Business Model Canvas: Explained with Examples
Got a new business idea, but don’t know how to put it to work? Want to improve your existing business model? Overwhelmed by writing your business plan? There is a one-page technique that can provide you the solution you are looking for, and that’s the business model canvas.
In this guide, you’ll have the Business Model Canvas explained, along with steps on how to create one. All business model canvas examples in the post can be edited online.

What is a Business Model Canvas
A business model is simply a plan describing how a business intends to make money. It explains who your customer base is and how you deliver value to them and the related details of financing. And the business model canvas lets you define these different components on a single page.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that lets you visualize and assess your business idea or concept. It’s a one-page document containing nine boxes that represent different fundamental elements of a business.
The business model canvas beats the traditional business plan that spans across several pages, by offering a much easier way to understand the different core elements of a business.
The right side of the canvas focuses on the customer or the market (external factors that are not under your control) while the left side of the canvas focuses on the business (internal factors that are mostly under your control). In the middle, you get the value propositions that represent the exchange of value between your business and your customers.
The business model canvas was originally developed by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur and introduced in their book ‘ Business Model Generation ’ as a visual framework for planning, developing and testing the business model(s) of an organization.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Business Model Canvas
Why do you need a business model canvas? The answer is simple. The business model canvas offers several benefits for businesses and entrepreneurs. It is a valuable tool and provides a visual and structured approach to designing, analyzing, optimizing, and communicating your business model.
- The business model canvas provides a comprehensive overview of a business model’s essential aspects. The BMC provides a quick outline of the business model and is devoid of unnecessary details compared to the traditional business plan.
- The comprehensive overview also ensures that the team considers all required components of their business model and can identify gaps or areas for improvement.
- The BMC allows the team to have a holistic and shared understanding of the business model while enabling them to align and collaborate effectively.
- The visual nature of the business model canvas makes it easier to refer to and understand by anyone. The business model canvas combines all vital business model elements in a single, easy-to-understand canvas.
- The BMC can be considered a strategic analysis tool as it enables you to examine a business model’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges.
- It’s easier to edit and can be easily shared with employees and stakeholders.
- The BMC is a flexible and adaptable tool that can be updated and revised as the business evolves. Keep your business agile and responsive to market changes and customer needs.
- The business model canvas can be used by large corporations and startups with just a few employees.
- The business model canvas effectively facilitates discussions among team members, investors, partners, customers, and other stakeholders. It clarifies how different aspects of the business are related and ensures a shared understanding of the business model.
- You can use a BMC template to facilitate discussions and guide brainstorming brainstorming sessions to generate insights and ideas to refine the business model and make strategic decisions.
- The BMC is action-oriented, encouraging businesses to identify activities and initiatives to improve their business model to drive business growth.
- A business model canvas provides a structured approach for businesses to explore possibilities and experiment with new ideas. This encourages creativity and innovation, which in turn encourages team members to think outside the box.
How to Make a Business Model Canvas
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model.
Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
While you can create a business model canvas with whiteboards, sticky notes, and markers, using an online platform like Creately will ensure that your work can be accessed from anywhere, anytime. Create a workspace in Creately and provide editing/reviewing permission to start.
Step 2: Set the context Clearly define the purpose and the scope of what you want to map out and visualize in the business model canvas. Narrow down the business or idea you want to analyze with the team and its context.
Step 3: Draw the canvas Divide the workspace into nine equal sections to represent the nine building blocks of the business model canvas.
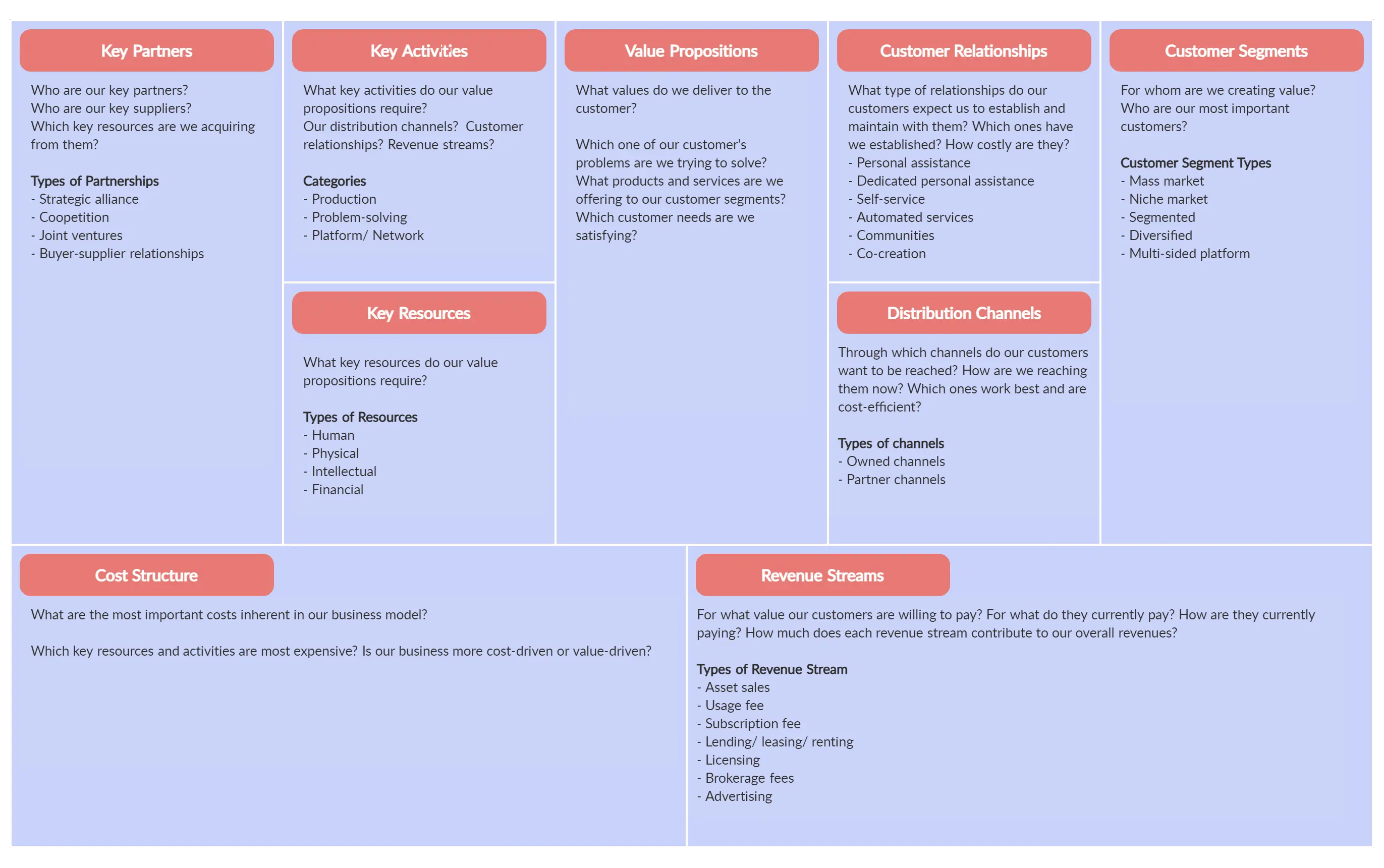
Step 4: Identify the key building blocks Label each section as customer segment, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, and cost structure.
Step 5: Fill in the canvas Work with your team to fill in each section of the canvas with relevant information. You can use data, keywords, diagrams, and more to represent ideas and concepts.
Step 6: Analyze and iterate Once your team has filled in the business model canvas, analyze the relationships to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges. Discuss improvements and make adjustments as necessary.
Step 7: Finalize Finalize and use the model as a visual reference to communicate and align your business model with stakeholders. You can also use the model to make informed and strategic decisions and guide your business.
What are the Key Building Blocks of the Business Model Canvas?
There are nine building blocks in the business model canvas and they are:
Customer Segments
Customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partners, cost structure.
- Value Proposition
When filling out a Business Model Canvas, you will brainstorm and conduct research on each of these elements. The data you collect can be placed in each relevant section of the canvas. So have a business model canvas ready when you start the exercise.
Let’s look into what the 9 components of the BMC are in more detail.
These are the groups of people or companies that you are trying to target and sell your product or service to.
Segmenting your customers based on similarities such as geographical area, gender, age, behaviors, interests, etc. gives you the opportunity to better serve their needs, specifically by customizing the solution you are providing them.
After a thorough analysis of your customer segments, you can determine who you should serve and ignore. Then create customer personas for each of the selected customer segments.
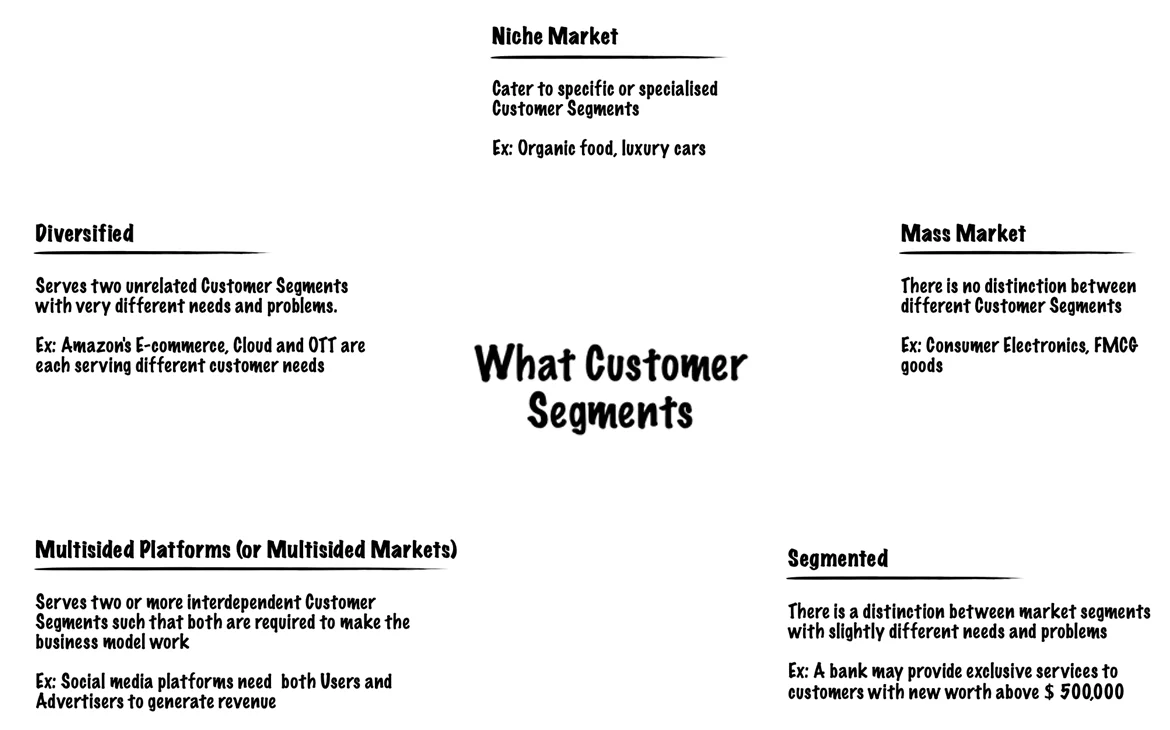
There are different customer segments a business model can target and they are;
- Mass market: A business model that focuses on mass markets doesn’t group its customers into segments. Instead, it focuses on the general population or a large group of people with similar needs. For example, a product like a phone.
- Niche market: Here the focus is centered on a specific group of people with unique needs and traits. Here the value propositions, distribution channels, and customer relationships should be customized to meet their specific requirements. An example would be buyers of sports shoes.
- Segmented: Based on slightly different needs, there could be different groups within the main customer segment. Accordingly, you can create different value propositions, distribution channels, etc. to meet the different needs of these segments.
- Diversified: A diversified market segment includes customers with very different needs.
- Multi-sided markets: this includes interdependent customer segments. For example, a credit card company caters to both their credit card holders as well as merchants who accept those cards.
Use STP Model templates for segmenting your market and developing ideal marketing campaigns
Visualize, assess, and update your business model. Collaborate on brainstorming with your team on your next business model innovation.
In this section, you need to establish the type of relationship you will have with each of your customer segments or how you will interact with them throughout their journey with your company.
There are several types of customer relationships
- Personal assistance: you interact with the customer in person or by email, through phone call or other means.
- Dedicated personal assistance: you assign a dedicated customer representative to an individual customer.
- Self-service: here you maintain no relationship with the customer, but provides what the customer needs to help themselves.
- Automated services: this includes automated processes or machinery that helps customers perform services themselves.
- Communities: these include online communities where customers can help each other solve their own problems with regard to the product or service.
- Co-creation: here the company allows the customer to get involved in the designing or development of the product. For example, YouTube has given its users the opportunity to create content for its audience.
You can understand the kind of relationship your customer has with your company through a customer journey map . It will help you identify the different stages your customers go through when interacting with your company. And it will help you make sense of how to acquire, retain and grow your customers.
This block is to describe how your company will communicate with and reach out to your customers. Channels are the touchpoints that let your customers connect with your company.
Channels play a role in raising awareness of your product or service among customers and delivering your value propositions to them. Channels can also be used to allow customers the avenue to buy products or services and offer post-purchase support.
There are two types of channels
- Owned channels: company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc.
- Partner channels: partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc.
Revenues streams are the sources from which a company generates money by selling their product or service to the customers. And in this block, you should describe how you will earn revenue from your value propositions.
A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models,
- Transaction-based revenue: made from customers who make a one-time payment
- Recurring revenue: made from ongoing payments for continuing services or post-sale services
There are several ways you can generate revenue from
- Asset sales: by selling the rights of ownership for a product to a buyer
- Usage fee: by charging the customer for the use of its product or service
- Subscription fee: by charging the customer for using its product regularly and consistently
- Lending/ leasing/ renting: the customer pays to get exclusive rights to use an asset for a fixed period of time
- Licensing: customer pays to get permission to use the company’s intellectual property
- Brokerage fees: revenue generated by acting as an intermediary between two or more parties
- Advertising: by charging the customer to advertise a product, service or brand using company platforms
What are the activities/ tasks that need to be completed to fulfill your business purpose? In this section, you should list down all the key activities you need to do to make your business model work.
These key activities should focus on fulfilling its value proposition, reaching customer segments and maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue.
There are 3 categories of key activities;
- Production: designing, manufacturing and delivering a product in significant quantities and/ or of superior quality.
- Problem-solving: finding new solutions to individual problems faced by customers.
- Platform/ network: Creating and maintaining platforms. For example, Microsoft provides a reliable operating system to support third-party software products.
This is where you list down which key resources or the main inputs you need to carry out your key activities in order to create your value proposition.
There are several types of key resources and they are
- Human (employees)
- Financial (cash, lines of credit, etc.)
- Intellectual (brand, patents, IP, copyright)
- Physical (equipment, inventory, buildings)
Key partners are the external companies or suppliers that will help you carry out your key activities. These partnerships are forged in oder to reduce risks and acquire resources.
Types of partnerships are
- Strategic alliance: partnership between non-competitors
- Coopetition: strategic partnership between partners
- Joint ventures: partners developing a new business
- Buyer-supplier relationships: ensure reliable supplies
In this block, you identify all the costs associated with operating your business model.
You’ll need to focus on evaluating the cost of creating and delivering your value propositions, creating revenue streams, and maintaining customer relationships. And this will be easier to do so once you have defined your key resources, activities, and partners.
Businesses can either be cost-driven (focuses on minimizing costs whenever possible) and value-driven (focuses on providing maximum value to the customer).
Value Propositions
This is the building block that is at the heart of the business model canvas. And it represents your unique solution (product or service) for a problem faced by a customer segment, or that creates value for the customer segment.
A value proposition should be unique or should be different from that of your competitors. If you are offering a new product, it should be innovative and disruptive. And if you are offering a product that already exists in the market, it should stand out with new features and attributes.
Value propositions can be either quantitative (price and speed of service) or qualitative (customer experience or design).
What to Avoid When Creating a Business Model Canvas
One thing to remember when creating a business model canvas is that it is a concise and focused document. It is designed to capture key elements of a business model and, as such, should not include detailed information. Some of the items to avoid include,
- Detailed financial projections such as revenue forecasts, cost breakdowns, and financial ratios. Revenue streams and cost structure should be represented at a high level, providing an overview rather than detailed projections.
- Detailed operational processes such as standard operating procedures of a business. The BMC focuses on the strategic and conceptual aspects.
- Comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. The business model canvas does not provide space for comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. These should be included in marketing or sales plans, which allow you to expand into more details.
- Legal or regulatory details such as intellectual property, licensing agreements, or compliance requirements. As these require more detailed and specialized attention, they are better suited to be addressed in separate legal or regulatory documents.
- Long-term strategic goals or vision statements. While the canvas helps to align the business model with the overall strategy, it should focus on the immediate and tangible aspects.
- Irrelevant or unnecessary information that does not directly relate to the business model. Including extra or unnecessary information can clutter the BMC and make it less effective in communicating the core elements.
What Are Your Thoughts on the Business Model Canvas?
Once you have completed your business model canvas, you can share it with your organization and stakeholders and get their feedback as well. The business model canvas is a living document, therefore after completing it you need to revisit and ensure that it is relevant, updated and accurate.
What best practices do you follow when creating a business model canvas? Do share your tips with us in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs About the Business Model Canvas
- Use clear and concise language
- Use visual-aids
- Customize for your audience
- Highlight key insights
- Be open to feedback and discussion
More Related Articles

Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.

Business Model Canvas (BMC)

What is the Business Model Canvas
Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a framework that helps determine how a business creates, delivers, and captures values. It is a visual representation of the important aspects or parts to consider when designing a Business Model.
BMC aids in constructing a shared understanding of a business by condensing it into a simple, relevant, and intuitively understandable one-page visual while not oversimplifying the complexities of how enterprises function.
This concept has been applied and tested around the world and is used in organizations such as GE, P&G, Nestlé, IBM, Ericsson, and Deloitte, including Government Services of Canada and many more [1],[2] .
The Nine Building Blocks
BMC describes a business through nine basic building blocks that show the logic of how a business intends to make money. These nine blocks cover the four main areas of a business: Customers, Offer, Infrastructure, and Financial Viability.
BMC acts as a shared language for describing, visualizing, assessing, and changing business models. It is like a blueprint for a strategy to be implemented through organizational structures, processes, and systems.
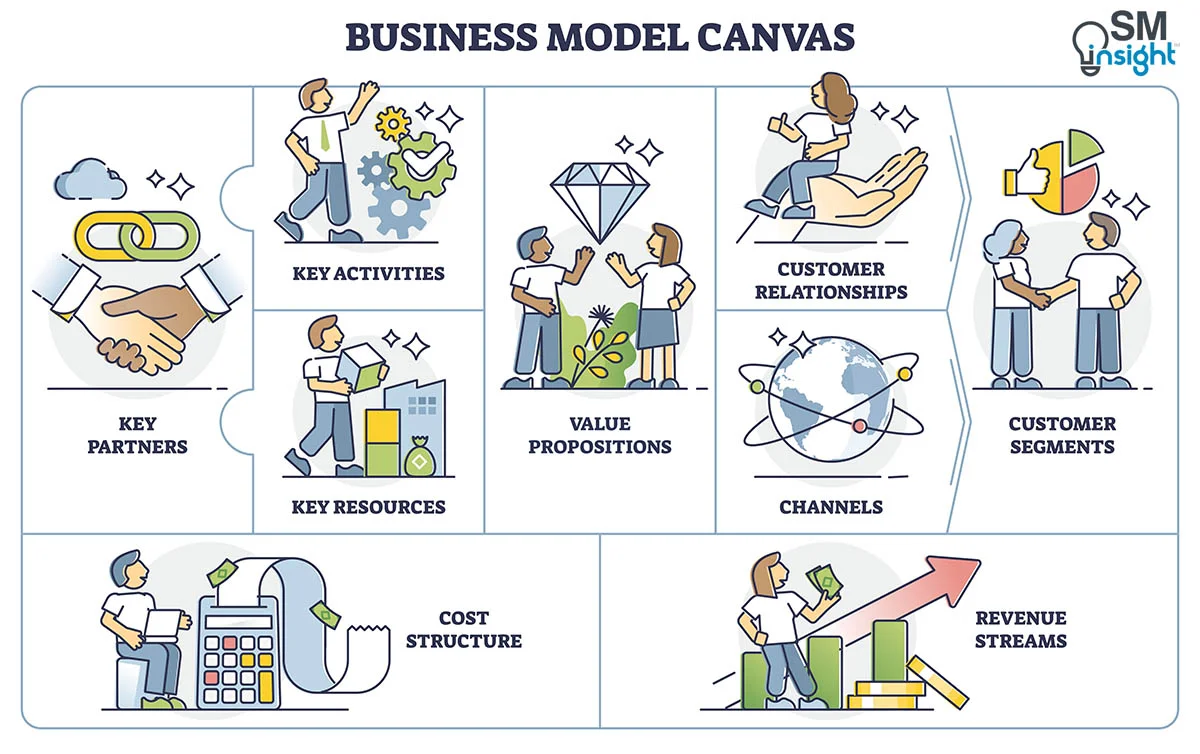
Each of these blocks is explained in more detail as follows:
1. Customer Segments (CS)
These are the groups of people or organizations that a business aims to reach and serve. Customers are the heart of a business model, and without (profitable) customers, a business cannot survive.
Customers are grouped into distinct segments with common needs, common behaviors, or other attributes. Customer groups represent separate segments if:
- Their needs require and justify a distinct offer.
- They are reached through different Distribution Channels.
- They require different types of relationships.
- They have substantially different profitability.
- They are willing to pay for different aspects of the offer.
An organization must make a conscious decision about which segment(s) to serve and which segments to ignore. Once this decision is made, a business model can be carefully designed around a strong understanding of specific customer needs.
The following two questions, if answered with clarity, help a business identify its CS.
- For whom are we creating value?
- Who are our most important customers?
- What are the customer archetypes?
Examples of some of the Customer Segments are shown in the figure:
2. Value proposition (VP)
Value Proposition describes the bundle of products and services that create value for a specific Customer Segment chosen by a business.
A VP is the reason why customers turn to one company over another. VP must solve a customer’s problem or satisfy a need. A business can have more than one VP, but each must consist of a selected bundle of products and/or services that caters to the requirements of a specific Customer Segment.
While some VPs may be innovative and represent a new or disruptive offer, others may be similar to existing market offers but with added features and attributes.
An organization’s VP must answer the following questions with clarity:
- What value do we deliver to the customer?
- Which one of our customer’s problems are we helping to solve?
- Which customer needs are we satisfying?
- What bundles of products and services are we offering to each CS?
Elements from some of the following can contribute to customer value creation:
3. Channels (CH)
Channels describe how a company communicates with and reaches its Customer Segments to deliver a Value Proposition.
Channels are customer touch points that play an important role in the customer experience and serve several functions, including:
- Raising awareness about a company’s products and services
- Helping customers evaluate a company’s Value Proposition
- Allowing customers to purchase specific products and services
- Delivering a Value Proposition to customers
- Providing post-purchase customer support
To establish an effective channel, a company must first answer the following:
- Through which Channels do our Customer Segments want to be reached?
- How are we reaching them now?
- How are our Channels integrated?
- Which ones work best?
- Which ones are most cost-efficient?
- How are we integrating them with customer routines?
There are five distinct phases (figure below) through which a channel passes, and it could cover more than one of these phases at a time.
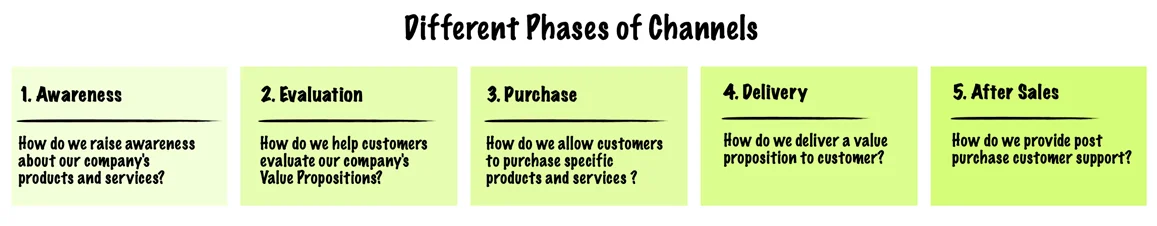
Channels can be either direct, indirect or hybrid, as shown:
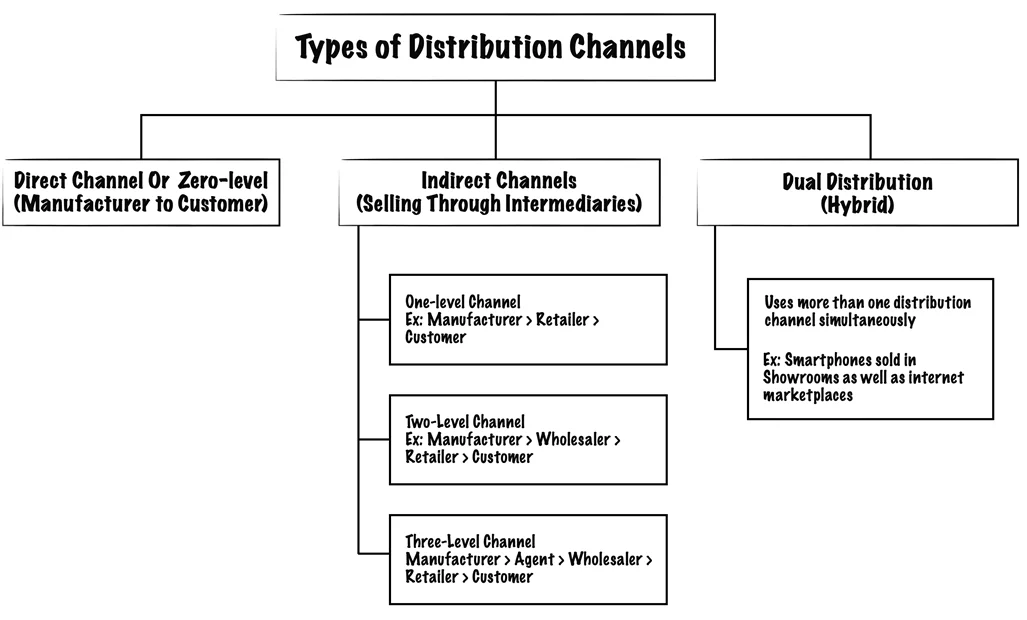
Finding the right mix of Channels to satisfy how customers want to be reached is crucial in bringing a Value Proposition to market and can create a great customer experience.
4. Customer Relationships (CR)
Customer Relationships describe the types of relationships a company establishes with specific Customer Segments. Relationships can range from personal to automated. An organization’s CR strategy may be driven by one of the following motivators:
- Customer acquisition
- Customer retention
- Boosting sales (upselling)
A business can arrive at the optimum CR by asking the following questions:
- What type of relationship does each of our Customer Segments expect us to establish and maintain with them?
- Which ones have we established?
- How costly are they?
- How are they integrated with the rest of our business model?
Several categories of Customer Relationships may co-exist in a company’s relationship with a particular Customer Segment. Some of which are:
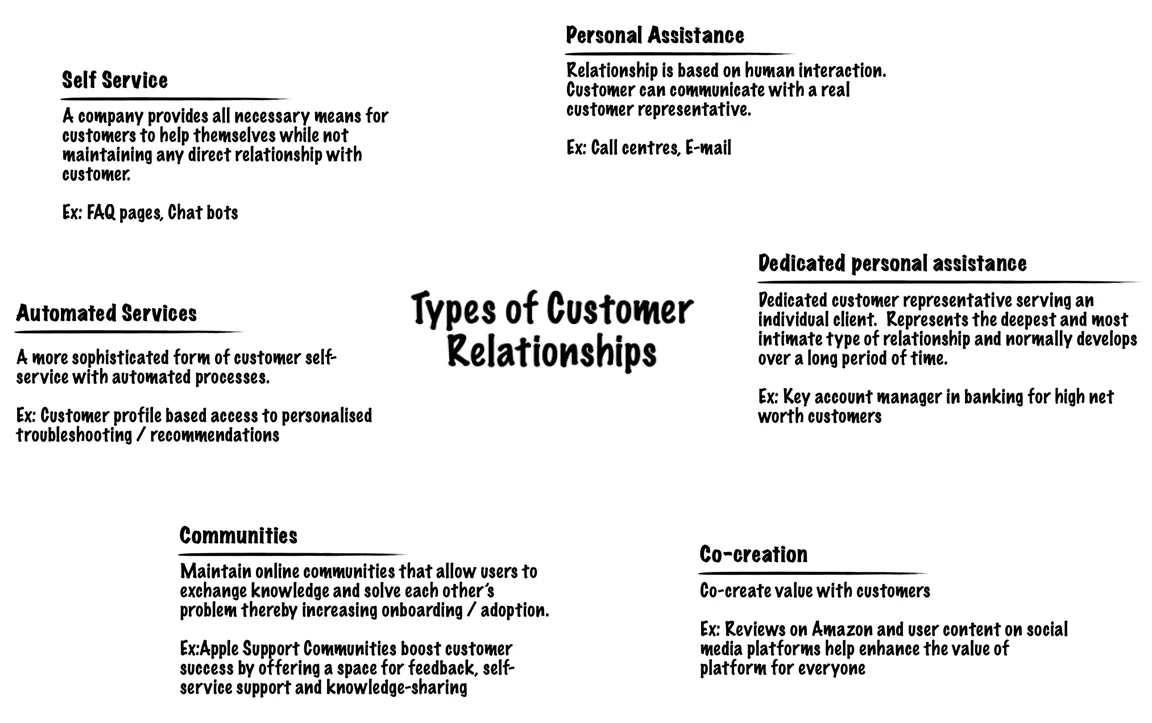
5. Revenue Streams (RS)
Revenue Streams represent the company’s cash (earnings) from each Customer Segment and are like the arteries of any business.
There are two distinct categories of Revenue Streams:
- Transaction Revenues which are one-time customer payments
- Recurring Revenues that are ongoing payments to either deliver a Value Proposition to customers or provide post-purchase customer support
A business can arrive at its ideal revenue stream by asking the following questions:
- For what value are our customers willing to pay?
- For what do they currently pay?
- How are they currently paying?
- How would they prefer to pay?
- How much does each Revenue Stream contribute to overall revenues?
There are several ways a business can generate revenue, such as:
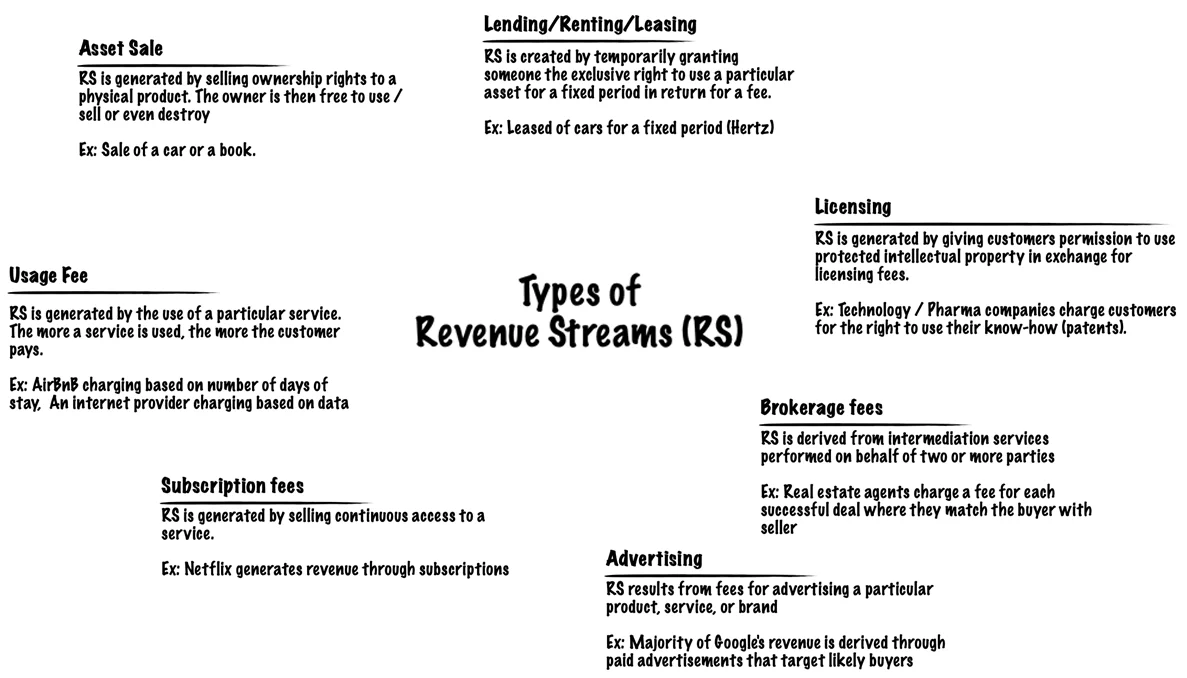
A business may have one or more Revenue Streams, each with different pricing mechanisms. The choice of pricing mechanism greatly influences the revenues generated.
There are two main types of pricing mechanisms, Fixed and Dynamic, as follows:
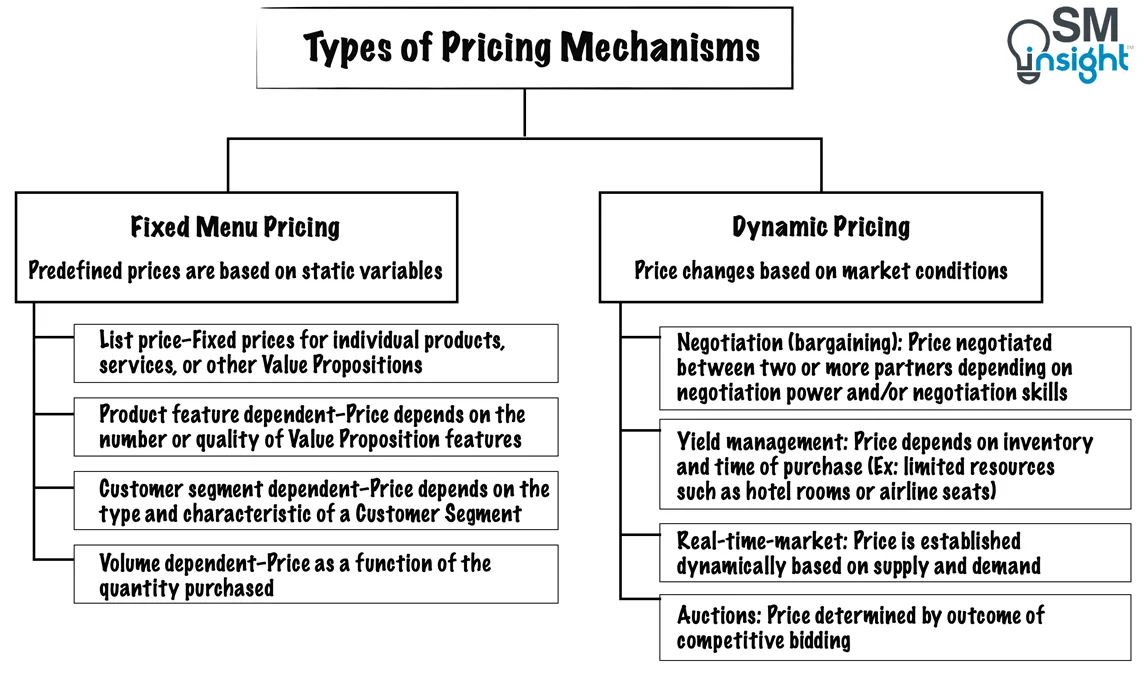
6. Key Resources (KR)
The Key Resources describe the most important assets required to make a business model work.
These resources allow an enterprise to create and offer a Value Proposition, reach markets, maintain relationships with Customer Segments, and earn revenues. Different Key Resources are needed depending on the type of business model.
For example, a chip fabrication business like TSMC [9] requires capital-intensive facilities worth billions of dollars, while a chip designer like NVIDIA [10] would need skilled manpower as its Key Resource.
Key Resources can be owned or leased by a business or acquired from its key partners. They can be identified by answering the following questions:
- What Key Resources do our Value Propositions require?
- What resources are required to sustain our Distribution Channels, Customer Relationships and Revenue Streams?
Key Resources can be categorized as follows:
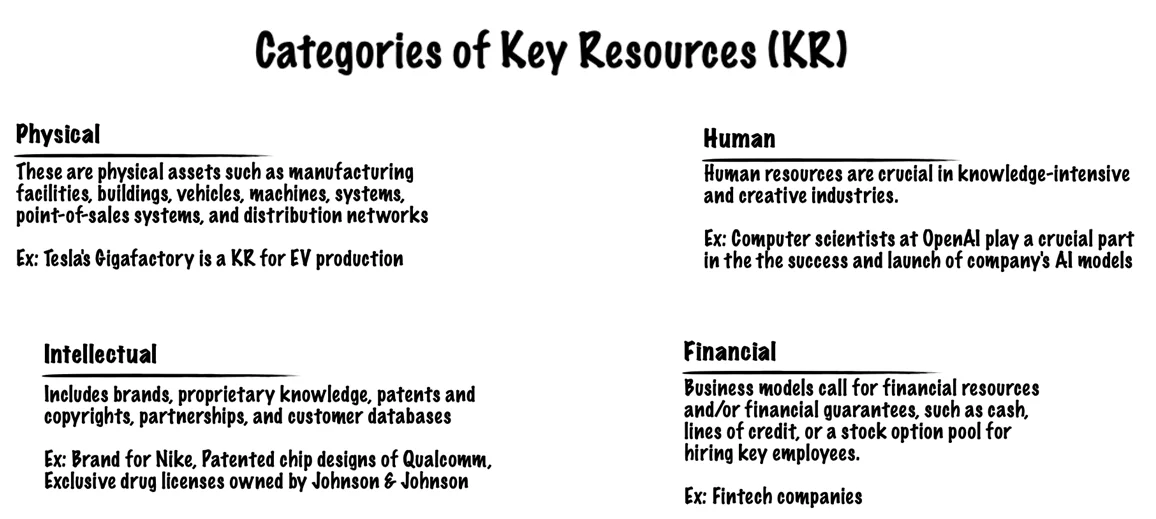
7. Key Activities (KA)
Key Activities describe the most important things a company must do to make its business model work. They are required to create and offer a Value Proposition, reach markets, maintain Customer Relationships, and earn revenues.
Key Activities differ depending on the business model type. For example, Microsoft’s Key Activity is software development, while for Dell, it is Supply Chain Management. For a consultancy firm like McKinsey, Key Activity is problem-solving.
A business can identify its Key Activities by answering the following questions:
- What Key Activities do our Value Propositions require?
- What activities directly contribute to maintaining our Distribution Channels, Customer Relationships and Revenue Streams?
Key Activities can be categorized as follows:
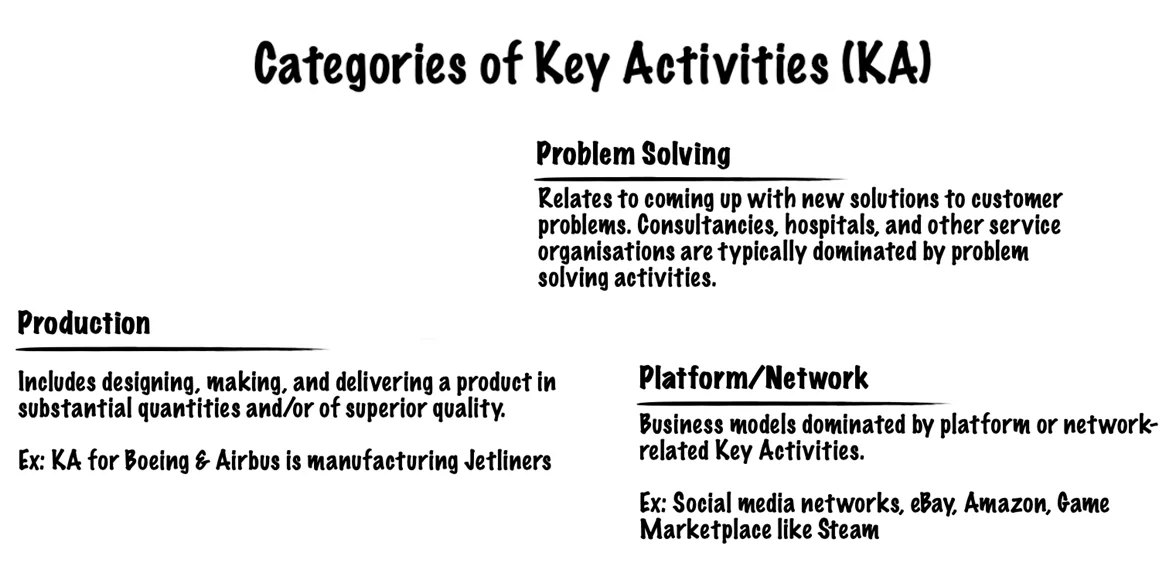
8. Key Partnerships (KP)
The Key Partnerships describe the network of suppliers and partners that make the business model. There are four types of partnerships:
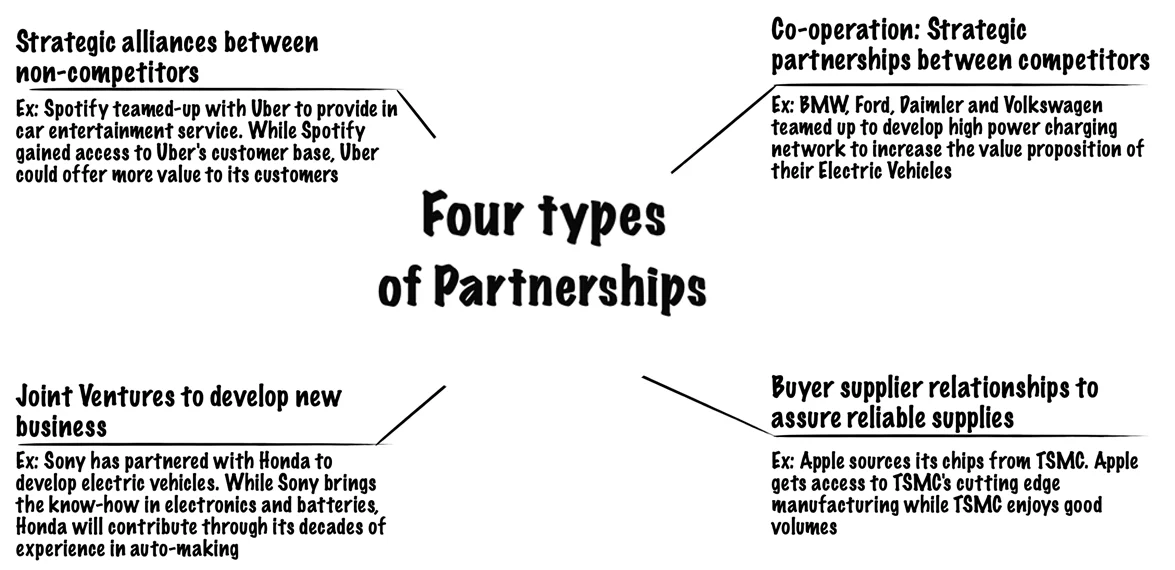
A business must ask the following questions before forming partnerships:
- Who are our key partners?
- Who are our key suppliers?
- Which Key Resources are we acquiring from partners?
- Which Key Activities do partners perform?
Primarily, there are three motivations for a business when creating partnerships, as shown:
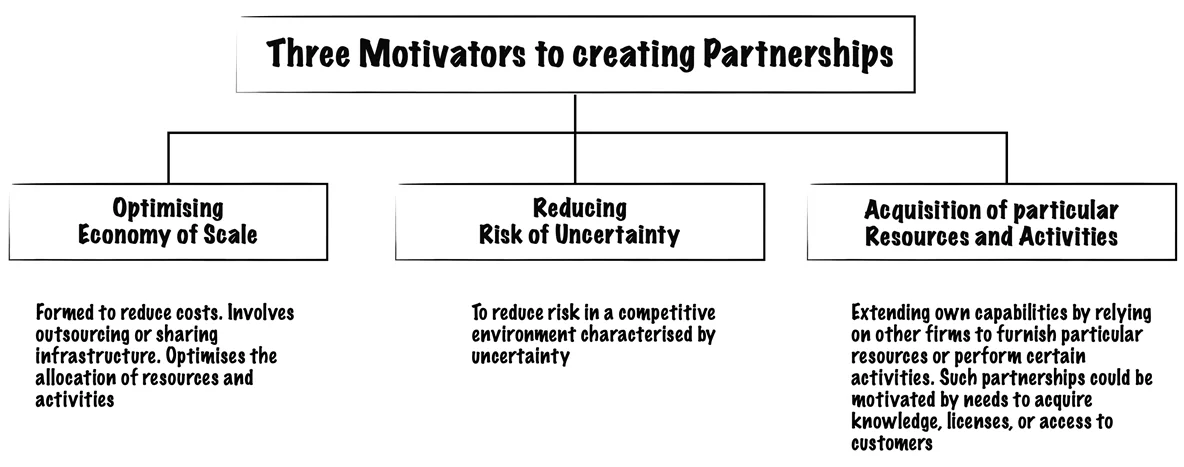
9. Cost Structure (CS)
Cost Structure describes all costs incurred to operate a business model. A business incurs costs in creating and delivering value, maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue. Costs are business-specific, where some are more cost-driven than others.
A business must answer the following questions to arrive at an optimum cost structure:
- What are the most important costs inherent in our business model?
- Which Key Resources are most expensive?
- Which Key Activities are most expensive?
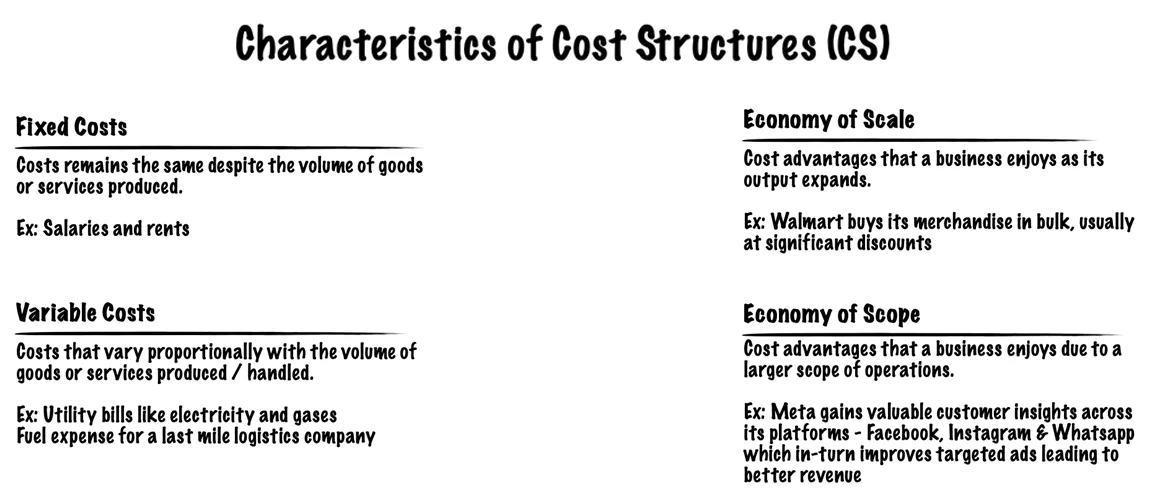
While costs should be minimized in every business model, it is useful to distinguish between two broad classes of business model Cost Structures:
- Cost Driven : This model focuses on minimizing costs wherever possible. This approach aims at creating and maintaining the leanest possible Cost Structure, using low-price Value Propositions, maximum automation, and extensive outsourcing. Examples: No frills airlines like Southwest & easyJet, Fast food joints such as McDonald’s & KFC.
- Value Driven: Premium Value Propositions and a high degree of personalized service usually characterize value-driven business models. Examples: Luxury hotels, Expensive Cars like Rolls-Royce
Cost Structures can have the following characteristics:
Putting-it-all together
The nine business model Building Blocks form the basis for a handy tool, which is called the Business Model Canvas (figure below). This tool resembles a painter’s canvas preformatted with nine blocks that allow painting pictures of new or existing business models. It is a hands-on tool that fosters understanding, discussion, creativity, and analysis.
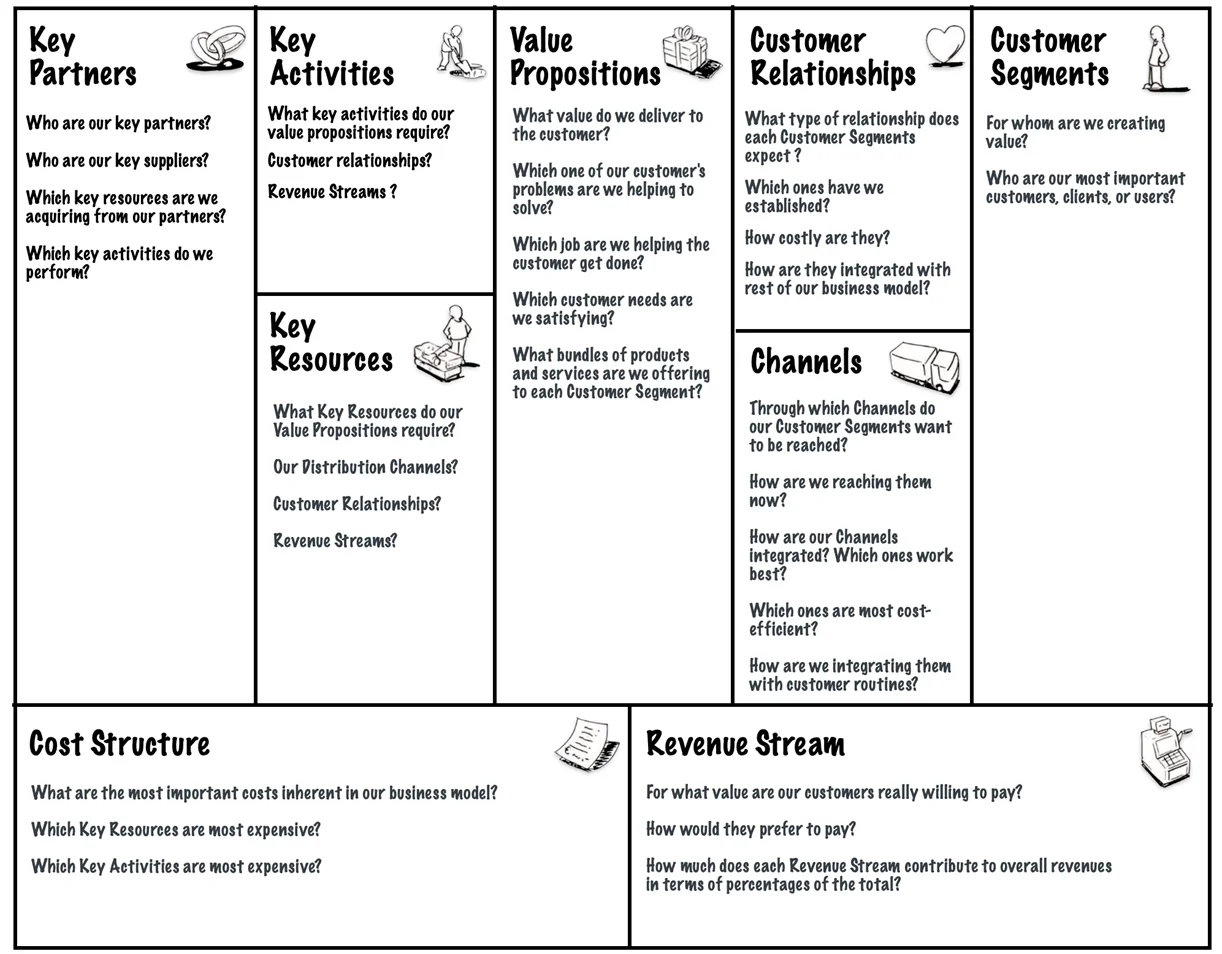
BMC works best when printed out on a large surface such that groups of people can jointly note, sketch, and discuss business model elements.
Example of Business Model Canvas
Nespresso [17] , a fully owned daughter company of Nestlé, changed the dynamics of the coffee industry by turning a transactional business (selling coffee through retail) into one with recurring revenues (selling proprietary pods through direct channels).
The two-part strategy involved selling their patented coffee machine to retail customers first to lock them into the brand. This generated a recurring demand for coffee refills (pods) that led to constant revenues. These pods were sold directly through mail/website/own stores, thereby eliminating middlemen/dealers, which further increased profits [1] .
Nespresso’s strategy plotted on a Business Model Canvas looks as follows:
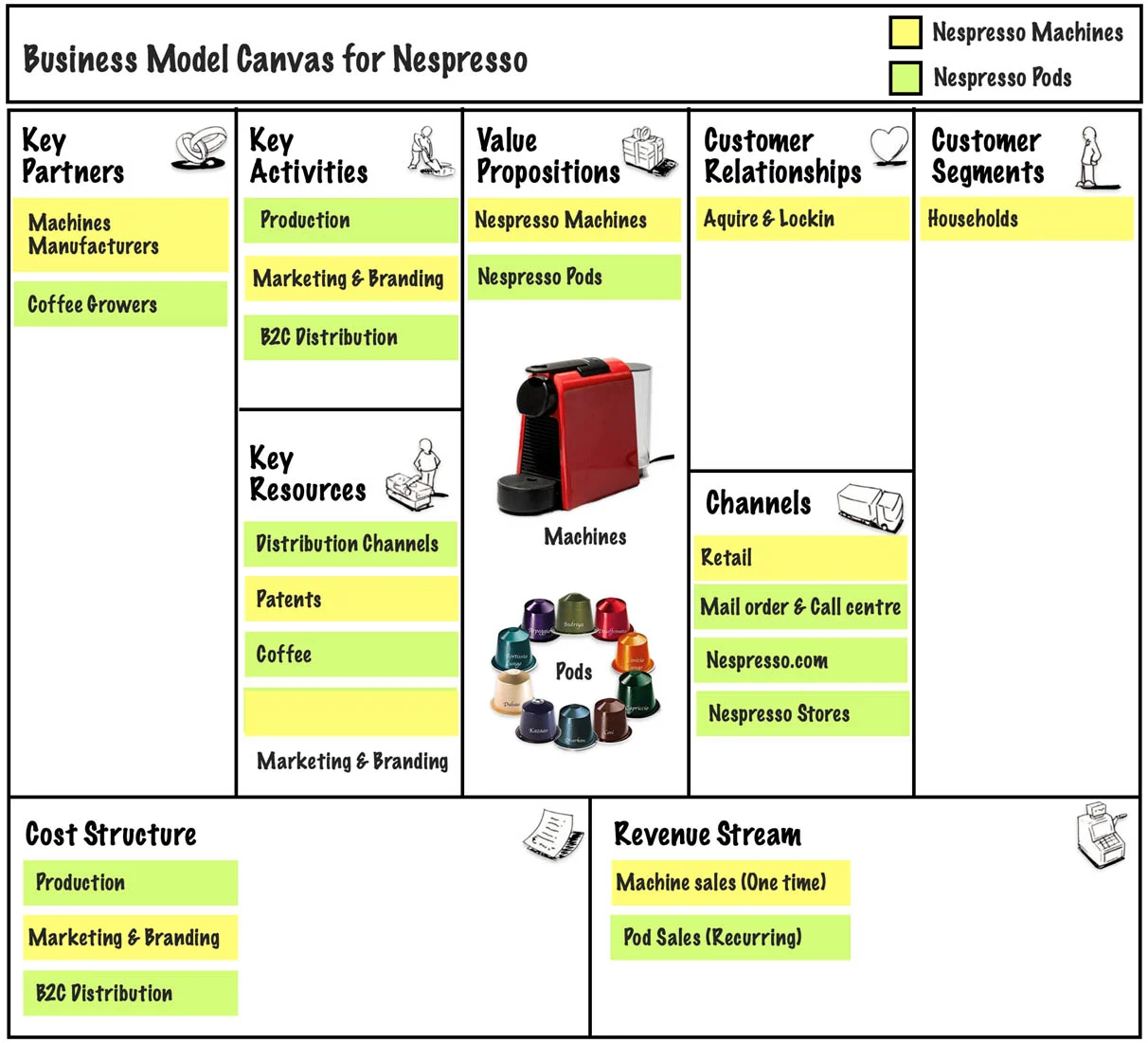
Business Model Canvas helped Nespresso establish a solid and enduring foundation by engaging consumers directly and bringing a barista-like experience within the reach of a home or an office.
Advantages & Limitations
- Encourages Collaboration – collaborative framework, which helps put different business stakeholders in sync. This improves the likelihood of generating new ideas and their quality.
- Facilitates testing of ideas before launch – allows business owners, strategists, and managers to think through business ideas as well as test concepts that would otherwise get tested with potential customers where the stakes are higher.
- Customer-centered approach – Key customer segments, relationships, activities, and value propositions are all elements that focus on creating, delivering, and capturing value for customers.
- Clarity – Analyzing the business through the lens of nine blocks brings better clarity and structure to the business model.
Limitations
- Lacks a section for defining the start-up’s mission statement, which is crucial to understanding the goals and objectives of any business.
- Overlooks the importance of a profit mechanism beyond costs and revenues, including decisions on how to use potential profits.
- The order of the canvas is not intuitive, making it difficult to read and understand the strategic decisions in a logical sequence.
- Does not depict interconnections between different elements, which can have a significant impact on the overall business model.
- Fails to acknowledge the company’s role within its ecosystem, including its impact on the environment and local communities.
- External factors such as competition, history, and other industry-specific factors are absent from the canvas, which can greatly influence the success of a business model.
1. “A Better Way to Think About Your Business Model”. Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/2013/05/a-better-way-to-think-about-yo . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
2. “Business Model Generation”. Alexander Osterwalder, https://www.strategyzer.com/books/business-model-generation . Accessed 28 Jul 2023
3. “The Apple M1 is a revolution that is changing the computing world”. Citymagazine, https://citymagazine.si/en/apple-m1-is-a-revolution-that-changes-the-computer-world/ . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
4. “Mass Customization”. Corporate Finance Institute, https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/management/mass-customization/ . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
5. “Moka Pot”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moka_pot . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
6. “NetJets Homepage”. NetJets, https://www.netjets.com/en-us/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
7. “Distribution Channels – Definition, Types, & Functions”. Feedough, https://www.feedough.com/distribution-channels-definition-types-functions/ . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
8. “Lease from Hertz”. Hertz, https://www.hertz.com/rentacar/rental-car/car-lease . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
9. “TSMC”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TSMC . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
10. “NVIDIA”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nvidia . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
11. “BMW, Daimler, Ford and Volkswagen team up on high-power charging network”. Techcrunch, https://techcrunch.com/2017/11/03/bmw-daimler-ford-and-volkswagen-team-up-on-high-power-charging-network/ . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
12. “Honda And Sony Combine Talents To Build Electric Vehicles”. Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/peterlyon/2022/06/26/honda-and-sony-announce-joint-venture-to-build-electric-vehicles/ . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
13. “Uber and Spotify launch car music playlist partnership”. BBC, https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-30080974 . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
14. “Walmart Has the Scale and Infrastructure to Generate Positive Gains”. Yahoo Finance, https://finance.yahoo.com/news/walmart-scale-infrastructure-generate-positive-201822628.html . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
15. “Demand-Side Economies of Scope in Big Tech Business Modelling and Strategy”. MDPI, https://www.mdpi.com/2079-8954/10/6/246 . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
16. “The Business Model Canvas”. Strategyzer, https://www.strategyzer.com/canvas/business-model-canvas . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
17. “HomePage”. Nespresso, https://www.nespresso.com/us/en/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
18. “Business Model Canvas of Nespresso”. Alex Osterwalder, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dhQh-tryXOg . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
19. “Nespresso Capsule”. Electromall, https://electromall.net/product/nespresso-capsule/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
20. “The Best Nespresso Machine (But It’s Not for Everyone)”. Newyork Times, https://www.nytimes.com/wirecutter/reviews/best-nespresso-machine/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
21. “Business Model Canvas”. Think Design, https://think.design/user-design-research/business-model-canvas/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
22. “6 Problems with the Business Model Canvas”. The Pourquoi Pas, https://www.thepourquoipas.com/post/problems-with-the-business-model-canvas . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
- McKinsey 7S Model
- Elaboration Likelihood Model of Persuasion
- The Johari Window Model
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Business model canvas: Creating a Value Proposition
Featured in:

© Entrepreneurial Insights based on the concept of Alex Osterwalder
In this article, we will explore, 1) what is a value proposition , 2) elements of the value proposition , 3) designing a value proposition , and 4) a case study .
WHAT IS A VALUE PROPOSITION?
In simple terms , a value proposition makes a case for why a customer should pick one product over another, citing the unique value the product provides over its contenders.
The Business Model Canvas value proposition provides a unique combination of products and services which provide value to the customer by resulting in the solution of a problem the customer is facing or providing value to the customer. This is the point of intersection between the product you make and the reason behind the customer’s impulse to buy it. A product can have a single value proposition or multiple value propositions.
Most start-ups fail to define their value proposition before they launch their products . This is because entrepreneurs tend to give too much credence to the ‘idea’ they have and run with it as opposed to exploring how this idea would actually perform in the market.
It is important for a product to solve a problem in a unique way. The problem could be unworkable, unavoidable, urgent or underserved. On the other end of the spectrum, the need for your product or service could be blatant, critical, aspirational or latent. A blatant need, as the word suggests, is one openly voiced and expressed by the customer. A latent need, conversely, is one which the customer himself may not be aware of having. A critical need is an immediate need that the customer MUST have fulfilled.
[slideshare id=22445632&doc=20130603pioniergaragevaluepropositiondesigner-130604141640-phpapp02]
ELEMENTS OF THE VALUE PROPOSITION
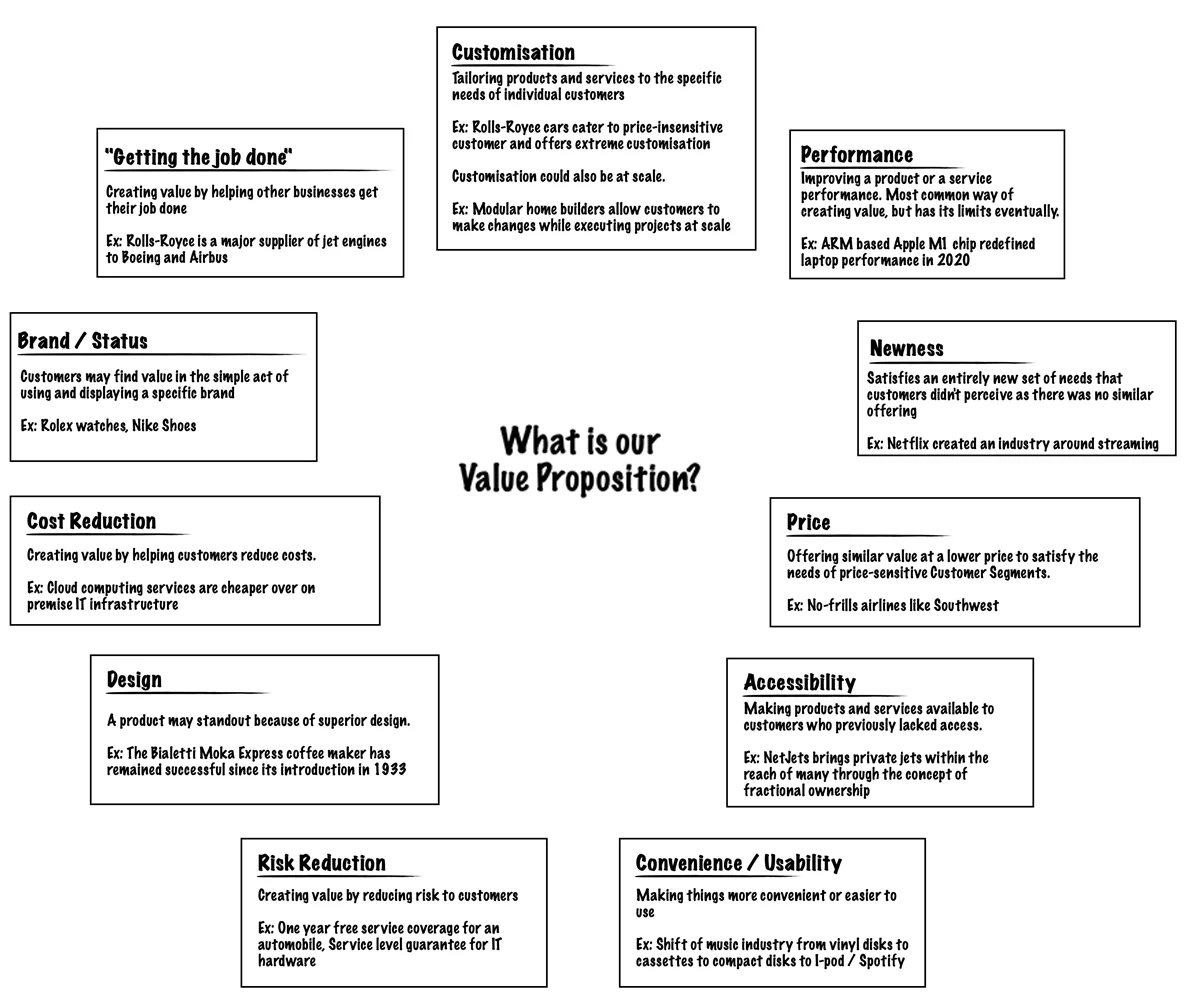
Some value propositions are based on the newness or novelty factor that they provide. This element usually comes into play for technology-intensive products.
The telecommunications industry was spawned through the newness element. Originally the market for cellphones was very small but once the technology became more mainstream the market for the product expanded exponentially with increasingly advanced cellphones and smartphones being created to take advantage of the telecommunications technology.
Performance
Better performance has been the hallmark of many product offerings over the years with most industries managing to thrive for decades on improved performance versions of the same products. Intel doubles the speed of its chip every year, resulting in faster computers able to support much more sophisticated software.
Customization
The modern consumer believes in self-expression and individualism. They expect the products they use to be an extension of their personality and a medium through which they can communicate their values and priorities to the world. Providing the option to tailor the product to the consumer’s preferences adds value for the customer. In recent times products have gained heavily on market share through utilizing concepts such as mass customization or customer co-creation. Where traditionally customization has resulted in prohibitively expensive products, today this option provides the opportunity for customers to put their personal stamp on a product while still providing economies of scale.
Nike lets its customers customize their shoes through NikeID on their website. A consumer can go online and create a completely original design with their preferred color palette, placement, color and size of the swoosh etc for their shoes. They can see what the end product will look like visually, play around with different permutations till they reach a result that suits their tastes and then order the final product when they are ready.
Getting the job done
When a product helps a consumer or business reach the end goal, its value proposition is getting the job done. Rolls Royce is best known for the cars they make but one of their major value propositions is getting the job done through the jet engines they manufacture and service for Boeing as well as providing financing through leasing.
A product whose value proposition is ‘getting the job done’ enhances the customer’s productivity and helps the customer to focus on more relevant details.
Most clothing labels rake in a higher price tag because of the superior design they have. Prada charges top dollar for something as simple as a T-shirt because of the strength of its designs.
Brand/ Status
Design and brand/status can be clustered together because their appeal is quite similar. Just as people will show loyalty to a brand because of its design, people will also show loyalty to a design because of the perceived status the brand name itself lends to the owner or user.
Almost everyone today owns and wears a watch on a regular basis but the brand of the watch could vary from your local watchmaker/ jeweler to the iconic brand Rolex. A Rolex is more than just a watch though, it is a statement that the wearer has money and status, since even a simple Rolex is exorbitantly expensive compared to regular brands.
Ultimately a brand/ status intensive product will help the customer look and feel in control, important and part of the in-crowd.
One of the most common elements a value proposition is based on is price . There are many companies that enter into the market with the premise that they are providing a product or service which is cheaper than the existing options in the market. However, organizations competing on price, or in some cases, even offering free services, usually have different business models to sustain the organization.
One example is the spate of ‘no frills’ airlines that sprung up like Southwest airlines. Southwest offered fares equivalent to a bus-ride, however, in a complete about face from the traditional airline, they did away with all the extra services which formed the pomp and show traditional airlines charged a premium for. In doing so, Southwest opened air travel up to a section of the market which had been previously untapped; the common man.
Cost Reduction
Products and services catered towards enhancing customer experience by reducing the cost a customer would ultimately incur cater to the cost reduction value proposition.
Technology has played a great role in helping consumers reduce costs. One such example is Salesforce.com which allows customers to use a customer relationship management software for a fee, voiding the need for the customer to buy the software, hardware and install and run it, each action associated with a significant cost.
Risk Reduction
The less risk associated with purchasing a product or service, the more value a customer derives from it. A reduction of the risk associated with a purchase provides peace of mind to a consumer. One example of this is the one year service warranty received when buying a used car. In the buyer’s mind, the risk of buying a second hand vehicle is diminished by the comfort of having the warranty.
Essentially a product whose value proposition is Risk Reduction aims to make people feel safer, whether real or imagined safety, as well as guarantees a solution to a problem he/ she is facing for a time bound period.
Accessibility
Another key ingredient for an effective and robust value proposition is making a previously inaccessible product or service available to a consumer segment. Innovative technologies and variations in business models have both led to offering accessibility to unserviced customers. NetJets is a wonderful example of providing accessibility. The company allows individuals and corporations to have access to private jets, which has traditionally been cost prohibitive and therefore unavailable to many who did not have the cash reserves to afford this luxury.
Convenience/ Usability
Providing consumers with a product that increases their convenience or is characterized by ease of use is a very strong value proposition and one on which some companies have built empires and legends around. One example of this type of value proposition is Apple which through its iconic iPod provided consumers with a convenient way to listen to music and by pairing it with iTunes, increased the convenience factor significantly; since now users could easily search, download and play songs, all through one medium!
DESIGNING A VALUE PROPOSITION

When designing a value proposition we often use traditional tools and models instead of thinking outside the box or taking into consideration how much technology, businesses and consumers have evolved. Ultimately, we need to understand whether what an organization delivers actually matters or is it relevant to a customer’s needs.
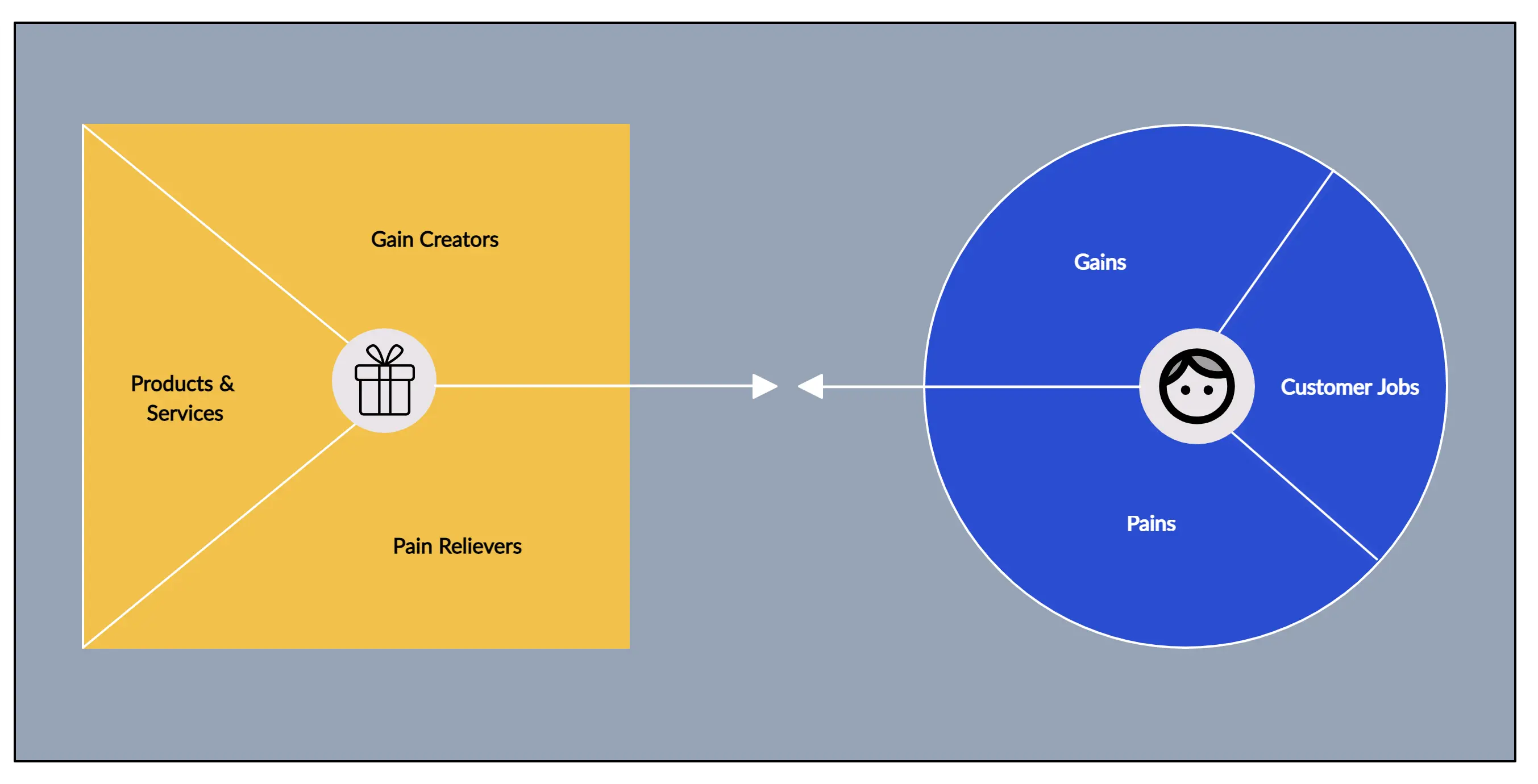
A value proposition can be more effectively designed by utilizing a value proposition canvas, which is essentially an equation of three key ingredients. First, the entrepreneur needs to understand the customer in its entirety by creating a customer profile through analyzing customer jobs, their pains and their gains. This is followed by a value map which clarifies the products and services offered to the customer, their pain relievers and gain creators. Finally a Fit will be achieved when a match is achieved between the Customer Profile and the Value Map.
Products and Services
It is important in the beginning to do an evaluation of the products and services around which your value proposition is built.
Products can be either tangible or intangible. They can also be characterized as digital or financial. When designing and evaluating your value proposition, it is crucial to get inside the customers head. A useful exercise would be to rank your product and services offerings in order of importance to the consumer. For this, the company needs to understand the appeal of the product. Is it a must-have for the customer because it fulfills a basic need? Or does it serve a functional, social or emotional requirement?
Pain Relievers
Your product or service must solve a problem the customer is facing. In essence it is relieving a chronic pain that the customer goes through on a regular basis and which no other product has been able to alleviate to the same degree. This pain could take the form of emotional stress, higher costs and increased risks
An effective way to evaluate your product is to analyze whether it generates lower usage of customer resources such as time, effort or money; Produces a positive change in the customer’s life by reducing his/ her frustration, monotony or boredom; resolve the challenges customers may face, reduce the chances of negative social stigmas and behaviors, reduce risks, alleviate stress, reduce chances of error, eliminate barriers between the customer and a possible solution etc.
By ranking the intensity with which each of these pains impacts your customer and the frequency of their occurrence, an entrepreneur can build up a detailed analysis of the pain relievers the various products and services in his/ her repertoire represent for customers.
Gain Creators
In this section, an entrepreneur needs to evaluate how the products and services in his portfolio lead to customer gains. An effective metric would be to understand how aspects of your products and services would enhance the customer experience by fulfilling his/ her expectations and wishes and even going beyond to surprise and delight him/ her.
The entrepreneur can analyze whether the product or service results in savings that delight the customer, has results that meet or surpass customer expectations, produce better results than the alternatives the customer is currently using, result in positive social relationships and status, fulfill a customer need and are easy to adopt, among other concerns.
By ranking the intensity with which each of these gains impact your customers and the frequency of their occurrence, an entrepreneur can build up a detailed analysis of the gain creators the various products and services in his/ her repertoire represent for customers.
Steps for using the Framework
In short, following are the main steps for using the framework effectively and efficiently;
- Jot down all the products and services in your portfolio which combine to make up your value proposition
- Describe how your value proposition contributes to eliminate your target customer’s pain points. Separate sticky notes should be used for each pain reliever
- Describe how your value proposition contributes a positive result for your target customer. Separate sticky notes should be used for each gain creator.
- Ultimately all three elements; products and services, pain relievers and gain creators should be ranked according to their relative importance to the target customer.
Best practices & Common mistakes when using the Framework
Best practices.
- List only the combination of products and services that directly provide value to the relevant customer segment.
- Pain reliever and gain creators list characteristics of your products and services that are of relevance to the target customers.
- Products and services will be of value to customers only if they match the target segment’s profile, pains and gains
- It is imperative for an entrepreneur to understand that no product or service will be able to meet all the pains and gains in a customer’s profile. Instead the entrepreneur needs to prioritize which pains and gains their product and service should match.
Common Mistakes
- Mention all the products and services in your portfolio regardless of the specific customer segment they target.
- Categorize your products and services as either pain relievers or gain creators.
- Add additional pain relievers and gain creators even if they don’t match the pains or gains in your target segment’s profile
- Try to resolve all pains or gains of the target segment.
[slideshare id=9945937&doc=customersegmentsandvaluepropositionforslideshare3-111030040451-phpapp01]
Evernote is an online company aiming to provide mobile professionals with the capability to take notes while they are on the move.
The main webpage provides a detailed overview of how the product and its various features can help its target market store organize and interpret a seemingly random hodgepodge of information and data. The website makes the features of the service as well as the overall experience come alive for the consumers, helping them understand how they can benefit by using the service.
The trifecta of the service features, the advantages of using Evernote and the overall customer experience are matched exactly to the customers wants, needs and fears. The company has also created further bifurcation of its customer segment so that each page is tailored to a specific kind of customer with the inherent benefits the customer can reap mentioned as well, creating a rudimentary level of customization.
The website’s value proposition is a quick and simple tool that syncs easily with other platforms so sharing ideas is convenient.
- One workspace for all
- Write everyday
- Work together
- Gather research
- Find everything fast
- Share your ideas
- Stay in sync
- Removes the need to carry notebooks, consolidated notes or other forms of data around
- Removes the need for complicated slides during meetings
- Single place to save online material available on a topic of interest
- Economically accessible for individuals without requiring a heavy investment in hardware or software
- Provides a common working space for a team to share ideas and information
- Provides access to freelancers, and individuals to a free service where his or her notes are backed up and available to him at a moment’s notice,
- Cost effective for individuals who can use the service for free
- Provides tools that help customers effectively and efficiently plan and execute projects.
Comments are closed.
Related posts
4 Reasons Your Company Needs a Brand Ambassador Program
Your company may not be doing very well. Not only are your sales low, several customer service …
The Innovation Process: Definition, Models, Tips
Innovation refers to the introduction of a new good or a new quality of a good, method of …
408,000 + job opportunities

Not yet a member? Sign Up
join cleverism
Find your dream job. Get on promotion fasstrack and increase tour lifetime salary.
Post your jobs & get access to millions of ambitious, well-educated talents that are going the extra mile.
First name*
Company name*
Company Website*
E-mail (work)*
Login or Register
Password reset instructions will be sent to your E-mail.
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
The Business Model Canvas
What is the business model canvas.
The business model canvas is a tool designers use to map out a business or product’s key actors, activities and resources, the value proposition for target customers, customer relationships, channels involved and financial matters. It gives an overview to help identify requirements to deliver the service and more.
“A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value.” — Alexander Osterwalder, Co-creator of the Business Model Canvas
Learn about the business model canvas and how it helps in design.
- Transcript loading…
The Business Model Canvas – Flexible Chart, Early-Warning System and More
In service design , two tools are essential to use early in your design process: the business model canvas and the value proposition canvas . You can use the business model canvas to build an overview of changes to be made to an existing business (e.g., a merger) or of a totally new business opportunity or market gap . At the start of your design process, it’s vital to map out the business model of your service to see how it will fit into the marketplace. You’ll also need to ensure what you propose can bring maximum value to both your customers and business, and keep doing so in terms of customer retention, profitability and more.
To gain the most accurate vision of a proposed product or service, it’s essential to understand all the components and dynamics of not only the customer experience but also the service as a whole ecosystem . This ecosystem contains all the channels and touchpoints that must work together to deliver and sustain maximum value to the customer.
This canvas gives you several important advantages, namely these:
It’s collaborative – so you can bring the various partners together on the same page to generate and analyze ideas, and have an early testing ground for concepts before you advance to service staging a prototype.
It’s human-centered – so you can keep close track on how to create and maximize value for customers as well as stakeholders and other partners.
It makes it easier to collect rich data – if you have a clear purpose and strategy in mind.
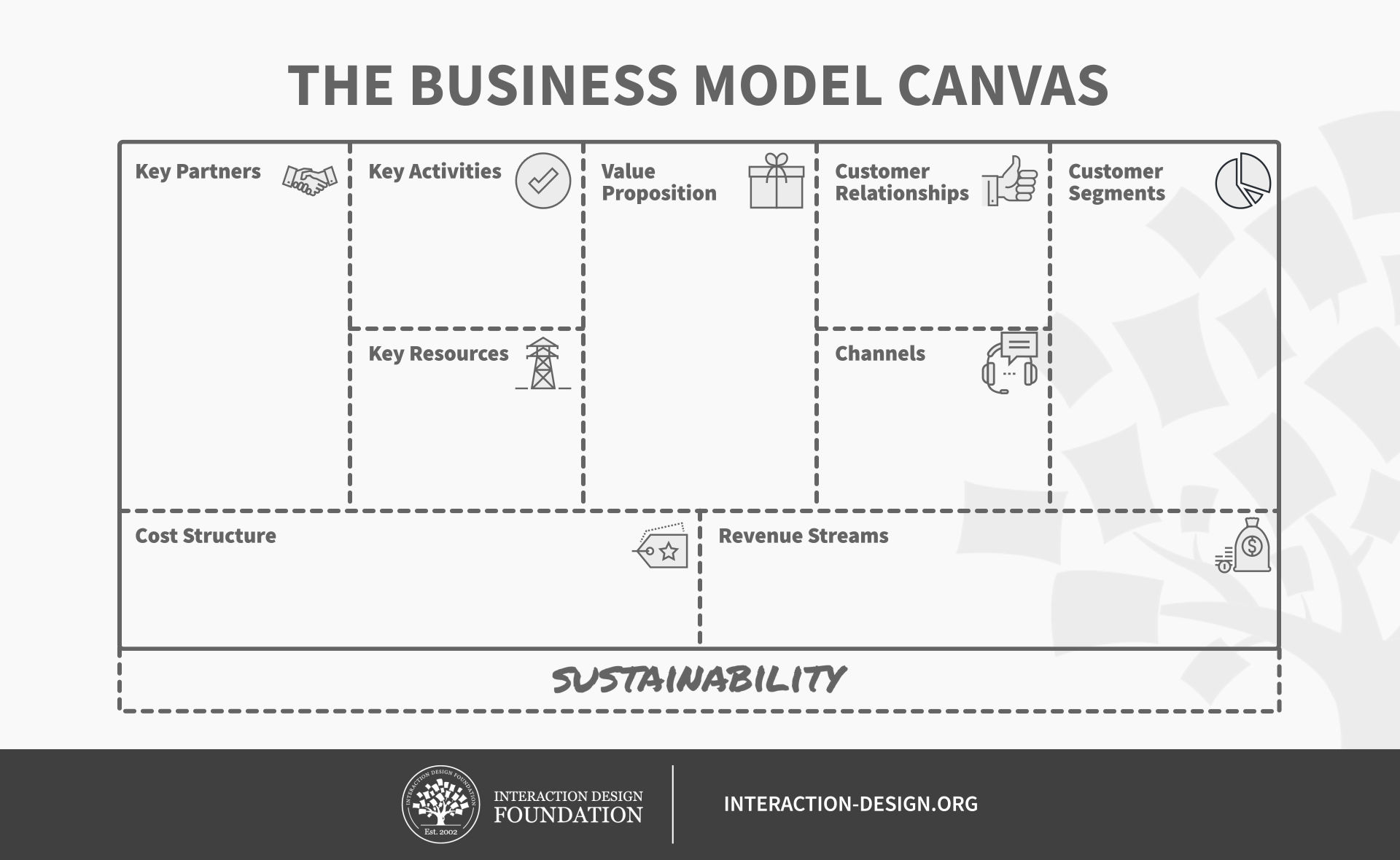
A business model canvas typically contains 10 boxes:
Key Partners – The people who will help you fulfill the key activities, using the key resources.
Key Activities – Those vital actions that go into the everyday business to get things done; these are all the activities needed to realize and maintain the value proposition, and to power everything else involved.
Key Resources – The tools needed to get those things done, stretching across all areas the canvas covers to include, for example, customer retention.
Value Proposition – The item you think will create value for your customer: e.g., a new idea, a price drop. This is a summary of what your business will deliver to customers, and feeds into the value proposition canvas, the tool you’ll use to expand this.
Customer Relationships – Where you envision the relationship each customer segment expects: e.g., customer acquisition, retention and upselling (i.e., How do you get customers? How do you keep customers? How do you continue to create value for them?).
(Note: boxes 5 and 4 are closely linked as everything you do revolves around retaining the customer and considering the customer lifecycle.)
Customer Segments – Your most important customers (e.g., seniors); consider the value of personas here.
Channels – How you deliver the value proposition. Will it be online, through physical means or a combination? Here, you identify which channels are the best (both desirable for customers as well as cost-efficient and cost-effective for the brand).
Cost Structure – Here you find the most essential cost drivers. This allows you to consider the return on investment (ROI).
Revenue Streams – Where you find potential revenue sources (e.g., advertising).
Sustainability – How sustainable your offering is overall, to the environment, to the social good, etc.
© Strategyzer AG, modified, CC-BY-SA-3.0
How to Build a Business Model Canvas
For the best results, follow these guidelines and aim to fill in all the gaps, looking out for cause-and-effect relationships that run between boxes/throughout:
Complete the top seven boxes (Key Partners to Customer Segments) – using all the information you can gather from your research.
Complete the next boxes:
Cost Structure – Determine the cost drivers from the Key Partners, Activities and Resources boxes; and
Revenue Streams – Determine these from the Customer Relationships, Customer Segments and Channels boxes.
Once you have established these, you can work to estimate them in monetary terms.
Complete the Sustainability box – according to the insights you’ve found.
Here’s an example of a business model canvas as a work in progress:
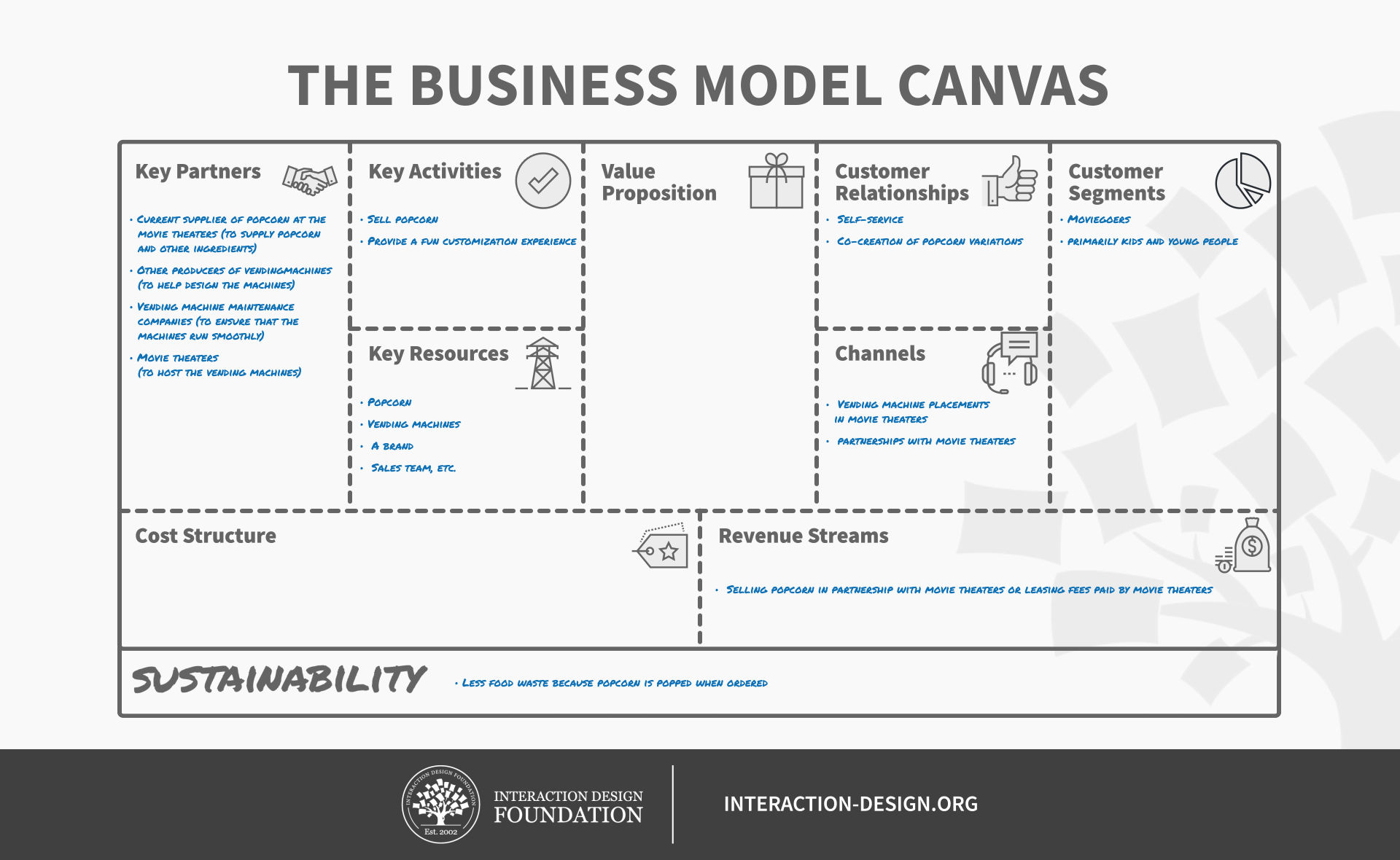
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0
Overall, remember your canvas is a flexible tool. It’s also a living document that you can revisit and use to find the most effective alternatives. With a clear sense of goals, a keen eye for detail and ear for input, and a readiness to refine this canvas, you can use it to fine-tune the best service prototype every time.
Learn More about The Business Model Canvas
Take our Service Design course , featuring a template for service blueprints.
Read this example-rich piece by experienced strategy designer Justin Lokitz for tips on using the business model canvas .
Find some additional tips on how to make the most of your business model canvas here .
Literature on the Business Model Canvas
Here’s the entire UX literature on the Business Model Canvas by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about the Business Model Canvas
Take a deep dive into Business Model Canvas with our course Service Design: How to Design Integrated Service Experiences .
Services are everywhere! When you get a new passport, order a pizza or make a reservation on AirBnB, you're engaging with services. How those services are designed is crucial to whether they provide a pleasant experience or an exasperating one. The experience of a service is essential to its success or failure no matter if your goal is to gain and retain customers for your app or to design an efficient waiting system for a doctor’s office.
In a service design process, you use an in-depth understanding of the business and its customers to ensure that all the touchpoints of your service are perfect and, just as importantly, that your organization can deliver a great service experience every time . It’s not just about designing the customer interactions; you also need to design the entire ecosystem surrounding those interactions.
In this course, you’ll learn how to go through a robust service design process and which methods to use at each step along the way. You’ll also learn how to create a service design culture in your organization and set up a service design team . We’ll provide you with lots of case studies to learn from as well as interviews with top designers in the field. For each practical method, you’ll get downloadable templates that guide you on how to use the methods in your own work.
This course contains a series of practical exercises that build on one another to create a complete service design project . The exercises are optional, but you’ll get invaluable hands-on experience with the methods you encounter in this course if you complete them, because they will teach you to take your first steps as a service designer. What’s equally important is that you can use your work as a case study for your portfolio to showcase your abilities to future employers! A portfolio is essential if you want to step into or move ahead in a career in service design.
Your primary instructor in the course is Frank Spillers . Frank is CXO of award-winning design agency Experience Dynamics and a service design expert who has consulted with companies all over the world. Much of the written learning material also comes from John Zimmerman and Jodi Forlizzi , both Professors in Human-Computer Interaction at Carnegie Mellon University and highly influential in establishing design research as we know it today.
You’ll earn a verifiable and industry-trusted Course Certificate once you complete the course. You can highlight it on your resume, CV, LinkedIn profile or on your website.
All open-source articles on the Business Model Canvas
Service design - design is not just for products.

The Relationship Between Visual Design and User Experience Design
- 2 years ago
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!

The Value Proposition Canvas
Value Proposition Canvas is a tool for marketing experts, product owners, and value creators. This method from the bestselling innovation book Value Proposition Design is applied in leading organizations and start-ups worldwide.

Why use the Value Proposition Canvas?
Precisely define your customer profiles.
Identify your customer's major Jobs-to-be-done, the pains they face when trying to accomplish their Jobs-to-be-done and the gains they perceive by getting their jobs done.
Visualize the value you create
Define the most important components of your offering, how you relieve pain and create gains for your customers.
Achieve product-market fit
Adjust your Value Proposition based on the insights you gained from customer evidence and achieve Product-Market fit.
The Value Proposition Canvas explained
A 2 minute overview of the Value Proposition Canvas, a tool for marketing experts, product owners, and value creators. This method from the bestselling innovation book Value Proposition Design is applied in leading organizations and start-ups worldwide.

About the speakers
Download your free copy of this whitepaper now, explore other examples, get strategyzer updates straight in your inbox.
Mastering Value Propositions
An online course that includes 8+ hours of high-quality videos and exercises to learn how to design value propositions that your customers want.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 11 min read
The Business Model Canvas
Understanding what makes your company successful.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Do you know what your company's business model is? How well do you understand it? And why does this matter?
A company's business model determines how it generates its revenue, operates successfully, and makes a profit. If your company's business model is out of date or wrong for its market, then it's likely to fail.
Understanding your company's business model is an important part of developing the "commercial awareness" you need to solve problems effectively, make good decisions, and become known as a trusted leader in your organization.
This article explores a useful model that you can use to think about your business model.
What Is the Business Canvas Model?
Alex Osterwald and Yves Pigneur developed their Business Model Canvas in 2010.
They collaborated with 470 members of the Business Model Innovation Hub – an online forum for business professionals and researchers – who contributed case studies, examples, and critical comments to their research. As such, the Business Model Canvas represents the collective experience of a community of business people.
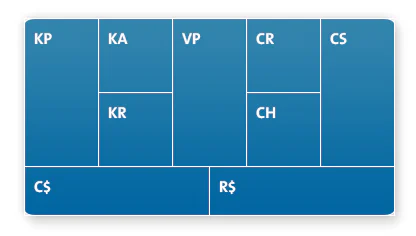
It appears as a template of nine basic building blocks, as shown in figure 1, below. These form a blueprint, based on which business models can be systematically designed, explained and challenged.
Figure 1: The Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is the property of BusinessModelGeneration.com / strategyzer.com , and it is distributed under a Creative Commons copyright license .
How to Use the Business Model Canvas
To use the Business Model Canvas, think about each building block using the questions below. You may want to download our worksheet to help with this.
CS: Customer Segments
Your customer segments are your target markets – the specific groups of people or organizations that your business serves.
Instead of trying to satisfy everyone, all of the time, group your customers according to common attributes like their location, needs, or behaviors, and decide which segments to focus on. This way, you can deliver a product or service that is closely tailored to the specific needs of particular groups.
See our article on market segmentation for more on this.
Record your results in the CS block of the canvas.
VP: Value Propositions
The value propositions block defines how you'll deliver value to your customers. You can create value in many ways, including offering a low price, a high standard of design, good accessibility, convenience, and high performance. Consider these questions:
- How do you create value for your target market?
- What problem or need does your product or service solve for the customer?
- How does your product or service differ from your competitors' offerings?
If you are struggling to crystallize your value proposition, conduct a USP Analysis and Core Competency Analysis to assess how your product or service stands out from those of your competitors.
Write your value proposition in the VP block of the Business Model Canvas.
R$: Revenue Streams
In this block, you analyze how each customer segment pays for your product or service.
There are many different ways to pay for a product or service. For example, is the price fixed, or will you charge customers for each use, by subscription, or with ongoing payments? Will any negotiation or bargaining be involved? And who, ultimately, is the customer? (Your customer may be an advertiser, for example, rather than the user of the service.)
Consider these additional questions:
- What do your customers currently pay for similar products or services?
- How do they pay for this?
- What do you charge for your product or service?
- Do customers get any free services or perks that your competitors don't offer?
Record this in the R$ block of the Business Model Canvas.
CH: Channels
The word "channel" refers to the way you deliver your value proposition to each customer segment. Channels include a direct sales force, web sales, own brand stores, partner stores, and wholesalers. Consider these questions:
- How do you make your customers aware of your products and services?
- What channels do your customers prefer to use?
- How will you help customers evaluate your value proposition?
- How do customers want to buy your products and services?
- How do you provide customer support?
Record your answers in the CH block of the Business Model Canvas.
CR: Customer Relationships
This block defines the type of relationship you want to foster with each of your customer segments. There are several categories to consider here.
- Dedicated personal assistance – This is where the wants and needs of each customer are handled by a dedicated customer service representative. For example, many types of business dedicate an account manager to highly valued clients.
- Personal assistance – Here, customers can communicate with a customer service professional during and after the sales process. This can happen in person at the point of sale, or through a call center, email, or IM.
- Self-service – Customers can purchase products without assistance.
- Automated Service – An automated service recognizes individual customers through a login or other identifier. This provides a customized service that "remembers" the customer's preferences and presents options accordingly.
- Communities – Here, the organization builds communities using social networking and blogs to encourage customers to communicate with one another, share ideas, and solve problems.
- Co-creation – In these relationships, organizations go beyond the traditional customer-vendor relationship by encouraging customers to take a more active role in shaping what the product or service might be. For example, some companies encourage their customers to review their products, or create content that can be shared with others.
To think about how your business develops relationships with customers, you can use the Buy-Sell Hierarchy , Focus Groups , and Customer Experience Mapping to understand what your customers want from their experience, and then use this information to build the customer relationships you need.
Record your findings in the CR block of the Business Model Canvas.
KR: Key Resources
Your key resources are the things you most need to make your business model work, and different types of business need different types of resource.
Key resources may be owned by your company, leased, or used through some other arrangement with key partners.
Consider these questions:
- What human resources will you need?
- What financial resources will you need?
- What physical resources will you need?
- What intellectual property resources will you need?
Conduct a VRIO analysis to explore how you can make best use of the resources you have available.
Make a record of these key resources in the KR block of the Business Model Canvas.
KA: Key Activities
Your key activities are the most important business processes that your organization must use to operate successfully. Examples of these include designing, manufacturing, and delivering a product; providing new solutions to customers; or providing a platform on which customers are able to complete transactions.
List your key activities in the KA block of the Business Model Canvas.
KP: Key Partnerships
This is the network of partners, stakeholders and suppliers that you rely upon to make your business model work. Consider these questions:
- What strategic alliances do you have in place to bring your product or service to market?
- What partnerships are needed to access key resources such as areas of expertise, raw materials, or access to customers?
- What partnerships allow you to access economies of scale?
- Who have you joined forces with to minimize risk and uncertainty?
- Who are the key stakeholders for your product or service? How can you create strategic partnerships with these people?
Conduct a Stakeholder Analysis to identify who has the most power and influence. And, as you evaluate potential partners, use our 10 Cs of Supplier Evaluation checklist to evaluate them carefully.
Write your key partnerships – both potential and present – in the KP block of the Business Model Canvas.
C$: Cost Structure
The last block you need to analyze is your cost structure. This looks at all of the operating costs that your business incurs as part of its business model. These costs should be easy to identify, now that you've defined your key resources, activities, and partnerships.
Record your findings in the C$ block of the Business Model Canvas.
Applying What You Have Learned
By working through the Business Model Canvas for your own company, you'll get a good insight into the things that really matter for your business.
You can use this understanding to make informed decisions about business areas that you are responsible for by checking, in particular, that your decision won't undermine the wider business in any way. You can also quickly identify business areas that will be improved by your decision, and this will help you "sell" your recommendations.
It also gives you a head start when you're scanning the business news or industry press for changes that will positively or negatively affect your business. You'll know the core things that your business depends on, and you can watch out for changes that affect these.
Another advantage of the Business Model Canvas is that it clarifies how your own part of the company affects, and is affected by, other departments. This helps all parts of the business co-operate with one another more efficiently.
The Business Model Canvas was developed by Alex Osterwald and Yves Pigneur, in collaboration with a community of business professionals at the Business Model Innovation Hub. It is a useful tool for designing and analyzing business models in an objective, structured way.
The Business Model Canvas incorporates nine building blocks:
Block 1: Customer segments.
Block 2: Value propositions.
Block 3: Channels.
Block 4: Customer relationships.
Block 5: Revenue streams.
Block 6: Key resources.
Block 7: Key activities.
Block 8: Key partnerships.
Block 9: Cost structure.
You can use the Business Model Canvas to develop a new business model, or refresh an outdated one; analyze the viability of a new business idea; and even to analyze your competitors' business models to discover opportunities for making your own business stand out.
Download Worksheet
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Expert Interviews
Wrong Fit, Right Fit: Why How We Work Matters More Than Ever
With André Martin
Reducing Stress With the Demand-Control Model
How Demand and Autonomy Shape How We Experience Work
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Gain essential management and leadership skills
Busy schedule? No problem. Learn anytime, anywhere.
Subscribe to unlimited access to meticulously researched, evidence-based resources.
Join today and take advantage of our 30% offer, available until May 31st .
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

How to Manage Your Deadlines

How to Be a More Engaging Speaker
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Do nothing: how to stop overmanaging and become a great leader.
J. Keith Murnighan
Book Insights
From Technical Expert to Manager
Learning the Management Skills You Need in Your New Role
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Pain points podcast - receiving feedback.
Accepting What Others Say About You
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- Integrations
- Learning Center
How to Build a Product Roadmap Based on a Business Model Canvas
Could you list all of the key building blocks you need to develop, manage, maintain, market, and sell a product on a single sheet of paper? With the business model canvas, you can! Using the business model canvas approach is a great way to force yourself to focus on the most strategically important elements of your product. As the name suggests, the typical use case for this tool is to outline the fundamental building blocks of a business, but it also can work really well for a product.
Today we’ll show you how the business model canvas works and how you can use it to come up with a high-level product strategy.
What is a Business Model Canvas?
As you can see from the sample example below (thanks, Strategyzer.com), a business model canvas is a one-page summary describing the high-level strategic details needed to get a business (or product) successfully to market.
The categories or buckets contained in a canvas can be customized. But most will look similar to the one here—covering such key areas as:
- The product’s value propositions (what it does and promises)
- Customer segments (who it’s for)
- Key activities (the steps the team must complete to make it successful)
- Key resources (what personnel, tools, and budget the team will have access to)
- Channels (how the organization will market and sell it)
- Customer relationships (how the team will support and work with its customer base)
- Key partners (how third parties will fit into the plan)
- Cost structure (what it costs to build the product as well as how to sell and support it)
- Revenue streams (how the product will make money)
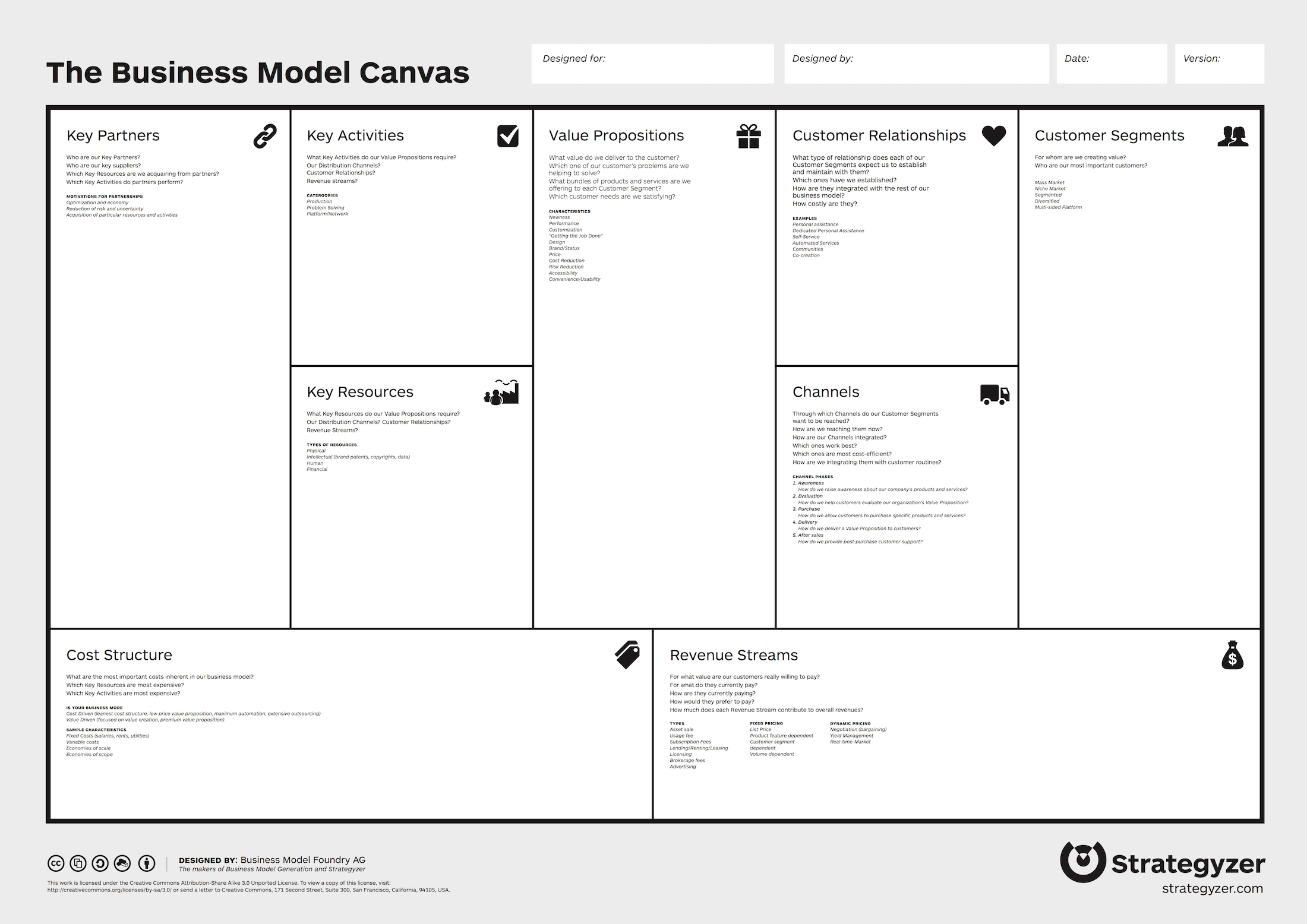
If you think about it, that’s a fairly comprehensive set of building blocks you’ll need to think through for your product before you begin developing it. There will certainly be additional factors that’ll affect your strategy, but if you can fill in these high-level details—which, as you can see, should fit comfortably on a single page—you’ll have a useful strategic guide for developing your product roadmap.
Why Should I Use a Business Model Canvas to Develop a Product Roadmap?
Okay, but why? What’s the benefit of building a business model canvas (or the, even more, stripped-down variation, the lean canvas) to guide my product roadmap ?
There are plenty of reasons. But simply put, you can think of a business model canvas as a mission statement for your product roadmap. It’s a handy reference you can refer to, to make sure your roadmap always reflects all the strategic elements needed for your product’s success.
Tweet This: “Think of a business model canvas as a mission statement for your product roadmap.”
Our co-founder Jim Semick has a couple of great short videos explaining the business model canvas concept, which you can check out in the player below.
As Jim explains, here are a few of the benefits of using a business model canvas to think through product strategies:

1. You can use a business model canvas to roadmap quickly.
You can use this canvas approach in just a few hours (and as Jim says, you can even do it with sticky-notes).
This way, rather than trying to write out every detail about your product plan beforehand, you can just document the highlights—and then you can get rolling translating the canvas into your product roadmap.

2. A business model canvas will be more agile.
One problem with the old structure of documenting a business model—the traditional business plan—was that it was almost always inaccurate as soon as the author finished drafting it.
These meaty plans included detailed cost estimates, revenue projections going years into the future, and long-term plans for growing the staff. How could any of that remain accurate for long?
In product terms, you can think of the business plan as resembling an MRD (Market Requirements Document). It’s long, detailed, and probably mostly untrue by the time it’s done.
But because you can put a canvas together so quickly, it will much more accurately reflect your strategic thinking and your company’s current reality. And if things change, it’ll be easier than a long and detailed plan to adjust. This brings us to Jim’s third benefit…
3. Business model canvas roadmaps allow you to pivot as needed.
If you build a business model canvas to guide your business roadmap , and something happens that forces you to re-prioritize or pivot your product , it will be a lot easier to update this short, high-level document than it would be if you had some monster MRD or business plan to tear apart and edit.
With a one-page business model canvas acting as the strategic undergirding for your roadmap, you’ll always be able to quickly spot any items or plans that need updating whenever priorities change or new realities demand that you adjust your approach.
How Can I Use A Business Model Canvas to Guide My Product Roadmap?
The alexa example.
Let’s talk through a hypothetical example, using Amazon’s Echo device (“Alexa”) as our guide.
Imagine that as they were talking through what belonged in the “Revenue Streams” bucket of the business model canvas, Amazon’s Echo team came up with three sources of revenue to start with:
1) Selling Echo devices.
2) Using the device to sell other stuff as customers ask it to connect to the Amazon marketplace. (“Alexa, please add laundry detergent pods to my shopping cart.”)
3) Licensing Echo’s proprietary speech-recognition technology to other businesses.
Now, if the Echo product team put these on their business model canvas, they’d know that they need to make room for budget, time, and resources on their product roadmap for all of these revenue streams.
Another Hypothetical Example of the Business Model Canvas: Channels
Or think about the Channels bucket in the business model canvas. If your team was building out a canvas, maybe you’d have several ideas for reaching customers:
1) The in-house sales team. 2) Affiliate partners. 3) Word-of-mouth advertising from users.
It’s easy to write. But how are you going to translate that “word-of-mouth” strategy into an actual plan?
Maybe you’ll need to budget time and resources for developing things right into your product that make it easier for users to share their experiences with friends, such as a handy tool to help them tweet about it. Maybe you’ll even want to include an “Invite a friend” feature that lets users easier send a trial license to friends, or a couponing feature that offers some reward to a user who brings in two more users.
The point is, your business model canvas can serve as a great strategic reminder of the things you’ve determined are important enough to make it onto your product roadmap .
So you can always look back and see immediately—it’s just one page, after all—if you’re still working on all of the essential elements of your product, or if you’ve inadvertently strayed from them and gotten lost in the wrong details.
That’s why we’re big proponents of the business model canvas approach to guiding your product roadmap .
Do you have an opinion about using the business model canvas approach for developing and documenting your product’s strategy? Feel free to share them in the comments section.

Product Management Training: 5 Excellent Resources
If you want to become a software developer, one option is to major in computer science or software engineering in...
A Product Manager’s Role in SAFe®
Agile started with software development. Although many organizations have found the principles beneficial. The ability to quickly assess, adjust, and...
5 Roadmap Templates for Product Executives
Product roadmaps shouldn’t be a one-size-fits-all proposition, as different stakeholders care about various elements and require different levels of detail....
Continue exploring
You can search or explore specific categories.
Product Updates
Company news and updates, templates and workbooks, remote product management, product metrics and analytics, product strategy example, product managers, prioritization and backlog, tools and resources, customer-centricity, product leadership, product management, roadmap and roadmap management, product strategy, agile & product development, career and interviews, try productplan free for 14 days, share on mastodon.
- Scroll to top
- / Sign Up
Value Proposition Canvas Template and Examples – Step-by-Step Guide
The Value Proposition Canvas provides a framework that centers your customers. It supports understanding the problem your customer is truly trying to solve so that you can design an elegant and effective solution.
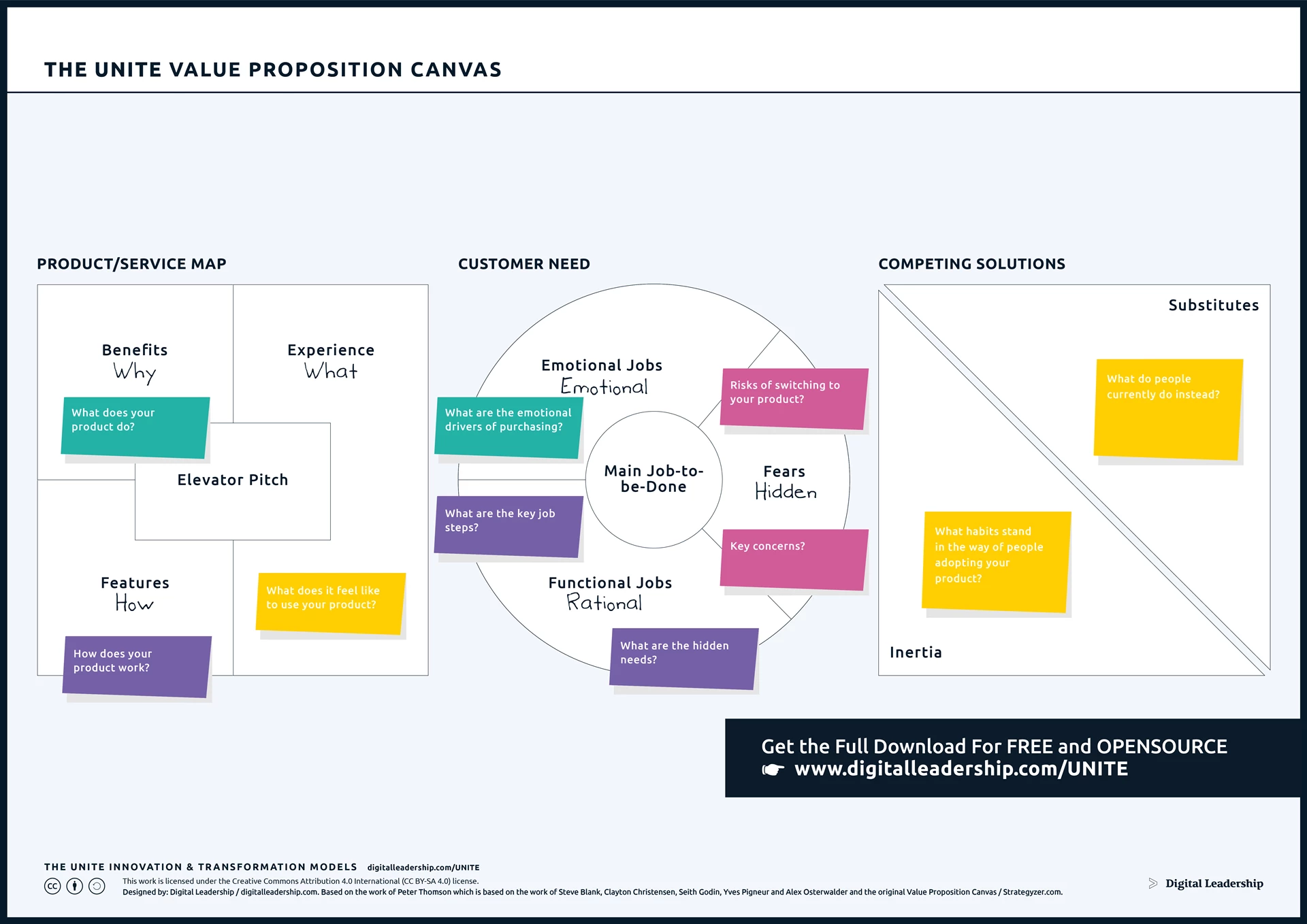
Get the Full Package for FREE & OpenSource
- Get instant access to this model including a full presentation, related tools and instructions!
- You will equally get instant access to all 50+ UNITE Innovation & Transformation Models!
- Completely FREE and OpenSource!

Table of Contents
Understanding and effectively communicating your value proposition to customers is important in business. One powerful tool for achieving this is the Value Proposition Canvas developed by Alex Osterwalder , a part of the Business Model Canvas that evolves dynamically, birthing new value propositions by uncovering unmet customer needs through the “Jobs to be Done” theory . The Value Proposition Canvas is a great tool serves as a framework to guarantee that a product or service aligns with the values and needs of the customer. By adopting a value proposition canvas approach , businesses can fill in the value and tailor their offerings to address specific customer pain points and desires. With a clear understanding of customers’ problems and needs, businesses can develop compelling value propositions that resonate with their target audience and differentiate themselves in competitive markets.
Understanding your customers’ desires helps you grasp what they want to achieve while addressing obstacles get in the way. In the circles of a successful value proposition framework, the value proposition is represented by the Value Proposition Canvas and Business Model Canvas .
In this complete guide, let’s take a look at the intricacies of the Value Proposition Canvas, providing a step-by-step template help you understand your customers’ needs trying to satisfy them and help them fulfill the gains. and real-world examples to illustrate its application. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or embarking on a startup journey, mastering the Value Proposition Canvas can significantly enhance your business strategy and success.
What is Value Proposition Canvas
The Value Proposition Canvas functions as a framework to guarantee that a product or service is strategically aligned with the customer’s values and needs. Developed by Dr. Alexander Osterwalder, the Value Proposition Canvas ensures a harmonious fit between the product and the market. The Value Proposition Canvas provides a structured approach to identifying customer pains, gains, and jobs to be done , as well as mapping how products or services alleviate customer pains and create gains.
In crafting a Value Proposition Canvas to map customer needs effectively, it’s imperative to start with a thorough understanding of your target customers’ profiles. This involves identifying the jobs they need to accomplish in their work or life, the obstacles they face, and the outcomes they desire. By recognizing the jobs customers need to fill and the outcomes they seek, you can develop products or services that address their specific needs and help them fulfill their goals. This process ensures that your offerings align closely with customer expectations and provide meaningful value.
The alignment between the customer profile and the value proposition map is essential for ensuring that businesses achieve product-market fit. This alignment involves identifying how each element of the value proposition map corresponds to specific aspects of the customer profile, thereby ensuring that products or services effectively address customer needs and deliver value.
Value Proposition Canvas Template For Mapping Customer Needs
The Value Proposition Canvas Template is divided into three key parts:
- The Customer Profile in the center allows you to get into your customer’s head and thus clarify their jobs to be done.
- The Product Value Map on the left helps you describe how you intend to create value for that customer. The ultimate objective is to achieve fit between the Customer Profile and the Product Value Map. You have achieved that fit once the product solves a clear Job to be Done
- The substitutes section outlines what people are currently using to solve their JTBD and identifies inertias that might prevent them from switching to your solution, even if it is superior. Most organizations struggle to understand the alternative solutions. Gaining a customer means not only serving their need but overcoming their resistance to trying something new.
Each part plays a crucial role in understanding and addressing customer needs effectively.

Customer jobs refer to the tasks, activities, or problems that customers are trying to solve in their work or life. These jobs can be functional, emotional, or social in nature. Understanding functional jobs helps you identify what customers are trying to achieve, while emotional and social jobs reveal deeper insights into their desires and aspirations.
- Main Jobs to be Done : This represents the primary goal or task the customer intends to accomplish. Sometimes, customers may have latent needs that they aren’t consciously aware of, which can be unveiled through exploring their jobs to be done.
- Functional Jobs : These are the practical tasks or requirements that customers need to fulfill. They often reflect rational motivations and can be mapped out in detail using a Job Map .
- Emotional Jobs : Emotional drivers influence decision-making by representing desires and aspirations for improvement in various aspects of life. These desires, while sometimes abstract, can significantly impact purchasing behavior.
Crafting the Jobs to Be Done Customer’s Job Statement model helps to distill the essence of the customer’s job into a concise and actionable statement. This model emphasizes understanding the customer’s Needs, Tasks, and Objectives, as well as the associated Context and Constraints. By utilizing this framework, businesses can gain deeper insights into the functional, emotional, and social dimensions of the customer’s job, enabling them to tailor their products or services more effectively to meet customer needs and desires.

Your download is now available!
You can now access the complete JTBD Customer’s Job Statement Package, including a full presentation, related models and instructions for use.
The UNITE Jobs-To-Be-Done Statement & Map
Customer pains in value proposition.
Pains represent the obstacles, challenges, or frustrations that customers encounter while trying to accomplish their jobs. These can range from tangible issues such as high costs to intangible concerns such as fear of change. By understanding your customers’ pains, you can develop solutions that address their specific needs and alleviate their frustrations.
Customer Gains in value proposition
Gains are the benefits, outcomes, or positive results that customers expect or desire from successfully completing their jobs or overcoming their pains. These can include functional gains like increased efficiency, emotional gains such as peace of mind, or social gains like enhanced social status. By exceeding customers’ expectations and delivering meaningful gains, you can create value and build lasting relationships with your customers.
2. Product Value Proposition Map
The product section of the canvas uses the widely accepted marketing syntax of features and benefits with the addition of a box for “experience” (taken from the fields of Design Thinking and customer experience architecture). Once businesses have a thorough understanding of customers’ needs and problems, jobs include proceeding to develop pain relievers and gain creators in the value map . Pain relievers are the features or solutions offered by products or services that alleviate customer pains and address the obstacles that prevent customers from achieving their desired outcomes. On the other hand, gain creators are the features or solutions that provide specific benefits or outcomes to customers, thereby fulfilling their needs and desires. Once you have a clear understanding of your customer profile, you can map out how your products or services address their needs and provide value. The Value Proposition Map consists of three key elements:
Pain Relievers:
Pain relievers are the features, attributes, or solutions offered by your products or services that alleviate customer pains and help them overcome obstacles in getting the job done. Whether it’s simplifying complex tasks, reducing costs, or saving time, pain relievers play a crucial role in enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Gain Creators:
Gain creators are the features, attributes, or solutions that deliver specific benefits or outcomes to customers, thereby fulfilling their needs and wants. By understanding your customers’ desires and aspirations, you can develop gain creators that exceed their expectations and provide added value. Whether it’s improving their emotional well-being, enhancing their social status, or fulfilling their existential needs, gain creators contribute to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Products and Services:
This section of the Value Proposition Map outlines the specific products or services that your business offers to address customer needs, pains, and gains. It provides a tangible representation of how your offerings align with customer requirements and create value. Whether you’re introducing a new product or improving existing ones, focusing on customer wants and needs is essential for success.
We recommend starting the crafting of your Elevator Pitch immediately to provide yourself with an initial version to iterate. Embracing even imperfect drafts can be valuable! You can then refine it progressively. The Elevator Pitch typically adheres to a standard structure, streamlining the process for you.

Download the Complete eXtended Business Model Canvas Package, including instructions for putting it to work for you today.
The UNITE Business Model Canvas
The Value Proposition Canvas plays a vital role within the Business Model Canvas, a strategic management tool widely utilized in various industries. Within the Business Model Canvas framework , the value proposition embodies the distinctive amalgamation of products or services provided by a business to meet precise customer demands and set itself apart from rivals. Through a deep comprehension of customer challenges and aspirations, coupled with the alignment of products or services to adequately address those needs, organizations can not only attract customers but also drive revenue and foster long-term growth. Let’s delve into the correlation between the value proposition and the business model canvas:
What is value proposition in business model canvas? And its importance?
In the Business Model Canvas, the value proposition represents the unique combination of products or services that a business offers to meet specific customer needs and differentiate itself from competitors. It serves as the core element of the business model, driving revenue generation and customer acquisition.
The importance of the value proposition in the Business Model Canvas lies in its ability to define the value that a business delivers to customers and articulate why customers should choose its offerings over alternatives. By clearly defining and communicating its value proposition, a business can attract customers, generate revenue, and sustain long-term growth.
The key measure of success for a Business Model is the ability to create and capture value. Many Business Model Innovations fail to capture enough value because their solution is poorly conceived. The Value Proposition Canvas is therefore a critical step in designing your overall Business Model.
The Value Proposition Canvas, alongside concepts like the Lean Canvas, serves as a comprehensive guide for businesses seeking to understand and address customer needs effectively. By focusing on how their product adds value and considering both positive outcomes and negative social consequences, businesses can better comprehend what motivates customers to buy and align their offerings accordingly. It’s crucial to always start with the customer, recognizing their desires and aspirations, while also acknowledging the challenges that may obstruct them from fulfilling those needs.
Through this process, businesses can identify the specific problems their customers are trying to solve and craft solutions that help fulfill their goals. By understanding the jobs customers need to accomplish and finding the right approach to satisfy those needs, businesses can create value propositions that resonate with their target audience. Ultimately, the Value Proposition Canvas provides a framework consisting of two essential components—the leftward square focusing on customer profiles and the rightward circle emphasizing value propositions. Leveraging this tool, businesses can develop a deeper understanding of their customers’ needs, refine their offerings, and ultimately achieve success in the marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what are the 6 components of the value proposition canvas.
The six components of the Value Proposition Canvas include:
- Customer Jobs
- Customer Pains
- Customer Gains
- Pain Relievers
- Gain Creators
- Products or Services
2. What are the 9 elements of business model canvas?
The nine elements of the Canvas are:
- Customer Segments
- Value Propositions
- Customer Relationships
- Revenue Streams
- Key Resources
- Key Activities
- Key Partnerships
- Cost Structure
3. Why use a value proposition canvas?
The Value Proposition Canvas helps businesses gain a deeper understanding of their customers’ needs, pains, and gains , enabling them to develop products or services that address those needs effectively. It also facilitates communication and alignment across internal teams, guiding strategic decision-making, and fostering innovation.
4. Gain creators vs pain relievers, What is the Difference?
Gain creators are features or attributes of a product or service that deliver specific benefits or outcomes to customers, fulfilling their desires or expectations. Pain relievers, on the other hand, are solutions offered by a product or service that alleviate customer pains or challenges, making it easier for them to achieve their goals. While gain creators focus on enhancing customer satisfaction, pain relievers address obstacles or frustrations that customers encounter.
- FREE LIVE TRAINING
How To Overcome The 90% Failure Rate in Innovation
Learn the winning formula from over 80+ successful innovation projects
SAVE MY FREE SPOT NOW

Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator & bestselling author!
Your e-mail address: * Your first name: *

One Last Step..
Help us better understand the UNITE community
Free guide to improve your innovation success rate*
Our 35-page comprehensive innovation guide covers the key areas why innovation fails. While it cannot cover all the solutions (that would take books to fill), it provides you with a convenient starting point for your analysis and provides further resources and links to the corresponding UNITE models, ultimately allowing you to work towards a doubling and tripling your chances of success.

Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the entire Internet!
LOG IN VIA E-MAIL
Forgot password?
New to Digital Leadership? Create your account

Get access to the UNITE Models now!
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the internet!
First name *
Last name *
Professional E-mail *
Choose Your Password *
Confirm Your Password *
I want to be kept up-to-date and accept the privacy statement *
By signing up, you agree to receive news and accept the privacy statement (mandatory)
Already have an account? Log in
Verify your e-mail address now by entering the 6-digit code we’ve just sent to your inbox
Don't receive Code? Resend code
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bhutan Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland State of Palestine Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United States United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Seniority * Please Select Junior Consultant Senior Consultant Manager Senior Manager Director VP SVP Partner CXO Board Member
Areas of interest * Innovation Digital Transformation Culture & Organization IT Strategy & Bus. Alignment Customer Experience
Editable UNITE models (PowerPoint) included
Most of our models and canvases are designed to be applied!
To help you personalize them to your exact business requirements, you can download fully editable versions of the UNITE models available (PowerPoint format)!
They are straightforward to work with, and you can directly incorporate them into your presentations as you need…thus saving countless hours of replication!
PS: did you know that you are also getting hi-res print-ready versions for your workshops?
Monthly live webinars
Each month we host our exclusive, invitation-only webinar series where one of our industry-leading experts updates our members on the latest news, progress and concepts around business strategy, innovation and digital transformation, as well as other related topics.
You will receive the book in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
Bi-weekly live group Q&A sessions
These sessions are your opportunity to bring any questions or challenges you’re facing and receive expert guidance on the spot.
Come and be a part of engaging discussions where your unique concerns are heard and addressed.
1x personal coaching session / month
If you are occasionally looking for a sparring partner or you need limited support, then this option will be ideal for you. Coaching sessions are 1-2 hours where we can discuss any challenge or opportunity you are currently facing.
If you need a few more hours outside of this provision, then these could be billed transparently.
Unlimited video call support! – it’s like always making the right decision!
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. Because we typically find that the occasional hour just doesn’t cut it – particularly if you and your team are in the midst of a large and complex project.
Your time with Stefan is therefore unlimited (fair usage applies) – in his function as coach and sparring partner. That does mean that you will still have to do the work – we cannot take that off you, unless you hire us as consultants. But you will get valuable strategic insight and direction to make sure you are always focusing your efforts where they will lead to the best results.
One personal coaching session / month + unlimited support via e-mail & WhatsApp
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. If you generally know what you are doing but want a sparring partner to frequently raise questions to, this is the perfect choice!
In addition to your monthly 1-1 live coaching sessions with Stefan, you will also get unlimited support from him via email and WhatsApp messaging (fair usage applies). This not only allows you to get valuable strategic direction in your calls, but also gives you instant access to expert help as you work through your plans each month.
The fact that support is text-based means that we can speed up our responses to you while keeping the overall cost of support down.
Welcome gift of our book “How to Create Innovation” (digital + physical editions)*
As a welcome gift, you will receive the both the digital and physical version of our book “How to Create Innovation”, which covers numerous relevant resources and provides additional deep dives into our UNITE models and concepts.
The print version will be shipped out to you on sign-up. The digital version will be emailed to you, and comes in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
1x major workshop or 2x smaller workshops / month
1x major or 2x smaller workshops based on the UNITE models.
- Topics covered: almost any challenge under the header of #strategy, #innovation or #transformation, leveraging the UNITE models.
- Hands-On Learning: solve your challenges while learning the practical application of the UNITE models and walk away with concrete plans and tools to take your next steps.
- Industry thought leadership: facilitated by Stefan, the founder of Digital Leadership and the main author of the UNITE models, ensuring top-tier guidance and knowledge sharing.
- Collaborative approach: engage in interactive sessions that foster collaboration, idea exchange, and real-time problem-solving among peers and industry leaders.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular workshops ensure ongoing development in your organization staying ahead of industry trends and customer needs.
Access all of our UNITE models, (incl. editable & print versions)
All of our Professional plans offer full access to the following:
- 6x UNITE model package downloads are included per month, if you need something in addition to these however, please let us know!
- Hi-res, print-ready versions you can use in your workshops
- Fully editable PowerPoint versions where applicable – personalize to your needs.
- Exclusive access to our vault of never-before-published strategic materials. We have much more to share – a lot of our concepts have never been published!
Exclusive access to our private UNITE community (upcoming)
We are currently in the process of launching our brand new community., we are designing our community to specifically help you:.
- Get answers to questions (“How do I …”)
- Share leading practices & knowledge
- Jointly develop new models
- Network amongst a highly qualified group of peers
Please, select the reason
Cancelling your plan will deactivate your plan after the current billing period ends. You will not be charged further, but also won’t be able to access [exclusive features/services].
- Cost-related issues
- Unsatisfied with the service
- Features I need are missing
- Switching to a different service
- Other (Please specify)
Book Your Initial Blueprint Session Now
Simply fill out the below form and book in a time for our initial session that works for you. This initial session is free, no strings attached, and is where we can discuss your Blueprint needs more in-depth before moving forward.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher
Founder of digital leadership.

Adam D. Wisniewski
Partner for it strategy & business alignment.

Get in touch with Digital Leadership
Speak to our team today to find the best solution for your business to grow and scale.
We are here to support you across the entire lifecycle in all topics related to #digital, #innovation, #transformation and #marketing!

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher Founder of Digital Leadership
Contact Us!
Contact form, contact details, book a call.
Title, first name & last name * Email address * Phone number Please let us know how we can best support you! *
By clicking “Send”, I agree to Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Let’s have a conversation!
“Please be invited to reach out! We are happy to help and look forward to a first meeting!”
+41 (0) 44 562 42 24
Schedule Your Call With Our Team
Find a time on our calender that best suits you !

Founder and CEO of Digital Leadership
SCHEDULE YOUR INITIAL CALL
A Quick Survey!
What is the main challenge you're currently facing in your business?
You Want To Drive Change?
Let’s find the best solution for your business to grow and scale sustainably!
Let’s kick start it!
We will uncover your current business situation and goals and provide you with a bespoke solution that helps you drastically grow your business working with us.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, M.B.A.

Feedback about our consulting that we are proud of
Read the reviews and make sure that this is not a waste of time, but a super effective tool.

You want to drive change?
Schedule your free business assessment call with our founder.
On this call, we will uncover your current business situation and goals and talk about how to drive change and solve your need.
Choose the meeting type that applies to your needs and schedule a time to meet with someone from our team. We look forward to speaking with you soon!
Thanks, We’ve Received Your Updated Details

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment Call With Adam D. Wisniewski
Welcome to our scheduling page.

Let’s Design your Customer Experience Blueprint !
In a uniquely designed 60 or 90 minute session* , we will …
- > identify where to start with near-certainty
- > define what approach it takes to create success in your organization
Based on the Blueprinting session, you will receive a tailored blueprint that aligns with your objectives, vision and goals, ensuring that your initiative is a success from start to finish.

In this session, you will be working together with Patrick Zimmermann, Associate Partner for Customer Experience

Let’s Design your Culture & Org-Change Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Dr. Andreas Rein, Partner at Digital Leadership for Culture & Org Change
Let’s Design your Innovation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Sascha Martini, Partner at Digital Leadership for Innovation and Digital Transformation
Let’s Design your Transformation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, Founder of Digital Leadership Stefan is a global thought leader in the innovation space
Let’s Design your IT Strategy & Business Alignment Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Adam D. Wisniewski, Partner for IT Strategy & Business Alignment

Patrick Zimmermann

Sascha Martini

Dr. Andreas Rein
Write a personalized review! Log in
Create Review

The 9-Step Business Model Canvas Explained (2023 Update)
Written by Raquel Alberdi
Business | entrepreneurship, 16 comments(s).

Blog » The 9-Step Business Model Canvas Explained (2023 Update)

“A major mistake made by many start-ups around the world is focusing on the technology, the software, the product, and the design, but neglecting to ever figure out the business . And by “business” we simply mean how the company makes money by acquiring and serving its customers”.
-Reid Hoffman
After meeting with hundreds of entrepreneurs and business owners over the years I believe the LinkedIn co-founder and Blitzscaling author Reid Hoffman’s got it spot on.
People tend to focus on specific parts of their business, such as which software packages are being used, which is the cheapest supplier, how to optimize internal processes…?
They get so bogged down in the details of the day-to-day running that they lose the overall vision of their business.
Without this vision they are unable to scale, they make marginal profits, miss opportunities, struggle to innovate, and end up running “just another” business.
Another handy metaphor in understanding this common mistake is the soldier in the trenches .
Every meter of ground gained comes at a heavy cost, mistakes are made, and progress is hard-fought and slow…a day-to-day experience for 99% of entrepreneurs and businessmen.
But when you do have that 360 vision you see the entire battlefield. Decisions are much clearer, fewer mistakes are made, and progress is fast and methodical.
Fortunately, a business model framework exists that gives you both vision and clarity .
The Business Model Canvas provides entrepreneurs, business owners, and strategists with a tool to analyze, structure, and evolve a business while always keeping the bigger picture front of mind.
So let’s take a closer look at how it works.
Table of Content
What is the Business Model Canvas?
Created by Swiss entrepreneur and Strategyzer co-founder, Alexander Osterwalder, the Business Model Canvas is a visual representation of the 9 key building blocks that form the foundations of every successful business. It’s a blueprint to help entrepreneurs invent, design, and build models with a more systematic approach.
Why is it so popular within the business community?
Its simplicity. The business model canvas allows us to carry out a high-level analysis without drilling down and getting lost in the details. You just draw out the 9 building blocks on a blank canvas, fill them in as each concept relates to your business, and hang it somewhere everybody can see.
It’s a visual overview of your entire business on a single canvas.
While the Business Model Canvas is an extremely fluid concept and hyper-specific to individual companies, each canvas is still broken down into these 9 key building blocks:
Customer Segments
Value propositions, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partners.
When laid out on the canvas the model will look something like this:

While you’ve probably come across each of the 9 building blocks before, the attractiveness of the Business Model Canvas is that it confines them to a single page , not a traditional 42-page document.
This makes it a lot easier to digest, as well as assess existing business models or map out new ideas.
How do I fill out the Business Model Canvas?
To start your Business Model Canvas you will need to breakdown and analyze each of the 9 building blocks.
A good way to approach this is to gather the heads from marketing, sales, operations, finance, and manufacturing (if product-based) and pencil-in a morning where you can all meet together.
Then, after drawing a mock canvas onto a whiteboard, proceed to dissect and discuss each of the 9 building blocks as they relate to your business. You can use sticky notes to better organize your thoughts around the canvas.
If you are an entrepreneur or new business owner working alone and don’t have a team to bounce your ideas off, not to worry. You can still carry out your analysis before sharing it with a like-minded entrepreneurial community or forum, like those found on ThePowerMBA , to get useful, insightful feedback.
Whichever way you decide to approach it, I recommend you complete each block in the following order:
- Cost structure
For continuity, I’m going to use the fashion retail giant Zara when analyzing each of the 9 key building blocks.
If you’d like to skip to another case study similar to your own business, navigate to the table of contents at the top of the page and select one of the other business model canvas examples.

The first block of the Business Canvas Model is about understanding who is the most important customer(s) you’re delivering value to. Or, in other words, who are they? What do they do? And why would they buy your product or service?
Not a single company exists without its clients, making customer segments the best block to start with while drawing out your business model canvas.
A great exercise to define your customer segments is to brainstorm and create your company’s buyer persona (s) .
Buyer personas are fictional depictions of an ideal or hypothetical client. Typically when brainstorming a buyer persona you’d want to define certain characteristics (age, demographic, gender, income, industry, pain points, goals, etc.)
However, remember at this stage we want a snapshot of our customer segment. There’s no need to jump into great detail just yet.
In the case of Zara, there are three distinct customer segments to whom they offer different products.
The products created for each of these customer segments (clothing, shoes, and accessories) are not trans-consumable. That is to say, a woman’s dress is highly unlikely to be worn by a 7-year-old child.
Once we know exactly who it is we are targeting, it’s time to look at what we as a company have to offer.

The second phase is about figuring out your company’s value propositions , and importantly, your UVP (unique value proposition). The “what” that makes customers turn to you, over your competitors? Which of their problems are you best at solving?
Each value proposition consists of a bundle of products or services that fulfill the needs of a buyer persona from your customer segment. It’s the intersection between what your company offers, and the reason or impulse customers have for purchasing.
Some popular questions to ask while determining your UVP are:
- Which specific customer pain point are you trying to solve?
- What job are you helping customers get done?
- How does your UVP eliminate customer pain points?
- What products or services do you provide that answer this specific pain point?
So let’s try and apply this to Zara. Why do people choose to purchase from them, over their competitors?
Zara’s principal value propositions are fairly clear. They offer various ranges of stylish men’s, women’s, and children’s clothing and accessories at an affordable price.
But there’s more to it than that.
If we dive a little deeper we see Zara’s value propositions are more complex, which are behind the success of the brand:
Fast fashion
Zara adds new clothes and designs to its collections every 2-3 weeks, both in its stores and online. It keeps the brand updated, fresh, and modern while maintaining its all-important medium price point
Great eCommerce experience
Once you enter Zara’s online store you’re presented with a clean, easy-to-navigate, and high-end feel. The customer segments are visible on the left navigation bar with a search tab to further aid customers with their online experience.

Localized stores
You can find a store in nearly all major retail locations (shopping malls, retail outlets, airports, etc.) meaning accessibility is not an issue for the majority of consumers.
Flagship stores
Zara demonstrates its aesthetic evolution to customers through its flagship stores. The recent opening of their Hudson Yards , New York City flagship is a great example of this. Customers shop around its vivid, minimalist layout offering them an experience aligned with the brand’s deeper, eco-friendly values.

Zara Hudson Yards, New York

The next step is to ask yourself how you are reaching your customers, and through which channels ?
This includes both the channels that customers want to communicate with you as well as how they’ll receive your products or services.
Is it going to be a physical channel? (store, field sales representatives, etc.) Or is it a digital channel? (mobile, web, cloud, etc.).
Zara has 3 primary channels in which they communicate and deliver products to its customers:
- Direct sales through their stores
- Online (both app and website)
- Social media
Customers can go to a traditional “bricks and mortar” store to browse, model, and purchase different items of clothing at one of their retail stores.
Alternatively, they can shop online or through their mobile application and have the product delivered straight to their door or nearest store. The choice is completely up to them!
So that covers Zara’s commercial channels, but what about how they communicate with customers?
While they do communicate through their mobile app, their predominant channel is social media.
What’s more, they’re really, really good at it.
For example, did you know that Zara invests less than 0.3% of its sales revenue into advertising?
This is only possible due to an A-rated social media presence . Customer queries are not only dealt with quickly, but recommended re-works are sent back to HQ, forwarded onto in-house designers who then apply the feedback to future collections.
This customer-first approach through fluid communication channels has saved them thousands of dollars in marketing, strengthened their brand, and created a loyal customer base.
You should only step away from this building block once you’ve decided how each of your customer segments want to be reached.

Once you have acquired customers, you will need to think about how you can build , nurture, and grow those relationships.
Now, this can be automated and transactional like large eCommerce brands Amazon or Alibaba. Or, it could be at the complete opposite end of the scale and require a more personal relationship you’d typically have with a bank or your local bike shop.
Zara’s relationship with its customers is threefold, and lies somewhere in the middle of transactional and personal:
- Salesperson at store
- Brand through social media
- Sentimental attachment to a product
Yes, you have the initial transactional touchpoint at the store or online, something relatively impersonal and for many the only interaction they’ll have with the brand.
However, customers (especially in the fashion industry) are encouraged to continue to interact with a brand through social media platforms.
As we mentioned before when discussing channels, Zara has a very effective communication system in place. Not only can people instantly get in touch with the brand, but also engage with new posts, images, and collections uploaded to social media.
This personal approach to customer relationship building can, in some cases, lead to the natural growth of brand ambassadors and communities .
An attachment can also develop between customers and particular garments or accessories from one of their collections. The sentimental attachment to these products also creates another potential form of brand loyalty.

Now that you’ve described how you are going to create real value for your customers, it’s time to look at how you plan to capture that value.
What are your revenue streams? Is it going to be a transactional, direct sales strategy ? Are you going to consider a freemium mode l, where you give a portion of your product or service away for free with the idea of converting later on down the line?
If you’re a SaaS company such as SalesForce or Strava , then it’s likely that a licensing or subscription revenue model will be more appropriate.
At Zara, it’s extremely simple. They make their money by selling clothes and accessories either at a store or online.

As you can see, we’ve filled in the entire right-hand side of our business model canvas. We touched upon:
Customer segments
- Value propositions
- Revenue streams
- Distribution channels
Now it’s time to move over to the left side of the business canvas model and look at what we need, internally , to deliver our value propositions.

To start with, let’s take a look at key resources.
The key resources are all things you need to have, or the assets required to create that value for customers.
This could be anything from intellectual property (patents, trademarks, copyrights, etc.) to physical holdings (factories, offices, delivery vans, etc.) right down to finances (the initial cash flow perhaps needed to start your brand).
Another key resource every company needs to consider is its human capital . Are you going to need highly specialized software engineers? Or field-based sales teams?
They are relatively capital-heavy resources that need to be factored into your business model.
In the case of Zara, they are going to need a number of key resources if they hope to deliver their propositions:
- Stock management
- A large, interconnected network of physical stores
- A strong brand
- Logistics and supply chain infrastructure
Stock is vital for both online and offline customers.
If they are unable to supply their range of products and meet customer demands, satisfaction levels fall and they have a serious problem on their hands.
A large distribution network of brick and mortar stores combined with a strong brand name help mitigate these factors, as well as reinforce any ongoing marketing activities and communication efforts.
Finally, an efficient logistics process within Zara is critical, especially when you consider the complexities involved with such a large-scale operation.
They will require the necessary technology to analyze data on inventory, storage, materials, production, and packaging, with the staff to execute each of these stages and manage the delivery of the final products.

The next step is to define the key activities – the areas you need to be good at to create value for your customers.
To mix it up a little let’s take a look at a slightly different business in Uber .
Their key activities can be broken down into:
- Web and mobile app development
- Driver recruitment
- Marketing: customer acquisition
- Customer service activities : drivers’ ratings, incidents, etc.
They need a fast, clean UX for their customers using the app, drivers to carry out their service, and the ability to both market the product and deal with any customer queries.
Zara’s key activities will differ to those of Uber. Some of the things they need to consider would be:
- Manufacturing
- Retail process (point of sale and 3rd party management)
- Distribution channel / logistics
Design is a key activity as Zara’s value proposition is to provide stylish garments at an affordable price. Their collections need to be constantly updated to follow the latest fashion trends at the time.
To produce their collections Zara will also require manufacturing capabilities. Now Zara doesn’t own their own factories (we will get to that in the Key Partners section) but they still need to be involved in the garment manufacturing process.
Everything from fabric selection to pattern making, to detailing and dyeing affects the outcome of the final product which of course they have to then go on and sell.
The effective management of the retail and distribution channels (online, offline, shipping, and communication with providers) is also key. A breakdown in either of these activities, such as a poor relationship with an important provider will have serious consequences for the business.

Most modern business models now require brands to build out and work with various key partners to fully leverage their business model.
This includes partnerships such as joint ventures and non-equity strategic alliances as well as typical relationships with buyers, suppliers, and producers.
A great example of a strategic partnership would be between ThePowerMBA and Forbes . In exchange for exposure of our brand to the magazine’s global audience, we provide expertise and content on high-level business education programs.
As we touched upon when discussing key activities , Zara requires strategic partnerships with many different providers if they are to design and produce their collections.
Another key partner is their major holding company, Inditex .
Inditex has several subsidiaries including Massimo Dutti , Pull & Bear , and Oysho . Being a subsidiary of Inditex means they share a consolidated balance sheet, stakeholders, management and control, and various legal responsibilities.
While as a subsidiary Zara is afforded certain freedoms when it comes to design, delivery, and the general running of the company, the overall strategy will need to be aligned with Inditex and its other subsidiaries.

The final step of the Business Model Canvas is to ask yourself, how much is it going to cost to run this model?
This includes some of the more obvious needs such as manufacturing costs, physical space, rent, payroll, but also areas such as marketing activities.
If you are unsure of exactly what to include in your cost structure take a look at a Profit and Loss statement ( P&L ) from a competitor or company in a similar industry to yours. You’ll find many items overlap such as research and development ( R&D ), cost of goods sold, admin expenses, operating costs, etc.
Once that’s done you should prioritize your key activities and resources and find out if they are fixed or variable costs .
As Zara is such a large, corporate business they are going to have both fixed costs (rent, payroll, point of sales personnel) and variables, such as costs associated with the fluctuating sale of goods, purchase of materials and, manufacturing costs.
Once you’ve completed these 9 steps, your Business Canvas Model should look something like this:
Business Model Canvas Examples
Hopefully, you were able to get a good feel for the effectiveness of the business model canvas with our run-through of Zara.
However, if you found it difficult to follow due to the stark difference between your industries, I’m going to quickly go through 3 more companies to demonstrate the tool’s flexibility:
- Netflix (Media service/production)
- Vintae (Vineyard)
Even if these business model canvas examples don’t align exactly with your industry, I honestly believe that studying different models gives you a competitive advantage in your professional career regardless.
If you’re currently employed by a company, you’ll better understand how your specific role helps the company achieve some of its “long-term” goals.
Alternatively, if you are a business owner yourself (or perhaps thinking of starting your own business) you’ll have a better understanding of your business and where potential opportunities lay.
I’m sure you’re familiar with our next business model canvas example candidate, Netflix .
The global media company offers an online streaming service of various movies, documentaries, and TV programs produced in-house or licensed 3rd-party content. Their success sparked a revolution in the online media world with the likes of Amazon, Apple, Disney, HBO, and Hulu all rushing to launch their own online video streaming platforms.
Netflix started life as an online DVD rental company, basically a web version of the more popular (at least at that time) “bricks and mortar” Blockbuster.
Co-founder Reed Hastings predicted as far back as 1999 that the future of media was in online streaming, saying “postage rates were going to keep going up and the internet was going to get twice as fast at half the price every 18 months.”
It wouldn’t be until 2007 that Hasting’s prediction would become true when Netflix, as we now know it, was born.
So let’s take a current look at their business model canvas:

As you probably know, there are very few people out there who haven’t subscribed, watched, or at least heard of Netflix. There is content for everybody: wildlife documentaries, sci-fi movies, rom coms, action-thrillers, you name it – it’s there.
That’s why their customer segment can be classified as a “ mass market ” as the base is just so diverse.
All people require is a computer, TV, internet, and/or smartphone and they’re good to go. For most developed markets, that covers just about everybody.
Value Proposition
Whether on the train to work, sitting in the car (if you’re not driving!), or relaxing at home in front of the TV, you can consume their online, on-demand video streaming service.
They also have a huge library of content for consumers to choose from, ensuring that people keep coming back, as well as increasing their mass-market appeal.
They also produce high-quality, original content to differentiate themselves from their competitors.
Most people access Netflix either through their website or mobile/TV App . Another popular channel that you may have picked up on is their affiliate partners .
You’ve perhaps signed up for a mobile, TV, and internet package where the provider offers Netflix as an extra to sweeten the deal, so to speak.
That would be an example of an affiliate partnership between Netflix and mobile service providers.
I doubt many consumers have had direct contact with Netflix unless it’s to resolve a subscription issue or general query. It’s very much a self-automated service – you download the app, select the program you wish to watch, and hit play.
Very simple, very effective.
Again, this doesn’t need much embellishment. Netflix generates money from the different tiers and packages put together in their subscription services.
This varies depending on the region to account for local markets, but on the whole, it’s sold at a low price point.
Originally, Netflix’s Key Resources would have been their unrivaled DVD collection combined with a cost-effective mail-order system.
Nowadays it’s undoubtedly the rights to stream online video content. Netflix has brokered deals with some of the biggest production studios worldwide.
Combined with their huge library of in-house productions , it’s more than enough to encourage customers to renew their subscriptions.
To help sustain interest in their product, Netflix understands they need to serve-up relevant content for each sub-sector of their mass audience. Therefore their machine learning algorithm selects content for consumers based on streaming habits (what they watched, at what time, etc,.) to personalize the customer experience.
This explains why over 80% of all content streamed on Netflix was cherry-picked by this algorithm, making it a Key Resource for their business model.
Also, Netflix accounts for a whopping 12.6% of global bandwidth usage . The literal capacity to stream their services must be met meaning bandwidth must also be included here.
Content procurement is arguably their biggest Key Activity. They need to find people to produce and deliver their original content, including actors, studios, writers, etc. as well as secure the licensing and streaming rights from 3rd party producers such as Sony, Warner Bros, and Disney.
Finally, they need a fast, easy-to-use application to host their online streaming service. This needs to be available for both TV and mobile devices if they are to deliver their “on-demand” value proposition.
K ey Partners
Seeing as Netflix’s entire business model is largely based around streaming 3rd party content, key partnerships need to be built with production studios . No content, no Netflix!
Also, as we touched upon earlier Netflix is one of the largest consumers of bandwidth worldwide. If the speed and delivery of their streaming service are to be continued then deals will also need to be made with internet service providers (ISPs).
Netflix’s biggest expenditures come from both their in-house content procurement and 3rd party licensing agreements . The high-quality standard of video streamed on Netflix is only possible due to the speed and performance of its online platform and application , which has additional costs of staff, software, etc.
To show you just how flexible the business model canvas can be, I wanted to throw in a slightly leftfield example. Vintae is a Spanish wine producer who, after a detailed analysis of the business model canvas, was able to innovate and disrupt one of the world’s most competitive industries.
As some of you may know, the wine industry is extremely competitive. It’s also steeped in history and tradition , making it very challenging for newcomers to grab market share, let alone think about year-on-year growth and revenue.
However, CEO “Richi” Arambarri looked at the traditional “ bodega ” business model and saw a chink in its armor.
A “small” innovation in the business canvas model helped them to become one of the region’s most important winery groups, with over 10 installations and a presence across all regional denominations (Rioja, Priorat, Rias Baixas, etc.) with year on year growth of 30% – practically unheard of in such a competitive industry.
So how did Vintae analyze the business model canvas to find a niche in their market?
To answer that question, we must first look at the traditional winery business model .

As you can see, the wine industry has historically been patrimonial. Vineyards and estates are passed down through generations with the winery responsible for all phases of production, clarification, and distribution.
The traditional winery business canvas model suggests you must be the owner of the winery/vineyard where the wine is “manufactured”, meaning physical assets are a key resource of the business model.
So, if you wanted to start producing a Rioja, for example, you’d have to set up your vineyard in the region.
This is monumentally expensive as you need to:
- Purchase the land
- Plant a vineyard
- Absorb set-up and installation costs
- Deal with maintenance costs
It’s here where Vintae saw their opportunity.
What if we move vineyard ownership across the business model canvas from key resources to key partners ?
By leasing the equipment and space of large wineries (of which there was plenty), they could still produce their wine but reduce the cost and exposure associated with land purchase, crushing equipment, huge storage tanks, vineyard maintenance, and their bottling line.
This enabled them to focus on their sales, marketing, and distribution channels to create a better brand experience for their customers.
Also, it afforded them more flexibility when creating new wines as they were no longer confined to the limitations of grapes grown on their vineyard.
The lightness of this new business model eliminates maintenance overheads, channels energy into personalizing the customer experience, and allows for unprecedented levels of growth in one of the world’s most competitive industries.

Business Model Canvas Software
Although I did mention starting with a large whiteboard, sticky notes, and a pack of colorful sharpies there are several options in which you can digitize the business canvas model production process.
While I still believe the aforementioned process is extremely valuable (it gets your entire team’s input in a single hour-long session) you may decide it more viable for each member of management to pool their ideas digitally before sharing with the rest of the group.
If that’s the case, then take a look at some of the following software tools for creating your business model canvas.
Strategyzer
Created by the founders of the business model canvas Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur , Strategyzer offers a range of business model canvas templates for you to get started with.
If you opt for the paid model (there is a 30-day free trial period) they offer a series of various classes that teach you how to build and test different value propositions and business models.
A real-time built-in cost estimator analyzes the financial viability of some of your business ideas, identifying alternative areas you may wish to explore with your model.
All-in-all, it’s a great resource to play around with and test some of your business ideas, with the option to dive into further detail if you see fit.
Canvanizer is a free, easy-to-use web tool that allows you to share links between team members who are brainstorming ideas for a business model canvas, but working remotely.
Like Strategyzer, there are several business model canvas templates provided to help you get started with your analysis. The strength of this platform is its accessibility. Much like a Google Doc., several people can brainstorm on the same canvas simultaneously with changes being synchronized automatically.
Business Model Canvas Tool
A ThePowerMBA alumni, impressed by the simplicity and effectiveness of the tool, went ahead and created the free application Business Model Canvas Tool .
It’s an incredibly intuitive, and easy-to-use tool that allows you to create templates simply by clicking the + button in each building block.
Each business model canvas created can be downloaded and shared as a pdf. with the rest of the team.
Would You Like to Learn More about Business Models?
If, after going through our 9-step guide on how to use the Business Model Canvas you’d like to learn more about different business model analysis tools , take a look at our alternative MBA business program .
As you’ll see, the course gives students a 360-degree view of business and management practices – such as engines of growth, segmentation and targeting, and value propositions.
I highly recommend you go check it out.
Regardless, I’d love to hear what you thought about this guide. Was it helpful? Would you like to see additional business cases analyzed from your industry?
Let us know in the comments below.
FREE CLASSES
What’s it like to take one of our programs.
The best thing is to try it yourself with these classes that are totally FREE! Sign up and experience being part of the business school that has challenged the traditional educational model.
How much do you know about business?
Tools, concepts, business methodologies… Find out with this test! (it won’t take you more than 3 minutes)

You may also like

Intelligence cycle, the success for Decision Making processes
Apr 12, 2024 | Business
For centuries, intelligence has been one of the fundamental resources of the military institution: an unquenchable...

What is Herzberg’s theory and why is it beneficial for companies?
Apr 5, 2024 | Business
Motivation is an essential factor for people to give their best and it is something that should be applied in all...

Reasons why you should use geomarketing
Mar 29, 2024 | Marketing
Would you like more people to visit your store? It’s true that there are many ways to achieve this, but with...
16 Comments
Perfect thought
I am a DBA student. I have used your site a lot. Thank you for the information
Well defined steps, Thanks for good contents.
Dear Sir many thanks for you guideline. it was very effective for me. Thanks a Million
Well explained with practical business case
Wow, this article was incredibly helpful! I’ve heard about the Business Model Canvas before, but I wasn’t sure exactly how it worked or how to use it for my own business.
I need a sample of business model canvas for a beauty palour
you’ve done a great job. keep it up
This is a very insightful content with a step-by-step practical approach of how to write a BMC and what exactly it should contain.
My team and I literally used your guide to write a BMC for a project we were working on, and in just about an hour we were done.
Thank you so much for this content, it was really helpful.
Thank you very much Collins and we are glad you are using this tool.
Insightful! Gave me the clarity I needed for my upcoming business. Thank you so much.
Thank you very much for the business model example of ZARA. It was very very informative
This is a great explanation, the best i’ve seen. Thanks
Thank you very much for reading and sharing your comments
Really great tool for business and whom want to enter,. Thanks
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- How traditional business accepted, adapted and transformed using Digital marketing tools. – Current Affairs - […] Netflix Business Model Canvas […]
- Entrepreneur vs intrapreneur: What’s The Difference? 👀 - […] Business Model Canvas […]
- Buyer Persona, how to Create An In-Depth? (+ FREE Template) - […] you could use a buyer persona canvas (similar to the framework used for the business model canvas) to draw…
- Demystifying business model canvas – Karmen Skaro - […] Additional information on business model canvas find here and here. […]
- Saas Business Model (2023) - […] in this material you will learn all about SaaS as a business model. It’s an interesting material that will…
- What is the main objective of inferential statistics? (2023) - […] offers a lot of information about different phenomena or behaviors that are relevant for making business decisions. The results…
- How to Prepare a Canvas Business Model - The Passionate Seeker - […] you have filled out each building block of the Business Model Canvas, you will have a comprehensive overview of…
- The Business Model Canvas: A Comprehensive Guide for SMEs and Start-ups – AdvantEdge - […] Further insights and practical applications of the BMC can be found here: The Power MBA’s Guide. […]
- Top 5 Tips For Business Success by Freeduhm Team | Milyin - […] that market and have a chance to make money and become profitable. Additionally, you can use a business model…
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer

Denis Oakley & Co
I HELP BOLD LEADERS TRANSFORM THEIR BUSINESSES AND THE INDUSTRIES THEY COMPETE IN
February 10, 2018 By Denis Oakley
The Value Proposition in the Business Model Canvas: What Problem are We Solving?
This is the second lesson in our free business model canvas course . In this lesson we cover the role of the value proposition in the business model canvas. Customers have problems. They need solutions to THEIR problems. A value proposition solves the problem for them. Shell solves the problem of how people get to work. It provides the petrol that powers their cars. Google solves the problems of not knowing about X. It provides the most relevant useful results on the internet. Jim Bean solves the problem of emotional pain and loneliness by reducing inhibitions.
Photo by rawpixel.com on Unsplash
Customer Pain and the Value Proposition
So when we start thinking about the value proposition the first step is always to think about the problem that we are solving. There are some great questions that you can ask as you think about this.
- What is the pain
- Who has the pain
- How painful is it
- How is it being solved now
- How much will people pay to avoid it?
Let’s use knowledge as an example. There are frequent times during the day when i want to do something. Often I don’t know how to do it. It may be treating a child for a bumped head, finding a particular item in a shop, translating something someone says or learning how to water avocado trees.
The problem is that I do not know the information I need to do a good job for any of these tasks. the pain is that I have to spend lots of time finding out answers. alternatively I have to accept a substandard solution as I solve it myself.
In this case almost everyone in the developed world has a lot of problems that they don’t have immediate answers for. This is a function of the size and complexity of the society and the rate that it is changing at.
When I want to do lots of things the pain is pretty intense. In some cases it can be a matter of life or death – How do I say that
My daughter has been bitten by a sea snake
in Thai? (ลูกสาวของฉันได้รับการกัดโดยงูทะเล). In other cases it is trivial.
Right now this problem (in the 90’s) was being solved by asking friends or family, using encyclopaedia and calling companies in the yellow pages.
How much will people pay to avoid the pain of not having a good answer almost immediately. As it turned out, people didn’t want to pay. They’d always got the information for free. Why should they start paying for it now. And anyway how do you value the information in so many cases and for so many people?
We now know how Google developed it’s value proposition to answer these questions. This is the process that every business needs to go through as it determines the value that it provides to customers. It is no longer enough to say “We make X”. Too many industries are being disrupted to make that viable for more than a few years. You need to say “We are solving this problem” A value proposition is a clear way of doing that.
The Value Proposition in the Business Model Canvas
The Value Proposition in the business model canvas is the unique offer your company provides to the customers. It can be a product or service that solves the customer’s problem.
For example, Domino’s Pizza delivers hot fresh pizza to you within 30 minutes or else it is free.

Hence, Domino’s Pizza value proposition is the guaranteed short delivery time customers receive.
What is my Value Proposition?
Your value proposition has to be clear to convince customers to do business with you and benefit from it.
Here is a formula that will assist you in crafting a value proposition:
End Result Customer Wants + Specific Period of Time + Addresses the Objections
Example, Domino’s Pizza
(End Result) Customers want hot fresh pizza to be delivered to their doorstep.
(Specific Period of Time) Domino’s Pizza aims to deliver hot fresh pizzas in 30 mins.
(Address the Objections) If Domino’s Pizza fails to do so, customers do not have to pay for the pizza
*Tip* It is ideal to include all 3 categories into a value proposition but not necessary.
This formula allows your customers to immediately understand how the product benefits them. Customers choose Domino’s Pizza because they are guaranteed hot fresh pizza in 30 mins, if not they will receive other benefits (free pizza).
Moreover, it forces you to think more about the customer and less about the solution. This is emphasized over and over again as we have the tendency to focus on the (first) solution instead of listening to the customers’ problems.
Checklist The following will give you the confidence you are on the right track:
Will your value proposition tempt your customer to read further if it was used a the header of an article?
Check if your focus is on your customer problem instead of your product. Example: We sell green salad vs Take a healthy lunch and feel better each day
How to Build a Great Business Model Canvas – The FREE Course
- Introduction
- Value Propositions
- Marketing & Distribution Channels
- Customer Relationships
- Key Resources
- Key Activities
- Key Partners & Suppliers
About Denis Oakley
Explorer | Trail Runner | Mountain Lover
'Big' companies are civilisation. I stay in the wilderness guiding entrepreneurs and startups on their journey to becoming 'Big'.
Then I head back to the frontier
Strategy | Marketing | Operations
Ready to start?

I help entrepreneurs transform their industries through wiser choices
Outcome : More Traction, Bigger Rounds, Better Products
Method : Problems, Customers, Business Models, Strategy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model. Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
Before 2004, entrepreneurs suffered from prolonged and cumbersome business plans. Alexander Osterwalder facilitated the creation of a business model by introducing the Business Model Canvas (BMC).. By definition, it's a visual template that illustrates various objects of a business model.Osterwalder's original canvas includes nine elements, which we will have explained below in the article.
Value Proposition Canvas is a business model tool that helps you make sure that a company's product or service is positioned around customers' values and needs. The tool has been created by Alexander Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, and Alan Smith. The same authors of the Business Model Canvas, aiming to map the value perceived by customers.
Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a framework that helps determine how a business creates, delivers, and captures values. It is a visual representation of the important aspects or parts to consider when designing a Business Model. ... Business Model Generation [2]) 2. Value proposition (VP) Value Proposition describes the bundle of products and ...
The value proposition canvas is a tool that enables people to share a common mental model of the customer, how the business generates value and what possibilities exist to innovate. Creating a value proposition is a method of clearly defining aspects of a product or service that a customer might need and why.
The Business Model Canvas enables you to: Visualize and communicate a simple story of your existing business model. Use the canvas to design new business models, whether you are a start-up or an existing businessManage a portfolio of business models. You can use the canvas to easily juggle between "Explore" and "Exploit" business models.
The Business Model Canvas value proposition provides a unique combination of products and services which provide value to the customer by resulting in the solution of a problem the customer is facing or providing value to the customer. In this article, we will explore, what is a value proposition, elements of the value proposition, designing a ...
The business model canvas is a tool designers use to map out a business or product's key actors, activities and resources, the value proposition for target customers, customer relationships, channels involved and financial matters. It gives an overview to help identify requirements to deliver the service and more.
The Value Proposition Canvas. Download. April 9, 2024. 1. min read. topics. Value Proposition Canvas. Value Proposition Canvas is a tool for marketing experts, product owners, and value creators. This method from the bestselling innovation book Value Proposition Design is applied in leading organizations and start-ups worldwide.
The value proposition is of utmost importance when filling out a Business Model Canvas as it acts as the core foundation for the entire canvas. It shapes and informs other elements such as customer segments, channels, and revenue streams, ensuring a coherent and customer-centric approach. A strong value proposition enhances the clarity and ...
The Business Model Canvas was developed by Alex Osterwald and Yves Pigneur, in collaboration with a community of business professionals at the Business Model Innovation Hub. It is a useful tool for designing and analyzing business models in an objective, structured way. The Business Model Canvas incorporates nine building blocks: Block 1 ...
A business model canvas is defined as an organizational tool that helps visualize the development of a potential business model. Learn more about business model canvas examples, channels and key resources. ... These resources support the business model's value proposition, help it achieve a competitive advantage, and enable the efficient ...
The Business Model Canvas - Connecting Value Propositions to Customer Segments. The Problems or Needs that you identified earlier and used to build your Marketing Personas now come into play. The Value Proposition Canvas describes the details of how the value proposition and customer segments interact.
As Jim explains, here are a few of the benefits of using a business model canvas to think through product strategies: 1. You can use a business model canvas to roadmap quickly. You can use this canvas approach in just a few hours (and as Jim says, you can even do it with sticky-notes). This way, rather than trying to write out every detail ...
The Business Model Canvas Value Proposition. The Value Proposition section of the Business Model Canvas. If you have several customers all seeking the same product for a different primary benefit, and you message all of them about the same benefit, you will not get traction, you will simply waste your time, energy and budget. ...
Understanding and effectively communicating your value proposition to customers is important in business. One powerful tool for achieving this is the Value Proposition Canvas developed by Alex Osterwalder, a part of the Business Model Canvas that evolves dynamically, birthing new value propositions by uncovering unmet customer needs through the "Jobs to be Done" theory.
Created by the founders of the business model canvas Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, Strategyzer offers a range of business model canvas templates for you to get started with. If you opt for the paid model (there is a 30-day free trial period) they offer a series of various classes that teach you how to build and test different value ...
Summary: The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a visual tool for showing how an organization creates and delivers value to its customers, including descriptions of the key suppliers, activities, how it makes revenue, and the cost structures to deliver that value. From a business process improvement perspective, I think of the Business Model Canvas being very similar to the SIPOC Diagram we use in ...
See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. The simple, visual template of the Business Model Canvas has made it a favorite among entrepreneurs and business strategists. With its one-page, nine-points design, a Business Model Canvas allows stakeholders to quickly understand the key needs and goals of any business.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management template used for developing new business models and documenting existing ones. It offers a visual chart with elements describing a firm's or product's value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances, assisting businesses to align their activities by illustrating potential trade-offs.. The nine "building blocks" of the business ...
Build a business model canvas. Fill out each component of the business model canvas template with information on your customers, partners, key activities, value propositions, costs, and revenue streams. Easily add new text boxes or sticky notes to construct and align your business concept with your team. Personalize your business model canvas.
A business model canvas is a strategic management tool that helps companies visualize new and existing business models they develop. This one-page template allows you to examine the external and internal factors that could make or break your business, such as the infrastructure running your business, what value you're offering, the customers you serve, and the finances that keep your business ...
The Value Proposition in the business model canvas is the unique offer your company provides to the customers. It can be a product or service that solves the customer's problem. Domino's Pizza delivers hot fresh pizza to you within 30 minutes or else it is free. Hence, Domino's Pizza value proposition is the guaranteed short delivery time ...
The Business Model Canvas is not your ordinary Business Plan. It is much easier to use than a traditional business plan because it is simple to construct. In this interactive workshop, the instructor(s) will help you create your own Business Model Canvas - a visual chart with nine blocks describing your company's value proposition, customer segments, and relationships, key activities ...
Voluntourism is a unique tourism pattern which got considerable attention recently, especially after the COVID-19 pandemic and the intense search to promote and revive all the possible tourist patterns in order to support the tourism industry. This paper studied and analyzed voluntourism from a business perspective by developing Business Model Canvas (BMC) to support this tourism pattern.