We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]

What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]
Written by: Sara McGuire Oct 26, 2023

A marketing plan is a blueprint that outlines your strategies to attract and convert your ideal customers as a part of your customer acquisition strategy . It’s a comprehensive document that details your:
- Target audience: Who you’re trying to reach
- Marketing goals: What you want to achieve
- Strategies and tactics: How you’ll reach your goals
- Budget: Resources you’ll allocate
- Metrics: How you’ll measure success
In this article, I’ll explain everything you need to know about creating a marketing plan . If you need a little extra help, there are professionally designed marketing plan templates that’ll make the process much easier. So, let’s ditch the confusion and get started!
Click to jump ahead:
What is a marketing plan?
How to write a marketing plan .
- Marketing plan v.s. business plan
- Types of marketing plans
9 marketing plan examples to inspire your growth strategy
Marketing plan faqs.
A marketing plan is a report that outlines your marketing strategy for your products or services, which could be applicable for the coming year, quarter or month.
Watch this quick, 13-minute video for more details on what a marketing plan is and how to make one yourself:
Typically, a marketing plan includes:
- An overview of your business’s marketing and advertising goals
- A description of your business’s current marketing position
- A timeline of when tasks within your strategy will be completed
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) you will be tracking
- A description of your business’s target market and customer needs
- A description of how you will measure the performance of the strategy
For example, this marketing plan template provides a high-level overview of the business and competitors before diving deep into specific goals, KPIs and tactics:

Learning how to write a marketing plan forces you to think through the important steps that lead to an effective marketing strategy . And a well-defined plan will help you stay focused on your high-level marketing goals.
With Venngage’s extensive catalog of marketing plan templates , creating your marketing plan isn’t going to be hard or tedious. In fact, Venngage has plenty of helpful communications and design resources for marketers. If you’re ready to get started, sign up for Venngage for Marketers now. It’s free to register and start designing.

Whether you’re a team trying to set smarter marketing goals, a consultant trying to set your client in the right direction, or a one-person team hustling it out, Venngage for Marketers helps you get things done.
As mentioned above, the scope of your marketing plan varies depending on its purpose or the type of organization it’s for.
For example, you could create a marketing plan that provides an overview of a company’s entire marketing strategy or simply focus on a specific channel like SEO, social media marketing, content marketing and more, like in this example:

A typical outline of a marketing plan includes:
- Executive summary
- Goals and objectives
- User personas
- Competitor analysis/SWOT analysis
- Baseline metrics
- Marketing strategy
- Tracking guidelines
Below you will see in details how to write each section as well as some examples of how you can design each section in a marketing plan.
Let’s look at how to create a successful marketing plan (click to jump ahead):
- Write a simple executive summary
- Set metric-driven marketing goals
- Outline your user personas
- Research all of your competitors
- Set accurate key baselines & metrics
- Create an actionable marketing strategy
- Set tracking or reporting guidelines
1. Write a simple executive summary
Starting your marketing plan off on the right foot is important. You want to pull people into your amazing plan for marketing domination. Not bore them to tears.

One of the best ways to get people excited to read your marketing plan is with a well-written executive summary. An executive summary introduces readers to your company goals, marketing triumphs, future plans, and other important contextual facts.

Basically, you can use the Executive Summary as a primer for the rest of your marketing plan.
Include things like:
- Simple marketing goals
- High-level metrics
- Important company milestones
- Facts about your brand
- Employee anecdotes
- Future goals & plans
Try to keep your executive summary rather brief and to the point. You aren’t writing a novel, so try to keep it under three to four paragraphs.
Take a look at the executive summary in the marketing plan example below:

The executive summary is only two paragraphs long — short but effective.
The executive summary tells readers about the company’s growth, and how they are about to overtake one of their competitors. But there’s no mention of specific metrics or figures. That will be highlighted in the next section of the marketing plan.
An effective executive summary should have enough information to pique the reader’s interest, but not bog them down with specifics yet. That’s what the rest of your marketing plan is for!
The executive summary also sets the tone for your marketing plan. Think about what tone will fit your brand ? Friendly and humorous? Professional and reliable? Inspiring and visionary?
2. Set metric-driven marketing goals
After you perfect your executive summary, it’s time to outline your marketing goals.
(If you’ve never set data-driven goals like this before, it would be worth reading this growth strategy guide ).
This is one of the most important parts of the entire marketing plan, so be sure to take your time and be as clear as possible. Moreover, optimizing your marketing funnel is key. Employing effective funnel software can simplify operations and provide valuable customer insights. It facilitates lead tracking, conversion rate analysis, and efficient marketing optimization .
As a rule of thumb, be as specific as possible. The folks over at VoyMedia advise that you should set goals that impact website traffic, conversions, and customer success — and to use real numbers.
Avoid outlining vague goals like:
- Get more Twitter followers
- Write more articles
- Create more YouTube videos (like educational or Explainer videos )
- Increase retention rate
- Decrease bounce rate
Instead, identify key performance metrics (KPI) you want to impact and the percentage you want to increase them by.
Take a look at the goals page in the marketing plan example below:

They not only identify a specific metric in each of their goals, but they also set a timeline for when they will be increased.
The same vague goals listed earlier become much clearer when specific numbers and timelines are applied to them:
- Get 100 new Twitter followers per month
- Write 5 more articles per week
- Create 10 YouTube videos each year
- Increase retention rate by 15% by 2020
- Decrease bounce rate by 5% by Q1
- Create an online course and get 1,000 new leads
- Focus more on local SEO strategies
- Conduct a monthly social media report to track progress
You can dive even deeper into your marketing goals if you want (generally, the more specific, the better). Here’s a marketing plan example that shows how to outline your growth goals:

3. Outline your user personas
Now, this may not seem like the most important part of your marketing plan, but I think it holds a ton of value.
Outlining your user personas is an important part of a marketing plan that should not be overlooked.
You should be asking not just how you can get the most visitors to your business, but how you can get the right visitors.
Who are your ideal customers? What are their goals? What are their biggest problems? How does your business solve customer problems?
Answering these questions will take lots of research, but it’s essential information to get.
Some ways to conduct user research are:
- Interviewing your users (either in person or on the phone)
- Conducting focus groups
- Researching other businesses in the same industry
- Surveying your audience
Then, you will need to compile your user data into a user persona guide.
Take a look at how detailed this user persona template is below:

Taking the time to identify specific demographic traits, habits and goals will make it easier for you to cater your marketing plan to them.
Here’s how you can create a user persona guide:
The first thing you should add is a profile picture or icon for each user persona. It can help to put a face to your personas, so they seem more real.
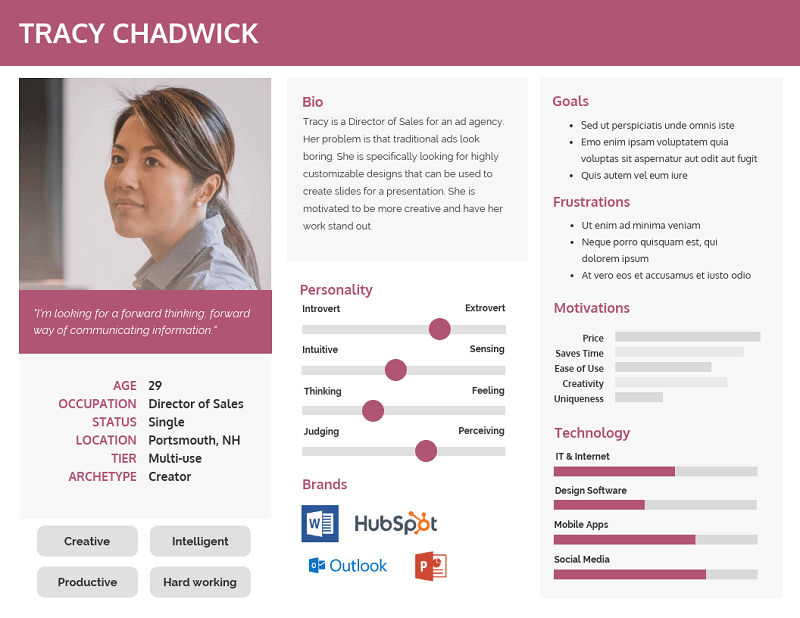
Next, list demographic information like:
- Identifiers
- Activities/Hobbies
The user persona example above uses sliding scales to identify personality traits like introversion vs. extroversion and thinking vs. feeling. Identifying what type of personality your target users tend to have an influence on the messaging you use in your marketing content.
Meanwhile, this user persona guide identifies specific challenges the user faces each day:

But if you don’t want to go into such precise detail, you can stick to basic information, like in this marketing plan example:

Most businesses will have a few different types of target users. That’s why it’s pertinent to identify and create several different user personas . That way, you can better segment your marketing campaigns and set separate goals, if necessary.
Here’s a marketing plan example with a segmented user persona guide:

The important thing is for your team or client to have a clear picture of who their target user is and how they can appeal to their specific problems.
Start creating robust user personas using Venngage’s user persona guide .
4. Conduct an extensive competitor analysis
Next, on the marketing plan checklist, we have the competitor research section. This section will help you identify who your competitors are, what they’re doing, and how you could carve yourself a place alongside them in your niche — and ideally, surpass them. It’s something you can learn to do with rank tracking software .
Competitor research is also incredibly important if you are starting a blog .
Typically, your competitor research should include:
- Who their marketing team is
- Who their leadership team is
- What their marketing strategy and strategic marketing plan are (this will probably revolve some reverse-engineering)
- What their sales strategy is (same deal)
- Social Media strategy (are they using discounting strategies such as coupon marketing to get conversions)
- Their market cap/financials
- Their yearly growth (you will probably need to use a marketing tool like Ahrefs to do this)
- The number of customers they have & their user personas
Also, take as deep a dive as you can into the strategies they use across their:
- Blog/Content marketing
- Social media marketing
- SEO Marketing
- Video marketing
- And any other marketing tactics they use
Research their strengths and weaknesses in all parts of their company, and you will find some great opportunities. Bookmark has a great guide to different marketing strategies for small businesses if you need some more information there.
You can use this simple SWOT analysis worksheet to quickly work through all parts of their strategy as well:

Click the template above to create a SWOT chart . Customize the template to your liking — no design know-how needed.
Since you have already done all the research beforehand, adding this information to your marketing plan shouldn’t be that hard.
In this marketing plan example, some high-level research is outlined for 3 competing brands:

But you could take a deeper dive into different facets of your competitors’ strategies. This marketing plan example analyses a competitor’s content marketing strategy:

It can also be helpful to divide your competitors into Primary and Secondary groups. For example, Apple’s primary competitor may be Dell for computers, but its secondary competitor could be a company that makes tablets.
Your most dangerous competitors may not even be in the same industry as you. Like the CEO of Netflix said, “Sleep is our competition.”
5. Set accurate key baselines & metrics
It’s pretty hard to plan for the future if you don’t know where your business stands right now.
Before we do anything at Venngage, we find the baselines so we can compare future results to something. We do it so much it’s almost like second nature now!
Setting baselines will allow you to more accurately track your progress. You will also be able to better analyze what worked and what didn’t work, so you can build a stronger strategy. It will definitely help them clearly understand your goals and strategy as well.
Here’s a marketing plan example where the baselines are visualized:

Another way to include baselines in your plan is with a simple chart, like in the marketing plan example below:

Because data can be intimidating to a lot of people, visualizing your data using charts and infographics will help demystify the information.
6. Create an actionable marketing strategy
After pulling all the contextual information and relevant metrics into your marketing plan, it’s time to break down your marketing strategy.
Once again, it’s easier to communicate your information to your team or clients using visuals .
Mind maps are an effective way to show how a strategy with many moving parts ties together. For example, this mind map shows how the four main components of a marketing strategy interact together:

You can also use a flow chart to map out your strategy by objectives:

However you choose to visualize your strategy, your team should know exactly what they need to do. This is not the time to keep your cards close to your chest.
Your strategy section may need to take up a few pages to explain, like in the marketing plan example below:

With all of this information, even someone from the development team will understand what the marketing team is working on.
This minimalistic marketing plan example uses color blocks to make the different parts of the strategy easy to scan:

Breaking your strategy down into tasks will make it easier to tackle.
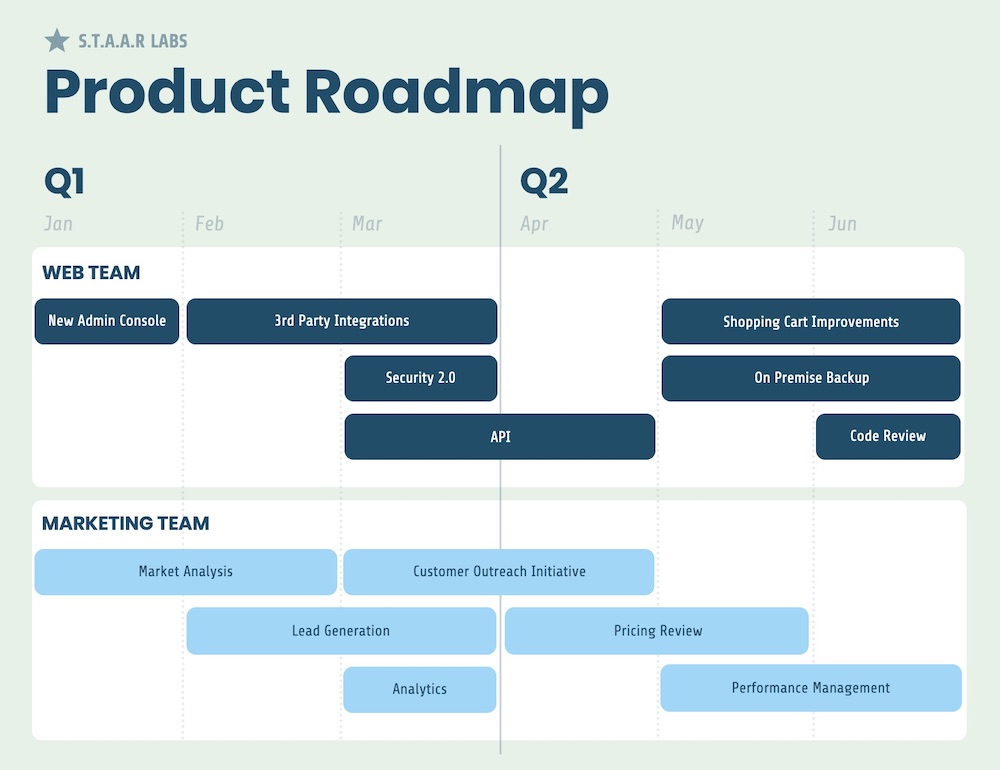
Another important way to visualize your marketing strategy is to create a project roadmap. A project roadmap visualizes the timeline of your product with individual tasks. Our roadmap maker can help you with this.
For example, this project roadmap shows how tasks on both the marketing and web design side run parallel to each other:
A simple timeline can also be used in your marketing plan:
Or a mind map, if you want to include a ton of information in a more organized way:

Even a simple “Next, Now, Later” chart can help visualize your strategy:

7. Set tracking or reporting guidelines
Close your marketing plan with a brief explanation of how you plan to track or measure your results. This will save you a lot of frustration down the line by standardizing how you track results across your team.
Like the other sections of your marketing plan, you can choose how in-depth you want to go. But there need to be some clear guidelines on how to measure the progress and results of your marketing plan.
At the bare minimum, your results tracking guidelines should specify:
- What you plan to track
- How you plan to track results
- How often you plan to measure
But you can more add tracking guidelines to your marketing plan if you see the need to. You may also want to include a template that your team or client can follow, for client reporting , ensure that the right metrics are being tracked.

The marketing plan example below dedicates a whole page to tracking criteria:

Use a task tracker to track tasks and marketing results, and a checklist maker to note down tasks, important life events, or tracking your daily life.
Similarly, the marketing plan example below talks about tracking content marketing instead:

Marketing plan vs. marketing strategy
Although often used interchangeably, the terms “marketing plan” and “marketing strategy” do have some differences.
Simply speaking, a marketing strategy presents what the business will do in order to reach a certain goal. A marketing plan outlines the specific daily, weekly, monthly or yearly activities that the marketing strategy calls for. As a business, you can create a marketing proposal for the marketing strategies defined in your company’s marketing plan. There are various marketing proposal examples that you can look at to help with this.
A company’s extended marketing strategy can be like this:
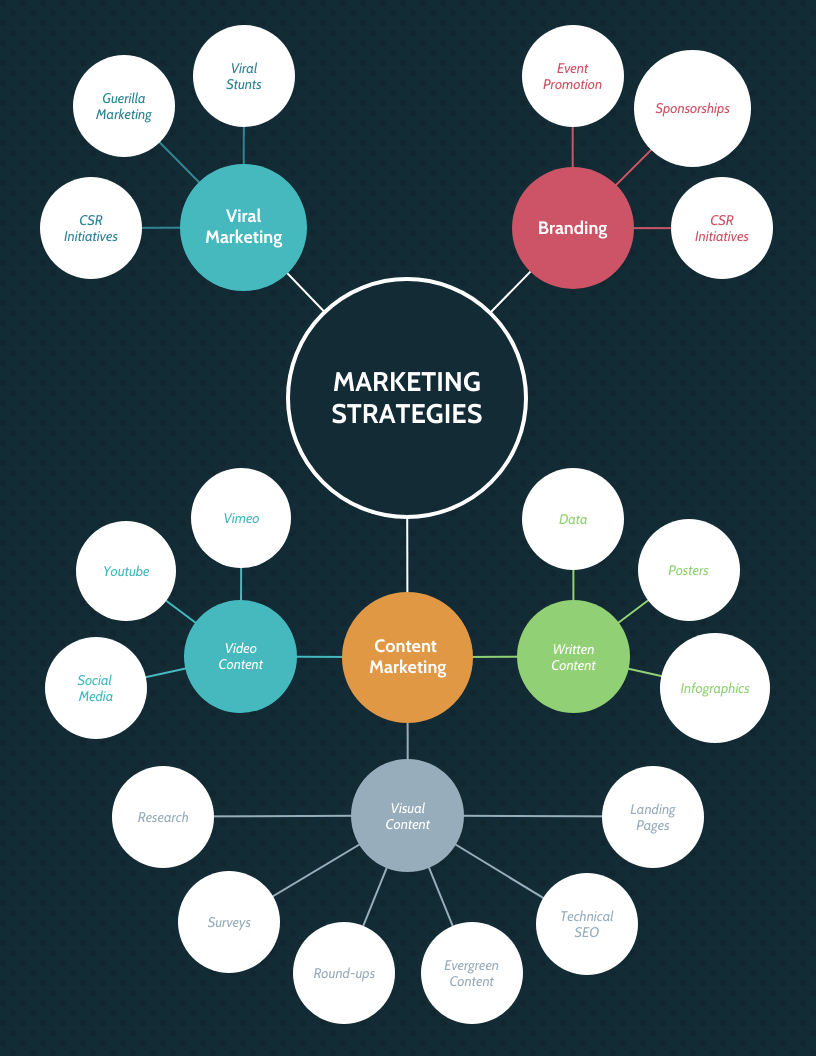
Notice how it’s more general and doesn’t include the actual activities required to complete each strategy or the timeframe those marketing activities will take place. That kind of information is included in a marketing plan, like this marketing plan template which talks about the content strategy in detail:

Marketing plan v.s business plan
While both marketing plans and business plans are crucial documents for businesses, they serve distinct purposes and have different scopes. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
Business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines all aspects of your business, including:
- Mission and vision
- Products or services
- Target market
- Competition
- Management team
- Financial projections
- Marketing strategy (including a marketing plan)
- Operations plan
Marketing plan on the other hand, dives deep into the specific strategies and tactics related to your marketing efforts. It expands on the marketing section of a business plan by detailing:
- Specific marketing goals (e.g., brand awareness, lead generation, sales)
- Target audience analysis (detailed understanding of their needs and behaviors)
- Product: Features, benefits, positioning
- Price: Pricing strategy, discounts
- Place: Distribution channels (online, offline)
- Promotion: Advertising, social media, content marketing, public relations
- Budget allocation for different marketing activities
- Metrics and measurement to track progress and success
In short, business plans paint the entire business picture, while marketing plans zoom in on the specific strategies used to reach your target audience and achieve marketing goals.
Types of marketing plans that can transform your business strategy
Let’s take a look at several types of marketing plans you can create, along with specific examples for each.
1. General marketing strategic plan / Annual marketing plan
This is a good example of a marketing plan that covers the overarching annual marketing strategy for a company:

Another good example would be this Starbucks marketing plan:

This one-page marketing plan example from coffee chain Starbucks has everything at a glance. The bold headers and subheadings make it easier to segment the sections so readers can focus on the area most relevant to them.
What we like about this example is how much it covers. From the ideal buyer persona to actional activities, as well as positioning and metrics, this marketing plan has it all.
Another marketing plan example that caught our eye is this one from Cengage. Although a bit text-heavy and traditional, it explains the various sections well. The clean layout makes this plan easy to read and absorb.

The last marketing plan example we would like to feature in this section is this one from Lush cosmetics.
It is a long one but it’s also very detailed. The plan outlines numerous areas, including the company mission, SWOT analysis , brand positioning, packaging, geographical criteria, and much more.

2. Content marketing plan
A content marketing plan highlights different strategies , campaigns or tactics you can use for your content to help your business reach its goals.
This one-page marketing plan example from Contently outlines a content strategy and workflow using simple colors and blocks. The bullet points detail more information but this plan can easily be understood at a glance, which makes it so effective.

For a more detailed content marketing plan example, take a look at this template which features an editorial calendar you can share with the whole team:

3. SEO marketing plan
Your SEO marketing plan highlights what you plan to do for your SEO marketing strategy . This could include tactics for website on-page optimization , off-page optimization using AI SEO , and link building using an SEO PowerSuite backlink API for quick backlink profile checks.
This SEO marketing plan example discusses in detail the target audience of the business and the SEO plan laid out in different stages:

4. Social media marketing plan
Your social media marketing plan presents what you’ll do to reach your marketing goal through social media. This could include tactics specific to each social media channel that you own, recommendations on developing a new channel, specific campaigns you want to run, and so on, like how B2B channels use Linkedin to generate leads with automation tools and expand their customer base; or like making use of Twitter walls that could display live Twitter feeds from Twitter in real-time on digital screens.
For B2C brands, you can target Facebook and Instagram. Gain Instagram likes to build trust for your brand’s profile and post engaging content on both platforms
Edit this social media marketing plan example easily with Venngage’s drag-and-drop editor:

5. Demand generation marketing plan
This could cover your paid marketing strategy (which can include search ads, paid social media ads, traditional advertisements, etc.), email marketing strategy and more. Here’s an example:

1. Free marketing plan template
Here’s a free nonprofit marketing plan example that is ideal for organizations with a comprehensive vision to share. It’s a simple plan that is incredibly effective. Not only does the plan outline the core values of the company, it also shares the ideal buyer persona.

Note how the branding is consistent throughout this example so there is no doubt which company is presenting this plan. The content plan is an added incentive for anyone viewing the document to go ahead and give the team the green light.
2. Pastel social media marketing campaign template
Two-page marketing plan samples aren’t very common, but this free template proves how effective they are. There’s a dedicated section for business goals as well as for project planning .
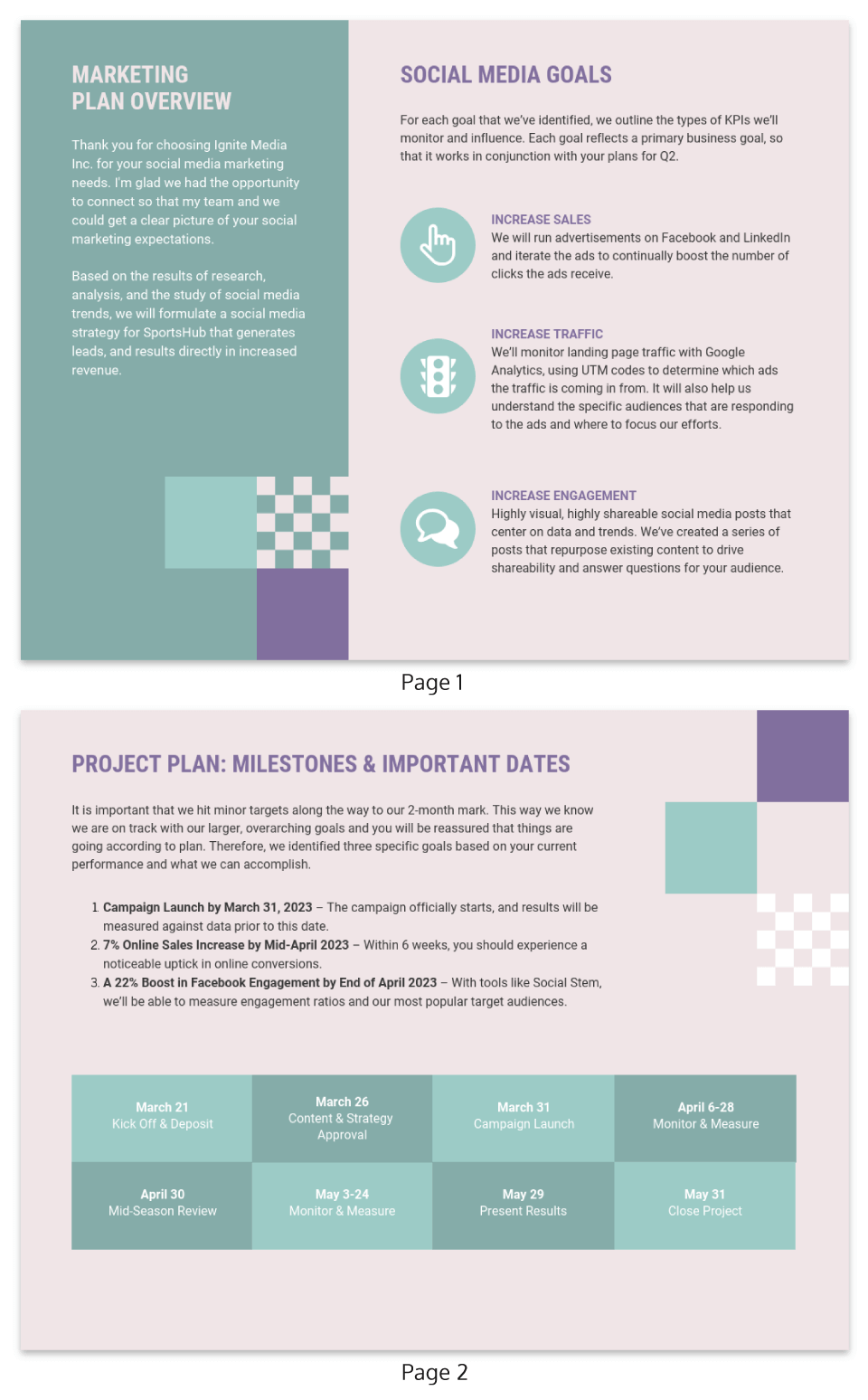
The milestones for the marketing campaign are clearly laid out, which is a great way to show how organized this business strategy is.
3. Small business marketing strategy template
This marketing plan template is perfect for small businesses who set out to develop an overarching marketing strategy for the whole year:
Notice how this aligns pretty well with the marketing plan outline we discussed in previous sections.
In terms of specific tactics for the company’s marketing strategy, the template only discusses SEO strategy, but you can certainly expand on that section to discuss any other strategies — such as link building , that you would like to build out a complete marketing plan for.
4. Orange simple marketing proposal template
Marketing plans, like the sample below, are a great way to highlight what your business strategy and the proposal you wan to put forward to win potential customers.

5. One-page marketing fact sheet template
This one-page marketing plan example is great for showcasing marketing efforts in a persuasive presentation or to print out for an in-person meeting.

Note how the fact sheet breaks down the marketing budget as well as the key metrics for the organization. You can win over clients and partners with a plan like this.
6. Light company business fact sheet template
This one-page sample marketing plan clearly outlines the marketing objectives for the organization. It’s a simple but effective way to share a large amount of information in a short amount of time.

What really works with this example is that includes a mission statement, key contact information alongside all the key metrics.
7. Marketing media press kit template
This press kit marketing plan template is bright and unmistakable as belonging to the Cloud Nine marketing agency . The way the brand colors are used also helps diversify the layouts for each page, making the plan easier to read.

We like the way the marketing department has outlined the important facts about the organization. The bold and large numbers draw the eye and look impressive.
8. Professional marketing proposal template
Start your marketing campaign on a promising note with this marketing plan template. It’s short, sharp and to the point. The table of contents sets out the agenda, and there’s a page for the company overview and mission statement.

9. Social media marketing proposal template
A complete marketing plan example, like the one below, not only breaks down the business goals to be achieved but a whole lot more. Note how the terms and conditions and payment schedule are included, which makes this one of the most comprehensive marketing plans on our list.

What should marketing plans include?
Marketing plans should include:
- A detailed analysis of the target market and customer segments.
- Clear and achievable marketing objectives and goals.
- Strategies and tactics for product promotion and distribution.
- Budget allocation for various marketing activities.
- Timelines and milestones for the implementation of marketing strategies.
- Evaluation metrics and methods for tracking the success of the marketing plan.
What is an executive summary in a marketing plan and what is its main goal?
An executive summary in a marketing plan is a brief overview of the entire document, summarizing the key points, goals, and strategies. Its main goal is to provide readers with a quick understanding of the plan’s purpose and to entice them to read further.
What are the results when a marketing plan is effective?
When a marketing plan is effective, businesses can experience increased brand visibility, higher customer engagement, improved sales and revenue, and strengthened customer loyalty.
What is the first section of a marketing plan?
The first section of a marketing plan is typically the “Executive Summary,” which provides a concise overview of the entire plan, including the business’s goals and the strategies to achieve them.
Now that you have the basics for designing your own marketing plan, it’s time to get started:
More marketing design guides and templates:
- Marketing Infographics: The Definitive Guide [Includes Infographic Templates]
- 20+ Business Pitch Deck Templates to Win New Clients and Investors
- 20+ White Paper Examples [Design Guide + White Paper Templates]
- The Evolution of Marketing [Timeline Infographic]
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Marketing |
- How to create a winning marketing plan, ...
How to create a winning marketing plan, with 3 examples from world-class teams

A marketing plan helps leaders clearly visualize marketing strategies across channels, so they can ensure every campaign drives pipeline and revenue. In this article you’ll learn eight steps to create a winning marketing plan that brings business-critical goals to life, with examples from word-class teams.
To be successful as a marketer, you have to deliver the pipeline and the revenue.”
In other words—they need a well-crafted marketing plan.
Level up your marketing plan to drive revenue in 2024
Learn how to create the right marketing plan to hit your revenue targets in 2024. Hear best practices from marketing experts, including how to confidently set and hit business goals, socialize marketing plans, and move faster with clearer resourcing.

7 steps to build a comprehensive marketing plan
How do you build the right marketing plan to hit your revenue goals? Follow these eight steps for success:
1. Define your plan
First you need to define each specific component of your plan to ensure stakeholders are aligned on goals, deliverables, resources, and more. Ironing out these details early on ensures your plan supports the right business objectives, and that you have sufficient resources and time to get the job done.
Get started by asking yourself the following questions:
What resources do I need?
What is the vision?
What is the value?
What is the goal?
Who is my audience?
What are my channels?
What is the timeline?
For example, imagine you’re creating an annual marketing plan to improve customer adoption and retention in the next fiscal year. Here’s how you could go through the questions above to ensure you’re ready to move forward with your plan:
I will need support from the content team, web team, and email team to create targeted content for existing customers. One person on each team will need to be dedicated full-time to this initiative. To achieve this, the marketing team will need an additional $100K in budget and one new headcount.
What is the vision?
To create a positive experience for existing customers, address new customer needs, and encourage them to upgrade. We’ll do this by serving them how-to content, new feature updates, information about deals and pricing, and troubleshooting guides.
According to the Sales Benchmark Index (SBI) , CEOs and go-to-market leaders report that more than 60% of their net-new revenue will come from existing customers in 2023. By retaining and building on the customers we have, we can maintain revenue growth over time.
To decrease the customer churn rate from 30% to 10%, and increase upgrades from 20% to 30% in the next fiscal year.
All existing customers.
The main channel will be email. Supporting marketing channels include the website, blog, YouTube, and social media.
The first half of the next fiscal year.
One of the most important things to do as you create your marketing strategy is to identify your target audience . As with all marketing, you need to know who you’re marketing to. If you’re having a hard time determining who exactly your target audience is, try the bullseye targeting framework . The bullseye makes it easy for you to determine who your target audience is by industry, geography, company size, psychographics, demographics, and more.
2. Identify key metrics for success
Now it’s time to define what key marketing metrics you’ll use to measure success. Your key metrics will help you measure and track the performance of your marketing activities. They’ll also help you understand how your efforts tie back to larger business goals.
Once you establish key metrics, use a goal-setting framework—like objectives and key results (OKRs) or SMART goals —to fully flush out your marketing objectives. This ensures your targets are as specific as possible, with no ambiguity about what should be accomplished by when.
Example: If a goal of your marketing plan is to increase email subscriptions and you follow the SMART goal framework (ensuring your objective is specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound) your goal might look like this: Increase email subscription rate from 10% to 20% in H1 .
3. Research your competition
It’s easy to get caught up in your company’s world, but there’s a lot of value in understanding your competitors . Knowing how they market themselves will help you find opportunities to make your company stand out and capture more market share.
Make sure you’re not duplicating your competitors’ efforts. If you discover a competitor has already executed your idea, then it might be time to go back to the drawing board and brainstorm new ways to differentiate yourself. By looking at your competitors, you might be surprised at the type of inspiration and opportunities you’ll find.
To stay ahead of market trends, conduct a SWOT analysis for your marketing plan. A SWOT analysis helps you improve your plan by identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Example: If your competitor launches a social media campaign identical to what you had planned, go back to the drawing board and see how you can build off their campaign. Ask yourself: How can we differentiate our campaign while still getting our message across? What are the weaknesses of their campaign that we can capitalize on? What angles did they not approach?
4. Integrate your marketing efforts
Here’s where the fun comes in. Let’s dive into the different components that go into building a successful marketing plan. You’ll want to make sure your marketing plan includes multiple supporting activities that all add up into a powerful marketing machine. Some marketing plan components include:
Lead generation
Social media
Product marketing
Public relations
Analyst relations
Customer marketing
Search engine optimization (SEO)
Conversational marketing
Knowing where your consumer base spends the most time is significant for nailing this step. You need to have a solid understanding of your target audience before integrating your marketing efforts.
Example: If your target audience is executives that spend a lot of time on LinkedIn, focus your social media strategy around placing branded content on LinkedIn.
5. Differentiate with creative content
Forty-nine percent of marketers say visual images are hugely important to their content strategy. In other words, a clear brand and creative strategy is an essential component to every marketing plan. As you craft your own creative strategy, here are some tips to keep in mind:
Speak to your audience: When defining your creative strategy, think about your audience—what you want them to feel, think, and do when they see your marketing. Will your audience find your creative work relevant? If your audience can’t relate to your creative work, they won’t feel connected to the story you’re trying to tell.
Think outside the box: Find innovative ways to engage your audience, whether through video, animations, or interactive graphics. Know what screens your creative work will live on, whether desktop, mobile, or tablet, and make sure they display beautifully and load quickly across every type of device.
Tie everything back to CTAs: It’s easy to get caught up in the creative process, so it’s important to never lose sight of your ultimate goal: Get your audience to take action. Always find the best way to display strong Calls to Action (CTAs) in your creative work. We live in a visual world—make sure your creative content counts.
Streamline creative production: Once you’ve established a strong creative strategy, the next step is to bring your strategy to life in the production stage. It’s vital to set up a strong framework for your creative production process to eliminate any unnecessary back and forth and potential bottlenecks. Consider establishing creative request forms , streamlining feedback and approval processes, and taking advantage of integrations that might make your designers’ lives easier.
Example: If your brand is fun and approachable, make sure that shows in your creative efforts. Create designs and CTAs that spark joy, offer entertainment, and alleviate the pressure in choosing a partner.
6. Operationalize your marketing plan
Turn your plan into action by making goals, deliverables, and timelines clear for every stakeholder—so teams stay accountable for getting work done. The best way to do this is by centralizing all the details of your marketing plan in one platform , so teams can access the information they need and connect campaign work back to company goals.
With the right work management tool , you can:
Set goals for every marketing activity, and connect campaign work to overarching marketing and business objectives so teams focus on revenue-driving projects.
Centralize deliverables for your entire marketing plan in one project or portfolio .
Mark major milestones and visualize your plan as a timeline, Gantt chart, calendar, list, or Kanban board—without doing any extra work.
Quickly loop in stakeholders with status updates so they’re always up to date on progress. This is extremely important if you have a global team to ensure efforts aren’t being duplicated.
Use automations to seamlessly hand off work between teams, streamlining processes like content creation and reviews.
Create dashboards to report on work and make sure projects are properly staffed , so campaigns stay on track.
With everything housed in one spot, you can easily visualize the status of your entire marketing plan and keep work on track. Building an effective marketing plan is one thing, but how you operationalize it can be your secret to standout marketing.
Example: If your strategy focuses on increasing page views, connect all campaign work to an overarching OKR—like “we will double page views as measured by the amount of organic traffic on our blog.” By making that goal visible to all stakeholders, you help teams prioritize the right work.
See marketing planning in action
With Asana, marketing teams can connect work, standardize processes, and automate workflows—all in one place.

7. Measure performance
Nearly three in four CMOs use revenue growth to measure success, so it’s no surprise that measuring performance is necessary. You established your key metrics in step two, and now it’s time to track and report on them in step eight.
Periodically measure your marketing efforts to find areas of improvement so you can optimize in real-time. There are always lessons to be learned when looking at data. You can discover trends, detect which marketing initiatives performed well, and course-correct what isn’t performing well. And when your plan is complete, you can apply these learnings to your next initiative for improved results.
Example: Say you discover that long-form content is consistently bringing in 400% more page views than short-form content. As a result, you’ll want to focus on producing more long-form content in your next marketing plan.
Marketing plan examples from world-class teams
The best brands in the world bring their marketing plans to life every day. If you’re looking for inspiration, check out these examples from successful marketing teams.
Autodesk grows site traffic 30% three years in a row
When the Autodesk team launched Redshift, it was initially a small business blog. The editorial team executed a successful marketing plan to expand it into a premier owned-media site, making it a destination for stories and videos about the future of making.
The team scaled content production to support seven additional languages. By standardizing their content production workflow and centralizing all content conversations in one place, the editorial team now publishes 2X more content monthly. Read the case study to learn more about how Autodesk runs a well-oiled content machine.
Sony Music boosts creative production capacity by 4X
In recent years the music industry has gone through a pivotal transition—shifting from album sales to a streaming business model. For marketing and creative teams at Sony Music, that meant adopting an “always on” campaign plan.
The team successfully executed this campaign plan by centralizing creative production and approvals in one project. By standardizing processes, the team reduced campaign production time by 75%. Read the case study to learn more about how Sony Music successfully scaled their creative production process.
Trinny London perfects new customer acquisition
In consumer industries, social media is crucial for building a community of people who feel an affinity with the brand—and Trinny London is no exception. As such, it was imperative that Trinny London’s ad spend was targeted to the correct audience. Using a work management tool, Trinny London was able to nail the process of creating, testing, and implementing ads on multiple social channels.
With the help of a centralized tool, Trinny London improved its ad spend and drove more likes and subscriptions on its YouTube page. Read the case study to learn more about how Trinny London capitalized on paid advertising and social media.
Turn your marketing plan into marketing success
A great marketing plan promotes clarity and accountability across teams—so every stakeholder knows what they’re responsible for, by when. Reading this article is the first step to achieving better team alignment, so you can ensure every marketing campaign contributes to your company’s bottom line.
Use a free marketing plan template to get started
Once you’ve created your marketing strategy and are ready to operationalize your marketing plan, get started with one of our marketing templates .
Our marketing templates can help you manage and track every aspect of your marketing plan, from creative requests to approval workflows. Centralize your entire marketing plan in one place, customize the roadmap, assign tasks, and build a timeline or calendar.
Once you’ve operationalized your entire marketing plan with one of our templates, share it with your stakeholders so everyone can work together in the same tool. Your entire team will feel connected to the marketing plan, know what to prioritize, and see how their work contributes to your project objectives . Choose the best marketing template for your team:
Marketing project plan template
Marketing campaign plan template
Product marketing launch template
Editorial calendar template
Agency collaboration template
Creative requests template
Event planning template
GTM strategy template
Still have questions? We have answers.
What is a marketing plan.
A marketing plan is a detailed roadmap that outlines the different strategies your team will use to achieve organizational objectives. Rather than focusing solely on the end goal, a marketing plan maps every step you need to reach your destination—whether that’s driving pipeline for sales, nurturing your existing customer base, or something in-between.
As a marketing leader, you know there’s never a shortage of great campaign and project ideas. A marketing plan gives you a framework to effectively prioritize work that aligns to overarching business goals—and then get that work done. Some elements of marketing plans include:
Current business plan
Mission statement
Business goals
Target customers
Competitive analysis
Current marketing mix
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Marketing budget
What is the purpose of a marketing plan?
The purpose of a marketing plan is to grow your company’s consumer base and strengthen your brand, while aligning with your organization’s mission and vision . The plan should analyze the competitive landscape and industry trends, offer actionable insights to help you gain a competitive advantage, and document each step of your strategy—so you can see how your campaigns work together to drive overarching business goals.
What is the difference between a marketing plan and a marketing strategy?
A marketing plan contains many marketing strategies across different channels. In that way, marketing strategies contribute to your overall marketing plan, working together to reach your company’s overarching business goals.
For example, imagine you’re about to launch a new software product and the goal of your marketing plan is to drive downloads. Your marketing plan could include marketing strategies like creating top-of-funnel blog content and launching a social media campaign.
What are different types of marketing plans?
Depending on what you’re trying to accomplish, what your timeline is, or which facet of marketing you’re driving, you’ll need to create a different type of marketing plan. Some different types of marketing plans include, but aren’t limited to:
General marketing plan: A general marketing plan is typically an annual or quarterly marketing plan that details the overarching marketing strategies for the period. This type of marketing plan outlines marketing goals, the company’s mission, buyer personas, unique selling propositions, and more. A general marketing plan lays the foundation for other, more specific marketing plans that an organization may employ.
Product launch marketing plan: A product launch marketing plan is a step-by-step plan for marketing a new product or expanding into a new market. It helps you build awareness and interest by targeting the right audience, with the right messaging, in the right timeframe—so potential customers are ready to buy your new offering right away. Nailing your product launch marketing plan can reinforce your overall brand and fast-track sales. For a step-by-step framework to organize all the moving pieces of a launch, check out our product marketing launch template .
Paid marketing plan: This plan includes all the paid strategies in your marketing plan, like pay-per-click, paid social media advertising, native advertising, and display advertising. It’s especially important to do audience research prior to launching your paid marketing plan to ensure you’re maximizing ROI. Consult with content strategists to ensure your ads align with your buyer personas so you know you’re showing ads to the right people.
Content marketing plan: A content marketing plan outlines the different content strategies and campaigns you’ll use to promote your product or service. When putting together a content marketing plan, start by identifying your audience. Then use market research tools to get the best insights into what topics your target audience is most interested in.
SEO marketing plan: Your SEO marketing plan should work directly alongside your content marketing plan as you chart content that’s designed to rank in search results. While your content marketing plan should include all types of content, your SEO marketing plan will cover the top-of-funnel content that drives new users to your site. Planning search engine-friendly content is only one step in your SEO marketing plan. You’ll also need to include link-building and technical aspects in order to ensure your site and content are as optimized as possible.
Social media marketing plan: This plan will highlight the marketing strategies you plan to accomplish on social media. Like in any general or digital marketing plan , your social media strategy should identify your ideal customer base and determine how they engage on different social media platforms. From there, you can cater your social media content to your target audience.
Related resources

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

What is content marketing? A complete guide
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
The Marketing Plan Section of the Business Plan
Writing The Business Plan: Section 5
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
- Products, Services, and Your USP
Pricing and Positioning Strategy
Sales and distribution plan, advertising and promotion plan.
The marketing plan section of the business plan explains how you're going to get your customers to buy your products or services. The marketing plan, then, will include sections detailing your:
- Products and services and your unique selling proposition (USP)
- Pricing strategy
- Sales and distribution plan
- Advertising and promotions plan
The easiest way to develop your marketing plan is to work through each of these sections, referring to the market research you completed when you were writing the previous sections of the business plan . (Note that if you are developing a marketing plan on its own, rather than as part of a business plan, you will also need to include a target market and a competitors' analysis section.)
Let's look at each of these four sections in detail.
Products, Services, and Your Unique Selling Proposition
Focus on the uniqueness of your product or service and how the customer will benefit from what you're offering. Use these questions to write a paragraph summarizing these aspects for your marketing plan:
- What are the features of your product or service?
- Describe the physical attributes of your product or service and any other relevant features such as what it does or how it differs from competitors' offerings.
- How will your product or service benefit the customer?
- Remember that benefits can be intangible as well as tangible; for instance, if you're selling a cleaning product, your customers will benefit by having a cleaner house, but they may also benefit by enjoying better health. Brainstorm as many benefits as possible to begin with, then choose to emphasize the benefits that your targeted customers will most appreciate in your marketing plan.
- What is it that sets your product or service apart from all the rest? In other words, what is your USP, the message you want your customers to receive about your product or service? This will be at the heart of your marketing plan.
Examples of Unique Selling Propositions
Unique selling propositions should be short (no more than a sentence) and concise. Here are a few great examples:
- Domino's Pizza : "We deliver hot, fresh pizza in 30 minutes or less, or it's free."
- FedEx Corporation : "When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight."
- M&Ms : "The milk chocolate melts in your mouth, not in your hand ."
- Dollar Shave Club: “Everything you need in the bathroom—from razor blades to grooming products—automatically delivered to your door. It doesn’t get any simpler than that.”
The pricing strategy portion of the marketing plan involves determining how you will price your product or service. The price you charge has to be competitive but still allow you to make a reasonable profit.
Being reasonable is key—you can charge any price you want to, but for every product or service there's a limit to how much the consumer is willing to pay. Your pricing strategy needs to take this consumer threshold into account.
The most common question small business people have about the pricing strategy section of the marketing plan is, "How do you know what price to charge?" Basically, you set your pricing through a process of calculating your costs, estimating the benefits to consumers, and comparing your products, services, and prices to others that are similar.
Set your pricing by examining how much it cost you to produce the product or service and adding a fair price for the benefits that the customer will enjoy. You may find it useful to conduct a breakeven analysis to determine your minimum threshold. Competitor pricing will also help guide you toward the fair market value and help you determine how high you can reasonably go.
The pricing strategy you outline in your marketing plan will answer the following questions:
- What is the cost of your product or service? Make sure you include all your fixed and variable costs when you're calculating this. The costs of labor and materials are obvious, but you may also need to include freight costs, administrative costs, and selling costs, for example.
- How does the pricing of your product or service compare to the market price of similar products or services?
- Explain how the pricing of your product or service is competitive. For instance, if the price you plan to charge is lower, why are you able to do this? If it's higher, why would your customers be willing to pay more? This is where the strategy aspect comes into play; will your business be more competitive if you charge more, less, or the same as your competitors, and why?
- What kind of return on investment (ROI) are you expecting with this pricing strategy, and within what time frame?
Remember, the primary goal of the marketing plan is to get people to buy your products or services. Here's where you detail how this is going to happen.
There are usually three parts to the sales and distribution section, although all three parts may not apply to your business.
Distribution Methods
- How is your product or service going to get to the customer? Will you distribute your product or service through a website, through the mail, through sales representatives, home delivery, or through retail?
- What distribution channel is going to be used? In a direct distribution channel, the product or service goes directly from the manufacturer to the consumer. In a one-stage distribution channel, it goes from manufacturer to retailer to consumer. The traditional distribution channel is from manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer. Outline all the different companies, people and technologies that will be involved in the process of getting your product or service to your customer.
- What are the costs associated with distribution?
- What are the delivery terms?
- How will the distribution methods affect production time frames or delivery? How long will it take to get your product or service to your customer?
If your business involves selling a product, you should also include information about inventory levels and packaging in this part of your marketing plan. For instance:
- How are your products to be packaged for shipping and for display?
- Does the packaging meet all regulatory requirements (such as labeling)?
- Is the packaging appropriately coded, priced, and complementary to the product?
- What minimum inventory levels must be maintained to ensure that there is no loss of sales due to problems such as late shipments and backorders?
Transaction Process
- What system will be used for processing orders, shipping, and billing?
- What methods of payment will customers be able to use?
- What credit terms will customers be offered? If you will offer discounts for early payment or impose penalties for late payment, they should be mentioned in this part of your marketing plan.
- What is your return policy?
- What warranties will the customer be offered? Describe these or any other service guarantees.
- What after-sale support will you offer customers and what will you charge (if anything) for this support?
- Is there a system for customer feedback so customer satisfaction (or the lack of it) can be tracked and addressed?
Sales Strategy
- What types of salespeople will be involved (commissioned salespeople, product demonstrators, telephone solicitors, etc.)?
- Describe your expectations of these salespeople and how sales effectiveness will be measured.
- Will a sales training program be offered? If so, describe it in this section of the marketing plan.
- Describe the incentives salespeople will be offered to encourage their achievements (such as getting new accounts, the most orders, etc.).
Essentially the advertising and promotion section of the marketing plan describes how you're going to deliver your USP to your prospective customers. While there are literally thousands of different promotion avenues available to you, what distinguishes a successful plan from an unsuccessful one is the focus—and that's what your USP provides.
So think first of the message that you want to send to your target audience. Then look at these promotion possibilities and decide which to emphasize in your marketing plan:
Advertising
The best approach to advertising is to think of it in terms of media—specifically, which media will be most effective in reaching your target market. Then you can make decisions about how much of your annual advertising budget you're going to spend on each medium.
What percentage of your annual advertising budget will you invest in applicable methods of advertising, such as:
- The internet (including business website, email, social media campaigns, etc.)
- Direct mail
- Door-to-door flyer delivery
- Cooperative advertising with wholesalers, retailers, or other businesses
- Directories
- Bench/bus/subway ads
Include not only the cost of the advertising but your projections about how much business the advertising will bring in.
Sales Promotion
If it's appropriate to your business, you may want to incorporate sales promotional activities into your advertising and promotion plan, such as:
- Offering free samples
- Point of purchase displays
- Product demonstrations
Marketing Materials
Every business will include some of these in its promotion plans. The most common marketing material is the business card, but brochures, pamphlets, and service sheets are also popular.
This is another avenue of promotion that every business should use. Describe how you plan to generate publicity. While press releases spring to mind, that's only one way to get people spreading the word about your business. Consider:
- Product launches
- Social media
- Special events, including community involvement
- Writing articles
- Getting and using testimonials
Your Business's Website
If your business has or will have a website and a business Facebook page, describe how these fit into your advertising and promotion plan.
Trade Shows
Trade shows can be incredibly effective promotion and sales opportunities if you pick the right ones and go equipped to put your promotion plan into action.
Other Promotion Activities
Your promotion activities are limited only by your imagination. But whether you plan to teach a course, sponsor a community event, or conduct an email campaign, you'll want to include it in your advertising and promotion plan. Sporadic, disconnected attempts to promote your product or service are bound to fail. Your goal is to plan and carry out a sequence of focused promotion activities that will communicate the message you want to send about your products or services.
No business is too small to have a marketing plan. After all, no business is too small for customers or clients. And if you have these, you need to communicate with them about what you have to offer.
Harvard Business Review. " How to Find Out What Customers Will Pay ." Accessed Jan. 16, 2020.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Understanding Business Plans
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
How to Write a Business Plan
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
Common Elements of a Business Plan
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
The Bottom Line
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to Create a Complete Marketing Strategy in 2024 [Data + Expert Tips]
Updated: March 29, 2024
Published: October 26, 2023
Creating a marketing strategy is essential to effectively nurture your customers, improve your business’s bottom line, and increase the ROI of your efforts.

A marketing strategy is especially critical if you want to use the highest ROI trends for 2024 : short-form video and social media. To get powerful results, you must carefully weave both emerging trends and proven strategies into your plan.
Let’s dive into the critical components of a complete marketing strategy in 2024, followed by some examples for inspiration.
Table of Contents
- What is a marketing strategy?
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
Marketing strategy components, why is a marketing strategy important, marketing strategy process, recommended resources, examples of successful marketing strategies, what to expect after following your marketing process steps, marketing strategy.
A marketing strategy covers a company’s overall approach for promoting its brand to a target audience. The process involves research, goal-setting, and positioning.
A completed marketing strategy typically includes brand objectives, target audience personas, marketing channels, key performance indicators, and more.
A marketing strategy will:
- Align your team to specific goals.
- Help you tie your efforts to business objectives.
- Allow you to identify and test what resonates with your target audience.
- Empower you to capitalize on emerging trends.
The last one is especially important. Keeping up with marketing trends is important for your strategy, but it could be a full-time job.
Why? Because almost 80% of marketers say this industry changed more in the last three years than it has in the past five decades.
Add to that the fact that 50% of marketers believe their marketing strategy in 2023 was only *somewhat effective,* which means there’s plenty of room for improvement.
In short, what worked for your marketing strategy in the past might not fly today.
A marketing strategy outlines the long-term goals and overall approach, while a marketing plan covers the specific actions and tactics to achieve those goals.
Phrased another way, marketing strategy guides the overall marketing efforts of a business. It includes goal-setting, market and competitor research, as well as messaging and positioning for a brand.
For example, say you’re creating a marketing strategy for a new fashion brand. Your strategy might target young urban professionals and position the brand as trendy and affordable.
But a marketing plan is a detailed tactical roadmap. It outlines the specific actions and tactics that should achieve the marketing strategy’s goals.
For example, the marketing plan for the fashion brand mentioned above might include:
- Targeted social media campaigns.
- Influencer partnerships.
- Online advertising timeline.
Both a marketing strategy and a marketing plan are essential for a business’s success.
To succeed in the fast-paced marketing world — and maintain a sense of relevance with your audience — it’s vital to stay ahead of the curve.
To help ease some of that uncertainty, we’re going to show you step-by-step how to create a comprehensive marketing strategy. But first, let’s go over the individual components that make up a strong marketing strategy.

Free Marketing Plan Template
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
- Pre-Sectioned Template
- Completely Customizable
- Example Prompts
- Professionally Designed
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
- Marketing Mix (4 Ps of Marketing)
- Marketing Objectives
- Marketing Budget
- Competitive Analysis
- Segmentation, Targeting, & Positioning
- Content Creation (Including Trending Content)
- Metrics & Key Performance Indicators
1. Marketing Mix
- Conduct market research.
- Define your goals.
- Identify your target audience and create buyer personas.
- Conduct competitive analysis.
- Develop key messaging.
- Choose your marketing channels.
- Create, track, and analyze KPIs.
- Present your marketing strategy.
1. Conduct market research.
Before you can begin creating your marketing strategy, you need to gather useful data for making informed decisions. Market research is like playing detective, but instead of solving crimes, you’re uncovering juicy details about your customers.
Market research will help your businesses make data-driven decisions for your marketing strategy. It also makes it easier to understand your target market, find gaps, and make the most of your resources.
This process is essential for understanding your customers and adapting to changing trends. If you’re new to this process, this complete market research guide and template can help.
Once you have the data you need, you’ll be ready to set some marketing goals.
2. Define your goals.
What do you want to achieve through your marketing efforts?
Whether it’s increasing brand awareness, driving sales, or diversifying your customer base, well-defined goals will guide your marketing strategy.
Your marketing strategy goals should reflect your business goals. They should also offer clear direction for marketing efforts.
For example, say one of your business goals is to increase market share by 20% within a year. Your goal as a marketer could include expanding into new target markets, updating your brand, or driving customer acquisition.
Other marketing goals might be to increase brand awareness or generate high-quality leads. You might also want to grow or maintain thought leadership in your industry or increase customer value.
Defining clear goals provides direction and clarity, guiding marketing efforts toward desired outcomes. It helps with resource allocation, decision-making, and measuring the success of marketing initiatives.
This SMART goal guide can help you with more effective goal-setting.
3. Identify your target audience and create buyer personas.
To create an effective marketing strategy, you need to understand who your ideal customers are. Take a look at your market research to understand your target audience and market landscape. Accurate customer data is especially important for this step.
But it’s not enough to know who your audience is. Once you’ve figured out who they are, you need to understand what they want. This isn’t just their needs and pain points. It’s how your product or service can solve their problems.
So, if you can’t define who your audience is in one sentence, now’s your chance to do it. Create a buyer persona that’s a snapshot of your ideal customer.
For example, a store like Macy’s could define a buyer persona as Budgeting Belinda, a stylish working-class woman in her 30s living in a suburb, looking to fill her closet with designer deals at low prices.
With this description, Macy’s Marketing department can picture Budgeting Belinda and work with a clear definition in mind.
Buyer personas have critical demographic and psychographic information, including age, job title, income, location, interests, and challenges. Notice how Belinda has all those attributes in her description.
For B2B SaaS companies, keep in mind that buyer personas don’t apply solely to the end user. When you’re selling a product to another business, you also have to address the decision-maker, the financial buyer, and the technical advisor, among other roles, says Head of Marketing at Entrapeer, Hillary Lyons .
“You need to be able to tailor your message to each of these unique personas even though most of them will never actually use the product,” says Lyons. “You have to sell each of them on the unparalleled benefit you provide without muddling your [overall] message.”
You don’t have to create your buyer persona with a pen and paper. In fact, HubSpot offers a free template you can use to make your own (and it’s really fun).
You can also use a platform like Versium , which helps you identify, understand, and reach your target audience through data and artificial intelligence.
Buyer personas should be at the core of your strategy.
4. Conduct competitive analysis.
Now that you have an understanding of your customers, it’s time to see who you’re competing with to get their attention.
To begin your competitive analysis, start with your top competitors. Reviewing their websites, content, ads, and pricing can help you understand how to differentiate your brand. It’s also a useful way to find opportunities for growth.
But how do you know which competitors are most important? This competitive analysis kit with templates will walk you through the process. It will help you choose and evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, and strategies of your competitors.
This process will help you find market gaps, spot trends, and figure out which marketing tactics will be most effective. Competitive analysis can also offer valuable insights into pricing, positioning, and marketing channels.
5. Develop key messaging.
You’ve figured out who you’re talking to, what they’ve already heard, and what they want to hear. Now, it’s time to share your brand’s unique value proposition .
In this step, you’ll craft key messaging that shows the benefits of your product or service and resonates with your target audience. This process should show off the research and work you have done up to this point. It should also incorporate your creativity, inventiveness, and willingness to experiment.
Well-crafted key messaging:
- Sets businesses apart from the competition.
- Resonates with the target audience.
- Is flexible enough to be consistent across all marketing channels.
- Builds brand credibility.
- Creates an emotional connection with customers.
- Influences buying decisions.
The key messaging in your marketing strategy is critical to driving engagement, loyalty, and business growth. These value proposition templates can help if you’re not sure how to draft this important messaging.
6. Choose your marketing channels.
You know what you have to say. Now, decide on the best marketing channels for your message. Your top goal for this stage of your strategy is to align your channel choices with your target persona’s media consumption habits.
Start with media channels you’re already using. Then, consider a mix of traditional and digital channels such as social media, TV, email marketing, podcast ads, SEO, content marketing, and influencer partnerships.
To streamline this process, think of your assets in three categories — paid, owned, and earned media.
To decide which marketing channels are best for your marketing strategy, look carefully at each channel. Think about which channels are best for reaching your audience, staying within budget, and meeting your goals.
For example, a business targeting a younger demographic might consider using TikTok or Reddit to reach its audience.
Don’t forget to take a look at emerging platforms and trends as you complete this review. You may also want to look at the content you’ve already created. Gather your materials in each media type in one location. Then, look at your content as a whole to get a clear vision of how you can integrate them into your strategy.
For example, say you already have a blog that’s rolling out weekly content in your niche (owned media). You might consider promoting your blog posts on Threads (owned media), which customers might then repost (earned media). Ultimately, that will help you create a better, more well-rounded marketing strategy.
If you have resources that don’t fit into your goals, nix them. This is also a great time to clean house and find gaps in your materials.
7. Create, track, and analyze KPIs.
Once you have a clear outline of your marketing strategy, you’ll need to think about how you’ll measure whether it’s working.
At this stage, you’ll shift from marketing detective to numbers nerd. With a little planning and prep, your analytics can unveil the mysteries of marketing performance and unlock super insights.
Review your strategy and choose measurable KPIs to track the effectiveness of your strategy. Create a system that works for your team to collect and measure your data.
Then, plan to check and analyze the performance of your strategy over time. This can help you refine your approach based on results and feedback.
Lexi Boese , an ecommerce growth strategist and co-founder of The Digital Opportunists, recommends making data a priority when building your marketing strategy this year.
“The more data you can use, the easier you can track your success,” she says. “This could be as simple as understanding which channels convert the highest amount of customers (to determine how your team should prioritize ad spend), or assessing whether you have a higher amount of first-time or returning customers to [determine] if you should focus on internal or external marketing.”
Analyzing KPIs helps businesses stay agile, refine their strategies, and adapt to evolving customer needs.
8. Present your marketing strategy.
A finished marketing strategy will pull together the sections and components above. It may also include:
Executive Summary
A concise overview that outlines the marketing goals, target audience, and key marketing tactics.
Brand Identity
You may want to create a brand identity as part of your strategy. Brand positioning, voice, and visual identity may also be helpful additions to your marketing strategy.
Marketing Plan and Tactics
Your marketing plan is the specific actions you’ll take to achieve the goals in your marketing strategy. Your plan may cover campaigns, channel-specific tactics, and more.
Not sure where to start? This free marketing plan template can help.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Demystifying Marketing's 6 Biggest Mixed Messages of 2024 with Jasper's Head of Enterprise Marketing

The Ultimate Guide to Marketing Strategies & How to Improve Your Digital Presence

9 Pivotal Marketing Trends to Watch in 2024, According to Experts

Diving Deep Into Marketing in Construction (My Takeaways)
![what is the business plan in marketing 11 Recommendations for Marketers in 2024 [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Marketing%20Recommendations.png)
11 Recommendations for Marketers in 2024 [New Data]
![what is the business plan in marketing The Top 5 B2C Marketing Trends of 2024 [New HubSpot Blog Data + Expert Insights]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/top%20b2c%20marketing%20trends.png)
The Top 5 B2C Marketing Trends of 2024 [New HubSpot Blog Data + Expert Insights]
![what is the business plan in marketing 5 Marketing Trends That Might Not Survive in 2024 [HubSpot Research + Expert Insights]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing%20trends%20that%20might%20not%20survive%202024.png)
5 Marketing Trends That Might Not Survive in 2024 [HubSpot Research + Expert Insights]
Everything You Need to Know About Webinar Marketing

7 Marketing Questions Teams are Asking in 2024 (+Data & Insights)

50 Small Business Marketing Ideas for 2024
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

- Case Studies
- Flexible Products

- Expert Insights
- Research Studies

- Creativity and Culture
- Management and Leadership
- Business Solutions
- Member Spotlight
- Employee Spotlight
What is a marketing plan and why is it important?
Before you spend a cent on marketing, you first have to understand the market and your customers.

Companies of all sizes have one thing in common: They all began as small businesses. Starting small is the corner for those just getting off the ground. Learn about how to make that first hire, deal with all things administrative, and set yourself up for success.
A marketing plan is a blueprint for launching new products, understanding the intricacies of your market, growing your audience, and promoting your company to customers who want what you’re selling.
With a well-designed marketing plan, you can design more effective promotions and impactful campaigns, reach your customers with targeted advertising, and track your business success with analytics. Without one, you might as well throw your marketing budget down a well and hope for the best.
If you’ve been tasked with creating a marketing plan for your company, there are some basic elements to keep in mind. Though every marketing plan will reflect the specific business and industry it’s been created for, most share a few common features and can be boiled down to just one or two simple objectives. In this article, we’ll outline some of the basic elements of a marketing plan and how to write one.
When you’re ready to put the plan into action, WeWork All Access and WeWork On Demand are there to support you with hundreds of dedicated workspaces around the world, so you can seamlessly collaborate on marketing strategy in a professional and stylish office space.
What is a marketing plan?
A marketing plan is a document outlining a company’s future marketing efforts and goals. It can be as short as a single page or made up of many smaller campaign plans from different marketing teams.
However large and complex those plans are, the idea remains the same: A marketing plan is created to organize, execute, and eventually measure the success of a business’s marketing strategy .
Types of marketing plans
Marketing plans come in as many different shapes and sizes as there are different kinds of business, but they can be broadly placed into one (or more) of a few different categories. Here are some of the most common you’ll encounter.
- Annual marketing plans. These types of marketing plans arrange campaigns according to when they’re expected to launch, rather than the content of the campaigns themselves. It’s a useful way to get an overview of a marketing strategy for the upcoming year, and to measure success continuously as time passes.
- Content marketing plans. This is a more content-focused way of approaching a marketing strategy, and highlights the specific channels and audiences you want to reach. Content marketing plans can look very similar to annual marketing plans, but are less concerned with the “when” and more with the “what” and the “how.”
- Product launch plans. Launching a new product or service requires a specific kind of marketing plan. The main goal is to successfully introduce the new product to the market. But these plans also include the strategies, tactics, and content needed in the buildup to the launch itself.
- Social media marketing plans. Social media channels are such a vital part of a company’s marketing goals that it’s often wise to create a separate social media marketing plan dedicated to creating advertising and promotional content on these platforms.
What is the purpose of a marketing plan?
A marketing plan lays out your business strategy for acquiring new customers and selling more products and services. But it also serves as a way of analyzing exactly how successful your marketing efforts have been so far. Knowing this information helps steer ongoing campaigns in the right direction, aligns your marketing with your company’s values, and ensures that future campaigns are better targeted and more effective.
To understand why a marketing plan is important, just consider what would happen without one. Your advertising budget would be spent based entirely on guesswork about where your potential customers can be found and what they’re looking for. You’d have no idea which of your campaigns contributed to increased sales figures. And you’d have no baselines from which to build more effective campaigns in the future.
How to create a marketing plan
Elements of a marketing plan.
The basic building blocks of any good marketing plan are focused on objectives, research, competitors, and content. These objectives should be clearly defined and easily measurable goals —ideally no more than two or three—and informed by as much consumer research as you can reasonably gather.
Whether your goal is increasing your Instagram followers, driving traffic to your site, or attracting more cheese fans to your cheese store, set a specific target by which to monitor the performance of any campaign. As you develop your marketing plan and learn what’s effective and what’s not, you can set more accurate targets and begin to hone in on the strategies that really work for your company.
A marketing plan should also describe your brand’s biggest competitors and the campaigns they’re running, as well as identify any openings in the market that would allow your company to grab market share. This is where SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis comes into its own, enabling a company to shape its marketing plan around its own strengths and weaknesses.
Lastly, a marketing plan should outline the content of each campaign. Will your pre-roll video content use animation or live actors? Can you offer discounts and voucher codes to new customers? Will you leverage your mailing list to notify existing customers of a new product launch?
Define a marketing plan strategy
If your marketing plan is a roadmap, then your marketing strategy is the road. The strategy describes which tools you’ll use to hit the targets laid out by the main marketing plan document, and how they’ll be applied.
Here’s where you get down to the fundamentals of selling. Depending on who you ask, there are as many as seven P’s of marketing, though most agree on four core elements: price, product, place, and promotion.
What are you selling? How much are you charging? Where will your customers see it? And how will you promote it to them? Marketing gurus will promise you that if you can answer all of these questions correctly, you’ll be guaranteed boundless success.
Of course, in the real world it’s not quite so straightforward. But the four main P’s are an ideal starting point for anyone creating a market plan from scratch.
How to measure the success of a marketing plan
An enormous amount of effort and investment is poured into monitoring the effectiveness of advertising campaigns, but at some level, consumer behavior becomes what’s known as a black box. You can measure what goes into it and what comes out the other end, but what happens inside the mind of a consumer can ultimately only be guessed at based on outcomes. Even the shoppers themselves can’t reliably report on why they choose certain products over others.
That’s why tracking a marketing plan’s performance alongside more specific KPIs (key performance indicators) is crucial. Advertising spend and sales figures aren’t linked in a simple or obvious way, so measuring success on a more granular level—such as increasing conversions or returning customers—helps create a much clearer picture of how well your marketing plan is doing.
Related articles

Final thoughts on creating a marketing plan
Marketing plans need to be squarely outlined and adhered to, but they shouldn’t be set in stone. You need to be able to course-correct when something isn’t landing, or lean more into campaigns when they’re working well.
Quick aside: This is particularly true when it comes to the content of social media marketing plans, which are truly effective only when they’re timely and topical. Memes are a perfect example of this: How often have you seen a promoted tweet deploy some forgotten joke from months ago, presumably because it had been left in somebody’s annual marketing plan?
But while it’s useful to have a flexible approach , it’s important that your marketing plan is resilient and doesn’t flip-flop or bounce wildly between ideas. Move the goalposts too much and your plan will quickly fall apart, leaving your campaign in chaos. Allow your strategies some time to settle in, and even if you don’t reach success, you will gain invaluable performance data for future projects.
Steve Hogarty is a writer and journalist based in London. He is the travel editor of City AM newspaper and the deputy editor of City AM Magazine , where his work focuses on technology, travel, and entertainment.
Rethinking your workspace?

Tom Hewitson, Chief AI Officer at leading AI training company General Purpose , offers tips for small businesses

Learn the differences between Class A, Class B, and Class C buildings based on their visual appeal, location, and amenities to see which of them best suits your business.

Short-term leases can offer startups and established companies some much-needed flexibility
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Business Plan vs. Marketing Plan
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on March 3, 2023 Updated on December 11, 2023

Starting a business usually requires both a business plan and a marketing plan. The first has many components, including a marketing section, and covers all facets of the business. The second is essentially an expanded and more detailed version of the marketing section of your business plan.
Both are dynamic documents that will change over time as you learn more about your business. This guide lays out all the details of what goes into a business plan and what is in a marketing plan.
- Business Plan Components
A business plan has eight essential components .
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary opens your business plan, but it’s the section you’ll write last . It summarizes the key points and highlights the most important aspects of your plan. Often investors and lenders will only read the executive summary; if it doesn’t capture their interest they’ll stop reading, so it’s important to make it as compelling as possible.
The components should include:
- The business opportunity – what problem are you solving in the market?
- Your idea, meaning the product or service you’re planning to offer, and why it solves the problem in the market better than other solutions.
- The history of the business so far – what have you done to this point? When you’re just getting started, this may be nothing more than coming up with the idea, choosing a business name , and forming a business entity.
- A summary of the industry, market size, your target customers, and the competition.
- A strong statement about how your company is going to stand out in the market – what will be your competitive advantage?
- A list of specific goals that you plan to achieve in the short term, such as developing your product, launching a marketing campaign, or hiring a key person.
- A summary of your financial plan including cost and sales projections and a break-even analysis.
- A summary of your management team, their roles, and the relevant experience that they have to serve in those roles.
- Your “ask”, if applicable, meaning what you’re requesting from the investor or lender. You’ll include the amount you’d like and how it will be spent, such as “We are seeking $50,000 in seed funding to develop our beta product”.
Remember that if you’re seeking capital, the executive summary could make or break your venture. Take your time and make sure it illustrates how your business is unique in the market and why you’ll succeed.
The executive summary should be no more than two pages long, so it’s important to capture the reader’s interest from the start.
2. Company Description/Overview
In this section, you’ll detail your full company history, such as how you came up with the idea for your business and any milestones or achievements.
You’ll also include your mission and vision statements. A mission statement explains what you’d like your business to achieve, its driving force, while a vision statement lays out your long-term plan in terms of growth.
A mission statement might be “Our company aims to make life easier for business owners with intuitive payroll software”, while a vision statement could be “Our objective is to become the go-to comprehensive HR software provider for companies around the globe.”
In this section, you’ll want to list your objectives – specific short-term goals. Examples might include “complete initial product development by ‘date’” or “hire two qualified sales people” or “launch the first version of the product”.
It’s best to divide this section into subsections – company history, mission and vision, and objectives.
3. Products or Services Offered
Here you’ll go into detail about what you’re offering, how it solves a problem in the market, and how it’s unique. Don’t be afraid to share information that is proprietary – investors and lenders are not out to steal your ideas.
Also specify how your product is developed or sourced. Are you manufacturing it or does it require technical development? Are you purchasing a product from a manufacturer or wholesaler?
You’ll also want to specify how you’ll sell your product or service. Will it be a subscription service or a one-time purchase? What is your target pricing? On what channels do you plan to sell your product or service, such as online or by direct sales in a store?
Basically, you’re describing what you’re going to sell and how you’ll make money.
4. Market Analysis
The market analysis is where you’re going to spend most of your time because it involves a lot of research. You should divide it into four sections.
Industry analysis
Research and describe exactly what’s happening in your industry, such as growth rate, market size, and current trends. Where is the industry predicted to be in 10 years? Provide links to your sources.
Detail your company’s place in the market. Will your product fit a certain niche? Is there a sub-industry your company will fit into? How will you keep up with industry changes?
Competitor analysis
Now you’ll dig into your competition. Detail your main competitors and how they differentiate themselves in the market. For example, one competitor may advertise convenience while another touts superior quality. Also highlight your competitors’ weaknesses.
Next, explain how you’ll stand out. Detail your competitive advantages and how you’ll sustain them. This section is extremely important and will be a focus for investors and lenders.
Target market analysis
Here you’ll describe your target market and whether it’s different from your competitors’. For example, maybe you have a younger demographic in mind?
You’ll need to know more about your target market than demographics, though. You’ll want to explain the needs and wants of your ideal customers, how your offering solves their problem, and why they will choose your company.
You should also lay out where you’ll find them, where to place your marketing and where to sell your products. Learning this kind of detail requires going to the source – your potential customers. You can do online surveys or even in-person focus groups.
Your goal will be to uncover as much about these people as possible. When you start selling, you’ll want to keep learning about your customers. You may end up selling to a different target market than you originally thought, which could lead to a marketing shift.
SWOT analysis
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and it’s one of the more common and helpful business planning tools.
First describe all the specific strengths of your company, such as the quality of your product or some unique feature, such as the experience of your management team. Talk about the elements that will make your company successful.
Next, acknowledge and explore possible weaknesses. You can’t say “none”, because no company is perfect, especially at the start. Maybe you lack funds or face a massive competitor. Whatever it is, detail how you will surmount this hurdle.
Next, talk about the opportunities your company has in the market. Perhaps you’re going to target an underserved segment, or have a technology plan that will help you surge past the competition.
Finally, examine potential threats. It could be a competitor that might try to replicate your product or rapidly advancing technology in your industry. Again, discuss your plans to handle such threats if they come to pass.
5. Marketing and Sales Strategies
Now it’s time to explain how you’re going to find potential customers and convert them into paying customers.
Marketing and advertising plan
When you did your target market analysis, you should have learned a lot about your potential customers, including where to find them. This should help you determine where to advertise.
Maybe you found that your target customers favor TikTok over Instagram and decided to spend more marketing dollars on TikTok. Detail all the marketing channels you plan to use and why.
Your target market analysis should also have given you information about what kind of message will resonate with your target customers. You should understand their needs and wants and how your product solves their problem, then convey that in your marketing.
Start by creating a value proposition, which should be no more than two sentences long and answer the following questions:
- What are you offering
- Whose problem does it solve
- What problem does it solve
- What benefits does it provide
- How is it better than competitor products
An example might be “Payroll software that will handle all the payroll needs of small business owners, making life easier for less.”
Whatever your value proposition, it should be at the heart of all of your marketing.
Sales strategy and tactics
Your sales strategy is a vision to persuade customers to buy, including where you’ll sell and how. For example, you may plan to sell only on your own website, or you may sell from both a physical location and online.
On the other hand, you may have a sales team that will make direct sales calls to potential customers, which is more common in business-to-business sales. Sales tactics are more about how you’re going to get them to buy after they reach your sales channel.
Even when selling online, you need something on your site that’s going to get them to go from a site visitor to a paying customer. By the same token, if you’re going to have a sales team making direct sales, what message are they going to deliver that will entice a sale?
It’s best for sales tactics to focus on the customer’s pain point and what value you’re bringing to the table, rather than being aggressively promotional about the greatness of your product.
Pricing strategy
Pricing is not an exact science and should depend on several factors. First, consider how you want your product or service to be perceived in the market. If your differentiator is to be the lowest price, position your company as the “discount” option.
Think Walmart, and price your products lower than the competition. If, on the other hand, you want to be the Mercedes of the market, then you’ll position your product as the luxury option.
Of course you’ll have to back this up with superior quality, but being the luxury option allows you to command higher prices. You can, of course, fall somewhere in the middle, but the point is that pricing is a matter of perception.
How you position your product in the market compared to the competition is a big factor in determining your price. Of course, you’ll have to consider your costs, as well as competitor prices. Obviously, your prices must cover your costs and allow you to make a good profit.
Whatever pricing strategy you choose, you’ll justify it in this section of your plan.
6. Operations and Management
This section is the real nuts and bolts of your business – how it operates on a day-to-day basis and who is operating it. Again, this section should be divided into subsections.
Operational plan
Your plan of operations should be specific , detailed and mainly logistical. Who will be doing what on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis? How will the business be managed and how will quality be assured? Be sure to detail your suppliers and how and when you’ll order raw materials.
This should also include the roles that will be filled and the various processes that will be part of everyday business operations. Just consider all the critical functions that must be handled for your business to be able to operate on an ongoing basis.
Technology plan
If your product involves technical development, you’ll describe your tech development plan with specific goals and milestones. The plan will also include how many people will be working on this development, and what needs to be done for goals to be met.
If your company is not a technology company, you’ll describe what technologies you plan to use to run your business or make your business more efficient. It could be process automation software, payroll software, or just laptops and tablets for your staff.
Management and organizational structure
Now you’ll describe who’s running the show. It may be just you when you’re starting out, so you’ll detail what your role will be and summarize your background. You’ll also go into detail about any managers that you plan to hire and when that will occur.
Essentially, you’re explaining your management structure and detailing why your strategy will enable smooth and efficient operations.
Ideally, at some point, you’ll have an organizational structure that is a hierarchy of your staff. Describe what you envision your organizational structure to be.
Personnel plan
Detail who you’ve hired or plan to hire and for which roles. For example, you might have a developer, two sales people, and one customer service representative.
Describe each role and what qualifications are needed to perform those roles.
7. Financial Plan
Now, you’ll enter the dreaded world of finance. Many entrepreneurs struggle with this part, so you might want to engage a financial professional to help. A financial plan has five key elements.
Startup Costs
Detail in a spreadsheet every cost you’ll incur before you open your doors. This should determine how much capital you’ll need to launch your business.
Financial projections
Creating financial projections, like many facets of business, is not an exact science. If your company has no history, financial projections can only be an educated guess.
First, come up with realistic sales projections. How much do you expect to sell each month? Lay out at least three years of sales projections, detailing monthly sales growth for the first year, then annually thereafter.
Calculate your monthly costs, keeping in mind that some costs will grow along with sales. Once you have your numbers projected and calculated, use them to create these three key financial statements:
- Profit and Loss Statement , also known as an income statement. This shows projected revenue and lists all costs, which are then deducted to show net profit or loss.
- Cash Flow Statement. This shows how much cash you have on hand at any given time. It will have a starting balance, projections of cash coming in, and cash going out, which will be used to calculate cash on hand at the end of the reporting period.
- Balance Sheet. This shows the net worth of the business, which is the assets of the business minus debts. Assets include equipment, cash, accounts receivables, inventory, and more. Debts include outstanding loan balances and accounts payable.
You’ll need monthly projected versions of each statement for the first year, then annual projections for the following two years.
Break-even analysis
The break-even point for your business is when costs and revenue are equal. Most startups operate at a loss for a period of time before they break even and start to make a profit. Your break-even analysis will project when your break-even point will occur, and will be informed by your profit and loss statement.
Funding requirements and sources
Lay out the funding you’ll need, when, and where you’ll get it. You’ll also explain what those funds will be used for at various points. If you’re in a high-growth industry that can attract investors, you’ll likely need various rounds of funding to launch and grow.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
KPIs measure your company’s performance and can determine success. Many entrepreneurs only focus on the bottom line, but measuring specific KPIs helps find areas of improvement. Every business has certain crucial metrics.
If you sell only online, one of your key metrics might be your visitor conversion rate. You might do an analysis to learn why just one out of ten site visitors makes a purchase. Perhaps the purchase process is too complicated or your product descriptions are vague.
Learning why your conversion rate is low gives you a chance to improve it and boost sales.
8. Appendices
In the appendices you can attach documents such as manager resumes or other documents that support your business plan.
- Marketing Plan Components
A marketing plan, as mentioned above, is a more detailed version of the marketing strategy section of your business plan. It includes six components.
1. Marketing Objectives
Start by detailing your short-term marketing goals. This could be “Reach 10,000 monthly site visitors by next year’” or “Acquire 500 new customers by May”. Be sure to set clear and attainable goals so your marketing team understands its targets.
2. Target Market
You’ll want to document exactly who you’re trying to reach with your marketing. You should’ve already done a target market analysis for your business plan, and you’ll use it here.
What Problem Are You Solving?
Whatever your product or service, it needs to solve a problem in the market. So, ask yourself, what problem does my business solve? Next, consider who faces that problem.
A plumbing company, for instance, solves the problem of broken pipes. Who deals with that problem? Homeowners and property owners and managers.
Depending on your business, it may not be obvious who has the problem you’re solving. If it’s not clear, do more research. Either way, knowing who faces the problem you’re solving is just the beginning. You need to know much more about your target customers.
Research Your Market and Competition
Now, dig into your market with some online research. Do some Google and Bing searches about your target demographic, where they shop and live, what appeals to them and so on.
Next, check out your competition to see who they’re marketing to. It may help to study their marketing through the eyes of a consumer.
What need do they fill? Who would find their marketing appealing? Where do they advertise? If their ads appear on TikTok, they’re looking to attract a younger market.
This market research should give you a general profile of your target market – but that’s not enough.
Talk to Potential Customers
To learn more about your target market, go straight to the source. The best way to learn their needs and wants, why they’d buy your product and how they’ll use it, is to ask them via a phone or email survey.
If you’ve yet to make any sales, it’s probably best to post your survey online then promote it on social media by offering a small reward, such as a gift certificate. Just make sure you ask the right questions to get the information you’re looking for.
You can also hold in-person focus groups and offer your goods at a discount for participants.
Create Customer Profiles
Now it’s time to build detailed profiles of your target customers. You may have found that your product will appeal to more than one group of people. These are called customer segments, and all your segments together make up your target market.
Create descriptions of each group with all the information you’re learned. These profiles should include:
- Pain points: the problems they have that you’re solving
- Benefits your product provides
- Their interests: what do they care about?
- Buying patterns: where do they shop?
- Age, location, income level, other factual information
3. Value Proposition
Now you can use these profiles to craft a value proposition that will serve as the foundation of all your marketing. You may need to devise more than one value proposition to target different segments.
Your value propositions should be no more than two sentences long and answer the following questions:
- How is it better than competitors’ products
An example might be “Payroll software that handles all the payroll needs of small business owners, making life easier for less.”
Remember that you need to align your value proposition with the wishes of your target market.
4. Marketing Activities
Now you’ll layout the specific marketing activities that you plan to conduct. Your target market analysis should have told you where you’re most likely to find potential customers, so if you found out that your potential customers use TikTok, you can post and run ads there.
You’ll want to only perform the marketing activities that are most likely to reach your potential customers so that you’re not wasting marketing dollars. If getting found online is important to you, focus on search engine optimization (SEO) and social media ads.
Make the activities as specific as possible, such as “Run a TikTok ad promoting ____ for three months.”
5. Marketing Budget
Now, determine what these activities will cost and set a budget. When you go through this process, you may find that you need to adjust your marketing to stick to the budget you can afford.
Your marketing budget needs to align with your goals. If one of your goals is to obtain 500 new customers, which will generate $10,000 in revenue, you can’t spend more than that on marketing. You have to make sure you’re getting a good return on your investment, or at least breaking even.
Now you’ll determine your key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge the success of your marketing.
If you sell only online, one of your key marketing metrics might be your visitor conversion rate. You might do an analysis to learn why just one out of ten site visitors makes a purchase.
Perhaps the purchase process is too complicated or your product descriptions are vague. The point is, learning why your conversion rate is low gives you a chance to improve it and boost sales.
Similarly, if you’re not getting enough site visitors, you may need to revisit your SEO strategies.
A business plan outlines the overall mission, objectives, and strategies of a business, encompassing aspects like operations, finances, and organizational structure.
In contrast, a marketing plan focuses specifically on strategies and tactics to promote products or services, detailing target audiences, promotional methods, and market positioning.
While the business plan provides a comprehensive view of the entire business, the marketing plan hones in on attracting and retaining customers.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
- Mobile Forms
- INTEGRATIONS
- See 100+ integrations
- FEATURED INTEGRATIONS
- See more Integrations
- See more CRM Integrations

- See more Storage Integrations
- See more Payment Integrations

- See more Email Integrations
- Jotform Teams
- Enterprise Mobile
- Prefill Forms
- HIPAA Forms
- Secure Forms
- Assign Forms
- Online Payments
- See more features
- Multiple Users
- Admin Console
- White Labeling
- See more Enterprise Features
- Contact Sales
- Contact Support
- Help Center
- Jotform Books
- Jotform Academy
Get a dedicated support team with Jotform Enterprise.
Apply to Jotform Enterprise for a dedicated support team.
- Sign Up for Free

- Marketing Plan
Marketing plan vs business plan: What’s the difference?
For business owners, nonprofit directors, and community group leaders, the process of writing a business plan or creating a marketing plan can seem intimidating. They may know the ins and outs of what they do every day and have fantastic ideas on how to grow and market their organizations, but the act of putting it on paper often feels like stepping into a world with opaque rules and confusing jargon.
Fortunately, the reality of both business and marketing plans is that they aren’t nearly as complicated as many people think. In fact, most business owners have written both without realizing it, even if only in an informal manner.
Creating a formal business or marketing plan uses a lot of the same steps business owners already take when sketching out new marketing ideas on a napkin or doing some quick back-of-the-envelope math to figure out how to expand into a new city.
But before moving forward with the process, it’s important to know which one you need. In other words, what’s the difference between a marketing plan and a business plan?
Create a marketing plan that works for your business with Jotform’s easy-to-use marketing form templates .
The biggest difference between a business plan and a marketing plan is the scope of what they cover. While both documents can be quite lengthy and thorough, they don’t address the exact same information.
A business plan is typically a much broader document that covers every aspect of your business: operations, supply chains, human resources, materials costs, and — yes — marketing. In fact, a marketing plan will usually be a section of a business plan.
Marketing plans tend to focus much more narrowly on the specifics of making customers aware of and likely to buy a product or service. A marketing plan may touch on some of the same things a business plan does, like the cost of goods sold, but only as they relate to being able to sell those goods to consumers.
Another key difference between the two is how far into the future they look. Business plans, for example, tend to cover a much longer period than marketing plans. A typical window for a business plan, for example, is about five years. A typical window for a marketing plan, on the other hand, will be a year to three years.
The two are updated differently as well. Business plans rarely need to be replaced or updated unless there’s a significant change in the business — a completely new product category, a new business model, or some global event that changes the way a company performs its core function.
Marketing plans are often updated every year. They tend to be part of the yearly budgeting activities that help business owners plan how they will allocate resources to various departments.
This makes sense when you think about it. Companies change their marketing much more often than they change their business model.
The reasons for creating a marketing plan and a business plan are often similar but not identical. Most often, business owners create both to secure financing. Banks and investors frequently ask for business and marketing plans before agreeing to loan money or invest in the company.
But external demands aren’t the only or even the most important reasons to write both kinds of plans. A business plan is a great way to formalize the ideas behind how and why a company works the way it does. It’s a fantastic way for business owners to put down on paper many of the things they’ve been intuitively doing, and cement processes and procedures for running a company.
Business plans are also great at helping you to prepare for future needs. By going through the exercise of writing a full business plan, business owners get an idea of where they are and what kinds of initiatives and resources they need to meet their goals.
Marketing plans are also incredibly useful internally. As we mentioned above, they are an important part of the annual budgeting process. Sitting down and thinking through all of the marketing needs can help both validate a company’s marketing initiatives as well as determine the ideal amount of money to allocate toward marketing.
The bottom line
A marketing plan is a part of a business plan. That’s the easiest way to remember the difference between the two. The business plan shapes everything about the way a company works, and lays out big-picture goals and ideas.
The marketing plan paints a more detailed picture of how the company will use marketing to achieve the goals laid out in the business plan. The marketing plan is department level and has to coexist with plans for other departments — HR, operations, legal and regulatory, and others.
Both plans are important in successfully running a company, but the business plan is more important because it will at least outline some marketing initiatives. For business owners who only have time to create one, the business plan is the logical choice.
Thank you for helping improve the Jotform Blog. 🎉
RECOMMENDED ARTICLES

How to Create a Marketing Plan

5 templates to use in your marketing planning

9 ways marketing departments use Jotform

How to offer a free consultation

Marketing during the maturity stage of your business

How to find brand ambassadors

Marketing Manager Mindset 2023 Survey Results

Tips for hiring a brand ambassador

Webinar: Defining your marketing event and promotion strategy
Implementing cross-channel marketing in your business

How marketing evolves with the stages of your business

How to speed up your sales during Black Friday 2023

5 marketing strategies to launch your startup

How to build a brand on social media

Brand ambassador interview questions

How to track marketing campaigns

How to optimize your Black Friday discount campaigns with Jotform

How to create a marketing budget

How to write a creative brief

How to define your target audience

5 tips for creating a brand ambassador marketing strategy

How to create a marketing plan timeline

How to create Black Friday sale forms with Jotform

How to create the right marketing goals for your business

How to market during the growth stage of your business
Send Comment :

1 Comments:
122 days ago
dear as far as i read your passage about marketing and business plan i would like to request that you send me some samples of business and marketing plan in FMCG scope thank you
Filter by Keywords
Crafting an Effective Marketing Plan: Steps, Examples, and Templates
Sudarshan Somanathan
Head of Content
May 14, 2024
You’d have heard people say, “our product speaks for itself, we don’t need marketing.” Boy, are they mistaken!
The reason is simple: Marketing directly and indirectly brings sales. It is a powerful growth engine.
For this very reason, business leaders spend significant time and energy creating and implementing marketing strategies and plans. In this blog post, we get into the weeds of it.
What is a Marketing Plan?
1. content marketing plan, 2. social media marketing plan, 3. new product launch marketing plan, 4. digital marketing plan, 5. growth marketing plan, barriers to successful marketing plan implementation, step 1: use your market research, step 2: see what your competitors are doing, step 3: set your marketing goals and targets, step 4: design your marketing campaigns/projects, step 5: set up your marketing project, step 6: collaborate in real-time, step 7: implement and monitor with analytics, 1. what are the 7 parts of a marketing plan, 2. what are the 7 steps of marketing plan, 3. what are the 10 essential elements in a marketing plan.
A marketing plan is the collection of activities that an organization intends to undertake during a specific period to achieve its objectives. Some of the defining characteristics of a marketing plan are:
- Derived from your company’s marketing strategy : Plan is the actionable part of the strategy
- Goal-oriented : Marketing plans are designed to achieve goals such as lead generation, customer acquisition, brand awareness, etc.
- Medium to long term : A marketing plan is generally made for a period of 12-18 months
- Comprehensive : A marketing plan includes goals, budgets, channels, activities, campaigns, resources, and more
More importantly, a marketing plan acts as a roadmap for creating, executing, monitoring, and evaluating tactics and activities.
Types of Marketing Plans
Marketing plans can be of various types. You can make marketing plans for a brand, a product, a channel, a specific campaign, or an offer. Some of the most common types of marketing plans are as follows.
A content marketing plan is the blueprint that guides the creation, publication, and management of content to attract and engage the right audience. A good content marketing plan is:
Creative : Collaborating with designers, videographers, animators, subject matter experts, etc., to create differentiating content.
Multimedia : Combining text with images, infographics, videos, podcasts, and more!
Scheduled : On a content calendar to make sure that you publish and distribute content regularly.
Distribution-driven : With details on the platform, frequency, style, and schedule on which the content will be distributed.
Content marketing metrics
Some of the commonly used metrics are:
- Readership: No. of visitors to the content piece
- Engagement: Time spent reading an article or watching a video
- Advocacy: No. of shares or comments
- Conversion: No. of signups or subscriptions after reading content
Unlike content, which is an asset, social media is a collection of channels, such as Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, and TikTok. A good social media marketing plan is:
Channel-specific : Designing content in a way that suits the platform. For instance, pithy text for Twitter and short vertical videos for TikTok.
Customer-centricity : Choosing the right channels based on the target customer.
Engagement tactics : Defining the expected action from the customer such as likes/comments/link clicks.
Social media marketing metrics
Commonly used metrics are:
- Responses or replies to posts
- Inquiries in form fills or direct private messages
- Likes and shares
- Followers and network reach
A product launch can be a game-changer for business. To make it happen, a product launch marketing plan needs to be extraordinary. Here’s what that might entail.
What’s new : Outlining the new product, its positioning, and differentiation
Why buy : Including a strong reason why they should buy your product now
How : Tactics, such as press releases, newspaper ads, email campaigns, social media blitz, etc.
Marketing efforts : Assets, channels, marketing budget, and resources you’re using for the activity
Commonly used product launch marketing metrics are:
- Reach: No. of live streams or total number of impressions
- Buzz: No. of shares, comments, re-tweets, and other social messages about the launch
- Sentiment analysis: Ratio of positive messages to negative/neutral
A comprehensive digital marketing plan consists of activities for:
- Search engine optimization
- Search engine advertising
- Content marketing
- Social media marketing
- Email marketing
- Virtual events and sponsorships
A digital marketing plan serves as a guideline for the team to expand their activities across channels. In addition, it also outlines:
Targeting : Specific groups of people based on demographics, interests, and behaviors
Personalization : Messages designed to be most relevant to the target audience
Remarketing : Customize and retarget customers effectively
Interactivity : Interactive quizzes, games, puzzles, etc., to engage the customer
Adaptability : Adapting to market trends, consumer feedback, or the evolving digital landscape, publishing your new campaigns in an agile and incremental manner
Digital marketing metrics
Some of the most commonly used metrics are:
- Revenue generated from digital channels
- Leads generated from digital channels
- Offline leads accelerated by digital channels
- Market reach in the form of social media reach, search impressions, or website visits
In the world of SaaS, growth marketing is a full-funnel approach where teams take responsibility for the customer journey from acquisition to retention, using data-driven and experimental approaches to optimize performance and scalability.
A good growth marketing plan is characterized by the following.
- Data-driven approach
- Continuous experimentation
- Focus on the entire lifecycle
- Community building
- Nifty use of resources
As beneficial as it is, a marketing plan is not easy to create or implement. If you’re in a marketing team, here are the barriers you might encounter.
While creating or implementing a marketing plan, a million things could go wrong. In the interest of time, we outline a handful here.
Firstly, let’s explore external factors that are barriers to successful marketing plan implementation.
The market has changed : Markets go through ups and downs every few years. Recently, markets are slowing down and customers are choosing to spend only on necessities. Even what one defines as a necessity might change, if the economy doesn’t improve.
A marketing plan that does not address these changes is bound to fail. For instance, if you’re positioning a luxury handbag as a fashion statement, you might not get much traction. However, if you position it as an investment, you will likely attract more attention.
Customers have changed : This can be a number of situations. Your customers have grown older and no longer wear Crocs. They’ve become more aware and no longer prefer sugar-filled aerated drinks. They’ve paid off their student debt and can afford more expensive products. No marketing plan can make them buy stuff they’ve grown out of.
Technology has become advanced : Technology is evolving rapidly, with new products being launched every day. If your marketing plan depends on an older technology, it is bound to be ineffective.
Regulation is evolving : In the interest of the public, regulators continue to tighten compliance. For instance, in the tobacco industry, advertising regulations get stricter constantly. If you are an e-cigarette company with a detailed plan to market to teenagers, a change in regulation is going to put an end to that!
Not all your barriers are external. In fact, an organization’s ability to implement a successful campaign can be hindered by its own shortcomings as well. Here are some examples.
Your organization is resistant to change : Traditional mindsets and resistance to change limit the flexibility and responsiveness needed for successful implementation. This is especially true for experimental marketing tactics like TikTok.
Team dynamics : A successful marketing plan needs various teams to work together. For instance, a campaign that spans search, email marketing, and social media needs these teams to interact and build on each other in real time. Without that, you might be running into a failed marketing plan.
Resource limitations : Not having the resources you need can affect marketing outcomes. This could be the shortage of a campaign manager, social media budget, or the right analytics tool.
So, how to overcome these challenges and create an effective marketing plan? Let’s find out.
How to Create an Effective Marketing Plan
An effective marketing plan depends on a number of factors, like research, budgets, channels, and more. To take care of all of them effectively, you need a robust marketing planning process and a powerful project management tool like ClickUp for marketing teams .
Once you have the basics ready, here’s how you can go about creating an effective marketing plan.
By the time you get to the marketing plan stage, your organization and product teams are likely to have already conducted a lot of research about the product, target market, pricing, etc. Understand the insights and use them in your plan.
Use the demographics, interests, and behavioral data about prospects for targeted messaging.
Example
Let’s say you’re selling low-fat ice cream. Your target market is likely to be:
Demographics : 25-40 year old, urban, middle/upper class. Use this as the primary segmentation in your Facebook/Instagram ad campaigns.
Interest : Health and fitness-related influencers, athleisure brands, other low-fat food and beverages brands, etc. Narrow your targeting to those who have these interests.
Behavioral data : Likely to post pictures of food and exercise, participate in marathons, or belong to cycling/trekking groups. Focus on these behaviors to target further. If you are competing on price as your differentiation, A/B test offers and discounts.
ClickUp Docs is a great collaborative tool to document key insights from market research that would be meaningful to your marketing plan. You can also use ClickUp AI to summarize insights and make them easier to access/use.

ClickUp templates
Set yourself up for success with ClickUp’s Marketing Action Plan template . Use this marketing plan template to design your campaigns, track your progress, meet your deadlines, collaborate with your team, and achieve your goals all in one place.
If you’re thinking long-term, try ClickUp’s Marketing Roadmap templates , a set of ready-to-use toolkits for defining and integrating your goals with tasks.
If that’s too comprehensive for you, here are several other marketing plan templates for you to choose from.
While you obviously won’t copy their campaigns, you need to keep an eye out if you want to be differentiated. Analyze competitor campaigns as a team, and debate what’s great and what’s not.
It is at this stage that you brainstorm various marketing strategies and choose the one that’s right for you.
As a low-fat ice cream maker, your primary competition might be other low-fat ice cream makers. However, it’ll be prudent to think about the problem you’re solving and other solutions that customers are using. For instance, this could be anything from fruit salad to green tea.
Begin by making a list of everyone who might be a competitor. Use ClickUp Whiteboards to debate and brainstorm with remote teams. Conduct SWOT analysis, trace customer journeys, organize ideas and more.
Then, narrow down to your direct and indirect competitors. Study their marketing efforts to identify the market gaps.

For thorough research, try ClickUp’s market analysis template to carefully evaluate five types of competitors.
- Direct: They have the same products as you
- Indirect: Their products are different from what you offer but target the same market
- Potential: They aren’t in the market right now but may be in the future
- Future: They are like potential competitors but are likely to enter the market in the immediate future
- Replacement: They offer an alternative to your product
If you need something simpler, try the ClickUp campaign manager’s SWOT analysis template . Use this for your primary competitor’s campaigns to get a clear picture of where the gaps are.
At this stage, ClickUp’s go-to-market templates will be exceptionally useful.
ClickUp GTM strategy template : For task lists in various GTM stages, such as discovery, analysis, research, planning, implementation, and reporting.
ClickUp GTM strategy whiteboard template : For a visual and interactive way to brainstorm and plan marketing activities
Before you make any plans, crystallize your marketing objectives.
- Make them SMART goals
- Ensure your goals are published in an easily accessible place
- Track progress toward your goals
ClickUp Goals is designed to help you with all this and more. With ClickUp, you can consolidate all your goals, break them down into targets, set timelines, automatically track progress, and keep your teams motivated.

We’ve discussed some possible goals in the types of marketing plans section above. Apply that to your efforts. As a low-cost ice cream vendor, your marketing goals might be:
- Increase store foot-falls by 20 month-on-month
- Increase online orders by 40% month-on-month
- Generate $10,000 in sales from Labor Day social media campaign (measured as the number of coupons encashed)
- Increase returning customer order value by 25%
Whether you’re a solo marketer or part of a larger team, ClickUp’s Marketers Goal Setting template will help you stay on track and crush your marketing goals.
This is the most important step in your marketing plan, where you put all the ideas to paper (or ClickUp, of course).
A typical marketing plan will have the following.
Brand message : Your equivalent of ‘Just Do It’ or ‘The Happiest Place On Earth’
Campaign breakdown : The messaging and offers you’re going to advertise throughout the year. For low-fat icecream, this could be Sunday deals, 4th of July discounts, Christmas Specials, etc.
Channel breakdown : First identify all the channels you want to target, and then clarify which campaign goes to which channel.
For instance, you might launch a campaign on Instagram asking customers to gift 10% off by posting their customized referral code on Stories, which anyone can use for 24 hours. This won’t work for Twitter, so you need another plan.
Budgets : Allocate budgets for each campaign and channel. Focus on your best converting channels. Optimize regularly.
Of all the marketing plan templates, ClickUp Content Management template remains popular. Plan and create content across multiple channels—website, blog, social, and email.
Streamline the end-to-end workflow from request intake, to planning with docs, to maintaining an editorial calendar, to delivery of content.
Looking for something specific for each channel, no sweat. ClickUp’s free content calendar templates have everything you need.
A successful marketing plan needs a robust way to execute it. ClickUp’s project management for marketing teams has everything you need.
Use ClickUp tasks , sub-tasks, and folders to organize your activities. Assign users for each task contextually. For instance, assign your social media tasks to the copywriter, designer, and channel manager.
Use the Workload view and aggregate planning strategies for better resource management. See if you’re designer is overloaded with work and reallocate some of their load.
Use ClickUp Forms to capture information from internal or external stakeholders. For example, if your Times Square store has a unique idea, encourage them to fill a form and get their work done.
Connect tasks to goals and targets to automatically track progress. Use the ClickUp Calendar view to schedule marketing activities effectively. Turn on the timeline view to see if you have overlaps or dependencies.

A marketing plan has hundreds of activities going on at the same time. Managing this can become too chaotic too quickly. Prevent that with ClickUp’s real-time collaboration capabilities.
Chat with colleagues, exchange feedback on creatives, and ping team mates in real-time to get marketing done like clockwork.
You can collaborate with a number of users for a range of activities, such as:
- Placing orders with vendors for marketing assets, ads, etc.
- Discussing feedback and improvements on advertisement designs
- Interacting with social media influencers, responding to their comments/questions

For marketing output, such as design, copy, or campaigns to be effective, you need a clear brief. Yet, not everyone can write a good brief. So, we’ve brought help.
ClickUp’s creative brief templates allow you to write briefs in minutes for a number of use cases, including product briefs, SEO content briefs, design briefs, campaign briefs, and more. Each of the above is a free marketing plan template for you to download, customize, and implement to your needs.
You can’t call a campaign successful if you don’t track performance. Use ClickUp to track performance.
Set up KPIs : Key performance indicators (KPIs) like conversion rates, website traffic, customer engagement, and sales figures are essential in measuring the success of a marketing plan. Choose the ones that are relevant to you.
Listen to feedback : Collect and analyze customer feedback on your marketing campaigns. This can be through active ways such as surveys or focus groups or passive methods like social media listening.
Experiment : Data-driven marketing depends on experimenting with various permutations and combinations of messaging, design, channel, etc. So keep trying multiple versions of the same thing.

If you’re experimenting with your campaigns, ClickUp’s got the right foundation for you.
Whether your experiments are as simple as red CTA vs. blue CTA or something more targeted like offering discounts in price vs. freebies, monitor and track them with ClickUp’s A/B testing template .
Plan Like a Pro With ClickUp
The importance of a good marketing plan cannot be overstated. It impacts revenue, profitability, expenses, customer experience, market capitalization, shareholder value, and more.
To ensure that your marketing plan is effective, you need a versatile project management tool like ClickUp.
With ClickUp, you can break down your projects into manageable tasks/subtasks, create checklists to maintain quality standards, set goals and track progress, customize views, and plan with drag-and-drop capabilities.
Integrate effortlessly with your marketing tool stack or use ClickUp as the native CRM with powerful features.
Bolster your marketing strategy. Try ClickUp for free today.
FAQs About Marketing Plans
The four Ps marketing mix has been extended to accommodate more complex activities of the digital world. The 7Ps of marketing are product, price, place, promotion, people, packaging, and process.
- Product is what you offer (including services)
- Price is the perceived value of a product, the dollars your customers are willing to pay
- Place is the point of distribution
- Promotion is the messaging about your product
- People are all the entities your customers meet in their journey, including salespeople, vendors, partners, resellers, etc.
- Packaging refers to the brand design on the product
- Process refers to the workflows that contribute to the customer experience
The seven steps of the marketing plan are:
- Using your market research
- Conducting competition research
- Goal setting
- Designing marketing activities
- Setting up marketing projects
- Enabling collaboration
- Monitoring performance
To be comprehensive and effective, a marketing plan needs a few essential elements. Here are the top ten.
- Goals : What targets are you working towards?
- Target audience : What is the demographic, interest, and preference profile of your prospective customers?
- Messaging : What is the unified message you’re giving your customer?
- Channels : Where are you distributing your marketing messages?
- Assets : What assets like content, design, landing pages, etc. are you using?
- Budget : How much are you spending on marketing and how do you break that down?
- Timelines : How are your marketing campaigns scheduled to optimize outcomes?
- Teams : Who is responsible for what?
- Tools : What tools are you using, including the marketing planning software ?
- Reviews : How often do you review the performance of your marketing efforts?
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months

- Growth Marketing
- Content Strategy
- SEO Strategy
- Health Care
- Guide to Growth Marketing
- Guide to Digital PR
- SEO Strategy: The Ultimate Guide
- Website Content Strategy Guide

How To Create Marketing Plans for Small Businesses
Big businesses make big plans. They also create elaborate marketing schemes to put those plans into action.
It’s easy for SMB (small and medium business) owners and their teams to feel that a full-fledged marketing plan is out of their reach. While they may lack the resources to go toe to toe with larger competitors in the market, though, that makes the strategic planning and guidance of small business marketing efforts that much more valuable.
Let’s go over what it means to create marketing plans for small businesses, why having a small business marketing strategy is so important for success, and how your business can create its own master marketing plan.
What are Marketing Plans for Small Businesses?
A marketing plan, at its most fundamental level, is a series of steps that you can take to promote your brand and its products and services to consumers. In other words, a marketing plan isn’t your actual marketing activity. It’s the strategy or guidelines that you create to set those initiatives in motion.
In the context of marketing plans for small businesses, this could include anything from creating a website to crafting an email drip campaign, drafting a social media marketing campaign, building credibility through digital PR , and more. A small business marketing plan takes the limited resources of a small business and considers how that entity can effectively reach its target audience with its marketing.
Why are Marketing Plans for Small Businesses Important?
Grasping the goal of a marketing plan is the easy part. For a small business team with finite time and resources, justifying the investment in a marketing plan is where things can bog down.
It’s tempting to redirect your team’s efforts toward activities with more immediate or tangible results, such as sales or product development. When you take the time to invest in a genuine growth-oriented marketing plan , though, you can provide a long-term blueprint for growth that you simply can’t recreate through other areas of business activity.
The goal of a marketing plan is to create basic parameters, such as a schedule and marketing budget, that help you optimize your promotional resources. Developing the plan itself may require some extra investment, but the benefits are well worth it.
By planning ahead of time, you give yourself the opportunity to consider all of your marketing options. It also allows you to either establish or revisit key factors, such as your target audience, primary selling points, and your competition. From there, you can decide which marketing activities are the most cost-effective and beneficial for your brand, as well as the order in which you need to execute them.
For example, a marketing plan might reveal that paying for ongoing PPC (pay-per-click) ads is exorbitant and expensive over the long term. It also may reveal that the money saved from slashing your PPC ads in half allows you to invest in a content marketing strategy. From there, you can plot out the steps required to generate, optimize, and promote that content (see the next section) as an effective way to put your marketing in motion.
Small business marketing plans also allow you to gauge the ROI of your marketing investments over time. This gives you the ability to make adjustments and maximize results as you go along. It also frees you up to be more creative in your long-term approach to marketing by building on past successes that you otherwise might not have known about.
What Should You Include in Marketing Plans for Small Businesses?
If you’re sold on the concept of developing a marketing plan for your small business but aren’t quite sure where to start, you’ve come to the right place. In the following section, we’ll break
down a step-by-step analysis of how you can turn your marketing ambitions into a solid plan of action that can guide you.
Step 1: Define Your Goals
It’s easy to skip this step, but trust us, you don’t want to do that. Most small business owners think they know their marketing goals — and in a certain sense, that’s true. As an involved executive of a smaller enterprise, you probably have your finger on the pulse of your organization more than most leaders.
But that proximity to daily operations and activities can also make it easy to cloud out the big-picture stuff at times. Before you establish your marketing plan, take a minute to step back.
What are you trying to accomplish with your marketing in the next year? What about the next five years? Do you want to generate revenue? Build brand awareness? Increase online visibility? Spark long-term growth?
Each goal is related to your marketing, but the differences are important. Get each specific marketing goal in place before you flesh out your plan.
Step 2: Identify Your Audience
Your target audience should be the central focal point of your entire operation. When you develop products, you should consider whom they serve. When you bring them to market, you want to consider how to communicate to a select group of consumers that they’re available to solve their problems.
Make sure you have a buyer persona in place that reflects precisely whom you’re trying to market to and what their pain points are. If you’ve already considered what your customer base looks like, use this step to review that data and ensure that it’s informed by up-to-date market research.
Step 3: Consider Resources and Competition
As a final step to set the stage for your planning, review what resources you have available. As a small business, do you have a marketing team, or does that responsibility overlap with other employees (or yourself)? How much time do you have to invest in marketing? What is your marketing budget? What assets do you already have, such as a CRM or social media marketing tools?
Also, consider conducting a fresh round of competitive analysis. You likely did this when you were pulling together your business plan. Go back and observe how your competitors are marketing themselves to your target audience. Note the pros and cons of their efforts.
Step 4: Identify the Marketing Tactics You Can Use
Now comes the marketing magic. Once you’ve considered your goals, target audience, resources, and competition, it’s time to bring it all together.
Consider the marketing tactics you have available and which ones best meet your current marketing needs. Then, weave these marketing ideas into a plan that considers resources and timelines. A few common marketing tactics that work well for small businesses include:
- Creating a strong website : This becomes your central online presence and a place to host your blogs, user-generated content, landing pages, and other content marketing.
- Optimizing your website : SEO is important. Optimizing your site with long-tail keyword phrases, links, and technical SEO (think metadata, mobile-friendly, etc.) is a powerful way to maximize your content creation efforts.
- Build up off-site marketing : Create a social media presence using platforms your target audience prefers. Nurture email marketing, as well, including drip campaigns, newsletters, and targeted announcements.
- Organize leads in a CRM : As a small business owner, you want to stay organized. When your marketing begins to gain momentum, have a customer relationship management (CRM) platform ready to keep things organized and under control.
Remember, you’re a small business with limited marketing resources. Consider which tactic is particularly relevant to your brand at the moment, and invest in those areas first.
Step 5: Establish Success Metrics and Feedback Loops
Finally, consider how you’ll track your marketing over time. Use tools like Google Analytics 4 to keep tabs on important marketing metrics, such as ranking for brand keywords, measuring organic traffic, and tracking conversions.
Also, request feedback from customers and team members and then use that information to hone your marketing activities moving forward. If you’re unsure how to adapt your plan (or create one in the first place), consider working with a growth marketing agency that can bring a cost-effective degree of experience and knowledge to bear on your brand’s marketing initiatives.
Building Master Marketing Plans for Small Businesses
As a small business, you may have limited time, money, and tools to work with. However, that doesn’t mean investing in a marketing plan isn’t worth it.
On the contrary, creating an effective marketing strategy helps you ensure that every ounce of resources you pour into promoting your business has a purpose. This gives you the best chance of sparking genuine, measurable growth, which can enable you to build larger marketing budgets, plans, and strategies in the future.
More From Forbes
The most important marketing metric is driving business growth.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Marketing's job is to drive business growth.
Over the past few years, many CEOs have encountered the same problem: the organization's media is more efficient than ever, but the business isn’t growing.
As digital, CRM, and more have evolved to create an abundance of digitally-infused customer experience activities, marketers have become responsible for an ever-growing list of options for how to spend their marketing dollars. While these innovations and the MarTech solutions that come with them have added immense value for the industry, they have also posed challenges for CMOs who’ve become deeply focused on optimizing each and every channel to ensure their reporting to the C-suite demonstrates value. The bigger picture – driving business growth – took a back seat.
Understandably, CEOs and their CFO counterparts appreciate some level of cost certainty for their marketing spend. Optimizing for channels provides comfort because it helps manage cost. Marketing’s job, however, is to drive growth – not simply manage cost.
Now, the industry’s best are demanding a shift to reposition marketing as a growth driver. In doing so, they’re fostering realignment on what marketing is responsible for among CEOs, CFOs, and beyond – all for the betterment of the business. Here’s how they’re doing it.
Prioritize Cultural Relevance and Brand
Don’t let performance marketing bog you down. For brands with some scale, prioritizing a marketing mix model that includes driving cultural relevance through brand marketing can make a big difference.
When Does ‘Bridgerton’ Season 3, Part 2 Come Out On Netflix? See The Release Schedule
Samsung galaxy s24 series users really want to turn off one of its best features, a storm of 3 000 ukrainian bomblets blew up four russian jets at their base in crimea.
According to research from X (Twitter ), a quarter of consumer’s purchasing decisions are linked to a brand’s cultural involvement. Consumers aged 18-35, who have long been a priority due to their purchasing power, feel even more strongly that the brands they purchase align with culture. These aren’t just idyllic consumer responses – there’s proof.
When travel company Airbnb lost 80% of its business due to the Covid-19 pandemic, it simply could not afford to let marketing manage costs; it needed to be a growth driver. CEO, Brian Chesky, and Global Head of Marketing, Hiroki Asai, aligned on a shift from primarily performance-driven marketing to instead focus on brand campaigns – connecting with customers rather than buying them.
As Asai shared on the Marketing Today podcast, “When you’re over-indexed on performance, you don’t really have the opportunity to put a narrative out there to tell your story.” Instead, a brand-forward approach allowed Airbnb to do just that, linking it to the culture of modern traveling. According to Asai, those brand campaigns, “strike a chord and get to a deeper shared experience of humor or awe or irony about travel that we all love.”
By 2023, Airbnb made the Fortune 500 list for the first time ever, citing a revenue jump of 40.2% year over year .
With results like that, Chief Financial Officer Dave Stephenson praised the approach stating , “Our brand marketing results are delivering excellent results overall with a strong rate of return, and it’s been so successful that we’re actually expanding to more countries.”
Think Beyond the Television Screen
While Airbnb did make a splash through some memorable television spots, modern brand marketing requires thinking beyond that screen.
With endless content options, it’s become increasingly difficult to win consumer attention. The Interactive Advertising Bureau recently reported that in 2024, digital video spend is expected to surpass linear for the first time. At the same time, research from Bulbshare found that 99% of Gen Z say they’ll hit ‘skip’ on an ad if it’s an option. As media dollars and consumer behaviors shift, a holistic marketing mindset must be applied to build brand.
Soda brand Poppi, whose team has called it a “ creator-first brand ,” has leaned in on influencer partnerships and experiences as part of its brand strategy. Most recently, they took a big swing by engaging one of the most well-known TikTok influencers, Alix Earle, for their activation at the popular music festival Coachella. While many brands set up experiential activations and wide-ranging influencer partnerships, Poppi invested big in Earle – her cultural relevance, 6.6 million TikTok followers, and power to drive trends.
In a custom luxury house with over-the-top Poppi branding and merchandise, Earle’s partnership generated 4.5 million engagements, reaching over 275 million people. Poppi’s previous influencer partnerships have helped catapult the brand to the number one selling soft drink on Amazon, entering 5 million monthly new households in 2024.
As director of brand awareness and culture, Sophia Sesto shared with Ad Age , “You can’t 100% measure what it does in terms of a sale, but I'm already seeing so many videos in our TikTok tags, viral or not, with people talking about the ‘Alix Earle effect’ and going to the store and buying Poppi … It really is just [about] looking for brand awareness.”
Step Back, Evaluate, and Build a Winning Strategy
Taking big brand swings can require a little faith, but they don’t need to be built without data. Marketers looking to make a shift can start small, evaluate new ways to measure impact, and gradually develop a plan that works for the entire C-suite.
Brand marketing may not pay off as predictably as performance marketing, but the strategic shift will set you up for greater long-term business success. It’s time for marketers to drive a move away from the performance marketing obsession; they must be less safe and tactical and more strategic and growth-focused. When the CEO, CMO, and CFO realign on marketing’s role - and the levers that must be pulled to drive real business growth - the company will ultimately win.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
How to Start a Small Business in 10 Steps

Learn how to start a small business from scratch with expert guidance. Get essential tips and steps for launching your dream journey successfully.

Brett Grossfeld
Share article.
Do you have a killer idea that you think would be perfect for launching a small business? If you believe what you see on TikTok, becoming an entrepreneur is just about as easy as posting a 30-second video. But in the real world, launching a small business can be a bit more challenging.
Starting a small business may seem daunting, but if you ask those same business owners if it’s worth the risk — few would trade the opportunity to shape their own destiny.
But where to start? Thankfully, you don’t need to have everything figured out before going out on your own. Successful small business owners are constantly learning from their mistakes — and improving their ideas and dreams along the way.
If you’re ready to take the leap and become a small business owner, keep reading.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
What is a small business, how much does it cost to start a small business, how to start a small business in 10 steps, what do you need to start a small business, start small — but think big.
Small businesses are generally defined by the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) as independent operations having fewer than 200 employees. And the majority of small businesses in the United States have fewer than five employees, according to the U.S. Census Bureau .
But the number — or lack — of employees doesn’t necessarily define a “small business.” A business’s size can also be determined by the number of sales, the range of individual business locations, and other factors.
Along with size requirements, the SBA considers a company to be small if it’s:
- Independently owned and operated
- Not dominant in its field
- Physically located and operated in the U.S. (or a U.S. territory)
If your company meets the SBA’s definition of a small business, many government programs offer resources and local assistance for you to turn your dreams into reality.
Start Your Small Business With Big Things

Grow Your SMB All In One Platform

DEMO: See For Yourself For Free With Starter Suite

Build Your SMB Marketing Strategy With This Free Guide

TRAILHEAD: Starter Suite Quick Look
If you’re skilled in a certain trade — say, bookkeeping — you can launch a business with almost no money . But if your idea needs to be fleshed out and developed by researchers, scientists, and engineers, your startup costs can run into the hundreds of thousands of dollars and beyond. But most startup costs fall somewhere in the middle.
Factors that influence cost
A sole proprietor working from home is going to have very different startup costs than a Silicon Valley startup flush with venture capital funds. But it doesn’t matter if you have $1,000 or $1 million to launch your small business — you’ll need to have a budget.
Are you moving the clutter out of your garage to make room for a desk? Or are you going to hire an architect to remodel a warehouse space in a trendy neighborhood? Obviously, both businesses are going to have wildly different expenses.
Think about your budget and what you can afford to get started. And it’s good to assume that unexpected expenses will pop up along the way — especially in your first year of business.
What kinds of costs to expect
The SBA has a worksheet that will help you calculate typical expenses for a small business, including one-time expenses such as:
- Rent : This includes security deposit, first month’s rent and utilities. If you’re working from home, you can deduct a percentage of your rent or mortgage on your taxes .
- Improvement costs: Anything that you might spend on your physical place of business to make it suitable for work.
- Inventory : If you’re selling a product, you’ll need goods to keep up with customer demand.
- Employees : This includes payroll, payroll taxes, and health insurance.
- Professional services: Accountants, lawyers, and consultants will all need to be paid
- Supplies : Think office supplies, such as paper and pencils, and operating supplies, like computers and printers.
- Marketing: Business cards, stationery, flyers, and advertising all fall under this category.
- Miscellaneous : This includes licenses, permits, legal fees, signage, technology, and accounting software. Everything else — liability insurance, repairs, maintenance, and dues.
The most difficult part of starting a small business is committing to your vision. It’s easier if you break down the process into small, achievable goals. Here are 10 steps that will get you on your way:
1. Do your research
If you don’t do basic market research before you launch your business, you may be down for the count before you even get started. Ask neighbors, friends, and even your barista if they would be interested in your product or service — and ask how much they’d be willing to pay for it.
Conduct competitor research, local and global searches, and even offer surveys to consumers to see what the need versus want ratio is.
2. Write a business plan
A business plan is your roadmap; it helps guide you as you start and grow your company. If you need capital to get started, most investors will want to review a business plan before they commit to any financing.
To organize your ideas, download and fill out a business plan template . A well-written business plan provides clarity, confirms the math, and helps you establish goals so your business has the best chance of success.
3. Choose a business name
Finding the perfect brand name is a vital step in launching a new business. But hiring a professional naming company doesn’t come cheap — it can cost as much as $100,000 , according to Fast Company.
If that’s outside your budget, there are countless AI-powered business name generators available online, and Fiverr has entrepreneurs who will help brainstorm business names for three figures or less.
4. Decide on your location
Take a look at the taxes, zoning laws, and regulations in your location. You may find that operating your business in a different location could offer financial advantages. Review the fees, costs, and tax benefits of each state to see which location makes the most sense for your business . A strategic move may put you ahead of the game before you even open the doors.
5. Get your finances in order
Startup costs discourage many would-be entrepreneurs, but the reality is that many successful businesses got started with little more than a vision, discipline, and hard work. However, if you really need cash for that newly opened business bank account, here are four ways of getting that money:
- Self-funding: If you have the means, you may use your own earnings to kickstart your business or see out financial counsel to work it into your budget.
- Outside investors: For a stake in your company, relatives or venture capitalists may be willing to invest in your business.
- Small business loans: If you want to keep full ownership of your business, a small business loan may be the way to go.
- Crowdfunding: If you’re feeling creative and confident, try sites such as Kickstarter or GoFundMe to generate capital.
6. Take care of the legal stuff
Register your business in the state where it was formed — and make sure that you’re set up to pay state income and unemployment tax. Review whether your local municipality requires filing for a license or permit to operate your business.
To satisfy Uncle Sam, apply for an EIN from the IRS . Confirm that no one else is using your business name by contacting your state filing office or online database. Some business structures require using a doing business as (DBA) name, and you may be required to open a business bank account.
7. Develop a marketing plan
Once you have a terrific name for your company locked down, you’ll want to create an online presence for your business. Be consistent on your social media channels , ideally creating accounts on the channels — meeting them online where they are.
Develop a website that’s intuitive and filled with all the information your customers need. Your marketing may also include advertising campaigns and public relations.
8. Set up your CRM software
To enhance your marketing efforts and grow your small business, try customer relationship management ( CRM) for Small Business . This will be your solution for storing and managing prospect and customer information such as contact information, accounts, leads, and sales opportunities — all in one single source of truth.
With Salesforce’s Starter Suite , you can start in minutes and easily manage your marketing, sales, and customer service as your business scales.
9. Launch your product or service
Congratulations: You’ve done all the hard work and you’re ready to introduce your product to the world. Make sure to announce your launch on social media — and consider throwing a media-friendly bash to celebrate.
10. Keep your customers happy
When you use CRM software, you can keep track and personalize support for all your customers. And happy customers are good for business — 80% of them say the experience a company provides is just as important as its products or services .
The United States has more than 33 million small businesses, according to the U.S. Chamber of Commerce , and that number represents 99.9% of all U.S. businesses. And most of those small businesses started the same way — with an entrepreneur and an idea. But it takes more than just a dream to launch a small business.
So, where to start?
It’s time to take some notes. First, start outlining your business plan. If you’re stuck, ask yourself these four questions when developing your plan :
- Goals : What do you need to accomplish to achieve your vision?
- Methods : What are the steps you need to follow to get you there?
- Measurements : How will you determine when each objective has been met?
- Obstacles : What could throw you off course along the way?
Once you’ve written a business plan and are feeling confident, you’re ready to establish:
A name for your business
A great business name should succinctly identify your company and its audience. Brainstorm and get feedback from friends, family, and potential customers. And before you fall in love with your new company name, make sure that an established business in your industry isn’t already using that name.
A location for your business
Choosing where to conduct business is one of the most important decisions you can make for your small business. While staying close to home may be your first instinct, a change of venue may prove to be financially advantageous.
A business structure
For tax purposes and protection of personal assets, you need to choose a business structure that offers the right balance of legal protections and benefits. Common business structures include sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company (LLC), corporation, and cooperative.
A legal presence
If you want personal liability protection, legal protection, and tax benefits for your company, you’ll need to register your business with state and local governments.
Federal and state tax ID numbers
Your Employer Identification Number (EIN) works like a personal Social Security number, but for your business. You need an EIN to pay state and federal taxes for your company.
Licenses and permits
Whether your business needs to apply — and pay for — licenses and permits depends on your business activities, location, and government rules. Review regulations from city, state, and federal agencies.
A business bank account
Opening up a bank account exclusively for business use will help keep your personal finances separate, making life easier at tax time. There are several banks that will allow you to open a business checking account with a zero balance, but traditionally banks will require an opening deposit of anywhere from $1,000 to $25,000.
Start-up funds
Even if you open a business checking account with a zero balance, you’re going to want to have some funds to cover basic operating expenses. The SBA offers guidance on obtaining funding for your small business, including loans, grants, and investors.
Starting a new business may feel like a gamble, but business insurance will help you cover your bet. The right insurance policy will help protect you against accidents, natural disasters, and lawsuits.
You should also consider:
Customer relationship management
A CRM platform keeps your customer data organized and provides the foundation to build connected customer experiences (that can be made even better through artificial intelligence). Starting with a suite of sales, service, marketing, and commerce tools is easy.
Invoice and billing software
While it is possible to keep track of your financial records on a traditional paper ledger, modern invoice and billing software makes the process much, much easier.
A graphic designer
A well-designed logo can make or break a business. The Nike “swoosh” was created by a graphic design student — and the $35 Nike initially spent paid for itself many times over.
Many small businesses exist with just a presence on social media, but having a professionally designed website adds legitimacy to your business.
Marketing experts
Like graphic design, marketing expenses are costs that many small business owners initially want to avoid. But strategically investing in a marketing campaign can be a boon for a small business that wants to make noise in a crowded marketplace.
A Human Resources department
Once your business grows to a certain size, it’s time to create a human resources (HR) department — or, at least, to hire an HR professional. This professional can focus on things such as labor law compliance, employee recruitment, employee engagement and development, and compensation and benefits management while you manage your business.
An assistant
For most small businesses starting out, hiring an assistant to perform administrative and clerical duties is something of a luxury. If your budget is tight, consider a virtual assistant .
What are some popular small business ideas?
If you have a unique idea for a small business, great. But some of the best small business ideas build on your strengths and experience. What do you love to do? What lights you up when you are helping the community? Do you have a pull to do something more?
What are the odds that my small business will succeed?
Starting a small business is no guarantee of success. Approximately 80% of small businesses survive their first year, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The survival rate decreases to 50% after five years and 30% after 10 years.
What are some Fortune 500 companies that started small?
Not all big companies started with millions of dollars in venture capital. Some of America’s biggest brand names had far more modest beginnings . Apple famously got started in a Silicon Valley garage, while Mattel was building dollhouse furniture from picture frame scraps in its early days.
What are the most business-friendly states?
Before setting up shop in New York or California, consider launching your small business in North Dakota, Indiana, Arkansas, South Dakota, or North Carolina. These states offer the best conditions to start a business , according to Forbes Advisor.
What can I deduct for my small business at tax time?
(Almost) everyone knows that you can deduct entertainment and travel expenses as a small business owner. But you can also deduct software subscriptions, office furniture, and interest on small business loans, according to NerdWallet .
Taking the leap to start your own small business is just the first step on your entrepreneurial path. But you’re in good company. Nearly half of all U.S. employees are employed by a small business — and more than 80% of those small businesses are solo ventures , according to Forbes Advisor. There’s no better time than the present to start turning your dreams into reality.
Want to grow your new small business? Sign up for a Salesforce free trial .
Just For You

Generative AI Regulations – What They Could Mean For Your Business

What Is ERP? (A Beginners Guide)

Explore related content by topic
- Future of Work
- Salesforce CMS
- Small Business
- B2B Commerce
- Best Practices
- Sales Strategy
- Sales Fundamentals

Brett Grossfeld is a Product Marketing Manager supporting Salesforce's CRM, data, and AI tools. He's written for multiple websites across various industries and interests, including tech, wellness, and modern customer experiences.
Get the latest articles in your inbox.

How To Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps

AI For Small Business is Here — Get Ready With These Tips

How to Write a Business Proposal for Small Businesses

Digital Marketing for Small Business: Here’s How You Can Do It

27 Top Sales Influencers You Should Follow in 2024

What Is an SMB and What Do You Need to Know to Be Successful?

4 Ways Your Contact Center Can Get Started With Generative AI

Email Marketing for Small Business: Here’s All You Need to Know

360 Highlights
Yes, I would like to receive the Salesforce 360 Highlights newsletter as well as marketing emails regarding Salesforce products, services, and events. I can unsubscribe at any time.
By registering, you confirm that you agree to the processing of your personal data by Salesforce as described in the Privacy Statement .

Thanks, you're subscribed!

New to Salesforce?
- What is Salesforce?
- Best CRM software
- Explore all products
- What is cloud computing
- Customer success
- Product pricing
About Salesforce
- Salesforce.org
- Sustainability
Popular Links
- Salesforce Mobile
- AppExchange
- CRM software
- Salesforce LIVE
- Salesforce for startups
- América Latina (Español)
- Brasil (Português)
- Canada (English)
- Canada (Français)
- United States (English)
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
- España (Español)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- France (Français)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Nederland (Nederlands)
- Sverige (Svenska)
- United Kingdom (English)
- All other countries (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- Malaysia (English)
- ประเทศไทย (ไทย)
© Copyright 2024 Salesforce, Inc. All rights reserved. Various trademarks held by their respective owners. Salesforce, Inc. Salesforce Tower, 415 Mission Street, 3rd Floor, San Francisco, CA 94105, United States
I’m in awe of business owners & founders. Some are self-confessed unemployable, unable to work for the man, so they risk it all to market their dream, idea, or a solution to others’ problems. Others plan their escape to entrepreneurship whilst trapped inside a corporate cubicle. Having spent 25 years as a corporate monster myself, and another 15 running my own successful business, 'The Small Business Big Marketing Spotlight' podcast is laser-focussed on bringing business owners real stories of the ups and downs of growing a business they love in 2024 and beyond. No sugar-coatings, no fancy lingo; just practical insights and tips across all aspects of business - Marketing, HR, tech, finance, scaling, to name a few. Thank you for listening … Tim Reid (Your curious host). Connect with Tim Reid: https://www.linkedin.com/in/timothyjreid Be a Guest: https://smallbusinessbigmarketing.com/contact Book Tim Reid: https://timreid.com.au
The Small Business Big Marketing Spotlight with Tim Reid Tim Reid
- MAY 14, 2024
Adam Pisk of BruntWork | Offshore Outsourcing
Today’s bright spark is Adam Pisk, the co-founder of BruntWork, an offshore outsourcing business headquartered in Sydney with offices in The Philippines, Colombia, Eastern Europe and beyond.
[Trailer] For Motivated Business Owners Keen To Grow In 2024 & Beyond
Real stories of the ups & downs of growing a business in 2024 and beyond. No sugar-coatings, no fancy lingo; just practical insights and tips across all aspects of business from those in the know.
Top Podcasts In Business

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan. A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics. A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute ...
Marketing Plan: A marketing plan is a business's operational document for advertising campaigns designed to reach its target market . A marketing plan pulls together all the campaigns that will be ...
Marketing plan v.s business plan. While both marketing plans and business plans are crucial documents for businesses, they serve distinct purposes and have different scopes. Here's a breakdown of the key differences: Business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines all aspects of your business, including:
A marketing plan is a document that a business uses to execute a marketing strategy. It is tactical in nature, and, as later sections of this article explore, it typically includes campaign objectives, buyer personas, competitive analysis, key performance indicators, an action plan, and a method for analyzing campaign results.
What is a Marketing Plan? A marketing plan is a document that lays out the marketing efforts of a business in an upcoming period, which is usually a year. It outlines the marketing strategy, promotional, and advertising activities planned for the period. Elements of a Marketing Plan. A marketing plan will typically include the following elements:
A general marketing plan lays the foundation for other, more specific marketing plans that an organization may employ. Product launch marketing plan: A product launch marketing plan is a step-by-step plan for marketing a new product or expanding into a new market. It helps you build awareness and interest by targeting the right audience, with ...
A marketing plan is the strategy a business uses to get its products or services in front of its target customer. It includes who the target market is, the channels used to reach them, and the messaging that will help the business sell its products. The purpose of a marketing plan isn't to create a step-by-step, never-fail manual.
If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture. 2. Feasibility Business Plan. This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing ...
Marketing plans can take various forms and serve different purposes depending on a company's goals and circumstances. Here are several types of marketing plans commonly used in the business world: Annual Marketing Plan: This is the most common type of marketing plan and covers marketing strategies and activities for the upcoming year. It ...
Strategy: Segmentation, Targeting and Positoning (STP) and the tactics forming the 7Ps of the marketing mix. Action: Budget, resourcing including team and tools and marketing technology (Martech) and 90-day action plans. As a marketer, every activity will fall into either an opportunity, strategy, or action.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
The terms are often used interchangeably or together: marketing business plan. But each plan is different and here's what sets them apart. Business plans cover a business's overall strategy, from the branding strategy to the company-wide marketing strategies. A marketing plan solely concentrates on a specific marketing strategy or a branch of ...
Mine the research you conducted, as well as your own insights, for this information. Be brutally honest. This is the basis for your entire marketing plan, so if you lie to yourself here, your ...
The marketing portion of a business plan addresses four main topics: product, price, promotion, and place. A business plan is a blueprint for taking an idea for a product or service and turning it into a commercially viable reality. The marketing portion of the business plan addresses four main topics:
Sales and distribution plan. Advertising and promotions plan. The easiest way to develop your marketing plan is to work through each of these sections, referring to the market research you completed when you were writing the previous sections of the business plan. (Note that if you are developing a marketing plan on its own, rather than as part ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A business plan documents the highest-level strategy for an organization, including essentials such as mission, vision, values, assets, human resources, and more. A marketing plan documents how your team will execute a marketing strategy. The marketing strategy is based on the "north star" vision, which is documented in the business plan.
Marketing encompasses every part of a plan to turn a prospective consumer into a happy and satisfied customer. It includes everything from market research to advertising. The goal of marketing is ...
This SMART goal guide can help you with more effective goal-setting. 3. Identify your target audience and create buyer personas. To create an effective marketing strategy, you need to understand who your ideal customers are. Take a look at your market research to understand your target audience and market landscape.
A marketing plan is a document outlining a company's future marketing efforts and goals. It can be as short as a single page or made up of many smaller campaign plans from different marketing teams. However large and complex those plans are, the idea remains the same: A marketing plan is created to organize, execute, and eventually measure ...
In contrast, a marketing plan focuses specifically on strategies and tactics to promote products or services, detailing target audiences, promotional methods, and market positioning. While the business plan provides a comprehensive view of the entire business, the marketing plan hones in on attracting and retaining customers.
The biggest difference between a business plan and a marketing plan is the scope of what they cover. While both documents can be quite lengthy and thorough, they don't address the exact same information. A business plan is typically a much broader document that covers every aspect of your business: operations, supply chains, human resources ...
A marketing plan is the collection of activities that an organization intends to undertake during a specific period to achieve its objectives. Some of the defining characteristics of a marketing plan are: ... A product launch can be a game-changer for business. To make it happen, a product launch marketing plan needs to be extraordinary. Here ...
A small business marketing plan takes the limited resources of a small business and considers how that entity can effectively reach its target audience with its marketing. Why are Marketing Plans for Small Businesses Important? Grasping the goal of a marketing plan is the easy part. For a small business team with finite time and resources ...
This strategic business plan template spans 7 pages to get you set up with a solid foundation for your business's strategic plan. ... You should have an objective for each section of your strategic plan: marketing, finance, human resources and so on. Set SMART goals, which stand for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic and Timely. ...
The bigger picture - driving business growth - took a back seat. Understandably, CEOs and their CFO counterparts appreciate some level of cost certainty for their marketing spend. Optimizing ...
To organize your ideas, download and fill out a business plan template. A well-written business plan provides clarity, confirms the math, and helps you establish goals so your business has the best chance of success. 3. Choose a business name. Finding the perfect brand name is a vital step in launching a new business.
The Small Business Big Marketing Spotlight with Tim Reid on Apple Podcasts. 2 episodes. I'm in awe of business owners & founders. Some are self-confessed unemployable, unable to work for the man, so they risk it all to market their dream, idea, or a solution to others' problems. Others plan their escape to entrepreneurship whilst trapped ...
The Planet Fitness $10-a-month membership plan is a powerful marketing tool and a central part of its strategy. But the largest gym chain in the United States is hiking that monthly fee for the ...