Teaching Commons Conference 2024
Join us for the Teaching Commons Conference 2024 – Cultivating Connection. Friday, May 10.

Summative Assessment and Feedback
Main navigation.
Summative assessments are given to students at the end of a course and should measure the skills and knowledge a student has gained over the entire instructional period. Summative feedback is aimed at helping students understand how well they have done in meeting the overall learning goals of the course.
Effective summative assessments
Effective summative assessments provide students a structured way to demonstrate that they have met a range of key learning objectives and to receive useful feedback on their overall learning. They should align with the course learning goals and build upon prior formative assessments. These assessments will address how well the student is able to synthesize and connect the elements of learning from the entirety of the course into a holistic understanding and provide an opportunity to provide rich summative feedback.
The value of summative feedback
Summative feedback is essential for students to understand how far they have come in meeting the learning goals of the course, what they need further work on, and what they should study next. This can affect later choices that students make, particularly in contemplating and pursuing their major fields of study. Summative feedback can also influence how students regard themselves and their academic disciplines after graduation.
Use rubrics to provide consistency and transparency
A rubric is a grading guide for evaluating how well students have met a learning outcome. A rubric consists of performance criteria, a rating scale, and indicators for the different rating levels. They are typically in a chart or table format.
Instructors often use rubrics for both formative and summative feedback to ensure consistency of assessment across different students. Rubrics also can make grading faster and help to create consistency between multiple graders and across assignments.
Students might be given access to the rubric before working on an assignment. No criteria or metric within a summative assessment should come as a surprise to the students. Transparency with students on exactly what is being assessed can help them more effectively demonstrate how much they have learned.
Types of summative assessments
Different summative assessments are better suited to measuring different kinds of learning.
Examinations
Examinations are useful for evaluating student learning in terms of remembering information, and understanding and applying concepts and ideas. However, exams may be less suited to evaluating how well students are able to analyze, evaluate, or create things related to what they've learned.
Presentation
A presentation tasks the student with teaching others what they have learned typically by speaking, presenting visual materials, and interacting with their audience. This can be useful for assessing a student's ability to critically analyze and evaluate a topic or content.
With projects, students will create something, such as a plan, document, artifact, or object, usually over a sustained period of time, that demonstrates skills or understanding of the topic of learning. They are useful for evaluating learning objectives that require high levels of critical thinking, creativity, and coordination. Projects are good opportunities to provide summative feedback because they often build on prior formative assessments and feedback.
With a portfolio, students create and curate a collection of documents, objects, and artifacts that collectively demonstrate their learning over a wide range of learning goals. Portfolios usually include the student's reflections and metacognitive analysis of their own learning. Portfolios are typically completed over a sustained period of time and are usually done by individual students as opposed to groups.
Portfolios are particularly useful for evaluating how students' learning, attitudes, beliefs, and creativity grow over the span of the course. The reflective component of portfolios can be a rich form of self-feedback for students. Generally, portfolios tend to be more holistic and are often now done using ePortfolios .
Created by the Great Schools Partnership , the GLOSSARY OF EDUCATION REFORM is a comprehensive online resource that describes widely used school-improvement terms, concepts, and strategies for journalists, parents, and community members. | Learn more »

Summative Assessment
Summative assessments are used to evaluate student learning, skill acquisition, and academic achievement at the conclusion of a defined instructional period—typically at the end of a project, unit, course, semester, program, or school year. Generally speaking, summative assessments are defined by three major criteria:
- The tests, assignments, or projects are used to determine whether students have learned what they were expected to learn. In other words, what makes an assessment “summative” is not the design of the test, assignment, or self-evaluation, per se, but the way it is used—i.e., to determine whether and to what degree students have learned the material they have been taught.
- Summative assessments are given at the conclusion of a specific instructional period, and therefore they are generally evaluative, rather than diagnostic—i.e., they are more appropriately used to determine learning progress and achievement, evaluate the effectiveness of educational programs, measure progress toward improvement goals, or make course-placement decisions, among other possible applications.
- Summative-assessment results are often recorded as scores or grades that are then factored into a student’s permanent academic record, whether they end up as letter grades on a report card or test scores used in the college-admissions process. While summative assessments are typically a major component of the grading process in most districts, schools, and courses, not all assessments considered to be summative are graded.
Summative assessments are commonly contrasted with formative assessments , which collect detailed information that educators can use to improve instruction and student learning while it’s happening. In other words, formative assessments are often said to be for learning, while summative assessments are of learning. Or as assessment expert Paul Black put it, “When the cook tastes the soup, that’s formative assessment. When the customer tastes the soup, that’s summative assessment.” It should be noted, however, that the distinction between formative and summative is often fuzzy in practice, and educators may have divergent interpretations and opinions on the subject.
Some of the most well-known and widely discussed examples of summative assessments are the standardized tests administered by states and testing organizations, usually in math, reading, writing, and science. Other examples of summative assessments include:
- End-of-unit or chapter tests.
- End-of-term or semester tests.
- Standardized tests that are used to for the purposes of school accountability, college admissions (e.g., the SAT or ACT), or end-of-course evaluation (e.g., Advanced Placement or International Baccalaureate exams).
- Culminating demonstrations of learning or other forms of “performance assessment,” such as portfolios of student work that are collected over time and evaluated by teachers or capstone projects that students work on over extended periods of time and that they present and defend at the conclusion of a school year or their high school education.
While most summative assessments are given at the conclusion of an instructional period, some summative assessments can still be used diagnostically. For example, the growing availability of student data, made possible by online grading systems and databases, can give teachers access to assessment results from previous years or other courses. By reviewing this data, teachers may be able to identify students more likely to struggle academically in certain subject areas or with certain concepts. In addition, students may be allowed to take some summative tests multiple times, and teachers might use the results to help prepare students for future administrations of the test.
It should also be noted that districts and schools may use “interim” or “benchmark” tests to monitor the academic progress of students and determine whether they are on track to mastering the material that will be evaluated on end-of-course tests or standardized tests. Some educators consider interim tests to be formative, since they are often used diagnostically to inform instructional modifications, but others may consider them to be summative. There is ongoing debate in the education community about this distinction, and interim assessments may defined differently from place to place. See formative assessment for a more detailed discussion.
While educators have arguably been using “summative assessments” in various forms since the invention of schools and teaching, summative assessments have in recent decades become components of larger school-improvement efforts. As they always have, summative assessments can help teachers determine whether students are making adequate academic progress or meeting expected learning standards, and results may be used to inform modifications to instructional techniques, lesson designs, or teaching materials the next time a course, unit, or lesson is taught. Yet perhaps the biggest changes in the use of summative assessments have resulted from state and federal policies aimed at improving public education—specifically, standardized high-stakes tests used to make important decisions about schools, teachers, and students.
While there is little disagreement among educators about the need for or utility of summative assessments, debates and disagreements tend to center on issues of fairness and effectiveness, especially when summative-assessment results are used for high-stakes purposes. In these cases, educators, experts, reformers, policy makers, and others may debate whether assessments are being designed and used appropriately, or whether high-stakes tests are either beneficial or harmful to the educational process. For more detailed discussions of these issues, see high-stakes test , measurement error , test accommodations , test bias , score inflation , standardized test , and value-added measures .

Alphabetical Search
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, what is the difference between formative and summative assessment, formative assessment.
The goal of formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing feedback that can be used by instructors to improve their teaching and by students to improve their learning. More specifically, formative assessments:
- help students identify their strengths and weaknesses and target areas that need work
- help faculty recognize where students are struggling and address problems immediately
Formative assessments are generally low stakes , which means that they have low or no point value. Examples of formative assessments include asking students to:
- draw a concept map in class to represent their understanding of a topic
- submit one or two sentences identifying the main point of a lecture
- turn in a research proposal for early feedback
Summative assessment
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark.
Summative assessments are often high stakes , which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include:
- a midterm exam
- a final project
- a senior recital
Information from summative assessments can be used formatively when students or faculty use it to guide their efforts and activities in subsequent courses.
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links
Join us for our next live demo on Thursday, April 4th to get a closer look at the Otus platform
Assessments
Grading & Reporting
Data & Analytics
Progress Monitoring
Request A Demo
Common Assessments
Standards-based grading, data-driven decisions, multi-tiered systems of support (mtss), portrait of a graduate, family engagement, product updates, implementation & support, partners & integrations, success stories, in the news, the ultimate guide to summative assessments.
Guides | 20 minutes
What are examples of summative assessments?
What are summative assessments in education.
Summative Assessments are—in simple words—the way educators determine what a student has learned. They are typically tests or cumulative assignments that provide teachers with insights into the overall success of their instructional methods. Summative assessments also reveal if students have or have not mastered the learning targets or standards. Additionally, summative assessments provide school administrators, districts, and other key decision makers with actionable data and insight into how successfully a curriculum or teacher performs.

Summative assessments must be created following specific guidelines, which are outlined in detail below. In brief, summative assessments must provide valid, reliable data points that can be compared across classrooms, across time, and across graders in order to measure student growth and teacher, district, or curriculum efficacy.

What does a summative assessment measure?
Summative assessments measure student learning along with teacher and curriculum effectiveness. Unlike formative assessments , which are often low-stake check-ins, summative assessments are typically high stakes, serving not only as the cumulation of a unit, semester, or school year, but also frequently serving as the key factor in a student’s grade or an administrator’s decision about a teacher or curriculum.
Teachers who incorporate mastery learning into their instructional process rely heavily on summative assessments to measure whether or not a student has mastered the content taught. When they have finished their units, teachers offer a summative—or cumulative—test, project, or essay to determine if students have reached the key learning targets. If a student does not reach a predetermined score (80%, according to most mastery learning models), teachers adjust what content comes next and often provide strategic interventions to provide students with the time needed to truly master the content. In this way, summative assessments can be thought of as formative, in that teachers inform next steps based on summative results.
Why are summative assessments used in education?
Summative assessments are highly valued in education due to the valuable data they provide. Unlike formative assessments, which are typically more subjective and rarely designed to be used across classrooms or schools for comparative purposes, summative assessments are created for validity and reliability.
Validity in summative assessments—or the ability of an assessment to actually measure what it is supposed to measure—ensures that teachers can be confident that students have or have not mastered the key learning objective. Additionally, valid summative assessments mean that educators and administrators are able to trust the summative assessment’s data about whether or not a teacher or curriculum performed as expected. A summative assessment’s validity ensures that decisions are made according to the true learning targets and not some side topic that may have unintentionally found its way into the assessment.
Reliability in summative assessments—or the ability of an assessment to reproduce consistent outcomes across time and setting regardless of grader—ensures that teachers and administrators are making decisions using accurate data, not outlying data. This is especially important in situations where a teacher’s salary or a controversial curriculum hangs in the balance.
Many educators have found that online tools allow them to more effectively gather and analyze data for validity and reliability, and to measure trends over time. Additionally, online tools allow teachers to quickly spot anomalies so they know which students need enrichment or intervention.
How do you write a summative assessment?
Summative assessments must be written according to a few specific guidelines.

First, in order to ensure a summative assessment is valid, teachers must:
- Determine the key learning objectives or standards that they will teach.
- Decide on what format will best showcase whether or not that objective or standard has been met. In some cases, a multiple choice test might work best; in others, teachers may need to choose something more along the lines of an essay or project.
- Ensure that students understand the learning objectives, the method of the summative assessment, and the grading scale or rubric. Students are far more likely to not only perform better on summative assessments but also to engage and take ownership in their learning when they clearly understand what they are being asked to do and why.
- Plan and teach curriculum that closely aligns with the learning objectives and parallels the summative assessment.
Second, in order to ensure a summative assessment is reliable, teachers must:
- Create a comprehensive grading plan—or rubric—to ensure data is consistently and correctly gathered.
- Ensure classroom instruction and curriculum follows the same plan across classrooms or year over year, depending on how the teacher is planning to use the data from the summative assessments.
- Decide on how the summative assessment will be given in order to ensure consistent results across classrooms or time. Does it always need to be given at a specific time of day or of year? Does the classroom need to be set up a certain way? Does the teacher provide specific prompts or help during the assessment?
- Create and execute the summative assessment according to the predetermined guidelines. Many teachers find it helpful to bring their summative assessments to their Professional Learning Communities (PLCs) for help in spotting questions that could take away from the test’s validity or reliability.
- Grade the summative assessment according to the predetermined guidelines. Many teachers find it helpful to bring in “blind graders”—fellow staff or other experts to grade the assessments without any background knowledge of students or classroom instruction.
Third, teachers should take time to analyze the results of their summative assessment. Did students master the learning targets or standards ? Did this unit drive their understanding and comprehension forward? Or will they need intervention and help before moving on to the next unit or goal? Teachers should then make decisions about how to proceed.
Fourth, teachers should report findings to the stakeholders—students, parents, administrators, and the like. Students are far more likely to improve their learning when they receive descriptive feedback—clear, exact descriptions of what a student got right or wrong, and more importantly, why they made certain mistakes and how to correct them.
Finally, many teachers find it valuable to bring the results of their summative assessments back to their PLCs. While there, teachers find support in analyzing data, understanding results, and creating intervention plans .
How do summative assessments fit in with the 5 types of assessment?
There are five foundational types of assessments:
- Diagnostic assessments , or pre-assessment, which teachers use to gauge students’ pre-knowledge and zone of proximal development. These typically occur once at the beginning of a unit.
- Formative assessments , which teachers use to determine where student knowledge is at mid-unit. These typically occur frequently throughout the unit.
- Summative assessments , which teachers use to determine student growth at the end of a unit. These typically occur once at the end of a unit.
- Interim assessments , which districts use to measure specific grades across schools. These typically occur once a year.
- Benchmark assessments , which bigger bodies (e.g. states) use to measure overarching student growth and school effectiveness. These typically occur once a year.
Typically, teachers create their diagnostic assessments to mirror their summative assessments in order to easily compare the results of a summative assessment to its unit’s diagnostic assessment. This allows teachers to quickly and easily see if students grew in the desired knowledge during the unit.

Additionally, many teachers work to align the majority of their formative assessments with their summative assessments. For example, teachers may use questions similar to the questions found on the summative assessments as exit tickets throughout the unit. They do this to tap into the “testing effect” of formative assessments: by allowing students to “test” themselves in a low-stakes environment, they are enabling students to recall up to 67% more of what they’ve learned on the final summative assessment than students would have via other study methods.
While summative assessments are not always interim and benchmark assessments, these two categories would fall under the same umbrella as summative assessments, as both teachers and administrators use interim and benchmark assessments to not only determine what students have learned, but to make decisions about staffing, curriculum, or school success.
While there is no one right summative assessment, it is important that teachers use or create summative assessments that will provide valid, reliable data across classrooms or year over year. For example, many teachers use:

- Curriculum Tests : Although a teacher may tweak the test created by the curriculum here or there to align with their state or district’s learning targets, using the curriculum test provides a large degree of validity and reliability, and teachers can easily use the same test (with the same tweaks) in every class for as long as they use that curriculum.
- Rubrics : It is essential that teachers create strong, detailed rubrics when they choose to use writing assignments or final projects. Although it may take the teacher a few rounds with their Professional Learning Communities (PLCs) and iterations in classrooms, eventually teachers should land on a rubric that they can use year over year for reliable data.
- Multiple Choice Tests : These are perhaps the easiest summative assessments to use in terms of gathering and comparing data. However, it can be easy to create multiple-choice questions that don’t align well with the learning objectives, which compromises the validity of the test. Teachers do well to bring their multiple-choice tests to PLCs to get peer feedback on their summative assessments before bringing them to their class.
Again, it’s important to note that regardless of what type of assessments teachers choose to use, these assessments should be used to gauge student learning and make critical decisions about how to enhance the learning process so students receive the best learning opportunities possible.
Privacy Overview

Explainer: what’s the difference between formative and summative assessment in schools?
Senior Lecturer in Educational Assessment, Macquarie University
Disclosure statement
Rod Lane does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Macquarie University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
The recent Gonski report argues Australia needs assessment and reporting models that capture both achievement progress and long-term learning progress. This, according to the review panel, involves low-stakes, low-key, and regular formative assessments to support learning progressions. The report used international evidence on individualised teaching to demonstrate ongoing formative assessment and feedback is fundamental to supporting students to do better in school.
The NSW Education Minister, Rob Stokes, has called for NAPLAN to be replaced in “haste” with less high stakes tests. Mark Scott, the secretary of the NSW Department of Education, echoed Stokes’ remarks. He stated :
I think [NAPLAN] will become obsolete because the kinds of information that the new assessment schemes will give us will be richer and deeper and more meaningful for teachers, for parents and for education systems.
So, what’s the difference between formative and summative assessment? And when should each be used? Formative and summative assessment have different purposes and both have an important role to play in a balanced assessment program.

Formative assessment
Formative assessment includes a range of strategies such as classroom discussions and quizzes designed to generate feedback on student performance. This is done so teachers can make changes in teaching and learning based on what students need.
It involves finding out what students know and do not know, and continually monitoring student progress during learning. Both teachers and students are involved in decisions about the next steps in learning.
Read more: Marking answers with a tick or cross won't enhance learning
Teachers use the feedback from formative tasks to identify what students are struggling with and adjust instruction appropriately. This could involve re-teaching key concepts, changing how they teach or modifying teaching resources to provide students with additional support. Students also use feedback from formative tasks to reflect on and improve their own work.
Regular classroom tasks, whether formal (for example, traditional pen and paper tests) or informal (such as classroom discussions), can be adapted into effective formative tasks by:
making students aware of the learning goals/success criteria using rubrics and carefully tracking student progress against them
including clear instructions to guide students through a series of activities to demonstrate the success criteria. A teacher might, for example, design a series of activities to guide students through an inquiry or research process in science
providing regular opportunities for feedback from the teacher, other students or parents (this feedback may be face-to face, written, or online)
making sure students have opportunities to reflect on and make use of feedback to improve their work. This may involve asking students to write a short reflection about the feedback on their draft essay and using this to improve their final version.
There are many advantages of formative assessment:
feedback from formative assessment helps students become aware of any gaps between their goal and their current knowledge, understanding, or skill
tasks guide students through the actions necessary to hit learning goals
tasks encourage students to focus their attention on the task (such as undertaking an inquiry or research process) rather than on simply getting the right answer
students and teachers receive ongoing feedback about student progress towards learning goals, which enables teachers to adjust their instructional approach in response to what students need
students build their self-regulation skills by setting learning goals and monitoring their progress towards them
results of formative assessments can also be used for grading and reporting.

Summative assessment
This includes end of unit examinations and the NSW Higher School Certificate (HSC) examination.
Summative assessment provides students, teachers and parents with an understanding of the pupil’s overall learning. Most commonly thought of as formal, time-specific exams, these assessments may include major essays, projects, presentations, art works, creative portfolios, reports or research experiments. These assessments are designed to measure the student’s achievement relative to the subject’s overall learning goals as set out in the relevant curriculum standards.
The design and goals of summative assessments are generally standardised so they can be applied to large numbers of students, multiple cohorts and time periods. Data collected on individual student, cohort, school or system performance provides schools and principals with a tool to evaluate student knowledge relative to the learning objectives. They can also compare them with previous cohorts and other schools.
Read more: Evidence-based education needs standardised assessment
The measurement and evaluation of student achievement this way gives us necessary information about how we can continuously improve learning and teaching.
There are a number of limitations of summative assessment. While formative assessments usually provide feedback for the student to review and develop their learning, summative assessments are rarely returned to students. When assessments provide only a numerical grade and little or no feedback, as the NSW HSC does, it’s hard for students and teachers to pinpoint learning needs and determine the way forward.
Additionally, being a form of “high stakes” assessment, results may be perceived as a way of ranking students. For high achieving students there is recognition and reward, while for the lower performing students there is potential embarrassment and shame. Neither of these things should be associated with an equal opportunity education system.
The author would like to acknowledge the work of David McDonald, a PhD student at Macquarie University in assessment, in writing this article.
- School assessment

Biocloud Project Manager - Australian Biocommons

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

School of Social Sciences – Public Policy and International Relations opportunities

Deputy Editor - Technology
Math teaching support you can trust

resources downloaded

one-on-one tutoring sessions

schools supported
[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities
Engage your students with our ready-to-go packs of no-prep games and activities for a range of abilities across Kindergarten to Grade 5!
Formative And Summative Assessment: The Differences Explained
Tim handley.
The assessment landscape in schools is often confusing and ever-changing. With the debate between the merits of formative vs summative assessments raging on, it can be difficult to know when to use either of these assessment types in your classroom. That’s why, in this article, we will discuss when you should use either type of assessment and explain why.
Formative vs summative assessments – what is the difference?
What is formative assessment, what is summative assessment, formative and summative assessments should be adaptable, formative vs summative assessment comparison chart, formative assessment – constantly assessing ‘in the moment’., how to bring formative assessments into your classroom, formative assessment ideas for your class, ensure each formative assessment routine has a purpose, don’t leave any potholes – why formative assessment is important, 4 things you must remember regarding summative assessment, formative vs summative assessments – the pros and cons.

When teachers discuss assessment, they often refer to two types – ‘formative’ and ‘summative’, however the distinctions and lines between the two types of assessment can often be blurred and misunderstood.
This article will compare and contrast formative and summative assessments to give you a true view of the difference between both types.
Formative assessment is the use of day-to-day assessments to gauge and explore students’ understanding of a topic.
It is best thought of as an assessment for learning.
Formative assessments are what we carry out to help inform the learning ‘in the moment’. Formative assessment is continuous, informal and should have a central and pivotal role in every math classroom.
If used correctly, it will have a high impact on current learning and help you guide your instruction and teaching by giving ongoing feedback on learners’ progress.
Having an assessment with low stakes allows students to develop their skills, confidence and user experience before attempting a summative assessment with high stakes. It also makes room for self-assessment.
Summative assessments take place after students’ have completed a block of work, whether that be at the end of a unit or at the end of a quarter. They are a more formal way to sum up student progress and are often compared against a standard benchmark.
They are best thought of as assessments of learning.
There are different types of summative evaluations that we carry out ‘after the event’, often periodic (rather than continuous), and they are often measured against a set standard.
Summative assessment can be thought of as helping to validate and ‘check’ formative assessment – it is a periodic measure of how children are, overall, progressing in their mathematics learning.
If formative assessment has been continually carried out, then the results of summative assessment shouldn’t yield any surprises.
Some common examples of summative assessment include:
- Final projects
Importantly, it is not the ‘form’ that assessment takes that determines whether it is formative or summative, instead it is how it is being used.
For example, ‘test style questions’ can be used both as formative assessment (perhaps as exit tickets – questions given to students at the end of the lesson to check student understanding) or summative (perhaps as an end of an instructional unit test or check).
It is important that in all subjects, but especially in math, that we use a combination of both assessment strategies, but that formative assessment, due to its constant nature, makes up the bulk of our assessment activities.
This Venn diagram shows the difference and similarities between the two assessment types very clearly.
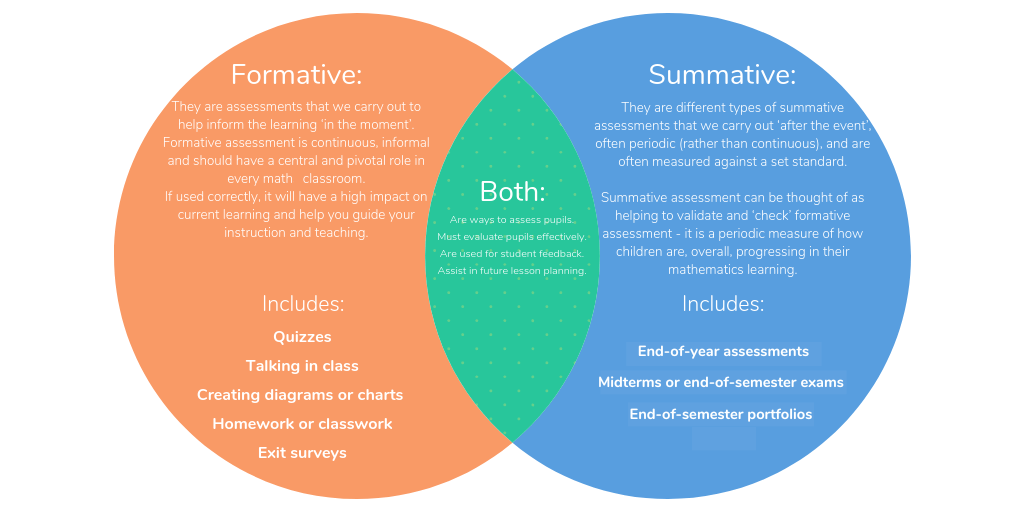
Formative assessment is an intrinsic part of both teaching and student progression. This form of assessment does not rely upon tests and results, but rather the ability to adapt to classroom blockers as they arise.
It should indicate what a good piece of work is and why this is the case, but it also gives you as a teacher a chance to see when things are not going so well and act upon it and see improvements.
Good formative feedback will enable both the teacher and student to plan together what the next stage of their progression will be and future learning goals.
During a lesson, all adults in the classroom should be on a ‘constant assessment mission’ through interactions with students.
Teachers should be moving around the room, interacting with each child, and assessing their progress towards the learning objective in real-time.
In the moment, assessment can take many forms:
• You could use a question from your shared learning to assess where you need to give independent work, or which students need further support
• It could be as simple as asking key questions to students during their independent work
• You could use ‘exit tickets’ to assess children’s understanding at the end of a lesson
However, it is important that this ‘in the moment’ assessment that is carried out has a purpose, and that this information is used to adapt the learning experiences and opportunities that you are providing to each child.
The information obtained from formative assessments can help you understand the student’s learning processes and adapt to this in future lesson plans.
If your assessment shows that students are secure, then how are you going to deepen their learning?
If your assessment shows that students have some misconceptions, then how are you going to support these?
These are just two of the questions you should be asking yourself throughout a formative assessment.
If you are looking for a way to bring formative assessments into your classroom, take a look at our blog containing your Math Intervention Must-Have: Formative Diagnostic Assessment Tests.
There are a lot of different assessment routines you can use to keep up with the progression of your math class.
Common types of formative assessment include:
- Group activities
- Class projects
- Presentations
Make sure that your assessment ‘routines’ have purpose and use.
For example, if you are going to do the ‘math lesson classic’ and ask children to show you an answer on a mini-whiteboard, make sure you are actually looking at the answers given by all students.
You should then be using these to inform the next step in your lesson and the learning for each student.
I have observed many lessons where teachers have carried out the mini-whiteboard ‘routine’, not actually looked at the responses given, and carried on with what they had planned regardless.
Remember- it is not the activity or ‘thing’ that you do that represents effective assessment, but what you do with the information you gather from it.
It is through effective in-lesson assessment that you can ensure that each student is supported and challenged, and that every student is learning rather than constantly rehearsing what they already know.
I often use a ‘pothole’ analogy with the schools I work with. Imagine a local council were filling in potholes but that their road maintenance vehicles were themselves creating new holes in the road.
They wouldn’t be doing a very good job at improving the overall quality of the road surface would they?
Yet, schools often inadvertently do the same with math. They are often very good at carrying out a plethora of intervention activities to fill gaps (or potholes) that have been ‘left’ from previous years, but, at the same time, often allow new gaps (or potholes) to be created.
It is therefore important that we use our constant, ‘in the moment’ assessment to help ensure that no new gaps are being allowed to form in a student’s mathematical understanding and learning.
Make sure that you use your ‘in the moment’ and ‘end of lesson’ assessment to help fill any new gaps that are starting to emerge.
Then, at the end of the math lesson, you formatively check that all students are secure with the objective for that lesson, and if not, you carry out some form of intervention to help address these gaps.
If you are not going to address the gaps now, then who is and when?
Summative assessment helps to demonstrate the extent of students’ success in meeting specific goals. It is a method that can be used to quantify achievement, and due to its data driven nature, it is a great way to provide a numerical basis for a student’s next step.
However, while the principles of summative assessment are simple, there are 4 key points you need to consider before implementing it in your classroom.
1- Assessment systems vs framework – What are you assessing against?
Despite the power of ‘in the moment’ formative assessment, schools do need a way to track the attainment and progress of students throughout the school.
It is this need that means that schools also need to consider the assessment framework they are using- i.e. what you are assessing against. This decision is often one that is taken at district level.
However, it is important that you are clear about the difference between your assessment system and the framework you are using.
Often with my work in schools, I am told that they are using ‘student asset’, ‘classroom monitor’, ‘target tracker’ (and many others) as their assessment. In fact, these are all assessment systems – bits of software that allow you to record and track student’s progress against a framework that has been chosen by your school.
They are not what you are using to ‘assess’- merely what you are using to record your assessment.
These assessment systems all allow you to select (and often create your own) framework upon which to assess your students – and it is these frameworks that are vitally important.
2- Balancing the frameworks is crucial
When choosing, or creating, the assessment framework that you are using, it’s important to consider the balance of objectives and target areas of mathematics within the framework.
Some end-of-grade tests may give a higher weight towards number based objectives, with number, calculations and proportionality making up between 75-85% of a child’s final result.
Yet, most grades have an even split between all standard domains.
This essentially means that a child could be legitimately marked as ‘secure’ or ‘working at aged related expectations’ against the whole curriculum, on the basis of their strength in geometry, but they wouldn’t be classed as ‘secure’ or ‘working at aged related expectations’ in a standardized test.
It is therefore important that whatever framework you use is balanced, and includes an equal weighting of standards-based questions.
There are many ways in which you can do this, including:-
• Use built-in ‘weighting’ functions of some assessment systems that allow you to weight each objective.
• Assess against key objectives only, which overall, have the balance of number vs non-number objectives.
• Group objectives together, creating the overall numbers vs non-number balance.
• Use a commercially available assessment framework which has the weighting work done for you.
3- Teacher assessment plays a huge role in summative assessment
Once your school has decided on a framework to use for assessment, next comes the question of how it is actually used.
These frameworks can be used both in a purely ‘summative’ way, or in a formative way that leads to, over time, an accurate summative assessment.
The traditional use of these frameworks is for schools to ask for each child to be assessed against the framework at set points – for example, midway through the school year or end-of-grade tests.
This often leads to ‘assessment panic’ with teachers feeling overwhelmed having to create the assessment against many objectives for all students in their task in a short period of time.
If this is the only way in which these frameworks are used, then these are being used purely summatively – it is the teacher’s judgment at the end of a quarter/year.
Due to the stress of having to meet a deadline and make a judgment against each objective for all students in your class, this can often mean that these summative only teacher assessments are not as accurate as many would like.
Luckily, you can adapt these assessments very easily
However, these frameworks can also be used in a more formative way – with teachers being encouraged to record the learning progress towards objectives on the framework or rubric as they are being taught .
An example of this is recording and amending judgements each week as a result of the ‘ongoing’ assessment. This leads to an ever-changing snapshot of each child’s performance, which can be really powerful.
This can be used to inform interventions and subsequent teaching, and help to identify common misconceptions, giving the assessment framework used by your school both a summative and formative use.
These assessments can then just be finalized in time for whatever deadline of ‘snapshot’ date your school set.
It is fantastic that many schools and districts are favoring teacher assessment to provide this ‘data.’
Teacher assessment is incredibly powerful, and gives teachers the professional autonomy that they deserve.
4- Testing can’t be forgotten about either
Many schools will also choose to use some form of testing alongside their assessment frameworks.
This can be seen as helping to validate teacher assessment judgments, and can also help to ensure there are no ‘nasty’ surprises when it comes to state standardized tests.
However, testing is only as good as the quality of the tests that you use. It is important that the tests your schools rely on have the same degree of ‘standardization’.
They should be standardized so you know how children across the country perform, and be based on a clear test development framework, and have been trialed and refined in schools.
Some popular tests that have been developed in this way include STAR Math and Terra Nova.
Regardless of what tests are used, it is also important that schools and teachers understand that they provide a snapshot of the performance on the day the test was taken.
Children, just like adults, all have ‘good’ and ‘bad’ days, and it is important that these tests are seen as a supplement to good quality teacher assessment, not a replacement for it.
Both formative and summative assessment have a very important role to play in the classroom and in schools. However, it is very important to ensure that you find the right balance between the two approaches for your own class’s learning needs.
Constant formative assessment can prove difficult if not implemented properly, but consistent assessment of students strengths and weaknesses can prove invaluable in helping them to progress.
Summative assessment can often not show the whole picture of a students’ progression, but it is a fantastic way of getting a data driven overview of how a student has progressed and grown over a period of time.
The goal of this blog was to summarize the difference between formative and summative assessment, and the conclusion is that both approaches have their flaws, but they can also both provide a valuable insight into how a class is getting on throughout the school year.
All that is left is to use assessments of both kinds to inform your teaching!
Do you have students who need extra support in math? Give your students more opportunities to consolidate learning and practice skills through personalized math tutoring with their own dedicated online math tutor. Each student receives differentiated instruction designed to close their individual learning gaps, and scaffolded learning ensures every student learns at the right pace. Lessons are aligned with your state’s standards and assessments, plus you’ll receive regular reports every step of the way. Personalized one-on-one math tutoring programs are available for: – 2nd grade tutoring – 3rd grade tutoring – 4th grade tutoring – 5th grade tutoring – 6th grade tutoring – 7th grade tutoring – 8th grade tutoring Why not learn more about how it works ?
The content in this article was originally written by math consultant and author Tim Handley and has since been revised and adapted for US schools by elementary math teacher Katie Keeton.
3rd to 6th Grade Math Test [FREE]
Always searching for high quality, pedagogically sound, off-the-shelf questions you can trust? Help students prepare for your state’s math tests with these practice assessments carefully created by our math experts to save you time.
Includes 40 multiple choice questions with detailed answers to support test prep, covering a range of topics and aligned to state standards.
Privacy Overview

What is summative assessment? How to further learning with final exams

Grading can be learning, for both students and teachers.
By completing this form, you agree to Turnitin's Privacy Policy . Turnitin uses the information you provide to contact you with relevant information. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time.
Understanding the meaning and function of summative assessment helps clarify its role within education as a critical component of bridging teaching and learning. In this post, we take a closer look at summative assessment’s qualities with the end goal of ensuring that summative assessment supports learning and informs teaching.
Assessment is a term that describes tests, quizzes, exams, and assignments that measure student learning. Each of these methodologies can provide students and teachers with insights. Educators receive data on what students have and have not learned and gain observations into teaching efficacy and exam design. Students, in turn, recognize any learning gaps they might have, and when they receive feedback, understand next steps to further learning.
The most high-stakes type of assessment is called summative assessment. Summative assessment often comes at the endpoint of learning, whether at the end of a unit, course, or curriculum, serving largely as a pure evaluation of knowledge.
It’s easy to consider summative assessments as a final chapter to learning, but summative assessments can also act as a milestone and inform next steps for both educators and students. By examining the definition of summative assessment as well as its capabilities, educators can embrace its strengths, bolster its shortcomings, and foster learning.
Summative assessment is a specific type of assessment that evaluates learning and offers little opportunity for providing student feedback because of its positioning at the end of a learning unit. They are usually high-stakes, contributing to a large portion of a student’s course grade (e.g., final exams) or an exam that has a high impact on a student’s educational outcome. (e.g., standardized exams or entrance exams). Summative assessments include heavily weighted midterm exams, final exams, licensure tests, and standardized exams like A levels in the UK, SATs in the United States, Matriculation Exams in Finland, National Boards in India, or the CSAT in South Korea.
In such a high-stakes context, failing or struggling on summative assessments can negate student effort in other areas of study. On the other hand, summative assessment can be an effective tool to evaluate student knowledge and in the realm of licensure and certification exams, determine qualification for beginning a career.
While we aim to focus discussion on summative assessment, it’s important to describe another type of assessment to provide context; formative assessments not only evaluate learning but provide feedback to students and data to instructors. While formative assessments may or may not be given a grade, they most certainly further learning and occur throughout the course to support student learning needs, and often provide a safe space for failure . Formative assessments include assignments, tests, in-class activities, quizzes, and even midterm exams when they include feedback and opportunities for instructor intervention.
Best practices in formative assessment include providing timely and actionable feedback to students before the next assessment ( Hattie & Timperley, 2007 ).
While formative assessment is the measurement and support of learning as it takes place, summative assessments are evaluations of what a student has learned at the end of a given period (e.g., semester or training course). By assessing students at the end of a module, course, or curriculum, educators gain insight into how well their students have mastered the content and how effective their teaching methods were.
Even though summative assessments are situated at a point where students will find it hard to action results, data from summative assessments can still be used to inform curriculum planning and teaching, as well as any future exam adjustments.
That said, when possible, it’s important to balance formative and summative assessments within a term or curriculum. Fortifying summative assessments with prior formative assessments can support a student’s educational journey. Students who understand what they know and what they need to know in order to move forward are more likely to be prepared for final evaluation. Furthermore, preparing students for final evaluation with frequent opportunities to fail safely and receive feedback reduces stress, increases learning outcomes, and can mitigate academic misconduct .
While every type of assessment has its function to evaluate, every type of assessment, too, can be maximized for learning and teaching. Mid-course exams, for example, have the potential for both summative and formative qualities, serving to evaluate mastery (summative) and provide feedback to promote student learning (formative).
Without feedback, a midterm exam is purely summative. And while a summative component to a mid-course exam is reasonable, there is a lot more potential to them. It is important to provide feedback on mid-course exams so that students understand what they do and do not know and have the tools to bridge learning gaps for the next assessment and ultimately their final exam.
When assessments are provided with timely and actionable feedback, students have the information they need to facilitate their own learning; in this way, even high-stakes midterm exams can pivot towards formative learning opportunities for students. Additionally, summative assessments contain information critical for teacher and curriculum intervention as well as future exam design.
While formative assessments hinge on providing students with immediate feedback to help with the learning process, summative assessments happen after the student learning occurs. However, this doesn’t mean that communicating students’ performance is any less important.
For students to understand what content they have mastered and which topics might need additional study time, they need a detailed breakdown of their performance.
Categorizing summative assessment questions can give instructors the granular performance data they (and their students) need. By tagging exam items to course topics or learning objectives, faculty can provide the detailed feedback students need to be more focused in their study efforts.
Summative assessments are an important part of the assessment process and are incredibly valuable to both students and faculty. By ensuring high-stakes exams are secure, and providing students with performance feedback, educators can gain insight into how well students have learned the content and how well instructors have presented it.
Summative assessments evaluate content mastery. Generally, they are end-of-course or end-of-year exams; however, these are not the only applicable uses of summative assessments. Evaluating student learning could also come at the end of a chapter or learning module with mid-course exams.
Summative exams can also be multi-functional, as they, like all assessments, are rich with data. When item analysis and psychometrics accompany summative assessment, instruction is bolstered. When an assessment occurs at the end of a course or year or curriculum, data insights help educators make adjustments to teaching and curriculum so that future learning can be bolstered. When category-tagging is employed in tools like ExamSoft, educators can pinpoint student preparation for things like licensure exams. And conducting item analysis can inform effective exam design.
Summative assessments are by nature, high-stakes, and very stressful.
Who hasn’t woken from a nightmare in panic about missing or failing a final exam, even decades out from school? The reality that summative assessments can make or break academic success is deeply implanted in our psyche.
While there is little disagreement among educators about the need for or utility of summative assessments, debates and disagreements tend to center on issues of fairness and effectiveness, especially when summative-assessment results are used for high-stakes purposes.
Fair and inclusive assessments uphold accurate assessments. When exams are not fair nor inclusive, they become vulnerable to misconduct, resulting in missed learning opportunities. When exams do not cover what was taught, students may feel stressed and vulnerable. These missed opportunities can compound and widen learning gaps.
Assessments need to contain a variety of formats and question styles to measure different components of learning and include different learning styles. Summative assessments, when poorly designed, reward memorization rather than deep understanding of concepts. Encouraging competition between students, which can happen when grading on a curve, can also increase stress and decrease fairness.
Additionally, when test-takers are not sure how they will be evaluated, summative assessments can be unfair and inaccurate. Providing rubrics to students and graders ensures clarity of expectations and ensuing measurement of learning.
When summative assessments are stressful, do not accurately measure learning, aren’t preceded with learning opportunities beforehand, and/or don’t test what has been taught, they also become more vulnerable to academic misconduct and shortcut solutions like cheating, plagiarism, and AI Writing misuse.
Assessments are a checkpoint for student learning and teaching efficacy; consequently, accurate student responses are critical to increasing learning outcomes.
Most summative assessments are given with the understanding that the student’s score counts toward their final grade. As such, keeping these secure from academic dishonesty is paramount to providing a fair experience for all exam-takers. Though many educational institutions are moving to computer-based testing (CBT), taking exams on laptops or other devices brings a new list of potential security issues, such as access to the internet or other applications during an exam. An effective way to ensure exam integrity is testing software that does not allow use of the internet during an exam and prevents students from accessing other applications on their device.
Preventing academic dishonesty by blocking exam-takers’ information sources isn’t the only point to consider; ensuring students don’t share assessment items is also a concern. Once a test question is compromised, it’s no longer a valid measurement of student learning. Thus, keeping questions secure is vital.
Assessment security is a focus of Professor Phillip Dawson, an authority on assessment security from Deakin University in Australia, who defines assessment security as: “Measures taken to harden assessment against attempts to cheat. This includes approaches to detect and evidence attempts to cheat, as well as measures to make cheating more difficult.”
Dawson suggests a multilayered approach to assessment design, with seven standards for assessment security that institutions ought to consider:
- Coverage across a program - how much of a degree should be secured?
- Authentication - how do we ensure the student is who they say they are?
- Control of circumstances - how can we be sure the task was done in the intended circumstances?
- Difficulty to cheat metrics - we need to know how hard it may be to cheat a task.
- Detection accuracy metrics - we need to know if our detection methods work.
- Proof metrics - we need to be able to prove cases of cheating.
- Prevalence metrics - we need to know approximate rates of undetected, detected, and proven cheating ( Dawson, 2021 ).
According to Professor Roseanna Bourke, Director of Educational Psychology programme and Institute of Education at Massey University, there is a link between student cheating and student understanding and investment in the assigned tasks; when students don’t understand questions and lack confidence, learning itself becomes the barrier ( Bourke, Integrity Matters, n.d. ).
Providing support to students throughout a course or curriculum mitigates academic dishonesty in summative assessments. When students feel seen and supported with formative feedback in their educational journey, they are less likely to cheat. Additionally, rubrics can make clear the purpose of each question.
As stated, summative assessment is useful when the data exchange is maximized and accurate. Not only should it provide information about content mastery to instructors, it can also act as a reservoir of statistics about learning trends, item analysis, and exam effectiveness. Finally, and when possible, summative exams can take on formative qualities when feedback is provided. All of these data points directly benefit student learning.
Because it is a platform to demonstrate a culmination of knowledge, designing summative assessments is particularly critical to make the test accessible and inclusive for all different types of learners, and thus promote accurate measurement and data insights. Exam design principles include:
- Test what has been taught; aligning summative assessment with instruction models and promotes integrity for students.
- Design assessments that focus on measuring both breadth and depth of student knowledge and consider eliminating components that do not inform learning. Offer a variety of assessment formats. Multiple-choice questions can effectively breadth of knowledge in a limited time while short-answer and long-answer formats can evaluate higher-order thinking.
- Offering a variety of formats and questions styles within a summative assessment can also accommodate different learning styles. When diverse formats are offered, a larger spectrum of learning can be assessed. Additionally, diverse formats provide different ways for students to demonstrate their learning.
- And consider eliminating grading on a curve, which can increase competition between students, some of whom may be cheating ( UC Berkeley, 2020 ). Researchers Schinske and Tanner state, “Moving away from curving sets the expectation that all students have the opportunity to achieve the highest possible grade” ( Schinske & Tanner, 2014 ).
- A rubric, too, benefits students by clarifying expectations and acts as added assurance that tests align to previously-communicated learning goals.
Finally, the summative assessment itself is a living document, one that can be continuously optimized.
Analyze student responses to ensure assessments are fair, and to examine answer patterns to see if shortcut solutions have been utilized. Item analysis , or formally examining student responses and patterns, can show whether or not summative assessments are accurately assessing student knowledge. The data (Did every student get one particular question wrong? Did every student get one particular question correct? What kinds of answers are your test questions eliciting? Did you get the answers you expected?) can inform both exam design and teaching. Furthermore, item analysis supports exam robustness by highlighting questions on exams that may need adjustment.
Category tagging , a feature in ExamSoft assessment software, can offer more in-depth insights into future testing. A nursing program, for instance, can evaluate readiness for certification and the strength of curriculum to prepare students for standardized exams. Of course, category tagging can also fortify summative assessment within the curriculum.
In conclusion, summative assessments function largely as a way to evaluate learning at critical learning junctions, whether at the end of a term, end of a curriculum, or for advancement into the next level of schooling or licensure. The nature of summative assessments make them high-stakes, sometimes to the extent that they can negatively impact all prior learning. Moreover, they lack the opportunity for feedback, given their position in the educational journey.
That said, summative assessments are not wholly an endpoint. They are an intersection rich with data for educators to inform teaching, curriculum, and exam design. For students, too, there can be opportunities to learn, either by feedback or via data analysis, their own learning gaps and how to bridge them.
When educators maximize the potential of summative assessment, they can foster learning.
- Health Science
- Business Education
- Computer Applications
- Career Readiness
- Teaching Strategies
« View All Posts
Assessment | Career and Technical Education (CTE) | Classroom Planning
Formative vs. Summative Assessments: What's the Difference?
- Share This Article
March 19th, 2024 | 8 min. read

Brad Hummel
Coming from a family of educators, Brad knows both the joys and challenges of teaching well. Through his own teaching background, he’s experienced both firsthand. As a writer for iCEV, Brad’s goal is to help teachers empower their students by listening to educators’ concerns and creating content that answers their most pressing questions about career and technical education.
Print/Save as PDF
Whether you’re an administrator, supervisor, or teacher, you’ve heard of formative assessments and summative assessments . They're both essential parts of any curriculum map . But what do these terms actually mean?
In a nutshell, formative assessments are quizzes and tests that evaluate how someone is learning material throughout a course .
Summative assessments are quizzes and tests that evaluate how much someone has learned throughout a course .
In the classroom, that means formative assessments take place during a course, while summative assessments are the final evaluations at the course’s end.
That's the simple answer, but there's actually a lot more that makes formative and summative assessments different. To fully understand formative vs. summative assessments, you'll need to understand the details of these two important forms of assessment.
In this article, we'll take a closer look at formative and summative quizzing and assessing. When you've finished reading, you'll understand how to better test student knowledge in your classroom.
What Are Formative Assessments?
Formative assessments are evaluations of someone’s learning progress in a classroom.
Common formative assessments include:
- Presentations
- Group activities
Formative assessments work great when they’re used on a regular basis. That regularity could be based on a calendar (every Monday, every Thursday, etc.) or your lesson plans (every unit).
They’re also more flexible than summative assessments. You don’t always have to use pencil and paper to get a feel for your students’ progress. Instead, you can use in-class games, group presentations, and hands-on activities to evaluate student progress.
Ultimately, the formative assessments you use are up to you. After all, no one knows your classes better than you. So if you’d prefer to get an overview of how well your students are learning, you can use a group-style assessment like a game. If you want to know where each student struggles, you can use an individual assessment like a quiz.
This flexibility is perfect for keeping students engaged in your class. It lets you stick to a syllabus while mixing up the exact task each student has to perform. That way, you don’t fall into a predictable routine of teach-test-teach-test. Instead, you have a varied routine of teach-game-quiz-teach-presentation-project or another interesting format.
By the time your course ends, you’ll have a full understanding of how students are learning as you teach a subject. Then, you can keep all of your grades to look for patterns among different class sections.
Is there an area where students seem to do worse than others? Could you adjust a lesson and shoot for better results?
Naturally, you’ll never get a class that’s straight A’s from top to bottom. But you can still design your classroom assessments to work for as many students as possible!
Top 3 Formative Assessment Examples
Formative assessments are excellent opportunities to let your students flex their creative muscles.
Even if a student isn’t much of a writer or artist, they can still have a little fun with these assessments.
1. Make an Advertisement
Have your students create an advertisement for a concept they just learned. Use visuals and text to really sell an idea.
This makes students apply what they’ve learned into a creative exercise, which helps with long-term retention.
2. Idea Comparisons
Instruct students to lay out the main ideas of a new concept they learned. Then, have them compare that concept to another to see where they agree and disagree.
In addition to helping students remember these concepts, this exercise makes them apply previous knowledge to a new format so they can remember it better in the future.
3. Misconceptions
After you introduce a concept to students, introduce a popular misconception about it. Have students discuss why the misconception is false and where it may have started.
This exercise makes students think critically about what they’ve just learned while showing them how to debunk misinformation.
How Do You Track Formative Assessments?
You can track formative assessments in one of three ways: by grade, by feel, and with student data .
Let's take a closer look at using each of these methods to monitor student progress.
Track by Grade
First, you can track them by grade . This gives you a specific, concentrated view of how a student (or group of students) learns. However, graded assessments are sources of stress for many students. So if you want to make a unit fun or loose, graded assessments may not work well for you.
Track by Feel
Second, you can track them by feel . This is more based on your teacher instinct, allowing you to pick which students need additional support based on your observation. On the downside, you can’t “show” this information to your administrators. If you have certain standards to meet throughout a marking period, you won’t be able to prove you’ve fulfilled those standards without grades.
Track with Student Data
Finally, you can track formative assessments with student data . This is non-graded information that may reflect how your students are learning, such as questions they've frequently answered incorrectly or subject areas where they've had trouble. After all, not everything has to be a grade!
When you have a comprehensive data management system in place, tracking with student data can be the most effective way to measure student progress.
With all of that said and done, let’s next consider summative assessments.
What Are Summative Assessments?
Summative assessments are evaluations of what someone has learned throughout a course.
Common summative assessments include:
- Final exams
- End-of-class projects
Summative assessments almost always take place at the end of a course unless a teacher decides to break a course into more manageable chunks. They’re often cumulative, and they’re used to evaluate a student’s long-term information retention.
In summative assessments like final exams , you can include questions from the first week or two of a course to ensure students retained introductory information. In other assessments like papers, your students can pull from a full marking period of learning to apply to a topic.
Either way, your students have to do some serious reflecting and critical thinking to bring together the information from an entire course.
This is a great way to ensure students retain essential information from one course to another. So if you teach introductory courses, summative assessments are perfect to set students up for success in their next classes.
That’s important because a student’s success in your classroom is just one step for them. When you prepare them for the next step, you make it easier for them to succeed in the future as well.
In that way, summative assessments serve two purposes:
First , they evaluate what someone learned while they’ve been in your class.
Second , they evaluate how prepared someone is to go to the next academic level.
Combined with the rest of a student’s performance in class, summative quizzing and assessments are excellent ways to gauge progress while ensuring long-term information retention.
Top 3 Summative Assessment Examples
Summative assessments are traditionally more structured and standardized than formative assessments.
Still, you have a few options to shake things up that go beyond a pen-and-paper test.
1. In-depth reports
Instruct students to choose a topic that resonated with them in class and report in-depth on it. This is a great opportunity for students to take an idea and run with it under your supervision.
These reports often showcase a student’s interest, and you’ll be able to evaluate a student’s engagement level in the class by how they approach the report.
The goal is a passionate, intelligent, and comprehensive examination of a concept that matters to a student.
2. Cumulative, individual projects
Have your students pick a project to complete. This project should somehow reflect what they’ve learned throughout the course.
Projects are great for any practical application class from health science to physics. Creating a cross-section of the human heart, designing a diet, or creating a protective egg-drop vessel are all fun ways students can show off their knowledge of a topic.
3. Personal evaluation papers
Require students to apply principles from your class to their personal lives. These papers are excellent fits for psychology, nutrition, finance, business, and other theory-based classes.
In a nutshell, personal evaluations let students look at themselves through a different lens while exploring the nuances of the principles they learned in class. Plus, it lets students do something everyone loves — talk about themselves!
Now that you have a few ideas on summative assessments, how can you track their success?
How Do You Track Summative Assessments?
While everyone has their own ideas on this topic, grades are the best way to evaluate someone’s success with a summative assessment.
How you grade is ultimately up to you. Presentations are great ways to grade someone based on a number of factors, including soft skills like public speaking. Written exams or project-based assessments are ideal to see a student’s full-scope understand of your class after a marking period.
Whatever you choose, stick to a consistent grading scale so you can identify your own strengths and weaknesses in the classroom as students complete your course.
What’s More Important: Formative or Summative Assessments?
Many new teachers have this question — are formative or summative assessments more important?
In a perfect world, they’re equally important. Formative assessments let students show that they’re learning, and summative assessments let them show what they’ve learned.
But American public education values summative assessments over formative assessments. Standardized tests — like the SATs — are great examples of high-value summative assessments.
It’s rare to find the same emphasis on formative quizzing and assessments. That’s because formative assessments act like milestones while summative assessments show the bottom line.
We encourage teachers to look at these assessments as two sides of the same coin. Formative and summative assessments work together flawlessly when implemented properly.
With all of that in mind, you only have one question left to answer. How are you going to add these assessments to your curriculum ?
Use Formative and Summative Assessments and Meet Your Challenges
As a teacher, you’ll likely need to employ both summative and formative assessments in your curriculum. An effective balance of these assessments will help you understand your students’ needs while meeting your standards.
However, CTE teachers face challenges in the classroom each day that sometimes get in the way of connecting with students and preparing them for these assessments.
If you want to feel less overwhelmed and spend more time helping your students succeed, download your free guide . You’ll learn about five of the most significant challenges teachers face and how you can overcome them.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
An assessment plan must come first, not last, in the educational process.
Classroom assessment “appears to be one of the most potent forces influencing education.” (Cooks, 1998).
Formative Assessment
Formative assessment refers to the ongoing process that teachers and students engage in when selecting a learning goal(s), taking stock of current student performance is in relation to the goal, and the action steps needed to move students closer to the goal. This ongoing process is implemented through formative assessments, assessments that can easily be incorporated in the day-to-day classroom activities and that measure the students’ performance and progress. Informal assessments are content and performance driven and include questioning of and discussion with students, student work (exit slips; assignments), and direct observation of students working. Rather than being used for grading, this ongoing formative assessment (that gather data for learning) is used to inform instructional planning decisions. Unlike formative assessments, summative assessments (that gather data of learning) are used to assess students’ academic achievement and evaluate how students perform when compared to a larger group of students. These formal assessments include standardized tests that are graded in a formulated manner (ie: criterion-referenced tests, norm-referenced tests, achievement tests, and aptitude tests). Assessments implemented following completion of units of study/learning are also often referred to as summative. These are the classroom assessments that are graded, showing students’ levels of mastery of a unit of content when it has been completed.
Formative assessment data is used to guide instruction. It is collected in a pre-assessment prior to the creation of lesson objectives and instructional activities (as outlined in the previous chapter), as well as throughout a lesson (informally during learning activities and often through a post assessment implemented in the closing of a lesson. This formative data is informative regarding students’ current performance related to the content standard/objective. As addressed in chapter two, the resulting assessment data must be organized and analyzed to effectively inform the appropriate ‘next steps’ in moving students towards their academic goals. Knowing details regarding exactly what students understand/can do guides the determination of appropriate lesson objectives (and often flexible groupings) for subsequent lessons.
This cycle of formative assessment continues throughout a unit of instruction, which often ends with a summative assessment of learning.
(What Teachers Really Need to Know About Formative Assessment by Laura Greenstein, ASCD)
Organizing Data
It is expected that assessments implemented in the closing of a lesson clearly align with, or target, the lesson’s objective. Numerical data that can be analyzed and reflected upon must be presented. Additionally, qualitative data (often in the form of descriptive observation notes) is critical to modifying instruction according to students’ needs. This feedback should be collected in an organized manner so that it may be analyzed in a way that informs future instruction. One way to do so is the use of:
Clipboards and Post-its
Circle the room with a clipboard to track student engagement and progress during independent and group work. Then, use the notes to follow-up with direct, quick feedback to students. Notes can later be transferred to student folders, binders, or checklists following the lesson.
Class Checklists and Data Forms
Use a template (such as one made in a Google Doc) to create a helpful document on which to organize data. It is quite simple to use repeatedly for varying sets of data and may look like this:
Graphs can be used to show students’ performance data visually and can be especially helpful to consider patterns of understanding across groups of students. Observing individual student performance and adding related anecdotal notes of error analysis is a necessary addition to graphs, which most commonly provide holistic or whole class results.
Many teachers are using smartphones to record students’ conversations as they circulate to various areas of the classroom. This provides opportunities to observe more than one group’s discussion at a time. iPads and apps like FlipGrid are also often used to collect student thoughts and reflections which provide invaluable information regarding student understanding.
Formative Pre-Assessment Data in the CPS Lesson Plan
In your lesson planning at The Center for Educator Preparation, you are expected to present a description, date, and numerical data from a pre-assessment that provides evidence of the students’ need in relation to the lesson objective. Analysis of this data must be presented that addresses patterns of understanding and misunderstanding in students’ work.
It is vital that lesson objectives are determined as a result of the analysis of students’ pre-assessment data and that planned post-assessment (an exit ticket or other end of lesson assessment) directly align to the lesson objective. This post-assessment will serve as a formative assessment to plan the ‘next steps’ in future lessons and will be addressed as you reflect on your instruction.
Consider how you will record and organize student assessment data (whether during or after the lesson) in a way that promotes data analysis. Describe the process you plan to take to track, organize, and analyze the data you gather during your lesson. In sequential lessons be sure that the assessment considers the data gathered in the preceding lesson. Show any adjustments in a new color or font.
Summative Assessment
Summative assessment is implemented at the end of a unit and is used to evaluate students’ mastery of content. Examples include a final project, test, written report, or performance task. This assessment is typically graded or used to mark students’ progress toward a competency.
Formative and Summative Assessment in the CPS Lesson Plan
The CPS lesson plan intentionally asks students to consider the lesson assessment immediately following the writing of the lesson objective and analysis of pretest data so that planning of instruction is done with ‘the end in mind’, a backward design planning approach (Cite UbD).
First, consider what mastery of the lesson objective looks like. Consider what students will be expected to say and do once they have fully mastered the lesson objective. Design an assessment that provides an opportunity for students to do these things. Consider including open ended opportunities in which students are able to show the depth of their understanding (in regard to the objective). Describe the assessment you design and provide an image of it directly in the lesson plan, or attach a copy in the plan.
CPS’s Aligned Lesson Plan Section
Cps’s aligned loft evaluation criteria and annotations, cps’s aligned lesson plan rubric criteria.
Lesson Planning 101 Copyright © 2019 by Deborah Kolling and Kate Shumway-Pitt is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Search form
- About Faculty Development and Support
- Programs and Funding Opportunities
Consultations, Observations, and Services
- Strategic Resources & Digital Publications
- Canvas @ Yale Support
- Learning Environments @ Yale
- Teaching Workshops
- Teaching Consultations and Classroom Observations
- Teaching Programs
- Spring Teaching Forum
- Written and Oral Communication Workshops and Panels
- Writing Resources & Tutorials
- About the Graduate Writing Laboratory
- Writing and Public Speaking Consultations
- Writing Workshops and Panels
- Writing Peer-Review Groups
- Writing Retreats and All Writes
- Online Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- About Teaching Development for Graduate and Professional School Students
- Teaching Programs and Grants
- Teaching Forums
- Resources for Graduate Student Teachers
- About Undergraduate Writing and Tutoring
- Academic Strategies Program
- The Writing Center
- STEM Tutoring & Programs
- Humanities & Social Sciences
- Center for Language Study
- Online Course Catalog
- Antiracist Pedagogy
- NECQL 2019: NorthEast Consortium for Quantitative Literacy XXII Meeting
- STEMinar Series
- Teaching in Context: Troubling Times
- Helmsley Postdoctoral Teaching Scholars
- Pedagogical Partners
- Instructional Materials
- Evaluation & Research
- STEM Education Job Opportunities
- Yale Connect
- Online Education Legal Statements
You are here
Formative and summative assessments.
Assessment allows both instructor and student to monitor progress towards achieving learning objectives, and can be approached in a variety of ways. Formative assessment refers to tools that identify misconceptions, struggles, and learning gaps along the way and assess how to close those gaps. It includes effective tools for helping to shape learning, and can even bolster students’ abilities to take ownership of their learning when they understand that the goal is to improve learning, not apply final marks (Trumbull and Lash, 2013). It can include students assessing themselves, peers, or even the instructor, through writing, quizzes, conversation, and more. In short, formative assessment occurs throughout a class or course, and seeks to improve student achievement of learning objectives through approaches that can support specific student needs (Theal and Franklin, 2010, p. 151).
In contrast, summative assessments evaluate student learning, knowledge, proficiency, or success at the conclusion of an instructional period, like a unit, course, or program. Summative assessments are almost always formally graded and often heavily weighted (though they do not need to be). Summative assessment can be used to great effect in conjunction and alignment with formative assessment, and instructors can consider a variety of ways to combine these approaches.
Examples of Formative and Summative Assessments
Both forms of assessment can vary across several dimensions (Trumbull and Lash, 2013):
- Informal / formal
- Immediate / delayed feedback
- Embedded in lesson plan / stand-alone
- Spontaneous / planned
- Individual / group
- Verbal / nonverbal
- Oral / written
- Graded / ungraded
- Open-ended response / closed/constrained response
- Teacher initiated/controlled / student initiated/controlled
- Teacher and student(s) / peers
- Process-oriented / product-oriented
- Brief / extended
- Scaffolded (teacher supported) / independently performed
Recommendations
Formative Assessment Ideally, formative assessment strategies improve teaching and learning simultaneously. Instructors can help students grow as learners by actively encouraging them to self-assess their own skills and knowledge retention, and by giving clear instructions and feedback. Seven principles (adapted from Nicol and Macfarlane-Dick, 2007 with additions) can guide instructor strategies:
- Keep clear criteria for what defines good performance - Instructors can explain criteria for A-F graded papers, and encourage student discussion and reflection about these criteria (this can be accomplished though office hours, rubrics, post-grade peer review, or exam / assignment wrappers ). Instructors may also hold class-wide conversations on performance criteria at strategic moments throughout a term.
- Encourage students’ self-reflection - Instructors can ask students to utilize course criteria to evaluate their own or a peer’s work, and to share what kinds of feedback they find most valuable. In addition, instructors can ask students to describe the qualities of their best work, either through writing or group discussion.
- Give students detailed, actionable feedback - Instructors can consistently provide specific feedback tied to predefined criteria, with opportunities to revise or apply feedback before final submission. Feedback may be corrective and forward-looking, rather than just evaluative. Examples include comments on multiple paper drafts, criterion discussions during 1-on-1 conferences, and regular online quizzes.
- Encourage teacher and peer dialogue around learning - Instructors can invite students to discuss the formative learning process together. This practice primarily revolves around mid-semester feedback and small group feedback sessions , where students reflect on the course and instructors respond to student concerns. Students can also identify examples of feedback comments they found useful and explain how they helped. A particularly useful strategy, instructors can invite students to discuss learning goals and assignment criteria, and weave student hopes into the syllabus.
- Promote positive motivational beliefs and self-esteem - Students will be more motivated and engaged when they are assured that an instructor cares for their development. Instructors can allow for rewrites/resubmissions to signal that an assignment is designed to promote development of learning. These rewrites might utilize low-stakes assessments, or even automated online testing that is anonymous, and (if appropriate) allows for unlimited resubmissions.
- Provide opportunities to close the gap between current and desired performance - Related to the above, instructors can improve student motivation and engagement by making visible any opportunities to close gaps between current and desired performance. Examples include opportunities for resubmission, specific action points for writing or task-based assignments, and sharing study or process strategies that an instructor would use in order to succeed.
- Collect information which can be used to help shape teaching - Instructors can feel free to collect useful information from students in order to provide targeted feedback and instruction. Students can identify where they are having difficulties, either on an assignment or test, or in written submissions. This approach also promotes metacognition , as students are asked to think about their own learning. Poorvu Center staff can also perform a classroom observation or conduct a small group feedback session that can provide instructors with potential student struggles.
Instructors can find a variety of other formative assessment techniques through Angelo and Cross (1993), Classroom Assessment Techniques (list of techniques available here ).
Summative Assessment Because summative assessments are usually higher-stakes than formative assessments, it is especially important to ensure that the assessment aligns with the goals and expected outcomes of the instruction.
- Use a Rubric or Table of Specifications - Instructors can use a rubric to lay out expected performance criteria for a range of grades. Rubrics will describe what an ideal assignment looks like, and “summarize” expected performance at the beginning of term, providing students with a trajectory and sense of completion.
- Design Clear, Effective Questions - If designing essay questions, instructors can ensure that questions meet criteria while allowing students freedom to express their knowledge creatively and in ways that honor how they digested, constructed, or mastered meaning. Instructors can read about ways to design effective multiple choice questions .
- Assess Comprehensiveness - Effective summative assessments provide an opportunity for students to consider the totality of a course’s content, making broad connections, demonstrating synthesized skills, and exploring deeper concepts that drive or found a course’s ideas and content.
- Make Parameters Clear - When approaching a final assessment, instructors can ensure that parameters are well defined (length of assessment, depth of response, time and date, grading standards); knowledge assessed relates clearly to content covered in course; and students with disabilities are provided required space and support.
- Consider Blind Grading - Instructors may wish to know whose work they grade, in order to provide feedback that speaks to a student’s term-long trajectory. If instructors wish to provide truly unbiased summative assessment, they can also consider a variety of blind grading techniques .
Considerations for Online Assessments
Effectively implementing assessments in an online teaching environment can be particularly challenging. The Poorvu Center shares these recommendations .
Nicol, D.J. and Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006) Formative assessment and self‐regulated learning: a model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education 31(2): 2-19.
Theall, M. and Franklin J.L. (2010). Assessing Teaching Practices and Effectiveness for Formative Purposes. In: A Guide to Faculty Development. KJ Gillespie and DL Robertson (Eds). Jossey Bass: San Francisco, CA.
Trumbull, E., & Lash, A. (2013). Understanding formative assessment: Insights from learning theory and measurement theory. San Francisco: WestEd.
YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN

The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning routinely supports members of the Yale community with individual instructional consultations and classroom observations.

Reserve a Room
The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning partners with departments and groups on-campus throughout the year to share its space. Please review the reservation form and submit a request.

Instructional Enhancement Fund
The Instructional Enhancement Fund (IEF) awards grants of up to $500 to support the timely integration of new learning activities into an existing undergraduate or graduate course. All Yale instructors of record, including tenured and tenure-track faculty, clinical instructional faculty, lecturers, lectors, and part-time acting instructors (PTAIs), are eligible to apply. Award decisions are typically provided within two weeks to help instructors implement ideas for the current semester.
Skip to Content
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
- Summative Assessments: Types
Below are some types of assessments that are commonly used to gauge learning at the end of a unit or course. While the focus here is primarily on the use of these assessments for summative purposes, these can also be utilized as formative assessments , to track student learning during a course. For each, we make suggestions for ways to design these assessments to be equity-minded and recommend further readings and resources.
Exams typically consist of a set of questions that are aimed at eliciting a specific response. They can include a range of question formats, such as multiple choice questions, fill-in-the-blank questions, labeling diagrams, or providing short answer questions. When designing exam questions, it is important to consider the principles of equity-minded assessment. This involves making exam questions that are:
- Relevant : Test concepts are aligned with the course learning objectives. Additionally, questions involve applying course concepts to problems and situations that are relevant to students’ interests and skills.
- Authentic: Require students to apply skills that may be utilized in their professional and personal lives (e.g., critical thinking and collaboration). Questions also test a range of learning outcomes from those requiring lower-order cognitive skills such as recollection or understanding to those requiring higher-order cognitive skills such as evaluation and application of concepts (e.g., case studies that allow application of concepts to real-world problems).
- Rigorous: Focus on application of skills or creation of new knowledge to novel or complex situations, rather than recollection of facts. Can involve multi-step problem solving or require students to justify a given answer through reasoning.
- Transparent: Explicit about the knowledge and skills being tested in the exam. The scoring system for each question is known to students while taking the exam (e.g., each question specifies if answers are marked for both accuracy and process or if there is negative marking for writing the wrong answer). Providing students with practice questions that illustrate the types of questions they may encounter on the exam can especially help international and first-generation students who may be unfamiliar with predominant assessment strategies.
- Inclusive: Describe scenarios, names, or contexts that reflect the lived experiences of diverse students, without assuming specific cultural knowledge. Questions do not rely on knowledge of concepts that are not already taught in the course. Characterized by use of clear, concise, and unambiguous language (e.g., avoid double negative statements, jargon, complex words). This is particularly important when instructors are unavailable to clarify what the particular question is testing, for example in online exams and in large classes.
Open-book or group-based exams that require critical thinking, collaboration, and analytical skills to arrive at an answer may be one way to implement exams that follow the above principles (Johanns et al., 2016; Martin et al., 2014). Incorporating exam wrappers as a follow-up is known to promote good learning strategies by helping students self-assess and engage in metacognition (Lovett, 2013). Explore some additional resources on writing good multiple choice exam questions (Brame 2013), incorporating group-exams (Chen 2018) or exam wrappers (Carnegie Mellon University). Also consider our guidelines on best practices for designing summative assessments and effective online exam design and administration .
References:
Brame, C. (2013) Writing good multiple choice test questions . Vanderbilt University.
Chen, Y. (2018). Collaborative learning through group testing . Center for Teaching and Learning, Kent State University.
Division of Learning and Teaching. (2022, March 30). Exams . Charles Sturt University.
Lovett, M. C. (2013). Make exams worth more than the grade: Using exam wrappers to promote metacognition . In Kaplan, M., Silver, N, Lavaque-Manty, D., & Meizlish, D. Using reflection and metacognition to improve student learning . Stylus Publishing: Sterling, VA., pp. 18-52.
Johanns, A., Dinkens, J., & Moore, J. (2017). A systematic review comparing open-book and closed-book examinations: Evaluating effects on development of critical thinking skills . Nursing Education in Practice , 27, 89-94.
Martin, D., Friesen, E., & De Pau, A. (2014). Three heads are better than one: A mixed methods study examining collaborative versus traditional test-taking with nursing students . Nurse Education Today , 34 (6), 971–977.
Projects are a powerful way to assess student learning in a relevant, authentic, rigorous, transparent, and inclusive manner. Projects typically involve a sequence of steps that must be completed within a defined timeline to create a novel product. Examples of common products include:
1. Presentations:
These usually involve a slide deck (e.g., PowerPoint) or poster designed to support an oral exposition describing the motivation and outcome of a project. Compared to written papers or portfolios, presentations can be efficient forms of assessment to test higher-order thinking, application, and communication skills since grading can take place in real-time. However, presentations can be time consuming to execute, particularly in classes with high student enrollment ( > 150 students). Presentations conducted in small groups and, when possible, during lab or recitation sections may be one of the ways to incorporate presentations in large classes. Group presentations are also good avenues to promote peer-based learning along with skills in collaboration, communication, and time management. Learn more about designing oral presentations (McCaroll, 2016), best practices to design group projects (Carnegie Mellon University) and evaluate group projects (Cornell University)
2. Research Papers:
Typically assigned in upper-level classes, research papers tend to involve a structured written report describing the motivation, methods, results, and conclusions of a project (research-based or literature syntheses) following the IMRaD format with a reference list. These assessments help students demonstrate their organizational, critical thinking, and writing skills in a manner relevant and authentic to research-based disciplines in which such papers are the dominant mode of communication.
For students, structuring and organizing thoughts in a research paper tends to be difficult without adequate practice and support. Additionally, for instructors, research papers can be difficult to grade and provide feedback in a timely manner, given the volume of content produced by each student. Scaffolding student work and incorporating opportunities for peer feedback are some ways in which these problems can be mitigated. Scaffolding may involve providing adequate guidance to students on conducting literature searches and training them on the use of tools such as citation managers or AI search engines . Providing appropriate rubrics in advance for students to evaluate their own work or engage in peer-assessments are other ways in which students can receive timely feedback before submitting their work. Use Ohio State University’s guiding questions to effectively design research or inquiry-based assessments .
3. Essays or Commentaries:
Essays are longer written papers that ask students to respond to a prompt by explaining a point of view in response to a prompt along with supporting evidence. Since essays are open-ended, they allow students to demonstrate their understanding and interpretation in a creative and individualistic style. Essays are helpful in assessing student understanding and skill across various dimensions, particularly their literary, creative or critical thinking skills. However, similar to research papers, essays can be difficult for students to write and can be difficult for instructors to grade in a timely manner. Scaffolding, providing a clear rubric, writing samples and incorporating peer feedback are few ways in which essays can be implemented in a rigorous, transparent and inclusive manner, without being burdensome for students and instructors. It is also important to consider and comply with norms set by FERPA , when sharing work of students from past classes. More examples can be found on WAC Clearinghouse’s resource on designing writing assignments (Kiefer, 2018).
With the increased accessibility and ease of AI writing tools, however, instructors must take care to be explicit about the appropriate use of AI in writing given the potential for plagiarism. This may include having a syllabus statement on the use of AI in grading policies and assessments, discussing the ethics of plagiarism, training students on using AI as a writing assistant (e.g., to provide structure, check for grammar or spelling), and being transparent about the benefit for students to fully engage in the writing process (Matthews, 2023). Learn more about teaching & learning in the age of AI on our website.
4. Digital Storyboards:
With the ease and accessibility of digital media, some final projects can involve more creative depictions of a project from conception to outcome in the form of artwork, films, photographs or audio-based storyboards. Storyboards can be a powerful medium of communication since it helps an audience visualize the main message of a written text in an easy and digestible manner. Storyboards can involve a variety of elements, e,g., original artwork, curation of images, background music, a narrative script or dialogue, all of which are laid out in an intentional order that together tell a story. As such storyboards are rigorous and authentic forms of assessments, since they require students to employ multiple, higher order thinking skills and learn to collaborate with peers to present their point of view. Thus, storyboards can particularly benefit from scaffolding.
One way to scaffold may be to provide prompts that draw student attention to varied elements of a sample storyboard, in a sequential manner and help students evaluate how the elements support the narrative. Following this, instructors may have students complete parts of an existing sample storyboard to master each element. Finally, instructors should attempt to provide a clear rubric that is transparent about the skills being evaluated and the level of performance expected of students. In order to be inclusive and just, instructors should also consider student access to material needed to produce a high-quality storyboard since such material tends to be fairly expensive. This may include providing access to a repository of art material, videography equipment etc. through a library or local repository and/or arranging for funds that allow students to procure necessary equipment or software. Explore Macalaster University’s compilation of resources to design digital storyboard projects and evaluate storyboards . More examples can also be found on University of Houston’s repository of digital stories (Dogan, 2021).
Projects are equity-minded assessments if they are:
- Relevant: Include tasks such as application of knowledge, presentation skills, critical thinking or collaboration skills, each of which should correspond to learning goals of a course.
- Authentic: Engage students to apply knowledge and skills to address a novel problem. Ideally, the problem addressed is at the intersection of real-world application of knowledge or skills, needs of a discipline, and students' own interests.
- Rigorous: Require application of higher-order cognitive skills such as critical thinking, synthesis, and application of knowledge to a new context over multiple steps. For example, to produce a research paper, students need to identify a gap in the field, read primary literature, conduct analyses/experiments, verify findings using multiple sources, and write findings in a logical and cohesive manner. However, it is important for these projects to be well-structured and potentially be scaffolded wherein instructors provide more guidance on components of a project early on, and gradually have students independently complete the work as they gain more competency. Scaffolding provides students with adequate support to achieve the high standards set by rigorous assessments.
- Transparent: Explicit about the learning objectives and the metrics by which performance will be assessed. Provide students with a detailed rubric listing the criteria for evaluation and standards of performance expected in advance. Providing samples of successful projects completed by students in the past can also help make projects more transparent.
- Inclusive: Allows for diverse student interests, voices, and forms of creative expression in how the project is designed and presented.
Explore Champlain University’s guidelines on designing project assignments and Boston University’s suggestions for implementing project-based learning .
Center for Teaching and Learning. (2021, May 06). Project-Based Learning: Teaching Guide . Boston University
Division of Learning and Teaching (2022, March 30). Essay . Charles Sturt University.
Dogan, B. (2021). Example stories . The Educational Uses of Digital Storytelling Website. University of Houston College of Education.
Matthews, D. (2023, March 14). If you’re not using CHATGPT for your writing, you’re probably making a mistake . Vox.
Portfolios refer to a collection of work curated by students to provide evidence for the quality of work they have done and have the potential to do in the future (Vitale & Romance, 2005). Portfolios can include all or a selection of work done in a course and usually also include a component of reflective writing (Dibrell, n.d.). Although more common in performance-based disciplines such as humanities and art, portfolios can also be used in science and engineering to similarly evaluate demonstrated proficiency and potential (e.g., CV , research statements , ePortfolios/websites ). Alternately, portfolios may be composed of research papers, presentations, or concept maps . Portfolios align with equity-minded assessments when they are:
- Relevant: Include a wide repertoire of student work that is related to the course content and objectives, as well as student interests and goals.
- Authentic: Evaluate learning that simultaneously draws on multiple levels of cognitive demand, including synthesis, application and creation of new knowledge. Further, the work is typically aligned directly with future professional career paths that students will pursue.
- Rigorous: Consists of a sample of work drawn from a larger body of work that students complete throughout the course. The work typically requires students to employ a range of higher order thinking skills including analytical reasoning, collaboration, problem solving etc.
- Transparent: Co-creating rubrics with students in the class allows making expectations for the assessment explicit and inclusive of student voice. This is important because students and instructors may differ in their aesthetic sensibilities, making portfolios difficult to evaluate in a consistent manner. Utilizing a checklist or single-point rubric when grading student portfolios is recommended since such rubrics help provide a more uniform application of standards (meets/does not yet meet expectations), while leaving scope for subjective feedback on what students have done well and what they could improve on.
- Inclusive: Enables diverse student voice and expression since students curate their own collection. In some cases, allow students to include early pieces of work to evaluate the extent to which students have grown and expanded their skillset. Consider securing funds to reimburse students for materials, tools or other resources needed to complete the portfolio, making such assessments inclusive for students from marginalized backgrounds.
Explore tools such as digication to learn more about systematic ways to evaluate and assign portfolios in a transparent manner. Click on the respective links to view examples of CU undergraduate student portfolios in art , engineering and English . You can also find more examples on ASSETT’s BuffsCreate , a service providing all CU learners access to a subdomain and support to create an ePortfolio.
Dibrell, D. (n.d.). Designing reflective writing assignments . The University of Texas, Rio Grande Valley.
Vitale, M. R. & Romance, N. R. (2005). Portfolios in science assessment: A knowledge-based model for classroom practice . In J. J. Mintzes, J. H. Wandersee, & J. D. Novak (Eds.), Assessing Science Understanding: A Human Constructivist View, Educational Psychology. Burlington: Academic Press. (pp. 167–196). Burlington, VT: Academic Press.
Further readings and resources:
You can find additional resources and references below to learn more about incorporating different types of summative assessments and feedback in your class. Particularly notable is the NILOA Assignment Library , which provides a detailed description of best practices in incorporating the above assessments in each discipline in an equity-minded manner. Charles Sturt University also has a substantive overview of assessment types and best practices in designing them . For individualized support, you may also schedule a consultation with our team .
Division of Learning and Teaching. (2022, March 30). Assessment types . Charles Sturt University.
Montenegro, E., & Jankowski, N. A. (2020, January). A new decade for assessment: Embedding equity into assessment praxis (Occasional Paper No. 42). Urbana, IL: University of Illinois and Indiana University, National Institute for Learning Outcomes Assessment (NILOA).
Chan, J. C. K. & Ahn, D. (2023). Unproctored online exams provide meaningful assessment of student learning . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . 120 (31): e230202012
- Assessment in Large Enrollment Classes
- Classroom Assessment Techniques
- Creating and Using Learning Outcomes
- Early Feedback
- Five Misconceptions on Writing Feedback
- Formative Assessments
- Frequent Feedback
- Online and Remote Exams
- Student Learning Outcomes Assessment
- Student Peer Assessment
- Student Self-assessment
- Summative Assessments: Best Practices
- Assessing & Reflecting on Teaching
- Departmental Teaching Evaluation
- Equity in Assessment
- Glossary of Terms
- Attendance Policies
- Books We Recommend
- Classroom Management
- Community-Developed Resources
- Compassion & Self-Compassion
- Course Design & Development
- Course-in-a-box for New CU Educators
- Enthusiasm & Teaching
- First Day Tips
- Flexible Teaching
- Grants & Awards
- Inclusivity
- Learner Motivation
- Making Teaching & Learning Visible
- National Center for Faculty Development & Diversity
- Open Education
- Student Support Toolkit
- Sustainaiblity
- TA/Instructor Agreement
- Teaching & Learning in the Age of AI
- Teaching Well with Technology
Part 2: Backwards Design and Designing Assessments
Summative assessment.
Summative assessments are used to evaluate student learning, skill acquisition, and academic achievement at the conclusion of a defined instructional period—typically at the end of a project, unit, course, semester, program, or school year. Generally speaking, summative assessments are defined by three major criteria:
- The tests, assignments, or projects are used to determine whether students have learned what they were expected to learn. In other words, what makes an assessment “summative” is not the design of the test, assignment, or self-evaluation, per se, but the way it is used—i.e., to determine whether and to what degree students have learned the material they have been taught.
- Summative assessments are given at the conclusion of a specific instructional period, and therefore they are generally evaluative, rather than diagnostic—i.e., they are more appropriately used to determine learning progress and achievement, evaluate the effectiveness of educational programs, measure progress toward improvement goals, or make course-placement decisions, among other possible applications.
- Summative-assessment results are often recorded as scores or grades that are then factored into a student’s permanent academic record, whether they end up as letter grades on a report card or test scores used in the college-admissions process. While summative assessments are typically a major component of the grading process in most districts, schools, and courses, not all assessments considered to be summative are graded.
Summative assessments are commonly contrasted with formative assessments , which collect detailed information that educators can use to improve instruction and student learning while it’s happening. In other words, formative assessments are often said to be for learning, while summative assessments are of learning. Or as assessment expert Paul Black put it, “When the cook tastes the soup, that’s formative assessment. When the customer tastes the soup, that’s summative assessment.” It should be noted, however, that the distinction between formative and summative is often fuzzy in practice, and educators may have divergent interpretations and opinions on the subject.
Some of the most well-known and widely discussed examples of summative assessments are the standardized tests administered by states and testing organizations, usually in math, reading, writing, and science. Other examples of summative assessments include:
- End-of-unit or chapter tests.
- End-of-term or semester tests.
- Standardized tests that are used to for the purposes of school accountability, college admissions (e.g., the SAT or ACT), or end-of-course evaluation (e.g., Advanced Placement or International Baccalaureate exams).
- Culminating demonstrations of learning or other forms of “performance assessment,” such as portfolios of student work that are collected over time and evaluated by teachers or capstone projects that students work on over extended periods of time and that they present and defend at the conclusion of a school year or their high school education.
While most summative assessments are given at the conclusion of an instructional period, some summative assessments can still be used diagnostically. For example, the growing availability of student data, made possible by online grading systems and databases, can give teachers access to assessment results from previous years or other courses. By reviewing this data, teachers may be able to identify students more likely to struggle academically in certain subject areas or with certain concepts. In addition, students may be allowed to take some summative tests multiple times, and teachers might use the results to help prepare students for future administrations of the test.
It should also be noted that districts and schools may use “interim” or “benchmark” tests to monitor the academic progress of students and determine whether they are on track to mastering the material that will be evaluated on end-of-course tests or standardized tests. Some educators consider interim tests to be formative, since they are often used diagnostically to inform instructional modifications, but others may consider them to be summative. There is ongoing debate in the education community about this distinction, and interim assessments may defined differently from place to place. See formative assessment for a more detailed discussion.
While educators have arguably been using “summative assessments” in various forms since the invention of schools and teaching, summative assessments have in recent decades become components of larger school-improvement efforts. As they always have, summative assessments can help teachers determine whether students are making adequate academic progress or meeting expected learning standards, and results may be used to inform modifications to instructional techniques, lesson designs, or teaching materials the next time a course, unit, or lesson is taught. Yet perhaps the biggest changes in the use of summative assessments have resulted from state and federal policies aimed at improving public education—specifically, standardized high-stakes tests used to make important decisions about schools, teachers, and students.
While there is little disagreement among educators about the need for or utility of summative assessments, debates and disagreements tend to center on issues of fairness and effectiveness, especially when summative-assessment results are used for high-stakes purposes. In these cases, educators, experts, reformers, policy makers, and others may debate whether assessments are being designed and used appropriately, or whether high-stakes tests are either beneficial or harmful to the educational process. For more detailed discussions of these issues, see high-stakes test , measurement error , test accommodations , test bias , score inflation , standardized test , and value-added measures .
- Summative Assessment. Authored by : S. Abbott (Ed.). Provided by : Great Schools Partnership. Located at : http://edglossary.org/summative-assessment/ . Project : The Glossary of Education Reform. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Your browser is unsupported
We recommend using the latest version of IE11, Edge, Chrome, Firefox or Safari.
Center for the Advancement of Teaching Excellence
Summative assessments.
Nicole Messier, CATE Instructional Designer February 7th, 2022
WHAT? Heading link Copy link
Summative assessments are used to measure learning when instruction is over and thus may occur at the end of a learning unit, module, or the entire course.
Summative assessments are usually graded, are weighted more heavily than other course assignments or comprise a substantial percentage of a students’ overall grade (and are often considered “high stakes” assessments relative to other, “lower stakes” assessments in a course), and are required assessments for the completion of a course.
Summative assessments can be viewed through two broad assessment strategies: assessments of learning and assessments as learning.
- Assessment of learning (AoL) provides data to confirm course outcomes and students the opportunity to demonstrate proficiency in the learning objectives.
- Assessment as learning (AaL) provides student ownership of learning by utilizing evidence-based learning strategies, promoting self-regulation, and providing reflective learning.
A summative assessment can be designed to provide both assessment of learning (AoL) and assessment as learning (AaL). The goal of designing for AaL and AoL is to create a summative assessment as a learning experience while ensuring that the data collected is valid and reliable.

Want to learn more about these assessment strategies? Please visit the Resources Section – CATE website to review resources, teaching guides, and more.
Summative Assessments Heading link Copy link
Summative assessments (aol).
- Written assignments – such as papers or authentic assessments like projects or portfolios of creative work
- Mid-term exam
- Performances
Although exams are typically used to measure student knowledge and skills at the end of a learning unit, module, or an entire course, they can also be incorporated into learning opportunities for students.
Example 1 - Exam Heading link Copy link
Example 1 - exam.
An instructor decides to analyze their current multiple-choice and short-answer final exam for alignment to the learning objectives. The instructor discovers that the questions cover the content in the learning objectives; however, some questions are not at the same cognitive levels as the learning objectives . The instructor determines that they need to create some scenario questions where students are asked to analyze a situation and apply knowledge to be aligned with a particular learning objective.
The instructor also realizes that this new type of question format will be challenging for students if the exam is the only opportunity provided to students. The instructor decides to create a study guide for students on scenarios (not used in the exam) for students to practice and self-assess their learning. The instructor plans to make future changes to the quizzes and non-graded formative questions to include higher-level cognitive questions to ensure that learning objectives are being assessed as well as to support student success in the summative assessment.
This example demonstrates assessment of learning with an emphasis on improving the validity of the results, as well as assessment as learning by providing students with opportunities to self-assess and reflect on their learning.
Written assignments in any form (authentic, project, or problem-based) can also be designed to collect data and measure student learning, as well as provide opportunities for self-regulation and reflective learning. Instructors should consider using a type of grading rubric (analytic, holistic, or single point) for written assignments to ensure that the data collected is valid and reliable.
Summative Assessments (AaL) Heading link Copy link
Summative assessments (aal).
- Authentic assessments – an assessment that involves a real-world task or application of knowledge instead of a traditional paper; could involve a situation or scenario specific to a future career.
- Project-based learning – an assessment that involves student choice in designing and addressing a problem, need, or question.
- Problem-based learning – similar to project-based learning but focused on solutions to problems.
- Self-critique or peer assessment
Example 2 - Authentic Assessment Heading link Copy link
Example 2 - authentic assessment.
An instructor has traditionally used a research paper as the final summative assessment in their course. After attending a conference session on authentic assessments, the instructor decides to change this summative assessment to an authentic assessment that allows for student choice and increased interaction, feedback, and ownership.
First, the instructor introduced the summative project during the first week of class. The summative project instructions asked students to select a problem that could be addressed by one of the themes from the course. Students were provided with a list of authentic products that they could choose from, or they could request permission to submit a different product. Students were also provided with a rubric aligned to the learning objectives.
Next, the instructor created small groups (three to four students) with discussion forums for students to begin brainstorming problems, themes, and ideas for their summative project. These groups were also required to use the rubric to provide feedback to their peers at two separate time points in the course. Students were required to submit their final product, references, self-assessment using the rubric, and a reflection on the peer interaction and review.
This example demonstrates an authentic assessment as well as an assessment of learning (AoL) and assessment as learning (AaL). The validity and reliability of this summative assessment are ensured using a rubric that is focused on the learning objectives of the course and consistently utilized for the grading and feedback of the summative project. Data collected from the use of grading criteria in a rubric can be used to improve the summative project as well as the instruction and materials in the course. This summative project allows for reflective learning and provides opportunities for students to develop self-regulation skills as well as apply knowledge gained in an authentic and meaningful product.
Another way to create a summative assessment as a learning opportunity is to break it down into smaller manageable parts. These smaller parts will guide students’ understanding of expectations, provide them with opportunities to receive and apply feedback, as well as support their executive functioning and self-regulation skills.
WHY? Heading link Copy link
We know that summative assessments are vital to the curriculum planning cycle to measure student outcomes and implement continuous improvements. But how do we ensure our summative assessments are effective and equitable? Well, the answer is in the research.
Validity, Reliability, and Manageability
Critical components for the effectiveness of summative assessments are the validity, reliability, and manageability of the assessment (Khaled, 2020).
- Validity of the assessment refers to the alignment to course learning objectives. In other words, are the assessments in your course measuring the learning objectives?
- Reliability of the assessment refers to the consistency or accuracy of the assessment used. Are the assessment practices consistent from student to student and semester to semester?
- Manageability of the assessment refers to the workload for both faculty and students. For faculty, is the type of summative assessment causing a delay in timely grading and feedback to the learner? For students, is the summative assessment attainable and are the expectations realistic?
As you begin to design a summative assessment, determine how you will ensure the assessment is valid, reliable, and manageable.
Feedback & Summative Assessments
Attributes of academic feedback that improve the impact of the summative assessment on student learning (Daka, 2021; Harrison 2017) include:
- Provide feedback without or before grades.
- Once the grade is given, then explain the grading criteria and score (e.g., using a rubric to explain grading criteria and scoring).
- Identify specific qualities in students’ work.
- Describe actionable steps on what and how to improve.
- Motivate and encourage students by providing opportunities to submit revisions or earn partial credit for submitting revised responses to incorrect answers on exams.
- Allow students to monitor, evaluate, and regulate their learning.
Additional recommendations for feedback include that feedback should be timely, frequent, constructive (what and how), and should help infuse a sense of professional identity for students (why). The alignment of learning objectives, learning activities, and summative assessments is critical to student success and will ensure that assessments are valid. And lastly, the tasks in assessments should match the cognitive levels of the course learning objectives to challenge the highest performing students while elevating lower-achieving students (Daka, 2021).
HOW? Heading link Copy link
How do you start designing summative assessments?
Summative assessments can help measure student achievement of course learning objectives as well as provide the instructor with data to make pedagogical decisions on future teaching and instruction. Summative assessments can also provide learning opportunities as students reflect and take ownership of their learning.
So how do you determine what type of summative assessment to design? And how do you ensure that summative assessment will be valid, reliable, and manageable? Let’s dive into some of the elements that might impact your design decisions, including class size, discipline, modality, and EdTech tools .
Class Size and Modality
The manageability of summative assessments can be impacted by the class size and modality of the course. Depending on the class size of the course, instructors might be able to implement more opportunities for authentic summative assessments that provide student ownership and allow for more reflective learning (students think about their learning and make connections to their experiences). Larger class sizes might require instructors to consider implementing an EdTech tool to improve the manageability of summative assessments.
The course modality can also influence the design decisions of summative assessments. Courses with synchronous class sessions can require students to take summative assessments simultaneously through an in-person paper exam or an online exam using an EdTech tool, like Gradescope or Blackboard Tests, Pools, and Surveys . Courses can also create opportunities for students to share their authentic assessments asynchronously using an EdTech tool like VoiceThread .
Major Coursework
When designing a summative assessment as a learning opportunity for major coursework, instructors should reflect on the learning objectives to be assessed and the possible real-world application of the learning objectives. In replacement of multiple-choice or short answer questions that focus on content memorization, instructors might consider creating scenarios or situational questions that provide students with opportunities to analyze and apply knowledge gained. In major coursework, instructors should consider authentic assessments that allow for student choice, transfer of knowledge, and the development of professional skills in place of a traditional paper or essay.
Undergraduate General Education Coursework
In undergraduate general education coursework, instructors should consider the use of authentic assessments to make connections to students’ experiences, goals, and future careers. Simple adjustments to assignment instructions to allow for student choice can help increase student engagement and motivation. Designing authentic summative assessments can help connect students to the real-world application of the content and create buy-in on the importance of the summative assessment.
Summative Assessment Tools
EdTech tools can help to reduce faculty workload by providing a delivery system for students to submit work as well as tools to support academic integrity.
Below are EdTech tools that are available to UIC faculty to create and/or grade summative assessments as and of learning.
Assessment Creation and Grading Tools Heading link Copy link
Assessment creation and grading tools.
- Blackboard assignments drop box and rubrics
- Blackboard quizzes and exams
Assessment creation and grading tools can help support instructors in designing valid and reliable summative assessments. Gradescope can be utilized as a grading tool for in-person paper and pencil midterm and final exams, as well as a tool to create digital summative assessments. Instructors can use AI to improve the manageability of summative assessments as well as the reliability through the use of rubrics for grading with Gradescope.
In the Blackboard learning management system, instructors can create pools of questions for both formative and summative assessments as well as create authentic assessment drop boxes and rubrics aligned to learning objectives for valid and reliable data collection.
Academic Integrity Tools
- SafeAssign (undergraduate)
- iThenticate (graduate)
- Respondus LockDown Browser and Monitoring
Academic integrity tools can help ensure that students are meeting academic expectations concerning research through the use of SafeAssign and iThenticate as well as academic integrity during online tests and exams using Respondus Lockdown Browser and Monitoring.
Want to learn more about these summative assessment tools? Visit the EdTech section on the CATE website to learn more.
Exam Guidance
Additional guidance on online exams is available in Section III: Best Practices for Online (Remote Proctored, Synchronous) Exams in the Guidelines for Assessment in Online Environments Report , which outlines steps for equitable exam design, accessible exam technology, and effective communication for student success. The framing questions in the report are designed to guide instructors with suggestions, examples, and best practices (Academic Planning Task Force, 2020), which include:
- “What steps should be taken to ensure that all students have the necessary hardware, software, and internet capabilities to complete a remote, proctored exam?
- What practices should be implemented to make remote proctored exams accessible to all students, and in particular, for students with disabilities?
- How can creating an ethos of academic integrity be leveraged to curb cheating in remote proctored exams?
- What are exam design strategies to minimize cheating in an online environment?
- What tools can help to disincentive cheating during a remote proctored exam?
- How might feedback and grading strategies be adjusted to deter academic misconduct on exams?”
GETTING STARTED Heading link Copy link
Getting started.
The following steps will support you as you examine current summative assessment practices through the lens of assessment of learning (AoL) and assessment as learning (AaL) and develop new or adapt existing summative assessments.
- The first step is to utilize backward design principles by aligning the summative assessments to the learning objectives.
- To collect valid and reliable data to confirm student outcomes (AoL).
- To promote self-regulation and reflective learning by students (AaL).
- Format: exam, written assignment, portfolio, performance, project, etc.
- Delivery: paper and pencil, Blackboard, EdTech tool, etc.
- Feedback: general (how to improve performance), personalized (student-specific), etc.
- Scoring: automatically graded by Blackboard and/or EdTech tool or manual through the use of a rubric in Blackboard.
- The fourth step is to review data collected from summative assessment(s) and reflect on the implementation of the summative assessment(s) through the lens of validity, reliability, and manageability to inform continuous improvements for equitable student outcomes.
CITING THIS GUIDE Heading link Copy link
Citing this guide.
Messier, N. (2022). “Summative assessments.” Center for the Advancement of Teaching Excellence at the University of Illinois Chicago. Retrieved [today’s date] from https://teaching.uic.edu/resources/teaching-guides/assessment-grading-practices/summative-assessments/
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES Heading link Copy link
Academic Planning Task Force. (2020). Guidelines for Assessment in Online Learning Environments .
McLaughlin, L., Ricevuto, J. (2021). Assessments in a Virtual Environment: You Won’t Need that Lockdown Browser! Faculty Focus.
Moore, E. (2020). Assessments by Design: Rethinking Assessment for Learner Variability. Faculty Focus.
Websites and Journals
Association for the Assessment of Learning in Higher Education website
Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education. Taylor & Francis Online Journals
Journal of Assessment in Higher Education
REFERENCES Heading link Copy link
Daka, H., & Mulenga-Hagane, M., Mukalula-Kalumbi, M., Lisulo, S. (2021). Making summative assessment effective. 5. 224 – 237.
Earl, L.M., Katz, S. (2006). Rethinking classroom assessment with purpose in mind — Assessment for learning, assessment as learning, assessment of learning. Winnipeg, Manitoba: Crown in Right of Manitoba.
Galletly, R., Carciofo, R. (2020). Using an online discussion forum in a summative coursework assignment. Journal of Educators Online . Volume 17, Issue 2.
Harrison, C., Könings, K., Schuwirth, L. & Wass, V., Van der Vleuten, C. (2017). Changing the culture of assessment: the dominance of the summative assessment paradigm. BMC Medical Education. 17. 10.1186/s12909-017-0912-5.
Khaled, S., El Khatib, S. (2020). Summative assessment in higher education: Feedback for better learning outcomes
Formative and Summative Assessment
Assessment helps instructors and students monitor progress towards achieving learning objectives. Formative assessment is used throughout an instructional period to treat misconceptions, struggles, and learning gaps. Summative assessments evaluate learning, knowledge, proficiency, or success at the conclusion of an instructional period.
Below you will find formative and summative descriptions along with a diagram, examples, recommendations, and strategies/tools for the next steps.
Descriptions
Formative assessment (Image 1, left) refers to tools that identify misconceptions, struggles, and learning gaps along the way and assess how to close those gaps. It includes practical tools for helping to shape learning. It can even bolster students’ ability to take ownership of their education when they understand that the goal is to improve learning and not apply final marks (Trumbull and Lash, 2013). It can include students assessing themselves, peers, or even the instructor, through writing, quizzes, conversation, and more. Formative assessment occurs throughout a class or course and seeks to improve student achievement of learning objectives through approaches that can support specific student needs (Theal and Franklin, 2010, p. 151). In the classroom, formative assessment centers on practice and is often low-stakes. Students may or may not receive a grade.
In contrast, summative assessments (Image 1, right) evaluate student learning, knowledge, proficiency, or success after an instructional period, as a unit, course, or program. Summative assessments are almost always formally graded and often heavily weighted (though they do not need to be). Summative assessment can be used to significant effect in conjunction and in alignment with formative assessment, and instructors can consider a variety of ways to combine these approaches.

Examples of Formative and Summative Assessments
Formative: l earn and practice.
- In-class discussions
- Clicker questions (e.g., Top Hat)
- 1-minute reflection writing assignments
- Peer review
- Homework assignments
Summative: Assess performance
- Instructor-created exams
- Standardized tests
- Final projects
- Final essays
- Final presentations
- Final reports
- Final grades
Formative Assessment Recommendations
Ideally, formative assessment strategies improve teaching and learning simultaneously. Instructors can help students grow as learners by actively encouraging them to self-assess their skills and knowledge retention, and by giving clear instructions and feedback. Seven principles (adapted from Nicol and Macfarlane-Dick, 2007 with additions) can guide instructor strategies:
1. Keep clear criteria for what defines good performance
Instructors can explain criteria for A-F graded papers and encourage student discussion and reflection about these criteria (accomplish this through office hours, rubrics, post-grade peer review, or exam/assignment wrappers . Instructors may also hold class-wide conversations on performance criteria at strategic moments throughout the term.
2. Encourage students' self-reflection.
Instructors can ask students to utilize course criteria to evaluate their own or peers’ work and share what kinds of feedback they find most valuable. Also, instructors can ask students to describe their best work qualities, either through writing or group discussion.
3. Give students detailed, actionable feedback
Instructors can consistently provide specific feedback tied to predefined criteria, with opportunities to revise or apply feedback before final submission. Feedback may be corrective and forward-looking, rather than just evaluative. Examples include comments on multiple paper drafts, criterion discussions during 1-on-1 conferences, and regular online quizzes.
4. Encourage teacher and peer dialogue around learning
5. promote positive motivational beliefs and self-esteem.
Students will be more motivated and engaged when assured that an instructor cares for their development. Instructors can design assignments to allow for rewrites/resubmissions in assignments to promote learning development. These rewrites might utilize low-stakes assessments, or even automated online testing that is anonymous, and (if appropriate) allows for unlimited resubmissions.
6. Provide opportunities to close the gap between current and desired performance
Related to the above; instructors can improve student motivation and engagement by making visible any opportunities to close gaps between current and desired performance. Examples include opportunities for resubmission, specific action points for writing or task-based assignments, and sharing study or process strategies that an instructor would use to succeed.

7. Collect information to help shape teaching
Instructors can feel free to collect useful information from students to provide targeted feedback and instruction. Students can identify where they are having difficulties, either on an assignment or test or in written submissions. This approach also promotes metacognition, as students reflect upon their learning.
Instructors may find various other formative assessment techniques through CELT’s Classroom Assessment Techniques .
Summative Assessment Recommendations
Because summative assessments are usually higher-stakes than formative assessments, it is especially important to ensure that the assessment aligns with the instruction’s goals and expected outcomes.
1. Use a Rubric or Table of Specifications
Instructors can use a rubric to provide expected performance criteria for a range of grades. Rubrics will describe what an ideal assignment looks like, and “summarize” expected performance at the beginning of the term, providing students with a trajectory and sense of completion.
2. Design Clear, Effective Questions
If designing essay questions, instructors can ensure that questions meet criteria while allowing students the freedom to express their knowledge creatively and in ways that honor how they digested, constructed, or mastered meaning.
3. Assess Comprehensiveness.
Effective summative assessments allow students to consider the totality of a course’s content, make deep connections, demonstrate synthesized skills, and explore more profound concepts that drive or find a course’s ideas and content.
4. Make Parameters Clear
When approaching a final assessment, instructors can ensure that parameters are well defined (length of assessment, depth of response, time and date, grading standards). Also, knowledge assessed relates clearly to the content covered in course; and provides students with disabilities required space and support.
5. Consider Anonymous Grading.
Instructors may wish to know whose work they grade, to provide feedback that speaks to a student’s term-long trajectory. If instructors want to give a genuinely unbiased summative assessment, they can also consider a variety of anonymous grading techniques (see hide student names in SpeedGrader Canvas guide ).
Explore Assessment Strategies and Tools
Instructional strategies.
CELT’s online resources are organized to help an instructor sequentially work through the teaching process.
Learning Technology
A listing with applications that have been proven to meet the ISU’s security, accessibility, and purchasing standards.
Academic Integrity
Explore the following approaches and methods which emphasize prevention and education.
- Nicol, D.J. and Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006) Formative assessment and self‐regulated learning: a model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education 31 (2): 2-19.
- Theall, M. and Franklin J.L. (2010). Assessing Teaching Practices and Effectiveness for Formative Purposes. In: A Guide to Faculty Development . KJ Gillespie and DL Robertson (Eds). Jossey Bass: San Francisco, CA.
- Trumbull, E., & Lash, A. (2013). Understanding formative assessment: Insights from learning theory and measurement theory . San Francisco: WestEd.
Formative and Summative Assessment, by the Center for Excellence in Learning and Teaching (CELT) at Iowa State University is licensed under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 . This work, Formative and Summative Assessment, is a derivative of Formative and Summative Assessment developed by the Yale University Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning(retrieved on June 23, 2020) from https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/Formative-Summative-Assessments.
- eLearning Platform
- eLearning Content
- Access 800 Courses on our Platform
- Bespoke eLearning
- Virtual Training
- Our Pricing
- Request a Demo
- Content Partnerships
- Whitepapers
- Most Popular Blogs
- Personal Learning Journeys
- Training Feedback Form
- Training Needs Analysis Template
- Personal Development Plan Template
- Learning and Development Strategy
- Talent Management Strategy
- Kirkpatrick Evaluation Model
- Microlearning
- Informal Learning
- 70 20 10 Learning
Home » Blog » Formative and Summative Assessments: Examples and Differences
Formative and Summative Assessments: Examples and Differences

One of the primary benefits of using formative and summative assessments is that you aren’t forced to choose between them. They work exceptionally well when used in combination.
In this article, we’ll be breaking down precisely what formative and summative assessments are, the key differences between them, the benefits of their use, and providing a range of examples to help illustrate how they can be implemented in the classroom.
If you’re looking for an effective way to assess student learning and measure progress, read on to find out how formative and summative assessments can help.

Learn How To Create Personal Learning Journeys For FREE!
Formative assessments: definition and purpose.
Before we get into examples of their use, it’s essential that we first define precisely what both formative and summative assessments are and how they differ.
Formative assessments are employed regularly throughout a set learning period, be that a chapter, unit, or term, and help track progress and identify areas where students may struggle or need more support.
They also give the teacher and course designer the data they need to improve the learning experience and make any necessary changes that may be required throughout a system.
Rather than strict exams, formative assessments are usually relatively low-stakes, meaning they do not always need to be graded or even marked. This helps to create a non-threatening atmosphere and encourages students to take risks in their learning without fear of failure.
Formative assessment tasks usually rely on feedback from both students and the teacher, with learners receiving feedback on performance as soon as possible.
Uses of Formative Assessments
As mentioned, one of the primary uses of a formative assessment is to gauge student understanding and identify knowledge gaps that may need extra work.
Formative assessments can also be used to help inform curricular decisions, provide valuable data on the effectiveness of a course or lesson, and allow students to monitor their progress over time.
In addition, formative assessments are valuable in helping teachers gain real-time insight into a group’s collective understanding, allowing them to rapidly adapt their training or lessons accordingly.
Benefits of Using Formative Assessments
There are a range of benefits to employing formative assessments as part of your teaching strategy, including the following:
- Improved student or employee engagement and motivation – By allowing students to track their learning journey, you can help them take ownership of their learning experience. This can be highly motivating for students, as it encourages a sense of progress and accomplishment.
- Better assessment of real-world understanding – By using formative assessments that involve practical skills or application, you can better understand how well your students understand the real-world implications of the content they are studying.
- Enables rapid identification of areas of difficulty for learners – Through formative assessments, you can quickly identify areas that students may be struggling with. This helps to ensure that these areas are addressed rapidly and effectively.
- Allows teachers to tailor their lessons to the needs of the group – Teachers and course designers can use the data from formative assessments to tailor their studies according to the group’s needs and ensure that they meet all learning objectives.

Examples of Formative Assessments
To clarify how formative assessments can be used, below are a few examples of tasks that could be used both in the classroom and in a digital learning environment.
Classroom-Based Examples
The following examples can be valuable to employ in a classroom setting:
1. Quizzes and polls
Simple and easy to execute, quizzes and polls are a low-effort way of gauging student understanding at regular intervals throughout a lesson.
2. Peer feedback and self-assessment
Peer-based feedback sessions and self-assessment questionnaires can help identify areas where students may need extra support or guidance while giving vital insight into how students perceive their progress.
3. Class discussions and debates
Encouraging students to discuss their different perspectives on a given topic or concept allows teachers to better understand how well they comprehend the material. It also gives students the opportunity to have their ideas heard and helps create a sense of solidarity within the classroom.
Online and Digital Examples
With the rise in the use of digital learning tools and technologies , there is also a range of online-based practices that can be used as formative assessments, including:
1. Interactive quizzes and games
The gamification of quizzes or other learning activities can provide an engaging way to assess student understanding and offer real-time feedback.
2. Virtual simulations and case studies
Where more vocational skills are being taught, virtual simulations and case studies can test students’ problem-solving capabilities in a low-stakes environment.
3. Online discussion forums and feedback platforms
One of the benefits of using an online learning platform is the wide range of features available to assess student understanding. Discussion forums, peer feedback platforms, and automated feedback systems can all be used as formative assessment tools.

Summative Assessments: Definition and Purpose
Compared to formative assessments, summative assessments are conducted at the end of a defined learning period and often represent the final grade for the course.
To provide a comprehensive assessment grade, summative assessments evaluate a student’s overall understanding and performance of the skill or concept studied.
They can also be used to track educational progress over time, such as in standardised testing, as well as help to inform curricular decisions and the effectiveness of teaching methods.
Uses of Summative Assessments
Summative assessments test student mastery of content, assess their overall understanding of a subject or topic area and generally give them a final mark.
For teachers and course designers, a summative assessment allows them to measure the effectiveness of their teaching and make any necessary changes or improvements.
Summative assessments can also be used to compare student performance across different classes, courses, and programs.
Benefits of Summative Assessments
As with formative assessments, there is a range of benefits associated with the use of summative assessments, including:
- Provides an overall assessment score – Summative assessments can provide a more accurate assessment of student understanding and performance, offering an overall grade or score.
- Helps track educational progress over time – Educators can track student progress to identify improvement areas through standardised testing or other summative assessments.
- Helps inform curricular decisions – Summative assessments can assess the effectiveness of a particular course or program and help inform future curricular choices.
- Offers an efficient way to measure learning outcomes – By providing an overall assessment grade, summative assessments offer a convenient way to measure the success of a teaching strategy in one go.

Examples of Summative Assessments
To clarify how summative assessments can be implemented, here are a few examples of traditional assessment methods, such as essays and exams, and performance-based assessments, such as presentations and projects.
Traditional Assessment Methods
Below are some examples of traditional assessment methods:
1. Examinations and final tests
Examinations are widely used to assess student knowledge and understanding at the end of a course or program. They are easy to implement and provide a quick and efficient way to evaluate student performance.
2. Term papers and essays
Essays and term papers are another traditional assessment method used alongside examinations. Essays test students’ ability to analyse a given topic or concept in detail, providing insight into their understanding of the subject matter.
3. Projects and presentations
Where skill-based or vocational courses are being taught, projects and presentations can test a student’s performance in class. These assessments allow students to demonstrate their understanding of the subject matter and show their ability to apply and transfer the knowledge in a practical context.
Performance-Based Assessments
Performance-based assessments are best employed when assessing practical skills or processes. Examples of performance-based summative assessments include:
1. Practical exams and demonstrations
Practical tests and demonstrations are often used to assess students’ physical abilities, such as in sports or vocational courses. These assessments test a student’s understanding of a particular skill or concept by having them demonstrate it in a real-world setting.
2. Portfolios and showcases
Where creative or design-based courses are being taught, portfolios and showcases allow students to demonstrate their understanding of the concepts in a practical way. These assessments require students to use their creative skills to produce a tangible output, such as an artwork or multimedia presentation.
3. Capstone projects and dissertations
Dissertations and capstone projects are often used to assess students’ understanding of complex topics or skills. These assessments require students to demonstrate their knowledge of the subject matter by producing an in-depth research or project that meets specific criteria.

Critical Differences Between Formative and Summative Assessments
Now that you have a fuller understanding of what both formative and summative assessments represent and how they can be employed, here’s a summary outlining the key differences between the two:
Timing and Frequency
One of the most essential distinctions between the two types of assessment is when they are conducted. Formative assessments occur throughout the course and act as checkpoints to monitor student progress.
In contrast, summative assessments are shown at the end of a defined learning period and only count towards an overall grade or score.
Purpose and Focus
Formative assessments are designed to provide feedback on understanding and inform instruction in real-time. In contrast, summative assessments evaluate student performance of a skill or concept and can help inform curriculum decisions.
Feedback and Evaluation Process
The feedback and evaluation process for formative and summative assessments differs significantly. Formative assessments are designed to offer real-time feedback on performance.
In contrast, summative assessments provide an overall assessment score or grade that reflects the student’s understanding of the subject matter at the end of a course or program.

Which is the Right Assessment Approach to Utilise?
Choosing the correct assessment approach for your students ultimately depends on the goals you are trying to achieve, the type of course or program being taught and the knowledge and skills that need to be assessed.
To help you decide, consider the following:
Considerations for Selecting Formative Assessments
Some of the critical considerations for making use of formative assessments include:
- Regular feedback – Formative assessments should be implemented regularly to ensure students receive regular feedback on their understanding and performance.
- Low-stakes testing – As formative tests don’t count towards an overall grade, they should be designed as low-stakes tests to help encourage participation.
- Inform instruction – Formative assessment results can inform instruction in real-time, allowing educators to tailor their teaching approach to student needs.
Considerations for Selecting Summative Assessments
When making use of summative assessments, it’s essential to consider the following points:
- Assessment goals – Before designing a summative assessment, clearly define the purposes of the evaluation and how it will be used to evaluate student performance.
- Assessment criteria – When creating a summative assessment, ensure that you set clear and concise evaluation criteria that allow students to demonstrate their understanding fully.
- Inter-rater reliability – To ensure fairness and accuracy, consider having multiple assessors score each student’s work when creating a summative assessment.
Using Both Formative and Summative Assessments in Learning and Development
As mentioned, one of the primary benefits of using formative and summative assessments in learning and development is that they can provide a more comprehensive evaluation of student performance.
By implementing both assessment forms, educators can better understand their student’s progress and tailor their instruction for maximum impact.
Formative assessments can measure progress and inform instruction in real-time, while summative assessments provide an overall score or grade that indicates learning success.
Final Thoughts
While formative and summative assessments have apparent differences, such as in their purpose, timing and feedback mechanisms, there are significant benefits to using both assessment types in learning and development.
Educators can better assess student performance and tailor instruction by implementing formative and summative assessments. Additionally, the use of both reviews provides a comprehensive view of understanding that can be used to inform curriculum decisions.
If you are looking for more guidance and resources on creating and implementing formative and summative assessments, check out the other articles on the Skillshub blog .
As an eLearning company , we are committed to creating efficient and impactful learning experiences. Our team are experts in developing eLearning content , so skillshub can help create customised learning materials tailored to your organisation’s needs. To learn more about our services, get in touch with us today.

Sean McPheat
Sean is the CEO of Skillshub. He’s a published author and has been featured on CNN, BBC and ITV as a leading authority in the learning and development industry. Sean is responsible for the vision and strategy at Skillshub, helping to ensure innovation within the company.
Updated on: 20 September, 2023
Would your connections like this too? Please share.

You might also be interested in…

What is Ebbinghaus’s Forgetting Curve and How to Overcome it

What Is a Learner-Centred Approach and Why Is It Important

Importance and Benefits of Providing Employee Training

10 Important Steps for Building Relationships at Work

Exploring Different Types of Learning Styles

Employee Engagement Strategies for a Productive Workplace
- elearning Content
- Get In Touch
- Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning
- Instructional Guide
- Formative and Summative Assessment
Assessment is the process of gathering data. More specifically, assessment is the ways instructors gather data about their teaching and their students’ learning (Hanna & Dettmer, 2004). The data provide a picture of a range of activities using different forms of assessment such as: pre-tests, observations, and examinations. Once these data are gathered, you can then evaluate the student’s performance. Evaluation, therefore, draws on one’s judgment to determine the overall value of an outcome based on the assessment data. It is in the decision-making process then, where we design ways to improve the recognized weaknesses, gaps, or deficiencies.
Types of Assessment
There are three types of assessment: diagnostic, formative, and summative. Although are three are generally referred to simply as assessment, there are distinct differences between the three.
There are three types of assessment: diagnostic, formative, and summative.
Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessment can help you identify your students’ current knowledge of a subject, their skill sets and capabilities, and to clarify misconceptions before teaching takes place (Just Science Now!, n.d.). Knowing students’ strengths and weaknesses can help you better plan what to teach and how to teach it.
Types of Diagnostic Assessments
- Pre-tests (on content and abilities)
- Self-assessments (identifying skills and competencies)
- Discussion board responses (on content-specific prompts)
- Interviews (brief, private, 10-minute interview of each student)
Formative Assessment
Formative assessment provides feedback and information during the instructional process, while learning is taking place, and while learning is occurring. Formative assessment measures student progress but it can also assess your own progress as an instructor. For example, when implementing a new activity in class, you can, through observation and/or surveying the students, determine whether or not the activity should be used again (or modified). A primary focus of formative assessment is to identify areas that may need improvement. These assessments typically are not graded and act as a gauge to students’ learning progress and to determine teaching effectiveness (implementing appropriate methods and activities).
A primary focus of formative assessment is to identify areas that may need improvement.
Types of Formative Assessment
- Observations during in-class activities; of students non-verbal feedback during lecture
- Homework exercises as review for exams and class discussions)
- Reflections journals that are reviewed periodically during the semester
- Question and answer sessions, both formal—planned and informal—spontaneous
- Conferences between the instructor and student at various points in the semester
- In-class activities where students informally present their results
- Student feedback collected by periodically answering specific question about the instruction and their self-evaluation of performance and progress
Summative Assessment
Summative assessment takes place after the learning has been completed and provides information and feedback that sums up the teaching and learning process. Typically, no more formal learning is taking place at this stage, other than incidental learning which might take place through the completion of projects and assignments.
Rubrics, often developed around a set of standards or expectations, can be used for summative assessment. Rubrics can be given to students before they begin working on a particular project so they know what is expected of them (precisely what they have to do) for each of the criteria. Rubrics also can help you to be more objective when deriving a final, summative grade by following the same criteria students used to complete the project.
Rubrics also can help you to be more objective when deriving a final, summative grade by following the same criteria students used to complete the project.
High-stakes summative assessments typically are given to students at the end of a set point during or at the end of the semester to assess what has been learned and how well it was learned. Grades are usually an outcome of summative assessment: they indicate whether the student has an acceptable level of knowledge-gain—is the student able to effectively progress to the next part of the class? To the next course in the curriculum? To the next level of academic standing? See the section “Grading” for further information on grading and its affect on student achievement.
Summative assessment is more product-oriented and assesses the final product, whereas formative assessment focuses on the process toward completing the product. Once the project is completed, no further revisions can be made. If, however, students are allowed to make revisions, the assessment becomes formative, where students can take advantage of the opportunity to improve.
Summative assessment...assesses the final product, whereas formative assessment focuses on the process...
Types of Summative Assessment
- Examinations (major, high-stakes exams)
- Final examination (a truly summative assessment)
- Term papers (drafts submitted throughout the semester would be a formative assessment)
- Projects (project phases submitted at various completion points could be formatively assessed)
- Portfolios (could also be assessed during it’s development as a formative assessment)
- Performances
- Student evaluation of the course (teaching effectiveness)
- Instructor self-evaluation
Assessment measures if and how students are learning and if the teaching methods are effectively relaying the intended messages. Hanna and Dettmer (2004) suggest that you should strive to develop a range of assessments strategies that match all aspects of their instructional plans. Instead of trying to differentiate between formative and summative assessments it may be more beneficial to begin planning assessment strategies to match instructional goals and objectives at the beginning of the semester and implement them throughout the entire instructional experience. The selection of appropriate assessments should also match course and program objectives necessary for accreditation requirements.
Hanna, G. S., & Dettmer, P. A. (2004). Assessment for effective teaching: Using context-adaptive planning. Boston, MA: Pearson A&B.
Just Science Now! (n.d.). Assessment-inquiry connection. https://www.justsciencenow.com/assessment/index.htm
Selected Resources

Suggested citation
Northern Illinois University Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. (2012). Formative and summative assessment. In Instructional guide for university faculty and teaching assistants. Retrieved from https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide
- Active Learning Activities
- Assessing Student Learning
- Direct vs. Indirect Assessment
- Examples of Classroom Assessment Techniques
- Peer and Self-Assessment
- Reflective Journals and Learning Logs
- Rubrics for Assessment
- The Process of Grading
Phone: 815-753-0595 Email: [email protected]
Connect with us on
Facebook page Twitter page YouTube page Instagram page LinkedIn page
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Book Bracket Template. For March and Beyond!
Formative, Summative, and More Types of Assessments in Education
All the best ways to evaluate learning before, during, and after it happens.

When you hear the word assessment, do you automatically think “tests”? While it’s true that tests are one kind of assessment, they’re not the only way teachers evaluate student progress. Learn more about the types of assessments used in education, and find out how and when to use them.
Diagnostic Assessments
Formative assessments, summative assessments.
- Criterion-Referenced, Ipsative, and Normative Assessments
What is assessment?
In simplest terms, assessment means gathering data to help understand progress and effectiveness. In education, we gather data about student learning in variety of ways, then use it to assess both their progress and the effectiveness of our teaching programs. This helps educators know what’s working well and where they need to make changes.
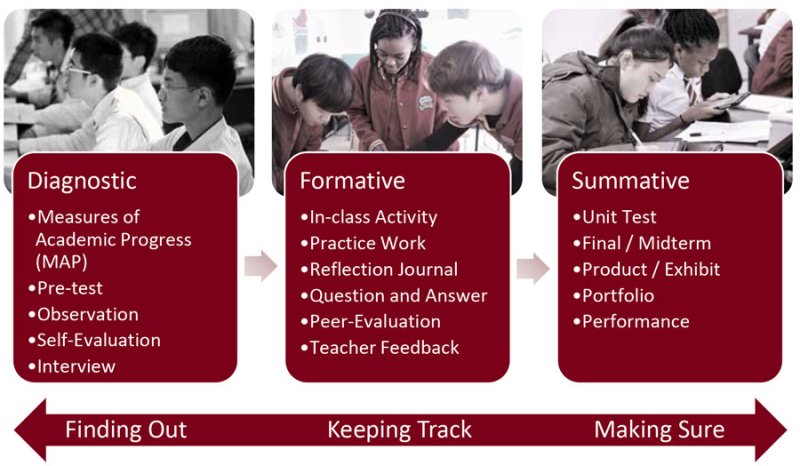
There are three broad types of assessments: diagnostic, formative, and summative. These take place throughout the learning process, helping students and teachers gauge learning. Within those three broad categories, you’ll find other types of assessment, such as ipsative, norm-referenced, and criterion-referenced.
What’s the purpose of assessment in education?
In education, we can group assessments under three main purposes:
- Of learning
- For learning
- As learning
Assessment of learning is student-based and one of the most familiar, encompassing tests, reports, essays, and other ways of determining what students have learned. These are usually summative assessments, and they are used to gauge progress for individuals and groups so educators can determine who has mastered the material and who needs more assistance.
When we talk about assessment for learning, we’re referring to the constant evaluations teachers perform as they teach. These quick assessments—such as in-class discussions or quick pop quizzes—give educators the chance to see if their teaching strategies are working. This allows them to make adjustments in action, tailoring their lessons and activities to student needs. Assessment for learning usually includes the formative and diagnostic types.
Assessment can also be a part of the learning process itself. When students use self-evaluations, flash cards, or rubrics, they’re using assessments to help them learn.
Let’s take a closer look at the various types of assessments used in education.

Diagnostic assessments are used before learning to determine what students already do and do not know. This often refers to pre-tests and other activities students attempt at the beginning of a unit.
How To Use Diagnostic Assessments
When giving diagnostic assessments, it’s important to remind students these won’t affect their overall grade. Instead, it’s a way for them to find out what they’ll be learning in an upcoming lesson or unit. It can also help them understand their own strengths and weaknesses, so they can ask for help when they need it.
Teachers can use results to understand what students already know and adapt their lesson plans accordingly. There’s no point in over-teaching a concept students have already mastered. On the other hand, a diagnostic assessment can also help highlight expected pre-knowledge that may be missing.
For instance, a teacher might assume students already know certain vocabulary words that are important for an upcoming lesson. If the diagnostic assessment indicates differently, the teacher knows they’ll need to take a step back and do a little pre-teaching before getting to their actual lesson plans.
Examples of Diagnostic Assessments
- Pre-test: This includes the same questions (or types of questions) that will appear on a final test, and it’s an excellent way to compare results.
- Blind Kahoot: Teachers and kids already love using Kahoot for test review, but it’s also the perfect way to introduce a new topic. Learn how Blind Kahoots work here.
- Survey or questionnaire: Ask students to rate their knowledge on a topic with a series of low-stakes questions.
- Checklist: Create a list of skills and knowledge students will build throughout a unit, and have them start by checking off any they already feel they’ve mastered. Revisit the list frequently as part of formative assessment.

Formative assessments take place during instruction. They’re used throughout the learning process and help teachers make on-the-go adjustments to instruction and activities as needed. These assessments aren’t used in calculating student grades, but they are planned as part of a lesson or activity. Learn much more about formative assessments here.
How To Use Formative Assessments
As you’re building a lesson plan, be sure to include formative assessments at logical points. These types of assessments might be used at the end of a class period, after finishing a hands-on activity, or once you’re through with a unit section or learning objective.
Once you have the results, use that feedback to determine student progress, both overall and as individuals. If the majority of a class is struggling with a specific concept, you might need to find different ways to teach it. Or you might discover that one student is especially falling behind and arrange to offer extra assistance to help them out.
While kids may grumble, standard homework review assignments can actually be a pretty valuable type of formative assessment . They give kids a chance to practice, while teachers can evaluate their progress by checking the answers. Just remember that homework review assignments are only one type of formative assessment, and not all kids have access to a safe and dedicated learning space outside of school.
Examples of Formative Assessments
- Exit tickets : At the end of a lesson or class, pose a question for students to answer before they leave. They can answer using a sticky note, online form, or digital tool.
- Kahoot quizzes : Kids enjoy the gamified fun, while teachers appreciate the ability to analyze the data later to see which topics students understand well and which need more time.
- Flip (formerly Flipgrid): We love Flip for helping teachers connect with students who hate speaking up in class. This innovative (and free!) tech tool lets students post selfie videos in response to teacher prompts. Kids can view each other’s videos, commenting and continuing the conversation in a low-key way.
- Self-evaluation: Encourage students to use formative assessments to gauge their own progress too. If they struggle with review questions or example problems, they know they’ll need to spend more time studying. This way, they’re not surprised when they don’t do well on a more formal test.
Find a big list of 25 creative and effective formative assessment options here.

Summative assessments are used at the end of a unit or lesson to determine what students have learned. By comparing diagnostic and summative assessments, teachers and learners can get a clearer picture of how much progress they’ve made. Summative assessments are often tests or exams but also include options like essays, projects, and presentations.
How To Use Summative Assessments
The goal of a summative assessment is to find out what students have learned and if their learning matches the goals for a unit or activity. Ensure you match your test questions or assessment activities with specific learning objectives to make the best use of summative assessments.
When possible, use an array of summative assessment options to give all types of learners a chance to demonstrate their knowledge. For instance, some students suffer from severe test anxiety but may still have mastered the skills and concepts and just need another way to show their achievement. Consider ditching the test paper and having a conversation with the student about the topic instead, covering the same basic objectives but without the high-pressure test environment.
Summative assessments are often used for grades, but they’re really about so much more. Encourage students to revisit their tests and exams, finding the right answers to any they originally missed. Think about allowing retakes for those who show dedication to improving on their learning. Drive home the idea that learning is about more than just a grade on a report card.
Examples of Summative Assessments
- Traditional tests: These might include multiple-choice, matching, and short-answer questions.
- Essays and research papers: This is another traditional form of summative assessment, typically involving drafts (which are really formative assessments in disguise) and edits before a final copy.
- Presentations: From oral book reports to persuasive speeches and beyond, presentations are another time-honored form of summative assessment.
Find 25 of our favorite alternative assessments here.
More Types of Assessments
Now that you know the three basic types of assessments, let’s take a look at some of the more specific and advanced terms you’re likely to hear in professional development books and sessions. These assessments may fit into some or all of the broader categories, depending on how they’re used. Here’s what teachers need to know.
Criterion-Referenced Assessments
In this common type of assessment, a student’s knowledge is compared to a standard learning objective. Most summative assessments are designed to measure student mastery of specific learning objectives. The important thing to remember about this type of assessment is that it only compares a student to the expected learning objectives themselves, not to other students.
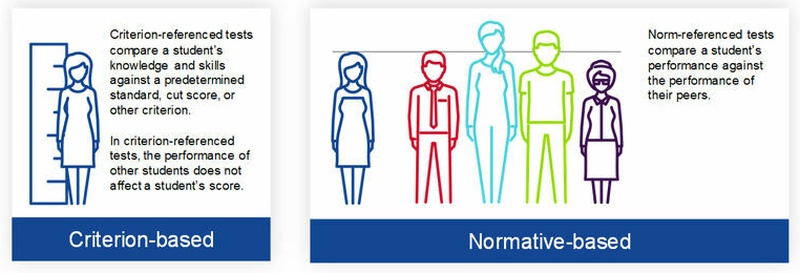
Many standardized tests are criterion-referenced assessments. A governing board determines the learning objectives for a specific group of students. Then, all students take a standardized test to see if they’ve achieved those objectives.
Find out more about criterion-referenced assessments here.
Norm-Referenced Assessments
These types of assessments do compare student achievement with that of their peers. Students receive a ranking based on their score and potentially on other factors as well. Norm-referenced assessments usually rank on a bell curve, establishing an “average” as well as high performers and low performers.
These assessments can be used as screening for those at risk for poor performance (such as those with learning disabilities) or to identify high-level learners who would thrive on additional challenges. They may also help rank students for college entrance or scholarships, or determine whether a student is ready for a new experience like preschool.
Learn more about norm-referenced assessments here.
Ipsative Assessments
In education, ipsative assessments compare a learner’s present performance to their own past performance, to chart achievement over time. Many educators consider ipsative assessment to be the most important of all , since it helps students and parents truly understand what they’ve accomplished—and sometimes, what they haven’t. It’s all about measuring personal growth.
Comparing the results of pre-tests with final exams is one type of ipsative assessment. Some schools use curriculum-based measurement to track ipsative performance. Kids take regular quick assessments (often weekly) to show their current skill/knowledge level in reading, writing, math, and other basics. Their results are charted, showing their progress over time.
Learn more about ipsative assessment in education here.
Have more questions about the best types of assessments to use with your students? Come ask for advice in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out creative ways to check for understanding ..

You Might Also Like

What Is Formative Assessment and How Should Teachers Use It?
Check student progress as they learn, and adapt to their needs. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
- Prodigy Math
- Prodigy English
From our blog
- Is a Premium Membership Worth It?
- Promote a Growth Mindset
- Help Your Child Who's Struggling with Math
- Parent's Guide to Prodigy
- Assessments
- Math Curriculum Coverage
- English Curriculum Coverage
- Game Portal
10 Summative Assessment Examples to Try This School Year

Written by Jordan Nisbet
Hey teachers! 👋
Turn math assessments into enjoyable experiences with Prodigy's game-based approach. Get ready for eager learners!
- Teaching Strategies
- A formative and summative assessment definition
- Difference between formative and summative assessment
- Pros and cons of summative assessment
- 9 effective and engaging summative assessment examples
- Helpful summative assessment strategies
When gauging student learning, two approaches likely come to mind: a formative or summative assessment.
Fortunately, feeling pressure to choose one or the other isn’t necessary. These two types of learning assessment actually serve different and necessary purposes.
Definitions: What’s the difference between formative and summative assessment?

Formative assessment occurs regularly throughout a unit, chapter, or term to help track not only how student learning is improving, but how your teaching can, too.
According to a WestEd article , teachers love using various formative assessments because they help meet students’ individual learning needs and foster an environment for ongoing feedback.
Take one-minute papers, for example. Giving your students a solo writing task about today’s lesson can help you see how well students understand new content.
Catching these struggles or learning gaps immediately is better than finding out during a summative assessment.
Such an assessment could include:
- In-lesson polls
- Partner quizzes
- Self-evaluations
- Ed-tech games
- One-minute papers
- Visuals (e.g., diagrams, charts or maps) to demonstrate learning
- Exit tickets
So, what is a summative assessment?

Credit: Alberto G.
It occurs at the end of a unit, chapter, or term and is most commonly associated with final projects, standardized tests, or district benchmarks.
Typically heavily weighted and graded, it evaluates what a student has learned and how much they understand.
There are various types of summative assessment. Here are some common examples of summative assessment in practice:
- End-of-unit test
- End-of-chapter test
- Achievement tests
- Standardized tests
- Final projects or portfolios
Teachers and administrators use the final result to assess student progress, and to evaluate schools and districts. For teachers, this could mean changing how you teach a certain unit or chapter. For administrators, this data could help clarify which programs (if any) require tweaking or removal.
The differences between formative and summative assessment
While we just defined the two, there are five key differences between formative and summative assessments requiring a more in-depth explanation.
Formative assessment:
- Occurs through a chapter or unit
- Improves how students learn
- Covers small content areas
- Monitors how students are learning
- Focuses on the process of student learning
Summative assessment:
- Occurs at the end of a chapter or unit
- Evaluates what students learn
- Covers complete content areas
- Assigns a grade to students' understanding
- Emphasizes the product of student learning
During vs after
Teachers use formative assessment at many points during a unit or chapter to help guide student learning.
Summative assessment comes in after completing a content area to gauge student understanding.
Improving vs evaluating
If anyone knows how much the learning process is a constant work in progress, it’s you! This is why formative assessment is so helpful — it won’t always guarantee students understand concepts, but it will improve how they learn.
Summative assessment, on the other hand, simply evaluates what they’ve learned. In her book, Balanced Assessment: From Formative to Summative, renowned educator Kay Burke writes, “The only feedback comes in the form of a letter grade, percentage grade, pass/fail grade, or label such as ‘exceeds standards’ or ‘needs improvement.’”

Little vs large
Let’s say chapter one in the math textbook has three subchapters (i.e., 1.1, 1.2 and 1.3). A teacher conducting formative assessments will assign mini tasks or assignments throughout each individual content area.
Whereas, if you’d like an idea of how your class understood the complete chapter, you’d give them a test covering a large content area including all three parts.
Monitoring vs grading
Formative assessment is extremely effective as a means to monitor individual students’ learning styles. It helps catch problems early, giving you more time to address and adapt to different problem areas.
Summative assessments are used to evaluate and grade students’ overall understanding of what you’ve taught. Think report card comments: did students achieve the learning goal(s) you set for them or not?
😮 😄 😂 #reportcard #funny #memes #comics #samecooke #schooldays #music #classic #letsgo #gooutmore #showlove pic.twitter.com/qQ2jen1Z8k — Goldstar Events (@goldstar) January 20, 2019
Process vs product
“It’s not about the destination; it’s about the journey”? This age-old saying sums up formative and summative assessments fairly accurately.
The former focuses on the process of student learning. You’ll use it to identify areas of strength and weakness among your students — and to make necessary changes to accommodate their learning needs.
The latter emphasizes the product of student learning. To discover the product’s “value”, you can ask yourself questions, such as: At the end of an instructional unit, did the student’s grade exceed the class standard, or pass according to a district’s benchmark?
In other words, formative methods are an assessment for learning whereas summative ones are an assessment of learning .
Now that you’ve got a more thorough understanding of these evaluations, let’s dive into the love-hate relationship teachers like yourself may have with summative assessments.
Perceived disadvantages of summative assessment
The pros are plenty. However, before getting to that list, let’s outline some of its perceived cons. Summative assessment may:
1) Offer minimal room for creativity
Rigid and strict assignments or tests can lead to a regurgitation of information. Some students may be able to rewrite facts from one page to another, but others need to understand the “why” before giving an answer.
2) Not accurately reflect learning
“Teaching to the test” refers to educators who dedicate more time teaching lessons that will be emphasized on district-specific tests.
A survey conducted by Harvard’s Carnegie-Knight Task Force on the Future of Journalism asked teachers whether or not “preparing students to pass mandated standardized tests” affects their teaching.
A significant 60% said it either “dictates most of” or “substantially affects” their teaching. While this can result in higher scores, curriculum distortion can prevent students from learning other foundational subject areas.
3) Ignore (and miss) timely learning needs

Because summative assessment occurs at the end of units or terms, teachers can fail to identify and remedy students’ knowledge gaps or misconceptions as they arise.
Unfortunately, by this point, there’s often little or no time to rectify a student’s mark, which can affect them in subsequent units or grades.
4) Result in a lack of motivation
The University of London’s Evidence for Policy and Practice conducted a 19-study systematic review of the impact summative assessment and tests have on students’ motivation for learning.
Contrary to popular belief, researchers found a correlation between students who scored poorly on national curriculum tests and experienced lower self-esteem, and an unwillingness to put more effort into future test prep. Beforehand, interestingly, “there was no correlation between self-esteem and achievement.”
For some students, summative assessment can sometimes be seen as 'high stakes' testing due to the pressure on them to perform well. That said, 'low-stakes' assessments can also be used in the form of quizzes or practice tests.
Repeated practice tests reinforce the low self-image of the lower-achieving students… When test scores are a source or pride and the community, pressure is brought to bear on the school for high scores.
Similarly, parents bring pressure on their children when the result has consequences for attendance at high social status schools. For many students, this increases their anxiety, even though they recognize their parents as being supportive.
5) Be inauthentic
Summative assessment has received criticism for its perceived inaccuracy in providing a full and balanced measure of student learning.
Consider this, for example: Your student, who’s a hands-on, auditory learner, has a math test today. It comes in a traditional paper format as well as a computer program format, which reads the questions aloud for students.
Chances are the student will opt for the latter test format. What’s more, this student’s test results will likely be higher and more accurate.
The reality is that curricula — let alone standardized tests — typically don’t allow for this kind of accommodation. This is the exact reason educators and advocates such as Chuck Hitchcock, Anne Meyer, David Rose, and Richard Jackson believe:
Curriculum matters and ‘fixing’ the one-size-fits-all, inflexible curriculum will occupy both special and general educators well into the future… Students with diverse learning needs are not ‘the problem’; barriers in the curriculum itself are the root of the difficulty.
6) Be biased
Depending on a school district’s demographic, summative assessment — including standardized tests — can present biases if a group of students is unfairly graded based on their race, ethnicity, religion, gender, or social class.
In his presentation at Kansas State University, emeritus professor in the UCLA Graduate School of Education and Information Studies, Dr. W. James Popham, explained summative assessment bias:
This doesn’t necessarily mean that if minority students are outperformed on a summative test by majority students that the test is biased against that minority. It may instead indicate that the minority students have not been provided with the appropriate instruction…
An example of content bias against girls would be one in which students are asked to compare the weights of several objects, including a football. Since girls are less likely to have handled a football, they might find the item more difficult than boys, even though they have mastered the concept measured by the item.
Importance and benefits of summative assessment

Overall, these are valid points raised against summative assessment. However, it does offer fantastic benefits for teachers and students alike!
Summative assessment can:
1) Motivate students to study and pay closer attention
Although we mentioned lack of motivation above, this isn’t true for every student. In fact, you’ve probably encountered numerous students for whom summative assessments are an incredible source of motivation to put more effort into their studies.
For example, final exams are a common type of summative assessment that students may encounter at the end of a semester or school year. This pivotal moment gives students a milestone to achieve and a chance to demonstrate their knowledge.
In May 2017, the College Board released a statement about whether coaching truly boosts test scores:
Data shows studying for the SAT for 20 hours on free Official SAT Practice on Khan Academy is associated with an average score gain of 115 points, nearly double the average score gain compared to students who don’t use Khan Academy. Out of nearly 250,000 test-takers studied, more than 16,000 gained 200 points or more between the PSAT/NMSQT and SAT…
In addition to the 115-point average score increase associated with 20 hours of practice, shorter practice periods also correlate with meaningful score gains. For example, 6 to 8 hours of practice on Official SAT Practice is associated with an average 90-point increase.
2) Allow students to apply what they’ve learned

It’s one thing to memorize multiplication tables (which is a good skill), but another to apply those skills in math word problems or real-world examples.
Summative assessments — excluding, for example, multiple choice tests — help you see which students can retain and apply what they’ve learned.
3) Help identify gaps in student learning
Before moving on to a new unit, it’s vital to make sure students are keeping up. Naturally, some will be ahead while others will lag behind. In either case, giving them a summative assessment will provide you with a general overview of where your class stands as a whole.
Let’s say your class just wrote a test on multiplication and division. If all students scored high on multiplication but one quarter of students scored low on division, you’ll know to focus more on teaching division to those students moving forward.
4) Help identify possible teaching gaps

Credit: woodleywonderworks
In addition to identifying student learning gaps , summative assessment can help target where your teaching style or lesson plans may have missed the mark.
Have you ever been grading tests before, to your horror, realizing almost none of your students hit the benchmark you hoped for? When this happens, the low grades are not necessarily related to study time.
For example, you may need to adjust your teaching methods by:
- Including/excluding word problems
- Incorporating more visual components
- Innovative summative assessments (we list some below!)
5) Give teachers valuable insights

Credit: Kevin Jarrett
Summative assessments can highlight what worked and what didn’t throughout the school year. Once you pinpoint how, where and what lessons need tweaking, making informed adjustments for next year becomes easier.
In this world nothing can be said to be certain, except death and taxes… and, for teachers, new students year after year. So although old students may miss out on changes you’ve made to your lessons, new ones get to reap the benefits.
This not only improves your skills as an educator, but will ensure a more enriching educational experience for generations of students to come.
6) Contribute positively to learning outcomes
Certain summative assessments also provide valuable data at district, national, and global levels. Depending on average test scores, this can determine whether or not certain schools receive funding, programs stay or go, curriculum changes occur, and more. Burke writes:
Summative assessments also provide the public and policymakers with a sense of the results of their investment in education and give educators a forum for proving whether instruction works – or does not work.
The seven aims of summative assessment

Dr. Nancy P. Gallavan, a professor of teacher education at the University of Central Arkansas, believes teachers can use performance-based summative assessments at any grade level.
However, in an article for Corwin , she suggests crafting yours with seven aims in mind:
- Accompanied with appropriate time and task management
- Achievable as in-class activities and out-of-class assignments
- Active involvement in planning, preparation, and performance
- Applicable to academic standards and expectations
- Appropriate to your students’ learning styles, needs, and interests
- Attractive to your students on an individual and group level
- Authentic to curricular content and context
Ideally, the assessment method should also measure a student’s performance accurately against the learning objectives set at the beginning of the course.
Keeping these goals in mind, here’s a list of innovative ways to conduct summative assessments in your classroom!
Summative assessment examples: 9 ways to make test time fun

If you want to switch things up this summative assessment season, keep reading. While you can’t change what’s on standardized tests, you can create activities to ensure your students are exhibiting and applying their understanding and skills to end-of-chapter or -unit assessments. In a refreshing way.
Why not give them the opportunity to express their understanding in ways that apply to different learning styles?
Note : As a general guideline, students should incorporate recognition and recall, logic and reasoning, as well as skills and application that cover major concepts and practices (including content areas you emphasized in your lessons).
1) One, two, three… action!
Write a script and create a short play, movie, or song about a concept or strategy of your choosing.
This video from Science Rap Academy is a great — and advanced — example of students who created a song about how blue-eyed children can come from two brown-eyed parents:
Using a tool such as iPhone Fake Text Generator , have students craft a mock text message conversation conveying a complex concept from the unit, or each chapter of that unit.
Students could create a back-and-forth conversation between two historical figures about a world event, or two friends helping each other with complex math concepts.
Have your students create a five to 10-minute podcast episode about core concepts from each unit. This is an exciting option because it can become an ongoing project.
Individually or in groups, specific students can be in charge of each end-of-chapter or -unit podcast. If your students have a cumulative test towards the end of the year or term, the podcast can even function as a study tool they created together.

Credit : Brad Flickinger
You can use online tools such as Record MP3 Online or Vocaroo to get your class started!
4) Infographic
Creating a detailed infographic for a final project is an effective way for students to reinforce what they’ve learned. They can cover definitions, key facts, statistics, research, how-to info, graphics, etc.
You can even put up the most impressive infographics in your classroom. Over time, you’ll have an arsenal of in-depth, visually-appealing infographics students can use when studying for chapter or unit tests.
5) Compare and contrast
Venn diagrams are an old — yet effective — tool perfect for visualizing just about anything! Whether you teach history or social studies, English or math, or something in between, Venn diagrams can help certain learners visualize the relationship between different things.
For example, they can compare book characters, locations around the world, scientific concepts, and more just like the examples below:
6) Living museum
This creative summative assessment is similar to one, two, three… action! Individuals will plan and prepare an exhibit (concept) in the Living Museum (classroom). Let’s say the unit your class just completed covered five core concepts.
Five students will set up around the classroom while the teacher walks from exhibit to exhibit. Upon reaching the first student, the teacher will push an imaginary button, bringing the exhibit “to life.” The student will do a two to three-minute presentation; afterwards, the teacher will move on to the next one.
7) Ed-Tech games
Now more than ever, students are growing up saturated with smartphones, tablets, and video games. That’s why educators should show students how to use technology in the classroom effectively and productively.
More and more educators are bringing digital tools into the learning process. Pew Research Center surveyed 2,462 teachers and reported that digital technologies have helped in teaching their middle and high school students.
Some of the findings were quite eye-opening:
- 80% report using the internet at least weekly to help them create lesson plans
- 84% report using the internet at least weekly to find content that will engage students
- 69% say the internet has a “major impact on their ability to share ideas with other teachers
- 80% report getting email alerts or updates at least weekly that allow them to follow developments in their field
- 92% say the internet has a “major impact” on their ability to access content, resources, and materials for their teaching
- 67% say the internet has a “major impact” on their ability to interact with parents and 57% say it has had such an impact on enabling their interaction with students
To make the most of EdTech, find a tool that actually engages your students in learning and gives you the insightful data and reports you need to adjust your instruction
Tip: Teaching math from 1st to 8th grade? Use Prodigy!
With Prodigy Math, you can:
- Deliver engaging assessments: Prodigy's game-based approach makes assessments fun for students.
- Spot and solve learning gaps: See which students need more support at the touch of a button.
- Reduce test anxiety: Prodigy has been shown to build math confidence.
Plus, it's all available to educators at no cost. See how it works below! 👇
8) Shark Tank/Dragon’s Den
Yes, just like the reality TV show! You can show an episode or two to your class or get them to watch the show at home. Next, have students pitch a product or invention that can help change the world outside of school for the better.
This innovative summative assessment is one that’ll definitely require some more thought and creativity. But it’s important that, as educators, we help students realize they can have a huge positive impact on the world in which they live.
9) Free choice
If a student chooses to come up with their own summative assessment, you’ll need to vet it first. It’ll likely take some collaboration to arrive at something sufficient.
However, giving students the freedom to explore content areas that interest them most could surprise you. Sometimes, it’s during those projects they form a newfound passion and are wildly successful in completing the task.

We’re sure there are countless other innovative summative assessment ideas out there, but we hope this list gets your creative juices flowing.
With the exclusion of standardized state and national tests, one of the greatest misconceptions about summative assessments is that they’re all about paper and pencil. Our hope in creating this list was to help you see how fun and engaging summative assessments can truly be.
10) Group projects
Group projects aren't just a fun way to break the monotony, but a dynamic and interactive form of summative assessment. Here's why:
- Collaborative learning: Group projects encourage students to work as a team, fostering their communication and collaboration skills. They learn to listen, negotiate, and empathize, which are crucial skills in and beyond the classroom.
- Promotes critical thinking: When students interact with each other, they get to explore different perspectives. They challenge each other's understanding, leading to stimulating debates and problem-solving sessions that boost critical thinking.
- In-depth assessment: Group projects offer teachers a unique lens to evaluate both individual performances and group dynamics. It's like getting a sneak peek into their world - you get to see how they perform under different circumstances and how they interact with each other.
- Catering to different learning styles: Given the interactive nature of group projects, they can cater to different learning styles - auditory, visual, and kinesthetic. Every student gets a chance to shine!
However, it's important to set clear instructions and criteria to ensure fairness. Remember, it's not just about the final product - it's about the process too.
Some interesting examples of group projects include:
- Create a Mini Documentary: Students could work together to research a historical event and create a mini documentary presenting their findings.
- Plan a Community Service Project: This could involve identifying a problem in the local community and creating a detailed plan to address it.
- Design a Mobile App: For a more tech-focused project, students could identify a problem and design an app that solves it.
Summative assessment strategies for keeping tests clear and fair

In addition to using the summative assessment examples above to accommodate your students’ learning styles, these tips and strategies should also help:
- Use a rubric — Rubrics help set a standard for how your class should perform on a test or assignment. They outline test length, how in-depth it will be, and what you require of them to achieve the highest possible grades.
- Design clear, effective questions — When designing tests, do your best to use language, phrases, and examples similar to those used during lessons. This’ll help keep your tests aligned with the material you’ve covered.
- Try blind grading — Most teachers prefer knowing whose tests they’re grading. But if you want to provide wholly unbiased grades and feedback, try blind grading. You can request your students write their names on the bottom of the last test page or the back.
- Assess comprehensiveness — Make sure the broad, overarching connections you’re hoping students can make are reasonable and fluid. For example, if the test covers measurement, geometry and spatial sense, you should avoid including questions about patterning and algebra.
- Create a final test after, not before, teaching the lessons — Don’t put the horse before the carriage. Plans can change and student learning can demand different emphases from year to year. If you have a test outline, perfect! But expect to embrace and make some changes from time to time.
- Make it real-world relevant — How many times have you heard students ask, “When am I going to use this in real life?” Far too often students assume math, for example, is irrelevant to their lives and write it off as a subject they don’t need. When crafting test questions, use culturally-relevant word problems to illustrate a subject’s true relevance.
Enter the Balanced Assessment Model
Throughout your teaching career, you’ll spend a lot of time with formative and summative assessments. While some teachers emphasize one over the other, it’s vital to recognize the extent to which they’re interconnected.
In the book Classroom Assessment for Student Learning , Richard Stiggins, one of the first educators to advocate for the concept of assessment for learning, proposes something called “a balanced assessment system that takes advantage of assessment of learning and assessment for learning.”
If you use both effectively, they inform one another and “assessment becomes more than just an index of school success. It also serves as the cause of that success.”
In fact, Stiggins argues teachers should view these two types of assessment as “in sync.”
They can even be the exact same thing — only the purpose and the timing of the assessment determine its label. Formative assessments provide the training wheels that allow students to practice and gain confidence while riding their bikes around the enclosed school parking lot.
Once the training wheels come off, the students face their summative assessment as they ride off into the sunset on only two wheels, prepared to navigate the twists and turns of the road to arrive safely at their final destination.
Conclusion: Going beyond the test
Implementing these innovative summative assessment examples should engage your students in new and exciting ways.
What’s more, they’ll have the opportunity to express and apply what they’ve learned in creative ways that solidify student learning.
So, what do you think — are you ready to try out these summative assessment ideas? Prodigy is a game-based learning platform teachers use to keep their students engaged.
Sign up for a free teacher account and set an Assessment today!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Summative assessments are given to students at the end of a course and should measure the skills and knowledge a student has gained over the entire instructional period. Summative feedback is aimed at helping students understand how well they have done in meeting the overall learning goals of the course. ... Portfolios usually include the ...
Some of the most well-known and widely discussed examples of summative assessments are the standardized tests administered by states and testing organizations, usually in math, reading, writing, and science. Other examples of summative assessments include: End-of-unit or chapter tests. End-of-term or semester tests.
Many original conceptualizations of formative assessment include summative assessment as a necessary component before any feedback can be provided (Taras, 2005). More recent thinking about the relationship between the two suggests more of a cyclical relationship. Formative assessments that measure students' individual progress can be used to ...
Summative assessment tips for teachers. 1. Design a summative assessment based on its purpose. 2. Offer clear instructions throughout the assessment. 3. Ensure consistency in summative assessments from year to year. 4. Prepare students in advance.
Summative assessments are implemented at the end of a unit, set of units, or entire course to assess and evaluate the extent to which students have achieved the learning objectives (knowledge, skills, and behaviors) for that period of instruction. ... Some examples include: Breaking down summative assessments, such as major projects and papers ...
Examples of summative assessments may include: Written Assessment: Students will be tasked with writing an original piece, such as a narrative or analytical essay. Performance Assessment: With ...
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark. Summative assessments are often high stakes, which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include: a midterm exam. a final project. a paper. a senior recital.
Summative assessment, summative evaluation, or assessment of learning is the assessment of participants in an educational program. Summative assessments are designed to both assess the effectiveness of the program and the learning of the participants. ... Grading systems can include a percentage, pass/fail, or some other form of scale grade ...
A summative assessment's validity ensures that decisions are made according to the true learning targets and not some side topic that may have unintentionally found its way into the assessment. ... Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. _jsuid: 1 year:
Summative assessments are generally standardised and rarely provide feedback. Shutterstock Summative assessment. This includes end of unit examinations and the NSW Higher School Certificate (HSC ...
Formative and summative assessments should be adaptable. Importantly, it is not the 'form' that assessment takes that determines whether it is formative or summative, instead it is how it is being used. For example, 'test style questions' can be used both as formative assessment (perhaps as exit tickets - questions given to students ...
Summative assessment is a specific type of assessment that evaluates learning and offers little opportunity for providing student feedback because of its positioning at the end of a learning unit. They are usually high-stakes, contributing to a large portion of a student's course grade (e.g., final exams) or an exam that has a high impact on ...
Summative assessments are quizzes and tests that evaluate how much someone has learned throughout a course. In the classroom, that means formative assessments take place during a course, while summative assessments are the final evaluations at the course's end. That's the simple answer, but there's actually a lot more that makes formative and ...
Unlike formative assessments, summative assessments (that gather data of learning) are used to assess students' academic achievement and evaluate how students perform when compared to a larger group of students. These formal assessments include standardized tests that are graded in a formulated manner (ie: criterion-referenced tests, norm ...
In short, formative assessment occurs throughout a class or course, and seeks to improve student achievement of learning objectives through approaches that can support specific student needs (Theal and Franklin, 2010, p. 151). In contrast, summative assessments evaluate student learning, knowledge, proficiency, or success at the conclusion of ...
Summative Assessments: Types. Below are some types of assessments that are commonly used to gauge learning at the end of a unit or course. While the focus here is primarily on the use of these assessments for summative purposes, these can also be utilized as formative assessments, to track student learning during a course.
Some of the most well-known and widely discussed examples of summative assessments are the standardized tests administered by states and testing organizations, usually in math, reading, writing, and science. Other examples of summative assessments include: End-of-unit or chapter tests. End-of-term or semester tests.
Attributes of academic feedback that improve the impact of the summative assessment on student learning (Daka, 2021; Harrison 2017) include: Provide feedback without or before grades. Once the grade is given, then explain the grading criteria and score (e.g., using a rubric to explain grading criteria and scoring).
Descriptions. Formative assessment (Image 1, left) refers to tools that identify misconceptions, struggles, and learning gaps along the way and assess how to close those gaps. It includes practical tools for helping to shape learning. It can even bolster students' ability to take ownership of their education when they understand that the goal is to improve learning and not apply final marks ...
Examples of performance-based summative assessments include: 1. Practical exams and demonstrations . Practical tests and demonstrations are often used to assess students' physical abilities, such as in sports or vocational courses. These assessments test a student's understanding of a particular skill or concept by having them demonstrate ...
Summative Assessment. Summative assessment takes place after the learning has been completed and provides information and feedback that sums up the teaching and learning process. Typically, no more formal learning is taking place at this stage, other than incidental learning which might take place through the completion of projects and assignments.
Assessment for learning usually includes the formative and diagnostic types. Assessment can also be a part of the learning process itself. When students use self-evaluations, flash cards, or rubrics, they're using assessments to help them learn. ... Summative assessments are often tests or exams but also include options like essays, projects ...
Summative assessment examples: 9 ways to make test time fun. If you want to switch things up this summative assessment season, keep reading. While you can't change what's on standardized tests, you can create activities to ensure your students are exhibiting and applying their understanding and skills to end-of-chapter or -unit assessments.
testing window, scheduled to begin on April 15, 2024. This manual includes an assessment overview, guidelines for test security, details on student tools and accommodations, testing scripts, and other pertinent information. It is crucial to thoroughly review this manual to ensure a smooth and successful testing process.
3. When are ELPA Summative scores for Grade 9 -12 tests truly finalized? a. Scores for the Grade 9-12 ELPA Summative are not final until scoring has been completed using information carried per Honoring Student Proficiency on the HS ELPA Summative. You can find the dates for this scoring completion in Table 24 in the Test Administration Manual. 4.