If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.

Unit 1: Algebra foundations
Unit 2: solving equations & inequalities, unit 3: working with units, unit 4: linear equations & graphs, unit 5: forms of linear equations, unit 6: systems of equations, unit 7: inequalities (systems & graphs), unit 8: functions, unit 9: sequences, unit 10: absolute value & piecewise functions, unit 11: exponents & radicals, unit 12: exponential growth & decay, unit 13: quadratics: multiplying & factoring, unit 14: quadratic functions & equations, unit 15: irrational numbers, unit 16: creativity in algebra.
- 888-309-8227
- 732-384-0146
New User Registration
Forgot Password
Glencoe McGraw-Hill Algebra 1, Grade: 9 Publisher: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe mcgraw-hill algebra 1, title : glencoe mcgraw-hill algebra 1, publisher : glencoe/mcgraw-hill, isbn : 0078738229, isbn-13 : 9780078738227, use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement glencoe mcgraw-hill algebra 1., textbook resources.
- Call us toll-free
- FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- Contact Lumos Learning – Proven Study Programs by Expert Teachers
Follow us: Lumos Learning -->
- 2024 © Lumos Learning
- Privacy Policy - Terms of Service - Disclaimers
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc... Read More
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc., the Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any state of the Union. Neither PARCC, Inc., nor The Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any member state has endorsed this product. No portion of any fees or charges paid for any products or services Lumos Learning offers will be paid or inure to the benefit of PARCC, Inc., or any state of the Union
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not aff... Read More
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC, was not... Read More
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC,was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved... Read More
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the prod... Read More
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved... Read More
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved... Read More
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved... Read More
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved... Read More
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.

Home > CCA > Chapter 8 > Lesson 8.1.1
Lesson 8.1.1, lesson 8.1.2, lesson 8.1.3, lesson 8.1.4, lesson 8.1.5, lesson 8.2.1, lesson 8.2.2, lesson 8.2.3, lesson 8.2.4, lesson 8.2.5.
© 2022 CPM Educational Program. All rights reserved.
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Answers Chapter 8 Graphing Quadratic Functions
Looking for the Topic-wise Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Answers Chapter 8 Graphing Quadratic Functions for growing your Math Skills? Then, learn thoroughly & solve all BIM Algebra 1 Ch 8 Graphing Quadratic Functions Questions covered in the chapter test, quiz pages. Big Ideas Math Answers’ main intention is to provide good quality of education and make students move on the right path.
Ace up your preparation and Develop Problem Solving Skills by referring to the Ch 8 Graphing Quadratic Functions Big Ideas Math Book Algebra 1 Solution Key . All exercises questions & answers of BIM Algebra 1 Graphing Quadratic Functions Chapter 8 are free to access and download through the below direct links.
Big Ideas Math Book Algebra 1 Answer Key Chapter 8 Graphing Quadratic Functions
Here, we have given a complete guide of Chapter 8 BIM Algebra 1 Graphing Quadratic Functions Answers in quick links. Click on the Topic-wise Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Solutions of Chapter 8 and clear all your queries regarding the concepts. Also, you can refer to the covering Questions from Practice Test, Chapter Test, Cumulative Practice, Performance Test, etc in this Chapter 8 Big Ideas Math Answer Key.
Seek whatever Homework Help you might need and enhance your math proficiency. Also, you can attempt the Chapter 8 Graphing Quadratic Functions Assessments easily by solving all exercise questions covered in the Big Math Ideas Algebra 1 Textbook Answers.
- Graphing Quadratic Functions Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency – Page 417
- Graphing Quadratic Functions Mathematical Practices – Page 418
- Lesson 8.1 Graphing f(x) = ax2 – Page (419-424)
- Graphing f(x) = ax2 8.1 Exercises – Page (423-424)
- Lesson 8.2 Graphing f(x) = ax2 + c – Page (425-430)
- Graphing f(x) = ax2 + c 8.2 Exercises – Page (429-430)
- Lesson 8.3 Graphing f(x) = ax2 + bx + c – Page (431-438)
- Graphing f(x) = ax2 + bx + c 8.3 Exercises – Page (436-438)
- Graphing Quadratic Functions Study Skills: Learning Visually – Page 439
- Graphing Quadratic Functions 8.1 – 8.3 Quiz – Page 440
- Lesson 8.4 Graphing f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k – Page (441-448)
- Graphing f(x) = a(x – h)2 + k 8.4 Exercises – Page (446-448)
- Lesson 8.5 Using Intercept Form – Page (449-458)
- Using Intercept Form 8.5 Exercises – Page (455-458)
- Lesson 8.6 Comparing Linear, Exponential, and Quadratic Functions – Page (459-468)
- Comparing Linear, Exponential, and Quadratic Functions 8.6 Exercises – Page (465-468)
- Graphing Quadratic Functions Performance Task: Asteroid Aim – Page 469
- Graphing Quadratic Functions Chapter Review – Page (470-472)
- Graphing Quadratic Functions Chapter Test – Page 473
- Graphing Quadratic Functions Cumulative Assessment – Page (474-475)
Graphing Quadratic Functions Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
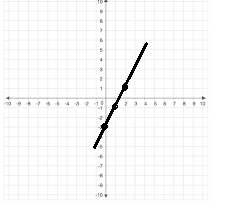
Graph the linear equation.
Evaluate the expression when x = −2. Question 5. 5x 2 – 9 Answer: Given, 5x 2 – 9 Now we have to substitute x = -2 in the above expression 5(-2) 2 – 9 = 5(4) – 9 = 20 – 9 = 11
Question 6. 3x 2 + x – 2 Answer: Given, 3x 2 + x – 2 Now we have to substitute x = -2 in the above expression 3(-2) 2 + (-2) – 2 = 3(4) – 2 – 2 = 12 – 4 = 8
Question 7. -x 2 + 4x + 1 Answer: Given, -x 2 + 4x + 1 Now we have to substitute x = -2 in the above expression -(-2) 2 + 4(-2) + 1 = -4 – 8 + 1 = -12 + 1 = -11
Question 8. x 2 + 8x + 5 Answer: Given, x 2 + 8x + 5 Now we have to substitute x = -2 in the above expression (-2) 2 + 8(-2) + 5 = 4 – 16 + 5 = -7
Question 9. -2x 2 – 4x + 3 Answer: Given, -2x 2 – 4x + 3 Now we have to substitute x = -2 in the above expression = -2(-2) 2 – 4(-2) + 3 = -2(4) + 8 + 3 = -8 + 8 + 3 = 3
Question 10. -4x 2 + 2x – 6 Answer: Given, -4x 2 + 2x – 6 Now we have to substitute x = -2 in the above expression -4(-2) 2 + 2(-2) – 6 = -16 – 4 – 6 = -26
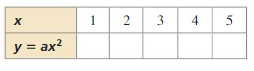
Graphing Quadratic Functions Mathematical Practices
Mathematically proficient students try special cases of the original problem to gain insight into its solution.
Monitoring Progress
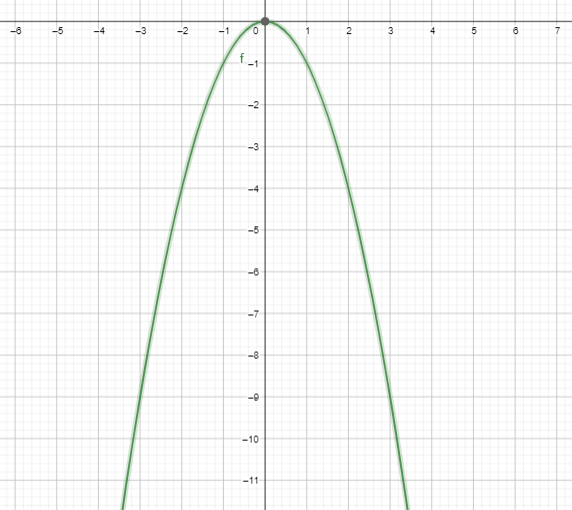
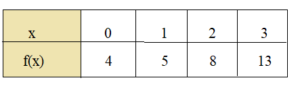
Question 9. How are the graphs in Monitoring Progress Questions 1-8 similar? How are they different? Answer: All the graphs from 1-8 are quadratic. The quadrants of the graphs are different and they are not equal to zero.
Lesson 8.1 Graphing f(x) = ax 2
Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of a quadratic function of the form f(x) = ax 2 ?
EXPLORATION 1

Communicate Your Answer
Question 2. What are some of the characteristics of the graph of a quadratic function of the form f(x) = ax 2 ? Answer: The graph of a quadratic function is U-shaped and known as a parabola. Parabolas have several recognizable features that characterize their shape and placement on the Cartesian plane.

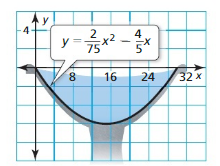
Question 9. The cross section of a spotlight can be modeled by the graph of y = 0.5x 2 , where x and y are measured in inches and -2 ≤ x ≤ 2. Find the width and depth of the spotlight. Answer:
Graphing f(x) = ax 2 8.1 Exercises
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
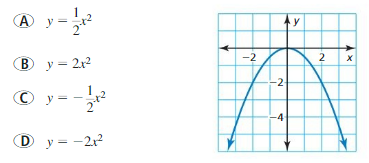
Question 1. VOCABULARY What is the U-shaped graph of a quadratic function called? Answer: The U-shaped graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola.
Question 2. WRITING When does the graph of a quadratic function open up? open down? Answer: When a < 0 it opens down When a > 0 it opens up
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
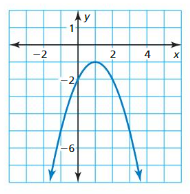
Question 22. When is each function decreasing? Answer: f is decreasing when g < 0. g is decreasing when x > 0

Question 24. REASONING Is the x-intercept of the graph of y = x 2 always 0? Justify your answer. Answer: The x-intercept is the intersection of the graph of the function with the x-axis and thus y = 0. Thus let us replace y with 0 in the given function 0 = ax 2 0 = x 2 0 = x Then we note that 0 is the only x-intercept.

ABSTRACT REASONING In Exercises 26–29, determine whether the statement is always, sometimes, or never true. Explain your reasoning. Question 26. The graph of f(x) = x 2 is narrower than the graph of g(x) = x 2 when a > 0. Answer: The given statement is sometimes true, because the graph f(x) = x 2 is narrower than the graph of g(x) = x 2 if a > 1, wider if a < 1 and equaly wide of a = 1.

Question 28. The graph of f(x) = x 2 is wider than the graph of g(x) = x 2 when 0 < |a| < 1. Answer: The given statement is sometimes true, because the graph f(x) = x 2 is narrower than the graph of g(x) = x 2 if a > 1, wider if -1< a < 0 or 0 < a < 1.

Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Evaluate the expression when n = 3 and x = −2. Question 32. n 2 + 5 Answer: n 2 + 5 =3 2 + 5 = 9 + 5 = 14
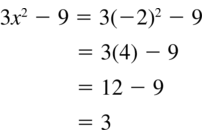
Question 34. -4n 2 + 11 Answer: -4n 2 + 11 = -4(3) 2 + 11 = -4(9) + 11 = -36 + 11 = -25
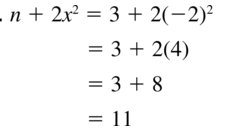
Lesson 8.2 Graphing f(x) = ax 2 + c
Essential Question How does the value of c affect the graph of f(x) = -ax 2 + c?
EXPLORATION 2
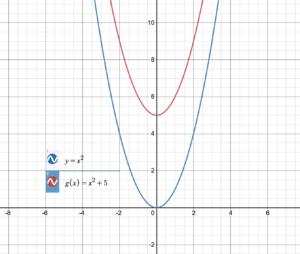
Question 3. How does the value of c affect the graph of f(x) = ax 2 + c? Answer: Given equation f(x) = ax 2 + c ‘c’ tell us the intercept of graph.

Question 5. Let f(x) = 3x 2 – 1 and g(x) = f (x) + 3. a. Describe the transformation from the graph of f to the graph of g. Then graph f and g in the same coordinate plane. b. Write an equation that represents g in terms of x. Answer: g(x) = f(x) + 3 g(x) = (3x 2 – 1 )+ 3 = 3x 2 + 2
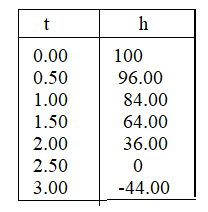
Question 6. Explain why only nonnegative values of t are used in Example 4. Answer:
Graphing f(x) = ax 2 + c 8.2 Exercises
Question 1. VOCABULARY State the vertex and axis of symmetry of the graph of y = ax 2 + c. Answer: The graph of y = ax 2 + c has a vertex of (0, c) and an axis of symmetry of x = 0
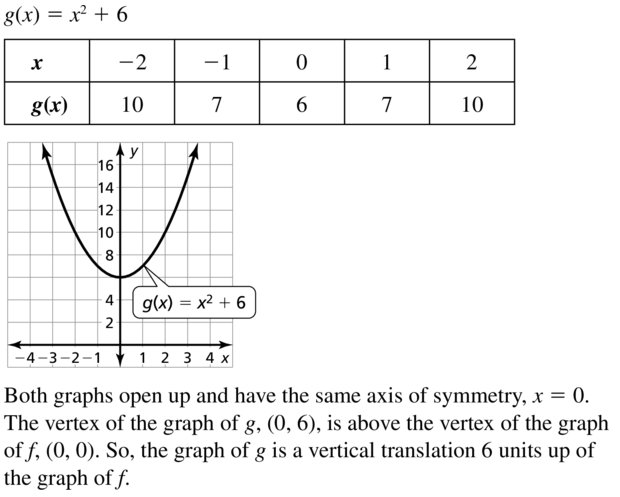
Question 2. WRITING How does the graph of y = ax 2 + c compare to the graph of y = ax 2 ? Answer: y = ax 2 y = ax 2 + c The graph of the function y = ax 2 + c is the graph of the function y = ax 2 translated up with c units if c > 0 and down with |c| units if c < 0
0Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
Question 20. y = x 2 – 36 Answer: y = x 2 – 36 x 2 – 36 = 0 x 2 = 36 x = ±6
Question 22. f(x) = -x 2 + 49 Answer: f(x) = -x 2 + 49 -x 2 + 49 = 0 -x 2 = -49 x = ±7
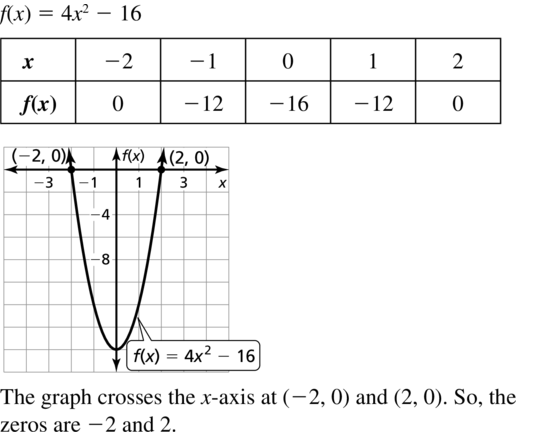
Question 24. f(x) = 3x 2 – 27 Answer: f(x) = 3x 2 – 27 3x 2 – 27 = 0 3x 2 = 27 x 2 = 9 x = ±3
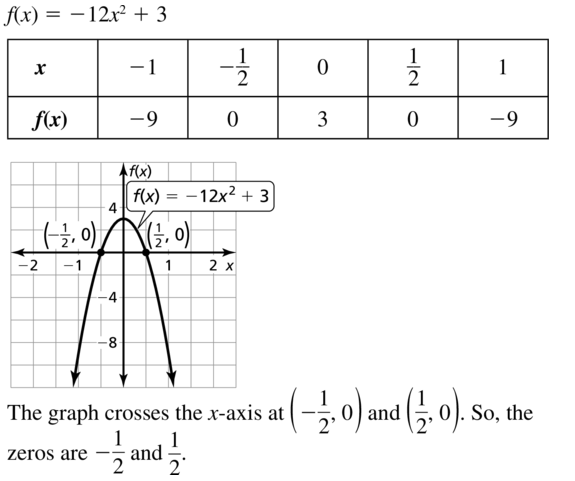
Question 26. f(x) = -8x 2 + 98 Answer: f(x) = -8x 2 + 98 -8x 2 + 98 = 0 -8x 2 = -98 x = ±7/2
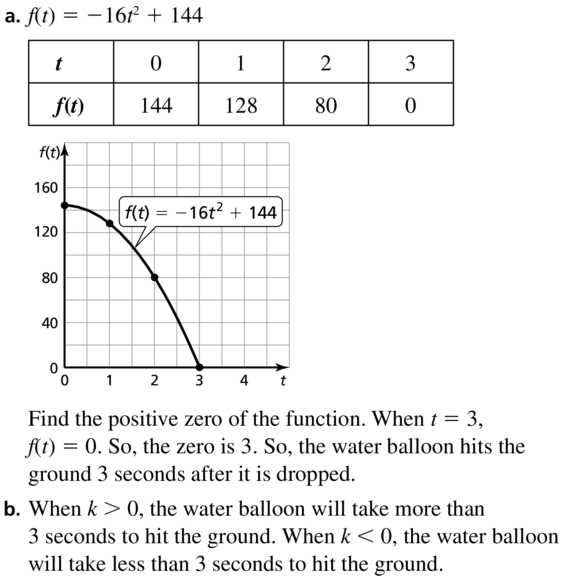
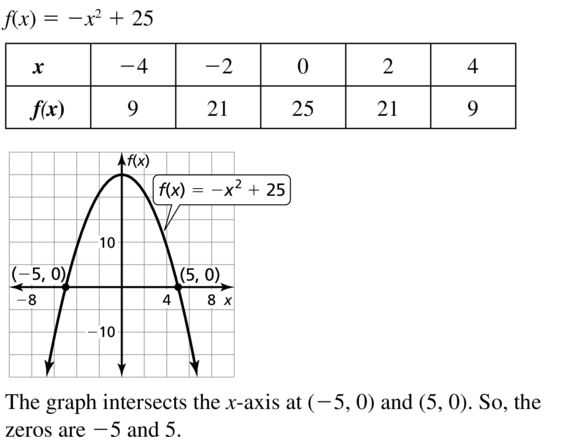
Question 28. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS The function y = -16x 2 + 36 represents the height y (in feet) of an apple x seconds after falling from a tree. Find and interpret the x- and y-intercepts. Answer: y = -16x 2 + 36 -16x 2 + 36 = 0 x 2 = 36/16 x = ±√9/4 x = ±3/2 = ±1.5 So, the x-intercepts are (-1.5, 0) and (1.5, 0) x = -1.5 does not make sense in the context of the problem x = 1.5 represents 1.5s, the time the apple will hit the ground. To find the y-intercept set x = 0 and solve for y: y = -16(0) + 36 y = 36 The y-intercept is (0, 36) y = 36 represents 36 ft, the initial height the apple was dropped.
In Exercises 29–32, sketch a parabola with the given characteristics.
Question 34. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that in the equation y = ax 2 + c, the vertex changes when the value of a changes. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning. Answer: No, a only determines how narrow the function is and if it is reflected about the x-axis (if a < 0). If c changes however, then the vertex will also change.
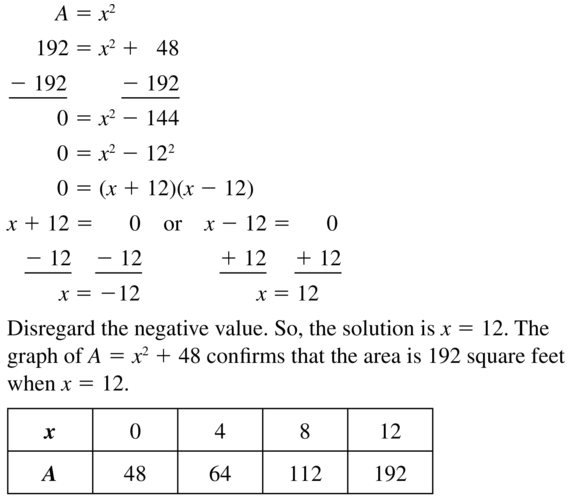
Evaluate the expression when a = 4 and b = −3. Question 42. \(\frac{a}{4b}\) Answer: Given, \(\frac{a}{4b}\) a = 4 and b = -3 \(\frac{4}{4(-3)}\) \(\frac{4}{-12}\) = \(\frac{1}{-3}\)
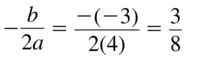
Question 44. \(\frac{a-b}{3 a+b}\) Answer: Given, \(\frac{a-b}{3 a+b}\) a = 4 and b = -3 \(\frac{4-(-3)}{3 4 – 3}\) \(\frac{7}{3}\)
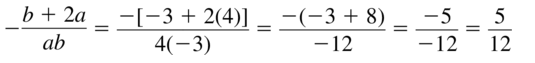
Lesson 8.3 Graphing f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c
Essential Question How can you find the vertex of the graph of f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c?
Comparing x-Intercepts with the Vertex Work with a partner. a. Sketch the graphs of y = 2x 2 – 8x and y = 2x 2 – 8x + 6. b. What do you notice about the x-coordinate of the vertex of each graph? c. Use the graph of y = 2x 2 – 8x to find its x-intercepts. Verify your answer by solving 0 = 2x 2 – 8x. d. Compare the value of the x-coordinate of the vertex with the values of the x-intercepts.
EXPLORATION 3
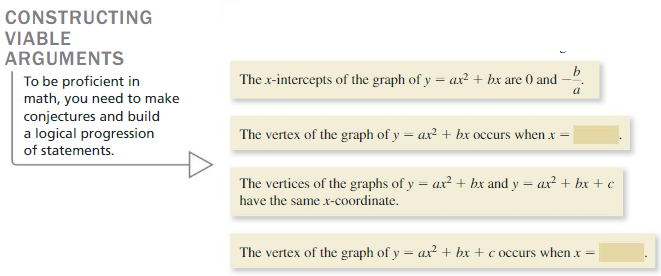
Question 4. How can you find the vertex of the graph of f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c? Answer:
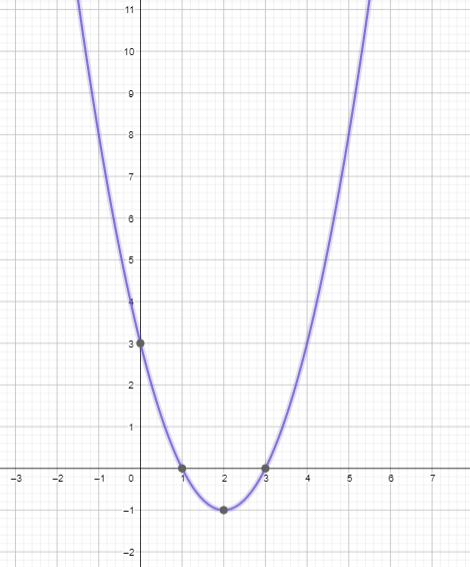
Find (a) the axis of symmetry and (b) the vertex of the graph of the function. Question 1. f(x) = 3x 2 – 2x Answer: Given, f(x) = 3x 2 – 2x y = 3x 2 – 2x Differentiate y’ = 6x – 2 6x – 2 = 0 6x = 2 x = 2/6 x = 1/3 y = 3(1/3) 2 – 2(1/3) y = 1/3 – 2/3 y = -1/3 Hence the vertex is (1/3, -1/3)
Question 2. g(x) = x 2 + 6x + 5 Answer: g(x) = x 2 + 6x + 5 y = x 2 + 6x + 5 Differentiate y’ = 2x + 6 2x + 6 = 0 2x = -6 x = -6/2 x = -3 y = x 2 + 6x + 5 y = (-3) 2 + 6(-3) + 5 y = 9 – 18 + 5 y = -4 Hence the vertex is (-3, -4)
Question 3. h(x) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)x 2 + 7x – 4 Answer: Given, h(x) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)x 2 + 7x – 4 y = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)x 2 + 7x – 4 Differentiate y’ = -x + 7 0 = -x + 7 x = 7 y = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)x 2 + 7x – 4 y = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)(7) 2 + 7(2) – 4 y = –\(\frac{49}{2}\) + 14 – 4 y = -24.5 + 10 y = -14.5 Hence the vertex is (7, -14.5)
Tell whether the function has a minimum value or a maximum value. Then find the value. Question 7. g(x) = 8x 2 – 8x + 6 Answer: Graph the function above and graph y = x 2 g(x) = 8x 2 – 8x + 6 x = -b/2a x = 8/2(8) = 1/2 = 0.5 Substitute in 0.5 for x and you get 4 for y your vertex is 0.5, 4 axis of symmetry equation is x – 0.5
Question 8. h(x) = – \(\frac{1}{4}\)x 2 + 3x + 1 Answer: maximum value; 10
Question 9. The cables between the two towers of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge in Washington form a parabola that can be modeled by y = 0.00016x 2 – 0.46x + 507, where x and y are measured in feet. What is the height of the cable above the water at its lowest point? Answer: Given, The cables between the two towers of the Tacoma Narrows Bridge in Washington form a parabola that can be modeled by y = 0.00016x 2 – 0.46x + 507, where x and y are measured in feet. x = -b/2a = -(-0.37)/2(0.000098) = 1888 Now substitute 1888 for x in the equation to find the y-coordinate of the vertex. y = 0.00016(1888) 2 – 0.46(1888) + 507 = 203 The cable is about 203 feet above the water at its lower point.
Question 11. Which balloon reaches its maximum height faster? Explain your reasoning. Answer:
Graphing f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c 8.3 Exercises
Question 1. VOCABULARY Explain how you can tell whether a quadratic function has a maximum value or a minimum value without graphing the function. Answer: The equation of a quadratic function is of the form ax2 + bx + c and if a < 0 then the function will have a maximum value of if a > 0 then the function will have a minimum value.

Question 8. y = 3x 2 + 2x Answer: y = 3x 2 + 2x The axis of symmetry when a = 3 and b = 2 x = -b/2a x = -1/3 The axis of symmetry is -1/3 Now use the function to find the y-coordinate of the vertex y = 3x 2 + 2x y = 3(-1/3) 2 + 2(-1/3) y = -1/3 Thus the vertex is (-1/3, -1/3)
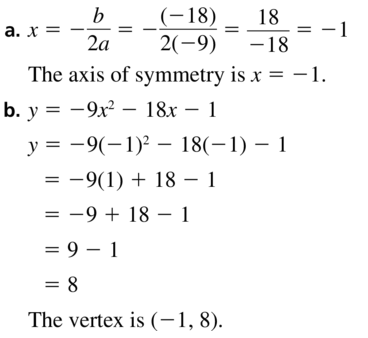
Question 10. f(x) = -6x 2 + 24x – 20 Answer: Given, f(x) = -6x 2 + 24x – 20 a = -6 and b = 24 x = -b/2a = -24/2(-6) = 2 The axis of symmetry is x = 2, so the x-coordinate of the vertex is 2. Use the function to find the y-coordinate of the vertex. f(x) = -6x 2 + 24x – 20 = -6(2) 2 + 24(2) – 20 = -24 + 48 – 20 = 4 Vertex is (2, 4)
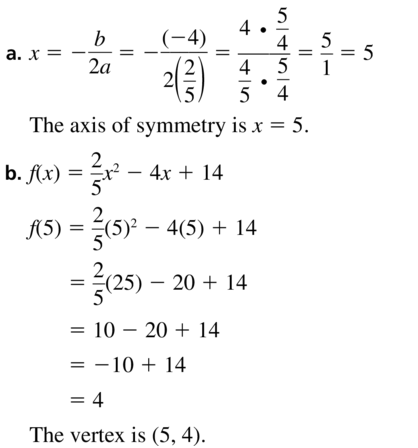
Question 12. y = – \(\frac{3}{4}\) x 2 + 9x – 18 Answer: y = – \(\frac{3}{4}\) x 2 + 9x – 18 a = – \(\frac{3}{4}\) and b = 9 x = -b/2a Substitute – \(\frac{3}{4}\) for a and 9 for b x = – 9/2(-\(\frac{3}{4}\)) x = 6 Thus the axis of symmetry is x = 6 y = – \(\frac{3}{4}\) (6) 2 + 9(6) – 18 = 9 The vertex is (6, 9)

Question 22. f(x) = -5x 2 + 10x + 7 Answer: Since the leading coefficient is negative, the function has a maximum value. f(x) = -5x 2 + 10x + 7 Axis of symmetry: x = -10/-10 = 1 f(x) = -5(1) 2 + 10(1) + 7 = 12 Maximum value is 12.
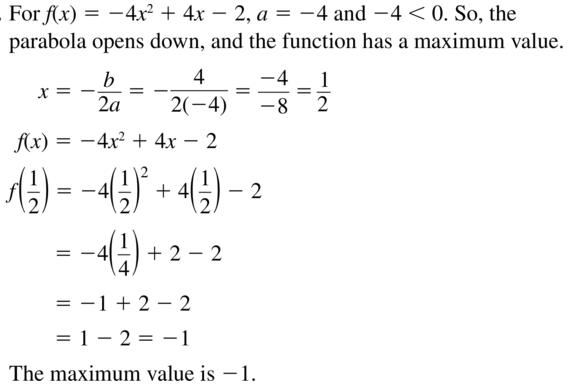
Question 24. y = 2x 2 – 10x + 13 Answer: Since the leading coefficient is positive, the function has a minimum value. y = 2x 2 – 10x + 13 Axis of symmetry is x = 5/2 y = 2(5/2) 2 – 10(5/2) + 13 = 1/2 Minimum value: 1/2
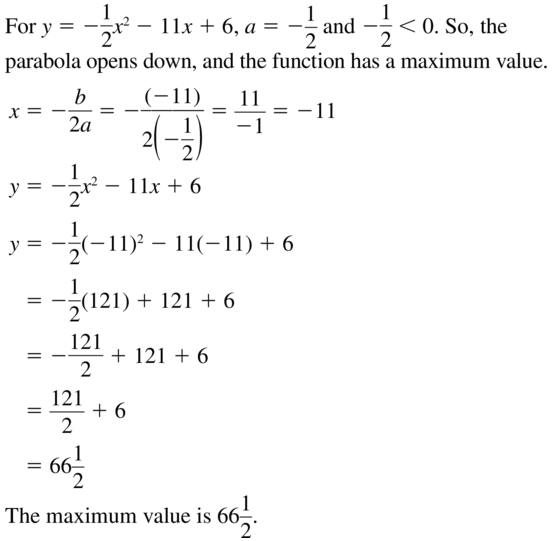
Question 26. f(x) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)x 2 – 5x + 27 Answer: f(x) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)x 2 – 5x + 27 Since a>0, the minimum value for function exists. The minimum value is attained at the vertex of parabola. x = –\(\frac{b}{2a}\) x = \(\frac{25}{2}\) y0 = f(\(\frac{25}{2}\)) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)(\(\frac{25}{2}\)) 2 – 5(\(\frac{25}{2}\)) + 27 = -4.25 The minimum value is -4.25

Question 28. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS The function h(t) = -16t 2 + 16t represents the height (in feet) of a horse t seconds after it jumps during a steeplechase. a. When does the horse reach its maximum height? b. Can the horse clear a fence that is 3.5 feet tall? If so, by how much? c. How long is the horse in the air? Answer: a. h(t) = -16t 2 + 16t t0 = –\(\frac{16}{2(-16)}\) = 1/2 Horse reaches its maximum height at t = 0.5s
b. y0 = h(1/2) = -16(1/2) 2 + 16(1/2) = -4 + 8 = 4 Since, the maximum value is 4 feet, the fence would be cleared by 0.5 feet. c. Let t1 be the time at which horse hits the ground. Then h(t1) = 0 and t1 > 0 h(t1) = 0 -16t1 2 + 16t1 = 0 -16t(t1 – 1) = 0 t1 = 0 or 1 Since t1 > 0, we have t1 = 1s
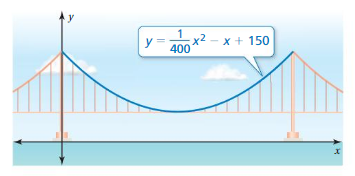
Question 30. REASONING Find the axis of symmetry of the graph of the equation y = ax 2 + bx + c when b = 0. Can you find the axis of symmetry when a = 0? Explain. Answer: x = –\(\frac{b}{2a}\) when b = 0 x = 0 when a = 0 x = undefined because of division by 0. Infact, there is no axis of symmetry because the equation will become linear. y = bx + c
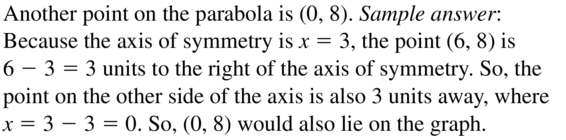
Question 32. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that it is possible to draw a parabola through any two points with different x-coordinates. Is your friend correct? Explain. Answer: f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c A parabola passing through 2 points give two linear equations with 3 variables that need to satisfied. Let (x0, y0) and (x1, y1) be two points through which parabola passes. ax0 2 + bx0 + c = y0 – c ax1 2 + b1 + c = y1 – c Thus there would be the infinite number of parabolas passing through the two points.
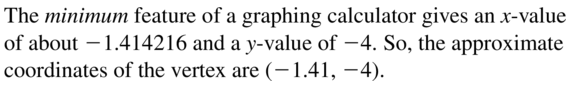
b. Using a different revenue model, the store expects to sell five more calculators for each $4 decrease in price. Which revenue model results in a greater maximum monthly revenue? Explain. Answer: R(n) = (120 – 4n)(80 + 5n) R(n) = -20n² + 280n + 9600 n = -b/2a a = -20 and b = 280 n = – 280/2(-20) = 7 R(n) = (120 – 4(7))(80 + 5(7)) = 10580 The vertex is at (7, 10580) This means that the maximum revenue is $10580 which is less than the original revenue at $10800. Therefore, the original revenue results in a greater maximum monthly revenue.
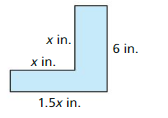
Answer: The initial height is the y-intercept which is y = 1.5 b. Estimate the maximum height of the arrow. Answer: Approximately 1.6 meters c. How far does the arrow travel? Answer: Find the x-coordinate where y = 0 which is at x = 90 x = 90 meters

Question 44. REASONING For a quadratic function f, what does f(-\(\frac{b}{2a}\)) represent? Explain your reasoning. Answer: Since x = –\(\frac{b}{2a}\) represents the x-coordinate of the vertex, the f(-\(\frac{b}{2a}\)) is the y-coodinate of the vertex.
Describe the transformation(s) from the graph of f(x) = |x| to the graph of the given function. Question 50. q(x) = |x + 6| Answer: The graph is shifted to the left by 6.

Question 52. g(x) = |x – 2| + 5 Answer: The graph is shifted to the right by 2 and up by 5.
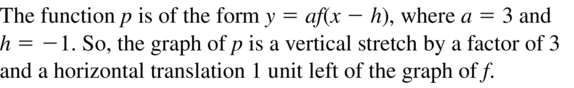
Graphing Quadratic Functions Study Skills: Learning Visually
8.1– 8.3 What Did You Learn?

Core Concepts Section 8.1 Characteristics of Quadratic Functions, p. 420 Graphing f(x) = ax 2 When a > 0, p. 421 Graphing f (x) = ax 2 When a < 0, p. 421
Section 8.2 Graphing f(x) = ax 2 + c, p. 426
Section 8.3 Graphing f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c, p. 432 Maximum and Minimum Values, p. 433
Mathematical Practices
Question 1. Explain your plan for solving Exercise 18 on page 423. Answer:
Question 2. How does graphing a function in Exercise 27 on page 429 help you answer the questions? Answer:
Question 3. What definition and characteristics of the graph of a quadratic function did you use to answer Exercise 44 on page 438? Answer:
Study Skills: Learning Visually
- Draw a picture of a word problem before writing a verbal model. You do not have to be an artist.
- When making a review card for a word problem, include a picture. This will help you recall the information while taking a test.

Graphing Quadratic Functions 8.1 – 8.3 Quiz
Tell whether the function has a minimum value or a maximum value. Then find the value. Question 17. f(x) = 5x 2 + 10x – 3 Answer: f(x) = 5x 2 + 10x – 3 x = -10/10 = -1 f(x) = 5(-1) 2 + 10(-1) – 3 = -8 Minimum value: -8
Question 18. f(x) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)x 2 + 2x + 16 Answer: Since the leading coefficient is negative, the parabola contains a maximum value f(x) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)x 2 + 2x + 16 x = -2/-1 = 2 f(x) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)(2) 2 + 2(2) + 16 = 18 Maximum value: 18
Question 19. y = -x 2 + 4x + 12 Answer: y = -x 2 + 4x + 12 Since a < 0, maximum value exists. The maximum value is attained at vertex. x0 = -b/2a = – 4/2(-1) = 2 y0 = y(2) = -(2) 2 + 4(2) + 12 = -4 + 8 + 12 = 16
Question 20. y = 2x 2 + 8x + 3 Answer: y = 2x 2 + 8x + 3 x = -8/4 x = 2 y = 2(-2) 2 + 8(-2) + 3 y = -5 Minimum value is -5
Question 21. The distance y (in feet) that a coconut falls after t seconds is given by the function y = 16t 2 . Use a graph to determine how many seconds it takes for the coconut to fall 64 feet. Answer: y = 16t 2 16t 2 = 64 t 2 = 4 t = 2
Question 22. The function y = -16t 2 + 25 represents the height y (in feet) of a pinecone t seconds after falling from a tree. a. After how many seconds does the pinecone hit the ground? Answer: The pinecone hits the ground at y = 0 0 = -16t 2 + 25 16t 2 = 25 t 2 = 25/16 t = 5/4 = 1.25 seconds
b. A second pinecone falls from a height of 36 feet. Which pinecone hits the ground in the least amount of time? Explain. Answer: The constant 25 represents the initial height of 25 feet. Therefore, the first pinecone will hit the ground in the least amount of time.
Lesson 8.4 Graphing f(x) = a(x – h) 2 + k
Essential Question How can you describe the graph of f(x) = a(x – h) 2 ?
Question 3. How can you describe the graph of f(x) = a(x – h) 2 ? Answer:

Determine whether the function is even, odd, or neither. Question 1. f(x) = 5x Answer: Given function f(x) = 5x f(-x) = 5(-x) f(-x) = -5x Thus the function is odd
Question 2. g(x) = 2x Answer: Given function g(x) = 2x g(-x) = 2(-x) = -2x Thus the function is odd
Question 3. h(x) = 2x 2 + 3 Answer: Given function h(x) = 2x 2 + 3 h(-x) = 2(-x) 2 + 3 = 2x 2 + 3 Thus the function is even.
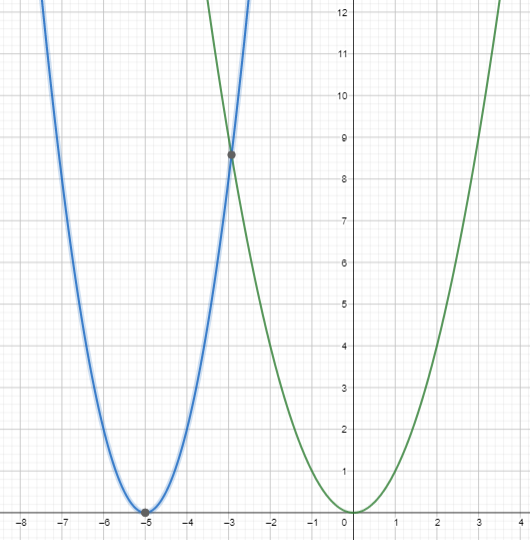
Question 8. Consider function g in Example 3. Graph f(x) = g(x) – 3 Answer:
Question 9. WHAT IF? The vertex is (3, 6). Write and graph a quadratic function that models the path. Answer:
Graphing f(x) = a(x – h) 2 + k 8.4 Exercises
Question 1. VOCABULARY Compare the graph of an even function with the graph of an odd function. Answer: The graph of an even function is symmetric about the y-axis. The graph of an odd function is symmetric about the origin.
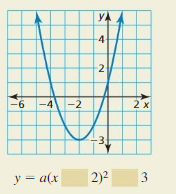
Question 2. OPEN-ENDED Write a quadratic function whose graph has a vertex of (1, 2). Answer: f(x) = a(x – 1) 2 + 2 Equation must have a vertex at (1, 2)
Question 3. WRITING Describe the transformation from the graph of f(x) = ax 2 to the graph of g(x) = a(x – h) 2 + k. Answer: The graph of g is a horizontal translation h units right if h is positive or |h| units left if h is negative and a vertical translation k units up if k is positive or |k| units down if k is negative of the graph of f.
Question 6. g(x) = 3x 2 Answer: Given function g(x) = 3x 2 g(-x) = 3(-x) 2 g(-x) = 3x 2 Even
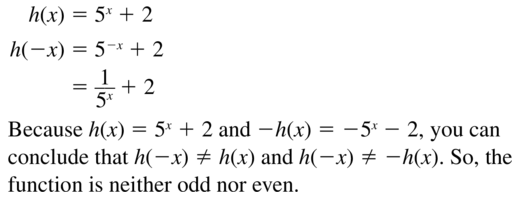
Question 8. m(x) = 2x 2 – 7x Answer: m(x) = 2x 2 – 7x m(-x) = 2(-x) 2 – 7(-x) m(-x) = 2x 2 + 7x Neither
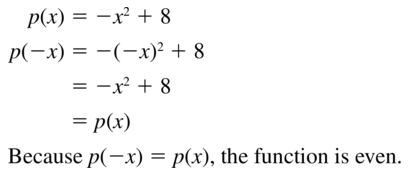
Question 10. f(x) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)x Answer: f(x) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)x f(-x) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)(-x) f(-x) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x Odd
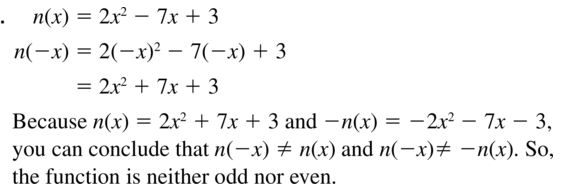
Question 12. r(x) = -6x 2 + 5 Answer: To determine is function odd, even, neither, you should replace x with -x. 1. If r(-x) = -r(x) function is odd 2. If r(-x) = r(x) function is even r(x) = -6x 2 + 5 r(-x) = -6(-x) 2 + 5 r(-x) = -6x 2 + 5 Thus r(-x) = r(x) Even
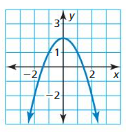
Question 20. f(x) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)(x – 6) 2 Answer: f(x) = \(\frac{1}{4}\)(x – 6) 2 Find the axis of symmetry and vertex: Since h = 6, the axis of symmetry is x = 6 and the vertex is (6, 0)
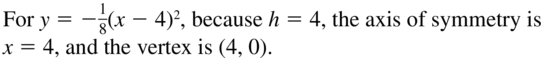
Question 22. y = -5(x + 9) 2 Answer: y = -5(x + 9) 2 Find the axis of symmetry and vertex: Since h = -9, the axis of symmetry is x = -9 and the vertex is (-9, 0)
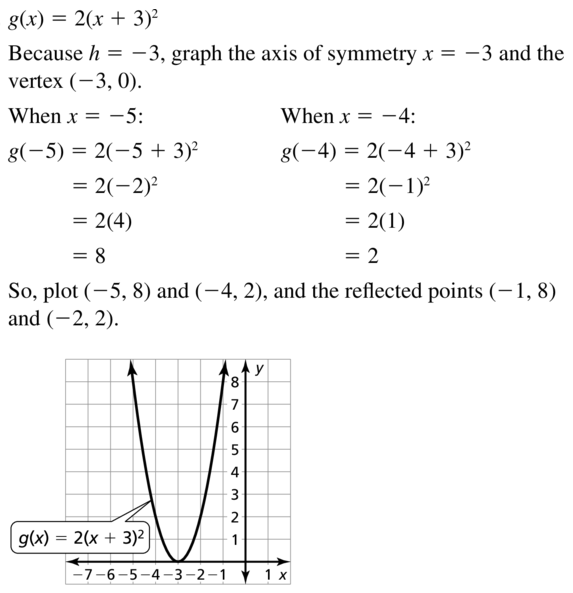
Question 32. f(x) = 3(x – 3) 2 + 6 Answer: Given, f(x) = 3(x – 3) 2 + 6 Vertex: (3, 6) Axis of symmetry: x = 3
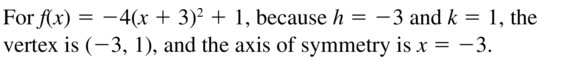
Question 34. y = -(x – 6) 2 – 5 Answer: y = -(x – 6) 2 – 5 Vertex: (6, -5) Axis of symmetry: x = 6
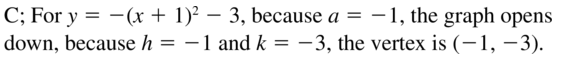
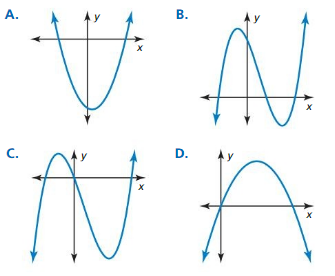
Question 36. y = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)(x – 1) 2 + 3 Answer: y = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)(x – 1) 2 + 3 This equation belongs to Graph A because it is the only graph with a vertex of (1, 3) and a reflection over the x-axis.
Question 38. y = 2(x + 1) 2 – 3
Answer: Given, y = 2(x + 1) 2 – 3 This equation belongs to Graph B because it is the only graph with a vertex of (-1, -3) and a vertical stretch by a factor of 2.
Question 46. r(x) = f(x + 2) Answer: Given, f(x) = (x – 2)² + 1 r(x) = f(x + 2) Rewrite r(x): r(x) = x² + 1 Match with a graph: The function r(x) belongs to Graph C because it is the only graph with a vertex at (0, 1)

Question 48. p(x) = f(x) – 3
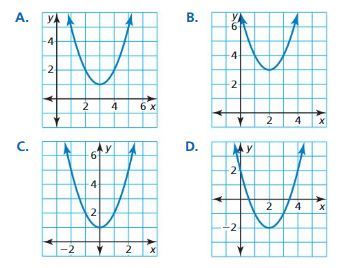
Answer: f(x) = (x – 2)² + 1 p(x) = f(x) – 3 Rewrite p(x): p(x) = (x – 2)² – 2 Match with a graph: The function p(x) belongs to Graph D because it is the only graph with a vertex at (2, -2)

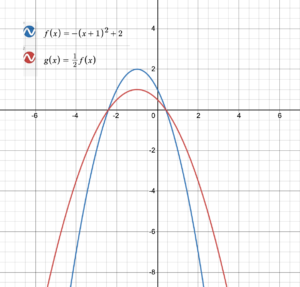
Question 50. f(x) = -(x + 1) 2 + 2; g(x) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)f(x) Answer: g(x) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)f(x) \(\frac{1}{2}\)(-(x + 1) 2 + 2) = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)(x + 1) 2 + 1. In given function g(x) = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)(x + 1) 2 + 1 a. a vertical contraction by a factor of \(\frac{1}{2}\) b. a vertical shift of 1 unit downward c. reflection about the x-axis d. horizontal shift of 1 unit to the right of the parent function y = ax 2
c. Compare the graphs. On which possession does the kicker punt closer to his goal line? Explain. Answer: The graph of g(x) is a translation left 5 units of f(x), The kicker kicks closer to his goal line the second time.
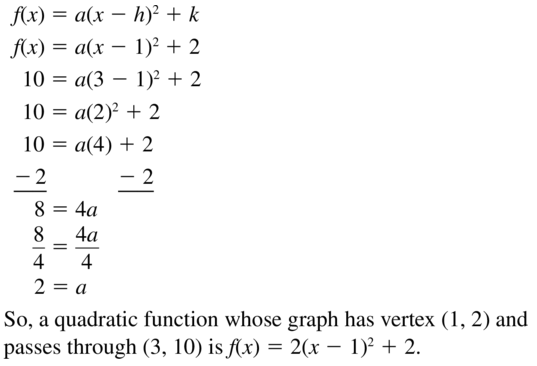
Question 58. vertex: (-3, 5); passes through (0, -14) Answer: Vertex form is f(x) = a(x – h) 2 + k f(x) = a(x + 3) 2 + 5 -14 = a(0 + 3) 2 + 5 -14 = a(3) 2 + 5 9a + 5 = -14 9a = -14 – 5 9a = -19 a = -19/9 f(x) = -19/9(x + 3) 2 + 5

Question 60. vertex: (1, 8); passes through (3, 12) Answer: Vertex form is f(x) = a(x – h) 2 + k f(x) = a(x – 1) 2 + 8 12 = a(3 – 1) 2 + 8 12 = a(2) 2 + 8 4a + 8 = 12 4a = 12 – 8 4a = 4 a = 1 f(x) = 1(x – 1) 2 + 8

Question 62. vertex: (-5, -1); passes through (-2, 2) Answer: Vertex form is f(x) = a(x – h) 2 + k f(x) = a(x + 5) 2 – 1 2 = a(-2 + 5) 2 – 1 2 = a(3) 2 – 1 9a – 1 = 2 9a = 3 a = 1/3 f(x) = 1/3(x + 5) 2 – 1

Question 66. y = 3x 2 + 6x – 1 Answer: Given, y = 3x 2 + 6x – 1 x = -b/2a x = -6/6 x = -1 y = 3(-1) 2 + 6(-1) – 1 y = 3 – 6 – 1 y = -4 Vertex: (-1, -4) f(x) = a(x – h) 2 + k y = a(x + 1) 2 – 4 -1 = a(0 + 1) 2 – 4 -1 = a – 4 a = -1 + 4 a = 3 f(x) = 3(x + 1) 2 – 4

Question 68. f(x) = -x 2 + 4x + 2 Answer: Given, f(x) = -x 2 + 4x + 2 x = -b/2a x = -4/2(-1) x = -2 y = -(-2) 2 – 4(-2) + 2 y = -4+8+2 y = 6 Vertex: (-2, 6) f(x) = a(x – h) 2 + k y = a(x + 2) 2 + k 2 = a(0 + 2) 2 + 6 2 = 4a + 6 4a + 6 = 2 a = -1 f(x) = -(x + 2) 2 + 6
Question 69. REASONING Can a function be symmetric about the x-axis? Explain. Answer: A function cannot be symmetric about the x-axis because it would not pass the vertical line test.
Question 72. f(x) = 2(x – 1)) 2 + 1 h(x) = f(x – 5) Answer: given, f(x) = 2(x – 1)) 2 + 1 h(x) = f(x – 5) The graph of h(x) is a horizontal translation right 5 units of the graph of f(x) y = 2(x – 6) 2 + 1

Question 74. f(x) = -(x + 5)) 2 – 6 h(x) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)f(x) Answer: Given, f(x) = -(x + 5)) 2 – 6 h(x) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)f(x) The graph of h(x) is a vertical shrink by a factor of 1/3 of the graph of f(x) y = –\(\frac{1}{3}\)(x + 5) 2 – 2
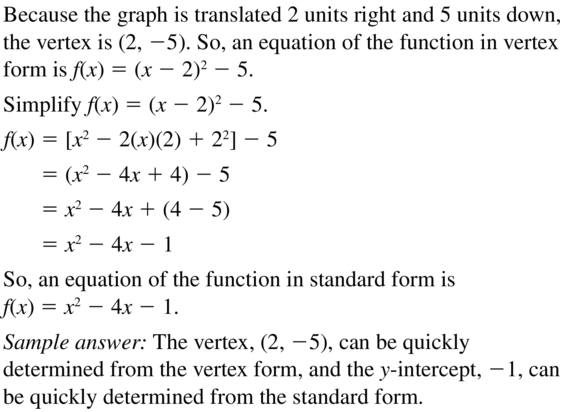
Question 76. THOUGHT PROVOKING Which of the following are true? Justify your answers. a. Any constant multiple of an even function is even. Answer: Let f(x) be an even function. Let g(x) = af(x) g(-x) = af(-x) Since f is even function, we get g(-x) = af(x) = g(x) Thus, g is an even function. b. Any constant multiple of an odd function is odd. Answer: Let f(x) be an odd function. Let g(x) = af(x) g(-x) = af(-x) Since f is even function, we get g(-x) = a(-f(x)) = -g(x) Thus, g is an odd function. c. The sum or difference of two even functions is even. Answer: Let f, h be even function. Let g(x) = f(x) + ah(x) g(-x) = f(-x) + ah(-x) Since f, h are even functions. Let g(x) = f(x) + ah(x) g(-x) = f(-x) + ah(-x) g(x) = f(x) + ah(x) = g(x) Thus g is an even function
d. The sum or difference of two odd functions is odd. Answer: Let f, h be odd function. Let g(x) = f(x) + ah(x) g(-x) = f(-x) + ah(-x) Since f, h are even functions. Let g(x) = f(x) + ah(x) g(-x) = -f(x) + a(-h(x)) = -g(x) Thus g is an odd function
e. The sum or difference of an even function and an odd function is odd. Answer: f(x) = x² h(x) = x g(x) = f(x) + h(x) f(1) = h(1) = 1, g(1) = 2 ≠ -g(-1) = 0 Thus, g is not odd function
Question 78. REASONING Compare the graphs of y = 2x 2 + 8x +8 and y = x 2 without graphing the functions. How can factoring help you compare the parabolas? Explain. Answer: y = 2x 2 + 8x +8 y = 2(x 2 + 4x +4) y = 2(x+2)(x + 2) y = 2(x+2)² The graph is a translation left 2 units and a vertical stretch by a factor of 2 of the graph y = x 2

Solve the equation. Question 80. x(x – 1) = 0 Answer: Given, x(x – 1) = 0 x = 0 or x – 1 = 0 x = 0 or x = 1
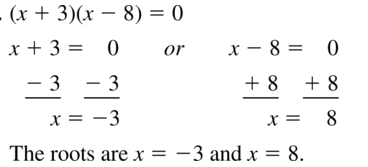
Question 82. (3x – 9)(4x + 12) = 0 Answer: Given, (3x – 9)(4x + 12) = 0 3x – 9 = 0 or 4x + 12 = 0 3x = 9 or 4x = -12 x = 3 or x = -3
Lesson 8.5 Using Intercept Form
Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q)?
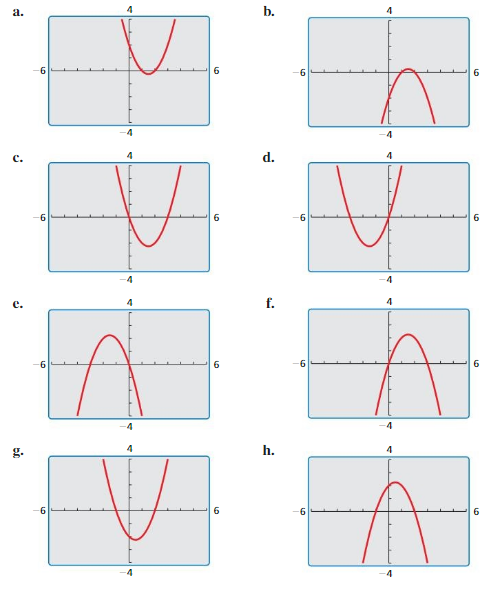
Question 2. What are some of the characteristics of the graph of f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q)? Answer:

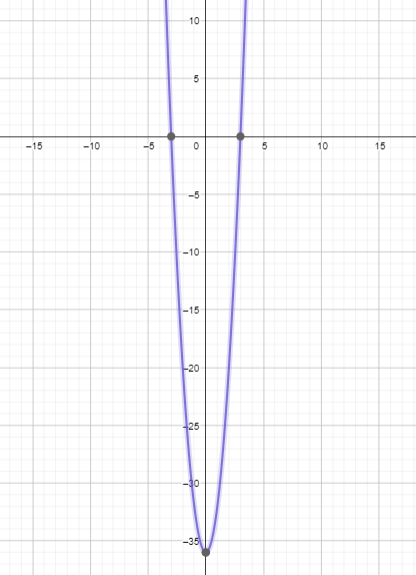
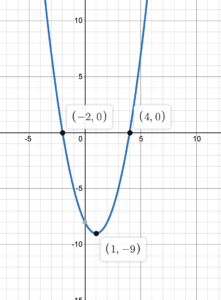
x-intercept:(-1, 0) and (4, 0) Range: {y ∈ R : y ≤ 25/2}
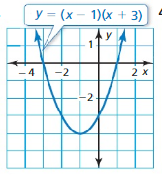
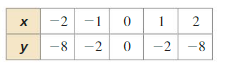
Find the zero(s) of the function. Question 4. f(x) = (x – 6)(x – 1) Answer: f(x) = (x – 6)(x – 1) (x – 6)(x – 1) = 0 x² – 6x -x + 6 = 0 x – 6 = 0 or x – 1 = 0 x = 6 or x = 1
Question 5. g(x) = 3x 2 – 12x + 12 Answer: Given, g(x) = 3x 2 – 12x + 12 3x 2 – 12x + 12 = 0 3x 2 – 12x + 12 = 0 3( x 2 – 4x + 4) = 0 x 2 – 4x + 4 = 0
Question 6. h(x) = x(x 2 – 1) Answer: Given, h(x) = x(x 2 – 1) x(x 2 – 1) = 0 x = 0 or x 2 – 1 = 0 x = 0 or x = 1
Write a quadratic function in standard form whose graph satisfies the given condition(s). Question 9. x-intercepts: -1 and 1 Answer:
Question 10. vertex: (8, 8) Answer: Let a = 1 f(x) = a(x – h)² + k f(x) = 1(x – 8)² + 8 f(x) = (x – 8)² + 8 f(x) = x² – 16x + 64 + 8 f(x) = x² – 16x + 72
11. passes through (0, 0), (10, 0), and (4, 12) Answer:
Question 12. passes through (-5, 0), (4, 0), and (3, -16) Answer:
Question 15. The zeros of a cubic function are -3, -1, and 1. The graph of the function passes through the point (0, -3). Write the function. Answer:
Using Intercept Form 8.5 Exercises
Question 1. COMPLETE THE SENTENCE The values p and q are __________ of the graph of the function f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q). Answer: The values p and q are x-intercepts of the graph of the function f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q).
Question 2. WRITING Explain how to find the maximum value or minimum value of a quadratic function when the function is given in intercept form. Answer: The intercept form is: f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q) x = (p+q)/2 Substitute the x-coordinate to the function to find the y-coordinate which is the maximum or minimum value.
Question 6. g(x) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) x(x + 8) Answer: g(x) = \(\frac{2}{3}\) x(x + 8) x – intercepts of parabola in intercept form are given p = 0 and q = -8 Axis of symmetry is x = (p + q)/2 = (0 – 8)/2 = -4
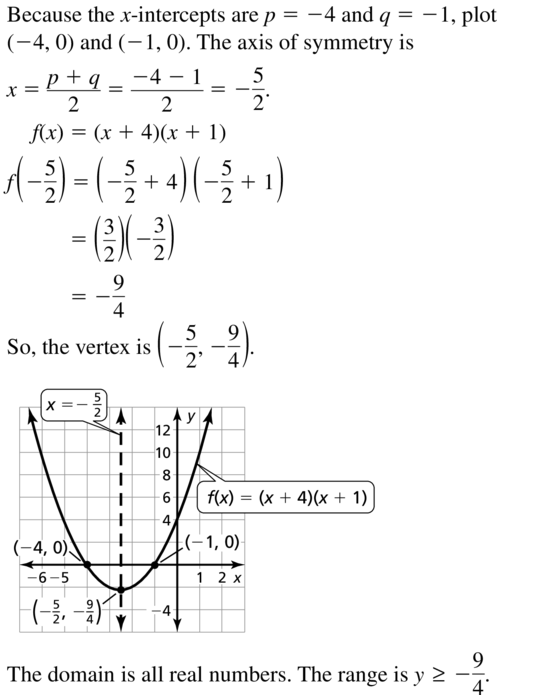
Question 22. f(x) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)(x + 5)(x – 1) Answer: f(x) = \(\frac{1}{3}\)(x + 5)(x – 1) \(\frac{1}{3}\)(x + 5)(x – 1) = 0 x + 5 = 0 or x – 1 = 0 x = -5 or x = 1
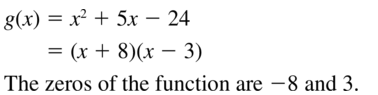
Question 24. y = x 2 – 17x + 52 Answer: Given, y = x 2 – 17x + 52 x 2 – 17x + 52 = 0 x 2 – 4x – 13x + 52 = 0 x(x – 4) – 13(x – 4) = 0 (x – 4)(x – 13) = 0 x – 4 = 0 or x – 13 = 0 x = 4 or x = 13
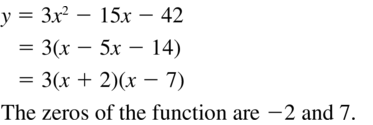
Question 26. g(x) = -4x 2 – 8x – 4 Answer: g(x) = -4x 2 – 8x – 4 -4x 2 – 8x – 4 = 0 (x + 1) 2 = 0 x + 1 = 0 x = -1
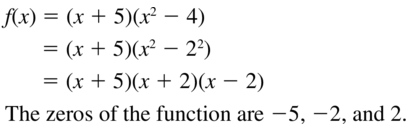
Question 28. h(x) = (x 2 – 36)(x – 11) Answer: h(x) = (x 2 – 36)(x – 11) (x 2 – 36)(x – 11) = 0 (x + 6)(x – 6)(x – 11) = 0 x + 6 = 0 or x – 6 = 0 or x – 11 = 0 x = -6 or 6 or 11

Question 30. y = x 3 – x 2 – 9x + 9 Answer: y = x 3 – x 2 – 9x + 9 x 3 – x 2 – 9x + 9 = 0 x 2 (x – 1) -9(x – 1) = 0 (x – 1)(x² – 9) = 0 (x – 1)(x – 3)(x + 3) = 0 x – 1 = 0 or x – 3 = 0 or x + 3 = 0 x = 1 or x = 3 or x = -3
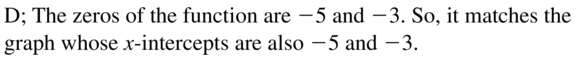
Question 46. vertex: (4, 8) Answer: f(x) = a(x – h)² + k V(h, k) = (4, 8) h = 4, k = 8 f(x) = a(x – 4)² + 8 a = 1 f(x) = 1(x – 4)² + 8 f(x) = (x – 4)² + 8 = x² – 8x + 24
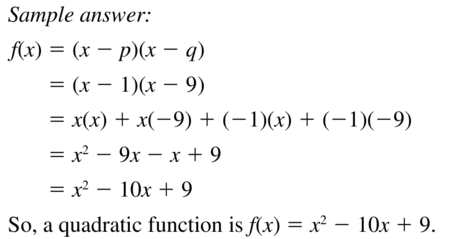
Question 48. x-intercepts: -2 and -5 Answer: Given, x-intercepts: -2 and -5 f(x) = a[x – (-2)][x – (-5)] f(x) = a(x + 2)(x + 5) a = 1 f(x) = 1(x + 2)(x + 5) f(x) = (x + 2)(x + 5) = x² + 5x + 2x + 10 = x² + 7x + 10
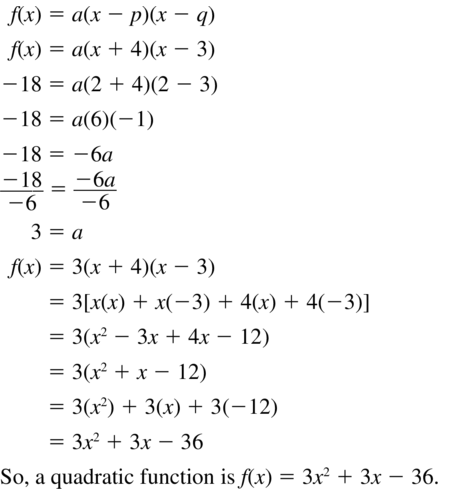
Question 50. passes through (-5, 0), (-1, 0), and (-4, 3) Answer: f(x) = a[x – (-5)][x – (-1)] f(x) = a(x + 5)(x + 1) a(-4 + 5)(-4 + 1) = 3 -3a = 3 a = -1 f(x) = -1(x + 5)(x + 1) f(x) = -(x² + x + 5x + 5) – x² – 6x – 5

Question 52. passes through (0, 0) and (6, 0) Answer: The points of parabola (0, 0) and (6, 0) f(x) = a[x – 0][x – 6] f(x) = ax(x – 6) a=1 f(x) = x(x – 6) f(x) = x² – 6x

Question 74. x-intercepts: -7, -5, and 0 Answer: Given the x-intercepts use the intercept form: f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q)(x – r) a = 1 f(x) = 1(x – (-7))(x – (-5))(x – 0) f(x) = (x + 7)(x + 5)(x) f(x) = x² + 12x² + 35x

Question 76. passes through (0, 6) Answer: Note that the given is not x-intercept Since we need a cubic function, we need 3 intercepts. For simplicity’s sake we will use (-1, 0), (1, 0) and (2, 0) Given the x-intercepts use the intercept form: f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q)(x – r) f(x) = a(x – (-1))(x – 1)(x – 2) Use the other point (0, 6) to find the value of a: 6 = a(0 + 1)(0 – 1)(0 – 2) 6 = 2a a = 3 f(x) = 3(x + 1)(x – 1)(x – 2) f(x) = 3x³ – 6x² – 3x + 6
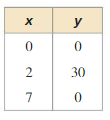
b. The basketball player releases another shot from the point (13, 0) and makes the shot. The shot also passes through the point (10, 1.4). Write a quadratic function in standard form that models the path of the shot. Answer: Two intercepts are given (3, 0) and (13, 0) y = a(x – p)(x – q) y = a(x – 3)(x – 13) Use the other point (10, 1.4) to find the value of a 1.4 = a(10 – 3)(10 – 13) 1.4 = -21a a = –\(\frac{1}{15}\) f(x) = –\(\frac{1}{15}\) (x – 3)(x – 13) f(x) = –\(\frac{1}{15}\) (x² – 16x + 39)

Question 88. y = x 2 – x – 12 Answer: The given is a quadratic function, so it is either A or D. Substituting x = 0, the y-intercept is y = (0) 2 – 0 – 12 = -12 This corresponds to Graph A.

Question 90. y = x 3 – 4x 2 – 11x + 30 Answer: The given is a cubic function. So it is either B or C. Substituting x = 0, the y-intercept is y = x 3 – 4x 2 – 11x + 30 y = (0) 3 – 4(0) 2 – 11(0) + 30 = 30 This corresponds to Graph B.
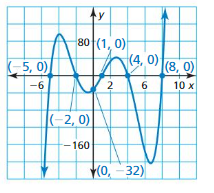
Question 96. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that any quadratic function can be written in standard form and in vertex form. Is your friend correct? Explain. Answer: My friend is correct Any quadratic function can be written in vertex form. y = a(x² – 2hx + h²) + k b = -2ahx c = h² + k Any quadratic function can be written in standard form. When a quadratic function is in standard form, completing the square can be applied so that it can be transformed to vertex form.
PROBLEM SOLVING In Exercises 100 and 101, write a system of two quadratic equations whose graphs intersect at the given points. Explain your reasoning. Question 100. (-4, 0) and (2, 0) Answer: Given the x-intercepts (-4, 2) use the intercept form: y = a(x – p)(x – q) y = a(x – (-4))(x – 2) y = a(x + 4)(x – 2) y = a(x² + 2x – 8) To find 2 equations let a be any constant value other than 0 y = x² + 2x – 8 y = -x² – 2x + 8
Question 104. What tends to happen to the number of calories as the number of grams of fat increases? Answer: As the number of grams of fat increases, the number of calories also increases.
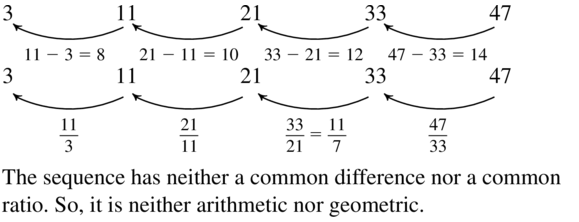
Question 106. -2, -6, -18, -54, . . . Answer: -6/-2 = -18/-6….. geometric sequence
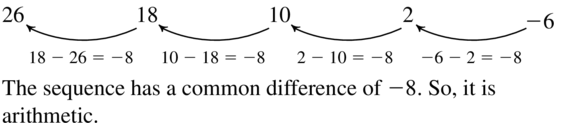
Question 108. 4, 5, 9, 14, 23, . . . Answer: 5 – 4 ≠ 9 – 5 not an arithmetic sequence 5/4 ≠ 9/5 not geometric sequence
Lesson 8.6 Comparing Linear, Exponential, and Quadratic Functions
Essential Question How can you compare the growth rates of linear, exponential, and quadratic functions?
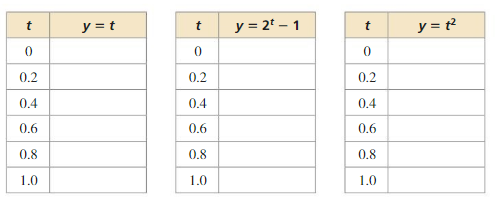
Question 3. How can you compare the growth rates of linear, exponential, and quadratic functions? Answer:
Question 4. Which function has a growth rate that is eventually much greater than the growth rates of the other two functions? Explain your reasoning. Answer:
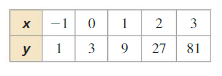
Plot the points. Tell whether the points appear to represent a linear, an exponential, or a quadratic function. Question 1. (-1, 5), (2, -1), (0, -1), (3, 5), (1, -3) Answer:
Question 2. (-1, 2), (-2, 8), (-3, 32), (0, \(\frac{1}{2}\)), (1, \(\frac{1}{8}\)) Answer:
Question 3. (-3, 5), (0, -1), (2, -5), (-4, 7), (1, -3) Answer:
Question 6. Compare the websites in Example 4 by calculating and interpreting the average rates of change from Day 0 to Day 10. Answer:
Question 7. WHAT IF? Tinyville’s population increased by 8% each year. In what year were the populations about equal? Answer:
Comparing Linear, Exponential, and Quadratic Functions 8.6 Exercises

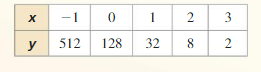
Question 2. WRITING How can you decide whether to use a linear, an exponential, or a quadratic function to model a data set? Answer: If consecutive y-values have a constant first difference, a linear function must be used to model a data set. If consecutive y-values have a constant second difference, a quadratic function must be used to model a data set. If a common ratio exists consecutive y-values, an exponential function must be used to model a data set.
Question 38. USING STRUCTURE Write a function that has constant second differences of 3. Answer: If the second difference is constant, then it must be a quadratic function. Let the first difference be: 1, 4, 7, 10 Therefore, a possible sequence with the first difference shown above is 0, 1, 5, 12, 22 Find a quadratic function that passes through: (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 5), (3, 12), (4, 22) Choose any 3 points: (0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 5) Us the model y = ax² + bx + c At (0, 0): 0 = a(0)² + b(0) + c c = 0 At (0, 0): 0 = a(1)² + b(1) + c a + b + c = 1 At (2, 5): 0 = a(2)² + b20) + c 4a + 2b + c = 5 Substitute c = 0 a + b + c = 1 a + b = 1 4a + 2b = 5 Solving a and b, a = 1.5, b = -0.5 y = 1.5x² – 0.5x

Question 44. \(\sqrt [ 3 ]{ 125 }\) Answer: 5
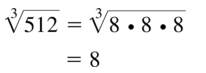
Question 46. \(\sqrt [ 5 ]{ 243 }\) Answer: 3
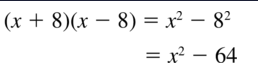
Question 48. (4y + 2)(4y – 2) Answer: Given, (4y + 2)(4y – 2) 4y(4y – 2) + 2(4y – 2) 16y² – 8y + 8y – 4 16y² – 4
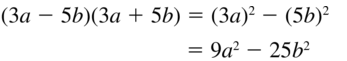
Question 50. (-2r + 6s)(-2r – 6s) Answer: Given, (-2r + 6s)(-2r – 6s) -2r(-2r – 6s) + 6s(-2r – 6s) 4r² + 12rs – 12rs – 36s² 4r² – 36s²

Graphing Quadratic Functions Performance Task: Asteroid Aim
8.4–8.6 What Did You Learn?
Question 1. How can you use technology to confirm your answer in Exercise 64 on page 448? Answer:
Question 2. How did you use the structure of the equation in Exercise 85 on page 457 to solve the problem? Answer:
Question 3. Describe why your answer makes sense considering the context of the data in Exercise 20 on page 466. Answer:
Performance Task: Asteroid Aim

Graphing Quadratic Functions Chapter Review
8.1 Graphing f(x) = ax 2 (pp. 419–424)
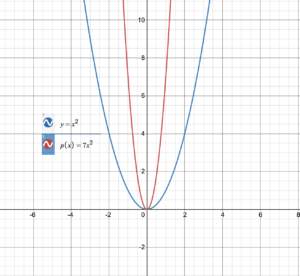
8.2 Graphing f(x) = ax 2 + c (pp. 425–430)
8.3 Graphing f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c (pp. 431–438)
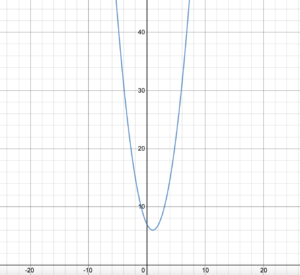
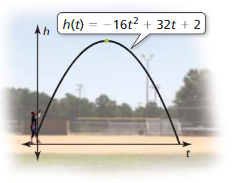
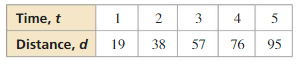
Question 13. The function f(t) = -16t 2 + 88t + 12 represents the height (in feet) of a pumpkin t seconds after it is launched from a catapult. When does the pumpkin reach its maximum height? What is the maximum height of the pumpkin? Answer: The trajectory of the pumpkin will be a parabola, so the time required for the pumpkin to reach maximum speed is actually the x-coordinate of the vertex of the parabola and the maximum height is the y-coordinate of the vertex. f(t) = -16t 2 + 88t + 12 f(t) = -16(t 2 + 2 . t . \(\frac{11}{4}\)+ (\(\frac{11}{4}\))² – (\(\frac{11}{4}\))² – \(\frac{3}{4}\)) f(t) = -16((t – \(\frac{11}{4}\))² – \(\frac{133}{16}\)) f(t) = -16(t – \(\frac{11}{4}\))² + 133 f(t) = -16(t – 2.75)² + 133 Pumpkin reaches a maximum speed 2.75 seconds after it is launched and the maximum height is 133 feet.
8.4 Graphing f(x) = a(x − h) 2 + k (pp. 441–448)
Determine whether the function is even, odd, or neither. Question 14. w(x) = 5 x Answer: Function is even if f(-x) = f(x) and function is odd if f(-x) = -f(x) So we replace x with w(x) with -x w(-x) = 5 -x = \(\frac{1}{5 x }\) notice that w(-x) is not equal to -w(x) = -5 x or w(x) So, the function w(x) is neither odd nor even.
Question 15. r(x) = -8x Answer: Function is even if f(-x) = f(x) and function is odd if f(-x) = -f(x) So we replace x with r(x) with -x r(-x) = -8(-x) = 8x notice that r(-x) is equal to r(x) so function r(x) is odd function.
Question 16. h(x) = 3x 2 – 2x Answer: Function is even if f(-x) = f(x) and function is odd if f(-x) = -f(x) So we replace x with h(x) with -x h(-x) =3(-x) 2 – 2(-x) = 3x 2 + 2x notice that h(-x) is not equal to -h(x) or h(x) So, the function w(x) is neither odd nor even.
Question 21. Write a quadratic function whose graph has a vertex of (3, 2) and passes through the point (4, 7). Answer: The vertex form of the quadratic function is y = a(x – h)² + k where (h, k) is the vertex. It is given that the vertex is (3, 2) y = a(x – 3)² + 2 As the graph passes through the point (4, 7). We can insert a point in the equation to get a 7 = a(4 – 3)² + 2 7 – 2 = a . 1 a = 5 Therefore the equation that satisfies the given vertex and point is y = 5(x – 3)² + 2
8.5 Using Intercept Form (pp. 449–458)
8.6 Comparing Linear, Exponential, and Quadratic Functions (pp. 459−468)
Question 30. The balance y (in dollars) of your savings account after t years is represented by y = 200(1.1)t. The beginning balance of your friend’s account is $250, and the balance increases by $20 each year. (a) Compare the account balances by calculating and interpreting the average rates of change from t = 2 to t = 7. (b) Predict which account will have a greater balance after 10 years. Explain. Answer: average rates of change from t = 2 to t = 7 t(7) – t(2)/7 – 2 = 29.55 My friend’s balance is given by y = 20t + 250 t(7) – t(2)/7 – 2 = (250 + 140 – 250 + 40)/5 = 100/5 = 200 My saving account has more money and is growing faster than my friend’s saving account.
Graphing Quadratic Functions Chapter Test
where b is the common ratio. Thus the tentative equation of the function that represents the given table of values f(x) = a . b x Use the point (0, 8) to find the value of a: 8 = a . 2 0 8 = a(1) 8 = a Therefore the function that represents the given table of values is f(x) = 8 . 2 x Thus is equivalent to the function f(x) = 2³ . 2 x+3
Write a quadratic function in standard form whose graph satisfies the given conditions. Explain the process you used. Question 10. passes through (-8, 0), (-2, 0), and (-6, 4) Answer: Given the x-intercepts (-8, -2) use the intercept form: f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q) Substitute the intercepts and simplify: f(x) = a(x – (-8))(x – (-2)) f(x) = a(x + 8)(x+2) Use the other point, (-6, 4) to find the value of a: 4 = a(-6 + 8)(-6 + 2) 4 = -8a Thus the function f(x) = -1/2(x + 8)(x + 2) f(x) = -1/2x² – 5x – 8
Question 11. passes through (0, 0), (10, 0), and (9, -27) Answer: Given the x-intercepts (0, 10) use the intercept form f(x) = a(x – p)(x – q) f(x) = a(x – 0)(x – 10) f(x) = a(x)(x – 10) Use the other point, (9, -27) to find the value of a: -27 = a(9)(9 – 10) -27= -9a a = 3 Therefore the function is f(x) = 3(x)(x – 10) f(x) = 3x² – 30x
Question 12. is even and has a range of y ≥ 3 Answer: The quadratic is even if it is symmetric about the y-axis so the symmetry is the y-axis. The range implies that the parabola opens upward and the vertex is at (0, 3) Use the vertex form: y = a(x – h)² + k At vertex (h, k) = (0, 3) y = a(x – 0)² + 3 Let a = 1 y = (1)(x – 0)² + 3 y = x² + 3
Question 13. passes through (4, 0) and (1, 9) Answer: Let the parabola be in the form y = ax² + bx Set up 2 equations using the points At(4, 0): 0 = 16a + 4b At (1, 9): 9 = a + b b = 9 – a 0 = 16a + 4(9 – a) 0 = 16a + 36 – 4a -12a = 36 a = -3 b = 9 – (-3) y = -3x² + 12x
Question 15. You are playing tennis with a friend. The path of the tennis ball after you return a serve can be modeled by the function y = -0.005x 2 + 0.17x + 3, where x is the horizontal distance (in feet) from where you hit the ball and y is the height (in feet) of the ball. a. What is the maximum height of the tennis ball? Answer: The maximum height is the y-coordinate of the vertex. x = -b/2a where a = -0.005 and b = 0.17 x = –\(\frac{0.07}{2(-0.005)}\) = 17 The y-coordinate is y = -0.005(17)² + 0.17(17) + 3 y = 4.445
b. You are standing 30 feet from the net, which is 3 feet high. Will the ball clear the net? Explain your reasoning. Answer: The ball will clear the net if at x = 30, the height, y, is greater than 3 feet. y = 0.005(30)² + 0.17(30) + 3 y = 3.6 ft Since 3.6ft > 3 ft, then the ball will clear the net.
Question 16. Find values of a, b, and c so that the function f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c is (a) even, (b) odd, and (c) neither even nor odd. Answer: a. The function is even is it satisfies: f(-x) = f(x) a(-x)² + b(-x) + c = ax 2 + bx + c ax 2 – bx + c = ax 2 + bx + c For this equation to be true, we can let b = 0 so that a and c any value. A possible answer is a = 1, b = 0, c = 2 b. The function is odd if it satisfies: f(-x) = -f(x) a(-x)² + b(-x) + c = -(ax 2 + bx + c) ax 2 – bx + c = -ax 2 – bx – c For this equation to be true, we can let a = c = 0 so that b can be any value. A possible answer is a = 0, b = 1, c = 0 c. The function is neither odd nor even when a, b and c are non-zeros A possible answer is: a = 1, b = 2, c = 3
Graphing Quadratic Functions Cumulative Assessment
Question 2. Find all numbers between 0 and 100 that are in the range of the function defined below.(HSF-IF.A.3) f(1) = 1, f(2) = 1, f(n) = f(n – 1) + f(n – 2) Answer: The recursive rule is the Fibonacci sequence where each term is the sum of the previous terms. Use the recursive rule until the term is greater than 100 where it is not included: f(1) = 1 f(2) = 1 f(3) = f(2) + f(1) = 1 + 1 = 2 f(4) = f(3) + f(2) = 2 + 1 = 3 f(5) = f(4) + f(3) = 3 + 2 = 5 f(6) = f(5) + f(4) = 5 + 3 = 8 f(7) = f(6) + f(5) = 8 + 5 = 13 f(8) = f(7) + f(6) = 13 + 8 = 21 f(9) = f(8) + f(7) = 21 + 13 = 34 f(10) = f(9) + f(8) = 34 + 21 = 55 f(11) = f(10) + f(9) = 55 + 34 = 89 f(12) = f(11) + f(10) = 89 + 55 = 144 Therefore, the numbers that are in between 0 and 100 are: 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55 and 89.
Question 3. The function f(t) = -16t 2 + v 0 t + s 0 represents the height (in feet) of a ball t seconds after it is thrown from an initial height s0 (in feet) with an initial vertical velocity v0 (in feet per second). The ball reaches its maximum height after \(\frac{7}{8}\) second when it is thrown with an initial vertical velocity of ______ feet per second. Answer: The maximum height corresponds to the vertex where the x-coordinate is x = -b/2a t = – v 0 /2(-16) 7/8 = v 0 /32 v 0 = 28 Thus the initial velocity is 28ft/s.
Question 5. Your friend claims that quadratic functions can have two, one, or no real zeros. Do you support your friend’s claim? Use graphs to justify your answer. Answer: Yes, he is correct. There are 2 real zeros when the graph crosses the x-axis. There is only 1 real zero when the graph touches the x-axis. There is no real zero when the graph does not cross/touch the x-axis.
b. Order the functions from least to greatest according to the average rates of change between x = 1 and x = 3. Answer: Compare the rate of change using average rate of change = f(b) – f(a)/b-a p(x) = -40-(-16)/3-1 = -12 r(x) = 40-0/3-1 = 40/2 = 20 s(x) = 18-(72)/3-1 = -27 t(x) = -5-3/3-1 = -4 Compare the absolute values of the rate of change, the order from least to greatest is: t(x), p(x), r(x), s(x)

b. Describe the domain of the function. Is the domain discrete or continuous? Answer: The domain is the set of natural numbers in context with the given problem and is discrete as the number of games must be whole numbers.
c. Write a function that models the data. Answer: (x1, y1) → (2, 90) (x2, y2) → (4, 180) y – y1 = m(x – x1) m = 45 substitute: y – 90 = 45(x – 2) y – 90 = 45x – 90 y = 45x
d. Can the referee earn exactly $500? Explain. Answer: No, because 500 not a multiple of 45 as shown above.
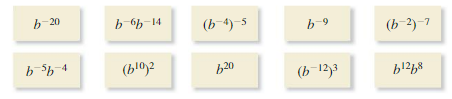
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Get started
- Pre-Algebra
A quicker path to better grades
We have gathered all your curriculum-based courses, assignments, hints, tests, and solutions in one easy-to-use place
- Integrated I
- Integrated II
- Integrated III
Can't find your textbook?
More math. less studying.
A personal private tutor for each student. Free from preassure and study anxiety.
CPM Educational Program
- Core Connections Integrated I, 2013
- Core Connections Algebra 1, 2013
- Core Connections Geometry, 2013
- Core Connections Algebra 2, 2013
- Core Connections Integrated I, 2014

- Core Connections Integrated II, 2015

- Core Connections: Course 1

- Core Connections: Course 2

- Core Connections: Course 3

- Core Connections Integrated III, 2015
Expert Textbook Solutions
Browse your textbook to find expert solutions, hints, and answers for all exercises. The solutions are always presented as a clear and concise, step-by-step explanation with included theory and helpful figures, graphs, and diagrams. Mathleaks covers the most commonly adopted textbooks with more than 250000 expert solutions.
Mathleaks Solver
With Mathleaks, you’re not tied to your textbook for solutions. Instead, scan and solve exercises with our math solver, which instantly reads the problem by using the camera on your smartphone or tablet. Access the solver through the Mathleaks app or on our website. The Mathleaks solver works for Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, and Algebra 2.
Mathleaks Community
Get access to the world's most popular math community with Mathleaks. You can connect with other students all over the US who are studying with the same textbook or in the same math course.
Study math more efficiently using Mathleaks for CPM Educational Program textbooks.
Be Prepared
ⓐ 8; ⓑ −1; ⓒ -729
ⓐ x 6 x 6 ; ⓑ y 6 y 6 ; ⓒ z 12 z 12
1 y 8 1 y 8
53 60 53 60
64 x 6 y 15 64 x 6 y 15
1 125 1 125
2 x 2 + 11 x − 8 2 x 2 + 11 x − 8
8 + 2 a − a 2 8 + 2 a − a 2
81 − 90 y + 25 y 2 81 − 90 y + 25 y 2
49 − 9 x 2 49 − 9 x 2
y 2 − 6 y + 9 y 2 − 6 y + 9
x = 5 2 x = 5 2
n = 2 or n = 4 n = 2 or n = 4
( − ∞ , 1 2 ] ( − ∞ , 1 2 ]
f ( 2 ) = 2 , f ( −1 ) = −7 , f ( 0 ) = −4 f ( 2 ) = 2 , f ( −1 ) = −7 , f ( 0 ) = −4
domain: [ 0 , ∞ ) ; range: [ 0 , ∞ ) domain: [ 0 , ∞ ) ; range: [ 0 , ∞ )
ⓐ −4 , 0. 5 – , 7 3 , 3 , 81 ; −4 , 0. 5 – , 7 3 , 3 , 81 ; ⓑ 7 ; 7 ; ⓒ −4 , − 7 , 0. 5 – , 7 3 , 3 , 81 −4 , − 7 , 0. 5 – , 7 3 , 3 , 81
2 x 2 − x − 15 2 x 2 − x − 15
5 + 15 2 5 + 15 2
ⓐ −8 −8 ⓑ 15
ⓐ 10 ⓑ −11 −11
ⓐ not a real number ⓑ −9 −9
ⓐ −7 −7 ⓑ not a real number
ⓐ 3 ⓑ 4 ⓒ 3
ⓐ 10 ⓑ 2 ⓒ 4
ⓐ −3 −3 ⓑ not real ⓒ −2 −2
ⓐ −6 −6 ⓑ not real ⓒ −4 −4
ⓐ 6 < 38 < 7 6 < 38 < 7 ⓑ 4 < 93 3 < 5 4 < 93 3 < 5
ⓐ 9 < 84 < 10 9 < 84 < 10 ⓑ 5 < 152 3 < 6 5 < 152 3 < 6
ⓐ ≈ 3.32 ≈ 3.32 ⓑ ≈ 4.14 ≈ 4.14 ⓒ ≈ 3.36 ≈ 3.36
ⓐ ≈ 3.61 ≈ 3.61 ⓑ ≈ 4.38 ≈ 4.38 ⓒ ≈ 3.15 ≈ 3.15
ⓐ | b | | b | ⓑ w ⓒ | m | | m | ⓓ q
ⓐ | y | | y | ⓑ p ⓒ | z | | z | ⓓ q
ⓐ | y 9 | | y 9 | ⓑ z 6 z 6
ⓐ m 2 m 2 ⓑ | b 5 | | b 5 |
ⓐ | u 3 | | u 3 | ⓑ v 5 v 5
ⓐ c 4 c 4 ⓑ d 4 d 4
ⓐ 8 | x | 8 | x | ⓑ −10 | p | −10 | p |
ⓐ 13 | y | 13 | y | ⓑ −11 | y | −11 | y |
ⓐ 3 x 9 3 x 9 ⓑ 3 | q 7 | 3 | q 7 |
ⓐ 5 q 3 5 q 3 ⓑ 3 q 5 3 q 5
ⓐ 10 | a b | 10 | a b | ⓑ 12 p 6 q 10 12 p 6 q 10 ⓒ 2 x 10 y 4 2 x 10 y 4
ⓐ 15 | m n | 15 | m n | ⓑ 13 | x 5 y 7 | 13 | x 5 y 7 | ⓒ 3 w 12 z 5 3 w 12 z 5
ⓐ 12 2 12 2 ⓑ 3 3 3 3 3 3 ⓒ 2 4 4 2 4 4
ⓐ 12 3 12 3 ⓑ 5 5 3 5 5 3 ⓒ 3 9 4 3 9 4
ⓐ b 2 b b 2 b ⓑ | y | y 2 4 | y | y 2 4 ⓒ z z 2 3 z z 2 3
ⓐ p 4 p p 4 p ⓑ y y 3 5 y y 3 5 ⓒ q 2 q 6 q 2 q 6
ⓐ 4 y 2 2 y 4 y 2 2 y ⓑ 3 p 3 2 p 3 3 p 3 2 p 3 ⓒ 2 q 2 4 q 2 4 2 q 2 4 q 2 4
ⓐ 5 a 4 3 a 5 a 4 3 a ⓑ 4 m 3 2 m 2 3 4 m 3 2 m 2 3 ⓒ 3 | n | 2 n 3 4 3 | n | 2 n 3 4
ⓐ 7 | a 3 | b 2 2 a b 7 | a 3 | b 2 2 a b ⓑ 2 x y 7 x 2 y 3 2 x y 7 x 2 y 3 ⓒ 2 | x | y 2 2 x 4 2 | x | y 2 2 x 4
ⓐ 6 m 4 | n 5 | 5 m n 6 m 4 | n 5 | 5 m n ⓑ 2 x 2 y 9 y 2 3 2 x 2 y 9 y 2 3 ⓒ 2 | x y | 5 x 3 4 2 | x y | 5 x 3 4
ⓐ −4 −4 ⓑ no real number no real number
ⓐ −5 5 3 −5 5 3 ⓑ no real number
ⓐ 5 + 5 3 5 + 5 3 ⓑ 2 − 3 2 − 3
ⓐ 2 + 7 2 2 + 7 2 ⓑ 2 − 5 2 − 5
ⓐ 5 4 5 4 ⓑ 3 5 3 5 ⓒ 2 3 2 3
ⓐ 7 9 7 9 ⓑ 2 5 2 5 ⓒ 1 3 1 3
ⓐ | a | | a | ⓑ | x | | x | ⓒ y 3 y 3
ⓐ x 2 x 2 ⓑ m 2 m 2 ⓒ n 2 n 2
2 | p | 6 p 7 2 | p | 6 p 7
2 x 2 3 x 5 2 x 2 3 x 5
ⓐ 4 | m | 5 m | n 3 | 4 | m | 5 m | n 3 | ⓑ 3 c 3 4 c 3 d 2 3 c 3 4 c 3 d 2 ⓒ 2 x 2 5 x 2 4 | y | 2 x 2 5 x 2 4 | y |
ⓐ 3 u 3 6 u v 4 3 u 3 6 u v 4 ⓑ 2 r 5 3 s 2 2 r 5 3 s 2 ⓒ 3 | m 3 | 2 m 2 4 | n 3 | 3 | m 3 | 2 m 2 4 | n 3 |
ⓐ 5 | y | x 6 5 | y | x 6 ⓑ 2 x y y 2 3 3 2 x y y 2 3 3 ⓒ | a b | a 4 2 | a b | a 4 2
ⓐ 2 | m | 3 5 | n 3 | 2 | m | 3 5 | n 3 | ⓑ 3 x y x 2 3 5 3 x y x 2 3 5 ⓒ 2 | a b | a 2 4 3 2 | a b | a 2 4 3
ⓐ 7 z 2 7 z 2 ⓑ −5 2 3 −5 2 3 ⓒ 3 | m | 2 m 2 4 3 | m | 2 m 2 4
ⓐ 8 m 4 8 m 4 ⓑ −4 −4 ⓒ 3 | n | 2 4 3 | n | 2 4
ⓐ t t ⓑ m 3 m 3 ⓒ r 4 r 4
ⓐ b 6 b 6 ⓑ z 5 z 5 ⓒ p 4 p 4
ⓐ ( 10 m ) 1 2 ( 10 m ) 1 2 ⓑ ( 3 n ) 1 5 ( 3 n ) 1 5 ⓒ 3 ( 6 y ) 1 4 3 ( 6 y ) 1 4
ⓐ ( 3 k ) 1 7 ( 3 k ) 1 7 ⓑ ( 5 j ) 1 4 ( 5 j ) 1 4 ⓒ 8 ( 2 a ) 1 3 8 ( 2 a ) 1 3
ⓐ 6 ⓑ 2 ⓒ 2
ⓐ 10 ⓑ 3 ⓒ 3
ⓐ No real solution ⓑ −8 −8 ⓒ 1 8 1 8
ⓐ No real solution ⓑ −4 −4 ⓒ 1 4 1 4
ⓐ x 5 2 x 5 2 ⓑ ( 3 y ) 3 4 ( 3 y ) 3 4 ⓒ ( 2 m 3 n ) 5 2 ( 2 m 3 n ) 5 2
ⓐ a 2 5 a 2 5 ⓑ ( 5 a b ) 5 3 ( 5 a b ) 5 3 ⓒ ( 7 x y z ) 3 2 ( 7 x y z ) 3 2
ⓐ 9 ⓑ 1 729 1 729 ⓒ 1 8 1 8
ⓐ 8 ⓑ 1 9 1 9 ⓒ 1 125 1 125
ⓐ −64 −64 ⓑ − 1 64 − 1 64 ⓒ not a real number
ⓐ −729 −729 ⓑ − 1 729 − 1 729 ⓒ not a real number
ⓐ x 3 2 x 3 2 ⓑ x 8 x 8 ⓒ 1 x 1 x
ⓐ y 11 8 y 11 8 ⓑ m 2 m 2 ⓒ 1 d 1 d
ⓐ 8 x 1 5 8 x 1 5 ⓑ x 1 2 y 1 3 x 1 2 y 1 3
ⓐ 729 n 3 5 729 n 3 5 ⓑ a 2 b 2 3 a 2 b 2 3
ⓐ m 2 m 2 ⓑ 5 n m 1 4 5 n m 1 4
ⓐ u 3 u 3 ⓑ 3 x 1 5 y 1 3 3 x 1 5 y 1 3
ⓐ − 2 − 2 ⓑ 11 x 3 11 x 3 ⓒ 3 x 4 − 5 y 4 3 x 4 − 5 y 4
ⓐ −4 3 −4 3 ⓑ 8 y 3 8 y 3 ⓒ 5 m 4 − 2 m 3 5 m 4 − 2 m 3
ⓐ −2 7 x −2 7 x ⓑ − 5 x y 4 − 5 x y 4
ⓐ − 3 y − 3 y ⓑ 3 7 m n 3 3 7 m n 3
ⓐ 9 2 9 2 ⓑ 2 2 3 2 2 3 ⓒ 3 3 3 3
ⓐ 7 3 7 3 ⓑ −10 5 3 −10 5 3 ⓒ −3 2 3 −3 2 3
ⓐ − m 3 2 m − m 3 2 m ⓑ x 2 5 x 3 x 2 5 x 3
ⓐ − p 3 p − p 3 p ⓑ 4 y 4 y 2 3 − 2 y 4 n 2 3 4 y 4 y 2 3 − 2 y 4 n 2 3
ⓐ 12 15 12 15 ⓑ −18 4 3 −18 4 3
ⓐ 27 2 27 2 ⓑ −36 2 3 −36 2 3
ⓐ 288 x 3 5 288 x 3 5 ⓑ 8 y 6 y 2 4 8 y 6 y 2 4
ⓐ 144 y 2 5 y 144 y 2 5 y ⓑ −36 a 3 a 4 −36 a 3 a 4
ⓐ 18 + 6 18 + 6 ⓑ −2 4 3 − 2 3 3 −2 4 3 − 2 3 3
ⓐ −40 + 4 2 −40 + 4 2 ⓑ −3 − 18 3 −3 − 18 3
ⓐ −66 + 15 7 −66 + 15 7 ⓑ x 2 3 − 5 x 3 + 6 x 2 3 − 5 x 3 + 6
ⓐ 41 − 14 11 41 − 14 11 ⓑ x 2 3 + 4 x 3 + 3 x 2 3 + 4 x 3 + 3
1 + 9 21 1 + 9 21
−12 − 20 3 −12 − 20 3
ⓐ 102 + 20 2 102 + 20 2 ⓑ 55 + 6 6 55 + 6 6
ⓐ 41 − 12 5 41 − 12 5 ⓑ 121 − 36 10 121 − 36 10
ⓐ 5 s 8 5 s 8 ⓑ 2 a 2 a
ⓐ 5 q 2 6 5 q 2 6 ⓑ 2 b 2 b
ⓐ 9 x 2 y 2 9 x 2 y 2 ⓑ −4 x y −4 x y
ⓐ 10 n 3 m 10 n 3 m ⓑ −3 p q 2 −3 p q 2
4 x y 2 x 4 x y 2 x
4 a b 3 b 4 a b 3 b
ⓐ 5 3 3 5 3 3 ⓑ 6 8 6 8 ⓒ 2 x x 2 x x
ⓐ 6 5 5 6 5 5 ⓑ 14 6 14 6 ⓒ 5 x x 5 x x
ⓐ 49 3 7 49 3 7 ⓑ 90 3 6 90 3 6 ⓒ 5 3 y 2 3 3 y 5 3 y 2 3 3 y
ⓐ 4 3 2 4 3 2 ⓑ 150 3 10 150 3 10 ⓒ 2 5 n 2 3 5 n 2 5 n 2 3 5 n
ⓐ 27 4 3 27 4 3 ⓑ 12 4 4 12 4 4 ⓒ 3 5 x 3 4 5 x 3 5 x 3 4 5 x
ⓐ 125 4 5 125 4 5 ⓑ 14 4 4 14 4 4 ⓒ 2 4 x 3 4 x 2 4 x 3 4 x
− 3 ( 1 + 5 ) 4 − 3 ( 1 + 5 ) 4
4 + 6 5 4 + 6 5
5 ( x − 2 ) x − 2 5 ( x − 2 ) x − 2
10 ( y + 3 ) y − 3 10 ( y + 3 ) y − 3
( p + 2 ) p − 2 2 ( p + 2 ) p − 2 2
( q − 10 ) q − 10 2 ( q − 10 ) q − 10 2
m = 23 3 m = 23 3
z = 3 10 z = 3 10
no solution no solution
x = 2 , x = 3 x = 2 , x = 3
y = 5 , y = 6 y = 5 , y = 6
x = −6 x = −6
x = −9 x = −9
x = 8 x = 8
x = 6 x = 6
m = 7 m = 7
n = 3 n = 3
a = 63 a = 63
b = 311 b = 311
x = 3 x = 3
x = − 6 5 x = − 6 5
x = 4 x = 4
x = 9 x = 9
x = 5 x = 5
x = 0 x = 4 x = 0 x = 4
3.5 3.5 seconds
42.7 42.7 feet
54.1 54.1 feet
ⓐ f ( 6 ) = 4 f ( 6 ) = 4 ⓑ no value at x = 0 x = 0
ⓐ g ( 4 ) = 5 g ( 4 ) = 5 ⓑ no value at f ( −3 ) f ( −3 )
ⓐ g ( 4 ) = 2 g ( 4 ) = 2 ⓑ g ( 1 ) = −1 g ( 1 ) = −1
ⓐ h ( 2 ) = 2 h ( 2 ) = 2 ⓑ h ( −5 ) = −3 h ( −5 ) = −3
ⓐ f ( 4 ) = 2 f ( 4 ) = 2 ⓑ f ( −1 ) = 1 f ( −1 ) = 1
ⓐ g ( 16 ) = 3 g ( 16 ) = 3 ⓑ g ( 3 ) = 2 g ( 3 ) = 2
[ 5 6 , ∞ ) [ 5 6 , ∞ )
( − ∞ , 4 5 ] ( − ∞ , 4 5 ]
( −3 , ∞ ) ( −3 , ∞ )
( 5 , ∞ ) ( 5 , ∞ )
( − ∞ , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , ∞ )
ⓐ domain: [ −2 , ∞ ) [ −2 , ∞ ) ⓑ
ⓒ range: [ 0 , ∞ ) [ 0 , ∞ )
ⓐ domain: [ 2 , ∞ ) [ 2 , ∞ ) ⓑ
ⓐ domain: ( − ∞ , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , ∞ ) ⓑ
ⓒ range: ( − ∞ , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , ∞ )
ⓐ 9 i 9 i ⓑ 5 i 5 i ⓒ 3 2 i 3 2 i
ⓐ 6 i 6 i ⓑ 3 i 3 i ⓒ 3 3 i 3 3 i
6 2 i 6 2 i
7 3 i 7 3 i
ⓐ 6 + 5 i 6 + 5 i ⓑ 6 − 3 i 6 − 3 i
ⓐ −2 − 6 i −2 − 6 i ⓑ 2 + 9 i 2 + 9 i
12 + 20 i 12 + 20 i
12 − 6 i 12 − 6 i
−11 − 7 i −11 − 7 i
−5 − 10 i −5 − 10 i
−21 + 21 i −21 + 21 i
9 − 40 i 9 − 40 i
−12 − 22 3 i −12 − 22 3 i
6 + 12 2 i 6 + 12 2 i
4 17 + 16 17 i 4 17 + 16 17 i
2 5 + 4 5 i 2 5 + 4 5 i
3 2 − 3 2 i 3 2 − 3 2 i
4 5 − 2 5 i 4 5 − 2 5 i
Section 8.1 Exercises
ⓐ 8 ⓑ −9 −9
ⓐ 14 ⓑ −1 −1
ⓐ 2 3 2 3 ⓑ −0.1 −0.1
ⓐ not real number ⓑ −17 −17
ⓐ −15 −15 ⓑ not real number
ⓐ 8 ⓑ 3 ⓒ 1
ⓐ −2 −2 ⓑ not real not real ⓒ −2 −2
ⓐ −5 −5 ⓑ not real not real ⓒ −4 −4
ⓐ 8 < 70 < 9 8 < 70 < 9 ⓑ 4 < 71 3 < 5 4 < 71 3 < 5
ⓐ 14 < 200 < 15 14 < 200 < 15 ⓑ 5 < 137 3 < 6 5 < 137 3 < 6
ⓐ ≈ 4.36 ≈ 4.36 ⓑ ≈ 4.46 ≈ 4.46 ⓒ ≈ 3.14 ≈ 3.14
ⓐ ≈ 7.28 ≈ 7.28 ⓑ ≈ 5.28 ≈ 5.28 ⓒ ≈ 4.61 ≈ 4.61
ⓐ u ⓑ | v | | v |
ⓐ | y | | y | ⓑ m m
ⓐ | x 3 | | x 3 | ⓑ y 8 y 8
ⓐ x 12 x 12 ⓑ | y 11 | | y 11 |
ⓐ x 3 x 3 ⓑ | y 3 | | y 3 |
ⓐ m 2 m 2 ⓑ n 4 n 4
ⓐ 7 | x | 7 | x | ⓑ −9 | x 9 | −9 | x 9 |
ⓐ 11 m 10 11 m 10 ⓑ −8 | a | −8 | a |
ⓐ 2 x 2 2 x 2 ⓑ 2 y 2 2 y 2
ⓐ 6 a 2 6 a 2 ⓑ 2 b 4 2 b 4
ⓐ 12 | x y | 12 | x y | ⓑ 13 w 4 | y 5 | 13 w 4 | y 5 | ⓒ 2 a 17 b 2 2 a 17 b 2
ⓐ 11 | a b | 11 | a b | ⓑ 3 c 4 d 6 3 c 4 d 6 ⓒ 4 x 5 y 22 4 x 5 y 22
Answers will vary.
Section 8.2 Exercises
ⓐ 2 2 4 2 2 4 ⓑ 2 2 5 2 2 5
ⓐ 2 4 4 2 4 4 ⓑ 4 4 3 4 4 3
ⓐ | y 5 | y | y 5 | y ⓑ r r 2 3 r r 2 3 ⓒ s 2 s 2 4 s 2 s 2 4
ⓐ n 10 n n 10 n ⓑ q 2 q 2 3 q 2 q 2 3 ⓒ | n | n 2 8 | n | n 2 8
ⓐ 5 r 6 5 r 5 r 6 5 r ⓑ 3 x 4 x 2 3 3 x 4 x 2 3 ⓒ 2 | y | 3 y 2 4 2 | y | 3 y 2 4
ⓐ 11 | m 11 | 2 m 11 | m 11 | 2 m ⓑ 3 m 2 5 m 2 4 3 m 2 5 m 2 4 ⓒ 2 n 5 n 3 5 2 n 5 n 3 5
ⓐ 7 | m 3 n 5 | 3 m n 7 | m 3 n 5 | 3 m n ⓑ 2 x 2 y 2 6 y 3 2 x 2 y 2 6 y 3 ⓒ 2 | x y | 2 x 4 2 | x y | 2 x 4
ⓐ 8 | q r 3 | 3 q r 8 | q r 3 | 3 q r ⓑ 3 m 3 n 3 2 n 3 3 m 3 n 3 2 n 3 ⓒ 3 a 2 b 2 a 4 3 a 2 b 2 a 4
ⓐ −6 4 3 −6 4 3 ⓑ not real
ⓐ −2 −2 ⓑ not real
ⓐ 5 + 2 3 5 + 2 3 ⓑ 5 − 6 5 − 6
ⓐ 1 + 3 5 1 + 3 5 ⓑ 1 + 10 1 + 10
ⓐ 3 4 3 4 ⓑ 2 3 2 3 ⓒ 1 3 1 3
ⓐ 5 3 5 3 ⓑ 3 5 3 5 ⓒ 1 4 1 4
ⓐ x 2 x 2 ⓑ p 3 p 3 ⓒ | q | | q |
ⓐ 1 y 2 1 y 2 ⓑ u 2 u 2 ⓒ | v 3 | | v 3 |
4 | x 3 | 6 x 11 4 | x 3 | 6 x 11
5 m 2 3 m 4 5 m 2 3 m 4
7 r 2 2 r 10 7 r 2 2 r 10
2 | q 3 | 7 15 2 | q 3 | 7 15
ⓐ 5 r 4 3 r s 4 5 r 4 3 r s 4 ⓑ 3 a 2 2 a 2 3 b 3 a 2 2 a 2 3 b ⓒ 2 | c | 4 c 4 | d | 2 | c | 4 c 4 | d |
ⓐ 2 | p 3 | 7 p | q | 2 | p 3 | 7 p | q | ⓑ 3 s 2 3 s 2 3 t 3 s 2 3 s 2 3 t ⓒ 2 | p 3 | 4 p 3 4 | q 3 | 2 | p 3 | 4 p 3 4 | q 3 |
ⓐ 4 | x y | 3 4 | x y | 3 ⓑ y 2 x 3 2 y 2 x 3 2 ⓒ | a b | a 4 2 | a b | a 4 2
ⓐ 1 2 | p q | 1 2 | p q | ⓑ 2 c d d 2 3 5 2 c d d 2 3 5 ⓒ | m n | 2 | m n | 2
ⓐ 3 p 4 p | q | 3 p 4 p | q | ⓑ 2 2 4 2 2 4 ⓒ 2 x 2 x 5 2 x 2 x 5
ⓐ 5 | m 3 | 5 | m 3 | ⓑ 5 5 3 5 5 3 ⓒ 3 | y | 3 y 2 4 3 | y | 3 y 2 4
Section 8.3 Exercises
ⓐ x x ⓑ y 3 y 3 ⓒ z 4 z 4
ⓐ u 5 u 5 ⓑ v 9 v 9 ⓒ w 20 w 20
ⓐ x 1 7 x 1 7 ⓑ y 1 9 y 1 9 ⓒ f 1 5 f 1 5
ⓐ ( 7 c ) 1 3 ( 7 c ) 1 3 ⓑ ( 12 d ) 1 7 ( 12 d ) 1 7 ⓒ 2 ( 6 b ) 1 4 2 ( 6 b ) 1 4
ⓐ ( 21 p ) 1 2 ( 21 p ) 1 2 ⓑ ( 8 q ) 1 4 ( 8 q ) 1 4 ⓒ 4 ( 36 r ) 1 6 4 ( 36 r ) 1 6
ⓐ 9 ⓑ 5 ⓒ 8
ⓐ 2 ⓑ 4 ⓒ 5
ⓐ −6 −6 ⓑ −6 −6 ⓒ 1 6 1 6
ⓐ not real ⓑ −3 −3 ⓒ 1 3 1 3
ⓐ not real ⓑ −6 −6 ⓒ 1 6 1 6
ⓐ not real ⓑ −10 −10 ⓒ 1 10 1 10
ⓐ m 5 2 m 5 2 ⓑ ( 3 y ) 7 3 ( 3 y ) 7 3 ⓒ ( 4 x 5 y ) 3 5 ( 4 x 5 y ) 3 5
ⓐ u 2 5 u 2 5 ⓑ ( 6 x ) 5 3 ( 6 x ) 5 3 ⓒ ( 18 a 5 b ) 7 4 ( 18 a 5 b ) 7 4
ⓐ 32,768 ⓑ 1 729 1 729 ⓒ 9
ⓐ 4 ⓑ 1 9 1 9 ⓒ not real
ⓐ −27 −27 ⓑ − 1 27 − 1 27 ⓒ not real
ⓐ c 7 8 c 7 8 ⓑ p 9 p 9 ⓒ 1 r 1 r
ⓐ y 5 4 y 5 4 ⓑ x 8 x 8 ⓒ 1 m 1 m
ⓐ 81 q 2 81 q 2 ⓑ a 1 2 b a 1 2 b
ⓐ 8 u 1 4 8 u 1 4 ⓑ 8 p 1 2 q 3 4 8 p 1 2 q 3 4
ⓐ r 7 2 r 7 2 ⓑ 6 s t 6 s t
ⓐ c 2 c 2 ⓑ 2 x 3 y 2 x 3 y
Section 8.4 Exercises
ⓐ 3 2 3 2 ⓑ 7 m 3 7 m 3 ⓒ 6 m 4 6 m 4
ⓐ 9 5 9 5 ⓑ 12 a 3 12 a 3 ⓒ 6 2 z 4 6 2 z 4
ⓐ 4 2 a 4 2 a ⓑ 0
ⓐ 3 c 3 c ⓑ 4 p q 3 4 p q 3
ⓐ −2 3 −2 3 ⓑ −2 5 3 −2 5 3 ⓒ 3 2 4 3 2 4
ⓐ 7 3 7 3 ⓑ 7 2 3 7 2 3 ⓒ 3 5 4 3 5 4
ⓐ a 2 2 a a 2 2 a ⓑ 0
ⓐ 2 c 3 5 c 2 c 3 5 c ⓑ 14 r 2 2 r 2 4 14 r 2 2 r 2 4
4 y 2 4 y 2
ⓐ −18 6 −18 6 ⓑ −64 9 3 −64 9 3
ⓐ −30 2 −30 2 ⓑ 6 2 4 6 2 4
ⓐ 72 z 2 3 72 z 2 3 ⓑ 45 x 2 2 3 45 x 2 2 3
ⓐ −42 z 5 2 z −42 z 5 2 z ⓑ −8 y 6 y 4 −8 y 6 y 4
ⓐ 14 + 5 7 14 + 5 7 ⓑ 4 6 3 + 3 4 3 4 6 3 + 3 4 3
ⓐ 44 − 3 11 44 − 3 11 ⓑ 3 2 4 + 54 4 3 2 4 + 54 4
60 + 2 3 60 + 2 3
ⓐ 30 + 18 2 30 + 18 2 ⓑ x 2 3 − 2 x 3 − 3 x 2 3 − 2 x 3 − 3
ⓐ −55 + 13 10 −55 + 13 10 ⓑ 2 x 2 3 + 8 x 3 + 6 2 x 2 3 + 8 x 3 + 6
23 + 3 30 23 + 3 30
−439 − 2 77 −439 − 2 77
ⓐ 14 + 6 5 14 + 6 5 ⓑ 79 − 20 3 79 − 20 3
ⓐ 87 − 18 6 87 − 18 6 ⓑ 163 + 60 7 163 + 60 7
9 x 2 3 − 4 9 x 2 3 − 4
− 5 4 − 5 4
10 c 2 3 − 9 c 3 3 10 c 2 3 − 9 c 3 3
17 q 2 17 q 2
−42 9 3 −42 9 3
29 − 7 17 29 − 7 17
54 − 36 2 54 − 36 2
6 + 3 2 3 6 + 3 2 3
Section 8.5 Exercises
ⓐ 4 3 4 3 ⓑ 4 3 4 3
ⓐ 10 m 2 7 10 m 2 7 ⓑ 3 y 3 y
ⓐ 5 6 r 2 5 6 r 2 ⓑ 2 x 3 2 x 3
ⓐ 6 p q 2 6 p q 2 ⓑ − 2 a 2 b − 2 a 2 b
ⓐ 8 m 4 3 n 4 8 m 4 3 n 4 ⓑ − 2 x 2 3 y 2 − 2 x 2 3 y 2
2 x 2 7 y 2 x 2 7 y
2 a b 2 a 3 2 a b 2 a 3
ⓐ 5 6 3 5 6 3 ⓑ 2 3 9 2 3 9 ⓒ 2 5 x x 2 5 x x
ⓐ 6 7 7 6 7 7 ⓑ 2 10 15 2 10 15 ⓒ 4 3 p p 4 3 p p
ⓐ 25 3 5 25 3 5 ⓑ 45 3 6 45 3 6 ⓒ 2 6 a 2 3 3 a 2 6 a 2 3 3 a
ⓐ 121 3 11 121 3 11 ⓑ 28 3 6 28 3 6 ⓒ 9 x 3 x 9 x 3 x
ⓐ 343 4 7 343 4 7 ⓑ 40 4 4 40 4 4 ⓒ 2 4 x 2 4 x 2 4 x 2 4 x
ⓐ 9 4 3 9 4 3 ⓑ 50 4 4 50 4 4 ⓒ 2 3 a 3 4 a 2 3 a 3 4 a
−2 ( 1 + 5 ) −2 ( 1 + 5 )
3 ( 3 + 7 ) 3 ( 3 + 7 )
3 ( m + 5 ) m − 5 3 ( m + 5 ) m − 5
2 ( x + 6 ) x − 6 2 ( x + 6 ) x − 6
( r + 5 ) r − 5 2 ( r + 5 ) r − 5 2
( x + 2 2 ) x − 8 2 ( x + 2 2 ) x − 8 2
Section 8.6 Exercises
x = 14 x = 14
no solution
x = −4 x = −4
m = 14 m = 14
v = 17 v = 17
m = 7 2 m = 7 2
u = 3 , u = 4 u = 3 , u = 4
r = 1 , r = 2 r = 1 , r = 2
x = 10 x = 10
x = −8 x = −8
x = 7 x = 7
z = 21 z = 21
x = 42 x = 42
r = 3 r = 3
u = 3 u = 3
r = −2 r = −2
x = 1 x = 1
x = −8 , x = 2 x = −8 , x = 2
a = 0 a = 0
u = 9 4 u = 9 4
a = 4 a = 4
x = 1 x = 5 x = 1 x = 5
8.7 8.7 feet
4.7 4.7 seconds
Section 8.7 Exercises
ⓐ f ( 5 ) = 4 f ( 5 ) = 4 ⓑ no value at x = 0 x = 0
ⓐ g ( 4 ) = 5 g ( 4 ) = 5 ⓑ g ( 8 ) = 7 g ( 8 ) = 7
ⓐ F ( 1 ) = 1 F ( 1 ) = 1 ⓑ F ( −11 ) = 5 F ( −11 ) = 5
ⓐ G ( 5 ) = 2 6 G ( 5 ) = 2 6 ⓑ G ( 2 ) = 3 G ( 2 ) = 3
ⓐ g ( 6 ) = 2 g ( 6 ) = 2 ⓑ g ( −2 ) = −2 g ( −2 ) = −2
ⓐ h ( −2 ) = 0 h ( −2 ) = 0 ⓑ h ( 6 ) = 2 4 3 h ( 6 ) = 2 4 3
ⓐ f ( 0 ) = 0 f ( 0 ) = 0 ⓑ f ( 2 ) = 2 f ( 2 ) = 2
ⓐ g ( 1 ) = 0 g ( 1 ) = 0 ⓑ g ( −3 ) = 2 g ( −3 ) = 2
[ 1 3 , ∞ ) [ 1 3 , ∞ )
( − ∞ , 2 3 ] ( − ∞ , 2 3 ]
( 2 , ∞ ) ( 2 , ∞ )
( − ∞ , −3 ] ∪ ( 2 , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , −3 ] ∪ ( 2 , ∞ )
[ − 3 8 , ∞ ) [ − 3 8 , ∞ )
ⓐ domain: [ −1 , ∞ ) [ −1 , ∞ ) ⓑ
ⓒ [ 0 , ∞ ) [ 0 , ∞ )
ⓐ domain: [ −4 , ∞ ) [ −4 , ∞ ) ⓑ
ⓐ domain: [ 0 , ∞ ) [ 0 , ∞ ) ⓑ
ⓒ [ 2 , ∞ ) [ 2 , ∞ )
ⓐ domain: ( − ∞ , 3 ] ( − ∞ , 3 ] ⓑ
ⓒ ( − ∞ , 0 ] ( − ∞ , 0 ]
ⓒ ( − ∞ , ∞ ) ( − ∞ , ∞ )
Section 8.8 Exercises
ⓐ 4 i 4 i ⓑ 11 i 11 i ⓒ 2 2 i 2 2 i
ⓐ 10 i 10 i ⓑ 13 i 13 i ⓒ 3 5 i 3 5 i
9 3 i 9 3 i
8 2 i 8 2 i
8 + 7 i 8 + 7 i
14 + 2 i 14 + 2 i
−2 + 2 i −2 + 2 i
8 + 5 i 8 + 5 i
7 − 13 i 7 − 13 i
25 − 2 2 i 25 − 2 2 i
−12 + 18 i −12 + 18 i
−38 + + 9 i −38 + + 9 i
27 + 15 i 27 + 15 i
−7 + 24 i −7 + 24 i
−5 + 12 i −5 + 12 i
−44 − 4 i 3 −44 − 4 i 3
−20 − 2 2 i −20 − 2 2 i
2 25 + 11 25 i 2 25 + 11 25 i
6 13 + 9 13 i 6 13 + 9 13 i
− 12 13 − 8 13 i − 12 13 − 8 13 i
4 3 − 1 3 i 4 3 − 1 3 i
− 3 4 + 1 2 i − 3 4 + 1 2 i
Review Exercises
ⓐ 15 ⓑ −4 −4
ⓐ 2 ⓑ 3 ⓒ 3
ⓐ 8 < 68 < 9 8 < 68 < 9 ⓑ 4 < 84 3 < 5 4 < 84 3 < 5
ⓐ 5 5 3 5 5 3 ⓑ 2 2 6 2 2 6
ⓐ 4 | s 7 | 5 s 4 | s 7 | 5 s ⓑ 2 a 3 a 2 5 2 a 3 a 2 5 ⓒ 2 | b | 2 b 6 2 | b | 2 b 6
ⓐ 6 7 6 7 ⓑ 2 3 2 3 ⓒ 1 2 1 2
ⓐ 1 2 | p q | 1 2 | p q | ⓑ 2 c d 5 d 2 3 2 c d 5 d 2 3 ⓒ | m n | 2 | m n | 2
ⓐ r r ⓑ s 3 s 3 ⓒ t 4 t 4
ⓐ 5 ⓑ 3 ⓒ 2
ⓐ −2 −2 ⓑ 1 3 1 3 ⓒ −5 −5
ⓐ 125 ⓑ 1 27 1 27 ⓒ 16
ⓐ 6 3 6 3 ⓑ b 9 b 9 ⓒ 1 w 1 w
ⓐ 4 2 4 2 ⓑ 9 p 3 9 p 3 ⓒ 2 x 3 2 x 3
37 y 3 37 y 3
ⓐ 126 x 2 x 126 x 2 x ⓑ 48 a 5 a 2 3 48 a 5 a 2 3
ⓐ 71 − 22 7 71 − 22 7 ⓑ x 2 3 − 8 x 3 + 15 x 2 3 − 8 x 3 + 15
ⓐ 27 + 8 11 27 + 8 11 ⓑ 29 − 12 5 29 − 12 5
− 7 ( 2 + 6 ) 2 − 7 ( 2 + 6 ) 2
64.8 64.8 feet
− ∞ , 10 7 − ∞ , 10 7
23 + 14 i 23 + 14 i
Practice Test
5 x 3 5 x 3
2 x 2 y 9 x 2 y 3 2 x 2 y 9 x 2 y 3
ⓐ 1 4 1 4 ⓑ −343 −343
x 7 4 x 7 4
− x 2 3 x − x 2 3 x
36 x 4 2 36 x 4 2
2 − 7 3 2 − 7 3
7 x 2 x 3 | y 3 | y 7 x 2 x 3 | y 3 | y
3 ( 2 − 3 ) 3 ( 2 − 3 )
−12 + 8 i −12 + 8 i
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/intermediate-algebra-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Lynn Marecek, Andrea Honeycutt Mathis
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Intermediate Algebra 2e
- Publication date: May 6, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/intermediate-algebra-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/intermediate-algebra-2e/pages/chapter-8
© Jan 23, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Algebra 1 Common Core - 9780133185485, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Chapter 1:Foundations for Algebra. Section 1-1: Variables and Expressions. Section 1-2: ... Section 8-1: Adding and Subtracting Polynomials. Section 8-2: Multiplying and Factoring.
Our resource for Algebra 1: Homework Practice Workbook includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers ...
Homework Practice Workbook -07-660294-X 978--07-660294- Answers For Workbooks The answers for Chapter 8 of these workbooks can be found in the back of this Chapter Resource Masters booklet. ... Chapter 8 3 Glencoe Algebra 1 Anticipation Guide Quadratic Expressions and Equations
Use Mathleaks to get learning-focused solutions and answers to Algebra 1 math, either 8th grade Algebra 1 or 9th grade Algebra 1, for the most commonly used textbooks from publishers such as Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Big Ideas Learning, CPM, McGraw Hill, and Pearson. Getting helpful and educational math answers and solutions to high school ...
8-13. a. (2x + 3)(x + 1) b. One corner should contain 4x , while the other should contain 6x ; (3x + 4)(x + 2) . c. Their sum is 7x, and their product is 12x2 . d. The product 12x2 should be placed at the top of the diamond problem, 7x at the bottom, and terms 3x and 4x should be in the middle.
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!
1PT. Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 1. Consider the following problem. A total distance travelled by F by his scooter is given. He travelled the same route back. To find out how far he travelled in all, Let the distance travelled in one way is x. Therefore, multiply this distance by 2 to get the total distance travelled in all.
Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 1. When two numbers in exponential form are multiplied with one another and their bases are same then the exponents are to be added. So. Also two numbers in exponential form are equal if their bases are same and the exponents are also same. In 4 5 and 16 5 the powers are same but the bases are not same.
Glencoe McGraw-Hill Algebra 1 grade 9 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 9, Title: Glencoe McGraw-Hill Algebra 1, Publisher: Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 0078738229 ... Chapter 8: Factoring: Apps Videos Practice Now; Lesson 1: Monomials and Factoring. apps. videocam. create. Lesson 2: Factoring Using the Distributive Property. apps.
©Glencoe/McGraw-Hill iv Glencoe Algebra 1 Teacher's Guide to Using the Chapter 8 Resource Masters The Fast FileChapter Resource system allows you to conveniently file the resources you use most often. The Chapter 8 Resource Mastersincludes the core materials needed for Chapter 8. These materials include worksheets, extensions, and assessment options.
Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 2. Step 1: Find all points that satisfy the equation. To determine these points choose arbitrary values (some positive, some negative and zero) of and use the equation to determine the corresponding values of. Make a table for equation.
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Big Ideas Math Algebra 1: A Common Core Curriculum - 9781608408382, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Chapter 1:Solving Linear Equations. Section 1.1: Solving Simple Equations. Section 1.2: Solving Multi-Step Equations. Section 1.3: Solving Equation with ...
Textbook solutions for BIG IDEAS MATH Algebra 1: Common Core Student Edition 2015… 1st Edition HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT and others in this series. View step-by-step homework solutions for your homework. Ask our subject experts for help answering any of your homework questions!
CPM Education Program proudly works to offer more and better math education to more students.
Big Ideas Math Book Algebra 1 Answer Key Chapter 8 Graphing Quadratic Functions. Here, we have given a complete guide of Chapter 8 BIM Algebra 1 Graphing Quadratic Functions Answers in quick links. Click on the Topic-wise Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Solutions of Chapter 8 and clear all your queries regarding the concepts. Also, you can refer to ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Glencoe Algebra 1 - 9780079039897, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Chapter 0:Preparing for Algebra. Section 0-1: Plan for Problem Solving. Section 0-2: Real Numbers. Section 0-3: Operations with Integers. ... Chapter 8 Study Guide and Review. Page 551 ...
With Mathleaks, you'll have instant access to expert solutions and answers to all of the CPM math questions you may have from the CPM Educational Program publications such as Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, Algebra 2, and Geometry. Mathleaks offers the ultimate homework help and much of the content is free to use.
Chapter ; 8.1 Chapter ; 8.2 Chapter ; 8.3 Chapter ; 8.4 Chapter ; 8.5 Chapter ; 8.6 Chapter ; 9.R Chapter ; 9.1 Chapter ; 9.2 ... Understanding Holt Mcdougal Larson Algebra 1 0th Edition homework has never been easier than with Chegg Study. ... Why buy extra books when you can get all the homework help you need in one place?
Prentice Hall Math Algebra 1 Student Edition | 1st Edition. ISBN-13: 9780133659467 ISBN: 0133659461 Authors: Basia Hall, Sadie Chavis Bragg, William G Handlin, Allan E Bellman, Randall I Charles Rent | Buy. Alternate ISBN: 9780131657229.
Intermediate Algebra 2e Chapter 8. Intermediate Algebra 2e Chapter 8. Close. Contents Contents. Highlights. Print. Table of contents. Preface; 1 Foundations. Introduction; 1.1 Use the Language of Algebra; 1.2 Integers; ... Answers will vary. Section 8.2 Exercises. 55. 3 3 3 3. 57. 5 5 5 5. 59. 7 3 7 3.
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities. 7th Edition • ISBN: 9780134119281 (3 more) Michael Sullivan. 10,040 solutions. Get your Pearson Math homework done with Quizlet! Browse through thousands of step-by-step solutions to end-of-chapter questions from the most popular Pearson Math textbooks. It's never been a better time to #LearnOn.