- Child Program
- Adult Program
- At-Home Program
Take the Quiz
Find a Center
- Personalized Plans
- International Families
- Learning Disorders
- Processing Disorders
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Behavioral Issues
- Struggling Kids
- Testimonials
- The Science Behind Brain Balance
- How It Works

End Homework Anxiety: Stress-Busting Techniques for Your Child
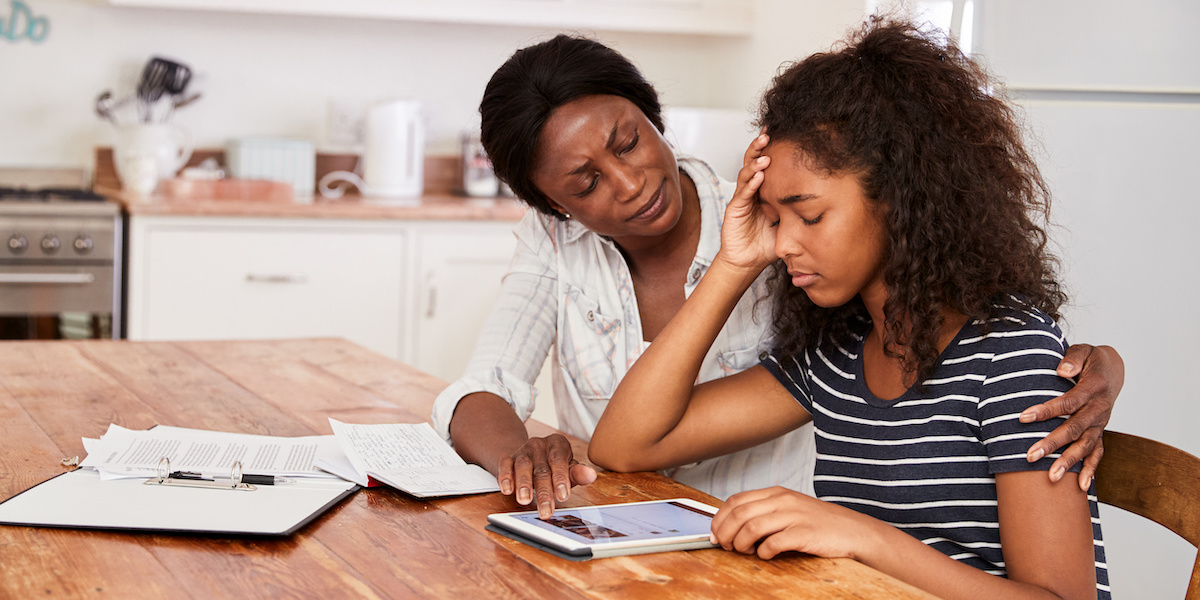

Sometimes kids dread homework because they'd rather be outside playing when they're not at school. But, sometimes a child's resistance to homework is more intense than a typical desire to be having fun, and it can be actually be labeled as homework anxiety: a legitimate condition suffered by some students who feel intense feelings of fear and dread when it comes to doing homework. Read on to learn about what homework anxiety is and whether your child may be suffering from it.
What is Homework Anxiety?
Homework anxiety is a condition in which students stress about and fear homework, often causing them to put homework off until later . It is a self-exacerbating condition because the longer the student puts off the homework, the more anxiety they feel about it, and the more pressure they experience to finish the work with less time. Homework anxiety can cripple some kids who are perfectly capable of doing the work, causing unfinished assignments and grades that slip.
What Causes Homework Anxiety?
There are many causes of homework anxiety, and there can be multiple factors spurring feelings of fear and stress. Some common causes of homework anxiety include:
- Other anxiety issues: Students who tend to suffer anxiety and worry, in general, can begin to associate anxiety with their homework, as well.
- Fear of testing: Often, homework is associated with upcoming tests and quizzes, which affect grades. Students can feel pressure related to being "graded" and avoid homework since it feels weighty and important.
- General school struggle: When students are struggling in school or with grades, they may feel a sense of anxiety about learning and school in general.
- Lack of support: Without a parent, sibling, tutor, or other help at home, students may feel that they won't have the necessary support to complete an assignment.
- Perfectionism: Students who want to perform perfectly in school may get anxious about completing a homework assignment perfectly and, in turn, procrastinate.
Basic Tips for Helping with Homework Anxiety
To help your child with homework anxiety, there are a few basic tips to try. Set time limits for homework, so that students know there is a certain time of the day when they must start and finish assignments. This helps them avoid putting off homework until it feels too rushed and pressured. Make sure your student has support available when doing their work, so they know they'll be able to ask for help if needed. Teaching your child general tips to deal with anxiety can also help, like deep breathing, getting out to take a short walk, or quieting racing thoughts in their mind to help them focus.
How can the Brain Balance Program Help with Homework Anxiety?
Extensive scientific research demonstrates that the brain is malleable, allowing for brain connectivity change and development and creating an opportunity for improvement at any age. Brain Balance has applied this research to develop a program that focuses on building brain connectivity and improving the foundation of development, rather than masking or coping with symptoms.
If you have a child or a teenager who struggles with homework anxiety, an assessment can help to identify key areas for improvement and create an action plan for you and your child. To get started, take our quick, free online assessment by clicking the link below.
Get started with a plan for your child today.
Related posts, what is dyslexia.
By Dr. Rebecca Jackson
Brain-Healthy Chicken Pot Pie
Gluten-Free, Dairy-Free, Brain-Healthy Chicken Pot Pie Recipe
What is ADHD?
Call us at 800.877.5500
Webinar Sign Up
Call 800-877-5500
Home › Study Tips › Tackling Homework Anxiety: Your Guide to a Calmer Study Life
Tackling Homework Anxiety: Your Guide to a Calmer Study Life
- Published April 3, 2024

Table of Contents
Navigating schoolwork can sometimes feel like you’re trying to sail through a storm. With assignments, projects, and revision piling up, it’s no surprise that many of us end up feeling a tad overwhelmed. This isn’t just about the usual stress of meeting deadlines; it’s about that extra layer of worry that can throw us off balance – something you might have heard referred to as homework anxiety. But fear not! Understanding what it is and learning some clever ways to manage it can really make a difference in how we handle our school workload.
So, What Exactly is Homework Anxiety?
Imagine your homework as a giant wave coming right at you. Homework anxiety is the feeling you get right before it crashes over you – a mix of worry, stress, and fear that can really shake you up emotionally and physically. It might come from the sheer volume of work, a fear of not doing well, putting too much pressure on yourself to be perfect, not quite getting the hang of the material, or just feeling swamped with managing your time. Symptoms can range from simply putting things off to feeling physically unwell or struggling to focus.
Spotting the Signs
Knowing the signs of homework anxiety can help you notice early and do something about it. These signs can include:
- Feeling constantly worried or filled with dread about homework.
- Physical issues like headaches or feeling run down.
- Finding it hard to concentrate or finish your homework.
- Avoiding your homework or finding any reason to do something else.
- Getting easily frustrated or feeling stuck.
How to Wave Goodbye to Homework Anxiety
1. Get Your Ducks in a Row: Keeping your work organised can help ease that feeling of being overwhelmed. Break your tasks down into smaller bits and give yourself clear deadlines.
2. Stick to a Study Schedule: Finding a routine that works for you and sticking to it can help keep the anxiety at bay. Work out when and where you study best and make it a habit.
3. Don’t Be Shy, Ask for Help: If you’re struggling with something, asking your teachers for a bit of clarity can go a long way in calming those nerves.
4. Pick Your Battles: Work out which tasks need your immediate attention and which ones can wait. Starting with the most urgent ones can make everything else feel more manageable.
5. Take a Deep Breath: Or several. Mixing in relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or a bit of exercise can help clear your head and improve your focus.
6. Balance is Key: Don’t forget to mix in things you enjoy alongside your study. Regular breaks and fun activities can be the perfect antidote to study stress.
7. Give Yourself a Pep-Talk: Swap out those nagging negative thoughts with some positivity! Reminding yourself of what you’ve already achieved can give you a nice confidence boost.
8. Lean on Your Squad: Talking things through with family, friends, or even teachers can give you a fresh perspective and some much-needed support. And sometimes, it might be worth chatting with a professional to find new ways to tackle your anxiety.
Final Notes:
Dealing with homework anxiety is definitely a challenge, but it’s one you can overcome with the right approach and support. Keeping an eye out for the warning signs and adopting some of these strategies can help you face your schoolwork with a bit more confidence and a lot less stress. Remember, it’s all about finding that sweet spot between doing your best and taking care of yourself. Here’s to smoother sailing ahead!
Related Content
It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Study shedding new light on Earth's global carbon cycle could help assess liveability of other planets
2 hours ago

Team is first ever to measure qubits with ultrasensitive thermal detectors, evading Heisenberg uncertainty principle

A microbial plastic factory for high-quality green plastic
11 hours ago

Can the bias in algorithms help us see our own?
13 hours ago

Humans have converted at least 250,000 acres of estuaries to cities and farms in last 35 years, study finds
14 hours ago

Mysterious bones may have belonged to gigantic ichthyosaurs

Hurricane risk perception drops after storms hit, study shows

Peter Higgs, physicist who proposed the existence of the 'God particle,' dies at 94

Scientists help link climate change to Madagascar's megadrought
16 hours ago
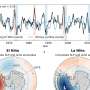
Heat from El Niño can warm oceans off West Antarctica—and melt floating ice shelves from below
17 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Motivating high school physics students with popcorn physics.
Apr 3, 2024
How is Physics taught without Calculus?
Mar 29, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Mar 24, 2024
The changing physics curriculum in 1961
Suggestions for using math puzzles to stimulate my math students.
Mar 21, 2024
The New California Math Framework: Another Step Backwards?
Mar 14, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
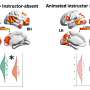
Research reveals significant effects of onscreen instructors during video classes in aiding student learning
Mar 25, 2024

Prestigious journals make it hard for scientists who don't speak English to get published, study finds
Mar 23, 2024

Using Twitter/X to promote research findings found to have little impact on number of citations
Mar 22, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
The Truth About Homework Stress: What Parents & Students Need to Know
- Fact Checked
Written by:
published on:
- December 21, 2023
Updated on:
- January 9, 2024
Looking for a therapist?
Homework is generally given out to ensure that students take time to review and remember the days lessons. It can help improve on a student’s general performance and enhance traits like self-discipline and independent problem solving.
Parents are able to see what their children are doing in school, while also helping teachers determine how well the lesson material is being learned. Homework is quite beneficial when used the right way and can improve student performance.
This well intentioned practice can turn sour if it’s not handled the right way. Studies show that if a student is inundated with too much homework, not only do they get lower scores, but they are more likely to get stressed.
The age at which homework stress is affecting students is getting lower, some even as low as kindergarten. Makes you wonder what could a five year old possibly need to review as homework?
One of the speculated reasons for this stress is that the complexity of what a student is expected to learn is increasing, while the breaks for working out excess energy are reduced. Students are getting significantly more homework than recommended by the education leaders, some even nearly three times more.
To make matters worse, teachers may give homework that is both time consuming and will keep students busy while being totally non-productive.
Remedial work like telling students to copy notes word for word from their text books will do nothing to improve their grades or help them progress. It just adds unnecessary stress.
Explore emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in affordable online therapy. With 30,000+ licensed therapists and plans starting from only $65 per week, BetterHelp makes self-care accessible to all. Complete the questionnaire to match with the right therapist.
Effects of homework stress at home
Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.
Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students.
Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and time spent doing homework, a child can get headaches, sleep deprivation or even ulcers.
And homework stress doesn’t just impact grade schoolers. College students are also affected, and the stress is affecting their academic performance.
Even the parent’s confidence in their abilities to help their children with homework suffers due increasing stress levels in the household.
Fights and conflict over homework are more likely in families where parents do not have at least a college degree. When the child needs assistance, they have to turn to their older siblings who might already be bombarded with their own homework.
Parents who have a college degree feel more confident in approaching the school and discussing the appropriate amount of school work.
“It seems that homework being assigned discriminates against parents who don’t have college degree, parents who have English as their second language and against parents who are poor.” Said Stephanie Donaldson Pressman, the contributing editor of the study and clinical director of the New England Center for Pediatric Psychology.
With all the stress associated with homework, it’s not surprising that some parents have opted not to let their children do homework. Parents that have instituted a no-homework policy have stated that it has taken a lot of the stress out of their evenings.
The recommended amount homework
The standard endorsed by the National Education Association is called the “10 minute rule”; 10 minutes per grade level per night. This recommendation was made after a number of studies were done on the effects of too much homework on families.
The 10 minute rule basically means 10 minutes of homework in the first grade, 20 minute for the second grade all the way up to 120 minutes for senior year in high school. Note that no homework is endorsed in classes under the first grade.
Parents reported first graders were spending around half an hour on homework each night, and kindergarteners spent 25 minutes a night on assignments according to a study carried out by Brown University.
Making a five year old sit still for half an hour is very difficult as they are at the age where they just want to move around and play.
A child who is exposed to 4-5 hours of homework after school is less likely to find the time to go out and play with their friends, which leads to accumulation of stress energy in the body.
Their social life also suffers because between the time spent at school and doing homework, a child will hardly have the time to pursue hobbies. They may also develop a negative attitude towards learning.
The research highlighted that 56% of students consider homework a primary source of stress.
And if you’re curious how the U.S stacks up against other countries in regards to how much time children spend on homework, it’s pretty high on the list .
Signs to look out for on a student that has homework stress
Since not every student is affected by homework stress in the same way, it’s important to be aware of some of the signs your child might be mentally drained from too much homework.
Here are some common signs of homework stress:
- Sleep disturbances
- Frequent stomachaches and headaches
- Decreased appetite or changed eating habits
- New or recurring fears
- Not able to relax
- Regressing to behavior they had when younger
- Bursts of anger crying or whining
- Becoming withdrawn while others may become clingy
- Drastic changes in academic performance
- Having trouble concentrating or completing homework
- Constantly complains about their ability to do homework
If you’re a parent and notice any of these signs in your child, step in to find out what’s going on and if homework is the source of their stress.
If you’re a student, pay attention if you start experiencing any of these symptoms as a result of your homework load. Don’t be afraid to ask your teacher or parents for help if the stress of homework becomes too much for you.
What parents do wrong when it comes to homework stress
Most parents push their children to do more and be more, without considering the damage being done by this kind of pressure.
Some think that homework brought home is always something the children can deal with on their own. If the child cannot handle their homework then these parents get angry and make the child feel stupid.
This may lead to more arguing and increased dislike of homework in the household. Ultimately the child develops an even worse attitude towards homework.
Another common mistake parents make is never questioning the amount of homework their children get, or how much time they spend on it. It’s easy to just assume whatever the teacher assigned is adequate, but as we mentioned earlier, that’s not always the case.
Be proactive and involved with your child’s homework. If you notice they’re spending hours every night on homework, ask them about it. Just because they don’t complain doesn’t mean there isn’t a problem.
How can parents help?
- While every parent wants their child to become successful and achieve the very best, it’s important to pull back on the mounting pressure and remember that they’re still just kids. They need time out to release their stress and connect with other children.
- Many children may be afraid to admit that they’re overwhelmed by homework because they might be misconstrued as failures. The best thing a parent can do is make home a safe place for children to express themselves freely. You can do this by lending a listening ear and not judging your kids.
- Parents can also take the initiative to let the school know that they’re unhappy with the amount of homework being given. Even if you don’t feel comfortable complaining, you can approach the school through the parent-teacher association available and request your representative to plead your case.
- It may not be all the subjects that are causing your child to get stressed. Parents should find out if there is a specific subject of homework that is causing stress. You could also consult with other parents to see what they can do to fix the situation. It may be the amount or the content that causes stress, so the first step is identifying the problem.
- Work with your child to create a schedule for getting homework done on time. You can set a specific period of time for homework, and schedule time for other activities too. Strike a balance between work and play.
- Understanding that your child is stressed about homework doesn’t mean you have to allow them not to try. Let them sit down and work on it as much as they’re able to, and recruit help from the older siblings or a neighbor if possible.
- Check out these resources to help your child with their homework .
The main idea here is to not abolish homework completely, but to review the amount and quality of homework being given out. Stress, depression and lower grades are the last things parents want for their children.
The schools and parents need to work together to find a solution to this obvious problem.
Take the stress test!
Join the Find-a-therapist community and get access to our free stress assessment!
Additional Resources
Online therapy.
Discover a path to emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in convenient and affordable online therapy. With a vast network of 30,000+ licensed therapists, they’re committed to helping you find the one to support your needs. Take advantage of their Free Online Assessment, and connect with a therapist who truly understands you. Begin your journey today.
Relationship Counceling
Whether you’re facing communication challenges, trust issues, or simply seeking to strengthen your connection, ReGain’ s experienced therapists are here to guide you and your partner toward a healthier, happier connection from the comfort of your own space. Get started.
Therapist Directory
Discover the perfect therapist who aligns with your goals and preferences, allowing you to take charge of your mental health. Whether you’re searching for a specialist based on your unique needs, experience level, insurance coverage, budget, or location, our user-friendly platform has you covered. Search here.
About the author
You might also be interested in
Therapist vs. Psychologist: Recognizing the Differences
Top Magnesium Side Effects to Look Out For
Does Green Tea Relieve Stress?
Disclaimers
Online Therapy, Your Way
Follow us on social media
We may receive a commission if you click on and become a paying customer of a therapy service that we mention.
The information contained in Find A Therapist is general in nature and is not medical advice. Please seek immediate in-person help if you are in a crisis situation.
Therapy Categories
More information
If you are in a life threatening situation – don’t use this site. Call +1 (800) 273-8255 or check these resources to get immediate help.
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., how to manage homework stress.
Feeling overwhelmed by your nightly homework grind? You’re not alone. Our Student Life in America survey results show that teens spend a third of their study time feeling worried, stressed, or stuck. If you’re spending close to four hours a night on your homework (the national average), that’s over an hour spent spent feeling panicky and still not getting your work done. Homework anxiety can become a self-fulfilling prophecy: If you’re already convinced that calculus is unconquerable, that anxiety can actually block your ability to learn the material.

Whether your anxiety is related to handling your workload (we know you’re getting more homework than ever!), mastering a particular subject like statistics, or getting great grades for your college application, stress doesn’t have to go hand-in-hand with studying .
In fact, a study by Stanford University School of Medicine and published in The Journal of Neuroscience shows that a student’s fear of math (and, yes, this fear is completely real and can be detectable in scans of the brain) can be eased by a one-on-one math tutoring program. At The Princeton Review this wasn’t news to us! Our online tutors are on-call 24/7 for students working on everything from AP Chemistry to Pre-Calc. Here’s a roundup of what our students have to say about managing homework stress by working one-one-one with our expert tutors .
1. Work the Best Way for YOU
From the way you decorate your room to the way you like to study, you have a style all your own:
"I cannot thank Christopher enough! I felt so anxious and stressed trying to work on my personal statement, and he made every effort to help me realize my strengths and focus on writing in a way that honored my personality. I wanted to give up, but he was patient with me and it made the difference."
"[My] tutor was 1000000000000% great . . . He made me feel important and fixed all of my mistakes and adapted to my learning style . . . I have so much confidence for my midterms that I was so stressed out about."
"I liked how the tutor asked me how was I starting the problem and allowed me to share what I was doing and what I had. The tutor was able to guide me from there and break down the steps and I got the answer all on my own and the tutor double checked it... saved me from tears and stress."

2. Study Smarter, Not Harder
If you’ve read the chapter in your history textbook twice and aren’t retaining the material, don’t assume the third time will be the charm. Our tutors will help you break the pattern, and learn ways to study more efficiently:
"[My] tutor has given me an easier, less stressful way of seeing math problems. It is like my eyes have opened up."
"I was so lost in this part of math but within minutes the tutor had me at ease and I get it now. I wasn't even with her maybe 30 minutes or so, and she helped me figure out what I have been stressing over for the past almost two days."
"I can not stress how helpful it is to have a live tutor available. Math was never and still isn't my favorite subject, but I know I need to take it. Being able to talk to someone and have them walk you through the steps on how to solve a problem is a huge weight lifted off of my shoulder."
3. Get Help in a Pinch
Because sometimes you need a hand RIGHT NOW:
"I was lost and stressed because I have a test tomorrow and did not understand the problems. I fully get it now!"
"My tutor was great. I was freaking out and stressed out about the entire assignment, but she really helped me to pull it together. I am excited to turn my paper in tomorrow."
"This was so helpful to have a live person to validate my understanding of the formulas I need to use before actually submitting my homework and getting it incorrect. My stress level reduced greatly with a project deadline due date."
4. Benefit from a Calming Presence
From PhDs and Ivy Leaguers to doctors and teachers, our tutors are experts in their fields, and they know how to keep your anxiety at bay:
"I really like that the tutors are real people and some of them help lighten the stress by making jokes or having quirky/witty things to say. That helps when you think you're messing up! Gives you a reprieve from your brain jumbling everything together!"
"He seemed understanding and empathetic to my situation. That means a lot to a new student who is under stress."
"She was very thorough in explaining her suggestions as well as asking questions and leaving the changes up to me, which I really appreciated. She was very encouraging and motivating which helped with keeping me positive about my paper and knowing that I am not alone in my struggles. She definitely eased my worries and stress. She was wonderful!"
5. Practice Makes Perfect
The Stanford study shows that repeated exposure to math problems through one-on-one tutoring helped students relieve their math anxiety (the authors’ analogy was how a fear of spiders can be treated with repeated exposure to spiders in a safe environment). Find a tutor you love, and come back to keep practicing:
"Love this site once again. It’s so helpful and this is the first time in years when I don’t stress about my frustration with HW because I know this site will always be here to help me."
"I've been using this service since I was in seventh grade and now I am a Freshman in High School. School has just started and I am already using this site again! :) This site is so dependable. I love it so much and it’s a lot easier than having an actual teacher sitting there hovering over you, waiting for you to finish the problem."
"I can always rely on this site to help me when I'm confused, and it always makes me feel more confident in the work I'm doing in school."
Stuck on homework?
Try an online tutoring session with one of our experts, and get homework help in 40+ subjects.
Try a Free Session
- Tutoring
- College
- Applying to College

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
Free MCAT Practice Test
Thank you! Look for the MCAT Review Guide in your inbox.
I already know my score.
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework
A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance and even alienation from society. More than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive, according to the study.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
• Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Check out our free educational resource library at MTT Education Station!
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

Maryland Teacher Tutors
Private Tutoring From Certified Teachers
Let’s Talk Homework Anxiety
December 6, 2021 by Natalie Mangrum

What is homework anxiety ?
Homework anxiety is situational anxiety focused on homework time. It’s really just anxiety about homework, not an actual anxiety diagnosis.
If your child is showing frustration and worry that centers around homework, then this applies to them. Note: if your child is showing signs of sleep trouble, headaches, bellyaches, social reclusiveness, etc., then it is a good idea to talk to a doctor about an actual anxiety diagnosis.
Natalie Mangrum, CEO of Maryland Teacher Tutors , discusses homework anxiety with psychotherapist Kristi from Baltimore Family Therapy
What are the signs to look for?
In younger students, this can look like defiance (tantrums, tears, refusal), and in older students it may be more verbalized (“I can’t do this,” “I’m not smart enough to do this”). Since competition is big among students as they get older, it can be worry about friends excelling while your child may be struggling.
Tips for managing homework anxiety
- Patience, patience, patience.
- If you are frustrated, take a break.
- Model what you want your child to do.
- Stick to a routine so your child knows what to expect and when. This routine depends on YOUR child – do they need a break after school, or should they get right to it?
- Have a homework spot.
- Use a planner.
- Make to-do lists.
- Do your “homework” (bills, e-mails, planning) at the same time so your child isn’t alone.
- If a child really needs help, have them reach out to their teacher themselves.
- Positive reinforcement is huge – don’t be afraid to introduce incentives.
- Remember to give positive feedback.
- An anxious parent begets an anxious child, so find what works for you and your child to ease the worry and create a positive environment for homework.
If your child is still struggling with homework anxiety, we can help. Contact us today .

Natalie Mangrum is the founder and CEO of Maryland Teacher Tutors. She is a reading specialist with a bachelors in elementary education and masters in education. As a parent to two young adults, and prior teacher, Natalie knows all too well the benefits of one-on-one tutoring and coaching for students . Her mission is to ensure that every aspect of MTT is done in a spirit of excellence! She enjoys alleviating the concerns of parents so they can breathe easy knowing their children are in good hands!
Join the newsletter


How to Reduce Homework Stress
If homework is a source of frustration and stress in your home, it doesn’t have to be that way! Read on to learn effective strategies to reduce your child’s homework stress.

Author Katie Wickliff
Published March 2024

If homework is a source of frustration and stress in your home, it doesn’t have to be that way! Read on to learn effective strategies to reduce your child’s homework stress.
- Key takeaways
- Homework stress can be a significant problem for children and their families
- An appropriate amount of quality homework can be beneficial for students
- Parents can help reduce homework stress in several key ways
Table of contents
- Homework stress effects
- How to reduce homework stress
As a parent who has felt the frustration of watching my child be reduced to tears because of her homework each night, I’ve often wondered: do these math worksheets and reading trackers really make a difference to a child’s academic success? Or does homework cause stress without having a positive impact on learning?
If your child experiences a significant amount of homework stress, you may feel at a loss to help. However, there are several things you can do at home to minimize the negative effects of this stress on your child–and you! We’ve put together a list of research-based practices that can help your child better handle their homework load.
The Effects of Homework Stress on Students
Does homework cause stress? Short answer: Yes. It’s been well documented that too much homework can cause stress and anxiety for students–and their parents. However, do the benefits of homework outweigh the costs? Is homework “worth” the frustration and exhaustion that our children experience?
Findings on the benefits of homework at the elementary school level are mixed, with studies showing that homework appears to have more positive effects under certain conditions for certain groups of students.
After examining decades of studies on the relationship between homework and academic achievement, leading homework researcher Harris M. Cooper has proposed the “10-minute rule,” suggesting that homework be limited to 10 minutes per grade level. For example, children in 3rd grade should do no more than 30 minutes of homework daily, while a 1st grader should do no more than 10 minutes of homework. The National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association both endorse this guideline as a general rule of thumb.
Because of these research findings, Doodle believes that an appropriate amount of quality homework can help students feel more positive about learning and can provide parents with a critical connection to their child’s school experience . But to keep learning positive, we need to reduce the amount of stress both students and parents feel about homework.
1. Routine, Routine, Routine
Creating an after-school routine and sticking to it helps children feel organized, but with sports, tutoring, or music lessons, many children have varying weekday schedules. As a former classroom teacher and private tutor, I suggest that families post a weekly schedule somewhere visible and communicate that schedule with their child.
At our house, we have a dry-erase calendar posted on the wall. Every Sunday evening, I write both of my children’s schedules for the following week–including homework time. We go through the calendar together, and they reference it often throughout the week. I can tell both my son and daughter feel better when they know when they’ll get their homework done.
2. Create a Homework Space
Ideally, your child should have a dedicated homework space. It doesn’t matter if that space is a desk, a dining room table, or a kitchen countertop. What does matter is that the homework area is tidy, because an unorganized homework area is very distracting.
3. Start Homework Early
Encourage your child to start their homework as early as possible. Help them review their assignments, make a plan for what needs to be completed, and then dive in. Naturally, children are more tired later in the evening which can lead to more stress.
4. Encourage Breaks
If you can see your child becoming frustrated or overwhelmed by their homework, encourage them to take a breather and come back to it later. As a teacher and tutor, I called this a “brain break” and believe these breaks are essential. Taking a short break will give your child a chance to step away from a frustrating problem or assignment.
5. It’s Okay to Ask for Help
Sometimes, homework can become just too stressful and overwhelming. In that case, it really is okay to stop. Children can learn to advocate for themselves by making a list of questions for their teacher and asking for help the next day. Depending on their age, you might need to help role-play how to approach their teacher with their frustrations.
Additionally, parents should never feel afraid to contact their child’s teacher to talk about homework issues. When I was teaching elementary school, I always wanted parents to feel comfortable reaching out about any issues, including homework stress.
6. Get Plenty of Rest
Sleep is critical to a child’s overall wellbeing , which includes their academic performance. Tired kids can’t concentrate as well, which can lead to feeling more overwhelmed about homework assignments. According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, kids aged 6-12 should get at least 9 hours of sleep each night.
7. Consider a Homework Group
Organizing a homework group a few times a week is another way for your child to view homework more positively. Working as a group encourages collaboration, while discussions can solidify concepts learned in class.
8. Encourage Positivity
No matter what your school experience was like, it’s important to model a growth mindset for your child. A growth mindset is the belief that your abilities can develop and improve over time. So if your child says something like “ I can’t do this! ” first acknowledge their frustration. Then, encourage them to say, “ I may not understand this yet, but I will figure it out. ” Speaking positively about tough experiences takes practice, but it will go a long way in reducing homework stress for your child.
9. Develop Skills With Fun Games
Feeling stressed about homework is no fun. Completing worksheets and memorizing facts is necessary, but playing games is a great way to inject some excitement into learning. Doodle’s interactive math app is filled with interactive exercises, engaging math games, and unique rewards that help kids develop their skills while having fun.
Lower Math Anxiety with DoodleMath
Does your child struggle with math anxiety? DoodleMath is an award-winning math app f illed with fun, interactive math questions aligned to state standards. Doodle creates a unique work program tailored to each child’s skill level to boost confidence and reduce math anxiety. Try it free today!

FAQs About Homework Stress
Many studies have shown that homework and stress often go hand-in-hand, often because many children feel pressure to perform perfectly or they have trouble managing their emotions–they get overwhelmed or flooded easily.
You can help your child reduce homework stress in several ways, including by establishing a routine, creating a homework space, encouraging breaks, and making homework fun with online games or math apps.

Lesson credits

Katie Wickliff
Katie holds a master’s degree in Education from the University of Colorado and a bachelor’s degree in both Journalism and English from The University of Iowa. She has over 15 years of education experience as a K-12 classroom teacher and Orton-Gillingham certified tutor. Most importantly, Katie is the mother of two elementary students, ages 8 and 11. She is passionate about math education and firmly believes that the right tools and support will help every student reach their full potential.

Parents, sign up for a DoodleMath subscription and see your child become a math wizard!
What we offer
Quick links
All rights reserved.

Are you a parent, teacher or student?
Get started for free!
Maths information pack
We ask for your contact info so we can send our info pack directly to your inbox for your convenience, exam prep information pack, case studies information pack.
Book a chat with our team

I’m new to Doodle

My school is already using Doodle

Information pack
We ask for your contact info so that our education consultants can get in touch with you and let you know a bit more about doodle., student login, which programme would you like to use.
DoodleMaths
DoodleTables
DoodleEnglish
DoodleSpell
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here:
18 Anxiety Worksheets for Adults, Teens & More

And yet, it can also be energizing, focusing our attention and preparing us for action — an evolutionary response to the unexpected, difficult, or downright dangerous (Workman & Reader, 2015).
It is not so much what happens but how we respond that matters the most (Joseph, 2013).
Therapists, counselors, and coaches can help by working with clients to change how they react to anxiety-inducing situations.
In this article, we introduce a collection of free worksheets for use by mental health professionals with their clients or as self-help activities.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF) for free . These science-based exercises will equip you and your clients with tools to better manage stress and find a healthier balance in your life.
This Article Contains
5 best anxiety worksheets, 4 anxiety worksheets for teens, 3 social anxiety worksheets, 3 anxiety activities for adults, cbt worksheets for anxiety, positivepsychology.com resources, a take-home message.
We can learn to break free from anxiety. With the right approaches, the same situations can have different outcomes (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
The following five worksheets encourage clients to recognize that they are not alone in their experiences and can, indeed, learn how to cope with anxiety.
The activities work on their own or can be combined. They support clients by helping them identify situations that cause anxiety, using mindfulness and meditation to restore a balanced perspective, and recognizing that someone should not be defined by the extreme emotions they are experiencing (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016; Southwick & Charney, 2018):
1. Anxiety Hierarchy
Intense fears, phobias, and stressful situations can be highly anxiety provoking. It is helpful to establish a list of challenging situations that result in extreme upset or negative emotions for clients (American Psychological Association, 2016).
Use the Anxiety Hierarchy exercise to list situations that lead to anxiety and rate them on a scale from 1 (mild discomfort) to 10 (extreme emotions such as panic).
Once these anxiety-inducing situations are listed and sorted in order, the practitioner can use graded exposure practices as part of systematic desensitization.
2. Breath Awareness While Waiting
Waiting for an event can leave us excited, concerned, nervous, or anxious. We may notice changes to our physiology (increased heart rate, sweating, and faster breathing), cognition (erratic thinking, poor decision-making, and a failing memory), and emotions (fear, upset, and panic ; Peterson, 2018).
Work with the client to identify times they are waiting during the week — for example, waiting for the bus, at the school gates, at an appointment — and how they expect to feel.
Then use this breath awareness practice for mindful breathing: slowly breathing in through the nose, holding, and slowly breathing out through the mouth. As unhelpful thoughts enter the mind, direct attention back to breathing.
3. Creating a Mindfulness Anxiety Plan
Our behavior often follows patterns, and so does our anxiety. It is possible to anticipate when anxiety might show up, especially when we become more in tune with our bodies and the events around us (Peterson, 2018).
By creating a mindfulness anxiety plan , we can be ready with a list of actions to perform when we begin to recognize our anxiety taking shape and in advance of situations that can be difficult. These actions should aim to improve our wellbeing and leave us less anxious throughout the day
For example, “If my anxiety is getting away from me, I will call my best friend.” Or “Every day, I will go outside for a walk at lunchtime and try to be more mindful.”
4. Who Am I Beyond My Anxiety?
We are not our emotions, but when fearful or anxious, we spend a great deal of time and energy focusing on what is wrong with us, forgetting our strengths (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
In this exercise , the client mindful reflects on the following prompts (among others):
I am someone who … I really like … My most important relationship is … I feel my best when …
Reading through the answers helps remind us that anxiety does not define who we are.
5. Funeral Meditation
Often, we stop ourselves from taking on or embracing a challenge for fear of failure or experiencing anxiety.
Despite its foreboding name, the Funeral Meditation is used within Acceptance and Commitment Therapy to help free ourselves from the grip of anxiety (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
This powerful meditation helps us reflect on what matters to us, recognizing that, at any time, we can start living in line with how we want to be remembered.
After several calming breaths, we imagine what our funeral would be like, including:
How do people look? Who would be there? What would they say? What would we like people to say about us?
Recognizing our values can help us eliminate anxiety and begin living the way we want.

The following worksheets can also be adapted for adult populations, and mental health practitioners will find them valuable when working with adolescents coping with anxiety.
1. Best and Worst
Children and teens can benefit from stepping back from anxiety-inducing situations to reflect upon how, despite being scary, they can also be exciting.
For example, joining a new class, school, or social group can bring with it feelings of anxiety. When also recognized as exciting, it can be energizing, leading to positive emotions such as hope, curiosity, and gratitude.
Work with your teen client to:
- Identify and capture a situation that makes them feel nervous or scared.
- Use the diagram to capture what is exciting in the left-hand circle and what is scary about the situation in the right-hand circle.
- Write down aspects of the situation that are both scary and exciting in the intersection between the two circles.
Identifying how something fills us with fear while providing energy can help us have a more balanced view regarding how to approach what is ahead.
2. FLARE for Anxiety and Fear
This helpful worksheet helps teach acceptance of difficult feelings (rather than hiding from or rejecting them) through self-acceptance and self-compassion (Khazan, 2019).
The FLARE acronym directs the client to:
- Feel each sensation. Become aware of their heart rate, breath, and body temperature.
- Label the sensations. Do they feel worried, fearful, or anxious?
- Allow the experience to remain as it is. They can say to themselves, “It is OK to feel this way.”
- Respond by refocusing on breathing, taking each breath slowly and making the out-breath longer than the in-breath.
- Expand awareness of their environment and reflect on what they are grateful for that day.
By focusing on positive emotions, the approach builds toward a spiral of positive feelings (Fredrickson, 2010).
3. Radio Doom and Gloom
Teenagers are vulnerable to focusing on the worst events, situations, and outcomes. As a result, it can almost seem like an endless radio program playing in the background, broadcasting negative stories and songs all day long.
While it’s not easy to turn down the volume on the radio (or turn it off completely), we can attend to it less. By learning to treat such negative thinking as background noise and focusing more on current activities, its impact and ability to heighten anxiety are reduced.
4. When I’m Scared
Children and adolescents (and even adults) feel scared sometimes. And that’s OK. It’s a perfectly normal fight-or-flight response to a perceived — or actual — uncomfortable or dangerous situation.
Talking to an adult can help.
When I’m Scared can be used with individual youths or in a group setting.
They are asked to write down what makes them frightened, how it affects their thinking, how it feels physically, and one thing might be that makes them feel better.

Download 3 Free Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to manage stress better and find a healthier balance in their life.
Download 3 Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Social anxiety leads to persistent fear and the avoidance of social situations because of concerns about being evaluated by others (Schneier & Goldmark, 2015).
Therapy and the use of interventions enable clients to increase their social engagement and form deep, meaningful relationships (Schneier & Goldmark, 2015).
The following worksheets are valuable for mental health professionals helping clients identify what triggers their anxious thinking and manage them through visualization and mindfulness.
1. A Mountain of Worries
Our worries can mount up. Stresses, concerns, upsets, and things going wrong may seem never-ending, with even the most minor problems blown out of proportion, leaving our anxiety out of control.
This exercise captures situations that bother us and is particularly helpful for social anxiety, where we can begin to identify and reflect on unhelpful thought patterns and learn to expect and plan for how to handle them.
2. Event visualization worksheet
Visualization can feel as real to the mind as experiencing a situation first-hand — especially a social one — and offers a safe and controlled environment to explore and experiment with existing and future challenges (Clough & Strycharczyk, 2015).
Visualizing an event, especially one we are worrying about, can be a powerful and helpful way of reducing concern and anxiety and gaining confidence without the risk of failure or being overwhelmed.
Use the worksheet to:
- Identify an event likely to cause anxiety.
- Visualize the event in as much detail as possible using all the senses.
- Imagine the people and the situation.
- Reflect on how being successful might feel.
Clients can repeat the visualization exercise several times until they feel comfortable and less anxious.
3. The Documentary of You
Anxiety can arise from any environment and is particularly common in social situations (Schneier & Goldmark, 2015).
Mindfulness can help us think about ourselves and our situations with more compassion and forgiveness and less judgment (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
In this exercise , the client imagines their life playing out as a movie on a screen. They capture on paper, nonjudgmentally, situations that leave them feeling anxious.
Following a series of grounding breaths, the client considers each one mindfully without becoming too involved.
Finally, they reflect on how reading the story now makes them feel. What is their degree of anxiety?

Changing your relationship with it can help us take charge of our lives (Forsyth & Eifert, 2016).
Try the following three activities to create coping strategies, identify what we can control while learning to accept everything else, and become more comfortable with discomfort.
1. Anxiety Strategy Cards
Preparation is a crucial part of managing anxiety. This sheet contains a list of cards to help clients develop strategies for events and situations where they feel out of control and stressed, with their anxiety building.
Each card offers a valuable reminder of a powerful technique that will help them restore their physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral balance.
For example:
When I feel anxious, I could try … controlled breathing. When I feel anxious, I could try … visualization. When I feel anxious, I could try … a grounding technique.
Use them with psychoeducation and technique training to build confidence in the client’s ability to handle and overcome tough times.
2. Control–Influence–Accept Model
We can’t control every situation, so it’s helpful to recognize those that can be influenced by our behavior and those that cannot.
The Control–Influence–Accept Model can stop individuals from feeling overwhelmed and experiencing feelings of hopelessness, frustration, and anxiety when they experience a loss of control or indecision (Thompson & Thompson, 2018).
The client is encouraged to perform each of the following:
- Identify a potentially tricky situation.
- Capture what can be controlled or influenced.
- What cannot be controlled or influenced must be accepted.
- List what needs to be accepted.
Having performed each step, the client reflects on how they now feel about the situation and whether they are left wishing to control or influence anything they have accepted.
3. Interoceptive Exposure
Anxiety has a strong physical element that we can use to increase awareness of panic-related physiological symptoms .
Interoceptive exposure is built on the premise that exposure to such sensations can increase our familiarity with them and our preparedness for future anxiety-inducing situations.
The worksheet uses activities that induce physical, cognitive, and emotional discomfort to replicate the sensations of panic and anxiety.
Note: These should only be used under the guidance of a physician or health professional in a suitably safe environment.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) treats anxiety by restructuring the client’s thinking, with the therapist exploring maladaptive expectations and worries related to upcoming events (Dobson & Dozois, 2021).
1. Anxiety Record
Reflecting on and sharing what makes us anxious can leave us feeling vulnerable, but it is essential. Understanding what leaves us feeling this way allows us to prepare for situations and learn appropriate coping skills.
One of the most powerful techniques is recognizing and, if possible, replacing unhelpful thinking.
Use the simple form in the worksheet to capture the following:
What does the anxiety feel like? When does it happen? What thoughts do you experience? How realistic are these thoughts? What thoughts could you replace them with? Are they more realistic?
Capturing our anxieties is an essential part of reducing them and bringing them under control.
2. Dealing with anxiety: Reverse the Rabbit Hole
The two words “what if?” can be anxiety- inducing, sending our thoughts racing down a rabbit hole of all that could go wrong.
What if I forget the words when I’m on stage? What if my date doesn’t like me?
Reframing an experience helps us experience it differently. We can turn a negative into a positive — reverse the rabbit hole.
In this exercise , we write negative outcomes in the left-hand column and then a corresponding reversed, positive outcome on the right.
What if I nail the speech? What if my date goes really well?
3. Tackling Anxious Thoughts
Anxiety can bias our thinking by making us buy into the likelihood of something terrible happening. As a result, it can be helpful to consider the following three points:
What is the worst potential consequence of this scenario? What is the best possible consequence of this scenario? What do you feel is the most likely consequence of this scenario?
Following these questions, the client thinks about how it would feel in a year’s time if the worst actually happened.
After all, even if the worst outcome becomes a reality, it may be less catastrophic than we imagine.

17 Exercises To Reduce Stress & Burnout
Help your clients prevent burnout, handle stressors, and achieve a healthy, sustainable work-life balance with these 17 Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises [PDF].
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
We have many resources available for therapists to support clients experiencing anxiety.
More extensive versions of the following tools are available with a subscription to the Positive Psychology Toolkit© , but they are described briefly below:
- Replacing Unhelpful Thoughts with Helpful Alternatives CBT is based on the premise that emotions and behaviors result from a person’s interpretation of a situation.
This exercise invites clients to examine the “helpfulness” of a thought they are having about a current challenging situation before formulating a more helpful alternative thought:
- Step one – Describe a challenging situation.
- Step two – Identify the automatic unhelpful thought.
- Step three – Rate the helpfulness of this thought.
- Step four – Come up with a more helpful alternative thought.
- Step five – Rate the helpfulness of this alternative thought.
- Step one – Visualize yourself in a relaxing environment.
- Step two – Add detail to the visualization by exploring all your senses.
- Step three – Enjoy the scene you have created and allow yourself to spend some time taking it all in.
- Step four – Close your eyes and continue taking slow, deep breaths as you visualize the stress leaving your body in waves with each exhale.
This exercise is valuable for stress reduction by connecting the sensations of relaxation with peaceful visual imagery during times of stress.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others manage stress without spending hours on research and session prep, check out this collection of 17 validated stress management tools for practitioners. Use them to help others identify signs of burnout and create more balance in their lives.
Anxiety is a normal reaction to life events and can be beneficial in many situations, alerting us to dangers and increasing our attention and readiness for action.
It is often less about our environment or the challenges we face, but how we interpret them.
As a result, anxiety can dramatically impair our ability to function and perform in education, work, and social environments (American Psychological Association, 2016).
Its effects are widespread, impacting 30% of adults at some point in their lives and preventing them from living normally (American Psychiatric Association, 2021). They can find themselves avoiding opportunities and shying away from challenges due to intrusive thoughts or concerns.
Anxiety disorders are treatable. Therapists and counselors can help clients manage anxiety-inducing situations by changing how they view them and learning to cope with stressful conditions.
The anxiety worksheets in this article can be used independently or together as interventions for better managing anxiety. When combined with ongoing therapeutic assessment, it is possible to see how clients bring their feelings under control and return to the lives they wish to lead.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Stress & Burnout Prevention Exercises (PDF) for free .
Ed: Updated March 2023
- American Psychiatric Association. (2021). What are anxiety disorders? Retrieved March 17, 2023, from https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/anxiety-disorders/what-are-anxiety-disorders
- American Psychological Association. (2016). Beyond worry: How psychologists help with anxiety disorders . Retrieved March 13, 2023, from https://www.apa.org/topics/anxiety/disorders
- Clough, P., & Strycharczyk, D. (2015). Developing mental toughness: Coaching strategies to improve performance, resilience and wellbeing . Kogan Page.
- Dobson, K. S., & Dozois, D. J. (2021). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies . Guilford Press.
- Forsyth, J. P., & Eifert, G. H. (2016). The mindfulness & acceptance workbook for anxiety: A guide to breaking free from anxiety, phobias & worry using acceptance & commitment therapy (2nd ed.). New Harbinger Publications.
- Fredrickson, B. (2010). Positivity: Groundbreaking research reveals how to release your inner optimist and thrive . Oneworld.
- Joseph, S. (2013). What doesn’t kill us: A guide to overcoming adversity and moving forward . Piatkus.
- Khazan, I. Z. (2019). Biofeedback and mindfulness in everyday life: Practical solutions for improving your health and performance . W.W. Norton & Company.
- Khesht-Masjedi, M. F., Shokrgozar, S., Abdollahi, E., Habibi, B., Asghari, T., Ofoghi, R. S., & Pazhooman, S. (2019). The relationship between gender, age, anxiety, depression, and academic achievement among teenagers. Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care , 8 (3), 799–804.
- Peterson, T. J. (2018). The mindfulness workbook for anxiety: The 8-week solution to help you manage anxiety, worry & stress . Althea Press.
- Schneier, F., & Goldmark, J. (2015). Social anxiety disorder. In D. J. Stein & B. Vythilingum (Eds.), Anxiety disorders and gender (pp. 49–67). Springer.
- Southwick, S. M., & Charney, D. S. (2018). Resilience: The science of mastering life’s greatest challenges . Cambridge University Press.
- Thompson, S., & Thompson, N. (2018). The critically reflective practitioner . Macmillan International Higher Education.
- Workman, L., & Reader, W. (2015). Evolutionary psychology: An introduction . Cambridge University Press.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Thank you. This helps so much I would definitely recommend this article especially for anxious people like me. Very generous of you guys.
I am a mental health professional Mental Health Skill Building and some of this information is very good for my clients. Thank you.
Thank you. So many resources and ideas in one place. We are in New Zealand. It is hard to access quality support here and too many don’t.
I am DYING for the ‘What if’ download. I do this all the time.
Awesome site – thank you!!
what an amazing website, jam packed with FREE and very useful information, thank you so much!!! I am currently working with a teenager and the ‘what-if’ worksheet alone is pure gold and just the thing I was looking for right now.
How do I get the What If worksheet?
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Overcome Languishing & Flourish: A Positive Psychology Guide
Amidst the turmoil of the recent pandemic, one positive psychology construct has captured more attention than any other. As societies worldwide had to endure lockdowns [...]

7 Trauma Response Types & How to Recognize Them
Over-sharing. Over-explaining. Trauma dumping. Hyperindependence. Hypersexualization. People pleasing. Do these sound like common traits your clients have? These may not be character traits but, instead, [...]

6 Best Diaphragmatic Breathing Exercises to Reduce Anxiety
Our brain controls our breathing largely without conscious awareness. We shower, watch football, listen to music, and sleep while our respiratory system functions in the [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (48)
- Coaching & Application (57)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (24)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (45)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (28)
- Positive Communication (20)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (17)
- Positive Parenting (3)
- Positive Psychology (33)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (35)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (31)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)
3 Stress Exercises Pack

Your Life Experiences May Have Contributed to Health Anxiety
How dysfunctional core beliefs about health develop and are reinforced over time..
Updated April 9, 2024 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- What Is Anxiety?
- Find a therapist to overcome anxiety
- Significant life experiences can contribute to the development and maintenance of health anxiety over time.
- Life experiences might include experiencing trauma or adversity, such as witnessing or experiencing illness.
- Core beliefs are deeply held beliefs formed through significant events and continually reinforced.
- Health anxiety is associated with several dysfunctional beliefs about health and illness.
Core beliefs are deeply ingrained beliefs we hold about ourselves, others, the future, and the world. They develop early in life through significant experiences. Core beliefs play a powerful role in how we process information. Once they develop and are set in motion, core beliefs are continuously reinforced throughout the rest of childhood and into adulthood. This is because we selectively attend to information that confirms our beliefs and ignore or dismiss information that does not support them. Due to these processes, our core beliefs only get stronger over time.
How My Life Experiences Led to Maladaptive Beliefs
I am a therapist and treat health anxiety with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT). But I also have a long personal history of dealing with health anxiety myself. Thanks to CBT, I am in a much different place today. I've been grateful to be able to help my clients work through similar issues that I have dealt with myself.
That said, let’s take a peek into my own history in the hopes that it might shed some light on how significant events in our lives can shape how we see the world.
For most of my childhood, things were pretty unstable. My father was abusive with substance use disorders: alcohol and meth. One day, when I was 7, my mom and little brother picked me up from school early, and we took off, forever leaving behind my father and the home we shared with him. This marked a positive change in our lives in many ways, but it was not without its challenges. We were hurt and broke, and my mom started getting terrible migraines , which only worsened over the years. Despite countless doctor visits, tests, and medical bills, we were left without an identifiable cause or effective treatment options. When I was 16, my mom died from an overdose of her pain medication .
These experiences as a child led me to develop maladaptive beliefs at a very young age, such as:
- The world is unsafe and unpredictable
- Serious disease is everywhere and unavoidable
- The field of medicine is incapable of treating diseases
- I am weak and vulnerable to disease
- Uncertainty about health is dangerous and unacceptable
Not surprisingly, anxiety kicked in around the first or second grade. While my friends at school seemed to be concerned about "normal" things like whether they were going to be able to play outside or have ice cream, I was crying about nuclear bombs and whether my mom was gonna die in a car crash on the way home from work. In general, I felt unsafe and expected the worst most of the time.
And then, around 9 or 10, the health anxiety came for me. I began to believe that serious diseases were extremely common and that those who weren’t plagued with a debilitating illness were among the lucky few. After all, if my only remaining parent is sick, then so many others out there must be experiencing something similar.
As I moved into my teenage years, and especially after my mom died, I began to assume that if someone is sick, then it is likely to be very serious and eventually terminal. Besides migraines, my mom had everything else going for her in the health department: she was young, took care of herself, had good genes , and followed all of the doctor’s orders. Yet, she still died. So, I concluded that if one is diagnosed with anything, they are as good as dead.
Core Beliefs Are Reinforced for Years
Once these health-related beliefs were solidified, then the process of reinforcement began. Essentially, I would scan my environment and selectively attend to all the pieces of “evidence” that supported my belief system.
- I paid special attention to situations when one of our relatives got sick or when I learned that a friend’s family member was sick or dying.
- I read all about various diseases in medical texts.
- I was overly focused in health class and became especially interested in the most deadly diseases we covered.
- I watched as many tragic movies and TV shows about the sick and dying as I could get my hands on.
I was so busy seeking out sickness and death that I failed to acknowledge that, aside from my mom, everyone in my life was pretty healthy and, well, alive.
Of course, these beliefs just progressively strengthened over the years. How could they not? In the world I had created for myself through all these activities, everyone was sick and dying. I remember, at one point as a teenager , thinking about how lucky I was that I had escaped sickness and death. I laugh at that now. Here I was, a young person with virtually no health issues, and I believed that my survival was some kind of miracle. It demonstrates just how biased and inaccurate my thinking had become through this whole process.

Your Homework
Your own life experiences that contributed to your health anxiety may not be as obvious or cliche as mine. But I am guessing if you did some digging, you’d find some situations or events that have significantly impacted you. Your health anxiety is likely the culmination of a variety of experiences. It can be helpful to understand what triggered the development of inaccurate beliefs. Still, it is much more important to identify what your beliefs are and how they have been (and are currently being) reinforced in your life. I'd like you to try to look at your own life through this lens and see what you find.
Consider the following questions:
- What significant events happened in your life? Did you or someone you love struggle with illness and/or die? Did you experience any adverse or traumatic events? Did it seem as though you were living in an unsafe and unpredictable world?
- How did these events shape your beliefs about health and illness? Grab my guide for a description of unhelpful core beliefs about health. Do you think any of these beliefs were influenced by the things that happened in your life?
- How were these beliefs then further reinforced/strengthened over time? Can you think of examples like those that I gave in terms of how I sought out information that supported these beliefs?
Remember, beliefs are not permanent. They can be reshaped. Doing so involves retraining or rewiring your brain to learn how to process information differently. You first learn how to identify all of the pieces of “evidence” that you think support your maladaptive belief. You then take the opportunity to reframe some of these pieces of evidence and challenge any inaccurate assumptions. Next, you want to develop a new, healthier, and more adaptive belief about health and begin to seek out evidence for that new belief.
Put some thought into this exercise. Gaining new insight can serve a positive purpose.

Brittney Chesworth, Ph.D., LCSW , is a psychotherapist with a private practice that focuses exclusively on the treatment of anxiety disorders through cognitive behavioral therapy and exposure therapy.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Use a calm voice. When kids feel anxious about homework, they might get angry, yell, or cry. Avoid matching their tone of voice. Take a deep breath and keep your voice steady and calm. Let them know you're there for them. Sometimes kids just don't want to do homework. They complain, procrastinate, or rush through the work so they can do ...
What is Homework Anxiety? Homework anxiety is a condition in which students stress about and fear homework, often causing them to put homework off until later. It is a self-exacerbating condition because the longer the student puts off the homework, the more anxiety they feel about it, and the more pressure they experience to finish the work ...
Homework anxiety is the feeling you get right before it crashes over you - a mix of worry, stress, and fear that can really shake you up emotionally and physically. It might come from the sheer volume of work, a fear of not doing well, putting too much pressure on yourself to be perfect, not quite getting the hang of the material, or just ...
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health ...
This list is hardly comprehensive. ADHD, autism spectrum disorder, social anxiety, generalized anxiety, panic disorder, depression, dysregulation, and a range of other neurodevelopmental and ...
failing to turn in homework. keeping to themselves at school rather than socializing with other kids. For kids whose school anxiety has persisted or increased in severity, physical symptoms may ...
Effects of homework stress at home. Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.. Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students. Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and ...
5. Practice Makes Perfect. The Stanford study shows that repeated exposure to math problems through one-on-one tutoring helped students relieve their math anxiety (the authors' analogy was how a fear of spiders can be treated with repeated exposure to spiders in a safe environment). Find a tutor you love, and come back to keep practicing ...
How To Avoid Homework Stress. Here are 10 tips to help your child learn how to make homework less stressful. 1. Stick to a Schedule. Help your child plan out his or her time, scheduling time for homework, chores, activities, and sleep. Keep this schedule handy so your child knows what he or she should be working on, and when.
Give extended time on tests and/or separate test-taking space to reduce performance anxiety. Allow use of word banks, cheat sheets, or fact cards for tests (for students who freeze or "go blank" during in-class tests). Set time limits for homework or reduce the amount of homework. Assure that work not completed in that time won't count ...
Homework is associated with some level of stress for most children. However, for youth with an anxiety disorder, the pressure of assignments, tests, and deadlines can provoke panic and can disable ...
Read on to learn more about homework anxiety and how you can he. Sometimes, kids don't want to do their homework. They procrastinate, protest, or rush through it so that they can move on to something more exciting. But for some kids, it runs deeper; homework makes them feel anxious and very stressed. Read on to learn more about homework ...
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance and even alienation ...
Homework anxiety is situational anxiety focused on homework time. It's really just anxiety about homework, not an actual anxiety diagnosis. If your child is showing frustration and worry that centers around homework, then this applies to them. Note: if your child is showing signs of sleep trouble, headaches, bellyaches, social reclusiveness ...
"Homework has perennially acted as a source of stress for students, so that piece of it is not new," Galloway says. "But especially in upper-middle-class communities, where the focus is on getting ahead, I think the pressure on students has been ratcheted up." Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well.
Encourage your child to start their homework as early as possible. Help them review their assignments, make a plan for what needs to be completed, and then dive in. Naturally, children are more tired later in the evening which can lead to more stress. 4. Encourage Breaks. If you can see your child becoming frustrated or overwhelmed by their ...
As with anxiety, there is a range of practical CBT homework activities that aid in treating depression. It should be noted that it is common for clients experiencing symptoms of depression to report concentration and memory deficits as reasons for not completing homework assignments (Garland & Scott, 2005).
Addressing anxiety concerns includes understanding how it affects your ability to complete assignments. In some cases, students may have a mental health concern such as an anxiety disorder, learning disorder, or ADHD. Here are a few ways to manage homework anxiety others have found helpful: * Address or acknowledge any mental health concerns.
Here, you breathe in for a count of 5, hold your breath for a count of 5, and then exhale for the duration for a count of 5. Close your eyes and repeat this entire exercise slowly till you feel like yourself again. Use this when your homework anxiety isn't allowing you to focus on what is in front of you. You can do this exercise any time you ...
CBT Worksheets for Anxiety. Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) treats anxiety by restructuring the client's thinking, with the therapist exploring maladaptive expectations and worries related to upcoming events (Dobson & Dozois, 2021).. 1. Anxiety Record. Reflecting on and sharing what makes us anxious can leave us feeling vulnerable, but it is essential.
worksheet. A safe space is a person, place, or activity that helps you feel calm, comfortable, and supported, and lets you be yourself. Your safe space is there for you no matter how you feel—happy or sad, talkative or quiet, brave or scared. A safe space is free of judgment and is full of acceptance.
Your Homework Your own life experiences that contributed to your health anxiety may not be as obvious or cliche as mine. But I am guessing if you did some digging, you'd find some situations or ...