- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax

How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.
Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.
Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Business Plan Template for New Product
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Thinking of launching a new product? You need a solid business plan to make your vision a reality. ClickUp's Business Plan Template for New Products is your secret weapon for success!
With this template, you can:
- Craft a strategic vision and roadmap for your product
- Conduct in-depth market analysis to understand your target audience and competition
- Create accurate financial projections to impress investors and secure funding
- Develop operational plans to guide every step of your product's development and launch
Don't let your brilliant idea go to waste. Use ClickUp's Business Plan Template for New Products to turn it into a thriving reality. Get started today!
Business Plan Template for New Product Benefits
Launching a new product can be an exciting but daunting endeavor. Using a business plan template for your new product can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Streamlining the process of organizing your strategic vision, market analysis, financial projections, and operational plans
- Attracting potential investors by showcasing a comprehensive and well-thought-out business plan
- Securing funding for your new product by demonstrating its potential for success
- Guiding the development and launch of your product by providing a clear roadmap and timeline
- Ensuring that you have considered all aspects of your business, from marketing to operations, for a successful product launch
Main Elements of New Product Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for New Product is the perfect tool to help entrepreneurs and business owners effectively plan and execute their product launch. This template includes:
- Custom Statuses: Easily track the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Utilize custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section to add additional details and organize your business plan.
- Custom Views: Access different views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide to gain a comprehensive overview of your business plan and easily navigate through different sections.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaborate with your team members in real-time with features like task comments, file attachments, and mentions.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrate with your favorite tools like Google Drive, Dropbox, and Slack to streamline your workflow and keep all your important documents in one place.
How To Use Business Plan Template for New Product
If you're looking to create a solid business plan for a new product, ClickUp's Business Plan Template can be a valuable tool. Follow these five steps to make the most of it:
1. Define your product and target market
Start by clearly defining your new product and identifying your target market. What problem does your product solve? Who is your ideal customer? Understanding these key aspects will help you tailor your business plan to meet the needs and preferences of your target market.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to outline your product and conduct market research to identify your target market.
2. Conduct a SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis is a crucial step in understanding the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of your new product. Evaluate your product's unique selling points, potential challenges, market trends, and competitive landscape. This analysis will help you identify areas of improvement and develop strategies to maximize your product's success.
Create custom fields in ClickUp to track and analyze each aspect of your SWOT analysis.
3. Develop your marketing and sales strategies
Your business plan should outline how you will market and sell your new product effectively. Determine your pricing strategy, distribution channels, promotional activities, and sales targets. It's important to tailor your strategies to your target market and align them with your overall business goals.
Use tasks in ClickUp to break down your marketing and sales strategies into actionable steps and assign them to team members.
4. Outline your financial projections
Include financial projections in your business plan to demonstrate the potential profitability and viability of your new product. Estimate your sales revenue, expenses, profit margins, and cash flow projections. This will help you understand the financial feasibility of your product and attract potential investors or stakeholders.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to create a financial spreadsheet and track your revenue, expenses, and profit projections.
5. Set milestones and timelines
Setting specific milestones and timelines is crucial to keep your new product development on track. Break down your business plan into actionable tasks and assign them to team members with clear deadlines. Regularly review and update your progress to ensure that you're meeting your milestones and making timely adjustments.
Use Milestones in ClickUp to set and track important project milestones and Automations to send reminders and notifications for upcoming deadlines.
By following these steps and utilizing ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you can create a comprehensive and well-structured business plan for your new product. This will help you stay organized, focused, and increase your chances of success in the market.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for New Product
Entrepreneurs and business owners can use the Business Plan Template for New Product in ClickUp to streamline the process of creating a comprehensive business plan for their upcoming product launch.
To get started, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant team members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a successful business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize the different sections of your business plan, such as executive summary, market analysis, financial projections, and marketing strategies.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- The Timeline View allows you to set deadlines and milestones for each section, ensuring that you stay on track and meet your goals.
- The Business Plan View provides a comprehensive overview of your entire plan, allowing you to easily navigate and make edits as needed.
- The Getting Started Guide View offers step-by-step instructions and tips to help you fill out each section of the business plan.
- Utilize the custom fields, such as Reference, Approved, and Section, to add additional information and categorize your plan.
- Collaborate with team members by assigning tasks, leaving comments, and attaching files to ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Monitor and analyze the progress of your business plan to make informed decisions and adjustments as needed.
- Business Plan Template for Pastors
- Business Plan Template for Curators
- Business Plan Template for Cinematographers
- Business Plan Template for Retail Clothing Store
- Business Plan Template for Beauty Industry Professionals
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
- 212 best farm names
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
May 24, 2021
Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles
Best Pressure Washer Guide (2024)
Becoming a successful pressure-washing company requires a combination of customer service, business skills, and having the best pressure washer to get the job done. That’s why we took the time to review the best pressure washers for different jobs.
We talked to Joshua Brown, who started Brown’s Pressure Washing , and Josiah Le Beau, their Operations Manager, to help you choose the best pressure washers for each cleaning job.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"] We’ll discuss nine pressure washers and cover all of the following. Click any of the links to jump straight to the pressure washer info you need right now.
What is the best pressure washer to buy?
How we tested the pressure washers, what to look for in a pressure washer.
- Do you prefer gas or electric pressure washers? [/su_note]

We reviewed nine of the best pressure washers on the market to establish what power washer provides the best cleaning power for your cleaning needs. We explain what we like and don’t like about every pressure washer and provide an overview of the performance and stats for the pressure washer. The best pressure washers are:
- Honda GX690 8 GPM (Brown’s top pick)
- Sun Joe SPX3000-MAX Electric Pressure Washer
- Greenworks 2000 PSI Electric Pressure Washer (best for patios)
- Karcher K5 Premium Electric Power Pressure Washer (best for cars)
- Greenworks 3000 PSI Brushless (best Electric Pressure Washer)
- WORX Hydroshot 320 PSI Cordless Power Cleaner (best compact pressure washer)
- Simpson Powershot 4400 PSI 4.0 GPM Gas Cold Water Pressure Washer
- Greenworks Pro 2300 PSI Brushless 2.3 GPM Electric Pressure Washer
- Best for first-time users: Sun Joe SPX3001 2030 PSI Electric Pressure Washer With Hose Reel
You can find most of these in the UpFlip Amazon Store , where we get a percentage of each sale to help bring more content to you.
Get ready to find out about the pressure washer power that puts most pressure washers to shame. Let’s start with one of the best gas pressure washers—the one Brown’s Pressure Washing uses on all their pressure washer trucks.
#1. Brown’s Top Pick: Honda GX690 8 GPM Pressure Washer
Using a Honda GX690 8 GPM pressure washer offers several benefits, but there are of course considerations to remember. Here are some pros and cons.
Why We Like the GX690
- High flow rate
- Powerful cleaning performance
- Professional-grade quality
- Versatility in cleaning tasks
- Efficient and time-saving
GX690 Drawbacks
- Larger and Heavier Equipment: Pressure washers with a Honda GX690 engine and an 8 GPM flow rate tend to be larger and heavier than to lower-powered models. This can make them more challenging to transport and maneuver, requiring additional effort and potentially limiting accessibility to tight spaces.
- Higher Cost: Pressure washers with a Honda GX690 engine and high flow rate typically come at a higher price point due to their professional-grade quality and power. The initial investment may be more significant compared to lower-powered or consumer-grade models. However, the cost may be justified for those with demanding cleaning needs.
- Noise and Emissions: Gas-powered pressure washers, including those with the Honda GX690 engine, can produce significant noise during operation. Proper hearing protection should be used. Additionally, gas engines emit exhaust fumes, meaning they should only be used in well-ventilated areas.
- Requires Fuel and Maintenance: Gas engines, including the Honda GX690, require fuel (gasoline) to operate. This adds an extra step of refueling and increases the potential for fuel-related issues. Gas engines also require regular maintenance, such as oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug checks, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
GX690 Performance
The Honda GX690 8 GPM pressure washer provides an exceptionally high flow rate of 8 gallons per minute (GPM). This allows for efficient and quick cleaning of large surfaces, making it ideal for commercial, industrial, or heavy-duty applications that require a significant volume of water.
The gas engine makes this one of the most powerful and therefore loudest gas washers on the market, so you’ll need hearing protection, and you can’t use a gas-powered pressure washer in enclosed spaces. Despite that, a Honda gas model is hands-down the most effective pressure washer for getting work done. Other pressure washers just don’t compare.
GX690 Stats
- Set of quick connect spray nozzles
- 22HP Honda GX690 gas engine
- Anti-vibration rubber isolators
- Battery cables
- Electric start
- External unloader
- Heavy duty general (gp) triplex plunger pump
- Powder coated
- Skid mounted
- Thermal relief valve
- V-Belt drive system
- 28,000 cleaning units
#2. Sun Joe SPX3000-MAX Electric Pressure Washer

Why We Like the SPX3000
- Affordability ($200 at time of writing)
- Safety features
- Compact design
- Dual detergent tanks
- Lower noise level
- Just 15 minutes to assemble
- Comes with great instructions
- Oversized wheels
SPX3000 Drawbacks
- No storage hoses
- Limited attachment choices
SPX3000 Performance
The best electric pressure washer we tested is the Sun Joe SPX3000 Electric power washer. This electric pressure washer delivers 2,030 pounds per square inch (PSI) at 1.76 Gallons Per Minute(GPM), which makes it perfect for most tasks.
The Sun Joe SPX3000 electric power washer includes:
- Dual soap/detergent tanks
- Five quick-connect spray tips
- 20-foot high-pressure hose
- Garden hose adapter
- 34-inch extension wand
- 35-foot power cord
The Sun Joe pressure washer is both quiet and effective, especially for a pressure washer at its pricing and size. The dual soap compartments are beneficial for a power washing company that focuses on cars or windows because you can switch the cleaner with ease.
The Sun Joe is one of the most useful power washers on the list, but it doesn’t come with attachments that are good for cleaning wood or concrete surfaces.
SPX3000 Stats
- Electric power
#3. Greenworks 2000 PSI Electric Pressure Washer (Best for Patios)

Why We Like the Greenworks 2000 PSI EPW
- Affordability ($220 at time of writing)
- Best pressure washer attachments for large surfaces
- Easy to assemble and use
- Effective on all surfaces
- Comparably quiet
- 24-minute assembly
- Comes with attachment storage
Greenworks 2000 PSI EPW Drawbacks
- Poorly written instruction manual
- Uses an offboard tank for cleaning fluids
- Not suitable for regular heavy-duty cleaning
- No soap dispenser instructions
Greenworks 2000 PSI EPW Performance
Greenworks 2,000 PSI Pressure Washer with an 11-inch surface cleaner is best at cleaning large flat surfaces like cars, driveways, fences, and siding.
The Greenworks 2,000 PSI Pressure Washer includes:
- 11-inch surface cleaner (great for house siding, driveways, and fences)
- Cleaning wand
- 20-foot hose
- Onboard storage
This would be the best portable pressure washer hands down if they improved the instructions and added an onboard soap tank.
Greenworks 2000 PSI EPW Stats
- Electric power source
#4. Karcher K5 Premium Electric Power Pressure Washer (Best Car Pressure Washer)

Why We Like the K5
- Affordability ($300 at time of writing)
- Great for cleaning cars
- Onboard detergent tank
- Two spray wands
- Onboard hose storage
- Lightweight
K5 Drawbacks
- Assembly instructions are a bit tricky to implement
- Does not seem built for long-term use in a commercial environment
- Fewer attachments than other brands
K5 Performance
The K5 is the best pressure washer for detailing cars. The Karcher K5 is the best electric pressure washer for cars because it provides up to 2,000 PSI at 1.4 GPM.
The K5 includes:
- onboard soap dispenser
- Vario cleaning wand: Use it for lighter cleaning
- Dirtblaster cleaning wand: Use for dirty jobs
- 25-foot high-pressure hose
- Water-cooled induction motor to extend useful life
While it’s a little pricier than some of the pressure washers on our list, the dual wands make this the best pressure washer for car detailing.
- 2,000 PSI pressure
Now you know the best pressure washer for car washing. Let’s look at the most powerful electric pressure washer.
#5. Greenworks 3000 PSI Brushless (Most Powerful Electric Pressure Washer)

Why We Like the Greenworks 3000 PSI Brushless EPW
- Affordability ($449 at time of writing)
- Dual speed motor
- Good onboard storage
- Large onboard detergent tank
- Powerful spray nozzles
- Easily understood labels
Greenworks 3000 PSI Brushless EPW Drawbacks
- Damages some surfaces
- Comparatively higher electric washer price point
Greenworks 3000 PSI Brushless EPW Performance
The Greenworks Pro 3,000 PSI Brushless Pressure Washer has a great combination of features and usability. It stands out among electric pressure washers because of its unique features, including:
- 14-amp brushless motor
- Large 1-gallon onboard soap tank
- 35-foot cord
- Cord swivel storage
- 5 nozzles (we love the Turbo Nozzle)
- No-leak attachment switching
This is the most powerful of the electric washers we tested and is comparable to some of the gas-powered washers—which most electric pressure washers are not.
The Greenworks 3000 PSI Brushless Electric Power Washer propels water at either 3000 PSI at 1.1 GPM or 1000 PSI at 2 GPM. Some attachments are actually capable of damaging wood or cars, so be cautious if you are using the stronger nozzles!
3000 PSI Brushless EPW Stats
- 1.1 or 2 GPM
#6. WORX Hydroshot 320 PSI Cordless Power Cleaner (Best Compact Power Washer)

Why We Like the Hydroshot
- Affordability ($129 at time of writing)
- Lightest power washer reviewed
- Quietest power washer reviewed
- 10-minute setup
- Best supply options
Hydroshot Drawbacks
- Low pressure
- Not for commercial cleaners
- Short battery life
Worx Hydroshot 20V Performance
This is not a commercial pressure washer, but if you have a customer who wants to maintain their space between cleanings, the Worx Hydroshot 20V Power Share 320 PSI Portable Power Cleaner might be the best pressure washer for home use.
Unlike most of the other options, it doesn’t come with nozzles and attachments. It’s just a battery and a sprayer. You can connect the Worx Hydroshot to a:
- 20-foot water tube and bucket
- Garden hose with the included adapter
- 2-liter bottle
The sprayer has five pressure settings, but at 320 PSI, you’ll still need to remove heavy dirt and grime with something else.
Worx Hydroshot Stats
- Battery powered
- Cordless wand
- 5-pressure spray wand
#7. Simpson Powershot 4400 PSI 4.0 GPM Gas Cold Water Pressure Washer

Why We Like the Powershot 4400
- Highest cleaning power
- 5 spray tips
- 50-foot-long hose
Powershot 4400 Drawbacks
- Most expensive on our list ($900 at time of writing)
- No built-in detergent tank
- Starter is tricky to use
- More challenging assembly
Powershot 4400 Performance
Time is money, and a high-powered gas-powered pressure washer saves time because it is more powerful than any electric counterpart.
The Simpson PowerShot Pro Gas Pressure Washer is one of the best gas-powered pressure washers because it delivers up to 4400 PSI at 4 GPM. This gas pressure washer cleared tough stains off of driveways and vehicles without using strong settings.
Powershot 4400 Stats
- Gas-powered engine
- 5 spray nozzle options
#8. Greenworks Pro 2300 PSI Brushless 2.3 GPM Electric Pressure Washer (Best for Beginners)

Why We Like the Green Works PRO 2300
- Very easy to set up and use
Green Works PRO 2300 Drawbacks
- Hoses tangle
Green Works PRO 2300 Performance
Beginners will find this the best pressure washer because it’s easy to use without damaging property—unlike more powerful gas pressure washers.
The Greenworks Pro 2300 PSI Pressure Washer is quick to set up, gets great gas pressure washer results, and comes with a ton of accessories.
Green Works PRO 2300 Stats
- 5 nozzles, plus water and detergent tank
#9. Sun Joe SPX3001 2030 PSI Electric Pressure Washer With Hose Reel (Great for First-Time Users)

Why We Like the SPX 3001
- Affordability ($168 at time of writing)
- Easy to use
SPX 3001 Drawbacks
- Handle is a bit flimsy
- Not very high-powered
SPX 3001 Performance
The Sun Joe SPX3001 is a great starter powerwasher because it’s relatively quiet and portable. Setting it up is easy and it will work on most surfaces.
For large amounts of dirt and debris, you will probably need something more powerful, though. You might also have challenges if you have to carry the pressure washer across surfaces like sand, which makes the wheels less functional.
SPX 3001 Stats
- 5 spray patterns

All the pressure washers reviewed were tested by Brown’s team members, who generously provided their input on which pressure washers they would recommend. We featured the gas-powered pressure washer that Brown’s currently uses in our number one spot because it can easily be considered the best pressure washer currently available.
Should Brown’s choose to upgrade their gas engine, we will provide a new review of the best pressure washers with the updated gas engine.
When looking for a pressure washer, there are several important factors to consider to ensure you get a model that suits your needs and performs effectively. Here's what to look for:
- Pressure Level (PSI): PSI stands for pounds per square inch and indicates the pressure output of the washer. 3,000+ PSI values are best for tougher cleaning tasks like removing oil stains from driveways or cleaning large surfaces. Lighter tasks like washing cars or furniture require lower PSI levels.
- Flow Rate (GPM): Gallons per minute (GPM) indicates how much water the pressure washer uses. A higher GPM can help you clean faster and more efficiently, but it also uses more water. Brown’s uses an 8 GPM motor .
- Power Source: Pressure washers can be powered by electricity or gas engines. Gas-powered models offer more mobility and higher power, making them preferable for professional power washers. Electric models are generally quieter, easier to start, and require less maintenance, but they typically have slightly lower power.
- Portability: Consider the weight, size, and overall portability of the pressure washer, especially if you need to move it around frequently. Some models come with wheels for easier mobility.
- Nozzles and Spray Tips: A variety of interchangeable nozzles or spray tips allow you to adjust the spray pattern and pressure according to the task. They can range from high-pressure pinpoint streams for tough cleaning to wider fan sprays for more delicate surfaces.
- Build Quality and Durability: Look for pressure washers with sturdy construction, preferably with metal components for better durability. Well-built machines are likelier to withstand the demands of frequent use.
- Attachments and Accessories: Check if the pressure washer comes with attachments like surface cleaners, extension wands, detergent tanks, and brushes. These can enhance the versatility of the washer and make certain tasks easier.
- Noise Level: Gas-powered pressure washers tend to be noisier than electric ones. If noise is a concern, opt for a quieter electric model.
- Price: Pressure washers come in a wide price range. While it's tempting to choose the cheapest option, investing a bit more in a quality machine can lead to better performance and longevity.
- Brand Reputation and Reviews: Research brands with a good reputation for producing reliable pressure washers. Reading user reviews and seeking recommendations can give you insights into real-world performance.
- Warranty and Customer Support: A good warranty indicates the manufacturer's confidence in their product's quality. Also, check to see if the manufacturer offers responsive customer support in case you encounter any issues. One way to test this is to call or email customer service with a few questions before you buy.
- Safety Features: Look for safety features such as automatic shut-off when the trigger is released, as well as features that prevent overheating and excessive pressure buildup.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly design with easy-to-access controls and a comfortable handle can make your cleaning tasks more enjoyable and efficient.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the maintenance needs of the pressure washer, such as cleaning filters, changing oil (for gas models), and winterizing if necessary.
Remember to assess your specific cleaning needs before making a decision. A pressure washer that suits your requirements will ensure that your cleaning tasks are completed effectively and efficiently.
Do you prefer gas or electric pressure washers?
Which pressure washer option do you prefer? What will you use it for? What other information would you like us to include in our reviews of pressure washers?
31 Best Self-Employment Ideas 2024
You don’t have to hire employees to be a business owner. Many people start working for themselves just because they want the freedom to be their own boss and set their own hours. Get ready! We’re going to share some of the best self-employment ideas for new business owners.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"]We’ve compiled a list of the best self-employed jobs you can find today. Click on any of the links below to jump straight to the section that interests you!
12 Unique Business Ideas for Self-Employment
Top 10 work-for-yourself jobs, self-employed jobs with no qualifications, self-employment ideas for over 50, faqs about self-employment jobs ideas.

#1. Phone or Electronics Repair
Average Annual Revenue: $560,320 Average Profit Margins: 5.7% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.4% Best for: Detail- and systems-focused entrepreneurs, electronics and repair experts
Check out our video on how Joe Pilat, of Joe’s Gaming & Electronics, started his business from scratch by repairing and refurbishing broken gadgets and electronics.
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rqce8NAZWYw&ab_channel=UpFlip"]
Cell phone repair alone was a $1.3 billion industry in 2022, and it makes sense why–97% of Americans own a cellphone, and 66% of them have damaged their phones in the past year.
Best for people considering self-employed jobs, 70% of cellphone repair shops are opened by local business owners with no prior industry experience.
You don’t need to open a brick-and-mortar storefront to start your own repair business, either. A mobile repair business, or one with pick-up and drop-off service, is even more convenient for customers and saves you the expense of a physical location.
#2. Grocery Delivery Service

Average Annual Revenue: $340,600 Average Profit Margins: 6.7% Startup Cost: $500-$250K Time To Revenue: 3+ months Annual Market Growth Rate: 3.6% Best for: Drivers, those that like to socialize and meet new people, those with networks with other business owners
Demand for last-mile grocery delivery soared during the pandemic, with online grocery sales exceeding $85 billion in 2022, more than double pre-pandemic figures.
At the same time, many grocery stores don’t have the staff, infrastructure, or capability to offer delivery in-house. This opens the door for self-employed entrepreneurs seeking a profitable business opportunity.
Starting a delivery service also lets you support other local small businesses while you gain financial freedom. That was one of Adam Haber’s main goals when he started Trellus, a same-day local delivery market. You can hear his advice on how to start a delivery business in this podcast interview:
#3. Project Management Services

Average Annual Revenue: $363,300 Average Profit Margins: 10.3% Startup Cost: $1K-$100K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.8% Best for: People with an expertise in organizing and delegating tasks, taking responsibility for managing the work of other people, and people with strong leadership and communication skills
The number of project managers in the workforce hasn’t kept up with the demand for them in recent years. That talent gap leaves space for those with project management skills to start a self-employed business and work for companies on a freelance basis.
As a freelance project manager, you get more freedom over when you work and the projects that you take on than when you work full-time for a company. There’s also a wide variety of work available, from software and IT projects to marketing and PR campaigns, construction projects, or just about any other industry you can name.
You can also make more money. Freelance project managers earn $451 per work day on average, which equates to roughly $117,000 a year, far higher than the $85,662 salary average reported for project managers on Indeed.
#4. Career Coaching and Resume Writing Service
Average Annual Revenue: $234K Average Profit Margins: 5.8% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.1% Best for: People that enjoy managing, mentoring, and coaching other people, and those that are detail-oriented and independent entrepreneurs with good interpersonal skills
A career coach helps other professionals make career progress. This often starts by helping them map out their career path. A career coach also often offers services like resume or cover letter writing, interview preparation, and offer negotiation advice.
People with a background in recruiting or HR are ideally suited to become self-employed as career coaches. This is also a great business idea for former executives and managers who have first-hand insights into what businesses look for in applicants.
#5. Tax Preparation

Average Annual Revenue: $1.57M Average Profit Margins: 18% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months (not including time training as a CPA) Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.7% Best for: CPAs, finance experts, entrepreneurs with strong math skills
Tax preparation is one of the few self-employment job ideas with a built-in demand. Every individual and business needs to file taxes, and that means tons of potential clients.
While you do need professional certification to start a tax prep business, it’s not hard to get, and there’s no fee to obtain one. Aside from this certification, all you’ll need is an understanding of the tax code and a few clients to start building your reputation and customer trust.
#6. Catering Business
Average Annual Revenue: $124,410 Average Profit Margins: 5.5% Startup Cost: $1K-$100K Time To Revenue: 6-18 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1% Best for: Chefs, cooks, bakers, and other food experts
For chefs, bakers, and other food service workers who want to become self-employed, a catering business is one of the most affordable ways to go about it.
Watch the video below on how Kyle Gourlie, the owner of Vet Chef, built a successful food truck business.
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YCnE13BaQlk&ab_channel=UpFlip"]
This can also be an ideal business plan for a home cook or baker who wants to break into the food industry without starting from the bottom of the hierarchy in a restaurant.
One reason for this is that you don’t need a storefront to start catering. Many use clients’ kitchens to prepare the food, or they rent a commercial kitchen when they need it. You can also easily scale a catering business by opening a food truck , cafe, or restaurant as you grow.
#7. Airbnb Hosting
Average Annual Revenue: $201K Average Profit Margins: 8.1% Startup Cost: $100K-$3.5M Time To Revenue: 6-18 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 2.2% Best for: Homeowners, frequent travelers, people with hospitality experience
If you’re looking for self-employed jobs from home, why not turn your home into a source of income? As an Airbnb host, you can rent out unused rooms, buy and fix up properties to rent, or convert a shed or garage into a mini-apartment.
The unique and varied properties available for rent are one of the biggest appeals of Airbnb for travelers, and unique places to stay often do quite well on the site.
However you go about it, Airbnb hosting can be a very lucrative business. Nicasa started from a single property in 2009 and has now grown to 22 properties that bring in $3 million in annual revenue. Hear how the business started in this YouTube interview:
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6m-MosXlpOE"]
#8. Tutoring
Average Annual Revenue: $18,170 Average Profit Margins: 13.1% Startup Cost: $100-$1K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 8.5% Best for: Teachers, educators, professors, and experts in a particular skill or knowledge area
Tutoring is among the top self-employed business ideas for recent graduates and a common way for college students to make a bit of extra cash.
You don’t need to be close to your school years to make a good living as a tutor, either. It’s also an excellent self-employed job for teachers, professors, and other education professionals who want to branch out on their own.
The trickiest part of starting a tutoring business for many is where to connect with students. The Tutor Resource’s guide to finding students is a great place to start. You can also grow your reputation online by posting how-to videos, informative blog posts, and other educational content that demonstrates your knowledge.
#9. Car Wrapping

Average Annual Revenue: $241,230 Average Profit Margins: 16.1% Startup Cost: $1K-$100K Time To Revenue: 1-6 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.8% Best for: Car enthusiasts, detail-oriented entrepreneurs, and those that enjoy working with their hands
People keep their cars longer than in the past, with the average age of a car on the road increasing by 44% since 1995 . Protective car wrapping helps cars and trucks look like new for longer. Offering that service is one of the best small business ideas for people who love cars.
Car wrapping can be a creative pursuit, too. A car can be wrapped in graphics just to change the look or for marketing and branding of company cars or driving billboards.
Between these two uses, there’s a high demand for car wrapping. Fred Roman started WrapCo in 2012 and has grown it to $70,000 in monthly revenue. See how in this YouTube interview:
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LM1wFesfapQ&list=PLaU6uY9Yy7XkECNQPPT_LNAxEghhffqv7&index=11"]
#10. Notary Public
Average Annual Revenue: $552,900 Average Profit Margins: 9.4% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: -0.5% Best for: People interested in legislative and legal topics, and those who have excellent reading and writing skills
Notaries are basically professional witnesses, verifying people’s identities when they sign contracts, give oaths, or other legally-binding agreements.
Some notaries work for other businesses, but many are working for yourself jobs. A self-employed business as a notary public can be very profitable, too. Roughly 33% of all mobile notaries earn more than $4,000 a month, and it’s double that figure for notaries with at least 3 years of experience.
While you do need a license to work as a notary, the process for getting licensed isn’t complicated. You can see the regulations state-by-state on the American Society of Notaries website.
#11. Be a Tour Guide
Average Annual Revenue: $995,900 Average Profit Margins: 6.6% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 3.5% Best for: Those with a love for local history and attractions, those who like to socialize and meet new people, and those who like to educate
If you live in a place that gets a lot of visitors, giving tours can be a fun and profitable business venture. The types of tours you give can depend on your location and interests. For example, a foodie could give a tour of local restaurants, or you could give haunted history tours if you’re into the supernatural.
The most difficult part of starting a tour guide business is often finding customers, especially since your target market tends to be people who don’t live near you. Having your own website and a strong online presence can help.
#12. Tailoring or Clothing Alterations

Average Annual Revenue: $27,825 Average Profit Margins: 8.3% Startup Cost: $500-$250K Time To Revenue: 3+ months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.6% Best for: Those that like to work with their hands, those that enjoy sewing and handicraft, fashionistas tuned into fashion trends
Tailoring is among the best home business ideas for fashionistas who love to sew. Depending on your skills and interests, you can focus on a niche like formalwear alterations or hand-made custom clothes, or provide a range of services to maximize your revenue.
#1. Real Estate Agent
Average Annual Revenue: $298,870 Average Profit Margins: 44.6% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: -0.3% Best for: Strong salespeople and negotiators, entrepreneurs who want a passive income
A realtor or real estate agent works on behalf of property buyers or sellers to help them get what they want out of the deal. If you’re an active listener with strong sales, organization, and negotiation skills, real estate can be a great business idea.
Now, you do need a license to become a real estate agent. The licensing requirements vary by state and usually involve around 60-120 hours of coursework followed by an exam. None require a degree beyond a high school diploma, so while you will need specific knowledge to excel in this field, that doesn’t need to be a barrier to entry.
Do you want to know how to become a successful real estate agent? Highly successful real estate agents can earn upwards of $500,000 a year! But, to make it into the highest tier of earners, you need to be aware of certain insider information which details the best path for how to become a successful real estate agent. Watch our video to uncover these secrets!
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lzgxxq_FYHY"]
Do you want to know how to be a real estate agent–and one that doesn’t fail in their first 5 years, like 87% of new agents? Santino Filipelli is the principal broker and owner of the $175K/month firm Modern Realty, and he’s sharing his tips and insight in this episode.
#2. Web Designer
Average Annual Revenue: $239K+ Average Profit Margins: 5.3% Startup Cost: $100-$1K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.4% Best for: Designers, programmers, or anyone with website building skills
Freelance web design is a profitable self-employment idea for people with strong visual design and computer skills. The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 23% increase in demand for website designers through 2031, making this a potentially lucrative business venture with a lot of opportunities.
You don’t need to be a tech expert to start your own business designing websites, either. While a basic understanding of HTML and other coding languages is helpful, people with expertise in WordPress templates, search engine optimization, and user experience can build a successful small business as a web designer.
#3. Freelance Writing

Average Annual Revenue: $712K/employee Average Profit Margins: 14.6% Startup Cost: $100-$200 Time To Revenue: 1 month to 3 years Annual Market Growth Rate: -1.5% Best for: Creative entrepreneurs with strong communication skills
Despite the doom and gloom predictions that AI will eliminate writing jobs, these tools still have major limitations and freelance writers are as in-demand as ever.
As a self-employed freelance writer, you can take on a huge variety of work. Some focus on online content like news articles and blogs, while others ghostwrite novels, memoirs, and other books for clients.
Freelance writing can also be combined with other skills to boost your self-employment income. For example, technical writing is a profitable option for tech industry experts, while those with healthcare experience can turn that into a career as a medical writer.
#4. Graphic Designer
Average Annual Revenue: $123,240 Average Profit Margins: 13.5% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 3+ months Annual Market Growth Rate: 2% Best for: Visual artists, creative entrepreneurs, and entrepreneurs with web design, user interface, or similar tech skills
Another creative profession that’s a great self-employment idea is graphic design. Just like with writing, there are a lot of ways you can earn money if you have these skills.
Some graphic designers work closely with web designers, creating the images that enhance this online content. Others create images for ads and marketing materials, design logos for companies, or upload their designs to print-on-demand sites like Redbubble .
Another great business opportunity for graphic designers is to open your own online shop through a site like Etsy. Vlad Kuksenko combined his graphic design expertise with his love of animals to start TagPup, now the site’s #1 pet products store.
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dqHBHA4AmU"]
#5. Affiliate Marketing
Average Annual Revenue: $60K-$160K Average Profit Margins: 8% Startup Cost: $500-$2K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 10.5% Best for: Bloggers, YouTubers, those with a large social media presence
If you have a substantial social media presence, affiliate marketing could be the right business idea for you. It’s also a good home business idea for bloggers, copywriters, and experts in search rankings, SEO, and other digital marketing skills.
Affiliate marketers promote products and services to earn money on commission from each sale made through their site. This can bring in a big income with a small time commitment if you’re able to generate a lot of traffic.
To make even more money, you can scale your business into a marketing agency. Affiliate marketer Matt Diggity started his own firm and now makes about $400,000 in monthly revenue:
The best part about affiliate marketing for many is that you work completely for yourself, not for clients. This gives you full control to set your own hours and pick what products you promote.
#6. Photography
Average Annual Revenue: $50K Average Profit Margins: 7.3% Startup Cost: $1K-$10K Time To Revenue: 1-6 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.3% Best for: Photographers and visual artists with strong customer service, communication, and organization skills
Photography is another of those self-employed businesses that can take a lot of forms. You can open a portrait studio, photograph events like weddings, or sell your pictures as stock photos through sites like Shutterstock or Getty Images , just to name a few options.
Another great way to make money as a photographer is to partner with other businesses. Mile High Productions specializes in drone photography and videography for real estate agents, commercial marketing, and similar clients, and makes upward of $35,000 a month doing it. Hear more advice from them in this YouTube interview:
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EUcv1HAAbns"]
Katelyn James Photography has grown into the premier online destination for photography education. The business’s revenue has grown along with its reputation, generating more than $200,000 every month. That’s way beyond the $24,000 a month goal Katelyn made starting a photography business in college.
#7. Direct Sales Consultant
Average Annual Revenue: $68,310 Average Profit Margins: 6.8% Startup Cost: $1K-$100K Time To Revenue: 3+ months Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.5% Best for: Salespeople, those with marketing skills, those that like to travel and socialize with other people
The classic door-to-door salesman is a type of direct sales consultant, though today, many connect with customers online or over the phone as well as face-to-face.
Being a direct sales consultant is similar to affiliate marketing in that you earn a commission for selling other people’s products to customers. The commission is higher in direct sales, though, usually around 20%-40%, so you can make money fast if you have strong sales skills.
#8. Landlord or Property Manager
Average Annual Revenue: $372,940 Average Profit Margins: 10.1% Startup Cost: $100K-$3.5M Time To Revenue: 6-18 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.3% Best for: Those that are interested in real estate investing, home repair, and maintenance
You can become a landlord by investing in real estate and renting it to tenants, or managing properties on behalf of others if you don’t have the cash on hand to invest.
Property management is among the most profitable self-employment ideas, too. Thach Nguyen averages $800,000 every month from his properties. Hear his advice and strategies in this YouTube interview:
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TWCzwn3R78A"]
#9. Social Media Consultant
Average Annual Revenue: $817K Average Profit Margins: 6.9% Startup Cost: $100-$10K Time To Revenue: 1-6 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.3% Best for: Social media experts, writers, and content creators, people with search engine optimization (SEO) expertise
In the interview below, we talk to the CEO and founder of Socialistics, learning how he turned a side hustle into a mid-six-figure business.
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kb1czTEK8f8&ab_channel=UpFlip"]
A strong presence on social media platforms is a must-have for many businesses today, but not every business owner is skilled with these platforms. If you are, self-employment as a social media consultant could be the right business idea for you.
Growth potential is one of the main advantages of starting a social media consulting business. It can be easily scaled into a digital marketing agency, as Eric Berman did with Brandetize. You can learn how he built his business in this podcast interview:
#10. Event Planning

Average Annual Revenue: $34,380 Average Profit Margins: 12.2% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 3+ months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1% Best for: Strong networkers, great party planners, outgoing and social entrepreneurs
An event planner does exactly what it sounds like: helps people and businesses put together big gatherings. These could be corporate events for companies or private events like weddings, Bar and Bat Mitzvahs, family reunions, or birthday and anniversary parties.
How much you can expect to earn as an event planner depends on what niche you focus on. The average salary of a corporate event planner in the US is around $63,000 a year , while wedding planners earn an average annual revenue of $112,000 .
#1. Start an Online Store
Average Annual Revenue: $60K-$120K Average Profit Margins: 5-15% Startup Cost: $100-$10K Time To Revenue: 30-90 days Annual Market Growth Rate: -9.3% Best for: Thrifters, collectors, hobbyists, and craftsmen
You can make money selling just about anything with an e-commerce business. For makers and artists, it’s a way to sell your wares to customers all over the world. You could also resell things like vintage clothes, collectibles, rare books, or whatever else tickles your fancy.
Whatever you decide to sell with your e-commerce business, you’ll need customers to buy it. This is why people with strong marketing skills tend to do the best with an e-commerce business.
Portland Razor Company built a community around their brand to grow their sales to $7,500 a month. You can hear how they did it in this YouTube interview:
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aXWiqmePZe0&list=PLaU6uY9Yy7XmTcFZcez2SJipVSL_iC_J8"]
E-commerce was still a fairly new industry when Unique Vintage started 22 years ago. The company has grown with the industry, earning accolades like being one of Inc 5000’s fastest-growing private companies in 2020 and Newsweek’s Best Online Shop for 2020/2021. In our interview with her, Unique Vintage founder Katie Echeverry explains how she started and grew this thriving online clothing store.
#2. Be a Virtual Assistant
Average Annual Revenue: $35K-$50K Average Profit Margins: 10.5% Startup Cost: $100-$200 Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.9% Best for: Outgoing and social entrepreneurs; those with strong scheduling, time management, and problem-solving skills
A virtual assistant business is one of the easiest to start from home. All you need is a reliable internet connection and a few clients who need help planning or organizing their life or business.
The type of work you do as a virtual assistant depends on your clients. It often involves things like replying to emails, making travel or dinner reservations, and other planning and logistic things.
The site 24/7 Virtual Assistants is a great place to find work if you’re thinking of starting this type of business.
#3. Start a Cleaning Service

Average Annual Revenue: $74,880 Average Profit Margins: 6.7% Startup Cost: $1K-$30K Time To Revenue: 1-6 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% Best for: Self-motivated, independent, and detail-oriented entrepreneurs
Life is messy–and that’s why cleaning services exist. Like other options on this list, there are a variety of niches you can go into, from residential home cleaning to janitorial services to outdoor work like window or gutter cleaning.
The 7-Figure Cleaning Business Blueprint is an excellent resource for anyone who’s considering self-employment in home cleaning services.
A cleaning business is a great option for a first-time entrepreneur because start-up costs are low and you don’t need special training to get started. Just ask Chris Mondragon. He and his wife started Queen Bee Cleaning Service in 2015 with just $5,000. Five years later, they’ve grown to a staff of 25 and earned a revenue of $1.5 million in 2021, with more than $3.2 million in cumulative sales.
If you’re more interested in something like power washing or roof cleaning, this interview with Northwest Pro Wash founder Spencer Claeys can give you some helpful insights.
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2lTDQb4HJH0&list=PLaU6uY9Yy7XmmBfiLC1KpSMZ3-Ms0vGtc&index=4"]
#4. Be a Child Care Provider
Average Annual Revenue: $143,110 Average Profit Margins: 0.9% Startup Cost: $0-$1K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 51.7% Best for: Those that enjoy childcare and like children
Busy parents need people they can trust to keep their kids safe and healthy when they’re not home. You can provide this service while being your own boss by starting a child care business.
The simplest and most affordable way to start is with nanny or babysitting services right in clients’ homes. If you want to scale, you can open your own daycare center, either out of your home or in a commercial space.
#5. Be a Personal Trainer
Average Annual Revenue: $16,867 Average Profit Margins: 10.9% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-6 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 0.6% Best for: Fitness buffs, exercise experts, people who excel at motivating others
Personal trainers work one-on-one with clients to help them lose weight, recover from injuries, prepare for athletic events, or simply improve their overall health. It’s one of the best self-employed business ideas for people who love to exercise and stay active on the job.
The average salary for a personal trainer in the US is $65,790 a year , but in truth, there’s no upper limit on what you can earn. Personal training is a big part of Bedros Keuilian’s multi-million dollar empire. You can hear how he built it in this YouTube interview:
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gXdFpkfXvGA"]
#1. Life Coach
Average Annual Revenue: $63,400 Average Profit Margins: 10.5% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.5% Best for: Therapists, productivity experts, people who love helping others
Being self-employed as a life coach can be a very rewarding job, helping other people to improve their personal life, mental health, relationships, career progress, or whatever else they struggle with.
People come to life coaches for their experience and wisdom, making this one self-employed job where being over 50 gives you an advantage over younger entrepreneurs.
#2. Personal Finance Consultant

Average Annual Revenue: $1,810,230 Average Profit Margins: 36.1% Startup Cost: $500-$5K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 8.2% Best for: Accountants and financial experts
This is another excellent way to leverage a lifetime of experience managing your personal finances into a self-employed job. People look to finance consultants to help them plan for retirement, save for their kids’ college, or prepare for a large purchase like a home or new business.
Bankers and accountants are especially well-suited to this type of work, and you’ll have the easiest time landing clients and earning their trust if you have certification like a CPA .
#3. Reselling
Average Annual Revenue: $60K-$120K Average Profit Margins: 5-15% Startup Cost: $100-$1K Time To Revenue: 30-90 days Annual Market Growth Rate: -9.3% Best for: Shoppers and collectors, thrifters and collectors
If you have an eye for spotting valuable items at garage sales, thrift stores, or storage unit auctions, you can make self-employment income selling these items for a profit.
Life-long collectors may not even need to buy inventory to resell if they have items around their home they’re willing to part with. You can also find free inventory on sites like Craigslist or Facebook Marketplace to get started with no investment.
You can turn your passion for collecting valuable items into a lucrative business, just like how Tia discovered when she was reselling clothes and sneakers. Check out the video below on how she managed.
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dJryzKeGwtU&ab_channel=UpFlip"]
An eBay shop or similar online store is the fastest and most affordable way to start reselling. That’s what Mike Wilson did to start Golden State Picker, a $30,000-a-month reselling business:
If you’d rather stay analog, you can open a storefront or rent a booth at a flea market or similar venue.
#4. Professional Organizer
Average Annual Revenue: $168,360 Average Profit Margins: 10.6% Startup Cost: $1K-$100K Time To Revenue: 1-3 months Annual Market Growth Rate: 1.2% Best for: Highly organized entrepreneurs, strong planners, communicators, and collaborators, creative problem-solvers
Professional organizers help people bring order to the chaos of daily life. It’s among the top self-employment ideas for seniors with high analytical reasoning, high empathy, and strong communication skills.
As an organizer, the main thing you bring to the table is your knowledge and guidance, so this is a very affordable business to start. There also isn’t too much physical work involved. While you may help move items, much of the work is helping people decide what to keep or dispose of and giving them strategies they can use to maintain the order you’ve created.
What are the 4 types of self employment?
The most common types of self-employment include:
- Freelancing - Also known as independent contractors, freelancers perform services for clients but control when and how they work.
- Gig work - This includes jobs like rideshare and delivery drivers. Gig workers choose which jobs they take on, but usually have less control over when and how they work than freelancers. However, these terms are often used interchangeably.
- Sole proprietor - A sole proprietor owns their own business selling a product or service. They may be a solo entrepreneur or have a team of employees.
- Partnership - This is when you own your own business along with a business partner.
Can I do self-employed business ideas from home?
For those wondering what kind of business I can start from home, you can start any of these self-employment business ideas from home.
What is the cheapest, most profitable business to start?
This depends on what skills and knowledge you bring to the table. However, on average, the businesses with low upfront costs that have the highest profit margins include affiliate marketing, Airbnb hosting, and digital marketing.
What are some self-employment ideas for nurses?
Having medical credentials opens up a lot of options for RNs, LPNs, or other nursing professionals. One option is to become a traveling nurse or nurse consultant who works in healthcare facilities as a contractor.
If you’d rather work with people in their homes, working as a personal trainer, nutritionist, or wellness consultant might be up your alley.
Senior care is a growing home health segment that opens up self-employment jobs for trained nurses.
What kind of business can I start from home?
Many of the business ideas listed here can be started easily out of a private home without needing a brick-and-mortar space. Any service-based business falls into this category, including things like event planning, cleaning, tutoring, writing, or any kind of coaching. Online stores can also be easily run from home.
What are some easy self-employment ideas for ladies?
Any of the self-business ideas listed in this article can be a great way for people of any gender to set their own hours and be their own boss.
The most popular self-employment ideas for women in the US, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , are professional services (such as accounting or consulting), education, health, and retail.
What are good self-employment ideas to earn passive income
Being a landlord or Airbnb host can generate a large, mostly-passive income stream, and can be fully passive income if you hire someone to work with guests or tenants.
Are you ready to start your own business and make your own hours?
We’ve provided you with dozens of self employment ideas for you to try.
Using this list is just the beginning. We aim to create content that helps people the most.
If you are self employed, we want to know what you think are the best self-employed jobs. What is your favorite business idea?
Food Truck for Sale: Ultimate Buying Guide 2024
Buying a food truck is the single largest investment a food truck business owner will make. That’s why we offer this guide on buying a food truck for sale.
We’ve interviewed a lot of business owners and they’ve provided advice on how to buy a food truck. We’ve also added additional information from research to help you buy or lease a food truck.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"] Click on any of the links below to find information about a food truck for sale.
Find creative food truck ideas
Create a food truck mockup, find food trucks for sale, get food truck financing, get food truck equipment, how to build a food truck, how to start a food truck business.
- Find a food truck to buy [/su_note]
How to buy a food truck for sale

You’ll want to perform the following process while buying a food truck:
- Build a food truck
- Start a food truck business
Before you even think about buying a food truck for sale, you need to know how the food truck business will make you money. That means you must decide what food and drinks you’ll serve in the food truck. Some food truck ideas include a:
- Pizza truck
- Concession trailer
- Mobile coffee shop
- Ice cream truck
- Breakfast food truck
- Seafood truck
- Lunch truck
- Dinner truck
- Food truck bar
Check out our interview with Saied Samaiel, who started Aybla Grill, which makes more than $50K a month.
Once you’ve decided what you’ll serve as a new food truck business owner, you’ll need to consider how to set up your food truck. If you don’t do it right, your food business success could be much slower.
It will be much easier for your new food truck to succeed if you plan before shopping for a food truck. You’ll want to create a concept design for your food truck, which means you’ll need to:

Measure food truck dimensions
Get a list of equipment you need (and all dimensions), draw the food truck layout.
Let’s look at each step to understand what you’ll need in a food truck for sale.

During the design stage, you’ll need to know the exterior and interior dimensions of food trucks. The outside dimensions of a food truck are useful to know so you can estimate how much it costs to wrap a food truck.
You’ll need the interior dimensions to know whether you can fit the equipment in the space. A food truck can be as small as a postal truck or up to 34 feet long. Most food trucks will be seven feet wide. You’ll also want to ensure the food truck is at least seven feet tall so people can stand comfortably.
In addition to considering different truck dimensions, your food truck business will need additional equipment to operate effectively. You’ll need to know the types of equipment you need and the size to make sure you can fit all the cooking equipment in the food truck you purchase.
Depending on the type of food truck offerings you’ll provide, you’ll need a variety of mobile cooking equipment. Your mobile commercial kitchen will need:
- Fire suppression system
- Food truck menu board
- Cash register/payment processor
- Outdoor furniture for guests (optional)
- Cooking equipment
- Food truck exhaust fan (or food truck vent hood)
- Refrigerator and freezer
- Food truck sink
- Storage for dry food
- Food truck awning
- Space for food truck supplies
- Drink machine
- Food truck oven
- Ice machine
- Food truck window
- Cooking utensils
- Air conditioning and heater
- Food truck water tank
As you can see, there are a lot of food truck appliances that need to fit into a fairly small cooking space. Fortunately, you have the option of buying food trucks fully equipped, which makes starting a food truck business much easier than designing your own storage setup and prep space from scratch.
Once you know the sizes of food trucks and the commercial equipment you need, you’ll need to map out the best way to fit it all in the vehicle.
A new business owner can choose three methods of planning the equipment layout.
- Do-it-yourself (DIY) design
Look for fully equipped food trucks for sale
Hire a mobile commercial kitchen design company.
There are pros and cons to taking each approach when buying a food truck for sale. Keep reading to find out more.
DIY food truck design

When you design your own food truck layout before buying a truck, you’ll want to look for a multipurpose food truck. You can choose to buy a new or used food truck that does not come with commercial equipment for cooking.
Designing the truck layout yourself comes with some challenges. For instance, you’re probably not trained to design and install a professional fire suppression system, work with gas appliances, or install HVAC equipment.
This may be the least expensive way of buying a new food truck for your dream food business, but if you can buy a used food truck for sale, you will probably find it much quicker and easier than building a food truck yourself.
Suggested layout for food trucks
A food truck owner will want to dispense the weight so it is as evenly distributed as possible to reduce the risk of fishtailing .
Whether you choose to have your food truck laid out clockwise (as pictured) or counterclockwise, you’ll want to consider the order in which you or your employees will perform your food prep and service processes.
For instance, a pizza truck might not have condiments and have a pizza-cutting station instead.
You’ll want dedicated spaces for the following, arranged in this order:
- Processing sales
- Cool storage
- Packaging or plating and finishing touches
Finally, you’ll serve your customers out of the second window.
If you serve drinks, you can have a self-service drink machine near the cashier or at the other end of the serving window. Either way, I suggest having it on the same side.
While the exact features of each food truck business will be different, the concepts are the same.

If you buy a fully equipped food truck, there’s no need to do design work. These will normally be more expensive than buying a truck without equipment, but you’ll know the food truck was designed by a professional.
There are plenty of places for a new owner to buy a food truck that is fully equipped with everything you need to start your mobile food truck business. Just search online for the type of food trucks you want to buy. Some common searches include:
- Food trucks for sale
- Used food trucks for sale
- Coffee truck for sale
- Food truck for sale near me
- Used food trailers for sale
- Food carts for sale
- Taco truck for sale
- Food truck trailers for sale
- Lunch truck for sale
- Food truck trailer for sale
- New food truck for sale
- Food trailer for sale
- Used food truck for sale
- Step van for sale
- Food cart for sale
You might also want to add modifiers to your search like “Near me”, state name, city name, or state abbreviation. Some popular searches for local food trucks for sale include:
- Food truck for sale Texas
- Food truck sale California
- Food trucks for sale Los Angeles
- Food trucks for sale Dallas
- Food trucks for sale in Georgia
You can buy custom food trucks if you need a unique system for your food business. That said, before you spend the extra time and money to have engineers design a pro fire suppression system and select the equipment for a custom-designed food truck, make sure you can’t find them premade.

You don’t want to request a custom design, then have the company you work with turn it into a commercially available option. This actually occurred when my dad had custom designs built. He commissioned someone to create a mold, then they started selling the design as a standard product.
While it was great for the company, it meant my dad fully paid for the product development process. Read your contracts when you commission custom work. To keep a product one of a kind, you’ll need to own all design work and any custom fabrications used to create the product.
The next step is looking at food trucks for sale. You’ll want to:
Choose the type of food truck for sale
- Establish how much the food truck will cost
- Decide where to buy the food truck

You can choose from a variety of food trucks. Here are some of the options:
- Concession trailers
Let’s look at the benefits of each of these options when you decide to become a mobile food vendor.
Why should I buy a food truck?
When you look for a food truck for sale, you’ll get a vehicle that has the kitchen and the driving equipment all in one piece. This makes the vehicle safer and easier to drive because there is no trailer attached to the food truck.
A new owner can buy a food truck fully equipped for a specific type of food sales, purchase a multipurpose food truck, or buy an empty food truck that can be fully customized.
Why should I consider concession trailers?

If you own a truck, you might save money buying a concession trailer. There’s also more space in a food trailer than in a food truck because there is no engine, transmission, or passenger space in the trailer.
A food trailer has the benefit of separating the food truck trailer from the engine and transmission. That means you can buy or sell the food truck trailer and the truck together or separately.
You can also leave the food trailer at a location if you’ll be working there for multiple days. This saves you money because you don’t have to tow the concession trailer with you everywhere.
What are the benefits of a food cart?
A food cart is less beneficial than a food truck because most are not motorized. These are a budget way of starting a mobile food business.
Food carts can make a great entry-level food business that is a stepping stone to eventually buying a food truck for sale. Some common food cart business ideas include:
- Ice cream cart
- Hot dog stand
- Drink stand
- Coffee shop
These machines will roll, but the owner must pull or push them to where they want to serve customers.
What are the benefits of a step van?

A step van is a type of food truck that allows you to access the cooking area from the cab.
This is advantageous because you can stop the truck and get to the cooking section without going outside, which is why many food truck business owners use them instead of box trucks.
How much is a food truck?
A food truck for sale can range anywhere from a couple of thousand dollars for a used food truck in poor condition to $200K for a brand-new, fully equipped food truck.
Saied explained:
[su_quote]A stationary food truck (one that stays at the same location each day) is more profitable than one you are driving to a different location each day.[/su_quote]
We’ll talk more about choosing a location for your food truck later.
How much is a food truck to rent?

Food truck rentals cost between $1,000 and $5,000 per month, depending on the terms of the fully equipped food truck rental. You will want to consider terms like:
- Equipment in the food truck
- Duration of services
- Licensing and health department inspections (included and excluded)
Consider renting a food truck so you can get your business started, earn revenue, and then qualify for food truck financing after you have proven your business model.
How much does a food truck cost to buy?
You can buy a food truck for as little as $6,000, but you can find less expensive alternatives.
How much is a used food truck?
According to Roaming Hunger, used food trucks will cost at least $6,000 unequipped or $8,000 with equipment. The prices can go up from there depending on the age of the equipment and the truck and whether it includes a business.
Where to buy a food truck

You can find a food truck for sale through companies like:
- Roaming Hunger
- Local food truck dealers
- Online marketplaces
- Food truck auction sites
- Business brokers
- Local food truck association
Food truck manufacturer
On the West Coast, Mobile Cuisine ranks Prime Design Food Trucks as their top manufacturer. The company builds, remodels, and repairs food trailers and trucks, so you can go to them to get all your equipment and your truck from one place.
On the East Coast, Mobile Cuisine suggests going to Mr. Trailers , which provides food trucks and mobile medical units.
Check out their blog for a list of manufacturers by state. Most food truck manufacturers are located in California, Texas, and Florida, but there are some in other states.
Now that you can answer “How much for a food truck?” and know where to buy them, let’s discuss getting food truck financing.

You can get food truck financing using seven different loan strategies.
- Business line of credit
- Business term loan
- Equipment financing
- Merchant cash advance
- Small Business Administration loan
- Vendor leasing programs
- Working capital loan
Check out our blog about food truck financing , then head over to National Business Capital to apply for food truck loans from the number one provider of online business loans.
This step will vary depending on whether you buy a fully equipped food truck or an empty step van, trailer, or box truck. If you bought a fully equipped vehicle, skip to the section about starting a food truck business. If you didn’t, make sure to read this and the next section.
What food truck equipment do I need?

When you enter the food truck industry, you’ll need:
- An enticing menu
- A refrigerator and freezer
- Exhaust fans
- Huge exterior lightboxes
- Storage space
- Cash register or point-of-sale (POS) machine
Don’t forget to get any specialized equipment based on your food truck needs.
Where to buy food truck equipment
Next, you’ll need to buy the equipment for your step van or trailer. You can purchase these products from some of the following places.
Restaurant supply house
A restaurant supply house is a place that sells food items to serve customers as well as equipment. Most are equipped to help you establish what you need to prep, cook, and serve food. You can go to your local store or shop online. Some popular restaurant supply houses include:
- RestaurantSupply.com: They carry equipment including Manitowac refrigeration machines, cooking equipment, and other products, but not food. They are a supplier for employee-owned Winco grocery stores. Check out Restaurant Supply .
- Web Restaurant Store: Check out Web Restaurant Store’s page for food truck tabletop equipment. They advertise having more than 400K products for sale.
- Amazon: Like every industry, you can get your storage and food prep products from Amazon Business .
Keep reading for other solutions a food truck owner could pursue.
Customization shop

A food truck business owner can also go to auto repair shops that focus on upgrading work vehicles. These companies should be located near you and offer services like:
- Food Truck Wraps: Help people see what you’re serving in your food truck van.
- Huge Exterior Light Boxes: At night, these will help people see the food truck name, menu, and price.
- Food Truck Logos: Nothing builds food truck brand awareness like a logo.
- Equipment Mounting: A mobile kitchen must have the equipment mounted to the food truck interior so it doesn’t fly around.
You might look for people who specialize in car wraps, mobile HVAC, and other features. Check out some food truck wrap ideas below.
Building a food truck requires the following steps.
Create a drawing of the food truck layout
- Strip the food truck
Gather all the equipment
Install concession window, install flooring, install electrical, install gas lines.
- Install plumbing in your food truck
Install a three-compartment sink
Install cooking equipment, install fire suppression system.
The following subsections are a summary of the step-by-step tutorials from Mobile Cuisine combined with my experience in construction management.
Keep reading for more information on how to build a food truck.
You want to have your step van or food trailer design mapped out before you begin. Otherwise, you might not be able to fit everything in the food truck. We discussed how to do this earlier in the blog. Revisit the section on creating a food truck mockup and measuring for equipment (above) for a refresher.
Next, you’ll want to gather all your storage, equipment, and tools so it is easy to start working on the food truck. I suggest laying out the equipment you want in the truck in the same relative position it will go into the step van so you can visualize it before installing it.
Strip the truck

When you buy a multipurpose food truck or trailer, you’ll need to strip out anything that could hinder you from doing business. This includes seats, trim, and anything else you don’t need.
Many people include this step later in the steps for building a food truck, but you need to at least cut out the hole before you do anything else.
Can you imagine how frustrating it would be to install something and then have to redo it because it doesn’t line up with the windows?

Once you have the window cut out for the step van, it’s time to install the floors. You’ll want to make sure you have slip-resistant materials that will not be damaged by heat, cold, or spills (meaning no carpet!).
Make sure the floor is level before installing the flooring materials onto the multipurpose food truck. You might also get slip-resistant kitchen mats like the ones pictured below. You’ll put them in once your food truck is complete.
You’ll need to install a breaker panel, electrical wiring, and lighting fixtures. You’ll probably want to hire or consult with an electrician to make sure you size them right.
If you decide to install the electrical yourself, please refrain from turning it on until after you install safety devices to prevent fires. It would be devastating if your food truck caught fire before you even used it.

A fire prevention system may be required for a food truck. Related equipment may include:
- Fire extinguishers
- Splash guards
- Gas monitors
- Properly secured appliances
- Flexible gas hoses
- Shut-off valves
- Other requirements depending on the business location
Once your multipurpose food truck is equipped with the proper security features, it’s time to install gas lines.
Gas lines will be used in many food truck applications to cook the food. Installing them is not hard, but you need to know what you’re doing.
Most states have laws holding people criminally liable for improper gas line installation.
For this reason, we won’t be providing step-by-step information. Please hire or at least consult a professional. Most HVAC providers are happy to help with work like this for a reasonable cost.
Install plumbing

You’ll need a freshwater reservoir, a waste water reservoir, and a pump in addition to piping and fittings. Check with your local health department about any special rules they’ll require you to follow.
Local health departments normally require a three-compartment sink in every food truck. The sink wells are for washing, rinsing, and sanitizing and make it possible to keep clean and dirty utensils separate.

Next, you’ll want to install the appliances to cook food. Secure them to the food truck wall and connect them to the electrical or gas power source.
At this point, you’ll likely need to get a fire inspection or health audit to make sure the unit meets all local requirements. We discuss this process in detail in the portion about how to start a food truck business below.
Buying a food truck for sale is only a portion of starting a food truck business. There are 11 steps to follow when you start and expand your food truck business.
- Learn about the food truck industry
- Generate food truck ideas
- Know how much it costs to start a food truck business
- Figure business operating costs
- Write a food truck business plan
- Determine financing options
- Obtain licenses and permits
- Buy your truck
- Secure your suppliers
- Streamline the process
- Build your food truck business and brand
Read our blog about starting a food truck for more details on the full process.
Find a food truck to buy

Now that you know how to find a food truck for sale, it’s up to you to find a seller, contact them, and buy your food truck. Sign up for our mailing list to be the first to know when we release our food truck business course. We’ll be sure to make room for you.
What else would you like to know about buying a food truck for sale?
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
Published: February 06, 2024
I believe that reading sample business plans is essential when writing your own.

hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(53, 'e9d2eacb-6b01-423a-bf7a-19d42ba77eaa', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
As you explore business plan examples from real companies and brands, it’s easier for you to learn how to write a good one.
But what does a good business plan look like? And how do you write one that’s both viable and convincing. I’ll walk you through the ideal business plan format along with some examples to help you get started.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Format
Business plan types, sample business plan templates, top business plan examples.
Ask any successful sports coach how they win so many games, and they’ll tell you they have a unique plan for every single game. To me, the same logic applies to business.
If you want to build a thriving company that can pull ahead of the competition, you need to prepare for battle before breaking into a market.
Business plans guide you along the rocky journey of growing a company. And if your business plan is compelling enough, it can also convince investors to give you funding.
With so much at stake, I’m sure you’re wondering where to begin.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Fill out the form to get your free template.
First, you’ll want to nail down your formatting. Most business plans include the following sections.
1. Executive Summary
I’d say the executive summary is the most important section of the entire business plan.
Why? Essentially, it's the overview or introduction, written in a way to grab readers' attention and guide them through the rest of the business plan. This is important, because a business plan can be dozens or hundreds of pages long.
There are two main elements I’d recommend including in your executive summary:
Company Description
This is the perfect space to highlight your company’s mission statement and goals, a brief overview of your history and leadership, and your top accomplishments as a business.
Tell potential investors who you are and why what you do matters. Naturally, they’re going to want to know who they’re getting into business with up front, and this is a great opportunity to showcase your impact.
Need some extra help firming up those business goals? Check out HubSpot Academy’s free course to help you set goals that matter — I’d highly recommend it
Products and Services
To piggyback off of the company description, be sure to incorporate an overview of your offerings. This doesn’t have to be extensive — just another chance to introduce your industry and overall purpose as a business.
In addition to the items above, I recommend including some information about your financial projections and competitive advantage here too.:
Keep in mind you'll cover many of these topics in more detail later on in the business plan. So, keep the executive summary clear and brief, and only include the most important takeaways.
Executive Summary Business Plan Examples
This example was created with HubSpot’s business plan template:

This executive summary is so good to me because it tells potential investors a short story while still covering all of the most important details.
.webp?width=500&height=418&name=executive-summary-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
Image Source
Tips for Writing Your Executive Summary
- Start with a strong introduction of your company, showcase your mission and impact, and outline the products and services you provide.
- Clearly define a problem, and explain how your product solves that problem, and show why the market needs your business.
- Be sure to highlight your value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential.
- Keep it concise and support ideas with data.
- Customize your summary to your audience. For example, emphasize finances and return on investment for venture capitalists.
Check out our tips for writing an effective executive summary for more guidance.
2. Market Opportunity
This is where you'll detail the opportunity in the market.
The main question I’d ask myself here is this: Where is the gap in the current industry, and how will my product fill that gap?
More specifically, here’s what I’d include in this section:
- The size of the market
- Current or potential market share
- Trends in the industry and consumer behavior
- Where the gap is
- What caused the gap
- How you intend to fill it
To get a thorough understanding of the market opportunity, you'll want to conduct a TAM, SAM, and SOM analysis and perform market research on your industry.
You may also benefit from creating a SWOT analysis to get some of the insights for this section.
Market Opportunity Business Plan Example
I like this example because it uses critical data to underline the size of the potential market and what part of that market this service hopes to capture.

Tips for Writing Your Market Opportunity Section
- Focus on demand and potential for growth.
- Use market research, surveys, and industry trend data to support your market forecast and projections.
- Add a review of regulation shifts, tech advances, and consumer behavior changes.
- Refer to reliable sources.
- Showcase how your business can make the most of this opportunity.
3. Competitive Landscape
Since we’re already speaking of market share, you'll also need to create a section that shares details on who the top competitors are.
After all, your customers likely have more than one brand to choose from, and you'll want to understand exactly why they might choose one over another.
My favorite part of performing a competitive analysis is that it can help you uncover:
- Industry trends that other brands may not be utilizing
- Strengths in your competition that may be obstacles to handle
- Weaknesses in your competition that may help you develop selling points
- The unique proposition you bring to the market that may resonate with customers
Competitive Landscape Business Plan Example
I like how the competitive landscape section of this business plan below shows a clear outline of who the top competitors are.
.webp?width=500&height=405&name=competitive-landscape-business-plans-examples%20(1).webp)
It also highlights specific industry knowledge and the importance of location, which shows useful experience in this specific industry.
This can help build trust in your ability to execute your business plan.
Tips for Writing Your Competitive Landscape
- Complete in-depth research, then emphasize your most important findings.
- Compare your unique selling proposition (USP) to your direct and indirect competitors.
- Show a clear and realistic plan for product and brand differentiation.
- Look for specific advantages and barriers in the competitive landscape. Then, highlight how that information could impact your business.
- Outline growth opportunities from a competitive perspective.
- Add customer feedback and insights to support your competitive analysis.
4. Target Audience
Use this section to describe who your customer segments are in detail. What is the demographic and psychographic information of your audience?
If your immediate answer is "everyone," you'll need to dig deeper. Here are some questions I’d ask myself here:
- What demographics will most likely need/buy your product or service?
- What are the psychographics of this audience? (Desires, triggering events, etc.)
- Why are your offerings valuable to them?
I’d also recommend building a buyer persona to get in the mindset of your ideal customers and be clear on why you're targeting them.
Target Audience Business Plan Example
I like the example below because it uses in-depth research to draw conclusions about audience priorities. It also analyzes how to create the right content for this audience.
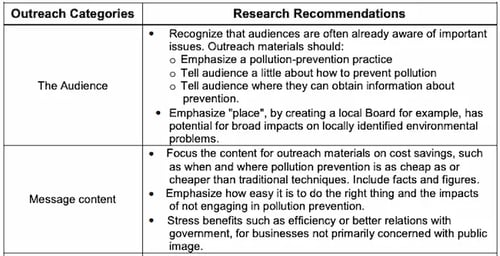
Tips for Writing Your Target Audience Section
- Include details on the size and growth potential of your target audience.
- Figure out and refine the pain points for your target audience , then show why your product is a useful solution.
- Describe your targeted customer acquisition strategy in detail.
- Share anticipated challenges your business may face in acquiring customers and how you plan to address them.
- Add case studies, testimonials, and other data to support your target audience ideas.
- Remember to consider niche audiences and segments of your target audience in your business plan.
5. Marketing Strategy
Here, you'll discuss how you'll acquire new customers with your marketing strategy. I’d suggest including information:
- Your brand positioning vision and how you'll cultivate it
- The goal targets you aim to achieve
- The metrics you'll use to measure success
- The channels and distribution tactics you'll use
I think it’s helpful to have a marketing plan built out in advance to make this part of your business plan easier.
Marketing Strategy Business Plan Example
This business plan example includes the marketing strategy for the town of Gawler.
In my opinion, it really works because it offers a comprehensive picture of how they plan to use digital marketing to promote the community.
Tips for Writing Your Marketing Strategy
- Include a section about how you believe your brand vision will appeal to customers.
- Add the budget and resources you'll need to put your plan in place.
- Outline strategies for specific marketing segments.
- Connect strategies to earlier sections like target audience and competitive analysis.
- Review how your marketing strategy will scale with the growth of your business.
- Cover a range of channels and tactics to highlight your ability to adapt your plan in the face of change.
6. Key Features and Benefits
At some point in your business plan, you'll need to review the key features and benefits of your products and/or services.
Laying these out can give readers an idea of how you're positioning yourself in the market and the messaging you're likely to use. It can even help them gain better insight into your business model.
Key Features and Benefits Business Plan Example
In my opinion, the example below does a great job outlining products and services for this business, along with why these qualities will attract the audience.

Tips for Writing Your Key Features and Benefits
- Emphasize why and how your product or service offers value to customers.
- Use metrics and testimonials to support the ideas in this section.
- Talk about how your products and services have the potential to scale.
- Think about including a product roadmap.
- Focus on customer needs, and how the features and benefits you are sharing meet those needs.
- Offer proof of concept for your ideas, like case studies or pilot program feedback.
- Proofread this section carefully, and remove any jargon or complex language.
7. Pricing and Revenue
This is where you'll discuss your cost structure and various revenue streams. Your pricing strategy must be solid enough to turn a profit while staying competitive in the industry.
For this reason, here’s what I’d might outline in this section:
- The specific pricing breakdowns per product or service
- Why your pricing is higher or lower than your competition's
- (If higher) Why customers would be willing to pay more
- (If lower) How you're able to offer your products or services at a lower cost
- When you expect to break even, what margins do you expect, etc?
Pricing and Revenue Business Plan Example
I like how this business plan example begins with an overview of the business revenue model, then shows proposed pricing for key products.

Tips for Writing Your Pricing and Revenue Section
- Get specific about your pricing strategy. Specifically, how you connect that strategy to customer needs and product value.
- If you are asking a premium price, share unique features or innovations that justify that price point.
- Show how you plan to communicate pricing to customers.
- Create an overview of every revenue stream for your business and how each stream adds to your business model as a whole.
- Share plans to develop new revenue streams in the future.
- Show how and whether pricing will vary by customer segment and how pricing aligns with marketing strategies.
- Restate your value proposition and explain how it aligns with your revenue model.
8. Financials
To me, this section is particularly informative for investors and leadership teams to figure out funding strategies, investment opportunities, and more.
According to Forbes , you'll want to include three main things:
- Profit/Loss Statement - This answers the question of whether your business is currently profitable.
- Cash Flow Statement - This details exactly how much cash is incoming and outgoing to give insight into how much cash a business has on hand.
- Balance Sheet - This outlines assets, liabilities, and equity, which gives insight into how much a business is worth.
While some business plans might include more or less information, these are the key details I’d include in this section.
Financials Business Plan Example
This balance sheet is a great example of level of detail you’ll need to include in the financials section of your business plan.
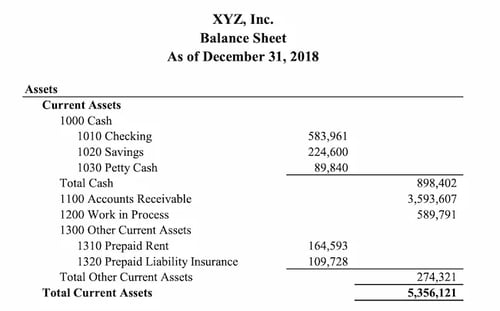
Tips for Writing Your Financials Section
- Growth potential is important in this section too. Using your data, create a forecast of financial performance in the next three to five years.
- Include any data that supports your projections to assure investors of the credibility of your proposal.
- Add a break-even analysis to show that your business plan is financially practical. This information can also help you pivot quickly as your business grows.
- Consider adding a section that reviews potential risks and how sensitive your plan is to changes in the market.
- Triple-check all financial information in your plan for accuracy.
- Show how any proposed funding needs align with your plans for growth.
As you create your business plan, keep in mind that each of these sections will be formatted differently. Some may be in paragraph format, while others could be charts or graphs.
The formats above apply to most types of business plans. That said, the format and structure of your plan will vary by your goals for that plan.
So, I’ve added a quick review of different business plan types. For a more detailed overview, check out this post .
1. Startups
Startup business plans are for proposing new business ideas.
If you’re planning to start a small business, preparing a business plan is crucial. The plan should include all the major factors of your business.
You can check out this guide for more detailed business plan inspiration .
2. Feasibility Studies
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization.
3. Internal Use
You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders. In my opinion, internal business plans are useful for alignment and building support for ambitious goals.
4. Strategic Initiatives
Another business plan that's often for sharing internally is a strategic business plan. This plan covers long-term business objectives that might not have been included in the startup business plan.
5. Business Acquisition or Repositioning
When a business is moving forward with an acquisition or repositioning, it may need extra structure and support. These types of business plans expand on a company's acquisition or repositioning strategy.
Growth sometimes just happens as a business continues operations. But more often, a business needs to create a structure with specific targets to meet set goals for expansion. This business plan type can help a business focus on short-term growth goals and align resources with those goals.
Now that you know what's included and how to format a business plan, let's review some of my favorite templates.
1. HubSpot's One-Page Business Plan
Download a free, editable one-page business plan template..
The business plan linked above was created here at HubSpot and is perfect for businesses of any size — no matter how many strategies we still have to develop.
Fields such as Company Description, Required Funding, and Implementation Timeline give this one-page business plan a framework for how to build your brand and what tasks to keep track of as you grow.
Then, as the business matures, you can expand on your original business plan with a new iteration of the above document.
Why I Like It
This one-page business plan is a fantastic choice for the new business owner who doesn’t have the time or resources to draft a full-blown business plan. It includes all the essential sections in an accessible, bullet-point-friendly format. That way, you can get the broad strokes down before honing in on the details.
2. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

We also created a business plan template for entrepreneurs.
The template is designed as a guide and checklist for starting your own business. You’ll learn what to include in each section of your business plan and how to do it.
There’s also a list for you to check off when you finish each section of your business plan.
Strong game plans help coaches win games and help businesses rocket to the top of their industries. So if you dedicate the time and effort required to write a workable and convincing business plan, you’ll boost your chances of success and even dominance in your market.
This business plan kit is essential for the budding entrepreneur who needs a more extensive document to share with investors and other stakeholders.
It not only includes sections for your executive summary, product line, market analysis, marketing plan, and sales plan, but it also offers hands-on guidance for filling out those sections.
3. LiveFlow’s Financial Planning Template with built-in automation
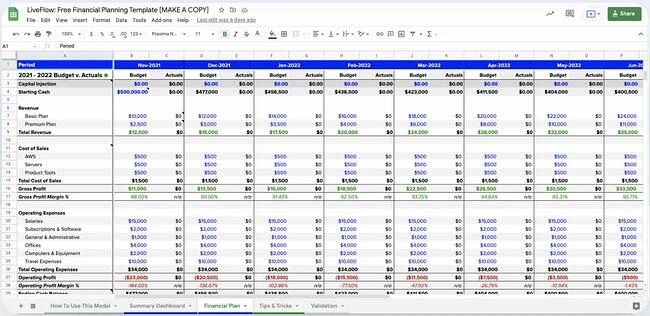
This free template from LiveFlow aims to make it easy for businesses to create a financial plan and track their progress on a monthly basis.
The P&L Budget versus Actual format allows users to track their revenue, cost of sales, operating expenses, operating profit margin, net profit, and more.
The summary dashboard aggregates all of the data put into the financial plan sheet and will automatically update when changes are made.
Instead of wasting hours manually importing your data to your spreadsheet, LiveFlow can also help you to automatically connect your accounting and banking data directly to your spreadsheet, so your numbers are always up-to-date.
With the dashboard, you can view your runway, cash balance, burn rate, gross margins, and other metrics. Having a simple way to track everything in one place will make it easier to complete the financials section of your business plan.
This is a fantastic template to track performance and alignment internally and to create a dependable process for documenting financial information across the business. It’s highly versatile and beginner-friendly.
It’s especially useful if you don’t have an accountant on the team. (I always recommend you do, but for new businesses, having one might not be possible.)
4. ThoughtCo’s Sample Business Plan

One of the more financially oriented sample business plans in this list, BPlan’s free business plan template dedicates many of its pages to your business’s financial plan and financial statements.
After filling this business plan out, your company will truly understand its financial health and the steps you need to take to maintain or improve it.
I absolutely love this business plan template because of its ease-of-use and hands-on instructions (in addition to its finance-centric components). If you feel overwhelmed by the thought of writing an entire business plan, consider using this template to help you with the process.
6. Harvard Business Review’s "How to Write a Winning Business Plan"
Most sample business plans teach you what to include in your business plan, but this Harvard Business Review article will take your business plan to the next level — it teaches you the why and how behind writing a business plan.
With the guidance of Stanley Rich and Richard Gumpert, co-authors of " Business Plans That Win: Lessons From the MIT Enterprise Forum ", you'll learn how to write a convincing business plan that emphasizes the market demand for your product or service.
You’ll also learn the financial benefits investors can reap from putting money into your venture rather than trying to sell them on how great your product or service is.
This business plan guide focuses less on the individual parts of a business plan, and more on the overarching goal of writing one. For that reason, it’s one of my favorites to supplement any template you choose to use. Harvard Business Review’s guide is instrumental for both new and seasoned business owners.
7. HubSpot’s Complete Guide to Starting a Business
If you’re an entrepreneur, you know writing a business plan is one of the most challenging first steps to starting a business.
Fortunately, with HubSpot's comprehensive guide to starting a business, you'll learn how to map out all the details by understanding what to include in your business plan and why it’s important to include them. The guide also fleshes out an entire sample business plan for you.
If you need further guidance on starting a business, HubSpot's guide can teach you how to make your business legal, choose and register your business name, and fund your business. It will also give small business tax information and includes marketing, sales, and service tips.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of starting a business, in addition to writing your business plan, with a high level of exactitude and detail. So if you’re in the midst of starting your business, this is an excellent guide for you.
It also offers other resources you might need, such as market analysis templates.
8. Panda Doc’s Free Business Plan Template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is one of the more detailed and fleshed-out sample business plans on this list. It describes what you should include in each section, so you don't have to come up with everything from scratch.
Once you fill it out, you’ll fully understand your business’ nitty-gritty details and how all of its moving parts should work together to contribute to its success.
This template has two things I love: comprehensiveness and in-depth instructions. Plus, it’s synced with PandaDoc’s e-signature software so that you and other stakeholders can sign it with ease. For that reason, I especially love it for those starting a business with a partner or with a board of directors.
9. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers several free business plan templates that can be used to inspire your own plan.
Before you get started, you can decide what type of business plan you need — a traditional or lean start-up plan.
Then, you can review the format for both of those plans and view examples of what they might look like.
We love both of the SBA’s templates because of their versatility. You can choose between two options and use the existing content in the templates to flesh out your own plan. Plus, if needed, you can get a free business counselor to help you along the way.
I’ve compiled some completed business plan samples to help you get an idea of how to customize a plan for your business.
I chose different types of business plan ideas to expand your imagination. Some are extensive, while others are fairly simple.
Let’s take a look.
1. LiveFlow
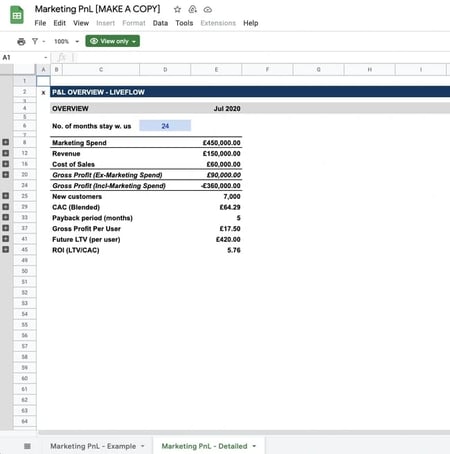
One of the major business expenses is marketing. How you handle your marketing reflects your company’s revenue.
I included this business plan to show you how you can ensure your marketing team is aligned with your overall business plan to get results. The plan also shows you how to track even the smallest metrics of your campaigns, like ROI and payback periods instead of just focusing on big metrics like gross and revenue.
Fintech startup, LiveFlow, allows users to sync real-time data from its accounting services, payment platforms, and banks into custom reports. This eliminates the task of pulling reports together manually, saving teams time and helping automate workflows.
"Using this framework over a traditional marketing plan will help you set a profitable marketing strategy taking things like CAC, LTV, Payback period, and P&L into consideration," explains LiveFlow co-founder, Lasse Kalkar .
When it came to including marketing strategy in its business plan, LiveFlow created a separate marketing profit and loss statement (P&L) to track how well the company was doing with its marketing initiatives.
This is a great approach, allowing businesses to focus on where their marketing dollars are making the most impact. Having this information handy will enable you to build out your business plan’s marketing section with confidence. LiveFlow has shared the template here . You can test it for yourself.
2. Lula Body

Sometimes all you need is a solid mission statement and core values to guide you on how to go about everything. You do this by creating a business plan revolving around how to fulfill your statement best.
For example, Patagonia is an eco-friendly company, so their plan discusses how to make the best environmentally friendly products without causing harm.
A good mission statement should not only resonate with consumers but should also serve as a core value compass for employees as well.
Patagonia has one of the most compelling mission statements I’ve seen:
"Together, let’s prioritise purpose over profit and protect this wondrous planet, our only home."
It reels you in from the start, and the environmentally friendly theme continues throughout the rest of the statement.
This mission goes on to explain that they are out to "Build the best product, cause no unnecessary harm, and use business to protect nature."
Their mission statement is compelling and detailed, with each section outlining how they will accomplish their goal.
4. Vesta Home Automation

This executive summary for a smart home device startup is part of a business plan created by students at Mount Royal University .
While it lacks some of the sleek visuals of the templates above, its executive summary does a great job of demonstrating how invested they are in the business.
Right away, they mention they’ve invested $200,000 into the company already, which shows investors they have skin in the game and aren’t just looking for someone else to foot the bill.
This is the kind of business plan you need when applying for business funds. It clearly illustrates the expected future of the company and how the business has been coming along over the years.
5. NALB Creative Center
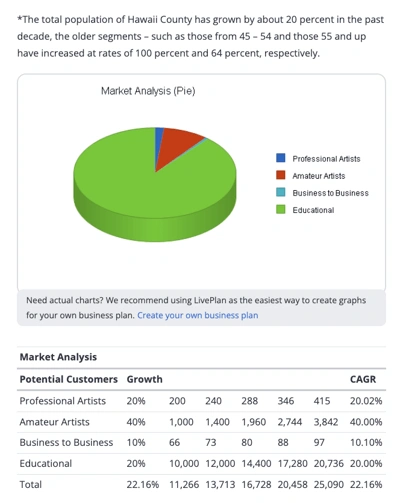
This fictional business plan for an art supply store includes everything one might need in a business plan: an executive summary, a company summary, a list of services, a market analysis summary, and more.
One of its most notable sections is its market analysis summary, which includes an overview of the population growth in the business’ target geographical area, as well as a breakdown of the types of potential customers they expect to welcome at the store.
This sort of granular insight is essential for understanding and communicating your business’s growth potential. Plus, it lays a strong foundation for creating relevant and useful buyer personas .
It’s essential to keep this information up-to-date as your market and target buyer changes. For that reason, you should carry out market research as often as possible to ensure that you’re targeting the correct audience and sharing accurate information with your investors.
Due to its comprehensiveness, it’s an excellent example to follow if you’re opening a brick-and-mortar store and need to get external funding to start your business .
6. Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS)
If you’re looking for a SaaS business plan example, look no further than this business plan for a fictional educational software company called Curriculum Companion Suites.
Like the business plan for the NALB Creative Center, it includes plenty of information for prospective investors and other key stakeholders in the business.
One of the most notable features of this business plan is the executive summary, which includes an overview of the product, market, and mission.
The first two are essential for software companies because the product offering is so often at the forefront of the company’s strategy. Without that information being immediately available to investors and executives, then you risk writing an unfocused business plan.
It’s essential to front-load your company’s mission if it explains your "Why?" and this example does just that. In other words, why do you do what you do, and why should stakeholders care? This is an important section to include if you feel that your mission will drive interest in the business and its offerings.
7. Culina Sample Business Plan

Culina's sample business plan is an excellent example of how to lay out your business plan so that it flows naturally, engages readers, and provides the critical information investors and stakeholders need.
You can use this template as a guide while you're gathering important information for your own business plan. You'll have a better understanding of the data and research you need to do since Culina’s plan outlines these details so flawlessly for inspiration.
8. Plum Sample Business Plan

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![business plan new product How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![business plan new product 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![business plan new product The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast
Finish your plan faster with step-by-step guidance, financial wizards, and a proven format.

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily, just like you can leverage an example business plan template to write your plan, we also have a gallery of over 50 pitch decks for you to reference.
With this gallery, you have the option to view specific industry pitches or get inspired by real-world pitch deck examples.
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Forming a new product development business plan
Table of Contents
Creating a product idea
Outline the concept and idea, do market research , create a pitch, business planning for your new product development , creating the product, consider the finances, determine a price point , research profitability, marketing your new product , product launch , create incentives , keep your finances in good shape.
Introducing new products can be a good way to grow your small business. In fact, a survey with Neilson found that 63% of those surveyed liked when businesses offered new products. These products can bring awareness to your brand and fit a consumer’s needs. They’re also a good way to earn more income.
But product development can be time-consuming and lead to profits if it’s not well-planned.
This guide will discuss how to create a new product development business plan, including:
- Marketing your new product
If you’re wondering how to create a new product development business plan, you may want to start with brainstorming.
The idea for your new product is the first step in developing new things to sell for your business. These ideas should keep your target customer and market in mind. Try to consider what your customer wants from your product . For example, if you have a baking business, you may think of ideas for baked goods or baking tools.
The idea will be the actual product you may develop, whereas the concept is its purpose and plan. You may want to create a list of ideas to narrow down to a final concept.
When considering your ideas, outline a few key factors for its development. Ask yourself about the functionality of the product. Is it solving a problem or answering a question? Would your customers be interested in buying it? Is it realistic to create and sell?
Once you narrow down your idea and concept, do market research to understand the product’s marketability. You might look at similar product listings, prices, and reviews to get an idea of demand.
Compile some information on your target audience . Determine how stable this market is and how long it may last. If the trend doesn’t last long, you may not be able to profit from the interest before it goes away.
Also, outline potential competitors to see how difficult it may be to convince buyers to pick your product. Then, determine what you can do to stand out.
With your idea and concept, put together a pitch. This pitch can be the beginning of your new product development business plan. The pitch will include a product description , a development plan, and potential customer benefits. You could also put together a sample.
Then, give this pitch to a few people you trust. If they agree that it could be a beneficial and successful product, you can get started on a more detailed business plan for the product development.
The development plan will outline how you’ll create the product and sell it to customers to earn money from it. We’ll cover a few things you may want to consider in this business plan.
First, determine what you’ll need and how you’ll put the finished product together. You may want to get quotes from vendors to get materials for your new product. If it’s more of a service than a product, outline what it will offer and how you’ll successfully achieve the service for customers.
To develop your product, you’ll need to determine the money you’ll need. Start by deciding how much it will cost to make the new product. Then, decide how many you might make for a release.
Use your vendor quotes to estimate the cost of production. When putting together a budget for your development plan, look at startup costs and ongoing expenses for the new product. Then, determine if your business’s cash flow can support these. If not, you may need to consider funding options or start saving for the product development.
Once you outline the cost of production, use that information to determine how much you’ll charge for your new product. You may want to establish a competitive price so buyers may choose yours over competitor’s.
Your pricing will need to promote profitability. To do this, establish a profit margin, or markup, which is the product’s price divided by the cost of the production. This might be about 10-20% or more, depending on the industry and the demand.
After deciding on your product price, project how much you could earn from it. Consider how many products you might sell in the first few months. Plus, decide how many you’ll need to sell to cover your startup costs and begin earning revenue from that new product.
You may also want to consult your current customers to see if they’re interested in the product. In addition, consider putting together a focus group to see what a sample of people thinks of the new product. With this new information, you can set sales goals and create a timeline towards profitability.
The last part of your new product development business plan will be to decide how you’ll market that product to earn sales. You’ll need to create buzz around it’s release.
To build awareness and promote sales, you can create a product launch event that celebrates the product and demonstrates its usefulness. Consider sending out a newsletter that announces it’s release or posting on social media with a launch countdown.
Since it’s a new product, you may want to incentivise it to potential customers to try it. You could offer existing customers a discount or free trial of the new product. A trial can help you understand the product’s effectiveness and see if it needs any tweaking. Then, consider asking these customers to review the product for others to see how well it works.
As you plan for new product development, you’ll need to manage your finances to support your business growth. Financial management can be stressful and time-consuming when you’re self-employed. That’s why thousands of business owners use the Countingup app to make their financial admin easier.
Countingup is the business current account with built-in accounting software that allows you to manage all your financial data in one place. With features like automatic expense categorisation, invoicing on the go, receipt capture tools, tax estimates, and cash flow insights, you can confidently keep on top of your business finances wherever you are.
You can also share your bookkeeping with your accountant instantly without worrying about duplication errors, data lags or inaccuracies. Seamless, simple, and straightforward!
Find out more here .

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
What insurance does a self-employed hairdresser need.
As a self-employed hairdresser, you’re open to risks in your everyday work. Whether
What are assets and liabilities in a business?
Anyone going into business needs to be familiar with assets and liabilities. They
Personal car for business use: How does it work?
Access to a car is a must for most businesses, meaning that travel
Advantages and disadvantages of using personal savings in business
Have you got a new business idea? And are you considering using your
How to pay Corporation Tax
Corporation Tax is the main tax your limited company has to pay every
How long do CHAPS & BACS payments take?
If you are making transfers frequently between banks in the UK, you have
11 common costs of running a business
When running a business, the various costs can quickly add up. If you
How to buy a vehicle through a limited company
Buying a vehicle through a limited company works similarly to how you may
What is a sales strategy? (with example)
When you run a small business, it’s important to consider how you’ll optimise
Preparing business packages for distribution
You may think shipping your product is as easy as popping it in
How to use cloud services for a business
The development of cloud computing is a game changer for businesses big and
How do EU imports and exports work?
In January 2022, the UK introduced new EU imports and exports regulations. If
Need a business plan? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB1 Business Plan
- EB2 Visa Business Plan
- EB5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- UK Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- UK Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Planning
- Landlord Business Plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- eCommerce business plan
- Online Boutique Business Plan
- Mobile Application Business Plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food Delivery Business Plan
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
New Product Launch Business Plan Sample
Sep.30, 2013
Average rating 3.7 / 5. Vote count: 12
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
New product launch business plan for starting your own business
Clueless on how to add a new product line to your enterprise? Well, adding a product line is not a simple process. It isn’t just hiring a few more people and acquiring additional equipment.
Establishing a new product line needs adjustments on all organizational levels, and your operational plan & strategic plan. It may require you to carry out marketing analysis and overall risk assessment again. And therefore, you require a comprehensive business plan to launch a new product no matter how established your business already is.
A good practice is to get developed a business plan online or by industry experts near you so that all features of the new product launch can be taken care of.
To help you fathom how a new product launch in the market is introduced we are providing a sample business plan guide adopted by NYC House Cleaners when they added construction debris cleanup to their services.
Executive Summary
2.1 the business.
NYC House Cleaners was a cleaning company founded in New York. The company was established in 2009 and in 2021, the enterprise owner decided to add a new product line and broaden his services to the city’s construction sector. In this sample, we will provide some segments of the business plan for launching a new product following which the owner successfully launched a new product.
2.2 Management of new product launch
Management of a new product launch is just as complicated and expedient as that of initiating a new startup. Only by properly following the steps for launching a new product can you ensure better management.
In this business plan for franchise , we will explain how to launch a product line and how to adjust all the segments of your previous business plan according to the new needs.
2.3 Customers of new product launch
The buyers (of your new product line) depend on the type of your basic business. In the case of NYC House Cleaners, they were contractors, construction managers, disaster management organizations, and construction firms.
2.4 Business Target
Presenting a new product, you would have certain fiscal and social expectations. In your business plan for a new product launch , it is expedient to pen them down so you can remain focused on achieving them.
The business targets of NYC House Cleaning are demonstrated in the graph below.
Company Summary
3.1 company owner.
NYC House Cleaning is owned by Frank Max. Max is a Harvard graduate with a passion to provide unparalleled services to consumers and make profits.
3.2 Why the new product launch is being started
In almost 10 years, Max was able to strengthen the business working with which he started. To bring innovation, and explore more opportunities, he decided to launch a new product.
3.3 How the new product launch will be started
Step1: Create Business Plan New Product
The foremost step is to study as many business plans for new products as are available. They will help you understand the process for different types of businesses. After that, you should delineate launching a new product plan.
In case, you lack a professional business diploma or degree, you should consider hiring a business consulting firm to make for you a new product business plan sample. You can have a great deal of insight into what that plan would look like by reading this sample product business plan.
Step2: Execute the Plan
The second step is to execute and administer each part of your business plan. You have to recruit more people with qualifications that match your product specification. You will have to develop sales strategy and marketing strategy accordingly.
Step3: Use the Web
The forthcoming step is to make your consumers aware of the new product or service. Using the web and social media will be the best choice as your reach can grow multiple times using them.
Step4: Manage and Grow
After you have integrated the new product into all the business features, you will have to develop a brief strategy on how to grow your business even further by capitalizing on the new product.
Operational and Strategic Planning
Services of new product launch.
When you have concluded which product or service you want to add, the forthcoming step is to thoroughly investigate how to launch a product line. For a systematic approach, you should discuss all the features of the new product in very specific terms in your business plan for product launch.
If you don’t know how that can be accomplished, you can study business plans for new products available online like this one. In this business plan sample for new product launches, we will explain what type of new products are usually added by enterprises.
- Extension of Service
Enterprises whose model is based on service provision usually extend the service line. This includes either providing the same set of services to other areas or increasing services on the list.
- New Product
This includes adding an entirely new product to your business. This needs a proper business plan sample for new product since the areas to consider are the same as they were when you launched your business.
- Product Mix
This category caters to the scenario when a startup entirely shifts its range of products.
- Changing Product Features
This includes adding new features or bringing innovation to an already existing product or service.
In this product business plan sample we will explain how NYC House Cleaners extended their services. You can also see the new arrangement and staff in the later segments of this product business plan example.
Marketing Analysis of new product launch
Excellent work.
excellent work, competent advice. Alex is very friendly, great communication. 100% I recommend CGS capital. Thank you so much for your hard work!
Even if you have already carried out the flawless market analysis in your operational plan, you are required to do it again when making a marketing plan for the launch of new product . It includes understanding market statics and dynamics and taking them down in your business plan for the new product launch.
For micro-trends, you should include a portfolio of your business rivals, their offerings, services, and sales. In your new product marketing launch plan, you should outline how you can outperform your competitors. Macro trends such as interest rates and inflation can also impact your earnings profoundly, that’s why it is expedient to consider them as well in your marketing launch plan new product.
In this sample business plan for new product we will explain marketing steps to launch a new product. Based on your type of business, you may also benefit from business plan for video game or Mexican restaurant business plan .
5.1 Market Trends
In the United States, it is quite common for businesses to keep on adding new products and service lines. It is because technological changes are happening at a pace never witnessed before. Either it is needed to bring innovation to the service or product or drop the prior product altogether.
5.2 Marketing Segmentation
When you are marketing for launching a new product, you are actually adding customer segments to your business. To make sure you meet the new criteria, it is incumbent to mention the new consumer groups in your sample marketing plan for the new product launch. This will help you in reaching a wider audience as well as gathering best business ideas.
If you are marketing a new product launch , your consumer groups would depend on your niche. For instance, in the case of tobacco shop business plan , they will mostly be adults and seniors. If you make oyster farming business plan , they can be youngsters, teens, adults as well as seniors.
In this new product launch marketing plan example, we are listing a generic list of groups that can be your consumers for the new product.
5.2.1 Individuals
If you are a restaurant, a gym, or a service provider whose prior consumers belonged to individuals of all ages, your customer groups will likely remain the same.
5.2.2 Small Businesses
In case you run a business that offered services like hardware or software outsourcing, office management, office cleaning, and business consulting, then your consumers will mostly belong to small enterprises.
5.2.3 Large Businesses
Based on services, large and already established businesses can be a customer group as well.
5.2.4 Manufacturing Industries
If your new product line provides raw materials for manufacturing industries whether they deal in food, chemicals, or technical products, then your consumers will fall in this category.
5.3 Business Target
By adding a product line, NYC House Cleaners intended to:
- Acquire a CSAT score of 90+ concerning the new product
- Make at least $55k in monthly profits by the end of the first five years
5.4 Product Pricing
NYC House Cleaners decided to keep the prices of construction debris cleaning in the same range as their competitors.
Marketing Strategy of new product launch
if you are presenting a new product, you have to look for marketing strategies for a new product launch so that your consumers learn about it. You can meet your monetary expectations from the new product only if you successfully carry out your product launch marketing strategy.
In this business plan for new product sample, we are providing NYC House Cleaners’ marketing strategy to launch a new product.
6.1 Competitive Analysis
- Our biggest competitive advantage is that we have built the name and reputation of our brand by providing excellent customer service during the past years.
- We have been in contact with enterprises and contractors who will hire us for professional cleanup.
- We are situated in a location where construction cleaning service is not offered by most startups.
6.2 Sales Strategy
- We will contact our target consumers by sending our sales executive and digital business cards.
- We will offer a 20% discount to our consumers for the first two months of our launch.
- We will promote ourselves through the web and social media.
6.3 Sales Monthly
6.4 sales yearly, 6.5 sales forecast, personnel plan of new product launch.
For putting forward a new product, you need to have a team that is acquainted with the new production procedure. While drafting your business plan for launching a new product, you should clearly define the personnel you would require to carry out additional responsibilities.
In this business plan sample for a new product , we are providing the general staff that you can need to hire to incorporate a fresh product line. You may need to hire more people according to the product specification and adjust your business plan to launch a new product accordingly.
7.1 Company Staff
- 1 Operation Manager to manage the distribution
- 1 Social Media Manager to make the product known
- 1 Sales Executive to reach out to enterprises
- 1 Web Developer to develop a website for a new product launch
- 1 Customer Care Executive to assist consumers with the new product
- 1 Business Strategy Consultant to help integrate the new functionality
- 2 Technical Assistants
7.2 Average Salary of Employees
Financial plan of new product launch.
Even if you had done accurate fiscal planning for your enterprise at the initiation time, you will need to still do it again to incorporate the new product. A new product launch will have its risks, investments and profits associated. To make sure you can generate profits and strengthen your business by putting forward the new product, it is expedient to renew financial planning in your business plan for a new product launch.
Sometimes, financial planning for a new product line is considered more complex than the one for a startup. It is because, for the new product launch, you have to carefully analyze if and how you can use your prior resources to build manpower and funding for the new venture.
In this new product launch business plan template, we are documenting the financial plan of NYC House Cleaners. These segments are taken after Max had incorporated revised figures for the product launch in his new product launch business plan.
If you are looking for legal assistance or document destruction business plan , you can have a general idea from here.
8.1 Important Assumptions
8.2 break-even analysis, 8.3 projected profit and loss, 8.3.1 profit monthly, 8.3.2 profit yearly, 8.3.3 gross margin monthly, 8.3.4 gross margin yearly, 8.4 projected cash flow, 8.5 projected balance sheet, 8.6 business ratios.
Download New Product Launch Business Plan Sample in pdf
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Vegetable Farming Business Plan

Trading Business Plan

How To Write A Textile Manufacturing Business Plan

Start a Vending Machine Business in 2024: A Detailed Guide

Oil and Gas Business Plan

What Is Strategic Planning: Definition and Process

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is a product plan and how to create one in 6 steps

Whenever I read about the next hot, new start-up with unicorn potential, I can’t help but think of Pinky and the Brain .

Both titular characters in the mid-90s animated TV series are genetically modified laboratory mice. Brain is hyper-intelligent; Pinky, not so much.
Brain’s primary objective? World domination:
Pinky : Gee, Brain. What are we going to do tonight? Brain : The same thing we do every night, Pinky. Try to take over the world.
In each episode, Brain devises a diabolical yet half-baked plan — for example, manipulating the world’s biggest magnet to form discarded satellites to spell “Brain is your ruler” — that invariably ends up foiled.
What does this have to do with product management?
Devise a product plan to take over the world
If you want to make an impact with your product and solve all your customers’ problems, don’t be like Brain; take the time to devise a product plan before you make your first move on your quest for market domination.
Creating roadmaps and backlogs is a great start, but product planning covers a much wider scope.
In this guide, we’ll define what product planning means, why it’s important, and the components and steps involved in creating a product plan.
What is a product plan?
Product planning covers all the steps, activities, and decisions a company must perform and make to develop a successful product.
A product can be defined as an input-outcome device. The input is the customer value proposition and the outcome is the company’s profit. Product planning includes everything you need to do internally to get from input to outcome.
It starts with a recognized customer need — after all, customers don’t just buy a product, they buy what the product will do for them to solve a problem they are having. It ends when the product has reached the end of its usefulness from a business perspective.
What is the purpose of product planning?
Product planning encompasses the actions and components that contribute to achieving a specific outcome. Product management is all about realizing outcomes.
Before jumping into the how and what, let’s first understand why product planning is important by outlining its six objectives:
- Company survival
- Meet customer needs
- Increase sales
- Understand and manage strengths and weaknesses
- Better manage capacity
- Plan effectively
1. Company survival
The eye of the tiger, survival of the fittest — or as P. Diddy said, it’s all about the Benjamins .
Product planning allows you to focus, remain viable, and understand your ability to innovate. It also helps you clarify how to introduce, grow, and sunset products in highly competitive markets.
2. Meet customer needs
The customer is at the heart of any product. Thorough product planning will set you up to understand and meet your customers’ needs. This, in turn, helps you quickly move customers from evaluators to champions through the product-led growth flywheel .
3. Increase sales
Your product can be lightyears ahead with brilliant solutions to customer problems, yet if they are not interested in the solution and don’t buy the product, your product fails.
For example, virtual reality seems to have finally found product-market fit . VR technology though, is not new.
In the 90s, VR was on the rise and forecasted sales potential was off the charts. Unfortunately, VR systems such as the Virtual Boy failed to deliver; its poor ergonomics and underwhelming stereoscopic effect gave users terrible headaches.
With better product planning, Nintendo might’ve been able to craft a more sophisticated product that satisfied customer expectations and, as a result, increased sales.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
4. Understand and manage strengths and weaknesses
Product planning allows you to look introspectively and analyze your strengths and weaknesses in light of market requirements. What does your product do really well? What qualities distinguish it from competitors? What does your product lack and what do competitors do better?
By asking and answering questions like these, you’ll gain a better understanding of what you can take advantage of and what you need to improve in your product.
5. Better manage capacity
What’s one thing every company has in common? Limited resources in terms of capital, material, and human resources. Product planning enables you to plan these optimally and get the most out of them.
6. Plan effectively
When you’re building products, you have many competing priorities . Will you invest in new features, enhance and improve existing ones, reduce technical debt , or spend more time on improving discovery and delivery processes ? Product planning allows you to meet your long-term strategic plans.
6 considerations for product planning
Now that we understand why product planning is essential, how do you go about doing it?
Creating a successful product plan involves the following considerations:
- Research before development
- Choose a delivery method
- Coordinate activities
- Set a price
- Commercialize the product
- Abandon unprofitable products
1. Research before development
Energy to get going: Check. Confidence it will work out: Check.
Validation that the idea will deliver what customers need? [Buzzer sounds].
Before jumping into the deep end of product development, start with extendive market and user research. The insights gathered therein will help you establish what characteristics and requirements your product must fulfil to meet customers’ needs.
2. Choose a delivery method
All roads lead to Rome. The question is, which is the most efficient?
This is even more applicable when it comes to product delivery. Which delivery method will enable you to develop your product or feature exact how the customer needs it to be?
3. Coordinate activities
Product planning aims to coordinate all the initiatives and activities around the product and its investments. Doing so allows you to improve your competitive position and strive for market leadership. It also helps you quickly respond to changing market conditions.
4. Set a price
Product planning helps you determine the ideal price point for your product.
More great articles from LogRocket:
- How to implement issue management to improve your product
- 8 ways to reduce cycle time and build a better product
- What is a PERT chart and how to make one
- Discover how to use behavioral analytics to create a great product experience
- Explore six tried and true product management frameworks you should know
- Advisory boards aren’t just for executives. Join LogRocket’s Content Advisory Board. You’ll help inform the type of content we create and get access to exclusive meetups, social accreditation, and swag.
The insights gathered during product planning can help you determine the best pricing strategy. For example, is your product most suitable for value-based, competitive, price skimming, cust-plus, penetration, economy, or dynamic pricing?
5. Commercialize the product
Product planning helps you uncover and validate the viability, feasibility, and desirability of your product.
Desirability speaks to satisfaction of customer needs and the commercialization of the product. This measure helps you ensure viability and, hopefully, rake in profits.
Product planning also considers how to best introduce the product to the market and continuously measure success post-launch .
6. Abandon unprofitable products
All good things eventually come to an end. Every decision in a product is a business decision, and there will come a time that further investment in a product or product feature becomes unprofitable.
At that point, a decision has to be made whether or not to sunset the product or feature.
Good product planning throughout the product lifecycle helps you recognize when it is time to abandon the product and sunset it in a structured way with minimal impact on customers.
How to create a product plan in 6 steps
OK, enough small talk. It’s time to deep-dive into the product planning process.
Product planning involves six steps:
- Market and user research
- Concept ideation
- Screening and testing
- Introduction and launch
- Product lifecycle
1. Market and user research
Before you start to build, it’s crucial to understand the problem you’re trying to solve, the market drivers, competitors, and customer needs. You can generate insights on all of the above through market research.
Competitive analysis , a subset of market research, is a structured approach to identifying and analyzing competitors.
Both are conducted to identify markets, investigate market positioning , and analyze the business’s success.
Through customer segmentation research, which is especially important to new businesses, larger customer groups are divided into different groups with personas.
The personas form the basis of user research, which is aimed at understanding potential customers’ problems, habits, interests, motivations, and more.
2. Concept ideation
A great product starts with a great concept and initial validation of that concept. This step is arguably the most fun and creative step.
During the concept development stage, you define what you are trying to build by figuring out how well it solves the identified problem, how easy it is to use, what it will cost the customer, the look and feel of the application, and so on.
A key step in this process step is product discovery and a continuation of user research, which enables you to uncover the problems the persona faces and the solution to aim for.
Concept ideation sources can be both external and internal. Externally, market and user research influence concept ideation. Internally, concept ideas originate from sales, customer support, marketing, engineering, designers, user research, executives, and investors.
3. Screening and testing
During screening and testing, the ideas generated during the concept ideation phase are critically evaluated.
The goal is to groom out ideas that are either inconsistent with the product vision , undesirable, and/or impractical.
After evaluation, the next step is to rigorously prioritize ideas . As the Highlander said, “ There can only be one .” This is not to say you should only test one idea; it just means you should pursue the most promising tests first.
There are plenty of prioritization frameworks to choose from with some of the most commonly used include:
- Value vs. effort
- MoSCoW method
- Opportunity scoring
Once you have a prioritized list, you should devise a hypothesis and experiment to verify or disprove it.
In product testing, customers are given an opportunity to try a prototype. This helps you understand whether customers understand the product idea, what they like or dislike about it, and whether they would ultimately buy and use it.
The concept ideation, screening, and testing as a whole are often covered in the Double Diamond approach, which is a design process to help you discover, define, develop and deliver solutions.
4. Introduction and launch
After a few iterations of screening and testing, the new features and usability improvements deemed ready to pursue and develop trickle through and are ready for development and launch.
In this step, the idea is converted into a product. It’s the PM’s job to schedule activities to ensure a successful product launch with a high adoption rate .
When ready, the product is launched and commercialized. If your product planning is sound, it should be poised to compete with existing products and maximize market share and profits.
5. Product lifecycle
After the product is launched, the real fun begins. Now it’s time to measure and analyze usage to gather new insights about whether or not your product launch was successful.
Using these insights, you can modify and enhance the product, introduce new features, improve usability, and help the product move from introduction to growth.
At a certain point, you’ll reach product maturity. The number of customers and sales will stabilize. Eventually, new investments in the product will have a harder time generating additional revenue. It will become increasingly challenging to compete.
Eventually, the product will decline, and the number of customers and sales along with it. This might be due to existing competition or the introduction of new products that are more advanced and better serve the customer’s needs.
Think about how the Walkman was surpassed by the Discman, which was overtaken by the mp3 player, and, eventually, an app on your phone.
6. Sunsetting
When a product is in decline, it’s time to sunset it. Sunsetting is also known as the end of life and usually involves deprecating the product.
Though it might feel difficult to say goodbye to a product that you birthed, nurtured, and watched grow, sunsetting a product is a perfectly natural part of the product lifecycle.
During the sunsetting phase, it is important to be diligent. You should devise a playbook or checklist to ensure all activities, such as communication, code clean-ups, and so on are covered during the end-of-life period.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #product strategy

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Drive growth with these 7 customer feedback tools
A customer feedback tool is a software solution or platform designed to collect, analyze, and manage feedback from customers.

Leader Spotlight: Motivating teams to hit customer-centric outcomes, with Kristina Bailey
Kristina Bailey discusses the careful balance of knowing the business outcomes you want to achieve while balancing customer outcomes.

Exploring augmented products: Beyond the core offering
Augmented products leverage technology and additional services to provide enhanced functionality, convenience, and value to users.

A guide to acceptance test-driven development (ATDD)
ATDD is an agile methodology involving collaboration to define acceptance criteria before starting any development.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Product Management
- New product development process
New Product Development - The 7-Step Process Explained
Browse topics.
Delivering innovative products can help you gain a competitive advantage, but maintaining that advantage requires continuously delivering new products that keep pace with your customers' evolving needs. New product development is the key to building and keeping market share and customer loyalty.
What is new product development?
New product development is the end-to-end process of creating a product that has never been brought to market—from idea to concept, prototyping, developing, testing, and launch. It involves building a product strategy and roadmap to successfully guide cross-functional teams and stakeholders through the entire process.
Unlike product enhancements and upgrades that modify and improve existing products, new product development addresses the unique challenges of designing and delivering brand-new products. This article discusses the seven stages of new product development, some challenges Agile teams face along the way, and how you can succeed.
The 7 stages of new product development
Successful Agile software development takes careful planning and good project management practices . The seven stages of new product development guide you through the process by breaking the work into stages or steps.
1. Generating ideas
Every new product begins with a problem and ideas to solve it. Ideas may come from within the company, such as the customer service team, or from outside via customer and market research. In this phase, it's important to gather all ideas without discrimination. The more ideas you can brainstorm, the better.
Products such as Jira Product Discovery help product teams structure the chaos of prolific ideas. Ideas can be supported by data, customer feedback, sales input, support tickets, and more to help shape what the product team should focus on, creating ongoing feedback loops. Idea generation is most effective as a team activity with the outcome of developing the essential elements for a new product.
To help you prioritize ideas, methods such as a SWOT or Competitive analysis take the guess-work out of the process. When generating ideas, having a clear understanding of where opportunities exist and knowing how the competition stacks up can lead to brainstorming disruptive and game-changing ideas.
2. Screening ideas
Agile teams can use Jira Product Discovery matrixes to view a large number of ideas, using criteria such as impact, effort, and confidence level before scoring and selecting which ideas to move into the next phase. Gathering and organizing product ideas in a centralized tool makes it easier for product teams to prioritize which ideas or features will drive the most impact.
Scoring ideas by product development effort versus the overall impact of the solution is an excellent way to focus on those with the most impact. The SWOT and competitive analysis templates from step 1 can provide the foundation for where to place priorities.
You can also identify good ideas that are simply not right for this new product but may be suitable for future products and the goals of the team. Screening ideas can be difficult, but aligning each good idea to your goals and comparing its impact to other ideas will help identify the most impactful opportunities.
3. Creating a product strategy
After selecting ideas to develop into a new product, it's time to create your product strategy. This is a concise definition of the need that the new product meets. A good product strategy includes the vision, target market or user, position in the industry, features and benefits, and the value the new product brings to the business. This phase involves creating a clear definition of the requirements.
Confluence offers a strategic plan template that can help you refine your strategy messaging, remove ambiguity, and clearly communicate the goal. From here, the Confluence requirements template walks you through the process of outlining your objectives and success metrics, listing assumptions and options to address them, and adding supporting documentation. These efforts include prototyping and validating with customers, ensuring the product being built will be something that customers actually want.
4. Building a product roadmap
A product roadmap is an action plan. It outlines product functionality and release schedules and helps you manage new product development. Think of the roadmap as the core communication tool for short- and long-term efforts that align with your business goals. It's a shared source of truth for a product’s vision, direction, priorities, and progress over time. Creating a great product roadmap keeps your entire team working together and moving in the same direction (try our product roadmap template ). They also make it easy to check in on the work at any time throughout the product development life cycle.
Product teams using Jira Product Discovery can then share their product strategy using always-up-to-date, custom roadmaps to present which ideas will be built, when, and why.
5. Prototyping
Time to market is critical for new product development, and your ability to rapidly prototype and develop products ensures viable solutions. Jira Product Discovery’s integration with software development tools like Jira makes it easy to seamlessly connect your entire software delivery lifecycle.
Defects and change requests are simply a fact of new product development, but concise tracking and issue management keep everyone on your team informed, organized, and on schedule. Testing can span both internal quality assurance (QA) teams as well as customers and end users engaged in alpha, beta, or user acceptance testing. Jira is the leading tool that Agile teams use for testing, in part because it optimizes the QA workflow by writing and managing test scripts, tracking test cases, and managing defects.
The product roadmap template from the previous step, along with other Confluence project planning templates , also inform testing and help ensure you miss nothing.
7. Product launch
You only get one chance to make a good first impression, and launching a new product requires careful planning and delivery. Every step in the process is a building block to a successful launch. Confluence’s product launch template helps ensure a smooth launch.
Additionally, sales and marketing, HR, and legal teams are already using your product strategy and roadmap to align messaging, identify opportunities, and ensure regulatory compliance. Using Jira , they can seamlessly connect their work with the product team’s. It provides a streamlined UI and integrations with the tools they use daily, such as Gantt charts and spreadsheets.
4 main types of product development
There are four types of product development, including:
- New product development : These are products that haven’t been released in the market before, such as software applications that solve new or novel customer problems.
- New product categories : These products may not be new to the marketplace, but they are new to the company developing them. For example, a software company may expand their offering to include products within the category they currently develop, such as adding tax accounting to their portfolio of personal finance applications.
- Product line extensions : These expand the products offered within the organization’s existing range of products, such as adding new industries within a category. For example, a company may develop accounting software for the construction industry and decide to extend their accounting software to the airline industry.
- Product enhancements : These are new features and capabilities within existing products. Companies generally design them to provide customers with new or added value. Enhancements respond to changes in the market, performance issues, or new competitive products.
Example of new product development
Whether creating a new product that hasn’t been seen in the market before, or expanding an existing application to address new geographic locations, understanding the time it will take to develop is essential.
Jira insights help teams make data-driven decisions based on their own historical progress. Insights can come from every aspect of the product development process and provide continuous improvement opportunities with each new product development project.
3 challenges teams encounter in the new product development process
Great tools can help alleviate the challenges of new product development. Understanding these challenges and how to address them can keep your team on track for a successful launch.
1. Defining clear requirements
When speed is important, the requirements often become an ironclad set of instructions. While clear requirements are necessary, Agile teams must have a shared understanding of and empathy for the customer. Include various members of your team in requirements-gathering activities, such as customer interviews. When designers, developers, and QA share an understanding of user stories, they can produce results more quickly and accurately without maintaining rigid rules.
Confluence’s requirements template gives you the power to capture and update assumptions, use cases, UX design, and scope together.
2. Estimating the development effort
Working with realistic project timelines is essential for bringing new products to market and gaining a competitive advantage. However, product development tasks are notoriously difficult to estimate, and new product development can be even harder. Break work into smaller tasks for more accurate estimates. In addition to giving you more flexibility with resource assignments, smaller tasks minimize the impact on your overall project when something takes longer than expected.
Many Agile teams have switched from traditional estimates to story points—units that measure the effort teams require to fully implement a user story. A user story is an informed explanation of a feature from the user's perspective. With Jira, Agile teams track story points, reflect, and quickly recalibrate estimates.
3. Siloed tools
Collaboration is a critical component in your team's success and the success of their products. Development teams use a variety of specialized tools, such as visual design tools for creating mock-ups and instant messaging apps for hosting team discussions. No single tool can provide the specialized functionality for all the needs of the development team. Jira Product Discovery and Jira integrate with a wide range of specialized development tools to easily collect and incorporate important information.
How long does new product development take?
The time to develop a new product can vary widely based on the complexity of that product. For example, developing an application that securely processes credit card payments may take magnitudes longer than developing software to track exercise statistics. But a few tips can help reduce the time to market while maintaining quality.
Expert tips from Atlassian for new product development
Understand the customer.
Begin with the customer’s needs in mind. The time you spend early, interviewing customers and gathering input, helps create a clear product strategy. The entire team should understand the problem they are solving for the customer. It will keep the team on track when they make decisions during development.
Foster team collaboration
When the team has the tools for seamless collaboration, generating ideas, prioritizing issues, and solving problems is much easier. Today’s product development teams include a wide range of cross-functional roles. The best way to prevent silos and keep the team working together is with collaboration, respect, and genuine appreciation for each other’s contributions. Centralized tools such as Jira Product Discovery and Jira help foster this.
Define the requirements
A good product specification outlines the purpose, what the client needs the product to do, the technical and functional requirements to achieve that, design mockups, and even release plans. This foundational document takes time to create, but it helps teams refine and clarify fuzzy requirements and align on the scope of the project.
Optimize resource allocation
Resource allocation is among the hardest aspects of new product development, so the roadmap must be well-defined before you begin. Understand the tasks included in the project, their dependencies, and the resources required. Visual workflows can help teams identify when you underutilize or overcommit resources. They can also highlight bottlenecks and roadblocks to allow teams to quickly adjust and stay on track.
Jira makes new product development easier
Jira provides success tools for new product development teams to collaborate on and manage work from idea to product launch. Agile teams have made Jira the leading solution for new product development.
Jira Product Discovery is a dedicated tool that aids teams in crucial stages of product development. It helps Agile teams gather and prioritize ideas and align everyone with product roadmaps.
With Jira Product Discovery matrixes and criteria, you can easily select which ideas to move ahead with, enhancing the experience of product development.
How to Manage Scrum Remote Teams
Learn about what scrum remote teams are, as well as how to manage them. Read about benefits, challenges and helpful tools to use.
Distributed Teams: Strategies for Success
Do you work on a distributed team, maybe remote or virtual? Learn how to manage, structure and build culture with a distributed agile team.
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Sign out of AWS Builder ID
- AWS Management Console
- Account Settings
- Billing & Cost Management
- Security Credentials
- AWS Personal Health Dashboard
- Support Center
- Expert Help
- Knowledge Center
- AWS Support Overview
- AWS re:Post
- Amazon Q Business ›
Amazon Q Business pricing
Amazon Q Business pricing offers two subscription models—Amazon Q Business Lite and Amazon Q Business Pro—so you can choose the right plan for everyone in your company.
Amazon Q Business Lite
$3 per user/mo., the amazon q business lite subscription provides users access to basic functionality such as asking questions and receiving permission-aware responses., amazon q business pro, $20 per user/mo., the amazon q business pro subscription provides users access to the full suite of amazon q business capabilities, including access to amazon q apps (preview), and amazon q in quicksight (reader pro)., index pricing.
Amazon Q Business offers two index types for production and proof of concept (PoC) workloads:
The Starter Index is deployed in a single Availability Zone, making it ideal for PoCs and developer workloads.
- Priced at $0.140 per hour for one unit (limit five units per application)
- 100 hours of connector usage
- 20,000 documents or 200 MB of extracted text, whichever comes first
The Enterprise Index is deployed across three Availability Zones, making it best for production workloads.
- Priced at $0.264 per hour for one unit
The free trial terms for Amazon Q Business and Amazon Q in QuickSight are as follows.
Note the following about free trials:
- The free trial terms change on July 1, 2024, and are different for Amazon Q Business and QuickSight. For customers subscribing the same user to both products with an Amazon Q Business Pro subscription, the free trial for that users will end whenever the first free trial expires. For example, if a user is added to an Amazon Q Business application and a QuickSight account at the same time through an Amazon Q Business Pro subscription, their free trial will end after 30 days. As another example, if a user is added to an Amazon Q Business application on day 1 with an Amazon Q Business Pro subscription and later added to a QuickSight account on day 15, then their free trial will end on day 45.
- A free trial applies per user. If a user has used their free trial in one Amazon Q Business application or QuickSight account, they will not get a second free trial in another application.
Pricing examples
You are an enterprise company with 5,000 employees looking to deploy Amazon Q Business. You decide to purchase Amazon Q Business Lite for 4,500 users and Amazon Q Business Pro for 500 users. You have 1 million enterprise documents across sources like SharePoint, Confluence, and ServiceNow that need indexing with an Enterprise Index. Your monthly charges will be as follows:
Enterprise Index for 1M documents will need 50 index units of 20K capacity each (assuming that the extracted text size of 1M documents is less than 200 MB * 50 units = 10 GB) :
- $0.264 per hour * 50 units * 24 hours * 30 days = $9,504
User subscriptions:
- 4,500 users * $3 per user/month = $13,500
- 500 users * $20 per user/month = $10,000
- Total user subscriptions: $23,500
In summary, your monthly charges are as follows::
- Enterprise Index: $9,504
- User subscriptions: $23,500
- Total per month: $33,004
In the preceding scenario, you decided to upgrade 300 of the Lite users to Amazon Q Business Pro, considering that those employees could benefit from the advanced features. Additionally, you decided to cancel Amazon Q Lite subscriptions for 10 users who left the company. You made these changes on the 10th day of the month. Upgrades are prorated, and downgrades/cancellations apply starting next month. Therefore, for the remainder of that month, you will be charged the full monthly rate for the 4,200 Lite users. The 500 Pro users will also be billed for the full month. The 300 upgraded users will be prorated, with 10 days billed at the Lite rate and 20 days at the upgraded Pro rate.
Therefore, for the current month, your user subscription charges are as follows:
- $3 * 4,200 + $20 * 500 + [$3 * (10/30) + $20 * (20/30)] * 300 = $26,900
Starting next month, you will have (4,500 - 300 - 10 = 4,190) users with Lite and (500 + 300 = 800) users with Pro. Therefore, your charges from the next month are as follows:
- $3 * 4,190 + $20 * 800 = $28,570 per month
Since you didn’t change anything on index capacity, your index charges remain the same at $9,360 per month.
In summary, your monthly charges starting next month are as follows:
- Enterprise Index: $9,360
- User subscriptions: $28,570
- Total per month: $37,930
You have 1,000 employees at your company. Your IT team uses Amazon Q Business to answer employee questions. They assigned Amazon Q Business Lite subscriptions to all 1,000 employees. The IT help desk chatbot contains 10,000 documents.
Separately, your sales team uses Amazon Q Business for 100 sales reps to help them answer customer questions, create presentations, and implement actions using plugins. You assigned these 100 sellers the Amazon Q Business Pro plan. Their sales chatbot contains 200,000 documents. You granted the sales team access to QuickSight so that they can create documents and presentations using sales data, access dashboards with natural language data summaries, and ask questions about the data.
With Amazon Q Business, subscriptions are deduplicated, and users are charged once for the highest tier. So, the 100 sales reps are charged at the Pro rate, while the 900 other employees are charged at the Lite rate. Amazon Q Business users are charged separately across each AWS IAM Identity Center instance, so all applications must use the same IAM Identity Center instance to be charged only once per user.
Your monthly user charges are as follows:
- 100 users at $20 Pro rate: 100 * $20 = $2,000
- 900 users at $3 Lite rate: 900 * $3 = $2,700
- Total user subscriptions: $2,000 + $2,700 = $4,700
For indexing, you have two separate apps: the 10K document IT chatbot and the 200K document sales chatbot.
The IT chatbot requires 1 index unit at $0.264 * 24 hours * 30 days * 1 unit = $190.08 per month.
The larger sales chatbot needs 10 index units at $0.264 * 24 hours * 30 days * 10 units = $1,900.80 per month.
In total, your estimated monthly charges are as follows:
- User subscriptions: $4,700
- IT chatbot index: $190.08
- Sales chatbot index: $1,900.80
- Amazon Q in QuickSight enablement fee: $250/month/account
- Total per month: $4,700 + $190.08 + $1,900.8 +$250 = $7040.88
- Amazon Q Apps will be available to all users (including Amazon Q Business Lite and Pro) until June 30, 2024. Beginning July 1, 2024, Amazon Q Apps will only be available to Amazon Q Business Pro users.
Note : Customers using Amazon Q Business only will not be charged for user subscriptions (Amazon Q Business Lite/Amazon Q Business Pro) until June 30, 2024. However, in that period, customers will be charged for Amazon Q Business Index after a free trial of 750 hours or 30 days. Customers using Amazon Q in QuickSight will be charged for user subscriptions (Amazon Q Business Pro, $20 per user) after a 30-day free trial for up to four users.
User subscriptions are created per Amazon Q Business application or QuickSight account. Each admin can independently create, update, or delete subscriptions for users for their specific Amazon Q Business application or QuickSight account. AWS will deduplicate subscriptions across all Amazon Q Business applications and QuickSight accounts, and charge each user only once for their highest subscription level. Note that deduplication will apply only if the Amazon Q Business applications and QuickSight accounts share the same IAM Identity Center instance. User subscriptions are prorated when created or upgraded based on the number of days left in the calendar month. Any cancellations or downgrades are not prorated and apply starting in the next calendar month. The charges for user subscription starts only after first use by the user.

Ending Support for Internet Explorer
Portugal's EDP cuts investment plan, still sees 35% rise in 2024 profit
- Medium Text
- Company EDP Renovaveis SA Follow
- Company EDP Energias de Portugal SA Follow
Sign up here.
Reporting by Sergio Goncalves; Editing by Susan Fenton
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

McDonald's to launch $5 meal deal to lure low-income diners, Bloomberg News reports
McDonald's is preparing to launch a $5 meal deal at its U.S. restaurants to draw more inflation-hit customers back to its outlets, Bloomberg News reported on Friday, citing a person familiar with the matter.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Apple’s New iPad Ad Leaves Its Creative Audience Feeling … Flat
An ad meant to show how the updated device can do many things has become a metaphor for a community’s fears of the technology industry.

By Tripp Mickle
Tripp Mickle has been writing about Apple since 2016.
The trumpet is the first thing to be squished. Then the industrial compressor flattens a row of paint cans, buckles a piano and levels what appears to be a marble bust. In a final act of destruction, it pops the eyes out of a ball-shaped yellow emoji.
When the compressor rises, it reveals Apple’s latest commodity: the updated iPad Pro.
Tim Cook, Apple’s chief executive, posted the advertisement, called “Crush,” on Tuesday after the company held an event to announce new tablets. “Meet the new iPad Pro: the thinnest product we’ve ever created,” Mr. Cook wrote, adding, “Just imagine all the things it’ll be used to create.”
Meet the new iPad Pro: the thinnest product we’ve ever created, the most advanced display we’ve ever produced, with the incredible power of the M4 chip. Just imagine all the things it’ll be used to create. pic.twitter.com/6PeGXNoKgG — Tim Cook (@tim_cook) May 7, 2024
For decades, Apple has been the toast of the creative class. It has won over designers, musicians and film editors with promises that its products would help them “Think Different.”
But some creators took a different message from the one-minute iPad ad. Rather than seeing a device that could help them create, as Mr. Cook suggested, they saw a metaphor for how Big Tech has cashed in on their work by crushing or co-opting the artistic tools that humanity has used for centuries.
The image was especially unnerving at a time when artists fear that generative artificial intelligence, which can write poetry and create movies, might take away their jobs.
“It’s unusual in its cruelty,” said Justin Ouellette, a software designer in Portland, Ore., who does animation work and is a longtime Apple product user. “A lot of people see this as a betrayal of its commitment to human creative expression and a tone deafness to the pressures those artists feel at this time.”
Apple didn’t respond to requests for comment.
It was the latest in a series of recent promotional slip-ups by a company that is widely considered to be a marketing juggernaut. Its marketing of the Apple Vision Pro , released in January, struggled to help that device break through with many customers. Last year, Apple was criticized for making an awkward sketch that cast Octavia Spencer as Mother Earth , lording over a corporate meeting about the company’s effort to become carbon neutral by 2030.
Apple has been regarded as an advertising visionary since the 1980s. Its “ 1984” Super Bowl commercial to introduce the Macintosh computer is among the most famous commercials ever made. The ad, which was developed by the Chiat/Day agency, showed an actor throwing a sledgehammer through a screen projecting the face of a “Big Brother” figure that was meant to be a metaphor for IBM.
When Steve Jobs returned to Apple in 1997 after 12 years away, he sought to reclaim its marketing magic. Together he and Lee Clow, the advertising creative behind the “1984” spot, developed the “Think Different” campaign. It paved the way to the famous “Get a Mac” spots, featuring a Mac and PC , and the original iPhone ad , which showed people in classic films and television shows picking up a phone and saying, “Hello.”
Apple’s marketing pitched its products as easy to use. It billed PCs and Android phones as devices for business executives working on spreadsheets, while Macs and iPhones were tools for film editors, photographers and writers.
But Apple’s advertising has been uneven over the last dozen years or so. It yanked a 2012 campaign that showcased its Apple Store “geniuses” on planes. Critics dismissed a subsequent spot, “Designed by Apple in California,” as “ lame .”
In the wake of those hiccups, Mr. Cook shifted oversight of advertising from Phil Schiller, the company’s longtime head of marketing, to Tor Myhren, a former president and chief creative officer at Grey, the ad agency that created the E-Trade baby.
Under Mr. Myhren, who joined in 2016, Apple has developed some of its ads with its own creative team and others in collaboration with an outside agency, Media Arts Lab. It has been recognized at the Cannes Lions Awards, the leading event for the ad industry, for a spot on AirPods called “Bounce,” which showed a man bounding off the sidewalk as he listened to music. Last year, Apple was named Creative Brand of the Year because of its “R.I.P. Leon” ad, in which a man sent an iPhone message saying a lizard in his care had died, then deleted it when the lizard suddenly rolled over off its back.
Mr. Myhren and Media Arts Lab didn’t respond to requests for comment about who was behind the “Crush” spot.
Michael J. Miraflor, the chief brand officer at Hannah Grey, a venture capital firm, said on X that Apple’s ad had effectively offended and turned off its core customer base, achieving the opposite of what it had done with its “1984” commercial.
“It’s not even that it’s boring or banal,” Mr. Miraflor wrote . “It makes me feel … bad? Bummed out?”
Tripp Mickle reports on Apple and Silicon Valley for The Times and is based in San Francisco. His focus on Apple includes product launches, manufacturing issues and political challenges. He also writes about trends across the tech industry, including layoffs, generative A.I. and robot taxis. More about Tripp Mickle

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
1 Defining a Business Plan. 2 How to Design a Product Business Plan. 2.1 Step One - Research, Research, Research. 2.2 Step Two - Determine Your Plan's Purpose. 2.3 Step Three - Create a Product Profile. 2.4 Step Four - Document Every Aspect of Your Product. 2.5 Step Five - Set Up a Strategic Marketing Plan. 2.6 Step Six - Make ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
All product organizations have started seeing the importance of a business plan before approving a new product idea. A good business plan has numerous benefits, the most fundamental being an opportunity to think through the idea before investing time and resources. The following are the key traits of a good business plan. Clarity of vision
An example of the items bag shop BAGGU would include in the products and services section of its business plan. BAGGU. Describe new products you'll launch in the near future and any intellectual property you own. Express how they'll improve profitability. ... Here is an example of a marketing plan for a new business: 8. Provide a logistics ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for New Products is your secret weapon for success! With this template, you can: Craft a strategic vision and roadmap for your product. Conduct in-depth market analysis to understand your target audience and competition. Create accurate financial projections to impress investors and secure funding.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Feasibility business plans focus on that business's product or service. Feasibility plans are sometimes added to startup business plans. They can also be a new business plan for an already thriving organization. 3. Internal Use. You can use internal business plans to share goals, strategies, or performance updates with stakeholders.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
7 business plan examples: section by section. The business plan examples in this article follow this example template: Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business. Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists. Market analysis.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
A product business plan is a document that provides justification for a new product or product release, including the product's potential and the quantifiable risks. The business plan is then used to communicate with leadership and investors so they may be able to decide which ventures to fund and which to delay or terminate.
A business plan is a document describing a business, its products or services, how it earns (or will earn) money, its leadership and staffing, its financing, its operations model, and many other details essential to its success. ... Whether you've written a business plan for a new online business idea, a retail storefront, ...
To develop your product, you'll need to determine the money you'll need. Start by deciding how much it will cost to make the new product. Then, decide how many you might make for a release. Use your vendor quotes to estimate the cost of production. When putting together a budget for your development plan, look at startup costs and ongoing ...
3.3 How the new product launch will be started. Step1: Create Business Plan New Product. The foremost step is to study as many business plans for new products as are available. They will help you understand the process for different types of businesses. After that, you should delineate launching a new product plan.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Product management is all about realizing outcomes. Before jumping into the how and what, let's first understand why product planning is important by outlining its six objectives: Company survival. Meet customer needs. Increase sales. Understand and manage strengths and weaknesses. Better manage capacity.
New product development is the end-to-end process of creating a product that has never been brought to market—from idea to concept, prototyping, developing, testing, and launch. It involves building a product strategy and roadmap to successfully guide cross-functional teams and stakeholders through the entire process.
This page details the steps to take to develop a new product. A well thought-out product development plan can help you avoid wasting time, money and business resources. Your plan will: help you organise your product planning and research. understand your customers' views and expectations. accurately plan and resource your project.
Pfizer Inc. (NYSE: PFE) today announced that Andrew Baum, M.D., will join the company as Chief Strategy and Innovation Officer, Executive Vice President. Dr. Baum will be a member of Pfizer's Executive Leadership Team reporting to Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, Dr. Albert Bourla. He joins Pfizer from Citi, where he served as Head of Global Healthcare, Managing Director Equity Research.
Note the following about free trials: The free trial terms change on July 1, 2024, and are different for Amazon Q Business and QuickSight. For customers subscribing the same user to both products with an Amazon Q Business Pro subscription, the free trial for that users will end whenever the first free trial expires.
Portugal's largest utility company, EDP , cut its three-year investment plan on Friday, citing worsening market conditions, but maintained its guidance for more than 35% growth in net profit this ...
Meet the new iPad Pro: the thinnest product we've ever created, the most advanced display we've ever produced, with the incredible power of the M4 chip. Just imagine all the things it'll be ...