- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes

You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Create a Business Budget for Your Small Business

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A business budget estimates future revenue and expenses in detail, so that you can see whether you’re on track to meet financial expectations for the month, quarter or year. Think of your budget as a point of comparison — you run your actual numbers against it to determine if you’re over or under budget.
From there, you can make informed business decisions and pivot accordingly. For example, maybe you find that your expenses are over budget for the quarter, so you may hold off on a large equipment purchase.
Here’s a step-by-step guide for creating a business budget, along with why budgets are crucial to running a successful business.
» MORE: What is accounting? Definition and basics, explained
QuickBooks Online
How does a business budget work?
Budgeting uses past months’ numbers to help you make financially conservative projections for the future and wiser business decisions for the present. If you’ve had a few bad months and predict another slow one, you can prepare to minimize expenses where possible. If business has been booming and you’re bringing in new customers, maybe you invest in buying more inventory to satisfy increased demand.
Creating a business budget from scratch can feel tedious, but you might already have access to tools that can help simplify the process. Your small-business accounting software is a good place to start, since it houses your business’s financial data and may offer basic budgeting reports.
To create a budget in QuickBooks Online , for example, you break down your estimated income and expenses across each area of your business. Then, the software calculates figures like gross profit, net operating income and net income for you.
You can then compare actual versus projected figures side by side by running a Budget vs. Actuals report. Businesses that need more in-depth features, like cash flow forecasting or the ability to use different projection methods, might subscribe to business budgeting software in addition to accounting software.
If your small business doesn’t have access to these features or has simple financials, you can download free small-business budget templates to manually create and track your budget. Regardless of which option you choose, your business will likely benefit from hiring an accountant to help manage your budget, course-correct when the business gets off track, and make sure taxes are being paid correctly.
Why is a business budget important?
A business budget encourages you to look beyond next week and next month to next year, or even the next five years.
Creating a budget can help your business do the following:
Maximize efficiency.
Establish a financial plan that helps your business reach its goals.
Point out leftover funds that you can reinvest.
Predict slow months and keep you out of debt.
Estimate what it will take to become profitable.
Provide a window into the future so you can prepare accordingly.
Creating a business budget will make operating your business easier and more efficient. A business budget can also help ensure you’re spending money in the right places and at the right time to stay out of debt.
How to create a business budget in 6 steps
The longer you’ve been in business, the more data you’ll have to inform your forward-looking budget. If you run a startup, however, you’ll want to do extensive research into typical costs for businesses in your industry, so that you have working estimates for revenue and expenses.
From there, here’s how to put together your business budget:
1. Examine your revenue
One of the first steps in any budgeting exercise is to look at your existing business and find all of your revenue sources. Add all those income sources together to determine how much money comes into your business monthly. It’s important to do this for multiple months and preferably for at least the previous 12 months, provided you have that much data available.
Notice how your business’s monthly income changes over time and try to look for seasonal patterns. Your business might experience a slump after the holidays, for example, or during the summer months. Understanding these seasonal changes will help you prepare for the leaner months and give you time to build a financial cushion.
Then, you can use those historic numbers and trends to make revenue projections for future months. Make sure to calculate for revenue, not profit. Your revenue is the money generated by sales before expenses are deducted. Profit is what remains after expenses are deducted.
2. Subtract fixed costs
The second step for creating a business budget involves adding up all of your historic fixed costs and using them to reliably predict future ones. Fixed costs are those that stay the same no matter how much income your business is generating. They might occur daily, weekly, monthly or yearly, so make sure to get as much data as you can.
Examples of fixed costs within your business might include:
Debt repayment.
Employee salaries.
Depreciation of assets.
Property taxes.
Insurance .
Once you’ve identified your business’s fixed costs, you’ll subtract those from your income and move to the next step.
3. Subtract variable expenses
As you compile your fixed costs, you might notice other expenses that aren’t as consistent. Unlike fixed costs, variable expenses change alongside your business’s output or production. Look at how they’ve fluctuated over time in your business, and use that information to estimate future variable costs. These expenses get subtracted from your income, too.
Some examples of variable expenses are:
Hourly employee wages.
Owner’s salary (if it fluctuates with profit).
Raw materials.
Utility costs that change depending on business activity.
During lean months, you’ll probably want to lower your business’s variable expenses. During profitable months when there’s extra income, however, you may increase your spending on variable expenses for the long-term benefit of your business.
4. Set aside a contingency fund for unexpected costs
When you’re creating a business budget, make sure you put aside extra cash and plan for contingencies.
Although you might be tempted to spend surplus income on variable expenses, it’s smart to establish an emergency fund instead, if possible. That way, you’ll be ready when equipment breaks down and needs replacing, or if you have to quickly replace inventory that's damaged unexpectedly.
5. Determine your profit
Add up all of your projected revenue and expenses for each month. Then, subtract expenses from revenue. You may also see the resulting number referred to as net income . If you end up with a positive number, you can expect to make a profit. If not, that’s a loss — and that can be OK, too. Small businesses aren’t necessarily profitable every month, let alone every year. This is especially true when your business is just starting out. Compare your projected profits to past profits to confirm whether they’re realistic.
Looking for accounting software?
See our overall favorites, or choose a specific type of software to find the best options for you.
on NerdWallet's secure site
6. Finalize your business budget
Are the resulting profits enough to work with, or is your business overspending? This is your opportunity to set spending and earning goals for each month, quarter and year. These goals should be realistic and achievable. If they don’t line up with your projections, make sure to establish a strategy for making up the difference.
As time goes on, regularly compare your actual numbers to your budget to determine whether your business is meeting those goals, and course correct if necessary.
» MORE: Ways your small business can spend smarter
A business budget projects future revenue and expenses so you can create a smart, realistic spending plan. As the year progresses, comparing your actual numbers against your budget can help you hold your business accountable and make sure it reaches its financial goals.
A business budget includes projected revenue, fixed costs, variable costs and the resulting profits. You can also factor in contingency funds for unforeseen circumstances like equipment failure.
On a similar note...

The Ultimate Guide to Budgeting for Small Businesses
By Andy Marker | March 4, 2022
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Creating a budget for your small business can be daunting, but doing so is essential for any successful company. We’ve rounded up expert tips and created a step-by-step guide for designing a strong small business budget.
Included on this page, you’ll learn why a budget is necessary for small businesses and how to create a budget using Excel . Plus, you’ll find a free, downloadable small business budget starter kit .
What Is a Small Business Budget?
A small business budget is a detailed outline of your financial status and projection, based on your historical financial data. It includes your projected income and expenses and is used to determine where your money is best spent.

Ahmet Yüzbaşıoğlu, the Co-Founder of Peak Plans , explains the importance of budgeting for small businesses: “The success of your business is determined by the quality of your decisions. If you want to make informed decisions, you must have a budget. A budget can help you create a plan for the future, whether it's for your company as a whole or for smaller departments. More importantly, [a budget] gives you guidelines with which to make decisions. If budgeting is not yet a part of your business strategy, it may be worth considering it as an option to provide you with insights that can help you to better plan for all aspects of your company.”
Do Small Businesses Need a Budget?
All businesses should have a budget, especially small ones with less room for errors. A small business can better weather periods of low income by knowing exactly where its money is going, forecasting sales, and identifying what can be cut when needed.

Stephen Light, the Co-Owner of Nolah Mattress , gives his take on why all small businesses should have a budget in place: “For small businesses, creating an effective budget is one of the most important tools to carve a successful path to profitability. Budgets are crucial for allocating funds efficiently and curbing any unnecessary or wasteful spending, [which is] an easy trap to fall into if you don’t have a framework or goalposts to stay within. Budgets are especially important to small business owners who might be using their personal funds.”
How Much Should a Small Business Budget Be?
Your budget should be based on historical financial data and not exceed what you expect to make in the budgeted period. Be realistic with your numbers and projections so that you do not find yourself in a position you cannot recover from.
Your budget should take into account all of your sources of revenue and all of your expenses, as well as an additional percentage for any emergencies or surprises.
“Small businesses should absolutely be sure to pad their budget with contingency funds for unseen expenses,” suggests Light.
Larger businesses tend to make budgets annually , but for a small business, especially at first, it is a good idea to break down your budget monthly. To get started and identify a realistic monthly budget for your business check out our small business monthly budget templates for Google Sheets.
Importance of Budgeting in a Small Business
A budget helps a small business anticipate challenges, achieve and track financial targets, and secure investment opportunities. A well-considered budget should help a small business to encounter fewer unforeseen expenses and more opportunities.
Below are some benefits of having a strong budget:
- Make Informed Decisions: A company can make more informed decisions more efficiently when they have a budget. A good budget is built on historical data and allows you to learn from your experience. “Budgeting is a great strategy for maintaining informed control of your business. You can use data insights to plan with greater clarity and organize all of your finances in one place. This allows your leadership team to have the necessary information to drive their decision-making processes more efficiently, which is a great way for your business to act on its data,” explains Yüzbaşıoğlu.
- Identify Growth Opportunities: With a budget in place, you can identify the most profitable projects for your company. Use your budget data over time to see where current resource allocation provides the most payoff. As Yüzbaşıoğlu says, “You can use budgeting to create assumptions about your business projections by measuring the effects of different investments on your business. For example, you can make conclusions about how much revenue an investment in sales will bring in with the information gathered from your marketing efforts. By evaluating different scenarios, you can consider your options for best achieving your goals. Observing different scenarios will soon help you find which strategies work best for your business.”
- Weather Leaner Business Times: All businesses should expect to encounter lean times. Having a budget in place can help you stay afloat by tracking which times are historically slow and by establishing an emergency fund. Knowing when to spend your money can be just as important as what you spend it on.

- Manage Risk: A well-crafted budget can help you to identify potential risks by gaining visibility into your spending. If you don’t track your money, it is easy to spend much more than you had planned (on an unsound investment). “Looking ahead is important for risk management ,” says Yüzbaşıoğlu. “Budgeting is a good way of looking ahead and contains similar methodologies as risk management. A budget allows you to look ahead and see how your activities in different areas will affect the company’s cash flow, earnings, and profitability.”
- Measure Performance: Having access to current and historical financial data from your business allows you to measure financial performance year over year. Without tracking this information, you cannot know which goals you are meeting. “Budgets are the most important tools that managers use to measure how well an organization is doing. Although budgets are commonly perceived to exist for financial purposes only, they can also be key tools to provide insight into how an organization and its departments are performing. Identifying variances — such as differences in expenses and costs and increase or decrease in sales and profits — will give a good overview to management about the performance of the company and its departments,” explains Yüzbaşıoğlu.
- Set Company Goals: A budget is a great place to start goal setting. Whether you aim to spend less over time or drive more sales, a budget gives you concrete numbers on which to base your financial goals. “When all parties are on the same page about the strategic goals of the company and the means of attaining them, it is much simpler to monitor success and work together to keep the organization on track to achieve its goals,” suggests Mains.
What Should a Small Business Budget Include?
A small business budget should include all income and expenses the business accrues over a given period. These numbers may change month to month, so it is important to either use an average, or to overestimate expenses and underestimate income.

Linn Atiyeh, the CEO and Founder of Bemana , highlights some major small business budget expenses that may not be immediately obvious. “[The expenses] need to include everything, from the employees themselves to the office spaces that they work in. They need to include technology, software, onboarding, training, client acquisition, insurance payments, marketing, product development, employee compensation, and any other anticipated costs,” she says.
The following bullets outline what to include in your budget:
- All Income and Expenses: Your budget should consider the entirety of your income and expenses. Note fixed and variable costs. It may also be beneficial to keep track of which expenses you can easily cut during lean times.
- Small Business Financial Plan: When creating your budget, consult your financial plan. If you do not have one, create an income statement and a cash flow statement . “You must incorporate your cash flow in your projections. Cash flow refers to the total amount of money that flows into and out of a firm. If you have positive cash flow in your firm over a certain period of time, this means that more money is flowing into your business than is leaving it,” says Mains. To learn more, read our how-to guide on creating a small business financial plan.
- Historical Sales Numbers: If you have them, use your historical sales numbers to project your income during the same time period in the future. If you don’t have historical data, start tracking it. As you continue to track this information, you will get a better idea of how much money your company is making and spending at different times of the year.
- Sales Forecasts: Create a sales forecast and use it to estimate your projected income. This information will help give you a target number for your budget.
- Emergency Fund: Any strong budget will include some wiggle room for emergencies and surprise expenses. Most sources recommend keeping three to six months’ worth of business expenses in an emergency fund — but remember that some money saved is better than none at all.
- Seasonal and Industry Trend Information: Most industries have slow seasons and busy seasons, and it is important to know when those times are. If you don’t have this information from your own business, a quick Google search can often tell you the answer.
- Growth Projections: Factor any expectations for major growth into your budget, such as opening a new storefront, buying new equipment, or hiring and training a new department.
How to Create a Budget for a Small Business
To create a budget for your small business, determine how much money your company spends and makes, and estimate how it will do so in the future. We’ve outlined how to create a budget in the steps below:
1. Gather Your Financial Information
This includes all income and expense information from previous years and any previous budget information you may have.

“To begin with, collect financial data, predictions, and market analysis to aid in the development of your small company's budget planning,” suggests Lattice Hudson, Business Coach and Owner of Lattice and Co . “To design your budget, consider the company's overall business and overall strategy in addition to the crucial financial data and analytics.”
2. Add Up Your Income
Use a small business budget template or spreadsheet to itemize and add up your income. Consider using a tool that tracks itemized income monthly so that you can more easily note changes over time.
3. Subtract Fixed Costs
Your fixed costs won’t change month to month, so they are the easiest to subtract from your income. Fixed costs might include rent, salaried employees, and non-variable utilities.
4. Determine and Subtract Variable Expenses
Not all costs are fixed, so you may need to do a little digging to determine some of your expenses. Calculate how much the company spent on hourly employees, variable utilities, and break room snacks and business lunches.
“Variable costs are those that change from month to month depending on your company's success, [such as] consumption-based utilities, delivery charges, transport costs, and sales commissions. When your earnings are greater, you may spend more on variable costs, but when your earnings are lower, you should aim to cut back where you can,” says Hudson.
5. Profit and Loss Statement
Prepare a profit and loss statement from the data you’ve collected. Outline how much your company made and spent in a given time period. This will be the first indicator of what your budget numbers should look like.
6. Outline a Forward-Looking Budget
Create your budget using the numbers from historical profit and loss statements. Your income and expenses may grow or shrink over time, so it is important to calculate an average or to add a buffer to your expenses. Your budget should always have money left over for incidentals, as well as allocation to an emergency fund.
Hays Bailey, the CEO and Founder of Sheqsy , recommends that you also include allocations for expansions or growth if you can see either on the horizon.
7. Review on a Schedule
Review your budget periodically. Track your income and expenses monthly, and update your budget as things change. “Over time, you will gain a better understanding of your company's operations and will be able to make more informed decisions regarding your budgeting plan,” says Hudson.
How to Create a Small Business Budget Spreadsheet in Excel
Microsoft Excel makes it easy to organize and chart your small business budget over time. The following tutorial lays out step by step how to use a template in Excel to add up your income and expenses and determine your business’s cash flow.
Gather and Organize All Relevant Financial Information for Your Business
To start your budget, you will need to gather and organize all of your financial information for the previous period. This includes income statements, expense reports, cash flow documentation, and any other relevant documents. If this is your first budget and you do not have these items, organize your bank statements, invoices, payroll information, and receipts.
By organizing your data into these documents, each month becomes easier to track than the last. The more you stay organized, the simpler it will be to maintain your budget.
Download a Small Business Budget Template
- Download the small business budget template for Microsoft Excel.
Record Your Monthly Income
Record Your Monthly Expenses
Record Your Cash Flow
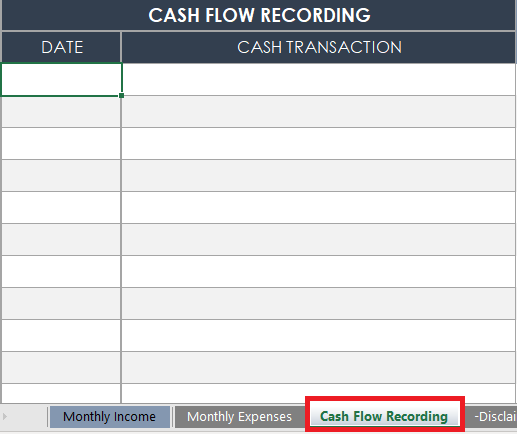
Save and Update Your Budget Regularly
Store your budget template on an accessible drive and update it regularly. Small businesses should update their budget and cash flow as often as possible to stay up to date.
Small Business Budget Example
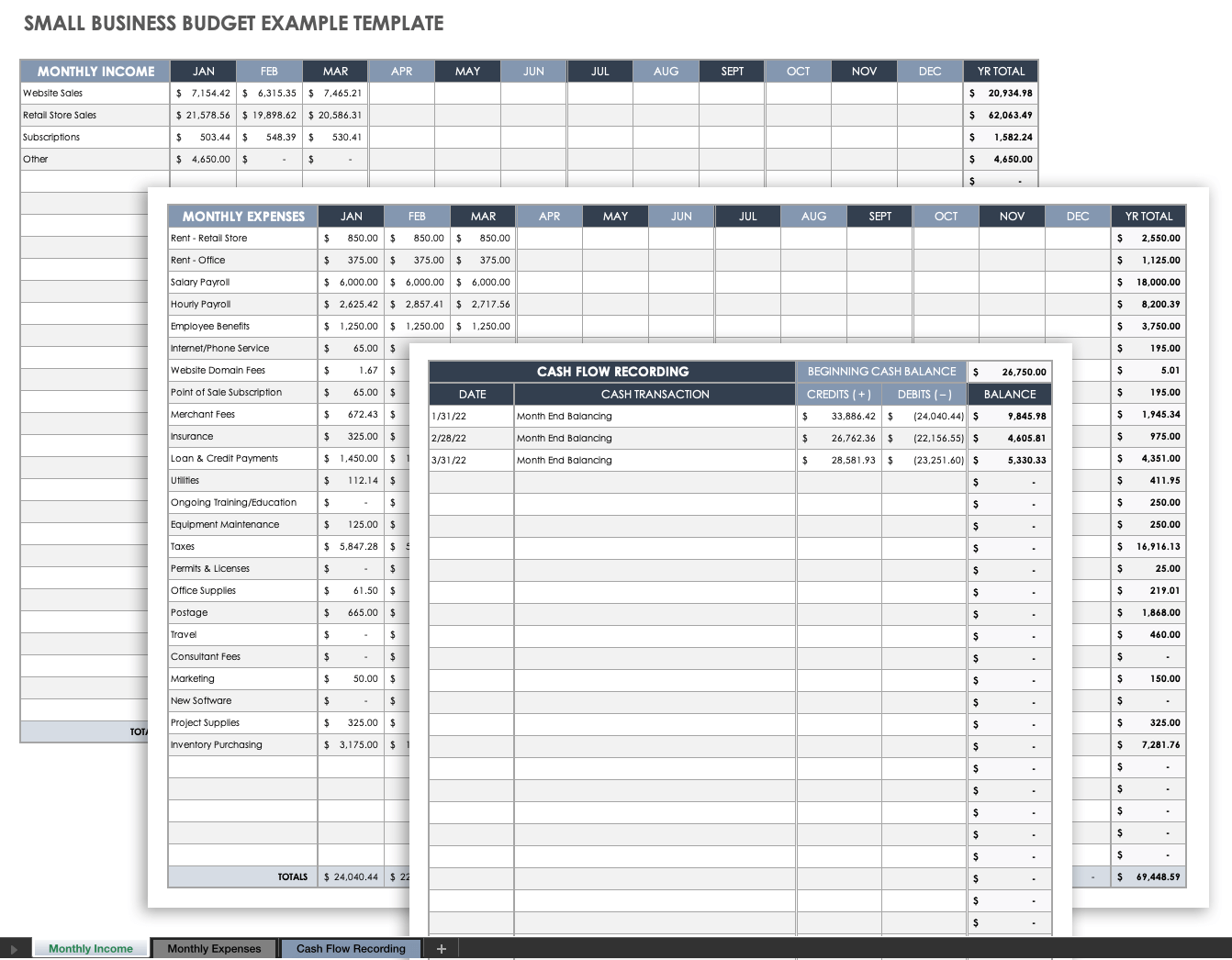
Download Small Business Budget Example Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
In this example of a small business budget, we’ve listed sample income, expense, and cash flow information using categories that are relevant to a small retail business. This template is fully customizable and can be used for a small business in any industry. You can also download a blank version of this template in the small business budget starter kit below.
Tips for Creating a Small Business Budget
Creating a budget for your small business can be daunting. To help you get started, we’ve gathered expert tips, from finding a mentor to setting realistic goals.
- Be Realistic: Keep all financial estimates in the realm of reality. Use historical financial data from your own past whenever possible. “My best tip is to avoid any wishful thinking or dreaming about best-case scenarios because it’s always better to use the real data from years past and to be realistic — you’ll avoid disappointment and tricky financial situations that way,” suggests Light.
- Note Changing Costs: Products and services don’t always cost the same amount every year. Be sure that the expenses listed in your budget are accurate at all times. “Be very mindful of the rapid rate at which prices can change and to get as many quotes as possible to inform your budget,” says Atiyeh. “On the first of these points, you may incorrectly assume that the amount you paid for a service in the past is still a good indicator of how much it would cost today. However, services are priced based on a multitude of factors, such as demand and market circumstances. Keep this in mind when creating a budget.”
- Find a Mentor: Doing so can cut down on the time it might take you to learn about business budgeting on your own. “Find someone who has experience in making budgets. Making a budget is technical and it requires experience if you want it to be done right. Of course, you are also allowed to do it on your own, but expect that it is going to take time and that you are in for lots of revisions,” warns Bailey.
- Overestimate Your Costs: Overestimating your costs helps ensure that your finances aren’t threatened when surprises come up or projects go over budget. You will be much better equipped to weather financial hardship if you’ve made room in your budget to respond to unexpected changes. “If your company works on a project-by-project basis, you are well aware that every customer is unique and no two projects will be precisely the same in their outcome. It is often impossible to forecast when a project may run over budget,” says Mains. “So much of running a company is about anticipating and responding to the unexpected. For small company owners, failure to predict an expenditure or its scale may be devastating and may cause the organization to become crippled before it has had a chance to mature and develop. Company owners must overestimate their costs to protect themselves from financial risk. This is a survival strategy that will assist business owners to protect themselves against danger and failure.”

What Specific Types of Businesses Should Consider when Budgeting for a Small Business
Budgeting for any business involves adding up income, subtracting expenses, and identifying where to spend and save money. Because different industries require different strategies, we’ve created a list of things to consider for specific small business types.

“One thing that is unique to small businesses as a whole is that there are so many different types of businesses. This means that there is no one-size-fits-all budget plan for small businesses. Each business should tailor its budget plan to its own specific needs and circumstances,” explains Lindsey Hyland, Founder of Urban Organic Yield .
- Seasonal Businesses: Some small businesses, such as those based around holidays or gardening, operate at a much higher business volume at certain times of the year. These businesses need to consider that their busy season will bring in much more income than their slow season(s). One way to tackle this is to take an average of your monthly income for the year and use that as your monthly operating budget. Don’t project based on the biggest numbers — use the smaller numbers or an average. For these businesses, it is especially important to establish an emergency fund so that a surprise expense during the slow season doesn’t become a catastrophe.
- Recruitment and Staffing: Businesses that deal with recruitment and staffing need to have a finger on the pulse of the businesses they work with. Do outside research into the growth or downscaling of other businesses to determine budget numbers for a given period. “Since my company is in the industrial and equipment recruiting industry, one unique challenge that we face is having to incorporate the needs of other businesses into our budget. For instance, it's important that we stay mindful of how much these businesses are upscaling or downscaling their operations at any given time, as that directly impacts the provision of our services,” says Atiyeh.
- E-commerce: Online businesses may have fewer fixed costs, such as rent, but may have more variable ones. Shipping costs, shipping zones, import taxes, and shipping supplies will change based on sales volume, so find an average or inflated number that works for these budget items. Companies that operate exclusively online should also invest in a well-made, working website and have a system in place for potential returns. These two things will help improve remote customer service, which can lead to more sales — and a larger budget — in the future.
- Nonprofits: Not-for-profit businesses are funded in a variety of ways, including through grants, donations, and dues. For these businesses, it is even more important to keep the budget as realistic as possible at all times, as there is commonly less money to move around. For more information and to help keep your budget balanced, peruse our list of free nonprofit budget templates .
- Inventory Business: Remember that it can be very expensive to keep large amounts of inventory on hand. Buying more of a product to sell can sometimes be cheaper because of the economy of scale, but ensure you have the space and capacity to hold on to things that don’t sell right away. Consider that you may need to spend more on rent and temperature control for a place to store these items.
- Custom Orders: The price of a custom order is not only the cost of the finished product, but a combination of factors. Determine a cost for your time and labor for conception, execution, materials, and delivery, and factor those into your expenses.
- Startups: Budgeting for a company with no existing financial history can be tough. Company owners will need to do research on the industry and use those numbers to create a rough estimate for their budget. When you are estimating a budget from scratch, be sure to overestimate your costs to mitigate risks. It is always a good idea to ask professionals and people with experience. Visit this list of free customizable startup budget templates to get started.
- Construction: Construction companies need to factor in the cost of all associated permits and insurance on top of all of the general costs of doing business. Permits and insurances may change based on the specific job you are doing, so it is critical to factor those costs into the relevant monthly budget. To help keep you organized, check out this list of free construction budget templates .
- Service: Businesses based on service need to put a larger portion of their budget toward staff training and retention. Better employees mean better service, and much of an employee's ability comes from their training. Additionally, you do not want to lose the valuable employees you spend time and money training, so these businesses need to factor in rising pay scales for more qualified staff.
- All Small Businesses: Do not forget to factor in taxes and fees involved in running your business. If you don’t know what they are, ask a professional for help. “There are a shocking number of people that do not make any self-employment tax payments to the IRS for lack of fear or know-how,” says Stevenson.
How to Manage a Small Business Budget
Manage your small business budget by spending within your means and saving money where you can. Make sure your budget is as realistic as possible, and update and revise it on a regular basis.
- Spend Within Your Means: Whenever possible, do not spend more money than you make. Use loans and credit wisely so as not to dig yourself into a hole. “Make do with what you have, start small with the free versions of software before you upgrade. Save for equipment. Make room in the budget later if you can’t afford it now,” advises Stevenson.
- Get Multiple Quotes: When you work with other businesses, it is in your best interest to get multiple quotes. You can use these quotes to negotiate the prices of goods or services that you need to run your own business, and save money in your budget. “By getting as many quotes as possible, you can build a more accurate understanding of the true prices of what you'll need throughout the period of time that you're budgeting for. By getting quotes from several sources rather than just one or two, you can make sure that your estimates are fair and accurate,” suggests Atiyeh.
- Revisit Your Budget Regularly: Circumstances can easily change from month to month or year to year. “The best way to stay on budget is to revisit the budget regularly. Budgets shouldn’t be set and then put away, they should be consistently reassessed and adjusted. If you’re committed to tweaking and allowing your budget to evolve with a watchful eye, you’re far more likely to stay within its bounds,” says Light.
- Be Realistic from the Outset: It is easy to get carried away with lofty goals and underestimated expenses. The closer your budget reflects reality, the easier it will be to stick to the plan. “Don’t underestimate expenses just to make your budget look conservative, because a budget that’s unrealistic is so much worse than not having a budget at all. It is misleading and it can cause lots of problems in the long run,” warns Bailey.
How to Do a Small Business Budget Efficiently
There are three key ways to help ensure that you manage your small business’s budget efficiently: Use the tools that are available to you, review your financial data on a schedule, and seek help when you need it.
- Use Software Tools: There are many software tools that can help you to create a budget. Many offer free trials so that you can find the one that works best for you. You may also find that a template suits your needs.
- Hire Help: Consider using the professional services of a financial advisor, or hire an accountant to manage your budget. For many businesses, hiring someone to manage the money is an inevitability that should be considered sooner than later.
- Create a Review Schedule: Small businesses should record budgets monthly. Track and store your monthly budget data so that you can reference it for future months and make changes as needed.
Small Business Budget Starter Kit
Download Small Business Budget Starter Kit
We’ve created this small business budget starter kit to help you get started creating and maintaining a budget. We’ve included a blank budget template from the example above, plus powerful cash flow and income statement templates to help keep you organized and on track. We’ve also included a customizable budget checklist so that you can ensure you’re tracking all of the information you need, every time.
Small Business Budget Template
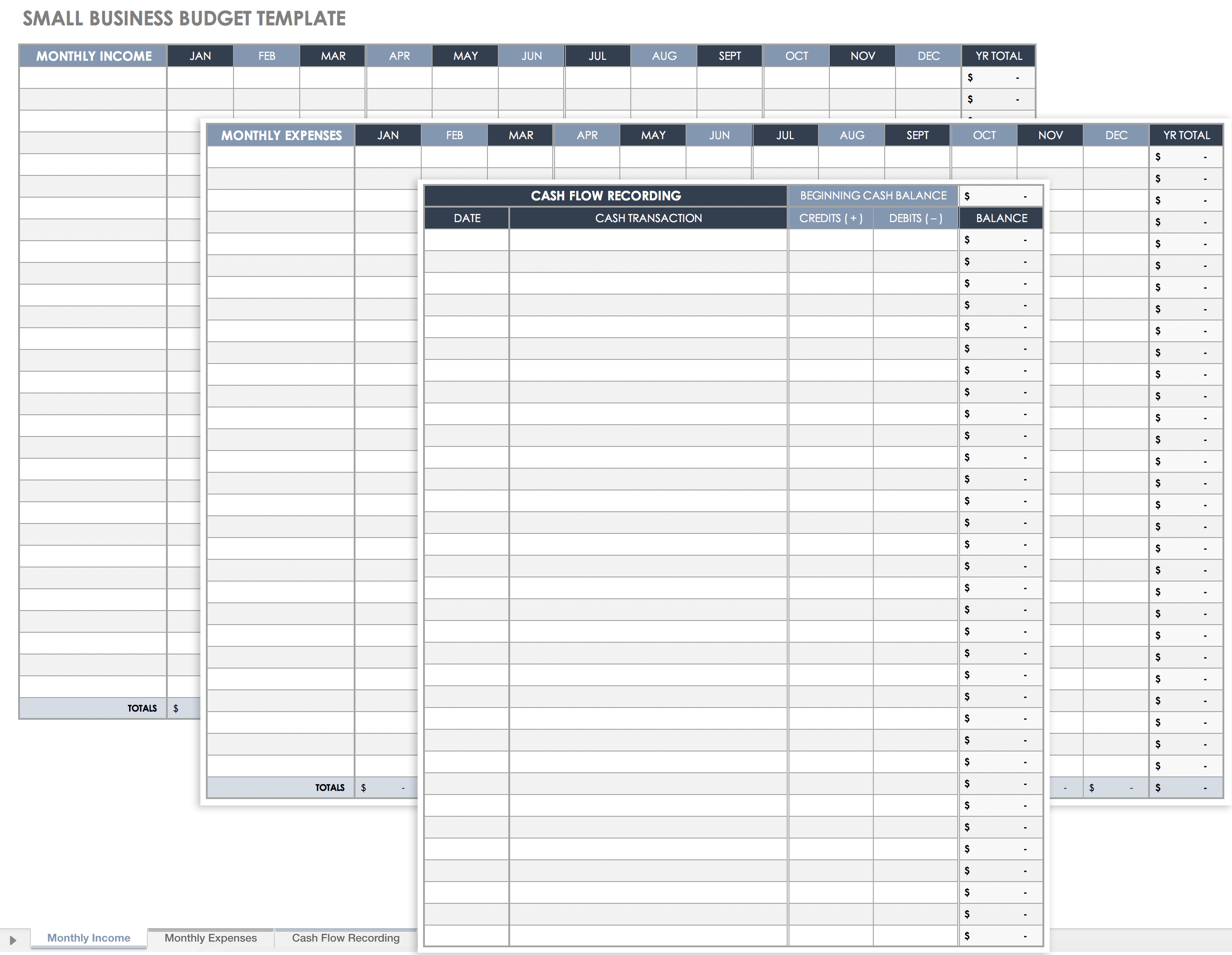
Download Small Business Budget Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets | Smartsheet
Use this blank small business template to calculate your income, expenses, and a simplified cash flow. This powerful template adds up your itemized income and expenses each month, giving you a running total while in progress and a yearly total once completed.
Small Business Budget Checklist
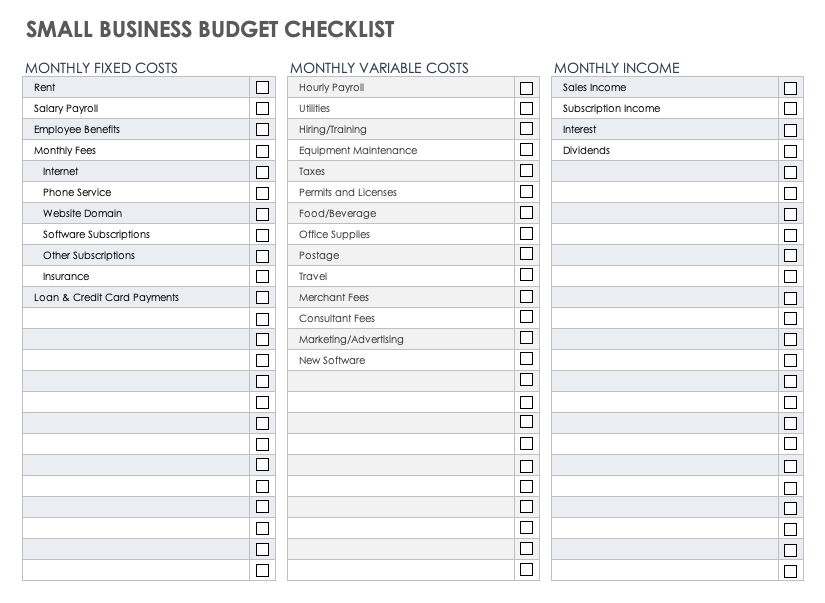
Download Small Business Budget Checklist Microsoft Excel | Adobe PDF | Google Sheets
This customizable small business budget checklist will help ensure that you’ve included all income and expenses in your monthly budget. The checklist includes a list of some of the most common business expenses, but you can edit it as needed.
Small Business Income Statement Template
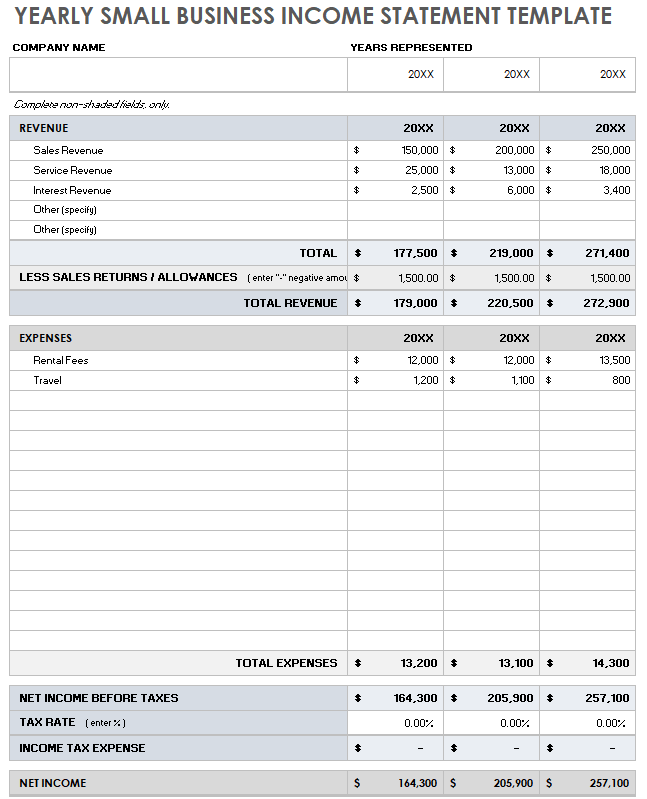
Download Small Business Income Statement Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this small business income statement template to track your company’s total income and expenses over time. Customize it to track by month, quarter, or year, and use it to complete the income and expense information on your budget template.
Small Business Cash Flow Statement Template
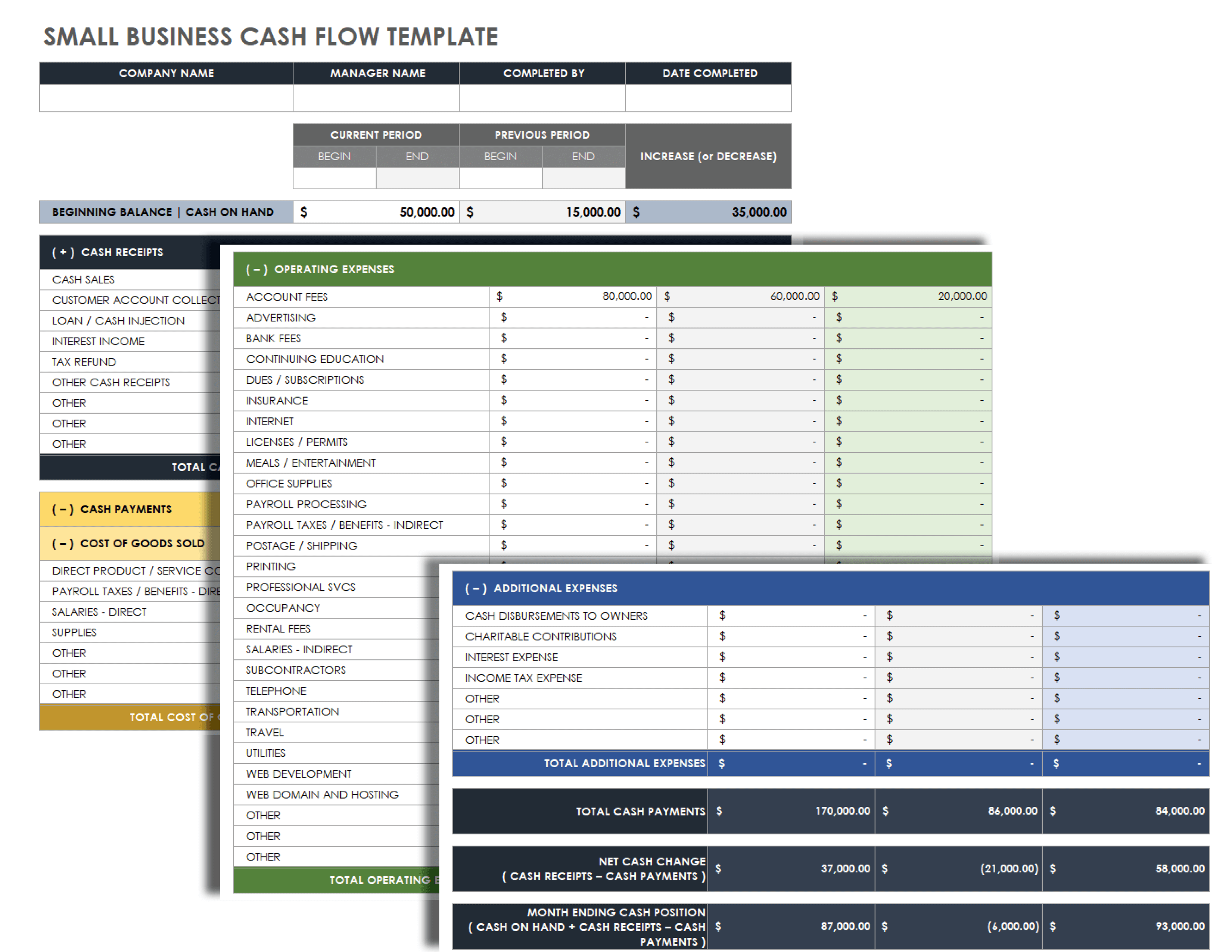
Download Small Business Cash Flow Statement Template Microsoft Excel | Google Sheets
Use this small business cash flow statement template to follow your cash income and expenses. Input your cash flow in the appropriate cell, and compare the current to the previous time period. The template will generate your total cash payments and ending cash position, which will help you fill in your budget template.
Streamline Small Business Budgeting Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Discover a better way to connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform that empowers your team to get more done, faster.
With Smartsheet, you can align your team on strategic initiatives, improve collaboration efforts, and automate repetitive processes, giving you the ability to make better business decisions and boost effectiveness as you scale.
When you wear a lot of hats, you need a tool that empowers you to get more done in less time. Smartsheet helps you achieve that. Try free for 30 days, today .
Connect your people, processes, and tools with one simple, easy-to-use platform.
Accounting | How To
How To Create a Small Business Budget [+Free Template]
Published June 20, 2023
Published Jun 20, 2023
REVIEWED BY: Tim Yoder, Ph.D., CPA
WRITTEN BY: Eric Gerard Ruiz, CPA
This article is part of a larger series on Bookkeeping .
- 1. Create a Budget Process
- 2. Determine Key Assumptions in Budgeting
- 3. Create the Sales Budget
- 4. Create the Inventory and Purchases Budget
- 5. Create the COGS Budget
- 6. Create the Sales & Administrative Budget
- 7. Create the Capital Budget
- 8. Create the Cash Budget
- 9. Assemble Proforma Financial Statements
Common Problems in Budgeting
Bottom line.
Creating a business budget is an important step in planning. A small business budget starts with creating the budgeting process, the operating budgets, such as sales, inventory and purchases, cost of goods sold (COGS), and sales and administrative, and ends with the financial budgets, such as cash, capital, and proforma financial statements.
To help you get started, we’ve provided a very simplified version of a budget spreadsheet to illustrate how information from each area of your business is combined to form an annual budget. We’ll discuss how to use this spreadsheet throughout our article.
FILE TO DOWNLOAD OR INTEGRATE
FILE TO DOWNLOAD
Thank you for downloading!
Budgeting is an important subset of managerial accounting. Read our small business guide to managerial accounting and learn how managerial accounting concepts can be applied in a small business setup.
Step 1: Create a Budget Process
The budget process shows how the different departments of the business create a budget. Without a process, budgeting would be chaotic, and it would result in inefficiencies. In the budget process, you need to consider the following:
- Budget period: When are budgets created, reviewed, implemented, and evaluated against actual performance?
- Budgeting method: How are budgets created? Is it created from scratch (zero-based budgeting)? Is it based on actual results with adjustments (incremental budgeting)?
- Budget involvement: Who creates the budgets?
- Budget committee: Who oversees and approves the budgets?
- Budget manual: What are the guidelines for creating budgets?
Budget Period
The first thing to consider in the budget process is the budget period. How long should budgets be prepared? When will it be implemented? The budget period can be any time before the next business year begins. Hence, you can create next year’s budget three months prior to the end of the current year.
The crucial periods for budget planning are as follows:
- Budget preparation : The time at which managers and heads create a budget for their department.
- Budget review and approval : The time at which top management will review and approve all lower-level budgets.
- Budget implementation : The time at which all concerned parties will act upon planned activities stated in the budget. This phase runs until the effectiveness of the budget lasts.
- Budget accountability : The time at which top management will assess if the business is meeting its budgetary goals. This phase runs intermittently during the year, such as monthly, quarterly, or semiannually, especially during performance evaluation and review.
As a small business, you need not be particular about the phases. You can modify the phases depending on small business needs.
Budgeting Method
There are four different types of budgeting methods, but for small businesses, we picked only two, as they are the most appropriate for the setup:
- Zero-based budgeting : This is a budgeting technique that starts from scratch. It doesn’t use information from past budgets. Instead, departments and managers need to justify every dollar in the budget without referring to past performance or past budgeting practices.
- Incremental budgeting : This is a budgeting technique that uses actual figures from the past years and adjusts with a certain percentage. For example, if actual sales last year is $20,000, the incremental budgeted sales could be 10 percent more or $22,000.
Budget Involvement
Small businesses must consider what kind of involvement is needed during the budgeting process, given that budgets can be used to measure the performance of departments and managers. There are two kinds of budget involvement—for small businesses, authoritative budgeting is suitable if the small business owner is heavily involved in daily operations. Alternatively, participatory budgeting applies if the owner delegates decision-making to managers.
1. Authoritative budgeting
Also known as top-down budgeting, this budget involvement strategy only includes top management in the budgeting process, where operating personnel and lower-level employees have little to no say in the budget. It takes less time to create since there are fewer employees involved.
However, some operating personnel and lower-level employees may disagree with top management’s estimates in the budget. At the least, this strategy creates discord between top management and operating personnel due to conflicting views. But if prepared appropriately, authoritative budgeting reflects the business’ vision, mission, and goals better.
2. Participatory budgeting
This is also called bottom-up budgeting, and this budget involvement strategy includes operating personnel and lower-level employees in creating a budget. It is a budget co-created by everyone involved or affected by the budget being created.
It enhances the relationship between top management and operating personnel since everyone has a say in the budget. However, this strategy can take time since more employees are involved in the budgeting process. Also, some lower-level managers can use this opportunity to insert some budgetary slack so that they look good during performance.
Budget Committee
The budget committee is responsible for compiling all lower-level budgets and assembling them into one package called the master budget and reviewing and approving budgets from different departments. For small businesses, the composition of the budget committee can be the small business owners, chief executive officer (CEO), treasurer, budget coordinator, and chief accountant.
The role of the budget coordinator is to reach out to lower-level managers and communicate the wishes of the budget committee. If you’re a family-grown small business, family members, including the small business accountant or finance officer, can be committee members.
Budget Manual
The first order of business of the budget committee is to create a budget manual, which outlines the budgeting process. Lower-level managers and department heads will use the budget manual when creating lower-level budgets. The budget committee may also set specific budget formats and deadlines.
A budget manual standardizes the budgeting process—it ensures fairness and comparability among departments and managers. With this manual in place, you can prevent the instance of inserting unfamiliar line items in the budget or using different sources in forecasting budgeted figures.
The budget manual should include the following:
- Statements of budgetary purpose
- Budgetary activities, such as budget preparation, budget hearing and evaluation, budget approval, budget execution, and budget accountability
- Schedule of budgetary activities and deadlines
- Sample budgets
- Key assumptions used in budgeting
You can create a budget easily using QuickBooks Online. Its budgeting functions create budgets per account in the chart of accounts. Read our QuickBooks Online review for detailed information on our recommendation.
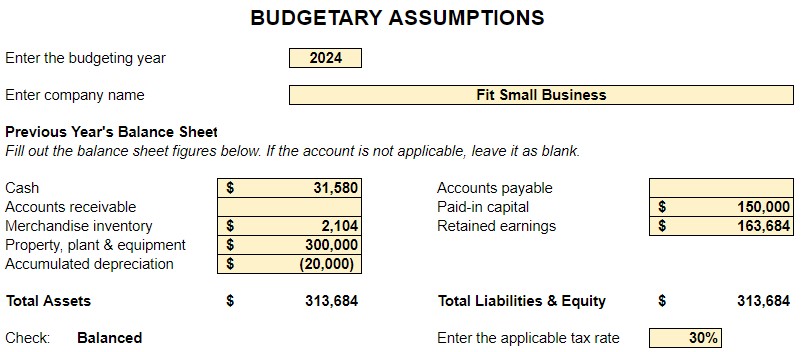
Step 2: Determine Key Assumptions in Budgeting
After performing the groundwork for budgeting, the next step is determining the key assumptions. These assumptions make it easy to prepare budgets since not all information is readily available until it happens. These assumptions are not arbitrary because they must be based on past experience and good business practices.
Examples of assumptions are:
- Sales forecast
- Selling price per unit
- Cost per unit
- Estimated discounts given to customers
- Estimated sales returns
- Desired ending inventory per month or quarter
- Number of raw materials used to produce one good unit
- Number of labor hours needed to produce one good unit
- Number of overhead hours (if any) needed to produce one good unit
- Inventory cost flow method used, such as first-in, first-out (FIFO), last-in, first-out (LIFO), or average cost
- Cash collection patterns
- Cash payments patterns
- Cash retention policies
Input your assumptions in the second tab of our downloadable spreadsheet. When done, all of the reports will automatically populate. It’s the quality of your assumptions that will determine if your budget is realistic. As you improve your budgeting process, you’ll come up with additional assumptions to include in the process.
Step 3: Create the Sales Budget
The sales budget is the first budget that should be prepared because almost all budgets will depend on the information in it. It is the responsibility of the sales department to forecast and create the sales budget of the company, and it is crucial that the department forecast sales reasonably using the appropriate forecasting method. Our article about sales forecasting discusses the method of sales forecasting and shows how CRM software can help.
Below is an example of the sales budget taken from our small business master budget template.
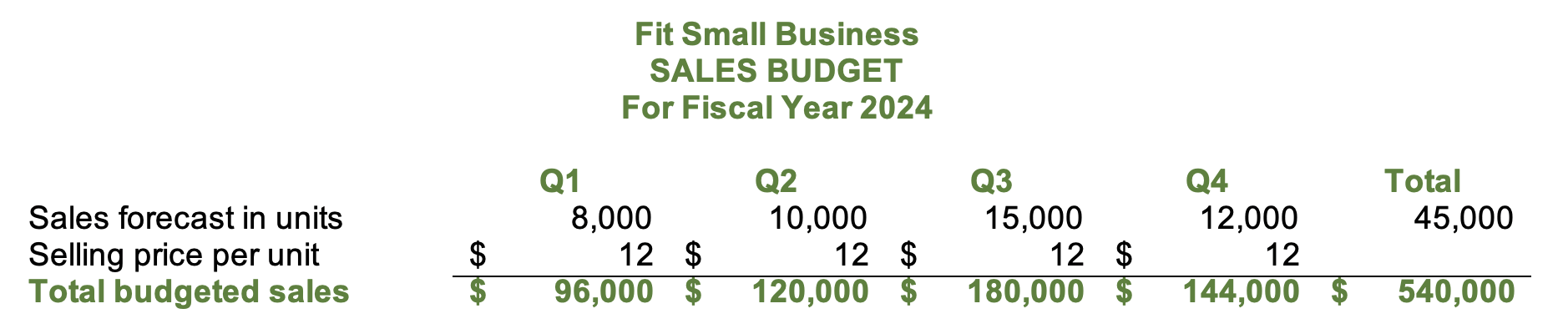
Sales budget
Step 4: Create the Inventory & Purchases Budget
There are two ways to call this budget: merchandising companies can call it inventory and purchases budget while manufacturing companies can call it production budget. However, the information shown in this budget remains the same. The inventory or production budget shows the number of units needed to meet the sales demand.
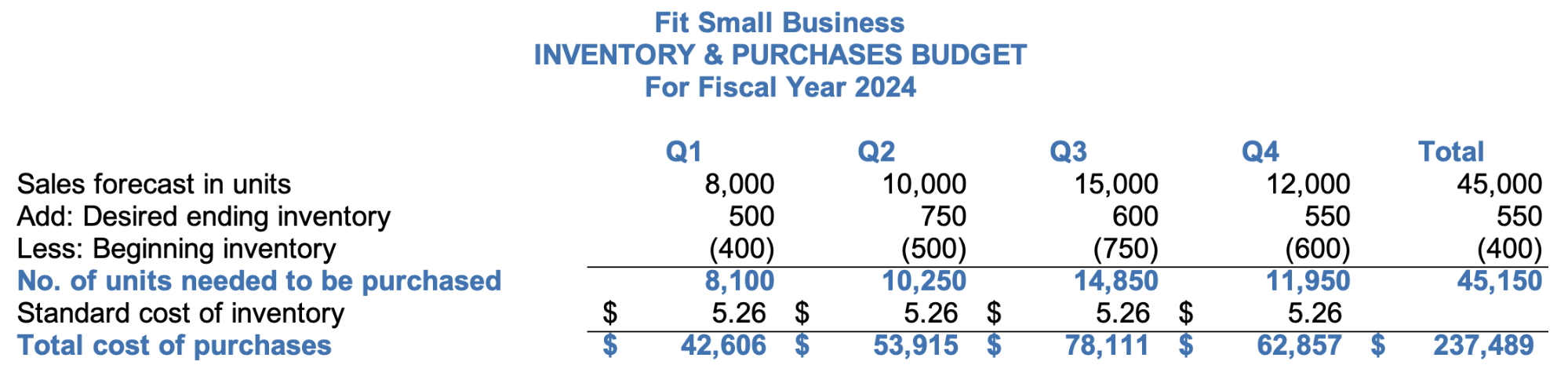
Inventory budget
The image above shows the sample inventory budget in our free template. One of our assumptions is that the business intends to keep 5% of next quarter’s sales forecast as current quarter’s ending inventory. In Q1, desired ending inventory is 500 units, which is 5% of 10,000 units of Q2’s sales forecast.
After determining the number of units needed, multiply them to the standard cost of inventory to get the total cost of inventory. The standard inventory cost is also the budgeted cost of inventory. Since some inventory prices fluctuate, setting standard costs makes it easy for us to budget.
When adding values in the total column, do not sum up the values in the beginning and desired ending inventory rows. Instead, the total beginning inventory in the total column should be the Q1 beginning inventory, while the total ending inventory should be the Q4 ending inventory.
Step 5: Create the COGS Budget
The next logical step after budgeting inventory and purchases is to determine the COGS. Through the COGS budget, we can estimate the level of COGS per quarter. This budget is necessary for preparing the proforma income statement.
Below is the COGS budget from our small business budget template:
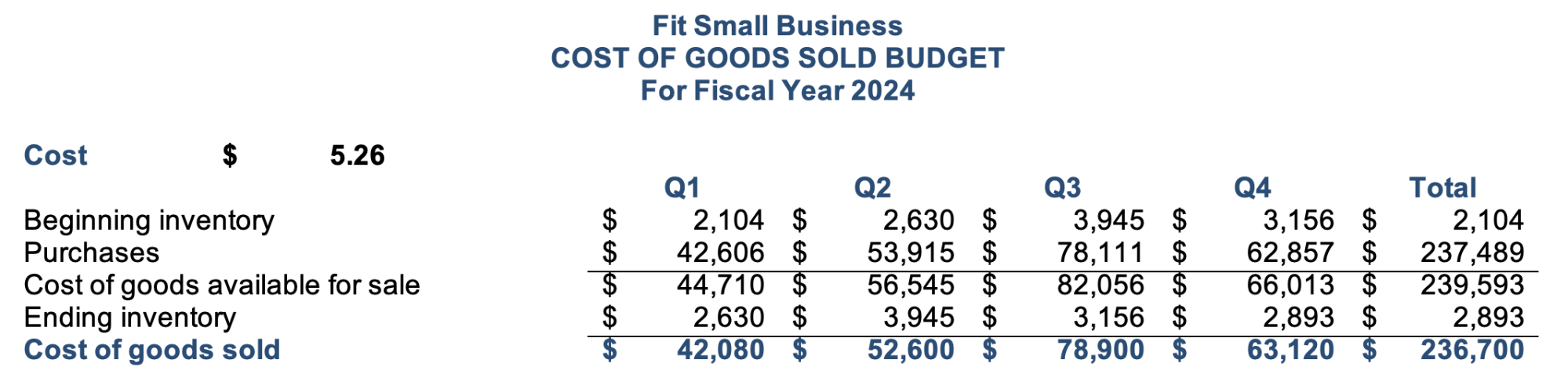
COGS budget
Step 6: Create the Sales & Administrative Budget
The sales and administrative (S&A) budget presents the budgeted costs for sales expenses, office expenses, and administrative expenses. This is necessary for budgeting the salaries of employees and other fixed expenses. The image below shows the sales and administrative budget from our template:
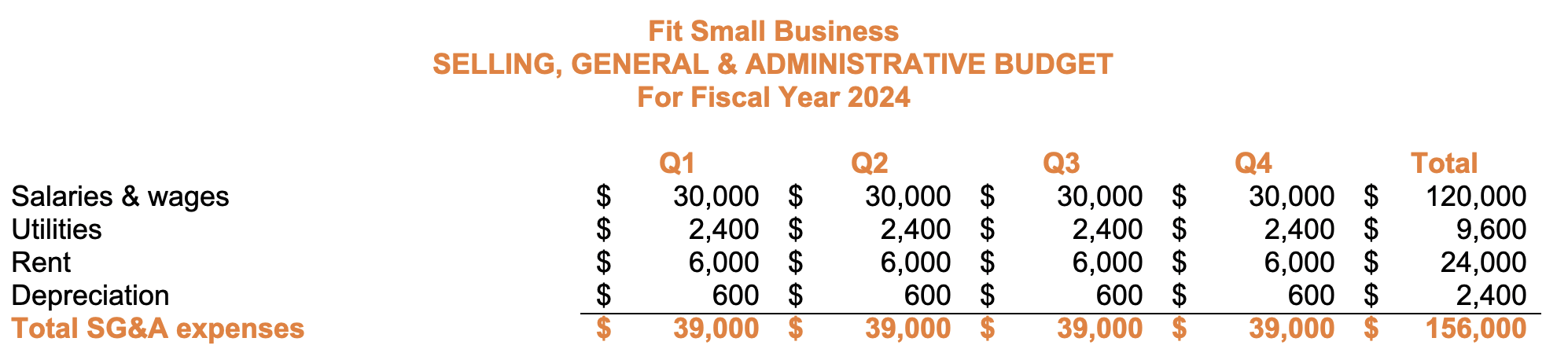
S&A budget
Most expenses in this budget are fixed costs. That’s why the amounts are the same for every quarter. Manufacturing companies may also call this budget a “fixed overhead budget.”
Step 7: Create the Capital Budget
A capital budget shows all the planned capital expenditures during the year. In our capital budget example below, there are no figures because the sample company didn’t plan any capital decisions for 2024. However, we’ve included common capital decisions for you to fill out when you use our template. For instance, a bank loan is a capital inflow while the purchase of equipment is a capital outflow.

Capital budget
The capital budget in our downloadable spreadsheet does not auto-populate from the assumptions tab. Instead, enter your budgeted loans and purchases directly in the report.
Step 8: Create the Cash Budget
The last budget that you need to prepare is the cash budget, which shows all the cash inflows and outflows from all budgets. Almost all budgets above affect cash flow. For example, the sales budget can show all cash inflows from cash sales and subsequent cash collections from credit sales.
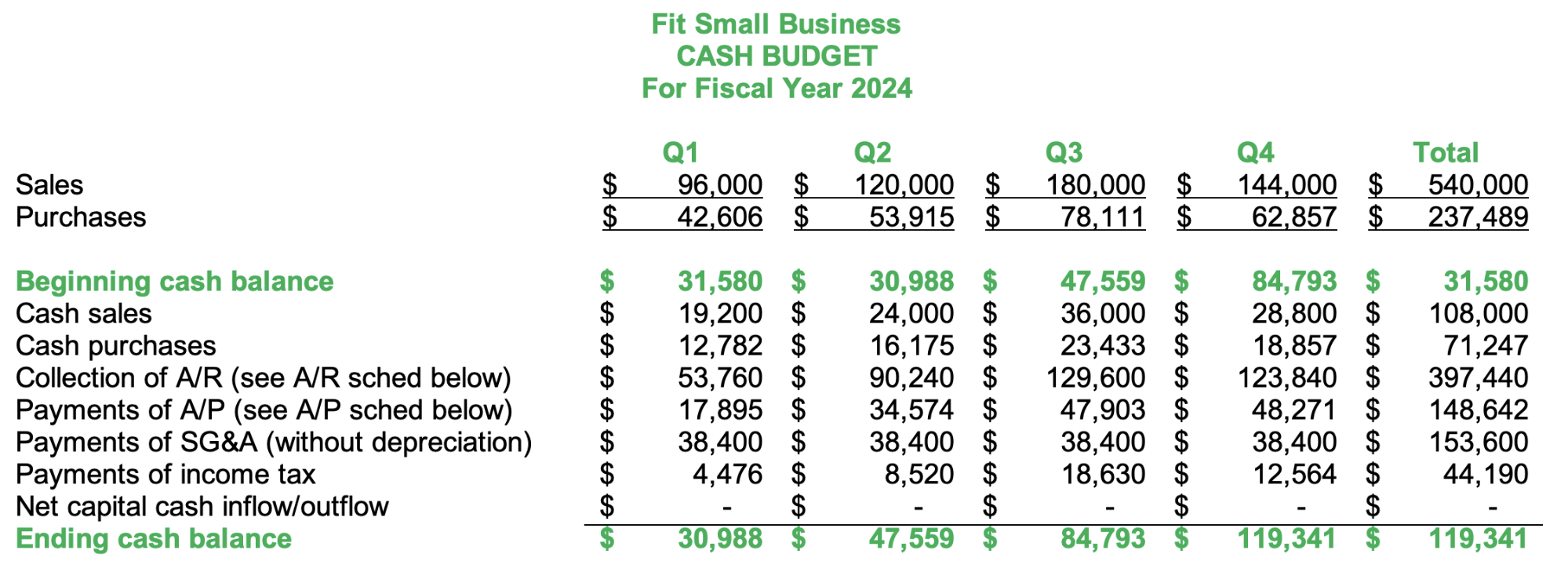
Cash budget
Accounts Receivable & Accounts Payable Schedule
Collections from accounts receivables (A/R) and payments of accounts payable (A/P) are integral parts of the cash budget. Creating the A/R and A/P schedules helps in computing the ending balance of A/R and A/P and the amount of cash collections and payments per quarter. Below are the supporting A/R and A/P schedules for our cash budget above:
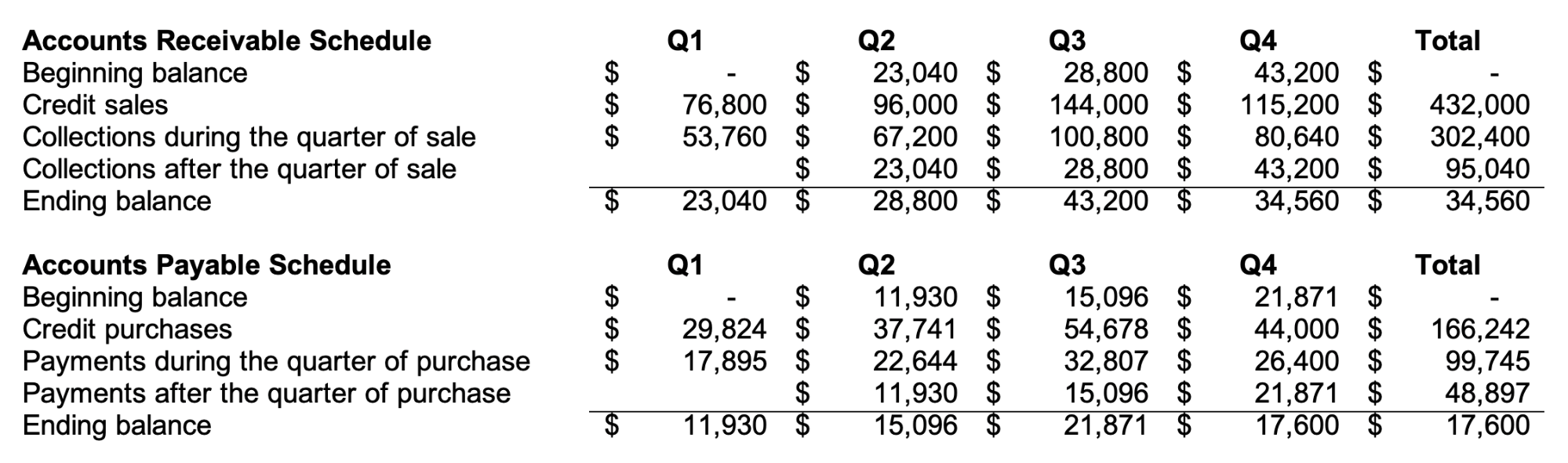
A/R and A/P schedules
Step 9: Assemble the Proforma Financial Statements Based on Budgeted Figures
The ultimate result of the budgeting process is the proforma financial statements, which are the budgeted or projected results of planned activities. If the budget goes as planned, the actual financial statements should be near the proforma financial statements. Below are the proforma income statement and balance sheet in our small business budget template.
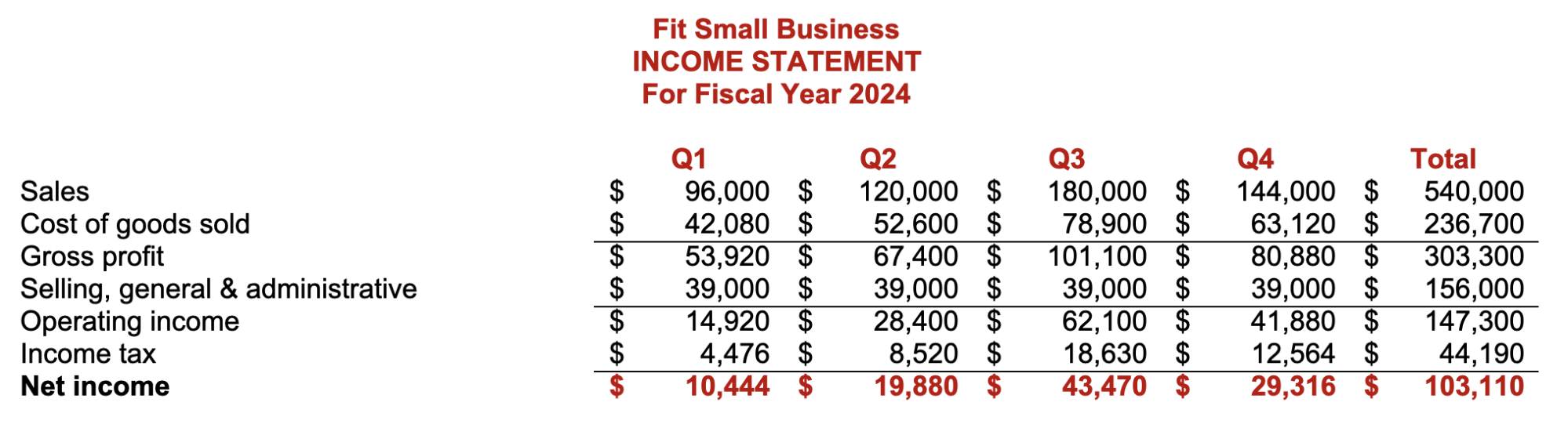
Proforma Income Statement
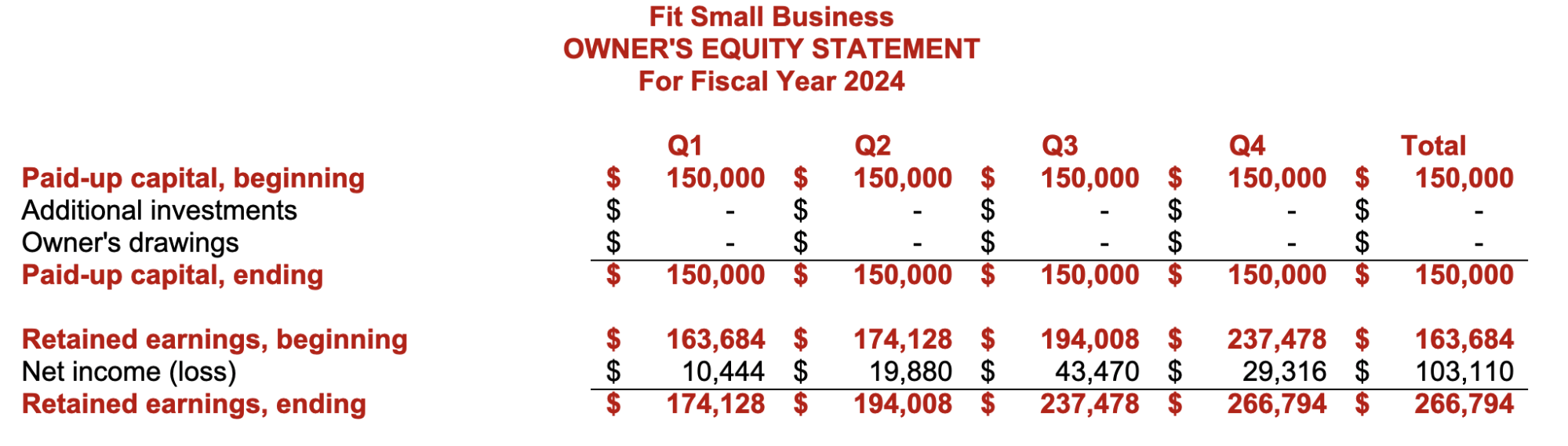
Proforma Owner’s Equity Statement
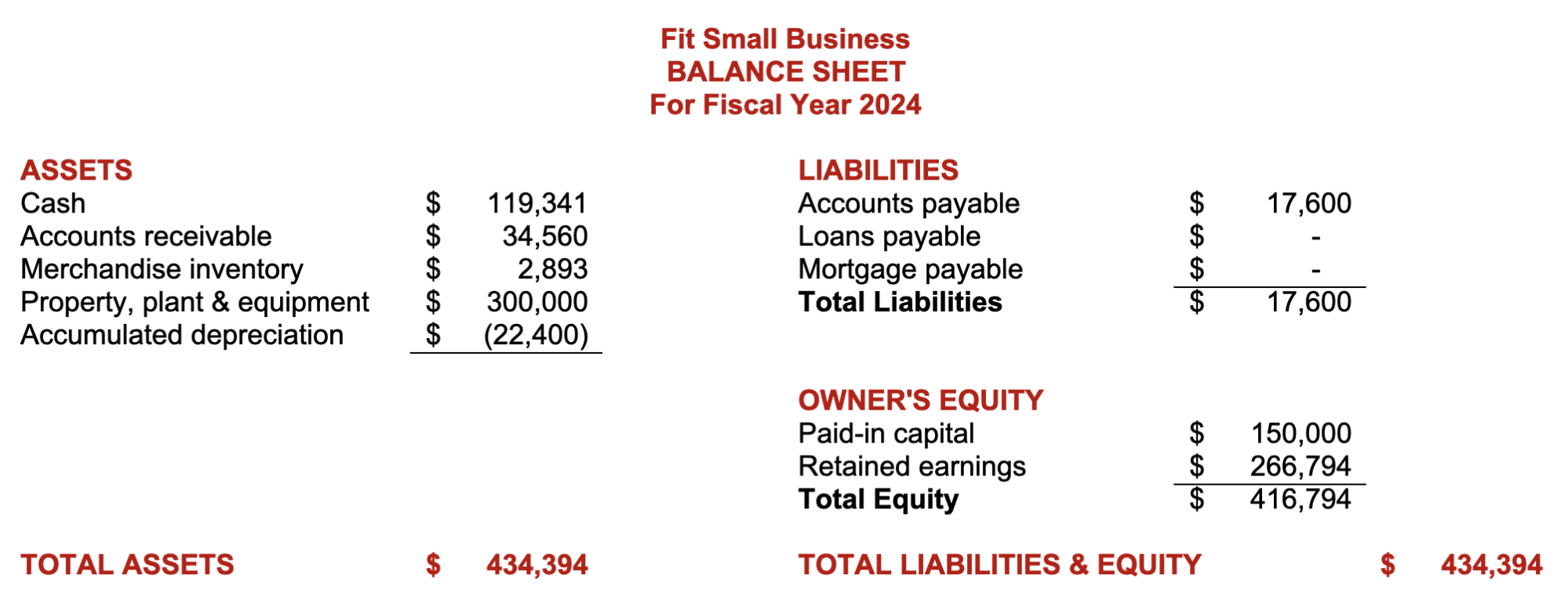
Proforma Balance Sheet
Budgeting helps businesses plan on future events and meet company goals. However, it is likely that you will experience difficulties and problems during the budgeting process. The four problems we’ll discuss are budgetary slack, goal incongruence, budget myopia, and standard setting.
Budgetary slack and goal incongruence occur when managers are not aligned with the business’s overall goals and objectives, while budget myopia happens when the business forgets to consider the impact of short-term decisions in the long run. Lastly, standard setting often poses a problem when standards are too high or ideal. Let’s discuss each of them in greater detail below.
Budgetary Slack
Sometimes, managers and heads can use budgets to preempt results to their favor. This unethical practice is called budgetary slack or budget padding. Budget slacks occur when managers underestimate revenue goals and overestimate expense goals and when the business follows the participatory budget involvement strategy.
When time for evaluation arrives, budget slacks will make the manager’s performance as exemplary. Managers tend to include budgetary slacks when top management is too strict and punitive whenever budgets aren’t met.
For example, the sales manager underestimates the sales forecast at $50,000 for the first quarter, knowing that they can achieve actual sales of $70,000. This example shows how budgetary slack can affect performance evaluation and create a false reflection of the company’s ability to generate revenue.
Goal Incongruence
Budgets are goals. When goals of management and employees don’t meet, the budget will not reflect the results that’s best for the business as a whole. Preventing goal incongruence enhances the quality of the budget. The goal of employees should be aligned with the business’s goals, and top management should provide opportunities for employees to pursue their career growth within the business.
Improper communication of business goals and ineffective leadership are the common causes of goal incongruence. As a small business owner or manager, you should show employees that you are committed to them with respect to their professional goals and that you expect them to align themselves with the business’s overall goals.
Budget Myopia
Budget myopia occurs when budgeting focuses only on short-term goals without considering how these goals will affect the company in the future. Managers become “myopic” in budgeting when they see budgets as measures for performance—they forget that the main objective of budgeting is to plan, organize, and manage the firm’s resources. As a result, budget realignments occur because there is a failure to plan future events.
Standard Setting
Another hurdle in budgeting is setting standards, which are tools for planning and controlling. If used inappropriately, they can cause problems in the budgeting process. It is important that you have to set your standards at a practical level.
Practical standards allow room for error or inefficiencies. It gives employees a chance to learn and improve their outputs without affecting performance. Unwise managers often impose ideal standards or standards that require optimum performance and perfection.
As a result, imposing ideal standards results in employee burnout, decreased productivity, and negative employee morale. Discouraged employees might also result in dysfunctional behavior that might be detrimental to the company.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is budgeting important.
Budgets help in planning and managing business resources. Since plans and goals require an outflow of resources, budgets help the business determine the right amount of resources needed to achieve the goal.
Who should have an active participation in the budgeting process for small businesses?
The small business owner should have an active role in helping managers and supervisors craft their budgets. As the owner, you should guide your employees to align their goals with the business’ overall goals.
With our small business budget guide and template, you can create a small business master budget. We hope that the template will help you understand why budgeting is crucial to the planning, organizing, and controlling business operations.
About the Author

Find Eric Gerard On LinkedIn
Eric Gerard Ruiz, CPA
Eric is an accounting and bookkeeping expert for Fit Small Business. He has a CPA license in the Philippines and a BS in Accountancy graduate at Silliman University. Since joining FSB, Eric has used his expertise and authority in curating and writing content about small business accounting and bookkeeping, accounting software, financial accounting and reporting, managerial accounting, and financial management.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Managing Your Money
How to Create a Business Budget
Last Updated: November 18, 2021 Approved
This article was co-authored by Samantha Gorelick, CFP® . Samantha Gorelick is a Lead Financial Planner at Brunch & Budget, a financial planning and coaching organization. Samantha has over 6 years of experience in the financial services industry, and has held the Certified Financial Planner™ designation since 2017. Samantha specializes in personal finance, working with clients to understand their money personality while teaching them how to build their credit, manage cash flow, and accomplish their goals. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. In this case, several readers have written to tell us that this article was helpful to them, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 181,357 times.
Building a realistic budget is an effective way to help keep your business profitable. To create your budget, you'll need to make a revenue forecast, estimate your costs, and leave enough room for a reasonable profit margin. Don't worry though—it's easier than it sounds. Our how-to guide will walk you through the simple steps of creating your own financial plan, even if you're a total beginner to budgeting!
Understand the Basics of Budgeting

- For example, assume your business is planning for next year. A budget will outline your estimated revenues, and then include a plan for expenses that is less than those revenues, so that you can earn a profit.
- A balanced budget means your revenues are equal to your expenses. A surplus means your revenues exceed expenses, and a deficit means expenses exceed revenues. As a business, your budget should always strive to be in a surplus state.

- A budget should guide every single business expenditure. For example, if you realize midway through a year that your business desperately needs updated computers, you can consult your budget to see how much estimated surplus revenue you will generate for the remainder of the year. You can then explore costs for computer upgrades and see if that fits within the surplus figure while allowing you to earn a profit, or alternatively, if you have the additional revenue to support taking out a loan for the computers.

- Sales: Sales refer to how much total money your business brings in from all sources. A budget will involve an estimate or forecast of your future sales.
- Total costs: Total costs are what it costs your business to generate your sales. These include fixed costs (like rent), variable costs (like materials used to make your products), and semi-variable costs (like salaries).
- Profits: Profits are equal to revenues minus total costs. Since profit is the goal of business, your budget should include expenses that are low enough to earn you a decent return on your investment.
Forecasting Revenue

- Remember that revenue forecasts are rarely accurate. The point is to provide the best possible estimate using the knowledge you have. [6] X Research source
- Always be conservative. This means assume you will receive sales volumes and pricing on the low end of the possible range.

- For example, assume you are opening a therapy practice. Therapists in your region may charge $100 to $200 per hour. Compare your qualifications, experience, and service offerings to your competition, and estimate your price. You may decide $100 is wise.
- If you offer multiple products and services, make sure to research prices for those too.

- Do you have any customers or contracts lined up? If so, include these. You can then assume referrals from customers and advertising will add to these volumes over the year.
- Compare to existing businesses. If you have colleagues who have established businesses, ask them what their volumes were like early on. For a therapy practice, your colleagues may tell you during their first year they averaged about 10 client hours a week.
- Look at what drives sales volumes. If you are opening a therapy practice, for example, your reputation, referrals, and advertising will bring in people. You could decide that based on these resources, one new client every two weeks is reasonable. You could then go further and make an estimate that each client will pay for one hour a week, and last for an average of six months.
- Once again, remember that revenue forecasts are purely estimates.

- Look at pricing. Do you have reason to believe your prices will increase or decrease?
- Look at volume. Are more people going to be purchasing your product or service? If your business has been growing by 2% annually, you can assume the same for the following year if no significant changes have occurred. If you plan on aggressively advertising, you could bump that up to 3%.
- Look at the market. Is your market growing? For example, imagine that you run a coffee shop in a downtown neighborhood. You may be aware that the neighborhood is rapidly growing due to new people moving in. This could be reason to add to your growth forecast.
Creating the Budget

- Contact an accountant if you are having difficulties. Chartered Professional Accountants in the UK and Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) in the US are trained to advise businesses in the area of budgeting, and for a fee they can assist you in any aspect of the budget creation process.
- A simple online search of "business budget template" can yield thousands of results. You can even find custom templates for your particular type of business.

- Research online or ask a financial adviser what the typical margins for your kind of business should be.
- If 10% is typical for your business, you know that if you are forecasting $100,000 of revenues, your expenses should equal no more than $90,000.

- Add up all these costs to get an idea of your fixed costs for the next year.
- If you have past financial data, use these fixed costs and adjust them for any rent increases, bill increases, or new costs.

- This will vary depending on how much you sell, which is why it is known as a variable cost. You can use your revenue forecast to determine this. For example, if you estimate you will sell 12 cars in your first year, your inventory costs will be the cost to purchase 12 cars.

- Add up all your estimated semi-variable costs.

- Are your total costs less than your revenues?
- Do your total costs provide a profit margin greater than or equal to your target?
- If the answer to either of these questions are no, you will need to look into making cuts. To do this, look at all your costs, and examine what you can do without. Labor costs are one of the most flexible areas to find savings (though you risk upsetting your employees when you cut hours). You can also look into finding a location with lower rents, or reducing utilities costs.
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ Samantha Gorelick, CFP®. Financial Planner. Expert Interview. 6 May 2020.
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/budget.asp
- ↑ http://www.inc.com/encyclopedia/businessbudget.html
- ↑ http://www.entrepreneur.com/article/76418
- ↑ http://articles.bplans.com/how-to-forecast-sales/
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/semivariablecost.asp
About This Article

To create a business budget, start by forecasting your yearly expenditures. To do this, add together fixed costs like rent, insurance, and property taxes. Then, add variable costs like inventory purchases and semi-variable costs like internet packages or employee salaries. Compare this number to your forecasted yearly revenue, which you can determine by comparing to last year’s revenue, or if you’re a new business, by doing market research to figure out what similar businesses make in a year. If your revenue is lower than your expenditures, figure out places you can cut from your budget. To learn how market forecasting can help give you an accurate estimate, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Kathleen Coyle
Mar 9, 2017
Did this article help you?
Daniel Aremu
May 17, 2018
Aug 17, 2016
Kirti Singh
Feb 14, 2017
Mohammad Zia
Nov 3, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve

A How-To Guide for Creating a Business Budget
Amanda Smith
Reviewed by
September 23, 2022
This article is Tax Professional approved
Most business owners know how important a business budget is when it comes to managing expenses and planning for the future—but in a challenging economic environment like the one we’ve been experiencing, your business budget takes on even greater significance.
With inflation running rampant and the possibility of a recession looming, business owners need to be able to forecast their cash flow, manage their expenses, and plan for the future. Creating a detailed business budget is the first step.
Whether you want to revamp your budgeting method, or you’ve never created a business budget before, this guide will walk you through the process.
I am the text that will be copied.
What is a business budget?
A budget is a detailed plan that outlines where you’ll spend your money monthly or annually.
You give every dollar a “job,” based on what you think is the best use of your business funds, and then go back and compare your plan with reality to see how you did.
A budget will help you:
- Forecast what money you expect to earn
- Plan where to spend that revenue
- See the difference between your plan and reality
What makes a good budget?
The best budgets are simple and flexible. If circumstances change (as they do), your budget can flex to give you a clear picture of where you stand at all times.
Every good budget should include seven components:
1. Your estimated revenue
This is the amount you expect to make from the sale of goods or services. It’s all of the cash you bring in the door, regardless of what you spent to get there. This is the first line on your budget. It can be based on last year’s numbers or (if you’re a startup ), based on industry averages.
2. Your fixed costs
These are all your regular, consistent costs that don’t change according to how much you make—things like rent, insurance, utilities, bank fees, accounting and legal services, and equipment leasing.
Further reading: Fixed Costs (Everything You Need to Know)
3. Your variable costs
These change according to production or sales volume and are closely related to “ costs of goods sold ,” i.e., anything related to the production or purchase of the product your business sells. Variable costs might include raw materials, inventory, production costs, packaging, or shipping. Other variable costs can include sales commission, credit card fees, and travel. A clear budget plan outlines what you expect to spend on all these costs.
The cost of salaries can fall under both fixed and variable costs. For example, your core in-house team is usually associated with fixed costs, while production or manufacturing teams—anything related to the production of goods—are treated as variable costs. Make sure you file your different salary costs in the correct area of your budget.
Further reading: Variable Costs (A Simple Guide)
4. Your one-off costs
One-off costs fall outside the usual work your business does. These are startup costs like moving offices, equipment, furniture, and software, as well as other costs related to launch and research.
5. Your cash flow
Cash flow is all money traveling into and out of a business. You have positive cash flow if there is more money coming into your business over a set period of time than going out. This is most easily calculated by subtracting the amount of money available at the beginning of a set period of time and at the end.
Since cash flow is the oxygen of every business, make sure you monitor this weekly, or at least monthly. You could be raking it in and still not have enough money on hand to pay your suppliers.
6. Your profit
Profit is what you take home after deducting your expenses from your revenue. Growing profits mean a growing business. Here you’ll plan out how much profit you plan to make based on your projected revenue, expenses, and cost of goods sold. If the difference between revenue and expenses (aka “ profit margins ”) aren’t where you’d like them to be, you need to rethink your cost of goods sold and consider raising prices .
Or, if you think you can’t squeeze any more profit margin out of your business, consider boosting the Advertising and Promotions line in your budget to increase total sales.
7. A budget calculator
A budget calculator can help you see exactly where you stand when it comes to your business budget planning. It might sound obvious, but getting all the numbers in your budget in one easy-to-read summary is really helpful.
In your spreadsheet, create a summary page with a row for each of the budget categories above. This is the framework of your basic budget. Then, next to each category, list the total amount you’ve budgeted. Finally, create another column to the right—when the time period ends, use it to record the actual amounts spent in each category. This gives you a snapshot of your budget that’s easy to find without diving into layers of crowded spreadsheets.
See the sample below.
Pro tip: link the totals on the summary page to the original sums in your other budget tabs . That way when you update any figures, your budget summary gets updated at the same time. The result: your very own budget calculator.
You can also check out this simple Startup Cost Calculator from CardConnect. It lays out some of the most common expenses that you might not have considered. From there, you can customize a rough budget for your own industry.
Small business budgets for different types of company
While every good budget has the same framework, you’ll need to think about the unique budgeting quirks of your industry and business type.
Seasonal businesses
If your business has a busy season and a slow season, budgeting is doubly important.
Because your business isn’t consistent each month, a budget gives you a good view of past and present data to predict future cash flow . Forecasting in this way helps you spot annual trends, see how much money you need to get you through the slow months, and look for opportunities to cut costs to offset the low season. You can use your slow season to plan for the next year, negotiate with vendors, and build customer loyalty through engagement.
Don’t assume the same thing will happen every year, though. Just like any budget, forecasting is a process that evolves. So start with what you know, and if you don’t know something—like what kind of unexpected costs might pop up next quarter— just give it your best guess . Better to set aside money for an emergency that doesn’t happen than to be blindsided.
Ecommerce businesses
The main budgeting factor for ecommerce is shipping. Shipping costs (and potential import duties) can have a huge impact.
Do you have space in your budget to cover shipping to customers? If not, do you have an alternative strategy that’s in line with your budget—like flat rate shipping or real-time shipping quotes for customers? Packaging can affect shipping rates, so factor that into your cost of goods sold too. While you’re at it, consider any international warehousing costs and duties.
You’ll also want to create the best online shopping experience for your customers, so make sure you include a good web hosting service, web design, product photography, advertising, blogging, and social media in your budget.
Inventory businesses
If you need to stock up on inventory to meet demand, factor this into your cost of goods sold. Use the previous year’s sales or industry benchmarks to take a best guess at the amount of inventory you need. A little upfront research will help ensure you’re getting the best prices from your vendors and shipping the right amount to satisfy need, mitigate shipping costs, and fit within your budget.
The volume of inventory might affect your pricing. For example, if you order more stock, your cost per unit will be lower, but your overall spend will be higher. Make sure this is factored into your budget and pricing, and that the volume ordered isn’t greater than actual product demand.
You may also need to include the cost of storage solutions or disposal of leftover stock.
Custom order businesses
When creating custom ordered goods, factor in labor time and cost of operations and materials. These vary from order to order, so make an average estimate.
Budgeting is tricky for startups—you rarely have an existing model to use. Do your due diligence by researching industry benchmarks for salaries, rent, and marketing costs. Ask your network what you can expect to pay for professional fees, benefits, and equipment. Set aside a portion of your budget for advisors—accountants, lawyers, that kind of thing. A few thousand dollars upfront could save you thousands more in legal fees and inefficiencies later on.
This is just scratching the surface, and there’s plenty more to consider when creating a budget for a startup. This business startup budget guide from The Balance is a great start.
Service businesses
If you don’t have a physical product, focus on projected sales, revenue, salaries, and consultant costs. Figures in these industries—whether accounting, legal services, creative, or insurance—can vary greatly, which means budgets need flexibility. These figures are reliant on the number of people required to provide the service, the cost of their time, and fluctuating customer demand.
Small business budgeting templates
A business budget template can be as simple as a table or as complex as a multi-page spreadsheet. Just make sure you’re creating something that you’ll actually use.
Create your budget yearly—a 12-month budget is standard fare—with quarterly or monthly updates and check-ins to ensure you’re on track.
Here are some of our favorite templates for you to plug into and get rolling.
- The Balance has a clear table template that lists every budget item, the budgeted amount, the actual amount, and the difference between the two. Use this one if you’re looking to keep it simple.
- Capterra has both monthly and annual breakdowns in their Excel download. It’s straightforward, thorough, and fairly foolproof.
- Google Sheets has plenty of budget templates hiding right under your nose. They’re easy to use, and they translate your figures into clear tables and charts on a concise, visual summary page.
- Smartsheet has multiple resources for small businesses, including 12-month budget spreadsheets, department budget templates, projection templates, project-by-project templates, and startup templates. These templates are ideal if you’re looking for a little more detail.
- Scott’s Marketplace is a blog for small businesses. Their budget template comes with step-by-step instructions that make it dead simple for anyone.
- Vertex42 focuses on Excel spreadsheets and offers templates for both product-based and service-based businesses, as well as a business startup costs template for anyone launching a new business.
Budgeting + bookkeeping = a match made in heaven
Making a budget is kind of like dreaming: it’s mostly pretend. But when you can start pulling on accurate historical financials to plan the upcoming year, and when you can check your budget against real numbers, that’s when budgets start to become useful.
The only way to get accurate financial data is through consistent bookkeeping.
Don’t have a regular bookkeeping process down pat? Check out our free guide, Bookkeeping Basics for Entrepreneurs . We’ll walk you through everything you need to know to get going yourself, for free.
If you need a bit more help, get in touch with us. Bookkeeping isn’t for everyone, especially when you’re also trying to stay on top of a growing business—but at Bench, bookkeeping is what we do best.
Related Posts

How Revenue Recognition Works: A 5-Step Guide
What is revenue recognition and does it affect your business?

Best Free Accounting Software for Small Businesses
Accounting software can be your secret weapon when it comes to managing your small business finances. But you don't have to spend big for features you won't use.

Why Your Small Business Should Invest in Accounts Payable Software
Accounts payable software is an important tool for your business. It can help you manage bill pay, track vendor payments, and maintain cash flow.
Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
Get a regular dose of educational guides and resources curated from the experts at Bench to help you confidently make the right decisions to grow your business. No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

How to Create a Small Business Budget in 5 Simple Steps
Want to protect the financial health of your small business? You need a business budget. Here's how to create one.

When you build a business, there are a lot of things to stay on top of, from marketing and finding new clients to building a website and establishing your digital presence. But there’s one element that you want to stay on top of from the very beginning—and that’s your business budget.
Having a detailed and accurate budget is a must if you want to build a thriving, sustainable business. But how, exactly, do you create one? What are the steps for business budget planning?
As a small business owner, let’s take a look at how to create a business budget in five simple, straightforward steps.
What’s a Business Budget—and Why Is It Important?
Before we jump into creating a business budget, let’s quickly cover what a business budget is—and why it’s so important for small businesses.
A business budget is an overview of your business funds. It outlines key information on both the current state of your finances (including income and expenses) and your long-term financial goals. Because your budget will play a key role in making sound financial decisions for your business, it should be one of the first tasks you tackle to improve business success.
And, as a financially savvy owners, you’ll also want to have a budget in place to help you:
- Make sound financial decisions. In many ways, your business budgets are like a financial road map. It helps you evaluate where your business finances currently stand—and what you need to do to hit your financial goals in the future for business growth.
- Identify where to cut spending or grow revenue. Your business budgets can help you identify areas to decrease your spending or increase your revenue, which will increase your profitability in the process, outline unexpected costs, and help your sustain your business goals.
- Land funding to grow your business. If you’re planning to apply for a business loan or raise funding from investors, you’ll need to provide a detailed budget that outlines your income and expenses.
Now that you understand why budget creation is so important to your business decisions, let’s jump into how to do it.
Business Budget Step 1: Tally Your Income Sources

First things first. When building a small business budget, you need to figure out how much money your business is bringing in each month and where that money is coming from – this will hep create an operating budget based on your business income.
Your sales figures (which you can access using the Profit & Loss report function in FreshBooks) are a great place to start. From there, you can add any other sources of income for your business throughout the month.
Your total number of income sources will depend on your business model.
For example, if you run a freelance writing business, you might have multiple sources of income from:
- Freelance writing projects
- A writing course you sell on your website
- Consulting with other writers who are starting small businesses
Or, if you run a brick-and-mortar retail business, you may only have one source of income from your store sales.
However many income sources you have, make sure to account for any and all income that’s flowing into your business—then tally all those sources to get a clear picture of your total monthly income to build your master business budget template.
Business Budget Step 2: Determine Fixed Costs
Once you’ve got a handle on your income, it’s time to get a handle of your costs—starting with fixed costs.
Your fixed costs are any expenses that stay the same from month to month. This can include expenses like rent, certain utilities (like internet or phone plans), website hosting, and payroll costs.
Review your expenses (either via your bank statements or through your FreshBooks reports) and see which costs have stayed the same from month to month. These are the expenses you’re going to categorize as fixed costs.
Once these costs are determined, add them together to get your total fixed and variable costs expense for the month.
TIP: If you’re just starting your business and don’t have financial data to review, make sure to use projected costs. For example, if you’ve signed a lease for office space, use the monthly rent you will pay moving forward.
Business Budget Step 3: Include Variable Expenses
Related articles.

Variable costs don’t come with a fixed price tag—and will vary each month based on your business performance and activity. These can include things like usage-based utilities (like electricity or gas), shipping costs, sales commissions, or travel costs.
Variable expenses will, by definition, change from month to month. When your profits are higher than expected, you can spend more on the variables that will help your business scale faster. But when your profits are lower than expected, consider cutting these variable costs until you can get your profits up.
At the end of each month, tally these expenses. Over time, you’ll get a sense of how these expenses fluctuate with your business performance or during certain months, which can help you make more accurate financial projections and budget accordingly.
Business Budget Step 4: Predict One-Time Spends
Many of your business expenses will be regular expenses that you pay for each month, whether they’re fixed or variable costs. But there are also costs that will happen far less frequently. Just don’t forget to factor those expenses when you create a budget as well.
If you know you have one-time spends on the horizon (for example, an upcoming business course or a new laptop), adding them to your budget can help you set aside the financial resources necessary to cover those expenses—and protect your business from unexpected costs in the form of a sudden or large financial burden.
On top of adding planned one-time spends to your budget, you should also add a buffer to cover any unplanned purchases or expenses, like fixing a damaged cell phone or hiring an IT consultant to deal with a security breach. That way, when an unexpected expense pops up (and they always do), you’re prepared!
Business Budget Step 5: Pull It All Together
You’ve gathered all of your income sources and all of your revenue and expenses. What’s next? Pulling it all together to get a comprehensive view of your financial standing for the month.
On your businesses master budget, you’ll want to tally your total income and your total expenses (i.e., adding your total fixed costs, variable expenses, cost of goods, and one-time spends)—then compare cash flow in (income) to cash flow out (expenses) to determine your overall profitability.
Having a hard time visualizing what a business budget looks like in action? Here’s an operating budget example to give you an idea of what your new business budget might look like each month:
A Client Hourly Earnings: $5,000 B Client Hourly Earnings: $4,500 C Client Hourly Earnings: $6,000 Product Sales: $1,500 Loans: $1,000 Savings: $1,000 Investment Income: $500
Total Income: $19,500
Fixed Costs
Rent: $1,000 Internet: $50 Payroll costs: $5,000 Website hosting: $50 Insurance: $50 Government and bank fees: $25 Cell phone: $50 Accounting services : $100 Legal services: $100
Total Fixed Costs: $6,425
Variable Expenses
Sales commissions: $2,000 Contractor wages: $500 Electricity bill: $125 Gas bill: $75 Water bill: $125 Printing services: $300 Raw materials: $200 Digital advertising costs: $750 Travel and events: $0 Transportation: $50
Total Variable Expenses: $4,125
One-Time Spends
Office furniture: $450 Office supplies for new location: $300 December business retreat: $1,000 New time tracking software: $500 Client gifts : $100
One-Time Spends: $2,350
Expenses: $12,900
Total Income ($19,500) – Total Expenses ($12,900) = Total Net Income ($6,600)
Above all, once you have a clear sense of your profitability for the month, you can use it to make the right financial decisions for your small business moving forward.

For example, if you realize you’re in the red and spending more than you earn, you might cut your spending and focus on finding new clients . Alternatively, if your income is significantly higher than your expenses, you might consider investing your profits back into your business (like investing in new software or equipment).
Use Your Business Budget to Stay on Track
Putting in the work to create a budget for your small business may seem like a hassle. But while it takes a bit of time and energy, it’s worth the extra effort. Thorough business budgeting gives you the financial insights you need to make the right decisions for your business to grow, scale, and prosper in the future.
This post was updated in October 2023

Written by Deanna deBara , Freelance Contributor
Posted on June 20, 2017
Freshly picked for you

Thanks for subscribing to the FreshBooks Blog Newsletter.
Expect the first one to arrive in your inbox in the next two weeks. Happy reading!
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Small Business
6 Steps to a Better Business Budget
A top-notch budget can help propel your business success
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/100378251brianbeersheadshot__brian_beers-5bfc26274cedfd0026c00ebd.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
You've just purchased or opened a small business and you know your trade. But when it comes to bookkeeping—and more specifically, budgeting —your skill set is lacking. The good news is that it is possible to come up with a budget (or at least a good estimation of what will be needed in terms of dollars and cents) fairly easily.
Estimating and matching expenses to revenue (real or anticipated) is important because it helps small business owners to determine whether they have enough money to fund operations, expand the business, and generate income for themselves. Without a budget or a plan, a business runs the risk of spending more money than it is taking in, or conversely, not spending enough money to grow the business and compete.
Key Takeaways
- A business budget helps owners determine if they have enough money to fund operations, expand, and generate income.
- Without a budget, a company runs the risk of spending money it doesn't have, not spending enough to compete, or failing to build a solid emergency fund.
- To create a budget, check industry standards to determine the average costs of doing business and create a spreadsheet estimating the amount of money you'll need to allocate toward your costs.
- Factor in some slack in your budget to cover unexpected costs and review areas where you could cut costs if times get tough.
- Review your budget every few months and shop around for new suppliers to save money on products or services for your business.
Getting Started With a Business Budget
Every small business owner tends to have a slightly different process, situation, or way of budgeting. However, there are some parameters found in nearly every budget that you can employ.
For example, many business owners must make rent or mortgage payments. They also have utility bills, payroll expenses, cost of goods sold (COGS) expenses (raw materials), interest, and tax payments. The point is every business owner should consider these items and any other costs specifically associated with the business when setting up shop or taking over an existing business.
With a business that is already up and running, you can make assumptions about future revenue based on recent trends in the business. If the business is a startup , you'll have to make assumptions based on your geographic area, hours of operation, and by researching other local businesses. Small business owners can often get a sense of what to expect by visiting other businesses that are for sale and asking questions about weekly revenue and traffic patterns.
After you've researched this information, you should then match the business's revenue with expenses. The goal is to figure out what an average weekly expense for overhead, utilities, labor, raw materials, etc. would look like. Based on this information, you may then be able to estimate or forecast whether you'll have enough extra money to expand the business or to tuck away some money into savings. On the flip side, owners may realize that in order to have three employees instead of two, the business will have to generate more in revenue each week.
These six simple tips will help you put together a top-notch small business budget:
1. Check Industry Standards
Not all businesses are alike, but there are similarities. Therefore, do some homework and peruse the internet for information about the industry , speak with local business owners, stop into the local library, and check the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) website to get an idea of what percentage of the revenue coming in will likely be allocated toward cost groupings.
Small businesses can be extremely volatile as they are more susceptible to industry downturns than larger, more diversified competitors. So, you only need to look for an average here, not specifics.
2. Make a Spreadsheet
Prior to buying or opening a business, construct a spreadsheet to estimate what total dollar amount and percentage of your revenue will need to be allocated toward raw materials and other costs. It's a good idea to contact any suppliers you'd have to work with before you continue on. Do the same thing for rent, taxes, insurance(s), etc. It's also important you understand the different types of budgets you'll need to set up for your small business and how to implement them.
3. Factor in Some Slack
Remember that although you may estimate that the business will generate a certain rate of revenue growth going forward or that certain expenses will be fixed or can be controlled, these are estimates and not set in stone. Because of this, it's wise to factor in some slack and make sure that you have more than enough money socked away (or coming in) before expanding the business or taking on new employees.
4. Look to Cut Costs
If times are tight and money must be found somewhere in order to pay a crucial bill, advertise, or otherwise capitalize on an opportunity, consider cost-cutting . Specifically, take a look at items that can be controlled to a large degree. Another tip is to wait to make purchases until the start of a new billing cycle or to take full advantage of payment terms offered by suppliers and any creditors. Some thoughtful maneuvering here could provide the business owner with much-needed breathing and expansion room.
5. Review the Business Periodically
While many firms draft a budget yearly, small business owners should do so more often. In fact, many small business owners find themselves planning just a month or two ahead because business can be quite volatile, and unexpected expenses can throw off revenue assumptions. Establishing a budget planning calendar can be an effective tool for business owners to ensure they have enough capital to meet their business needs.
6. Shop Around for Services/Suppliers
Don't be afraid to shop around for new suppliers or to save money on other services being performed for your business. This can and should be done at various stages, including when purchasing or starting up a business, when setting annual or monthly budgets, and during periodic business reviews.
The Bottom Line
Budgeting is an easy, but essential process that business owners use to forecast (and then match) current and future revenue to expenses. The goal is to make sure that enough money is available to keep the business up and running, to grow the business, to compete, and to ensure a solid emergency fund.
University of California, Irvine, Accounting & Fiscal Services. " Understanding Fiscal Years and Fiscal Periods ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-485221701-581f4df15f9b581c0b6e2256.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to Create a Business Budget for Your Small Business

According to a study done by CBinsights, a few of the top reasons why small businesses fail include include pricing and cost issues, losing focus and running out of cash. These issues can be prevented by having a realistic budget in place.
Before you can focus on the budget, however, you need to identify what aspects of your business you’d like to improve. This will allow you to decide what can be done with your funds. Based on that list, you can set up short-term and long-term goals.
These goals will be directly affected by your incoming and outgoing cash. A short-term goal can be paying off a debt or purchasing new equipment. Long-term goals, like keeping aside marketing expenses, are crucial because they are connected to the overall growth of your business.
You should be practical about the goals you set. They should be purely based on your business’ capacity to spend and save. Once you have your goals in place, you can create an effective, foolproof budget by following these steps.
1. Analyze costs
Before you start drafting a budget, you must research the operating costs involved in your business. Knowing your costs inside and out gives you the baseline knowledge needed to craft an effective spending plan.
If you create a rough budget and later discover that you need more money for your business activities, this will jeopardize your goals. Your budget should be such that you can increase your revenue and profit enough as your business expands to handle your growing expenses. Your budget should factor in fixed, variable, one-time, and unexpected costs. Some examples of a fixed expense are rent, mortgages, salaries, internet, accounting services, and insurance. Examples of variable costs include cost of goods sold and commissions for labor.
There is not much harm in overestimating the costs involved since you will need enough cash to handle your future expenditures. If your business is new, then you must include start-up costs as well. Planning the budget this way will help you make informed decisions and tackle any unwanted financial surprises.
2. Negotiate costs with suppliers
This step will be useful for those businesses which have been functional for more than a year and are dependent on suppliers to sell products. Before you get started on your yearly budget, have a chat with your suppliers and try getting discounted rates for the materials, products, or services you need before you make your payments.
Negotiations allow you to create trustworthy relationships with your suppliers. This will be helpful when incoming cash is thin. For example, you might have a seasonal business. When you have enough cash saved, you can pay advance amounts to your suppliers as compensation for the times when you are unable to make payments. The main goal here is to find efficient ways to reduce cost of doing business.
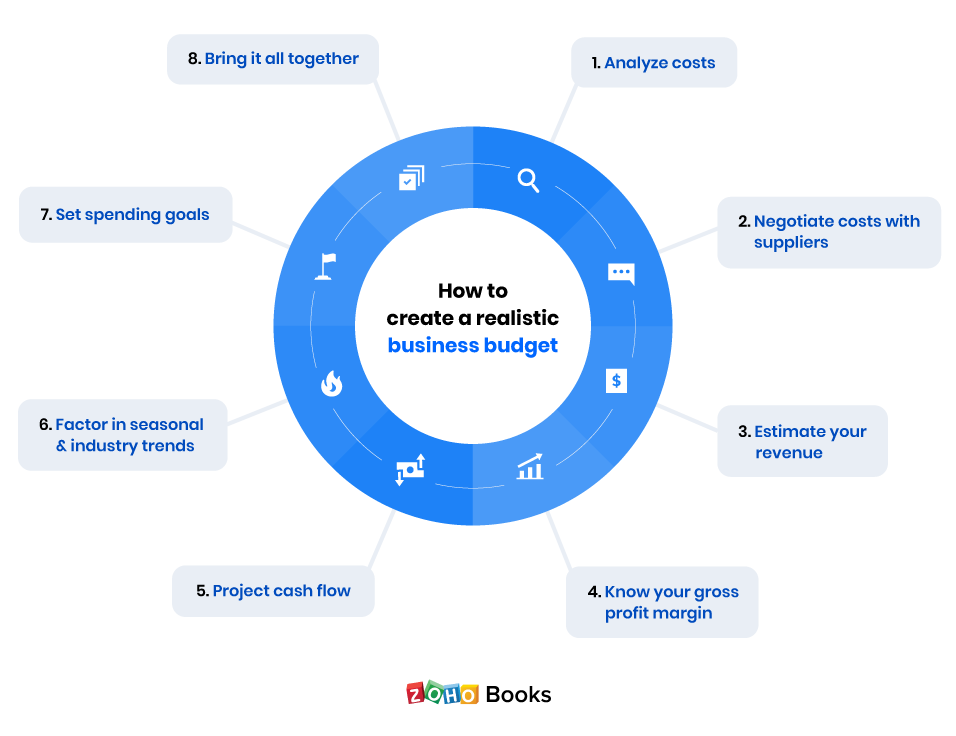
3. Estimate your revenue
Many businesses have failed in the past by overestimating revenue and borrowing more cash to meet operational needs. This defeats the very purpose of creating a budget. To keep things realistic, it’s a good idea to analyze previously recorded revenue. Businesses must track revenue periodically on a monthly, quarterly and annual basis.
Your previous year’s revenue figures can act as a reference point for the upcoming year. It’s important to rely solely on this empirical data. This will help you set realistic goals for your team, leading to the eventual growth of your business.
4. Know your gross profit margin
The gross profit margin is the cash you are left with after your business has dealt with all the expenses at the end of the year. It gives insight into the financial health of your business. Here’s an example of why you need to understand this parameter while creating a budget.
Suppose your business made a revenue $5,000,000 and yet there are debts to be paid. At the end of the year, your expenses are more than your revenue, which is not a good sign for a growing business. This tells you that you must identify the expenses that are not benefiting the business in any way and eliminate them. The best way to do this would be to list out the cost of goods sold for all materials and deduct them from the overall sales revenue. This information is needed to get a real picture on how your business is faring, allowing you to increase profit and reduce costs.
5. Project cash flow
There are two components to cash flow : customer payments and vendor payments. You need to balance these two components to keep the cash flowing in your organization.
To do your best to ensure timely customer payments, it’s important to have flexible payment terms and the ability to receive payments through common payment channels. Unfortunately you will need to deal with customers who might not comply to the stated terms. This might affect your cash flow forecast due to missing payments.
You can encourage payment by giving customers a grace period and creating strict business policies for paying late. Beyond this, you must have some money allocated in your budget for ‘bad debt,’ in case the customer never pays.
When you know your incoming cash flow, you can fix an amount for your employee salaries and travel expenses. You can also allocate some money to pay off your fixed vendor expenses. If you are still left with cash, you can then spend on business initiatives such as professional development or new equipment.
6. Factor in seasonal and industry trends
It’s unrealistic to expect that you will achieve every business goal and reach your estimates every month. In an annual cycle, there will be months where your business will be booming, and there may be a few months where sales are slow. Due to seasonal inconsistency and industry trends, you will have to spend cash effectively so that the business isn’t at risk of shutting down during slower periods.
To overcome this challenge while creating a budget, gather insights as to when your business performs better. The aim should be to generate enough revenue during peak months to sustain the business during off seasons.
For example, let’s assume that you are a business owner of a winter clothing company. Your products are on demand only during that season, so most of your revenue comes during that period. For the rest of the year, you can use the earnings to keep the business going and market to specific target groups, like hikers or travelers. This will help you gauge how successful your products are during off seasons, what revenue to expect, and how much to save during your peak periods.
7. Set spending goals
Making a budget is more than just adding your costs and subtracting them from your earnings. How wisely you spend your money determines how well your business will fare. Goals provide a system to check if your money is being spent on the right areas to avoid unwanted expenses.
For example, if you are spending money on stationary that is going unused for operational or marketing efforts, it may be time to cut those costs. This money can be better applied to your marketing campaigns, bringing in more leads and revenue. Gauge and invest in those expenses that would benefit your business in the long run.
8. Bring it all together
Once you have gathered all the information from the previous steps, it’s time to create your budget. After you have subtracted your fixed and variable expenses from your income, you will get an idea of the amount that you can work with. Be prepared to tackle the unexpected one-time expenses that come your way. You can then find ways to use the money effectively to achieve your short-term and long-term goals.
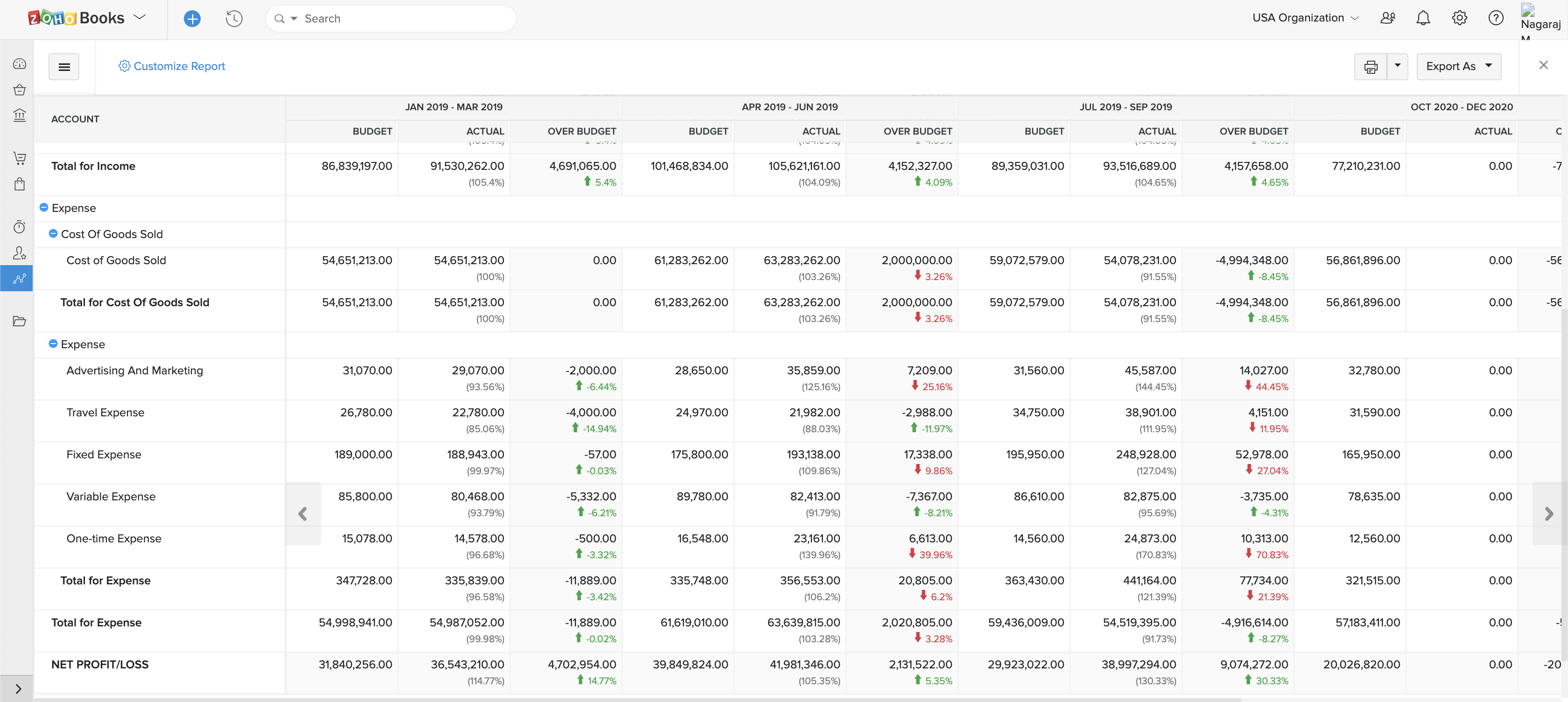
Role of accounting software in budgeting
Budgeting for a business is a large task, which is why you might need assistance. Creating a budget will involve analyzing costs, estimating revenue, and projecting cash flow. Having an accounting system in place will give you real-time information about your finances, helping you to create a feasible budget.
The key to creating a good budget is to evaluate the previous years’ data and draw realistic projections. An accounting system can give you access to all this information in one place, no matter when you need it.
The effectiveness of a budget also depends on how well any projected goals have been achieved by your business. To check this, an accounting system generates financial reports that record your actuals, and those can then be compared with the budget. Comparing your budget with your actuals is an important step to gauge the effectiveness of a budget.
Budgeting is an essential process, especially for small businesses, as it allows business owners to estimate and allocate money for different business activities. Preparing a budget also gives you a clear idea of the money that can be used to achieve business goals and ensure that there is enough in hand to handle a crisis. For small businesses, it might get a bit difficult to make estimations for the whole year as the initial stages of growing an organization are often volatile. In such cases, you can create smaller budget estimates for a duration of two or three months and keep reviewing it for better results. When an accounting system is introduced, the process becomes even more manageable. You can easily handle tasks like projecting cash flow or estimating costs, and you can set realistic goals for your business.
Related Posts
- Business Budget: What is it & Why is it important?
- How Is Cash Flow Calculated?
Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Great article, Easy to read, straight to the point, very informative.
Wonderful article! Just what I needed
a valuable information for person like me who doesn’t has finance background.
wonderful said,
I really like this article, it is very easy to read, gives an idea and try to make the budget process a much easier task
Simple and precise article
You might also like
Switch to smart accounting. try zoho books today.
How to create a business budget
Advertiser disclosure.
We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Our goal is to help you make smarter financial decisions by providing you with interactive tools and financial calculators, publishing original and objective content, by enabling you to conduct research and compare information for free - so that you can make financial decisions with confidence.
Bankrate has partnerships with issuers including, but not limited to, American Express, Bank of America, Capital One, Chase, Citi and Discover.
How We Make Money
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
- Share this article on Facebook Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter Twitter
- Share this article on LinkedIn Linkedin
- Share this article via email Email

- • Small business loans
- • Bad credit loans

- • Funding inequality
- Connect with Emily Maracle on LinkedIn Linkedin
The Bankrate promise
At Bankrate we strive to help you make smarter financial decisions. While we adhere to strict editorial integrity , this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for how we make money .
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. We’ve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts , who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our banking reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most — the best banks, latest rates, different types of accounts, money-saving tips and more — so you can feel confident as you’re managing your money.
Editorial integrity
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions.
Key Principles
We value your trust. Our mission is to provide readers with accurate and unbiased information, and we have editorial standards in place to ensure that happens. Our editors and reporters thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you’re reading is accurate. We maintain a firewall between our advertisers and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from our advertisers.
Editorial Independence
Bankrate’s editorial team writes on behalf of YOU – the reader. Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions. We follow strict guidelines to ensure that our editorial content is not influenced by advertisers. Our editorial team receives no direct compensation from advertisers, and our content is thoroughly fact-checked to ensure accuracy. So, whether you’re reading an article or a review, you can trust that you’re getting credible and dependable information.
How we make money
You have money questions. Bankrate has answers. Our experts have been helping you master your money for over four decades. We continually strive to provide consumers with the expert advice and tools needed to succeed throughout life’s financial journey.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that our content is honest and accurate. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions. The content created by our editorial staff is objective, factual, and not influenced by our advertisers.
We’re transparent about how we are able to bring quality content, competitive rates, and useful tools to you by explaining how we make money.
Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range, can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range of offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.
Our writers and editors used an in-house natural language generation platform to assist with portions of this article, allowing them to focus on adding information that is uniquely helpful. The article was reviewed, fact-checked and edited by our editorial staff prior to publication.
Key takeaways
- A business budget is a financial plan that helps estimate a company's revenue and expenses, making it an essential tool for small businesses
- The steps to creating a business budget include choosing budget and accounting software, listing expenses and forecasting revenue
- If a business finds itself in a budget deficit, strategies such as cutting costs, negotiating with suppliers and diversifying revenue streams can help
As a small business owner, keeping your finances organized through a business budget is crucial to running a successful company.
Business budgeting involves creating a financial plan that estimates future revenue and expenses to make informed financial decisions, which can ultimately move the needle on your business’s financial goals and help it grow in profitability.
What is a business budget?
A business budget is a financial plan that outlines the company’s current revenue and expenses. The budget also forecasts expected revenue that can be used for future business activities, such as purchasing equipment. It sets targets for your business’s revenue, expenses and profit and helps you determine if you’ll have more money coming in than you pay out.
A business budget is an essential tool that helps you make wise business decisions. Without it, it’s difficult to gauge your business’s financial health.
What is the difference between a cash flow statement and a business budget?
A cash flow statement (CFS) is a financial document that summarizes the movement of cash coming in and going out of a company. The CFS gauges how effectively a company manages its finances, including how it manages debt responsibilities and funds day-to-day operations.
It’s similar to a business budget in that you can see expenses and revenue. But while a budget gives a moment-in-time snapshot of your business’s financial performance compared to forecasts, the cash flow statement focuses on the actual inflows and outflows of money through your business.
Follow these steps to ensure a well-developed budget, from understanding your expenses to generating revenue and adjusting expenses to balance the budget.
1. Choose a budget and accounting software
First, you’ll want to store your expense and revenue information with accounting software to help you track your numbers and generate reports. Some software may also help you assign categories to the transactions, identify tax deductions and file taxes. Quickbooks is an example of accounting software.
Some business bank accounts also have accounting software built in, helping you stay organized by keeping your accounting and banking in one place.
2. List your business expenses
The next step in creating a small business budget is to list all your business expenses. Here are the types of expenses you want to include in your budget:
- Fixed expenses: Fixed expenses cost a fixed amount monthly or within the assessed period. Those costs include rent, insurance, salaries and loan payments.
- Variable expenses: Variable expenses can change monthly or over time, making them trickier to budget. This might include materials, direct labor, utility bills or marketing expenses.
- Annual or one-time costs: Some costs only occur a few times per year, while others you’ll only pay for as needed, such as buying new equipment. You still want to budget for these expenses by allocating a portion of your weekly or monthly budget toward one-time expenses.
- Contingency funds: Unexpected business costs can throw a wrench in your budget if not planned for. Such costs could include emergency repairs, necessary equipment purchases, sudden tax increases or unforeseen legal fees. To plan for these costs, you can create a contingency or emergency fund that’s separate from your operational budget.
- Maintenance costs: To allocate funds for maintenance costs, begin by including regular inspections and maintenance in your budget. Then, make sure to leave room for changes and unexpected maintenance costs.
3. Forecast your revenue
To estimate your future revenue, start by deciding on a timeline for your forecast. A good place to start is the previous 12 months. Your accounting software may also include revenue forecasting as one of its features, which can automate this step for you.
The timeline and your recent past growth can help you understand how much revenue you’ll generate in the future. Consider external factors that could drive revenue growth, such as planned business activities like expansion, marketing campaigns or new product launches.
You’ll also want to think about anything that might slow your growth. Many businesses experience seasonal fluctuations, which can impact your budget if you don’t plan for it. To account for these changes, list the minimum expenses required to keep your business running. Use your financial statements to understand these costs, and consider averaging out irregular expenses over the year to avoid surprises.
Ideally, your business should build a cash reserve during profitable periods to cover expenses during slower seasons. If necessary, consider various financing options, such as a business credit card or line of credit, that you can draw from to manage cash flow during peak or off times.
4. Calculate your profits
The next step in creating a business budget is to calculate your business profits. You can look at your total profits by calculating revenue minus expenses. That way, you see how much money you have to work with, called your working capital .
You should also understand your profit margins for each of your products and services, which can help you set prices or decide whether to offer a new product or service.
How to calculate your profit margins
To find out your gross profit margin, you’ll first need to calculate the gross profit. To calculate your business’s gross profit, subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your total revenue. COGS includes all the expenses related to producing your products and services.
Once you have the gross profit, use the gross profit margin formula: (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue x 100. This will give you a percentage that shows how much profit you gain from that particular product after accounting for the product’s costs.
5. Make a strategy for your working capital
Knowing what to do with extra revenue, which is your working capital, is crucial for managing your business finances and growth. Here’s how to get started with a financial strategy that propels your business goals forward:
- Set spending limits for different categories in your budget. When listing your expenses, you should have set a dollar amount for each category. You can estimate this by a monthly average or a general forecasted amount.
- Set realistic short- and long-term goals. These goals will motivate you to stick to your budget and guide your spending decisions.
- Compare your actual spending with your net income and priorities. Look at the areas you’re spending and consider whether you need to reallocate money to different categories. Consider separating expenses into business needs and extras.
- Adjust your budget and actual spending. Adjust your spending to ensure you do not overspend and can allocate money towards your goals. If you need to cut spending, consider the categories that are extras, such as types of marketing that you don’t know will generate a return on investment.
6. Review your budget and forecasts regularly
Finally, review your budget regularly. By frequently checking in on your budget, you can identify any discrepancies between your planned and actual expenses and adjust accordingly. This allows you to proactively handle any financial issues that may arise rather than reacting to them after they’ve become a problem.
Regular reviews also allow you to refine your budgeting process and improve its accuracy over time. Keep in mind that your budget is not set in stone but rather a tool to guide your financial decisions and help you achieve your business goals.
What to do if you have a deficit in your business budget
Finding a deficit in your small business budget can be alarming, but there are several strategies you can employ to handle this situation.
- Do a cash flow analysis. Begin by doing a cash flow analysis to review what your business is earning and spending money on. Identify potential problems and adjust the budget as needed to prevent overspending.
- Cut nonessential business costs. Cutting spending may involve eliminating nonessential costs and transferring funds from other categories to overspent categories. Your goal is a balanced or profitable budget.
- Negotiate with suppliers. Be transparent in your communications with suppliers and explain your quality standards and why you’re seeking cost reduction. Explore options for cost reduction that do not compromise quality, such as process improvements or ordering in larger quantities.
- Create a lean business model. By removing anything that doesn’t benefit your customer, your business can potentially save time and resources. Lean business models focus on continually improving processes and customer experience without adding additional resources, time or funds.
- Add revenue and diversify revenue streams. Raising revenue requires a realistic plan with measurable goals to increase sales and overall business income. You can also consider other products and services you could offer that would make your business profitable.
- Use financing to cover temporary gaps. Applying for a small business loan can help pay bills during an unplanned shortfall. Since this will add an expense to your budget, make sure you can handle the loan repayments and your regular expenses.
- Plan for a deficit. In some cases, a planned budget deficit might be a strategic decision, such as investing in new opportunities that promise long-term benefits.
Bottom line
Having a well-developed business budget is crucial for making informed decisions. You can effectively manage your small business’s finances by tracking and analyzing your business’s inflows and outflows, forecasting your expected revenue and adjusting your budget to stay balanced.
Even in the face of a budget deficit, there are various strategies you can use to keep your business profitable, including negotiating costs with your suppliers, assessing your business operations and offering new products and services.
With a solid business budget in place, you can confidently navigate financial challenges and drive long-term success for your small business.
Frequently asked questions
What are the benefits of a business budget, what are the components of a business budget, how do you calculate fixed and variable costs in a business budget.

Related Articles

How to get a small business loan without collateral

How to get a small business loan when self employed

How to finance a small business for the holidays

How to start a small business
Small Business Resources is now the Center for Business Empowerment.
Suggested Keywords
Center for Business Empowerment
How to create a budget for your business
January 16, 2024 | 7 minute read
If you want to increase the odds of having a successful small business, start by creating a budget. A budget is a powerful tool. It helps you understand how much money you have and what you’ve spent where — and provides clues about how much money you’ll need in the short and long term. It can also help shape key business decisions like whether to add staff and equipment or where to cut expenses to avoid cash flow issues .
A budget is critical, particularly at a time when companies are coping with rising costs. Seventy-nine percent of small business owners polled in Bank of America’s 2023 Small Business Owner Report said they are concerned about inflation and 68% said they are worried about commodity prices. Here’s how to create a budget and use it to make the best decisions today, tomorrow and in the future.
What is a business budget?
Simply put, a budget is a spending plan based on your business’ income and expenses. It shows your available capital, estimates spending and assists in predicting revenue. The information in your budget can help you plan your company’s next moves. A budget looks at activities for a specified time. Think of it as a tool to help you allocate resources toward the strategic priorities in your business plan.
What are the benefits of creating a business budget?
Budgeting enables you to allocate financial resources more effectively, track variances and make changes to your spending plan as needed. A budget provides a much-needed assist in maintaining daily operations, giving you the intel to deploy your cash more strategically so you don’t face a cash flow crunch. It can identify when you need to raise financing. Debt is a fact of life in many businesses. A budget can help you manage debts with controlled and planned financial activities.
A budget can also help you stay ready for the unexpected. Staying within your budget and creating a safety net for emergencies will give you a firmer financial foundation.
Types of business budgets
When it comes to business budgets, it’s not one and done. There are several types that may be helpful in your business.
Master budget
This type of budget uses inputs from financial statements, your cash forecast and your financial plan to create a single document you can use to keep your finger on the pulse of your business. Your management team can use it to plan the activities needed to reach business goals. Typically, small businesses use spreadsheets to create their master budgets or consider using budgeting software too, as it may help minimize mistakes.
Operating budget
This budget shows your projected revenue and expenses for a given period. Think of it as a profit and loss report , but for the future. The operating budget includes fixed and variable costs, as well as non-operating expenses. Capital expenditures are usually excluded from an operating budget. Each line item should be backed up with key details.
Fixed costs occur monthly.
Variable costs, like utilities , change depending on factors like usage.
Capital costs are one-time expenses, such as the purchase of a building.
The operating budget gives you a reality check on whether you’re spending according to plan. While this budget is often prepared at the start of each year, don’t set it and forget it. Update it throughout the year, be it monthly or quarterly, so you always know where your business stands.
Capital budget
Companies sometimes create a capital budget when they are looking to make a large purchase, such as a large piece of factory equipment or a new technology system that will require a substantial investment. This allows the finance team to determine the impact on cash flow and plan accordingly.
Cash budget or cash flow budget
This document will give you an estimate of how money comes in and goes out during a certain time horizon. You create a cash budget using the conclusions you draw from sales forecasts and production, and by estimating payables and receivables.
Labor budget
If you will hire employees , this type of budget is helpful in planning for the money you’ll need to meet payroll, not only for regular employees, but also for any temporary and seasonal staff.
Budgeting methods you can use
There’s more than one way to budget. Here are some common methods:
An incremental budget
This takes the current period’s budget or actual performance, uses it as a base and then adjusts it in incremental amounts to account for any increases in costs. Typically, when you put together an incremental budget, you use the rate of inflation as a guide for fine-tuning the amounts. One plus of budgeting this way is that it is relatively easy to do.
Zero-based budgeting
Here, you’re budgeting from scratch. You must scrutinize every expense or potential expense before deciding to add it to your budget. This helps you align your business goals with your expenses. Unlike other types of budgeting, it doesn’t focus on historical results. A zero-based budget is ideal when you’re looking to reduce expenses.
Activity-based budgeting
Actions speak louder than words. This type of budgeting looks at the inputs required to reach the targets or outputs set by the company. Say your business wants to achieve $5 million in revenue. First, you need to figure out the activities that need to happen to make that revenue a reality and then determine the costs of carrying out those activities.
Participative budgeting
There are more cooks in the kitchen with participative budgeting, which is often used by larger small businesses. Both middle management and lower levels of management share in the responsibility of putting together the budget. The budget begins with lower management then moves to middle managers before top management weighs in and signs off. An upside of this type of budgeting is that information is shared, and when management and staff are on the same page in terms of goals, they’re more likely to achieve those goals.
How to create a business budget
Creating a business budget takes several steps:
- Calculate your revenue . Include all your revenue streams, preferably over at least the last 12 months, to determine your monthly income. If your business is new, you can research what’s typical in your industry and use that as a guide to come up with estimates.
- Add up your fixed costs . Fixed costs are things like rent, payroll and debt repayment.
- Determine variable costs . In addition to utilities, these may include billable labor, materials, transaction fees and commissions.
Using a budget to make better decisions
If you make your budget a regular resource, you’ll be rewarded for your budgeting efforts. As you make spending decisions, consult your budget frequently and use it as a reality check. If you have budgeted for X amount and go beyond it, you’ll have some explaining to do, even if you’re only answering to yourself. Being disciplined can be challenging, but ultimately it will position your business for growth , both today and in the future.
Explore more

How to create a sales forecast

Understanding free cash flow
Important Disclosures and Information
QuickBooks is registered trademark of Intuit, Inc., used under license. Bank of America does not deliver and is not responsible for the products, services or performance of Intuit, Inc. You are responsible for separately purchasing QuickBooks, QuickBooks Online, or QuickBooks Online Payroll, and Bank of America makes no warranties nor accepts any liability for such software.
Internet access may be required. Internet service provider fees may apply. Other bank fees may apply. See the Business Schedule of Fees available at bankofamerica.com/businessfeesataglance for details.
Bank of America and/or its affiliates or service providers may receive compensation from third parties for clients' use of their services.
Bank of America, Merrill, their affiliates and advisors do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice. Consult your own legal and/or tax advisors before making any financial decisions. Any informational materials provided are for your discussion or review purposes only. The content on the Center for Business Empowerment (including, without limitations, third party and any Bank of America content) is provided “as is” and carries no express or implied warranties, or promise or guaranty of success. Bank of America does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, reliability, completeness, usefulness, non-infringement of intellectual property rights, or quality of any content, regardless of who originates that content, and disclaims the same to the extent allowable by law. All third party trademarks, service marks, trade names and logos referenced in this material are the property of their respective owners. Bank of America does not deliver and is not responsible for the products, services or performance of any third party.
Not all materials on the Center for Business Empowerment will be available in Spanish.
Certain links may direct you away from Bank of America to unaffiliated sites. Bank of America has not been involved in the preparation of the content supplied at unaffiliated sites and does not guarantee or assume any responsibility for their content. When you visit these sites, you are agreeing to all of their terms of use, including their privacy and security policies.
Credit cards, credit lines and loans are subject to credit approval and creditworthiness. Some restrictions may apply.
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated (also referred to as “MLPF&S" or “Merrill") makes available certain investment products sponsored, managed, distributed or provided by companies that are affiliates of Bank of America Corporation (“BofA Corp."). MLPF&S is a registered broker-dealer, registered investment adviser, Member SIPC , and a wholly owned subsidiary of BofA Corp.
Banking products are provided by Bank of America, N.A., and affiliated banks, Members FDIC, and wholly owned subsidiaries of BofA Corp.
“Bank of America” and “BofA Securities” are the marketing names used by the Global Banking and Global Markets division of Bank of America Corporation. Lending, derivatives, other commercial banking activities, and trading in certain financial instruments are performed globally by banking affiliates of Bank of America Corporation, including Bank of America, N.A., Member FDIC. Trading in securities and financial instruments, and strategic advisory, and other investment banking activities, are performed globally by investment banking affiliates of Bank of America Corporation (“Investment Banking Affiliates”), including, in the United States, BofA Securities, Inc., which is a registered broker-dealer and Member of SIPC , and, in other jurisdictions, by locally registered entities. BofA Securities, Inc. is a registered futures commission merchant with the CFTC and a member of the NFA.
Investment products:
The Best Free Business Budget Templates
Published: October 12, 2023
Business budgets are a source of truth for your income and expenses. That includes all the money you spend — from A/B testing your marketing campaigns to your monthly office rent.

While organizing the numbers may sound difficult, using a business budget template makes the process simple. Plus, there are thousands of business budget templates for you to choose from.

We’ll share seven budget templates that can help organize your finances. But first, you’ll learn about different types of business budgets and how to create one.

What is a Business Budget?
A business budget is a spending plan that estimates the revenue and expenses of a business for a period of time, typically monthly, quarterly, or yearly.
The business budget follows a set template, which you can fill in with estimated revenues, plus any recurring or expected business expenses.
For example, say your business is planning a website redesign. You'd need to break down the costs by category: software, content and design, testing, and more.
Having a clear breakdown will help you estimate how much each category will cost and compare it with the actual costs.
Image Source
Types of Budgets for a Business
Master budget, operating budget, cash budget, static budget, departmental budget, capital budget, labor budget, project budget.

Business budgets aren’t one size fits all. In fact, there are many different types of budgets that serve various purposes. Let’s dive into some commonly used budgets:
Think of a master budget as the superhero of budgets — it brings together all the individual budgets from different parts of your company into one big, consolidated plan. It covers everything from sales and production to marketing and finances.
It includes details like projected revenues, expenses, and profitability for each department or business unit. It also considers important financial aspects like cash flow, capital expenditures, and even creates a budgeted balance sheet to show the organization's financial position.
The master budget acts as a guide for decision-making, helps with strategic planning, and gives a clear picture of the overall financial health and performance of your company. It's like the master plan that ties everything together and helps the organization move in the right direction.
Your operating budget helps your company figure out how much money it expects to make and spend during a specific period, usually a year. It not only predicts the revenue your business will bring in, but also outlines expenses it will need to cover, like salaries, rent, bills, and other operational costs.
By comparing your actual expenses and revenue to the budgeted amounts, your company can see how it's performing and make adjustments if needed. It helps keep things in check, allowing your business to make wise financial decisions and stay on track with its goals.
.png)
Free Business Budget Templates
Manage your business, personal, and program spend on an annual, quarterly, and monthly basis.
- Personal Budget Template
- Annual Budget Template
- Program Budget Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A cash budget estimates the cash inflows and outflows of your business over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year. It provides a detailed projection of cash sources and uses, including revenue, expenses, and financing activities.
The cash budget helps you effectively manage your cash flow, plan for cash shortages or surpluses, evaluate the need for external financing, and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
By utilizing a cash budget, your business can ensure it has enough cash on hand to meet its financial obligations, navigate fluctuations, and seize growth opportunities.
A static budget is a financial plan that remains unchanged, regardless of actual sales or production volumes.
It’s typically created at the beginning of a budget period and doesn’t account for any fluctuations or changes in business conditions. It also assumes that all variables, such as sales, expenses, and production levels, will remain the same throughout the budget period.
While a static budget provides a baseline for comparison, it may not be realistic for businesses with fluctuating sales volumes or variable expenses.
A departmental budget focuses on the financial aspects of a specific department within your company, such as sales, marketing or human resources.
When creating a departmental budget, you may look at revenue sources like departmental sales, grants, and other sources of income. On the expense side, you consider costs such as salaries, supplies, equipment, and any other expenses unique to that department.
The goal of a departmental budget is to help the department manage its finances wisely. It acts as a guide for making decisions and allocating resources effectively. By comparing the actual numbers to the budgeted amounts, department heads can see if they're on track or if adjustments need to be made.
A capital budget is all about planning for big investments in the long term. It focuses on deciding where to spend money on things like upgrading equipment, maintaining facilities, developing new products, and hiring new employees.
The budget looks at the costs of buying new stuff, upgrading existing things, and even considers depreciation, which is when something loses value over time. It also considers the return on investment, like how much money these investments might bring in or how they could save costs in the future.
The budget also looks at different ways to finance these investments, whether it's through loans, leases, or other options. It's all about making smart decisions for the future, evaluating cash flow, and choosing investments that will help the company grow and succeed.
A labor budget helps you plan and manage the costs related to your employees. It involves figuring out how much your business will spend on wages, salaries, benefits, and other labor-related expenses.
To create a labor budget, you'll need to consider factors like how much work needs to be done, how many folks you'll need to get it done, and how much it'll all cost. This can help your business forecast and control labor-related expenses and ensure adequate staffing levels.
By having a labor budget in place, your business can monitor and analyze your labor costs to make informed decisions and optimize your resources effectively.
A project budget is the financial plan for a specific project.
Let's say you have an exciting new project you want to tackle. A project budget helps you figure out how much money you'll need and how it will be allocated. It covers everything from personnel to equipment and materials — basically, anything you'll need to make the project happen.
By creating a project budget, you can make sure the project is doable from a financial standpoint. It helps you keep track of how much you planned to spend versus how much you actually spend as you go along. That way, you have a clear idea of whether you're staying on track or if there are any financial challenges that need attention.
How to Create a Business Budget
While creating a business budget can be straightforward, the process may be more complex for larger companies with multiple revenue streams and expenses.
No matter the size of your business, here are the basic steps to creating a business budget.
1. Gather financial data.
Before you create a business budget, it’s important to gather insights from your past financial data. By looking at things like income statements, expense reports, and sales data, you can spot trends, learn from past experiences, and see where you can make improvements.
Going through your financial history helps you paint a true picture of your income and expenses. So, when you start creating your budget, you can set achievable targets and make sure your estimates match what's actually been happening in your business.
2. Find a template, or make a spreadsheet.
There are many free or paid budget templates online. You can start with an already existing budget template. We list a few helpful templates below.
You may also opt to make a spreadsheet with custom rows and columns based on your business.
3. Fill in revenues.
Once you have your template, start by listing all the sources of your business’ income. With a budget, you’re planning for the future, so you’ll also need to forecast revenue streams based on previous months or years. For a new small business budget, you’ll rely on your market research to estimate early revenue for your company.
When you estimate your revenue , you're essentially figuring out how much money you have to work with. This helps you decide where to allocate your resources and which expenses you can fund.
4. Subtract fixed costs for the time period.
Fixed costs are the recurring costs you have during each month, quarter, or year. Examples include insurance, rent for office space, website hosting, and internet.
The key thing to remember about fixed costs is that they stay relatively stable, regardless of changes in business activity. Even if your sales decrease or production slows down, these costs remain the same.
However, it's important to note that fixed costs can still change over the long term, such as when renegotiating lease agreements or adjusting employee salaries.
5. Consider variable costs.
Variable costs will change from time to time. Unlike fixed costs, variable costs increase or decrease as the level of production or sales changes.
Examples include raw materials needed to manufacture your products, packaging and shipping costs, utility bills, advertising costs, office supplies, and new software or technology.
You may always need to pay some variable costs, like utility bills. However, you can shift how much you spend toward other expenses, like advertising costs, when you have a lower-than-average estimated income.
6. Set aside time for business budget planning.
Unexpected expenses might come up, or you might want to save to expand your business. Either way, review your budget after including all expenses, fixed costs, and variable costs. Once completed, you can determine how much money you can save. It’s wise to create multiple savings accounts. One should be used for emergencies. The other holds money that can be spent on the business to drive growth.
Fill out the form to get the free templates.
How to manage a business budget.
There are a few key components to managing a healthy business budget.
Budget Preparation
The process all starts with properly preparing and planning the budget at the beginning of each month, quarter, or year. You can also create multiple budgets, some short-term and some long-term. During this stage, you will also set spending limits and create a system to regularly monitor the budget.
Budget Monitoring
In larger businesses, you might delegate budget tracking to multiple supervisors. But even if you’re a one-person show, keep a close eye on your budget. That means setting a time in your schedule each day or week to review the budget and track actual income and expenses. Be sure to compare the actual numbers to the estimates.
Budget Forecasting
With regular budget tracking, you always know how your business is doing. Check in regularly to determine how you are doing in terms of revenue and where you have losses. Find where you can minimize expenses and how you can move more money into savings.
Why is a Budget Important for a Business?
A budget is crucial for businesses. Without one, you could easily be drowning in expenses or unexpected costs.
The business budget helps with several operations. You can use a business budget to keep track of your finances, save money to help you grow the business or pay bonuses in the future, and prepare for unexpected expenses or emergencies.
You can also review your budget to determine when to take the next leap for your business. For example, you might be dreaming of a larger office building or the latest software, but you want to make sure you have a healthy net revenue before you make the purchase.
Best Free Business Budget Templates
1. marketing budget template.
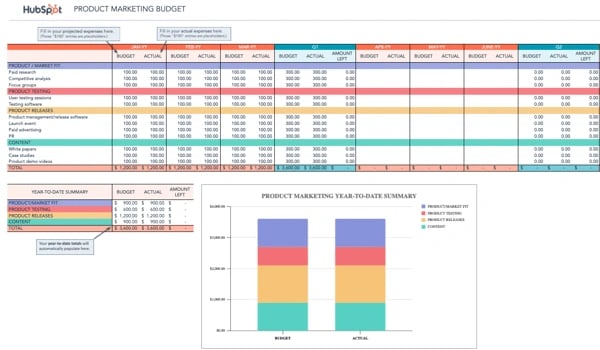
Knowing how to manage a marketing budget can be a challenge, but with helpful free templates like this marketing budget template bundle , you can track everything from advertising expenses to events and more.
This free bundle includes eight different templates, so you can create multiple budgets to help you determine how much money to put toward marketing, plus the return on your investment.
2. Small Business Budget Template
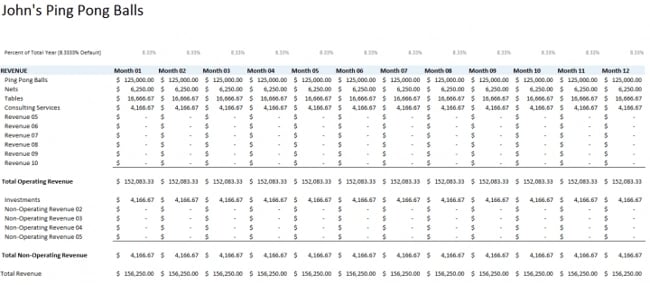
For small businesses, it can be hard to find the time to draw up a budget, but it’s crucial to help keep the business in good health.
Capterra offers a budget template specifically for small businesses. Plus, this template works with Excel. Start by inputting projections for the year. Then, the spreadsheet will project the month-to-month budget. You can input your actual revenue and expenses to compare, making profits and losses easy to spot.
3. Startup Budget Template
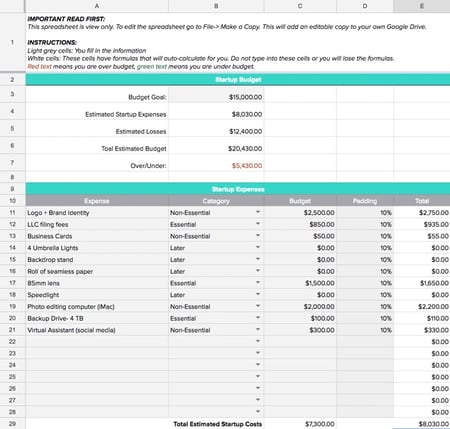
What if you don’t have any previous numbers to rely on to create profit and expense estimates? If you are a startup, this Gusto budget template will help you draw up a budget before your business is officially in the market. This will help you track all the expenses you need to get your business up and running, estimate your first revenues, and determine where to pinch pennies.
4. Free Business Budget Template
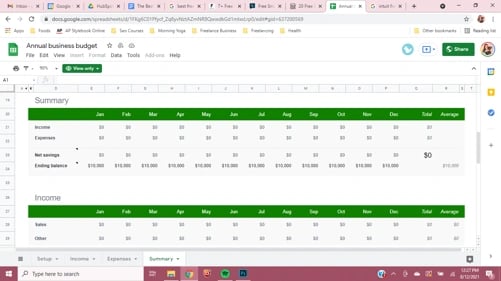
You might be familiar with Intuit. Many companies, big and small, rely on Intuit’s services like Quickbooks and TurboTax. Even if you don’t use the company’s paid financial services, you can take advantage of Intuit’s free budget template , which works in Google Sheets or Excel.
It features multiple spreadsheet tabs and simple instructions. You enter your revenue in one specific tab and expenses in another. You can also add additional tabs as needed. Then, like magic, the spreadsheet uses the data in the income and expense tabs to summarize the information. This template can even determine net savings and the ending balance.
5. Department Budget Sheet
A mid- to large-size company will have multiple departments, all with different budgetary needs. These budgets will all be consolidated into a massive, company-wide budget sheet. Having a specific template for each department can help teams keep track of spending and plan for growth.
This free template from Template.net works in either document or spreadsheet formats. This budget template can help different departments keep track of their income and spending.
6. Project Budget Template
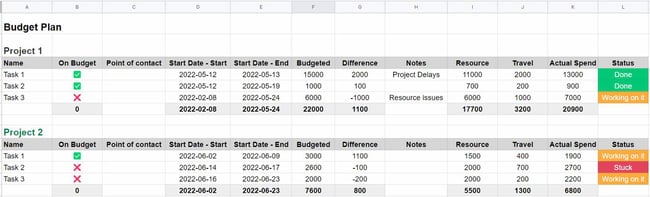
Every new project comes with expenses. This free budget template from Monday will help your team estimate costs before undertaking a project. You can easily spot if you're going over budget midway through a project so you can adjust.
This template is especially useful for small companies that are reporting budgets to clients and for in-house teams getting buy-in for complex projects.
7. Company Budget Template
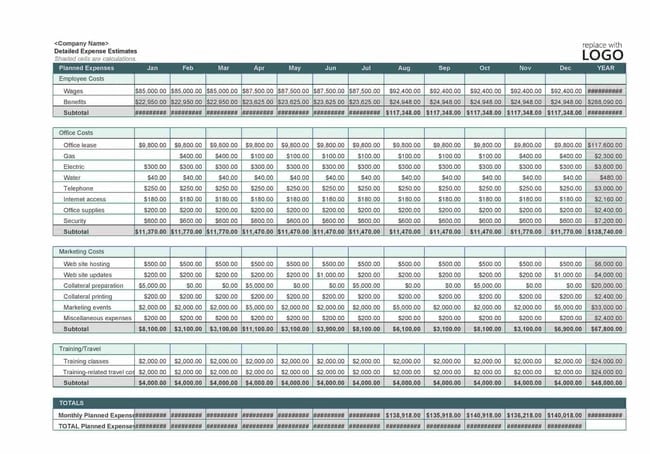
Want to keep track of every penny? Use this template from TemplateLab to draw up a detailed budget. The list of expenses includes fixed costs, employee costs, and variable costs. This business template can be especially useful for small businesses that want to keep track of expenses in one, comprehensive document.
Create a Business Budget to Help Your Company Grow
Making your first business budget can be daunting, especially if you have several revenue streams and expenses. Using a budget template can make getting started easy. And, once you get it set up, these templates are simple to replicate.
With little planning and regular monitoring, you can plan for the future of your business.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in September 2021 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![how to create a budget for a new business Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20to%20spend%20your%20marketing%20budget_featured.webp)
Marketing Budget: How Much Should Your Team Spend in 2024? [By Industry]
![how to create a budget for a new business How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20marketing%20leaders%20are%20navigating%20recession.webp)
How Marketing Leaders are Navigating Recession [New Data]
![how to create a budget for a new business 3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-marketers-are-navigating-recession.jpg)
3 Ways Marketers are Already Navigating Potential Recession [Data]
![how to create a budget for a new business Marketing Without a Budget? Use These 10 Tactics [Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing%20without%20budget.jpg)
Marketing Without a Budget? Use These 10 Tactics [Expert Tips]

24 Ways to Spend Your Marketing Budget Next Quarter

Startup Marketing Budget: How to Write an Incredible Budget for 2023
![how to create a budget for a new business How to Manage Your Entire Marketing Budget [Free Budget Planner Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/free-marketing-budget-templates_5.webp)
How to Manage Your Entire Marketing Budget [Free Budget Planner Templates]

10 Best Free Project Management Budget Templates for Marketers

What Marketing Leaders Are Investing in This Year

The Best Free Business Budget Worksheets
6 templates to manage your business, personal, and program spend on an annual, quarterly, and monthly basis.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Operations & Success
How To Create a Business Startup Budget
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/DanielRathburn-a16946b87e45469aaae5b4998db2397a.jpeg)
Questions to Ask Before You Begin Your Budget
- Step 1: Plan for "Day One" of Your Business Startup
Step 2: Estimate Monthly Fixed and Variable Expenses
Step 3: estimate monthly sales, step 4: create a cash-flow statement, tips for creating your business startup budget, frequently asked questions.
getty images / the balance
One of the most important tasks for building a start-up company is creating a budget . A proper budget allows you to view the business' expected revenue, expenses, and cash needs for current and future months, quarters, and calendar or fiscal years.
Since you have no past financial data to go on, you must create the budget using your best guess on income and expenses (otherwise known as a profit and loss statement) . Before you begin, consider why you need to spend the time to create a budget. Even if you don't need bank financing, creating a budget is still a valuable exercise for any new and continuing business.
Key Takeaways
- A budget is a key component of your startup business plan .
- The most difficult part of creating a budget for a new business is estimating your sales.
- You should start by calculating your "day one" costs—the expenses needed to open your physical or virtual doors and begin accepting customers.
- Next up is calculating your fixed and variable costs and your estimated monthly sales.
- Creating a cash-flow statement is also an important part of creating your new business' budget.
Some questions to ask yourself before you begin creating your start-up business' budget:
- What do you need to open the doors of your business on the first day?
- What will your fixed and variable costs be on a continuing basis?
- What can you contribute to keep costs low?
- What can you get as donations from friends and relatives?
- What can you do without?
Keep your "must-haves" to the minimum. The less you need for your business startup, the sooner you can start making a profit.
Step 1: Plan for "Day One" of Your Business Startup
Begin by determining what you will need on "day one" of your business—costs necessary to open the doors (or to take your website live) and begin accepting customers.
A "day one" start-up budget can be broken down into four categories (depending on your situation, some of the categories may not apply to your business.) The categories are:
Facilities Costs
Facilities costs include all the costs of setting up a leased or purchased location for your store, office, warehouse, or other building. These costs may be called leasehold improvements or tenant improvements. For example, you may need walls or a bathroom or a special secure area in your office or building.
If you are working from home, you probably won't have location costs but you may have costs to fix up a room in your home for an office or a small production area in your garage.
Facilities costs also include lease security deposits and signage.
Fixed Assets
What are the fixed assets (sometimes called capital expenditures ) such as furniture, equipment, and vehicles needed to set up your location and start your business? Fixed assets also include computers and machinery, furniture, and anything for your office, store, or warehouse that is needed to set up your business.
Materials and Supplies
Different from assets, materials and supplies include office supplies and any advertising and promotion materials. You will need an initial supply of these to get started.
Other Miscellaneous Costs
Miscellaneous costs include the initial fees to an accountant to help you set up your accounting system, local licenses and permits , insurance deposits, and legal fees to register your business with government entities (like your state) and prepare operating documents.
In your listing of these startup costs, include items you are contributing to the business, like a computer and office furniture. Note the cost of these items in your list so you can get credit for them as collateral for a business loan.
Fixed Expenses
Fixed expenses are costs that don't change and aren't dependent on the number of customers you have. Gather information on your fixed expenses each month. Some of the most common monthly fixed expenses include:
- Phones (business phones and cell phones)
- Credit card processing—monthly fees (transaction fees are variable)
- Website service fees
- Equipment lease payments
- Office supplies
- Dues and subscriptions to professional publications
- Advertising, publicity, and promotion commitments, like social media or continuing online ads
- Business insurance
- Professional fees (legal and accounting)
- Employee pay/benefits. (This category is semi-fixed, because you may be able to lower your employee costs at times.)
- Miscellaneous expenses
- Business loan payment
Variable Expenses
Variable expenses are expenses that will change with the number of customers you work with every month. These might include:
- Postage, mailing, packaging, and shipping costs
- Commissions on sales
- Production costs
- Raw materials
- The wholesale price of goods to be re-sold
If you have a service business, you may not need many variable expenses.
Estimating your profits and sales is probably the most difficult part of a budget because, for a new company, you don't have a track record on which to base your estimate. You might want to do three different sales projections:
- Best-case scenario, in which you show your most optimistic estimate for first-year sales.
- Worst-case scenario, in which you show your least optimistic scenario, with very little sales during the first six months to a year.
- Likely scenario, somewhere in between. The likely scenario would be the one to show your lender.
To be realistic in your budgeting, you must assume that not all sales will be collected. Depending on the type of business you have and the way customers pay, you might have a greater or smaller collections percentage.
Include a collections percentage along with your estimate of sales for each month. For example, if you estimate sales in month one to be $50,000 and your collection percentage is 85%, show your cash for the month to be $42,500.
Calculate the variable costs of sales for each month based on sales for the month. For example, if your estimated sales for a month are 2,500 units and your variable costs are $5.50 per unit, total variable costs for the month would be $13,750.
Add monthly variable costs to monthly fixed costs to get total monthly costs (expenses).
If you are selling products, you might want to calculate your break-even point to include with your budget. The break-even point shows when you will start making a profit on each sale.
Cash flow is literally the amount of money going into and out of your business each month.
Begin your cash flow statement by combining total costs with total collections of money from all sales for each month. Remember that sales and collections might be different, unless you have a cash or credit business. For the cash flow statement, you'll need to use collections.
The monthly cash flow totals should look something like this:
- Monthly sales $50,000
- Collected $42,500
- Total fixed costs $26,900
- Total variable costs $13,750
- Total cash balance $2,150
The $2,150 represents your total cash balance for the month, not your profit.
By changing your sales figures using the three scenarios above, you can see the result in your cash balance at the end of each month. This cash balance can give you information about your cash needs and how much you might need to borrow for working capital.
Managing your cash flow is a key tool for keeping your new business afloat. And cash flow is more important than profits. You can be making a profit on paper, but if you don't have money in the bank, your business won't be able to pay its bills.
- Use youraccounting software program to create your budget, so you can use existing accounts and make changes more easily. If you don't have an accounting software program, you can use a spreadsheet program.
- Most lenders require three years of cash flow statements on a month-by-month basis, and three years of quarterly and annual income statements (P&Ls).
- Income taxes are a variable expense, and you don't know what taxes you will have to pay until you calculate your net income. Don't include taxes in fixed expenses or variable expenses but make these a separate category.
Estimate sales LOW and expenses HIGH. Everything always costs more and takes longer than you think it will, and it will take longer to get sales going than you think it will.
What are the four steps to creating a budget for your small business?
One: Calculating your "day one" costs: the expenses absolutely necessary to open your business and begin accepting customers. Two: Estimating your monthly fixed and variable expenses. Three: Estimating monthly revenue. Four: Create a cash-flow statement.
What are the most common expenses for small businesses?
Some of the most common monthly fixed expenses for small businesses and start-ups include rent, utilities, equipment, website service fees, insurance, and labor. Common variable expenses include packaging, production, and shipping costs, sales commissions, and raw materials.
- Building Your Site
- Promote Your Site
- Entrepreneurship
- Design & Inspiration
- Tips & Tricks
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Business Budget Plan
A well-structured business budget plan is crucial for success. It serves as a financial stability and growth roadmap, allowing companies to allocate resources wisely and make informed decisions. Understanding the basics of business budgeting is essential for any entrepreneur or business owner looking to create a solid financial plan to help them achieve their goals.
The Importance of Business Budget Planning
Business budget planning is not just about crunching numbers; it's about setting clear financial goals and outlining strategies to achieve them. It provides a framework for managing expenses, maximizing revenue , and ensuring the long-term sustainability of a company. Without a well-thought-out budget plan, businesses may struggle to stay afloat in today's competitive market.
Understanding the Basics of Business Budget
At its core, a business budget is an estimate of future income and expenses based on historical data and current trends. It involves identifying all sources of revenue and categorizing various types of expenses, including fixed costs (rent, salaries) and variable costs (utilities, marketing). Understanding these fundamental concepts is essential for creating an effective budget plan.
Benefits of Creating a Business Budget Plan
The benefits of creating a business budget plan are manifold. It clarifies where money is being spent and helps identify areas where costs can be reduced or investments can be made to drive growth. Additionally, having a well-structured budget plan can instill confidence in stakeholders, such as investors or lenders who want to see evidence of sound financial management .
Now that we've laid the groundwork for understanding the importance of business budget planning and its basics, let's delve deeper into the process by assessing your financial situation and setting achievable goals.
Assessing Your Financial Situation

Sarah Horsman Template from Strikingly
Now that you understand the importance of business budget planning, it's time to assess your financial situation. This involves analyzing your current revenue and expenses, identifying fixed and variable costs, and projecting future income and expenses.
Analyzing Current Revenue and Expenses
You must clearly understand your current revenue and expenses to create a business budget plan that works for your company . This involves looking at your sales figures, incoming cash flow, and all the money going out of your business. By analyzing these numbers, you can gain valuable insights into where your money is coming from and where it's going.
Identifying Fixed and Variable Costs
When creating a business budget plan, it's crucial to distinguish between fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs, such as rent or salaries, remain constant regardless of your level of production or sales. Variable costs, like raw materials or shipping expenses, fluctuate with production levels or sales volume. Identifying these costs will help you make more accurate financial projections.
Projecting Future Income and Expenses
Looking ahead is an essential part of business budget planning. You can anticipate potential financial challenges or opportunities by projecting future income and expenses based on historical data and market trends. This will enable you to make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic investments.
Remember that creating a business budget plan is not just about crunching numbers; it's about setting the stage for sustainable growth and success in the long run.
Setting Financial Goals
Now that you understand the basics of business budget planning, it's time to set your financial goals . Establishing short-term and long-term objectives can create a roadmap for your business's financial success. Whether increasing revenue or reducing expenses, having clear goals will guide your budgeting decisions.
Establishing Short-term and Long-term Objectives
To effectively create a business budget plan, it's crucial to establish both short-term and long-term financial objectives. Short-term goals could include reducing overhead costs by a certain percentage within six months, while long-term goals might involve doubling your annual revenue within three years. These objectives provide direction for allocating funds and making strategic financial decisions.
Allocating Funds for Growth and Expansion
One of the key benefits of creating a business budget plan is the ability to allocate funds for growth and expansion. Whether you're looking to invest in new equipment, expand your product line, or open additional locations, setting aside funds in your budget allows you to pursue these opportunities without compromising your financial stability .
Planning for Contingencies and Emergencies
In business, unexpected events can have a significant impact on your finances. Planning for contingencies and emergencies is essential when creating a business budget plan. You can protect your business from potential financial hardships by setting aside a portion of your budget for unforeseen circumstances, such as economic downturns or equipment breakdowns.
Creating the Budget Plan
Now that you understand the importance of business budget planning, it's time to create a solid business budget plan. When choosing the right budgeting method, consider your company's size, industry, and financial goals. Whether it's zero- or activity-based budgeting, select a method that aligns with your business objectives and ensures accurate financial management .
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method
Selecting the right budgeting method is crucial for effective business budget planning. Zero-based budgeting involves justifying every expense from scratch, while activity-based budgeting focuses on cost allocation based on activities. Whichever method you choose, ensure it aligns with your company's financial objectives and provides a clear resource allocation roadmap.
Allocating Funds to Different Departments
When creating a business budget plan, allocating funds to different departments is essential based on their specific needs and priorities. Consider departmental goals, operational requirements, and revenue generation potential when distributing financial resources. This approach ensures each department has the necessary funds to function effectively within the business framework.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Budget as Needed
Once you've allocated funds to different departments in your business budget plan, monitoring and adjusting the budget as needed is essential. Regularly review your financial performance against the set targets and adjust based on changing market conditions or internal dynamics. Flexibility ensures that your business remains agile and responsive to evolving economic landscapes.
By carefully choosing the right budgeting method, allocating funds to different departments thoughtfully, and monitoring and adjusting the budget as needed, you can create a robust business budget plan that sets your company up for long-term success in managing its finances effectively.
Implementing the Budget Plan

Quantum Template from Strikingly
Now that you have created a solid business budget plan, it's time to implement it. This step involves communicating the budget to key stakeholders, training employees on budgetary guidelines, and integrating the budget into daily operations.
Communicating the Budget to Key Stakeholders
It is crucial to inform all relevant stakeholders about the business budget plan. This includes shareholders, managers, and other decision-makers who must know the financial goals and constraints. Clear communication will ensure everyone is on the same page and can work towards common objectives.
Training Employees on Budgetary Guidelines
Employees play a vital role in adhering to the budget plan. Providing them with comprehensive training on budgetary guidelines will help them understand their responsibilities in managing costs and staying within allocated funds. This will empower them to make informed decisions that align with the company's financial objectives.
Integrating the Budget into Daily Operations
Incorporating the business budget plan into daily operations requires a strategic approach. It involves aligning all activities with the financial goals outlined in the budget, ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently, and making adjustments as needed to stay within budgetary limits. This integration fosters a culture of financial responsibility throughout the organization.
By effectively implementing your business budget plan through clear communication, employee training, and seamless integration into daily operations, you can set your company up for financial success while achieving your long-term objectives.
Tracking and Evaluating Performance

Monitoring Budget Variance and Deviations
Once you have implemented your business budget plan, it's crucial to regularly monitor the budget variance and identify any deviations from the projected expenses and revenue. This will help you understand where adjustments need to be made and where you may exceed or fall short of your financial goals.
Conducting Regular Financial Reviews
Regular financial reviews are essential for evaluating the performance of your business budget plan. By conducting these reviews, you can assess whether your actual income and expenses align with what was projected in the budget. This will allow you to make informed decisions on where to allocate funds or where to cut back to stay on track with your financial objectives.
Making Informed Decisions Based on Budget Analysis
Analyzing the data from your business budget plan is key to making informed decisions for your company's future. By understanding how well your budget is performing, you can strategically plan for growth, expansion, and any potential contingencies or emergencies that may arise.
Continuously tracking and evaluating the performance of your business budget plan is vital for maintaining financial stability and achieving long-term success. By closely monitoring variance, conducting regular reviews, and making informed decisions based on budget analysis, you can ensure that your business stays on track toward its financial goals.
Tips for Successfully Implementing Your Business Budget Plan: Striking a Balance Between Dreams and Dollars
Every business owner knows the importance of a budget—it's the roadmap to financial stability and growth. But crafting a brilliant budget is only half the battle. The real test lies in implementation. How do you translate those meticulously planned numbers into tangible results? Here are some key tips to ensure your business budget plan becomes a reality, not just a document gathering dust on a shelf:
1. Set SMART Goals
Your budget shouldn't exist in a vacuum. It should be tightly woven into your business goals. But instead of vague aspirations, set SMART goals: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound . This clarity provides a clear direction for allocating resources and tracking progress.
2. Foster Collaboration
Budgeting isn't a solo act. Involve key stakeholders in the process, from department heads to team members. This collaborative approach fosters buy-in, ensures everyone understands their role in achieving financial goals, and harnesses diverse perspectives for smarter decision-making.
3. Embrace Transparency
Open communication is crucial. Share the budget with relevant team members, not just financial experts. This transparency builds trust, empowers employees to make informed decisions, and encourages a culture of financial responsibility.
4. Track and Monitor
Don't let your budget become a static document. Regularly track actual spending against the planned figures. Identify any discrepancies, analyze the causes, and make adjustments as needed. This active monitoring allows you to course-correct before small deviations snowball into major issues.
5. Leverage Technology

Strikingly Landing Page
- Easy to use. Strikingly is a user-friendly platform that is easy to use, even for those without experience in website design .
- Affordable. Strikingly offers a variety of affordable plans to fit any budget.
- Mobile-friendly. Strikingly's websites are mobile-friendly, so you can reach your customers wherever they are.

Strikingly Website on a Mobile Device
- SEO-friendly. Strikingly's websites are SEO-friendly so that you can improve your website's ranking in search results.
Strikingly is a valuable tool to help businesses create and manage their online presence . Strikingly's features can also be helpful for businesses when creating a business budget plan.
6. Review and Adapt
The business landscape is dynamic. Be prepared to adapt your budget as circumstances change. Regularly review your plan, considering market shifts, new opportunities, and unforeseen challenges. A flexible approach ensures your budget remains relevant and responsive to the ever-evolving environment.
7. Celebrate Successes
Don't forget to celebrate your wins! Recognizing positive financial milestones and acknowledging the collective effort motivates everyone and reinforces the importance of adhering to the budget plan.
8. Build a Culture of Accountability
Create a culture where all share financial responsibility. Hold yourself and your team accountable for staying within budget limits. This fosters a sense of ownership and promotes responsible financial behavior across the organization.
9. Communicate Effectively
Regularly communicate budget updates, performance metrics, and any necessary adjustments to the team. This transparency keeps everyone informed, engaged, and empowered to contribute to the business's financial success.
10. Continuously Improve
Never stop learning and evolving. Regularly evaluate your budgeting process, identify areas for improvement, and implement new strategies to optimize your financial management. Remember, a successful budget is a living document, constantly adapting and growing alongside your business.
By following these tips and embracing tools like Strikingly , you can transform your business budget plan from a theoretical framework into a powerful tool for driving growth and achieving your financial aspirations. Remember, successful budgeting is a journey, not a destination. It requires ongoing commitment, collaboration, and a continuous focus on improvement. So, embark on your financial journey confidently and watch your business reach new heights of success.
A well-structured business budget plan can lead to long-term financial stability and growth. It helps identify areas for cost savings, allocate funds for expansion, and plan for contingencies, ultimately leading to improved profitability and sustainability for your business.
Remember that creating a well-structured business budget plan is crucial for the success and sustainability of your business. By following these steps and incorporating these tips into your planning process, you can ensure that your business is on the path to financial success and growth.
Trusted by millions of entrepreneurs & creatives.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Prepare a Budget for an Organization: 4 Steps

- 16 Nov 2021
An organization’s budget dictates how it leverages capital to work toward goals. For this reason, the ability to prepare a budget is one of the most crucial skills for any business leader —whether a current or aspiring entrepreneur, executive, functional lead, or manager.
Before preparing your first organizational budget, it’s important to understand what goes into a budget and the key steps involved in creating one.
What Is a Budget?
A budget is a document businesses use to track income and expenses in a detailed enough way to make operational decisions.
Budgets are typically forward-looking in nature. Income is based on projections and estimates for the periods they cover, as are expenses. For this reason, organizations often create both short- (monthly or quarterly) and long-term (annual) budgets, where the short-term budget is regularly adjusted to ensure the long-term budget stays on track.
Access your free e-book today.
Most organizations also prepare what’s known as an “actual budget” or “actual report” to compare estimates against reality following the period covered by the budget. This allows an organization to understand where it went wrong in the budgeting process and adjust estimates moving forward.
Budget vs. Cash Flow Statement
If the definition above sounds similar to a cash flow statement , you’re right: Your organization’s budget and cash flow statement are similar in that they both monitor the flow of money into and out of your business. Yet, they differ in key ways.
First, a budget typically offers more granular details about how money is spent than a cash flow statement does. This provides greater context for making tactical business decisions, such as considering where to trim business expenses.
Related: The Beginner’s Guide to Reading & Understanding Financial Statements
Second, a budget is, quite literally, a tool used to direct work done within an organization. The cash flow statement plays a different role by offering a higher-level overview of how money moves into, throughout, and out of an organization.
Instead of thinking of the two documents as competing, view them as complementary, with each playing a role in driving your business’s performance.
Steps to Prepare a Budget for Your Organization
The steps below can be followed whether creating a budget for a project, initiative, department, or entire organization.
1. Understand Your Organization’s Goals
Before you compile your budget, it’s important to have a firm understanding of the goals your organization is working toward in the period covered by it. By understanding those goals, you can prepare a budget that aligns with and facilitates them.
Related: The Advantages of Data-Driven Decision-Making
For example, consider a business that regularly experiences year-over-year revenue growth that’s offset by rising expenses. That organization might benefit from focusing efforts on better controlling expenses during the budgeting process.
Alternatively, consider a company launching a new product or service. The company may invest more heavily in the fledgling business line to grow it. With this goal, the company may need to trim expenses or growth initiatives elsewhere in its budget.
2. Estimate Your Income for the Period Covered by the Budget
To allocate funds for business expenses, you first need to determine your income and cash flow for the period to the best of your ability.
Depending on the nature of your organization, this can be a simple or complicated process. For example, a business that sells products or services to known clients locked in with contracts will likely have an easier time estimating income than a business that depends on active sales activity. In the second case, it would be important to reference historical sales and marketing data to understand whether the market is changing in a way that might cause you to miss or exceed historical trends.
Related: How to Read & Understand an Income Statement
Beyond income from sales activity, you should include other income sources, such as returns on investments, asset sales, and bond or share offerings.

3. Identify Your Expenses
Once you understand your projected income for the period, you need to estimate your expenses. This process involves three main categories: fixed costs, variable expenses, and one-time expenses.
Fixed costs are any expenses that remain constant over time and don’t dramatically vary from week to week or month to month. In many cases, those expenses are locked in by some form of contract, making it easy to anticipate and account for them. This category usually includes expenses related to overhead, such as rent payments and utilities. Phone, data, and software subscriptions can also fall into this category, along with debt payments. Any expense that’s regular and expected should be included.
Related: 6 Budgeting Tips for Managers
Variable expenses are those your business incurs, which vary over time depending on several factors, including sales activities. Your shipping and distribution costs, for example, are likely to be higher during a period when you sell more product than one when you sell less product. Likewise, utilities such as water, gas, and electricity will be higher during periods of increased use. This is especially true for businesses that manufacture their own products. Sales commissions, materials costs, and labor costs are other examples of variable expenses.
Both fixed expenses and variable expenses are recurring in nature, making it easy to account for them (even if variable expenses must be projected). One-time expenses , also called “one-time spends,” don’t recur and happen more rarely. Purchasing equipment or facilities, developing a new product or service, hiring a consultant, and handling a security breach are all examples of one-time expenses. Understanding major initiatives—and what it will take to accomplish them—and what you’ve spent in previous years on similar expenses can help account for them in your budget, even if you’re unsure of their exact values.
4. Determine Your Budget Surplus or Deficit
After you’ve accounted for all your income and expenses, you can apply them to your budget. This is where you determine whether you have enough projected income to cover all your expenses.
If you have more than enough income to cover your expenses, you have a budget surplus. Knowing this, you should determine how to use additional funds best. You may, for example, move the money into a rainy day fund you can access should your actual income fall short of projections. Alternatively, you may deploy the funds to grow your business.
On the other hand, if your expenses exceed your income, you have a budget deficit. At this point, you must identify the best path forward to close the gap. Can you bring in additional funds by selling more aggressively? Can you lower your fixed or variable expenses? Would you consider selling bonds or shares of company stock to infuse the business with additional capital?

An Important Financial Statement
The person responsible for generating a budget varies depending on an organization’s nature and its budgetary goals. An entrepreneur or small business owner, for example, is likely to prepare an organizational budget on their own. Meanwhile, a larger organization may rely on a member of the accounting department to generate a budget for the entire business. Individual department heads or functional leads might also be called on to submit budget proposals for their teams.
With this in mind, anyone who aspires to start their own business or move into an organizational leadership position can benefit from learning how to prepare a budget.
Do you want to take your career to the next level? Consider enrolling in our eight-week Financial Accounting course or three-course Credential of Readiness (CORe) program to learn financial concepts that can enable you to unlock critical insights into business performance and potential. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
Get expert advice delivered straight to your inbox.
How to Make a Budget: Your Step-by-Step Guide
12 Min Read | Jan 4, 2024

Making a budget might seem overwhelming at first, but hear this: You can do it. How? By breaking down the process a bit. Because no one eats an elephant by swallowing it whole. (You go one bite at a time.) And no one leaps into budgeting like a pro. (You take it one step at a time.)
So, here we go—bite by bite, step by step. Here’s how to make a budget in five steps.
- List Your Income
- List Your Expenses
- Subtract Expenses From Income
- Track Your Transactions
- Make a New Budget Before the Month Begins
What Is a Budget?
Real quick though, let’s define the word budget . A budget is just a plan. It’s not a restriction on spending—it’s a plan for what you’ll do with your money. It’s a plan for what’s coming in and what’s going out.
When you learn how to make a budget—and do it every month—you’re giving your money purpose. You’re taking control. Goodbye, money anxiety. Hello, money goals.
Keep reading to see how to make it happen so you can make a budget that works for you.
How to Make a Budget in 5 Steps
No matter how you feel about budgeting right now, no matter what money goals you have, and no matter your income—you can make (and keep!) a budget in just five steps.
But first, decide if you’re making a budget on paper, with a spreadsheet, or in an app. (I know a great app called EveryDollar . It’s what I use to budget—and it’s the best. Just saying.) Either way, it’s totally okay to start by writing out everything on a sheet of paper.
Pro tip: Before you dive into the steps, open up your online bank account or grab your bank statements. That will give you the info you need as you start filling out numbers in your budget.
Step 1: List Your Income
Income is any money you plan to get during that month—that means your normal paychecks and any extra money coming your way through a side hustle, garage sale, freelance work or anything like that.
You work weekends as a barista or babysitter? That’s income, and it goes in your budget.
Create separate income budget lines for every paycheck you (and your spouse) get, plus anything extra coming in. (Note: You’re working with net income here, meaning what you bring in after taxes or anything else that’s taken out of your paycheck.) Here’s an example:
His Paycheck 1: $1,500 Her Paycheck 1: $1,500 His Paycheck 2: $1,500 Her Paycheck 2: $1,500 Side Hustle: $500
Total Income: $6,500
If you’ve got an irregular income , take a look at what you’ve made the last few months and list the lowest amount as this month’s planned income budget line. You can adjust later in the month if you make more and add that extra money to your money goal or another budget line.
Step 2: List Your Expenses
Now that you’ve planned for the money coming in, you can plan for the money going out. It’s time to list your expenses! (Yep, this is when that bank account or statement gets super helpful.)
Pro tip: When you’re making a budget, before you put in all the things you’ll pay for this month, set aside money for giving. I believe in putting 10% of your income here—it’s a great way to start your budget with a spirit of generosity ! Next, budget for your savings goals, like an emergency fund (depending on your Baby Step, which I'll talk about more in a minute). You've got to pay yourself first before you pay everyone else!
What’s next?
Cover your Four Walls. That’s food, utilities, shelter and transportation . Make a budget category for each of these and create budget lines underneath for your specific expenses.
Start budgeting with EveryDollar today!
Think of a budget category as a folder and the lines as the files inside it. Or the category is like a playlist, and the lines are like the songs. Or . . . okay, you get it.
Here’s what it might look like for you (but with your numbers, of course!):
Budget Category: Food Groceries: $700
Budget Category: Utilities Electricity: $130 Water: $60 Natural Gas: $40
Budget Category: Shelter/Housing Mortgage: $1,450 HOA Fees: $50
Budget Category: Transportation Gasoline: $180
Some of these are called fixed expenses —aka the expenses that stay the same every month, like your rent or mortgage.
Other expenses change up, like groceries or gasoline. By the way, that grocery budget line is super hard to guess at first, so just start with a really good estimate based on your past spending. You’ll learn better what you actually need here in the months ahead.
Next, list all other monthly expenses. Start with the essentials: I’m talking about insurance, debt , childcare, etc. Then work in a miscellaneous line and any nonessentials like personal spending, fun money and entertainment.
Then use your online bank account or those bank statements to estimate what you plan to spend for everything.
Here’s a quick callout. If you’re working to save money, get out of debt , or hit some other money goal, you’ll get there way quicker if you cut back on the nonessential spending.
If you don’t know what goal to focus on right now, check out the 7 Baby Steps . This plan breaks the most important money goals into easy-to-understand, actionable steps!
Make new budget categories for your new budget lines. Of course, if you spend money eating out, you can just add a line called Restaurants under your food category—as long as you remember groceries are a necessity , but drive-thrus or fancy three-course meals out are not .
Step 3: Subtract Expenses From Income
Math time! (It won’t be too bad. But it is totally necessary. Let’s do this.)
Subtract all your expenses from your income. This number should equal zero, meaning you just made a zero-based budget.
This is key: A zero-based budget doesn’t mean you let your bank account reach zero. (Leave a little buffer in there of about $100–300.) It also doesn’t mean you blow all your money.
Zero-based budgeting just means you give every dollar a job to do : spending, giving, saving or paying off debt . It’s all accounted for and given a purpose. It’s the reason I love this method.
You work hard for your money, right? Well, it should work hard for you! Every. Single. Dollar.
Okay, though, what do you do if you subtract your expenses from your income—and you’ve got money left over? Don’t leave it there. You’ll end up mindlessly spending it on coffees , convenience store candy, and those one-click deals of the day. Get those dollars to work by putting any “extra” money toward your current money goal .
What if you end up with a negative number? It’ll be okay. You just need to cut expenses until your income minus your expenses equals zero. (Hint: Start with those eating-out and entertainment budget lines. If restaurants are your love language, this will hit hard, but you can’t spend more than you make. You’ve got this!)
If you’re still struggling to make ends meet, don’t forget the power of the side hustle or overtime. Just remember not to increase your spending when you increase your income. Your extra cash needs to cover your budgeted expenses.
Is the math stressing you out a little? Listen, let EveryDollar do that for you. Our free budgeting app is made for this zero-based budgeting stuff, and you won’t have to keep running back to the calculator to get it right.
Okay, so that’s it for making a budget. The next two steps are all about sticking with it .
Step 4: Track Your Transactions (All Month Long)
Ready for one of the biggest secrets for how to budget—and do it really, really well? Good, because I don’t want to keep it a secret. Here it is: Track. Your. Transactions.
Every single one.
Putting the plan on paper, in your spreadsheet, or in your app is just a bunch of good intentions without this step. It’s like writing down a goal to run a marathon, making a training plan, lacing up your shoes . . . and flopping on the couch with a bag of donuts.
What am I even talking about? Tracking your transactions means you account for everything that happens with your money all month long .
When you fill up the gas tank , subtract that expense from transportation. When you pay the rent, subtract that expense from housing. When you buy a coffee on the way to the office, subtract that expense from your personal spending (or whatever budget line you made for the perk that helps you work).
Track your transactions regularly. That might be once a week. Or at the end of each day. Or it might mean you log a purchase before you leave the grocery store parking lot. Whatever works for you and gets every expense tracked.
As you’re tracking, make adjustments as you need to. Yes, really! This is your budget. You make it work for you. If the electricity bill comes in higher than you thought, just tweak another budget line to make up for it. If the water bill comes in lower, then celebrate and move that money over to your current money goal—or add it to a budget line that went over.
I can’t say enough good things about tracking your transactions. But to sum up, I love this budgeting step because it’s how you:
- Stay accountable to your budget, yourself and your money goals. (Also your spouse, if you’re married! And remember EveryDollar? You two can share an account so you’re budgeting as a team!) No secrets. No pretending a purchase didn’t happen.
- Keep from overspending, because as you enter expenses, you see what you have left in every budget line! Instantly, you’ll know what’s left so you don’t overspend.
- Stay on top of the budget. Your budget is not a set-it-and-forget-it project. It’s not a slow cooker. When you track transactions, you get in your budget all the time, and you can make adjustments so you know where your money is going—all the time.
- Learn and adjust your spending habits so you can get back on track with your goals and finally make them happen. One monthly budget at a time.
Step 5: Make a New Budget Before the Month Begins
While your budget shouldn’t change too much from month to month, the fact is, no two months are exactly the same. That’s why you create a new budget every single month —before the month begins. Then you can stare down certain expenses and say, “You will not be a surprise to my bank account, thank you very much.”
When you’re ready to start your next budget, just copy over this month’s budget to the next, and then make changes for anything new that’s coming.
Here are some examples of month-specific expenses to prep for:
- Celebrations like birthdays and anniversaries: Never forget those.
- Holidays: Do you need decor, gifts or a feast at the ready?
- Seasonal purchases: Don’t forget to budget for back-to-school season , fall coffee-flavor releases, and your spring kickball league.
- Semiannual expenses: Do you pay your auto insurance twice a year? Do you need an oil change next month?
- Annual expenses: Is it time for your yearly eye exam? Do you need to budget for your pet to get his shots at the vet?
Here’s one way to handle getting these changing expenses into your budget:
- Create a budget category called something like Month-Specific Stuff or Alternating Expenses or Discretionary (if you like huge words).
- Then add whatever lines you need for that month and delete the ones from last month you no longer need.
Where does the money come from? You can cut back spending somewhere else and move that money over to this category. Taking $5–20 from a couple budget lines really adds up. Literally. Or if you can, crank up your income for the month. (Time for an extra freelance gig!)
Hey, if this part sounds complicated or clunky, that’s because it can be at the beginning. It takes people about three months to really get the hang of budgeting, so give yourself some grace and keep working on it! The benefits of budgeting will far outweigh the effort.
Why Making a Budget Is So Important
What are the benefits? Why is it worth it? Because when you budget, you’re telling your money where to go—so you don’t have to wonder where it went. You’re showing your money who’s in charge. (You.)
Budgeting is how you make any money goals happen—it’s how you make progress with your finances! It puts you in control. It gives you permission to spend your money your way.
I could go on and on and on because I honestly believe making a budget—and living that budgeting life—is one of the most important decisions you’ll make with your finances.
How to Make a Budget With Confidence
That’s it! That’s how to make a budget—and why you should. So, now it’s time to do it! It’s time to get confident with your money.
But what about being confident with budgeting? Hey, let EveryDollar help! This free tool makes budgeting easier, which is always a win. Download EveryDollar. Budget every month. You got this!
Save more. Spend better. Budget confidently.
Get EveryDollar: the free app that makes creating—and keeping—a budget simple . (Yes, please.)
Did you find this article helpful? Share it!

About the author
Rachel Cruze
Rachel Cruze is a #1 New York Times bestselling author, financial expert, host of The Rachel Cruze Show, and co-host of Smart Money Happy Hour. Rachel writes and speaks on personal finance, budgeting, investing and money trends. As a co-host of The Ramsey Show, America’s second-largest talk radio show, Rachel reaches millions of weekly listeners with her personal finance advice. She’s appeared on Good Morning America and Fox News and been featured in TIME, REAL SIMPLE and Women’s Health, among others. Through her shows, books, syndicated columns and speaking events, Rachel shares fun, practical ways to take control of your money and create a life you love. Learn More.
How to Create a Zero-Based Budget
Zero-based budgeting is a method of budgeting where your income minus expenses equals zero. Follow these steps to make a zero-based budget each month.
How to Set Financial Goals: 6 Steps
Want to make more progress with your money? Setting the right financial goals is the first step!
- Personal Finance
- Managing Wealth
- Small Business
- Corporate & Institutional
- Our Commitments
- Explore Products & Solutions
- Spending Responsibly
How to Make a Budget Spreadsheet

- A budget spreadsheet simplifies tracking income and expenses, aligning daily spending with overall financial goals.
- Key steps include choosing a user-friendly tool like Excel ® or Google Sheets ® , setting up detailed budget categories, and deciding on a tracking period (monthly, quarterly, yearly).
- Effective budget management involves inputting actual financial data, utilizing formulas for automatic calculations, and comparing planned versus actual spending.
- Regular updates to the budget spreadsheet are crucial for adapting to financial changes and staying on track with goals.
A budget is a powerful tool that helps you make informed spending and savings decisions. It provides the freedom to spend with confidence, knowing your actions align with bigger-picture financial goals.
Tracking income and expenses by hand may seem like a hassle, but a well-designed budget spreadsheet makes it easy.
Knowing how to make a budget spreadsheet that’s customized to your needs allows you to effectively track finances without the need for expensive software or specialized financial knowledge.
In the following guide, we’ll walk through the process, from selecting the right platform to categorizing expenses and monitoring your progress. It’s an easy solution you can implement right away.
What Is a Budget Spreadsheet and How Is It Used?
A budget spreadsheet is a simple tool for organizing and tracking income and expenses. It provides a clear view of money coming in and going out over a set period of time, typically weekly or monthly. Assigning categories to each income and expense makes it easy to identify trends and uncover potential savings opportunities. Pre-planning weekly or monthly spending also helps ensure there’s enough left over to allocate toward saving for short-term and longer-term financial goals.
Regularly updating and reviewing a budget spreadsheet turns it into an active financial management tool. It helps you spot patterns, such as seasonal increases in utility bills, and proactively adjust the spending and savings goals to reflect changes in income, expenses, or financial priorities.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Budget Spreadsheet
There is a wide range of tools and software for creating and managing a budget, but how do you make a budget spreadsheet that works well over the long term? To choose a platform that suits your needs, consider the following factors:
- Ease of use : The best budgeting tool is one you use consistently. Look for an option that’s easy to set up and navigate. This will help ensure you’re comfortable making regular updates.
- Accessibility : Consider whether the tool is accessible across devices, such as your phone, tablet, or computer.
- Cost : Free options often work as well as paid tools, allowing for simple budget tracking without additional expense.
- Advanced features : Consider whether the tool offers advanced features such as customizable categories, automatic calculations, and charts and graphs to enhance the budgeting experience.
Popular Spreadsheet Tools: Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets
Microsoft Excel ® and Google Sheets ® are two of the most popular spreadsheet programs. Both are user-friendly and offer a range of budgeting features.
Microsoft Office Excel
Excel, the spreadsheet tool included in Microsoft Office Suite ® , is ideal for those who prefer a detailed budgeting approach and want customizable options. It comes with a range of budgeting templates, allowing for quick, easy setup without the need to manually create rows, columns, and formulas. You’ll find options available for everything from a standard household budget to budgets made specifically for planning events or tracking holiday spending .
Google Sheets
Google Sheets is a user-friendly option that is free to use with a Google account. It includes several pre-made budget templates, including monthly and annual budgets. Sheets are stored in Google Drive ® , a cloud-based platform that allows you to access the budget from wherever you are. This ensures the budget is available from your computer, tablet, or smartphone.
The Advantages Of Using a Premade Template
Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets both offer the ability to build a budget spreadsheet from scratch. However, choosing a pre-made budget template offers a ready-made structure, saving time and allowing you to focus on entering financial information right away.
The templates are designed with the user experience in mind, offering clear categories and useful formulas. While they provide a ready-to-use foundation, they’re often fully editable, allowing for small changes to better align the budget spreadsheet with your personal financial goals.
Setting Up Your Budget Categories and Time Frame
Organizing financial transactions into relevant categories helps you easily identify spending habits and make adjustments to help maintain a positive cash flow. The number of categories used depends on your situation, goals, and personal preferences. Begin with two primary categories: Income and Expenses. Then, break these down into relevant sub-categories.
Income Categories
When tracking your income, you may include categories such as:
- Rental income
- Investment income
- Freelance income
Expense Categories
There are several options for tracking budget categories. Depending on your goals and personal preferences, you may choose broad categories or track with greater detail.
General vs. Detailed
General expense categories may include items such as:
- Mortgage/rent
- Credit card payments
- Pet expenses
If you prefer more detail, consider tracking individual bills by creating another layer of sub-categories. For example, the utilities category may include:
- Electric bill
- Heating bill
While detailed categories take more time to set up initially, the additional information can help you identify areas where you could cut costs.
Fixed vs. Variable
You may also categorize expenses based on whether they are fixed or variable. For example, fixed expenses include rent or mortgage, insurance premiums, car payments, and other expenses that remain fairly consistent from month to month.
Variable expenses include items that change from month to month, such as dining out, hobbies, and shopping. Since variable expenses are typically easier to cut if necessary, adding this category can help with financial evaluations.
Savings and Investments
Finally, consider adding a budget category for savings and investments . This may include:
- Contributions to savings accounts
- Emergency fund savings
- Retirement account contributions
- Contributions to other investments
Budgeting for savings and investments helps prioritize these goals, ensuring you’ve set aside money for planned contributions rather than relying on leftover funds.
Determining Your Budget Period
Once you’ve determined key categories, decide how frequently to track, review, and update the budget. Many individuals use monthly or weekly tracking. However, depending on your needs, you may track more or less frequently. Quarterly, annual, or multi-year tracking can help with bigger-picture goals, while weekly or daily tracking helps you stay focused on short-term, specific goals.
You may find it helpful to combine several time periods, for example, using an annual budget to gain clarity on long-term trends and habits while tracking more frequently to allow for real-time adjustments.
Crafting Your Budget: Entering Income and Expenses
Now that the spreadsheet is ready, it’s time to input your financial information. While entering data and crunching numbers may not feel exciting, keep in mind that the spreadsheet will perform all of the calculations almost instantly — turning a potentially tedious task into a quick and satisfying experience. Here’s how to get started.
1. Input Your Data
Since you may not remember all income and expenses offhand, begin by pulling out your last few bank account and credit card statements. Enter each deposit and expense as a separate line item and choose the correct categories.
2. Utilize Formulas
Once you’ve entered all the data, use formulas to quickly perform key calculations, such as totaling expenses, calculating the difference between your income and expenses, or averaging spending to find monthly patterns.
If you’ve used a budget spreadsheet, the formulas are likely already included and will run automatically. Many spreadsheet tools also include pre-made formulas, which you can add for additional analysis.
3. Compare Planned vs. Actual Income and Expenses
Consider setting up separate columns for your projected and actual income and expenses, plus a column for the variance between these figures. This setup offers clear insights into how closely you’re meeting financial targets and areas that need attention. If this is not part of the premade template, add formulas to automatically complete the calculations.
Regularly Monitoring and Updating Your Budget
Many situations can affect your budget, from a pay raise to a change in expenses or a shift in financial goals. It’s important to regularly review and update the spreadsheet to ensure it remains an effective financial tool. During the review process, make changes as needed so it continues to accurately reflect your financial situation.
Regularly reviewing your budget spreadsheet also helps highlight spending patterns, identify areas for savings, and ensure your finances remain in alignment with short-term and longer-term goals.
Generally, a monthly update is sufficient. However, if you’re actively working to reduce debt or meet a short-term savings goal, weekly updates may prove more beneficial.
Empower Your Personal Finance with a Custom Budget Spreadsheet
Creating a budget spreadsheet is an important step toward taking control of your finances. The key is to start simple, stay consistent, and make adjustments along the way.
Once you’re comfortable with the process of regularly reviewing and updating the spreadsheet, it becomes a powerful tool that guides spending and savings decisions, helping you achieve bigger-picture financial goals.
For more information and financial management tips, read PNC Bank’s Personal Finance Insights . Here, you’ll find various topics designed to help you gain financial knowledge and empower your financial future.
- Manage Daily Finances
- Balance Financial Goals

Apply for a checking account today.
Apply for a checking account
with $0 minimum to open online and Low Cash Mode® to help avoid overdrafts.

Important Legal Disclosures and Information
1. Wall Street Journal, accessed April 2, 2024 https://www.wsj.com/articles/as-gas-prices-surge-stations-now-hold-up-to-175-of-your-money-when-you-swipe-11656277411
Excel is a trademark of the Microsoft group of companies.
Google is a trademark of Google LLC.
Visa ® is a registered trademark of Visa International Service Association and used under license.
PNC Bank, National Association Member FDIC .
These articles are for general information purposes only and are not intended to provide legal, tax, accounting or financial advice. PNC urges its customers to do independent research and to consult with financial and legal professionals before making any financial decisions. This site may provide reference to Internet sites as a convenience to our readers. While PNC endeavors to provide resources that are reputable and safe, we cannot be held responsible for the information, products or services obtained on such sites and will not be liable for any damages arising from your access to such sites. The content, accuracy, opinions expressed and links provided by these resources are not investigated, verified, monitored or endorsed by PNC.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Dear Life Kit
- Life Skills
Want to lend a friend money? Ask yourself if you can afford to never see it again

Andrew Limbong

Michelle Singletary and her husband used to lend money to her friends on a regular basis, until one incident "taught us a lesson," she says.
They lent money to a couple in their circle who didn't pay them back on time. "Then we attended a party at their house and noticed this new big-screen TV. And we're thinking, 'So you can buy a $1,500 TV, but you can't give our money back?'"
Singletary, a personal finance columnist for The Washington Post , didn't like that she was pocket-watching her friends. "So my husband and I decided we would only give money we didn't need to get back."
Lending money to friends and family is a tricky business. It can unite people in times of hardship. But it can also complicate relationships, especially because "so much of our financial decisions involve emotions," says Singletary, who is the author of a number of books on money management, including What to Do With Your Money When Crisis Hits: A Survival Guide.
When a loved one asks to borrow a significant amount of money, you have your own budget to consider — and your relationship, she says. What's your history together? How do you know whether you're in a position to help? Financial experts offer guidance on this topic, including how to say no without feeling guilty and what to do if you're asked to cosign a loan.
We want to hear from you: What are your thoughts on lending money?
Don't lend money. gift it.

The experts we spoke to agreed on this point: Don't lend money to people. If you have the funds and want to help out, give it to them as a gift instead. That way, you don't have to worry about the borrower paying you back or what to do if they don't.
"As individuals, we are not in the business of lending money. We don't know how to do it because there are a lot of feelings involved," says Singletary. "That's why it should be left up to financial institutions."

What is the new etiquette for tipping?
Avoid getting into a situation where the borrower wants to "write up a contract or have terms" on their loan, says financial educator Berna Anat , author of Money Out Loud: All the Financial Stuff No One Taught Us . They imply a contractual obligation, which may put a strain on relationships.
For that reason, Anat says, "if I'm giving money, I'm assuming it's a gift. It's not going to get paid back. So from my end, I know it's money I'm willing to lose."
DO let your budget guide your decision

"Ask yourself: Am I really in a position to be gifting money right now?" says Wendy De La Rosa , an assistant professor at the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania.
If you have extra money to share, then by all means, give the money. But if you have to pull from the funds you've set aside for critical expenditures like your rent, your car payment or tax money, "you are jeopardizing yourself," she says. It also puts you in a vulnerable financial position if the borrower does not pay you back.
DO create boundaries around whom you support

Guilt can play a role in deciding whether to give money to a loved one, says De La Rosa, especially if you were able to climb into a higher tax bracket than the one you grew up in. You probably had some help along the way and might feel some responsibility to pay it back somehow.

How to save money when you're broke
If this sounds like your situation, De La Rosa says to make a shortlist of the people whom you're willing to give money to. Maybe it's direct family only or just your close crew of friends. You can't exhaust your own funds to help everyone.
Don't forget to talk about those boundaries with your partner, says De La Rosa. "I was born in the Dominican Republic. Lots of people sacrificed to bring us here. My husband grew up in Texas. We had to be very clear when we got married about who was in our circle."
DO offer other ways to help

You checked your finances, and you realize you're not in any position to give anyone money. How do you say, "No, but I still care about you?"
Offer other ways to help, say our experts. It's not going to be easy. If someone is coming to you for money, it probably wasn't their first option. They're probably in a bad situation and don't see any other way out. They're vulnerable. And your turning them down is going to hurt.
De La Rosa had to have a "no" conversation with a member of her extended family. "It was painful," she says. But instead of giving the person money, she helped them with their budget. She listed their debts, set up spreadsheets and figured out an action plan to get them out of the hole. "They saw I was there with them. And they really appreciated it."
So think about other ways to assist your loved one during this difficult time. Offer to bring them dinner. Help them with child care so they can pick up a few more shifts at work.
DON'T cosign a loan

If a friend or relative asks you to cosign a loan, don't do it, say our experts. Cosigning a loan means you're agreeing to be responsible for someone else's debt. If the main borrower misses payments, you must repay the loan.
It also means that the debt is on your credit profile, says Singletary. "That could prevent you from getting a loan or make the loan you need more expensive."
Early in her career as a journalist, Singletary asked her grandmother to cosign a car loan. And her grandmother told her: "Let me get this straight. So the bank, which has way more money than I do, turned you down? Now you want to put my finances on the line?"
"That was the end of the conversation," says Singletary. Ultimately, she realized her grandmother was right. "I caught the bus until I could save up enough to get the loan."
Has a friend or family member ever asked to borrow money from you? Tell us about a time when you decided to pitch in — or a time when you had to say no. How did you make your decision? We may feature your response in a story on NPR. Email [email protected] with the subject line "Lending money."
The digital story was written by Malaka Gharib and edited by Meghan Keane. The visual editor is Beck Harlan. We'd love to hear from you. Leave us a voicemail at 202-216-9823, or email us at [email protected].
Listen to Life Kit on Apple Podcasts and Spotify , and sign up for our newsletter .
- Life Kit: Money
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
FACT SHEET: President Biden Takes Action to Protect American Workers and Businesses from China’s Unfair Trade Practices
President Biden’s economic plan is supporting investments and creating good jobs in key sectors that are vital for America’s economic future and national security. China’s unfair trade practices concerning technology transfer, intellectual property, and innovation are threatening American businesses and workers. China is also flooding global markets with artificially low-priced exports. In response to China’s unfair trade practices and to counteract the resulting harms, today, President Biden is directing his Trade Representative to increase tariffs under Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974 on $18 billion of imports from China to protect American workers and businesses. The Biden-Harris Administration’s Investing in America agenda has already catalyzed more than $860 billion in business investments through smart, public incentives in industries of the future like electric vehicles (EVs), clean energy, and semiconductors. With support from the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, CHIPS and Science Act, and Inflation Reduction Act, these investments are creating new American jobs in manufacturing and clean energy and helping communities that have been left behind make a comeback. As President Biden says, American workers and businesses can outcompete anyone—as long as they have fair competition. But for too long, China’s government has used unfair, non-market practices. China’s forced technology transfers and intellectual property theft have contributed to its control of 70, 80, and even 90 percent of global production for the critical inputs necessary for our technologies, infrastructure, energy, and health care—creating unacceptable risks to America’s supply chains and economic security. Furthermore, these same non-market policies and practices contribute to China’s growing overcapacity and export surges that threaten to significantly harm American workers, businesses, and communities. Today’s actions to counter China’s unfair trade practices are carefully targeted at strategic sectors—the same sectors where the United States is making historic investments under President Biden to create and sustain good-paying jobs—unlike recent proposals by Congressional Republicans that would threaten jobs and raise costs across the board. The previous administration’s trade deal with China failed to increase American exports or boost American manufacturing as it had promised. Under President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, nearly 800,000 manufacturing jobs have been created and new factory construction has doubled after both fell under the previous administration, and the trade deficit with China is the lowest in a decade—lower than any year under the last administration. We will continue to work with our partners around the world to strengthen cooperation to address shared concerns about China’s unfair practices—rather than undermining our alliances or applying indiscriminate 10 percent tariffs that raise prices on all imports from all countries, regardless whether they are engaged in unfair trade. The Biden-Harris Administration recognizes the benefits for our workers and businesses from strong alliances and a rules-based international trade system based on fair competition. Following an in-depth review by the United States Trade Representative, President Biden is taking action to protect American workers and American companies from China’s unfair trade practices. To encourage China to eliminate its unfair trade practices regarding technology transfer, intellectual property, and innovation, the President is directing increases in tariffs across strategic sectors such as steel and aluminum, semiconductors, electric vehicles, batteries, critical minerals, solar cells, ship-to-shore cranes, and medical products. Steel and Aluminum The tariff rate on certain steel and aluminum products under Section 301 will increase from 0–7.5% to 25% in 2024. Steel is a vital sector for the American economy, and American companies are leading the future of clean steel. Recently, the Biden-Harris Administration announced $6 billion for 33 clean manufacturing projects including for steel and aluminum, including the first new primary aluminum smelter in four decades, made possible by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and the Inflation Reduction Act. These investments will make the United States one of the first nations in the world to convert clean hydrogen into clean steel, bolstering the U.S. steel industry’s competitiveness as the world’s cleanest major steel producer. American workers continue to face unfair competition from China’s non-market overcapacity in steel and aluminum, which are among the world’s most carbon intensive. China’s policies and subsidies for their domestic steel and aluminum industries mean high-quality, low-emissions U.S. products are undercut by artificially low-priced Chinese alternatives produced with higher emissions. Today’s actions will shield the U.S. steel and aluminum industries from China’s unfair trade practices. Semiconductors The tariff rate on semiconductors will increase from 25% to 50% by 2025. China’s policies in the legacy semiconductor sector have led to growing market share and rapid capacity expansion that risks driving out investment by market-driven firms. Over the next three to five years, China is expected to account for almost half of all new capacity coming online to manufacture certain legacy semiconductor wafers. During the pandemic, disruptions to the supply chain, including legacy chips, led to price spikes in a wide variety of products, including automobiles, consumer appliances, and medical devices, underscoring the risks of overreliance on a few markets. Through the CHIPS and Science Act, President Biden is making a nearly $53 billion investment in American semiconductor manufacturing capacity, research, innovation, and workforce. This will help counteract decades of disinvestment and offshoring that has reduced the United States’ capacity to manufacture semiconductors domestically. The CHIPS and Science Act includes $39 billion in direct incentives to build, modernize, and expand semiconductor manufacturing fabrication facilities as well as a 25% investment tax credit for semiconductor companies. Raising the tariff rate on semiconductors is an important initial step to promote the sustainability of these investments. Electric Vehicles (EVs) The tariff rate on electric vehicles under Section 301 will increase from 25% to 100% in 2024. With extensive subsidies and non-market practices leading to substantial risks of overcapacity, China’s exports of EVs grew by 70% from 2022 to 2023—jeopardizing productive investments elsewhere. A 100% tariff rate on EVs will protect American manufacturers from China’s unfair trade practices. This action advances President Biden’s vision of ensuring the future of the auto industry will be made in America by American workers. As part of the President’s Investing in America agenda, the Administration is incentivizing the development of a robust EV market through business tax credits for manufacturing of batteries and production of critical minerals, consumer tax credits for EV adoption, smart standards, federal investments in EV charging infrastructure, and grants to supply EV and battery manufacturing. The increase in the tariff rate on electric vehicles will protect these investments and jobs from unfairly priced Chinese imports. Batteries, Battery Components and Parts, and Critical Minerals The tariff rate on lithium-ion EV batteries will increase from 7.5%% to 25% in 2024, while the tariff rate on lithium-ion non-EV batteries will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2026. The tariff rate on battery parts will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2024. The tariff rate on natural graphite and permanent magnets will increase from zero to 25% in 2026. The tariff rate for certain other critical minerals will increase from zero to 25% in 2024. Despite rapid and recent progress in U.S. onshoring, China currently controls over 80 percent of certain segments of the EV battery supply chain, particularly upstream nodes such as critical minerals mining, processing, and refining. Concentration of critical minerals mining and refining capacity in China leaves our supply chains vulnerable and our national security and clean energy goals at risk. In order to improve U.S. and global resiliency in these supply chains, President Biden has invested across the U.S. battery supply chain to build a sufficient domestic industrial base. Through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, the Defense Production Act, and the Inflation Reduction Act, the Biden-Harris Administration has invested nearly $20 billion in grants and loans to expand domestic production capacity of advanced batteries and battery materials. The Inflation Reduction Act also contains manufacturing tax credits to incentivize investment in battery and battery material production in the United States. The President has also established the American Battery Materials Initiative, which will mobilize an all-of-government approach to secure a dependable, robust supply chain for batteries and their inputs. Solar Cells The tariff rate on solar cells (whether or not assembled into modules) will increase from 25% to 50% in 2024. The tariff increase will protect against China’s policy-driven overcapacity that depresses prices and inhibits the development of solar capacity outside of China. China has used unfair practices to dominate upwards of 80 to 90% of certain parts of the global solar supply chain, and is trying to maintain that status quo. Chinese policies and nonmarket practices are flooding global markets with artificially cheap solar modules and panels, undermining investment in solar manufacturing outside of China. The Biden-Harris Administration has made historic investments in the U.S. solar supply chain, building on early U.S. government-enabled research and development that helped create solar cell technologies. The Inflation Reduction Act provides supply-side tax incentives for solar components, including polysilicon, wafers, cells, modules, and backsheet material, as well as tax credits and grant and loan programs supporting deployment of utility-scale and residential solar energy projects. As a result of President Biden’s Investing in America agenda, solar manufacturers have already announced nearly $17 billion in planned investment under his Administration—an 8-fold increase in U.S. manufacturing capacity, enough to supply panels for millions of homes each year by 2030. Ship-to-Shore Cranes The tariff rate on ship-to-shore cranes will increase from 0% to 25% in 2024. The Administration continues to deliver for the American people by rebuilding the United States’ industrial capacity to produce port cranes with trusted partners. A 25% tariff rate on ship-to-shore cranes will help protect U.S. manufacturers from China’s unfair trade practices that have led to excessive concentration in the market. Port cranes are essential pieces of infrastructure that enable the continuous movement and flow of critical goods to, from, and within the United States, and the Administration is taking action to mitigate risks that could disrupt American supply chains. This action also builds off of ongoing work to invest in U.S. port infrastructure through the President’s Investing in America Agenda. This port security initiative includes bringing port crane manufacturing capabilities back to the United States to support U.S. supply chain security and encourages ports across the country and around the world to use trusted vendors when sourcing cranes or other heavy equipment. Medical Products The tariff rates on syringes and needles will increase from 0% to 50% in 2024. For certain personal protective equipment (PPE), including certain respirators and face masks, the tariff rates will increase from 0–7.5% to 25% in 2024. Tariffs on rubber medical and surgical gloves will increase from 7.5% to 25% in 2026. These tariff rate increases will help support and sustain a strong domestic industrial base for medical supplies that were essential to the COVID-19 pandemic response, and continue to be used daily in every hospital across the country to deliver essential care. The federal government and the private sector have made substantial investments to build domestic manufacturing for these and other medical products to ensure American health care workers and patients have access to critical medical products when they need them. American businesses are now struggling to compete with underpriced Chinese-made supplies dumped on the market, sometimes of such poor quality that they may raise safety concerns for health care workers and patients. Today’s announcement reflects President Biden’s commitment to always have the back of American workers. When faced with anticompetitive, unfair practices from abroad, the President will deploy any and all tools necessary to protect American workers and industry.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.

Cost of living help and a future made in Australia
Investing in a future made in australia.
Investing in a Future Made in Australia and the skills to make it a reality
Print or save page
On this page
Attracting investment in key industries
Making Australians the beneficiaries of change
A Future Made in Australia is about creating new jobs and opportunities for every part of our country by maximising the economic and industrial benefits of the move to net zero and securing Australia’s place in a changing global economic and strategic landscape.
The Government’s $22.7 billion Future Made in Australia package will help facilitate the private sector investment required for Australia to be an indispensable part of the global economy.
For more information refer to the Future Made in Australia fact sheet [PDF 438KB]
Better deploying capital in priority areas
The Future Made in Australia package will realise Australia’s potential to become a renewable energy superpower, value‑add to our resources and strengthen economic security by better attracting and enabling investment in priority areas. The Government will create a Future Made in Australia Act and establish a National Interest Framework that identifies priority industries and ensures investments associated with them are responsible and targeted.
The Framework will have a focus on industries that contribute to the net zero transformation where Australia has a comparative advantage, and where Australia has national interest imperatives related to economic resilience and security.
Strengthening and streamlining approvals
This Budget provides a faster pathway to better decisions on environmental, energy, planning, cultural heritage and foreign investment approvals.
This includes:
- $134.2 million to better prioritise approvals for renewable energy projects of national significance, and support faster decisions on environment, cultural heritage and planning approvals.
- Working with the states and territories through the Energy and Climate Change Ministerial Council to accelerate electricity grid connections.
- $20.7 million to improve engagement with communities impacted by the energy transition and accelerate the delivery of key energy projects.
- $15.7 million to strengthen scrutiny of high‑risk foreign investment proposals, enhance monitoring and enforcement activities and support faster decisions.
The Government will also encourage foreign investment by providing refunds of 75 per cent of application fees for unsuccessful competitive bids.
Promoting sustainable finance
The Government is committing $17.3 million to mobilise private sector investment in sustainable activities. This includes extending Australia’s sustainable finance taxonomy to the agriculture sector and developing a labelling regime for financial products marketed as sustainable.
The Government will also examine opportunities to improve data quality and provide $1.3 million to develop and issue guidance for best practice transition plans.
Making Australia a renewable energy superpower
Powering australia with cheaper, cleaner, more reliable energy.
Australia’s potential to produce abundant renewable energy is a powerful source of comparative advantage. To realise this, the Government is unlocking more than $65 billion of investment in renewable capacity through the Capacity Investment Scheme by 2030.
This Budget helps Australians benefit from cheaper, cleaner energy sooner by investing $27.7 million to integrate consumer energy resources like batteries and solar into the grid.
The New Vehicle Efficiency Standard will save Australians around $95 billion at the bowser by 2050 and reduce transport emissions.
Unlocking investment in net zero industries and jobs
This Budget accelerates growth of new industries by establishing the $1.7 billion Future Made in Australia Innovation Fund and delivering a 10‑year extension of funding to the Australian Renewable Energy Agency. It also delivers the $44.4 million Energy Industry Jobs Plan and $134.2 million for skills and employment support in key regions.
The Future Made in Australia package establishes time‑limited incentives to invest in new industries. The Hydrogen Production Tax Incentive will make Australia’s pipeline of hydrogen projects commercial sooner, at an estimated cost of $6.7 billion over the decade. This Budget also expands the Hydrogen Headstart program by $1.3 billion.
Boosting demand for Australia’s green exports
The Government is making it easier for businesses and trading partners to source low‑emissions products by building better markets and product standards for green products.
This Budget provides $32.2 million to fast‑track the initial phase of the Guarantee of Origin scheme, focused on renewable hydrogen, and bring forward the expansion of the scheme to accredit the emissions content of green metals and low‑carbon liquid fuels. The Government is also working closely with trading partners to identify opportunities to drive greater supply chain transparency and better market recognition of high environmental, social and governance standards in the critical minerals sector.
Realising the opportunities of the net zero transformation
Australia is committed to reaching net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 and is developing six sector plans covering:
- electricity and energy
- agriculture and land
- the built environment.
This Budget continues investment in effective emissions abatement, including through $63.8 million to support emissions reduction efforts in the agriculture and land sector.
The Government is also investing $399 million to establish the Net Zero Economy Authority and support the economy‑wide net zero transformation. This Budget also invests an additional $48 million in reforms to the Australian Carbon Credit Unit scheme and $20.7 million to improve community engagement.
Strengthening resources and economic security
Backing a strong resources sector.
The Government is investing $8.8 billion over the decade to add more value to our resources and strengthen critical minerals supply chains. This Budget establishes a production tax incentive for processing and refining critical minerals at an estimated cost of $7 billion over the decade. It commits up to $1.2 billion in strategic critical minerals projects through the Critical Minerals Facility and the Northern Australia Infrastructure Facility, and pre‑feasibility studies for common user precincts.
This is in addition to $566.1 million to support Geoscience Australia to map all of Australia’s critical minerals, strategic materials, groundwater and other resources essential for the transition to net zero.
Manufacturing clean energy technologies
The Government is committing $1.5 billion to manufacturing clean energy technologies, including the $1 billion Solar Sunshot and $523.2 million Battery Breakthrough Initiative. These investments will be delivered by ARENA.
Strengthening supply chains
To support the delivery of the 82 per cent renewable energy target, the Government has formed the National Renewable Energy Supply Chain Action Plan with states and territories. The Government will invest an additional $14.3 million working with trade partners to support global rules on unfair trade practices and to negotiate benchmarks for trade in high quality critical minerals.
Digital, science and innovation
Investing in new technologies and capabilities.
The Government is investing $466.4 million to partner with PsiQuantum and the Queensland Government to build the world’s first commercial‑scale quantum computer in Brisbane.
The Government will undertake a strategic examination of Australia’s research and development (R&D) system with $38.2 million invested in a range of science, technology, engineering, and maths programs.
The Government is providing $448.7 million to partner with the United States in the Landsat Next satellite program to provide access to critical data to monitor the earth’s climate, agricultural production, and natural disasters.
Modernising and digitising industries
This Budget commits $288.1 million to support Australia’s Digital ID System. A National Robotics Strategy will also be released to promote the responsible production and adoption of robotics and automation technologies for advanced manufacturing in Australia.
Reforming tertiary education
The Government is committing $1.6 billion over 5 years, and an additional $2.7 billion from 2028–29 to 2034–35 to reform the tertiary education system and deliver Australia's future workforce.
This includes $1.1 billion for reforms to university funding and tertiary system governance.
Over $500 million will be provided for skills and training in priority industries and to support women’s participation in these sectors.
The Government will set a tertiary attainment target of 80 per cent of the working‑age population by 2050.
Supporting students on placements
The Government will establish Commonwealth Prac Payments (CPP) for students undertaking mandatory placements. From 1 July 2025, the payment will provide more than 73,000 eligible students, including teachers, nurses, midwives and social workers with $319.50 per week during their placements.
Felicity is a full‑time student receiving Youth Allowance, living by herself. She is studying a Bachelor of Nursing and must stop paid work during her mandatory prac placement. During her prac, Felicity receives $712.05 per week from the Government including: $319.50 of CPP, $285.55 of Youth Allowance (YA), $103.50 of Commonwealth Rent Assistance (CRA) and $3.50 of Energy Supplement.
Felicity receives $351.55 a week more than she would have in 2023 before indexation and the changes to YA, CRA and CPP in the current and 2023–24 Budget

Broadening access to university
From January 2026, needs‑based funding will provide per student funding contributions for under‑represented students. The Government will also provide $350.3 million to fully fund university enabling courses and increase pathways for prospective students to university.
Skills pipeline for priority industries
Skills and training for Future Made in Australia industries
The Government will expand eligibility to the New Energy Apprenticeships Program to include work in the clean energy sector, including in construction and advanced manufacturing. This will provide access to $10,000 incentive payments and support our target of 10,000 new energy apprentices.
The Government will commit $30 million to turbocharge the VET teaching workforce for clean energy courses and $50 million to upgrade and expand clean energy training facilities.
The Government will invest $55.6 million to establish the Building Women’s Careers program to support women’s participation in key industries including clean energy and advanced manufacturing.
Supporting apprentices and building the construction workforce
The $5,000 support payments to apprentices in priority occupations will be maintained for another 12 months to 1 July 2025, up from $3,000 in the absence of any changes. Employers of these apprentices will receive a $5,000 hiring incentive, up from $4,000 in the absence of changes. This will provide certainty to apprentices while the Strategic Review of the Apprenticeship Incentive System is underway.
The Government will also invest $88.8 million to deliver 20,000 new fee‑free TAFE places including pre‑apprenticeships in courses relevant to the construction sector. The Government will provide $1.8 million to deliver streamlined skills assessments for around 1,900 migrants from comparable countries to work in Australia’s housing construction industry.
Strengthening our defence industry capability
An integrated and focused approach to defending Australia
The Government is investing an additional $50.3 billion over ten years to implement the 2024 National Defence Strategy to meet Australia’s strategic needs.
Overall funding for Defence will reach $765 billion over the decade. Defence’s Integrated Investment Program has been rebuilt to create a focused Australian Defence Force, accelerate delivery of priority capabilities, and provide certainty to grow Australia’s defence industry. This includes funding for the Royal Australian Navy’s surface combatant fleet and establishing a guided weapons and explosive ordnance manufacturing capability earlier.
The Government is reforming Defence’s budget to support the National Defence Strategy and delivery of priority capabilities.
Developing defence industry and skills
Industry development grants funding of $165.7 million will also help businesses to scale up and deliver the Sovereign Defence Industrial Priorities, which include continuous naval shipbuilding and sustainment, and development and integration of autonomous systems.
The Government is providing $101.8 million to attract and retain the skilled industrial workforce to support Australian shipbuilding and delivery of conventionally armed, nuclear powered submarines. This includes a pilot apprenticeship program in shipbuilding trades and technologies.
Investing in civil maritime capabilities
The Government is providing $123.8 million to maintain and enhance civil maritime security capabilities. This includes $71.2 million to increase the Australian Border Force’s on‑water response and aerial surveillance capabilities.
Securing Australia’s place in the world
Strengthening relationships and simplifying trade
A stable, prosperous and resilient Pacific region
The Government is delivering over $2 billion in development assistance to the Pacific in 2024–25. This includes the Australia‑Tuvalu Falepili Union.
Investing in our relationship with Southeast Asia
Following the launch of Australia’s Southeast Asia Economic Strategy to 2040, the Government is committing $505.9 million to deepen ties with the region.
Australia recently celebrated 50 years of partnership with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). At the ASEAN‑Australia Special Summit, the Government announced a range of new and expanded initiatives, including a $2 billion Southeast Asia Investment Financing Facility to boost Australian trade and investment.
Simplifying trade
The Government will abolish 457 nuisance tariffs from 1 July 2024, streamlining $8.5 billion in annual trade and eliminating tariffs on goods such as toothbrushes, fridges, dishwashers, clothing and sanitary products.
The Government will provide $29.9 million to coordinate trade simplification and deliver the Digital Trade Accelerator program, and $10.9 million to enhance the Go Global Toolkit to support exporters.
The Government is expanding the Australia‑India Business Exchange, diversifying trade and helping more Australian businesses build commercial ties with India and across South Asia. There will be $2 million to support Australian agricultural exporters entering the Chinese markets.
Support for small businesses
Helping small businesses
This Budget’s Small Business Statement reaffirms the Government’s commitment to deliver a better deal for small businesses, with $641.4 million in targeted support.
For more information refer to the small business fact sheet [PDF 0.98MB]
Improving cash flow
The Government is providing $290 million to extend the $20,000 instant asset write‑off for 12 months. There will be $25.3 million to improve payment times to small businesses and $23.3 million to increase eInvoicing adoption.
Easing cost pressures and reducing the administrative burden
This Budget provides $3.5 billion of energy bill relief, including rebates of $325 to around one million small businesses.
The Government is reducing the administrative burden for small business by abolishing 457 nuisance tariffs and delivering $10 million to provide additional support for small business employers administering the Paid Parental Leave scheme.
Supporting confidence and resilience in the small business sector
This Budget invests a further $10.8 million in tailored, free and confidential financial and mental wellbeing supports for small business owners.
The Government is providing $20.5 million to the Fair Work Ombudsman to help small businesses understand and comply with recent workplace relations changes.
There will be $3 million to implement the Government’s response to the Review of the Franchising Code of Conduct, including remaking and enhancing the Code, and an additional $2.6 million to support more small businesses through alternative dispute resolution.
A more resilient Australia
Preparing for the future
The Government is preparing Australia for future droughts and heightened risk of natural disasters.
Disaster resilience and preparedness
The Government will provide $138.7 million to improve Australia’s response and resilience to natural hazards and disasters. Support includes: funding for the National Emergency Management Agency to supply communities with vital goods, equipment, and temporary accommodation during an emergency, aerial firefighting capability, and mental health support. This is in addition to the $11.4 billion previously committed for Disaster Recovery Funding Arrangements for the states and territories.
The Government is establishing a pilot program for Australia’s Strategic Fleet. These vessels will improve Australia’s capacity to respond and support communities and supply chains during crises.
Preparing for drought and climate change
This Budget provides $174.6 million from the National Water Grid Fund to deliver new water infrastructure projects that will enhance water security, boost agricultural production and help drought proof regional communities.
The Government will provide $519.1 million from its Future Drought Fund to help farmers and rural communities manage the impacts of climate change and prepare for future droughts.

This investment will build the drought resilience of more farmers like Victorian cropper Ed Rickard.
The Fund supported Ed in developing a better farm business plan, which identified his need for weather stations and soil moisture probes. It also helped him implement a succession plan that ensured his farm’s long-term viability.
Back to top
Social Trends
Never stop moving.

Starting an Online Business on a Budget

Dreaming of starting your own online business but worried about the financial commitment? You’re not alone. The good news is that launching an enterprise online has never been more accessible or affordable. With strategic planning and creativity, you can turn your entrepreneurial dreams into reality, even on a tight budget.
Identifying Your Niche
Finding your niche is the first step to setting the foundation of your budget-friendly online business. It should be a unique intersection of your passion, skills, and a market need. This process requires research and introspection but is crucial for creating a business that stands out in the digital landscape.
Leveraging Free Tools
Thankfully, many tools and resources can help get your online business off the ground without breaking the bank. From designing your logo and marketing materials using free graphic design software to managing projects and customer relationships with free management tools, the internet is full of cost-effective solutions for new entrepreneurs.
Creating a compelling online presence is crucial for any online business. With the right tools, designing a functional and visually appealing website can be straightforward and cost-effective. Exploring top website builders can help you find platforms that align with your business needs, allowing you to create a professional-looking website without extensive technical knowledge or a significant financial investment.
Building a Community
Engaging with your audience and building a community around your brand can be a cost-effective way to maintain interest and loyalty among your customers. Utilize social media, forums, and email newsletters to connect with your audience, share valuable content, and encourage customer feedback and interaction.
Scaling Wisely
As your online business grows, it’s important to scale wisely. Reinvest profits back into the business cautiously, focusing on the areas that offer the highest return on investment. This might mean expanding your product line, investing in marketing, or enhancing your website. Decide based on data and customer feedback to ensure sustainable growth.
Starting Small
One of the keys to starting an online business on a budget is to start small. Launch with a minimum viable product (MVP) – a version of your product with just enough features to satisfy early customers and provide feedback for future product development. This strategy minimizes initial costs while allowing you to test and improve your offering.
Adapting and Innovating
The online marketplace is constantly evolving, so staying adaptable and open to innovation is crucial for long-term success. Keep an eye on industry trends, technological advancements, and shifts in consumer behavior to continuously adapt and innovate your offerings. This proactive approach can set your business apart in a competitive digital world.
Smart Marketing
Marketing is essential for any business, but it doesn’t have to be expensive. Social media platforms offer a powerful way to reach potential customers for little to no cost. Content marketing , email marketing, and leveraging SEO are all budget-friendly strategies that can help you build a robust online presence and attract your target audience.
Utilizing Customer Feedback
Actively seeking and utilizing customer feedback is pivotal in refining your offerings and enhancing your business strategy. Encourage reviews, conduct surveys, and engage directly with your customers through social media to gather insights. This direct line of communication not only fosters stronger relationships but also provides valuable data that can inform your business decisions.
Focus on SEO
Maximizing the visibility of your online business through search engine optimization (SEO) is a cost-efficient method to attract more visitors without heavy advertising spending. Understanding and applying the fundamentals of SEO to your website and content can significantly impact your organic reach and rankings on search engines.
Starting an online business on a budget is entirely possible with the right approach, tools, and mindset. By identifying your niche, starting small, leveraging free or inexpensive resources, focusing on building a community, and incorporating strategies like customer feedback, SEO, and adaptability into your growth plan, you can launch and expand a successful online business without a hefty initial investment. The digital world is ripe with opportunities for those willing to explore, innovate, and commit to their vision.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Profit is what remains after expenses are deducted. 2. Subtract fixed costs. The second step for creating a business budget involves adding up all of your historic fixed costs and using them to ...
Ahmet Yüzbaşıoğlu, the Co-Founder of Peak Plans, explains the importance of budgeting for small businesses: "The success of your business is determined by the quality of your decisions.If you want to make informed decisions, you must have a budget. A budget can help you create a plan for the future, whether it's for your company as a whole or for smaller departments.
Step 1: Review your revenue. The first step toward creating a budget is to examine your revenue: not just the total for any given time, but specifics, such as months when revenue rose or dipped ...
Step 1: Create a Budget Process. The budget process shows how the different departments of the business create a budget. Without a process, budgeting would be chaotic, and it would result in inefficiencies. In the budget process, you need to consider the following: Budget period: When are budgets created, reviewed, implemented, and evaluated ...
1. Get a template online. The best way to start creating a budget is by getting a template online. A template will have all the available information, and your job will simply be to fill in the spaces with your estimates. This prevents you from needing to spend time building complex spreadsheets.
4. Your one-off costs. One-off costs fall outside the usual work your business does. These are startup costs like moving offices, equipment, furniture, and software, as well as other costs related to launch and research. 5. Your cash flow. Cash flow is all money traveling into and out of a business.
Subtract all of these from your revenue to move closer to your profit. 3. Determine variable expenses. This part's a little trickier; you can't calculate an exact number for these expenses because they change month to month. That's why it's best to base your budget on the figures from the most recent financial year.
Just follow these six simple steps to create a business budget that clarifies your business's focus and how you intend to achieve all of your goals. 1. Look at your revenue. Start by calculating your sales revenue as well as any other income, like interest on your savings or investments.
Business Budget Step 4: Predict One-Time Spends. Many of your business expenses will be regular expenses that you pay for each month, whether they're fixed or variable costs. But there are also costs that will happen far less frequently. Just don't forget to factor those expenses when you create a budget as well.
2. Make a Spreadsheet. Prior to buying or opening a business, construct a spreadsheet to estimate what total dollar amount and percentage of your revenue will need to be allocated toward raw ...
Having an accounting system in place will give you real-time information about your finances, helping you to create a feasible budget. The key to creating a good budget is to evaluate the previous years' data and draw realistic projections. An accounting system can give you access to all this information in one place, no matter when you need ...
How to create a small business budget in 6 steps. Now that you understand how important a budget is, here's how you can create one so you can ensure smooth business operation and facilitate efficient cash flow: 1. Separate your business finances from your personal finances. This is one of the cardinal rules to succeed in business.
1. Write down your revenue streams. Your revenue is the money you earn in exchange for your products or services. You'll start your small- business budget by listing all the ways you make money. Look at last month's P&L—or even just your checking account statement—to help you account for all your revenue streams.
2. List your business expenses. The next step in creating a small business budget is to list all your business expenses. Here are the types of expenses you want to include in your budget: Fixed ...
Creating a business budget takes several steps: Calculate your revenue. Include all your revenue streams, preferably over at least the last 12 months, to determine your monthly income. If your business is new, you can research what's typical in your industry and use that as a guide to come up with estimates.
Best Free Business Budget Templates. 1. Marketing Budget Template. Image Source. Knowing how to manage a marketing budget can be a challenge, but with helpful free templates like this marketing budget template bundle, you can track everything from advertising expenses to events and more.
In This Article. View All. Questions to Ask Before You Begin Your Budget. Step 1: Plan for "Day One" of Your Business Startup. Step 2: Estimate Monthly Fixed and Variable Expenses. Step 3: Estimate Monthly Sales. Step 4: Create a Cash-Flow Statement. Tips for Creating Your Business Startup Budget. Frequently Asked Questions.
To effectively create a business budget plan, it's crucial to establish both short-term and long-term financial objectives. Short-term goals could include reducing overhead costs by a certain percentage within six months, while long-term goals might involve doubling your annual revenue within three years. These objectives provide direction for ...
Subscribe: https://bit.ly/2HJlq46You can't manage a small business without a budget. So today, I'm going to simplify small business budgeting and help you ge...
8 steps to create an effective business budget. A good business budget is detailed yet flexible. It should act as a living document that you reevaluate and adjust often as your business grows and evolves. Here are eight steps to help you create an effective budget for your own business.
4. Determine Your Budget Surplus or Deficit. After you've accounted for all your income and expenses, you can apply them to your budget. This is where you determine whether you have enough projected income to cover all your expenses. If you have more than enough income to cover your expenses, you have a budget surplus.
Budgets are essential for tracking the financial health of your business. Your budget is your planned income and spending. It helps you to allocate funds for particular items and activities. Your budget also helps you to: set business goals. make good business decisions. get finance.
Let's do this.) Subtract all your expenses from your income. This number should equal zero, meaning you just made a zero-based budget. This is key: A zero-based budget doesn't mean you let your bank account reach zero. (Leave a little buffer in there of about $100-300.) It also doesn't mean you blow all your money.
5. Sit down and make your budget. Now it's time to make your budget. This step will depend on your approach. If you're using a zero-based budget, then you'll divide all of your money into specific ...
A budget spreadsheet simplifies tracking income and expenses, aligning daily spending with overall financial goals. Key steps include choosing a user-friendly tool like Excel ® or Google Sheets ®, setting up detailed budget categories, and deciding on a tracking period (monthly, quarterly, yearly).; Effective budget management involves inputting actual financial data, utilizing formulas for ...
Below, 11 members of Business Journals Leadership Trust discuss their top marketing tips for new founders working with a tight budget. From providing top-notch customer service to leveraging ...
Lending money to friends and family is a tricky business. It can unite people in times of hardship. But it can also complicate relationships, especially because "so much of our financial decisions ...
As part of the President's Investing in America agenda, the Administration is incentivizing the development of a robust EV market through business tax credits for manufacturing of batteries and ...
The Future Made in Australia package establishes time‑limited incentives to invest in new industries. The Hydrogen Production Tax Incentive will make Australia's pipeline of hydrogen projects commercial sooner, at an estimated cost of $6.7 billion over the decade. This Budget also expands the Hydrogen Headstart program by $1.3 billion.
Finding your niche is the first step to setting the foundation of your budget-friendly online business. It should be a unique intersection of your passion, skills, and a market need. This process requires research and introspection but is crucial for creating a business that stands out in the digital landscape. Leveraging Free Tools