- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is Market Segmentation?
- How It Works
- Determining Your Market Segment
- Limitations
- Market Segmentation FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
Market Segmentation: Definition, Example, Types, Benefits
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/picture-53886-1440626964-5bfc2a89c9e77c005876da24.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
Market segmentation is a way of aggregating prospective buyers into groups or segments, based on demographics, geography, behavior, or psychographic factors in order to better understand and market to them.
Key Takeaways
- Market segmentation seeks to identify targeted groups of consumers to tailor products and branding in a way that is attractive to the group.
- Markets can be segmented in several ways such as geographically, demographically, or behaviorally.
- Market segmentation helps companies minimize risk by figuring out which products are the most likely to earn a share of a target market and the best ways to market and deliver those products to the market.
- With risk minimized and clarity about the marketing and delivery of a product heightened, a company can then focus its resources on efforts likely to be the most profitable.
- Market segmentation can also increase a company's demographic reach and may help the company discover products or services they hadn't previously considered.
Investopedia / Matthew Collins
Understanding Market Segmentation
Companies can generally use three criteria to identify different market segments:
- Homogeneity , or common needs within a segment
- Distinction , or being unique from other groups
- Reaction , or a similar response to the market
For example, an athletic footwear company might have market segments for basketball players and long-distance runners. As distinct groups, basketball players and long-distance runners respond to very different advertisements. Understanding these different market segments enables the athletic footwear company to market its branding appropriately.
Market segmentation is an extension of market research that seeks to identify targeted groups of consumers to tailor products and branding in a way that is attractive to the group. The objective of market segmentation is to minimize risk by determining which products have the best chances of gaining a share of a target market and determining the best way to deliver the products to the market. This allows the company to increase its overall efficiency by focusing limited resources on efforts that produce the best return on investment (ROI).
Market segmentation allows a company to increase its overall efficiency by focusing limited resources on efforts that produce the best return on investment (ROI).
Types of Market Segmentation
There are four primary types of market segmentation. However, one type can usually be split into an individual segment and an organization segment. Therefore, below are five common types of market segmentation.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is one of the simple, common methods of market segmentation. It involves breaking the market into customer demographics as age, income, gender, race, education, or occupation. This market segmentation strategy assumes that individuals with similar demographics will have similar needs.
Example: The market segmentation strategy for a new video game console may reveal that most users are young males with disposable income.
Firmographic Segmentation
Firmographic segmentation is the same concept as demographic segmentation. However, instead of analyzing individuals, this strategy looks at organizations and looks at a company's number of employees, number of customers, number of offices, or annual revenue .
Example: A corporate software provider may approach a multinational firm with a more diverse, customizable suite while approaching smaller companies with a fixed fee, more simple product.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation is technically a subset of demographic segmentation. This approach groups customers by physical location, assuming that people within a given geographical area may have similar needs. This strategy is more useful for larger companies seeking to expand into different branches, offices, or locations.
Example: A clothing retailer may display more raingear in their Pacific Northwest locations compared to their Southwest locations.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation relies heavily on market data, consumer actions, and decision-making patterns of customers. This approach groups consumers based on how they have previously interacted with markets and products. This approach assumes that consumers prior spending habits are an indicator of what they may buy in the future, though spending habits may change over time or in response to global events.
Example: Millennial consumers traditionally buy more craft beer, while older generations are traditionally more likely to buy national brands.
Psychographic Segmentation
Often the most difficult market segmentation approach, psychographic segmentation strives to classify consumers based on their lifestyle, personality, opinions, and interests. This may be more difficult to achieve, as these traits (1) may change easily and (2) may not have readily available objective data. However, this approach may yield strongest market segment results as it groups individuals based on intrinsic motivators as opposed to external data points.
Example: A fitness apparel company may target individuals based on their interest in playing or watching a variety of sports.
Other less notable examples of types of segmentation include volume (i.e. how much a consumer spends), use-related (i.e. how loyal a customer is), or other customer traits (i.e. how innovative or risk-favorable a customer is).
How to Determine Your Market Segment
There's no single universally accepted way to perform market segmentation. To determine your market segments, it's common for companies to ask themselves the following questions along their market segmentation journey.
Phase I: Setting Expectations/Objectives
- What is the purpose or goal of performing market segmentation?
- What does the company hope to find out by performing marketing segmentation?
- Does the company have any expectations on what market segments may exist?
Phase 2: Identify Customer Segments
- What segments are the company's competitors selling to?
- What publicly available information (i.e. U.S. Census Bureau data) is relevant and available to our market?
- What data do we want to collect, and how can we collect it?
- Which of the five types of market segments do we want to segment by?
Phase 3: Evaluate Potential Segments
- What risks are there that our data is not representative of the true market segments?
- Why should we choose to cater to one type of customer over another?
- What is the long-term repercussion of choosing one market segment over another?
- What is the company's ideal customer profile, and which segments best overlap with this "perfect customer"?
Phase 4: Develop Segment Strategy
- How can the company test its assumptions on a sample test market?
- What defines a successful marketing segment strategy?
- How can the company measure whether the strategy is working?
Phase 5: Launch and Monitor
- Who are key stakeholders that can provide feedback after the market segmentation strategy has been unveiled?
- What barriers to execution exist, and how can they can be overcome?
- How should the launch of the marketing campaign be communicated internally?
Benefits of Market Segmentation
Marketing segmentation takes effort and resources to implement. However, successful marketing segmentation campaigns can increase the long-term profitability and health of a company. Several benefits of market segmentation include;
- Increased resource efficiency. Marketing segmentation allows management to focus on certain demographics or customers. Instead of trying to promote products to the entire market, marketing segmentation allows a focused, precise approach that often costs less compared to a broad reach approach.
- Stronger brand image. Marketing segment forces management to consider how it wants to be perceived by a specific group of people. Once the market segment is identified, management must then consider what message to craft. Because this message is directed at a target audience, a company's branding and messaging is more likely to be very intentional. This may also have an indirect effect of causing better customer experiences with the company.
- Greater potential for brand loyalty. Marketing segmentation increases the opportunity for consumers to build long-term relationships with a company. More direct, personal marketing approaches may resonate with customers and foster a sense of inclusion, community, and a sense of belonging. In addition, market segmentation increases the probability that you land the right client that fits your product line and demographic.
- Stronger market differentiation. Market segmentation gives a company the opportunity to pinpoint the exact message they way to convey to the market and to competitors. This can also help create product differentiation by communicating specifically how a company is different from its competitors. Instead of a broad approach to marketing, management crafts a specific image that is more likely to be memorable and specific.
- Better targeted digital advertising. Marketing segmentation enables a company to perform better targeted advertising strategies. This includes marketing plans that direct effort towards specific ages, locations, or habits via social media.
Market segmentation exists outside of business. There has been extensive research using market segmentation strategies to promote overcoming COVID-19 vaccination hesitancy and other health initiatives.
Limitations of Market Segmentation
The benefits above can't be achieved with some potential downsides. Here are some disadvantages to consider when considering implementing market segmentation strategies.
- Higher upfront marketing expenses. Marketing segmentation has the long-term goal of being efficient. However, to capture this efficiency, companies must often spend resources upfront to gain the insight, data, and research into their customer base and the broad markets.
- Increased product line complexity. Marketing segmentation takes a large market and attempts to break it into more specific, manageable pieces. This has the downside risk of creating an overly complex, fractionalized product line that focuses too deeply on catering to specific market segments. Instead of a company having a cohesive product line, a company's marketing mix may become too confusing and inconsistently communicate its overall brand.
- Greater risk of misassumptions. Market segmentation is rooted in the assumption that similar demographics will share common needs. This may not always be the case. By grouping a population together with the belief that they share common traits, a company may risk misidentifying the needs, values, or motivations within individuals of a given population.
- Higher reliance on reliable data. Market segmentation is only as strong as the underlying data that support the claims that are made. This means being mindful of what sources are used to pull in data. This also means being conscious of changing trends and when market segments may have shifted from prior studies.
Examples of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is evident in the products, marketing, and advertising that people use every day. Auto manufacturers thrive on their ability to identify market segments correctly and create products and advertising campaigns that appeal to those segments.
Cereal producers market actively to three or four market segments at a time, pushing traditional brands that appeal to older consumers and healthy brands to health-conscious consumers, while building brand loyalty among the youngest consumers by tying their products to, say, popular children's movie themes.
A sports-shoe manufacturer might define several market segments that include elite athletes, frequent gym-goers, fashion-conscious women, and middle-aged men who want quality and comfort in their shoes. In all cases, the manufacturer's marketing intelligence about each segment enables it to develop and advertise products with a high appeal more efficiently than trying to appeal to the broader masses.
Market segmentation is a marketing strategy in which select groups of consumers are identified so that certain products or product lines can be presented to them in a way that appeals to their interests.
Why Is Market Segmentation Important?
Market segmentation realizes that not all customers have the same interests, purchasing power, or consumer needs. Instead of catering to all prospective clients broadly, market segmentation is important because it strives to make a company's marketing endeavors more strategic and refined. By developing specific plans for specific products with target audiences in mind, a company can increase its chances of generating sales and being more efficient with resources.
What Are the Types of Market Segmentation?
Types of segmentation include homogeneity, which looks at a segment's common needs, distinction, which looks at how the particular group stands apart from others, and reaction, or how certain groups respond to the market.
What Are Some Market Segmentation Strategies?
Strategies include targeting a group by location, by demographics—such as age or gender—by social class or lifestyle, or behaviorally—such as by use or response.
What Is an Example of Market Segmentation?
Upon analysis of its target audience and desired brand image, Crypto.com entered into an agreement with Matt Damon to promote their platform and cryptocurrency investing. With backdrops of space exploration and historical feats of innovation, Crypto.com's market segmentation targeted younger, bolder, more risk-accepting individuals.
Market segmentation is a process companies use to break their potential customers into different sections. This allows the company to allocate the appropriate resource to each individual segment which allows for more accurate targeting across a variety of marketing campaigns.
PubsOnline. " Millennials and the Takeoff of Craft Brands ."
Crypto.com. " Fortune Favors the Bold ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Term-Definitions_Target-market-49a03b58f6d54ddd88d46521f248fc8a.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Brand Experience
Market Segmentation
What is market segmentation?
The benefits of market segmentation, the basics of segmentation in marketing, types of market segmentation, how to get started with segmentation, market segmentation strategy, market segmentation use case examples, ensuring effective segments, common segmentation errors, qualtrics solutions for market segmentation, see how qualtrics strategic brand works, market segmentation: definition, types, benefits, & best practices.
21 min read Market segmentation helps you send the right message, every time, by efficiently targeting specific groups of consumers. Here’s how it works.
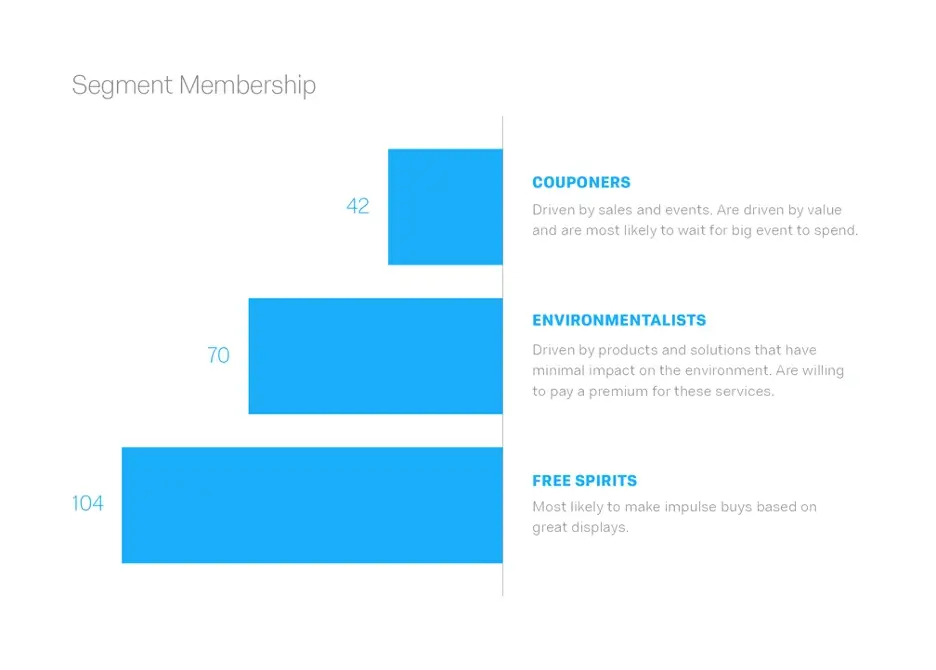
By understanding your market segments, you can leverage this targeting in product, sales, and marketing strategies . Market segments can power your product development cycles by informing how you create product offerings for different segments like men vs. women or high income vs. low income.
Read on to understand why segmentation is important for growth and the types of market segmentation to use to maximize the benefits for your business.
Free eBook: How to drive profits with customer segmentation
Companies who properly segment their market enjoy significant advantages. According to a study by Bain & Company , 81% of executives found that segmentation was crucial for growing profits. Bain also found that organizations with great market segmentation strategies enjoyed a 10% higher profit than companies whose segmentation wasn’t as effective over a 5-year period.
Other benefits include:
- Stronger marketing messages : You no longer have to be generic and vague – you can speak directly to a specific group of people in ways they can relate to, because you understand their characteristics, wants, and needs.
- Targeted digital advertising : Market segmentation helps you understand and define your audience’s characteristics, so you can direct your online marketing efforts to specific ages, locations, buying habits, interests etc.
- Developing effective marketing strategies : Knowing your target audience gives you a head start about what methods, tactics and solutions they will be most responsive to.
- Better response rates and lower acquisition costs : will result from creating your marketing communications both in ad messaging and advanced targeting on digital platforms like Facebook and Google using your segmentation.
- Attracting the right customers : targeted, clear, and direct messaging attracts the people you want to buy from you.
- Increasing brand loyalty : when customers feel understood, uniquely well served, and trusting, they are more likely to stick with your brand .
- Differentiating your brand from the competition : More specific, personal messaging makes your brand stand out .
- Identifying niche markets : segmentation can uncover not only underserved markets, but also new ways of serving existing markets – opportunities which can be used to grow your brand.
- Staying on message : As segmentation is so linear, it’s easy to stay on track with your marketing strategies, and not get distracted into less effective areas.
- Driving growth : You can encourage customers to buy from you again , or trade up from a lower-priced product or service.
- Enhanced profits : Different customers have different disposable incomes; prices can be set according to how much they are willing to spend . Knowing this can ensure you don’t oversell (or undersell) yourself.
- Product development : You’ll be able to design new products and services with the needs of your customers top of mind, and develop different products that cater to your different customer base areas.
Companies like American Express , Mercedes Benz , and Best Buy have all used segmentation strategies to increase sales, build better products, and engage better with their prospects and customers.
Understanding segmentation starts with learning about the various ways you can segment your market as well as different types of market segmentation. There are four primary categories of segmentation, illustrated below.
With segmentation and targeting, you want to understand how your market will respond in a given situation, like what causes people to purchase your products. In many cases, a predictive model may be incorporated into the study so that you can group individuals within identified segments based on specific answers to survey questions .
Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation sorts a market by elements such as age, education, household income, marital status, family size, race, gender, occupation, and nationality. The demographic approach is one of the simplest and most commonly used types of market segmentation because the products and services we buy, how we use those products, and how much we are willing to spend on them is most often based on demographic factors. It’s also seen as a simple method of predicting future behavior, because target audiences with similar characteristics often behave in similar ways.
How to start demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation is often the easiest because the information is the most readily available. You can send surveys directly to customers to determine their demographic data, or use readily available third party data such as government census data to gather further information.
Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation can be a subset of demographic segmentation, although it can also be a unique type of market segmentation in its own right. As its name suggests, it creates different target customer groups based on geographical boundaries. Because potential customers have needs, preferences, and interests that differ according to their geographies, understanding the climates and geographic regions of customer groups can help determine where to sell and advertise, as well as where to expand your business.
How to start geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation data again can be solicited from customers through surveys or available third party market research data, or can be sourced from operational data such as IP addresses for website visitors.
Firmographic segmentation
Firmographic segmentation is similar to demographic segmentation, except that demographics look at individuals while firmographics look at organizations. Firmographic segmentation would consider things like company size, number of employees and would illustrate how addressing a small business would differ from addressing an enterprise corporation.
How to start firmographic segmentation
Firmographic segmentation data can be found in public listings for companies and information that the business makes available, as well as trade publications. Again, surveying existing and potential customers can help to build out this data.
Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral Segmentation divides markets by behaviors and decision-making patterns such as purchase, consumption, lifestyle, and usage. For instance, younger buyers may tend to purchase bottled body wash, while older consumer groups may lean towards soap bars. Segmenting markets based on purchase behaviors enables marketers to develop a more targeted approach, because you can focus on what you know they are looking for, and are therefore more likely to buy.
How to start behavioral segmentation
Of all the types of market segmentation, behavioral segmentation is likely best started with the information you have on an existing customer base. Though it can be bolstered by third party market research data, the information you already have on customer purchase and usage behavior will be the best predictor of future behavior.
Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation considers the psychological aspects of consumer behavior by dividing markets according to lifestyle, personality traits, values, opinions, and interests of consumers. Large markets like the fitness market use psychographic segmentation when they sort their customers into categories of people who care about healthy living and exercise.
How to start psychographic segmentation
Pychographic segmentation relies on data provided by the consumers themselves. Though market research might provide insights on what particular segments are most likely to believe or prefer, psychographic segmentation is best completed with information direct from the source. You can use survey questions with a qualitative focus to help draw out insights in the customers’ own voice.
On-demand webinar: How to drive product design and profits with customer segmentation
There are five primary steps to all marketing segmentation strategies:
- Define your target market : Is there a need for your products and services? Is the market large or small? Where does your brand sit in the current marketplace compared to your competitors?
- Segment your market : Decide which of the five criteria you want to use to segment your market: demographic, firmographic, psychographic, geographic, or behavioral. You don’t need to stick to just one – in fact, most brands use a combination – so experiment with each one to figure out which combination works best for your needs.
- Understand your market : You do this by conducting preliminary research surveys, focus groups, polls , etc. Ask questions that relate to the segments you have chosen, and use a combination of quantitative (tickable/selectable boxes) and qualitative (open-ended for open text responses) questions.
- Create your customer segments : Analyze the responses from your research to highlight which customer segments are most relevant to your brand.
- Test your marketing strategy : Once you have interpreted your responses, test your findings by creating targeted marketing, advertising campaigns and more for your target market, using conversion tracking to see how effective it is. And keep testing. If uptake is disappointing, relook at your segments or your research methods and make appropriate changes.
Why should market segmentation be considered a strategy? A strategy is a considered plan that takes you from point A to point B in an effective and useful way. The market segmentation process is similar, as there will be times you need to revisit your market segments, such as:
In times of rapid change: A great example is how the Covid-19 pandemic forced a lot of businesses to rethink how they sell to customers. Businesses with physical stores looked at online ordering, while restaurant owners considered using food delivery services.
If your customers change, your market segmentation should as well, so you can understand clearly what your new customers need and want from you.
On a yearly basis: Market segments can change year over year as customers are affected by external factors that could alter their behavior and responses.
For example, natural disasters caused by global warming may impact whether a family chooses to stay living in an area prone to more of these events. On a larger scale, if your target customer segment moves away from one of your sales regions, you may want to consider re-focussing your sales activities in more populated areas.
At periodic times during the year: If you’ve explored your market and created market segments at one time of the year, the same market segments may have different characteristics in a different season. Seasonal segmentation may be necessary for better targeting.
For example, winter has several holidays, with Christmas being a huge influence on families. This holiday impacts your market segments’ buying habits, how they’ll behave (spending more than normal at this time than any other) and where they will travel (back home for the holidays). Knowing this information can help you predict and prepare for this period.
When considering updating your market segmentation strategy, consider these three areas:
- Acknowledge what has changed: Find out what has happened between one time period and another, and what have been the driving forces for that change. By understanding the reasons why your market is different, you can make key decisions on whether you want to change your approach or stay the course.
- Don’t wait to start planning: Businesses are always adapting to long-te r m trends , so refreshing market segmentation research puts you in a proactive place to tackle these changes head-on. Once you have your market segments, a good idea is to consider the long-term complications or risks associated with each segment, and forward-plan some time to discuss problem-solving if those issues arise.
- Go from “what” to “why” : Why did those driving forces come about? Why are there risks with your target market? At Qualtrics, we partner with companies to understand the different aspects of target markets that drive or slow success. You’ll have the internal data to understand what’s happening; we help unleash insight into why with advanced modeling techniques. This helps you get smart market segmentation that is predictive and actionable, making it easier for future research and long-term segment reporting.
Where can you use market segmentation in your business? We’ve collected some use case scenarios to help you see how market segmentation can be built out across several departments and activities:
Market and opportunity assessments
When your business wants to enter into a new market or look for growth opportunities, market segmentation can help you understand the sales potential. It can assist in breaking down your research, by aligning your findings to your target audience groups.
For example, When you’ve identified the threats and opportunities within a new market, you can apply your customer segment knowledge to the information to understand how target customers might respond to new ideas, products, or services.
Segmentation and targeting
If you have your entire market separated into different customer segments, then you have defined them by set criteria, like demographics, needs, priorities, common interests, or behavioral preferences .
With this information, you can target your products and services toward these market segments, making marketing messages and collateral that will resonate with that particular segment’s criteria.
Customer needs research
When you know a lot about your customers, you can understand where your business is connecting well with them and where there can be improvements.
Market segmentation can help with customer needs research (also known as habits and practices research) to deliver information about customer needs, preferences, and product or service usage. This helps you identify and understand gaps in your offerings that can be scheduled for development or follow-up.
Product development
If the product or service you’ve developed doesn’t solve a stated problem of your target audience or isn’t useful, then that product will have difficulty selling. When you know what each of your market segments cares about an/d how they live their lives, it’s easier to know what products will enrich or enhance their day-to-day activities.
Use market segmentation to understand your customers clearly , so that you can save time and money developing products and services that your customers will want to purchase.
Campaign optimization
Marketing and content teams will value having detailed information for each customer segment, as this allows them to personalize their campaigns and strategies at scale. This may lead to variations in messaging that they know will connect better with specific audiences, making their campaign results more effective.
When their marketing campaigns are combined with strong calls to action targeted to the specific segment, they will be a powerful tool that drives your target market segments towards your sales channels.
After you determine your segments, you want to ensure they’ll be useful. A good segmentation analysis should pass the following tests:
- Measurable : Measurable means that your segmentation variables are directly related to purchasing a product. You should be able to calculate or estimate how much your segment will spend on your product. For example, one of your segments may be made up of people who are more likely to shop during a promotion or sale.
- Accessible : Understanding your customers and being able to reach them are two different things. Your segments’ characteristics and behaviors should help you identify the best way to meet them. For example, you may find that a key segment is resistant to technology and relies on newspaper or radio ads to hear about store promotions, while another segment is best reached on your mobile app. One of your segments might be a male retiree who is less likely to use a mobile app or read email, but responds well to printed ads.
- Substantial : The market segment must have the ability to purchase. For example, if you are a high-end retailer, your store visitors may want to purchase your goods but realistically can’t afford them. Make sure an identified segment is not just interested in you, but can be expected to purchase from you. In this instance, your market might include environmental enthusiasts who are willing to pay a premium for eco-friendly products, leisurely retirees who can afford your goods, and successful entrepreneurs who want to show off their wealth.
- Actionable : The market segment must produce the differential response when exposed to the market offering. This means that each of your segments must be different and unique from each other. Let’s say that your segmentation reveals that people who love their pets and people who care about the environment have the same purchasing habits. Rather than having two separate segments, you should consider grouping both together in a single segment.
Market segmentation is not an exact science. As you go through the process, you may realize that segmenting based on behaviors doesn’t give you actionable segments, but behavioral segmentation does. You’ll want to iterate on your findings to ensure you’ve found the best fit for the needs of your marketing, sales and product organizations.
We’ve outlined the do’s , so here are some of the dont’s :
- Avoid making your segments too small or specialized : Small segments may not be quantifiable or accurate, and can be distracting rather than insightful
- Don’t just focus on the segment rather than the money : Your strategy may have identified a large segment, but unless it has the buying power and wants or needs your product, it won’t deliver a return on investment
- Don’t be inflexible : Customers and circumstances change, so don’t let your segments become too entrenched – be prepared to let them evolve.
Market segmentation doesn’t need to be complicated to be effective. We would advise, though, to get automated from the beginning . Forget spreadsheets – choose market segmentation software to measure and streamline your marketing strategy; as you grow, the technology will scale with you.
Innovative features such as XM Directory allow you to build your own customer segments and start personalizing experiences at scale based on the rich insights into your critical customer groups.
If you want to get a feel for your market segmentation upfront, before taking a step towards a streamlined and integrated system, trust us to take you through the research with our Market Segmentation Research service .
Related resources
Market fragmentation 9 min read, behavioral segmentation 20 min read, psychographic segmentation 11 min read, geographic segmentation 14 min read, demographic segmentation 14 min read.
Brand Perception
Brand Sentiment 18 min read
Brand intelligence 12 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Market segmentation — definition, types, and examples

If you’re a marketer or business owner, you know that segmentation is an effective way to expand your market and reach new customers.
But even if you understand market segmentation, sometimes you need a little inspiration to start doing it yourself. In this article, we’ll explore the key segment types with real-world examples to jump-start your company’s foray into market segments and help you improve your overall marketing efforts.
This post will cover:
What is market segmentation?
Types of market segmentation, demographic segmentation, examples of demographic segmentation, psychographic segmentation, examples of psychographic segmentation.
- Geographic segmentation
- Examples of geographic segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation
- Examples of behavioral segmentation
- Firmographic segmentation
- Examples of firmographic segmentation
Benefits of market segmentation
Frequently asked questions (faq).
Market segmentation is the practice of grouping customers together based on shared characteristics — including demographic information or common interests and needs. It’s a strategy for dividing a large, broader target audience into specific groups to create tailored and personalized marketing campaigns.
A market segment refers to the individuals who are grouped together based on their shared characteristics. The idea is that these people have similarities as consumers and respond similarly to marketing efforts. So companies need to communicate to them in a particular way, rather than just messaging their audience as a homogenous whole.
Businesses segment their market in different ways. Market segments should be based on extensive research of their potential customers’ demographics, lifestyles, needs, personalities, and more.
There are various types of segmentation that help businesses market to their target audience groups. We’ll go over the five main types of market segmentation and provide examples of each one.
Demographic segmentation is grouping customers based on data points like age, gender, marital status, occupation, and more. It’s essentially the “who” segment of your market. This is the most common type of segmentation because it’s easily identifiable. Demographic segmentation can help you understand the individuals that make up your audience and how to target your marketing efforts to them.
Demographic segmentation is typically sorted by characteristics like:
- Level of education
- Family size or status
- Professional occupation or role in a company
Demographic segmentation provides objective information on who is interested in your product or service. While it’s best to use other methods of segmentation as well, demographics provide an excellent starting point for marketers to group their audience.
Here are a couple examples of how demographic segmentation can be used:

Brooks Running Shoes and Dick’s Sporting Goods partnering on empowerment . Brooks and Dick’s are great real-life examples of using demographic segmentation to capture customer interest. The companies partnered to celebrate National Girls and Women in Sports Day with their “Empower Her” collection. It included a variety of women’s shoes and clothing, including products with phrases like “Dream Chaser” and “Respect Her Run.”
HelloFresh targeting female social media users . Lots of different people use meal delivery subscriptions, and marketing efforts often focus on making dinner prep easier for busy young professionals or families. But HelloFresh wanted to specifically target its primary market segment. Knowing its audience was 80% women and primarily between the ages of 30 and 50, HelloFresh created a female-oriented influencer campaign that produced buzz on foodie social media.
Demographic segmentation provides excellent initial information, but to understand the customer thought process, you need to use other segmentation methods too.
Psychographic segmentation is the “why” segment of your market. In this segmentation, you analyze how your audience thinks and create a strategy targeted toward customers’ attitudes and beliefs. These groups will likely have similar psychological characteristics, personal values, aspirations, and political opinions.
Companies generally divide psychographic segments based on:
- Personality
- Hobbies and interests
- Lifestyle choices
- Social or political views
- Values and beliefs
Psychographic segmentation is more difficult to segment because it’s more subjective. Social media analytics can be a helpful tool, but you should also plan to conduct interviews and surveys and hold focus groups to gather all the information you can about your audience.
Here’s an example of psychographic segmentation:
Marvel Studios marketing toward movie fanatics . Marvel creates engaging social media posts that generate excitement and anticipation for its upcoming films. The studio posts countdowns to the days leading up to the movie and includes clips likely to pique its audience’s interest. Marvel can market to people based on their interests in comic books, superheroes, film, and more.
This segmentation is what makes customers who they are. But who they are can be influenced by other factors, such as where they are.
Geographic market segmentation
Geographic market segmentation is the “where” segment of your market. In this type, customers are segmented based on their geographic location. These people will live in the same city or state — perhaps even in the same zip code — and are likely to have similar attitudes, needs, and cultural preferences based on their geography.
Companies generally separate geographic segments by:
- Climate region
- Population density
- Rural, urban, or suburban setting
Examples of geographic market segmentation
Geographic segmentation works best for companies that are trying to focus their efforts on a particular area. It could involve simple changes, such as adapting product offerings or the language used in marketing to fit the main language of a region or slang that would typically be used in one area.
Some examples of geographic market segmentation include:

McDonald’s adjusting items for individual countries . McDonald’s started out as an American restaurant company, but as it grew to become a global mega-brand and expanded its locations all around the world, it adjusted some of its menu items to match the cuisine of different countries. For example, rather than just the typical burger and fries, there’s the Veggie Maharaja Mac in India, the McSpaghetti in the Philippines, and poutine in Canada.
Climate impacting fashion. One general example of geographic segmentation could be based on weather. If your company sells clothing, your marketing may vary by region. In colder regions you may want to highlight coats and beanies, while in a warmer area tank tops and shorts will be more suitable.
Physical environment has a huge impact on why customers purchase the way they do. It’s also important to analyze how they interact and respond to your brand.
Behavioral market segmentation
Behavioral market segmentation is the “how” segment of your market. This approach examines customer behavior and how people engage with your brand. From this type of segmentation, you can better understand how they may respond to changes in prices, new promotions, and more.
Audiences can be grouped by:
- Spending habits
- Browsing habits
- Interactions with your brand
- Loyalty to your brand
- Product feedback
Examples of behavioral market segmentation
Behavioral segmentation, like the other types, helps you gain a deeper understanding of who your client base is. This category, however, goes beyond noting stereotypical characteristics of the customer and reveals their interactions and spending tendencies.
Some examples of behavioral segmentation are:
Guinness advertising non-alcoholic beer. Guinness is a global brand with a loyal following of beer drinkers, but industry research shows there are millions of people who choose not to consume alcohol. To market to this growing group during the popular Six Nations Rugby Cup, Guinness produced clever ads for its new product “Guinness Clear” with slogans like “Make it a night you’ll remember.”
Amazon honing in on buying habits. Amazon displays recent customer purchases to show shoppers other products they may be interested in. For example, if someone purchased a soccer ball, they may get advertisements on their social media platforms for shin guards, cleats, and other soccer equipment.
Behavioral market segmentation gives businesses a close look into how customers interact with brands and spend their money.
Firmographic market segmentation
Firmographic segmentation is the B2B version of demographic segmentation. It’s the study and classification of B2B customers using information from similar company characteristics. This segmentation type is popular for firms to find businesses that would benefit the most from their product.
Companies generally separate the firmographic segment based on:
- Turnover and profit numbers
- Industry type
- Business size
- Number of employees
- Ownership (public, private, or government)
- Organizational trends (for example, more companies going remote)
- Average sales cycle
Examples of firmographic market segmentation
Most of the market segments detailed in this article focus on B2C marketing, but firmographic segmentation is helpful for B2B companies to create engaging campaigns.

Upwork advertising in New York City. Upwork is a popular platform for companies to hire freelancers. Since New York is one of the largest population centers and business hubs in the world, Upwork created a marketing campaign with digital billboards and other ads prominently placed around the city to attract the attention of businesses that might need freelancers.
There are many reasons why segmentation can create more personalized experiences for each customer. By doing research and keeping up with industry trends, your business can expand its market and improve marketing ROI.
Market segmentation provides a number of benefits for businesses. Not only does it help your teams better understand your audience and create the right messaging to attract customers and grow your reach, but it produces a stronger brand image, more efficient use of resources, a higher rate of success, and a better customer experience.
With market segmentation, you can:
- Identify high-value customers and the similarities and differences between different groups of customers.
- Create more personalized communications and more targeted marketing efforts.
- Reach new markets by showcasing your unique product or service and adjusting your messaging.
- Build better brand awareness and stand out by understanding individual customer needs and creating personalized experiences.
- Cut down on wasted marketing dollars by creating more impactful and efficient campaigns.
- Improve your products by meeting specific market expectations based on what customers want.
- Make it easier to learn about your audience and create more cost-effective campaigns in the future.
- Gain better marketing ROI by using existing data to improve the customer experience.
What is meant by market segmentation?
Market segmentation is the practice of grouping customers together based on certain characteristics they may share.
What are the types of market segmentation?
There are four main types of market segmentation — demographic, psychographic, geographic, and behavioral. But there are other types that your business can take advantage of as well, such as firmographic for B2B marketing.
What are the advantages of market segmentation?
Market segmentation helps you establish who your target market is and customize your message for individuals. It allows your business to expand across new markets and improve products to keep up with changing customer needs.
How do you identify market segments?
By becoming an expert on your business, doing extensive industry research, and categorizing people by identifiable characteristics, you can use the information to group potential customers that might be interested in your products or services.
What makes a good market segment?
A good market segment should be easily identifiable and different from other segments. The sample sizes of these segments should be large and able to be assessed for feedback.
Evaluate your marketing software for market segmentation capabilities
Your business can reach new markets by using market segmentation. When you’re ready to get started, evaluate your current marketing software to see how it handles segmentation. If there are gaps, look into a new solution.
Acting on insights requires an audience. Create and activate engaged audiences on any channel or device with Adobe Audience Manager .
Audience Manager turns insights into action so your teams can create memorable customer experiences and extend your reach further than before. As a data management solution, Audience Manager collects and merges information from practically any source — building intelligent audience segments that give you a complete view of your customers.
Watch the two-minute product tour to learn more.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/market-segmentation
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/psychographic-segmentation
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/get-a-quick-refresher-on-market-segmentation

What Is Market Segmentation? Importance for Your Business
April 12, 2023
by Hannah Tow

In this post
Types of market segmentation, why is market segmentation important, how to do market segmentation .
- Common market segmentation mistakes
How to implement your own market segmentation strategy
You’ve spent time and money creating the perfect marketing strategy, and you want your message to resonate well with your potential customers, right?
Communication is an art, and it’s incredibly easy for a message to become lost, confused, or avoided altogether as the size of your audience increases. The larger your audience grows, the broader their preferences, needs, and opinions become which can put your marketing message at risk of being irrelevant to the majority of people you’re attempting to reach.
This is exactly why segmenting your target market is crucial. Making use of marketing automation software can help better manage a large audience and create a segmented, personalized, and targeted marketing experience. This practice allows you to focus your marketing efforts on individual customer segments so that you can better cater to their specific wants and needs.
This method gives your brand an advantage over your competitors because you can prove to potential customers that you understand them and know what they need best.
What is market segmentation?
Market segmentation is a business practice that brands use to divide their target market into smaller, more manageable groups of people based on common ground they share to optimize their marketing, advertising, and sales efforts. Simply put, customers of each market segment have similar characteristics that businesses can leverage to advance their efforts.
Market segmentation aims to introduce a tailored message that will be received successfully. This is advantageous for companies with a product or service in the marketplace that boasts multiple benefits or uses for different types of customers.
Accept the fact that you can’t be everything to everybody, and as a marketer, you can’t solve everyone’s problem or appeal to every single person. This is exactly why market segmentation is such an effective growth strategy to implement.
Tip: Before starting with market segmentation, you must have a solid marketing mix . This is your foundation for everything that comes next in this article.
As you can imagine, you can take many different approaches when segmenting your target market.
This article will walk you through the four main types and real-life market segmentation examples to help you get started. Learning from those who have done it right will help your brand garner that success you’re looking for.

Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation targets customers based on a predefined geographic border. Differences in interests, values, and preferences vary dramatically throughout cities, states, and countries, so it’s important for marketers to recognize these differences and advertise accordingly.
Think about products such as parkas and bathing suits.
Parkas will be sold most of the year in the colder northern half of the country, whereas southern areas may only be able to find parkas in specialty stores during the wintertime. On the other hand, bathing suits are sold year-round in the warmer states but are typically only sold during the spring and summer in the cooler states.
Another example of geographic segmentation is the iconic fast-food chain McDonald’s. If you’ve never traveled to another country and stepped foot in a McDonald’s, you’re in for a surprise!
Would you believe that in the Philippines, McDonald’s sells McSpaghetti? And in Hong Kong, they sell ramen flavored french fries?
These are all ways McDonald’s has segmented its customers based on geographic location to better cater to food preferences and different cuisines around the world.
“ When it comes to paid search campaigns, geographic targeting is the most important segment to get right. ” Ryan Moothart PPC Architect, Portent
Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation divides a market through variables such as age, gender, education level, family size, occupation, ethnicity, income, and more. This form of segmentation is widely used due to specific products catering to obvious individual needs relating to at least one demographic element.
Perhaps the most obvious variable of them all, age is a crucial element for marketers to understand thanks to the fast-paced nature of preference changes within the various stages of life.
Even media consumption differs greatly between each generation, so it’s important to recognize your target age range and which channels they use to consume information to ensure your tailored message reaches them appropriately.
An example of demographic segmentation is when clothing companies cater to multiple age groups. For instance, Lululemon sells athletic clothing to adult men and women of all ages, but they also cater to girls between the ages of 6 and 15.
By analyzing its current customer base, Lululemon saw an opportunity to serve a new market and expand its business.
Many clothing companies cater to a variety of age groups to reach as many customers as possible. Think H&M, Old Navy, and Zara. All of these companies cater to men, women, and children of all ages, and they have distinct labels, advertising, and styles for each segment.
Psychographic segmentation
Unlike geographic segmentation and demographic segmentation, psychographic segmentation focuses on the intrinsic traits your target customer possesses.
Psychographic traits can range from values, personalities, interests, attitudes, conscious and subconscious motivators, lifestyles, opinions, and more.
To understand your target audience on this level, methods such as focus groups, surveys, interviews, audience testing , and case studies can all prove to be successful in compiling this type of conclusion.
Think about the lifestyle of someone who lives in a small beach town and surfs for a living versus someone who lives in a big city working in corporate America. These two people have incredibly different wants and needs on a daily basis, and marketers must recognize those differences to be successful.
For example, Starbucks does a fantastic job segmenting its customers based on psychographic traits. We all know that not everyone loves coffee or prefers to drink it, but that doesn’t stop Starbucks from appealing to just about everyone.
Starbucks sells chocolate milk, cake pops, granola bars, cheese sticks, and more for the little kids that accompany mom or dad on their morning coffee run. Of course, those items aren’t strictly for the kids, but those items sure are tempting when you have a fussy one.
What about for those sophisticated coffee drinkers who care about quality and bean sources? Starbucks appeals to them by selling a variety of exotic beans sourced from regions all over the world. And what about those who don’t really drink coffee, but all of their friends do, and they enjoy an afternoon hang out at Starbucks? Think frappuccinos, lemonades, teas, and juices.
It’s one thing to sell products that can appeal to everyone, but it’s a whole new ball game when those products make every single person feel individually catered to. This is what Starbucks does through its messaging to create a sense of belonging.
They cater to each segment’s wants and needs through targeted marketing campaigns to ensure their coffee brand is inclusive to all, even if you aren’t a coffee drinker.
“ The biggest danger is assuming that your market is perfectly sliced and diced just because you're making sales. ” John Donnachie Director, ClydeBank Media
Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation has similar measurements to psychographic segmentation, but instead, it focuses on specific reactions and the ways customers go through their decision making and buying processes.
Attitudes towards your brand, the way they use and interact with it, and their knowledge base are all examples of behavioral segmentation. Collecting this type of data is similar to the way you would find psychographic data.
Brand loyalty is an excellent example of behavioral segmentation. While reading this article, I bet that you can think of one brand that you consistently purchase and trust enough to buy its newly launched product without even reading the reviews.
This type of brand loyalty produces a consistent buying pattern which is categorized as a behavioral trait. Marketers work hard to get customers to love and stay loyal to their brand for a consistent purchase cycle.
To target customers that have great brand loyalty, many companies will offer rewards programs to enhance this behavior with the hope of capturing new loyal customers as well.
For example, the makeup and beauty company, Sephora, has an excellent rewards program for its loyal customers. The more you spend at their store, the more points you rack up, which can be redeemed for generous samples. In addition to that, they offer free services, special access to sales, and more!
By targeting and rewarding those who already had an affinity to their brand, Sephora was able to build an impressive community that their target market wants to be a part of.
Now that you understand the four major types of market segmentation, you’re probably wondering what the major benefits are of implementing them.
The importance of this strategy goes far beyond placing your target market into cohesive segments.
Customer retention
For starters, those cohesive customer segments will lead to great customer retention . Capturing customers at the beginning of a perfectly tailored customer journey will provide an excellent brand experience and increase the likelihood that they will stay loyal to your brand.
Based on a recent study , 3 out of 4 customers are ready to make a significant move – switching brands – following a single negative experience. This is not just a minor bump in the road; it's a pivotal moment. What's even more alarming is that 52% of dissatisfied customers won't keep their dissatisfaction to themselves. They will also make sure their friends and family hear about it, actively discouraging them from purchasing the brand that let them down. Market segmentation safeguards your brand. By slicing your target market into smaller and more manageable groups, you're not just optimizing your efforts but also building a stronghold against negative experiences. It helps you outpace negative experiences with positive interactions and prevent potential brand defection before it even begins.
If every message and product shared with them resonates in some way, they will have a difficult time saying no to you.
Grow your business
Market segmentation can help you discover new ways to reach your current customers but also help you find new markets of potential customers you haven’t previously reached. Analyzing your customers in-depth will help you uncover unknown needs or problems that they face that your brand can solve.
This discovery can lead to new product lines, rebrands, or new brands, all to catapult the growth of your business by appealing to your current customers better, as well as new consumers that were previously uninterested.
Lower spend rate
If you know how to speak to your customers correctly, you’re more efficient with your efforts, which means you spend less money. It’s as simple as that.
Gone are the days of your team spinning its wheels, trying to come up with something that will stick. You'll get it right by segmenting your customers correctly every single time.
To implement a marketing strategy, it's important to understand how to perform market segmentation. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you divide your target audience and cater to their needs in a personalized manner.
- Define your target market: Understand your audience by asking yourself the right questions. Is it a small or large market? Is there a need for the product or service offered? Who are the competitors? Learning more about your target market will help you gain clarity on the next steps.
- Segment your market: We've seen the different types of market segmentation present. The next step is figuring out which segment or a combination of segments you would target.
- Understand each market segment: Conducting primary research through discussions, polls, and surveys will help understand the needs of each group and develop each customer persona . This will help you cater to their needs in the best possible way.
- Create customer segments: Analyze the findings from the previous step to create your final customer segments.
- Test your marketing strategy: Once the analysis is complete, test the marketing strategy through various campaigns or A/B tests to further understand the effectiveness. Relook at the strategy if required.
Common market segmentation mistakes
Now that you understand the basics of market segmentation and have seen it in practice, it’s time to focus on the common mistakes marketers can make when segmenting their target market for the first time.
Creating too small of segments
This can be rather easy to do if you’re trying to ensure that you have every last detail included. If a segment is created too small, you’ll lose the buying power of that group as well as create a segment with non-quantifiable metrics.
At the end of the day, every single person is vastly different. You cannot appeal to every aspect of every person.
Not updating your strategy as your customer base changes
People change, and they can change fast. It’s in your brand’s best interest to refresh its strategy and resurvey its customers from time to time.
Choose a cycle that makes sense for your business and stick to it. This can be a quarterly refresh, yearly, or every couple of years; if you’re seeing big changes within your customers, perform a refresh then, too.
Targeting the segment instead of the money
You may have segmented a large customer base that aligns with your strategy, but if that segment doesn’t have the buying power or a legitimate need for your product, then you won’t have a positive ROI.
Market segmentation can be a laborious and complicated task, and mistakes in the beginning stages may seem inevitable. Being aware of these common downfalls will better prepare you and your team so you don’t make them in the future.
It’s time to put what you’ve learned to use. Here are five steps that lay the process out simply, plus the two strategies that are most commonly used to guide them. Once you’ve got these basics down and you have a solid foundation for your strategy, branch out, and make it uniquely your own.
Before getting started, consider using marketing automation software to streamline and measure your efforts effectively. As your strategy becomes more complex and your campaigns grow larger, you’ll be happy with the amount of time and resources you were able to save from having everything automated from the very beginning.
Concentrated strategy
As the name suggests, a concentrated marketing strategy is when a company chooses only one market to focus all of their time, money, and efforts on. This strategy is usually chosen by smaller businesses or those that are just taking off and starting to make a name for themselves in the marketplace.
Success is typically seen when targeting a smaller group of people since the strategy has to appeal to the entire segment. Appealing to an entire segment becomes challenging when the segment is too large.
You should be aware that your growth opportunity is limited when using this strategy. Once you’ve capitalized on your market and are seeing great success, consider tapping into other similar markets to continue to drive growth.
Differentiated strategy
On the other hand, a differentiated marketing strategy is when a company focuses on two or more markets. Companies that utilize this strategy market their products to many different segments, they just change their messaging to appeal to all of the differences.
Although a differentiated marketing strategy requires a lot more effort, time, and money than a concentrated marketing strategy would, it typically yields more success since there are many more avenues to profit.
1. Define your market
Where does your brand fit within the current market landscape? Is there a need for the solution you promise to provide? How large is the market? These are all important questions to consider when starting this step.
2. Segment your market
This is where it gets fun. Decide which of the four segmentation methods you’re going to use, but don’t feel confined by one segmentation method.
It’s common for brands to implement more than one segmentation technique and take a combination approach, so play around with each and find the perfect mix for your brand.
3. Understand your market
Ask your target market questions related to your chosen segmentation categories. You should get to know your target market through and through at this step. You can use surveys , focus groups, polls, and more to obtain your answers. Make sure you’re asking questions that will provide quantifiable answers.
4. Build your customer segments
Interpret the responses you receive to create dynamic customer segments that are unique to your brand. You can use a customer support tool too. Make sure that you’re focusing on the buying power of the segments and not creating any that are too small. Look over the common mistakes one last time to ensure you’re not making any!
5. Test your strategy
Ensure that you have interpreted your responses accurately by testing it on your target market. Implement conversion tracking early. It’s one of the best ways to determine the effectiveness of your strategy.
If you’re not relating to your customers with the segments you’ve created, you’ll need to review your survey methods and analysis. Be sure your chosen strategy has unique characteristics from others in the marketplace to stand out.
By determining the proper strategy for your needs and following the basic steps outlined above, you can ensure your market segmentation strategy will be effective and successful.
Take your marketing strategy to the next level
Market segmentation is a highly effective strategy for every marketing team. It proves to your customers that you understand them by providing a tailored message that resonates with specific facets of their lives. Knowing how to get a message across successfully will help your brand grow exponentially.
Remember, your success won’t last long if you’re not constantly testing your strategy. To be competitive, you must always be on top of your game.
Market segmentation comes down to knowing your customer base and providing a personalized experience for them. For a seamless customer journey across your segments, learn how to implement an omnichannel marketing strategy next.
You've hit the bullseye!
Targeting the right audience can be quite tricky. Using the right marketing automation software can help ease the process.

Hannah is a former content marketing associate at G2. She graduated from the University of Missouri with a degree in Journalism. In her free time, Hannah enjoys running with her dog, Teddy, traveling to new and exciting places, and capturing the beautiful places she travels to with her DSLR camera. (she/her/hers)
Recommended Articles

Contributor Network
Personalized Marketing: All You Need to Know
Personalized marketing is all the rage for modern businesses.
by Savan Kharod

5 Steps to Become an Influencer Marketing Manager
Ten years ago, the concept of hiring a social media manager seemed outlandish to most brands.
by Haley Fraser

Your Local Marketing Guide: Reach Customers in Your Area
Marketing locally is very different from reaching a global audience.
by Tom Kotze
Never miss a post.
Subscribe to keep your fingers on the tech pulse.
By submitting this form, you are agreeing to receive marketing communications from G2.

Fill your (MarTech) cup
Stay current on SaaS-y news and the latest MarTech trends delivered in a 5-minute monthly newsletter.
The No-Nonsense Guide to Market Segmentation (With Tips and Examples)
Marketing to the wrong segment can feel like barking up the wrong tree, or more specifically, barking up tens of thousands of wrong trees.
Nearly everybody in sales has, at one point or another, heard someone reasoning that simply adding more people to the funnel will improve their sales numbers while preserving their conversion rate. If you’re a sales rep making 30 calls a day, you might reasonably extrapolate that making 60 calls a day would double your closed deals. Unfortunately, it’s not that straightforward.
Building a sales process can be complicated. What one audience might find valuable might just be noise for another.
That’s where effective customer segmentation can bring in some serious value for your business. Different demographics respond differently to marketing campaigns, and finding the right target market for your products or services can help you tailor your marketing strategies to be the most impactful they can be.
This guide to marketing segmentation will help you find your target audience and choose the best market segmentation strategies.
Table of Contents
What is market segmentation, what are the benefits of market segmentation, the 10 most common types of market segmentation.
- Market segmentation strategies
- How to do your own market segmentation
Frequently asked questions about market segmentation
Market segmentation in a nutshell.
Market segmentation is the process of qualifying companies (or people) into groups that respond similarly to specific marketing strategies. This is the first critical step in creating a marketing and sales process tailored to differentiate your business in the market and resonate across multiple demographics.
Market segmentation divides customers into segments based on shared characteristics, behaviors, or other attributes so you can create marketing strategies that appeal to entire groups. Your marketing segmentation strategy will be mainly influenced by what your product is and which types of companies are already buying it.
The history of market segmentation
The expression “market segmentation” was first coined by Wendell R. Smith in his 1956 publication Product Differentiation and Market Segmentation as Alternative Marketing Strategies . Smith wrote that modern marketing appeals to selective rather than primary buying motives.
In other words, consumers are actively contrasting products against one another rather than simply purchasing a product to satisfy an immediate need. This realization was the inception of the modern market segmentation we practice today.
Before 1956, there wasn’t a huge market variety, and general stores tended to carry only one or two brands’ versions of the same product. As time went on, more and more emerging brands began offering similar products and thus needed to differentiate themselves with branding and by targeting different markets.
It wasn’t enough to just manufacture ketchup, you had to identify your brand as America’s ketchup , or kids’ ketchup , or fancy ketchup .

Market segmentation provides several benefits to small teams and enterprises alike, including:
- Bang for your buck: With tailor-made, demographic-specific messages and advertising, companies can more effectively communicate with their audiences, begin boosting their conversion rates, and actually spend less on broad advertising.
- Better conversion rate: The more information you have about your various audiences, the more specificity you can add to your outreach, which will help your prospects convert more easily.
- Customer retention: By marketing towards customers who have already gone through their own buyer’s journey, segmentation makes it easier to keep them engaged and pitch them with occasional upgrades. And with the segment data you’ve captured, you know how to talk to them.
- Expanding your efforts: Segmentation can be a great way to pursue new markets that have something in common with your current markets.
See Nutshell in action
Join a live demo to see our powerful, easy-to-use CRM at work!
SEE A LIVE DEMO

Market segmentation helps savvy marketers categorize their target customers based on shared characteristics to keep their efforts focused and effective. Below are the 10 most common types of market segmentation:
1. Demographic segmentation
Demographic market segmentation is the most commonly used form of market segmentation and entails categorizing your market based on age, gender, income, profession, race, religion, education, location, family situation, etc.
Demographic segmentation examples:
- Switch to the cartoon channel and check out those commercials. Do Nerf guns and neon-colored slime appeal to someone your age? Yeah us too, bad example .
- Commercials for vacation homes may target people across ages, genders, locations, and other demographics, but they all appeal to customers with disposable income who are interested in travel.
2. Psychographic segmentation
More specific characteristics are categorized under the umbrella of psychographic segmentation. Less tangible than demographic segmentation, this classification method includes details like lifestyle, personality, beliefs, values, and social class.
This evaluation is important because two individuals can possess identical demographic information but make purchasing decisions completely differently, and thus require different marketing.
Psychographic segmentation examples:
- Health and wellness advertisements might not go a long way with someone who prefers to spend their money on video games and energy drinks, even if they work in the same industry and live in the same apartment building.
- Advertisements for large social gatherings (events, clubs, bars) might not appeal to introverts who would much rather snuggle up with a book than be surrounded by other people.
3. Behavioral segmentation
At its core, behavioral segmentation is the act of categorizing prospects based on their actions, usually within your marketing funnel. For instance, prospects who visited a landing page for an upcoming event might benefit from receiving a personalized invitation.
Segmenting your market based on behaviors is typically done by marketers within their marketing automation software , but any company with a mailing list has already performed behavioral segmentation simply by tracking prospects who have signed up to receive emails.
Behavioral segmentation examples:
- Sending emails to website visitors who have left items in their cart. “But wait…come back!”
- A retargeting campaign that only displays ads to people who have previously purchased an item.
4. Geographic segmentation
Geographic market segmentation takes into account prospects’ locations to help determine marketing strategies. Although SaaS sales are relatively unaffected, a salesperson of gigantic coats knows to avoid pitching to Arizona residents.

Geographic segmentation variables and examples:
- Climate: Swimwear brands shouldn’t be targeting Alaska residents in January.
- Cultural preferences (based on location): For obvious reasons, the McDonald’s in Germany sells beer.
- Population type: A bicycle company may segment its audience differently depending on the population type—rural (mountain bikes; thicker tires; more durable), urban (road bikes; thin tires; lightweight), etc.
- Density: A giant strip mall may require a high density of foot traffic to thrive.
5. Price segmentation
Price segmentation alters the price of similar products and services sold to different consumer groups. If you ever forced your kids to pretend to be under a certain age to qualify for the “kids eat free” special, then you understand the power and utility of price segmentation.
However, price segmentation can get much more granular. It can be used to identify customers who may be willing to pay more for a particular product or service that they perceive to be more valuable.
Done correctly, price segmentation can capture the maximum amount of revenue for each transaction.
Price segmentation examples:
- Broad: Senior discount, veteran discount, coupons, etc.
- Granular: Computer processors are priced differently when sold to a company as a part (like inside an iMac) than when sold to a consumer as a standalone product.
- Even more granular: A marketing consultancy may base its prices entirely on the value it can generate for each of its client’s unique situations.
6. Firmographic segmentation
Instead of categorizing consumers based on age, location, income, etc, firmographic segmentation categorizes companies based on industry, annual revenue, job function, company size, location, status, performance, etc.
For B2B marketers, utilizing firmographic segmentation is non-negotiable to a high-performing marketing strategy.
Just as the demographic segmentation variables can help you form a buyer persona at the consumer level, firmographic segmentation can help you develop a buyer persona at the company level.
Firmographic segmentation examples:
- Running different ads for different industries—real estate, finance, legal firms, etc.
- A B2B sales team only targeting companies with revenues over $100m.
7. Generational segmentation
Generational segmentation is almost comparable to the “age” variable in demographic segmentation. However, generational market segmentation goes beyond age by considering the difference in preferences, habits, lifestyles, and attitudes of a particular generation.
It’s self-evident that the generations are vastly different. Someone born in the 1960s will likely have experienced a different culture than someone born in the 2000s.
Generational segmentation examples
- Utilizing more memes on Facebook to target a larger percentage of Millennials.
- Altering your content publishing schedule to mornings to target a larger percentage of Baby Boomers.
8. Life stage segmentation
Life stage segmentation is the process of dividing your market based on the life stage of your target audience. Someone who is married with 5 kids may respond well to an emotional advertisement about convertibles during their midlife crisis.
Life stage segmentation examples
- Ads about life insurance may not appeal to sophomores in college, but they may appeal to someone who just started a family.
- Someone who just entered the workforce for the first time may be more interested in a new apartment than someone who is retired.
9. Seasonal segmentation
Seasonal segmentation targets people based on their purchasing habits during certain periods of the year. It can include actual seasons (spring, summer, fall, winter), events (Coachella, Super Bowl), and holidays (Christmas, Mother’s Day).
Seasonal segmentation examples
- A local you-pick berry farm may want to target their ads based on the fruit in season.
- A flower shop that specializes in same-day delivery may want to ramp up its ad spend around Mother’s Day targeting forgetful children.
10. Technographic segmentation
Much like firmographic market segmentation, technographic segmentation only applies to B2B audiences. It’s used to target companies based on the types of technology they’re using. Whether it’s a customer relationship management (CRM) platform, a website CMS, or a niche-specific software tool, utilizing technographic segmentation can help enhance sales and marketing efforts.
Technographic segmentation examples
- A company that develops WordPress plugins would have no business targeting companies that use a different CMS, like Wix.
- It would make sense for a SaaS company to target businesses using an app it just integrated with.
Want even more sales and marketing tips from our experts?
Sign up for our free newsletter!
SIGN UP FOR THE NEWSLETTER

Market segmentation strategies (and their pros and cons)
Every market segmentation strategy is different but most of them follow one of two fundamental outlines:
1. Concentration strategy
Concentration strategy is when a company determines that its efforts are best focused solely on a single market segment. This strategy is particularly great for small, growing businesses that have demonstrated a viable use case within a specific market. Focusing on one segment will allow the company to invest more time, energy, and resources into one specific market, which minimizes advertising spend and potentially mitigates wasting efforts across multiple segments.
Concentration strategy is like putting all your cards on the table—if it doesn’t work out, it can end badly. If the market segment hasn’t been properly vetted and turns out to be a bust, all of your marketing efforts could be wasted. Be sure to do some careful planning and execute thorough market testing before committing your business to a single market segment.
- Pros: High conversion percentages, repeatable marketing practices, less marketing spend
- Cons: “All-or-nothing,” growth potential is limited to segment size
2. Multi-segment strategy
Multi-segment marketing, or differentiated marketing, is when a company’s marketing strategies are designed to advertise one product to more than one market segment.
Although apparently “safer” than concentration strategy, multi-segment marketing is a much larger tax on a company’s marketing spend, as it requires completely different campaigns for each market segment.
However, if a particular segment is extremely receptive and converts well, it’s easy to tailor your strategy to market more directly to that segment.
- Pros: Safer, appeals to more consumers, diverse marketing, high growth potential
- Cons: Lower conversion percentages, greater marketing spend
How to do your own market segmentation in phases
Ready to complete market segmentation for your company? Here are three phases to follow during the process that will help you ensure you’re analyzing your markets effectively:
Phase 1: Gather the data
First things first, it’s time to gather data so that you can use it to form your market segments. There are many ways to go about it—some people like to buy pre-made lead lists and others prefer to do their own research .
Two helpful methods of researching prospects are webforms and surveys. You can place high-quality data behind webforms that requires site visitors to submit their name, email address, and other information to access the content. Surveys can get specific information from potential buyers in exchange for tangible rewards, like a gift card or special offer.
If you’re doing your own research, you can frame your searches along the following categories:
- Researching by company size: Size can mean a number of things, but is most often measured by the number of employees, number of customers, or overall sales revenue a company claims. Some companies have greater transparency on their websites, which makes reaching out to the correct person much easier.
- Researching by industry: It’s unlikely that your product is applicable across all industries, which is why industry segmentation exists. Industry segmentation will help you ensure that you’re not wasting your time by targeting a company with no need for your product.
- Researching by location: If you’re offering a location-specific product or service, like landscaping services within the local community, your geographic market segmentation is probably pretty airtight: You probably use handy tools like lead maps , and engage in local marketing wherever possible. For other industries, like IT staffing, your reach might be international. Whatever your product, location is a crucial thing to know about a company, because it will help you decide which sales tactics to use and when to send your emails if you’re communicating across time zones, at the least.
- Researching by needs: This method of segmentation entails qualifying companies based on whether they need your products or services. While this definition is straightforward, the process behind making this determination may not be, depending on what you’re offering. If you sell landscaping services, you can use Google Maps to look up a company’s HQ. If their office is in a tower in New York City, they probably don’t need any landscaping.
Reporting & analytics in Nutshell
Learn more about Nutshell’s reporting and analytics features
SEE REPORTING FEATURES

Phase 2: Sort the data into segments
There are many ways to go about sorting data. Most involve expensive analysts, marketers, and lots and lots of time. Although the DIY route is faster, it is no substitute for a comprehensive market segmentation strategy.
Assuming time and money are an obstacle, you can approximate your own market segmentation by compiling your data into one single source and running filters on it to manually group your prospects and companies together by segments.
Remember, ask yourself the following:
- Is this segment measurable?
- Is this segment large enough to earn a profit?
- Is this segment stable, and not going to vanish after a short time?
- Is this segment reachable with my marketing strategies?
- Is this segment homogenous, and will they respond similarly to my marketing strategies?
Phase 3: Plug in your marketing channels
Now that your segments have been firmly established, it’s time to connect the dots and breathe life into your marketing. This means establishing a plan for each of your marketing tools and channels and coming up with real ways to reach your segments with them.
You’ll be attributing different marketing and sales tactics to each stage of your pipeline and determining what sticks. The good news is that your market segments are clearly defined and you’ll be able to speak to them clearly.
The real challenge is continuously improving your efforts with trial and error to get the best possible conversion rates.
There’s a good, old-fashioned way to map this out quickly and easily:
- Draw your pipeline stages horizontally across a sheet of paper.
- Above each pipeline stage, jot your marketing channels, like Linkedin, emails, or webinars, with blank space in between them.
- Below each marketing channel, write exactly how you will use this tool at this pipeline stage, like “email prospects a link to a recorded webinar.”
Repeat this exercise for each market segment to help establish a concise and repeatable process for marketing to your various audiences. You can fully flesh out your segmented marketing strategy by configuring your sales software and email automation around the outline you’ve created, and then make tweaks as needed.
To this end, some CRMs have reporting and performance tracking as well as custom reporting to help you figure out what’s working and what needs to change.
Still have questions about market segmentation? Check out the FAQs below for answers to some common questions:
What are some common challenges faced when implementing market segmentation?
Here are a few of the challenges you may encounter when implementing your market segmentation strategy:
- Creating segments that are too broad: Your product or service may appeal to several different market segments, but trying to appeal to too many can lead to ineffective marketing and high ad spending.
- Creating segments that are too narrow: The opposite problem can also arise. Small segments might be difficult to quantify and distract from other segments with greater buying power.
- Not being flexible: Just because a particular segment is currently buying from you doesn’t mean they always will. Be willing to reevaluate your market segments over time to maximize your marketing spending and revenue.
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a target market segment?
Five key factors to consider when selecting market segments for your marketing strategies are:
- Whether the segment is measurable
- Whether the segment is large enough to generate a profit for your business
- If the segment is stable and won’t vanish after a short time
- If the segment is reachable by your marketing strategies
- Whether the segment is homogenous and will respond similarly to your marketing strategies
How can you effectively redefine your target market?
If you’ve determined that your target market no longer fits, you can always identify new markets . Here are a few tips for doing so:
- Identify trends and patterns: Do companies that make a certain amount of annual revenue seem to be shying away from your offerings? If you want to reach those customers, identify any patterns in which products or services they choose instead and strategize for how to provide the value they’re looking for.
- Listen to customer feedback: Your current (or former) customers are valuable sources of feedback. Consider what they’re saying about your product or service and whether you’re meeting their needs. You may be able to identify new opportunities.
- Diversify your marketing channels: Using multiple channels to reach your target market can be a highly effective way to increase exposure for your brand. Consider diving into new channels like content marketing, email marketing, SEO, and online advertising to drive engagement with your target audience.
Additional resources:
- Sales tactics encyclopedia: 19 strategies for prospecting, qualifying, and closing
- The complete guide to researching sales prospects: 13 tools to help you understand your buyers
- The ultimate guide to cold calling
- 16 B2B cold email templates that sales experts swear by
- How to build a sales process: The complete guide
- Buying a lead list: The pros, the cons, and the things that might land you in jail
Now you’ve got your demographics clearly segmented, your strategy figured out, and your sales processes mapped tightly to your market segments.
Because of this, you should have a clear understanding of how to talk to your prospects, and how to differentiate your outreach efforts based on the market segment.
The challenges that lie ahead are rooted in constantly adjusting your marketing—testing your messages, your tactics, and measuring your audiences’ responses.
If you’re ready to put your sales and marketing automation into action, get started with a free trial of Nutshell today!
Give our powerful, easy-to-use CRM a try for free for 14 days!
START YOUR FREE TRIAL
Ready to try Nutshell for Free?

The 16 Must-Attend Sales Conferences

The Five (Or So) Worst Cold Emails We’ve Ever Seen

10+ Best Survey Apps of 2023: Hear From Your Audience
What is nps and how can it help you make more sales, how to implement a sales process: the complete guide, how to use a sales activity report to coach your sales team.
Join 30,000+ other sales and marketing professionals. Subscribe to our Sell to Win newsletter!

Target Market Segmentation
Target market segmentation helps you market better to potential customers. Let's take a look at what this means and how you can grow your small business.
Download Template
Fill the form below to download this template
Thank for you submitting the information.
Click below to download template.
Calculating Stripe fees for customer payments is easy with our calculator. Enter the payment amount to calculate Stripe's transaction fees and what you should charge to receive the full amount.
Our calculations are based on Stripe's per-transaction fees of 2.9% plus $0.30.
Calculate how much you’ll pay in Square fees for online, in-person, and manually-entered payments.
Enter your loan information to get an estimated breakdown of how much you'll pay over the lifetime of your loan.
PayPal fees can be confusing. Our calculator helps you understand how much you’ll pay in fees for common transaction methods.
arget market segmentation helps you market better to potential customers. It's crucial to boost sales and increase the chances of long-term success. Let's take a closer look at what this term means and how you can use it to focus your marketing efforts.
What is Target Market Segmentation, and Why Does It Matter?
Target marketing segmentation is where you divide your potential customers into segments. You'll then focus on a few segments (or groups of people) that align most with your product or services. Doing so helps you tap into their needs and desires to attract new sales and increase longevity. You can also drill it down further by creating a marketing strategy for more specific groups of people - such as using different promotions and how you deliver your products or services. That way, it helps your marketing campaigns be more cost-effective, allowing you to spend time only on one focus at a time. Let's say you have a wedding and event photography business . Instead of spending thousands of dollars on print ads in random publications, you'll first see who your target customers are. Based on this information, you'll then focus your marketing campaigns by placing ads in publications where your target audience is most likely to see them. That way, it'll increase the chances you'll get a return on your investment.
How Do I Segment My Target Market?
The good news is that you can approach segmenting the market in many ways based on your company's market research. Four common ways are behavioral, demographic, geographic, and psychographic segmentation. Here's a bit more detail on the types of market segmentation:
Behavioral Segmentation
This segment looks at how consumers interact with brands and products. For instance, you can look at which platforms your ideal customer most frequents, their social media usage, and their customer journey online.
Demographic Segmentation
Businesses tend to feel this is the most important criteria to identify their target market. These include age, gender, education level, income level, social class, nationality, family size, marital status, and religion. Knowing these demographics about your ideal customer can help you with how you want to create marketing campaigns (Gen Xers may not understand the slang Gen Z tends to use, for instance).
Geographic Segmentation
Yes, this segment has to do with details on a consumer's location or where they live. Aside from nationality, you can consider their state, county, town, or city.
Psychographic Segmentation
Businesses can look at elements such as parts of a consumer's personality traits - like whether they lean towards being an extrovert or introvert. You can even consider a consumer's belief systems and lifestyles and consumer behavior.
.png)

How to Effectively Create Target Market Segmentation
Creating a target market analysis will help you understand the types of consumers you need to market to and will even help you break into niche markets. Don't worry; creating one isn't a difficult task, though you'll want to make sure you take the time to get it right to ensure effective marketing messages. Here are four steps you can take.
1. Gather Accurate and Current Data
Gathering details from outside sources can be incredibly valuable to help you gain better insights into your market segment, potential customers, and even your industry as a whole. Plus, if you're just starting out, you may not have enough internal data to get a good enough view of what customer groups you need to target based on customer needs. The challenge when gathering data is that there is plenty out there. Make sure what you're using is both current and accurate.
2. Divide up Market Based on Chosen Characteristics
Now's the time to wade through data and eliminate what isn't relevant to your target market. You'll want to create customer segmentations. Consumers who are most likely attracted to your brand, product, or service will share the same types of characteristics. Identifying these will ensure you're efficient when creating your messaging in your marketing campaigns. Here are some questions to help you get the ball rolling:
- What do my target customers have in common?
- How does my target customer research products and services?
- How does my target define themselves?
Once you have some shared characteristics, you can then use them to create customer profiles or personas. It will also help give you even better insight into what really matters to them, plus any trends and insights to help you develop more ideas to increase sales.
3. Gather Intel on Your Competitors
Understanding the competition in the market is critical. This will tell you exactly what your product or service is up against and what tactics you need to take on to compete. Ask questions like: How many businesses have a comparable offering to you? What's their pricing structure? What reach do they have? Who do they appeal to most? You may find that one group of people is very well served by competitors while another group has yet to be tapped into. Answering these questions will help you identify the most profitable group to target in your marketing plans, as well as identify what types of marketing communications may or may not have worked prior.
4. Use Market Segmentation As Part of Your Business Plan
Now that you've identified your target segment, it's time to use this knowledge as part of your overall business plan. Yes, you want to use the data to create better marketing plans, but this data can also help you tap into other insights. Think about how you can develop new products and services, order the right amount of stock, and even anticipate demand at certain months of the year. That is the essence of knowing your market. For instance, if you know you want to test certain products, look at how you can further segment your target market to see whether you should include this new item as part of your regular offerings. Or, if you know that sales are slow at a particular time of the year, you can look at the data to create campaigns to encourage quick sales.
Using Target Market Segmentation in Your Marketing Strategy
All in all, the goal of target market segmentation is to inform your company's overall business and marketing strategy. It'll help you easily create goals and develop ideas that are more audience-centric. Doing so means you know what they want and when they want it. This will increase brand loyalty in your customer base. Imagine how your business will benefit from this wealth of knowledge!
All-in-one money management
Take your business to new heights with faster cash flow and clear financial insights —all with a free Novo account. Apply in 10 minutes .
Small Business SEO Checklist: 9 Ways to Improve Rankings
How to optimize your google business profile in 2023, 5 tips for improving your business website, spend less time managing your finances.
Take your business to new heights with faster cash flow and clear financial insights—all with a free Novo account. Apply online in 10 minutes.
More Articles On
Small business guide to content marketing, how to expand your customer base and increase sales, the ultimate guide to marketing for small businesses.
Market Segmentation Strategy Solutions
Schedule a Call
Get a personalized walkthrough of thrivenumber™ from a member of our team..
A fervent believer in the promise of human powered growth, Russ leads CMG in partnering with companies to help them become aligned, agile, customer-driven enterprises that unleash the potential of their organizations with sustainable improvements in focus, teams, culture, and process our clients.
Mark leads CMG in partnering with Telecom companies to help them increase customers and accelerate revenue. His 25+ years of experience in growth, strategy and execution includes B2C and B2B multi-channel acquisition programs, customer experiences that surprise and delight, pricing that optimizes customer value, and innovative product development.
Knowing your target market is the first step in successfully selling your products and services, and one of the most important. A marketing segmentation strategy helps determine which customers you can build relationships with, how to group them, and what marketing actions to take to best reach your target market.
Creating a customized experience catered to customers lead to higher customer retention rates and more focused marketing campaigns. Market segmentation does the work of aggregating prospective buyers into groups with common needs that are likely to respond similarly to a marketing action.
This strategy can help determine which of your products and services are most wanted and where. Markets are typically grouped by Geography, Demographics, Psychographics, and Behavior. Determining the right marketing segmentation strategy for your business involves using one of or even a combination of these segments to reach a more targeted consumer base.
Create Your Marketing Segmentation Strategy
Identifying your marketing segmentation strategies ultimately involves answering these five important questions:
- Who is your consumer or business market?
- Where is your consumer or business market located?
- What is your consumer or business market interested in?
- How can you market your products and services to this market?
- Why are certain segments interested or not interested in your products or services?
Each of these strategies can be used to target a different customer base.
Demographic
Demographics are the most common form of segmentation. They divide customers by the structure of certain population traits:
- Marital Status
- Social Class
An example of marketing segmentation using demographics is to combine age and income information to target older, wealthy retirees looking to relocate to Florida to sell beachfront property.
Another demographic strategy would be marketing fantasy or war-based video games primarily to younger individuals ages 18-30.
Regional demographics can help you sell products and services, depending on where your customers live.
- International Marketing
Colleges looking to sell sports merchandise will sell items well within the state, but not so well outside home territory. Larger, non-collegiate conglomerates such as the NFL can expect a wider customer base in North America, but don’t need to bother merchandising as much overseas.
Psychographics
Psychographic or lifestyle segmentation targets customer hobbies and interests. This segmentation strategy caters to the most niche markets, where attractiveness, quality, and brand recognition are more important than price.
- Social Status
- Personality Type
One example of a psychographic segmentation strategy would be to target high-end musical equipment to music enthusiasts that want to collect the best gear or equipment as a status symbol for showcase collections.
Behavioral segmentation is relatively new in the digital age and takes into consideration information a company has collected through customer data reports, surveys, or marketing trends.
- Patterns of Use
- Price Sensitivity
- Brand Loyalty
- Benefits Sought
Consumers want the best brands at the best prices, and their buying patterns predict items and services they are more likely to buy. Amazon.com algorithms track your purchases and know that if you buy a book on grilling, you may also like to buy seasoning or barbecue tongs.
Restaurant menus are also broken up into price levels based on behavior, featuring specials, and seasonal items.
Combination Strategy
Selling snow gear to snowboarding hobbyists in Park City, Utah, combines geographic, psychographic, and demographic marketing segments. High-quality craftsmanship is expected, and customers will pay more for quality, innovative snowboards.
By utilizing a market segmentation strategy that is tailored to your target market in your organizations go-to-market strategy, you can optimize competitive positioning and better understand your customer. Putting in the work at this stage will pay off in the long run with customer retention, brand loyalty, and increased revenue.
Need help building your go-to-market strategy? Since 1998, CMG Partners have been leading strategic marketing consultants for some of the largest media and communications brands worldwide. Contact us to help you define your brand solutions strategy and push your organization to Transform, Grow, and Thrive.
Continue Reading
In this webinar we discuss using agile practices to help your organization overcome barriers to change, change is the only constant in today's business world, and organizations must adapt rapidly to stay competitive., tips for a leading your team into a successful q4, ensure that your team enters q4 2023 strongly and finishes the business year with rigor using these tips, cable growth driver series: residential opportunities, unpacking residential growth opportunities including: home automation & security, prepaid internet, and streaming tv.

Copyright © 2023 CMG Partners, LLC

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

11.5: Market Segmentation
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 97424
5. What are the five basic forms of consumer and business market segmentation?
Most organizations cannot target the total market for a specific product. For each separate part of the market that an organization wants to target, a marketing mix (a set of 5Ps) must be created. It would be very expensive to try to create a marketing mix for every part of the target market. Instead, companies cut up those targets into specific “segments” of the market that the organization is more strategically positioned to be successful in targeting. Segmentation also varies based on the target market being a consumer market or a business market.
The study of buyer behavior helps marketing managers better understand why people make purchases. To identify the target markets that may be most profitable for the firm, marketers use market segmentation , which is the process of separating, identifying, and evaluating the layers of a market to identify a target market. For instance, a target market might be segmented into two groups: families with children and families without children. Families with young children are likely to buy hot cereals and presweetened cereals. Families with no children are more likely to buy health-oriented cereals. Cereal companies plan their marketing mixes with this difference in mind. A business market may be segmented by large customers and small customers or by geographic area.
The five basic forms of consumer market segmentation are demographic, geographic, psychographic, benefit, and volume. Their characteristics are summarized in Table 11.2 and discussed in the following sections.
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation uses categories such as age, education, gender, income, and household size to differentiate among markets. This form of market segmentation is the most common because demographic information is easy to obtain. The U.S. Census Bureau provides a great deal of demographic data, especially about metropolitan areas. For example, marketing researchers can use census data to find areas within cities that contain high concentrations of high-income consumers, singles, blue-collar workers, and so forth. However, even though demographic information is easier to obtain than other types of information, it may not always be the best approach to segmentation because it is limited on what it can reveal about consumers.
Table 11.3 Source: Adapted from Frito Lay website, accessed October 1, 2017.
Many products are targeted to various age groups. Most music CDs, Pepsi, Coke, many movies, the Honda Fit, and thousands of other products are targeted toward teenagers and persons under 25 years old. In contrast, most cruises, medical products, fine jewelry, vacation homes, Teslas, and denture products are targeted toward people 50 years old and up. An example of how Frito Lay targets various age groups for three of its most popular products is shown in Table 11.3 .
Income is another popular way to segment markets. Income level influences consumers’ wants and determines their buying power. Housing, clothing, automobiles, and alcoholic beverages are among the many markets segmented by income. Budget Gourmet frozen dinners are targeted to lower-income groups, whereas the Stouffer’s line and California Pizza Kitchen frozen pizzas are aimed at higher-income consumers.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation means segmenting markets by region of the country, city or county size, market density, or climate. Market density is the number of people or businesses within a certain area. Many companies segment their markets geographically to meet regional preferences and buying habits. Pizza Hut, for instance, gives easterners extra cheese, westerners more ingredients, and midwesterners both. Both Ford and Chevrolet sell more pickup trucks and truck parts in the middle of the country than on either coast. The well-defined “pickup truck belt” runs from the upper Midwest south through Texas and the Gulf states. Ford“owns” the northern half of this truck belt and Chevrolet the southern half.
Psychographic Segmentation
Race, income, occupation, and other demographic variables help in developing strategies but often do not paint the entire picture of consumer needs. Demographics provide basic data that can be observed about individuals, but psychographics provide vital information that is often much more useful in crafting the marketing message. Demographics provide the skeleton, but psychographics add meat to the bones. Psychographic segmentation is market segmentation by personality or lifestyle. People with common activities, interests, and opinions are grouped together and given a “lifestyle name.” For example, Harley-Davidsondivides its customers into seven lifestyle segments, from “cocky misfits” who are most likely to be arrogant troublemakers, to “laid-back camper types” committed to cycling and nature, to “classy capitalists” who have wealth and privilege. Two different managers could be described by demographics as male, managers, 35 years old, with $80,000 per year income. A marketer who just saw the demographics might create one advertisement to reach both of them. However, if the marketer knew that one of the managers was president of his homeowner’s association and captain of a rugby league team and the other manager was a holder of opera season tickets and president of the Friends of the Public Library, the messages might be designed very differently in order to be more successful.
Benefit Segmentation
Benefit segmentation is based on what a product will do rather than on consumer characteristics. For years Crest toothpaste was targeted toward consumers concerned with preventing cavities. Recently, Crest subdivided its market. It now offers regular Crest, Crest Tartar Control for people who want to prevent cavities and tartar buildup, Crest for kids with sparkles that taste like bubble gum, and another Crest that prevents gum disease. Another toothpaste, Topol, targets people who want whiter teeth—teeth without coffee, tea, or tobacco stains. Sensodyne toothpaste is aimed at people with highly sensitive teeth.
Volume Segmentation
The fifth main type of segmentation is volume segmentation , which is based on the amount of the product purchased. Just about every product has heavy, moderate, and light users, as well as nonusers. Heavy users often account for a very large portion of a product’s sales. Thus, a firm might want to target its marketing mix to the heavy-user segment. For example, in the fast-food industry, the heavy user (a young, single male) accounts for only one in five fast-food patrons. Yet this heavy user makes over 60 percent of all visits to fast-food restaurants.
Retailers are aware that heavy shoppers not only spend more, but also visit each outlet more frequently than other shoppers. Heavy shoppers visit the grocery store 122 times per year, compared with 93 annual visits for the medium shopper. They visit discount stores more than twice as often as medium shoppers, and they visit convenience/gas stores more than five times as often. On each trip, they consistently spend more than their medium-shopping counterparts.
Business Market Segmentation
Business markets are segmented differently than consumer markets. Business markets may segment based on geography, volume, and benefits, just as consumer markets are. However, organizations might also segment based on use of the product (such as a petrochemical company having one market segment for purchasers who use polyethylene for instrumentation panels and one for purchasers who use polyethylene for car seats), characteristics of purchasing function (such as purchasing committees, purchasing managers, or purchasing departments), size of the client (one segment for large customers who have different needs than smaller customers), or industry (such as segmenting food systems into restaurants or government agencies such as schools or military bases), as well as other considerations related to characteristics of business customers.
Using Marketing Research to Serve Existing Customers and Find New Customers
How do successful companies learn what their customers value? Through marketing research, companies can be sure they are listening to the voice of the customer. Marketing research is the process of planning, collecting, and analyzing data relevant to a marketing decision. The results of this analysis are then communicated to management. The information collected through marketing research includes the preferences of customers, the perceived benefits of products, and consumer lifestyles. Research helps companies make better use of their marketing budgets. Marketing research has a range of uses, from fine-tuning existing products to discovering whole new marketing concepts.
For example, everything at the Olive Garden restaurant chain, from the décor to the wine list, is based on marketing research. Each new menu item is put through a series of consumer taste tests before being added to the menu. Hallmark Cards uses marketing research to test messages, cover designs, and even the size of the cards. Hallmark’s experts know which kinds of cards will sell best in which places. Engagement cards, for instance, sell best in the Northeast, where engagement parties are popular. Birthday cards for “Daddy” sell best in the South because even adult southerners tend to call their fathers Daddy.
Marketing research can use either primary data (where the organization actually gets the data and analyzes it) or secondary data (where the organization uses data that has already been developed and published by another entity and the organization is able to utilize the data for its own purposes). There are three basic research methods used for gathering primary data: survey, observation, and experiment.
With survey research , data is gathered from respondents—in person, through the internet, by telephone, or by mail—to obtain facts, opinions, and attitudes. A questionnaire is used to provide an orderly and structured approach to data-gathering. Face-to-face interviews may take place at the respondent’s home, in a shopping mall, or at a place of business.
Observation research is research that monitors respondents’ actions without direct interaction. In the fastest-growing form of observation research, researchers use cash registers with scanners that read tags with bar codes to identify the item being purchased. Technological advances are rapidly expanding the future of observation research. Arbitron research has developed a portable people meter (PPM) about the size of a cell phone that research participants clip to their belts or any article of clothing. They agree to wear it during all waking hours. Before the study participants go to sleep, they put the PPM in a cradle that automatically sends data back to Arbitron (now Nielsen Audio). The PPM will tell the marketing research company exactly which television programs the person watched and for how long. It also records radio programs listened to, any web streaming, supermarket piped-in music, or any other electronic media that the research participant encountered during the day. 5
In the third research method, experiment , the investigator changes one or more variables—price, package, design, shelf space, advertising theme, or advertising expenditures—while observing the effects of those changes on another variable (usually sales). The objective of experiments is to measure causality. For example, an experiment may reveal the impact that a change in package design has on sales.
CONCEPT CHECK
- Define market segmentation.
- List and discuss the five basic forms of consumer market segmentation.
- What are some additional forms of business segmentation?
- How does marketing research help companies make better use of their marketing budgets?
How to Write Up and Develop a Market Segmentation Plan
- Small Business
- Advertising & Marketing
- Marketing Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
How to Determine a Customer Base
How to approach new clients, how to conduct a high-level swot for business.
- How to Access Your Target Market
- Examples of Quantitative Marketing Objectives
A written market segmentation plan that has measurable targets attached to specific customer groups can help a business maximize profits. The more a business' owners understands the market, the better their chances of forming a strategy that reaches the most productive customer groups without wasting resources.
Divide and Conquer
Customer segmentation involves grouping customers together based on criteria relevant to your business. You can divide them up by any measure you choose, such as demographically or geographically, and clients can fit into more than one category. The goal is to separate out those segments that your business can serve most profitably, ideally in a way that makes them less prone to switching vendors based on a price decrease or marketing pitch from a competitor.
Market Analysis
The first part of a segmentation plan is market analysis. The plan should describe the industry and its major customer groups -- particularly the ones that your business is targeting. Identify the needs of both current and potential customers. Also note the size of the market and what percentage of it you can reasonably get. A big-picture trend analysis is also helpful. You want to finish this process knowing both why people buy what you are selling now and why that may change in the future.
Information Is Key
The more information you get about your market, the better a segmentation plan is going to be. In addition to commercially available sources, you may find it useful to gather your own data, perhaps by asking existing customers to fill out surveys or by gathering information from trade shows or conferences. It’s worth asking customers how they use your products or services to find out if they are using things in unintended ways that may provide additional means of generating sales, or if they are unaware of what you consider to be a key differentiator that gives you a comparative advantage over the competition.
Kick Customers Out
Don’t forget to also consider whether you’re currently serving customers that perhaps you shouldn’t be. If you’re spending a lot of money marketing your products to a group that isn’t responding and the return on investment is disappointing, it’s time to either come up with a more effective strategy for dealing with that group or abandon that segment to concentrate on more lucrative portions of the customer base.
Write it Up
Once you’ve decided which segments to target, it’s time to write up the findings. Be as specific as possible about your targeted segments, with a detailed action plan and measurable goals. If you continue to monitor the situation once the plan is in effect, you should know quickly whether everything is on the right track or changes need to be made and resources reallocated.
- SBA: Create Your Business Plan
- Mind of Marketing: What Is Customer Segmentation?
- Bain & Company: Customer Segmentation
- CIO: How to Do Customer Segmentation Right
- Strategy+Business: Making Customer Segmentation Deliver
Related Articles
What are the characteristics of market segments & target markets, market segmentation variables & characteristics, importance of setting goals from a marketing standpoint, customer characteristics for marketing, the importance of defining a target market, how to write a marketing analysis report, discuss the difference between market segmentation & target marketing, how to revise a strategic plan, how to write focus group objectives, most popular.
- 1 What Are the Characteristics of Market Segments & Target Markets?
- 2 Market Segmentation Variables & Characteristics
- 3 Importance of Setting Goals From a Marketing Standpoint
- 4 Customer Characteristics for Marketing
Segmentation, Targeting, & Positioning (STP Marketing): The Marketer's Guide
Published: December 06, 2023
As a content strategist, I like to ask my clients a lot of questions, starting with, "Who’s your target audience?"

But do you know what answer I always dread hearing? "Everyone"
While it’s nice to believe that everyone would be interested in purchasing your product or service, this definition (or lack thereof) creates way more work for you and also does a disservice to your actual target market. This is where segmentation, targeting, and positioning come into play.
![market segmentation of business plan → Download Now: Free Product Marketing Kit [Free Templates]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/08b5e1f4-5d26-405b-b986-29c99bd0cb14.png)
We developed this guide to help you understand how and why you should invest time into STP for better, more effective marketing. Let’s dive in.
What is segmentation, targeting, and positioning (STP Marketing)?
Segmentation, targeting, and positioning (often referred to as segmentation-targeting-positioning or STP marketing) is a consumer-centric approach to marketing communications. The STP model helps deliver more relevant, personalized messages to target audiences.

Free Product Go-to-Market Kit
Free templates to ensure that your whole team is aligned for your next product launch.
- Product Launch Template
- Product Roadmap Template
- Sales Plan Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
At its core, STP marketing helps you to better target your marketing messages and better serve your customer base.
Here's an example: I once created a marketing strategy for a fitness apparel brand. Rather than appeal to all fitness enthusiasts across the board, the brand wanted to target a specific segment within their target market: female yoga fans in their 30s and 40s.
Ultimately, our marketing campaign was much more efficient and cost-effective since we knew our audience, where to reach them, and what messages would resonate.
Conducting an STP Marketing Analysis
STP allows you to take a large, anonymous audience and define how your different products (or different components of the same product) relate to specific consumer segments within that larger audience — thus understanding how to position your product(s) and messaging to grab the attention of each segment.
Let’s unpack each part of the segmentation-targeting-positioning model.
1. Segmentation
.jpg?width=650&name=Audience%20Segmentation%20(1).jpg)
Segmentation refers to the process of dividing your audience into smaller groups based on certain characteristics. This process allows you to group your individual audience members into similar groups so you can better communicate your products, features, and benefits that may be most relevant to them.
You can segment your audience based on one or more of these criteria:
- Demographics , which typically answer the question of who your buyer is (e.g. age, gender, education, location, and profession)
- Psychographics , which answer the question of why your buyer buys (e.g. priorities, personality traits, and beliefs and values)
- Lifestyle traits , such as hobbies, entertainment preferences, and non-work activities
- Behavior , such as brand loyalty, channel preferences, and other shopping habits
Segmentation may sound a little familiar to another process we often discuss here on the HubSpot blog — creating buyer personas .
While the two are very similar, buyer personas help you create a handful of customer profiles that represent your broader audience. Segmentation allows you to split your audience into countless groups, each of which you can uniquely target.
For example, let’s say Paws & Tails is a Chicago pet-sitting company that offers pet-sitting, dog walking, and boarding services. Given the vast number of pet owners in the city, they need to segment their audience into smaller groups to better understand how to position their services.
Based on their research and current customer base, they split their audience into three main segments:
- Segment A is made up of high-income pet owners who work often and need daytime dog walking and pet pop-in visits.
- Segment B is made up of middle-class individuals and families who travel and need overnight boarding or pet-sitting services.
- Segment C is made up of older pet owners and retirees who need help caring for their pets.
2. Targeting
With your audience segments in hand, it’s time to move on to the targeting phase. First, however, you must decide which segments are worth targeting with your marketing. To decipher this, I like to ask myself the following questions about each segment:
- Is this segment composed of enough potential customers to justify targeting? Would it yield enough profits if the segment were to convert?
- Is it measurably different from the other segments?
- Is it accessible by all members of Marketing and Sales?
- Is your company equipped and able to serve the segment? Are there any physical, legal, social, or technological barriers that could prevent that?
Choosing what segments to target is a strategic decision. Thankfully, certain strategic planning models — the PESTLE analysis is a personal favorite — can help you better understand the viability of each segment.
It takes a lot of work to successfully target a segment of your audience. But from my experience, whether you’ve identified two segments or ten, don’t feel the need to target more than one segment at once. In fact, I've found that targeting one at a time can help you better position your marketing for each specific segment.
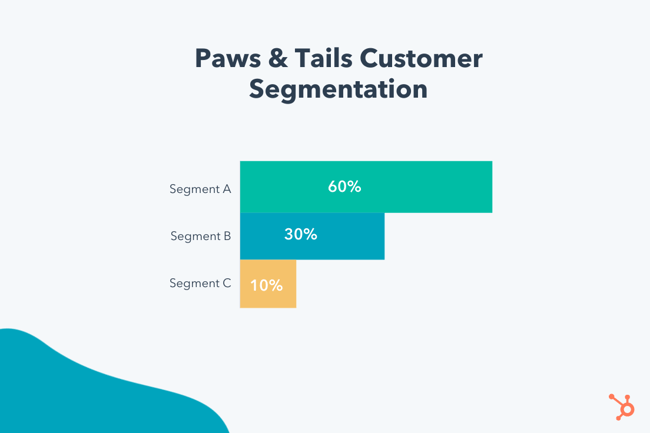
Following our example from before, Paws & Tails conducts research to better understand its Chicago audience. Paws & Tails finds that Segment A makes up 60% of its market size, Segment B makes up 30%, and Segment C makes up 10%. Moreover, Segment A has a higher average income and is willing to pay more for pet-sitting and walking services. Because of this, they choose to focus on Segment A.
3. Positioning
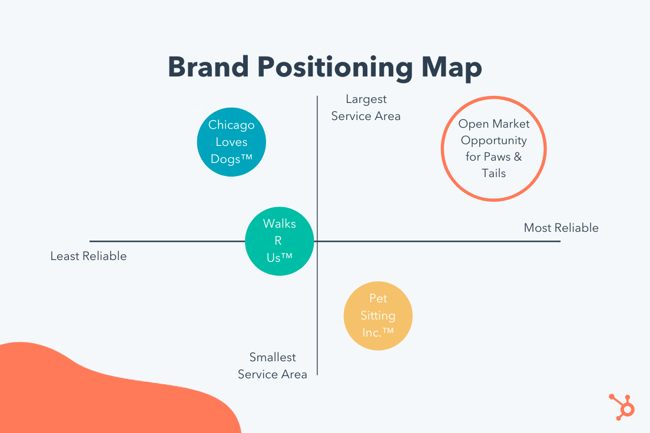
At this point, you should understand the demographics, psychographics, motivations, and pain points of the segments you’ve chosen to target, which can provide a place to start when it comes to positioning your product or service.
First, take a step back and examine your product or service through the perspective of your chosen segment. If you were in their shoes, why would you choose your product over a competitor’s? What features or benefits are most relevant to you, based on the motivations and pain points you’ve identified?
This information is important to defining your brand positioning and understanding how it stacks up next to your competitors. One way to understand where you, well, stand is by building a positioning map , which is “the visual plotting of specific brands against axes, where each axis represents an attribute that is known to drive brand selection.”
The segment you choose to target should dictate what two attributes you plot on your positioning map. For example, let’s say Paws & Tails decides Segment A selects pet-sitting brands based on two attributes: service area and reliability.
By understanding 1) what the target segment deems most important for brand selection and 2) where its competitors succeed (and fall short), Paws & Tails is able to identify an open market opportunity and position its marketing to best fit the needs and goals of its audience.
Using Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning in Marketing
The STP model is a priceless addition to any marketing strategy, regardless of your industry, product, or audience. It prioritizes efficient and effective marketing and ensures you’re delivering only the most relevant, targeted messaging across the board.
It also plays an important role in developing other strategies, such as your buyer personas, customer lifecycle stages, and core brand proposition.
By leading with a consumer-centric approach like STP, you can be sure that every inch of your marketing is relevant to your audience — thus, increasing the likelihood that they convert, purchase, and become lifelong customers.
Examples of Great Market Segmentation and Positioning
Brands are segmenting, targeting, and positioning their audiences and marketing constantly, oftentimes without us (consumers) even noticing. Ever seen a brand or product and thought “Huh, that’s perfect for me” or “Wow, right place at the right time”? Yeah … you’ve been subject to the STP model.
Let’s review a few examples of great marketing segmentation and positioning.
1. Panera Bread

Panera has successfully cornered the “health-conscious” and “ climate-conscious ” segment of the fast casual dining industry. Is Panera’s food so different from other fast casual options? Not entirely.
But by branding themselves with the perspective that “we believe that good food, food you can feel good about, can bring out the best in all of us”, Panera remains top-of-mind as a place to get high-quality food, fast.
2. AllBirds
How did AllBirds position itself to set itself apart from the competition? By elevating its eco-consciousness and placing that front and center in its marketing. According to the AllBirds website, the brand “crafts with planet-friendly natural materials, like merino wool and eucalyptus trees, because they're our best chance for a sustainable future.”
At first glance, AllBirds shoes don’t look too terribly different from other running or walking shoes. However, its audience segment that cares about sustainability and earth-conscious products knows the difference.
No longer can businesses simply segment their audiences by “men” and “women” — the individuals within each broad gender group vary too much, and razor brand Billie took note of this.
In an effort to extinguish the “pink tax,” Billie markets cost-friendly razors and associated products. Moreover, they work to normalize body hair and other forgotten or shamed parts of women’s bodies.
Through this positioning, Billie is able to set their products apart from competitors and create a strong, positive community around their brand.
The world of online dating is a busy, strange place. From Tinder to FarmersOnly.com, there seems to be a place for everyone to meet, well, anyone. Hinge came on the scene only a handful of years ago, yet it has skyrocketed to the top of the list of the most popular and reliable dating app.
Time and time again, I’ve heard that Hinge is a favorite because it works — meaning it helps people meet people and make real relationships. You wouldn’t think a dating app would position themselves to eventually be unnecessary, but that’s exactly what Hinge has done. In fact, its mission statement is to “[build] an app that’s designed to be deleted.”
By putting the needs and desires of its audience front and center, Hinge has created a more trustworthy, in-demand online dating experience and set itself apart from its competitors.
The Case for Using STP Marketing
The segmentation-targeting-positioning model is designed to help you better target your marketing messages and better serve your customer base. It’s a win-win for you and your customers!
This article was originally published October 29, 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Product Launch Checklist: How to Launch a Product, According to HubSpot's Experts
![market segmentation of business plan The 6 Stages of the Product Life Cycle [+Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/product-life-cycle_0.webp)
The 6 Stages of the Product Life Cycle [+Examples]

What Does Product Marketing Do?

Product Classification: What It Is & Its Impact on Marketing Efforts
How Benefit Segmentation Will Take Your Marketing Campaigns to the Next Level

How to Build a Product Ecosystem Buyers Will Want to Be In

9 Product Category Marketing Examples to Inspire Your Own

Product Attributes: What Marketers Need to Know

The Ultimate Guide to Product Marketing in 2023

5 Things Gen Z Will Spend Money On & Why Marketers Need to Care
Free planning and communication templates align your team for your next product launch.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Target Market Examples
Elon Glucklich
7 min. read
Updated March 20, 2024
Imagine your dream is to own a diner.
You have restaurant experience and a great location in mind – you just need the bank to approve your loan to get started.
But the bank has questions. A big one it wants answered is: who is your target market?
It might be tempting just to say, “hungry diners.” But you’ll need to dig deeper to truly define your target market .
In this article, we’ll use this diner scenario to walk through the market research process and illustrate what the final result could look like.
Questions about your target market
Before you even set foot in the bank, you should already have asked – and taken steps to answer – several key questions about your target market.
Let’s call our example business the Bplans Diner. Where is that perfect location you’ve found for the diner? Is it in a densely populated urban area, suburban neighborhood, or rural?
What are your hours of operation? Some diners cater to a breakfast crowd, while others might offer 24-hour dining to be a favorite among night owls. When you expect your peak hours could help determine whether you should expect to sell more omelets or hamburgers.
What’s the area’s median income, and what types of businesses or institutions are nearby? This information will help you determine pricing and marketing strategies for your diner. For instance, if your diner is located in a business district, you may want to offer lunch specials. But if it’s near a college or university, you might want to offer student discounts.
This is what a thorough target market analysis looks like, providing key insights and data to pinpoint the specific groups of customers most likely to patronize your diner. Gathering all of this information may sound intimidating, but it’s really just a matter of doing research. If you need help and guidance, check out our complete guide to conducting market research for your business .
Let’s look at an example of a target market analysis for this diner. Then, we’ll break it down and discuss each element in detail.
Example of a target market analysis

As you can see, the target market analysis follows the basic market segmentation process of splitting out potential customers into their demographic, geographic, psychographic and behavioral traits.
Next, let’s take a look at each in more detail. Afterward, we’ll look at how you can harness your target market analysis into actual business strategies.
- Demographic
You may have noticed that the demographic analysis in our example is very broad – 18 to 65 years old, including students, workers, and some seniors.
Finding your target market isn’t always about identifying a narrow demographic to cater to. In the case of a restaurant, it makes sense to focus on the geographic location and who currently frequents the area (more on that in the next section).
A different approach may be needed for a technology product that’s sold online. In that case, narrowing the demographic focus to specific age ranges or needs would be much more important than where the business is located.
In the case of the diner, we reached our decision by conducting a demographic analysis, examining the age ranges, occupations, and other concrete data points about potential customers near the proposed location (Reminder: we didn’t do this for the Bplans Diner, we’re just providing an example).
There are several ways to go about collecting this information for your business. The most straightforward is to get out in the neighborhood, take a look around and talk to people. Are you mostly seeing students, or families? Are there a lot of office workers in the area?
You can also look up data from the U.S. Census Bureau , which includes population, age, income and other useful information, often down to the neighborhood level.
After conducting this research, one valuable step is to create a detailed customer persona that represents the typical customer you expect for your business (we provide an example of a customer persona for the diner further down in this article).
While the demographic analysis considers the type of people who might frequent your business, the geographic analysis considers the characteristics of the neighborhood itself.
Our target market analysis for Bplans Diner noted that we plan to operate in an urban area near a university with heavy foot traffic and expect a fair amount of late-night diners.
A key reason for examining the geographic makeup of your businesses is to size up your competition. If there’s already a popular diner in the area you plan to target, getting customers could be a major challenge. But if there’s a lack of dining options or no one is serving diner-style food, you’re more likely to be successful. Determining the size of your market will help you create reasonable revenue projections.
We also mentioned the plan for Bplans Diner to cater to a late-night crowd. Examining the geographic makeup of the neighborhood will help you determine if there are the kinds of businesses – bars, music venues, or businesses such as hospitals where people are working all hours – to justify targeting this group.
- Psychographic
You know the demographics and geographic characteristics of your market. Now it’s time to consider the attitudes and values of your potential customers.
The psychographic analysis helps to understand the lifestyle of potential customers and how that might affect their preferences as consumers. If many of your potential customers are health-conscious, for instance, you’ll want to ensure your diner provides options like salads or gluten-free menu items. But if most customers are families looking for a place to bring their children, it may be important to keep classic items like hamburgers and french fries on the menu.
The best way to understand your potential customers’ attitudes is to get out and talk to them. Customer interviews are among the most powerful methods of validating a business idea , since you’ll get honest, real-time feedback from the kinds of people your business would depend on.
Finally, the behavioral analysis expands on customer psychographics by examining what customers do, given their values. This is another place where it’s worth considering the broad demographics of the diner’s target market – 18 to 65 years old, split among students, workers, and seniors.
They may all want the diner’s food, but their behaviors will vary widely. College students might be looking for a late-night study spot, or a place to meet up with friends for dinner before a concert or sporting event. But workers and seniors might be more interested in breakfast or lunch specials.
Each of these behaviors gives a business owner valuable information to target individual segments of their target audience. For instance, you might want to play popular music in the evenings to get young diners ready for a night out on the town. But you’ll want a quieter ambiance at the time of day when seniors are most likely to come in. The environment can be adjusted based on when certain customers frequent the business.
Addressing behavioral aspects like buying motivations and concerns of your potential customers will also help you effectively market your diner. For example, you could create marketing campaigns based on student discounts, late-night specials, or a family-friendly atmosphere, depending on your customers’ behaviors.
Connecting a target market analysis to business strategy
So far, we’ve touched on each of the components of a target market analysis for a diner: customer demographics, geographics, psychographics, and behaviors. (It’s also important to conduct an industry analysis to understand competitive and macroeconomic forces affecting your planning.)
With the target market analysis complete, you’re better equipped to demonstrate a thorough understanding of your customers to a lender.
Here are a few insights a business owner could use for the Bplans Diner, developed through the above analysis.
- Bplans Diner Competitive Analysis
Market Trends: Growing demand for late-night food options, increasing preference for healthy dining options.
Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses:
Competitor A: Strong brand but limited menu options.
Competitor B: Wide variety of options but lacking in ambiance.
- Bplans Diner Marketing Strategy
Product Differentiation: Offering a diverse menu that caters to various preferences, including healthy options.
Positioning: Establishing Bplans Diner as a reliable, quality, 24-hour dining option in the region.
Promotion: Utilizing social media to announce special night-time deals and promotions.
Get started with your business plan template
A target market analysis is a key part of any business plan. But it’s just one piece. At Bplans, we take some of the pain out of business planning. We’ve developed a free business planning template to help reduce entrepreneurs’ time to create a full, lender-ready business plan. Bplans has also collected over 550 free sample business plans across numerous industries. Find a plan in your industry to get inspiration for your plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Elon is a marketing specialist at Palo Alto Software, working with consultants, accountants, business instructors and others who use LivePlan at scale. He has a bachelor's degree in journalism and an MBA from the University of Oregon.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

8 Min. Read
How to Conduct an Industry Analysis

3 Min. Read
How to Use TAM, SAM, SOM to Determine Market Size

10 Min. Read
How to Create a Detailed User or Buyer Persona

9 Min. Read
How to Write a Customer Analysis
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Don't have a Shopify store?
5 Types of Market Segmentation with Examples
Drive 20-40% of your revenue with Avada

You’ve invested a large amount of money and much time into an efficient marketing strategy, and you really hope your message resonates perfectly with your potential customers. Is it right?
This is the reason why market segmentation is important. This practice enables you to concentrate your marketing efforts on each customer segment so you can better satisfy their demands. Your brand can leverage this method to combat your competitors as you show your potential customers that you understand them and apprehend what they need.
Therefore, to know more about What is Market Segmentation? 5 Market Segmentation Examples that will Inspire You , please read on.
Let’s start now!
Related posts
- What is Direct Response Marketing
- Types of Digital Marketing
- Reach vs Impression: What Are The Differences?
What is market segmentation?

Market segmentation is the process of classifying a market of potential customers into small groups or segments based on multiple features significant to you. In a group, customers share the same characteristics and react similarly to your messages.
The aim of segmentation is that you are capable of introducing a more tailor-made message that will be accepted successfully. This is beneficial for organizations that have a product or service in the marketplace that shows off different uses for different groups of customers.
Market Segmentation based on business types

So what criteria can we base on to implement market segmentation? Here are the two criteria we want to introduce to you:
B2C business

Except for professional customers or prosumers, customers are often more sensitive to price and tend to come up with an impulsive decision. Segmentation of these types of consumers shows their purchasing habits.
B2B business

B2B purchasers are a different type. They are not sensitive to price. As your products can save the business money and time or make money, then it’s worth it. Price is just a secondary factor.
They will consider how much it impacts on their workflow and how difficult it is to carry out.
5 Types of market segmentation and examples

Demographic Segmentation

Demographic segmentation is the easiest and the most popular applied type of market segmentation. Organizations utilize it to form broad segments of the population in terms of age, gender, location, religion, family size and so on.
These are typically black and white groups that provide you a profile of whether or not someone can purchase your products. For instance, if you offer a product for people 21 and beyond, then those who under that age would not be for you.
Correspondingly, products for men usually won’t be relevant to women unless you offer it as a gift.
Behavioral Segmentation
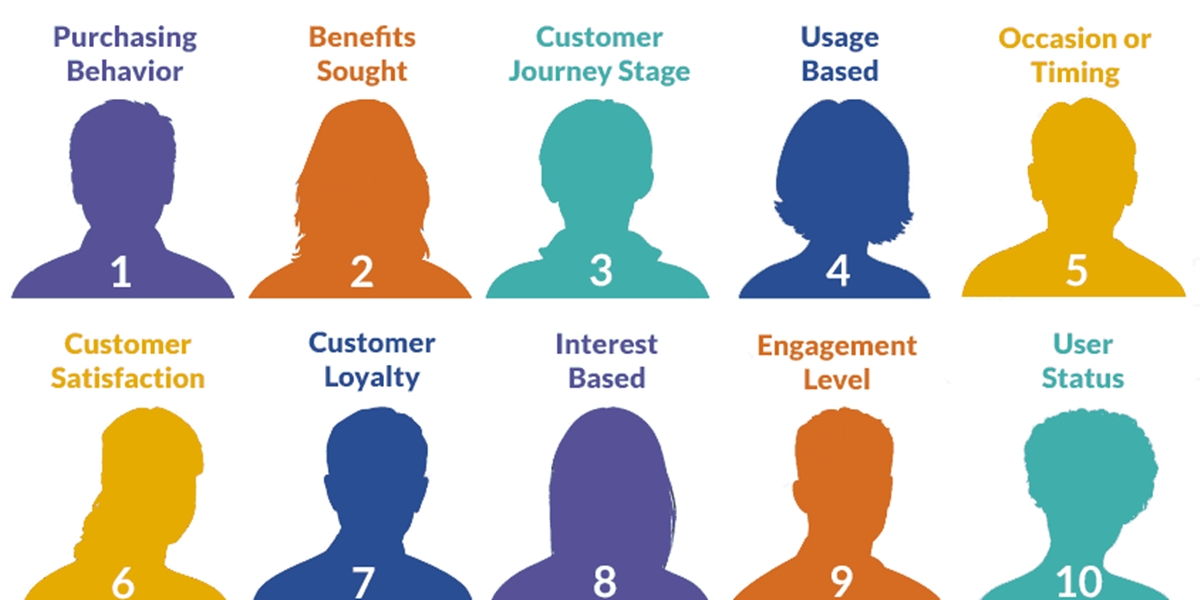

Behavioral segmentation involves the way people decide over time or react to stimuli. For instance, the method that a business uses during Christmas time will differ from the rest of the year.
They recognize that people are more receptive and may be willing to make bigger orders. Younger generation and athletes would love brands like Jordan and Air Max whereas older people would vote for brands like New Balance.
Geographic Segmentation
As its name, the market segmentation type divides people into different groups based on their physical location. This type may be helpful for your company as the demands of your consumers are different from area to area.
For instance, people living in the countryside wouldn’t need a subway but those who work in the city would.
It’s also possible for you to use geographic segmentation to bring special deals to your potential consumers. Besides, you can use it to acclimate the language and tone of your messages.
In Georgia, people would consider soda as coke until you ask several questions. In Chicago, every soda is called pop.
Psychographic Segmentation

Psychographic segmentation is used to form groupings based on customers’ lifestyles, interest and activities. Demographic segmentation shows you someone is a younger male, while psychographic segmentation tells you they go to the cinema on the weekends.
This type of segmentation indicates what customers do and why they purchase. It is quite similar to behavioral segmentation, but there exists a difference.
Behavioral segmentation lets us know that this demographic segment buys paper straws. Psychographic segmentation tells us this demographic segment buys paper straw because they can be recycled and the buyers are environmentally conscious.
Lenovo collaborated with Newstar, carried out market segmentation, and built personalized banners on their homepage that boosted click-through rates by 30% and conversion rates by 40%.
Firmographic segmentation
This type of market segmentation refers to analyzing and grouping business-to-business audiences and customers according to similar features that are important to your business. The way a firmographic grouping will search for one company may differ from the way it searches for another company.
Does this mean one organization is compatible with their firmographic segmentation and another is not?. No, it just means their KPIs are different from each other. For instance, a domestic brand may divide their leads based on location and these locations are north, south, east and west. Meanwhile, an international brand may also divide based on location, but their groups are Asia, Europe, South America, North America, Australia and so on.
Firmographic segmentation can have an effect on the way you access potential customers, the information you push forward as advantages, and the solutions being recommended. For instance, if you have an accounting solution that can be suitable for small businesses and enterprise customers, you would not use the same method to access them.
For small businesses, you can implement paid ads and try to achieve direct sign ups. For enterprise clients, you may concentrate on lead generation, demos, and create tailored solutions to satisfy their demands. Firmographic segmentation provides you with the insights to come up with those decisions.
Examples of successful market segmentation business

Automobile industry

The automobile industry can be a good example of market segmentation. Every person needs a car to travel. However, is traveling from one place to another is the one and only “need” on the basis of which brands market their products? Then why are there a lot of various makes, models and versions from one single company?
This is because purchasers mainly need private and convenient transportation. Nevertheless, there are some other considerations that people want to make. Some people want to buy a large and spacious car to have enough rooms for family members. Some may wish to own vehicles with strong power and high speed. And even others purchase a car as a status symbol.
Automobile companies totally understand how to identify and make use of these differences.
Regarding the Volkswagen Polo, what will spring to people’s minds would be some attributes such as robust, affordable and hatchback. But do you know the Volkswagen group produces Audi , Lamborghini and the Porsche among others?
Volkswagen has some different characteristics for different customer groupings. It can be trustworthy to some and elite to others. It has boosted the science of clustering purchasers with the same demands and invents a focused marketing mix for every cluster to position its vehicles as the perfect choice in the market.
Victoria’s secret

Victoria’s Secret deals are creating and marketing women lingerie and beauty products. They concentrated on women and “women” is the main market segment in their marketing campaign. Applying demographics segmentation, this company is also classifying their target market with product differentiation as PINK for adolescent girls.
The company Victoria’s Secret also uses geographic segmentation to serve their customers not only in America but also in the UK and Europe. They currently own more than a dozen stores.
Victoria’s lingerie brand is available in nearly 75 countries with about 1000 stores worldwide. It also owns 990 sales points in the USA. In addition, this company developed geographical segments to China in the lingerie market.
Moreover, as an example of psychological market segmentation, Victoria’s Secret also grouped its consumers according to women’s personalities and self-confidence. Victoria is growing towards a sexy, fashionable and open-minded trait.
Furthermore, in behavioral segmentation, this company has loyal consumers because Victoria makes them feel alive and self-assured. Clients buy Victoria lingerie product lines for prestige and they also go for this brand during birthdays and holidays.

In demographic segmentation, Coca Cola company aims to serve youngsters from 15 to 25 years old. This organization creates income level groups including different packing, for instance, returnable glass bottles, plastic bottles and tins with various pricing programs.
Using geographic segmentation, Coca Cola has many customer groups in different regions such as Asia Pacific, North America, Latin America, Europe, and Eurasia and Africa.
Besides, Coca Cola is considered a great example of psychographic segmentation. They created Diet Coke for those who are health conscious, offered a number of energy drinks for those who need energy particularly in sport, and also provided Real Gold for busy people in offices.
Plus, in behavioral segmentation, Coca Cola consumers are classified into segments on the basis of their knowledge of, attitude toward, use of and response to a product. Coca Cola buyers can be recognized according to occasions such as weddings, festivals or birthdays. Sometimes, to promote Coke - a drink to quench thirst and to refresh, the company includes prizes in the top cover.

Apple has divided the overall electronics market into mainly early adapters and wealthy market groupings.
Wells Fargo and JP Morgan

The bank industry is another great example of market segmentation. Both Wells Fargo and JP Morgan are large banks with a variety of different products that request market segmentation to best market them individually.
What are the benefits of market segmentation?

Segmentation marketing was invented to serve one main goal: increase ROI
With the aid of customer segmentation and personalized marketing strategies, organizations decrease the risk of implementing campaigns to uninterested customers. This improved campaign effectiveness concentrates resources on more ROI-generating efforts. Now we’ll look deeper to see how it exactly works.
Boosted competitiveness and market expansion
By concentrating on a certain subset of potential customers, your competitiveness in that market group naturally accelerates. If you’re concentrating mainly on retired seniors, investing much time and a lot of resources into them, your brand recall and brand loyalty are probably to be enhanced, knocking out other competitors.
Your market share can also rise by concentrating on specific market segments. For example, with a geography-based market campaign, you can begin market your products to San Francisco, then the bigger bay area, and consequently the state of California.
Enhanced time and money efficiency
If you launch marketing campaigns tailored particularly for distinct groups, you are able to prioritize consumer segments that are likely to get involved and convert. By putting more conversion efforts on them, rather than distributing resources evenly throughout all segments, tie and money are spent more effectively.
Better relationships and customer retention
The process of market segmentation refers to continually learning more about your customers so you can better satisfy their demands. The more you understand them, the stronger your interaction and your relationship with them becomes.
Closer relationships make it more difficult for them to leave you - improved customer retention . As you implement customer segmentation to track their changing situations - they age, have families, change jobs, grow more interests, have more purchasing patterns - you can certainly market to them. By offering products and services that intrigue consumers at different life stages, you are able to keep customers who might switch to your competitors.
Further readings
- Marketing to Children: The Good, The Bad and The Ugly
- What Is Market Orientation?
- How To Do Google Maps Markting?
Market Segmentation can help your business to target the right audience and the right goals. You can understand more about your customers, see how to better approach them and find new markets to expand.
If you feel it’s hard to have the exact data and implement it in your business, hope that the 5 Market Segmentation Examples can be useful. Let us know how you’re implementing Market Segmentation in the comment box or leave any questions you have.
Thank you for your time. Have a nice day!
Related Posts:
- Market development strategy: How to choose the right strategy for your business?
- What is a Go To Market strategy? 7 Steps to build a successful Go To Market strategy
- --> --> --> -->