Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More

Business Plan Examples for Students
Ajay Jagtap
- December 29, 2023
26 Min Read

Do you know what’s the most common mistake students and rookie entrepreneurs make while preparing their first business plan?
Of course, it’s the first business plan we’re talking about; there’ll definitely be a few. However, overcomplicating things and failing to consider a business plan example still remains the most common one.
That’s why we decided to come up with a solution. We’ve curated this list of top business plan examples for students to help you get going.
So whether you need a business plan for a college project, start a side hustle, or win a business competition, these examples are just what you need to create business plans that stand out.
Ready to dive in? Let’s start by understanding the key elements of a business plan example:
Key Elements of a Business Plan Example
Business planning is not as complicated of a process as people think it is; they’re just overcomplicating things. (Don’t think so?)
Let’s simplify the key elements that make up a comprehensive business plan; you’ll understand it better that way.
Executive Summary:
Company overview:, market analysis:, products and services:, sales and marketing strategies:, operations plan:, management team:, financial plan:.
That’s pretty much it about the key elements of a business plan example. Next, let’s explore the best business plan examples for students.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI assistant
Get 30% off for Students and educators

Top Business Plan Examples for Students
Now that you already know about the components of a business plan template, let’s review some of the best business plan examples for students.
1. Startup Business Plan Example
Upmetrics’ startup business plan example is the ideal solution for students planning to start up or participate in a business plan competition. This business plan template follows the SBA-approved business planning format used by thousands of successful entrepreneurs.
Whether your startup is about a new-age AI-based application, an online shopping site, or traditional IT consulting—this sample business plan is just what you need.
Unlike any traditional small business plan, this example of a startup business plan is lean and agile in approach, focuses on innovation, and emphasizes market validation.
2. Lean Business Plan Example
Since you’re transitioning from a student to an entrepreneur, you may not have enough time to spend on creating a detailed business plan. That’s where this lean business plan template can help.
It’s a condensed version of a traditional plan summarizing all its sections with a primary focus on covering only the critical aspects of the business.
This template is best for startups or businesses uncertain about business planning and student-turned-entrepreneurs with limited time and resources to prepare a business plan.
3. SBA Business Plan Example
Following an SBA-recommended business plan format is key to securing bank loans and business grants. Since it can be time-consuming to find a template that follows a similar outline as the SBA, this SBA-approved business plan example is the way to get started.
This SBA business plan template has nine primary sections, that include executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization, product description, marketing, funding request, and financial projections.
SBA business plan examples ensure you stay on track and don’t deviate from your funding needs.
4. One-Page Business Plan Example
As you may have already guessed, a one-page business plan is a one-page version of a traditional business plan. Since it’s a condensed version of a business plan, drafting it can be quite easy and quick compared to a lean or traditional plan.
Employees, partners, and vendors often use one-page business plans as a quick overview of your company and banks and investors as a summary of your operations.
While it may not be the ideal choice for entrepreneurs seeking investment or bank loans, students with side hustles and idea-stage startups can consider this option.
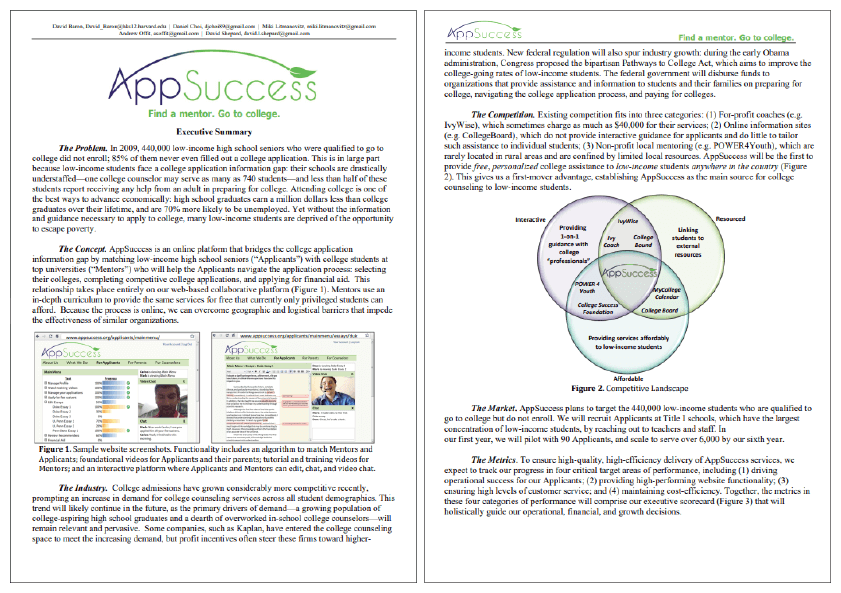
5. HBS Sample Business Plan
Harvard Business School’s new venture competition selected this sample business plan as a finalist in 2011.
This is a business plan of App Success, a collaborative web-based platform that connects low-income high school seniors with college students from top universities; this business will enable them to collaborate on college selection, college applications, and financial aid applications.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a mobile or web-based solution.
6. Kean University Sample Business Plan
Kean University organizes a business plan competition every year for its students where students prepare and present business plans to compete, and this is one of the sample business plans the University provides to participants to understand the format.
It’s a business plan of Blue Water Boatworks, Inc., a boat detailing and cleaning company specializing in servicing recreational fiberglass and aluminum watercraft.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a business related to housekeeping, cleaning, or maintenance.

7. UVM Sample Business Plan
If you are looking for a strategic business plan for a food business, the University of Vermont’s Fancy Foods Business Plan can be a guiding resource for you.
Despite the fact that it can be a good reference for detailed planning, it was written in 1998, so any statistics and numbers may not seem relevant to today’s market landscape. Make sure you keep that in mind.
You may closely follow this example as a reference if planning to start a food truck, restaurant, or any other business that serves food.
That was the list of best sample business plans for students. However, there’s more to talk about. You now have a business plan example, but what about pitching to investors? Let’s explore free pitch deck examples for students.
Free Pitch Deck Example for Students
Pitching to investors as a first-time founder can be exciting but also overwhelming at times. Worry not; we’ve got a solution—investor pitch templates. We’ve prepared a set of 8 investor pitch templates and examples for students and entrepreneurs to help create winning business pitches.
Whether you need a pitch to find an opportunity, ask for subject matter knowledge, or a problem-solving pitch, these investor pitch examples have got you covered. Download now.
How to write a winning plan for a business plan competition?
Creating a business plan is no different than creating one for a real business. Similar to how entrepreneurs prepare and present business plans to investors, Students in business plan competitions pitch to judges.
In short, the business planning process remains exactly the same. Let’s discuss how you can write a winning plan to help you win a business plan competition.
- Select a compelling business idea : everything starts with a compelling idea. Make sure you have a viable business idea to compete in the competition.
- Refer to winning business plan examples : Once you are sure about your business concept, refer to business plan examples from previous winners and how they planned the sections of their plan.
- Market Research & Industry Analysis : After referring to business plan examples, conduct industry research and market analysis to make your statistical and financial numbers accurate and realistic.
- Understand business model and revenue streams : Since you are preparing a business plan for a company that doesn’t exist, be sure about the business model and how the business will generate profit.
- Use AI business plan generator : Using an AI business plan generator like Upmetrics can be incredibly helpful in speeding up the business planning process. With industry-specific business plan templates and AI assistance to write your plan, you can write the first draft of your plan in literally no time.
- Presentation and visuals : Prepare visuals and graphs to make your business plan visually appealing and numbers digestible. You may not need to prepare these visuals if you use business plan software manually.
- Proofread and edit : Grammatical errors are the last thing judges want to see in a business plan. Make sure you proofread and edit your draft thoroughly before submitting it.
Easy as that, that’s the way to write a perfect business plan that can lead you to victory in any business plan competition on planet Earth. Let’s have a look at a real-life business and financial plan example.

Business and Financial Plan Example for Students
Having learned about business planning for students, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop sample business plan and financial statements prepared using Upmetrics.
1. Executive Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will be a new cafe in Phoenix, Arizona. The 1,500 square foot café will be located in the newly constructed Market Square Plaza on the northeast corner of 135th Street and Mission Street. The anchor tenant, the Price Chopper grocery store, has already taken occupancy, and the excellent location brings more than 10,000 shoppers weekly.
The Cooper’s Cup, aptly named for the aromatic brown liquid that will fill the cup, fills the void of original cafes in the market and stands out from its corporate peers with its fast food concepts and prompt services. The Cooper’s Cup is the alternative to fast food/commercial/coffee shops and offers a much calmer, civilized gourmet coffee experience.
There are no televisions in the cafe, the background music is subtle, and work from local artists will hang on the walls. The restaurant is well-appointed, with overstuffed leather chairs and sofas in a library-like setting. The cafe is reminiscent of times gone by – yet is cutting edge technologically with WIFI and state-of-the-art espresso machines.
The Cooper’s Cup measures its financial success in terms of increased market share and earnings. This is a tremendous opportunity with a total local market of $54 million! The keys to success will be offering quality gourmet coffees, taking advantage of its small size, and relying on an outstanding barista staff.
To achieve these goals, the cafe will present some of the area’s finest gourmet beans from local distributors. Because of its small size, the restaurant can enjoy larger margins through lower overhead. The cafe will hand-select baristas and offer salaries comparable to the chains. The baristas will be trained to cross-sell and sell higher-margin products.
The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper’s Cup are below:
- To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3
- Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3
- Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
Guiding Principles
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to values such as excellence, passion, quality, integrity, and leadership, allowing them to navigate challenges and provide for future opportunities. These core beliefs start with their commitment to their products and their employees. Cooper’s Cup rewards excellence and cherishes loyalty. The cafe will work with its employees to build strong businesses and a secure future.
Mission statement
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to its products and employees, which they believe is the recipe for market success.
Key to success
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from the competition. Below are their Keys to Success:
- Great Products : providing exemplary products at market prices – will make customers want to return again and again.
- Hire Quality Baristas : Pay employees rates similar to the larger chains with opportunities for long-term careers and opportunities for advancement with long-term plans to open a second facility.
- Convert Customers to Connoisseurs : Only 40% of the nation’s coffee drinkers consume premium ground and whole bean coffee – this will aid in the continued growth.
Financial Summary
2. Business Overview
The Cooper’s Cup will be a coffee house/cafe located in Phoenix, Arizona. The cozy cafe will be located in the newly completed Market Square Plaza in the Arizona City area. The cafe will serve gourmet coffee, espresso, drip coffee, lattes, and smoothies. The simple pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls. All pastries will be supplied daily by a local bakery.
The cafe will be owned and operated by Owen Jones, a veteran restaurateur with several years of experience running and managing chain restaurants. The cafe will be open for business Monday – Thursday 7-10, Fridays and Saturdays, 7-11, and closed Sundays.
The Cooper’s Cup will be formed as an S-Corporation owned by Mr. Doe.
Start-Up Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will have seating for 40 patrons. The rent is $2,075 a month, with a three-five-year lease available. The site comprises 1500 square feet of leased space consisting of a dining room, a coffee bar, two restrooms, and a storage room in the back.
This storefront needs to be plumbed and wired appropriately to be used as a restaurant. Painting, new floors, and countertops are also needed. A custom coffee bar needs to be built. With materials bought on sale and volunteer labor, the cost to renovate will be $71,725.
The coffeehouse equipment will consist of two commercial espresso machines, air pots and urns, a commercial blender, a commercial brewer, top-loading coffee bins, barista syrups, cold drink dispenser, frothing equipment, a commercial refrigerator, microwave, and stainless steel prep bar.
The cost of the equipment is $38,275. The furniture will consist of leather couches and chairs (purchased at auction), coffee tables, bookcases, and window treatments. The artwork will come from local artists and be sold on a consignment basis. The books were secured via donations. The total cost to furnish is $14,000. Other startup expenses will be dishes, furniture, rent deposit, and marketing.
Location and Facilities

The new coffeehouse is located in the highly desirable Phoenix, Arizona, area at the northeastern intersection of 135th Street and Mission Street in the Newmarket Square Plaza. The property is situated in an excellent location, with an easy 6-minute drive time to I-435 and 69 Highway.
The property is 95% leased with Price Chopper as the Anchor Tenant. Other tenants include LifeSpring Med Spa, Jane’s Canines (Pet Store & Boarding), Pride Cleaners Kahn Dental, and Swim U.
Price Chopper brings more than 10,000 shoppers per week to the center. The location comprises a population of 9,420 within a one-mile radius, 61,102 within a 2-mile radius, and 149,550 within a 5-mile radius – with a median household income of $120,856. Sprint / Nextel’s corporate office is within 2 miles of the site.
3. Market Analysis
Phoenix, Arizona, is an award-winning place to live and work and is considered the leading business community in the Midwest. National publications and organizations recognize Phoenix for its business environment and livability. Here’s a sampling: 6th Place, America’s Best Places to Live Money, Top 50 Cities to Live and Play, National Geographic Adventure, 3rd Hottest Town in the U.S., Money, Among 20 Best Places to Live & Work Employment Review, One of only 72 Sterling Tree Cities in the U.S., National Arbor Day Foundation, Top 10 best Locations to Raise a Family, Southern Business and Development, 1st Place, Kid Friendly Report Card, Population Connection, 2nd Best City in America to Live Business Development Outlook.
Phoenix is at the core of one of the most dynamic local markets in the U.S. It offers easy access to the Arizona City region’s amenities, and, as part of the Arizona City metropolitan area, it is within the most centrally located major market in the nation. I-35, I-435, I-635, and U.S. Highway 69 all pass through Phoenix, and no point in the city is more than 3.5 miles from a freeway. The city maintains an excellent arterial street network and plans to construct additional lane-miles as the area grows. Three airports serve the region. Arizona City International Airport (MCI) is just 25 interstate highway miles north of Phoenix. Johnson County Executive Airport—the second busiest in Arizona—provides complete services for private business jets and general aviation. New Century AirCenter, just 12 miles southwest of the city, offers available aviation services and accommodates cargo or passenger jets of any size.
Phoenix supplies some of the most highly educated workers in the nation, with 97% of Phoenix adults over age 25 holding at least a high school diploma. Johnson County, where Phoenix is located, ranks first among the country’s 231 counties with populations greater than 250,000. The county ranks sixth in the percentage of adults with at least a bachelor’s degree and 16th with a graduate or professional degree.
The Phoenix area has a population of 175,265, based on the 2010 census. The median household income is $77,881, and the median age is 37.9. (2010 U.S. Census)
Industry Analysis
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Peet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. Coffee shops are part of the specialty eatery industry, including retail outlets specializing in bagels, donuts, frozen yogurt, and ice cream products. (First Research)
Competitive Landscape
Consumer taste and personal income drive demand. The profitability of individual companies depends on the ability to secure prime locations, drive store traffic, and deliver high-quality products. Large companies have advantages in purchasing, finance, and marketing. Small companies can compete effectively by offering specialized products, serving a local market, or providing superior customer service. Specialty eateries, which include coffee shops, are labor-intensive: average annual revenue per worker is about $50,000. Coffee shops compete with convenience stores, gas stations, quick service, fast food restaurants, gourmet food shops, and donut shops. (First Research)
Market Size
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Pet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. (First Research)
Target Market and Segment Strategy
Most adult coffee drinkers said their lifelong habits began during their teenage years. 54% said they began drinking coffee between 13 and 19. Another 22% reported their coffee cravings started between 20 and 24. This means that 76% of adult coffee drinkers began drinking coffee by the time they were 24. So, despite a large amount of marketing and advertising directed at the younger age groups, savvy coffee shop owners will remember to cater some of their offerings to the adult and senior market. (National Coffee Drinking Study).
The Cooper’s Cup will offer a unique experience for coffee enthusiasts by providing a quiet, cozy, yet sophisticated cafe and a sense of refinement and peace in an otherwise hectic and fast-paced world. While other coffee shops cater to convenience with drive-throughs or loud music venues late into the night, the Cooper’s Cup will stand apart from its competitors with its quiet yet soothing ambiance, capturing a truly unique (and much-needed) market niche.
- Unique products (specialized roasts, local ingredients, locally-themed or named drinks, custom drinks by the star barista, etc.)
- Games, puzzles, mind benders, and other activities that encourage customers to linger over their coffee
- Hosting or sponsoring local events (entertainment, readings, book clubs, etc.)
- Using technology to creatively compete in marketing with big chains — services like FourSquare, Yelp, and Google Places can increase visibility in the local market.
- Delivering amazing service from knowledgeable baristas — spend lots of time training staff and utilizing online services like the American Coffee & Barista School.
- Selling coffee-related items (and tracking down any co-marketing opportunities with a local community college or another student-related group in the area)
4. Products and Services
Product/services descriptions.
The Cooper’s Cup’s primary offering is gourmet roasted coffees with mocha, carmelicious, white mocha, candy bar latte, and brewed coffee. Complementing the coffee will be a smoothie line including wild berry, strawberry, peach, mango, and lemonade. Rounding out the simple menu line will be pastries obtained from an outside supplier, freshly made and delivered daily. The pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls.

Product/Service Sourcing
The Cooper’s Cup has negotiated supplier agreements with several local food-service wholesalers and coffee wholesalers in the Phoenix area that have a reputation for quality and reliability:
- Mean Beans Coffee Roasters
- Phoenix Brewers
- Healthy Harvest Bread Co.
- Mary’s Organics
If one of the abovementioned specialty suppliers cannot meet their needs, the following national suppliers can provide all the food-service products they require. In addition, the following wholesalers will supply the cafe with general restaurant supplies:
- Lawrence Food Products Corp.
- Gerry Food Supply Inc.
Future Products/Services
Young families, which comprise Phoenix’s third largest market share, are often overlooked in the coffee market. Coffeehouses traditionally have not been considered ‘kid’ friendly. To overcome this hurdle, Cooper’s Cup has long-term plans (5 years) to open a 2nd coffee shop: A combination indoor play area/coffee bar. This concept allows parents and caregivers to meet and relax with other adults while the children can enjoy the indoor playground amenities.
Additional future services will include in-store sales for home purchases and an online store.
The website will have the option to purchase a prepaid gift card program – Prepaid gift cards provide immediate cash, reduce credit card transaction charges, and draw new customers to the business.
5. Sales and Marketing Strategies
Swot analysis.
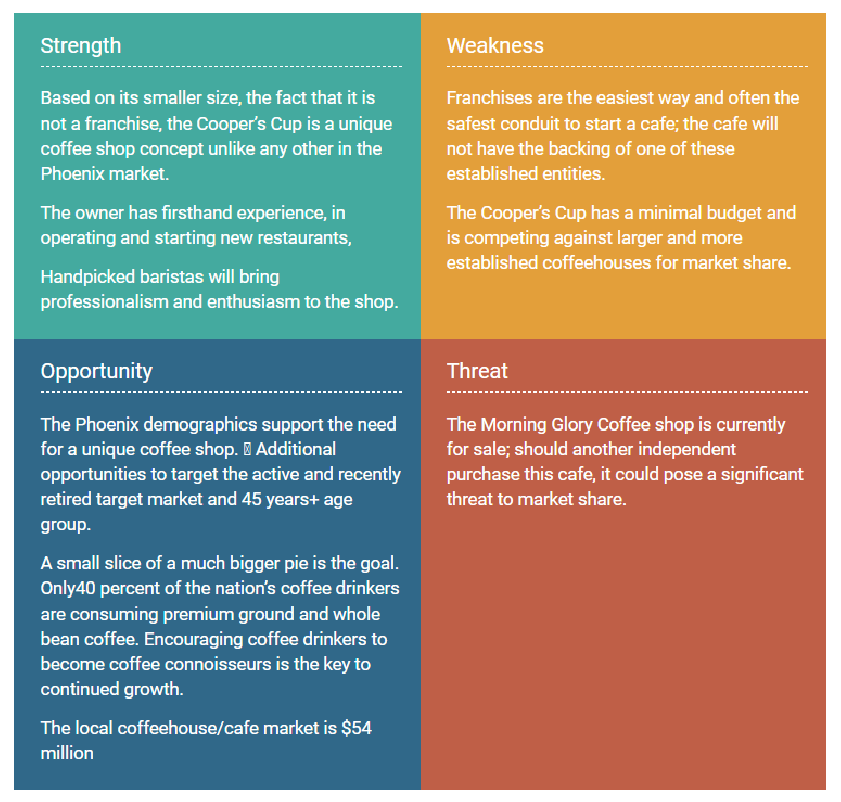
Unique Selling Proposition
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from a crowded sea of coffee chains and franchises. What sets it apart from the competition is primarily its smaller, cozier size combined with premium coffees served by knowledgeable baristas, providing so much energy and enthusiasm for its products.
Market Strategy and Positioning
The Cooper’s Cup utilizes a focus strategy on its Market. By specifically targeting three primary segments, they can cater specifically to their needs.
Senior Market (age 45+)
The Cooper’s Cup will target this Market simply by its well-selected location. Although this demographic group could readily drive downtown, they prefer a local cafe to unwind and relax and historically become some of the most loyal patrons.
Newly Hired Employees
The cafe will attract regular customers (weekly or more) – particularly the newly employed (first job) by providing free WIFI services and providing interesting games in the customer area.
Young Families
The third targeted Market, younger families, often find that coffeehouse is not ‘kid’ friendly. The company has long-term plans to create a combination coffee shop/play area so that parents and caregivers can meet with other adults while the children can enjoy the bounce houses, slides, and indoor playground equipment.
Pricing Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup primarily utilizes competition-based pricing. The cafe does not utilize coupons and discounts (other than opening promotions) because they believe that the most valuable customer demographic of daily coffee consumers is not influenced by discount programs or coupons.
Promotion and Advertising Strategy
- Online Advertising – The Cooper’s Cup will advertise regularly on popular social media sites like Facebook. Compared to traditional print advertising, this is a cost-effective tactic that will allow them to reach prospects in a highly targeted way (e.g., based on criteria such as age, gender, geography, etc.).
- Website – Cooper’s Cup will develop a simple Web site, which will provide basic information about the business, the menu, and links to their presence on the aforementioned social media channels.
- Radio Advertising – During the first six months of operation and the busy holiday shopping season, the business will advertise on local radio stations.
Sales Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup will use the following methods to increase sales revenue (as recommended by Andrew Hetzel on Better Coffee, Better Business):
- The menu will focus on the most profitable products sold. The cafe will always draw customer attention to the best products.
- As warranted, the cafe will raise prices to bolster its brand image. Prices communicate the perceived value of a product, so if set too low, the customers might assume that the beverages are inferior compared to the competition.
- Monitor flavoring inventory – Excess flavoring inventory ties up capital and valuable backroom space for storage. The cafe will utilize 4-6 varieties, including sugar-free offerings.
- Control waste and theft – audit sales and inventory reports to evaluate ingredient waste due to inefficient preparation, returned drinks, and employee consumption. Retail locations can easily waste 20% or more of their daily sales in these three key categories, which is a substantial and unnecessary loss.
- Monitor and evaluate hours of operation.
- Run employee sales contests – The baristas are the salespeople and have great influence over the customer ordering process. All baristas will have some form of sales and customer service training to make each transaction active rather than passive. Sales contests will emphasize high-margin items or cross-selling.
6. Operations Plan
Staffing and training.
An ongoing training and education program will ensure that each staff member learns and implements Cooper’s Cup’s exacting service and operational procedures standards. Staff meetings will reinforce service standards and principles. The Cafe will have detailed work descriptions and training programs for each position, from entry-level employees to the ongoing development of managers and owners. New employees will undergo an extensive training program. This ensures that each guest receives a quality experience from all employees, regardless of how long they have been employed. The Cafe embraces the concept of promoting from within. Excellence in one function typically leads to excellence in another. Regular staff evaluations and training will ensure motivation and address critical issues.
Inventory controls
The founder will be responsible for hiring and training managers who, in turn, will ensure that the day-to-day operations will comply with the standards set by Restaurant policy. Weekly management meetings will provide a forum to review and discuss financial and operational performance. Critical decisions related to purchasing, human resources, marketing, capital expenditures, and customer service will also be addressed.
Purchasing cost controls
Food preparation personnel will follow standardized recipes developed by the founders to control food costs and ensure consistency. The coffee shop will offer an innovative menu with nutritious food and beverages while achieving the most significant margin yield.
Customer Service
The hospitality business recognizes the client’s support experience is the critical driver to replicate business. The direction will Offer a superior degree of Professionalism by hiring individuals who deliver the ideal attitude to work and teaching them the skills required to accommodate guests. The restaurant will keep high levels of consumer satisfaction with talented, educated, and well-trained workers who understand and implement the fundamentals of fantastic service. Ongoing training will be provided to enable staff to perform their jobs with confidence and ability. Employees are well-spoken, well-versed, and trained to provide friendly, prompt, and professional service to each customer. This practice teaches employees who, by producing an exceptional customer experience, can optimize sales and raise their reimbursement. The team will have the knowledge and service required to create excellent daily service for every customer.
Technology & Software
While the quality of the cuisine and dining experience contributes significantly to a restaurant’s profitability, attention to business and financial details can transform small changes into significant returns. Critical sales, cost of sales, labor, inventory, marketing, and overhead metrics are monitored daily. Trends are evaluated, and constructive actions will be taken where improvement is needed. The management team will have access to the restaurant’s transactions and reports available in its real-time POS (point of sale) and accounting systems. Trends will be evaluated, and corrective action will be implemented as required.
7. Organization Structure
The Cooper’s Cup is formed as an S-Corporation wholly owned by John Doe.
Management Team
The Cooper’s Cup will be owned 100% by John Doe. Mr. Doe, a graduate of Arizona State University, has an undergraduate degree in business administration. During high school, he worked as a waiter in a local hospital coffee shop that purchased its beans from a local roaster. In addition to being an avid coffee drinker, this job allowed him to learn about the business first-hand. In college, Doe worked in a campus coffeehouse for four years, eventually becoming an assistant manager. Following graduation, Doe secured a business development position for a regional restaurant chain, which provided additional first-hand exposure to the food and beverage industry—especially the steps involved in establishing new locations.
Management Team Gaps
The Cooper’s Cup will rely on its POS (Point of Sale) system to generate daily accounting and cost activity reports. Mr. Doe will supply these to an outside bookkeeper for the preparation of annual income taxes.
Personnel Plan
Initially, the cafe will hire 1 manager, 5 baristas, and 2 part-time servers. In Year 2, the cafe plans to hire 1 additional full-time barista.
8. Financial Plan
Important assumptions.
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some month’s revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wane in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp-up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista’s salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
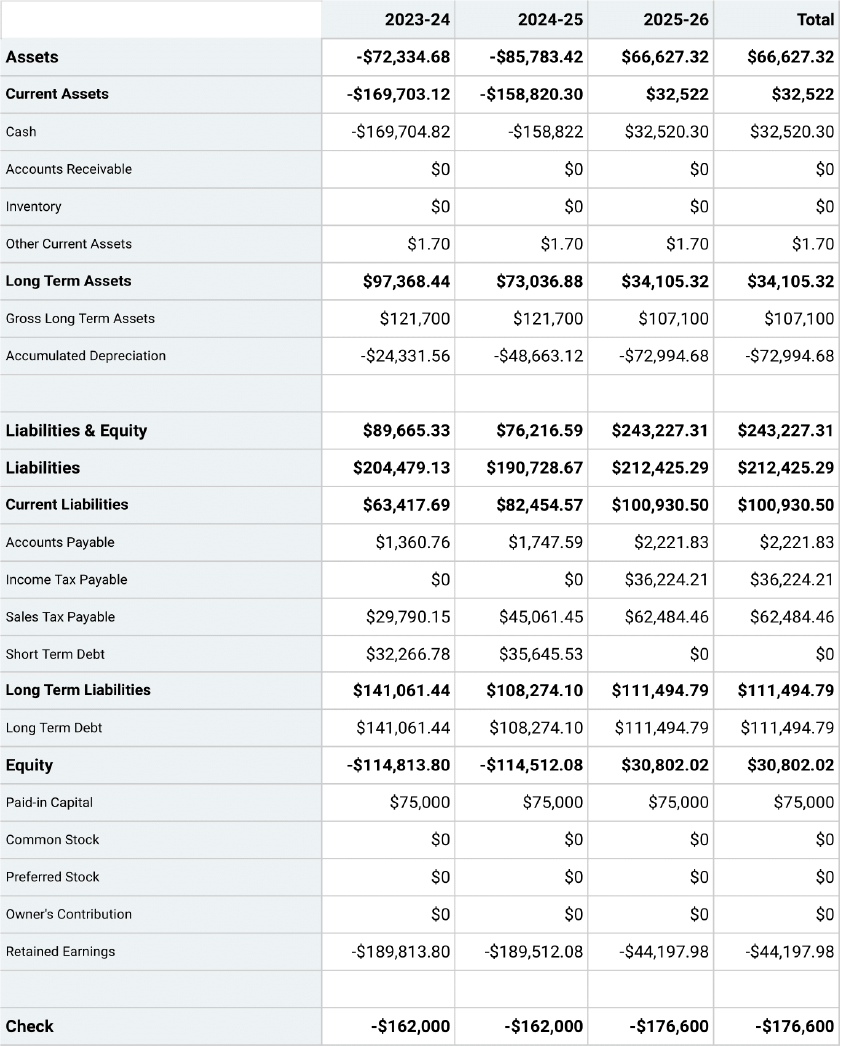
Projected Balance Sheet
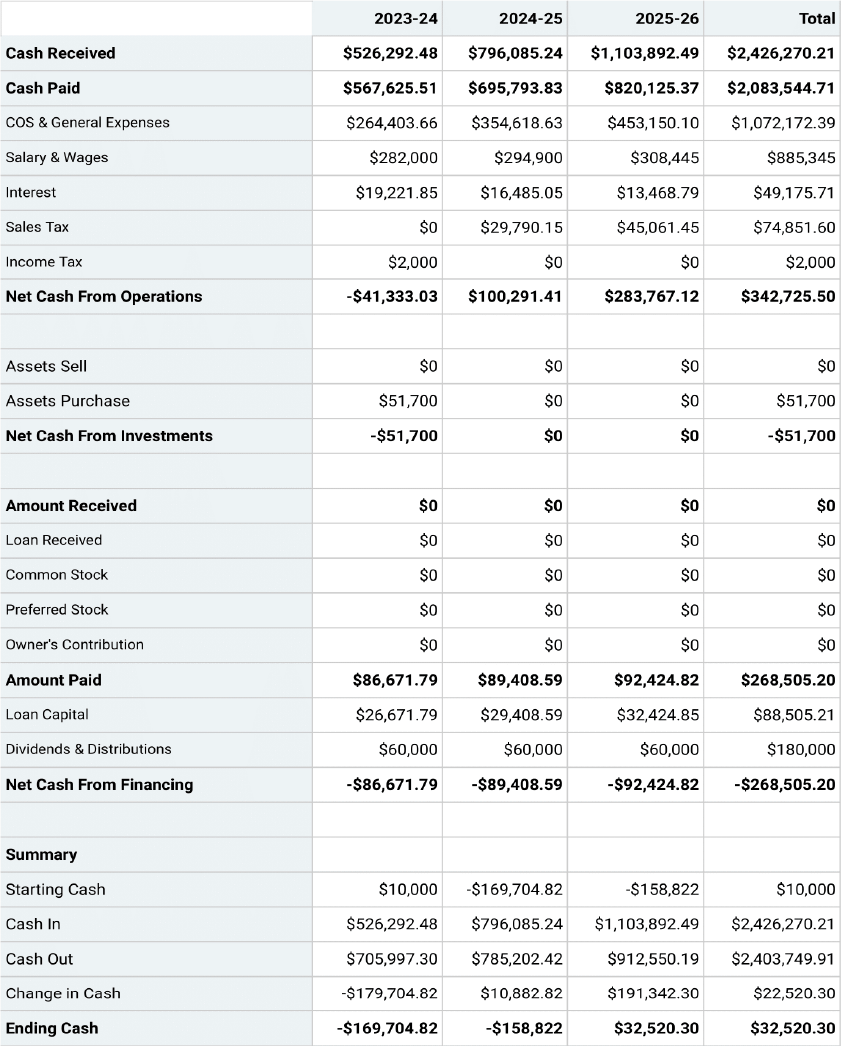
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
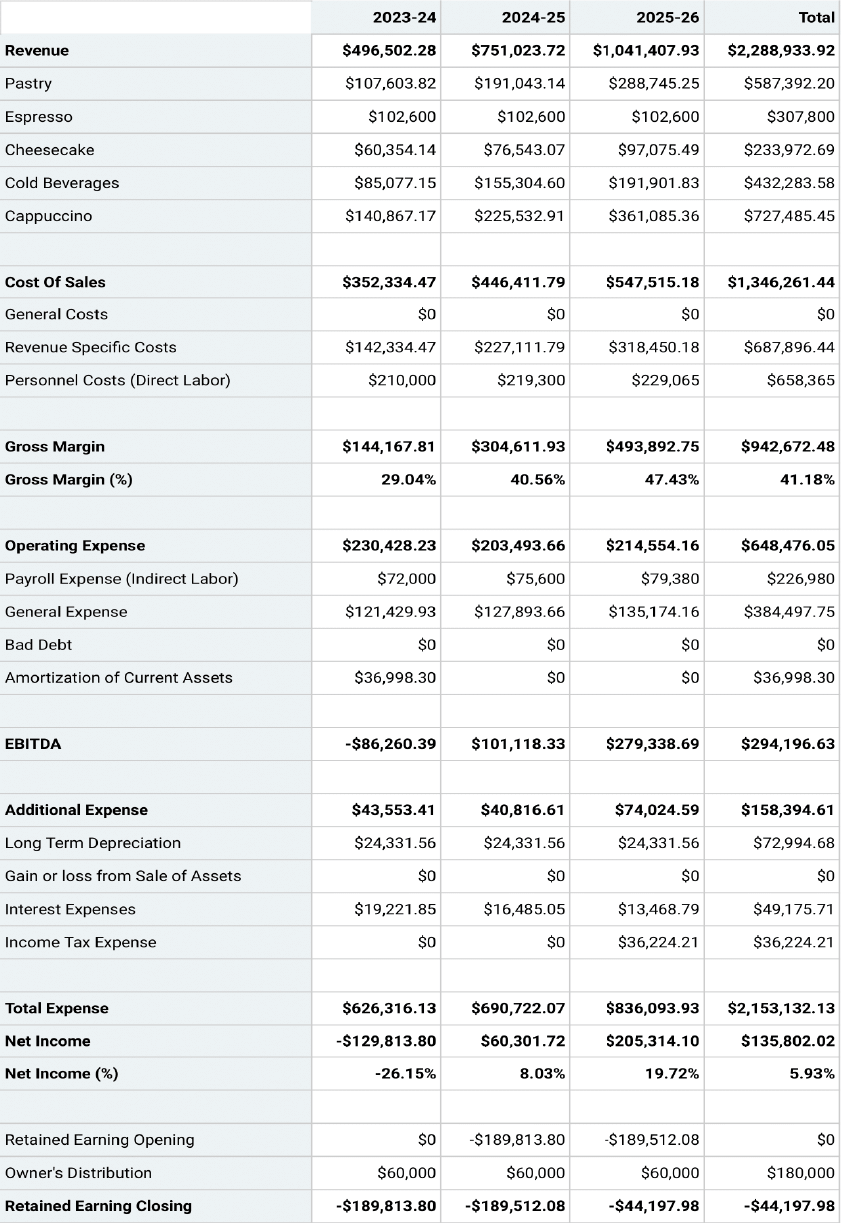
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
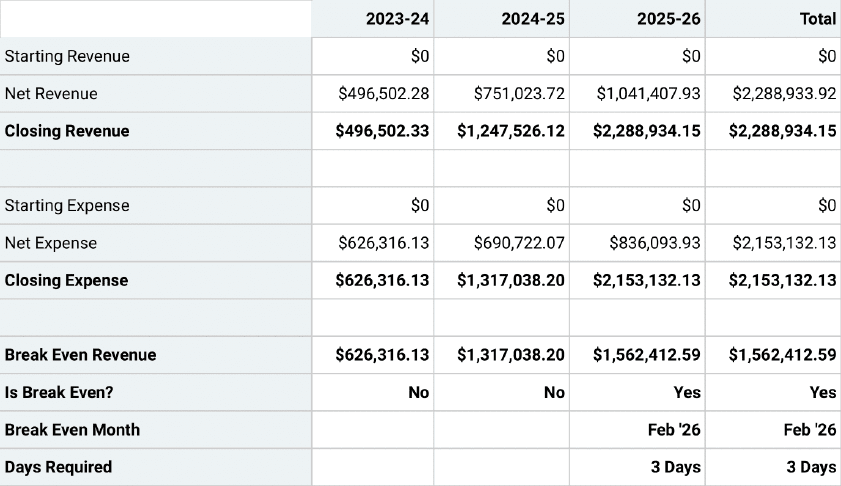
Break Even Analysis
Write Your Business Plan With Upmetrics
Whether you need a business plan to compete in a competition, win investors, or gain a competitive advantage in the market landscape, Upmetrics can help you get started.
Upmetrics is an AI business plan software that comes with AI assistance, financial forecasting features, and 400+ sample business plans so that you can prepare a business plan in no time.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your business plan in a snap.
Make your plan in half the time & twice the impact with Upmetrics
Fill-in-the-blanks, AI-assistance, and automatic financials make it easy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you write a business plan for a college project.
As mentioned earlier in the article, business planning for a college project or competition is no different than for a real business. You can write your business plan using these step-by-step instructions.
- Select a compelling business idea
- Refer to business plan examples
- Prepare a business plan outline
- Create a company description section
- Conduct market research and industry analysis
- Describe your product and services
- Outline sales and marketing strategies
- Create an operations plan
- Introduce management team
- Prepare financial projections
- Summarize your plan with an executive summary
What is a business plan for students?
A business plan is a necessary business document that highlights its purpose, business goals, product/service offerings, go-to marketing strategies, operations and financial plan, key people involved in the business operations, and other necessary details.
As a student, consider a business plan example as a document that helps you better understand business and industry dynamics and learn how a business operates inside out.
What is a business plan competition for students?
Business plan competitions are competitions mostly organized by universities for students passionate about entrepreneurship and the business world. These competitions offer students a platform to showcase their entrepreneurial skills while also providing opportunities for mentorship and networking.
How can I increase my chances of winning a business plan competition?
There cannot be a straightforward answer to this question, but there’s surely a method that can increase your chances of winning a competition—Using AI-powered business plan software.
Why? An AI tool will make you 10X more productive while writing a business plan and preparing financial forecasts. So you can spend more time researching the market and brainstorming business ideas.
Where can I find more business plan examples for students?
Upmetrics’ library of 400+ business plan examples could be an incredible source for students to find more industry-specific business plan examples. There are examples for almost every small business category, including real estate, retail, entertainment and media, food & beverages, and more.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates
Ready to kickstart your business planning.

– Don’t Miss It
See in 90 seconds how LivePlan simplifies
financials for students: Watch
Garretts Bike Shop
Provide real–world business plan examples for your students, inspire confidence in future entrepreneurs and easily create your class syllabus using industry–best business plans., liveplan gives students access to actual business plans so they can practice business planning in and outside of the classroom., it's not just a classroom project. it's your students planning for their futures..

Teach by example
LivePlan's examples of actual business plans show students how they can identify opportunities, meet challenges, and plan their path to profits. Just like real-world entrepreneurs.

No spreadsheets necessary
With all–in–one spreadsheet–free forecasting and pitching tools–students can use LivePlan to build a realistic business plan with accurate projections and compelling pitches. Analyze scenarios. Track progress. Set goals. All in LivePlan.

Works seamlessly with your classroom setup
With LivePlan you can simplify syllabus creation. LivePlan can also be used alongside classroom tools such as Blackboard and Canvas. LivePlan's optional instructional resources can enhance your syllabus with materials that introduce lean planning principles, growth metrics, financial forecasting, and more.
Instructors looking for a great tool to help students develop business plans need to look at Live Plan. The step–by–step process walks students through the entire process from Pitch to Financials. As the Instructor you can also have online access to their plan and provide feedback and comments as the plan develops.

Mike Allen Business Instructor, North Idaho College, Coeur d'Alene, ID
Bring out the best in every student
LivePlan's business plan examples help students turn ideas into top–notch business plans for class projects and startups. The tools, features, and instructional content allow you to focus on bringing out the best in your students for every plan and project.
Before using LivePlan, my students were intimidated by the business planning process. LivePlan breaks it down into manageable steps and takes the mystery out of developing a business plan.

Amy Schulz NACCE Vice President of Education, Membership and Associate Faculty, Feather River College, Quincy, CA
I used LivePlan to develop a business plan for a class project. Turns out, the project became part of a business plan competition where I placed second out of over 200 entries.

Sheila Austin Student
LivePlan provides your students with the tools to

Know the competition
No business operates in a vacuum. LivePlan incorporates real–world industry data, so students can better understand competitors, plan businesses around industry realities, and confidently execute data–driven strategies.

Build business dreams together
From sharing feedback and engaging in discussions, to simultaneously working on different parts of the plan, students can easily collaborate in groups using LivePlan.

Create a plan that fits their needs
Whether small or big, LivePlan can build out the right–sized business plan for your classroom projects. In LivePlan, students can develop a simple lean plan that focuses their ideas, or create a full business plan with all the details and steps necessary to persuade investors, attract partners, and turn their idea into a profitable reality.

With so much happening in the classroom, you need a tool that works with you, not one that makes you do extra work. Used by educators, consultants, entrepreneurs, and students all around the world, LivePlan has been regularly improved and streamlined so it's easy to use.

Develop confidence in their plan and themselves
It's one thing to plan a business. It's another thing to know how to talk about a business plan. Students can develop talking points and practice their pitch in LivePlan so they can discuss their enterprise with confidence and authority.
With LivePlan your students exceed expectations
With LivePlan, students create business plans that:
- Guide them from concept to actionable plan
- Build the confidence necessary to be entrepreneurs
- Combine pitching, forecasting, and collaboration
LivePlan streamlines projects for educators
LivePlan eases project management in the classroom, so instructors can:
- Pinpoint feedback and suggest improvements
- Monitor project progress
- Teach business planning instead of managing multiple apps
Go beyond business plan examples
LivePlan easily integrates into business courses, includes all materials and curriculum to support classroom business projects, and comes with free phone, email, and chat technical support.
The students very much appreciate the guidance the LivePlan program offers. I love the ability to act as a contributor to their plans. The help resources are phenomenal and easy to navigate.

John Shaw Assistant Professor of Management, Davis College of Business – Jacksonville University, Jacksonville, FL
See how LivePlan can upgrade your student's education
Fill out the form below and our LivePlan Partnership Team will be in touch shortly.
Get Your Free LivePlan Account Today
Thanks an educator advocate will be contacting you shortly to set up your free liveplan account..
If you'd like to talk to us before then, please call 1–888–498–6136 Phones are open M–F, 8am–5pm (Pacific time)
Teachers and students love LivePlan
LivePlan really facilitated communication between students who were in a team on the business plan project. Students could comment on sections of their business plan and collaborate on what to change in their plan without having to meet face–to–face.

Amy Valente Assistant Professor of Business, Cayuga Community College, Auburn, New York
LivePlan helped us easily set up the business plan for our startup during our MBA. As soon as the other students saw it, they also wanted LivePlan. The time we saved on planning we could use for operational tasks. It was the ideal solution for us.

The product we produced by using Live Plan was exceptional, far exceeded our expectations, and came out so much better than we could have ever done on our own.

This product is a game-changer. It allows the non–MBA founder to unleash their potential through strategic planning and beautiful design. Highly recommended.

Answers Neuroscience
LivePlan is simply awesome.

Amit Agrawal
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Business Plan Template for Students
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Thinking of starting your own business as a student? We've got you covered! ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students is the ultimate tool to help you turn your entrepreneurial dreams into reality.
With this template, you can:
- Develop a strategic and detailed plan for your business idea
- Outline your objectives, marketing strategies, and financial projections
- Structure your organizational hierarchy for effective management
- Impress potential investors and stakeholders with a professional and well-thought-out plan
- Stay organized and focused on your goals throughout the entire business development process
Don't let your student status hold you back from achieving your business goals. Get started with ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students today and pave the way for your future success!
Business Plan Template for Students Benefits
When students use the Business Plan Template, they gain a competitive edge and set themselves up for success by:
- Structuring their business ideas and goals in a comprehensive and organized manner
- Presenting a professional and well-thought-out plan to potential investors or stakeholders
- Creating a clear roadmap for their business, ensuring they stay on track and achieve their objectives
- Developing a solid understanding of key business components like marketing strategies and financial projections
- Gaining valuable experience in business planning and management, setting them up for future entrepreneurial endeavors.
Main Elements of Students Business Plan Template
When it comes to creating a solid business plan, ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students has got you covered. Here are the main elements you'll find in this template:
- Custom Statuses: Track the progress of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do, ensuring that every step is accounted for and easily manageable.
- Custom Fields: Utilize custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section to add important details to your business plan, keeping everything organized and accessible in one place.
- Custom Views: Explore different views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, enabling you to visualize your plan in various formats and dive deep into specific areas of your business plan.
- Collaboration: Collaborate seamlessly with your team by assigning tasks, leaving comments, and attaching files directly within ClickUp, streamlining the entire business planning process.
- Integrations: Integrate with other tools such as Google Drive, Dropbox, and Slack to streamline your workflow and ensure all relevant documents and communication are easily accessible.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students, you'll have all the tools you need to create a comprehensive, well-structured business plan that will impress potential investors and set you on the path to success.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Students
Creating a business plan as a student can be a daunting task, but with the help of ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you can break it down into manageable steps. Follow these six steps to create a comprehensive business plan that sets you up for success:
1. Define your business idea
Start by clearly defining your business idea. What product or service will you offer? Who is your target audience? What makes your business unique? Use the Docs feature in ClickUp to brainstorm and outline your business concept.
2. Conduct market research
Next, conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, competitors, and target market. Analyze market trends, customer preferences, and potential demand for your product or service. Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your research data.
3. Outline your business structure
Determine the legal structure of your business and outline its organizational structure. Will you operate as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation? Define the roles and responsibilities of key team members and any necessary partnerships. Utilize the Board view in ClickUp to visualize and assign tasks related to your business structure.
4. Develop a marketing strategy
Create a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your business and attract customers. Identify your unique selling propositions, target marketing channels, and budget for marketing activities. Use the Calendar view in ClickUp to plan and schedule your marketing campaigns.
5. Create a financial plan
Develop a financial plan that includes projected revenue, expenses, and profit margins. Determine your startup costs, pricing strategy, and sales projections. Use custom fields in ClickUp to track and calculate financial data accurately.
6. Set goals and milestones
Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your business. Break them down into smaller milestones and create a timeline to track your progress. Utilize the Goals feature in ClickUp to set and monitor your business goals.
By following these six steps and utilizing ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you can create a comprehensive and well-structured business plan that will guide you towards success in your entrepreneurial journey.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Students
Students who are aspiring entrepreneurs or learning about business management can use the ClickUp Business Plan Template to develop a comprehensive and structured plan for their business idea.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a solid business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your plan into different sections such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Marketing Strategy, Financial Projections, etc.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- The Timeline View will allow you to set deadlines and milestones for each section, ensuring you stay on track.
- The Business Plan View will give you an overview of the entire plan, allowing you to see how each section fits together.
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to use the template effectively.
Customize your business plan further by utilizing the three custom fields: Reference, Approved, and Section. These fields will help you keep track of external resources, approval status, and the specific section each task belongs to.
Monitor and analyze your progress using the various views and custom fields to ensure your business plan is comprehensive and well-structured.
- Business Plan Template for Jollibee
- Business Plan Template for Strategic Planning
- Business Plan Template for Woolworths
- Business Plan Template for Ui Designers
- Business Plan Template for Shoe Retailers
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
- Small Business
- Credit Cards
- Personal Finance
- Business Loans
- Business Bank Accounts
- Free Business Bank Accounts
- Business Insurance
- Business Energy
- Business Water
- Accounting software
- How Do Business Loans Work?
- How To Get A Business Loan
- Do I Need A Business Bank Account?
- How To Open A Business Bank Account
- Do I Need Business Insurance?
- Types Of Business Insurance
- How To Switch Business Energy Supplier
- How To Start A Business
- What is an SME?
- How To Go Self-Employed
- How To Grow Your Business
Whether you’re an established business or start-up, see the latest offers from leading business bank account providers
- Personal Loans
- Secured Loans
- Bad Credit Loans
- Guarantor Loans
- Car Finance
- Unsecured Vs Secured Loans
- How to Get a Loan
- Why Can’t I Get A Loan?
- What Are Joint Loans?
- What Is A Bank Loan?
- Am I Eligible For A Personal Loan?
- What You Need To Know About APR
- Paying Off A Loan Early
- Loans For People On Benefits
Compare loans and check your eligibility from a range of leading loan providers
- Best Mortgage Lenders
- Mortgage Rates
- Commercial Mortgages
- Mortgage Calculator
- Stamp Duty Calculator
- Mortgage Eligibility
- What Is Stamp Duty?
- Fixed Vs Variable Rate Mortgages
- What Is A Buy-To-Let Mortgage?
- What Is A Joint Mortgage?
- How Remortgaging Works
- How To Pay Off Your Mortgage Early
- How Long Does A Mortgage Offer Last?
- What Is A Shared Ownership Mortgage?
- What Is A Guarantor Mortgage?
- UK House Prices
- How To Open A Bank Account
- Student Bank Accounts
- How Overdrafts Work
- Can I Open A Bank Account For My Child?
- Regular Savings Accounts
- What Is A Personal Pension?
- ISA Or Savings Account?
- How To Choose A Credit Card
- Do I Need A Credit Card?
- Credit Card Charges And Fees
- Debit Vs Credit Cards
- Breakdown Cover
- Car Insurance
- Home Insurance
- Travel Insurance
- Life Insurance
- Do I Need Breakdown Cover?
- Do I Need Life Insurance?
- Types Of Life Insurance
- What Is Home Emergency Cover?
- How To Maintain Your Vehicle
- Benefits Of Life Insurance
- Can You Have Multiple Life Insurance Policies?
- What Does Car Warranty Cover?
- Business Finance
The Ultimate Guide to Starting a Business as a Student Entrepreneur
You’re currently studying at university (it’s expensive), and you believe you’ve spotted a gap in the market for an innovative new product or service that can help you make money. You’re certain you have what it takes to realise your vision and make a success of your idea.
However, you’re unsure what support is available from your university to get your idea off the ground. In this article we’ll guide you to taking advantage of the support available for your fledgling business from grants to incubator programmes and student entrepreneurship competitions.
What is entrepreneurship?
The problem is, entrepreneurship is a very broad term, and some definitions can serve to put off those best suited to running their own business with flair and originality. Entrepreneurship shouldn’t necessarily put you in the mind of Dragons’ Den , lengthy funding meetings with investors and grant applications, but for many it does, and this perspective can be off-putting to potential student entrepreneurs, the demographic most likely to drive innovation when they bring fresh energy and enthusiasm to the job market.
“A misconception is that the term ‘entrepreneur’ may not resonate with students and they do not see themselves as an entrepreneurial person.” Kirsty Badrock, Entrepreneurship Co-ordinator, Careers and Employability, University of Chester
In fact, entrepreneurship can apply to any way an individual makes money on their own; that is, not through traditional employment as an employee of a business.
Investopedia defines an entrepreneur as “An individual who creates a new business, bearing most of the risks and enjoying most of the rewards. They are commonly seen as an innovator, a source of new ideas, goods, services and business or procedures.”
“If you have ever made money – from babysitting to making greeting cards, Etsy or eBay – then you’ve been entrepreneurial, and if you can do it once you can do it again!” Joseph Buglass, Enterprise & Incubation Manager at University of Central Lancashire
There is a myth that you either have the entrepreneurial drive and skill set required to run a small business or you don’t. We want to dispel this belief and drive more student enterprise. We believe students should be encouraged and supported on their path to entrepreneurship.
Whether you have a unique idea that you think will make you millions and make the world a better place or you have a particular set of skills and ambition and would prefer to strike out on your own and hold your own destiny in your hands, you can become an entrepreneur.
Is there a typical student entrepreneur?
Santander Universities’ report reveals there is a strong entrepreneurial spirit among university students, with over 450,000 students currently running or planning to set up a business while at university. But what type of venture could you start during your degree, and can you secure investor attention and funding for your big idea?
- A third of student entrepreneurs plan to turn their business into a career when they graduate
- Student entrepreneurship generates £1 billion every year
What are the most common student ventures?
So it seems that student entrepreneurship is relatively healthy. But what fields do students favour?
- Technology – 27%
- Arts and crafts – 17%
- Clothing and textiles – 9%
- Administration and business services – 9%
- Tutoring – 8%
- Charity, voluntary and social work – 7%
Unsurprisingly, the most popular student entrepreneurial ventures are technology-based. All students have access to computers and the internet and, with a little entrepreneurial spark, students can set up their own businesses.
Likewise, arts and crafts businesses are popular, possibly because designing crafts can easily be undertaken from student accommodation without the need for business premises, and it’s an activity that can easily fit into leisure time. Examples of students’ arts and crafts companies are greetings card designers, homemade jewellery enterprises, and art and design services.
Can your student business turn into a career?
Santander Universities’ report shows positive trends across the country for many student entrepreneurs. As many as 33% of the student business owners surveyed said they plan to turn their business into their long-term career.
52 % said they will continue their business as a second job for additional income or run it as a hobby alongside full-time employment. 9% said their business would continue with guidance and support from others, and only 4% said they would close their business down on graduation.
What support can universities provide to student entrepreneurs?
There’s a wide variety of support available from most universities. You certainly aren’t on your own when starting a new business! All entrepreneurs need help, support and guidance; no business owner is an island.
The University of Chester for instance through its Venture Programme develops the entrepreneurial capabilities of students across all fields of study, and The University of Bristol were one of the first Russell Group universities to start such a programme with their Centre for Innovation and Entrepreneurship . They do this through enterprise skill development, creating a local entrepreneurial community to connect students with mentors and encouraging collaboration between student entrepreneurs and more.
Challenges bring out the best in an entrepreneur
A challenging environment brings out the best qualities in a would-be entrepreneur. Words such as innovation , problem-solving and creativity are synonymous with what we imagine an entrepreneur to be in the modern day. That’s why many university educators believe in giving students the tools necessary to become entrepreneurs, but not in giving only advice or judging an idea to be right or wrong.
“In fact, we avoid giving advice as much as we can. For example, we never tell a student that their idea won’t work, or that it is a bad idea. However, we ask them difficult questions like what problem are you solving? Every answer they give we disagree with or challenge them on further, irrespective of our opinion.” Simon Best, Programme Leader Msc Innovation Management and Entrepreneurship – Middlesex University London
By learning the skills needed to be an entrepreneur, students can apply their knowledge to the field wish to enter. It’s important that young entrepreneurs learn that it’s important to think creatively and be flexible if they are going to be successful running their own venture. That’s why learning to overcome challenges is vital to creating a thriving business.
What skills help entrepreneurs overcome challenges?
- Leadership skills
- Strategic thinking
Mentorship and networking
Some of the greatest entrepreneurs of our time believe they wouldn’t have achieved what they have without the close mentorship of someone they looked up to. A report by the Federation of Small Businesses revealed that 70% of entrepreneurs with a mentor remain in business for at least five years, while 45% of new businesses fail in the first five years .
Bill Gates considers Warren Buffett to be his mentor, and Steve Jobs thought of Ed Woolard – the Apple board member who encouraged Apple’s cofounder to return to the company after several years in the wilderness – as his mentor.
As a student entrepreneur, it’s a good idea to check if your university has a student entrepreneur mentorship programme. Many do. The university programme will connect students with local successful business people, perhaps even successful alumni of the university, demonstrating to young entrepreneurs that their visions of success are achievable.
“Although all aspects are important, I believe the one-to-one support provides the most value to start-up founders.” Marek Tokarski, Senior Enterprise Manager, Durham University
Incubator programmes
An incubator programme can help kickstart student-run businesses. Incubator programmes are structured programmes that provide support to startup companies through office space, training and networking opportunities. Incubator programmes are used as catalysts to drive growth and establish successful companies.
Many university business schools have incubator programmes; however, entry may be restricted, so check application deadlines as early as you can to avoid disappointment. Most student applications will be cut off before the beginning of each academic year.
If your university doesn’t have a startup incubator programme they may be able to recommend local incubators in the area that you can apply to.
You may be able to apply for grants from various bodies. Your university may have a grants programme for entrepreneurs.
The Prince’s Trust was set up to provide support for young people. They’ve been providing grants to young entrepreneurs since 1976. The Prince’s Trust Enterprise Programme provides funding and support for your business, including connecting you with a suitable mentor.
Other grant programmes for young people
- Enterprise Nation Student Startup of the Year
- Mayor’s Entrepreneur (London)
- Santander Universities Entrepreneurship Awards
Entrepreneurship competitions
There are many entrepreneurship competitions sponsored by businesses and various other bodies. Lots of these competitions offer significant prize money and provide the seed capital that many new ventures need to get off the ground, expand and set their sights higher.
- Unilever Young Entrepreneurs Award – environmental and social change businesses
- Baldwin’s KickStart Young Entrepreneur Awards
- Shell LiveWIRE Smarter Future Award
» MORE: Should I register as a sole trader or limited company?
Business ideas and execution
When most people think of an entrepreneur, they think of someone starting a tech business. The term has become closely linked to Silicon Valley tech entrepreneurs in recent years. Many people’s reply to the statement “Name the first entrepreneur that you can think of” would be either Steve Jobs or Mark Zuckerberg.
But the range of business ideas and fields developed by entrepreneurs is extremely wide. A more recent development is an individual monetising their online presence, such as bloggers and social media influencers. However, competition is fierce online, and this form of entrepreneurship isn’t necessarily as easy as some might believe.
Young entrepreneurs can be successful in many other areas, from hospitality to entertainment.
“Tech isn’t going to solve all our problems” Dave Jarman, Senior Lecturer in Entrepreneurship, Centre for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Bristol
The hospitality and entertainment industries have been some of the hardest-hit by the Coronavirus pandemic . These and other industries that have been financially impacted as a result of lockdown measures could represent an opportunity to new businesses looking to pick up the slack and provide essential services to Brits.
This brings into focus the purpose of your entrepreneurship. Some people start a small business at university as a means to an end, to boost their employability. For others, it’s a route to a full-time career, in which case it’s important that your business will have requisite demand and that it is scalable, so it can expand and develop throughout your working life.
“It’s those students who are developing knowledge or skills at University within a particular area who are more likely to be enterprising, for example, those studying within the Faculty of Arts and Media, the Faculty of Humanities and the Faculty of Science and Engineering.” Kirsty Badrock, Entrepreneurship Coordinator, Careers and Employability, University of Chester
As stated earlier, it’s not necessary to be an expert in your field. The most successful entrepreneurs, while talented and well informed in their industry, combine knowledge with hard work and constant personal development. One of the most valuable traits an entrepreneur can have is to learn from experience and apply hard-learnt lessons to future strategic planning.
“For an idea to be successful it requires four things. Desirability – will other people want it enough to use it and pay for it? Feasibility – does it actually work (well enough)? Viability – is there a business model that makes enough profit to sustain the enterprise? And credibility – does the founder have the competence and determination to persuade others they can make it happen? Dave Jarman, Senior Lecturer in Entrepreneurship, Centre for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Bristol
Disruptive has been a big buzzword in the entrepreneurial community since the mid-00s. But does your idea really have to be wholly unique or disruptive to established industry norms to be successful and scalable?
It’s an easy trap to fall into with all the discourse around disruptive technology. Take the rise of challenger banks, which has revolutionised the banking industry. Rather than focusing on how original or disruptive your idea is, a more valuable action is comparing your idea to what’s already available through rigorous competitive analysis.
Through market analysis you’ll be able to objectively assess the feasibility of your idea. This is such a vital process for any entrepreneur because, if you wish to grow your company, perhaps by seeking investment funds, you’re going to need to be able to provide powerful evidence of the demand in the market for your product, service, and brand.
» MORE: How to grow your small business online
Access to funding
For many entrepreneurs, raising capital is essential to bringing their vision to life. Funding might be needed for product manufacture, marketing and hiring employees.
Recognising your own strengths and weaknesses and being able to market yourself to stakeholders and decision makers are invaluable skills. Even if they don’t lead to a successful funding application, they will sharpen your pitching skills and understanding of all the functions of your business.
Aside from getting a firm grasp on your business’s feasibility, knowing your market also involves identifying whom you want to approach for capital. There is serious research work in identifying your potential investors.
The network you establish at university will help you get started. By making connections with local business people and your lecturers, you will have the support you need to identify the right investors for your business, and at the same time gain invaluable advice from experienced entrepreneurs. This is also where having a strong mentor can come in handy, because they’ll be able to give you firsthand advice on how they secured funding for their own businesses.
When approaching investors with your pitch, it can be invaluable to know whether they are likely to be receptive to your business model. You’ll understand this by approaching investors at the earliest possible stage. Before you make a formal approach for capital, it’s crucial to ensure your approach is correctly targeted when asking for capital by gauging the interest level of different investors. You can also investigate the track record of potential investors to see where their interests lie, and then ask yourself what the companies that have successfully won investment capital have done well. Take apart their business plan and apply it to your own where relevant.
“It’s good to get on investors’ radars early. It means that they can guide you on where you need to be before they’ll seriously consider giving you the investment you need.” Marek Tokarski, Senior Enterprise Manager, Durham University
“Do some research on your investors and ask yourself the following questions. What is their reputation like? What are they offering? Just money, or do they offer more support in the form of business expertise and mentoring? Do they have the same or similar values to yourself?” Joseph Buglass, Enterprise & Incubation Manager at University of Central Lancashire
Investment capital isn’t everything
Don’t despair if you cannot secure investment capital. There are other ways of securing funding, whether you pursue a grant or even put your own money into your business.
There is something to say for investing in your own business. It demonstrates that you believe in yourself and the strength of your ideas. Consider investing your savings in your own business, either as an alternative to securing capital or as a prudent capital injection into your business, which will both help it get off the ground and prove to investors your seriousness in making your enterprise work.
“Student entrepreneurs should also be able to demonstrate exactly what they are putting into their startup idea. Do they have enough faith in their idea to put in their own money? Their own time and resources?” Joseph Buglass, Enterprise & Incubation Manager at University of Central Lancashire
Grants and competitions are an alternative form of investment worth pursuing. However, you’ll still need to firmly prove the efficacy of your business plan. Check with your university the grants that are available to students either looking to start or already running their own businesses.
University grants will usually be available in much smaller amounts than those possible from venture capitalists or small business loans. The benefit of grants, however, is that they are generally not repayable and they will be easier to secure than venture capital, as investors bear a lot of risk should your business fail.
“Not getting venture capital isn’t the death knell of a startup that many assume” Dave Jarman, Senior Lecturer in Entrepreneurship, Centre for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Bristol
You might be thinking, what about business and startup loans? Business loans can be a valuable source of funding for a student entrepreneur. With a business loan, you could secure anywhere from a few thousand to millions of pounds. However, when researching loans it’s important to assess risks, evaluate the feasibility of repayment schedules and understand all the conditions of the loan before making yourself responsible for repayment.
Remember, if you’re considering applying for a business loan, you will need a dedicated business bank account .
Comparing business loans
As a student running your own business or as a prospective business owner, you’ll now be aware of the support available and the funding options open to you.
If you’re ready to invest in your business to enable scaling and are considering a small business loan, why not read our business loan guide.
We wish you luck with your venture. Small business owners are so important to a healthy economy, as you drive innovations, create jobs and fulfil consumer demand.
» MORE: What is business continuity planning?
About the Author
Nic Redfern is Finance Director at NerdWallet and an accomplished business and finance strategist with over 26 years' experience. Nic has been instrumental in the growth of several regional and…
Dive even deeper

How To Start a Candle Business
Are you a candle lover who waxes lyrical about starting your own business? Our guide will answer all the burning questions you need to consider before getting your candle business off the ground.
What is a VAT Loan?
The quarterly obligation of paying VAT returns to HMRC can be challenging for VAT-registered businesses for several reasons. VAT loans are a source of financing companies can use to avoid incurring late payment penalties by missing deadlines.
Top 6 Crowdfunding Sites UK
Raising money through crowdfunding could help you to start a business, launch a new project or expand the business to the next level. But determining the best crowdfunding platform for your business is a step that can turn crowdfunding failure into success.
How to Inspire Entrepreneurial Thinking in Your Students
Explore more.
- Course Design
- Experiential Learning
- Perspectives
- Student Engagement
T he world is in flux. The COVID-19 pandemic has touched every corner of the globe, profoundly impacting our economies and societies as well as our personal lives and social networks. Innovation is happening at record speed. Digital technologies have transformed the way we live and work.
At the same time, world leaders are collaborating to tackle the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals , which aim to address issues related to health, education, gender equality, energy, and more. Private sector leaders, too, are recognizing that it makes good business sense to be aware of corporations’ social and environmental impact.
So, how can we as educators prepare our students to succeed in this tumultuous and uncertain—yet hopeful and exhilarating—global environment? As the world changes, so do the skills students need to build their careers—and to build a better society. For students to acquire these evolving skills, we believe educators must help students develop an entrepreneurial mindset.
6 Ways You Can Inspire Entrepreneurial Thinking Among Your Students
An entrepreneurial mindset —attitudes and behaviors that encapsulate how entrepreneurs tend to think and act—enables one to identify and capitalize on opportunities, change course when needed, and view mistakes as an opportunity to learn and improve.
If a student decides to become an entrepreneur, an entrepreneurial mindset is essential. And for students who plan to join a company, nonprofit, or government agency, this mindset will enable them to become intrapreneurs —champions of innovation and creativity inside their organizations. It can also help in everyday life by minimizing the impact of failure and reframing setbacks as learning opportunities.
“As the world changes, so do the skills students need to build their careers—and to build a better society.”
Effective entrepreneurship professors are skilled at nurturing the entrepreneurial mindset. They, of course, have the advantage of teaching a subject that naturally demands students think in this way. However, as we will explore, much of what they do in their classroom is transferable to other subject areas.
We interviewed top entrepreneurship professors at leading global institutions to understand the pedagogical approaches they use to cultivate this mindset in their students. Here, we will delve into six such approaches. As we do, think about what aspects of their techniques you can adopt to inspire entrepreneurial thinking in your own classroom.
1. Encourage Students to Chart Their Own Course Through Project-Based Learning
According to Ayman Ismail, associate professor of entrepreneurship at the American University in Cairo, students are used to pre-packaged ideas and linear thinking. “Students are often told, ‘Here’s X, Y, Z, now do something with it.’ They are not used to exploring or thinking creatively,” says Ismail.
To challenge this linear pattern, educators can instead help their students develop an entrepreneurial mindset through team-based projects that can challenge them to identify a problem or job to be done, conduct market research, and create a new product or service that addresses the issue. There is no blueprint for students to follow in developing these projects, so many will find this lack of direction confusing—in some cases even frightening. But therein lies the learning.
John Danner, who teaches entrepreneurship at Princeton University and University of California, Berkeley, finds his students similarly inhibited at the start. “My students come in trying to understand the rules of the game,” he says. “I tell them the game is to be created by you.”
Danner encourages students to get comfortable navigating life’s maze of ambiguity and possibility and to let their personal initiative drive them forward. He tells them, “At best you have a flashlight when peering into ambiguity. You can shine light on the next few steps.”
In your classroom: Send students on an unstructured journey. Dive right in by asking them to identify a challenge that will hone their problem-finding skills and encourage them to work in teams to find a solution. Do not give them a blueprint.
For example, in our M²GATE virtual exchange program, we teamed US students with peers located in four countries in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. We asked them to identify a pressing social issue in MENA and then create a product or service to address it. One of the teams identified the high rate of youth unemployment in Morocco as an issue. They discovered that employers want workers with soft skills, but few schools provide such training. Their solution was a low-cost after-school program to equip students ages 8-16 with soft skills.
2. Help Students Think Broadly and Unleash Their Creativity
Professor Heidi Neck says her students at Babson College struggle with problem finding at the start of the entrepreneurial journey. “They are good at solving problems, but not as good at finding the problem to solve,” she explains. “For example, they know that climate change is a problem, and they’re interested in doing something about it, but they’re not sure what problem within that broad area they can focus on and find a market for.”
Professor Niko Slavnic, who teaches entrepreneurship at IEDC-Bled School of Management in Slovenia and the ESSCA School of Management in France, says he first invests time in teaching his students to unlearn traditional ways of thinking and unleash their creativity. He encourages students to get outside their comfort zones. One way he does this is by having them make paper airplanes and then stand on their desks and throw them. Many ask, “Should we do this? Is this allowed?” When his students start to question the rules and think about new possibilities, this indicates to Slavnic that they are primed for the type of creative exploration his course demands.
“When students start to question the rules and think about new possibilities, this indicates to Professor Niko Slavnic that they are primed for the type of creative exploration his course demands.”
In your classroom: Think about the concept of “unlearning.” Ask yourself if students are entering your class with rigid mindsets or attitudes based on rules and structures that you would like to change. For example, they may be coming into your classroom with the expectation that you, the instructor, have all the answers and that you will impart your wisdom to them throughout the semester. Design your course so that students spend more time than you do presenting, with you acting more as an advisor (the “guide on the side”).
3. Prompt Students to Take Bold Actions
Geoff Archer, an entrepreneurship professor at Royal Roads University in Canada, says Kolb’s theory of experiential learning underpins the entrepreneurial management curriculum he designed. Archer takes what he calls a “ready-fire-aim approach,” common in the startup world—he throws students right into the deep end. They are tasked with creating a for-profit business from scratch and operating it for a month. At the end of the semester, they must come up with a “pitch deck”—a short presentation providing potential investors with an overview of their proposed new business—and an investor-ready business plan.
This approach can be met with resistance, especially with mature learners. “They’re used to winning, and it’s frustrating and more than a bit terrifying to be told to do something without being given more structure upfront,” says Archer.
Professor Rita Egizii, who co-teaches with Archer, says students really struggled when instructed to get out and talk with potential customers about a product they were proposing to launch as part of their class project. “They all sat outside on the curb on their laptops. For them, it’s not normal and not okay to make small experiments and fail,” says Egizii.
Keep in mind that, culturally, the taboo of failure—even on a very small scale and even in the name of learning—can be ingrained in the minds of students from around the world.
The benefit of this permutation, explains Archer, is that students are writing plans based on actual experiences—in this case, customer interactions. Moving the starting blocks forward offers many benefits, including getting the students out of the classroom and out of their heads earlier, reminding them that the market’s opinion of their solution is far more important than their own. This also affords students more time to reflect and maximize the potential of their minimum viable product or experiment.
In your classroom: Invite students to bring their lived experiences and workplace knowledge into their studies. This can be just as powerful as the more famous exhortation to “get out of the classroom.” As Egizii sees it, “student-directed experiential learning provides a comfortable and relatable starting point from which they can then diverge their thinking.”
4. Show Students What They Can Achieve
For Eric Fretz, a lecturer at the University of Michigan, the key to launching his students on a successful path is setting the bar high, while at the same time helping them understand what is realistic to achieve. “You will never know if your students can jump six feet unless you set the bar at six feet,” he says.
His undergraduate students work in small teams to create a product in three months and generate sales from it. At the start of the semester, he typically sees a lot of grandiose ideas—a lot of “fluff and BS” as he calls it. Students also struggle with assessing the viability of their ideas.
To help, Fretz consults with each team extensively, filtering through ideas together until they can agree upon a feasible one that fulfills a real need. The real magic of his course is in the coaching and support he provides.
“People know when you’re investing in them and giving them your attention and energy,” Fretz says. He finds that coaching students in the beginning of the course helps assuage their concerns about embarking on an open-ended team project, while also supporting initiative and self-reliance.
In your classroom: Design ways to nudge your students outside their comfort zones, while also providing support. Like Fretz, you should set high expectations, but also adequately guide students.
5. Teach Students the Value of Changing Course
A key part of the entrepreneurial mindset is to be able to course-correct, learn from mistakes, and move on. Entrepreneurship professors position hurdles as learning opportunities. For example, Danner tells his students that his class is a laboratory for both aspiring and failing. He advises them to expect failure and think about how they are going to deal with it.
“A key part of the entrepreneurial mindset is to be able to course-correct, learn from mistakes, and move on.”
Ismail believes letting his students fail in class is the best preparation for the real world. He let one student team pursue a project for the entire semester around a product he knew had no potential. Two days before the end of the course, he told them as such. From his perspective, their frustration was the best learning experience they could have and the best training he could offer on what they will experience in real life. This reflects a key component of the entrepreneurial mindset— the ability to view mistakes as opportunities .
In your classroom: Build into your course some opportunities for students to make mistakes. Show them how mistakes are an opportunity to learn and improve. In entrepreneurship speak, this is called a “pivot.” Can you build in opportunities for students to face challenges and have to pivot in your course?
6. Communicate with Students Regularly to Establish New Ways of Thinking
Professor Neck realized that to nurture the entrepreneurial mindset in her students, she needed to provide them with opportunities to do so outside of class. She now encourages her students to establish a daily, reflective practice. She even designed a series of daily “mindset vitamins” that she sends to her students via the messaging platform WhatsApp. Students are not expected to reply to the messages, but rather to simply consume and absorb them.
Some messages relate specifically to entrepreneurship, such as: “How can you get started with nothing?” And others apply to life in general: “What has been your proudest moment in life so far? How can you create more moments like that? What did it feel like the last time you failed?”
In your classroom: Communicate with your students outside the classroom with messages that reinforce the mindset change you are seeking to achieve in your course. Social media and apps such as WhatsApp and Twitter make it easy to do so.
All Students Can Benefit from an Entrepreneurial Mindset
The COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated that an entrepreneurial mindset is critical for addressing today’s problems. Adapting to risk, spotting opportunity, taking initiative, communicating and collaborating, being flexible, and problem solving—these are ways in which we have responded to the pandemic. And they’re all part of the entrepreneurial mindset. By instilling this way of thinking in our students, we will equip them to handle tomorrow’s challenges—as well as to identify and take advantage of future opportunities.
Thinking about which of these entrepreneurial approaches you can adopt in your own teaching may require you to redesign portions of your courses or even create a new course from scratch. We encourage you to be open to experimenting and trying out some of these ideas. Like the best entrepreneurs, don’t be afraid to fail.
Also, be open with your students. Let them know you are trying out some new things and solicit their feedback. If needed, you can always pivot your class and involve them in the exercise of co-creating something better together. In the process, you will also be modeling the entrepreneurial mindset for your students.

Amy Gillett is the vice president of education at the William Davidson Institute , a non-profit located at the University of Michigan. She oversees design and delivery of virtual exchanges, entrepreneurship development projects, and executive education programs. Over the past two decades, she has worked on a wide variety of global programs, including 10,000 Women , equipping over 300 Rwandan women with skills to scale their small businesses, and the NGO Leadership Workshops—one-week training programs held in Poland and Slovakia designed to enhance the managerial capability and sustainability of nongovernmental organizations in Central and Eastern Europe.

Kristin Babbie Kelterborn co-leads the Entrepreneurship Development Center (EDC) at the William Davidson Institute. She collaborates with the EDC’s faculty affiliates to design and implement projects that support entrepreneurs in building and growing their businesses in low- and middle-income countries.
Related Articles

We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free
Business Plan: What It Is + How to Write One
Discover what a business plan includes and how writing one can foster your business’s development.
![business plan for students entrepreneurship [Featured image] Woman showing a business plan to a man at a desk](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/8jaIrEmfb9uCidnAGOr2F/c551eade2b440294787de7afd2acb369/GettyImages-1127726432__1_.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines financial planning.
In your research into business plans, you may come across different formats, and you might be wondering which kind will work best for your purposes.
Let’s define two main types of business plans , the traditional business pla n and the lean start-up business plan . Both types can serve as the basis for developing a thriving business, as well as exploring a competitive market analysis, brand strategy , and content strategy in more depth. There are some significant differences to keep in mind [ 1 ]:
The traditional business plan is a long document that explores each component in depth. You can build a traditional business plan to secure funding from lenders or investors.
The lean start-up business plan focuses on the key elements of a business’s development and is shorter than the traditional format. If you don’t plan to seek funding, the lean start-up plan can serve mainly as a document for making business decisions and carrying out tasks.
Now that you have a clear business plan definition , continue reading to begin writing a detailed plan that will guide your journey as an entrepreneur.
How to write a business plan
In the sections below, you’ll build the following components of your business plan:
Executive summary
Business description
Products and services
Competitor analysis
Marketing plan and sales strategies
Brand strategy
Financial planning
Explore each section to bring fresh inspiration to the surface and reveal new possibilities for developing your business. You may choose to adapt the sections, skip over some, or go deeper into others, depending on which format you’re using. Consider your first draft a foundation for your efforts and one that you can revise, as needed, to account for changes in any area of your business.
Read more: What Is a Marketing Plan? And How to Create One
1. Executive summary
This is a short section that introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, your goals for developing it, and why it will be successful. If you are seeking funding, summarize the basics of the financial plan.
2. Business description
Use this section to provide detailed information about your company and how it will operate in the marketplace.
Mission statement: What drives your desire to start a business? What purpose are you serving? What do you hope to achieve for your business, the team, your customers?
Revenue streams: From what sources will your business generate revenue? Examples include product sales, service fees, subscriptions, rental fees, license fees, and more.
Leadership: Describe the leaders in your business, their roles and responsibilities, and your vision for building teams to perform various functions, such as graphic design, product development, or sales.
Legal structure: If you’ve incorporated your business or registered it with your state as a legal entity such as an S-corp or LLC, include the legal structure here and the rationale behind this choice.
3. Competitor analysis
This section will include an assessment of potential competitors, their offers, and marketing and sales efforts. For each competitor, explore the following:
Value proposition: What outcome or experience does this brand promise?
Products and services: How does each one solve customer pain points and fulfill desires? What are the price points?
Marketing: Which channels do competitors use to promote? What kind of content does this brand publish on these channels? What messaging does this brand use to communicate value to customers?
Sales: What sales process or buyer’s journey does this brand lead customers through?
Read more: What Is Competitor Analysis? And How to Conduct One
4. Products and services
Use this section to describe everything your business offers to its target market . For every product and service, list the following:
The value proposition or promise to customers, in terms of how they will experience it
How the product serves customers, addresses their pain points, satisfies their desires, and improves their lives
The features or outcomes that make the product better than those of competitors
Your price points and how these compare to competitors
5. Marketing plan and sales strategies
In this section, you’ll draw from thorough market research to describe your target market and how you will reach them.
Who are your ideal customers?
How can you describe this segment according to their demographics (age, ethnicity, income, location, etc.) and psychographics (beliefs, values, aspirations, lifestyle, etc.)?
What are their daily lives like?
What problems and challenges do they experience?
What words, phrases, ideas, and concepts do consumers in your target market use to describe these problems when posting on social media or engaging with your competitors?
What messaging will present your products as the best on the market? How will you differentiate messaging from competitors?
On what marketing channels will you position your products and services?
How will you design a customer journey that delivers a positive experience at every touchpoint and leads customers to a purchase decision?
Read more: Market Analysis: What It Is and How to Conduct One
6. Brand strategy
In this section, you will describe your business’s design, personality, values, voice, and other details that go into delivering a consistent brand experience.
What are the values that define your brand?
What visual elements give your brand a distinctive look and feel?
How will your marketing messaging reflect a distinctive brand voice, including the tone, diction, and sentence-level stylistic choices?
How will your brand look and sound throughout the customer journey?
Define your brand positioning statement. What will inspire your audience to choose your brand over others? What experiences and outcomes will your audience associate with your brand?
Read more: What Is a Brand Strategy? And How to Create One
7. Financial planning
In this section, you will explore your business’s financial future. If you are writing a traditional business plan to seek funding, this section is critical for demonstrating to lenders or investors that you have a strategy for turning your business ideas into profit. For a lean start-up business plan, this section can provide a useful exercise for planning how you will invest resources and generate revenue [ 2 ].
Use any past financials and other sections of this business plan, such as your price points or sales strategies, to begin your financial planning.
How many individual products or service packages do you plan to sell over a specific time period?
List your business expenses, such as subscribing to software or other services, hiring contractors or employees, purchasing physical supplies or equipment, etc.
What is your break-even point, or the amount you have to sell to cover all expenses?
Create a sales forecast for the next three to five years: (No. of units to sell X price for each unit) – (cost per unit X No. of units) = sales forecast
Quantify how much capital you have on hand.
When writing a traditional business plan to secure funding, you may choose to append supporting documents, such as licenses, permits, patents, letters of reference, resumes, product blueprints, brand guidelines, the industry awards you’ve received, and media mentions and appearances.
Business plan key takeaways and best practices
Remember: Creating a business plan is crucial when starting a business. You can use this document to guide your decisions and actions and even seek funding from lenders and investors.
Keep these best practices in mind:
Your business plan should evolve as your business grows. Return to it periodically, such as every quarter or year, to update individual sections or explore new directions your business can take.
Make sure everyone on your team has a copy of the business plan and welcome their input as they perform their roles.
Ask fellow entrepreneurs for feedback on your business plan and look for opportunities to strengthen it, from conducting more market and competitor research to implementing new strategies for success.
Start your business with Coursera
Ready to start your business? Watch this video on the lean approach from the Entrepreneurship Specialization :
Article sources
1. US Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan , https://www.sba.gov/business-guide/plan-your-business/write-your-business-plan." Accessed April 19, 2022.
2. Inc. " How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan , https://www.inc.com/guides/business-plan-financial-section.html." Accessed April 14, 2022.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
How To Write A Business Plan: A Guide For Entrepreneurs (2023)
What Is A Business Plan?
Business Plan
A business plan is a document that describes your business idea and your plan to turn the idea into a profitable business.
Why Is A Business Plan Crucial?
1. business planning ensures resource optimization, 2. business planning enables you to plan for a strong startup team.

How To Write A Business Plan In 7 Simple Steps
- A lean business plan:
- A traditional business plan:
Step 1: Write An Interesting Executive Summary

- What problem do you solve?
- Who are your target customers?
- What product/service do you sell, and how is it different from what competitors offer?
- If you launched already, what are your sales and revenue thus far?
- What are your projections for sales and profitability?
- Why should an investor be excited about your idea?
Step 2: Describe Your Company

- Who they are: makers of the “world’s most comfortable” hammocks
- Their goal: empower their weavers—craftswomen from Northern Thailand—to break the cycle of poverty
- Why they’re different: They achieve their goals through training and sustainable job creation.
- An advisory board that makes up for any lack of experience you may have.
- Industry experience.
- Business model .
- Business mission and vision .
- Business name, registered address, and contact information.
- Founding story — how you came about your idea and why you pursued it.
- Business structure — sole proprietorship, partnership, or limited liability company (LLC). Include the ownership stake of every party as well.
- Management team, including their professional background, unique skills, and expertise.
- Short-term goals (achievable within 12 months) and long-term goals (achievable within 5 years).
Step 3: Share Your Market Analysis
- Define your competitive advantages .
- Clarify your unique selling proposition (USP).
- Develop strategies that outperform competitors.
- Choose the best marketing approaches for your products/services.
Step 4: Describe Your Products Or Services
Step 5: present your sales & marketing strategies.
- Impact and results of past marketing efforts
- Clear, realistic, and measurable sales targets
- Goals for future marketing efforts
- Deadlines for meeting set goals.
- Budget for all marketing activities.
- Marketing channels (e.g., word of mouth, social media, advertising, direct-to-consumer, retail stores, e-commerce, etc.)
Step 6: Share Your Financial Projections
- Projected sales over the next 18- 36 months, including high, medium, and low sales estimates
- Total costs of producing goods, including marketing, promotion, commissions, administration, salaries, etc.
- Profit and loss projections
- Break-even analysis
- Projected cash flow

Step 7: Outline Your Operations & Management Plan
- Organizational structure, i.e., who is in charge of each aspect of the business
- Expense and capital requirements to support the organizational structure
- Facility, equipment, and supply requirements
- Initial personnel requirements
Plan, Write, & Share Your Business Plan Using Marketing Calendar
1. create a project for your business plan, 2. schedule your business plan projects.

- Information to include
- Gather Data
- Create Visuals
- Review Outline
- Review Data, & Visuals
- Summarize key findings
- Write introduction
- Recommend an action plan
- Review Plan Draft
- Distribute The Plan To Stakeholders

Attach Documents

- Financial Statement Files
- Outline Document
- Graphic Data
- Additional Projects
Add Business Plan Details To The Project

3. Delegate Tasks To Your Team

4. Share Your Business Plan With Stakeholders

Ready To Write Your Business Plan?
February 24, 2023
Precious Oboidhe is a B2B SaaS content strategist for marketing agencies and tech brands. He works on creating strategies that convert while also making content. He is a skilled marketer who eases the workload for his clients by creating cohesive and on-brand content marketing assets. Precious’s freelance business is called Content Estate Marketing. His site also features a blog that he’s the author of. His blog features topics such as writing case studies, freelancing, website creation, copywriting, blogging, and SEO. Precious’s services include thought leadership ghostwriting, content strategy, content writing, and content refresh. He also provides services in SaaS research, content distribution, LinkedIn content strategy, case study interviews, and website copywriting.

Building a strong marketing team isn’t easy. A key part of sorting out marketing candidates starts with asking the right interview questions. In this post, you can find a list […]
CoSchedule has hosted many demos with Sprout Social customers looking to for a viable alternative due to recent price increases. But finding the right replacement can be overwhelming. CoSchedule Marketing […]
You may believe that spending time organizing takes time away from getting work done. The thinking goes that if one focuses on the work itself, everything else can be set […]

Business Plan Development Guide
(6 reviews)
Lee Swanson, University of Saskatchewan
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: OPENPRESS.USASK.CA
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Kevin Heupel, Affiliate Faculty, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 3/4/20
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element of the business plan. Some examples from actual business plans would be helpful.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
For the most part, the content is accurate. The content covers all important aspects of drafting a business plan. I thought the industry analysis could use more information about collecting primary and secondary sources; instead, this information was referenced in the marketing plan section.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Most of the content relies on cites as far back as 2006; however, when it comes to developing and writing a business plan nothing has changed. Thus, the content is current and there is no concern about it becoming obsolete in the near future.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is clear. There are no difficult terms used and the writing is simple. The text uses a lot of bullet points though, which gets tedious to read for a few pages.
Consistency rating: 5
The text does a good job of maintaining consistency in terms of framework and terminology. The text is organized where it's easy to find the information you want in a quick manner.
Modularity rating: 3
The text has a lot of bullet points and the paragraphs are dense. However, the use of subheading is excellent.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book is organized as if you're writing a business plan from start to finish, which is helpful as a practical guide.
Interface rating: 5
There are no navigation problems, distortion of images/charts, or any other display features that may distract or confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The text is free of grammatical errors. The sentence structure is simple with many bullet points, which helps to avoid any grammatical issues.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This book was written by a Canadian professor and provides references to Canadian sources. However, the information in this text can be used for U.S. schools.
This book is very short and provides a good, general overview about the process of creating and writing a business plan. It won't help a reader if he/she is confused about a certain part of the business plan. The reader will have to find another source, such as "Preparing Effective Business Plans" by Bruce Barringer, Ph.D. The book provides links to good resources and a finished business plan that the reader can reference. I would recommend the book for undergraduate courses.
Reviewed by Kenneth Lacho, Professor of Management, The University of New Orleans on 6/19/18
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or... read more
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or economic area relevant to this proposed business. 4. Business model ok as a guide. 5. Suggested mission statement to cover: product/business, target customer, geographical area covered. 6. Need detailed promotion plan, e.g., personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, networking publicity, and social media. 7. How do you find the target market? 8. Chapter 6 too much detail on debt and equity financing. 9. Discuss how to find sources of financing, e.g., angels. 10. Expand coverage of bootstring, crowdfunding. 11. Chapter 4 – good checklist. 12. Chapter 3 - overlaps. 13. Chapter 7 – 3 pages of executive summary – double or single spaced typing. Number all tables, graphs. 14. Some references out-of-date, mostly academic. Bring in trade magazines such as Entrepreneur.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
In my opinion, the content is accurate and error free.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The material is relevant to writing a business plan. I wonder if the Porter, SWOT VRIO, etc. material is too high level for students who may not be seniors or have non-business degrees (e.g., liberal arts). Porter has been around for a while and does have longevity. The author has to be more alert to changes in promotion, e.g., social media and sources of financing, e.g., crowdfunding.
Clarity rating: 3
As noted in No. 9, the tone of the writing is too academic, thus making the material difficult to understand. Paragraphs are too long. Need to define: Porter, TOWS Matrix, VRIO, PESTEL. A student less from a senior or a non-business major would not be familiar with these terms.
Consistency rating: 4
The text is internally consistent. The model approach helps keep the process consistent.
Modularity rating: 4
The process of developing a business plan is divided into blocks which are parts of the business plan. Paragraphs tend to be too long in some spots.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics are presented in a logical step-wise flow. The language style is too academic in parts, paragraphs too long. Leaves out the citations. Provides excellent check lists.
There are no display features which confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The text has no grammatical errors. On the other hand, I found the writing to be too academic in nature. Some paragraphs are too long. The material is more like an academic conference paper or journal submission. Academic citations references are not needed. The material is not exciting to read.
The text is culturally neutral. There are no examples which are inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book best for a graduate class.
Reviewed by Louis Bruneau, Part Time Faculty, Portland Community College on 6/19/18
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials.
Contents of the book were accurate, although it could have benefited from editing/proofreading; there was no evidence of bias. As to editing/proofreading, a couple of examples: A. “Figure 1 – Business Plan… “ is shown at the top of the page following the diagram vs. the bottom of the page the diagram is on. (There are other problems with what is placed on each page.) B. First paragraph under heading “Essential Initial Research” there is reference to pages 21 to 30 though page numbering is missing from the book. (Page numbers are used in the Table of Contents.)
The book is current in that business planning has been stable for sometime. The references and resources will age in time, but are limited and look easy to update.
Clarity rating: 5
The book is written in a straightforward way, technical terms that needed explanations got them, jargon was avoided and generally it was an easy read.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
The book lends itself to a multi-week course. A chapter could be presented and students could work on that stage of Plan development. It could also be pre-meeting reading for a workshop presentation. Reorganizing the book would be inappropriate.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
Generally, the book is free of interface problems. The financial tables in the Sample Plan were turned 90° to maintain legibility. One potential problem was with Figure 6 – Business Model Canvas. The print within the cells was too small to read; the author mitigated the problem by presenting the information, following Figure 6, in the type font of the text.
I found no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I require a business plan in a course I teach; for most of the students the assignment is a course project that they do not intend to pursue in real life. I shared the book with five students that intended to develop an actual start-up business; three of them found it helpful while the other two decided not to do that much work on their plans. If I were planning a start-up, I would use/follow the book.
Reviewed by Todd Johnson, Faculty of Business, North Hennepin Community College on 5/21/18
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan.
The content is accurate and seems to lack bias.
Content seems relevant and useful . It does not help an entrepreneur generate ideas, and is very light on crowdfunding and other novel funding source content. It is more traditional. This can be easily updated in future versions, however. "Social Media" appears once in the book, as does "Crowd Funding".
The book is comprehensive, but perhaps not written in the most lucid, accessible prose. I am not sure any college student could pick this up and just read and learn. It would be best used as a "teach along guide" for students to process with an instructor.
The text seems consistent. The author does a nice job of consistently staying on task and using bullets and brevity.
Here I am not so certain. The table of contents is not a good guide for this book. It does make the book look nicely laid out, but there is a lot of complexity within these sections. I read it uncertain that it was well organized. Yes there are many good bits of information, however it is not as if I could spend time on one swathe of text at a time. I would need to go back and forth throughout the text.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
Similar to the above. I did not like the flow and organization of this. An editor would help things be in a more logical order.
Interface rating: 2
The interface is just OK. It is not an attractice interface, as it presents text in a very dense manner. The images and charts are hard to follow.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
I a not certain of the origins of Saskatchewan, but I do feel this is a different read. It is more formal and dense than it has to be. This would be a difficult read for my students. I do not feel it is insensitive in any way, or offensive in any way.
I would not adopt this book if given the chance. It is too dense, and not organized very well, even though the information is very good. The density and lack of modularity are barriers to understanding what is obviously very good information.
Reviewed by Mariana Mitova, Lecturer, Bowling Green State University on 2/1/18
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to... read more
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to other resources add to the completeness of the textbook.
Content seems accurate.
Since the content is somewhat conceptual, the text will not become obsolete quickly. In addition, the author seems to be updating and editing content often hence the relevance to current developments is on target.
The text is very clear, written in clear and straight-to-the point language.
The organization of content is consistent throughout the entire text.
The textbook is organized by chapters, beginning with overview of the model used and followed by chapters for each concept within the model. Nicely done.
The flow is clear, logical and easy to follow.
Overall, images, links, and text are well organized. Some headlines were misaligned but still easy to follow.
No concerns for grammar.
No concerns for cultural irrelevance.
Reviewed by Darlene Weibye, Cosmetology Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/1/18
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning. read more
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning.
The text was accurate, and error-free. I did not find the book to be biased.
The content is up-to-date. I am reviewing the book in 2017, the same year the book was published.
The content was very clear. A business plan sample included operation timelines, start up costs, and all relevant material in starting a business.
The book is very consistent and is well organized.
The book has a table of contents and is broken down into specific chapters. The chapters are not divided into sub topics. I do not feel it is necessary for sub topics because the chapters are brief and to the point.
There is a great flow from chapter to chapter. One topic clearly leads into the next without repeating.
The table of contents has direct links to each chapter. The appearance of the chapters are easy to read and the charts are very beneficial.
Does not appear to have any grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I am incorporating some of the text into the salon business course. Very well written book.
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research
- Chapter 3 – Business Models
- Chapter 4 – Initial Business Plan Draft
- Chapter 5 – Making the Business Plan Realistic
- Chapter 6 – Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
- Chapter 7 – Finishing the Business Plan
- Chapter 8 – Business Plan Pitches
References Appendix A – Business Plan Development Checklist and Project Planner Appendix B – Fashion Importers Inc. Business Plan Business Plan Excel Template
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This textbook and its accompanying spreadsheet templates were designed with and for students wanting a practical and easy-to-follow guide for developing a business plan. It follows a unique format that both explains what to do and demonstrates how to do it.
About the Contributors
Dr. Lee Swanson is an Associate Professor of Management and Marketing at the Edwards School of Business at the University of Saskatchewan. His research focuses on entrepreneurship, social entrepreneurship, Aboriginal entrepreneurship, community capacity-building through entrepreneurship, and institutional-stakeholder engagement. Dr. Swanson’s current research is funded through a Social Sciences Humanities Research Council grant and focuses on social and economic capacity building in Northern Saskatchewan and Northern Scandinavia. He is also actively studying Aboriginal community partnerships with resource based companies, entrepreneurship centres at universities, community-based entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurial attitudes and intentions. He teaches upper-year and MBA entrepreneurship classes and conducts seminars on business planning and business development.
Contribute to this Page
- UConn Library
- Topic: Entrepreneurship & Business Plan Guide
- Business Plan (How to & Samples)
Topic: Entrepreneurship & Business Plan Guide — Business Plan (How to & Samples)
- Idea Generation
- Industry Information
- Competitors
- Market Research
- Financial Data
- Advertising & Promotion
- Small Business Advisors
- Products, R&D, Strategy
- Patents and Trademarks
- Grants, Loans, and Financing
- Franchises & Franchising
- Celebrating Connecticut
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is "a guide—a roadmap for your business that outlines goals and details how you plan to achieve those goals."--Tim Berry from Bplans site.
- An Introduction to Business Plans Introduction to a tutorial on business plans written by the staff at Entrepreneur magazine.
- Business Planning Guide Step-by-Step guide to write a Business Plan by Bplans site.
- Create Your Business Plan, from the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) The SBA has delivered millions of loans, loan guarantees, contracts, counseling sessions and other forms of assistance to small businesses.
What is included in a Business Plan?
The following components make up a business plan:
Table of Contents
Executive Summary : Appears first, written last. Provides a snapshot of your company explaining who you are, what you do, and why.
Mission & Vision: Here you define the purpose of your business (Mission) and a statement about your perception of the company's growth and potential (Vision). Include specific goals and objectives of the business
Business Description: Provide background information about the company including brief history of the business and list of key company principals.
Define Your Market: Describe the industry within which your business will operate, identify your target market, provide a general profile of your targeted clients, and describe what share of the market your currently have and/or anticipate. For this section of the business plan, your will undertake following types of research:
Industry Analysis : how is the industry structured, trends and statistics, key players, segmentation, sales and distribution channels etc.
Competitive Analysis : major competitors, strengths and weaknesses, how would you position yourself against the competition, market niche, product/service comparison
Customers: who are the customers (demographic data), what do they want, customer buying habits, market share/market size, consumer preferences
Advertising and Promotion : How will you reach out to potential customers? Where do they currently shop for product/service? Where will you advertise and how will you measure the effectiveness of your advertising and promotion efforts?
Pricing : strategy, policies, price list, break-even analysis
Location : Where is your business located? (home-based; retail; commercial, etc….), is the location of your business important? Any special zoning, land or building improvements needed to accommodate your operation? If location is important, what are the features of your location?
Products & Services: Describe all your products and services; explain how your products and services are competitive including unique features, benefits of the product or service, niche served, stage of product/service development, production, future growth.
Organization & Management: Describe how your company is organized including legal structure(sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation etc); identify any special licenses and/or permists your business operates with; provide brief bio of key managers within the company; include an organization chart if available.
Marketing & Sales Strategy: Identify and describe your maket -- who are your customers and what's the demand for your products and services; channels of dsitribution you will use; your sales strategy specific to pricing, promotion, products, and place.
Financial Management:
For new business include: estimate of start-up costs (all one-time expenses such as equipment, deposits, fees, etc.); projected balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement (1 year forward)
For existing business include: balance sheets (last 3 years), income statements (last 3 years), cash flow statements (12 months)
If applying for a loan: current personal financial statement on each principal; federal tax return for prior year
Appendices: This section may include company brochures, resumes of key employees, list of business equipment, copies of press articles and advertisements (if available), pictures of your business location and products, any applicable information about your industry and /or products, key business agreements such as lease, contracts etc.
(Adapted from: SBA's Business Plan Template )
Finding Sample Business Plans
- Business Plans Handbook/ Lynn M. Pearce, ed. Vol 13. Includes sample plans on numerous topics such as advertising, fitness center, landscaping, and technology solutions provider and more.
- Business Plans Handbook/ Lynn M. Pearce, ed. Vol. 19. Includes business plans for assisted living facility, auto dealing, bowling alley, commodities trading firm, digital presentations, farm, furniture store, gas station, laundry mat, web design, and more.
- Business Plans Handbook (via Reference for Business) Earlier volumes of the Business Plans Handbook are available at the above sites for free.
- BPlans.com Includes samples of business plans as well as advice and tips on writing a business plan, starting and running a business.
Why You Need a Business Plan?
You need a business plan:
- To see if you have a viable business idea
- To identify your (and your company's) strengths and weaknesses
- To assess the market for your product or service
- To size up the competition
- To determine your financial needs
- To attract investors
- To set up milestones and monitor your business
- << Previous: Idea Generation
- Next: Industry Information >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 1:46 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/entrepreneurship

23+ Free Entrepreneur Lesson Plans (Projects, Worksheets, etc.)
By: Author Amanda L. Grossman
Posted on Last updated: December 14, 2022
Need free entrepreneurship curriculum, lesson plans, and projects? Here's entrepreneur lesson plans for high school, middle school, and elementary.

So, you’re looking for entrepreneur lesson plans to help turn your kids or students into the innovators of tomorrow.
And not just to make them into entrepreneurs, but to benefit your kids and students with the following results of teaching entrepreneurship :
- Improved academic performance
- Increased problem-solving and decision-making capabilities
- Improved interpersonal relationships
- Higher self-esteem
But, exactly how are you supposed to teach entrepreneurship?
Entrepreneurs, among other qualities, need to be able to recognize opportunities in the marketplace. This means finding a need, and figuring out how to solve that need in a profitable way.
This can be as simple as a kidpreneur/kidpreneurship (or kidpreneur-in-the-making) opening a lemonade stand on a smoldering July day near a construction site, and as complicated as creating a machine knob specifically for tea growers in Japan.
And having this ability doesn't have to result in a person starting their own business; it works equally as well for your child if they work for someone else in the form of more merit raises, one-time bonuses for one-off projects, promotions, leverage in salary negotiations, etc.
In fact, the skill of recognizing an opportunity, and seizing it by writing my own job description resulted in me snagging my first job out of college (worth an awesome $40,000 + benefits to me at the time). More on that in a bit.
What are the other skills a child needs to learn to help them as an entrepreneur?
Psst: you'll also want to check out my resource list of youth entrepreneurship programs , entrepreneur biographies for kids , kid entrepreneur kits , and full review of the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox .
Article Content
How Do You Teach Entrepreneurship?
Teaching entrepreneurship is a bit trickier than, say, teaching algebra. With algebra, the equations come out with the same solutions, every time. But with entrepreneurship?
There are an endless number of variables that go into it, and an endless number of outcomes that can come out of it.
How are you supposed to teach for that?
One of the best ways to teach entrepreneurship is to choose entrepreneurial projects, activities, and lesson plans that aim at nurturing these entrepreneur skills:
- Ability to identify opportunities
- Self confidence
- At least basic knowledge of business finances/financial literacy
- Knows how to take measured risk
- Vision and creativity
Elementary School Entrepreneurship Curriculum
Excited to start teaching your elementary school-aged kids about entrepreneurship? Let me share some entrepreneurship lesson plans, resources, and curriculum with you.
Also, check out these 3 kid business plan examples .
1. Venture Lab
Who It’s For : Grades 1-12
Financial Aid : ( Free for non-commercial use ) Curriculum that organizations can purchase to use with students
Length of Program : 90-minute lessons
Location : N/A
Venture Lab offers a curriculum suited for 1st – 12th graders (curriculum is divided into lower elementary, upper elementary, and middle school/high school.) This is a course in a box with all of the lesson plans already completed and is meant to be utilized as part of regular coursework, after school programs, or camps.
Its focus is on teaching girls components of entrepreneurship such as STEAM concepts and design thinking.
2. Money Monsters Start their Own Business
Who It’s For : 4th – 8th grade
Students will read through the Money Monsters Start their Own Business book (PDF provided – 51 pages), and then play a game that has them experience the ups and downs of starting a business.
I love how a Toy Store Income Tracker is included so that each student can track their own earnings and see the numbers for themselves.
Psst: you'll also want to check out Federal Reserve Bank's webinar on teaching kids entrepreneurship , which will give you some lesson plan ideas.
Starting a Business Lesson Plans for Middle School
Do you want to teach your middle school kid (or student) how to start a business, and you need a lesson plan? I’ve actually created a Take Your Child to Work Day printable which will give you lots of ideas for your starting a business lesson plan.
More middle school business lesson plans for how to start a business (all free):
- Federal Reserve Bank's Jay Starts a Business (Grades 3-6; comes with teacher's manual with lesson plans)
- Free Kid Business Plan Templates
- Biz Kid’s Crash Course on Entrepreneurship for Middle School
- EverFI’s Venture Entrepreneurial Expedition (for grades 7-10).
- Small Business Administration’s Young Entrepreneurs course
- Foundation for Economic Education’s Booms and Busts , What is Entrepreneurship? , What is the Entrepreneur’s Role in Creating Value? , etc. (students can earn a Certificate of Achievement)
- TeenBusiness’s Entrepreneur Lesson Videos series
- Parade of Entrepreneurs Lesson Plan
- Lemonade Stand Worksheets , and my best Lemonade Stand Ideas
Psst: Try holding a market day in your class. Here are 22 things for kids to make and sell , 17 boy crafts to sell , and help pricing their products in this market day lesson plan .
Teaching Entrepreneurship to High School Students – Free Entrepreneurship Curriculum
There are some great curriculum and materials out there for teaching entrepreneurship in high school, many of which include entrepreneur worksheets for students.
Psst: you also might want to check out these 5 business books for teens , and 11 business games for students .
1. Alison’s Entrepreneurial Skills Path
Who It’s For : Business students, and people interested in learning about creating a business
Financial Aid : Free
Length of Program : 6 lessons, each between 1 and 3 hours
Alison is a free, online platform with tons of courses, and one of the paths you can go down is an entrepreneurial skills one.
Teachers of the courses include venture capitalists, professors at Harvard, and professional entrepreneurs.
Lessons include:
- Characteristics of the Successful Entrepreneur
- Critical Skills for Entrepreneurs
- Creating an Entrepreneur’s Checklist for Success
- Entrepreneurship – Creating the Business
- Key Elements of Entrepreneurial Success
- Why Entrepreneurs Should Think Big
2. Youth Entrepreneurs
Who It’s For : Students
Financial Aid : Schools pay for this program, with the cost based on how many students get free and reduced lunches
Length of Program : 1 year
With this program, students first focus on economics, then they focus on starting their own businesses.
3. Diamond Challenge Business Curriculum
Who It’s For : Kids and teens
Length of Program : 14 modules
Looking for a video business curriculum with instructional guides? The Diamond Challenge’s program covers the following:
- What is Entrepreneurship?
- Opportunity Recognition
- Opportunity Screening
- Types of Businesses
- Building a Business like a Scientist
- Using a Business Model Canvas
They also offer a Social Curriculum track that’s 6 video modules long, including:
- What is Social Entrepreneurship?
- Wicked Problems and Grand Challenges
- Social Entrepreneurship Processes and Challenges
4. INCubateredu
Who It’s For : 10th and 12th graders
Financial Aid : Free (at schools where it’s available)
Length of Program : 1 year (followed by acceleratoredu for the 2nd year)
Through Uncharted Learning’s program, 10 th to 12 th graders develop their own business, pitch their idea ta a shark-tank style event, and even have a chance at receiving funding.
5. JA BE Entrepreneurial®
Who It’s For : Grades 9-12
Financial Aid : Free for students
Length of Program : 7, 45-minute sessions
Location : Anywhere
Through your child’s school, they can take Junior Achievement’s Entrepreneurial program. The course teaches students how to create a business plan, plus how to start a venture.
Lessons covered include:
- What’s My Business?
- Who’s My Customer?
- What’s My Advantage?
- Competitive Advantages
- Ethics are Good for Business
- The Business Plan
6. JA Company Program Blended Model
Length of Program : 13 classes (2 hours/class), or as a 1-year program with 26 classes (1 hour/class)
Location : Anywhere (online course)
This is an online program that teaches high schoolers how to solve a problem/fill a need in their community through entrepreneurship.
- Start a Business
- Vet the Venture
- Create a Structure
- Launch the Business!
- Run the Business
7. The Mint's Be Your Own Boss
Who It’s For : Teens
Length of Program : 3 lessons
Starting with the Be Your Own Boss Challenge , The Mint takes your teen through the following three lesson:
- Planning Your Business
- Money & Your Business
- The Law & Your Business
8. Wharton High School's Entrepreneurship
Who It’s For : High School students
Length of Program : 50+ lesson plans
These lesson plans go through the following:
- Entrepreneurs and Entrepreneurial Opportunities
- Global Markets
- Business Plans
9. YE$ Youth Entrepreneurship
Who It's for : high school students
Cost : Free
Location : Anywhere (it's a PDF)
Here's a free PDF with tons of entrepreneur lesson plans and research done for educators, that is meant to go along with a 4-H program. You'll find some nuggets in here, plus, it's free!
Now let’s take a look at entrepreneurial projects that can teach your kids and teens all about starting a business with hands-on experiences.
10. Build a Business Plan
Who It's For : Middle School and High School
Location : Anywhere (online)
Check out this plug n' play business plan creator! You could send your students to this page to work through a business idea of theirs.
Then, at the end, they can print out their business plan!
Questions they'll need to answer include:
- Your big idea
- Who will buy
- How you'll spend and make money
Entrepreneur Worksheets for Students
While I would recommend taking on one of the projects below, or one of the hands-on lesson plans from above, there are also entrepreneur worksheets students can use to learn about businesses.
Here's a few of my favorites (all free):
- Lemonade Stand Free Printables (here's my best lemonade stand ideas , too)
- Lemonade Stand Worksheets
- Family Guide to Getting a Family Business Going (kid-centered)
- Small Business Administration's Lean Startup Business Plan
- Take your students through the DECA Idea Challenge (you'll need to pick your own everyday item to challenge students with, as the competition has ended for the year)
- Take your students through the DECA Entrepreneur of Tomorrow Challenge (again, the competition is over, but the PDF is still available for you to set up your own)
Psst: you might want to check out my review on the Teen Entrepreneur Toolbox .
2 Entrepreneurial Projects – What is an Entrepreneurial Project?
Entrepreneurial projects are a smart way to teach entrepreneurship to kids, because, as with any project, it gives them a chance to dive deeper into a topic that interest them (all under the guise of teaching them how to start and run a business).
Entrepreneur Project #1: Winter Beverage Outdoor Tasting Contest
It’s soooooo easy to sit inside all winter long and slowly accumulate cabin fever (plus a few pounds). That's why you've got to look for fun things to do in the winter.
Well today? We’re going to switch things up. I’ve created a family date night for you ( family winter activities !) that has both an indoor AND an outdoor component.
But don’t worry – with this fun winter activity we’ll keep things toasty throughout.
So, what’s the game plan? Each of your kid(dos) will make (rather, create ) a warm winter beverage recipe indoors . Then here's the twist: you’re going to host a family taste testing contest around your fire pit in the backyard.
Not only will this make a fun family memory, but your kid(dos) will actually walk away with more money knowledge in the process centered around the all-important lesson of how to make a profit!
Psst: Now that’s a money lesson I could have used as a kid, specifically as I’ve gone into biz for myself as an adult.
Host a Winter Beverage Outdoor Taste Testing
Finding fun things to do in the winter doesn't have to mean you're freezing your tootsies off. There's nothing better to keep you warm outdoors in the wintertime than a toasty drink. Well, a toasty drink around a roaring fire.
Here’s how it’s going down:
Step #1: Choose an Event Date
Build the anticipation for your family by choosing a date 1 to 2 weeks out (so that there’s time for you guys to complete the rest of the prep work).
Fill out the invitation on Page 1 of the free printable, and display prominently on your family’s bulletin board/gathering center in the kitchen so everyone knows the date of the big event.
Set the stage for the competition by having your family read their mission out loud. Other cool factors you can add in: make it a Friday or Saturday family date night, under the stars. Let the kids stay up a little past bedtime to complete.
Step #2: Your Kid(dos) Research Hot Drink Ideas to Enter into the Competition
Your kids are the ones entering the competition. They’ll be in the driver seat of actually creating their own recipe from scratch (with some inspiration from below).
There are lots of toasty, kid-friendly drink recipe ideas to get them started:
- Hot caramel apple cider
- Vanilla steamer with cinnamon
- Harry Potter Warm Butterbeer
They’ll get lots of help not only from looking up recipe examples on sites like Pinterest, but also from the worksheet in the free printable (Page 2).
Step #3: Shop for the Ingredients
Once your budding restaurant consultant has determined possible ingredients they’ll need for their signature drink, they’ll need you, Mama Bear, to purchase them.
Take the list your kid(dos) have created and go to the store (solo, or with them) to make the purchases.
Having trouble coming up with a pool of possible ingredients to buy? Use the lists below for inspiration of what to pick up (a few of these ingredients you probably already have at home) and let your kids create what they can from it:
- Bases : hot cocoa, apple cider, chai tea, milk
- Flavors : cinnamon, nutmeg, vanilla extract, flavor syrups
- Sweeteners : sugar, brown sugar, caramel
- Creamers : milk, half & half, almond milk, heavy cream, etc.
- Top-offs : whipped cream, caramel sauce, orange peels for zesting
Save your store receipt, as your kid(dos) will need this information to price their drinks later on.
Step #4: Your Kid(dos) Tinker + Perfect their Drink
Using the purchased ingredients as well as anything in your home they can find, host a kitchen lab session where your kid(dos) tinker with ingredients and perfect their super-secret, signature recipes (talk about fun things to do in the winter inside!).
They’ll write down the exact portion sizes to each ingredient that they use as they go along, which is important for the next step.
Step #5: Your Kid(dos) Figure Out the Profit Margin of their Signature Drink
Remember, the goal is to create a new drink for this restaurant that not only costs less than $5, but has at least a 60% profit margin for the owner.
Ahem: between you and me, that means their cost needs to come in under $2.00.
So, as your kid tinkers with ingredients, they need to keep price in mind.
Note: this step can seem a bit unwieldy, but is SO important for the whole process. Just know – I’m outlining both how to do this all by hand, as well as giving you shortcuts to online calculators where your kid(dos) will still learn the process by setting up the inputs and thinking through how it all fits together.
Of course, we’re not talking about the cost of the entire ingredient that you’ve purchased. After all, it’s unlikely they’ll use an entire carton of milk to create one drink. We’re talking about the small portion size that they used of the product.
In other words, they’re not going to get the cost of a single drink they’ve created from your grocery store receipt as it is now. They need to do some calculating based on the measurements of each ingredient that goes into each drink.
You need to know how much it costs to create just ONE of your super-secret signature drinks so that you can calculate the profit margin.
What’s a profit margin? It’s the percentage of what you keep as profit from each $1.00. For example, a 20% profit margin means that we earn $0.20 on every dollar. That means that the other 80% or $0.80 are expenses. Remember that Jack, the man from The Yeti Slide, needs a 60% profit margin, or $0.60 on each dollar in profit after expenses are taken out.
Step #1: Write down your ingredients + quantities.
Step #2: Convert each quantity in your recipe to the quantity on the product label.
Divide your ingredients up by dry ones (like cocoa powder), and wet ones (like heavy cream or vanilla extract).
Then use the appropriate table below to convert the amount in your recipe to the amount that’s found on the ingredient’s product label (front of package).
For example, if you used 3 teaspoons of cocoa powder (dry ingredient), then your conversion is to a ½ ounce (the cocoa powder can is in ounces). Or if you used 2 tablespoons of almond milk, you find on the Wet Conversion table that you used 1 fl. Oz. (the almond milk carton is in Fl. Oz.).
Hint: Can’t find the conversion or a little confused? You can plug the exact quantity of your ingredients into this liquid converter or this dry converter calculator online and convert it into the measurement found on your product label).
Conversion tables:
Dry Conversions
Liquid Conversions:
Step #3: Calculate the cost of each quantity of ingredient used.
Now you need to price each converted quantity of ingredient by figuring out how much each ounce or fluid ounce costs, and then multiplying it by the amount you’ve used.
Hint: A good estimate to use for dashes of spices such as cinnamon or nutmeg is $0.05.
- Write down the overall price of each ingredient used.
- Write down the converted amount you used of it.
- Divide the total amount in the product package by its price to find what each ounce or fluid ounce costs.
- Then multiply that by the converted amount you used.
- Write down the cost. Then add all of the individual ingredient costs to get your total expense to create the drink.
Example: I used 1 tablespoon (tbsp.) of heavy cream. One 8 fl. oz. container of heavy cream at the store costs $2.99. That is $0.37/ounce. I look at the conversion chart below, and see that 1 tbsp. converts to ½ ounce. So, I divide $0.37/2 ounces, and see that this ingredient for just one drink costs $0.186 (you can round up to $0.19).
Ingredient Cost: $2.99 _ Converted Amount Used: ½ fl. Oz. Total Product Amount: 8 fl. Oz. Cost per ounce: _$0.37/fl. Oz. Cost of Ingredient Used: $0.37 X ½ = $0.186 .
Looking for a shortcut? Here’s a free online tool for pricing out beverages . You’ll need the converted amounts.
Step #4: Calculate Your Profit Margin
Figure out how high your profit margin is if you sell the drink for $5.00.
Profit on Drink: $5.00 – total drink cost = _ $ _________.
Profit Per Dollar: Your answer from above \ Cost drink is sold for ($5.00) = $ Profit
Profit Margin: $ Profit X 100 = Profit Margin%
Step #6: Taste Judging Begins
By now you’ve set the scene for some fun things to do in the winter outdoors – think a crackling bonfire out in the backyard (or in your fire pit. Heck, you can de-hibernate the grill for some winter outdoor cooking/heating), plus a table/flat surface where your kids can place their super-secret signature creations.
Bust out some blankets, cover straw bales with table cloths…you get the idea. (And if you’re in Houston like we are? Well, a hoodie should suffice).
Have your kid(dos) place their drinks on the tasting mat, as well as fill in how much their drink costs and what the profit margin is (all calculations they’ll be guided through on the free printable).
Now they get to take a break, while the parents taste + score each one!
Included in the printable are both a tasting mat as well as a score card with specific criteria, such as inventiveness, taste, and profit margin.
Step #7: Declare the Winners
There are winners in a variety of categories, and then an overall drink that is chosen for The Yeti Slide's Yeti Roasts:
- Most Inventive
- Best Money-Maker
- Newest Yeti Slide Signature Drink
Looking for fun things to do in the winter? This two-part activity for your child that will leave them understanding profit margins like a pro, plus give your family an awesome family date night under the stars on a winter evening when you might otherwise be watching tv.
What could be better than that? If nothing else, you’ll have created quite the memory.
Entrepreneur Project #2: A System for Your Child to Identify a Need in Your Home + Propose a Solution
We want to encourage your child to come to you with things they see that could use improvement, and ways they could add value or provide a solution for you.
Let's go through how to do this.
Step #1 : Discuss with your child the idea that people need things + services.
Here's a conversation outline for you with a few blanks to fill in (where underlined) :
“People need things and services in their lives. They need things to maintain their health, they need things to make life more enjoyable. They need parts to make repairs to their belongings. They need really cool items to buy as gifts for others. They need better systems or processes to make things work more efficiently, which just means taking less time and less money and getting the same (or better) results. All over the world, people need things. In my own life, three needs that I've satisfied through purchasing something include X , Y , and Z . By purchasing them, they made my life easier because <<FILL IN SPECIFIC INFORMATION FOR EACH EXAMPLE YOU GAVE>> . Generally, when people need something, they are willing to pay money for the solution. That's why there are so many companies, all which provide products + solutions for people's needs.”
Pssst: MAN I wish I could go back 17 years and give myself this talk! Would've saved me several adult years of banging my head against the wall trying to understand how to make money.
Step #2 : Task your child with identifying a need around the house/property/car.
What could this look like?
A Few Examples for you + your kiddo :
- Find a more efficient way to organize the “command center” in your home.
- Use Google Maps or another program to find a more efficient route for your commute.
- Organize the wood pile + create newspaper logs that are fireplace-ready.
- Find a better way to organize/clean/maintain the video game center in your home.
- Clean out your car (I used to do this for my parents!) + add a car trash can to the back area so that in the future the kids can just use that instead of throwing things on the ground.
- Introduce a better laundry system for the family's clothes so that they actually all end up in the laundry room, sorted, and ready to be washed.
The possibilities are endless, and specific to what needs your child sees in your family life.
Step #3 : Once they've identified a need and come to you with it, you must decide if it's worth it to you to move forward. Don't be afraid if, after they've told you a need they think you have but that you don't actually have, to tell them that it isn't a current need of yours. Hey, the road to success is paved with failed products! This is excellent feedback so that they start to understand their “customer” and dig deeper. Perhaps they'll even start to ask YOU what you want from them!
Step #4 : What are both of your expectations for this job so that you know when the job is completed correctly?
Let them tell you what they propose to accomplish and what that would look like.
Then you share what you, as a paying customer, expect in results. Hash this out if need be (just like a real negotiation between a biz and their potential client).
This includes a deadline.
Step #5 : Now you need to ask them for a price.
I know, I know. You might be wondering, “why on earth am I going to let my child choose how much I'm willing to pay them for something they want to do around the house? Isn't it MY money?”
I totally get that. But remember that the nature of this lesson is to ignite that entrepreneurial spirit in them. Instead of you offering what you're willing to pay, have them go through the exercise of pricing their efforts. Then the negotiations start.
This sets them up for good negotiation + valuation skills in the future.
Determine the market price you'll pay, which is where their price (the supplier) and your price (based on how much you need what they're offering + a dash of several other things) meets. $__________.
Step #6 : Your child completes the work + notifies you.
Step #7 : Using the checklist you both created, provide oversight and see if everything is as it was supposed to be.
Step #8 : Pay the agreed upon rate once everything is up to par. And if they don't quite complete the project + deliver what they promised, it's up to you whether you want to make a partial payment, or not pay at all (satisfaction guaranteed could be added to this lesson as well).
If your child makes it through this process, then they will have successfully figured out a “market” need, fulfilled it, and gotten paid from their initiative. This is something that will no doubt shape their futures.
And if they don't quite succeed? Well the lessons are vast for all entrepreneurs as they traverse through the mistakes, failures, and successes.
It's really a win-win situation.
Let me show you what I mean, with an example in my own life.
How I Used this Skill Set to Write My Own First Job Offer Worth $40,000 + Benefits
While some of my dorm mates were floundering around trying to find employment, I was busy enjoying my last two months of college before entering the “real world”.
Why is that? Because I had a job waiting for me. And the only reason why I had that job was I spotted a need in a local company, and wrote my way into it.
I had interned for an organization in my small college town, and they ended up building a start-up company set to open its doors sometime around when I was due to graduate. One day I asked them if I could have a full-time job there come June. The director looked at me, and said, “go ahead and write up a job description of what you propose you would do here. Then we'll see.”
So I went back to my college dorm and worked on a job description. I thought about what the company was trying to achieve, and tied this into what I wanted to do with my life (at least what I thought I wanted to do at the time).
I wish I had saved a copy of the actual job description, but my sharp memory tells me it went something like this:
“Amanda L. Grossman will be the International Marketing & Sales contact at Chesapeake Fields. The International Marketing & Sales Person is responsible for researching new markets around the world where Chesapeake Fields' products would be well received. Primary responsibilities include understanding these markets, making contact with potential wholesalers and distributors, sending samples, and being the brand ambassador for Chesapeake Fields within these markets.”
With one minor change − they put sales in front of marketing in my job title − I got an offer from them for $40,000 + benefits to do just that. Within the one year I worked there, I ended up negotiating an initial container load of $27,000 worth of our product to a major food retailer in Taiwan.
Unfortunately, my job AND that company went under not long after my first and only year there. But writing my way into a company right out of college based on a need I saw that I could fill? Well that was enough to impress future employers who then hired me.
See how lucrative learning this skill could be for your child? I'd love to hear below what needs (perceived or actual ones) your child comes up with to fulfill.
- Latest Posts
Amanda L. Grossman
Latest posts by Amanda L. Grossman ( see all )
- 19 Unique Kid Piggy Banks (Plus How to Use Them for Money Lessons) - April 3, 2024
- 50 Banking Activities for Kids (Student Financial Literacy) - February 14, 2024
- 14 Christmas Activities for High School Students (they’ll Actually Find Cool) - December 1, 2023
Thursday 8th of June 2017
Uh, I totally love this post! My hubby and I are both entrepreneurs and want to instill the same in our children... definitely going to use these tips!!
Friday 9th of June 2017
*Squee*! Thanks, Lauren. I'd love to hear what your kiddos come up with:).
College Student Business Plan Template – Free Access
Harry Foster
Published on May 09, 2024, updated on May 14, 2024
Throughout undergraduate studies, there are abundant chances to engage in entrepreneurship competitions. These events not only enhance personal experiences and foster well-rounded skills but also hold the promise of transforming innovative business concepts into reality. Yet, for students unacquainted with professional jargon like market dynamics, operational frameworks, profit strategies, and risk assessment, crafting a comprehensive and polished business plan can pose challenges and bewilderment. This article, coupled with the collaborative online tool Boardmix Whiteboard , outlines the process of crafting a top-notch business plan tailored for college students. Its goal is to aid those gearing up for competitions or nurturing entrepreneurial ambitions.
1. Cover and Table of Contents
The cover and table of contents create the first impression when others review our plan. Therefore, accuracy is crucial.
- Cover: The cover should reflect basic project information, including the project logo, name, responsible person, affiliated school, advisor, and team members.
- Copyright Statement: A separate page for a more formal appearance.
- Table of Contents: It's recommended to include hyperlinks for easy navigation, saving time for reviewers during online evaluation.
2. Market Pain Point Analysis
This section explains the rationale behind our product. We need to integrate and explain current market issues, target user needs, reasons behind these issues, market size, and prospects. A clear and specific analysis of the market status will make our proposal more persuasive.
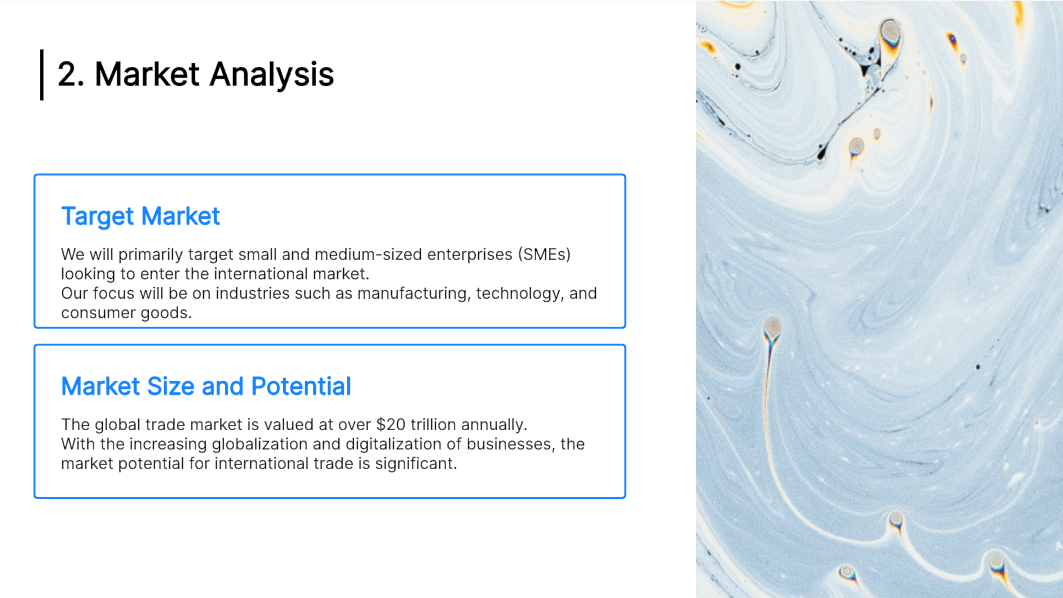
- Market Issue Description: Use cases, reports, stories, and data to illustrate the pain points vividly.
- Market Reason Analysis: Elaborate on the essence behind the issues, detailing each point.
- Market Size and Prospects: Identify the population or scenarios that need solutions and assess the prospects through data research. Boardmix Whiteboard offers a wealth of market analysis case resources for beginners.
3. Product Introduction
After clarifying market pain points, we need to explain and organize the solutions our team can propose, adhering to principles of specificity, clarity, and focus.
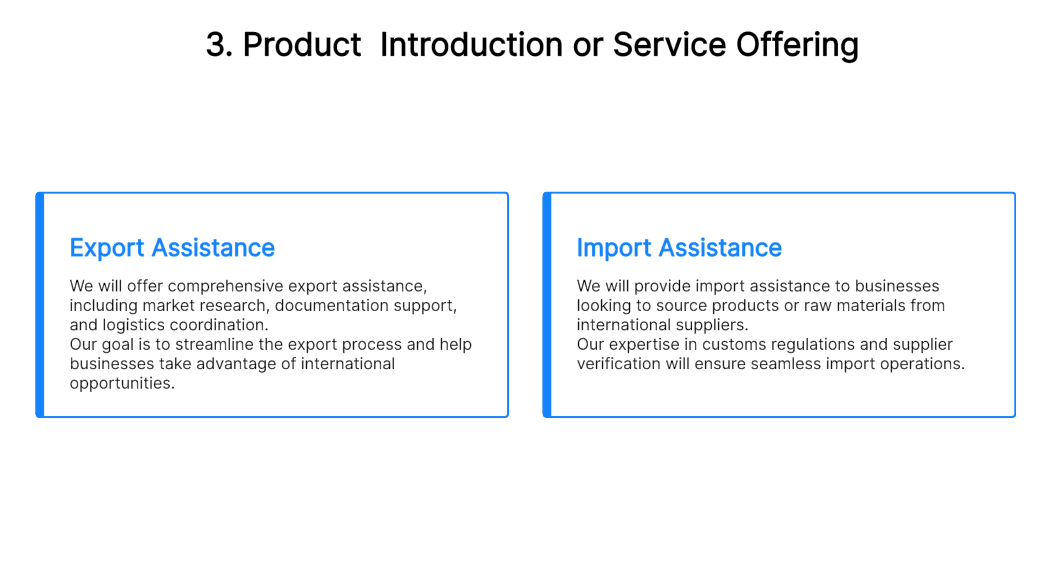
- Product Technology: Describe the technology used, functionalities, and problems solved, including technical parameters, approaches, and outcomes.
- Product Images: Provide physical, model, or operational flow images with explanatory text.
- Product Advantages: Highlight the product's innovation, market, and technical feasibility. Use Boardmix's built-in Competitive Analysis Template to compare our product with competitors on performance and price, making advantages more apparent.
4. Business Model Introduction
This section introduces the feasible operational model constructed by the entire team, centered around the product. It includes user pain points, customer segmentation, unique selling points, solutions, channels, key metrics, competitive barriers, cost analysis, and revenue analysis. A more intuitive method is to use the Business Model Canvas to introduce the business model.
5. Marketing Strategy
To make a product known to the public and market, we need to plan marketing strategies.
- Target Customer Analysis: Analyze who our target customers are, including their numbers, demand levels, and purchasing power.
- Promotion Strategy: How can we make customers aware of our product? What means and channels can we use?
6. SWOT Analysis
SWOT is a strategic analysis method representing a company's internal capabilities (strengths, weaknesses) and external environmental factors (opportunities, threats). Using it for project analysis can better illustrate the feasibility of implementation. Boardmix includes a built-in SWOT Analysis Template and case resources.
Try Boardmix for Free
7. Risk Analysis and Response
Conducting risk analysis and developing contingency plans are crucial to prevent business plan failure. Potential risks include financial, market, technical, transactional, and management risks.
8. Financial Data and Financing
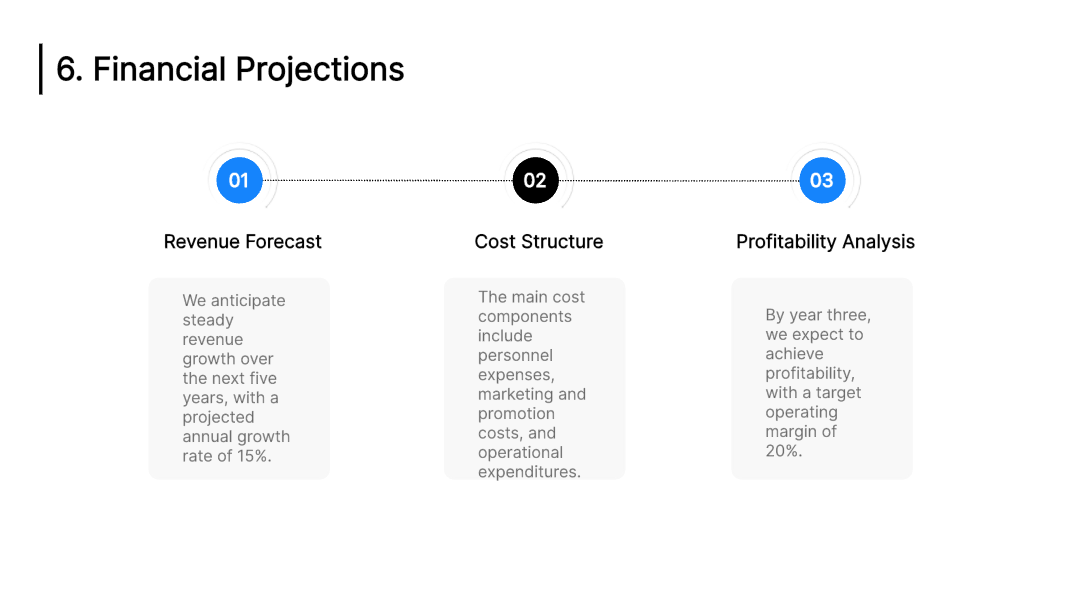
- Equity Structure and Financing Needs: Clarify the current equity structure, share distribution, reasons for holding shares, and expected financing in terms of share percentage and amount. Specify how the funds will be used.
- Financial Data Tables: Include profit analysis, sales forecasts, etc.
9. Team Member Introduction
- Project Members: List professional expertise, positions, and specific responsibilities. Include relevant achievements if applicable.
- Advisors: Research expertise in the project's field and industry, influence, achievements, and specific responsibilities.

10. Future Plans
It includes short-term and long-term plans with achievable goals.
11. Appendices
It includes certificates, patent introductions, other relevant project materials, research data, project practice images, etc.
This marks the completion of a thorough template for a university student entrepreneurship plan. Organize your materials in line with the provided information, and you're bound to make a lasting impression.
In the process of entrepreneurial planning, conducting extensive business analysis and planning is essential. Boardmix Whiteboard stands out as a robust and feature-rich online whiteboard software designed to foster creativity.
It simplifies the creation of diverse graphics and charts, offering an array of templates for knowledge organization and idea clarification, thus proving highly user-friendly for university students and beginners alike.
Additionally, Boardmix facilitates real-time collaborative editing, enabling online meetings, brainstorming sessions, and presentations, thereby enhancing team collaboration.
Furthermore, Boardmix boasts a wealth of high-quality case studies spanning enterprise management, marketing, operations, and various scenarios, serving as a valuable free learning platform. Boardmix Whiteboard is currently available for personal use at no cost. Give ti a try today!
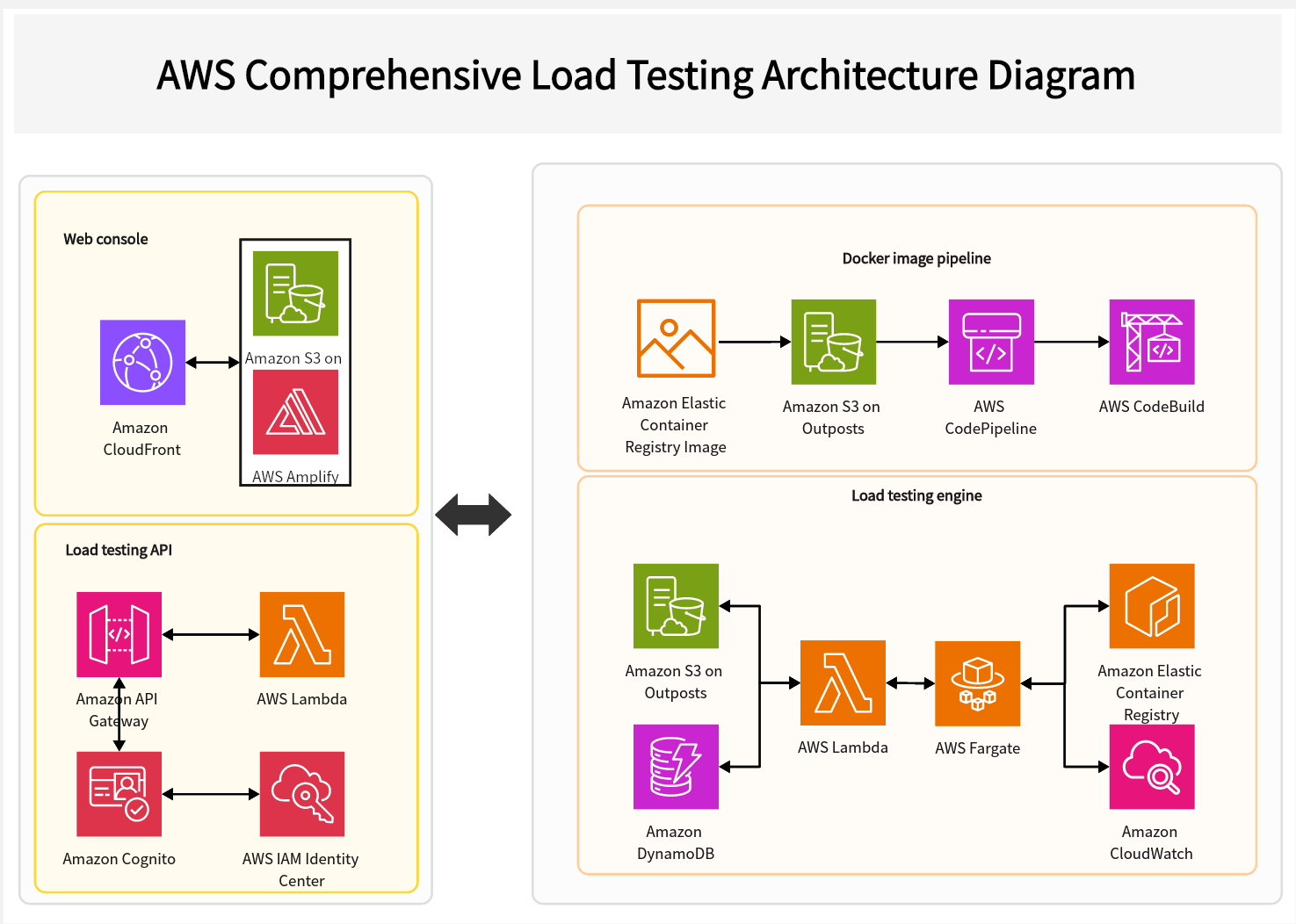
Top 9 Software for Crafting Architecture Diagrams with Ease
Brace Map Template: Free & Edite Online

What is Brace Map: A Thinking Map for Clarity


Top 20 Student Business-Plan Competitions
Say you have an awesome idea for a startup, something with real potential. There is, however, a pretty big problem: launching a business isn’t cheap, and as a student or recent graduate, it’s difficult to finance a business on your own. But, your idea is good. So what happens next? We’ve compiled a list of the top competitions aimed at current college undergraduates, graduate students, recent alumni, and high school students from all over the world to not only help you test your business model against what your peers are doing (and gain meaningful experience in the process), but also transform your idea into a reality.
1. High School Utah Entrepreneur Challenge
Hosted by the Lassonde Entrepreneur Institute at the University of Utah with sponsorship from Zions Bank, this competition is targeted at high schoolers with big ideas.
- What you need : A business idea that includes the following: a problem, a proposed solution, a targeted audience/customer and a prototype.
- Who can apply : Any Utah high-schooler aged 14-18. Teams are not required but can include up to 5 members.
- Where: This year’s events are expected to be virtual due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What you could win : Prizes vary in amount and type based on award received.
- 2020-21 Deadline : Apply by Feb. 17, 2021.
- Website : https://lassonde.utah.edu/hsuec/
2. Blue Ocean High School Entrepreneurial Leaders
A global, virtual pitch competition for high school students aimed to provide feedback, advance ideas, and launch students’ futures.
- What you need : A 3-5 minute pitch for a big idea.
- Who can apply : Any student currently in high school.
- Where: This is a virtual event conducted through video submissions.
- What you could win : The grand prize winner receives $1,000, with other awards receiving up to $750. There are also opportunities for high schools to receive grant money, too.
- 2020-21 Deadline : Apply by Feb. 19, 2021.
- Website : https://blueoceancompetition.org/
3. Get Seeded
Designed to help get ideas off the ground, this two-part milestone grant funding program seeks out students with measurable goals and helps fund the entrepreneurial process. This program is managed by the Lassonde Entrepreneur Institute at the University of Utah and sponsored by Chad and Kristen Anselmo and doxy.me.
- What you need : A startup with short-term measurable milestones (prototyping, marketing, etc.) that can be achieved within 30-90 days.
- Who can apply : Any college student in Utah.
- Where: The University of Utah in Salt Lake City, Utah, though location is subject to change due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What you could win : There are two grants opportunities: a microgrant of up to $500, and a Seed Grant for $501-1,500.
- 2020-21 Deadline : Regular grant intervals. See website for details.
- Website : https://lassonde.utah.edu/getseeded/
4. TechCrunch’s Startup Battlefield
A competition for early-stage startups to receive equity-free prize money, as well as general investors and media attention.
- What you need : A mid-stage startup with clear ideas and product or service in the development stages.
- Who can apply : Anyone with a startup idea is invited to participate.
- Where: The first round of competition is regional, and is subject to change due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
- What you could win : Global competition winners receive $100,000 in prize money.
- 2020-21 Deadline : Application dates have not yet been updated, as they vary by region.
- Website : https://techcrunch.com/
5. Hatch Pitch
Hosted with SXSW in Austin, Texas, until 2016, this is a competition focused on startups with information technology angles.
- What you need : A company in which the founders retain some portion of ownership, as well as a product or service that launched sometime in the past 2 years (or within 6 months after the Hatch Pitch event.)
- Who can apply : Anyone who meets the above criteria. There is no specific age limit or education requirement.
- Where: Houston, Texas, though location is subject to change due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What you could win : Winners can receive any amount of funding based on investors’ interest. All contestants receive active coaching and mentoring, as well as publicity for their concepts.
- 2020-21 Deadline : Applications are received on a rolling basis.
- Website : https://www.hatchpitch.com/apply-full-form
6. Rice University Business Plan Competition
A virtual three-day competition that accounts for pitches, feedback, and judge interaction, designed to give entrepreneurs real-world experience.
- What you need : A business in the seed, startup, or early growth stages
- Who can apply : Any full-time or part-time U.S. graduate students. Teams must have at least one graduate student and a faculty advisor, but only students can present.
- Where: Rice University in Houston, Texas.
- What you could win : The grand prize winner receives $125,000 in equity capital from a Houston investment group as well as $20,000 in cash and about $80,000 in services. This includes a year’s worth of office space.
- 2020-21 Deadline : Apply by Feb. 2, 2021, for the April 5-9, 2021 competition.
- Website : https://rbpc.rice.edu/
7. New Venture Championship, University of Oregon
This virtual competition attracts students who want to “create something extraordinary,” and can bridge the gap between a market need and a real solution.
- What you need : A business majorly owned by students that has a faculty advisor, looking for seed capital.
- Who can apply : Teams of 2-5 students who created, manage, and own their ventures and who are allocated at least 50% of the startup’s equity. At least one member of the team is required to be enrolled in a graduate program from any field.
- Where : Portland, Oregon.
- What you could win : Up to $50,000 in prize money is up for grabs. If you don’t make it to the top round, you can still compete in a lightning round for prize money during the finals.
- 2020-21 Deadline : Applications are due by Feb. 14, 2021, to compete in the qualifying round (Feb. 15 – March 20).
- Website : https://business.uoregon.edu/nvc/details
8. ClimateTech & Energy Prize @ MIT
A competition aimed at any student who wants to change the way we handle energy.
- What you need : A business focused on one of four categories: Generating Energy, Delivering Energy, Improving Energy Usage or Energy for Developing Economies.
- Who can apply : University teams from across the United States.
- Where : Cambridge, Massachusetts.
- What you could win : The top two teams in each category go on to compete for a $100,000 Grand Prize and other monetary prizes.
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Applications due on Feb. 5, 2021.
- Website : https://cep.mit.edu/intro
9. Baylor Business New Venture Competition
Hosted by Baylor University, this two-track competition is nationwide.
- What you need : A business in one of two competition tracks: Internet and Consumer Technology and Non-Internet and Consumer Technology Companies. Internet and Consumer Technology companies must aim to impact one of the following industries: Internet Services, Internet Security, Info Tech, Software Cloud, Mobile Tech, Mobile Apps, Mobile Commerce, Web/e-Commerce, Social Commerce, Social Networking, Social Media, Social Gaming, Video Gaming.
- Who can apply : Current students or recent alumni (within the last 15 months) in teams with 2-4 members.
- Where : Baylor University in Waco, Texas.
- What you could win: All prizes are in cash and range from a grand prize of $60,000 to $1,500 for second and third-round winners.
- 2021-2022 Deadlines : Dates have not yet been updated for the following year. The 2021 competition can be streamed from Mar. 25-27, 2021.
- Website : https://www.baylor.edu/business/newventurecompetition/
10. Innovation World Cup Series
This is a global competition split into categories where participants connect and compete in a convention setting.
- What you need : A business that is involved in the internet of things or wearable technology in the fields of Home, City, Lifestyle, Industrial, Transportation, Healthcare, and Retail.
- Who can apply : If you are 18 or older and in no way affiliated with Navispace, the host, you can apply.
- Where : Munich, Germany.
- What you could win: Prize pool of $500,000, with networking and exposure included
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Applications are open now, and due by Sept. 22, 2021.
- Website : https://www.innovationworldcup.com/13th-iot-wt-innovation-world-cup/
11. Utah Entrepreneur Challenge
A business-model competition for all college students in Utah. This competition is hosted by the Lassonde Entrepreneur Institute at the University of Utah and sponsored by Zions Bank.
- What you need : A business model of any type.
- Who can apply : University students currently enrolled in Utah colleges.
- Where : The University of Utah in Salt Lake City, Utah, though location is subject to change due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What you could win : Grand prize is up to $40,000 in cash, with additional prizes, like Best Speed Pitch, ranging in dollar amounts
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Applications close on Feb. 8, 2021.
- Website : http://lassonde.utah.edu/uec/
12. Postcode Lottery Green Challenge
One of the largest sustainable entrepreneurship competitions, participants compete with international entrepreneurs for the best green business plan.
- What you need : A business must have the potential to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions by a measurable amount, should be developed enough to execute should be realizable as a usable product or service within the next two years.
- Who can apply : Anyone 18 years or older whose business is located in Germany, Great Britain, the Netherlands, Norway, or Sweden.
- Where : The finals are hosted in Amsterdam, where you will present your idea to the jury (reasonable expenses covered for one person).
- What you could win : Grand prize winner receives €500,000. Second place receives €200,000, and other finalists receive €100,000.
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Dates have not yet been updated.
- Website : http://www.greenchallenge.info/entry-criteria
13. University Startup World Cup
This competition is hosted and organized by a Danish non-profit, Venture Cup. Their mission is to establish connections among student entrepreneurs internationally, as well as teach and advise young people about the world of business.
- What you need : Preferably, a business that fits into one of the following categories: Healthtech, Greentec, Fintech, Hightec & Robotics, or Information Communication technology. However, if your idea is cool enough, they’ll accept anything.
- Who can apply: Only student startups may enter. Therefore, all teams must have at least one person who is a student, faculty member, or recent graduate (within the year they’re applying). However, if you’re looking for team members, Venture Cup can help connect you to people with similar ideas.
- Where: The location is not certain due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- What you could win : Grand prize is $15,000.
- Website : https://venturecup.dk/uswc/
14. Get in the Ring
One-on-one, regional, and global face-off between startups that takes place in a literal ring.
- What you need : A “high potential” startup that is 8 years or younger with an innovative and scalable business idea or model.
- Who can apply : Anyone with a business fitting the above-described model.
- Where : The beginning stages of the competition are regional, and vary based on your location. Finals are hosted in a different location internationally every year. Travel cost to finals is covered.
- What you could win : GITR offers immense exposure for your business by placing you in a ring where you “battle” other entrepreneurs using your business pitch in front of investors and businesspeople. Grand prize winners receive a seat at the table with hand-picked advisors and investors, and title.
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Dates vary by region.
- Website : https://getinthering.co/gm2021/
15. U. Pitch
This national competition brings university students from all disciplines together to contend for the best 90-second pitch.
- What you need: A company or idea to start a for-profit company with headquarters in the U.S.
- Who can apply : Current university students or graduates within the last six months.
- Where : 100% virtual.
- What you could win : Up to $10,000 in prizes and cash.
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Applications open in the fall of 2021. You can sign up to get notified here .
- Website : https://futurefounders.com/startup/upitch/
16. Cartier Women’s Initiative Awards
This competition brings women from six regions of the world to showcase their ideas.
- What you need : A for-profit startup with at least one year of revenue.
- Who can apply : Only women may apply for this competition.
- Where : Finalists attend awards week in Singapore, where the final round commences.
- What you could win : Grand prize is $100,000. All runner ups receive $30,000.
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Application deadlines have not yet been updated.
- Website : https://application-form.cartierwomensinitiative.com/new-application
17. G-Startup Worldwide
This is a global competition that supports young entrepreneurs in the early stages of a startup with funding and a network of investors.
- What you need : A product that is making a positive impact, showing traction in the market, and is involved in AI, Mobile, IoT, Wearables, FinTech, Cyber Security, Smart Cars, AR/VR, Space, Robotics/Drones, Education, Enterprise, Health, AggTech, or Social and eCommerce.
- Who can apply : Any startup meeting the previous requirement that is registered as a company.
- Where : First rounds are regional. Finalists compete in Silicon Valley.
- What you could win : Winners of regional competitions receive cash prizes, travel opportunities, and networking invites.
- Website : http://g-startup.net/
18. Axel Springer Plug and Play
While competitive, this 100-day program is more of an accelerator than an out-right competition. They require 5% equity in exchange for participation.
- What you need : A business model for digital entrepreneurship.
- Who can apply : Anyone with an early-stage company and a Pitch-Deck.
- Where : Location varies. Check the website below for more details.
- What you could win : €50,000, valuable time to pitch in front of investors, and experience.
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Deadlines vary based on location and stage of company.
- Website : http://www.axelspringerplugandplay.com/#home-section
19. Citizen Entrepreneurship Competition
Inspired and promoted by the United Nations, this competition takes place through three stages of online submission and selection.
- What you need : Innovative ideas and projects with a societal impact. Must involve one or more of the United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals .
- Who can apply : Anyone aged 13-29 (or 30+ in the Adult Citizen Entrepreneurship category).
- Where: Winners are invited to the Summit in Berlin in October of every year.
- What you could win : Recognition at the Summit and the UN’s acknowledgement.
- 2020-21 Deadlines : Applications open in Spring 2021.
- Website : https://www.entrepreneurship-campus.org/about-the-competition/
20. CodeLaunch
Annual seed accelerator for people and groups with ideas for “apps” who are seeking seed funding. Entries are submitted online.
- What you need : Any software ideas are taken, even just having an idea for an app is acceptable.
- Who can apply : Anyone that fits the previous criteria.
- Where : Finals are hosted in Texas, dates change every year and might be impacted by COVID-19.
- What you could win : Applicants chosen to attend CodeLaunch pitch day compete in front of judges poised to invest. Overall winner receives custom software design, development, and/or website development, hosting services, and a partnership with Code Authority. Winners may also judge the following year’s competition.
- Website : https://www.codelaunch.com/
Share this:
About the author: jacqueline mumford, 2 thoughts on “ top 20 student business-plan competitions ”.
Thanks Jacqueline for this comprehensive list. I wish I had this information 15 years ago. Had a great idea, pitched it to some venture firms and was turned down and saw the same idea skyrocket to the top two years later when someone else came with the same idea and presented it in a much more convincing way to the investors.
The Draper Competition for Collegiate Women Entrepreneurs is another event that provides microfinancing for undergraduate women-led ventures. Total cash prize pool is $100,000. http://www.smith.edu/draper
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Launched at Lassonde
- Tips & Tricks
- Press Releases
- Publications & Reports
- In the News
- Marketing & Media Resources
- Latest News

- Study Entrepreneurship: Classes Start for Summer Monday, May 13, 2024
- Get Started with Your Business Idea Session Tuesday, May 14, 2024, 12:15 - 1pm
- Workshops: Market Research Wednesday, May 15, 2024, 1 - 2pm
JOIN THE COMMUNITY
Welcome to the hub for student entrepreneurs and innovators at the University of Utah. Subscribe or follow us for news and announcements. Learn More →
QUICK LINKS
About lassonde institute.
- Tours & Info Sessions
- Marketing & Media Resources
- Give to Lassonde
- Request Info
Lassonde Studios
- Apply to Live Here
- Housing Options
- Miller Cafe
News, Events & More
- Live at Lassonde Studios
- Lassonde Founders
- Summer at Lassonde
- Lassonde 400 Residential Program
- Make Program
- Hours with Experts
- Food Entrepreneur
- Arts Entrepreneur
- Utah Entrepreneur Challenge
- H.S. Utah Entrepreneur Challenge
- Bench to Bedside
- Company Launch
- Entrepreneurship Classes, Certificate and Degrees
- Master of Business Creation
- New Venture Development
- Lassonde Ambassadors
- Entrepreneur Club
- Student Leadership & Scholarship Opportunities
- Lassonde for Life
- Utah Founders
- Get Started with a Business Idea Sessions
- Community Engagement
- Global Entrepreneurship Program

550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast
Finish your plan faster with step-by-step guidance, financial wizards, and a proven format.

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the plans in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how you're business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remain stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a sample business plan.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a plan that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily we have a round-up of real-world pitch deck examples used by successful startups that you can review and reference as you build your pitch.
For more resources, check out our full Business Pitch Guide .
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right match for your business idea.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
British Council
- English, education and arts
- Our work in education
- Skills and employability
- Tools and resources
- Vocational Education Exchange
- Embedding enterprise and entrepreneurship in the vocational curriculum
Re-imagining the business plan for students

While the terms ‘enterprise’ and ‘entrepreneurship’ are often used interchangeably, there is a distinct difference between them, especially within the context of technical, vocational education and training (TVET).
‘Enterprising’ activities, which many TVET providers already focus on, enable students to develop interpersonal skills such as leadership, motivation, critical thinking, problem-solving, teambuilding, communication and presentation skills. ‘Entrepreneurship’ takes this a step further by encouraging students to explore the opportunity of self-employment by starting a new enterprise. There is a strong focus on developing business ideas, business acumen and skills such as product development, market research, finance and planning, and on providing access to pre-incubation services and business networks.
At Northern Regional College, in Northern Ireland, we embarked on an international TVET partnership with colleges from Spain, Portugal and Finland to explore a new approach to making enterprise education more entrepreneurial. Our area of focus? The business plan.
Completion of a business plan is a key measure of success for many enterprise start-up agency support programmes. To attract capital investment, the business plan remains, rightly or wrongly, the measurement of the entrepreneur’s commitment to the short to medium-term future of their business.
While many TVET colleges seeking to develop entrepreneurial thinking and action amongst their students emphasise the importance of the business plan, it is proven to be the least popular and, consequently, least practiced activity amongst TVET students.
A NEW APPROACH TO BUSINESS PLANNING
In response, our Erasmus+ partnership, Enterprise is VITAL, is piloting a new business planning model using language relevant to TVET students. The approach focuses on five core entrepreneurial characteristics: Vision, Innovation, Teamwork, Achievement and Leadership.
The model is an adaptation from the international bestselling book Winning from Within by EA Fox (2013), which highlights four intrinsic characteristics that need to be understood and developed for success.
Interestingly, these characteristics link with the standard template business plan:
- Dreamer : vision, innovation, creativity, star-gazing, future thinking, idea generation
- Thinker : research, data – facts, risk analysis (acceptable loss-thinking), market research
- Warrior : performance, tasks, to-do lists, deadlines, goals, milestones, plans
- Lover : people, relationships, networks, communication, contacts, customers.
By focusing on these emotionally descriptive words, TVET students are better able to understand the critical skills required for embarking on a new venture. The term ‘Lover’ evokes a positive response, suggesting the importance of developing a long-lasting mutual relationship. The term ‘Thinker’ underlines the importance of making time for data gathering and analysis within busy schedules. ‘Warrior’ is a call to action. ‘Dreamer’ invites innovative solutions to problems.
Our TVET students have understood and adapted to this model extremely quickly. It has encouraged them to engage in lively debate, and to discuss their ideas through problem-based learning projects. All of this ultimately leads to the development of a business plan, without actually using the term ‘business plan’.
In addition to language and digital competence, the EU recognises that transversal competencies including a sense of initiative and entrepreneurship, learning to learn, cultural awareness and social and civic responsibility are required to make individuals more flexible and mobile, and, therefore, responsive to the needs of a modern economy ( Key Competences for Lifelong Learning , 2006). The programme content of any entrepreneurship programme must consider the level and extent to which these transversal competences are being addressed.
During the first year of Enterprise is VITAL, our students fully embraced these transversal competencies. Working in mixed international teams, they developed their business ideas and their market pitch proposal during a business planning competition in Spain, based on this visual model.
The judging panel, comprising of local business leaders, entrepreneurs and independent start-up agency experts from Spain and the UK, commended the students on ‘their clarity of vision, understanding of the market place and customer needs, realistic financial forecasts and doable actions’. The students were also congratulated for ‘their insights into their own weaknesses and how to build their social capital’, which the judges said was rarely included in an enterprise pitch. What more could you ask for from a successful business plan?
To find out more about Enterprise is VITAL, contact Irvine Abraham at the Northern Regional College.
British Council Worldwide
- Afghanistan
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Czech Republic
- Hong Kong, SAR of China
- Korea, Republic of
- Myanmar (Burma)
- Netherlands
- New Zealand
- North Macedonia
- Northern Ireland
- Occupied Palestinian Territories
- Philippines
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Switzerland
- United Arab Emirates
- United States of America
For Teachers
Home » Teachers
Teaching by Topic: Entrepreneurship
Here are a bunch of tips, learning objectives, worksheets, and pre-built lesson plans to help you build your curriculum to teach students about entrepreneurship!

Entrepreneurship is essential for your students to understand. By learning successful entrepreneurial skills, your kids can increase their odds of achieving financial success.
You can find the materials you need to teach entrepreneurship, regardless of your students’ levels. Here are entrepreneurship lessons, worksheets, activities and games, and some key tips – by grade. We also include learning objectives that connect to the National Standards for Financial Education.
National Standards for Personal Finance Education
Download our free teachers' cheat sheet.
Our free cheat sheet covers every learning objective in the National Standards for Personal Finance Education and the corresponding Kids' Money Lesson Plans - we cover each and every standard!
Learning Objectives
Pre-K students are likely still too young to understand the concepts of entrepreneurship. However, they can work on money awareness, mainly coins, to grasp more advanced concepts in later grades. They should be able to:
- See how money works and understand the value of different coins.
Pre-K Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- Pre-K – Let’s Learn About Money!: In this lesson from Penn State University, students learn about wants vs. needs and understand how decision-making is part of money education. They complete several activities introducing them to money and set the foundation for more complex topics later.
Pre-K Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Coin Worksheets
- Coin Toss: Frog
- Counting Coins
- Coins and Dollars
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to Pre-K Students
- Pre-K students may think that coins are more valuable than bills.
- Use the idea of ownership and borrowing to teach basic money concepts.
- Explain the many ways to make money, including starting a business.
For more resources on other topics, check out our Pre-K Money Lesson Plans Center .
Kindergarten
The concept of entrepreneurship is still out of reach for many Kindergarteners, but they can learn characteristics that successful entrepreneurs share. They should be able to:
- Find ways to solve problems and analyze decision-making skills.
Kindergarten Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- Kindergarten – Discovering the Leader In Me: This lesson from leaderinme.org teaches students the value of leadership, a crucial component of entrepreneurship. They identify positive attributes about themselves, play games, and solve problems as they become better leaders.
Kindergarten Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- I’m In Charge of Me
- All About Me Leadership Poster
- Student Leadership
- Leadership KWL Chart
- I Am a Leader
Kindergarten Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- STEM Makerspace Activities
- Humpty Dumpty Takes a Risk
- Leadership Lanyards
- WISE Decisions
- Would You Rather Task Cards
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to Kindergarten Students
- Build strong character traits.
- Continue working on money identification, as they need to know money well for the upcoming concepts.
- Use songs, stories, and fables to show characters’ positive, entrepreneurial habits.
For more resources on other topics, check out our Kindergarten Money Lesson Plans Center .
1st-graders look at different careers, including the idea of entrepreneurship. They should be able to:
- Develop a list of possible careers of interest and determine the skills needed in those careers.
1st Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 1st Grade – Jobs I Like At Home and At School: In this lesson from mdek12.org, students look closely at jobs and why people have them. They participate in various activities while identifying strengths and interests for possible careers in the future.
1st Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Lemonade Stand
- Lemonade Stand Addition
- Would You Rather Career
- Career Interest Survey
- When I Grow Up
1st Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Run Your Own Lemonade Stand Activity
- Economics Business Plan
- Future Career Business Card Activity
- Career Day Packet
- Career Research
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 1st Graders
- Encourage kids to research and ask questions.
- Use the classroom store to show how earning income, spending, and saving work.
- Remind them that kids can start businesses, too.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 1st Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
2nd-grade students learn about entrepreneurial characteristics and further study specific careers. They should be able to:
- Research careers and see how entrepreneurs establish their own path.
2nd Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 2nd Grade – Tell Me About Your Job: This lesson plan from ed.sc.gov showcases various jobs, letting students see how communities and careers intersect. They research one career and give an oral presentation to the class about the job.
2nd Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- My Business Plan
- Entrepreneur Brainstorm
- Product Design Phase
- Leadership Roles Reflection Sheet
2nd Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- What Does It Mean to Be An Entrepreneur?
- A Career for Me Writing
- Design a Line of Caps
- Leaping Into Leadership Writing
- Lemonade Stand Math and Business Virtual Game
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 2nd Graders
- Focus on leadership and other entrepreneurial traits.
- Have students reflect in writing often.
- Use hands-on and practical activities to show how businesses work.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 2nd Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
3rd-graders learn more about specific ways to become an entrepreneur, including planning, decision-making, and risk-taking. They should be able to:
- Understand the motive of profit in entrepreneurship and describe various paths of entrepreneurs.
3rd Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 3rd Grade – So You Want to Be An Entrepreneur?: This lesson from Business Kidz shows kids the ways entrepreneurs can make money. It offers many activities and opportunities for kids to demonstrate their understanding of economic concepts.
3rd Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Entrepreneurship Profit vs. Loss Worksheet
- Dream It! Make It! Sell It!
- Entrepreneurship Enrichment
- STEAM Investigative Process for Entrepreneurs
- Create Your Own Business Worksheet
3rd Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Popcorn Farm-to-Table
- Entrepreneurship Activity Book for Beginners
- Kidpreneur: An Entrepreneurship Educational Resource
- Let’s Make a Profit
- Economics For Fun and Profit
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 3rd Graders
- Use role-play often.
- Build the idea of risk/reward tradeoffs.
- Show them several ways to start their own business.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 3rd Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
4th-grade students jump into more advanced entrepreneurial skills, including planning business operations and measuring success. They should be able to:
- Diagram the steps needed to set up a business and learn the role of the entrepreneur.
4th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 4th Grade – Isabel’s Car Wash: This lesson from the Kansas City Fed shows students essential entrepreneurial concepts and terminology. They see the importance of having a business plan and having a pitch to secure investors.
4th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Starting Your Own Business
- Elementary Entrepreneurs
- Entrepreneur Vocabulary
- Economics/Entrepreneurs
- Business Model Handout
4th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Comparing Jobs and Hobbies
- Graphing Ways to Make Money
- Exploring Opportunity Costs
- Jay Starts a Business
- Lemonade Stand Business Plan
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 4th Graders
- Use more advanced money math, like multiplication to long division, to improve their financial skills.
- Build as much entrepreneurship vocabulary with word walls and reflective journals.
- Challenge students to list as many ways to start a business as possible.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 4th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
5th-grade students discover various jobs and ways to earn income and see the type of person who becomes a successful entrepreneur. They should be able to:
- Identify risks and rewards involved in entrepreneurship and identify various historical entrepreneurs.
5th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 5th Grade – The Sweet Success of Milton Hershey: In this lesson from econedlink.org, students learn how the chocolate tycoon rose to riches and fame. They also look at the risks and rewards of being an entrepreneur.
5th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Startup Entrepreneurship 101 Vocabulary
- Jobs I Can Do To Earn Money
- Problem Solving
- My Favorite Entrepreneur
- My Interests and Dislikes
5th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Playing a Business Game
- Entrepreneurship Day
- Personal Finance for Young Learners
- Lemonade Stand Math
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 5th Graders
- Bring in guest speakers.
- Have a Career Day where students research and represent various careers.
- Increase math complexity, e.g., showing how taxes impact entrepreneurship.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 5th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
6th-grade students see how pursuing their passion can lead to income, and they break down the steps to make it happen. They should be able to:
- Use critical thinking and self-reflection to determine logical steps on the entrepreneurial journey.
6th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 6th Grade – I Can Be An Entrepreneur: This lesson from econedlink.org shows kids how to plan and develop entrepreneurial activities. They also learn how to calculate profit and loss in economic situations.
6th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Turning Hobbies Into Earnings
- Study an Entrepreneur
- Make Your Business Plan
- Plan Your Pitch
- Connect With a Mentor
6th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Getting Paid
- Resources For A Lemonade Stand
- Entrepreneur Math Project
- Target Market Persona
- Economics Causation Cards
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 6th Graders
- Introduce mentoring by partnering with students from higher grades.
- Work on public speaking and confidence-building exercises.
- Set up a classroom store and reward entrepreneurial successes.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 6th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
7th-graders dive further into how to market businesses, understanding that every decision has an outcome. They should be able to:
- See that responsible choices increase the chance for entrepreneurial success and understand a plan’s importance.
7th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 7th Grade – Crash Course On Starting A Business: This lesson from BizKids stresses the importance of analyzing decisions and taking responsibility in entrepreneurship. Students learn to make a business plan and market a product or service.
7th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Are You Ready to Take the Risk?
- Famous American Entrepreneurs
- Entrepreneur Think Sheet
- Small Business Loans
- Career Readiness
7th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Exploring Entrepreneurship
- Common Cents
- Entrepreneur Research Report
- Career Exploration Activity
- Career Webquest
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 7th Graders
- Use current events and famous figures from today to teach entrepreneurship.
- Begin to show kids the risks involved in entrepreneurship.
- Have students reflect on decisions continually.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 7th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
8th-grade students deepen their financial and entrepreneurial vocabulary and understand more advanced concepts. They should be able to:
- Research possible careers they can start on their own, determining risks and rewards involved in their choice.
8th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 8th Grade – Entrepreneurial Expedition: This lesson from everfi.com teaches students many entrepreneurial terms, starting a career, and finding success in business ventures. They learn how to create a personalized plan by watching case studies and completing personal development activities.
8th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Competitive Analysis Worksheet
- Business Plan
- Paychecks and Taxes
- Career Research Handout
- Interview Planning Sheet
8th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Drawing Your Own Business
- Coffee Shop Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurship Project
- Food Trucks Gallery Walk
- Business Plan Note-Taking Activity
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 8th Graders
- Have students work in small groups to mimic business startups.
- Attend virtual career fairs and presentations to get ideas.
- Have students research often.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 8th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
9th-grade students look at real-life examples of entrepreneurial success throughout the year. They should be able to:
- Identify characteristics shared by leading entrepreneurs and incorporate them into business planning.
9th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 9th Grade – Making Your Own Job: In this lesson from econedlink.org, students identify characteristics of entrepreneurs and discover examples of business success. They also compare entrepreneurial ventures with working in an organization.
9th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Understanding Jobs, Teens, and Taxes
- Becoming Familiar With Taxes
- Getting Banked
- Career Worksheet
9th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Gazillionaire
- Fistful of Dollars
- Cookie Tycoon
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 9th Graders
- Use current events.
- Challenge students to think about how they would improve on existing products and services.
- Play games and interactive activities that build entrepreneurial skills.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 9th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
10th-grade students focus on specific careers of interest and begin understanding the details of entrepreneurship in their chosen industry. They should be able to:
- Understand how funding works in entrepreneurship and how to secure loans to start a business.
10th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 10th Grade – Twenty-Two Cents: In this lesson from the Kansas City Fed, students learn about loans that entrepreneurs can receive. They see how lenders use specific criteria to determine who receives loans and the various interest rates involved.
10th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Business Entrepreneurship Vocabulary Sheet
- Entrepreneurial Self-Assessment Survey
- Career Research Graphic Organizer
- Career Exploration Worksheets
- Career Cluster
10th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Entrepreneurship Business Opportunity
- Environmental Entrepreneurism
- Location, Location, Location: Let’s Start a Business
- STEM Careers Research and Application
- Finding Your Vocation
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 10th Graders
- Provide daily time for research.
- Have one-on-one consultations to focus on career clusters and interests.
- Use virtual field trips, online resources, and guest speakers to enhance teaching.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 10th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
11th-graders dive into the details of entrepreneurship, learning how to plan and execute the steps to success. They should be able to:
- Identify characteristics that lead to successful entrepreneurship and understand the risks involved in forming your own business.
11th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- KMLP 11th Grade – The Entrepreneur’s Journey : This lesson plan shows students the path of entrepreneurship, from having an idea to scaling a product. They watch videos, read articles, and research a famous entrepreneur as they learn the ins and outs of starting a business.
11th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Tracking Income for a Farming Family
- Tracking Income for an Artist Family
- Choosing How to Get Paid
- Comparing Higher Education Choices
- Business Plan Graphic Organizer
11th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Finances 101 Game
- Understanding Taxes and Your Paycheck
- Creating a Poster On Life After High School
- Picturing Your Financial Self
- Researching the Gig Economy
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 11th Graders
- Show students that every entrepreneur experiences failures on the path to success.
- Break down taxes and interest, showing them the financial details behind entrepreneurship.
- Show them the importance of multiple income streams and how they can use entrepreneurial skills to support the approach.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 11th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .
12th-graders look at various practical ways to jump into entrepreneurship, and see how careful planning can lead to success. They should be able to:
- Identify successful strategies in entrepreneurship and analyze decision-making to reach outcomes.
12th Grade Entrepreneurship Lesson Plans
- 12th Grade – Three Types of Business Organizations: This lesson from econedlink.org shows students how they can set up a business in the future. They compare the costs and benefits of sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations, linking these ideas to their planned entrepreneurial ventures.
12th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets
- Restaurant Creation
- Business Letter
- Types of Business Sort
- Business Ownership Types
- Business Bell Work
12th Grade Entrepreneurship Games and Activities
- Balancing Fairness with Self-Interest
- Lights, Camera, Budget!
- Break-Even Analysis Activity
- Real World Business Soft Skills
- Business Profile Research Activity
Tips for Teaching Entrepreneurship to 12th Graders
- Use diverse grouping, letting students work independently, in pairs, and teams.
- Focus on soft skills, too.
- Use online tools and apps to expose students to real-life data and financial statistics.
For more resources on other topics, check out our 12th Grade Money Lesson Plans Center .

Student Entrepreneurs Go Head-to-Head in Business Plan Competition
Target market identified? Check. Competition researched? Check. Financials planned, location selected, advisory board recruited? Check, check, and check.
There is a lot more to being an entrepreneur than coming up with a great business idea. No one knows this better than the students who participated in the Cornell Hospitality Business Plan Competition, presented by the Leland C. and Mary M. Institute for Hospitality Entrepreneurship at the School of Hotel Administration. The competition began in November with 30 student teams submitting executive summaries; five finalist teams competed in the final round of the competition on April 6 during the 88th Annual Hotel Ezra Cornell.
“All of the concepts in the final round were outstanding. They were unique and filled a clear void in the market, and each has the potential to succeed in the real world,” said Neil Tarallo, PIHE academic director. “A good idea isn’t enough to attract investors, though, and the teams that really stood out were the ones that had fully rounded business plans and were ready to bring their concepts to life.”
Martin Andonov ’13 won the competition and the $15,000 first-place cash prize for his concept, Agora Hellenic Grill, a chain of Mediterranean fast-casual restaurants that will be based in London. Passionate about his nascent business and spurred by his win, Andonov will return to the United Kingdom after graduation to test his concept in a real-life setting and continue on his path to become an entrepreneur.
Andonov got the idea for Agora while he was studying abroad at the London School of Economics and was unsatisfied with his dining options. Citing the growth in interest in Mediterranean food, the rise in healthy eating, and the lack of restaurants filling this niche, he explained “there is a tremendous opportunity that, interestingly enough, nobody is capitalizing on.”
That eye for unrealized opportunities was common among all the finalist teams. Runner-up Voilà Mobile Crêperie—a food truck concept by Michael Perlman ’13, Ethan Joseph ’13, & Tareq Ali ’13—took home the $5,000 second-place prize. Third place and $2,500 went to Spencer Stein ’13, who developed the Solace, an in-room pain-relief product. The Stein Family Prize of $5,000 went to Robert Frisch MBA ’13 and Tara Lobo ’15, for a mobile, luxury eco-tent business, Cairn Tented Resorts. SakuraTerra Hospitality team of Satoko Nagahara MMH ’13, Christopher O’Donnell ’13, Zhuodan Huang MMH ’13, and Blake Golom MMH ’13, earned honorable mention for their a Japanese-style inn and spa.
“The students put a tremendous amount of work into the competition, and I love to watch the business plans develop over the course of the academic year. It is even more impressive to see how much the students grow throughout the competition. Everything from their confidence levels to their critical thinking skills to their time management skills grows,” said Susan Fleming, senior lecturer in management and organizational behavior, who co-chairs the competition with Tarallo.
The teams pitched their business concepts to judges Chris Hemmeter, Thayer Ventures; Bill Minnock ’79, Marriott International; Sandy Solomon, Sweet Street Desserts; and Jacob Wright, High Peaks Hospitality. Judges for the semi-final round were Moby Ahmed; Nick Bayer, Saxbys Coffee; Kenny Blatt ’81, Caribbean Property Group; Larry Hall, PAR Springer-Miller; Ken Hamlet ’66, Crestview Partners; Chris Hunsberger ’81, Four Seasons Hotels & Resorts; Warren Leeds ’84, Dartcor Management Services; and Mark Lomanno.
Sponsors for the 2013 competition were Marriott International, Four Seasons Hotels and Resorts, the Sun family, and the Stein Family.
To learn more about the Cornell Hospitality Business Plan Competition, visit the competition web page.
- Mercy University Entrepreneurship Program Inspires Future Innovators
- Mercy University News
- School of Business
- News & Events
Standing from left to right: Sofia Cialicu, associate director of Operations for Mercy's School of Business; Mercy alum Alex Boryk ’17, co-founder of Lunchbox; Mercy Trustee and alumnus Phillip Grant, CEO, Hunts Point Produce Market; Robert F. Bohn, director of Mercy’s entrepreneurship programs; Korhan Beba and Umran Beba of the Beba Innovation and Entrepreneurship Foundation; 2022 winner Tereva Bundy ’21; Elena Rivera-Cheek, CEO of C&A Digital and Victor Petenkemani, interim dean of the School of Business.
Seated from left to right: Student finalists and winners Joey Dos Santos, Eirick Elvestad, Sophia Resolme, Mason Gifford, Olga Ineza, Jorgen Krohn-Pettersen and Alyssa Politi.
This Spring, Mercy University’s School of Business hosted its 5th Annual Student-Preneur Conference to inspire future innovators. Sponsored by the Beba Innovation & Entrepreneurship Foundation, the event featured guest speakers, an entrepreneurial alliance panel, an entrepreneur expo, and the business plan competition finale, during which students got to display their business acumen.
“Our job is to prepare the next generation of entrepreneurs, so they can go on to help solve problems because that is what entrepreneurship is all about,” said Victor Petenkemani, interim dean of the School of Business. “Thank you, Professor Robert Bohn for leading this fantastic initiative along with our wonderful team in the School of Business.”
The event drew more than 180 attendees, including students, faculty, and staff, who participated in person at the Westchester campus and virtually. Students from local high schools, including Lincoln High School in Yonkers, New York, also got the chance to participate for the second year in a row.
This year’s keynote speaker was Mercy alum Alex Boryk ’17, co-founder of Lunchbox, a company that empowers restaurants by helping them build their own online ordering platforms. Featured in Forbes “30 Under 30” for being one of the brightest young entrepreneurs, Boryk’s passion for digital business began while he was still a student at Mercy.
“I benefited so much from the incredible networking opportunities and internships I received at Mercy,” said Boryk. “What you’re getting here is a well-rounded foundation in business, and you are building upon the skillset of knowing and getting the exposure of finding where you want to go.”
His advice to the students in the room, “always be open and embrace the unconventional, don’t create your own “no’s” in your head; it takes perseverance and grit, build a great team with the people who will run towards the fire and motivate each other, and always be willing to learn.”
The event also included an entrepreneurial alliance panel headed by Elena Rivera-Cheek, founder and CEO of C&A Digital, a leading Westchester-based strategic communications and consulting agency. She highlighted the importance of networking to build connections and recommended gaining some experience before attempting to start your own business. “Learn on a company, let them show you the way, and then start your own thing,” she added.
The day concluded with the anticipated Business Plan Competition Finale. Robert F. Bohn, Director of Mercy’s Entrepreneurship programs and the conference organizer, noted that this year, they had an unprecedented number of competitors thanks to the expansion of the contest to all students. “For the first time, we had cross-functional teams with students who come from different Schools and academic programs, making the competition a university wide engagement,” added Bohn. The competition drew students from finance, management, marketing, entrepreneurship, accounting, mental health counseling, health science, sport management and journalism.
Five student teams presented their business ideas to a panel of judges comprised of Boryk, Rivera-Cheek, Mercy Trustee Phillip Grant, M.B.A. ’08, CEO, Hunts Point Produce Market; Umran Beba, M.B.A., H.D. ’22 co-founder of the Beba Innovation and Entrepreneurship Foundation and Korhan Beba, its executive director and 2022 competition winner Tereva Bundy, M.S. '22, who has since successfully launched her online tutoring business.
The finalists were Simon Steffensen '25, Jaid Wazihullah '25, Paal Andreas Furuseth '24 with Friendly, an application to help find roommates, rooms and apartments in Europe; Isabella Masala '26, Evanice Garrisi '24, Alyssa Gonzalez '24 with MindFit, a place that combines exercise and mental health resources; Joey Dos Santos '25, Eirick Elvestad '24, Jorgen Krohn-Pettersen '25 with Rescue-Ready VR, a virtual reality application that offers in-depth training for emergency medical technicians and nurses; Alyssa Politi '24 with Self-Scent, a company that lets you personalize the scent of your perfume; and Mason Gifford '26, Olga Ineza '27 and Sophia Resolme '26 with Trace, a discrete, radio-frequency tracking sticker.
After much deliberation, the judges declared the winners. First place went to the team at Trace, who received a $4,500 prize. Second place went to Self-Scent and Rescue-Ready VR came in third place.
“It is so rewarding,” said Gifford about winning as a team. “Meeting night in and night out. It taught us a lot about time management.” Ineza added, “What we learned was to make the solution happen, and we came up with Trace.”
When asked what their inspiration was for the product, Resolme said, “We are constantly losing stuff. It seemed trivial but once we dove into it and saw stats, we thought it was a great idea.” To which, Ineza added, “We’d love to invest in a prototype.”
The winning team will represent Mercy University at the Collegiate Entrepreneurs Organization’s 41 st Annual Global Conference and Pitch Competition, which will be held from October 31 - November 2, 2024, in Tampa, FL.
For Margaret Ennin, a sophomore at Lincoln High School, attending the conference was truly inspiring. “Our generation can change the world, and this taught me the opportunities we have as entrepreneurs to change the world.”
" We look forward to Mercy University’s 6th Annual Student Preneur Conference next year. Our School of Business thanks the Beba Innovation & Entrepreneurship Foundation for their continued support to our students. Their commitment to Mercy University, and for their overall invaluable contribution, to the competition, and to the school, over the years, is vital to our future growth," concluded Bohn.
First place winners: Sophia Resolme, Mason Gifford and Olga Ineza with Trace
This video game is teaching college students entrepreneurship
A free mobile and PC game teaches students something classes can't: how to react in real time to a dynamically shifting market.
As BestColleges reports, Venture Valley , created by the Singleton Foundation for Financial Literacy and Entrepreneurship , is a multiplayer business-building game where you compete and cooperate with friends and others online for the best entrepreneurship outcomes.
All players start with a dog-walking service, earn in-game money to build their businesses and assets, and play cards to give themselves an advantage or their opponent a disadvantage.
Organizers of the mobile game started running competitions to give college students a shot at thousands of dollars to see who could create the most profitable businesses against opponents.
Oliver Stoner-German is a sophomore at the University of Arizona studying computer science and economics. He's also Venture Valley's first tournament winner .
Stoner-German found Venture Valley by walking around campus. He saw a Venture Valley competition flyer, started playing, and ended up winning, taking home the $2,500 prize. Afterward, he flew to Chicago for the Collegiate Entrepreneurs Organization's 39th Annual Global Conference & Pitch Competition and won $10,000.
Stoner-German learned from the game's quick, dynamic business world to market his real-life venture at the University of Arizona, Shelp — Student Help . Shelp is a peer-to-peer marketplace where students can request help with tutoring, cleaning up their room, moving in, or anything they can think of. Stoner-German created Shelp after he realized there wasn't a place where students could ask for help from other students. He said he saw tons of Snapchat stories of people asking for help and offering cash in return.
"I was like, there has to be a more secure and better way to do that," he told BestColleges. With Shelp, students can scroll through requests on the job board, message the poster, and make money.
"Most of the time, I found that if I asked my friends for advice or help with something, they would be more knowledgeable than the university itself because they were actually on the ground and going through everything," Stoner-German said.
Shelp fully launched in February and has about 1,000 downloads. But it didn't start as a hit. Stoner-German had to pivot his marketing strategy when the app soft-launched at the end of last year — something he learned from Venture Valley.
He said the biggest lesson Venture Valley taught him was how to react to the market and quickly pivot his strategy. In Venture Valley, each player's in-game businesses affect the market and player revenue through changes in employee wages, business type, selling prices, and marketing.
The Shelp team realized no one was downloading their app because no one knew about it, so they quickly started hosting events, offering rewards programs, and letting people know what the app is and how to use it.
Venture Valley helped Stoner-German with his first business — and it inspires most of its other players to start thinking about starting their own.
Venture Valley found that almost 70% of college students in its recent survey were more interested in starting businesses after playing the game. "These survey results continue to validate the power of gamified learning and further affirm the effectiveness of the Venture Valley game in teaching entrepreneurship and financial literacy," Singleton Foundation CEO Shelley Miles said in a press release. "The Venture Valley game will continue to empower this generation of students to navigate the complexities of the business world with confidence and strategic proficiencies."
The study also found that over 80% of college students thought the game was an effective way to teach business and entrepreneurship . And students aren't the only ones — professors are noticing, too.
"I was impressed by the description of the game since it enables students to apply fundamental business concepts in a fast-paced structure that the students find enjoyable and exciting," Tony Garcia, a finance department professor at Seton Hall University's Stillman School of Business, told BestColleges.
"I regard the game as a learning technique that is related to the case method since it requires the application of business concepts to a particular business situation." Garcia said he encouraged his students to participate in Venture Valley's collegiate cup and apply the concepts they learned from the app in class.
"Seeing how these puzzle pieces relate to each other helps the students understand a business as a complete picture rather than as a series of unrelated pieces," Garcia said.
According to Stoner-German, succeeding as an entrepreneur goes beyond what you learn in class — or in a video game. "You have to be the marketer, the coder, the finance person, and it's really fun and fulfilling," he told BestColleges.
"If you love the problem that you're solving and love your product and are really passionate about that, my biggest advice is to make sure that if you're going to pursue entrepreneurship, that you have to actually love the problem that you're solving and actually have to love the product."
This story was produced by BestColleges and reviewed and distributed by Stacker Media.
© Stacker Media, LLC.
This story was originally published May 10, 2024, 10:00 AM.
Get unlimited digital access
Try 1 month for $1
JetBlue bans political displays after antisemitism accusations
Too many flight attendants live out of cars, report shows
A top student loan company allegedly told staff to keep borrowers on hold
Newest WNBA team announces eye-catching new team name
U.S. airlines challenge Biden administration’s new transparency rules
Carnival Cruise Line takes a stand on cruise ship ducks
Foster Garvey Celebrates Entrepreneurship at 2024 Washington State University's Business Plan Competition
Foster Garvey is proud to have sponsored this year's Washington State University (WSU) Business Plan Competition . This event serves as a vital platform for student entrepreneurs to showcase their ideas, interact with seasoned entrepreneurs and compete for significant prize money.
This year’s standout, HappyPop , secured the $5,000 prize offered in the “ Foster Garvey Open Collegiate League ”. Founded by University of Washington undergraduates, HappyPop has introduced a twist to the snack market with their popped sorghum product. Inspired by traditional Indian flavors and modernized with a range of popular tastes, HappyPop caters to a growing market of health-conscious consumers.
Reflecting on the competition, Dan Wadkins , who served as a judge for the Foster Garvey League, praised the high level of participation and the quality of the business plans presented. "It’s inspiring to see such entrepreneurial drive among students," Dan remarked. "HappyPop's focus on a healthy lifestyle and innovative flavors particularly impressed the judges."
Foster Garvey extends its congratulations to all the participants of the competition, with a special mention to HappyPop for their outstanding achievement. We are eager to see how these young entrepreneurs will continue to evolve and impact their industries.

Related Services
- Food & Beverage
- Payment Portal
- Attorney Advertising
- Privacy & Disclaimer
© 2024 Foster Garvey PC. All Rights Reserved. Site by Firmseek
We use cookies to improve your experience on our website. By continuing to use our website, you agree to the use of cookies. To learn more about how we use cookies, please see our Cookie Policy .
Newsmoor.com is an educational website for online learning. It Provides information: on verbal and nonverbal communication elements, noise, models, and theories, print, broadcast, and online journalism, and feature article writing. It also includes business models, theories, plans, profile examples, advantages and disadvantages of several models, facts, research methodology, research proposal writing, assignment writing, a study abroad, including top public and private universities and educational consultants.
Business Plan Examples and Sample For Students
Business Plan Examples For Students. Business Proposal Examples for Students. Also, Business Plan Sample pdf for Students. Business Plan Examples For Students Entrepreneurship PDF.
Business Plan
The business plan refers to the company’s written statement explaining the company’s background and business details. This plan includes the executive summary of the company, product and service, operation, marketing, and financial plan.
The employee creates the business plan to represent and improve the organization’s image to stakeholders, customers, and affiliates. It proposes the business strategy entirely mentioning how the company profits and survives in markets. So, a business plan is also known as a business proposal that is crucial for corporate branding. The business plan is essential for every company to build rapport with stakeholders and business partners as well as achieve competitiveness.
The key elements of a business plan or proposal are an executive summary, background, product and service, organizational structure , sales and marketing strategy, financial and operational plan, and more.
Business Plan Examples
A business plan example refers to a business proposal sample that thoroughly explains the business, including the executive summary of the financial statement. It is also known as a business report example or business proposal format. An example of a business plan certainly includes the executive summary of the business, operating strategy, start-up financial projections, financial projections, etc. The business plan example for students is also known as the business report format.
Business plan writing is a mandatory assignment for students in entrepreneurship. It is also a compulsory assignment for business students. The importance of a business plan is growing day by day for selling products on digital platforms and managing the organization virtually.
The business proposal is also compulsory for getting a bank loan. The organization needs it to make agreements with other organizations. The bank authority surely asks the organization to submit a business plan with the bank loan application. The other names of a business plan are business proposal, report, profile, and more. A business plan example is also known as an example of a company profile , business proposal example, sample, and format.
Elements of Business Plan Example
The Nine Components of a Business Plan are as follows:
Business Plan Examples For Student Entrepreneurship
Today, the authors present a business plan example for students. They wrote it while they were students in entrepreneurship courses at the Faculty of Economics and Management University Putra Malaysia (UPM). The lecturer sets group assignments for the students; therefore, the students make the business plan example to complete the group assignment. Thus, this business plan or proposal example for students certainly assists business administration students. It also assists students in BBA, MBA, economics, finance, and business communication courses and researchers.
The author also wrote business plan examples for students about food and an Example of Business Report.

The students set the company name “BambooS.” It sells reusable and eco-friendly bamboo straws. Straws are a unique product in Malaysia that can be customized for length and diameter. Besides, the company offers engraving services for customers. So, customers can customize a meaningful word on the bamboo straw for engraving. In addition, it provides a designed pouch as packaging for our straw that looks smart.
Business Plan Example For Students

1.0 Executive Summary Of Business Plan
BambooS Sdn. Bhd. company was created by a group of 10 students in the Basic Entrepreneurship course. This company is named BambooS. It produces and sells bamboo-based products. The capital S in the company’s name stands for straw. The original idea came from a student. And we chose Bamboo as the main ingredient of the products. Currently, we focus on producing eco-friendly straws to serve our customers. The products are the best quality yet affordable straws.
Our product is also biodegradable as it is made from Bamboo. We also guarantee that customers can use our products many times. It is reusable and easy to wash and carry. The straw size is customizable. So customers choose the size based on their preferences. In addition, our specialty is not only in our product but also in our packaging.
There are ten members in a group and each member will contribute RM 100. The total paid-up capital is RM 1000. We set up our warehouse in the Serdang area to produce, package, and store our products. We are making the straw as per the customer’s demand and request. For the marketing part, we are advertising and promoting our product through social media sites, such as WhatsApp, Instagram, and Facebook, and e-commerce, such as Shopee. We adopt the lean canvas business model tool to assess the outcome of the business.
2.0 Background of the Company

2.2 Company overview

2.3 Vision And Mission Statement
2.3.1 vision statement.
To become the most notable company in Malaysia for producing eco-friendly bamboo straws.
2.3.2 Mission Statement
We want to fulfill the objective of satisfying customers with our eco-friendly products. We want to reduce pollution by using reusable straws anywhere and anytime.
2.4 Keys To Success
The Keys to Success for BambooS Include the following:
Table: 4 Keys of Success
2.5 Organizational Chart

3.0 Administration anD Human Resource Plan
3.1 business strategies.
Business strategy is crucial to maintain business growth.
The personal preferences of corporate management do not influence good business strategies. We emphasize every department’s function. It ensures the plans run smoothly to meet goals. We need to achieve them. We have put as much emphasis on the efficiency of each Department.
Our company has set several strategies to achieve the company objectives. However, these strategies have been made based on every Department’s suggestion.
a. Administration and Human Resources Department
- The admin and human resource department monitors all the business operations. It manages employees’ and management problems.
- It also solves problems that affect people management programs in the long run.
- Moreover, it follows the five-gap model of service quality to ensure service quality.
b. Marketing Department
- This department handles marketing of the product and promotional activities in order to reach the products to a vast amount of potential clients.
- It also promotes the business and mission of an organization through social media.
c. Operational Department
- This department ensures that all the equipment and material are ready to run the operation smoothly. It ensures that all products are of good quality. This department follows the eight principles of TQM to ensure product and service quality.
- Additionally, this department has the ultimate accountability for profit and loss and seeks to maximize shareholder return on investment.
3.2 Management Team

3.3 Job Descriptions

4.0 Market Plan
4.1 introduction.
BambooS Sdn. Bhd. support the “Save The Earth” campaign by producing eco-friendly Bamboo straws. These straws are environmentally friendly products. Therefore, these products are alternatives to plastic straws. The government has imposed restrictions on the use of plastic straws. They also create social awareness of to use of natural products.
Hence, It is an important driving factor of our market strategy. In addition, the surging demand for drinking beverages, including juices and Boba drinks and then the save the turtle campaign, is also propelling the demand for bamboo straws across the globe. Bamboo straws are reusable compared to plastic; they are better for health, durable & robust, and it is an environmentally friendly product. The products will contribute to reducing global warming and preventing climate change globally .
4.2 Objective of Marketing
Our objective in producing Bamboo straws is to encourage consumers to use natural, eco-friendly products. Why are bamboo straws better than metal? Firstly, Bamboo comes from a natural source. So it is naturally sturdy and easy to collect. We do not need to use chemicals to make straws.
Additionally, metal straws are not pocket-friendly compared to Bamboo. Moreover, metal will rust when in contact with water and oxygen. Bamboo stock is much cheaper, less work, and easy to collect. Our marketing strategy will focus mainly on reusable principles and are much more trendy to youngsters because we have an engraving service to attract them.
4.3 Analysis of Marketing
4.3.1 market trend.
The demand for bamboo straws has risen due to growing environmental attention. Additionally, plastic straws have been reduced due to state restrictions. However, the bamboo straw market is expected to achieve high growth shortly. In addition, BambooS Sdn. Bhd is a unique company in Malaysia. We produce our straw ourselves, and we provide safety and hygiene assurance. The buyer can engrave their name on the straw. Nowadays, customers want recognition for something they buy or support. They are also sincere about ‘Save the Earth’ and deserve to flex.
4.3.2 External Environment Analysis
Our first demographic psychographic and geographic target market is the University Putra Malaysia (UPM). Since we are students of UPM, it is easier to approach our target customers, including students and staff. Students tend to bring their water bottles or flasks to classes. It is one step toward being environmentally friendly; thus, we promote their effort by selling bamboo straws. In addition, we will promote our product at cafes or food courts at the faculty and library. We also establish a booth at super shops.
4.3.3 Internal Environment Analysis
(SWOT ANALYSIS)

4.3.4 Market Opportunities
Our bamboo straw comes with a pouch; thus, it is hygienic and easy to bring everywhere. We also provide a small brush to ensure deep cleaning of the inner straw. Our product is able to be used again and again. So students and staff can save money. They do not need to bring straws in large volumes. The structure of our bamboo straw is strong and sturdy; thus, it will not break if soaked in water for a long time, unlike paper straws.
4.4 Target Market
4.4.1 segmentation.
- S size is fit for ordinary drinks, fully liquid
- L size is suited for Boba drink or any drink that has topping.
- People use straws for drinking tea, juice, frappe, and Boba.
- Restaurants, cafes, food court, canteen, food stalls, super shops around UPM
4.4.2 Consumer Market and Buyer Behaviour
(i) Students and staff at UPM (ii) Cafe and Restaurant at UPM
4.4.3 Positioning
- New business strategy for eco-friendly products in the market.
- Our production, process, and packaging materials match zero pollution.
- Providing Engraved service
- Customized and Eco-friendly bamboo straws of different sizes
- Made of organic material
- Unique punch made by the jute bag.
4.5 4 P’s Marketing Strategy
4.5.1 product strategy.
To make our product unique, we ensure the quality and safety of our products always satisfy our customers.
Our product comes neatly packaged in a unique eco-friendly punch. It is made of a jute bag. The natural bag is designed to make people use bamboo straws every day.
Labeling/Customised
Our company provides customized products. We resize and engrave the bamboo straws to attract more customers. So, our customers can request any size and imprint their straw with any logo or design they like. Our product comes in two sizes: the regular size for the standard drink, fully liquid, and the large size for the Boba drink or drink that has topped. Customers can send us their logo or name on social media sites. Personalized bamboo straws look fantastic across social media.
4.5.2 Price Strategy
Price is the payment given by one party to the other in order to get the return for goods or services. It is necessary as it determines our profit and business survival. Two factors affect our pricing strategy to increase our profits. The internal factor that affects our pricing strategy is production and management cost. At the same time, the external factor is the competitive environment.
Our management team decided to sell the straw in four sets: A, B, C, and D. Our company decided to set the price at RM 10.00 for set A. This set includes the common Bamboo straw, brush, and pouch. Then SET B cost RM 12.00, including the Boba size straw, brush, and pouch. SET C and SET D are more special because they include the engraving service. The engraving cost is RM 8.00 for each Set. As we mentioned before, we resize products for clients. So our customers can personally request to resize the straw. We charge it costs RM 9.00 per set.
4.5.3 Place Strategy
Place strategy is also known as distribution strategy, wherein the organization decides the mode of distribution for the product. The pacing strategy plays an important role in selling the products. We have chosen the market, cafe, or restaurant adjacent to the University Putra Malaysia. Our main target market is UPM staff and students.
Furthermore, we also decided to make it easy for our customers to find our product by using the shopping app, Shopee apps. We chose these apps because Shopee is the best option if you want to start selling online at a low cost and big money.
4.5.4 Promotion Strategy
Promotion is the advertising process to provide information to different parties about the products. It is a communication process that influences the customer to buy products. In order to get customers’ attention and obtain a more significant market share, Bamboos Sdn. Bhd uses digital and internet marketing.
We have set up social media accounts, Instagram, Facebook, Shopee, and Blogspot, to promote our business. The marketing team will upload the promotional content to social media sites. This is because most people stay on social media sites mostly. With that, social media sites are the easiest way to buy anything we want without going out. Moreover, online shopping has become popular in this era, and all these social media sites have become the hottest sites, especially Instagram, which has a high rating in advertisements. Many companies use social media to sell their products and services by putting corporate information in their accounts.
Social Media Advantages
Social media are free sites where we can reach a large number of customers. Hence, we use social media to do hard and soft selling.
We fully develop every post to attract customers. In addition, we will always update our posts and story feeds. We ensure that customers are more exposed to our product. Next, we also use social media hashtags. We use hashtags such as #Bamboos, #SafeTheEarth, and more to make it easier for customers. The marketing team uses social media for the ordering process.
Similarly, we will place the generated links on each social media to encourage the product ordering process. Our company also makes sure transactions with our customers are easy. Finally, we also produce videos to promote our sales. The video will achieve the highest social media reach for views and engagement.
We tend to focus more on WhatsApp groups, Shopee, and Instagram since our target audience is UPM students. Many students are involved in WhatsApp groups, such as on faculty, college, hostels, and clubs. WhatsApp and Instagram are more popular among students as the places they spend most of their time. WhatsApp is the most popular social media site in Malaysia.
5.0 operations planning
5.1 location and address.
We will mainly sell the straw on social media sites. The production team will handle the production process. They resize and wash the Bamboo at the warehouse in Selangor, Malaysia. The social media sites are Instagram, Facebook, Shopee, Blogspot, and WhatsApp. Supplies will be directly delivered to the responsible members for further processing based on our buyer’s order.
5.2 Objective of Operations
We aim to produce and deliver good quality Bamboo Straw. Our team ensures that all products are effective and attractive. We also must gain customers’ trust and happiness with our service, including price and delivery. We also make sure our products are cleaned and safe for use. Our team is very responsive to making good-quality straws. In addition, our company has ultimate responsibility for profit and loss. However, we seek partners for more investment.
5.3 Operation Strategies
A few strategies have been set up to ensure that our business runs smoothly throughout the week and meets our objectives.

5.4 Supplier
The bamboo stock was from a supplier via the Shopee platform, and the pouch supplies were from Giftstalk Sdn. Bhd. The company logo’s printing service was also included when we ordered the pouch from suppliers. Moreover, we order coconut fiber cleaning brush stock and packing Boxes from Shopee. We also surveyed purchasing and made sure that our supplies were reasonable. All the supplies are ordered online and delivered to our company via specialized courier service companies.
The bamboo straw will be customized and delivered to the customer using J&T Express, Ninja Van, and cash-on-delivery service, which will ease our delivery.
Thus, we have decided on the following suppliers as our supply providers:
- Wing.DIY – Shopee- For Bamboo Stock
- GIFTSTALK SDN BHD)- For Pouch Supplies
- Gd. Pack -Shopee)- For Paper Boxes Stock – Sandpaper Holder with Plastic.
5.5 Process Planning

5.6 Implementation Schedule

5.7 Machinery and Equipment Including GST
6.0 Financial Plan
6.1 introduction.
A financial plan can be defined as a process of framing procedures and budgets regarding the financial activities of concern. This is done to ensure good financial and investment procedures.
Generally, the financial plan is used to know an investor’s current pay and future financial state by using current known variables to predict future income, asset values, and withdrawal plans.
A financial plan is one of the most crucial parts of a business. Some of the importance of a financial plan are:
- A financial plan provides the direction of one’s business.
- It also helps understand how finances impact one’s business.
- Additionally, it helps to manage income better.
6.2 Purpose of the Financial Department
A few purposes are as below:
- Firstly, it determines capital conditions.
- Secondly, it operates the fund nicely for different purposes.
- Finally, it maintains proper cash flow.
6.3 Project Implementation Cost

Source of Fund
Our money is used as the start-up capital with a contribution of RM100.00 per shareholder, bringing the total investment to RM 1000.00.
6.4 List of Expenses
Twelve partners funded a total of RM1000.00 to cover all business costs, which is RM 617.29. Expenses are in terms of buying raw materials, equipment, and delivery fees. We will not invest all amount to the business.
The equipment is counted as fixed cost as they are bought in bulk. Refer to 6.4 (List of Expenses) for detailed information.
6.5 Record of List of Sales
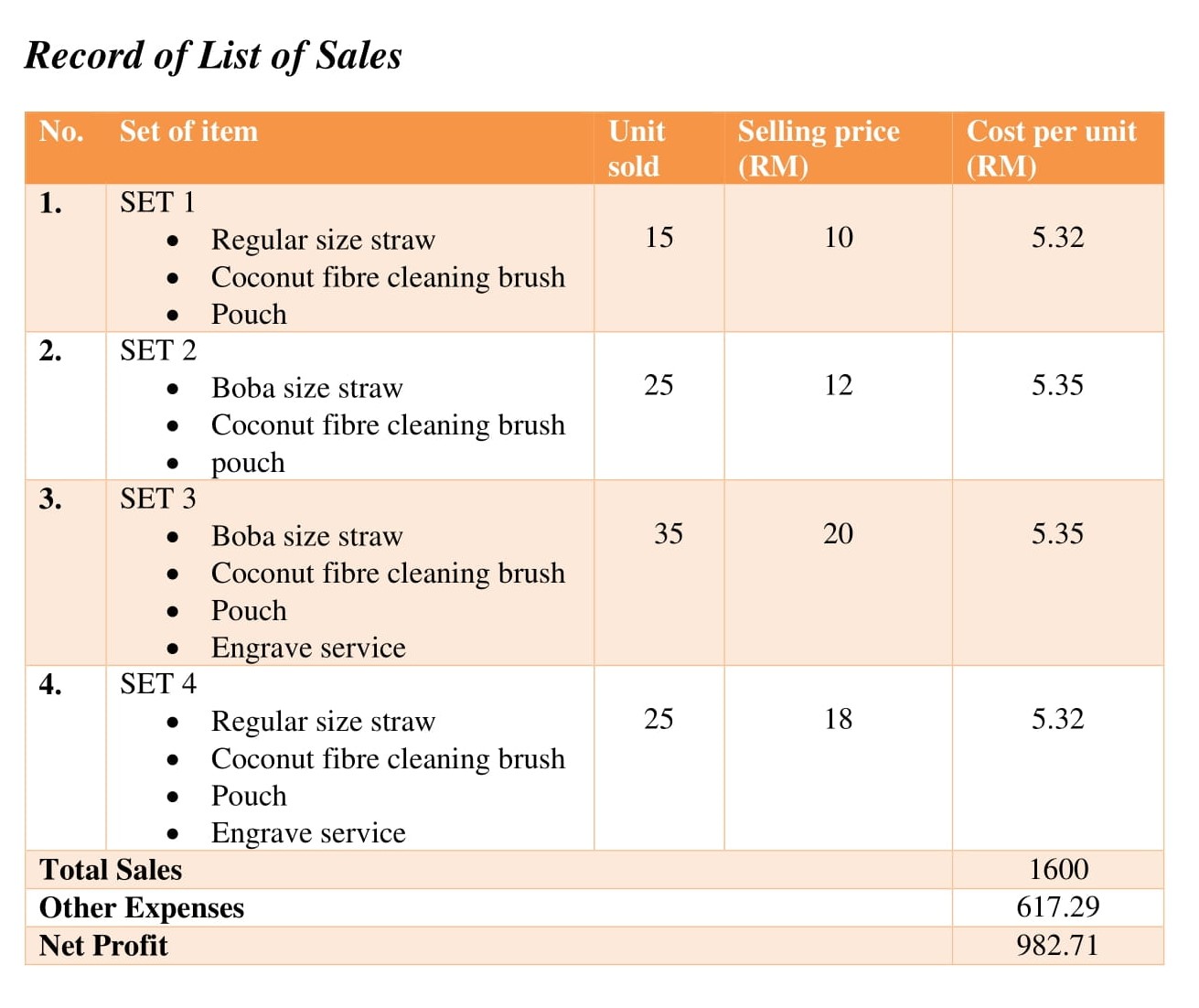
6.6 Income Statement
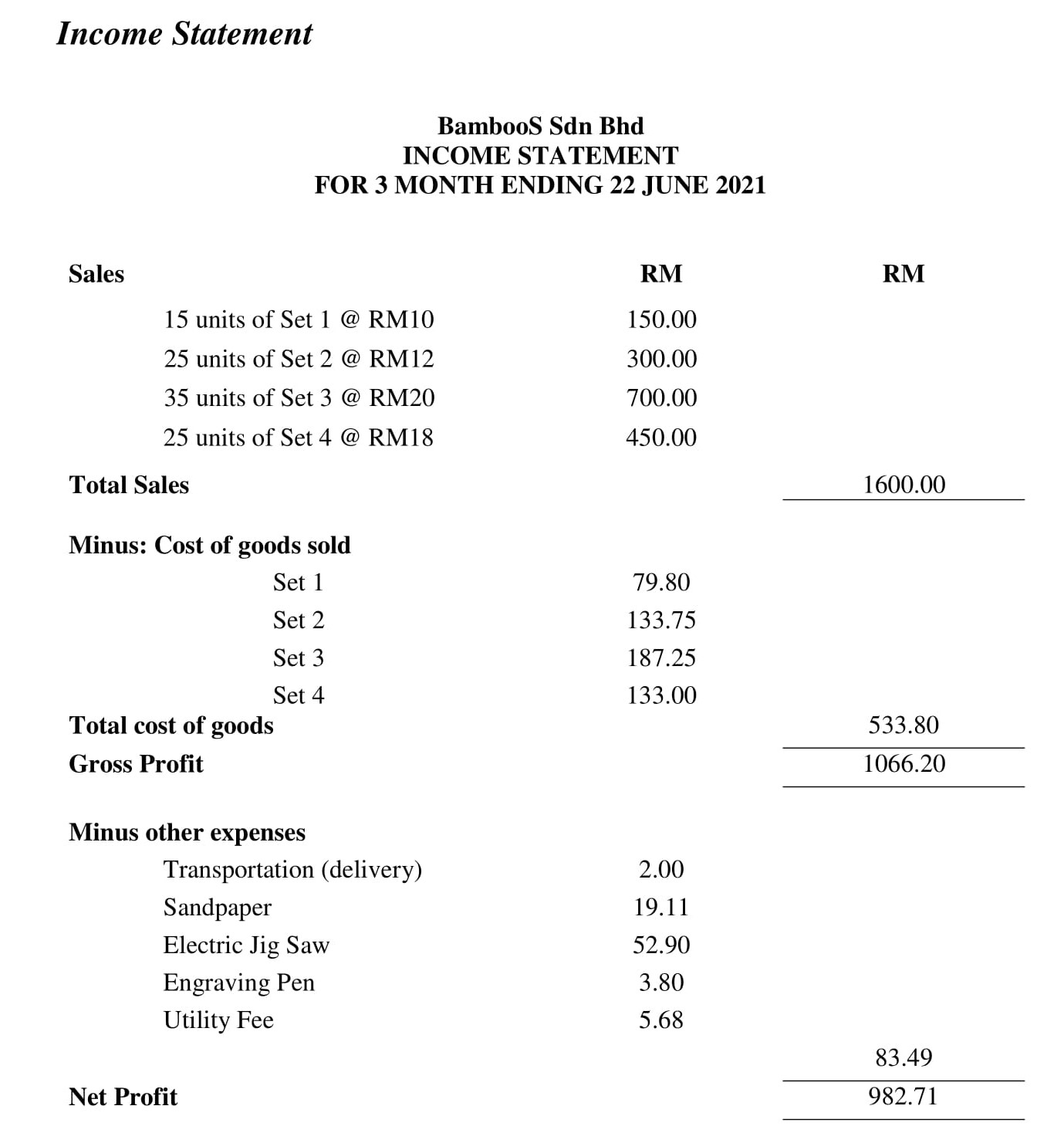
After one month of business, BambooS ended up with RM 1600.00 from 7 different products. This includes selling 15 units of Set 1, 25 of Set 2, 35 of Set 3, and 30 of Set 4. Leftovers for bamboo straws are found. The income statement shows that the business’s net profit after one month of operation is RM 988.39, approximately 98.8% of capital invested into the business.
6.7 Cash Flow Statement

The case flow statement shows that the initial capital on hand is RM 1000.00, and at the end of the business, the total surplus (after deducting all expenses) is RM 1982.71.
The RM 1982.71 includes RM 100 capital invested by every shareholder at the beginning of the business. By dividing the remaining money after deduction, each shareholder would find themselves receiving an extra RM 98.27. Hence, every
6.8 Balance Sheet
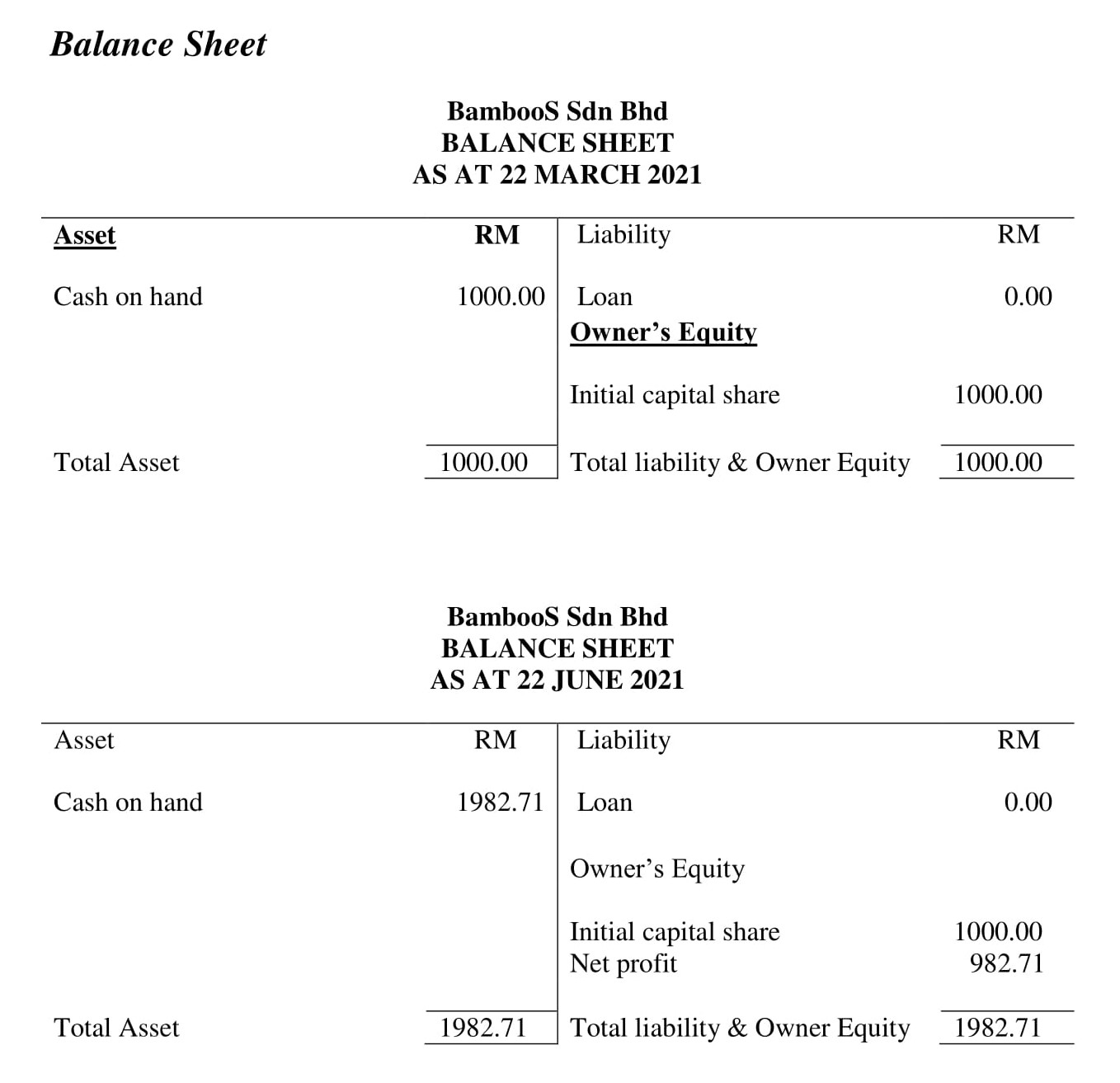
At the start of the business (22 March 2021), the initial capital share is RM 300.00. There is no liability such as a loan.
At the end of 9 weeks’ business (22 June 2021), the cash on hand increased to RM 1982.71, as well as the owner’s equity. The firm’s net worth is RM 1982.71, done by subtracting liabilities from assets.
6.9 Financial Analysis
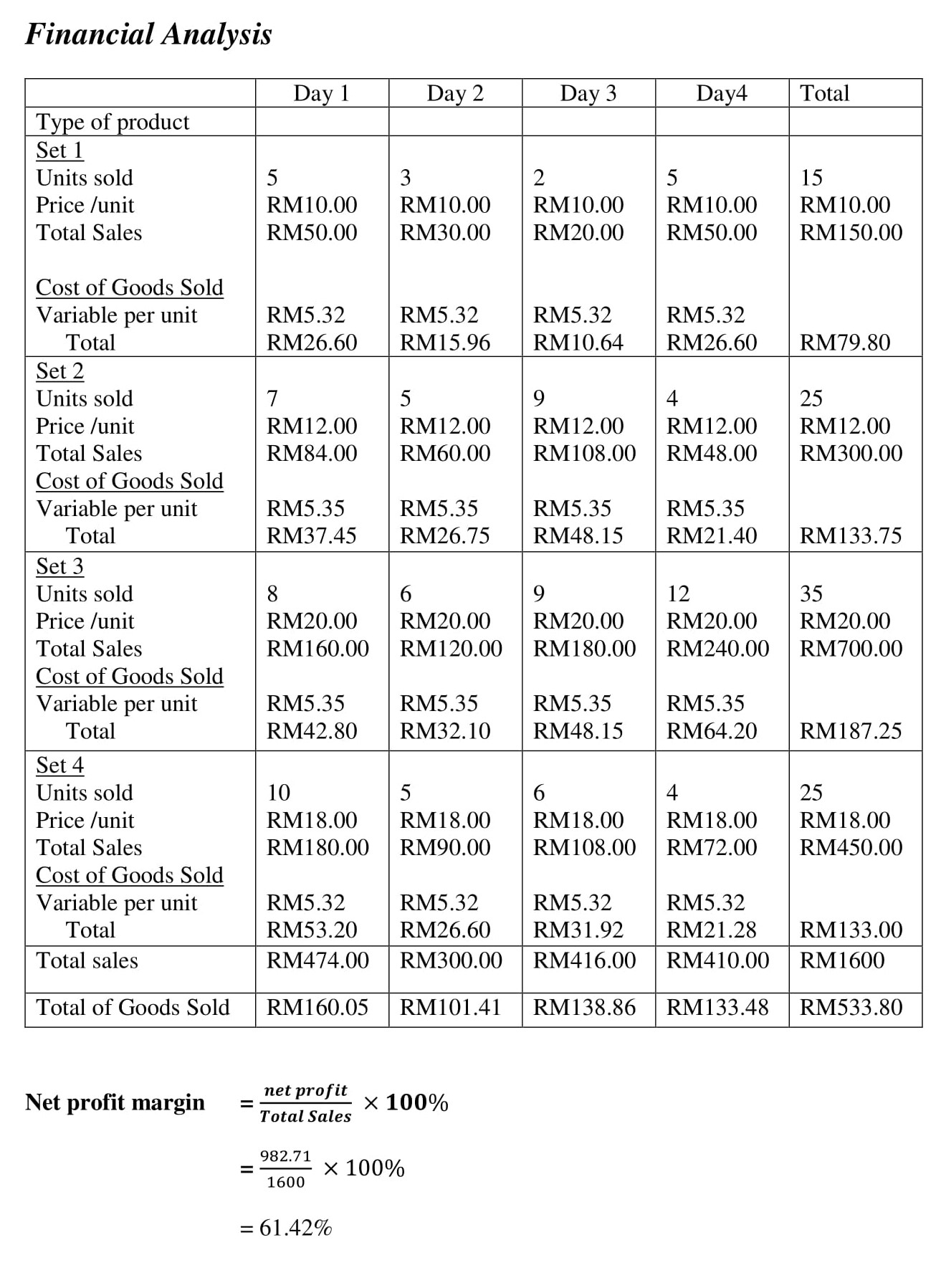
BambooS has a net profit margin of 61.42%. BambooS also has a break-even point of RM 126.50. Sales passing this break-even point means that BambooS can start making profits.
Set 1 has a break-even point of RM 11.90, and set 2 have it at RM 23.72. The break-even point for set 3 is RM 55.34, while set 4 has a break-even point of RM 35.58.
The interest for the business is 0.9827 or 98.27%. This means for every RM 1 capital invested in the business; the shareholders can get back RM 0.98 as profit.
7.0 Conclusion
Based on the business plan template or business proposal example that we have made, BambooS will give us profitable returns. The assumptions we made for these three months are conservative as we know that our company is still in the beginning, and the marketing and promotion are still in the early phase. The company sets systematic planning to reach the target. Thus, BambooS is very confident that our company will be able to grow in the future and become the most popular brand in the world.
We will always ensure that everyone in the company cooperates well in order to achieve the business target profit. We hope that BambooS will be the best company for producing eco-friendly straws in Malaysia. Our company assists UPM students and staff in reducing plastic usage.
Problem Faced and Solutions in Business
Every business will need to face many challenges to sustain success. As a new business, we also must face many things to achieve our business goal.
Firstly, we confirmed the product we would sell; everyone gave their opinions and ideas. This leads to 10 different products and services on the list. So we need to vote for the best one. We had faced a healthy argument on picking the best product. After discussion, we finally came out with the idea of producing an eco-friendly product. We focused on global warming issues and finally decided to produce and sell bamboo straws.
Moreover, we also have to face a conflict in fixing the vendors. We need to find the best vendors that offer the most reasonable price for us to produce the bamboo straw. The cost must be tele with our starting capital. In order to solve this, everyone has done their research on all the possible suppliers until we find the best one to choose from.
To avoid extreme market competitors, our team chose a blue ocean strategy to create a new market to achieve competitive advantages.
Business Proposal Examples For Students PDF
A business proposal is a short business plan. The business proposal describes the business process. However, a business proposal includes an executive summary, problem statements, product, finance, and solution. The example of a business proposal for students certainly guides others to create a business plan. This business plan sample teaches how to write business plan assignments for students. Students might learn how to write a simple business plan and proposal.
The importance of a business plan is crucial to stakeholders, employees, students, and entrepreneurs. Additionally, the business plan example assists employees in creating a professional business proposal.
Author: M M Kobiruzzaman
M M Kobiruzzaman, Content Writer View all posts by M M Kobiruzzaman
16 thoughts on “Business Plan Examples and Sample For Students”
this is wonderful ,,nice work
I need more info
Nice work keep on educating me I bet your help
Good Day! Can I ask your permission to use your template in my class discussion? It is very detailed and all the components present in this format.
Yes, You Can.
Great work,keep it up
great article . check out datatoleas.com
This template is the best I have seen It’s so detailed You have everything you are looking for
It’s a good sample for up coming entrepreneurs,keep it up 👍🏻
Mr Kobiruzzaman thanks so much am Kimera Kenneth from Uganda but your content is so useful.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Connecticut Small Business Development Center
Navigating entrepreneurship as an international student: visa and financing.

Live webinar event: May 29, 10 AM – 11:30 AM
If you’re an international student wanting to start a business but unsure about your immigration status and its implications, this webinar is for you!
Join Immigration Attorney Dana Bucin and CTSBDC Business Advisor Greg Lewis as they discuss immigration options available to international student entrepreneurs and the resources available to start a business.
This is a 90-minute virtual presentation that will cover important topics such as:
- US visas: How the system works.
- Visa options for international students and entrepreneurs.
- Tips and tactics for navigating employer sponsorships.
- Advantages and challenges of starting a business while being a student and after graduation.
- Balancing studying and working in the US.
We welcome your questions during and after the presentation.
This event is free to attend, but registration is required. After registering, please complete the pre-event survey and submit your questions about start-ups and issues related to entrepreneurship as an international student. Instructions:
You will receive an automatically generated e-mail after registration, including the WebEx and call-in details towards the bottom. We also send a reminder containing the join-in details 24 hrs. in advance of the event. Please note automated e-mails are sometimes re-routed to spam/junk boxes by e-mail providers
Register here
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Begin typing your search above and press return to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Business and Entrepreneurship
Network & navigate + faculty profile: beth ryan.
As part of BUSE #275-02 Self-Management & Freelancing course, the students organized a networking event to interact with professionals in their fields of interest. Since the content of the course focuses on preparing students for self-sustaining careers, the students wanted a chance to practice their networking skills with industry professionals. The instructor, Beth Ryan, responded to the students’ request and engaged them in the planning and execution of the event. The 46 students, representative of majors across the college, organized themselves into groups to plan, invite, and host local freelancers and entrepreneurs in creative industries such as photographers, videographers, illustrators, designers, music journalists, A&R reps, filmmakers, fashion stylists, branding experts and web developers, and social media experts.
This hands-on approach not only empowered students to take ownership of their learning but also fostered the development of essential skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and self-confidence. Through this event, they strengthened their networking abilities, essential for navigating the intricacies of creative industries. As they venture into self-sustaining careers, this served as an invaluable stepping stone to enhance their resumes and portfolios.

Faculty profile with Beth Ryan

Photo credit: Charles Hammond Jr.
Congratulations on your recent promotion to Professor of Instruction! How has this transition impacted your role within the Business and Entrepreneurship department?
It’s exciting to be a Professor of Instruction as I was one of the early members in the teaching track process at Columbia. This achievement is a result of the persistence and dedication aligned with the entrepreneurial spirit of our department. In addition to creating the student-led event, Network & Navigate, I have been creatively engaged at the College in other ways. I am particularly proud of being nominated by students to be a speaker at the TEDx Impulse Impact Columbia College . The inspiration for my Impulse. Action. Impact TEDx talk came from life experience as a creative professional. I have also been asked by college leadership to serve as the emcee for two of the 2024 commencement ceremonies, which is an incredible honor.
Can you share some insights into the recent networking event, “Network and Navigate,” organized by the students of the Self-Management & Freelancing course?
The idea for the event came from listening to the students in class and then pivoting to meet their needs. I responded to the student’s interest in an opportunity for some real-life networking experience and designed the second half of the course to co-create an inclusive event to bring industry connections to them. Students were able to build their ‘value network’ by meeting and interacting with creative industry professionals who provided advice and insights to help them navigate career paths beyond the classroom. Students articulated that networking events are often anxiety-producing, so I let them take the lead by inviting industry professionals and planning an event that would be more comfortable and inclusive.
Can you speak to the importance of experiential learning opportunities, such as networking events, in preparing students for self-sustaining careers in creative industries?
Giving students agency in-class activities empowers them to think and behave in creative and professional ways while increasing their abilities to critically think and problem-solve. Providing students with the hands-on opportunity of planning the event engaged them in their learning and helped them discover talents they didn’t know they had. It is a joyful experience to watch their self-confidence and self-efficacy skills increase as a result of planning and executing a creative industry project. Plus, they have real-life achievements to add to their resumes and portfolios.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Objectives. The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper's Cup are below: To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3. Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3. Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
LivePlan's business plan examples help students turn ideas into top-notch business plans for class projects and startups. The tools, features, and instructional content allow you to focus on bringing out the best in your students for every plan and project. Before using LivePlan, my students were intimidated by the business planning process.
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs, one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast ...
Get Started with ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Students. Students who are aspiring entrepreneurs or learning about business management can use the ClickUp Business Plan Template to develop a comprehensive and structured plan for their business idea. First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace.
2. Start a tutoring business. Help high school students with summer studies or younger students prep for the college classes you aced last semester. You can advertise your services on campus and across other marketing channels. Use a simple ecommerce website to sell time slots and showcase your skills and offerings. 3.
Many ambitious students will ask the question of whether you can start a business at university. The answer is a resounding yes. More than one in four, 26% of students plan to start a business ...
This reflects a key component of the entrepreneurial mindset— the ability to view mistakes as opportunities. In your classroom: Build into your course some opportunities for students to make mistakes. Show them how mistakes are an opportunity to learn and improve. In entrepreneurship speak, this is called a "pivot.".
And How to Create One. 1. Executive summary. This is a short section that introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, your goals for developing it, and why it will be successful.
Step 2: Describe Your Company. Your company description is the second component of your business plan. This section shows who you are, the problems your business solves, your goals, and why you are different. I'll illustrate using Yellow Leaf Hammocks.
Chapter 1 - Developing a Business Plan. Chapter 2 - Essential Initial Research. Chapter 3 - Business Models. Chapter 4 - Initial Business Plan Draft. Chapter 5 - Making the Business Plan Realistic. Chapter 6 - Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur. Chapter 7 - Finishing the Business Plan.
Supports any student entrepreneur interested in starting a new business or developing a product, as well as participants in the Entrepreneurship Bootcamp for Veterans (EBV) program. ... A business plan is "a guide—a roadmap for your business that outlines goals and details how you plan to achieve those goals."--Tim Berry from Bplans site.
Build a Business Plan. Who It's For: Middle School and High School. Cost: Free. Location: Anywhere (online) Check out this plug n' play business plan creator! You could send your students to this page to work through a business idea of theirs. Then, at the end, they can print out their business plan! Questions they'll need to answer include ...
This marks the completion of a thorough template for a university student entrepreneurship plan. Organize your materials in line with the provided information, and you're bound to make a lasting impression. Try Boardmix for Free. Conclusion. In the process of entrepreneurial planning, conducting extensive business analysis and planning is ...
Rice University Business Plan Competition. A virtual three-day competition that accounts for pitches, feedback, and judge interaction, designed to give entrepreneurs real-world experience. What you need: A business in the seed, startup, or early growth stages; Who can apply: Any full-time or part-time U.S. graduate students. Teams must have at ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
One defines student entrepreneurs as students who are engaged in preparing a business plan for a new or existing growth-oriented business (Katz et al., 2000). The second views student entrepreneurs as individuals who are actively pursuing academic coursework and are running a company at the same time (Ridder & Van Der Sijde, 2006).
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
Re-imagining the business plan for students. While the terms 'enterprise' and 'entrepreneurship' are often used interchangeably, there is a distinct difference between them, especially within the context of technical, vocational education and training (TVET). 'Enterprising' activities, which many TVET providers already focus on ...
Objectives/Purposes: In this introductory lesson, students will be able to: (1) describe what an entrepreneur is, (2) describe what a business plan is, and (3) begin creating a concept statement. Knowledge@Wharton Article: How Entrepreneurs Can Create Effective Business Plans (just the first section) Other Resources/Materials:
When looking at business plan template packages for teens, you are looking for business plan templates that will help you transition your business ideas to full-fledged businesses that will help adults see the vision. The 7 parts of a business plan include: Executive Summary; Business Description; Products and Services; Market Analysis
KMLP 11th Grade - The Entrepreneur's Journey: This lesson plan shows students the path of entrepreneurship, from having an idea to scaling a product. They watch videos, read articles, and research a famous entrepreneur as they learn the ins and outs of starting a business. 11th Grade Entrepreneurship Worksheets. Tracking Income for a ...
This section of your simple business plan template explores how to structure and operate your business. Details include the type of business organization your startup will take, roles and ...
Table for revised WHT 2018-2022. English 6 Q3 Week 1. Abaigarlessonplan-3 - Grade 9Lesson plan. LP4 Math-8 5-Triangle-Inequality. List of Student Teachers copy. Reseaerch 123.
There is a lot more to being an entrepreneur than coming up with a great business idea. No one knows this better than the students who participated in the Cornell Hospitality Business Plan Competition, presented by the Leland C. and Mary M. Institute for Hospitality Entrepreneurship at the School of Hotel Administration.
This Spring, Mercy University's School of Business hosted its 5th Annual Student-Preneur Conference to inspire future innovators. Sponsored by the Beba Innovation & Entrepreneurship Foundation, the event featured guest speakers, an entrepreneurial alliance panel, an entrepreneur expo, and the business plan competition finale, during which students got to display their business acumen.
The study also found that over 80% of college students thought the game was an effective way to teach business and entrepreneurship.And students aren't the only ones — professors are noticing, too.
Foster Garvey is proud to have sponsored this year's Washington State University (WSU) Business Plan Competition. This event serves as a vital platform for student entrepreneurs to showcase their ideas, interact with seasoned entrepreneurs and compete for significant prize money.
An example of a business plan certainly includes the executive summary of the business, operating strategy, start-up financial projections, financial projections, etc. The business plan example for students is also known as the business report format. Business plan writing is a mandatory assignment for students in entrepreneurship.
Visa options for international students and entrepreneurs. Tips and tactics for navigating employer sponsorships. Advantages and challenges of starting a business while being a student and after graduation. Balancing studying and working in the US. We welcome your questions during and after the presentation.
As part of BUSE #275-02 Self-Management & Freelancing course, the students organized a networking event to interact with professionals in their fields of interest. Since the content of the course focuses on preparing students for self-sustaining careers, the students wanted a chance to practice their networking skills with industry professionals. The instructor, Beth Ryan, responded to the ...