
- Search 33713
- Search 79239
- Search 1336


Facebook Business Model | How does Facebook make money?
Company: Facebook, Inc CEO: Mark Zuckerberg Year founded: 2004 Headquarter: Menlo Park, California, USA Number of Employees (June 2020): 52,534 Public or Private: Public Ticker Symbol: FB Market Cap (Nov 2020): $786.63 Billion Annual Revenue (2019): $70.697 Billion Profit |Net income (2019): $ 18.485 Billion
Products & Services: Facebook | Instagram | WhatsApp | Oculus | Facebook Marketplace | Facebook Media | Facebook Messenger | Facebook Ads | Facebook Watch | Facebook Games | Facebook Local | Facebook Business | Competitors: Apple in messaging| Google in advertising | Amazon in advertising | Tencent in social media & messaging | YouTube in video | Twitter | Snapchat | LinkedIn | Pinterest | Quora | Microsoft | Vkontakte |
Facebook has been a pioneer in triggering a social media revolution in the digital hemisphere. Today it has over 2 billion users worldwide, contributing to the globalization process every day. Initially exclusive to Harvard students in 2004, the site grew in popularity enough to inspire its founder Mark Zuckerberg to expand it in the public domain. The world was never the same once it hit the virtual landscape.
Regardless of the nationality, background, continent or location, as long as there is Internet connectivity present, then Facebook is always available for you to access. With the world more connected than ever, it is highly unlikely that people will ever abandon this platform even for alternative sites like Twitter , Snapchat or Instagram.
Table of Contents
Business Model Canvas of Facebook
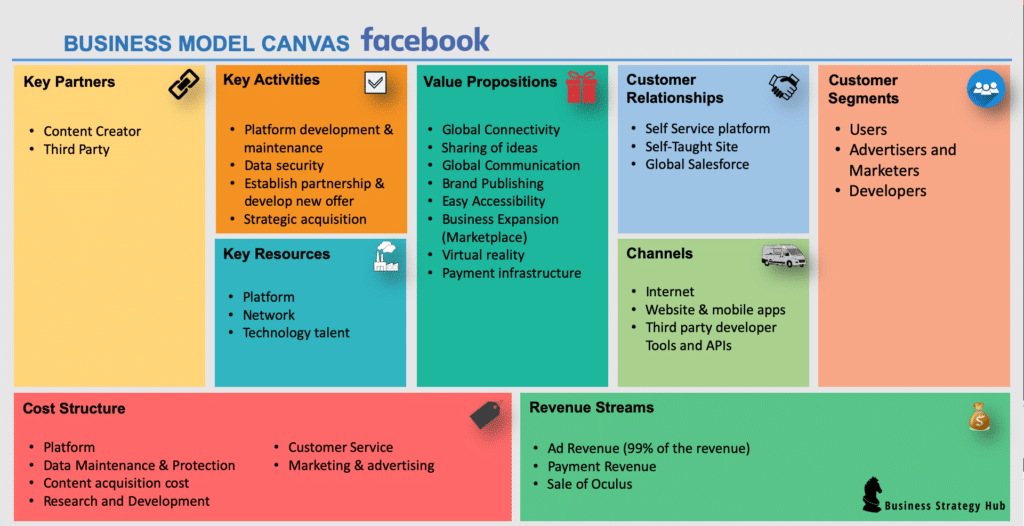
1. Customers of Facebook
Users – Facebook’s customers mostly comprise its users. Users who wish to communicate with different people and interact with those in the outside world. Facebook is now its own marketplace where users can buy and sell property like clothes and jewelry and even fundraise for their respective causes. Remote workers and colleagues working from home can use Facebook’s new Messenger Rooms that allows up to 50 people to meet virtually in a videoconference. [ 1 ]
Advertisers and Marketers – Brands and advertisers also form a part of its customer base that earns revenue for the company by placing offers and promotional ads.
Developers – The site also has its own App and Game development platform where users can play while the game developers like Zynga and Facebook both benefit.
2. Value Proposition of Facebook
Global Connectivity – Facebook has made it its mission to spread a free medium of communication and connectivity with people across the world regardless of their nationality, religion, culture or background.
Sharing of ideas – It is a platform where different people can interact with each other and expose themselves to different cultures, experiences, and ideas.
Global Communication – Many popular critics have noted the contribution of Facebook is enhancing common understandings and pioneering efforts in the globalization movement.
Brand Publishing – It is a platform where you can showcase your talents as well as play games whenever you want.
Easy Accessibility – There is no time limit where its network is concerned. Whatever you wish to search will be delivered in your domain.
Business Expansion (Marketplace) – It has also become a platform to utilize your business where you can sponsor, sell or buy from either your own company or any other company.
Virtual reality – With the acquisition of Oculus, Facebook is trying its hand in the field of virtual reality hardware.
Payment infrastructure – user can purchase digital goods or applications from developers using Facebook payment services.
Virtual meeting rooms – Messenger Rooms allow users to create virtual meeting rooms and open for up to 50 people to join and interact just like videoconferencing. While in a room, users can swap their background for a virtual one or apply Facebook’s augmented reality filters. [ 2 ]
Remote work tools and groups – Facebook added remote work tools on its app to facilitate collaboration between colleagues and freelancers. It includes Workplace Rooms that offer more features for professional workers to collaborate on the network. As of May 2020, Work Groups had more than 20 million active monthly users and 170,000 active groups. [ 3 ]
Live-streaming – Facebook also expanded its platform with new tools that enable users to live-stream sessions and events like wedding or birthday for friends and family to attend. The live-streaming feature is also used by professionals for remote work. [ 4 ]
3. Channel of Facebook
Internet – The first prerequisite is the Internet for its service; Facebook operates through the Internet via Laptops, Computers, Tablets or Smartphones.
Website & mobile apps – Then, it makes its usage of its website and mobile app to reach more users. Through its site, Facebook allows advertisers to market their products. Many public figures and celebrities have also contributed to its channeling efforts.
Third party developer Tools and APIs – These are used by developers for channeling purposes as well. Other partnerships assist in these purposes in their own distinct ways depending on the agreement.
4. Customer Relationships of Facebook
Self Service platform – Facebook’s network and site are user-friendly and easily accessible for its users. It assists new users through its instructions to form their own accounts and identities. The users gradually get the hang of it and realize how easy it can be utilized.
Self-Taught Site – It is basically a self-learning site. You can expand your online visibility by finding more friends through your new profile owing to Facebook’s community building applications.
Global Salesforce – Facebook has an extensive global sales organization that works directly with Advertising agencies and ad resellers. Sales work to attract, retain and support advertisers.
5. Key Partners of Facebook
Content Creator – Key Content Partners such as Movies, TV Shows, Gaming, Music and News articles. Facebook recently signed several deals for the right to show music videos on the platform. The partnership includes Universal Music Group , Sony Music Entertainment, and Warner Music Group, which are the three largest music houses. [ 5 ]
Third Party – Facebook’s platform continues to create new partners for it as it grows. Mobile operating system developer (iOS, Android), credit card companies (Visa, PayPal ), handset manufacturers ( Apple , Samsung ), and browser developers (Safari, Chrome, Firefox) have collaborated with Facebook.
6. Key Activities of Facebook
Platform development & maintenance – Facebook is a platform that produces a myriad of activities. One of them being its web development alongside App Development and game development.
Data maintenance and security – Invest in user data security and privacy.
Establish partnership & develop new offer – It offers other activities like projects, marketing, software development and other forms of innovation which it has been duly credited for.
Strategic acquisition – such as Instagram, WhatsApp , Oculus. Its most recent acquisition was a Swedish mapping start-up Mapillary that built a street-level imagery platform for creating maps using photos of members of the public. [ 6 ]
Maintaining government regulations – complying with laws in different countries is essential for Facebook operations.
Hire & retain talent
Sales, marketing and operations
- Sustainability – Facebook undertakes a variety of activities to attain its sustainability goals. It has invested heavily in green energy to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions and is now one of the largest buyers of renewable energy in the world. In 2019, 86% of its operations were powered by renewable energy, compared to 75% in 2018. [ 7 ]
7. Key Resources of Facebook
Platform – Facebook utilizes its platform as its primary resource to access more users and advertiser. The more users’ access and log in to its site the more subsidiaries it receives.
Network – Facebook’s network has provided limitless communication opportunities for its users despite their background.
Technology talent – Facebook takes immense pride in its technology and pool of talented employees. It was able to hire and retain. Thanks to its brand value.
8. Cost Structure of Facebook
Platform – Majority of the costs incurred by Facebook are directed in its platform that amasses millions of users worldwide.
Data Maintenance – Facebook incurs considerable costs from its Data Maintenance owing to how it manages, stores and protects its data, including the cost of data centers maintenance, equipment purchases, and upgrades.
Content acquisition cost – Facebook license and pay to content producers to increase user engagement.
Research and Development – Facebook focuses much of its time in the growth of its platform which demands costly investments.
Marketing & advertising – Facebook’s marketing strategy revolves around the audience and how it can expand that base. This tends to cost them exponentially.
Customer Service – Facebook values the feedback of its customers. It invests substantially in providing its services to customers who are new or require assistance in managing their accounts.
At a high level, according to Facebook’s 2018 annual report, here is a breakdown of its cost:
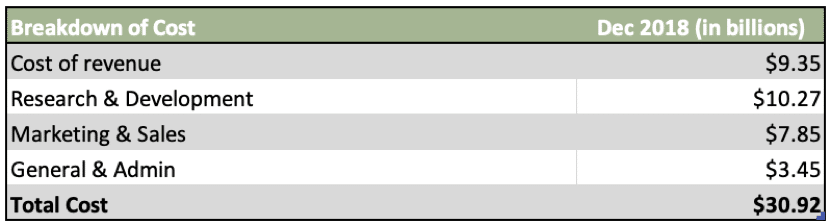
*Cost of revenue includes Operations expense, Datacenter, traffic and content acquisition cost, partner payment, and credit processing fees, etc.
*General & Administrative cost includes employees compensation and salaries, office maintenance, legal, HR, finance and administrative expense.
9. Revenue Stream of Facebook
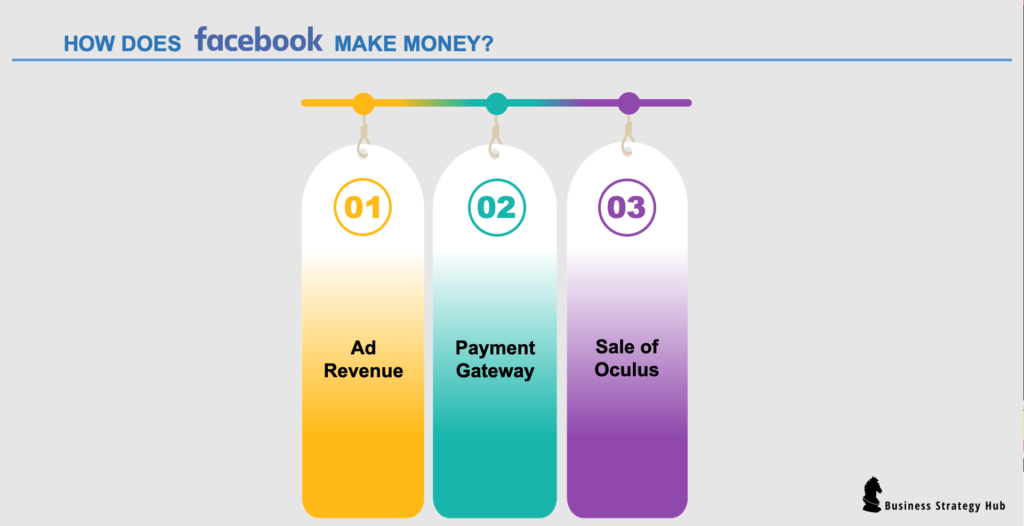
How does facebook make money .
Let’s see how does Facebook make money?
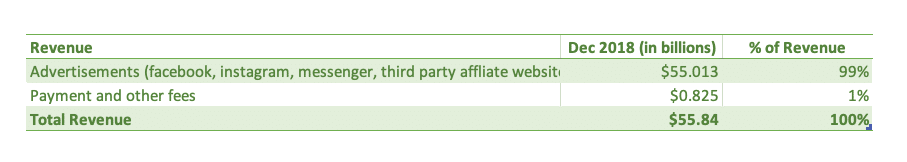
The most vital money making system for Facebook is in its advertising program. Most of its revenue (99%) is generated from advertising alone. It has always supported itself by its ads and will most definitely continue down this path. In Q3 2020, Facebook’s quarterly ad revenue was $21.2 billion , up by 22.1% compared to Q3 2019. [ 8 ]
Many have begun to spread conspiracy theories that Facebook will someday begin charging its users for utilizing or accessing their site. But these have been dismissed as mere rumors and fake news.
Self-Serve Advertising
- With Facebook’s self-serve platform for advertising, you simply have to seek out Facebook’s “Following” page and create your own campaign of advertising.
- These advertisements can be shown on sidebars such as events, groups, profile pages, and other applications on Facebook.
- Facebook uses its advertising strictly for a target audience, which is diverse according to age, gender, and relationship lines.
- It also relies heavily on restaurants, doctors, lawyers, and many small businesses or professionals to utilize its self-service advertising to generate its revenue.
Engagement Ads
- Apart from their self-serve advertisements, Facebook claims additional revenue from their “Engagement Ads” as well.
- These engagement ads are placed on Facebook’s homepage and are considered as key solutions for large advertising brands.
- All user has to do is log in, and he can interact with some of these ads on the right side of the site’s homepage.
- Facebook has been working to increase its recruitment of brand advertisers.
- Some of the work has been created in the form of the Brand Lift. This product encourages large brands to test their advertising campaigns in terms of their effectiveness.
- Through this, more advertisers can utilize the product and adopt Facebook as their main campaigner.
Payment Revenue
It’s the fees that Facebook receives from the developer community or wholesalers for utilizing Facebook’s payment infrastructure . Facebook charges a fee for any business transaction on its platform, whether it be :
- Marketplace featured deals
- Sale of digital products like Zynga poker chips,
- Sale of apps from developers,
- Money transfer to friends,
- Fund Raiser’s transaction fees etc.
Sale of Oculus
Facebook sells “ Oculus ” Virtual Reality (VR) products and makes a small portion of revenue from its sale. It introduced Oculus Go in 2018, starting at $199 that relied on the user’s smartphone for computing, and then later launched a more powerful all-in-one headset Oculus Quest, Oculus Rift, and Rift S, all going for $399 Quest.
In Q1 2020, Facebook shipped 55,000 units of Oculus Go , 141,000 Quest units, and a combined 87,000 units of the Rift and Rift S headsets. Oculus sales contributed to the revenue of $297 million from its non-advertising businesses. It announced that it stop the sale of Oculus Go in 2020 after demand declined in subsequent quarters. [ 9 ]
Future Revenue possibilities
WhatsApp, a giant social messaging platform, is still not monetized successfully to its full potential. Facebook can potentially make a huge amount of revenue from Whatsapp in the near future. Another potential revenue stream is its Libra cryptocurrency that was launched in 2019 but has faced pushback by lawmakers from countries across the world based on the company’s history of scandals. If the Libra project is successful, Facebook can become the biggest player in digital payments in the world as an alternative global transaction system. [ 10 ]
Read: How does WhatsApp make money?
In Conclusion
Facebook is a gift that just keeps on giving. It has continued to handle controversies and competition at a safe place without losing too much in terms of revenue or public image. Although many social media platforms have risen since its establishment, they are not as commonly used as Facebook.
Many sites like Twitter and Instagram have managed to provide adequate competition, but others like SnapChat, Pinterest, Tumblr and others continue to struggle in the hopes of catching up to their competitors.
All in all, Facebook is the one that will remain constant in the long run.
References & more information
- Bond, S. (2020, April 24). Facebook Launches Rival To Video-Meeting App Zoom . NPR
- Newton, C. (2020, Apr 24). Messenger Rooms are Facebook’s answer to Zoom and Houseparty for the pandemic . The Verge
- Hutchinson, A. (2020, May 21). Facebook Announces New Collaboration Tools for Workplace, Including First Steps into VR Offices . Social Media Today
- Perino, M. (2020, May 19). How to find live videos on Facebook on a computer or mobile device . Business Insider
- Wagner, K. (2020, July 31). Facebook Is Set to Finally Get the Rights to Show Music Videos . Bloomberg
- Shead, S. (2020, June 19). Facebook buys start-up in the latest push to take on Apple and Google at street-level mapping . CNBC
- Pierce, D. (2020, July 7). Facebook’s closer to its sustainability goals, but not quite there . Protocol
- Johnston, M. (2020, Nov 5). How Facebook Makes Money . Investopedia
- Rodriguez, S. (2020, June 23). Facebook cancels its cheapest VR headset to focus on pricier, more powerful models . CNBC
- Feiner, L. (2020, April 16). Facebook’s vision for a new cryptocurrency gets watered down as it attempts to woo regulators . CNBC
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.
A management consultant and entrepreneur. S.K. Gupta understands how to create and implement business strategies. He is passionate about analyzing and writing about businesses.
Add comment
Cancel reply, you may also like.

43 Recession Proof Businesses (2023)
Last updated: Sept 09, 2021 Recession is undoubtedly a time of high crisis, and you’d think that everything will slowly start crumbling. Well, that is not true in most cases. By most cases we mean businesses. We...
Wayfair’s Business Model | How does Wayfair make money?
Online home goods brands rake in over $86.41 billion in sales annually, accounting for a massive chunk of the US home decor segment. The convenience of online shopping, user-friendly apps, in-home services, and the...
Tesla Business Model (2023) | Tesla Business Model Canvas
Last updated: Oct 9, 2021 Company: TESLA, Inc. CEO: Elon Reeve Musk Subsidiary: SolarCity, Tesla Grohmann Automation, Maxwell Technologies Founders: Elon Musk, Martin Eberhard, JB Straubel, Marc...

How does Bumble work & make money?
Company: Bumble Founders: Whitney Wolfe Herd Year founded: 2014 Headquarter: Austin, TX Registered Users (2019): 75 million Valuation (2019): $3 Billion Annual Revenue (2018): $162 million Products &...

Roku Business Model | How does Roku make money?
The emergence of subscription video-on-demand (SVOD) changed how and when individuals consumed digital video content. Widespread internet availability, added flexibility, vast content libraries, adoption of mobile...
LinkedIn Business Model (2022)| How does LinkedIn make money?
Last updated: Out 9, 2021 Company: LinkedIn (a subsidiary of Microsoft Corporation) CEO: Jeff Weiner Year founded: 2002 Headquarter: Sunnyvale, California, USA Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 13,000...

Netflix Business Model (2023) | How does Netflix make money
Last Updated: Feb 3, 2023 Company: Netflix, Inc. Co-CEO: Ted Sarandos & Greg Peters Year founded: 1997 Headquarter: Los Gatos, USA Type: Public Ticker Symbol: NFLX (NASDAQ) Market Cap (Feb 2023): $ 162.95 Billion...
Etsy Business Model | How Does Etsy Make Money?
Technological advancements, increased adoption of mobile devices, globalization, better and cheaper internet connection, and safe payment gateways are driving the growth of online marketplaces like Etsy. But what is...

How Does Discord Make Money?
Company: Discord, Inc. CEO: Jason Citron Year founded: 2015 Industry: VoIP communication, Content delivery Headquarter: San Francisco, USA Type: Private Valuation (Dec 2018): $2.05 billion Products &...

How does Sweatcoin work and make money?
Company: Sweatcoin Founders: Oleg Fomenko and Anton Derlyatka Year founded: 2015 CEO: Oleg Fomenko and Anton Derlyatka Headquarter: London, England Type: Private Investor Funding: 6.3M Products &...
Recent Posts
- Who Owns Westin Hotels & Resorts?
- Who Owns Truist Bank?
- Who Owns Alfa Romeo?
- Who Owns Burt’s Bees?
- Top 15 Ruggable Competitors and Alternatives
- Top 15 Ticketmaster Competitors and Alternatives
- Who owns Kidz Bop?
- Top 20 Zapier Competitors and Alternatives
- Top 15 Boxabl Competitors and Alternatives
- Who Owns High Noon?
Business Strategy Hub
- A – Z Companies
- Privacy Policy
Subscribe to receive updates from the hub!
- Red Queen Effect
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Only the paranoid survives
- Co-opetition Strategy
- Mintzberg’s 5 Ps
- Ansoff Matrix
- Target Right Customers
- Product Life Cycle
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Bowman’s Strategic Clock
- Pricing Strategies
- 7S Framework
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Strategy Diamond
- Value Innovation
- PESTLE Analysis
- Gap Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Strategy Canvas
- Business Model
- Mission & Vision
- Competitors

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

How Does Facebook [Meta] Make Money? Facebook Business Model Analysis 2024
Facebook, the main product of Meta, is an attention merchant . As such, its algorithms condense the attention of over three billion monthly active users as of 2023. Meta generated nearly $ 135 billion in revenues in 2023, of which nearly $ 132 billion was from advertising (97.8% of the total revenues), $1.9 billion from Reality Labs (the augmented and virtual reality products arm), and over $1 billion in other revenue.
Table of Contents
Meta Business Model VTDF Breakdown
We describe the Meta business model via the VTDF framework developed by FourWeekMBA.
The history of Facebook: the former rocket ship turned into a heavy cruise ship
Back in the 2010s, a few years after Facebook had been founded, it represented one of the most impressive growth companies that ever existed, also for the Internet standard.
Indeed, Facebook and a few other companies opened the way, to what we call – in hindsight – Web 2.0.
In an early 2004 interview, Mark Zuckerberg, 20 at the time, side by side with WesMatch’s founder, Dan Stillman, explained what Facebook was about. Facebook would eventually wreck down WebMatch and all the other early players in the social network space ( Myspace, Friendster, and CampusHook to mention a few).
As Zuckerberg explained it at the time, Facebook was “an online directory that connects people through universities and colleges through their social networks.”
While today we give for granted a Facebook with billions of users, at the time with a hundred thousand users on the platform, it was very hard to tell how big it could become.

Facebook’s early growth trajectory (Source: Financial Prospectus).
When Facebook first launched, it was a rocket ship. The company used a staged rollout, where it would open its app to a larger and large set of users, not gradually, but exponentially.
In short, with its first release, in February 2004, it only proved the concept through Harvard. As growth picked up right on, and the product turned out to be very sticky among students at Harvard, Facebook opened to other top colleges, by the same year.
And this happened right after Facebook had built a very important feature, the Facebook Wall, which would become a place for users to post relevant staff and connect to each other.
This is how Facebook reached a million monthly active users.
After that, by early 2005, Facebook was already present in 800 college networks. By September and October of the same year, Facebook expanded to high schools and international networks. This, at the moment in which, it had introduced a new feature, photos , enabling users to upload their photos on the platform (a big deal at the time!).
By 2005, Facebook had reached 6 million monthly active users (a 6x growth ).
By September 2006, Facebook introduced another key feature, which was as powerful as the “Stories feature” that Snapchat would introduce seven years later, in 2013. That was Facebook’s News Feed!
By 2006, Facebook had grown into a 12 million monthly active user base.
By 2007, Facebook launched the Facebook Platform, a third-party application platform, enabling developers to build apps/features on top of Facebook. While this would be slowly shut down over the years (Facebook deprecated various APIs over time) it was a great experimental platform for quick users growth .
In the same year, also Facebook Pages was launched. The company reached 58 monthly active users.
In 2008-2009 Facebook’s expansion continued, with Facebook reaching over 360 million monthly active users.
In the same year, 2009, Facebook introduced the like button.
By 2012, as Facebook got ready for the IPO, it also reached a billion monthly active users!
And as it grew, it also played with its privacy policies, to make its advertising machine extremely profitable (a blessing and a curse that would follow the company for years).
Leveraging a powerful social graph, it leveraged network effects , and it quickly grew, from a social network for universities, to mass social media company.

The Facebook Social Graph of the early days! (Source: Facebook Prospectus).
Facebook was an incredible innovation for its time. With a very simple interface users could upload photos, update their status, and send messages to their friends and have complete control over what they wanted to share:

(Source: Facebook Prospectus).
Back then, when Facebook was getting ready for its IPO, Zuckerberg highlighted the company’s playbook, founded on what Zuck called “The Hacker Way” (which also turned into the name of the street – 1 Hacker Way, Menlo Park – where the main headquarter is situated).
This playbook would also become the standard, for those building Internet companies who had to leverage fast users’ adoption, and network effects .
It would inspire disciplines like growth hacking , and growth marketing , now become a standard in the Internet industry.
The manifesto said:
As part of building a strong company, we work hard at making Facebook the best place for great people to have a big impact on the world and learn from other great people. We have cultivated a unique culture and management approach that we call the Hacker Way The word “hacker” has an unfairly negative connotation from being portrayed in the media as people who break into computers. In reality, hacking just means building something quickly or testing the boundaries of what can be done. Like most things, it can be used for good or bad, but the vast majority of hackers I’ve met tend to be idealistic people who want to have a positive impact on the world.
Therefore, Zuckerberg reframed the meaning of hacker, not as something bad, but rather a mindset to be used to build valuable things in the world.
And he continued:
The Hacker Way is an approach to building that involves continuous improvement and iteration. Hackers believe that something can always be better, and that nothing is ever complete. They just have to go fix it — often in the face of people who say it’s impossible or are content with the status quo.
This would set the stage for the core mindset that Facebook had led for years of “moving fast, and breaking things.” This would be the main manifesto for years until Facebook had become such a popular company, that going too fast was no longer an option.
Indeed, in 2014, as Facebook had become a company generating over $12 billion in advertising revenues, and with almost 1.4 billion Monthly Active Users, the motto changed to “ Move fast with stable infrastructure.”
However, like Zuckerberg, explained, back in 2012 – when Facebook was getting ready for the IPO:
Hackers try to build the best services over the long term by quickly releasing and learning from smaller iterations rather than trying to get everything right all at once. To support this, we have built a testing framework that at any given time can try out thousands of versions of Facebook. We have the words “Done is better than perfect” painted on our walls to remind ourselves to always keep shipping.
He also added:
Hacking is also an inherently hands-on and active discipline. Instead of debating for days whether a new idea is possible or what the best way to build something is, hackers would rather just prototype something and see what works. There’s a hacker mantra that you’ll hear a lot around Facebook offices: “Code wins arguments.”
What about its culture?
Hacker culture is also extremely open and meritocratic. Hackers believe that the best idea and implementation should always win — not the person who is best at lobbying for an idea or the person who manages the most people.
How did Facebook incentivize this hacker mindset?
To encourage this approach, every few months we have a hackathon, where everyone builds prototypes for new ideas they have. At the end, the whole team gets together and looks at everything that has been built. Many of our most successful products came out of hackathons, including Timeline, chat, video, our mobile development framework and some of our most important infrastructure like the HipHop compiler.
This implied an initial program, a Bootcamp, which anyone (also future managers) had to go through:
To make sure all our engineers share this approach, we require all new engineers — even managers whose primary job will not be to write code — to go through a program called Bootcamp where they learn our codebase, our tools and our approach. There are a lot of folks in the industry who manage engineers and don’t want to code themselves, but the type of hands-on people we’re looking for are willing and able to go through Bootcamp.
In 2012, Facebook had reached over $5 billion in revenues. By 2016, that number would be more than 5x, reaching over $27 billion in revenues.
And by 2021, Facebook 4xed again its growth to $114.9 Billion in advertising revenues!
Facebook, metaverse, and rebranding as Meta
At the end of October 2021, Mark Zuckerberg announced the Facebook Inc. rebrand as Meta. A company focused and dedicated to building the Metaverse. Beyond buzzwords and corporate communication. What does that imply?
With the announcement, Facebook changed its name to Meta. It wasn’t just a name change (although it was perceived by many as such) but it also worked as organizational restructuring.
Indeed, with this move, Facebook, now Meta, wanted to show its bold move into VR/AR, which is seen by Zuckerberg as the next mass consumer platform after the smartphone.
In short, with this new organization, they are trying to go after, what today we call the Metaverse, which is something still hard to make sense of since its definition is being shaped now.
Thus, Facebook, now Meta, is trying to become a leading player in this new market. But to really understand that we need to look at the overall Facebook business model.

Before we get to that, it’s important to emphasize that Meta is still an advertising company. And how do you measure the success of an advertising company? There is a metric for that: ARPU !
It’s all about ARPU: How much are you worth to Facebook?

ARPU stands for average revenue per user. In short, how much money a company can get on average from each user?
In the Facebook case, we can take into account the monthly active users.
For a company like Facebook, for which over 97% of its revenues come from advertising the amount of time people spend on the so-called news feed is crucial to increase the profitability metrics of the company.
That isn’t only because Facebook is an advertising company , but also the way its business model was built.
If you think about Google, what makes the company able to monetize its users is not necessarily how much time they spend on the search results pages. Instead, that is based on how fast users can find what they need.
Once they click through that is how Google makes money .
Of course, things are changing fast both on Google and on Facebook .
Yet as of now the more time you spend on Facebook and the more you’re active on it, the more you allow it to make money.
What else? Not all users are born equal. In fact, according to the geography and the ad market of each country, the monetization strategy changes.

For instance, that is how much each user based on geography was worth to Facebook in 2023:
- US and Canada: $68.44.
- Europe: $17.29.
- Asia: $4.61.
- Rest of the World: $13.12.
Therefore, a user from the US or Canada as of 2023 is worth more than a user from Europe or the Asia-Pacific region. To make a comparison, a user from the US and Canada, on average, is worth nearly 4x more than a user in the rest of the world!
Of course, also within the US, there are the so-called power users, who are worth way more to the company.
For instance, think of an influencer profile, that has many millions of followers, and that when it posts, generates millions of interactions.
If you take, for instance, the most successful Instagram account in 2024, that of Cristiano Ronaldo, with over 600 million followers, you realize that this account alone might be worth hundreds of millions for the company, each year.
Compared to the account of average users, with a few followers, which generates very few engagements. Thus, when looking at ARPU, it’s important not to give it too much weight.
An analysis based on power users’ accounts and how those power users (like Cristiano Ronaldo) move their following across various social media platforms (imagine Ronaldo stopped posting on Instagram and only posted on TikTok) can tell us much more about the overall health of the platform user adoption.
This, of course, is a qualitative analysis.
From an internal standpoint, the long-term objective for Facebook is to keep increasing its monetization for each user, especially in the developing parts of the world where there is still space to grow the user base, which instead has stalled in the US and Canada.
At the same time, it needs to make sure to keep growing its user base and keep attracting power users, which can generate millions of interactions with each post. And this is a matter of product development, engineering, distribution , and brand appeal to newer generations!

If we look at the current landscape of Facebook’s monthly active users (this only comprises Facebook users), we can see how growth in US & Canada has mostly slowed down.
Snapshot of Facebook key stats and facts
- As reported officially by Facebook , the company’s main headquarter is situated at 1 Hacker Way , Menlo Park, California 94025.
- As we highlighted, the “ Hacker Way ” is Mark Zuckerberg’s key driving business strategy mindset.
- Facebook, now Meta, had f 67,317 by 2023.
- The company also reported over 3 billion monthly active users (remember that Facebook Inc., also comprises other products like Instagram , while they affect the Facebook bottom line, Facebook doesn’t report how much of it is coming from each product and doesn’t tell us the users count of those platforms).
- In 2023 Facebook, now Meta, generated nearly $ 135 billion in revenues.
- In 2023 Meta’s business model was driven by advertising revenues, which represented 97.8% of the total revenues.
What drove Facebook’s business model in 2024?

As we saw, Facebook, now Meta, makes money with an advertising business model . Almost all the revenue comes from targeted advertising.
Facebook’s revenue breakdown in 2023:
- Advertising (over 97.8% of revenues) : the company generated over $131 billion in advertising, primarily consisting of displaying ad products on Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, and third-party. As Facebook highlighted, in 2023, the number of ads delivered increased by 28%, as compared with approximately 18% in 2022. The price per ad decreased by 9% in 2023, compared to a 16% decrease in 2022. This happened due to the fact that Meta has been pushing formats (like Reels) that while grabbing more attention are also hard to monetize (for now) due to the format and geography.
- Payments and other fees (less than 1% of total revenues) : those revenues primarily consisted of the net fee received from developers using Payments infrastructure or revenue from the delivery of virtual reality platform devices and, most importantly, revenue from the delivery of consumer hardware devices.
- Reality Labs generated nearly $2 billion in revenues (less than 2% of the total revenues) from the delivery of consumer hardware products, such as Meta Quest (former Oculus) , Facebook Portal, wearables, and related software and content.
Facebook’s same mission statement, changed vision (hint: it’s all about the metaverse)
The company’s mission was “to give people the power to build community and bring the world closer together.”
As Facebook, became Meta, its mission statement stayed the same, however, its vision changed.
In fact, Meta’s mission is still to give people the power to build community and bring the world closer together.
The vision is “of helping to bring the metaverse to life.”
As the company highlighted in its 2021 financials:
We build technology that helps people connect, find communities, and grow businesses. Our useful and engaging products enable people to connect andshare with friends and family through mobile devices, personal computers, virtual reality (VR) headsets, wearables, and in-home devices. We also help peoplediscover and learn about what is going on in the world around them, enable people to share their opinions, ideas, photos and videos, and other activities withaudiences ranging from their closest family members and friends to the public at large, and stay connected everywhere by accessing our products. Meta is movingbeyond 2D screens toward immersive experiences like augmented and virtual reality to help build the metaverse, which we believe is the next evolution in socialtechnology
The pillars of Meta’s business model
Meta business model can be broken down into two main segments:
- Family of Apps ( comprising the main products which make the advertising business successful – like Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, WhatsApp).
- And Reality Labs : the suite of products related to the Metaverse (former Oculus, wearables, and marketplaces related to VR/AR).
And five main product pillars:
- Facebook , which main digital assets comprise the News Feed, Stories, Groups, Watch, Marketplace, Reels, Dating.
- Instagram , which main digital assets comprise Instagram Feed, Stories, Reels, Video, Live, Shops, and messaging.
- Messenger , which main features comprise chat, audio and video calls, and Rooms.
- WhatsApp which main application is mobile chat.
- And Meta Quest is the company’s flagship hardware for virtual reality on top of which Meta is trying to build its new supply chain of data.
And a “research factory”, which is Reality Labs, trying to build from scratch the whole Metaverse supply chain!
Facebook Reality Labs is an augmented and virtual reality laboratory that produces hardware and consumer devices. This is comprised of Oculus, a leader in VR headsets, which Facebook acquired in 2014 for $2.3 billion. Oculus Quest, the main product line of what has been rebranded as Facebook Reality Labs is the VR device, which will also play a key role in the development of the Metaverse .
We’ll see why the Metaverse plays such a key role in Facebook’s future. And it’s all about distribution .
Comparing the attention merchants’ business models

Before we jump forward, to understand Facebook’s fast move into the Metaverse. Let’s highlight some core similarities, and differences between Google and Facebook business models .
Let’s see two major similarities:
- Both Facebook (rebranded as Meta) and Google (rebranded as Alphabet), try to move away (or apparently do so) from ads, still making the most of their revenues from it . In 2021, Alphabet generated over $209 billion or over 81% of its total revenues from ads. Meta generated running on ads, primarily. Meta generated $114.9 billion or over 97% of its total revenues from ads! True, both companies are betting and investing in other areas, but that is where most revenues, at extremely high margins are generated.
- Both are asymmetric business models . As I explain here , asymmetric business models, work by offering a free, incredible tool/service/application, to users, at scale. While this is apparently free, the same free users represent the main asset for the company. Therefore, both Facebook and Google, 1. monetize their users’ traffic via advertising 2. are able to profit from users’ data , way more than the value of the data for a single user (thanks to network effects ). Thus, the data is much more valuable to Google/Facebook in their advertising marketplace, than to a single user 3. the way Google/Facebook can leverage the data is asymmetric , as they get two companies that combined are worth trillions, and the free user on the other side gets either easy to find information (Google) or entertainment/connection (Facebook). Worth highlighting also how benefits for society are created when more and more users freely use these applications at scale. However, also negative externalities arise (which are not accounted for in these companies’ balance sheets), which are carried by the collective.
Yet, similarities stop here, in fact, these two business models are fundamentally different, because:
- Search is a different mechanism than social media : in fact, where the search is a “pull mechanism” where users are looking for something, expressing their intent directly through search, social media is a “push communication mechanism,” where information is mostly shown in the news feed. Thus, the main effort for Facebook is to make sure this news feed stays relevant.
- Google is vertically integrated: Facebook primarily relies on its brand , and product to make sure its apps are easy to be found through Apple and Google mobile pipelines. However, where Google controls the operating system (Android), browser (Chrome), marketplace (Google Play), and some of the applications (like Google search), Facebook only has its brands. This means that if Google and Apple (as it happened already) were to unilaterally change their rules, this would affect the overall Facebook business model.
- The advertising marketplace : since Google primarily sells search ads the main effort for the company is to guess what’s the real intent behind the search. For Facebook instead, it’s all about micro-targeting the users, by knowing all their preferences. While the Facebook Advertising machine is much simpler to use and understand, the Google advertising machine has more subtleties to grasp.
Now that we clarified these distinctions, we can move to the Metaverse!
Facebook moves into the Metaverse!
The Facebook business model is quite simple: advertising . Even though there are two sources of income, most of the revenue comes from ads.
I wouldn’t be surprised to see the other sources of income, other than advertising, grow in the next years. That is good to diversify the revenue stream .
However, as of now, the company’s growth is tied to its ability to engage its daily active users.
Some users (for instance, North America and Europe) are worth more on Facebook because those areas are monetized differently. Also, there is one key metric that tells us if the value of Facebook will keep growing in the long run: ARPU .
As we saw, Facebook, together with Google, is the most profitable attention merchant. The company has emulated successfully the Google advertising machine.
With a couple of slight differences to emphasize.
First, Facebook’s ads are pushed to the users via targeting, wherein Google’s case these ads are pushed based on contextual search. Second, where Google’s distribution passes through ownership of hardware (Google manufactures the Pixel), browser (Google owns Chrome), mobile operating system (Google runs Android), and search. Thus, Google (Alphabet) is way more vertically integrated:
Facebook’s distribution is primarily based on strong brand names. With the acquisitions of Instagram, WhatsApp, and Oculus, Facebook has kept a strong distribution , yet primarily based on the strength of these brands.
Thus, from here we can really really explain the swift move that Facebook made into the Metaverse.
We can argue that Mark Zuckerberg’s Meta is in a Blitzscaling mode . Where it’s both trying to defend its business model, and attack the market, by creating a whole new industry, potentially bigger than mobile.
To understand this, we need to look at Apple’s privacy update on mobile devices.
Apple’s privacy change
The triggering move to Facebook’s rebrand has been the survival threat posed by Apple to the entire Facebook business model. In January 2021, Apple announced the “ Data Privacy Day ” where it explained:
“A Day in the Life of Your Data” helps users better understand how third-party companies track their information across apps and websites, while describing the tools Apple provides to make tracking more transparent and give users more control. The explainer sheds light on how widespread some of these practices have become. On average, apps include six “trackers” from other companies, which have the sole purpose of collecting and tracking people and their personal information.Data collected by these trackers is pieced together, shared, aggregated, and monetized, fueling an industry valued at $227 billion per year.

The Metaverse Supply Chain
In 2021, Founder’s letter Mark Zuckerberg highlighted:
We are at the beginning of the next chapter for the internet, and it’s the next chapter for our company too. In recent decades, technology has given people the power to connect and express ourselves more naturally. When I started Facebook, we mostly typed text on websites. When we got phones with cameras, the internet became more visual and mobile. As connections got faster, video became a richer way to share experiences. We’ve gone from desktop to web to mobile; from text to photos to video. But this isn’t the end of the line. The next platform will be even more immersive — an embodied internet where you’re in the experience, not just looking at it. We call this the metaverse, and it will touch every product we build.
In the metaverse, you’ll be able to do almost anything you can imagine — get together with friends and family, work, learn, play, shop, create — as well as completely new experiences that don’t really fit how we think about computers or phones today. We made afilm that explores how you might use the metaverse one day.
Facebook, now Meta emphasized its role in this development as:
Our role in this journey is to accelerate the development of the fundamental technologies, social platforms and creative tools to bring the metaverse to life, and to weave these technologies through our social media apps. We believe the metaverse can enable better social experiences than anything that exists today, and we will dedicate our energy to helping achieve its potential.
These statements which sound inspirational are actually explaining the long-term survival threat posed to Facebook, the rebrand as Meta, and its long-term success, achievable if Facebook managed to build the Metaverse!
What can you do in the Metaverse (for now)?
While Facebook’s vision for the Metaverse is limited for now, this might comprise various business worlds, domains, and ecosystems. In fact, Metaverse is a term that comprises VR/AR, crypto, and more.
Yet, In Facebook’s Meta vision, the Metaverse will have a few key killer features like gaming, fitness, and more:
Horizon Home
Messengers’ calls in VR
Work and Productivity
Key Highlights
- Facebook was founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg in his dorm room at Harvard. Since then the company has never stopped growing. If it were a country, Facebook would probably be the most crowded on earth. However, the ability of the company to increase its value over time is based on how much money on average can make for each user.
- Over 97% of Facebook’s revenues come from advertising. Therefore, unless things will change; the news feed is still the primary driver for monetizing Facebook’s content . A simple change in its algorithm can influence the mood of billions of people. Also, it can affect the value of the company by billions of dollars.
- Facebook swiftly moved into the Metaverse, as Apple’s privacy changes also threatened the company’s long-term survival. That is why Facebook, now Meta is committed to building the so-called Metaverse.
Key conclusions
- Though Meta claims to move toward the Metaverse, advertising through Facebook/Instagram is still the primary driver.
- While Facebook has kept growing in areas of the world like Asia and the rest of the world, its monetization and ARPU are still primarily tied to the US & Canada, which, in 2021 represented over 43% of the total revenues.
- In 2021, ARPU was $11.57 worldwide. While in US & Canada it was $60.57, in Europe it was $19.68, in Asia $4.89 and in the rest of the world, it was $3.43. This shows the great discrepancy inability to monetize the traffic in North America and Europe vs. other areas of the world.
- Most advertising revenues still come from mobile and from the main product: Instagram.
- Meta managed to increase substantially its revenues in 2021, primarily thanks to the number of ads delivered, which increased by 10% (compared to approximately 34% in 2020). The primary ad revenue driver was the price per ad increase of 24% in 2021 ( compared to a 5% decrease in 2020). This metric is extremely important as it shows that Facebook is squeezing users’ attention to drive up revenues.
- Reality Labs sales were primarily driven by Meta Quest (former Oculus), which turned out to be a great VR gaming console. Will it be able to make the jump and become the primary device for content creation, and consumption in virtual reality? That’s an open question.
- While other tech giants like Google and Apple are vertically integrated and control the whole supply chain of data. In fact, Apple runs iOS operating system on the iPhone and the Apple Store. While Google runs the Android operating system on Android Devices, and the Google Play marketplace on top of these devices. These are the mobile distribution pipelines that enable apps, like Facebook & Instagram to be experienced by billions of users.
- While Facebook’s family of apps still enjoys strong brands, thus, making it hard for companies like Apple and Google (which control the mobile distribution pipelines) to block users’ growth for the company. These companies can still affect negatively the Meta advertising machine, as they can change the rules of how users need to approve personalized advertising – unilaterally.
- While there is no clear sign of slowed revenues for Meta, in 2021. It’s worth emphasizing how the company kept growing its revenues by increasing the cost of advertising substantially (not a viable strategy in the long term).
- In addition, the company expects a substantial slow-down in 2022, as the effect of Apple’s privacy policy changes (users have to opt-in explicitly to targeted ads). In fact, Meta’s CFO has already announced a substantial – expected – decrease in profitability for the company in 2022.
- This means, that the move to the metaverse, for Facebook (now Meta) isn’t just a strategic move. That is a survival move! Where Facebook hasn’t integrated its supply chain over the years, primarily relying on third-party marketplaces (Apple Store and Google Play), to make its business model survive in the long-term, the company will need to build the hardware, operating system, software, and marketplace that might power up the next generation of mass consumer devices!
What organizational structure does Facebook run?
Facebook is characterized by a multi-faceted matrix organizational structure . The company utilizes a flat organizational structure in combination with corporate function-based teams and product-based or geographic divisions. The flat organization structure is organized around the leadership of Mark Zuckerberg, and the key executives around him. On the other hand, the function-based teams are based on the main corporate functions (like HR, product management, investor relations, and so on).

Is Facebook an important player in the digital advertising industry?
Facebook products come only after Google, in terms of revenue generation. Indeed, Facebook is among the largest digital advertising player, which generated nearly $114 billion in advertising revenues, in 2022.
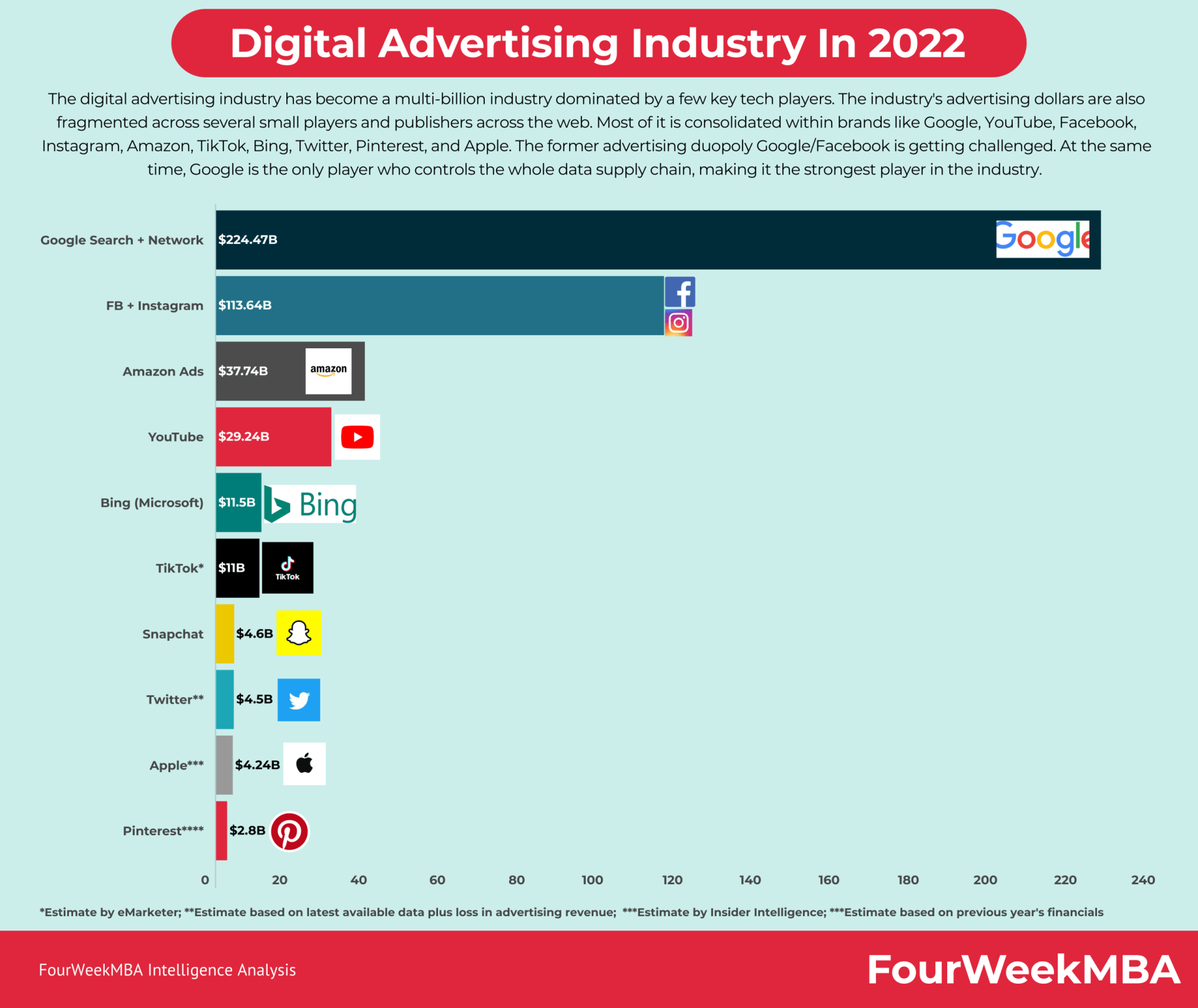
However, an important note here is that players like Amazon, and TikTok are growing very rapidly.
In addition to that, also Apple has built its advertising segment, and it has huge growth potential, given the fact, that the company controls the mobile pipeline (although Apple might want to keep that as hidden as possible, as it would in part conflict with its value proposition ).
Also, Amazon has a growing advertising business, which has the potential to become as big, or close, to that of Google and Facebook in the coming years.
Lastly, but also very important, TikTok’s advertising revenues are growing very quickly, thus posing a threat to the Google-Facebook duopoly.
In short, the digital advertising industry, which has been mostly resegmented around Google and Facebook, is now opening up to new competitors, that have the firepower to take over important market shares from the incumbent.
Main Free Guides:
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Business Development
- Digital Business Models
- Distribution Channels
- Marketing Strategy
- Platform Business Models
- Revenue Models
- Tech Business Models
- Blockchain Business Models Framework
Related Visual Stories
Who Owns Facebook

Facebook Business Model

Facebook Revenue Breakdown

Facebook Revenues

Facebook Employees

Facebook Revenue Per Employee

Facebook MAU
Facebook ARPU
Facebook ARPU 2010-2023
Facebook Profitability

Facebook Statistics
Facebook Organizational Structure

Instagram Business Model

WhatsApp Business Model
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
Profitable Business Models > Business models of large companies
Facebook’s Business Model Canvas: From College Experiment to Becoming the King of Social Media
- by Joanne Moyo
- August 26, 2021
TL;DR: Summary of the Facebook’s history
- Facebook’s success is due to its focus on innovation, platform development, and its ability to adapt quickly to changes in the social media landscape.
- Zuckerberg had been coding and programming since the age of 11, and he continued to develop his skills while attending college.
- The Social Network landscape in 2002 was dominated by Friendster, Myspace, and Second Life, all of which had free user bases and relied on advertising for revenue.
- Zuckerberg created Facemash, an early Facebook prototype that allowed Harvard students to compare female student’s pictures side by side and rank them based on attractiveness, but it was shut down before it even took off.
- Mark Zuckerberg created The Facebook, a social networking site exclusive to Harvard students, in February 2004.
- The Facebook platform was hit with its first lawsuit soon after its incorporation, with the plaintiffs alleging that Zuckerberg had stolen their idea.
- Zuckerberg and Saverin started selling small advertising spaces to companies and individuals to offset the cost of running and maintaining the platform servers while getting the company off the ground.
- Zuckerberg partnered with Sean Parker and Peter Thiel to help grow The Facebook in its early stages.
- Facebook focused on controlled and staged growth, which attracted investors, users, and great engineers and designers.
- Facebook’s Business Model Canvas: The Early Days
- 2006 was a big year for Facebook as they made several site improvements, went mobile, and partnered with Microsoft.
- Facebook had a busy year in 2008, hiring Sheryl Sandberg as COO, launching Facebook chat, Facebook Connect, and the Facebook for iPhone mobile app, and settling the ConnectU Lawsuit.
- 2009 saw the launch of the iconic like button, Facebook’s expansion into gaming, and the release of the Facebook Timeline.
- Facebook started as a social networking site for students, but has since evolved into a business, entertainment, and news platform.
- Facebook’s Business Model Canvas: The King of Social Media
Introduction
Undeniably, Facebook has become part of our daily routine. Opening the Facebook app on your phone has become second nature. The way Facebook has effortlessly integrated into the daily lives of users is by design. It’s hard to imagine life before Facebook, which is reflected in how well the company has done financially.
As of August 2021, the social media giant has been ranked with a market cap of more than $1.024 Trillion, making it the world’s 6th most valuable company. Facebook has 2.80 billion monthly active users and 1.84 billion daily active users.
A survey conducted in January 2021 found that of the five most popular social media platforms (YouTube, Facebook, WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and Instagram), Facebook owns four. This means that Facebook has significant control over crucial data and advertising.
From its inception in 2004, Facebook and its chief founder Mark Zuckerberg, have been at the forefront of innovation and the development of social media. It revolutionized the way people connected online and has made information sharing a breeze. Millions of businesses rely on the Facebook platform to advertise their products and services. Therefore giving Facebook the title of “King of Social Media” seems very apt.
Nevertheless, its rise to giant status has not been without missteps, controversies, and criticism. Marred with lawsuits from the very beginning, Facebook has managed to sustain its monopoly and dominance using various tactics, including a razor focus on innovation and platform development.
While the idea of a social network did not originate from Zuckerberg, his tenacity, adaptability, and quickness at launching the site gave him an advantage. Being a latecomer into the social network scene, Facebook has managed to disprove the proverbial theory that the early bird always gets the first worm.
So let’s take an in-depth look at how Facebook did it. How it managed to evolve from a free networking site for a few select college students to a multi-billion dollar empire with over a billion users worldwide.

2002-2005: How Facebook was born
2002: the history of zuckerberg’s programming passion & the state of social networking.
Mark Zuckerberg had been dabbling in coding and programming since the age of 11. Seeing a growing interest in the industry, his parents hired a software developer named David Newman to teach him. He successfully created an internal instant messaging program called ZuckNet for his father’s dentist’s practice through this tutoring.
A few years later, while attending an elite boarding school called Phillips Exeter Academy, Zuckerberg attracted the interest of Microsoft and AOL, who offered him a job. Both companies were looking at purchasing Synapse, a software that used AI to map a user’s music taste. Zuckerberg declined and chose to go to Harvard instead.
He decided to major in psychology and took several classes in computer science. This might seem like an odd choice for a kid with a knack for coding. However, his selection would prove to be very strategic in developing the very ‘addictive nature of Facebook and social media.
The Social Networking landscape
The Social Network landscape in 2002 was just in its infancy. Before Zuckerberg landed on his idea, several other social networking sites captured the interest of young teens and college students at that time.
There had been several early movers around the globe from as far back as the late 90s. When SixDegrees.com was launched in 1997, it became the first website to combine the basic features that we associate social media with today. Features such as; “…user profiles, listing of “friends,” and the ability to browse[ through a] friend’s list.” was developed by Six Degrees.
Three sites were trendy and quite successful before Facebook came onto the scene. These were; Friendster, Myspace, and Second Life. All three sites functioned on a non-subscription-based business model, meaning users could use the site for free. The aim was to make money by selling advertising to companies who want to reach the vast number of users.
Friendster, in particular, was launched in 2002. Within a few months, the company had more than three million monthly active users. Unfortunately, the Friendster platform was riddled with glitches and had too many restrictions for the user. These problems resulted in many early adopters migrating to MySpace the following year.
2003: Facemash, an Early Facebook Prototype & Competition from MySpace
Still, in his freshman year, Zuckerberg created an early Facebook prototype called Facemash. This new website allowed Harvard students to compare female student’s pictures side by side and rank them based on attractiveness.
Within a few hours, Facemash had garnered over 22 000 photo views. It was a smash hit; unfortunately, the website was shut down before it even took off. Zuckerberg didn’t have permission to use student photos from the Harvard student system for his website. Fortunately, he was not expelled for breaking the rules, and after a public apology, he set his sights on the next big thing.
That same year MySpace burst into the market and became an instant hit. It was a place for users to connect and build a private community to share blogs, groups, music, photos, and videos.
The platform was similar to Friendster’s model but focused more on sound infrastructure and scalability. It allowed users to personalize and continuously added new features based on user demand. By the end of the year, MySpace was established and dominated the social networking market.
2004: The Facebook is launched, tackling the first Lawsuit & Taking on MySpace & Friendster
Mark’s experience with his prototype helped him create a new site vastly different from Facemash. He noticed the mistakes and problems that sites like MySpace and Friendster were having.
Mainly the fact that Friendster was beginning to face challenges with managing their rapid new subscriber rate. The site often crashed, was slow to load, and the Friendster team didn’t bother with improving the platform design.
While MySpace was growing in leaps in bounds, Zuckerberg felt it necessary to control the growth of his new venture. He began working on a social networking site that connected Harvard students using their school email addresses and photos. Unlike MySpace, where the platform was open to anyone, The Facebook was exclusive to Harvard students only at first.
The platform was straightforward. Students could upload photos, share their interests and connect with people they knew at first.
Once he had worked on the platform for a few weeks, he told a few friends who suggested that Zuckerberg share the site on one of the school’s mailing lists. He launched the new site on the 4th of February 2004, incorporating it as a Florida LLC.
The strategy was a hit, and at least 1,200 students had signed up within a day of launch. The appeal was that this was a safe and exclusive place for Harvard students to meet each other.
The First Lawsuit from ConnectU
Barely a week after its first incorporation in February, The Facebook platform received the first of many lawsuits to follow. Zuckerberg was accused by three senior Harvard students of having stolen the idea from them.
The three students alleged that they had engaged Zuckerberg as a programmer to help them figure out a similar platform to The Facebook that they were calling ConnectU. This allegation soon developed into a full lawsuit. This started a cascade of legal issues that would plague Facebook for decades.
Monetizing the site
From the get-go, Zuckerberg saw the platform’s potential but needed a way to sustain it. So far,
Zuckerberg and his friend Eduardo Saverin absorbed the costs of operation from their own funds.
Borrowing the idea from MySpace who had lots of adverts running on their site, Saverin and Zuckerberg started a Flyer project to generate ad revenue in April. They started selling small advertising spaces to companies and individuals. They marketed services, job listings, T-Shirts, and other products from students.
While it wasn’t particularly sophisticated, it gave them a cushion to offset the cost of running and maintaining the platform servers while getting the company off the ground.
Within a month, at least 50% of all Harvard undergraduates had a profile. Around April 2004, The Facebook became available to college students from Yale, Columbia, and Stanford. Sensing the potential growth of the platform, Zuckerberg moved out of his Harvard dormitory in June and rented a house in Palo Alto, California, to serve as the company’s headquarters.
Getting Investors
He partnered with Sean Parker, who in 1999 had co-founded Napster, a file-sharing service that would change the way music was consumed. Parker became the first President of The Facebook when the company was incorporated in July in Delaware.
Parker went on the hunt for investors. After getting rejected by a few investors, he was directed to PayPal co-founder Peter Thiel. After an initial meeting with Zuckerberg and Parker, Thiel agreed to make a $500,000 investment for a 10.2% control of the company. Thiel became a member of the board and helped steer more people towards The Facebook.
As the year ended, The Facebook accepted membership from almost all universities in the U.S and Canada. They closed off their first year of operations with over 1 million active users and 7 employees.
2005: Early Expansion, Changing Name & Zuckerberg drops out
In May 2005 The Facebook received more capital. They got $12.7m from Accel and $1m from a venture capitalist Jim Breyer. All this money was being absorbed by the costs of operating, maintaining and developing the site. Selling ad space was still their only source of revenue. The platform was beginning to gain traction now, and a lot of people were paying attention.
Introducing Facebook.com
In August, they dropped the ‘the’ and renamed the company Facebook. They bought the facebook.com domain for a whopping $200,000 and continued to expand. Facebook continued to make improvements to the site, introducing a high school version of the platform in September and photos.
They expanded the site to allow Microsoft and Apple employees. They were soon ready to move beyond being a student platform. In October, Facebook expanded to the U.K and other countries, opening the site for up to 21 universities.
In November, Zuckerberg decided to drop out of Harvard and focus his efforts on running the company as CEO. By the end of the year, Facebook had expanded to Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Mexico, and Ireland. It had over 6 million users and 15 employees.
By avoiding the temptation to grow rapidly and instead opting for controlled and staged growth, Facebook built and developed a solid infrastructure to support the growing number of users. This attracted investors, users, and great engineers and designers who would create new products and features that catered to Facebook users. It was clear, Facebook was out for blood, and everyone could see it coming.
Facebook’s Business Model Canvas: The Early Days
At this point, Facebook’s Business Model Canvas looked like this:

2006-2012: Facebook to the World, Some Strategic Acquisitions & Going Public
2006: facebook becomes available to everyone and goes mobile.
2006 saw several significant changes to the site. Firstly, Facebook redesigned the group and events features to make them more accessible. They also launched a My Messages Page, a Browser Page, and several other improvements to their site. This made the site more user-friendly and convenient by allowing people to instantly connect with each other
Facebook took advantage of the rising availability of broadband and went mobile. They capitalized on the rise of smartphones and introduced additional networks that allowed people with corporate email addresses to join in May.
About two months later, Yahoo sent an acquisition offer of $1 billion to Facebook. Zuckerberg rejected it because he thought that Yahoo was grossly undervaluing Facebook’s potential. (Boy, was he right!)
As internet participation began to spread among diverse groups of people, social media was slowly becoming entrenched in the daily lives of individuals, schools, and families. Sensing this, Facebook lowered the age of users to 13, signally that they were a much ‘safer’ space for the youth and more family-friendly than MySpace.
Later that year, they launched the News Feed feature, which gathered users’ posts into one place. This made the site even more user-friendly. However, the change was met with resistance and outrage as certain users felt that Facebook was breaching their privacy. This outrage was to become a common thing for the company.
Partnership and Investment from Microsoft
Several vital things happened in 2007 for Facebook. Firstly, in October, Microsoft became highly interested in Facebook and purchased a 1.6% stake for $240 million. This new investment raised Facebook’s value to $15 billion. A month later, Facebook and Microsoft entered into a partnership intending to launch their Beacon ad program.
The aim of the program was to track a Facebook user’s behavior on third-party platforms. The product was highly unpopular and turned into a public relations nightmare because of user privacy concerns. Eventually, the many legal issues and lawsuits over the program forced Facebook and Microsoft to shut it down.
Acquisition of Parakey
The second significant event was Facebook’s first acquisition of a small startup called Parakey. Parakey was a crucial acquisition mainly because its founders Blake Ross and Joe Hewitt, were programming geniuses accredited for creating the Firefox web browser. They joined Facebook to help develop its platform and website.
Their programming and web development talents were immediately felt at Facebook with the launch of Facebook Marketplace for classified listings. The marketplace was a feature aimed at maximizing Facebook’s advertising revenue. The pair also helped create video posting and Facebook Ads and Pages. They were instrumental in developing the Facebook Application Developer platform aimed at developers who wanted to build their own applications and games integrated with Facebook.
It was clear that Facebook was now looking beyond personal user profiles. They were focusing on how businesses could use the site. By the end of the year, the platform had over 100,000 companies registered. Facebook’s value and appeal was accessibility, even for the smallest of businesses.
The decline of MySpace
The third critical event that occurred in 2007 was the beginning of MySpace’s decline. Although valued at a whopping $12 billion, MySpace was losing users to Facebook for several reasons. The platform was overloaded with advertising that made it extremely annoying to use. Its loading time was slower compared to Facebook. They were being beaten left, right and center in terms of innovation and features by Facebook. Facebook closed off the year with a membership of 58 million.
2008: Key Hires and settling lawsuits
Facebook started the year with a bang. In March, they hired Google executive Sheryl Sandberg as COO. Sandberg had extensive leadership experience and significant political acumen from her tenure as chief of staff for the Treasury Department under the Bill Clinton administration. This hire would prove crucial later on in the year when the financial crisis hit.
In April, Facebook launched Facebook chat, giving users an instant connection to their friends and family. The company also added Spanish as a language option, giving millions of Spanish speakers easier access to the side.
Another significant platform development was Facebook Connect, which allowed members to link their Facebook profiles to third-party sites. Lastly, they launched the Facebook for iPhone mobile app partnering with Apple.
Settling the ConnectU Lawsuit
After four years of back and forth, Facebook finally settles the lawsuit with the three senior Harvard students who claimed Zuckerberg had stolen their idea.
Navigating the Financial Crisis
When the global financial crisis hit, Facebook was just a small startup that relied heavily on ads for revenue. The situation made it challenging for this business model to survive. Fortunately, with Sandberg at the helm, Facebook managed to weather the storm by changing its advertising pricing and adapting the way it advertised.
2009: The Like Button Arrives and Product Expansion
2009 saw the launch of the iconic like button, allowing people to endorse other people’s posts. The launch was made possible through Facebook acquiring FriendFeed, a social media feed aggregator with many similar features to Facebook. As part of the acquisition, all 12 employees of FriendFeed joined Facebook, including its four founders, who played a crucial role in developing Google products such as Gmail and Google Maps.
Facebook also ventured into gaming, releasing Farmville in June. Within two months, the game had 10 million daily active users.
In 2011, Facebook purchased Snaptu, a small Israeli app developer tasked with redesigning and launching Facebook’s mobile app. Within a few years, the app had been downloaded by 100 million users. The same year Facebook retired the “Wall” and introduced the Facebook Timeline. This changed the platform’s user interface, reorganizing a user’s posts and putting them in chronological order.
2012: Disappointing IPO & Acquiring Instagram
The 18th of May, 2012, was a momentous day for Facebook. The company had the largest and most anticipated IPOs in history. They were offering 421,233,615 shares at $38 per share. Although they raised $16 billion through that offering, the IPO failed to meet expectations.
The stock fell immediately at opening, and the share prices plummeted by over 40% over the next few months. By August, Facebook had made a total loss of $50 billion. So why the lousy IPO turnout? The problem was that 57% of the shares sold on the IPO originated from Facebook insiders. This lack of confidence in the stock came from within Facebook itself.
Regardless of the disappointing IPO, the year 2012 saw Facebook make one of its most significant acquisitions. They bought Instagram, a photo-sharing social network that was integrated into the Facebook platform itself. This acquisition allowed Facebook to expand its user base and revenue from adverts. The year ends with Facebook announcing 1 billion active users.
2013-Present: A Maniacal focus on Advertising, Acquisitions & Product Launches
2013: htc phone fail.
In one of its few ill-advised ventures, Facebook partners with HTC to create a Facebook phone. The phone featured a home screen that was based on Facebook’s design and technology. It failed to garner any attention, and within a month, the selling price dropped from $99 to just $ 0.99. There were simply better phones on the market.
2014: Buying WhatsApp
In 2014, Facebook bought WhatsApp, a messaging app that increased Facebook’s reach. Despite already having a messaging system, Facebook wanted to have access to a younger user base and overseas users. This acquisition boosted Facebook’s presence in the mobile world, ensuring that their presence was felt one way or another.
2015-Present: Growing beyond Social Networking
From the years 2015 onward, Facebook continued to buy up everything in sight they felt was relevant for the company’s survival. Their advertising-dependent business model relied heavily on mining user’s data, behavior, and content. This landed them in trouble on several occasions, with privacy breaching complaints and lawsuits following them at every turn.
Nevertheless, Facebook continued to evolve beyond a place where students connect. It slowly grew into a business, entertainment, and news platform. Soon every business, organization, government, and individual was clamoring to be on Facebook. Its integration with third-party apps made it the most sought-after social media platform. Not to mention the thousands of updates, added features, and upgrades the platform introduced over the years.
Without a doubt, in today’s world, Facebook is the “King of Social Media”!
Facebook’s Business Model Canvas: The King of Social Media

- https://companiesmarketcap.com/facebook/marketcap/
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/272014/global-social-networks-ranked-by-number-of-users/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/gilpress/2018/04/08/why-facebook-triumphed-over-all-other-social-networks/?sh=2b526c4a6e91
- Tags: apple , facebook , google , microsoft , social media
Most Popular

Netflix’s Business Model Canvas Evolution (2021)

McDonald’s: Business Model Canvas, its evolution and company’s history

18 Must-Read Business Books

Check how Amazon’s main focus allowed the company to thrive. Amazon’s Business Model Canvas and how it changed from the very beginning.
- Business books reviews (27)
- Business Ideas (8)
- Business Model Canvas (9)
- Business models of large companies (26)
Business Tools

Download Free Business Model Canvas Template in Word / docx / PDF / SVG format
Inspire yourself with Business Ideas Generator
Get INSPIRING stories and TIPS on making your business model PROFITABLE!
- Recently trending business ideas
- Inspiring business models
- Examples of profitable businesses from all over the world
Related Posts

Twitter: Becoming The World’s Fastest Information Hub
Today, Twitter is one of the most recognizable and influential social media platforms on the planet. As of February 2022, Twitter is valued at $27.48

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Cost Structure
The last (but not least) segment on the Business Model Canvas is the cost structures. In this segment, you must ask yourself, how much will

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Key Partners
No man is an island; the same goes for your business. They are other companies, 3rd parties, and people that you will need to achieve

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Key Resources
On the Business Model Canvas, the Key Resources segment refers to the supplies, assets, and materials required to deliver your value proposition to your customer
Privacy Overview
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is a business model canvas? Overview with template

In 2013, I co-founded a startup in the Indian online gifting industry with three friends. It was my first involvement with a startup. Startups are fascinating — they’re small, agile, and quick. However, another key feature of startups is their ability to creatively solve problems.

At that time, we aimed to target India’s gifting market, which was more than 90 percent offline. We had plans to establish an online shop selling a wide variety of gifts. But before we got started, we decided to document our idea. Amidst many templates, we discovered the business model canvas, a lean tool for outlining business models. It was neat, straightforward, and free. This tool brought remarkable clarity to our idea.
Despite shutting down the startup in 2015, I gained a wealth of knowledge during those two years. One major takeaway was the tools and techniques I learned along the way. The business model canvas was one of them. Even after seven years, I still use the business model canvas in my role as a product manager.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how product managers and entrepreneurs can effectively use a business model canvas.
What is a business model canvas?
The business model canvas is a template introduced by Alexander Osterwalder in 2005 as part of his Ph.D. studies under the supervision of Yves Pigneur. The business model canvas outlines nine crucial elements of a business model in an easy-to-understand visual template: customer segments, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partnerships, and cost structure.
Various companies, including startups, scale-ups, and large software organizations, have utilized this template since its inception to simplify their business strategy and improve their understanding of the overall business structure. However, before we delve into what a business model canvas entails, it’s important to comprehend why simplifying business strategy and structure is essential.
The last company I was part of employed 10,000 individuals. It ran more than 20 different businesses, each generating millions in revenue. When operating on such a large scale, it’s vital to have a clear strategy that outlines the business models. This strategy should define who the customers are, identify key partners, elaborate on the value proposition, and explain the cost structure, among other things.
The strategic blueprint serves as a go-to source of information whenever confusion arises. While this is true for large corporations, it’s equally applicable to smaller scale-ups and startups. It’s crucial to understand the business strategy and models from the onset. This comprehension aids in crafting a framework that can be applied when tackling complex issues or determining priorities.
This is where the business model canvas proves invaluable. It assists in laying out business models in a straightforward, user-friendly format.
What are the 9 components of the business model canvas?
The business model canvas comprises nine key elements:
Customer segments
Value proposition, customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partnerships, cost structure.
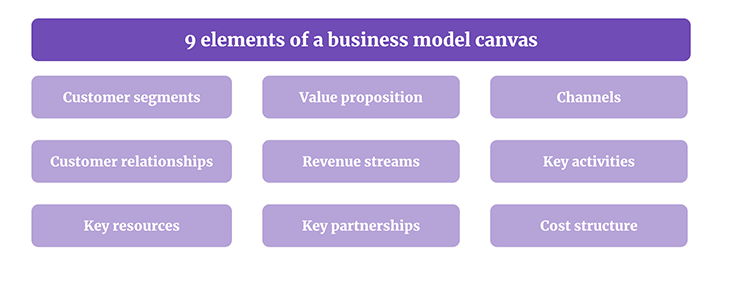
These components cover the three main areas of a business: desirability, viability, and feasibility. The nine components also aim to bring transparency and understanding to a broad audience, which can include upper management and internal teams such as engineering, design, product management, marketing, sales, legal, and customer service.
Collectively, these elements capture the essence of a business model. They help map the relationship between these elements and how they intertwine with one another. Let’s take a more in-depth look at each element.
Everything starts with the customers, which is why this is the first element of the business model canvas. This component identifies the different customer segments a company targets. These can vary across business models.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
For example, while working at Zalando (one of Europe’s largest fashion eCommerce companies), there were multiple business models. One focused on end customers, while another focused on partners selling products on Zalando. The business model canvas helps outline these customer segments in a single snapshot.
Try to avoid being too detailed. Mention who the partners are, but there’s no need to note the demographics, age, gender, etc., of the customer segment unless required.
This term refers to the unique advantage or value a business provides. It’s what sets the business apart from competitors. This could be a product or a service that the business uses to solve a customer’s problem.
For instance, Uber’s value proposition is its ability to help customers travel from point A to point B on demand.
Channels are the various ways through which a business intends to interact with customers and/or partners. For Airbnb, their website and apps are the primary channels. But they also leverage social media, offline hoardings, email marketing, and community forums to reach their audience.
This element addresses the various ways a business interacts with customers to improve satisfaction and the overall experience. Monitoring customer feedback and how they interact with a company’s product is critical in a competitive landscape.
Amazon, a company that prioritizes customer focus, includes 24/7 customer support, personalized recommendations, regular newsletters, ratings and reviews, Amazon Prime membership, and community engagement as part of its customer relationships.
This component lists the different ways a company plans to generate revenue. For Google, revenue streams include advertising, the Google Play Store, Google Cloud, and hardware sales.
This section includes all necessary activities needed to keep the business functioning smoothly and to deliver value to all users. Microsoft’s key activities, for example, include software development, hardware development, cloud computing, gaming, research and development, and VR.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
As the name implies, key resources are the essential tangible and intangible resources needed to keep the business operational. These resources incur costs, making their documentation vital. An online gift-selling company would require a website/app, collaborations with manufacturers, and marketing capabilities.
This element focuses on the partnerships or collaborations a business might have with other companies to better serve customers, reduce risks, and increase profits. For Facebook, key partners include regular users who generate content, advertisers, and influencers who create content at scale.
This element outlines the costs and expenses associated with a business. For companies like Google and Facebook, costs can be substantial given their value propositions. While it may be difficult to capture the cost structure of these giants in a small space, it becomes easier and beneficial for smaller companies.
For example, McDonald’s cost structure would include manufacturing costs, service-based costs (such as employee costs), franchise costs, and infrastructure costs.

What are the benefits of using a business model canvas?
Indeed, using a business model canvas offers many advantages for businesses of all sizes. To summarize, some of the key benefits include:
Visual representation
A business model canvas provides a visual overview of all the critical elements of a business. This allows stakeholders to see how these elements relate to each other, facilitating understanding and decision-making.
The visual nature of the canvas makes it accessible to various stakeholders, including top management, engineers, designers, customer service, and operations teams.
Clear collaboration, communication, and alignment
Developing and managing products often require the input and collaboration of multiple stakeholders . A business model canvas provides a clear, concise tool for aligning all these parties, promoting better communication and collaboration. It also helps product managers secure buy-in from stakeholders at an early stage, reducing risks and fostering better alignment, especially in a cross-functional environment.
Strategic long-term thinking and analysis
By design, a business model canvas encourages long-term strategic thinking. It helps identify business strengths and weaknesses, facilitates brainstorming new ideas and improvements, and shapes long-term strategies to better serve customers.
Flexibility
Businesses and ideas evolve, and a business model canvas accommodates these changes. It offers a flexible template that can be easily modified, often featuring version numbers to track document evolution. This flexibility supports an iterative approach, ensuring the canvas captures all necessary information as the business evolves.
Business model canvas template
The internet is replete with various business model templates. A quick Google search will return 34,200,000 results. Here’s a quick template that I created on Google Sheets:
Click here to access the business model canvas template. You can click File > Make a copy to download the canvas and customize it for your business.
Example of successful use of the business model canvas in product management
Here’s an example of a business model canvas for Facebook:
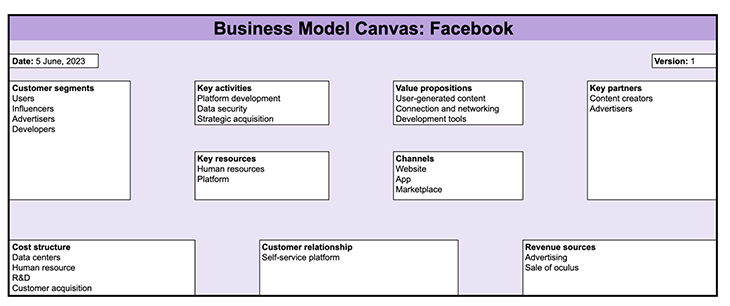
How do I create a business model canvas for my business?
After you fill out the nine components we went over earlier, there are some other key points to keep in mind to successfully create a business canvas model.
Involve all the stakeholders early on
Since a business model canvas has elements ranging from tech to marketing, sales, and customer service, it’s important to involve these stakeholders right at the start. This reduces the risk and helps to bring everyone on the same page.
Keep it simple
Don’t use complex sentences while explaining the pointers under every element. Use simple and short words. Simplicity will make it easier for the audience to consume the information effectively.
Be data-driven
Let every pointer included in the business model canvas be data-driven. This will help lay down a strong foundation for long-term decision-making.
Focus on an iterative approach
It’s difficult to come up with a business model canvas right at the first go. Hence, it’s important to keep an iterative approach and let the document evolve depending on the feedback from the contributors. You can use versioning to keep track of all the changes.
Consider external factors
Currently, the growth of many businesses is slow and it’s projected to be the same for the entire year. It’s important to consider these external factors while coming up with a business model canvas since it helps to consider factors that might not be in control of a business.
Conclusion and key takeaways
A business model canvas can be a very effective tool if used right away. Product managers can use this tool before starting a product or a feature. It can help them have clarity on the idea before the actual development work starts.
Also, since it involves all the major stakeholders right at the start, a business model canvas can help mitigate risks early on. It’s a great tool for validating business ideas, products, or a feature.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #tools and resources

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Drive growth with these 7 customer feedback tools
A customer feedback tool is a software solution or platform designed to collect, analyze, and manage feedback from customers.

Leader Spotlight: Motivating teams to hit customer-centric outcomes, with Kristina Bailey
Kristina Bailey discusses the careful balance of knowing the business outcomes you want to achieve while balancing customer outcomes.

Exploring augmented products: Beyond the core offering
Augmented products leverage technology and additional services to provide enhanced functionality, convenience, and value to users.

A guide to acceptance test-driven development (ATDD)
ATDD is an agile methodology involving collaboration to define acceptance criteria before starting any development.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Business Model Canvas (BMC)

What is the Business Model Canvas
Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a framework that helps determine how a business creates, delivers, and captures values. It is a visual representation of the important aspects or parts to consider when designing a Business Model.
BMC aids in constructing a shared understanding of a business by condensing it into a simple, relevant, and intuitively understandable one-page visual while not oversimplifying the complexities of how enterprises function.
This concept has been applied and tested around the world and is used in organizations such as GE, P&G, Nestlé, IBM, Ericsson, and Deloitte, including Government Services of Canada and many more [1],[2] .
The Nine Building Blocks
BMC describes a business through nine basic building blocks that show the logic of how a business intends to make money. These nine blocks cover the four main areas of a business: Customers, Offer, Infrastructure, and Financial Viability.
BMC acts as a shared language for describing, visualizing, assessing, and changing business models. It is like a blueprint for a strategy to be implemented through organizational structures, processes, and systems.
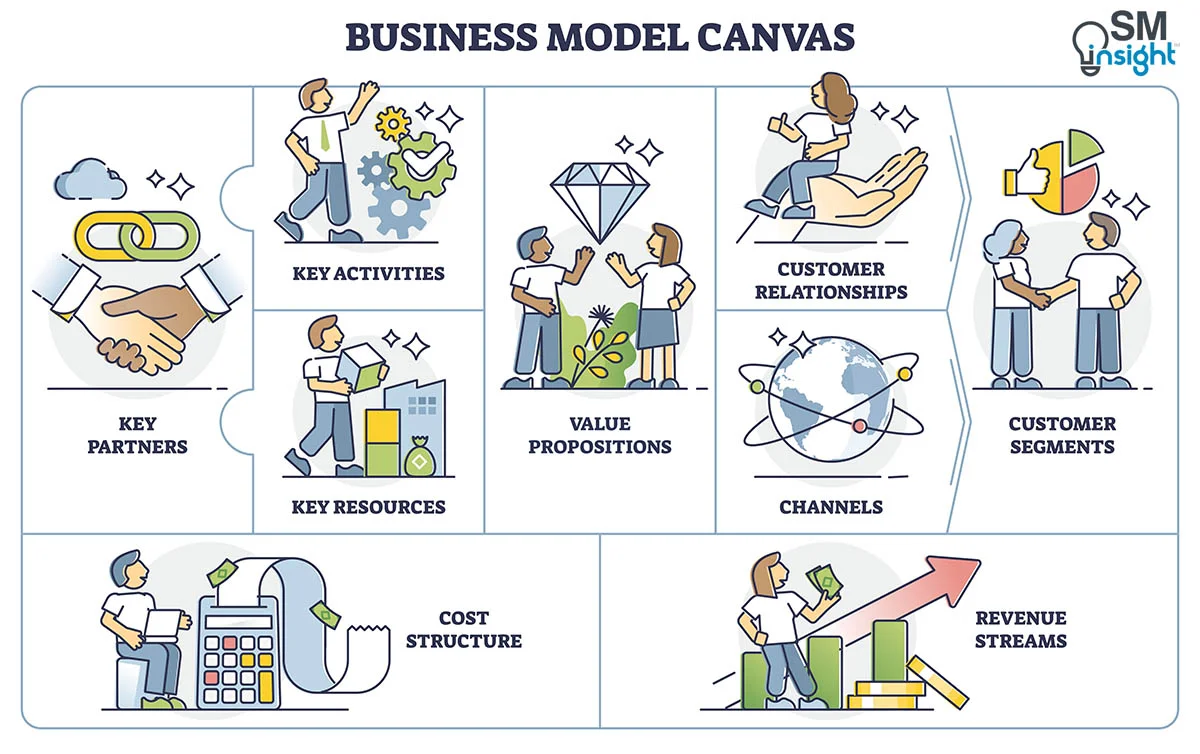
Each of these blocks is explained in more detail as follows:
1. Customer Segments (CS)
These are the groups of people or organizations that a business aims to reach and serve. Customers are the heart of a business model, and without (profitable) customers, a business cannot survive.
Customers are grouped into distinct segments with common needs, common behaviors, or other attributes. Customer groups represent separate segments if:
- Their needs require and justify a distinct offer.
- They are reached through different Distribution Channels.
- They require different types of relationships.
- They have substantially different profitability.
- They are willing to pay for different aspects of the offer.
An organization must make a conscious decision about which segment(s) to serve and which segments to ignore. Once this decision is made, a business model can be carefully designed around a strong understanding of specific customer needs.
The following two questions, if answered with clarity, help a business identify its CS.
- For whom are we creating value?
- Who are our most important customers?
- What are the customer archetypes?
Examples of some of the Customer Segments are shown in the figure:
2. Value proposition (VP)
Value Proposition describes the bundle of products and services that create value for a specific Customer Segment chosen by a business.
A VP is the reason why customers turn to one company over another. VP must solve a customer’s problem or satisfy a need. A business can have more than one VP, but each must consist of a selected bundle of products and/or services that caters to the requirements of a specific Customer Segment.
While some VPs may be innovative and represent a new or disruptive offer, others may be similar to existing market offers but with added features and attributes.
An organization’s VP must answer the following questions with clarity:
- What value do we deliver to the customer?
- Which one of our customer’s problems are we helping to solve?
- Which customer needs are we satisfying?
- What bundles of products and services are we offering to each CS?
Elements from some of the following can contribute to customer value creation:
3. Channels (CH)
Channels describe how a company communicates with and reaches its Customer Segments to deliver a Value Proposition.
Channels are customer touch points that play an important role in the customer experience and serve several functions, including:
- Raising awareness about a company’s products and services
- Helping customers evaluate a company’s Value Proposition
- Allowing customers to purchase specific products and services
- Delivering a Value Proposition to customers
- Providing post-purchase customer support
To establish an effective channel, a company must first answer the following:
- Through which Channels do our Customer Segments want to be reached?
- How are we reaching them now?
- How are our Channels integrated?
- Which ones work best?
- Which ones are most cost-efficient?
- How are we integrating them with customer routines?
There are five distinct phases (figure below) through which a channel passes, and it could cover more than one of these phases at a time.
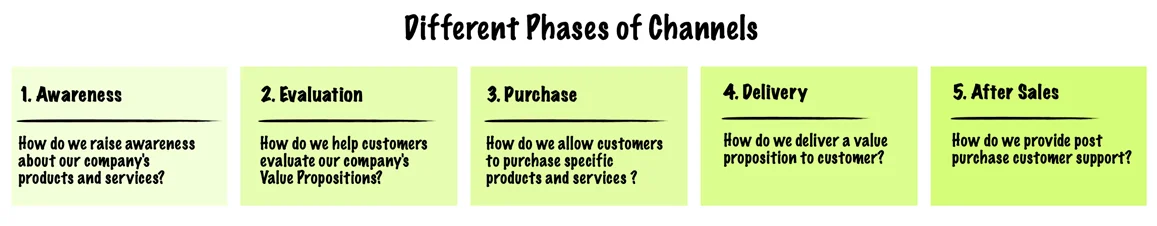
Channels can be either direct, indirect or hybrid, as shown:
Finding the right mix of Channels to satisfy how customers want to be reached is crucial in bringing a Value Proposition to market and can create a great customer experience.
4. Customer Relationships (CR)
Customer Relationships describe the types of relationships a company establishes with specific Customer Segments. Relationships can range from personal to automated. An organization’s CR strategy may be driven by one of the following motivators:
- Customer acquisition
- Customer retention
- Boosting sales (upselling)
A business can arrive at the optimum CR by asking the following questions:
- What type of relationship does each of our Customer Segments expect us to establish and maintain with them?
- Which ones have we established?
- How costly are they?
- How are they integrated with the rest of our business model?
Several categories of Customer Relationships may co-exist in a company’s relationship with a particular Customer Segment. Some of which are:
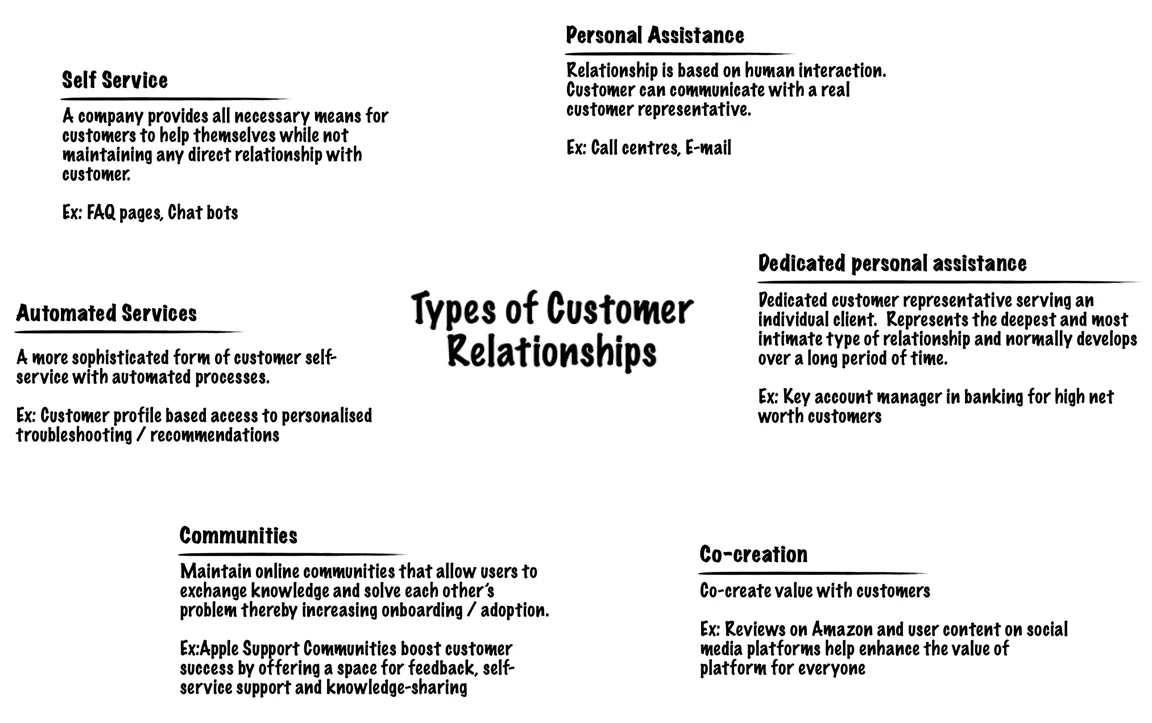
5. Revenue Streams (RS)
Revenue Streams represent the company’s cash (earnings) from each Customer Segment and are like the arteries of any business.
There are two distinct categories of Revenue Streams:
- Transaction Revenues which are one-time customer payments
- Recurring Revenues that are ongoing payments to either deliver a Value Proposition to customers or provide post-purchase customer support
A business can arrive at its ideal revenue stream by asking the following questions:
- For what value are our customers willing to pay?
- For what do they currently pay?
- How are they currently paying?
- How would they prefer to pay?
- How much does each Revenue Stream contribute to overall revenues?
There are several ways a business can generate revenue, such as:
A business may have one or more Revenue Streams, each with different pricing mechanisms. The choice of pricing mechanism greatly influences the revenues generated.
There are two main types of pricing mechanisms, Fixed and Dynamic, as follows:
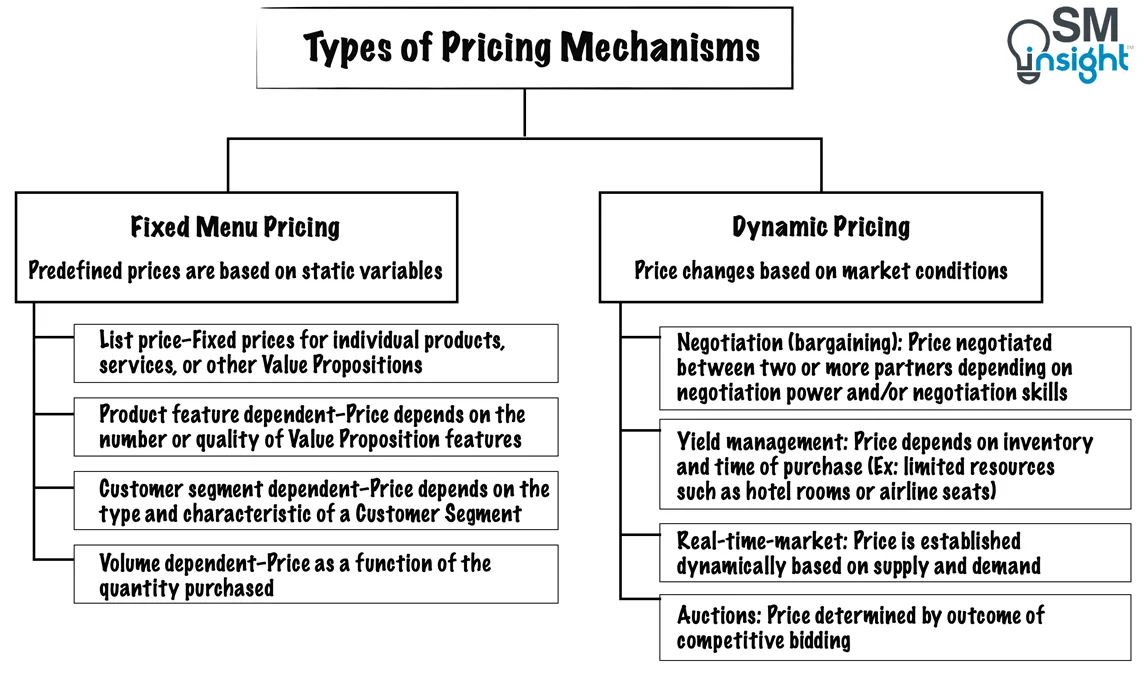
6. Key Resources (KR)
The Key Resources describe the most important assets required to make a business model work.
These resources allow an enterprise to create and offer a Value Proposition, reach markets, maintain relationships with Customer Segments, and earn revenues. Different Key Resources are needed depending on the type of business model.
For example, a chip fabrication business like TSMC [9] requires capital-intensive facilities worth billions of dollars, while a chip designer like NVIDIA [10] would need skilled manpower as its Key Resource.
Key Resources can be owned or leased by a business or acquired from its key partners. They can be identified by answering the following questions:
- What Key Resources do our Value Propositions require?
- What resources are required to sustain our Distribution Channels, Customer Relationships and Revenue Streams?
Key Resources can be categorized as follows:
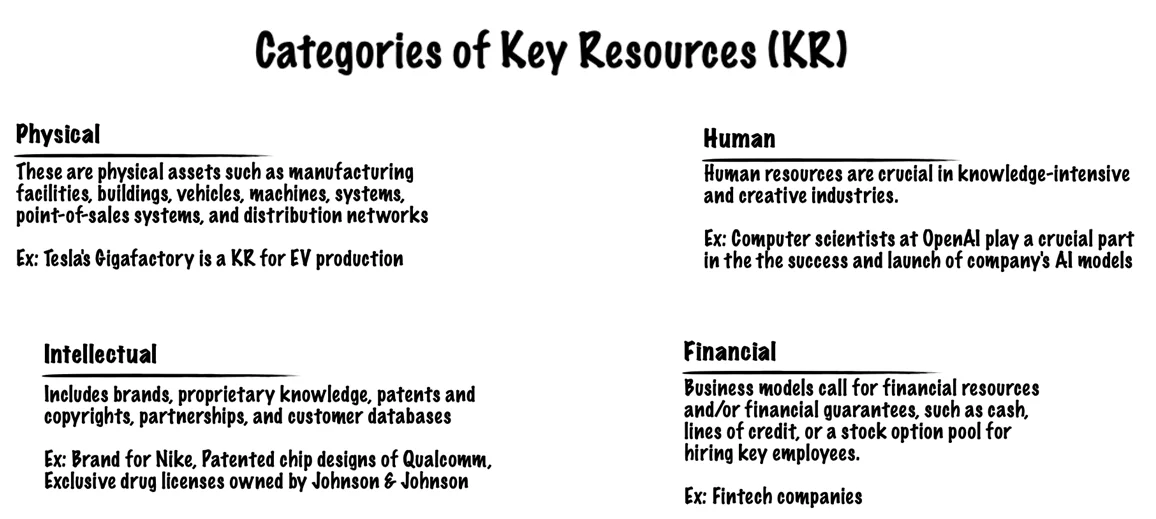
7. Key Activities (KA)
Key Activities describe the most important things a company must do to make its business model work. They are required to create and offer a Value Proposition, reach markets, maintain Customer Relationships, and earn revenues.
Key Activities differ depending on the business model type. For example, Microsoft’s Key Activity is software development, while for Dell, it is Supply Chain Management. For a consultancy firm like McKinsey, Key Activity is problem-solving.
A business can identify its Key Activities by answering the following questions:
- What Key Activities do our Value Propositions require?
- What activities directly contribute to maintaining our Distribution Channels, Customer Relationships and Revenue Streams?
Key Activities can be categorized as follows:
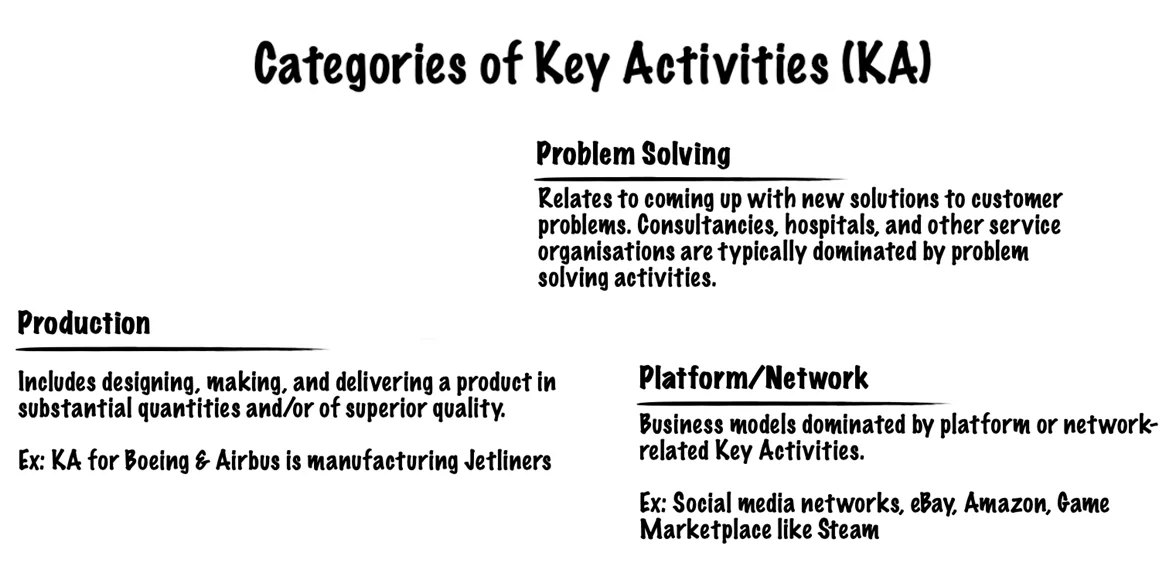
8. Key Partnerships (KP)
The Key Partnerships describe the network of suppliers and partners that make the business model. There are four types of partnerships:
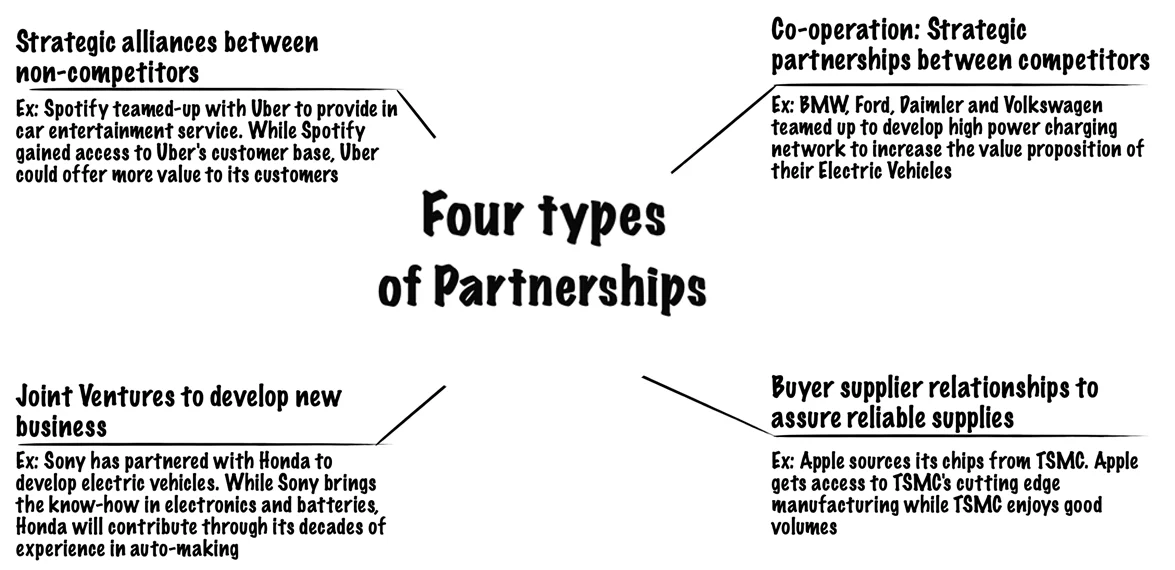
A business must ask the following questions before forming partnerships:
- Who are our key partners?
- Who are our key suppliers?
- Which Key Resources are we acquiring from partners?
- Which Key Activities do partners perform?
Primarily, there are three motivations for a business when creating partnerships, as shown:
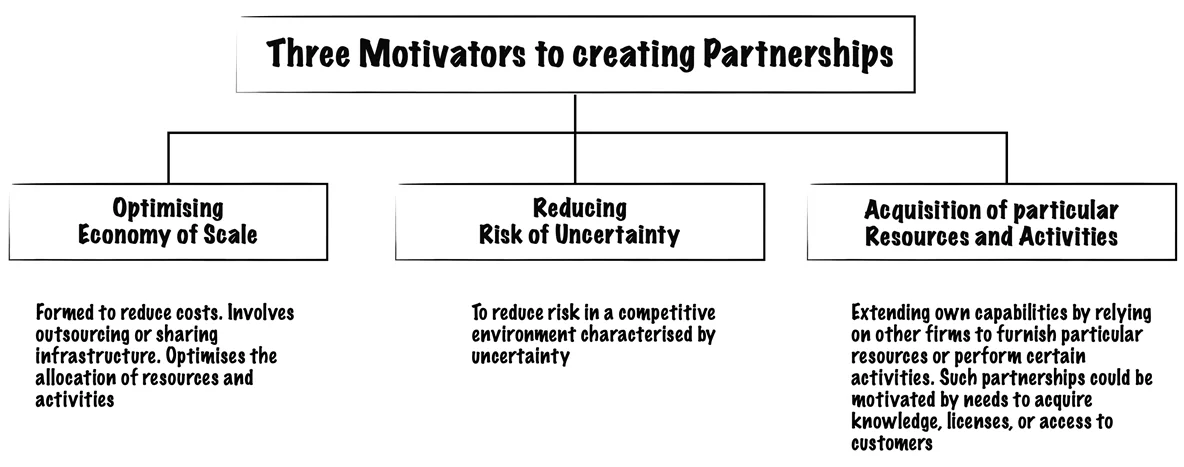
9. Cost Structure (CS)
Cost Structure describes all costs incurred to operate a business model. A business incurs costs in creating and delivering value, maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue. Costs are business-specific, where some are more cost-driven than others.
A business must answer the following questions to arrive at an optimum cost structure:
- What are the most important costs inherent in our business model?
- Which Key Resources are most expensive?
- Which Key Activities are most expensive?
While costs should be minimized in every business model, it is useful to distinguish between two broad classes of business model Cost Structures:
- Cost Driven : This model focuses on minimizing costs wherever possible. This approach aims at creating and maintaining the leanest possible Cost Structure, using low-price Value Propositions, maximum automation, and extensive outsourcing. Examples: No frills airlines like Southwest & easyJet, Fast food joints such as McDonald’s & KFC.
- Value Driven: Premium Value Propositions and a high degree of personalized service usually characterize value-driven business models. Examples: Luxury hotels, Expensive Cars like Rolls-Royce
Cost Structures can have the following characteristics:
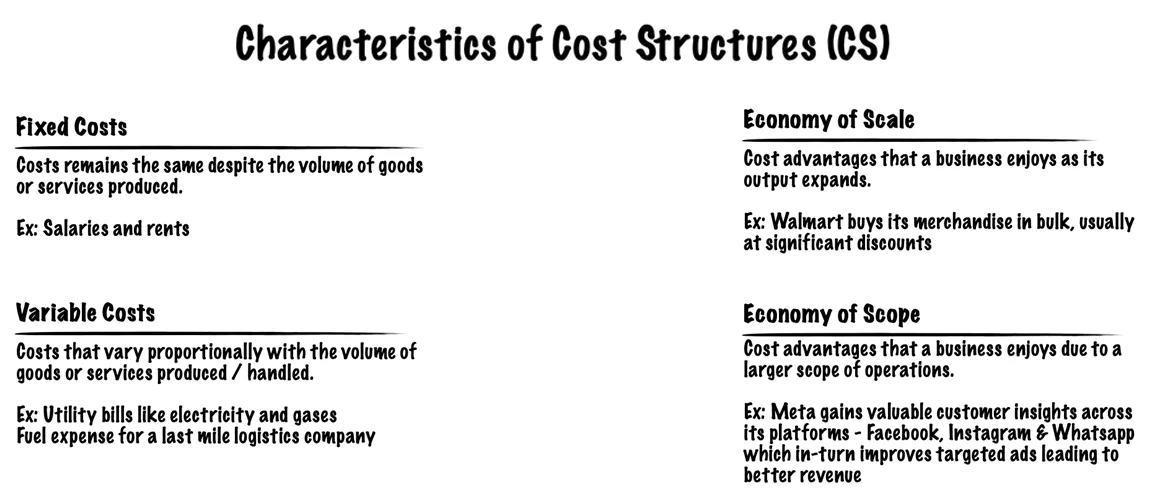
Putting-it-all together
The nine business model Building Blocks form the basis for a handy tool, which is called the Business Model Canvas (figure below). This tool resembles a painter’s canvas preformatted with nine blocks that allow painting pictures of new or existing business models. It is a hands-on tool that fosters understanding, discussion, creativity, and analysis.
BMC works best when printed out on a large surface such that groups of people can jointly note, sketch, and discuss business model elements.
Example of Business Model Canvas
Nespresso [17] , a fully owned daughter company of Nestlé, changed the dynamics of the coffee industry by turning a transactional business (selling coffee through retail) into one with recurring revenues (selling proprietary pods through direct channels).
The two-part strategy involved selling their patented coffee machine to retail customers first to lock them into the brand. This generated a recurring demand for coffee refills (pods) that led to constant revenues. These pods were sold directly through mail/website/own stores, thereby eliminating middlemen/dealers, which further increased profits [1] .
Nespresso’s strategy plotted on a Business Model Canvas looks as follows:
Business Model Canvas helped Nespresso establish a solid and enduring foundation by engaging consumers directly and bringing a barista-like experience within the reach of a home or an office.
Advantages & Limitations
- Encourages Collaboration – collaborative framework, which helps put different business stakeholders in sync. This improves the likelihood of generating new ideas and their quality.
- Facilitates testing of ideas before launch – allows business owners, strategists, and managers to think through business ideas as well as test concepts that would otherwise get tested with potential customers where the stakes are higher.
- Customer-centered approach – Key customer segments, relationships, activities, and value propositions are all elements that focus on creating, delivering, and capturing value for customers.
- Clarity – Analyzing the business through the lens of nine blocks brings better clarity and structure to the business model.
Limitations
- Lacks a section for defining the start-up’s mission statement, which is crucial to understanding the goals and objectives of any business.
- Overlooks the importance of a profit mechanism beyond costs and revenues, including decisions on how to use potential profits.
- The order of the canvas is not intuitive, making it difficult to read and understand the strategic decisions in a logical sequence.
- Does not depict interconnections between different elements, which can have a significant impact on the overall business model.
- Fails to acknowledge the company’s role within its ecosystem, including its impact on the environment and local communities.
- External factors such as competition, history, and other industry-specific factors are absent from the canvas, which can greatly influence the success of a business model.
1. “A Better Way to Think About Your Business Model”. Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/2013/05/a-better-way-to-think-about-yo . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
2. “Business Model Generation”. Alexander Osterwalder, https://www.strategyzer.com/books/business-model-generation . Accessed 28 Jul 2023
3. “The Apple M1 is a revolution that is changing the computing world”. Citymagazine, https://citymagazine.si/en/apple-m1-is-a-revolution-that-changes-the-computer-world/ . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
4. “Mass Customization”. Corporate Finance Institute, https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/management/mass-customization/ . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
5. “Moka Pot”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moka_pot . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
6. “NetJets Homepage”. NetJets, https://www.netjets.com/en-us/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
7. “Distribution Channels – Definition, Types, & Functions”. Feedough, https://www.feedough.com/distribution-channels-definition-types-functions/ . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
8. “Lease from Hertz”. Hertz, https://www.hertz.com/rentacar/rental-car/car-lease . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
9. “TSMC”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TSMC . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
10. “NVIDIA”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nvidia . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
11. “BMW, Daimler, Ford and Volkswagen team up on high-power charging network”. Techcrunch, https://techcrunch.com/2017/11/03/bmw-daimler-ford-and-volkswagen-team-up-on-high-power-charging-network/ . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
12. “Honda And Sony Combine Talents To Build Electric Vehicles”. Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/peterlyon/2022/06/26/honda-and-sony-announce-joint-venture-to-build-electric-vehicles/ . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
13. “Uber and Spotify launch car music playlist partnership”. BBC, https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-30080974 . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
14. “Walmart Has the Scale and Infrastructure to Generate Positive Gains”. Yahoo Finance, https://finance.yahoo.com/news/walmart-scale-infrastructure-generate-positive-201822628.html . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
15. “Demand-Side Economies of Scope in Big Tech Business Modelling and Strategy”. MDPI, https://www.mdpi.com/2079-8954/10/6/246 . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
16. “The Business Model Canvas”. Strategyzer, https://www.strategyzer.com/canvas/business-model-canvas . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
17. “HomePage”. Nespresso, https://www.nespresso.com/us/en/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
18. “Business Model Canvas of Nespresso”. Alex Osterwalder, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dhQh-tryXOg . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
19. “Nespresso Capsule”. Electromall, https://electromall.net/product/nespresso-capsule/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
20. “The Best Nespresso Machine (But It’s Not for Everyone)”. Newyork Times, https://www.nytimes.com/wirecutter/reviews/best-nespresso-machine/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
21. “Business Model Canvas”. Think Design, https://think.design/user-design-research/business-model-canvas/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
22. “6 Problems with the Business Model Canvas”. The Pourquoi Pas, https://www.thepourquoipas.com/post/problems-with-the-business-model-canvas . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
- McKinsey 7S Model
- Elaboration Likelihood Model of Persuasion
- The Johari Window Model
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.

Facebook’s Business Model: Unlocking Financial Success
Facebook, the world’s most popular social networking website, boasts approximately 1.13 billion daily active users and generated a staggering revenue of 27.63 billion in 2016. Furthermore, Instagram, the second most beloved social media network globally, is also under the ownership of the company.
In the face of intense competition, Facebook’s ability to maintain its dominant position and consistently increase its revenue year after year is truly remarkable.
While its primary competitor, Google Plus, failed to come close to Facebook’s success, it is worthwhile to examine the Facebook Business Model.
Before delving into how Facebook generates its revenue and its Revenue Model, let us first explore the companies that fall under the Facebook umbrella and its overarching business strategy.
Unveiling the Journey: A Concise History of Facebook
The facebook family of companies, meta’s business ventures, ownership of facebook, how does meta make money, facebook’s business strategy, understanding facebook’s expense sources, facebook’s business model, facebook’s competitors in the social media landscape, facebook’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Facebook’s evolution began in 2003 when Harvard students Mark Zuckerberg, Eduardo Saverin, Dustin Moskovitz, and Chris Hughes created Facemash, an appearance-based judgment platform. It faced a quick shutdown due to policy violations.
In January of the following year, they introduced thefacebok.com, a social network exclusively for Harvard students. It expanded to other universities, reaching over one million users by the end of 2004.
In 2005, it dropped the “the” and became Facebook, attracting high schoolers and international students, and boosting its user count to six million. Over the years, Facebook opened its doors to anyone above 13, surpassing MySpace in 2008 to become the leading social network.
In 2012, it became a public company, raising $16 billion in its IPO and achieving a valuation of $102.4 billion.
The Facebook business model encompasses a range of diverse companies:
- Facebook: A leading social media platform enabling users to connect, communicate, and share with friends, family, and like-minded individuals. Facebook generates its primary revenue through advertising, leveraging its wide user base and various features like Groups, Watch, and Marketplace;
- Instagram: A popular photo and video-sharing application where individuals and businesses worldwide can showcase their content. Meta monetizes Instagram through advertising, capitalizing on its users’ engagement and their inclination to discover and purchase products;
- Messenger and WhatsApp: Messenger serves as an instant messaging application that connects users across the Facebook and Instagram platforms, facilitating communication with friends, family, groups, and businesses. WhatsApp, on the other hand, is a widely used messaging application offering secure and simple communication for individuals and businesses globally. Both apps provide Meta with opportunities for monetization, including advertising and premium features that enhance customer support;
- Reality Labs: Meta’s Reality Labs is dedicated to developing augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) hardware, software, and content. AR/VR technologies are instrumental in Meta’s vision of creating the metaverse, a virtual world. Reality Labs offers Oculus virtual reality headsets for consumers and a marketplace where users can access and purchase apps and games for these devices. Additionally, Meta Portal provides dedicated devices for video calling, catering to the needs of consumers seeking enhanced collaboration and connections with friends and family.
Since its inception, Facebook has been owned by Mark Zuckerberg through his holding group, Facebook Inc. However, following the acquisition of Instagram and WhatsApp, Zuckerberg made the strategic decision to rebrand the holding group, separating the Facebook social network from the larger entity.
In October 2021, Facebook Inc. was renamed Meta Inc., with Mark Zuckerberg serving as its CEO and retaining ownership of all the companies within the group.
Facebook (the platform and apps) are free to users. So how does the company make any money at all? As noted above, its primary source of revenue is through digital advertising.
Due to the enormous number of users and social media reach, advertisers large and small consider Meta a prime opportunity to present ads to viewers. Meta provides various ways for them to advertise, such as self-serve and targeted ads.
Marketers can target specific types of people based on different factors such as age, gender, location, interests, and behaviors. They buy ads that are placed on various Meta social media platforms and apps, including Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp. Ads also appear on affiliated third-party applications and websites.
Ad prices are determined by an auction system based on bids and performance. Businesses are charged only for the number of clicks ads receive or the number of impressions (the number of times the ad is displayed).
A business that wants to run an advertisement sets a maximum budget and is charged a monthly billing based on the performance of the ad. While advertising provides Meta with the majority of its revenue, it’s not the company’s sole income focus.
In fact, by changing its name from Facebook to Meta Platforms, Meta signaled its plan to develop sources of revenue beyond advertising. Its Reality Labs is one such source.
Facebook’s business strategy revolves around expanding its user base and using targeted ads for revenue. It launched initiatives like internet.org to provide affordable or free internet access to unconnected populations. Acquisitions, such as Snaptu and Onavo, helped improve device compatibility and enhance user experiences.
Once users have access to Facebook, the focus shifts to monetization. Facebook successfully increased average revenue per user (ARPU) in the “Rest Of World” region, with a significant rise in ARPU from $0.28 in 2012 to $1.13 in Q2’16.
Increased daily usage time and ad impressions on Facebook, Instagram, and Messenger contribute to its substantial revenue generation and ongoing financial success.
To comprehend how Facebook generates revenue, we must also consider its various expenses. Over the years, the company has witnessed a substantial increase in its yearly expenditures, which encompass the following key categories:
- Cost of Revenue:
This includes expenses associated with the infrastructure that supports Facebook’s operations. It encompasses factors such as facility and server equipment costs, depreciation, energy, and bandwidth expenses, as well as support and maintenance expenditures.
- Research & Development:
Despite being the world’s leading social media network, Facebook faces competition and aims to sustain its position at the forefront. To achieve this, the company invests significantly in research and development.
R&D plays a critical role in enhancing user experience and continually improving and expanding Facebook’s offerings.
- Marketing and Sales Costs:
As a prominent global brand, Facebook incurs substantial expenses to maintain its market position. Marketing and sales costs encompass efforts to improve user interfaces and services, attract and retain users, support marketers and developers, and invest in product promotion.
These costs include amortization of intangible assets, payroll expenses, and other marketing and sales-related expenditures.
- General and Administrative:
General and administrative expenses cover compensation for administrative department employees, legal and accounting expenses, and other administrative costs associated with running the company.
Facebook’s Customer Segments:
- Users: Representing one-third of the world’s population, users form the largest customer segment of Facebook. They engage with friends and others, share content, and access entertainment and information. While users do not directly generate revenue for Facebook, their presence is vital in attracting advertisers;
- Businesses and advertisers: This segment contributes to Facebook’s revenue through advertising. Brands and businesses leverage Facebook’s targeted advertising capabilities to reach a qualified audience based on user data collected by the platform;
- Developers: The smallest customer segment comprises developers who create apps and games using Facebook’s platform.
Facebook’s Value Propositions:
- Users: Facebook allows users to connect and stay in touch with loved ones, offering entertainment, information, and a platform for sharing experiences and interests;
- Advertisers: Facebook provides targeted advertising options, allowing brands to reach their specific target audience effectively. The user-friendly advertising tools cater to both small businesses and larger enterprises;
- Developers: Facebook offers a robust platform for developing apps and games, providing exposure and a network of advertising service providers.
Facebook’s Channels:
- Facebook’s primary distribution channels are its website and app, where users connect and advertisers engage with their audience. The platform offers various channels, including feed, notifications, direct messages, stories, and integration with other products such as Instagram and WhatsApp.
Facebook’s Key Activities:
- Key activities include platform development and maintenance to ensure a positive user experience, infrastructure management, content moderation, user acquisition and engagement, data storage and security, talent acquisition, sales and marketing efforts, and fostering good practices within the network.
Facebook’s Key Partners:
- Content developers: Collaborating with developers for videos, games, and other content;
- Operating system, browser, and hardware developers: Working with partners to ensure compatibility and optimal performance;
- Digital influencers: Partnering with influential individuals who promote engagement on the platform;
- Businesses and brands: Collaborating with advertisers and companies that advertise or sell directly on Facebook;
- Marketing agencies: Working alongside agencies to facilitate advertising campaigns.
Facebook’s Cost Structure:
- Facebook’s cost structure includes platform maintenance, data storage, user acquisition costs, research and development investments, marketing and advertising expenses, customer support, general and administrative costs, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
In the dynamic world of social media, the company faces competition from various platforms and apps. Let’s delve into some of Facebook’s key competitors:
- Strong Brand: Despite its current ranking at 13th, Facebook remains a highly valuable brand, valued at over $35 billion;
- Diversified Portfolio: Acquisitions such as WhatsApp, Instagram, Messenger, and Oculus contribute to Facebook’s financial strength and diversify its offerings;
- Market Dominance: Facebook, along with its subsidiaries WhatsApp, Messenger, and Instagram, holds a significant market share in the social media industry;
- Loyal Customer Base: With approximately 30% of the world’s population using Facebook’s platforms, the company enjoys a vast and dedicated user base;
- Attractive Employer: Facebook’s HR policies position it as one of the top employers globally, allowing it to attract and retain top talent;
- Visionary Leadership: Mark Zuckerberg’s leadership provides stability, sustainability, and innovation for the business;
- Research and Development: Facebook invests a significant portion of its revenue in R&D, positioning itself as a leader in innovation;
- Effective Marketing Strategy: Facebook’s wide user base and targeted advertising capabilities contribute to its revenue generation.
Weaknesses:
- Privacy Concerns: Facebook’s reputation has suffered due to privacy issues and inadequate data protection measures;
- Overdependence on Advertising: The company heavily relies on social media and advertising for its revenue, limiting diversification opportunities;
- Fake News: Facebook faces criticism for its struggle to control the spread of misleading information.
Opportunities:
- Portfolio Diversification: Facebook can leverage its resources to expand into new industries and reduce dependence on social media and advertising;
- Integration with Other Applications: Opportunities exist for Facebook to integrate with various applications, such as e-commerce, podcasts, and gaming;
- Targeting Different Audiences: By introducing new features, Facebook can attract additional target segments beyond its current user base;
- Acquisitions: Facebook has the potential to continue acquiring companies, even outside the social media industry.
- Competition: Declining user numbers and the emergence of new platforms pose a threat to Facebook’s market share;
- Regulatory Challenges: Evolving regulations surrounding data safety, user privacy, and intellectual property may impact Facebook’s business model;
- Data Breaches: Security breaches and exposure of personal information can damage user trust and reputation;
- Digital Taxation: The adoption of digital taxes, such as in the UK and European Union, could negatively impact Facebook’s profits;
- Reputation Damage: Scandals, fake news, and other controversies have tarnished Facebook’s reputation and could lead to reduced usage.
Facebook’s business model has transformed online connectivity and content consumption, solidifying its dominance in the social media industry through platforms like Instagram, WhatsApp, and Oculus. Its primary revenue stream relies on targeted digital advertising to capitalize on its vast user base.
Despite privacy concerns and competition, Facebook thrives by fostering a strong brand, cultivating a loyal customer base, embracing visionary leadership, and investing in research and development.
By diversifying its portfolio and venturing beyond social media, the company aims to adapt to evolving market trends and explore new opportunities for growth and innovation.
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
How to Create a Business Model Canvas (With Template)
May 19, 2021 - 10 min read
Do you want to create a simple business plan? Something comprehensive, flexible, and easy to scribble on a napkin? You can do that with a business model canvas.
Every business has ever-changing, diverse interests. Illustrating all of this on a single sheet of paper may sound challenging — but by using a business model canvas template, your team can focus on the key elements of your business to ensure nothing slips through the cracks.
Business model canvas explained
"Lengthy business plans often increase the risk of failure," wrote Alex Osterwalder in his 2008 book “Business Model Generation.”
The business model canvas offers a way to avoid this, providing a simplified version of a business plan. A business model canvas is a simple, visual framework that helps teams outline the most fundamental elements of a business.
As a handy business tool, teams can use a business model canvas to map the nine core areas of a business, such as customer needs, value proposition, and platforms for customer acquisition.
This article will explain the business model canvas, its benefits, and how it can help your team develop a successful high-level business strategy and actionable roadmap .
How can a business model canvas help your business?
Many teams are so overwhelmed with operational issues that they don’t have time to focus on the core business strategy .
Utilizing the business model canvas helps create a unified framework that depicts this strategy alongside an action plan that teams can follow.
But how do you know if you need a business model canvas? If you are starting a business or even toying with an idea, a BMC can create a powerful visual representation of your concept. A business model canvas can also be a handy reference for your team as they move towards successful business outcomes. Here are five more ways in which a business model canvas can help your company.
It’s simple and easy to follow
Whether you have a business idea or are managing a large enterprise, having an easy-to-follow business plan can be immensely helpful. As a precise one-page document, teams can modify specific business model canvas elements as they go along without completely redoing a 50- or 100-page document.
Focused on being actionable
Every business plan needs to be actionable. Using a business model canvas helps you accurately define your organization’s core value proposition and keep it aligned to your business strategy.
Your focus could be to achieve profitability in the first year or gain a large market share. Stay competitive by defining actionable steps for your team within the business model canvas.
Flexible and scalable as the business evolves
No business stays the same forever but evolves as it interacts with diverse market dynamics, competitors, product innovations, and changing consumer needs.
To take your idea to market, you need a tool that connects the dots between what your customers want, your business's unique offering, and the desired profitability streams.
By creating a business model canvas template, you instantly get an edge over other market players engrossed in lengthy business plan documents.

Puts the customer first
Ignoring customers sets businesses up for failure . Companies flounder if they direct their energies solely towards making a great product or service. With a business model canvas template, your focus stays on the ultimate end-users of your product.
Having a business blueprint will force team members to think about what customers want, the primary issues they need help with, and how your product or service can do that.
Helps get team and executive buy-in
23% of businesses fail without the right team on their side. Every company needs team members with a diverse mix of skills, experiences, and talents.
Companies require a solid business blueprint for hiring team members or bringing in investors. Having a business model canvas can help get everyone on board with your organization’s core vision. Potential employees and investors can visualize how the different organizational parts interact and see how they can become an integral part of the company.
Promotes focus on the unique value proposition of your business
19% of companies fail due to being outperformed by their competitors. If there's no difference between your product and one from another firm, why should customers come to your company? Every business needs a clear value proposition that helps them stand out — that's where a business model canvas template comes in.
When you look at the nine core elements of a business model canvas (explained below), you'll quickly notice some factors are controllable to a certain extent, while others are more fractious.
Your company's core value proposition sits right in the middle. It acts as the central pillar around which all other elements exist, defining the fundamental nature of the business.
What goes into each segment?
To fill out a business model canvas, you should know what goes into each of the nine fundamental segments.
Have a business model canvas template ready before you and your team start brainstorming on each of these elements (you'll find one below) and then add the research and data into the relevant sections.
Customer segments In this fundamental business area, teams identify the core individuals they will help with their product or service. To do this, they create two to three buyer personas — potential customers that a business seeks to serve.
A buyer persona is a simple but detailed description of a prospective business customer. It assists with capturing the customer’s real-life problems and motivations, helping the business deliver what they want.
Value proposition The value proposition is the ultimate value that a customer will get from your product or service. It seeks to answer the question, “Why will a customer buy?” Here are a few popular value propositions for any organization:
- Customization ability
- Unique product design
- Innovation in product or service
- Exceptional service or product status
- Affordable pricing and clear pricing model definition
Channels In a business model canvas, channels are the platforms through which a company sells its product or service to end-users. To identify the best channel for your business, look at how you plan to connect with your customers.
A few possible channels can be:
- A self-owned retail store
- Direct sales staff
- Affiliate marketing platforms
- Google Adsense
A business can either own its channels or partner with other companies that have their own channels.
Customer relationships Customer relationships in a business model canvas define how the company will obtain, retain, and increase new customers. Let's take a look at how customer relationships are built:
- Identify how to obtain customers and from which platforms (e.g., Google, Facebook ads)
- Gain clarity on how to retain existing customers using different techniques (e.g., exceptional customer service)
- Discover how to increase the customer base of the business (e.g., sending text or email notifications to prompt website visits)
Revenue streams Revenue streams help the business owner decide how to generate revenue and achieve their predefined organizational goals . Key decisions with revenue streams include:
- Choosing from a one-time payment model or monthly subscriptions
- Keeping a free plus paid model or a wholly paid product or service with a free trial
- How payment from customers will be received — website payments, PayPal, or in-store
Key resources Key resources in your business model canvas represent the assets that are vital to your company’s operation. Business assets can include anything from the below categories:
- Physical assets , including machines, buildings, IT hardware, and vehicles
- Intellectual assets , including patents, copyrights, partnerships, brands, and employee skills
- Human assets , including talented employees in knowledge industries such as IT, law, and content marketing
- Financial assets , like cash balances in the bank or lines of credit
Key activities Want to make your business canvas model work? Make sure to list the key activities that will help expand the business's core value proposition. Key activities can come from any of the below categories:
- Production: How you will deliver your end product to the customers. You may need to order more stock or upgrade materials
- Platform: For example, the software used to sell your product, which may require upgrades or maintenance
- Problem-solving: For example, designing innovative solutions for issues that your customers face
Key partners Every business has some non-core activities that should preferably be outsourced. Key partners are the companies or individuals that complete these non-core activities.
Take a company like Facebook, for example — its key activity is to upgrade and maintain its platform. It doesn't create its own ads, so it also needs to strike deals with companies that wish to advertise on its platform.
Similarly, it doesn’t create its content — the users do. The primary reasons for choosing key partners can be:
- Achieving economies of scale
- Mitigating risk and unpredictability in business
- Acquiring resources and advertisements for its business (e.g., ads for Facebook)
Cost structure Once the key activities are outlined on the business model canvas, it's time to assign cost structures. Be clear and precise with the estimated business costs of the planned activities to ensure you reach your profitability goal.
Business model canvas example and template

- Customer segments: Facebook's customers can be divided into two distinct categories — advertisers and platform users
- Value proposition: The primary reasons platform users come to Facebook. Users feel connected to friends and families, while companies get more leads through advertising on the platform
- Channels: The website where all data is stored
- Customer relationships: Facebook incentivizes users to stay on the platform through notifications and new features, leading more companies to advertise on it
- Revenue streams: Facebook earns money through advertising, while companies gain new customers from Facebook ads
- Key resources: Facebook's key resources are its platforms — Facebook.com, the Messenger application, and Facebook Ads Manager for advertisers
- Key activities: Maintaining the website and its infrastructure are two of Facebook’s key strategic activities
- Key partnerships: Facebook's key partners are its users and advertisers
- Cost structures: Major costs incurred by Facebook include managing the software, backend engineering operations, product development, regular operations, and staff salaries
How to create a business model canvas (with template)
Ready to create your business model canvas? Before you begin, take some time to brainstorm answers to these questions related to the nine core fundamental areas of the canvas. Here's a simple business model canvas template exercise that can help your team get started.
- Customer segments: Can you identify your potential customers?
- Channels: Once the product or service is ready, how will customers discover it?
- Key partnerships: Can any non-core business activities be outsourced?
- Customer relationships: How will your business generate leads and retain and increase your customer base?
- Cost structures: Can the business classify its main costs and expenses into fixed and variable? Is there a way to align costs with the core value proposition and planned revenues?
- Revenue streams: Has the business decided on a profit margin? How will it make money?
- Key resources: Which core resources are critical for the business to succeed?
- Value proposition: Why will customers choose your business? Does the company satisfy any particular need with its product or service?
- Key activities: Are there any activities that help your business deliver its unique value proposition to customers?
Do I need a lean model canvas?
If your business is still an idea or in its infancy, choosing a lean model canvas makes more sense.
Inspired by the business model canvas, the lean model canvas was created by Ash Maurya . It is a one-page business plan template that distills the lean startup methodology into the original business model canvas.
Lean model canvas assimilates multiple essential data points to develop a simpler, start-up optimized version of a business model canvas. It adds four more building blocks to the business model canvas, namely:
- Problem: Identify the problem faced by the customer and focus on solving it
- Solution: Start with a minimum viable product that helps solve the customer problem effectively
- Unfair advantage: List the barriers to entry in a specific sector and your company’s competitive advantages
- Key metrics: Focus on one goal at one time to ensure you’re doing a good job
Lean model canvas drops four elements from the original business model canvas — key partners, key activities, key resources, and customer relationships.
While the original illustrates a more comprehensive business approach, the lean model canvas has a sharper customer orientation. Many start-ups prefer the lean model canvas to a traditional business plan for building an actionable roadmap.
The lean model canvas is a great fit for younger companies or those working with a tight time frame or budget to market with a more targeted problem resolution approach.
Why you should use Wrike to build a business model canvas
The business model canvas’ nine building blocks clearly illustrate the core business areas and their interrelationships. Whether you're trying to figure out the model for a company with three employees or 50,000, a business model canvas can be very useful.
Begin by mapping out the most crucial information about your business, then link the blocks to ensure every value proposition is linked to a revenue stream and a specific customer segment.
Using Wrike to build your business model canvas template, you can iterate faster, communicate with ease, and enable organization-wide success . With a centralized hub, your teams can configure custom dashboards easily and produce better quality work using premade templates . Implement what you've learned about the business model canvas by trying out a free two-week trial of Wrike today.

Yuvika Iyer
Yuvika is a freelance writer who specializes in recruitment and resume writing.
Related articles

What Is Business Process Outsourcing? A Guide
As businesses scale and grow, they often have requirements that cannot be addressed internally — whether because of resource or budgetary constraints. Business process outsourcing (BPO) can be a solution that enables organizations to grow and scale effectively. But exactly what is business process outsourcing? What are the risks associated with the practice, and how can corporate leaders use business process as a service (BPaaS) to their advantage? BPO meaning: What is business process outsourcing? Business process outsourcing describes a practice where specific tasks, functions, or processes within a company are contracted out to third-party organizations and vendors. These outside organizations have expertise in their specified area, which allows them to manage tasks and processes on behalf of other businesses. For example, a marketing agency, during their resource planning process, may choose to outsource their payroll and accounting functions in order to focus on the core competencies of their organization. There are three types of business process outsourcing: offshore, nearshore, and onshore outsourcing. Offshore outsourcing: The function is managed by an operator or vendor in a different country (often far away and in another time zone) Nearshore outsourcing: The function is managed by an operator or vendor in a neighboring/closeby country Onshore outsourcing: The function is managed by an operator or vendor within the same country — but could be in another state or region Business functions ideal for outsourcing may include admin, customer service, PR, data entry, HR, content moderation, and more. Business process outsourcing can improve efficiency and present significant cost savings for companies that may not have the resources to hire a team of in-house customer service specialists or payroll professionals, for example. In fact, Deloitte research indicates that 59% of companies who outsource say they do so with cost savings as a primary motivator. What is business process as service (BPaaS)? Business process as a service enables BPO by managing specific functions through cloud-based delivery systems. The global BPaaS market is extensive and expected to reach a value of $77.8 billion by 2023. Some well-known names in BPaaS include Accenture and IBM. BPaaS can help manage: Finance and accounting IT services eCommerce Customer service processes BPaaS leverages the capabilities of infrastructure as a service (IaaS), software as a service (SaaS), and platform as a service (PaaS) solutions in order to help companies manage and address their business objectives. Business process as a service also relies on automation in many cases, reducing the need for manual intervention. Who needs business process as a service (BPaaS)? Business process as a service can be beneficial for organizations across sizes and industries. For example, instead of hiring an outside firm to manage their finance and accounting needs, a company might instead execute this function via a cloud-based platform licensed through a monthly subscription model. This naturally brings costs down and offers a more flexible and scalable way of managing operations. Any company looking to manage processes without the costs associated with hiring, training, and managing an internal team or department may find that BPaaS is an effective solution. What are the benefits of outsourcing business processes? There are many benefits associated with outsourcing business processes. These benefits include cost and time savings, efficiency gains, the ability to focus on core business competencies, and more. Be sure to keep these in mind when contemplating outsourcing professional services key success factors, and which professional services agency is right for you.Cost savingsHigh costs associated with labor, training, management, and infrastructure can be a barrier as an organization scales and grows its operations. Outsourcing non-core processes can enable businesses to meet their objectives and operational needs while minimizing these internal costs and time commitments. Access to expertise and improved efficiencyBPO gives businesses access to vendors that have the necessary expertise, equipment, and personnel needed to execute a project or function on their behalf. This expertise means they are better equipped to provide cutting-edge, compliant, and effective services. Ability to focus on key business competencies As a company grows and scales, there is often a need for growth or expansion in other areas of the business. For example, a high-growth eCommerce company may need increased customer support capabilities to provide quality assistance to customer queries and issues. In this instance, outsourcing customer support staff to an agency or outside vendor allows the business to focus on its main competencies while also addressing customer challenges that can impact the bottom line. As is the case with most things, business process outsourcing can have its set of challenges and risks. Are there risks to business process outsourcing? Risks in business process outsourcing can include lower than expected or inconsistent quality of service, lack of visibility and collaboration with the vendor, and security considerations. Inconsistent delivery We’ve all been there. A service looks good on paper, but the results turn out to be inconsistent or of a lower standard than expected. This is always a risk, especially when outside vendors are involved. Lack of visibility and collaboration When handing over the keys to a business function, visibility and communication allow those within the organization to accurately track progress, success, and any challenges. Lack of visibility is a huge risk and could mean that a lower standard of service is inadvertently being passed on to customers. Privacy and security concerns Privacy and security are a top concern in business process outsourcing. In most cases, BPO will involve some degree of handling sensitive or confidential internal data. Engaging a vendor with lax digital security policies may make an organization vulnerable to breaches or attacks. As Deloitte notes, the tax implications of business process outsourcing should also be a consideration and factored into any business case. How to choose the right BPO vendor Choosing the right vendor can help avoid headaches, losses, and disputes. Here are some tips for choosing the right BPO partner for your business. Due diligenceDue diligence will involve researching the vendor and their reputation to determine if they have success and experience with your industry, project type, or company size. Understand costsWhile cost-saving is a major factor when establishing a BPO partnership, unexpected fees may make outsourcing pricier than initially thought. Evaluate security infrastructureWhen determining the suitability of a vendor, be sure to assess their ability to manage and protect sensitive information. Communicate clear objectives and KPIsClearly communicate objectives, expected outcomes, and KPIs and ensure they have the capacity to deliver. Ensure stabilityOutsourcing a business function can be risky if the third party is in a financially, legally, or otherwise unstable position. Overreliance on unstable vendors can be a unique challenge to overcome. How to organize your BPO with Wrike Streamline and simplify your business process outsourcing with Wrike. With Wrike, you can: Create and manage a risk register for your vendor and the outsourced function Invite vendors as external collaborators to share reports and status updates Share and store vendor meeting minutes using our actional meeting notes template Integrate data from 400+ applications like Salesforce, Marketo, and more Take advantage of the cost savings, time savings, and expertise that BPO and BPaaS can afford your business. Be sure to track and manage progress, communication, and risk using Wrike. Sign up for a free two-week trial and discover why 2 million+ people trust Wrike to manage and execute their tasks and projects.

The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Modeling
Struggling to optimize your business processes? Find out process modeling benefits and techniques for executing business process modeling projects successfully.

What Is Business Forecasting? Why It Matters
What is business forecasting? Forecasting helps organizations strategize and, when done right, can give you a competitive advantage. Read on to learn more.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.
Business Model Canvas: Explained with Examples
Got a new business idea, but don’t know how to put it to work? Want to improve your existing business model? Overwhelmed by writing your business plan? There is a one-page technique that can provide you the solution you are looking for, and that’s the business model canvas.
In this guide, you’ll have the Business Model Canvas explained, along with steps on how to create one. All business model canvas examples in the post can be edited online.
What is a Business Model Canvas
A business model is simply a plan describing how a business intends to make money. It explains who your customer base is and how you deliver value to them and the related details of financing. And the business model canvas lets you define these different components on a single page.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that lets you visualize and assess your business idea or concept. It’s a one-page document containing nine boxes that represent different fundamental elements of a business.
The business model canvas beats the traditional business plan that spans across several pages, by offering a much easier way to understand the different core elements of a business.
The right side of the canvas focuses on the customer or the market (external factors that are not under your control) while the left side of the canvas focuses on the business (internal factors that are mostly under your control). In the middle, you get the value propositions that represent the exchange of value between your business and your customers.
The business model canvas was originally developed by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur and introduced in their book ‘ Business Model Generation ’ as a visual framework for planning, developing and testing the business model(s) of an organization.
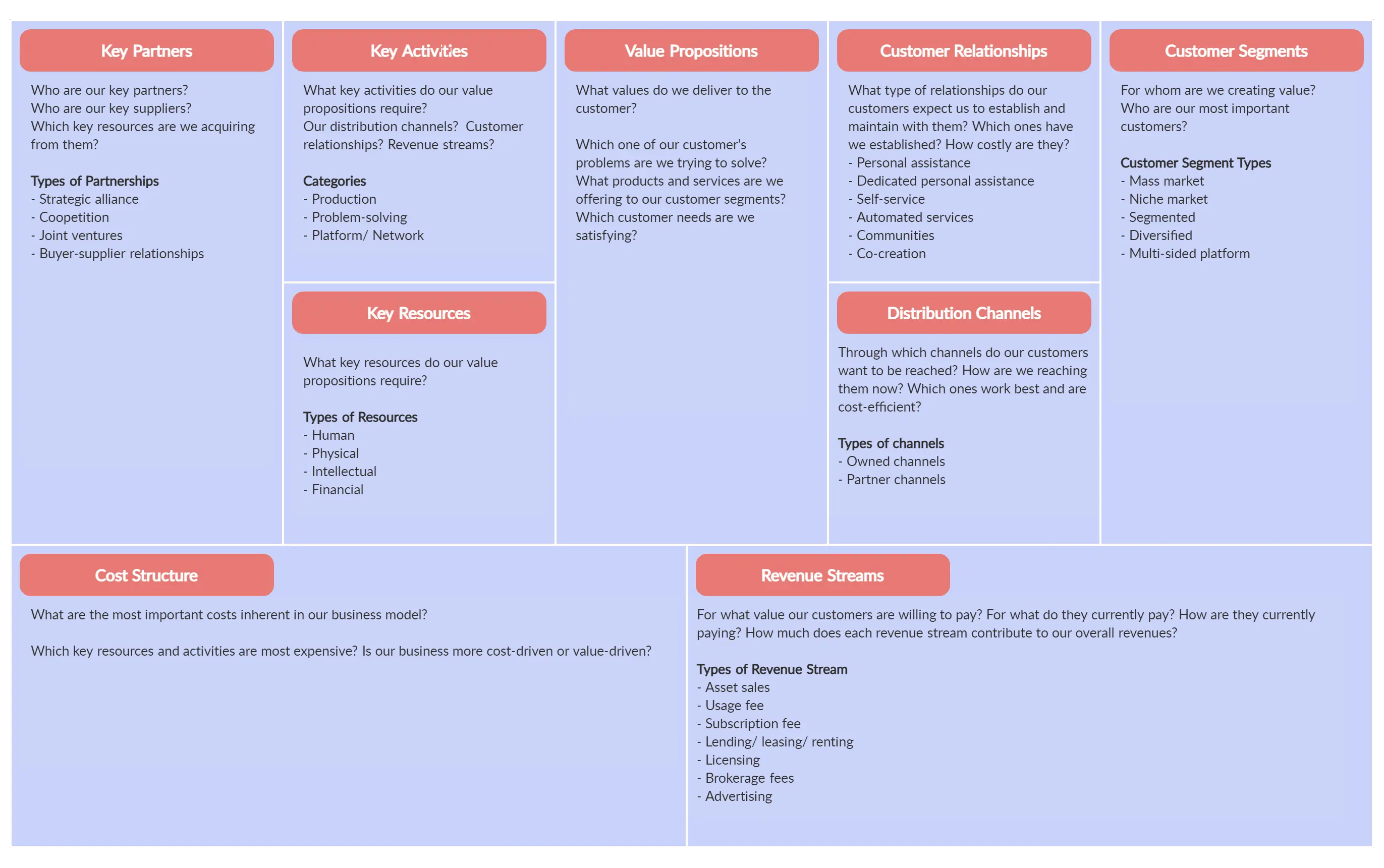
What Are the Benefits of Using a Business Model Canvas
Why do you need a business model canvas? The answer is simple. The business model canvas offers several benefits for businesses and entrepreneurs. It is a valuable tool and provides a visual and structured approach to designing, analyzing, optimizing, and communicating your business model.
- The business model canvas provides a comprehensive overview of a business model’s essential aspects. The BMC provides a quick outline of the business model and is devoid of unnecessary details compared to the traditional business plan.
- The comprehensive overview also ensures that the team considers all required components of their business model and can identify gaps or areas for improvement.
- The BMC allows the team to have a holistic and shared understanding of the business model while enabling them to align and collaborate effectively.
- The visual nature of the business model canvas makes it easier to refer to and understand by anyone. The business model canvas combines all vital business model elements in a single, easy-to-understand canvas.
- The BMC can be considered a strategic analysis tool as it enables you to examine a business model’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges.
- It’s easier to edit and can be easily shared with employees and stakeholders.
- The BMC is a flexible and adaptable tool that can be updated and revised as the business evolves. Keep your business agile and responsive to market changes and customer needs.
- The business model canvas can be used by large corporations and startups with just a few employees.
- The business model canvas effectively facilitates discussions among team members, investors, partners, customers, and other stakeholders. It clarifies how different aspects of the business are related and ensures a shared understanding of the business model.
- You can use a BMC template to facilitate discussions and guide brainstorming brainstorming sessions to generate insights and ideas to refine the business model and make strategic decisions.
- The BMC is action-oriented, encouraging businesses to identify activities and initiatives to improve their business model to drive business growth.
- A business model canvas provides a structured approach for businesses to explore possibilities and experiment with new ideas. This encourages creativity and innovation, which in turn encourages team members to think outside the box.
How to Make a Business Model Canvas
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model.
Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
While you can create a business model canvas with whiteboards, sticky notes, and markers, using an online platform like Creately will ensure that your work can be accessed from anywhere, anytime. Create a workspace in Creately and provide editing/reviewing permission to start.
Step 2: Set the context Clearly define the purpose and the scope of what you want to map out and visualize in the business model canvas. Narrow down the business or idea you want to analyze with the team and its context.
Step 3: Draw the canvas Divide the workspace into nine equal sections to represent the nine building blocks of the business model canvas.
Step 4: Identify the key building blocks Label each section as customer segment, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, and cost structure.
Step 5: Fill in the canvas Work with your team to fill in each section of the canvas with relevant information. You can use data, keywords, diagrams, and more to represent ideas and concepts.
Step 6: Analyze and iterate Once your team has filled in the business model canvas, analyze the relationships to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges. Discuss improvements and make adjustments as necessary.
Step 7: Finalize Finalize and use the model as a visual reference to communicate and align your business model with stakeholders. You can also use the model to make informed and strategic decisions and guide your business.
What are the Key Building Blocks of the Business Model Canvas?
There are nine building blocks in the business model canvas and they are:
Customer Segments
Customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partners, cost structure.
- Value Proposition
When filling out a Business Model Canvas, you will brainstorm and conduct research on each of these elements. The data you collect can be placed in each relevant section of the canvas. So have a business model canvas ready when you start the exercise.
Let’s look into what the 9 components of the BMC are in more detail.
These are the groups of people or companies that you are trying to target and sell your product or service to.
Segmenting your customers based on similarities such as geographical area, gender, age, behaviors, interests, etc. gives you the opportunity to better serve their needs, specifically by customizing the solution you are providing them.
After a thorough analysis of your customer segments, you can determine who you should serve and ignore. Then create customer personas for each of the selected customer segments.
There are different customer segments a business model can target and they are;
- Mass market: A business model that focuses on mass markets doesn’t group its customers into segments. Instead, it focuses on the general population or a large group of people with similar needs. For example, a product like a phone.
- Niche market: Here the focus is centered on a specific group of people with unique needs and traits. Here the value propositions, distribution channels, and customer relationships should be customized to meet their specific requirements. An example would be buyers of sports shoes.
- Segmented: Based on slightly different needs, there could be different groups within the main customer segment. Accordingly, you can create different value propositions, distribution channels, etc. to meet the different needs of these segments.
- Diversified: A diversified market segment includes customers with very different needs.
- Multi-sided markets: this includes interdependent customer segments. For example, a credit card company caters to both their credit card holders as well as merchants who accept those cards.
Use STP Model templates for segmenting your market and developing ideal marketing campaigns
Visualize, assess, and update your business model. Collaborate on brainstorming with your team on your next business model innovation.
In this section, you need to establish the type of relationship you will have with each of your customer segments or how you will interact with them throughout their journey with your company.
There are several types of customer relationships
- Personal assistance: you interact with the customer in person or by email, through phone call or other means.
- Dedicated personal assistance: you assign a dedicated customer representative to an individual customer.
- Self-service: here you maintain no relationship with the customer, but provides what the customer needs to help themselves.
- Automated services: this includes automated processes or machinery that helps customers perform services themselves.
- Communities: these include online communities where customers can help each other solve their own problems with regard to the product or service.
- Co-creation: here the company allows the customer to get involved in the designing or development of the product. For example, YouTube has given its users the opportunity to create content for its audience.
You can understand the kind of relationship your customer has with your company through a customer journey map . It will help you identify the different stages your customers go through when interacting with your company. And it will help you make sense of how to acquire, retain and grow your customers.
This block is to describe how your company will communicate with and reach out to your customers. Channels are the touchpoints that let your customers connect with your company.
Channels play a role in raising awareness of your product or service among customers and delivering your value propositions to them. Channels can also be used to allow customers the avenue to buy products or services and offer post-purchase support.
There are two types of channels
- Owned channels: company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc.
- Partner channels: partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc.
Revenues streams are the sources from which a company generates money by selling their product or service to the customers. And in this block, you should describe how you will earn revenue from your value propositions.
A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models,
- Transaction-based revenue: made from customers who make a one-time payment
- Recurring revenue: made from ongoing payments for continuing services or post-sale services
There are several ways you can generate revenue from
- Asset sales: by selling the rights of ownership for a product to a buyer
- Usage fee: by charging the customer for the use of its product or service
- Subscription fee: by charging the customer for using its product regularly and consistently
- Lending/ leasing/ renting: the customer pays to get exclusive rights to use an asset for a fixed period of time
- Licensing: customer pays to get permission to use the company’s intellectual property
- Brokerage fees: revenue generated by acting as an intermediary between two or more parties
- Advertising: by charging the customer to advertise a product, service or brand using company platforms
What are the activities/ tasks that need to be completed to fulfill your business purpose? In this section, you should list down all the key activities you need to do to make your business model work.
These key activities should focus on fulfilling its value proposition, reaching customer segments and maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue.
There are 3 categories of key activities;
- Production: designing, manufacturing and delivering a product in significant quantities and/ or of superior quality.
- Problem-solving: finding new solutions to individual problems faced by customers.
- Platform/ network: Creating and maintaining platforms. For example, Microsoft provides a reliable operating system to support third-party software products.
This is where you list down which key resources or the main inputs you need to carry out your key activities in order to create your value proposition.
There are several types of key resources and they are
- Human (employees)
- Financial (cash, lines of credit, etc.)
- Intellectual (brand, patents, IP, copyright)
- Physical (equipment, inventory, buildings)
Key partners are the external companies or suppliers that will help you carry out your key activities. These partnerships are forged in oder to reduce risks and acquire resources.
Types of partnerships are
- Strategic alliance: partnership between non-competitors
- Coopetition: strategic partnership between partners
- Joint ventures: partners developing a new business
- Buyer-supplier relationships: ensure reliable supplies
In this block, you identify all the costs associated with operating your business model.
You’ll need to focus on evaluating the cost of creating and delivering your value propositions, creating revenue streams, and maintaining customer relationships. And this will be easier to do so once you have defined your key resources, activities, and partners.
Businesses can either be cost-driven (focuses on minimizing costs whenever possible) and value-driven (focuses on providing maximum value to the customer).
Value Propositions
This is the building block that is at the heart of the business model canvas. And it represents your unique solution (product or service) for a problem faced by a customer segment, or that creates value for the customer segment.
A value proposition should be unique or should be different from that of your competitors. If you are offering a new product, it should be innovative and disruptive. And if you are offering a product that already exists in the market, it should stand out with new features and attributes.
Value propositions can be either quantitative (price and speed of service) or qualitative (customer experience or design).
What to Avoid When Creating a Business Model Canvas
One thing to remember when creating a business model canvas is that it is a concise and focused document. It is designed to capture key elements of a business model and, as such, should not include detailed information. Some of the items to avoid include,
- Detailed financial projections such as revenue forecasts, cost breakdowns, and financial ratios. Revenue streams and cost structure should be represented at a high level, providing an overview rather than detailed projections.
- Detailed operational processes such as standard operating procedures of a business. The BMC focuses on the strategic and conceptual aspects.
- Comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. The business model canvas does not provide space for comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. These should be included in marketing or sales plans, which allow you to expand into more details.
- Legal or regulatory details such as intellectual property, licensing agreements, or compliance requirements. As these require more detailed and specialized attention, they are better suited to be addressed in separate legal or regulatory documents.
- Long-term strategic goals or vision statements. While the canvas helps to align the business model with the overall strategy, it should focus on the immediate and tangible aspects.
- Irrelevant or unnecessary information that does not directly relate to the business model. Including extra or unnecessary information can clutter the BMC and make it less effective in communicating the core elements.
What Are Your Thoughts on the Business Model Canvas?
Once you have completed your business model canvas, you can share it with your organization and stakeholders and get their feedback as well. The business model canvas is a living document, therefore after completing it you need to revisit and ensure that it is relevant, updated and accurate.
What best practices do you follow when creating a business model canvas? Do share your tips with us in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs About the Business Model Canvas
- Use clear and concise language
- Use visual-aids
- Customize for your audience
- Highlight key insights
- Be open to feedback and discussion
More Related Articles

Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
How does Meta (Facebook) make money?
By Nikita Sheth | Verified by Andrew Boyd | Updated Aug. 17, 2023

- Meta, the parent company of Facebook, makes money from serving advertisements.
- Small business advertisement make up more than 95% of Facebook’s generated revenue.
- How else do they generate revenue?
Facebook has revolutionized the internet; it has completely changed the way people interact with each other and the way things are conducted. Facebook (Meta), which started off as a simple social network that allowed people to connect, has become a social media juggernaut, which now owns three of the biggest social media platforms; Instagram, WhatsApp, and Facebook.
Most of the income generated by Facebook is through advertisements; these advertisements are posted by small businesses mostly and make up more than 95% of Facebook’s generated revenue. Although there are some other revenue streams, the majority of Facebook’s revenue is generated through advertisements.
Coming up next
What does facebook do, how does facebook work, how does facebook make money, future growth engine, competitors.
Facebook is a social network; it began as a simple website that allowed people to connect via friend requests, post photos of themselves, and post comments. Gradually, Facebook expanded its functions; it allowed users to create groups, post stories, and do a bunch of other things that could not be done anywhere else.
Facebook also owns Instagram and WhatsApp, further expanding the functions performed by the company as a whole. Billions of people use Facebook and its subsidiaries, making it the largest social network in the world.
When it was first introduced, Facebook, or TheFacebook, as it was known back in the day, was intended to be a platform that allowed college students to connect and interact. However, today, anyone, anywhere around the globe can use Facebook and connect with anyone, anywhere.
Its working is simple, you create a profile, put up a profile photo, and start connecting with people. You can link your Facebook profile to Instagram and create a new Instagram profile without much hassle. The reason Facebook has become so popular is its simplicity and user-friendly interface; it is easy to understand even for those who do not know much about technology.
Facebook makes money by charging creators for advertisements on both Facebook and Instagram; it also generates a fraction of its revenue through the sale of hardware, Facebook Pay, and other applications.
Charging for ads on Facebook
Facebook charges a specific amount of money depending on the type of advertisement you intend to circulate. The charging fee can depend on numerous factors, the type of advertisement, the time period for which you want it displayed, the area where you want it to be displayed. Meta uses a state-of-the-art algorithm to find targeted audiences most relevant to the advertisement and display the advertisement to them, making Facebook ads the most effective type of marketing.
Charging for ads on Instagram
Meta also charges for ads on Instagram in a similar way to Facebook; you are charged based on certain criteria. It also uses the same algorithm, which finds an audience specific to your requirements and ensures a much better reach.
Selling hardware
Meta acquired Oculus in 2014, and ever since then, the sale of Oculus hardware has also made a percentage of the revenue generated by the corporation.
Facebook Pay
Facebook Pay allows you to send money to others; it works in a similar way to Venmo; it is another stream of income for the company.
Other applications
Jibbigo and Onavo are two other apps that allow Meta to make money.
Recently, Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg changed the name of the parent company that owns Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Oculus to Meta.
This is the first step towards a Metaverse, which will take social networking to the next level; holograms, physical projections, and even more realistic online interactions might become a reality in the near future.
Metaverse is an ambitious step in the right direction; if it materializes, it might be unlike anything ever seen before. Nevertheless, the privacy of users is of the utmost importance if Facebook wants metaverse to become a success. The data of the users needs to be safeguarded, and the company should make sure it does not end up in the wrong hands.
Facebook has competitors in nearly all the services it provides. In the advertisement domain, it has competitors like Google and Amazon, two tech giants.
As a social media platform, Facebook has seen its fair share of competition; it has various competitors like Snapchat, Twitter, Reddit , Pinterest, and numerous other platforms. However, Facebook remains at the top because of the diversity of services it provides. One of its fastest-growing competitors is Discord , the chat platform popular with YouTubers, gamers, streamers, and influencers.
As a video-sharing platform, Facebook also faces competition from YouTube.
- Layah Heilpern's net worth
- Ethan Klein's net worth
- Mike Cernovich's net worth
- Richard Cooper's net worth
- Benny Johnson's net worth
- George Janko's net worth
- Matt Walsh's net worth
- Robert F. Kennedy Jr.'s net worth
- Tom Bilyeu's net worth
- Lara Trump's net worth
Advertiser disclosure
At Finty we want to help you make informed financial decisions. We do this by providing a free comparison service as well as product reviews from our editorial staff.
Some of the products and services listed on our website are from partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we compare and the pages they are listed on. Partners have no influence over our editorial staff.
For more information, please read our editorial policy and find out how we make money .

Finty members get
I don't want rewards
I want rewards
Disclaimer: You need to be logged in to claim Finty Rewards. If you proceed without logging in, you will not be able to claim Finty Rewards at a later time. In order for your rewards to be paid, you must submit your claim within 45 days. Please refer to our T&Cs for more information.
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer

Denis Oakley & Co
I HELP BOLD LEADERS TRANSFORM THEIR BUSINESSES AND THE INDUSTRIES THEY COMPETE IN
September 13, 2018 By Denis Oakley
What is the Facebook Business Model?
What is Facebook’s business model? In this video, I explain what Facebook’s business model is using the business model canvas .
Facebook provides a platform where users can share experiences of value to them.

Facebook uses this content to gather data about users and sell the information to advertisers to enable them to sell more to consumers. Facebook takes a commission.
That’s the Facebook business model and it is an extremely valuable one – making it one of the world’s most valuable technology companies

- Business Model Strategy
- What Happened to Friendster?
- PrecisionBit Business Model Analysis – Predictive Image Analytics for Advertisers
- Penetrating Markets with Large Network Effects
- What are the Big Threats to Your Business Model?
About Denis Oakley
Explorer | Trail Runner | Mountain Lover
'Big' companies are civilisation. I stay in the wilderness guiding entrepreneurs and startups on their journey to becoming 'Big'.
Then I head back to the frontier
Strategy | Marketing | Operations
Ready to start?

I help entrepreneurs transform their industries through wiser choices
Outcome : More Traction, Bigger Rounds, Better Products
Method : Problems, Customers, Business Models, Strategy

The Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management and entrepreneurial tool. It allows you to describe, design, challenge, invent, and pivot your business model. This method from the bestselling management book Business Model Generation is applied in leading organizations and start-ups worldwide.

The Business Model Canvas enables you to:
- Visualize and communicate a simple story of your existing business model.
- Use the canvas to design new business models, whether you are a start-up or an existing businessManage a portfolio of business models
- You can use the canvas to easily juggle between "Explore" and "Exploit" business models.

About the speakers
Download your free copy of this whitepaper now, explore other examples.

Get Strategyzer updates straight in your inbox

Mastering business models
A self-paced online course with Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur.
Are you trying to improve your existing business model? Or trying to create a new one that can compete in today’s market?
This web app uses cookies to compile statistic information of our users visits. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. If you wish you may change your preference or read about cookies
Or explore sectors:
Why facebook's business model is so successful.

Facebook business model canvas
Facebook’s Company Overview
Facebook, Inc. builds products that enable people to connect and share through mobile devices and personal computers. The company enables people to share their opinions, ideas, photos and videos, and other activities. Its products include Facebook, Instagram, Messenger, WhatsApp, and Oculus. Facebook is a mobile application and website that enables people to connect, share, discover and communicate with each other on mobile devices and personal computers. Instagram is a mobile application that enables people to take photos or videos, customize them with filter effects, and share them with friends and followers in a photo feed or send them to friends. Messenger is a messaging application available for mobile and the Web on various platforms and devices. WhatsApp Messenger is a mobile messaging application that is used by people around the world. Oculus virtual reality technology and content platform allow people to play games, consume content and connect with others.
Country: California
Foundations date: 2004
Type: Public
Sector: Information & Media
Categories: Internet
Facebook’s Customer Needs
Social impact: self-transcendence
Life changing: provides hope, self-actualization, affiliation/belonging
Emotional: rewards me, badge value, fun/entertainment, attractiveness, provides access, design/aesthetics
Functional: organizes, connects, variety, informs, integrates, organizes, saves time, avoids hassles, sensory appeal, makes money
Facebook’s Related Competitors
Facebook’s business operations.
Advertising:
This approach generated money by sending promotional marketing messages from other businesses to customers. When you establish a for-profit company, one of the most critical aspects of your strategy is determining how to generate income. Many companies sell either products or services or a mix of the two. However, advertisers are frequently the source of the majority of all of the revenue for online businesses and media organizations. This is referred to as an ad-based income model.
Affiliation:
Commissions are used in the affiliate revenue model example. Essentially, you resell goods from other merchants or businesses on your website or in your physical store. You are then compensated for referring new consumers to the company offering the goods or services. Affiliates often use a pay-per-sale or pay-per-display model. As a result, the business can access a more diversified prospective client base without extra active sales or marketing efforts. Affiliate marketing is a popular internet business strategy with significant potential for growth. When a client purchases via a referral link, the affiliate gets a portion of the transaction's cost.
The aikido business model is often characterized as using a competitor's strength to get an edge over them. This is accomplished through finding weaknesses in a competitor's strategic position. In addition, it adds to marketing sustainability by exposing rivals' flaws, finding internal and external areas for development, and attracting consumers via specific product offers that deviate from the norm.
Benchmarking services:
Benchmarking is a technique for evaluating performance and gaining insights via data analytics. It may be used to conduct internal research on your firm or compare it to other businesses to enhance business processes and performance indicators following best practices. Typically, three dimensions are measured: quality, time, and cost. In this manner, they may ascertain the targets' performance and, more significantly, the business processes that contribute to these companies' success. The digital transformation era has spawned a slew of data analysis-focused software businesses.
Blue ocean strategy:
The blue ocean approach is predicated on the premise that market limits and industry structure are not predetermined and may be reconfigured via the actions and attitudes of industry participants. This is referred to as the reconstructionist perspective by the writers. Assuming that structure and market boundaries exist solely in managers' thoughts, practitioners who subscribe to this perspective avoid being constrained by actual market structures. To them, more demand exists, primarily untapped. The core of the issue is determining how to produce it.
Collaborative production:
Producing goods in collaboration with customers based on their input, comments, naming, and price. It represents a new form of the socioeconomic output in which enormous individuals collaborate (usually over the internet). In general, initiatives based on the commons have less rigid hierarchical structures than those found on more conventional commercial models. However, sometimes not always?commons-based enterprises are structured so that contributors are not compensated financially.
Combining data within and across industries:
How can data from other sources be integrated to generate additional value? The science of big data, combined with emerging IT standards that enable improved data integration, enables new information coordination across businesses or sectors. As a result, intelligent executives across industries will see big data for what it is: a revolution in management. However, as with any other significant organizational transformation, the difficulties associated with becoming a big data-enabled company may be tremendous and require hands-on?or, in some instances, hands-off?leadership.
Community-funded:
The critical resource in this business strategy is a community's intellect. Three distinct consumer groups comprise this multifaceted business model: believers, suppliers, and purchasers. First, believers join the online community platform and contribute to the production of goods by vendors. Second, buyers purchase these goods, which may be visual, aural, or literary in nature. Finally, believers may be purchasers or providers, and vice versa.
Conversational commerce:
It is a reference to the nexus between chat applications and business. That is the trend toward engaging with organizations through messaging and chat applications such as Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, Talk, and WeChat, or via speech technologies like Amazon's Echo, allowing users to engage with businesses via voice commands.
Corporate innovation:
Innovation is the outcome of collaborative creativity in turning an idea into a feasible concept, accompanied by a collaborative effort to bring that concept to life as a product, service, or process improvement. The digital era has created an environment conducive to business model innovation since technology has transformed how businesses operate and provide services to consumers.
Cross-selling:
Cross-selling is a business strategy in which additional services or goods are offered to the primary offering to attract new consumers and retain existing ones. Numerous businesses are increasingly diversifying their product lines with items that have little resemblance to their primary offerings. Walmart is one such example; they used to offer everything but food. They want their stores to function as one-stop shops. Thus, companies mitigate their reliance on particular items and increase overall sustainability by providing other goods and services.
Cross-subsidiary:
When products and goods and products and services are integrated, they form a subsidiary side and a money side, maximizing the overall revenue impact. A subsidiary is a firm owned entirely or in part by another business, referred to as the parent company or holding company. A parent company with subsidiaries is a kind of conglomerate, a corporation that consists of several distinct companies; sometimes, the national or worldwide dispersion of the offices necessitates the establishment of subsidiaries.
Culture is brand:
It requires workers to live brand values to solve issues, make internal choices, and provide a branded consumer. Developing a distinctive and enduring cultural brand is the advertising industry's holy grail. Utilizing the hazy combination of time, attitude, and emotion to identify and replicate an ideology is near to marketing magic.
Curated retail:
Curated retail guarantees focused shopping and product relevance; it presents a consumer with the most appropriate options based on past purchases, interactions, and established preferences. It may be provided via human guidance, algorithmic recommendations, or a combination of the two.
Customer data:
It primarily offers free services to users, stores their personal information, and acts as a platform for users to interact with one another. Additional value is generated by gathering and processing consumer data in advantageous ways for internal use or transfer to interested third parties. Revenue is produced by either directly selling the data to outsiders or by leveraging it for internal reasons, such as increasing the efficacy of advertising. Thus, innovative, sustainable Big Data business models are as prevalent and desired as they are elusive (i.e., data is the new oil).
Channel aggregation:
Consolidating numerous distribution routes into one to achieve greater economic efficiency. A business model for internet commerce in which a company (that does not manufacture or warehouse any item) gathers (aggregates) information about products and services from many competing sources and displays it on its website. The firm's strength is in its power to create an 'environment' that attracts users to its website and develop a system that facilitates pricing and specification matching.
Data as a Service (DaaS):
Data as a Service (DaaS) is a relative of Software as a Service in computing (SaaS). As with other members of the as a service (aaS) family, DaaS is based on the idea that the product (in this instance, data) may be delivered to the user on-demand independent of the provider's geographic or organizational isolation from the customer. Additionally, with the advent[when?] of service-oriented architecture (SOA), the platform on which the data sits has become unimportant. This progression paved the way for the relatively recent new idea of DaaS to arise.
A digital strategy is a strategic management and a business reaction or solution to a digital issue, which is often best handled as part of a broader company plan. A digital strategy is frequently defined by the application of new technologies to existing business activities and a focus on enabling new digital skills for their company (such as those formed by the Information Age and frequently as a result of advances in digital technologies such as computers, data, telecommunication services, and the World wide web, to name a few).
Digitization:
This pattern is based on the capacity to convert current goods or services into digital versions, which have several benefits over intangible products, including increased accessibility and speed of distribution. In an ideal world, the digitalization of a product or service would occur without compromising the consumer value proposition. In other words, efficiency and multiplication achieved via digitalization do not detract from the consumer's perceived value. Being digitally sustainable encompasses all aspects of sustaining the institutional framework for developing and maintaining digital objects and resources and ensuring their long-term survival.
Disruptive banking:
The banking industry's disruptors are changing the norms that have been in place for decades. These new regulations, however, will only be effective until the next round of disruption occurs. Banks and credit unions must thus be nimble and responsive. We need audacious tactics. 'Disruptive Innovation' is a term that refers to the process whereby a product or service establishes a foothold at the bottom of a market and then persistently climbs up the value chain, ultimately replacing existing rivals.
Disruptive trends:
A disruptive technology supplants an existing technology and fundamentally alters an industry or a game-changing innovation that establishes an altogether new industry. Disruptive innovation is defined as an invention that shows a new market and value network and ultimately disrupts an established market and value network, replacing incumbent market-leading companies, products, and alliances.
A business ecosystem is a collection of related entities ? suppliers, distributors, customers, rivals, and government agencies ? collaborating and providing a particular product or service. The concept is that each entity in the ecosystem influences and is impacted by the others, resulting in an ever-changing connection. Therefore, each entity must be adaptive and flexible to live, much like a biological ecosystem. These connections are often backed by a shared technical platform and are based on the flow of information, resources, and artifacts in the software ecosystem.
This model collects data and connects it to others; it is suggested to investigate the impact of advertising on consumer purchase dynamics by explicitly linking the distribution of exposures from a brand's media schedule to the brand purchase incidence behavior patterns over time. The danger is that we may be unable to react productively and cost-effectively to technological and market changes.
Fast fashion:
Fast fashion is a phrase fashion retailers use to describe how designs travel rapidly from the catwalk to catch current fashion trends. The emphasis is on optimizing specific supply chain components to enable these trends to be developed and produced quickly and affordably, allowing the mainstream customer to purchase current apparel designs at a reduced price.
Featured listings:
A highlighted listing is more important and noticeable than a regular listing, providing maximum exposure for your workplace to consumers searching in your region. In addition, customers are attracted to these premium listings because they include more pictures of your home ? and its excellent location.
Hidden revenue:
A hidden revenue business model is a revenue-generating strategy that excludes consumers from the equation, preventing them from paying for the service or product provided. For example, users of Google do not pay for the search engine. Rather than that, income streams are generated via advertising dollars spent by companies bidding on keywords.
Infomediary:
An infomediary acts as a personal agent for customers, assisting them to regain control over the information collected about them for marketing and advertising purposes. Infomediaries operate on the premise that personal data belongs to the individual represented, not necessarily the person who manages it.
Layer player:
Companies that add value across many markets and sectors are referred to be layer players. Occasionally, specialist companies achieve dominance in a specific niche market. The effectiveness of their operations, along with their economies of size and footprint, establish the business as a market leader.
Online lead generation is the technique of gathering or gaining a user's information ? often in return for an item, service, or information ? and then reselling that information to businesses interested in advertising to or selling to those gathering leads.
The long tail is a strategy that allows businesses to realize significant profit out of selling low volumes of hard-to-find items to many customers instead of only selling large volumes of a reduced number of popular items. The term was coined in 2004 by Chris Anderson, who argued that products in low demand or with low sales volume can collectively make up market share that rivals or exceeds the relatively few current bestsellers and blockbusters but only if the store or distribution channel is large enough.
Markets are conversations:
For professional services firms, the difference will be made by converting non-engaged customers into engaged customers. Product development will be obsolete. Customer relations and conversations will replace it. By sharing modular and beta products and services with your current and future customers, companies and their customers interact and collaborate in ongoing conversations. Not only will customers find and follow companies in online social networks, but it will also be the other way around as well.
Mobile first behavior:
It is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices. The term is “mobile first,” and it is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices.
Network builders:
This pattern is used to connecting individuals. It offers essential services for free but charges for extra services. The network effect is a paradox that occurs when more people utilize a product or service, the more valuable it becomes.
This method allows the modification of current structures via the use of cutting-edge technology, as shown by growing political unrest, a crisis in representation and governance, and upstart companies upending established sectors. Nevertheless, the nature of this transition is often exaggerated or severely underestimated. As a result, some cling to delirious fantasies of a new techno-utopia in which greater connection results in direct democracy and wealth.
Product innovation:
Product innovation is the process of developing and introducing a new or better version of an existing product or service. This is a broader definition of innovation than the generally recognized definition, which includes creating new goods that are considered innovative in this context. For example, Apple launched a succession of successful new products and services in 2001?the iPod, the iTunes online music service, and the iPhone?which catapulted the firm to the top of its industry.
Referral marketing is a technique for acquiring new consumers by advertising goods or services through recommendations or ordinary word of mouth. While these recommendations often occur spontaneously, companies may influence this via the use of suitable tactics. Referral marketing is a technique for increasing referrals through word of mouth, arguably the oldest and most trusted kind of marketing. This may be done by incentivizing and rewarding consumers. A diverse range of other contacts to suggest goods and services from consumer and business-to-business companies, both online and offline.
Reputation builders:
Reputation builders is an innovative software platform that enables companies to create, collect, and manage positive internet reviews. It was a pioneer in the utilization of user-generated material. The website services are provided for free to users, who supply the majority of the content, and the websites of related businesses are monetized via advertising.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Skunkworks project:
A skunkworks project is one that is created by a small, loosely organized group of individuals who study and develop a project with the primary goal of radical innovation. The terminology arose during World War II with Lockheed's Skunk Works project. However, since its inception with Skunk Works, the phrase has been used to refer to comparable high-priority research and development initiatives at other big companies that include a small team operating outside of their regular working environment and free of managerial restrictions. Typically, the phrase alludes to semi-secretive technological initiatives, such as Google X Lab.
Sponsorship:
In most instances, support is not intended to be philanthropic; instead, it is a mutually beneficial commercial relationship. In the highly competitive sponsorship climate of sport, a business aligning its brand with a mark seeks a variety of economic, public relations, and product placement benefits. Sponsors also seek to establish public trust, acceptability, or alignment with the perceived image a sport has built or acquired by leveraging their connection with an athlete, team, league, or the sport itself.
Tag management:
Tag management refers to the capability of the collaborative software to handle both your own and user-generated tags. Marketers use various third-party solutions to enhance their websites, video content, and mobile applications. Web analytics, campaign analytics, audience measurement, customization, A/B testing, ad servers, retargeting, and conversion tracking are examples of such systems. At its most fundamental level, tag management enables new methods for your business model to use data.
Take the wheel:
Historically, the fundamental principles for generating and extracting economic value were rigorous. Businesses attempted to implement the same business concepts more effectively than their rivals. New sources of sustained competitive advantage are often only accessible via business model reinvention driven by disruptive innovation rather than incremental change or continuous improvement.
Technology trends:
New technologies that are now being created or produced in the next five to ten years will significantly change the economic and social landscape. These include but are not limited to information technology, wireless data transmission, human-machine connection, on-demand printing, biotechnology, and sophisticated robotics.
Trading data:
Combining disparate data sets enables businesses to develop a variety of new offerings for complementary companies. Robustness is a property that describes a model's, test's, or system's ability to perform effectively when its variables or assumptions are changed, ensuring that a robust concept operates without fail under various conditions. In general, robustness refers to a system's capacity to deal with unpredictability while remaining practical.
Two-sided market:
Two-sided marketplaces, also called two-sided networks, are commercial platforms featuring two different user groups that mutually profit from the web. A multi-sided platform is an organization that generates value mainly via the facilitation of direct contacts between two (or more) distinct kinds of connected consumers (MSP). A two-sided market enables interactions between many interdependent consumer groups. The platform's value grows as more groups or individual members of each group use it. For example, eBay is a marketplace that links buyers and sellers. Google connects advertising and searchers. Social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook are also bidirectional, linking consumers and marketers.
Unlimited niches:
Online retailers provide specialized content to various niche client groups via continuing mass-customized customer relationships. The sector of technical content providers is a second client segment. Combining these two factors may result in an infinite number of niches. New material is produced and distributed through online channels, which implies that online retailers must prioritize platform maintenance and marketing in addition to service delivery.
User design:
A client is both the manufacturer and the consumer in user manufacturing. For instance, an online platform could offer the client the tools required to create and market the product, such as product design software, manufacturing services, or an online store to sell the goods. In addition, numerous software solutions enable users to create and customize their products to respond to changing consumer requirements seamlessly.
Virtual reality:
AR/VR is the fourth significant platform change (after PC, web, and mobile). First, CEOs must choose how to play. Business models are determined by installed bases, use cases, and unit economics; there is no one-size-fits-all answer; each situation is unique, and developers must do market research and analysis before making a choice. Relying on advertising-income is a handy strategy for unknown businesses or newcomers to the market. It allows them to use their prior expertise with mobile and online ad campaigns.
Embed code:
Recommended companies based on your search:
Diaspora Business Model
Tumblr business model, twitter business model.
Vizologi is a platform powered by artificial intelligence that searches, analyzes and visualizes the world’s collective business model intelligence to help answer strategic questions, it combines the simplicity of business model canvas with the innovation power of mash-up method .
See how Vizologi works View all features
You rock! Thank you for your interest. Before starting the canvas download, we would like to ask you to pay with a tweet.
Download paying with a tweet
Supercharge Your Business Strategy!
Before you download our exclusive content Subscribe to Vizologi’s FREE newsletter. Join 50k+ innovators shaping success with curated content. No spam, just pure value! @vizologi

Thanks for joining us!
Your exclusive content is on the way to your inbox. Ready to elevate your business with Vizologi?

COMMENTS
Learn how Facebook makes money from targeted advertisements and other sources, and explore its customer segments, value propositions, channels, and key activities. Download the PDF of the Facebook business model canvas and compare it with other social networks.
Understanding Facebook's Business Model. By Mark Zuckerberg, Founder, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. Facebook turns 15 next month. When I started Facebook, I wasn't trying to build a global company. I realized you could find almost anything on the internet—music, books, information—except the thing that matters most: people.
Business Model Canvas of Facebook. 1. Customers of Facebook. Users - Facebook's customers mostly comprise its users. Users who wish to communicate with different people and interact with those in the outside world. Facebook is now its own marketplace where users can buy and sell property like clothes and jewelry and even fundraise for their ...
Facebook, the main product of Meta is an attention merchant. As such, its algorithms condense the attention of over 2.91 billion monthly active users as of June 2021. Meta generated $117.9 billion in revenues, in 2021, of which $114.9 billion from advertising (97.4% of the total revenues) and over $2.2 billion from Reality Labs (the augmented and virtual reality products arm).
Facebook estimates there to be 5% fake and 11% duplicate accounts (with higher proportions in certain countries) - this is still a very big number (5%=125m, 11%=275m). Information shared around the Coronavirus has become the latest "infodemic" example. Engaging the users is mission-critical for any platform business.
Facebook is a social media platform that connects billions of people around the world. But how does it make money and sustain its growth? Learn about Facebook's business model, its sources of revenue, its innovation strategies and its impact on various industries and markets.
Business Model Canvas of Facebook: The Early Days 2006-2012: Facebook to the World, Some Strategic Acquisitions & Going Public 2006: Facebook becomes available to everyone and goes mobile. 2006 saw several significant changes to the site. Firstly, Facebook redesigned the group and events features to make them more accessible.
The business model canvas is a template introduced by Alexander Osterwalder in 2005 as part of his Ph.D. studies under the supervision of Yves Pigneur. The business model canvas outlines nine crucial elements of a business model in an easy-to-understand visual template: customer segments, value proposition, channels, customer relationships ...
Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a framework that helps determine how a business creates, delivers, and captures values. It is a visual representation of the important aspects or parts to consider when designing a Business Model. BMC aids in constructing a shared understanding of a business by condensing it into a simple, relevant, and ...
Conclusion. Facebook's business model has transformed online connectivity and content consumption, solidifying its dominance in the social media industry through platforms like Instagram, WhatsApp, and Oculus. Its primary revenue stream relies on targeted digital advertising to capitalize on its vast user base.
Business Model Canvas of Facebook. Business model canvas of Facebook explains the different aspects of a business model like customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relations, revenue stream, key activities, key resources, key partners and cost structure. Click to enlarge the image.
The Facebook Business Model Canvas explains the various components of the company's business model, including its value proposition, customer segments, and revenue streams. Some of Facebook's main competitors include Google, Twitter, and Instagram. In a SWOT analysis, Facebook's strengths include its large user base and strong brand, while its ...
Inspired by the business model canvas, the lean model canvas was created by Ash Maurya. It is a one-page business plan template that distills the lean startup methodology into the original business model canvas. Lean model canvas assimilates multiple essential data points to develop a simpler, start-up optimized version of a business model canvas.
Business Model Canvas Introduction. With our partners, understand why digital transformation is so important for businesses and how to apply it to your business strategy. Explore Program. March, 2021 3 min. With our partners, understand why digital transformation is so important for businesses and how to apply it to your business strategy.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model. Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
Meta, the parent company of Facebook, makes money from serving advertisements. Small business advertisement make up more than 95% of Facebook's generated revenue. How else do they generate revenue? Facebook has revolutionized the internet; it has completely changed the way people interact with each other and the way things are conducted.
In this video, I explain what Facebook's business model is using the business model canvas. Facebook provides a platform where users can share experiences of value to them. The Facebook value proposition is clear on its home page. Connect and share with the people in your life. Facebook uses this content to gather data about users and sell ...
Business Models. The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management and entrepreneurial tool. It allows you to describe, design, challenge, invent, and pivot your business model. This method from the bestselling management book Business Model Generation is applied in leading organizations and start-ups worldwide.
advertising community mobile communications media social blogging messaging social network news. Vizologi is a platform powered by artificial intelligence that searches, analyzes and visualizes the world's collective business model intelligence to help answer strategic questions, it combines the simplicity of business model canvas with the ...
Build a business model canvas. Fill out each component of the business model canvas template with information on your customers, partners, key activities, value propositions, costs, and revenue streams. Easily add new text boxes or sticky notes to construct and align your business concept with your team. Personalize your business model canvas.
Causes event by Funding Connection on Monday, May 13 2024
A introduction to the Business Model Canvas (invented by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur.) We look at the nine building blocks and explore three common mis...
Facebook -2.23 billion MAU's (Monthly Active Users) 2. YouTube -1.9 billion MAUs MAU's 3. WhatsApp -1.5 billion MAU's 4. Messenger -1.3 billion MAU's 5. WeChat -1.06 billion MAUs (Chinese Market) 6. ... Business Model Canvas Author: Susan Cornelius Created Date: