- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools

Writing a Business Plan Confidentiality Statement

Free Confidentiality Statement Template (NDA)
Ayush Jalan
- December 12, 2023
Every company has a unique identity that sets it apart from its rival companies in the industry. It is a combination of various aspects: The way you set your goals , your marketing strategy, your manufacturing process, or your entire business plan.
As crucial as it is to create a business plan that helps you stand out, it is perhaps just as crucial to protect your plan from any potential intellectual property theft. This is where a confidentiality statement for your business plan helps you safeguard your valuable assets.
A business plan confidentiality statement is a document that states that the information disclosed to the recipient can’t be disclosed to anyone outside the agreement. It is an agreement made between two parties before they enter a deal or exchange any sensitive information which is confidential.
Why Do You Need a Confidentiality Statement?
Even though trust is essential between partners or investors, there’s always a need to stay cautious while handing over your business plans. Even though the organization you plan to work with values confidentiality, everyone involved in it may not.
Your business plan is one of the most elaborate and classified documents. Before disclosing any information, the first and foremost thing is to sign a confidentiality statement. This will avoid the misuse of any information disclosed between the two parties.
How Does a Confidentiality Statement Protect You?
When a confidentiality statement is signed, it is agreed by both parties that they will not expose any of the information that is discussed or presented in the business plans. Additionally, the document should also mention the penalties in case of a violation of the agreement.
If the other party violates the statement of confidentiality, you can proceed legally and receive compensation for the damages you had to bear because of the violation. As per the contract, the compensation is paid.
The absence of a confidentiality statement is an invitation for others to use parts of your business plan. Although copyright laws can help you claim most of your information, some, still, stay unprotected.
Creating a Confidentiality Statement for the Business Plan
Most companies include a brief confidential statement on their business plan cover page. Although it is not a requirement, it delivers a quick message that the document is highly classified. Furthermore, it is essential to create an exclusive document.
To write a stringent confidentiality statement for your business plan, these are the elements that you must include:
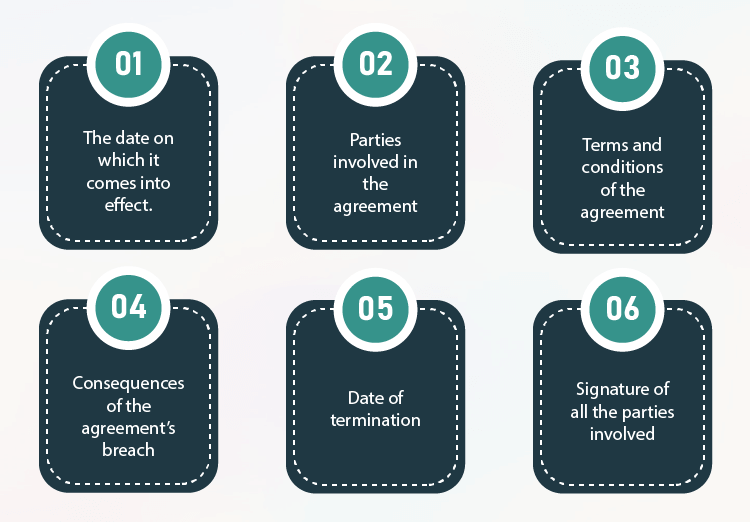
1. Date of Effect
The date of effect is the date from which the confidentiality statement becomes active. An agreement is not valid until all the parties sign it; the date of effect follows this.
2. Parties Involved in the Agreement
It is crucial to specify the parties that will sign the agreement. If someone, you want as a part of the confidentiality statement, hasn’t signed it, they’re not bound by the clauses mentioned in the document.
For instance, two companies are getting into a contract, and the CEOs, representing the entire company, are signing the document, it is essential to mention that all employees are also bound by the agreement even when they haven’t signed it.
3. Agreement Terms
Describe and mention all the terms that both parties are agreeing to. This is a crucial part of the agreement and hence, requires confidentiality. Anything that isn’t included is not protected.
Here, you can also include that the recipient needs written consent from the disclosing party—the owner of the information, in case any information needs to be disclosed to a third party who isn’t a part of the statement of confidentiality.
4. The Non-Confidential part
Along with mentioning the confidential part of your business plan, you also mention the non-confidential part of the agreement. In most cases, there’s a lot of information that is acquired from other sources. This information won’t show under confidential.
Information relevant to the receiving party won’t list under confidential, some of these are:
- The information they owned before the agreement
- If they legally received it from another source
- The information they need to disclose in a lawsuit or administrative proceeding
- If they have developed or are developing the information.
5. Consequences in case of Agreement’s breach
Here, you mention all the legal consequences that will follow if the receiving party violates the agreement. This can include the procedure and the monetary penalties. According to the uniqueness of the information exposed, the compensation can vary.
6. Limits of the Usage of Information
The objective of a statement of confidentiality is to restrict the usage of the information that is disclosed to the recipient. Here, you mention the extent to which the information can be used. Also, specify the standard of security that needs to be followed while handling confidential information.
7. Date of Termination
Every agreement has an expiry date, after which both parties are free of the binding clauses. This termination date is set based on various factors like the end of the partnership , the end of a project or an event, or simply the end of the period mentioned in the agreement.
8. Miscellaneous Clauses
This part of the agreement is usually at the end of the document, which includes any other clauses that don’t necessarily fit into the above categories, but the owner of the information wants to include.
9. Signatures of all Parties
Clearly, this is the most important part of an agreement. Without the signatures of all the parties, the document is pointless and of no value. The agreement, as mentioned previously, can’t go into effect unless everyone involved signs it.
We have written a confidentiality statement example for you, including the above-mentioned elements. This will help you get a better understanding of how to write a confidentiality statement for your business plan.
Business Plan Confidentiality Statement Example (Key Points)
This BUSINESS PLAN NON-DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT (hereinafter known as the “Agreement”) between ______ (hereinafter known as the “Company”) and ________ (hereinafter known as the “Recipient”) becomes effective as of this ____ day of ____, 20___ (hereinafter known as the “Effective Date”).
Article III: Term
– The Recipient’s obligations of non-use and non-disclosure concerning Confidential Information will remain in effect in perpetuity. – The Recipient’s obligations of non-use and non-disclosure concerning Confidential Information will remain in effect for ____ years from the Effective Date.
Article VIII: Governing Law
This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of ____________, without regard to conflict of law principles.
Article XII: Notices
Company’s Address ______________________________
Recipient’s Address ______________________________
Representative Signature: Date: Representative Printed Name: Representative Title:
Recipient Signature: Date: Recipient Printed Name:
Protect Your Information with a Confidentiality Statement
As a business owner, it is a duty to protect your ideas and marketing strategies . Create a confidentiality statement for your business plan and ensure that your business interests are safe and in good hands.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Related Articles

Strategic Marketing Process: A Full Step-by-Step Guide

Best Business Strategy for Growth in (2024)

Business Problem Statement Explained with Examples
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Free Help Wanted Ads
- Forms & Templates
- Sample Letters
- Type of Business

Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA)

The business plan non-disclosure agreement is intended for use when sharing a business plan with consultants, investors, contractors, potential employees, and anyone else evaluating your planned enterprise. Regardless of the size or complexity of your plan, it is likely to include confidential information that hopefully gives you an advantage over competitors. Such information could include your marketing plan, revenue forecast, and capital spending. Note, if you use an NDA with your business plan with one person, you must use NDAs for all who read it, and you should mark the plan as “confidential.”
Product Development NDA – Use when consulting with third (3rd) parties about a potential invention and its use and functionality.
BUSINESS PLAN NON-DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT This agreement (the “Agreement”) between _________________ (the “Disclosing Party”) and _________________ (the “Receiving Party”) is effective _________________ and is intended to prevent the unauthorized disclosure of Confidential Information (as defined below) contained in and relating to the business plan of Disclosing Party. The parties agree as follows: 1. Confidential Information “Confidential Information” is proprietary trade secret information contained within and relating to Disclosing Party’s business plan including but not limited to: business description, marketing plan, sales revenue forecast, profit and loss forecast, capital spending plan, cash flow forecast, future trends, personnel plan, business goals, personal financial statement, supporting documents and information conveyed in writing or in discussion that is indicated to be confidential. 2. Non-Disclosure Receiving Party will treat Confidential Information with the same degree of care and safeguards that it takes with its own Confidential Information, but in no event less than a reasonable degree of care. Without Disclosing Party’s prior written consent, Receiving Party will not: (a) disclose Confidential Information to any third party; (b) make or permit to be made copies or other reproductions of Confidential Information; or (c) make any commercial use of Confidential Information. Receiving Party will carefully restrict access to Confidential Information to those of its officers, directors and employees who are subject to non-disclosure restrictions at least as protective as those set forth in this Agreement and who clearly need such access to participate on Receiving Party’s behalf in the analysis and negotiation of a business relationship or any contract or agreement with Disclosing Party. Receiving Party will advise each officer, director or employee to whom it provides access to any Confidential Information that they are prohibited from using it or disclosing it to others without Disclosing Party’s prior written consent. 3. Return of Business Plan Materials Upon Disclosing Party’s request, Receiving Party shall within 30 days return all original materials provided by Disclosing Party and any copies, notes or other documents in Receiving Party’s possession pertaining to Confidential Information. 4. Exclusions This agreement does not apply to any information that: (a) was in Receiving Party’s possession or was known to Receiving Party, without an obligation to keep it confidential, before such information was disclosed to Receiving Party by Disclosing Party; (b) is or becomes public knowledge through a source other than Receiving Party and through no fault of Receiving Party; (c) is or becomes lawfully available to Receiving Party from a source other than Disclosing Party; or (d) is disclosed by Receiving Party with Disclosing Party’s prior written approval. 5. Term This Agreement and Receiving Party’s duty to hold Confidential Information in confidence shall remain in effect until _________________ or until whichever of the following occurs first: (a) Disclosing Party sends Receiving Party written notice releasing it from this Agreement, or (b) Confidential Information disclosed under this Agreement ceases to be a trade secret. 6. No Rights Granted This Agreement does not constitute a grant or an intention or commitment to grant any right, title or interest in Confidential Information to Receiving Party. 7. Warranty Disclosing Party warrants that it has the right to make the disclosures under this Agreement. 8. General Provisions (a) Relationships. Nothing contained in this Agreement shall be deemed to constitute either party a partner, joint venturer or employee of the other party for any purpose. (b) Severability. If a court finds any provision of this Agreement invalid or unenforceable, the remainder of this Agreement shall be interpreted so as best to effect the intent of the parties. (c) Integration. This Agreement expresses the complete understanding of the parties with respect to the subject matter and supersedes all prior proposals, agreements, representations and understandings. This Agreement may not be amended except in a writing signed by both parties. (d) Waiver. The failure to exercise any right provided in this Agreement shall not be a waiver of prior or subsequent rights. (e) Injunctive Relief. Any misappropriation of Confidential Information in violation of this Agreement may cause Disclosing Party irreparable harm, the amount of which may be difficult to ascertain, and therefore Receiving Party agrees that Disclosing Party shall have the right to apply to a court of competent jurisdiction for an order enjoining any such further misappropriation and for such other relief as Disclosing Party deems appropriate. This right of Disclosing Party is to be in addition to the remedies otherwise available to Disclosing Party. (f) Indemnity. Receiving Party agrees to indemnify Disclosing Party against any and all losses, damages, claims or expenses incurred or suffered by Disclosing Party as a result of Receiving Party’s breach of this Agreement. ( g) Attorney Fees and Expenses. In a dispute arising out of or related to this Agreement, the prevailing party shall have the right to collect from the other party its reasonable attorney fees and costs and necessary expenditures. (h) Governing Law. This Agreement shall be governed in accordance with the laws of the State of _________________. (i) Jurisdiction. The parties consent to the exclusive jurisdiction and venue of the federal and state courts located in _________________ in any action arising out of or relating to this Agreement. The parties waive any other venue to which either party might be entitled by domicile or otherwise. ( j) Successors & Assigns . This Agreement shall bind each party’s heirs, successors and assigns. Receiving Party may not assign or transfer its rights or obligations under this Agreement without the prior written consent of Disclosing Party. However, no consent is required for an assignment or transfer that occurs: (a) to an entity in which Receiving Party owns more than fifty percent of the assets; or (b) as part of a transfer of all or substantially all of the assets of Receiving Party to any party. Any assignment or transfer in violation of this section shall be void. Disclosing Party: _____________________________________________ (Signature) _____________________ (Typed or Printed Name) Title: _____________________ Date: _____________________ Receiving Party: _____________________________________________ (Signature) _____________________ (Typed or Printed Name) Title: _____________________ Date: _____________________
How to Write
EXPLANATION FOR BUSINESS PLAN NON-DISCLOSURE AGREEMENT
Below we provide an explanation for each of the provisions of the Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement.
Introductory Paragraph
Fill in your company name (you are the disclosing party). Fill in the name of the outside individual or company being granted access to your trade secrets (the Receiving Party). Finally, fill in the date the agreement will take effect. This can be the date it’s signed or a date in the future.
1. Confidential Information
This section defines what is protected against disclosure. Keep in mind that if you are disclosing information in conjunction with the plan, you should designate that information as confidential. If the information is spoken, you should announce the confidentiality.
2. Non-Disclosure
This clause makes clear that your trade secrets must be kept in confidence by the receiving party and may not be revealed to others without your prior written consent.
3. Return of Business Plan Materials
Here, the receiving party promises to return your business plan and related materials provided by your company, as well as copies, notes, and documents pertaining to the business plan. The agreement gives the receiving party 30 days to return the materials, but you can change this time period if you wish.
4. Exclusions
This provision describes all the types of information that are not covered by the agreement. These exclusions are based on court decisions and state trade secret laws that say these types of information do not qualify for trade secret protection.
This clause provides the receiving party with an expiration date for the agreement. The Agreement should last as long as the information is likely to remain a trade secret. Five years is a common period, but it can be much shorter, even as little as six months. In Internet and technology businesses, the time period may need to be shorter because of the fast pace of innovation.
6. No Rights Granted
This clause makes clear that you are not granting any ownership rights in the confidential information to the receiving party.
7. Warranty
A warranty is a promise. Here, you promise the receiving party that you have the right to disclose the information. This is intended to assure the receiving party that it won’t be sued by some third party claiming that the trade secrets belonged to it and that you had no right to reveal them to the receiving party.
8. General Provisions
These miscellaneous provisions (often referred to as “boilerplate”) are often grouped together at the end of an agreement.
Relationships . Most agreements include a provision like this one, disclaiming any relationship other than that defined in the agreement.
Severability . The severability clause provides that if you wind up in a lawsuit over the agreement and a court rules that one part of the agreement is invalid, that part can be cut out and the rest of the agreement will remain valid.
Integration . The integration provision verifies that the version you are signing is the final version and that neither of you can rely on statements made in the past.
Waiver . This provision states that even if you don’t promptly complain about a violation of the NDA, you still have the right to complain about it later.
Injunctive Relief . An injunction is a court order directing a person to do (or stop doing) something. If someone violated your NDA, you would want a court order directing that person to stop using your secrets.
Indemnity . Some NDAs require the receiving party to pay for all damages (lost profits, attorney fees or other expenses) incurred by the other party as a result of the receiving party’s breach of the non-disclosure agreement. This obligation is known as indemnification. Leaving out the indemnity provision does not prevent you from suing and collecting damages for a breach (contract law holds the receiving party responsible for a breach), but the clause makes it easier to claim damages.
Attorney Fees and Expenses. If you don’t include an attorney fees clause in your agreement, a judge may (in most states) order the award of attorney fees in cases where the theft of the trade secret was willful and malicious. It’s up to the judge, which makes things unpredictable. You are far better off using an attorney fees provision. However, don’t be surprised if the other party is opposed to the idea. Why? Because it is the receiving party that is usually sued, not vice-versa, and the receiving party may believe that the provision will encourage you to litigate.
Governing Law . You can choose any state’s laws to govern the agreement, regardless of where you live or where the agreement is signed. Most businesses favor the state where their headquarters are located.
Jurisdiction . The purpose of adding a jurisdiction provision to an NDA is to get each party to consent in advance to jurisdiction in one county or state and to give up the right to sue or be sued anywhere else.
Successors and Assigns . This provision binds any company that acquires either party.
Signing the agreement. Someone with the necessary authority must sign the agreement on behalf of each party. Each party should sign two copies and keep one. This way, both parties have an original signed agreement.

Adobe PDF – Microsoft Word (.docx)
Related NDA's:

Thank you for downloading!
How would you rate your free form.
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Business Plan Tips
How to Write a Business Plan Confidentiality Agreement
Are you about pitching your idea to investors? If YES, here is a detailed guide on how to write an ironclad confidentiality agreement for a business plan. Confidentiality statements are documents that are prepared for the safety of parties that are about to go into a business contract.
Also known as non-disclosure agreements, confidentiality statements help to preserve sensitive information that various business parties might bring to the table when transacting business. Business confidentiality statement in essence is a document that states that when a company’s business plan has been revealed, they will not be able to discuss the contents of it with anyone that is not part of the agreement.
Confidentiality or nondisclosure agreement has various uses in the world of business. An individual with a patentable invention or idea may need to enter into partnership with a manufacturer or marketing firm; and of course, he would want to keep his or her invention a secret.
Again, two companies considering a joint venture may need to share the names of their investors – but may not want those names to reach competitors’ ears. Confidentiality agreements can cover all these scenarios; the parties can tailor them to their specific needs before a meeting or negotiation, or over the course of a contractual relationship.
Tips to Note When Writing a Business Plan Confidentiality Statement
A. use the proper contract format.
The proper contract format that is generally used when writing a confidentiality statement is the standard contract format. In this writing format, single-spaced paragraphs with a double space between them is used. Each paragraph constitutes a separate term of the contract and are also numbered for specification. If you have any sub-paragraphs, indent them under the main paragraph and mark them with a letter, as though you were writing an outline.
B. Agreement type
There are two types of agreement to use when writing your confidentiality statement. A unilateral and mutual confidentiality agreement. A unilateral confidentiality agreement is used when only one party is disclosing information, while a mutual agreement is used when both or all parties involved are disclosing information.
You have to decide whether the confidential relationship established will be mutual or one-way. Mutual confidentiality agreements are necessary when you’re providing information to a company so they can provide you with something secret in return. For example, you may be disclosing your plans for a secret invention to a professional who will help you devise a marketing plan.
You need a one-way confidentiality agreement if you need to share confidential information with an employee or contractor who will not be sharing secrets of their own, simply doing work for you. There are also other scenarios where you may require either type of agreement, that is why you have to note the type of confidentiality agreement you need.
How to Write an Ironclad Business Plan Confidentiality Agreement
Provide a list of parties involved in the agreement.
When writing a confidential agreement, you must identify who are the parties to be covered by the agreement. If someone is to be involved in the agreement, but he or she is not listed, you must know that the agreement is not binding on them.
For example, if the agreement is between two companies, the CEO of the company may be able to sign for her entire company, but the agreement should also specify that all employees of the company who have access to the information are bound by its provisions.
Parties can be identified by referring to classes of people, such as “employees” or “engineers,” as long as the person signing the agreement has the authority to bind those people.
Unless the agreement forbids a contractor to have a subcontractor assist with the work, all subcontractors should be included as parties to the agreement as well. This is done so as not to leave any loopholes behind that people can take advantage of.
Describe what the other party is agreeing to
In this part, you need to make known the types of information you wish to keep confidential. This can include any sort of information that might be exchanged between the parties. For instance, if you are designing a software, you might include not only the code and design of the app itself, but also any prototypes, testing procedures and results, or reviews and comments from designers.
This portion of the agreement is designed to set the boundaries of confidential information without disclosing the information itself. It can also be stated that information cannot be disclosed without written consent of the Disclosing Party. The information should only be used for business purposes, and only on a “need to know” basis. And that the information can only be disclosed when the receiving party signs a non disclosure agreement.
List information excluded from confidentiality
Of course not all information should be hidden in a business arrangement. So, for this reason, you need to specify the information that are not under confidentiality. These information may not be a list of specific things, but broad categories of information that don’t have to be protected as confidential. Most of these categories are created by law.
For instance, if an information is already public knowledge then it is not be put under the category of protection. Likewise, information that the receiving party learns from a third party or of which they had prior knowledge cannot be considered confidential, and should be listed as non confidential.
One of the most important exclusions is that if the receiver creates something independently before entering the confidential relationship, it cannot be considered party of the confidentiality agreement even if it happens to use or include some of the same or similar secret information or processes.
Other things that are not under the confidentiality agreement include;
- An information the Receiving Party owned before the agreement
- If the Receiving Party legally received it from another source
- If the Receiving Party is required to disclose in a lawsuit or administrative proceeding
- If it is being or has been developed by the Receiving Party’s employees, consultants, or agents.
Describe what happens if the other party breaches the contract
Wherever there is a law, there must be consequences for breaking it. A typical remedy for this type of contract is an injunction. You can ask for a court order to stop the person who breached confidentiality from continuing to share the information in violation of the agreement.
In some federal cases, under the DTSA, a court may grant the owner the right to seize the property which may be used in “extraordinary circumstances.” You may also require the return of Confidential Information.
You also have the ability to sue for damages incurred as a result of the breach of confidentiality, which may include penalties. For example, in some states you may have the ability to get double or triple damages if the breach was intentional rather than accidental.
Some confidentiality agreements include stiff financial penalties if secret information is revealed to the general public. Others leave the consequences up to a judge or arbitrator to decide. How detailed you want to get with penalties generally relates to how unique the information being disclosed is, and how damaging it would be if it got out.
Establish the obligations of the party receiving the information
Confidentiality agreements typically limit the ways the receiving party can use the confidential information provided, as well as provide the standard for keeping and protecting confidential information.
For example, if you’re looking for investor evaluations of something you’ve invented, your confidentiality agreement may specify that the information can only be used for the purposes of evaluating the product and not in the evaluator’s own business.
If you’re having an employee or contractor sign a confidentiality agreement, you would probably want to limit your employee’s use of information to the performance of job duties directly related to the employment.
Many confidentiality agreements recite that receivers must keep the information disclosed to them in the same way they would keep their own confidential information. However, this statement only works if the receiving party has a known policy for handling confidential information.
Generally, confidentiality standards include limiting access to the information and taking basic precautions to keep the information secure so it doesn’t easily fall into outside hands. Such precautions might include, for example, using encryption for emails discussing the confidential information.
If your confidentiality agreement relates to software designs, inventions or technology, it should include a statement that the receiver of the information has no license, expressed or implied, in the information by virtue of its disclosure.
State when the agreement ends
Whatever has a beginning must have an end, and same applies to a confidentiality agreement. In writing one, you have to specify when the agreement is going to elapse, and when the parties can get out of the loop. State when the agreement ends and what notice must be given to the other party about the termination. You can set one of two options for when the agreement ends:
Your agreement should specify two time periods: the period during which disclosure will be made, and the time period thereafter during which the information should be kept confidential.
American confidentiality agreements typically last for a period of five years, although some may only last two or three years. The end point doesn’t have to be a specific date, but there should be a specific date used as a starting point. Otherwise it’s unclear when the agreement will take effect and for how long it will be enforceable.
If your agreement specifies a confidentiality period of two years, for example, but fails to establish when that two year period starts, the receiver of the information can argue that she didn’t believe the agreement had gone into effect yet.
Another way to set a specific starting date is to have the confidentiality period start from the date the agreement is signed. If you use this method, make sure you don’t disclose any secrets until you have the signature and the agreement is in force.
The confidentiality time period also may end when a certain event happens. For example, if you’re seeking evaluation of a new product, the confidentiality period may end when you market and distribute that product in stores.
Add any necessary miscellaneous provisions
This section is typically located towards the end. The miscellaneous section is sometimes called boilerplate. All agreements contain various clauses that don’t fit in any other section, such as which state’s law will apply and whether attorneys’ fees will be available to an injured party if they agreement is breached. These agreements are then put under the miscellaneous section. This section, though negligent, but should not be overlooked because of the details it is wont to contain.
Provide space for all parties to sign the agreement
For your confidentiality agreement to be binding, it has to be signed. For this reason, you have to provide a page where parties involved in the agreement would pen down their signatures. Without the agreement signed, it cannot go into effect.
With the use of a confidentiality statement, otherwise known as a non-disclosure agreement, the parties can keep nonpublic information under wraps. These contracts bind the parties to very specific pledges on the disclosure of information and are enforceable under the laws of the state where they are created.
More on Business Plan Tips
Business development
- Billing management software
- Court management software
- Legal calendaring solutions
Practice management & growth
- Project & knowledge management
- Workflow automation software
Corporate & business organization
- Business practice & procedure
Legal forms
- Legal form-building software
Legal data & document management
- Data management
- Data-driven insights
- Document management
- Document storage & retrieval
Drafting software, service & guidance
- Contract services
- Drafting software
- Electronic evidence
Financial management
- Outside counsel spend
Law firm marketing
- Attracting & retaining clients
- Custom legal marketing services
Legal research & guidance
- Anywhere access to reference books
- Due diligence
- Legal research technology
Trial readiness, process & case guidance
- Case management software
- Matter management
Recommended Products
Conduct legal research efficiently and confidently using trusted content, proprietary editorial enhancements, and advanced technology.
Fast track case onboarding and practice with confidence. Tap into a team of experts who create and maintain timely, reliable, and accurate resources so you can jumpstart your work.
A business management tool for legal professionals that automates workflow. Simplify project management, increase profits, and improve client satisfaction.
- All products
Tax & Accounting
Audit & accounting.
- Accounting & financial management
- Audit workflow
- Engagement compilation & review
- Guidance & standards
- Internal audit & controls
- Quality control
Data & document management
- Certificate management
- Data management & mining
- Document storage & organization
Estate planning
- Estate planning & taxation
- Wealth management
Financial planning & analysis
- Financial reporting
Payroll, compensation, pension & benefits
- Payroll & workforce management services
- Healthcare plans
- Billing management
- Client management
- Cost management
- Practice management
- Workflow management
Professional development & education
- Product training & education
- Professional development
Tax planning & preparation
- Financial close
- Income tax compliance
- Tax automation
- Tax compliance
- Tax planning
- Tax preparation
- Sales & use tax
- Transfer pricing
- Fixed asset depreciation
Tax research & guidance
- Federal tax
- State & local tax
- International tax
- Tax laws & regulations
- Partnership taxation
- Research powered by AI
- Specialized industry taxation
- Credits & incentives
- Uncertain tax positions
A powerful tax and accounting research tool. Get more accurate and efficient results with the power of AI, cognitive computing, and machine learning.
Provides a full line of federal, state, and local programs. Save time with tax planning, preparation, and compliance.
Automate workpaper preparation and eliminate data entry
Trade & Supply
Customs & duties management.
- Customs law compliance & administration
Global trade compliance & management
- Global export compliance & management
- Global trade analysis
- Denied party screening
Product & service classification
- Harmonized Tariff System classification
Supply chain & procurement technology
- Foreign-trade zone (FTZ) management
- Supply chain compliance
Software that keeps supply chain data in one central location. Optimize operations, connect with external partners, create reports and keep inventory accurate.
Automate sales and use tax, GST, and VAT compliance. Consolidate multiple country-specific spreadsheets into a single, customizable solution and improve tax filing and return accuracy.
Risk & Fraud
Risk & compliance management.
- Regulatory compliance management
Fraud prevention, detection & investigations
- Fraud prevention technology

Risk management & investigations
- Investigation technology
- Document retrieval & due diligence services
Search volumes of data with intuitive navigation and simple filtering parameters. Prevent, detect, and investigate crime.
Identify patterns of potentially fraudulent behavior with actionable analytics and protect resources and program integrity.
Analyze data to detect, prevent, and mitigate fraud. Focus investigation resources on the highest risks and protect programs by reducing improper payments.
News & Media
Who we serve.
- Broadcasters
- Governments
- Marketers & Advertisers
- Professionals
- Sports Media
- Corporate Communications
- Health & Pharma
- Machine Learning & AI
Content Types
- All Content Types
- Human Interest
- Business & Finance
- Entertainment & Lifestyle
- Reuters Community
- Reuters Plus - Content Studio
- Advertising Solutions
- Sponsorship
- Verification Services
- Action Images
- Reuters Connect
- World News Express
- Reuters Pictures Platform
- API & Feeds
- Reuters.com Platform
Media Solutions
- User Generated Content
- Reuters Ready
- Ready-to-Publish
- Case studies
- Reuters Partners
- Standards & values
- Leadership team
- Reuters Best
- Webinars & online events
Around the globe, with unmatched speed and scale, Reuters Connect gives you the power to serve your audiences in a whole new way.
Reuters Plus, the commercial content studio at the heart of Reuters, builds campaign content that helps you to connect with your audiences in meaningful and hyper-targeted ways.
Reuters.com provides readers with a rich, immersive multimedia experience when accessing the latest fast-moving global news and in-depth reporting.
- Reuters Media Center
- Jurisdiction
- Practice area
- View all legal
- Organization
- View all tax
Featured Products
- Blacks Law Dictionary
- Thomson Reuters ProView
- Recently updated products
- New products
Shop our latest titles
ProView Quickfinder favorite libraries
- Visit legal store
- Visit tax store
APIs by industry
- Risk & Fraud APIs
- Tax & Accounting APIs
- Trade & Supply APIs
Use case library
- Legal API use cases
- Risk & Fraud API use cases
- Tax & Accounting API use cases
- Trade & Supply API use cases
Related sites
United states support.
- Account help & support
- Communities
- Product help & support
- Product training
International support
- Legal UK, Ireland & Europe support
New releases
- Westlaw Precision
- 1040 Quickfinder Handbook
Join a TR community
- ONESOURCE community login
- Checkpoint community login
- CS community login
- TR Community
Free trials & demos
- Westlaw Edge
- Practical Law
- Checkpoint Edge
- Onvio Firm Management
- Proview eReader

NDAs and confidentiality agreements: What you need to know Protection of confidential information within an organization is usually a vital business priority. Learn what you need to know when structuring confidentiality agreements.
Nearly all businesses have valuable confidential information, and for many, confidential information is a dominant asset. Companies also share, receive, and exchange confidential information with and from customers, suppliers and other parties in the ordinary course of business and in a wide variety of commercial transactions and relationships.
Contractual confidentiality obligations are fundamental and necessary to help protect the parties that disclose information in these situations. Depending on the circumstances, these obligations can be documented in either:
- A free-standing confidentiality agreement (also known as a nondisclosure agreement or NDA)
- Clauses within an agreement that covers a larger transaction
When is a confidentiality agreement needed?
A range of commercial transactions and relationships involve either the disclosure of confidential information by one party to the other or a reciprocal exchange of information. In both cases, the parties should have a confidentiality agreement in place.
For example, confidentiality agreements may be used when evaluating or engaging a business or marketing consultant or agency, where the hiring company will necessarily disclose confidential information to enable the consultant to perform the assignment. They can also be used when soliciting proposals from vendors, software developers, or other service providers, which usually involves the exchange of pricing, strategies, personnel records, business methods, technical specifications, and other confidential information of both parties.
Finally, your company may need a confidentiality agreement when entering a co-marketing relationship, as an e-commerce business, with the operator of a complementary website or a similar type of strategic alliance.
Why is it necessary to have written confidentiality agreements?
- There are numerous reasons to enter into written confidentiality agreements, such as:
- Avoiding confusion over what the parties consider to be confidential.
- Allowing more flexibility in defining what is confidential.
- Delineating expectations regarding treatment of confidential information between the parties, whether disclosing or receiving confidential information.
- Enforcing written contracts is easier than oral agreements.
- Memorializing confidentiality agreements is often required under upstream agreements with third parties (for example, a service provider's customer agreement may require written confidentiality agreements with subcontractors).
- Maximizing protection of trade secrets, because under state law this protection can be weakened or lost (deemed waived) if disclosed without a written agreement.
- Covering issues that are indirectly related to confidentiality, such as non-solicitation.
- Maintaining standards that are expected of most commercial transactions and relationships.
The forms of confidentiality agreements
Depending on the type of transaction or relationship, only one party may share its confidential information with the other, or the parties may engage in a mutual or reciprocal exchange of information.
In unilateral confidentiality agreements, the nondisclosure obligations and access and use restrictions will apply only to the party that is the recipient of confidential information, but the operative provisions can be drafted to favor either party.
In mutual confidentiality agreements, each party is treated as both a discloser of its—and a recipient of the other party's—confidential information (such as when two companies form a strategic marketing alliance). In these situations, both parties are subject to identical nondisclosure obligations and access and use restrictions for information disclosed by the other party.
In some circumstances, the parties may share certain confidential information with each other but not on a mutual basis. Instead of entering into a fully mutual confidentiality agreement, the parties enter into a reciprocal confidentiality agreement, in which the scope and nature of the confidential information that each party will disclose is separately defined and their respective nondisclosure obligations and access and use restrictions may differ accordingly.
Limitations and risks of confidentiality agreements
Confidentiality agreements are very useful to prevent unauthorized disclosures of information, but they have inherent limitations and risks, particularly when recipients have little intention of complying with them. These limitations include the following:
- Once information is wrongfully disclosed and becomes part of the public domain, it cannot later be "undisclosed."
- Proving a breach of a confidentiality agreement can be very difficult.
- Damages for breach of contract (or an accounting of profits, where the recipient has made commercial use of the information) may be the only legal remedy available once the information is disclosed. However, damages may not be adequate or may be difficult to ascertain, especially when the confidential information has potential future value as opposed to present value.
- Even where a recipient complies with all the confidentiality agreement's requirements, it may indirectly use the disclosed confidential information to its commercial advantage.
Nondisclosure obligations
In general, recipients of confidential information are subject to an affirmative duty to keep the information confidential, and not to disclose it to third parties except as expressly permitted by the agreement. The recipient's duty is often tied to a specified standard of care. For example, the agreement may require the recipient to maintain the confidentiality of the information using the same degree of care used to protect its own confidential information, but not less than a reasonable degree of care.
Recipients should ensure there are appropriate exceptions to the general nondisclosure obligations, including for disclosures:
- To its representatives. Most confidentiality agreements permit disclosure to specified representatives for the purpose of evaluating the information and participating in negotiations of the principal agreement.
- Required by law. Confidentiality agreements usually allow the recipient to disclose confidential information if required to do so by court order or other legal process. The recipient usually must notify the disclosing party of any such order (if legally permitted to do so) and cooperate with the disclosing party to obtain a protective order.
Disclosing parties commonly try to ensure that recipients are required to have downstream confidentiality agreements in place with any third parties to which subsequent disclosure of confidential information is permitted. In these cases, either the recipient or the discloser may prefer to have these third parties enter into separate confidentiality agreements directly with the discloser.
Term of agreement and survival of nondisclosure obligations
Confidentiality agreements can run indefinitely, covering the parties' disclosures of confidential information at any time, or can terminate on a certain date or event.
Whether or not the overall agreement has a definite term, the parties' nondisclosure obligations can be stated to survive for a set period. Survival periods of one to five years are typical. The term often depends on the type of information involved and how quickly the information changes.
The information in this article was excerpted from Confidentiality and Nondisclosure Agreements. The full practice note, one of more than 65,000 resources, is available at the Thomson Reuters Practical Law website.
The information in this article was excerpted from Confidentiality and Nondisclosure Agreements . The full practice note, one of more than 65,000 resources, is available at the Thomson Reuters Practical Law website.
Related content

Title: Is your legal function prepared for global expansion?

Risk considerations for third-party relationships

The modern law department: designed to provide superior value

Check out Practical Law for sample NDA documents
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Legal Templates
Home Business Non-Disclosure Agreement Confidentiality
Confidentiality Agreement Template
Use our Confidentiality Agreement to protect your sensitive information.
- 4.9 577 Ratings

Updated January 2, 2024 Written by Josh Sainsbury | Reviewed by Brooke Davis
Use a confidentiality agreement if you need a party to keep specific information disclosed for a certain period or as long as the relationship with that party lasts, whether as a business or between individuals.
What is a Confidentiality Agreement?
Types of confidentiality agreements, when should i use a confidentiality agreement, what does a confidentiality agreement protect, what to include in a confidentiality agreement, confidentiality agreement sample, frequently asked questions.
A confidentiality agreement is a legally binding contract to protect confidential or proprietary information shared between businesses or individuals.
The parties agree not to disclose the information outlined in the agreement for the duration of the relationship or a specified period.
- Mutual: used when both parties disclose and receive information that must remain confidential.
- Unilateral: used when one party discloses confidential information (disclosing party) while the other party receives and promises to keep the information confidential (receiving party).
If you and another individual or business wish to pursue a relationship that requires disclosing confidential information, you should use a confidentiality agreement. For example, if you’re engaging with:
- Employees: New hires should sign an employee confidentiality agreement or a specified period after termination.
- Independent contractors: Prevent independent contractors from sharing sensitive information with competitors.
- Consulting firms: Ensure your internal information is safeguarded during and after an audit.
- Businesses: Protect your proprietary information when pursuing joint ventures, partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions.
- Interviewees: Protect the information shared with a candidate during the interview process with an interview confidentiality agreement .
If you’ve been asked to enter into a non-disclosure agreement, it’s essential to understand when you should (and shouldn’t) sign an NDA .
A confidentiality agreement protects any information you’ve categorized as confidential in your form:
- Marketing strategies : long- and short-term plans for marketing a company’s products and services to customers
- Product plans : every stage of product development from ideation and beta testing to product launch
- Financial information : all documentation and procedures that make up a company’s finances, including forecasts, reports, taxes, expenditures, profits, losses, and more
- Source code : original code created by programmers employed or contracted by the company
- Intellectual property : copyrights, patents, and trade secrets developed or purchased by the company
A standard confidentiality agreement should include the following information:
- Receiving and Disclosing Party : If either party is a business, you’ll need to specify which type (LLC, corporation, etc.) and where it was formed, as well as include a representative’s name, title, and contact information.
- Confidential Information : Specify the types of confidential information the agreement protects
- Non-Compete Clause : Decide whether or not to include a non-compete clause, and specify when the non-compete period ends.
- Non-Solicitation Clause : Restrict the receiving party from hiring your employees for some time by including a non-solicitation clause.
- Term: Outline how long the agreement will last — this is often how long the potential business relationship is.
- Duration : Define how long the receiving party must maintain confidentiality after the agreement ends.
- Jurisdiction : Establish which state’s laws will govern the agreement.
- Effective Date : Decide when the agreement goes into effect.
Here’s what a standard confidentiality agreement looks like:

How do I ensure my confidentiality agreement form is valid?
Although state laws differ, your confidentiality agreement form will be legally binding and enforceable if:
- It’s signed and dated by both the receiving and disclosing party
- The confidential information defined in the agreement is unavailable to the public
- The scope of the agreement is not overly broad
- An item listed as confidential, such as a product design, cannot be developed or replicated easily without access to the designs.
Just because the document is valid doesn’t mean the other party will adhere to it. Understand what to do if someone breaks your NDA .
Can confidentiality agreements be indefinite?
Yes, confidentiality agreements can be indefinite. Even if there’s a definite term, the obligations of the agreement can be stated to go on indefinitely.
However, most signatories to the agreement would prefer the document to expire at some point.
How long should a confidentiality agreement last?
A confidentiality agreement should last as long as you require the information to be confidential. Typical time frames are between one and five years, but they can be as long as needed.
The agreement should last an appropriate length of time to cover the disclosing party’s interests.
- Legal Resources
- Partner With Us
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information

The document above is a sample. Please note that the language you see here may change depending on your answers to the document questionnaire.
Thank you for downloading!
How would you rate your free template?
Click on a star to rate
Business Confidentiality Statement
Its a tool that businesses use when they discuss their business plan with others who will be given information that the company wishes to keep a secret. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
A business confidentiality statement is a tool that businesses use when they discuss their business plan with others who will be given information that the company values or wishes to keep a secret. In essence, it is a document that states that when a company's business plan is seen, they will not be able to discuss the contents of it with anyone outside of the agreement.
Confidentiality statements may also be referred to as non-disclosure statements that sales representative and other employees often sign but are typically used in regards to exposure to a company's business plan. They are intended to provide protection for both parties involved in a business plan or transaction.
How Can a Confidentiality Statement Protect You?
In every confidentiality agreement, there should be a provision that states that both parties will not disclose any of the information they are about to discuss or see in a business plan. In addition to that, there should also be a provision that covers damages which will occur in the event that a party breaches the agreement. This is often a place to list the monetary liability the party may be sued for.
If you do not have a confidentiality agreement in place when you write your business plan, then you are opening the door for anyone who sees your business plan to use parts of it without your permission. While copyright law may protect a large amount of it, not all of it will be protected.
If you do have a confidentiality agreement in place and someone does breach it , you will be entitled to some form of compensation and be able to possibly obtain a judgment from the breaching party. If you do not have an agreement in place, the courts are not likely to give you any damages if someone were to steal your idea.
When Do You Need a Confidentiality Agreement?
It is good practice to have a confidentiality agreement anytime that you make a business plan. Some of the benefits of having a confidentiality agreement include:
- You can make sure that your financial information stays private.
- You can protect your ides even though the plan may need to be seen by multiple parties.
You should request a signed confidentiality agreement when showing your business plan to anyone, even to a bank. Even though they work for an organization that values confidentiality, it does not mean that everyone working there will be ethical. Always make sure the agreement is signed before handing the business plan over.
Confidentiality Statement Business Plan
The downside of requiring a confidentiality agreement for your business is that it may turn off investors as it can signal distrust. They may feel that you think they plan on stealing your idea and may not be comfortable providing funds for the investment. Other reasons that you may choose not to use a confidentiality agreement include:
- It can make it seem as though you are a novice.
- Some people may find it offensive.
- You may not be able to secure funding and keep it confidential.
Who Signs a Confidentiality Statement of a Business Plan?
In typical fashion, confidentiality agreements would precede or accompany a business plan submission. When requiring the signing of a confidentiality agreement, you should require signing by anyone who you anticipate will see the plan to ensure the information contained in it is confidential.
Considerations
There are some considerations that need to be made before deciding to use a confidentiality agreement. The first is that your confidentiality agreement is not only protecting an invention, but it also should be used to protect:
- Business ideas.
- Strategies.
Until you have received financing or the investment you need to get your business started, anyone will be able to create an identical business without having to ask permission.
It is also important when drafting a confidentiality agreement that it is simply stated and clearly outlines what needs to be protected and what can occur if the agreement is violated. The agreement should be non-intimidating in its verbiage. you can use this agreement for anyone who you may be in contact with about your business before it is stared such as financers, clients, and potential vendors.
If you need help with a business confidentiality statement, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Confidentiality Agreement
- Purpose of a Confidentiality Agreement
- Confidentiality Contracts
- Penalty for Breach of Confidentiality
- How to Draft a Confidentiality Agreement
- Drafting Confidentiality Agreements: What You Need to Know
- Confidentiality Clause Sample
- Confidentiality Agreement Law
- Confidentiality Agreement for Business Partners
- Confidentiality Agreement Consideration

Understanding Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDA)
Written by Dave Lavinsky

When it comes to starting or expanding a business, creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial. A business plan is a written document that outlines the goals, strategies, financial projections, and other key details of a business venture. However, sharing sensitive business information, such as trade secrets, proprietary methods, or financial data, with potential investors, partners, or employees can pose risks. That’s where a Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) comes into play.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
This article will explain to you what an NDA is and provide a sample NDA. However, before discussing that, it is important to note that most investors and lenders will not sign an NDA. So, you’ll need to keep that in mind.
Typically on the cover of a business plan , we’ll include the following:
CONFIDENTIAL
This document includes confidential and proprietary information of and regarding [Your Company Name]. This document is provided for informational purposes only. You may not use this document except for informational purposes, and you may not reproduce this document in whole or in part, or divulge any of its contents without the prior written consent of [Company Name]. By accepting this document, you agree to be bound by these restrictions and limitations.
While such a statement is far from 100% legal protection, it may provide dissuade readers from divulging information about your business plan and company.
What is a Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement
A Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement, also known as a Confidentiality Agreement or NDA, is a legal contract that aims to protect the confidential and proprietary information shared in the plan from being disclosed or used by third parties without authorization. It establishes a legally binding agreement between the parties involved, and it helps to ensure that the sensitive information shared in the business plan remains confidential and is not misused.
The main purpose of a Business Plan NDA is to safeguard the intellectual property and confidential information of a business. This may include, but is not limited to:
- business strategies
- financial projections
- marketing plans
- customer lists
- trade secrets
- proprietary technology
- other sensitive information that gives a business a competitive advantage
By signing a Business Plan NDA, the recipient agrees to keep the information confidential and not to disclose, use, or exploit it for any purpose other than the intended business relationship.
What Key Elements are included in a Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement
A well-drafted Business Plan NDA typically includes the following key elements:
Definition of Confidential Information: Clearly specifying what information is considered confidential and protected under the agreement. This may include a broad or specific definition of confidential information, depending on the needs of the parties involved.
Obligations of the Receiving Party: Outlining the responsibilities of the recipient of the confidential information, including the duty to maintain confidentiality, restrictions on disclosure and use, and the requirement to return or destroy the information after the business relationship ends.
Permitted Disclosures: Identifying situations where the recipient may be allowed to disclose the confidential information, such as to legal or financial advisors, or as required by law.
Term and Termination: Establishing the duration of the NDA and specifying the conditions under which it can be terminated, such as by mutual agreement or by breach of the agreement.
Remedies for Breach: Outlining the consequences of breaching the NDA, such as damages, injunctive relief, or other remedies available under the law.
Governing Law and Jurisdiction: Specifying the applicable law and jurisdiction that will govern any disputes arising from the NDA.
Sample Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement:
Below is a sample business plan non-disclosure agreement (NDA). Since we are not lawyers, we recommend that have a lawyer review any NDAs you plan on using.
[Your Company Name]
[Recipient Name]
This Non-Disclosure Agreement (the “Agreement”) is made and entered into as of [Date] by and between Your Company Name (“Disclosing Party”) and Recipient Name (“Receiving Party”).
Definition of Confidential Information: The term “Confidential Information” shall mean any and all information disclosed by the Disclosing Party to the Receiving Party, including but not limited to business strategies, financial projections, marketing plans , customer lists, trade secrets, proprietary technology, and any other information that is not publicly available.
Obligations of the Receiving Party: The Receiving Party shall use the Confidential Information solely for the purpose of evaluating the possibility of a business relationship between the parties and shall not disclose or use the Confidential Information for any other purpose without the prior written consent of the Disclosing Party.
Permitted Disclosures: The Receiving Party may disclose the Confidential Information to its employees or advisors on a need-to-know basis, provided that such employees or advisors are bound by similar confidentiality obligations.
Term and Termination: This Agreement shall remain in effect for a period of [insert duration, e.g., 2 years] from the date of execution, unless terminated earlier by mutual written agreement or by breach of this Agreement. Upon termination, the Receiving Party shall promptly return or destroy all Confidential Information and provide written certification of such return or destruction to the Disclosing Party.
Remedies for Breach: In the event of a breach of this Agreement, the Disclosing Party shall be entitled to seek equitable relief, including but not limited to injunctive relief, as well as damages for any losses incurred as a result of the breach.
Governing Law and Jurisdiction: This Agreement shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of [insert applicable jurisdiction such as “California”]. Any disputes arising out of or in connection with this Agreement shall be resolved exclusively by the courts of [insert applicable jurisdiction].
Entire Agreement: This Agreement contains the entire understanding between the parties with respect to the subject matter hereof and supersedes all prior and contemporaneous agreements and understandings, whether oral or written, relating to the Confidential Information.
Binding Effect: This Agreement shall be binding upon and inure to the benefit of the parties hereto and their respective successors and assigns.
By signing below, the parties acknowledge and agree to the terms of this Agreement:
[insert name, signature and date lines]

Business Plan Confidentiality Agreement
A business plan confidentiality agreement (or NDA) is used when sharing a business idea or plan with consultants, investors, or anyone else that is evaluating your business. It establishes what information cannot be shared and prevents any misunderstandings. This confidentiality agreement is used as a legally binding document with the parties that are meeting each other. It will help establish definitions about trade secrets and when information can be shared.

Create a Personalized Business Plan Confidentiality Agreement Form online in under 5 minutes!
Build Your Document
Answer a few simple questions to make your document in minutes
Save and Print
Save progress and finish on any device, download and print anytime
Sign and Use
Your valid, lawyer-approved document is ready
The Importance of a Business Plan NDA
Risks of not using it, what to include in a business plan non-disclosure agreement.
Even when a business is new, there can still be plans or ideas that can be stolen. Having an NDA agreement for a business plan prevents your unique ideas from being misused by another party.
As with any confidentiality agreement, a business plan NDA will keep your information safe. You will know that your business idea will not be used by someone else. Your plan may have potential trade secrets and other company secrets that you do not want public. A statement of confidentiality will prevent that from happening.
Using a business plan disclosure agreement can prepare you for using NDAs for your business career, both with third parties and employees. Many businesses have trade secrets and confidential information that you want to control the release of. Using the nda template from the beginning will help your business establish good practices.
A business plan covers many different ideas and aspects of running a business. Marketing, competition, and finances are all included. This is valuable information that you want to protect, in many cases for the entire time you are running your business.
Business plans cover a lot of important information that you will want to protect, oftentimes for the entire time it’s operating. Keeping these plans safe will help your business have a successful start and continue to grow.
Aspects of your business plans that you will want to be protected by a business plan confidentiality agreement include market analysis and strategy, list of competitors, staffing and employee plans, and financial data.
This research and planning cover not only your business idea but what you have discovered about other businesses in a similar market. These plans can be protected with a non-disclosure agreement for a business plan to help you keep the right information safe.
When you don’t use a business plan confidentiality agreement you have the risk of your business idea being used or sold without your permission. It would be a shame if all of the time and energy that you spent on developing just the right ideas were used by someone else. Business plans being stolen is a real threat and you want to protect yourself from it.
If the worst-case scenario occurs and the business idea is stolen from you, a business plan confidentiality agreement will also give you recourse options, including compensation. It will save you time and money to establish what information was publicly known and what was revealed during the business plan meeting.
With a confidentiality agreement, all parties have agreed to what information was not allowed to be shared, making getting legal help easier. There will be less confusion with NDAs signed before any confidential information is shared.

A business plan non-disclosure agreement should include many similar aspects of other statements of confidentiality. These agreements define the terms of what is confidential and what can happen if there is a breach of contract.
1. Define Confidential Information
The first item to include in a non-disclosure agreement for a business plan is to define confidential information and how it applies in this document. It can include revenue predictions, spending plans, and predicted future trends among many other aspects of running a business. Without these terms being defined.
2. The Agreement of Confidentiality
The next item to include is the agreement of confidentiality on the receiving parties. This includes talking about what is the meeting, making copies of any documents, or making commercials from the topics discussed. This will also cover how the receiving party will handle being asked about confidential information.
In cases where documents and materials are being shared, a confidentiality agreement will also disclose that these materials be returned within a time frame. The receiving party cannot make copies or share this information without the consent of the business owner.
3. Exclusions
Exclusions are included in a business plan confidentiality agreement to cover what the receiving party already knew before the agreement, if information becomes public knowledge, or is available through other sources legally.
4. Duration
A non-disclosure agreement for a business plan also covers how long the agreement is in effect. This can be until a specified date or certain provisions are met, such as being released from the confidentiality agreement or the information stops being a trade secret.
5. Courts and Contracts
A statement of confidentiality will also include general provisions about if the agreement is determined to be void by a court and an agreement that the current contract supersedes previous contracts and agreements.
6. Legal Ramifications
Legal ramifications for a breach of the confidentiality agreement are also included. This can include legal action and pay for legal fees. These fees will be paid to the disclosing party or business owner, from the receiving party to cover damages and loss of business from the broken contract.
Once the business plan confidentiality agreement is signed and dated, the contract is placed into effect unless otherwise made void.
When drafting a confidentiality agreement for a business idea, you want to use the right language and organize it correctly. They can cover a lot of information and you want to ensure that all the right information is accounted for to protect your business plans.
Using an NDA when you're building a business plan
Starting a new company requires you to share your business plan with a variety of investors, banks, and potential partners. Here's how to protect your confidential information.
Find out more about business management

by Brette Sember, J.D.
Brette is a former attorney and has been a writer and editor for more than 25 years. She is the author of more than 4...
Read more...
Updated on: April 19, 2024 · 4 min read
Creating a basic business plan
Understanding nondisclosure agreements, what to include in a nondisclosure agreement, refusal to sign a nondisclosure agreement.
Starting a business is exciting, but there are a lot of steps to take to get from brilliant idea to successful company. The most important building block of your new venture is your business plan, which you'll be sharing with a lot of people. Because of this, you'll want to use a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) to ensure your hard work and planning remains confidential.

Creating a strategic business plan not only allows you to think through every aspect of your business, it provides a tool you can use to get investors, funding, new customers, and partners.
A well-developed business plan helps you recognize and deal with many possible impediments to your success in advance. It also helps you sharpen your strategy so that you can hit the ground running. A good business plan takes weeks or months to create and requires a lot of research and planning. A basic business plan should include:
- M arket analysis and strategy. This section looks at market trends, the segment of the market you will target, and the strategies you'll use.
- C ompetitors. List the companies you see as your direct competitors and how you will differentiate yourself from them.
- Staffing and employees. You might list specific people who will join your team or identify key roles and skills you need in employees.
- Financial data. Include sales predictions, capital, debts, and more—basically all the financial details of your company.
You can create a business plan using a template or work with a legal service provider or an attorney to create one. Be sure the document is thorough and complies with your state's laws.
A nondisclosure agreement states that your business will give an individual or another business information that they agree to keep secret. If the agreement is breached , you can seek compensation. Using an NDA signals that the information you're sharing is private and critically important to your business.
An NDA is usually one-sided , meaning you're providing confidential information to the other person only. However, it could be two-sided, or mutual, if both parties are sharing confidential information with each other, such as if you're in talks with a potential partner.
Before sharing your business plan with potential investors, customers, partners, or banks, you should first have them sign an NDA , which should include the following information:
- Definition. Describe clearly what you are characterizing as confidential so that there can be no misunderstanding. Generally, you want to state that your entire business plan is confidential, as well as any supporting material you provide and any discussions you have about the business plan.
- Jurisdiction. The agreement should indicate which state's laws apply to the agreement.
- End of relationship. If you and the other party receiving the business plan decide not to work with each other and terminate your business relationship, the information you provided should be returned to you, destroyed, or deleted.
- Length of agreement. An expiration date is normally included, as NDAs cannot be open-ended.
- Ownership of the information. The NDA should make it clear that just because you're sharing information, you're not giving the receiving party any ownership rights in the information.
- Other people. The party you're sharing the business plan with may need to show it to people who work for or with them, such as their accountant or lawyer. The agreement should state that the NDA is binding on those third parties as well.
- Signatures. The agreement should be signed by you and someone from the receiving party who has legal authority to enter into the agreement. The NDA should make it clear that this person has the authority to do so and that their signature is binding on their company.
You may find that large banks or investors won't sign your NDA. This can be frustrating, but because such large funders review hundreds of business plans or pitches every month, they may see doing so as an undue burden.
To protect yourself, you could bring a digital copy of your business plan to your meeting and not allow them direct access.
Another idea is to put the business plan online behind a password, making sure to change the password often. You could also withhold as much confidential information as possible until the investor is seriously interested.
An NDA offers an important way to protect yourself as you share your business plan and seek investors or partners. Taking this extra step can ensure your ideas and data are not stolen or shared without your permission.
You may also like

Why do I need to conduct a trademark search?
By knowing what other trademarks are out there, you will understand if there is room for the mark that you want to protect. It is better to find out early, so you can find a mark that will be easier to protect.
October 4, 2023 · 4min read

Do small businesses need NDAs?
In the course of doing business, it's inevitable that you'll have to share this confidential information with employees, colleagues, investors, etc. A little preparation now may save a legal headache—and a potential loss of business—later.
April 19, 2024 · 3min read

How to Start an LLC in 7 Easy Steps (2024 Guide)
2024 is one of the best years ever to start an LLC, and you can create yours in only a few steps.
May 16, 2024 · 22min read
Business Partner Magazine
Tips and advice for entrepreneurs, start-ups and SMEs
The Essential Guide to Confidentiality Agreements in Business Transactions
March 1, 2024 by BPM Team
Click here to get this post in PDF
Too long to read? Enter your email to download this post as a PDF. We will also send you our best business tips every 2 weeks in our newsletter. You can unsubscribe anytime.

In the labyrinth of business transactions, the confidentiality agreement, often known as a non-disclosure agreement (NDA), stands as the guardian at the gate, ensuring the safe exchange of secrets that could shape the future of the companies involved. This pivotal document is not just a formality but a critical tool designed to protect sensitive information from being mishandled or misappropriated during the delicate phases of negotiation and beyond. Its importance spans a wide range of scenarios, from mergers and acquisitions (M&A) to joint ventures, private placements, and even the hiring process, underscoring its versatility and indispensability in the corporate world.
Why the Written Word Matters
The decision to encapsulate confidentiality in a written form is driven by several compelling reasons. Foremost among these is the ease of enforcement compared to the nebulous territory of oral agreements or the reliance on common law protections. A written NDA offers a clear definition of what is deemed confidential, thereby minimizing disputes over breaches of confidentiality. It also provides a framework for the treatment of sensitive information, including provisions for lawful disclosure requirements.
Moreover, the preservation of trade secrets — a company’s crown jewels — hinges on their confidentiality. A breach in secrecy can waive these rights, leaving invaluable assets unprotected. NDAs often serve as the only binding commitment between parties until a definitive agreement is reached, covering not only confidentiality but also critical ancillary issues like non-solicitation and exclusivity. This underscores the written NDA’s role as a cornerstone of trust and security in business dealings.
Crafting the Shield: Structure, Timing, and Mutual Consideration
Initiating an NDA is typically the first step in exploring a potential M&A deal, setting the stage for a trustworthy relationship. The strategic timing of this agreement enables due diligence to commence without delay, ensuring that sensitive information is shielded right from the outset. While NDAs can stand alone, incorporating confidentiality clauses in initial term sheets or letters of intent (LOIs) should be done with caution, ensuring these provisions are explicitly binding. More information on term sheets and LOIs can be found here .
The nature of the NDA, whether unilateral or mutual, depends on the transaction at hand. Unilateral NDAs are common in cash M&A transactions, where the seller is the primary discloser. However, mutual NDAs are favored in joint ventures and equity-based transactions, reflecting the reciprocal exchange of information. The choice between unilateral and mutual agreements often involves strategic negotiation, balancing protection with the practicalities of information exchange.
Navigating the Limitations
Despite their critical role, NDAs are not impervious shields. The unauthorized disclosure of information, whether intentional or accidental, can irreparably breach confidentiality. Legal remedies, while available, may not always offer sufficient recompense for the loss of future value or the challenge of proving a breach. This highlights the importance of managing disclosure carefully and having contingency plans for information leaks.
Disclosure Dilemmas and Protections
In M&A transactions, timing and method of disclosure are key. The divulging of highly sensitive information should be delayed as long as possible to minimize risks. Employing security measures such as controlled access to data rooms or watermarking documents can further protect confidential information. Vendors must also navigate legal and contractual constraints on disclosure, ensuring compliance without compromising secrecy.
Special Considerations for Start-ups and Investments
For start-ups, the stakes are even higher. Their main asset often lies in their innovative ideas, making NDAs vital for discussions with potential investors or service providers. However, the reluctance of venture capital and private equity firms to sign NDAs poses a challenge, necessitating a balanced approach that protects the start-up’s interests without deterring potential investment.
Start-ups must approach the negotiation of NDAs with investors strategically. While some investors may refuse to sign NDAs due to concerns about restricting their ability to pursue similar opportunities or protecting their existing portfolio companies, there are ways for start-ups to mitigate these concerns while still safeguarding their sensitive information.
One approach is to limit the scope of the NDA to specific information that truly requires protection, such as proprietary technology, customer lists, or strategic plans, rather than seeking blanket confidentiality for all discussions. By focusing on protecting only the most critical information, start-ups can demonstrate their respect for investors’ concerns while still safeguarding their valuable assets.
Additionally, start-ups can explore alternative forms of protection, such as patents, trademarks , or copyrights, for their intellectual property. While these forms of protection may not offer the same level of secrecy as an NDA, they can still provide valuable legal recourse in the event of misappropriation or infringement.
Furthermore, start-ups should carefully evaluate the reputation and track record of potential investors before disclosing sensitive information. While it may be tempting to pursue investment from well-known firms or individuals, start-ups must prioritize trust and compatibility in their investor relationships. Working with investors who have a proven track record of respecting confidentiality and supporting their portfolio companies can provide invaluable peace of mind for start-up founders.
In summary, while NDAs are essential tools for protecting sensitive information in start-up investment discussions, start-ups must approach their negotiation strategically. By focusing on protecting only the most critical information, exploring alternative forms of protection, and prioritizing trust and compatibility in investor relationships, start-ups can navigate the complexities of confidentiality agreements with confidence and ensure that their valuable assets remain secure.
The Art of the Agreement: Balancing Detail and Accessibility
The complexity of an NDA should be tailored to the transaction, balancing the need for protection with the practicality of negotiation and compliance. For start-ups and small businesses, simplicity and clarity take precedence, ensuring the agreement is comprehensible to non-lawyers while adequately safeguarding sensitive information.
In conclusion, confidentiality agreements are foundational to the integrity and success of business transactions. They require careful consideration and skillful drafting to balance protection with practicality, ensuring that the secrets that fuel innovation and growth are securely guarded in the competitive arena of business. Given the complexities and nuances involved in crafting an NDA that adequately protects all parties’ interests while facilitating the smooth progression of business negotiations, hiring a business lawyer experienced in the intricacies and art of drafting such agreements is crucial. Their expertise can not only navigate the legal landscape effectively but also anticipate potential challenges, ensuring that your business’s confidential information remains safeguarded throughout the transaction process and beyond.
About the Author
Christopher Stienburg is a seasoned litigator, part of the business lawyers team at Roberts & Obradovic law firm. With extensive experience, he has successfully represented clients in complex employment law disputes, elder abuse and estates cases, professional misconduct claims, commercial disputes, personal injury claims, and more. A graduate of Osgoode Hall Law School, Christopher is dedicated to helping individuals and businesses navigate the legal landscape. To contact him, visit Roberts & Obradovic website.
You may also like: What to do if Your Business Partner has Breached your Partnership Agreement
Image source: Depositphotos.com
We earn commissions if you shop through the links on this page.
Digital Marketing Agency

Business Partner Magazine provides business tips for small business owners (SME). We are your business partner helping you on your road to business success.
Have a look around the site to discover a wealth of business-focused content.
Here’s to your business success!


How to Write a Business Plan Confidentiality Agreement
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans
Are you about pitching your idea to investors? If YES, here is a detailed guide on how to write an ironclad confidentiality agreement for a business plan. Confidentiality statements are documents that are prepared for the safety of parties that are about to go into a business contract.
Also known as non-disclosure agreements, confidentiality statements help to preserve sensitive information that various business parties might bring to the table when transacting business. Business confidentiality statement in essence is a document that states that when a company’s business plan has been revealed, they will not be able to discuss the contents of it with anyone that is not part of the agreement.
Confidentiality or nondisclosure agreement has various uses in the world of business. An individual with a patentable invention or idea may need to enter into partnership with a manufacturer or marketing firm; and of course, he would want to keep his or her invention a secret.
Again, two companies considering a joint venture may need to share the names of their investors – but may not want those names to reach competitors’ ears. Confidentiality agreements can cover all these scenarios; the parties can tailor them to their specific needs before a meeting or negotiation, or over the course of a contractual relationship.
Tips to Note When Writing a Business Plan Confidentiality Statement
A. use the proper contract format.
The proper contract format that is generally used when writing a confidentiality statement is the standard contract format. In this writing format, single-spaced paragraphs with a double space between them is used. Each paragraph constitutes a separate term of the contract and are also numbered for specification. If you have any sub-paragraphs, indent them under the main paragraph and mark them with a letter, as though you were writing an outline.
B. Agreement type
There are two types of agreement to use when writing your confidentiality statement. A unilateral and mutual confidentiality agreement. A unilateral confidentiality agreement is used when only one party is disclosing information, while a mutual agreement is used when both or all parties involved are disclosing information.
You have to decide whether the confidential relationship established will be mutual or one-way. Mutual confidentiality agreements are necessary when you’re providing information to a company so they can provide you with something secret in return. For example, you may be disclosing your plans for a secret invention to a professional who will help you devise a marketing plan.
You need a one-way confidentiality agreement if you need to share confidential information with an employee or contractor who will not be sharing secrets of their own, simply doing work for you. There are also other scenarios where you may require either type of agreement, that is why you have to note the type of confidentiality agreement you need.
How to Write an Ironclad Business Plan Confidentiality Agreement
Provide a list of parties involved in the agreement.
When writing a confidential agreement, you must identify who are the parties to be covered by the agreement. If someone is to be involved in the agreement, but he or she is not listed, you must know that the agreement is not binding on them.
For example, if the agreement is between two companies, the CEO of the company may be able to sign for her entire company, but the agreement should also specify that all employees of the company who have access to the information are bound by its provisions.
Parties can be identified by referring to classes of people, such as “employees” or “engineers,” as long as the person signing the agreement has the authority to bind those people.
Unless the agreement forbids a contractor to have a subcontractor assist with the work, all subcontractors should be included as parties to the agreement as well. This is done so as not to leave any loopholes behind that people can take advantage of.
Describe what the other party is agreeing to
In this part, you need to make known the types of information you wish to keep confidential. This can include any sort of information that might be exchanged between the parties. For instance, if you are designing a software, you might include not only the code and design of the app itself, but also any prototypes, testing procedures and results, or reviews and comments from designers.
This portion of the agreement is designed to set the boundaries of confidential information without disclosing the information itself. It can also be stated that information cannot be disclosed without written consent of the Disclosing Party. The information should only be used for business purposes, and only on a “need to know” basis. And that the information can only be disclosed when the receiving party signs a non disclosure agreement .
List information excluded from confidentiality
Of course not all information should be hidden in a business arrangement. So, for this reason, you need to specify the information that are not under confidentiality. These information may not be a list of specific things, but broad categories of information that don’t have to be protected as confidential. Most of these categories are created by law.
For instance, if an information is already public knowledge then it is not be put under the category of protection. Likewise, information that the receiving party learns from a third party or of which they had prior knowledge cannot be considered confidential, and should be listed as non confidential.
One of the most important exclusions is that if the receiver creates something independently before entering the confidential relationship, it cannot be considered party of the confidentiality agreement even if it happens to use or include some of the same or similar secret information or processes.
Other things that are not under the confidentiality agreement include;
- An information the Receiving Party owned before the agreement
- If the Receiving Party legally received it from another source
- If the Receiving Party is required to disclose in a lawsuit or administrative proceeding
- If it is being or has been developed by the Receiving Party’s employees, consultants, or agents.
Describe what happens if the other party breaches the contract
Wherever there is a law, there must be consequences for breaking it. A typical remedy for this type of contract is an injunction. You can ask for a court order to stop the person who breached confidentiality from continuing to share the information in violation of the agreement.
In some federal cases, under the DTSA, a court may grant the owner the right to seize the property which may be used in “extraordinary circumstances.” You may also require the return of Confidential Information.
You also have the ability to sue for damages incurred as a result of the breach of confidentiality, which may include penalties. For example, in some states you may have the ability to get double or triple damages if the breach was intentional rather than accidental.
Some confidentiality agreements include stiff financial penalties if secret information is revealed to the general public. Others leave the consequences up to a judge or arbitrator to decide. How detailed you want to get with penalties generally relates to how unique the information being disclosed is, and how damaging it would be if it got out.
Establish the obligations of the party receiving the information
Confidentiality agreements typically limit the ways the receiving party can use the confidential information provided, as well as provide the standard for keeping and protecting confidential information.
For example, if you’re looking for investor evaluations of something you’ve invented, your confidentiality agreement may specify that the information can only be used for the purposes of evaluating the product and not in the evaluator’s own business.
If you’re having an employee or contractor sign a confidentiality agreement, you would probably want to limit your employee’s use of information to the performance of job duties directly related to the employment.
Many confidentiality agreements recite that receivers must keep the information disclosed to them in the same way they would keep their own confidential information. However, this statement only works if the receiving party has a known policy for handling confidential information.
Generally, confidentiality standards include limiting access to the information and taking basic precautions to keep the information secure so it doesn’t easily fall into outside hands. Such precautions might include, for example, using encryption for emails discussing the confidential information.
If your confidentiality agreement relates to software designs, inventions or technology, it should include a statement that the receiver of the information has no license, expressed or implied, in the information by virtue of its disclosure.
State when the agreement ends
Whatever has a beginning must have an end, and same applies to a confidentiality agreement. In writing one, you have to specify when the agreement is going to elapse, and when the parties can get out of the loop. State when the agreement ends and what notice must be given to the other party about the termination. You can set one of two options for when the agreement ends:
Your agreement should specify two time periods: the period during which disclosure will be made, and the time period thereafter during which the information should be kept confidential.
American confidentiality agreements typically last for a period of five years, although some may only last two or three years. The end point doesn’t have to be a specific date, but there should be a specific date used as a starting point. Otherwise it’s unclear when the agreement will take effect and for how long it will be enforceable.
If your agreement specifies a confidentiality period of two years, for example, but fails to establish when that two year period starts, the receiver of the information can argue that she didn’t believe the agreement had gone into effect yet.
Another way to set a specific starting date is to have the confidentiality period start from the date the agreement is signed. If you use this method, make sure you don’t disclose any secrets until you have the signature and the agreement is in force.
The confidentiality time period also may end when a certain event happens. For example, if you’re seeking evaluation of a new product, the confidentiality period may end when you market and distribute that product in stores.
Add any necessary miscellaneous provisions
This section is typically located towards the end. The miscellaneous section is sometimes called boilerplate. All agreements contain various clauses that don’t fit in any other section, such as which state’s law will apply and whether attorneys’ fees will be available to an injured party if they agreement is breached. These agreements are then put under the miscellaneous section. This section, though negligent, but should not be overlooked because of the details it is wont to contain.
Provide space for all parties to sign the agreement
For your confidentiality agreement to be binding, it has to be signed. For this reason, you have to provide a page where parties involved in the agreement would pen down their signatures. Without the agreement signed, it cannot go into effect.
With the use of a confidentiality statement, otherwise known as a non-disclosure agreement, the parties can keep nonpublic information under wraps. These contracts bind the parties to very specific pledges on the disclosure of information and are enforceable under the laws of the state where they are created.
Related Posts:
- How to Successfully Present a Business Plan with PowerPoint
- How to Plan Your Growth Strategy (Writing a Business Plan)
- How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan
- Buying Business Plan Software – 10 Tough Questions to Ask
- Business Plan Pro Vs Live Plan: Which is the Best

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To write a stringent confidentiality statement for your business plan, these are the elements that you must include: 1. Date of Effect. The date of effect is the date from which the confidentiality statement becomes active. An agreement is not valid until all the parties sign it; the date of effect follows this. 2.
The primary purpose of a business plan confidentiality statement is to establish a legally binding agreement between the business and the intended readers or recipients of the business plan. This agreement emphasizes the confidential nature of the information contained within the business plan and serves as a formal acknowledgment of the ...
A business plan non-disclosure agreement, also known as a confidentiality agreement or an NDA, is designed to build trust in your business relationships. By learning from the beginning what type of information is confidential, you can safely explore all private aspects of your business venture.
BUSINESS PLAN NON-DISCLOSURE AND CONFIDENTIALITY AGREEMENT This Non-Disclosure and Confidentiality Agreement (this "Agreement") is entered into as of ... ☐ 'Business Operations' which includes all processes, proprietary information or data, ideas or the like, either in existence or contemplated related to Disclosing Party's daily and ...
Business Plan Confidentiality Agreement: The undersigned reader of [Company's Name] Business Plan hereby acknowledges that the information provided is completely confidential and therefore the reader agrees not to disclose anything found in the business plan without the express written consent of [Business Owner's Name].
Create Document. Updated December 22, 2022. A business plan non-disclosure agreement (NDA) allows someone to share a business plan without fear of a third party using it for their own benefit. Business plans are highly confidential, especially detailing a marketing strategy with a different approach to a specific market. An NDA makes the shared ...
Fill Now Download PDF (282.57 KB) Download Word (22.29 KB) The business plan non-disclosure agreement is intended for use when sharing a business plan with consultants, investors, contractors, potential employees, and anyone else evaluating your planned enterprise. Regardless of the size or complexity of your plan, it is likely to include ...
A confidentiality agreement—also called a "nondisclosure agreement" or "NDA"—is a legally binding contract where a person or business promises to treat specific information as a trade secret and promises not to disclose the secret to others without proper authorization. NDAs are sometimes used in other civil cases, such as where one party ...
A. Use the proper contract format. The proper contract format that is generally used when writing a confidentiality statement is the standard contract format. In this writing format, single-spaced paragraphs with a double space between them is used. Each paragraph constitutes a separate term of the contract and are also numbered for ...
A confidentiality agreement is a contract between two or more parties regulating the treatment of specified private information. While these agreements can exist in a variety of contexts, they are ...
A business plan non-disclosure agreement is a document intended to protect private information about your business plan.It notifies the other party that you intend to share confidential information. It lays out potential penalties that the other entity, often a company or a potential business partner, will have to pay if they disclose information about your business plan.
Confidentiality agreements can run indefinitely, covering the parties' disclosures of confidential information at any time, or can terminate on a certain date or event. Whether or not the overall agreement has a definite term, the parties' nondisclosure obligations can be stated to survive for a set period. Survival periods of one to five years ...
A standard confidentiality agreement should include the following information: Receiving and Disclosing Party: If either party is a business, you'll need to specify which type (LLC, corporation, etc.) and where it was formed, as well as include a representative's name, title, and contact information. Confidential Information: Specify the ...
In every confidentiality agreement, there should be a provision that states that both parties will not disclose any of the information they are about to discuss or see in a business plan. In addition to that, there should also be a provision that covers damages which will occur in the event that a party breaches the agreement.
A Confidentiality Agreement is often used in the workplace or during business negotiations that involve the disclosure of commercially sensitive information, such as:. When an employee or contractor gains access to new information not covered in the original contracts with their employer or client; When an employer gives a salary raise, bonus checks, or other compensation packages that they ...
What is a Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement. A Business Plan Non-Disclosure Agreement, also known as a Confidentiality Agreement or NDA, is a legal contract that aims to protect the confidential and proprietary information shared in the plan from being disclosed or used by third parties without authorization.
A business plan confidentiality agreement (or NDA) is used when sharing a business idea or plan with consultants, investors, or anyone else that is evaluating your business. It establishes what information cannot be shared and prevents any misunderstandings. This confidentiality agreement is used as a legally binding document with the parties that are meeting each other.
A nondisclosure agreement states that your business will give an individual or another business information that they agree to keep secret. If the agreement is breached, you can seek compensation. Using an NDA signals that the information you're sharing is private and critically important to your business. An NDA is usually one-sided, meaning ...
In conclusion, confidentiality agreements are foundational to the integrity and success of business transactions. They require careful consideration and skillful drafting to balance protection with practicality, ensuring that the secrets that fuel innovation and growth are securely guarded in the competitive arena of business.
Get PDF. A business confidentiality agreement form (or non-disclosure agreement) is a legally binding contract that an individual, or enterprise, must sign when handling specific information as a commerce secret. Additionally, both need to pledge to never disclose any information to someone else without the proper authorization.
Unilateral confidentiality agreement: This information is protected when one party discloses the information and the other party receives the information and agrees to keep it confidential. These are the things that need to be included in the confidentiality agreement that you drafted. Receiving and Disclosing Parties: If either of the parties ...
A. Use the proper contract format. The proper contract format that is generally used when writing a confidentiality statement is the standard contract format. In this writing format, single-spaced paragraphs with a double space between them is used. Each paragraph constitutes a separate term of the contract and are also numbered for specification.
A confidentiality agreement is exactly what it sounds like. In simple terms, it is a document stating that the person you disclose your business plan to will not disclose any of its contents to ...