When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Your Methods


Ensure understanding, reproducibility and replicability
What should you include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate?
Why Methods Matter
The methods section was once the most likely part of a paper to be unfairly abbreviated, overly summarized, or even relegated to hard-to-find sections of a publisher’s website. While some journals may responsibly include more detailed elements of methods in supplementary sections, the movement for increased reproducibility and rigor in science has reinstated the importance of the methods section. Methods are now viewed as a key element in establishing the credibility of the research being reported, alongside the open availability of data and results.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability.
For example, the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology project set out in 2013 to replicate experiments from 50 high profile cancer papers, but revised their target to 18 papers once they understood how much methodological detail was not contained in the original papers.
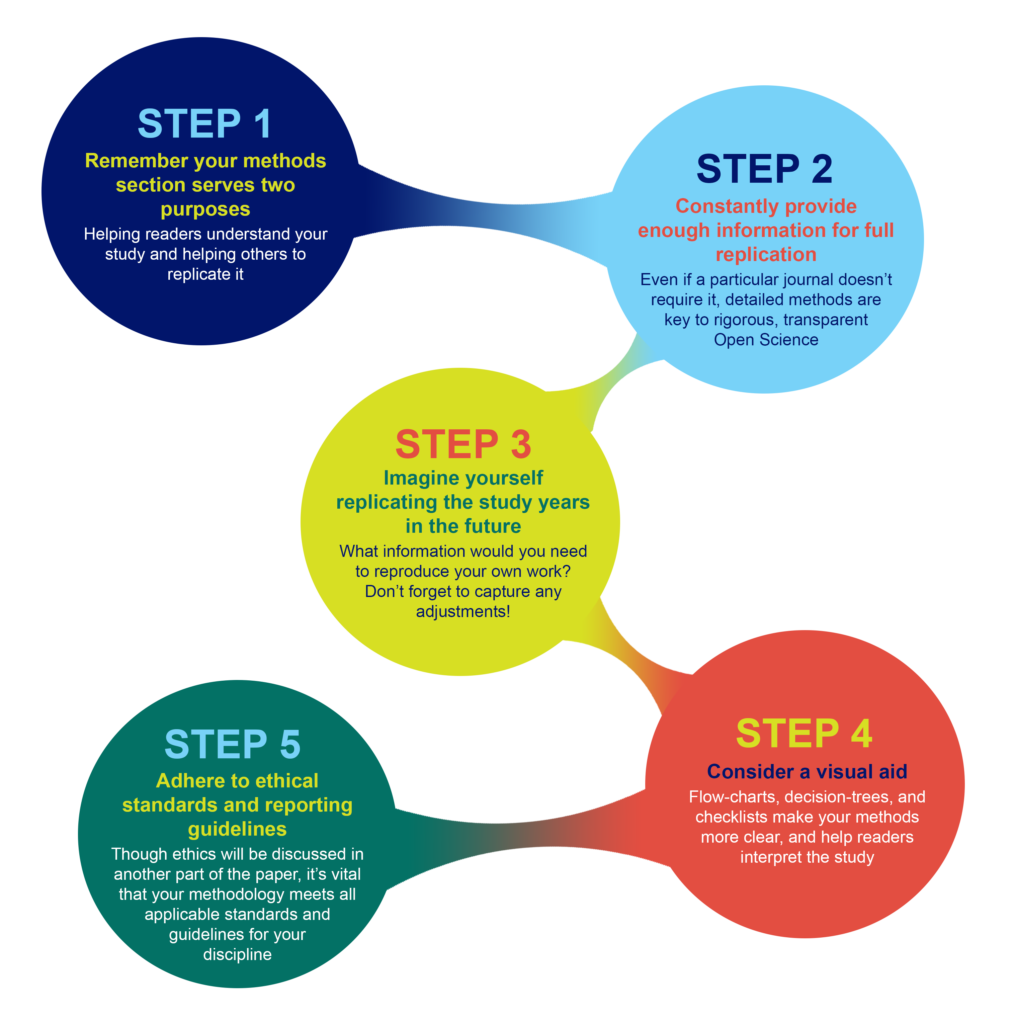
What to include in your methods section
What you include in your methods sections depends on what field you are in and what experiments you are performing. However, the general principle in place at the majority of journals is summarized well by the guidelines at PLOS ONE : “The Materials and Methods section should provide enough detail to allow suitably skilled investigators to fully replicate your study. ” The emphases here are deliberate: the methods should enable readers to understand your paper, and replicate your study. However, there is no need to go into the level of detail that a lay-person would require—the focus is on the reader who is also trained in your field, with the suitable skills and knowledge to attempt a replication.
A constant principle of rigorous science
A methods section that enables other researchers to understand and replicate your results is a constant principle of rigorous, transparent, and Open Science. Aim to be thorough, even if a particular journal doesn’t require the same level of detail . Reproducibility is all of our responsibility. You cannot create any problems by exceeding a minimum standard of information. If a journal still has word-limits—either for the overall article or specific sections—and requires some methodological details to be in a supplemental section, that is OK as long as the extra details are searchable and findable .
Imagine replicating your own work, years in the future
As part of PLOS’ presentation on Reproducibility and Open Publishing (part of UCSF’s Reproducibility Series ) we recommend planning the level of detail in your methods section by imagining you are writing for your future self, replicating your own work. When you consider that you might be at a different institution, with different account logins, applications, resources, and access levels—you can help yourself imagine the level of specificity that you yourself would require to redo the exact experiment. Consider:
- Which details would you need to be reminded of?
- Which cell line, or antibody, or software, or reagent did you use, and does it have a Research Resource ID (RRID) that you can cite?
- Which version of a questionnaire did you use in your survey?
- Exactly which visual stimulus did you show participants, and is it publicly available?
- What participants did you decide to exclude?
- What process did you adjust, during your work?
Tip: Be sure to capture any changes to your protocols
You yourself would want to know about any adjustments, if you ever replicate the work, so you can surmise that anyone else would want to as well. Even if a necessary adjustment you made was not ideal, transparency is the key to ensuring this is not regarded as an issue in the future. It is far better to transparently convey any non-optimal methods, or methodological constraints, than to conceal them, which could result in reproducibility or ethical issues downstream.
Visual aids for methods help when reading the whole paper
Consider whether a visual representation of your methods could be appropriate or aid understanding your process. A visual reference readers can easily return to, like a flow-diagram, decision-tree, or checklist, can help readers to better understand the complete article, not just the methods section.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to describing what you did, it is just as important to assure readers that you also followed all relevant ethical guidelines when conducting your research. While ethical standards and reporting guidelines are often presented in a separate section of a paper, ensure that your methods and protocols actually follow these guidelines. Read more about ethics .
Existing standards, checklists, guidelines, partners
While the level of detail contained in a methods section should be guided by the universal principles of rigorous science outlined above, various disciplines, fields, and projects have worked hard to design and develop consistent standards, guidelines, and tools to help with reporting all types of experiment. Below, you’ll find some of the key initiatives. Ensure you read the submission guidelines for the specific journal you are submitting to, in order to discover any further journal- or field-specific policies to follow, or initiatives/tools to utilize.
Tip: Keep your paper moving forward by providing the proper paperwork up front
Be sure to check the journal guidelines and provide the necessary documents with your manuscript submission. Collecting the necessary documentation can greatly slow the first round of peer review, or cause delays when you submit your revision.
Randomized Controlled Trials – CONSORT The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) project covers various initiatives intended to prevent the problems of inadequate reporting of randomized controlled trials. The primary initiative is an evidence-based minimum set of recommendations for reporting randomized trials known as the CONSORT Statement .
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – PRISMA The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) is an evidence-based minimum set of items focusing on the reporting of reviews evaluating randomized trials and other types of research.
Research using Animals – ARRIVE The Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments ( ARRIVE ) guidelines encourage maximizing the information reported in research using animals thereby minimizing unnecessary studies. (Original study and proposal , and updated guidelines , in PLOS Biology .)
Laboratory Protocols Protocols.io has developed a platform specifically for the sharing and updating of laboratory protocols , which are assigned their own DOI and can be linked from methods sections of papers to enhance reproducibility. Contextualize your protocol and improve discovery with an accompanying Lab Protocol article in PLOS ONE .
Consistent reporting of Materials, Design, and Analysis – the MDAR checklist A cross-publisher group of editors and experts have developed, tested, and rolled out a checklist to help establish and harmonize reporting standards in the Life Sciences . The checklist , which is available for use by authors to compile their methods, and editors/reviewers to check methods, establishes a minimum set of requirements in transparent reporting and is adaptable to any discipline within the Life Sciences, by covering a breadth of potentially relevant methodological items and considerations. If you are in the Life Sciences and writing up your methods section, try working through the MDAR checklist and see whether it helps you include all relevant details into your methods, and whether it reminded you of anything you might have missed otherwise.
Summary Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your methods is keeping it readable AND covering all the details needed for reproducibility and replicability. While this is difficult, do not compromise on rigorous standards for credibility!

- Keep in mind future replicability, alongside understanding and readability.
- Follow checklists, and field- and journal-specific guidelines.
- Consider a commitment to rigorous and transparent science a personal responsibility, and not just adhering to journal guidelines.
- Establish whether there are persistent identifiers for any research resources you use that can be specifically cited in your methods section.
- Deposit your laboratory protocols in Protocols.io, establishing a permanent link to them. You can update your protocols later if you improve on them, as can future scientists who follow your protocols.
- Consider visual aids like flow-diagrams, lists, to help with reading other sections of the paper.
- Be specific about all decisions made during the experiments that someone reproducing your work would need to know.

Don’t
- Summarize or abbreviate methods without giving full details in a discoverable supplemental section.
- Presume you will always be able to remember how you performed the experiments, or have access to private or institutional notebooks and resources.
- Attempt to hide constraints or non-optimal decisions you had to make–transparency is the key to ensuring the credibility of your research.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Methods Section for a Psychology Paper
Tips and Examples of an APA Methods Section
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
The methods section of an APA format psychology paper provides the methods and procedures used in a research study or experiment . This part of an APA paper is critical because it allows other researchers to see exactly how you conducted your research.
Method refers to the procedure that was used in a research study. It included a precise description of how the experiments were performed and why particular procedures were selected. While the APA technically refers to this section as the 'method section,' it is also often known as a 'methods section.'
The methods section ensures the experiment's reproducibility and the assessment of alternative methods that might produce different results. It also allows researchers to replicate the experiment and judge the study's validity.
This article discusses how to write a methods section for a psychology paper, including important elements to include and tips that can help.
What to Include in a Method Section
So what exactly do you need to include when writing your method section? You should provide detailed information on the following:
- Research design
- Participants
- Participant behavior
The method section should provide enough information to allow other researchers to replicate your experiment or study.
Components of a Method Section
The method section should utilize subheadings to divide up different subsections. These subsections typically include participants, materials, design, and procedure.
Participants
In this part of the method section, you should describe the participants in your experiment, including who they were (and any unique features that set them apart from the general population), how many there were, and how they were selected. If you utilized random selection to choose your participants, it should be noted here.
For example: "We randomly selected 100 children from elementary schools near the University of Arizona."
At the very minimum, this part of your method section must convey:
- Basic demographic characteristics of your participants (such as sex, age, ethnicity, or religion)
- The population from which your participants were drawn
- Any restrictions on your pool of participants
- How many participants were assigned to each condition and how they were assigned to each group (i.e., randomly assignment , another selection method, etc.)
- Why participants took part in your research (i.e., the study was advertised at a college or hospital, they received some type of incentive, etc.)
Information about participants helps other researchers understand how your study was performed, how generalizable the result might be, and allows other researchers to replicate the experiment with other populations to see if they might obtain the same results.
In this part of the method section, you should describe the materials, measures, equipment, or stimuli used in the experiment. This may include:
- Testing instruments
- Technical equipment
- Any psychological assessments that were used
- Any special equipment that was used
For example: "Two stories from Sullivan et al.'s (1994) second-order false belief attribution tasks were used to assess children's understanding of second-order beliefs."
For standard equipment such as computers, televisions, and videos, you can simply name the device and not provide further explanation.
Specialized equipment should be given greater detail, especially if it is complex or created for a niche purpose. In some instances, such as if you created a special material or apparatus for your study, you might need to include an illustration of the item in the appendix of your paper.
In this part of your method section, describe the type of design used in the experiment. Specify the variables as well as the levels of these variables. Identify:
- The independent variables
- Dependent variables
- Control variables
- Any extraneous variables that might influence your results.
Also, explain whether your experiment uses a within-groups or between-groups design.
For example: "The experiment used a 3x2 between-subjects design. The independent variables were age and understanding of second-order beliefs."
The next part of your method section should detail the procedures used in your experiment. Your procedures should explain:
- What the participants did
- How data was collected
- The order in which steps occurred
For example: "An examiner interviewed children individually at their school in one session that lasted 20 minutes on average. The examiner explained to each child that he or she would be told two short stories and that some questions would be asked after each story. All sessions were videotaped so the data could later be coded."
Keep this subsection concise yet detailed. Explain what you did and how you did it, but do not overwhelm your readers with too much information.
Tips for How to Write a Methods Section
In addition to following the basic structure of an APA method section, there are also certain things you should remember when writing this section of your paper. Consider the following tips when writing this section:
- Use the past tense : Always write the method section in the past tense.
- Be descriptive : Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your experiment, but focus on brevity. Avoid unnecessary detail that is not relevant to the outcome of the experiment.
- Use an academic tone : Use formal language and avoid slang or colloquial expressions. Word choice is also important. Refer to the people in your experiment or study as "participants" rather than "subjects."
- Use APA format : Keep a style guide on hand as you write your method section. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Make connections : Read through each section of your paper for agreement with other sections. If you mention procedures in the method section, these elements should be discussed in the results and discussion sections.
- Proofread : Check your paper for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.. typos, grammar problems, and spelling errors. Although a spell checker is a handy tool, there are some errors only you can catch.
After writing a draft of your method section, be sure to get a second opinion. You can often become too close to your work to see errors or lack of clarity. Take a rough draft of your method section to your university's writing lab for additional assistance.
A Word From Verywell
The method section is one of the most important components of your APA format paper. The goal of your paper should be to clearly detail what you did in your experiment. Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your study if they wanted.
Finally, if you are writing your paper for a class or for a specific publication, be sure to keep in mind any specific instructions provided by your instructor or by the journal editor. Your instructor may have certain requirements that you need to follow while writing your method section.
Frequently Asked Questions
While the subsections can vary, the three components that should be included are sections on the participants, the materials, and the procedures.
- Describe who the participants were in the study and how they were selected.
- Define and describe the materials that were used including any equipment, tests, or assessments
- Describe how the data was collected
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded, left-aligned and in title case.
The purpose of the methods section is to describe what you did in your experiment. It should be brief, but include enough detail that someone could replicate your experiment based on this information. Your methods section should detail what you did to answer your research question. Describe how the study was conducted, the study design that was used and why it was chosen, and how you collected the data and analyzed the results.
Erdemir F. How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):10-5. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.047
Kallet RH. How to write the methods section of a research paper . Respir Care . 2004;49(10):1229-32. PMID: 15447808.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
American Psychological Association. APA Style Journal Article Reporting Standards . Published 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

How to Write the Methods Section of a Scientific Article
What Is the Methods Section of a Research Paper?
The Methods section of a research article includes an explanation of the procedures used to conduct the experiment. For authors of scientific research papers, the objective is to present their findings clearly and concisely and to provide enough information so that the experiment can be duplicated.
Research articles contain very specific sections, usually dictated by either the target journal or specific style guides. For example, in the social and behavioral sciences, the American Psychological Association (APA) style guide is used to gather information on how the manuscript should be arranged . As with most styles, APA’s objectives are to ensure that manuscripts are written with minimum distractions to the reader. Every research article should include a detailed Methods section after the Introduction.
Why is the Methods Section Important?
The Methods section (also referred to as “Materials and Methods”) is important because it provides the reader enough information to judge whether the study is valid and reproducible.
Structure of the Methods Section in a Research Paper
While designing a research study, authors typically decide on the key points that they’re trying to prove or the “ cause-and-effect relationship ” between objects of the study. Very simply, the study is designed to meet the objective. According to APA, a Methods section comprises of the following three subsections: participants, apparatus, and procedure.
How do You Write a Method Section in Biology?
In biological sciences, the Methods section might be more detailed, but the objectives are the same—to present the study clearly and concisely so that it is understandable and can be duplicated.
If animals (including human subjects) were used in the study, authors should ensure to include statements that they were treated according to the protocols outlined to ensure that treatment is as humane as possible.
- The Declaration of Helsinki is a set of ethical principles developed by The World Medical Association to provide guidance to scientists and physicians in medical research involving human subjects.
Research conducted at an institution using human participants is overseen by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) with which it is affiliated. IRB is an administrative body whose purpose is to protect the rights and welfare of human subjects during their participation in the study.
Literature Search
Literature searches are performed to gather as much information as relevant from previous studies. They are important for providing evidence on the topic and help validate the research. Most are accomplished using keywords or phrases to search relevant databases. For example, both MEDLINE and PubMed provide information on biomedical literature. Google Scholar, according to APA, is “one of the best sources available to an individual beginning a literature search.” APA also suggests using PsycINFO and refers to it as “the premier database for locating articles in psychological science and related literature.”
Authors must make sure to have a set of keywords (usually taken from the objective statement) to stay focused and to avoid having the search move far from the original objective. Authors will benefit by setting limiting parameters, such as date ranges, and avoiding getting pulled into the trap of using non-valid resources, such as social media, conversations with people in the same discipline, or similar non-valid sources, as references.
Related: Ready with your methods section and looking forward to manuscript submission ? Check these journal selection guidelines now!
What Should be Included in the Methods Section of a Research Paper?
One commonly misused term in research papers is “methodology.” Methodology refers to a branch of the Philosophy of Science which deals with scientific methods, not to the methods themselves, so authors should avoid using it. Here is the list of main subsections that should be included in the Methods section of a research paper ; authors might use subheadings more clearly to describe their research.
- Literature search : Authors should cite any sources that helped with their choice of methods. Authors should indicate timeframes of past studies and their particular parameters.
- Study participants : Authors should cite the source from where they received any non-human subjects. The number of animals used, the ages, sex, their initial conditions, and how they were housed and cared for, should be listed. In case of human subjects, authors should provide the characteristics, such as geographical location; their age ranges, sex, and medical history (if relevant); and the number of subjects. In case hospital records were used, authors should include the subjects’ basic health information and vital statistics at the beginning of the study. Authors should also state that written informed consent was provided by each subject.
- Inclusion/exclusion criteria : Authors should describe their inclusion and exclusion criteria, how they were determined, and how many subjects were eliminated.
- Group characteristics (could be combined with “Study participants”) : Authors should describe how the chosen group was divided into subgroups and their characteristics, including the control. Authors should also describe any specific equipment used, such as housing needs and feed (usually for animal studies). If patient records are reviewed and assessed, authors should mention whether the reviewers were blinded to them.
- Procedures : Authors should describe their study design. Any necessary preparations (e.g., tissue samples, drugs) and instruments must be explained. Authors should describe how the subjects were “ manipulated to answer the experimental question .” Timeframes should be included to ensure that the procedures are clear (e.g., “Rats were given XX drug for 14 d”). For animals sacrificed, the methods used and the protocols followed should be outlined.
- Statistical analyses: The type of data, how they were measured, and which statistical tests were performed, should be described. (Note: This is not the “results” section; any relevant tables and figures should be referenced later.) Specific software used must be cited.
What Should not be Included in Your Methods Section?
Common pitfalls can make the manuscript cumbersome to read or might make the readers question the validity of the research. The University of Southern California provides some guidelines .
- Background information that is not helpful must be avoided.
- Authors must avoid providing a lot of detail.
- Authors should focus more on how their method was used to meet their objective and less on mechanics .
- Any obstacles faced and how they were overcome should be described (often in your “Study Limitations”). This will help validate the results.
According to the University of Richmond , authors must avoid including extensive details or an exhaustive list of equipment that have been used as readers could quickly lose attention. These unnecessary details add nothing to validate the research and do not help the reader understand how the objective was satisfied. A well-thought-out Methods section is one of the most important parts of the manuscript. Authors must make a note to always prepare a draft that lists all parts, allow others to review it, and revise it to remove any superfluous information.
m so confused about ma research but now m okay so thank uh so mxh
Mil gracias por su ayuda.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Infographic
- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
- Trending Now
Can AI Tools Prepare a Research Manuscript From Scratch? — A comprehensive guide
As technology continues to advance, the question of whether artificial intelligence (AI) tools can prepare…
Abstract Vs. Introduction — Do you know the difference?
Ross wants to publish his research. Feeling positive about his research outcomes, he begins to…

- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
Demystifying Research Methodology With Field Experts
Choosing research methodology Research design and methodology Evidence-based research approach How RAxter can assist researchers

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
How to Choose Best Research Methodology for Your Study
Successful research conduction requires proper planning and execution. While there are multiple reasons and aspects…

Top 5 Key Differences Between Methods and Methodology
While burning the midnight oil during literature review, most researchers do not realize that the…
How to Draft the Acknowledgment Section of a Manuscript
Discussion Vs. Conclusion: Know the Difference Before Drafting Manuscripts

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE : Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE : If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE : If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: May 18, 2024 11:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Methods Section for a Research Paper
A common piece of advice for authors preparing their first journal article for publication is to start with the methods section: just list everything that was done and go from there. While that might seem like a very practical approach to a first draft, if you do this without a clear outline and a story in mind, you can easily end up with journal manuscript sections that are not logically related to each other.
Since the methods section constitutes the core of your paper, no matter when you write it, you need to use it to guide the reader carefully through your story from beginning to end without leaving questions unanswered. Missing or confusing details in this section will likely lead to early rejection of your manuscript or unnecessary back-and-forth with the reviewers until eventual publication. Here, you will find some useful tips on how to make your methods section the logical foundation of your research paper.
Not just a list of experiments and methods
While your introduction section provides the reader with the necessary background to understand your rationale and research question (and, depending on journal format and your personal preference, might already summarize the results), the methods section explains what exactly you did and how you did it. The point of this section is not to list all the boring details just for the sake of completeness. The purpose of the methods sections is to enable the reader to replicate exactly what you did, verify or corroborate your results, or maybe find that there are factors you did not consider or that are more relevant than expected.
To make this section as easy to read as possible, you must clearly connect it to the information you provide in the introduction section before and the results section after, it needs to have a clear structure (chronologically or according to topics), and you need to present your results according to the same structure or topics later in the manuscript. There are also official guidelines and journal instructions to follow and ethical issues to avoid to ensure that your manuscript can quickly reach the publication stage.
Table of Contents:
- General Methods Structure: What is Your Story?
- What Methods Should You Report (and Leave Out)?
- Details Frequently Missing from the Methods Section
More Journal Guidelines to Consider
- Accurate and Appropriate Language in the Methods
General Methods Section Structure: What Is Your Story?
You might have conducted a number of experiments, maybe also a pilot before the main study to determine some specific factors or a follow-up experiment to clarify unclear details later in the process. Throwing all of these into your methods section, however, might not help the reader understand how everything is connected and how useful and appropriate your methodological approach is to investigate your specific research question. You therefore need to first come up with a clear outline and decide what to report and how to present that to the reader.
The first (and very important) decision to make is whether you present your experiments chronologically (e.g., Experiment 1, Experiment 2, Experiment 3… ), and guide the reader through every step of the process, or if you organize everything according to subtopics (e.g., Behavioral measures, Structural imaging markers, Functional imaging markers… ). In both cases, you need to use clear subheaders for the different subsections of your methods, and, very importantly, follow the same structure or focus on the same topics/measures in the results section so that the reader can easily follow along (see the two examples below).
If you are in doubt which way of organizing your experiments is better for your study, just ask yourself the following questions:
- Does the reader need to know the timeline of your study?
- Is it relevant that one experiment was conducted first, because the outcome of this experiment determined the stimuli or factors that went into the next?
- Did the results of your first experiment leave important questions open that you addressed in an additional experiment (that was maybe not planned initially)?
- Is the answer to all of these questions “no”? Then organizing your methods section according to topics of interest might be the more logical choice.
If you think your timeline, protocol, or setup might be confusing or difficult for the reader to grasp, consider adding a graphic, flow diagram, decision tree, or table as a visual aid.
What Methods Should You Report (and Leave Out)?
The answer to this question is quite simple–you need to report everything that another researcher needs to know to be able to replicate your study. Just imagine yourself reading your methods section in the future and trying to set up the same experiments again without prior knowledge. You would probably need to ask questions such as:
- Where did you conduct your experiments (e.g., in what kind of room, under what lighting or temperature conditions, if those are relevant)?
- What devices did you use? Are there specific settings to report?
- What specific software (and version of that software) did you use?
- How did you find and select your participants?
- How did you assign participants into groups?
- Did you exclude participants from the analysis? Why and how?
- Where did your reagents or antibodies come from? Can you provide a Research Resource Identifier (RRID) ?
- Did you make your stimuli yourself or did you get them from somewhere?
- Are the stimuli you used available for other researchers?
- What kind of questionnaires did you use? Have they been validated?
- How did you analyze your data? What level of significance did you use?
- Were there any technical issues and did you have to adjust protocols?
Note that for every experimental detail you provide, you need to tell the reader (briefly) why you used this type of stimulus/this group of participants/these specific amounts of reagents. If there is earlier published research reporting the same methods, cite those studies. If you did pilot experiments to determine those details, describe the procedures and the outcomes of these experiments. If you made assumptions about the suitability of something based on the literature and common practice at your institution, then explain that to the reader.
In a nutshell, established methods need to be cited, and new methods need to be clearly described and briefly justified. However, if the fact that you use a new approach or a method that is not traditionally used for the data or phenomenon you study is one of the main points of your study (and maybe already reflected in the title of your article), then you need to explain your rationale for doing so in the introduction already and discuss it in more detail in the discussion section .
Note that you also need to explain your statistical analyses at the end of your methods section. You present the results of these analyses later, in the results section of your paper, but you need to show the reader in the methods section already that your approach is either well-established or valid, even if it is new or unusual.
When it comes to the question of what details you should leave out, the answer is equally simple ‒ everything that you would not need to replicate your study in the future. If the educational background of your participants is listed in your institutional database but is not relevant to your study outcome, then don’t include that. Other things you should not include in the methods section:
- Background information that you already presented in the introduction section.
- In-depth comparisons of different methods ‒ these belong in the discussion section.
- Results, unless you summarize outcomes of pilot experiments that helped you determine factors for your main experiment.
Also, make sure your subheadings are as clear as possible, suit the structure you chose for your methods section, and are in line with the target journal guidelines. If you studied a disease intervention in human participants, then your methods section could look similar to this:
Since the main point of interest here are your patient-centered outcome variables, you would center your results section on these as well and choose your headers accordingly (e.g., Patient characteristics, Baseline evaluation, Outcome variable 1, Outcome variable 2, Drop-out rate ).
If, instead, you did a series of visual experiments investigating the perception of faces including a pilot experiment to create the stimuli for your actual study, you would need to structure your methods section in a very different way, maybe like this:
Since here the analysis and outcome of the pilot experiment are already described in the methods section (as the basis for the main experimental setup and procedure), you do not have to mention it again in the results section. Instead, you could choose the two main experiments to structure your results section ( Discrimination and classification, Familiarization and adaptation ), or divide the results into all your test measures and/or potential interactions you described in the methods section (e.g., Discrimination performance, Classification performance, Adaptation aftereffects, Correlation analysis ).
Details Commonly Missing from the Methods Section
Manufacturer information.
For laboratory or technical equipment, you need to provide the model, name of the manufacturer, and company’s location. The usual format for these details is the product name (company name, city, state) for US-based manufacturers and the product name (company name, city/town, country) for companies outside the US.
Sample size and power estimation
Power and sample size estimations are measures for how many patients or participants are needed in a study in order to detect statistical significance and draw meaningful conclusions from the results. Outside of the medical field, studies are sometimes still conducted with a “the more the better” approach in mind, but since many journals now ask for those details, it is better to not skip this important step.
Ethical guidelines and approval
In addition to describing what you did, you also need to assure the editor and reviewers that your methods and protocols followed all relevant ethical standards and guidelines. This includes applying for approval at your local or national ethics committee, providing the name or location of that committee as well as the approval reference number you received, and, if you studied human participants, a statement that participants were informed about all relevant experimental details in advance and signed consent forms before the start of the study. For animal studies, you usually need to provide a statement that all procedures included in your research were in line with the Declaration of Helsinki. Make sure you check the target journal guidelines carefully, as these statements sometimes need to be placed at the end of the main article text rather than in the method section.
Structure & word limitations
While many journals simply follow the usual style guidelines (e.g., APA for the social sciences and psychology, AMA for medical research) and let you choose the headers of your method section according to your preferred structure and focus, some have precise guidelines and strict limitations, for example, on manuscript length and the maximum number of subsections or header levels. Make sure you read the instructions of your target journal carefully and restructure your method section if necessary before submission. If the journal does not give you enough space to include all the details that you deem necessary, then you can usually submit additional details as “supplemental” files and refer to those in the main text where necessary.
Standardized checklists
In addition to ethical guidelines and approval, journals also often ask you to submit one of the official standardized checklists for different study types to ensure all essential details are included in your manuscript. For example, there are checklists for randomized clinical trials, CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) , cohort, case-control, cross‐sectional studies, STROBE (STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology ), diagnostic accuracy, STARD (STAndards for the Reporting of Diagnostic accuracy studies) , systematic reviews and meta‐analyses PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta‐Analyses) , and Case reports, CARE (CAse REport) .
Make sure you check if the manuscript uses a single- or double-blind review procedure , and delete all information that might allow a reviewer to guess where the authors are located from the manuscript text if necessary. This means that your method section cannot list the name and location of your institution, the names of researchers who conducted specific tests, or the name of your institutional ethics committee.

Accurate and Appropriate Language in the Methods Section
Like all sections of your research paper, your method section needs to be written in an academic tone . That means it should be formal, vague expressions and colloquial language need to be avoided, and you need to correctly cite all your sources. If you describe human participants in your method section then you should be especially careful about your choice of words. For example, “participants” sounds more respectful than “subjects,” and patient-first language, that is, “patients with cancer,” is considered more appropriate than “cancer patients” by many journals.
Passive voice is often considered the standard for research papers, but it is completely fine to mix passive and active voice, even in the method section, to make your text as clear and concise as possible. Use the simple past tense to describe what you did, and the present tense when you refer to diagrams or tables. Have a look at this article if you need more general input on which verb tenses to use in a research paper .
Lastly, make sure you label all the standard tests and questionnaires you use correctly (look up the original publication when in doubt) and spell genes and proteins according to the common databases for the species you studied, such as the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee database for human studies .
Visit Wordvice AI’s AI Text Editor to receive a free grammar check and English editing services (including manuscript editing , paper editing , and dissertation editing ) before submitting your manuscript to journal editors.
- Interlibrary Loan and Scan & Deliver
- Course Reserves
- Purchase Request
- Collection Development & Maintenance
- Current Negotiations
- Ask a Librarian
- Instructor Support
- Library How-To
- Research Guides
- Research Support
- Study Rooms
- Research Rooms
- Partner Spaces
- Loanable Equipment
- Print, Scan, Copy
- 3D Printers
- Poster Printing
- OSULP Leadership
- Strategic Plan
Scholarly Articles: How can I tell?
- Journal Information
- Literature Review
- Author and affiliation
- Introduction
- Specialized Vocabulary
Methodology
- Research sponsors
- Peer-review
The methodology section or methods section tells you how the author(s) went about doing their research. It should let you know a) what method they used to gather data (survey, interviews, experiments, etc.), why they chose this method, and what the limitations are to this method.
The methodology section should be detailed enough that another researcher could replicate the study described. When you read the methodology or methods section:
- What kind of research method did the authors use? Is it an appropriate method for the type of study they are conducting?
- How did the authors get their tests subjects? What criteria did they use?
- What are the contexts of the study that may have affected the results (e.g. environmental conditions, lab conditions, timing questions, etc.)
- Is the sample size representative of the larger population (i.e., was it big enough?)
- Are the data collection instruments and procedures likely to have measured all the important characteristics with reasonable accuracy?
- Does the data analysis appear to have been done with care, and were appropriate analytical techniques used?
A good researcher will always let you know about the limitations of his or her research.
- << Previous: Specialized Vocabulary
- Next: Results >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 3:26 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.oregonstate.edu/ScholarlyArticle
Contact Info
121 The Valley Library Corvallis OR 97331–4501
Phone: 541-737-3331
Services for Persons with Disabilities
In the Valley Library
- Oregon State University Press
- Special Collections and Archives Research Center
- Undergrad Research & Writing Studio
- Graduate Student Commons
- Tutoring Services
- Northwest Art Collection
Digital Projects
- Oregon Explorer
- Oregon Digital
- ScholarsArchive@OSU
- Digital Publishing Initiatives
- Atlas of the Pacific Northwest
- Marilyn Potts Guin Library
- Cascades Campus Library
- McDowell Library of Vet Medicine
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
How to Master the Methods Section of Your Research Paper

The Methods section is a fundamental component of any research paper, playing a crucial role in establishing the validity and reliability of your study. It serves as a detailed roadmap of the research process that you undertook, providing sufficient information for the replication of the study. An effectively written Methods section can enhance the impact and credibility of your research, giving your readers a clear understanding of how your findings were achieved.
The methods section essentially answers the questions:
- What did you do?
- How did you do it?
- What tools and procedures did you use?
- And how did you analyze the data you collected?
Providing thorough responses to these questions, it typically includes detailed descriptions of your research design , participants or subjects of study, equipment or materials used, the procedures you followed, and the statistical methods applied for data analysis.
In the following sections, we'll delve into each of these elements, providing you with a comprehensive guide on how to craft a compelling, informative, and rigorous Methods section for your research paper.
Understanding the purpose of the methods section
Adding validity and credibility to the research.
The Methods section plays a pivotal role in adding validity and credibility to your research. By detailing the procedures you used, it allows readers to evaluate the soundness of your methodology. A well-written Methods section makes your research transparent, enabling others to understand exactly what you did and how you did it. This transparency not only adds to the credibility of your work but also allows for an accurate evaluation of the results. The Methods section is where you demonstrate that your research has been conducted in a rigorous, systematic, and ethical manner.
Enabling replication of the study
Perhaps one of the most crucial roles of the Methods section is to allow other researchers to replicate your study. Replication is a key aspect of scientific research - it's how we ensure that findings are not mere flukes or products of bias. By providing a clear and detailed description of your methodology, others can repeat your study under the same conditions to see if they achieve similar results. This not only reinforces the robustness of your own research but also contributes to the collective knowledge in your field. Consequently, the Methods section must be thorough and precise, ensuring that every step of your process can be duplicated accurately.
Deciding what to include in your methods section
Elements to include in the methods section.
The Methods section should provide a clear and comprehensive account of how you conducted your study. The content can vary depending on your field of study and the nature of your research, but typically, you should include the following elements:
- Participants: Describe who took part in your study. This might include details about their demographics (age, gender, etc.), how they were selected, and how they were assigned to groups in the case of experimental research.
- Materials and Equipment: Detail the materials or equipment you used during your study. This can range from lab equipment in a scientific study, surveys or tests in a social science study, to software and data sources in a computational study.
- Procedure: Give a step-by-step account of what you did during your study. This should be detailed enough to enable another researcher to replicate your study exactly.
- Data Analysis Methods: Explain how you analyzed your data. This might include statistical analysis methods, coding procedures for qualitative data , or computational algorithms.
Balancing detail and brevity
While it's important to provide enough detail in your Methods section to allow for replication, it's also crucial to avoid including unnecessary or irrelevant information. Striking a balance between detail and brevity is key. You should aim to provide a complete account of your methodology without getting lost in minute details that don't significantly impact the understanding or replication of your research.
Ask yourself, "Would including this detail enhance the understanding of my study or the ability to replicate it?" If the answer is no, you can likely leave that detail out. Remember, the goal is to provide a thorough, yet concise and readable account of your research methods .
Writing the participants section
Describing the participants.
In describing your participants, or subjects, it's essential to provide clear demographic information. This includes, but is not limited to, aspects like age, sex, ethnicity, occupation, education level, or any other characteristic relevant to your study. These details help provide context and allow readers to understand who your research is applicable to. For instance, a study involving only teenagers will have different implications than one involving adults.
Discussing selection and assignment to groups
The process of participant selection and assignment to groups is fundamental to many research studies, especially those involving experimental design. You should describe how you recruited your participants (e.g., through random sampling, convenience sampling, etc. ), and how they were assigned to different conditions or treatment groups if applicable. This might include a description of any randomization or matching procedures used. Clarity in this section bolsters the transparency and replicability of your study.
Ethical considerations in participant selection and treatment
It's also vital to discuss any ethical considerations related to your participants. This includes obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy and confidentiality, and minimizing potential harm. If your study was reviewed and approved by an Institutional Review Board (IRB) or Ethics Committee, mention this in your Methods section. It's also appropriate to detail any steps you took to minimize potential bias or discrimination in participant selection. This not only demonstrates your commitment to ethical research practices but also contributes to the credibility of your study.
Writing the materials and equipment section
Detailing materials and equipment used in the study.
When detailing the materials and equipment used in your study, it's important to be as specific and precise as possible. This might include the make and model of equipment, the type and source of materials, and even the versions of software packages used. These specifics enable replication and also allow other researchers to understand the tools that contributed to your findings. This part of the Methods section might vary significantly depending on your field of research. For example, a biology study might detail the type of microscopes used, whereas a psychology study could discuss specific psychometric tests.
Providing information about unique or unusually used tools
If you used special or unique tools, or if you used standard tools in an unusual way, this should be clearly specified in the Materials and Equipment section. Describe these tools or methods in detail, and explain why they were necessary for your study. If a tool is rare or specialized, consider providing a citation or source where readers can learn more about it. If a standard tool was used in a novel or unconventional way, explain what you did and why. This not only adds interest to your paper, but also contributes to the complete understanding and potential replication of your research. Remember, transparency is key in this section, as it helps enhance the credibility of your study and its findings.
Writing the procedure section
Importance of including each step taken during the study.
The Procedure section serves as a step-by-step guide to your study, detailing each phase from start to finish. The significance of this section cannot be overstated, as it offers a comprehensive look at the "how" of your research. Each step you took, every decision you made, and all procedures you followed should be recorded in this section. This level of detail not only supports your study's validity but also enables others to replicate your study accurately, fostering scientific transparency.
Tips for writing clearly and concisely, yet with enough detail for replication
When detailing your procedures, clarity and conciseness are key. Strive to describe your methods in a way that's straightforward and easy to follow. Avoid jargon where possible, and when it's unavoidable, make sure to provide clear definitions.
Remember, while conciseness is important, so too is the inclusion of sufficient detail to allow for replication. One approach to ensuring the right level of detail is to write as though you are explaining your study to another researcher in your field. They should be able to read your Procedure section and know exactly how to carry out your study.
Considerations for describing experimental and control conditions
If your study involved experimental and control conditions, these should be described with particular care. Detail the experimental procedures, clearly stating what distinguishes the experimental group from the control group. This includes any stimuli or treatments that were administered, as well as how, when, and where they were delivered. In addition, it's essential to articulate any measures that were taken to minimize the effects of confounding variables. This precise detailing underscores the reliability of your research and enhances the likelihood of accurate replication.
Writing the data analysis section
Describing the statistical or other methods used to analyze the data.
In the Data Analysis section, your aim should be to clearly describe the statistical or other methods you used to analyze your data. Include specifics about the tests used, the software employed, and the reasoning behind choosing these particular methods. For statistical tests, mention the test name, the variables it was used for, and any specific variations of the test that were applied. If you conducted qualitative analysis, explain the coding process, thematic analysis, or other methods used. Providing this level of detail allows other researchers to assess the appropriateness and rigor of your data analysis.
Importance of including all steps of the analysis, not just the final results
Remember that the Data Analysis section is not just about presenting the final results, but also about revealing the process you used to get there. Including each step of your analysis provides a complete picture of your research journey and ensures that your methodology can be accurately replicated and evaluated by others. Whether it involves data cleaning, variable coding, preliminary analyses, or specific sequences of statistical tests, all these details contribute to the overall transparency of your research.
Explaining any adjustments for potential biases or confounds
Lastly, be sure to explain any adjustments or corrections you made to account for potential biases or confounding variables in your data. This may include controlling for certain variables, dealing with missing data, or using specific statistical techniques to address these issues. Clearly articulating these adjustments enhances the reliability and validity of your findings, and also provides a more comprehensive understanding of your research approach. This is also where you can discuss the limitations of your study and how you accounted for them in your analysis.
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
Typical errors in the methods section.
One common mistake in writing the Methods section is providing too little detail. A lack of specificity can make it difficult for others to replicate your study or fully understand your process. On the other hand, including too much detail, particularly irrelevant information, can dilute the focus of your Methods section and confuse your readers.
Another common error is forgetting to include important steps, such as the processes for data cleaning, preprocessing, or certain aspects of participant recruitment and management. Also, failing to adequately discuss ethical considerations, when relevant, can negatively impact the perceived credibility of your research.
Tips and strategies for avoiding these mistakes
In order to effectively avoid common errors when writing the Methods section of your research paper, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Create a Detailed Outline: Begin by outlining your Methods section in detail. This will help you ensure that all important elements of your research process are captured and not forgotten in the final write-up.
- Strive for Balance: Aim for a balance between brevity and comprehensiveness. Remember, your primary objective is to provide enough information so that someone else can replicate your study.
- Review for Relevance: After drafting your section, review it to ensure that all included information is relevant and necessary. If certain details do not directly contribute to understanding your method or facilitating replication, consider removing them.
- Include Ethical Considerations: Ethics are a crucial aspect of any research. Therefore, remember to discuss any ethical considerations and approvals related to your study.
- Get Feedback: Have colleagues or mentors review your Methods section. They can offer valuable feedback and catch any errors or omissions you may have overlooked. It's always beneficial to have another pair of eyes on your work.
Sample methods sections and analysis
Consider the following examples of well-written methods sections from different fields of study. These fictional examples illustrate the important elements discussed above:
Psychology study example
In this study, 100 undergraduate students (50 males and 50 females, aged 18-25) were randomly selected from XYZ University. The selection criteria included full-time enrollment status and willingness to participate in the study. All participants provided informed consent prior to participation, and the study received ethical approval from the University's Institutional Review Board.
The instruments used included a demographic questionnaire, the Big Five Personality Test, and an academic performance survey. The demographic questionnaire gathered data on participants' age, gender, major, and year in college. The Big Five Personality Test, a validated and reliable instrument, was used to assess participants' personality traits. Academic performance was gauged through self-reported grade point averages (GPAs).
The experiment was conducted in a quiet and well-lit room. Participants first completed the demographic questionnaire, followed by the personality test. Afterward, they reported their GPAs on the academic performance survey. All responses were recorded anonymously to protect participant confidentiality.
The data were analyzed using SPSS software, version 24. Pearson's correlation coefficient was used to assess the relationship between personality traits and academic performance.
Psychology study example analysis
The above example illustrates several good practices in writing a methods section.
- Clear description of participants: The researcher clearly stated the number, gender distribution, and age range of the participants, and also mentioned the selection criteria.
- Detailed information about materials: The researcher named the tests and surveys used and briefly described what they measure.
- Transparent procedure: The researcher provided a step-by-step guide to how the experiment was conducted, ensuring that it could be replicated by others.
- Explanation of data analysis: The researcher stated which software was used and what statistical tests were performed.
Environmental science study example
For this study, soil samples were collected from 10 different locations within the ABC National Park. The locations were chosen to represent a variety of habitats within the park, including grassland, wetland, and forest areas. The study was conducted in the spring season to ensure consistency in environmental conditions.
At each location, five soil samples were taken using a standard soil corer. The samples were taken from the top 10 cm of the soil, as this is where the majority of biological activity typically occurs. Each sample was immediately sealed in a sterile container to prevent contamination.
Back in the lab, the soil samples were analyzed for nutrient content and microbial diversity. Nutrient content, including levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, was measured using a soil nutrient testing kit from XYZ Company. Microbial diversity was assessed through DNA extraction and sequencing, using the DEF DNA extraction kit and the GHI sequencing platform.
The collected data were then analyzed using the JKL statistical software package. A one-way ANOVA was used to compare nutrient levels between the different habitats, while microbial diversity was evaluated using a diversity index.
In all cases, appropriate precautions were taken to minimize potential contamination and to ensure the accuracy of our measurements. This study was approved by the ABC National Park's Research Review Board.
Environmental science study example analysis
This example effectively demonstrates the correct structure and content for a methods section in environmental science.
- Clear explanation of sample collection: The researcher has detailed where, when, and how the soil samples were collected.
- Transparent process of sample analysis: The specific procedures and equipment used for analyzing the samples are clearly outlined, providing potential for replication.
- Methodical data analysis: The use of specific software and statistical tests is mentioned, providing clarity on how results were derived.
Linguistics study example
For this study, the use of passive voice in academic writing across disciplines was investigated. A corpus of 500 peer-reviewed journal articles was created, comprising 100 articles from each of the following disciplines: Social Sciences, Humanities, Natural Sciences, Applied Sciences, and Formal Sciences. Articles were selected randomly from journals indexed in the ABC Database from the year 2022.
The data collection tool was a script written in Python, utilizing the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) for text processing and analysis. The script identified and counted instances of passive voice in each article.
The articles were processed one by one, first being converted into plain text files to allow for easy processing. The Python script then ran on each text file, analyzing and storing the data on passive voice usage. This process was automated to minimize errors and ensure consistency.
For data analysis, the counts of passive voice instances were normalized by the total word count of each article to account for variations in article length. The differences in passive voice usage across disciplines were then statistically analyzed using a Chi-square test in the R software environment.
All procedures in this study were designed with consideration to copyright and fair use policies. The Python script used for this study is openly available for other researchers to use and modify.
Linguistics study example analysis
This example demonstrates effective writing of a methods section in a Linguistics study.
- Detailed description of the corpus: The researcher clearly defined the source and composition of the corpus, including the number of texts and their disciplinary distribution.
- Explanation of data collection tool and process: The researcher explained the software and process used for text analysis, providing enough detail for replication.
- Transparent data analysis: The researcher mentioned how they accounted for variations in article length and which statistical test was used for analysis.
Remember, although methods sections will differ across disciplines, they all should provide a clear, concise, and replicable roadmap of the research process.
The methods section of a research paper is a critical component that adds credibility to your research and allows others to replicate and verify your study. It involves providing detailed descriptions of the participants, materials and equipment used, the procedures followed, and the methods of data analysis.
While the exact content may vary depending on your research design and field of study, a well-crafted methods section will always focus on clarity, comprehensiveness, and transparency. The examples provided in this post illustrate good practices in diverse fields and can serve as a guide for you to construct your own.
Avoid common errors by creating a detailed outline, striving for balance in information, reviewing for relevance, including ethical considerations, and getting feedback from colleagues or mentors.
With these steps, you'll be well on your way to writing a high-quality methods section that bolsters your research paper's integrity and contributes meaningfully to your field.
Header image by Cytonn Photography .
Related Posts

Everything You Need To Know About Footnotes

What Makes a Good Research Question?
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Elevate your research paper with expert editing services
Covidence website will be inaccessible as we upgrading our platform on Monday 23rd August at 10am AEST, / 2am CEST/1am BST (Sunday, 15th August 8pm EDT/5pm PDT)
How to write the methods section of a systematic review
Home | Blog | How To | How to write the methods section of a systematic review
Covidence breaks down how to write a methods section
The methods section of your systematic review describes what you did, how you did it, and why. Readers need this information to interpret the results and conclusions of the review. Often, a lot of information needs to be distilled into just a few paragraphs. This can be a challenging task, but good preparation and the right tools will help you to set off in the right direction 🗺️🧭.
Systematic reviews are so-called because they are conducted in a way that is rigorous and replicable. So it’s important that these methods are reported in a way that is thorough, clear, and easy to navigate for the reader – whether that’s a patient, a healthcare worker, or a researcher.
Like most things in a systematic review, the methods should be planned upfront and ideally described in detail in a project plan or protocol. Reviews of healthcare interventions follow the PRISMA guidelines for the minimum set of items to report in the methods section. But what else should be included? It’s a good idea to consider what readers will want to know about the review methods and whether the journal you’re planning to submit the work to has expectations on the reporting of methods. Finding out in advance will help you to plan what to include.
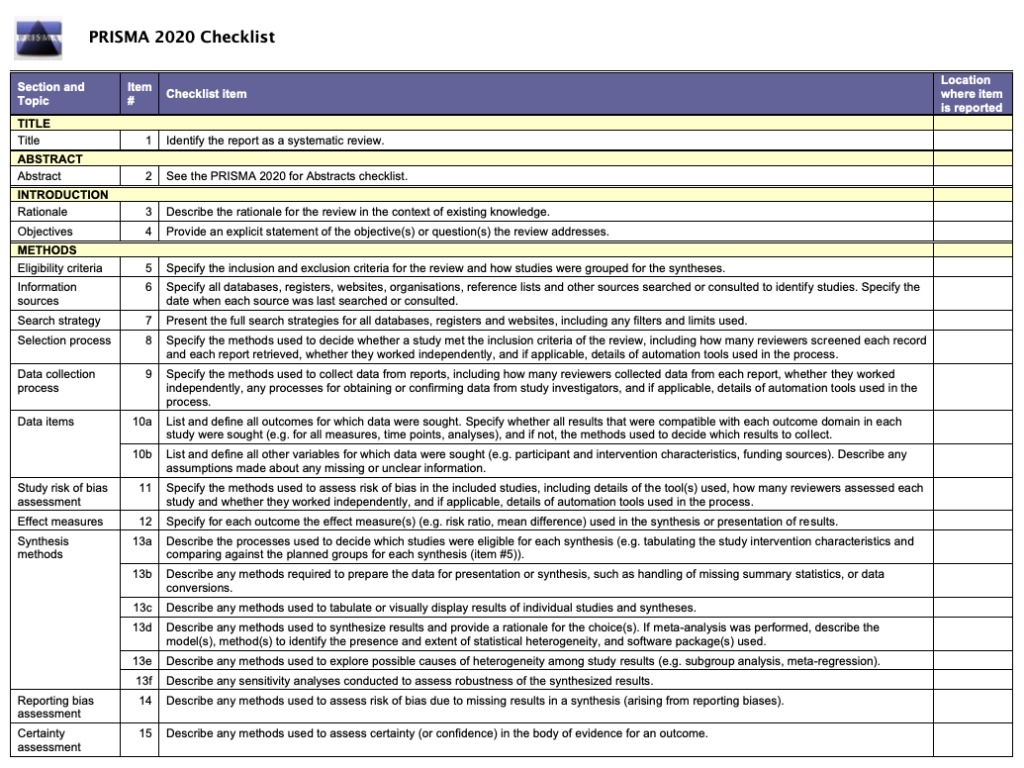
Describe what happened
While the research plan sets out what you intend to do, the methods section is a write-up of what actually happened. It’s not a simple case of rewriting the plan in the past tense – you will also need to discuss and justify deviations from the plan and describe the handling of issues that were unforeseen at the time the plan was written. For this reason, it is useful to make detailed notes before, during, and after the review is completed. Relying on memory alone risks losing valuable information and trawling through emails when the deadline is looming can be frustrating and time consuming!
Keep it brief
The methods section should be succinct but include all the noteworthy information. This can be a difficult balance to achieve. A useful strategy is to aim for a brief description that signposts the reader to a separate section or sections of supporting information. This could include datasets, a flowchart to show what happened to the excluded studies, a collection of search strategies, and tables containing detailed information about the studies.This separation keeps the review short and simple while enabling the reader to drill down to the detail as needed. And if the methods follow a well-known or standard process, it might suffice to say so and give a reference, rather than describe the process at length.
Follow a structure
A clear structure provides focus. Use of descriptive headings keeps the writing on track and helps the reader get to key information quickly. What should the structure of the methods section look like? As always, a lot depends on the type of review but it will certainly contain information relating to the following areas:
- Selection criteria ⭕
- Data collection and analysis 👩💻
- Study quality and risk of bias ⚖️
Let’s look at each of these in turn.
1. Selection criteria ⭕
The criteria for including and excluding studies are listed here. This includes detail about the types of studies, the types of participants, the types of interventions and the types of outcomes and how they were measured.

2. Search 🕵🏾♀️
Comprehensive reporting of the search is important because this means it can be evaluated and replicated. The search strategies are included in the review, along with details of the databases searched. It’s also important to list any restrictions on the search (for example, language), describe how resources other than electronic databases were searched (for example, non-indexed journals), and give the date that the searches were run. The PRISMA-S extension provides guidance on reporting literature searches.
Systematic reviewer pro-tip:
Copy and paste the search strategy to avoid introducing typos
3. Data collection and analysis 👩💻
This section describes:
- how studies were selected for inclusion in the review
- how study data were extracted from the study reports
- how study data were combined for analysis and synthesis
To describe how studies were selected for inclusion , review teams outline the screening process. Covidence uses reviewers’ decision data to automatically populate a PRISMA flow diagram for this purpose. Covidence can also calculate Cohen’s kappa to enable review teams to report the level of agreement among individual reviewers during screening.
To describe how study data were extracted from the study reports , reviewers outline the form that was used, any pilot-testing that was done, and the items that were extracted from the included studies. An important piece of information to include here is the process used to resolve conflict among the reviewers. Covidence’s data extraction tool saves reviewers’ comments and notes in the system as they work. This keeps the information in one place for easy retrieval ⚡.
To describe how study data were combined for analysis and synthesis, reviewers outline the type of synthesis (narrative or quantitative, for example), the methods for grouping data, the challenges that came up, and how these were dealt with. If the review includes a meta-analysis, it will detail how this was performed and how the treatment effects were measured.
4. Study quality and risk of bias ⚖️
Because the results of systematic reviews can be affected by many types of bias, reviewers make every effort to minimise it and to show the reader that the methods they used were appropriate. This section describes the methods used to assess study quality and an assessment of the risk of bias across a range of domains.
Steps to assess the risk of bias in studies include looking at how study participants were assigned to treatment groups and whether patients and/or study assessors were blinded to the treatment given. Reviewers also report their assessment of the risk of bias due to missing outcome data, whether that is due to participant drop-out or non-reporting of the outcomes by the study authors.
Covidence’s default template for assessing study quality is Cochrane’s risk of bias tool but it is also possible to start from scratch and build a tool with a set of custom domains if you prefer.
Careful planning, clear writing, and a structured approach are key to a good methods section. A methodologist will be able to refer review teams to examples of good methods reporting in the literature. Covidence helps reviewers to screen references, extract data and complete risk of bias tables quickly and efficiently. Sign up for a free trial today!

Laura Mellor. Portsmouth, UK
Perhaps you'd also like....

Top 5 Tips for High-Quality Systematic Review Data Extraction
Data extraction can be a complex step in the systematic review process. Here are 5 top tips from our experts to help prepare and achieve high quality data extraction.

How to get through study quality assessment Systematic Review
Find out 5 tops tips to conducting quality assessment and why it’s an important step in the systematic review process.

How to extract study data for your systematic review
Learn the basic process and some tips to build data extraction forms for your systematic review with Covidence.
Better systematic review management
Head office, working for an institution or organisation.
Find out why over 350 of the world’s leading institutions are seeing a surge in publications since using Covidence!
Request a consultation with one of our team members and start empowering your researchers:
By using our site you consent to our use of cookies to measure and improve our site’s performance. Please see our Privacy Policy for more information.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article?
In contrast to past centuries, scientific researchers have been currently conducted systematically in all countries as part of an education strategy. As a consequence, scientists have published thousands of reports. Writing an effective article is generally a significant problem for researchers. All parts of an article, specifically the abstract, material and methods, results, discussion and references sections should contain certain features that should always be considered before sending a manuscript to a journal for publication. It is generally known that the material and methods section is a relatively easy section of an article to write. Therefore, it is often a good idea to begin by writing the materials and methods section, which is also a crucial part of an article. Because “reproducible results” are very important in science, a detailed account of the study should be given in this section. If the authors provide sufficient detail, other scientists can repeat their experiments to verify their findings. It is generally recommended that the materials and methods should be written in the past tense, either in active or passive voice. In this section, ethical approval, study dates, number of subjects, groups, evaluation criteria, exclusion criteria and statistical methods should be described sequentially. It should be noted that a well-written materials and methods section markedly enhances the chances of an article being published.
How to Write a Materials and Methods Section of a Scientific Article?
Up to the 18 th Century scientific researches were performed on a voluntary basis by certain scientists. However from the second half of the 19 th century, scientific development has gained momentum with the contributions of numerous scientists including Edison, Fleming, and Koch. In parallel with these developments, apparently each scientific field, and even their branches made, and still making magnificent progressions from the end of the 18 th century. Secondary to these developments, scientific researches have been implemented systematically by universities, and various institutions in every part of the world as an integral component of national strategies. Naturally, the number of researchers who performed scientific investigations or sponsored by various institutions increased considerably. Also, as is known very well, all over the world scientists, and researchers move from one place to another to disseminate scientific knowledge. All of these scientific efforts, and activities reflect on clinical practice, and hundreds of thousands, and millions scientific articles which we can currently gain access into all of them online. As indicated by the investigator Gerard Piel, “Without publication, science is dead” which explains the importance of publication. In other words, if you don’t share your investigation and knowledge, they don’t mean anything by themselves. Although sharing the knowledge is essential for writing a scientific paper, nowadays writing a scientific article is mostly learnt as a master-apprentice relationship, and therefore certain standards have not been established. This phenomenon creates serious stress especially for young investigators in their early stage of writing scientific papers. Indeed investigators receiving their residency training confront this reality finally during writing of their dissertations. Though sharing knowledge is known as a fundamental principle in writing a scientific paper, it creates difficulties in the whole world. Relevant to this issue, in the whole world investigations have been performed, and books have been written on the subject of how to write a scientific paper. Accordingly, in our country mostly local meetings, and courses have been organized. These organizations, and investigations should be performed. Indeed, nowadays, in the first assessments, the rejection rate of the journals by internationally acknowledged scientific indexes as “Science Citation İndex (SCI)” and “Science Citation İndex Expanded (SCI-extended” which have certain scientific standards, increases to 62 percent. As a matter of fact only 25% of Class A journals have been included in the lists of SCI, and SCI-extended.
As we all know very well, scientific articles consist of sections of summary, introduction, material, and methods, discussion, and references. Among them, conventionally Materials and Methods section has been reported as the most easily written or will be written section. Although it is known as the most easily written section, nearly 30% of the reasons for rejection are related to this section per se. Therefore due care, and attention should be given to the writing of this section. In the writing process of the ‘Material and Methods’ section, all achievements performed throughout the study period should be dealt with in consideration of certain criteria in a specific sequence. Since as a globally anticipated viewpoint, ‘Materials and Methods’ section can be written quite easily, it has been indicated that if difficulties are encountered in writing a manuscript, then one should start writing from this section. In writing this section, study design describing the type of the article, study subjects to be investigated, methods, and procedures of measurements should be provided under four main headings. [ 1 , 2 ] Accordingly, in brief, we can emphasize the importance of providing clear-cut, adequate, and detailed information in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section to the scientists who will read this scientific article. Meeting these criteria carries great importance with respect to the evaluation of reliability of the investigation by the readers, and reviewers, and also informing them about procedural method, design, data collection, and assessment methods of the investigation, Priorly, as is the case in all scientific investigations, one should be reminded about the importance, and indispensability of compliance with certain standard writing rules. Accordingly, rules of grammar should be obeyed, and if possible passive voice of simple past tense should be used. Related to these rules, use of verbs ‘investigated’, ‘evaluated’ or ‘performed’ will be appropriate. Recently, expressions showing the ownership of the investigation as ‘we performed’, ‘we evaluated’, ‘we implemented’ have taken priority. Since the important point is communication of the message contained in the scientific study, the message should be clearly comprehensible. While ensuring clarity of the message, use of flourishing, and irrelevant sentences should be avoided. [ 1 , 3 ] According to another approach, since our article will be read by professionals of other disciplines, it is important to comply with certain rules of writing. To that end, standard units of measurements, and international abbreviations should be used. Abbreviations should be explained within parentheses at their first mention in the manuscript. For instance let’s analyze the following sentence” The patients were evaluated with detailed medical history, physical examination, complete urinalysis, PSA, and urinary system ultrasound” The abbreviation PSA is very well known by the urologist. However we shouldn’t forget that this article will be read by the professionals in other medical disciplines. Similarly this sentence should not be written as: “The patients were evaluated with detailed medical history, physical examination, complete urinalysis PSA (prostate-specific antigen), and urinary system ultrasound.” Indeed the abbreviation should follow the explanation of this abbreviation. Then the appropriate expression of the sentence should be. “The patients were evaluated with detailed medical history, physical examination, complete urinalysis, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and urinary system ultrasound.”
In addition to the abovementioned information, in the beginning paragraphs of ‘Materials and Methods’ section of a clinical study the answers to the following questions should be absolutely provided:
- The beginning, and termination dates of the study period.
- Number of subjects/patients/experimental animals etc. enrolled in the study,
- Has the approval of the ethics committee been obtained?
- Study design (prospective, retrospective or other). [ 1 , 2 , 4 – 7 ]
Still additional features of the study design (cross-sectional) should be indicated. Apart from this, other types of study designs (randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled or double-blind, parallel control etc.) should be revealed.
The heading of the section “Materials and Methods” can be changed to “Patients and the Method” in accordance with writing rules of the journal in question. Indication of starting, and termination dates of a clinical study will facilitate scientific interpretation of the article. Accordingly, outcomes obtained during development phase of a newly implemented method might be considered differently from those acquired during conventional use of this method. Besides, incidence of the diseases, and number of affected people might vary under the impact of social fluctuations, and environmental factors. Therefore with this justification study period should be specified. Number of cases included in the study should be absolutely indicated in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section. It will be appropriate to determine study population after consultation to a statistician-and if required-following “power analysis” Accordingly, the need for a control group will be indicated based on the study design. Nowadays, as a requirement of patient rights, obtainment of approval from ethics committee should be indicated with its registration number. In addition, acquirement of informed consent forms from patients should be indicated. Ethics Committee approval should be obtained in prospective studies performed with study drugs. Otherwise in case of occurrence of adverse effects, it should be acknowledged that in compliance with Article #90 of the Turkish Criminal Law, a 3-year prison sentence is given to the guilty parties. [ 8 ] Since issues related to the Ethics Committee are the subject of another manuscript, they won’t be handled herein.
The following paragraph exemplifies clearly the aforementioned arguments: “After approval of the local ethics committee (BADK-22), informed consent forms from the patients were obtained, and a total of 176 cases with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) were retrospectively evaluated between January 2011, and December 2012.” In a prospectively designed study, methods used to communicate with the cases including face-to-face interviews, phone calls and/or e-mail should be indicated. [ 1 , 2 ] Each paragraph or subheading in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section should be in accordance with the related ones in the ‘Results’ section. In other words, the sequence of paragraphs, and subheadings in the ‘Results’ section should be the same in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section.
As a next step, names of the groups, and distribution of the cases in these groups should be indicated. For instance: the statement “Cases were divided into 3 groups based on their LUTS scores as. Groups 1 (0–9; n=91), 2 (10–18; n=66), and 3 (≥19; n=20)” clearly delineates the scope of the study at baseline.. In the ‘Materials and Methods’ section the number of study subjects should be absolutely documented. Herein, after assignment of names to groups, in the rest of the manuscript, these names should be used. For example instead of saying: “Mean ages of the cases with LUTS scores between 0–9, 10–18, and ≥19 were determined to be 63.2±2.1, 62.8±4.5, and 65.7±3.9 years, respectively” it will be more comprehensible to use the expression: “Mean ages of the Groups 1, 2, and 3 were specified as 63.2±2.1, 62.8±4.5, and 65.7±3.9 years.” (p=0.478). Expressions indicated in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section should not be repeated in the “Results” section. Thus, errors of repetition will be precluded. Following the abovementioned information, the evaluation method of the cases enrolled in the study should be indicated. Hence, results of medical history, physical examination, and if performed laboratory or radiological evaluations-in that order-should be indicated. The application of survey study-if any-should be investigated, and documented. Therefore, the following sentences encompass all the information stated above: “The cases were evaluated with detailed medical history, physical examination, measurements of serum follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), testosterone (T) levels, complete urinalysis, urinary flow rate, direct urinary system roentgenograms, urinary system ultrasound, and if required cyctoscopy. Lower urinary system complaints, and erectile dysfunction were evaluated using International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), and International Erectile Function Scale (IIEF), respectively.” Apparently, questionnaire forms were used in the above-cited study. However, methods used for the evaluation of questionnaire forms, and significance of the results obtained, and if possible, the first performer of this survey should be written with accompanying references. In relation to the abovementioned questionnaires the following statements constitute standard expressions for the ‘Materials and Methods’ section: “International Prostate Symptom Score (IPPS) was used in the determination of the severity of prostatic symptoms. IPSS used to determine the severity of the disease, evaluate treatment response, and ascertain the symptomatic progression, is the most optimal scoring system recommended by European Association of Urology (EAU) which classifies the severity of the disease based on IPSS scores as mild (0–7), moderate (8–19), and severe symptomatic (20–35) disease. In the evaluation of sexual function International Erectile Function Scale (IIEF) was used. IIEF is one of the most prevalently used form for the patients who consulted for the complaints of sexual dysfunction Based on IIEF scores, the severity of the disease was classified as severe (1–10), moderate (11–16), mild to moderate (17–21), mild (22–25), and no ED (26–30).”
Whether the institutions of the authors working for should be written in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section can be a subject of debate, generally viewpoints favour provision of this information. However, in compliance with their writing rules, some journals do not favour open-label studies where name of the study site is indicated, and this principle is communicated to the author during editorial evaluation Besides, in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section, the brand of the study object, and its country of origin should be indicated. (ie. if radiological methods are used, then the brand of radiological equipment, and its manufacturing country should be specified. In a study entitled ‘The Impact of Computed Tomography in the Prediction of Post-Radical Nephrectomy Stage in Renal Tumours’ since the main topic of the study is computed tomography, the specifications of the equipment used should be explicitely indicated. On the other hand, the details of the medical method which can effect the outcomes of the study should be also recorded. Accordingly, the methods applied for percutaneous nephrolithotomy, ureterorenoscopy, varicocelectomy, transurethral prostatectomy, radical prostatectomy (perineal, open, laparoscopic or robotic should be absolutely indicated. Then inclusion, and exclusion criteria, and if used control group, and its characteristics should be documented. Thus the following paragraph about exclusion criteria will be appropriate: Patients with a history of neurogenic bladder, prostatic or abdominal operation, and transrectal ultrasound guided prostate biopsy (within the previous 6 months), those aged <40 or >70 years, individuals with a peak urine flow rate below 10 ml/sec, and residual urine more than 150 cc were not included in the study.” [ 1 – 3 , 9 ]
Some diseases mentioned in the “Materials and Methods” section require special monitorization procedures. In these cases the procedure of monitorization should be documented for the sake of the validity of the study in question. Accordingly, in conditions such as “nephrectomy, prostatectomy, orchidectomy, pyeloplasty, varicocelectomy, drug therapies, penile prosthesis, and urethral stricture” clinical follow-up protocols should be provided.
The abovementioned rules, and recommendations are most frequently valid for a clinical study, and some points indicated in experimental studies should be also considered. Types, weights, gender, and number of the animals used in animal studies should be absolutely specified. Besides condition of evaluation of experimental animals should be noted. Then as is the case with clinical studies, approval of the ethics committee should be obtained, and documented. Accordingly, the beginning paragraphs of the ‘Materials and Methods’ can be expressed as follows:
“In the study, 40 Wistar-Albino 6-month-old rats each weighing 350–400 g were used. After approval of the ethics committee (HADYEK-41) the study was performed within the frame of rules specified by the National Institute for animal experiments. The rats were divided into 3 groups. Hence, Group 1 (n=7) was accepted as the control group. The rats subjected to partial ureteral obstruction with or without oral carvedilol therapy at daily doses of 2 mg/kg maintained for 7 days constituted Groups 3 (n=8), and 2 (n=8), respectively. Each group of 4 rats was housed in standard cages with an area of 40×60 cm. The animals were fed with standard 8 mm food pellets, and fresh daily tap water. The rats were kept in the cages under 12 hours of light, and 12 hours of dark. Ambient temperature, and humidity were set at 22±2°C, and 50±10%, respectively.”
Herein, the method, and agent of anesthesia used (local or general anesthesia) in surgical procedures, and then the experimental method applied should be clearly indicated. For example the following sentences explain our abovementioned arguments; “All surgical procedures were performed under xylazine-ketamine anesthesia. In all groups, ureters were approached through midline abdominal incision. In Group 1, ureters were manipulated without causing obstruction. Results of biochemical, and pathological evaluations performed in Group 1 were considered as baseline values.”
“Through a midline abdominal incision partial ureteral obstruction was achieved by embedding two-thirds of the distal part of the left ureter into psoas muscle using 4/0 silk sutures as described formerly by Wen et al. [ 10 ] ( Figure 1 ). [ 11 ] All rats were subjected to left nephrectomies at the end of the experimental study.” As formulated by the above paragraph, if the method used is not widely utilized, then the first researcher who describes the method should be indicated with relevant references. One or more than one figures with a good resolution, and easily comprehensible legends should be also included in the explanation of the experimental model. For very prevalently used experimental models as torsion models cited in the “Materials and Methods” section, there is no need to include figures in the manuscript.

Partial ureteral obstruction model [ 11 ]
Appropriate signs, and marks placed on the figure will facilitate comprehension of the legends ( Figure 2 ).

Ureteral segments (black arrows) seen in a rat partial ureteral obstruction model [ 11 ]
The signs used will also improve intelligibility of the target. The figures should be indicated within parentheses in their first mention in the “Materials and Methods” section. Headings and as a prevalent convention legends of the figures should be indicated at the end of the manuscript.
If a different method is used in the study, this should be explained in detail. For instance, in a study where the effect of smoking on testes was investigated, the method, and the applicator used to expose rats to cigarette smoke should be indicated in the ‘Methods’ section following classical description. Relevant to the study in question, the following paragraph explaining the study method should be written: “A glass chamber with dimensions of 75 × 50 × 50 cm was prepared, and divided into 4 compartments with wire fences. The rats in the 2., and 4. cages were placed in these compartments. Each compartment contained 4 rats. Cigarette smoke was produced using one cigarette per hour, and smoke coming from the tip, and the filter of the lighted cigarette was pumped into the gas chamber with a pneumatic motor. The rats were exposed to smoke of 6 cigarettes for 6 hours. The compartments of the rats were changed every day so as to achieve balanced exposure of the rats to cigarette smoke.” [ 12 ]
Meanwhile, chemical names, doses, and routes of administration of the substances used in experimental studies should be indicated. If the substance used is a solution or an antibody, then manufacturing firm, and its country should be indicated in parenthesis. This approach can be exemplified as “Animals used in experiments were randomized into 4 groups of 8 animals. Each group was housed in 2 cages each containing 4 animals. The first group did not undergo any additional procedure (Group 1). The second group was exposed to cigarette smoke (Group 2). The third (Group 3), and the fourth (Group 4) groups received daily intraperitoneal injectable doses of 10 mg/kg resveratrol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The Group 4 was also exposed to cigarette smoke. [ 12 ]
After all of these procedures, method, and analytical procedure of histopathological examination used should be described-if possible-by a pathologist Similarly, biochemical method used should be referenced, and written by the department of clinical chemistry. It can be inferred that each division should describe its own method. In other words, histopathological, microbiological, and pharmacological method should be described in detail by respective divisions.
If we summarize all the information stated above, understandably sharing of the scientific knowledge is essential.. Since reproducibility of a study demonstrates the robustness of a study, with the detailed approaches indicated above, reproducibility of our study is provided, and the relevant questions of “How?”, and “How much?” are answered. Besides, since ‘Materials, and Methods’, and ‘Results’ sections will constitute a meaningful whole, explanations of all information related to the data mentioned in the ‘Results’ section should be provided. As an important point not to be forgotten, evaluation or measurement method used for each parameter indicated in the ‘Results’ section should be expounded in the “Materials and Methods” section. For example if you used an expression in the” Results” section like “median body mass index (BMI) of the patients was 27.42 kg/m 2 ”, then you should beforehand indicate that comparative evaluation of BMIs will be done in the “Materials and Methods” section. In addition, the description, and significance of the values expressed in the “Results” section should be indicated in the “Materials and Methods” section. In other words, it should be stated that the patients were evaluated based on their BMIs as normal (18–24.9 kg/m 2 ), overweight (25 kg/m 2 –40 kg/m 2 ), and morbid obesity (>40 kg/m 2 ). If you encounter difficulties in writing “Materials and Methods” section, also a valid approach for other sections, firstly simple headings can be written, then you can go into details. In brief, for every parameter, the reader should get clear-cut answers to the questions such as “How did they evaluate this parameter, and which criteria were used?”. [ 1 , 3 , 13 – 15 ]
The last paragraph of the ‘Materials, and Methods’ section should naturally involve statistical evaluations. This section should be written by statisticians. Accordingly, the preferred statistical method, and the justifications for this preference should be indicated. In conventional statistical evaluations, provision of details is not required. In information indicated above, the statement “For statistical analysis, ANOVA test, chi-square test, T test, Kruskal-Wallis test have been used.” is not required very much. Instead, more appropriate expression will be a statement indicating that recommendations of a knowledgeable, and an experienced statistician were taken into consideration or advanced statistical information was reflected on the statistical evaluations as follows: “Chi-square tests were used in intergroup comparisons of categorical variables, and categorical variables were expressed as numbers, and percentages. In comparisons between LUTS, and ED as for age, independent two samples t-test was used. In the evaluation of the factors effective on erectile dysfunction multivariate logistic regresssion test was used. P values lower than 0.05 were considered as statistically significant The calculations were performed using a statistical package program (PASW v18, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL).” Herein, the type of statistical package used for statistical methods should be emphasized.
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Manuscript
Affiliation.
- 1 Respiratory Care Services, Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, Arkansas. [email protected].
- PMID: 37643870
- PMCID: PMC10676260 (available on 2024-12-01 )
- DOI: 10.4187/respcare.11437
The methods section of a manuscript is one of the most important parts of a research paper because it provides information on the validity of the study and credibility of the results. Inadequate description of the methods has been reported as one of the main reasons for manuscript rejection. The methods section must include sufficient detail so that others could repeat the study and reproduce the results. The structure of the methods section should flow logically and chronologically. There are multiple components of methods sections, including study design, materials used, study procedures, and data analysis. Each element must be adequately described and thoroughly detailed to provide an understanding of how the results were obtained and how to interpret the findings. Studies that involved humans or animals must include an ethics statement of approval from the appropriate governing body. The methods section should explain how subjects were identified and should state inclusion and exclusion criteria. All materials used to complete the study should be described in detail, including equipment, drugs, gases, chemicals, treatments, interventions, or other items. Study procedures should outline all steps taken to obtain the results and clearly state the outcome measures. Subheadings might be helpful for organizing the methods section into subsections when there is a considerable amount of information to report. A well-written methods section will guide the reader through the research process and provide adequate information to evaluate study validity and reproduce the work. The purpose of this paper is to provide guidance for writing the methods section of a manuscript.
Keywords: manuscript; methods; publication; research; research paper; science writing; study protocol.
Copyright © 2023 by Daedalus Enterprises.
- Research Design*
We use cookies on this site to enhance your experience
By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies.
A link to reset your password has been sent to your email.
Back to login
We need additional information from you. Please complete your profile first before placing your order.
Thank you. payment completed., you will receive an email from us to confirm your registration, please click the link in the email to activate your account., there was error during payment, orcid profile found in public registry, download history, how to write a methods section in your research paper.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 17 August, 2020
- Academic Writing Skills
The Methods section is the part of a scientific paper that describes how the study was carried out. This section describes each technique that was used in the study and any relevant details about the materials, subjects, and so on. Some journals refer to this as the ‘Materials and Methods’ section, and some clinically-focused journals will refer to it as the ‘Patients and Characteristics’ section.
The primary aim of the Methods section is to describe how the study was performed in enough detail that another researcher could replicate it exactly if they wished to. It is always written in the past tense (e.g., ‘1 mL of solution was added to each sample’), and can be the easiest section of the paper to write; many researchers start with this section first when writing a paper.
How should the Methods section be organised?
A Methods section is divided into a number of subsections, each of which is dedicated to a single technique or collection of related techniques. The heading of each subsection should either clearly state the technique that subsection describes, if it only describes one, or the aim of the set of techniques, if the subsection describes multiple related techniques. For example, a subsection that only explains how qRT-PCR was carried out could simply be titled ‘qRT-PCR’, whereas a subsection describing complete blood count, enzyme tests, and cholesterol panel could be titled ‘Blood testing’.
Within each subsection, the information should be presented in order from the most general to the most specific. For example, in a study using human subjects, the entire study population should be described first (e.g. ‘Subjects were an average of 40 years old (range: 35–45), and 50% were male (23/46).’), followed by more detailed descriptions of each of the experimental or control groups within that population (e.g., ‘The subjects in group A smoked 1–2 times per week, the subjects in group B smoked 2–10 times per week, and the subjects in group C did not smoke.’).
Information within subsections should also ideally be presented in chronological order. For example, patient recruitment should be described before explaining how the recruited patients were divided into groups A, B, and C.
The subsections themselves should be presented in the same order in which the techniques that they describe are mentioned in the Results section. For example, if Figure 1 shows immunofluorescence microscopy images of cultured cells, the subsection describing the cell line and culture conditions, as well as the subsection describing how the microscopy was performed, should appear early on in the Methods section. Using this approach will help readers quickly and easily find the detailed information pertaining to each experiment as they read through the paper. The exception to this rule is ethics/consent statements and descriptions of statistical analyses, as discussed in more detail below.
What information should be included in the Methods section?
In addition to describing how each experiment was performed, the Methods section should provide detailed descriptions of all of the materials and equipment used to carry out those experiments. Generally speaking, most journals require that the supplier name and location (city and country) be specified for any specialized reagents and equipment mentioned in the Methods. It can also be helpful to provide catalogue numbers for highly specific materials, such as antibodies. As mentioned above, the ultimate goal is to provide enough detail to enable another researcher to reproduce each experiment exactly, so it helps to be as specific as possible.
In the case of studies involving experimental animals, an ethics statement should be included that clearly states whether ethical approval was obtained to perform the study and that cites the name of the ethics board that provided this approval. For studies involving human subjects, a similar ethics statement should be included, as well as a statement of whether the subjects consented to participate, and what type of consent this was (e.g., written or verbal, informed or otherwise).
Any statistical analyses performed as part of the study are typically described in the final subsection of the Methods. When writing this subsection, be sure to clearly reference the technique(s) described earlier in the section that each statistical test was applied to. For example, instead of saying: ‘Data were analysed by Student’s t-test.’, specify which data you are referring to: ‘The average values for group A and group B were compared by Student’s t-test.’
Some specialized types of studies need to comply with formal guidelines for reporting of methods (and other aspects of the study), so check carefully to see whether this applies to your situation. For example, papers reporting the results from randomised controlled trials should conform to CONSORT guidelines , and systematic reviews and analyses should comply with PRISMA guidelines for reporting. We recommend consulting any such relevant guidelines when writing the Methods section, and checking with your target journal to see whether any related documents such as checklists and/or flowcharts should be included in the Methods or as a supplemental file when the paper is submitted.
On a related note, some journals have specific requirements for Methods reporting, for example using the. STAR guidelines (Structured, Transparent, Accessible Reporting). It’s helpful to check the publisher website of your target journal as it may offer downloadable guidance for how to apply these standards to papers prior to submission.
How to reduce the word count of the Methods section
Given the extensive amount of information that needs to be presented in a Methods section, this part of the paper can sometimes become very lengthy and exceed your target journal’s word limit. Fortunately, there are a number of ways in which the word count can be reduced without omitting any crucial information.
For established or commonly used methods, it is appropriate to cite an article or other resource that describes that method in detail instead of providing a lengthy description in your own paper. For example: ‘Cells were harvested and sorted as described by Chen, et al. [1].’ If you used a previously published technique but modified it slightly to adapt it to your study, this same approach can be used; for example: ‘Western blotting was performed as described by Fouquet, et al. [2], with minor modifications, as follows: …’.
Another useful approach for decreasing the word count of the Methods section is to reference the supplier’s protocol for kits or any other reagents that come with specific instructions for use. For example: ‘Total protein was isolated using the Gerard Protein Extraction Kit (Gerard Bio, Inc., London, UK) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.’
Finally, tables can be used to present detailed information that may be too extensive to include the Methods or too difficult to interpret when incorporated into the text, such as lists of primers and their sequences, or lists of antibodies and their dilutions. While including this type of table in the main body of the text could distract readers from the study findings, many journals permit the inclusion of tables that support the methods in the Supplementary Information, so that the information is available if readers wish to seek it out, but does not interrupt the flow of the text.
If you are seeking additional support for writing or revising your Methods section, we are here to help. Charlesworth Author Services provide expert English language editing and publication support services. Why not get in touch with a member of our Charlesworth Author Services team for more information.
Our academic writing and publishing training courses, online materials, and blog articles contain numerous tips and tricks to help you navigate academic writing and publishing, and maximise your potential as a researcher. You can find out more about our Free author training webinar series by clicking here .
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Share with your colleagues
Related articles.

Writing a strong Methods section
Charlesworth Author Services 12/03/2021 00:00:00
Recommended webinars

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication: Module 8: Write a strong methods section
Charlesworth Author Services 05/03/2021 00:00:00

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication: Module 6: Choose great titles and write strong abstracts

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication: Module 7: Write a strong theoretical framework section

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication: Module 10: Enhance your paper with visuals

Bitesize Webinar: How to write and structure your academic article for publication: Module 9:Write a strong results and discussion section

Article Titles: The Do's and Don'ts
Charlesworth Author Services 25/04/2017 00:00:00
- Advanced search

Advanced Search
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Manuscript
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- Figures & Data
- Info & Metrics
The methods section of a manuscript is one of the most important parts of a research paper because it provides information on the validity of the study and credibility of the results. Inadequate description of the methods has been reported as one of the main reasons for manuscript rejection. The methods section must include sufficient detail so that others could repeat the study and reproduce the results. The structure of the methods section should flow logically and chronologically. There are multiple components of methods sections, including study design, materials used, study procedures, and data analysis. Each element must be adequately described and thoroughly detailed to provide an understanding of how the results were obtained and how to interpret the findings. Studies that involved humans or animals must include an ethics statement of approval from the appropriate governing body. The methods section should explain how subjects were identified and should state inclusion and exclusion criteria. All materials used to complete the study should be described in detail, including equipment, drugs, gases, chemicals, treatments, interventions, or other items. Study procedures should outline all steps taken to obtain the results and clearly state the outcome measures. Subheadings might be helpful for organizing the methods section into subsections when there is a considerable amount of information to report. A well-written methods section will guide the reader through the research process and provide adequate information to evaluate study validity and reproduce the work. The purpose of this paper is to provide guidance for writing the methods section of a manuscript.
- research paper
- science writing
- publication
- study protocol
- Introduction
Dissemination of research findings occurs through abstracts, posters, presentations, and manuscripts. 1 , - , 3 Writing the manuscript is considered the last step of the research process because it provides a detailed account of the research from start to finish. 4 , 5 The main components of a research paper include an abstract, the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusions. 3 , 4 Each section of the manuscript is important and has a specific role in describing the research story. However, the methods are one of the most critical sections of a manuscript because the details are used to evaluate and determine the validity of the study and credibility of the results. 6 Validity in research refers to reliability of the measured results: the extent to which the study accurately measured what it intended (internal validity) and how the results can be applied to the general population beyond the study (external validity). 6 , 7
The methods section describes what was done to answer the research question. 8 This section specifies how the research was done, the rationale for the procedures, what materials were used, and how the results were analyzed, all in a clear, concise, and organized manner. 6 The description of the research should provide enough detail so others could repeat the study and reproduce the results. 6 , 9 , 10 Much of the methods section should be written before the study is initiated. Indeed, for funded research, a detailed methods section is written as part of the grant application. There are several aspects of the methods sections, and the essential elements will vary, depending on the type of study. Submission requirements differ among journals; therefore, it is important to consult the instructions for authors for the specific journal to ensure that all necessary elements are included. 11 The purpose of this paper is to describe the different components of the methods section and provide guidance for writing the methods section of a research paper.
- General Considerations
An inadequate description of methods has been identified as one of the top reasons for manuscript rejection. 12 It has been suggested that including too much information is better than having insufficient detail because irrelevant content can later be omitted. 12 The methods section of a research paper is analogous to a recipe. 10 , 13 A recipe is composed of multiple elements, including the list and quantity of ingredients, equipment and tools needed and applicable settings, and the detailed instructions for how to create the recipe. Similar to a recipe, there are different elements of methods to describe in a manuscript. In general, common components of the methods section include a description of the study design, materials used, study procedures, measurements or calculations, and the statistical tests used to analyze the results. Materials used to conduct research are comparable with the ingredients, tools, and equipment for a recipe. Materials represent what was studied, including subjects, equipment or devices, and treatments or interventions. 6 , 14 The steps to create a recipe are akin to study procedures such as the process for data collection, measurements, calculations, and statistical analysis. A summary of the different elements of the methods section is included in Table 1 . The individual components for each element may vary, depending on the nature of the study.
- View inline
- Download powerpoint
Methods Section Elements
Although similarities exist between a recipe and the methods section of a research paper, the methods section should not be formatted to read like a recipe. 13 Use past tense for writing the methods section because the study has been completed and describes what was already done. 6 , 9 , 10 , 13 , 14 The methods section should be structured for logical and chronological flow. 6 , 14 , 15 Use of subheadings can be helpful for organizing the different components for the methods section when there is a substantial amount of detail to describe. 6 , 13 However, subheadings may not be required by some journals. An excessive use of subheadings can be distracting to the reader by interrupting the flow of the manuscript. There should not be a subheading for every paragraph. This is particularly distracting when each subheading is followed by a short 1- or 2-sentence paragraph. Paragraphs with fewer than 3 sentences should be avoided; combine the information with another paragraph unless the journal to which the paper will be submitted requires specific subheadings. Subheadings can be useful as an outline when writing the methods section but then might be omitted in the final manuscript.
A common error in manuscript writing is reporting results in the methods section and vice versa. A frequently occurring example is including the number of subjects who participated in the research in the methods section when it was unknown how many met inclusion criteria before study initiation and subject screening. The methods section should only include information available during the planning phase, before study initiation. 10 , 16 There are instances in which study procedures may have changed after the study commencement. This information would be reported in the methods section but the outcomes stated in the results section. The results section should reflect the data obtained from study procedures because this information would be unknown before the study was completed.
- Study Design
The methods section often begins with an overall description of the study design and key attributes, including the type of study, setting, time frame, and procedures. 14 , 15 This provides an overview and context for how the study was conducted with further details and specifics described in subsequent subsections. Study design has been described as a road map for the methods section to provide information for how to understand the approach and interpret the results. 14
Common study designs include observational, bench evaluation, systematic review, randomized controlled trial, survey, and others. Guidelines for writing the manuscript include the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) checklist for randomized controlled trials and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for systematic reviews. 17 , 18 Registration is another consideration for clinical trials and systematic reviews. The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) 16 requires registration of clinical trials on a public trials registry. Many journals, including R espiratory C are , follow the recommendations for publication set forth by this group. A randomized controlled trial should also include the blinding mechanism and different treatment groups as applicable. 17 Although registration of a systematic review is often not a prerequisite for publication, registering the protocol supports transparency, decreases potential bias, and can help prevent duplication of reviews. 18 An observational study should report if the design was retrospective, prospective, a secondary or post hoc analysis, or other category of observational design. 7
The setting where the study occurred, if it included data from a single-center or multiple centers, and the time frame in which it took place must be included because these factors have implications for clinical practice, generalizability, and validity. 7 Potential study settings might include an ICU (or specific ICU type), medical surgical ward, emergency department, out-patient clinic, home-care environment, or simulation laboratory. The time frame is an essential element for context because practices and trends change over time. A prime example of this is prone positioning for treatment of hypoxemic respiratory failure as use substantially increased during the COVID-19 pandemic. 19
- Ethics Statement
The United States Department of Health and Human Services defines a human subject “as a living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research obtains information or biospecimens through intervention or interaction with the individual, and uses, studies, or analyzes the biospecimens; or obtains, uses, studies, analyzes, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens.” 20 The methods section must include a statement regarding approval from an institutional review board (IRB) or ethics committee for research that included human subjects. 16 Quality improvement studies and certain types of surveys are often not considered human subject research and therefore may not require IRB oversight but the decision is made by the IRB. Quality improvement projects, depending on requirements of the institution or organization, can be performed without IRB approval in some cases; however, IRB approval is needed before publication or presentation outside of the institution, and human subject determination is made by the IRB, not the investigators.
Animal studies also require ethics approval to be reported in the methods section. Research that involves animals is subject to approval from the local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and must be conducted in accordance with national guidelines, for example, the National Institute of Health Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 21 For journals that do not have a specific requirement for where to include the ethics statement within the methods section, many authors typically incorporate it in the initial general description of the study or with the detailed description of the subjects. Some studies have included it at the beginning of the methods section.
Characteristics of the study population should be described. This includes basic demographics (eg, adults or children, age, sex) and general health status such as if the individuals were healthy volunteers or had a specific diagnosis or condition. This information is also needed for control groups. 4 Inclusion criteria for how subjects were identified and selected should be detailed as well as reasons for exclusion. For example, an evaluation of a disease management program included adults ages ≥ 65 years and with COPD who were admitted to 1 of 5 hospitals during a specified time frame. 22 Patients were excluded if they left against medical advice, died during admission, transferred to a hospital outside of the health system, entered hospice care, refused home care, or were unable to participate in education. 22 In this example, subject characteristics (adults with COPD), selection and identification (hospital admission during defined time frame), and exclusion criteria are clearly stated.
When referring to human subjects in research, the terms subject and patient are often used interchangeably, but there is a difference. 23 A patient receives care to improve health, and care is individualized in each particular case. When a patient participates in research, he or she becomes a subject. In research, care is designed to create information and is the same for all subjects based on the study protocol. The individual conducting the research is not always involved in the patient care provided, thus also making the distinction between subject and patient. A common error is to use the word subjects exclusively when writing the manuscript. However, individuals are patients before enrollment. When referring to the broader population of individuals who might benefit from the research findings, the word patients is likely more correct. Participant and volunteer are other terms that can be used in place of subject. Individuals who participated in survey research are typically referred to as respondents . 24
In addition to humans, research subjects may also involve animals or organisms such as cells. When animals are studied, the methods should describe the species, weight, age, and sex of the animals. 6 Ring et al 25 used ex vivo porcine lungs to evaluate the effect of breathing pattern and nebulization on exhaled viral content during mechanical ventilation. The authors reported that the lungs were sourced from a retail processing facility and were from 6-month-old Yorkshire hybrid pigs that weighed 118 kg. In addition, it was noted that approval to conduct the study was granted by the local Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. This publication demonstrates an appropriate description of animal subjects, including an ethics statement.
- Equipment and Other Materials
Identify all equipment and other materials used in the study, including devices, related accessories, drugs, or chemicals. At first mention of any device, provide the specific name of the item, model number if applicable, and manufacturer information. Many scientific journals do not usually allow use of trademark or registration symbols. 10 The ICMJE recommends that manufacturer name and location be included in parentheses. 16 For example, a study that evaluated the safety and feasibility of breathing high-dose nitric oxide in healthy volunteers used a Sievers 280i nitric oxide analyzer (GE Analytical Instruments, Boulder, Colorado) to measure nitric oxide gas concentration. 26 Subsequent mentions of equipment should be noted by generic name versus trade name when possible. It is important that the methods section does not project any bias that an author may have for a specific device or manufacturer.
Use of figures can be an effective means of providing a visual description of the equipment setup, especially when there are many components involved. This can also help reduce the amount of text and improve understanding of how the equipment was assembled. Figures can be either a photograph of the equipment or a graphic illustration (line drawing), but all components should be clearly labeled. An illustration of the setup used to deliver high-dose nitric oxide in the aforementioned study is provided in Figure 1 . 26 Use of a photograph to depict the experimental setup for measuring peak expiratory flow during mechanical insufflation-exsufflation is demonstrated in Figure 2 . 27 Photographs should be of good quality and include all relevant items. In both examples, all components are clearly identified and labeled.
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
Graphic illustration of an experimental setup. From Reference 26.
Photograph of an experimental setup. From Reference 27.
In addition to naming the specific equipment used in the study, settings should also be included in the methods section because these details are highly relevant for duplication of the study. For example, the evaluation of peak expiratory flow during mechanical insufflation-exsufflation provided the pressure settings used during therapy. 27 Not only is this important for repeating the study, but it is also essential for assessing the validity of the results. If the settings were not typical of those used in the study population or in clinical practice, then this would introduce limitations to interpreting and understanding the results.
Equipment preparation is another consideration for the methods section. Describe the calibration process and the frequency for equipment that requires calibration. The flow meter used to measure peak expiratory flow during mechanical insufflation-exsufflation was calibrated and validated annually by the manufacturer. 27 If manufacturer standards for calibration are not followed, then the accuracy of the results may be affected. It should be noted that calibration and validation represent two different processes. 4 Both should be described as applicable.
In addition to equipment, identify all drugs, chemicals, gases, or other materials used specifically for the study. The details for drugs and gases should include the concentration, dose, frequency, and route of administration. Gases should also note the flow used. Chemicals should be noted with the name and concentration as applicable. Use the generic name for drugs. If the trade name for a drug is relevant to the study, then follow the same process for identifying equipment brands and manufacturer information and use the generic name after initial identification. Preparation information may be needed in some cases. For example, detailed preparation information was provided for the bacteriophage used in the animal study conducted by Ring et al. 25 The process for how the bacteriophage was prepared was described in detail as well as the amounts used for the study.
- Study Procedures
The methods section should explicitly detail all procedures, treatments, or interventions used in the study. This portion of the methods section describes how study procedures were performed, the chronological order of procedures, measurements or calculations made, and the specific data elements collected. A rationale may be needed for some procedures, depending on the audience. 6 Outcome measures are often included in the subsection for study procedures, but some authors report them in the overall description for study design.
A comprehensive explanation of the procedures is vital for providing adequate details for reproducibility and validity regardless of the study design. A retrospective cohort study investigated outcomes of children treated with continuous albuterol that contains benzalkonium chloride and preservative-free solutions. 28 Collected data were clearly stated and included subject demographics, diagnosis, mortality risk score, albuterol dose and duration, use of adjunctive therapies, and respiratory support. The methods section for this paper also reported the source of the data extraction (electronic medical records, database, manual chart review) and the process for how therapies were initiated, escalated, and de-escalated (intensivist discretion). 28 The basis for the use of therapies in this study is an important consideration for generalizability because practices vary among institutions and some care might involve the use of protocols.
Diagrams and flow charts can be helpful for illustrating processes or workflow. An evaluation of sputum volume obtained with different cough augmentation techniques outlined the protocol in an illustrated timeline for the sequence of interventions and data collection ( Fig. 3 ). 29 The timeline provides clear information for the procedures that were done, when they were done, and the data elements collected. Data were collected at baseline, at the end of the intervention, and then 1 h after the intervention, followed by a minimum 4-h washout period before the second intervention and data collection. 29 Details with regard to who performed the interventions (5 experienced respiratory clinicians), how they were administered (cough augmentation technique and settings), and subject information (positioning) were comprehensively described.
Illustrated timeline of study protocol that depicts chronological order. From Reference 29.
Measurements obtained during study procedures should be identified along with a description of how they were obtained and the devices used. For example, the same study measured ventilator parameters before, during, and after interventions by using a Fluxmed GrH monitor (MBMED, Buenos Aires, Argentina). 29 Procedures for measurements or techniques with established references do not have to be described in detail and can be omitted if the procedure could be repeated without the specific details. 6 , 12 , 14 This is a common practice for measurements obtained during spirometry. In those instances, provide the reference for the previous work without providing all of the additional details. In a study that aimed to correlate baseline spirometry with airway hyper-responsiveness in methacholine challenge, the reported testing was performed according to published guidelines. 30 The guideline was referenced without providing all the specifics. On the contrary, studies that used novel methods would need to be further described. 6
The outcome measures that address the research question should be clearly stated. Outcome measures are the dependent or response variables assessed to evaluate the impact of the research that is established before beginning the study. 6 , 8 Outcome measures may include both primary and secondary outcomes. The primary outcome is the main measure of the research question, and secondary outcomes provide additional information for interpreting results. The retrospective evaluation of different albuterol solutions used ICU and hospital length of stay as primary outcomes and duration of continuous albuterol, use and duration of adjunctive therapies, and need for mechanical ventilation as secondary outcomes. 28 The primary outcome was sputum volume for the trial that assessed cough augmentation techniques, and secondary outcomes were respiratory mechanics and hemodynamics. 29
- Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis component is typically included as the last part of the methods section. This subsection describes how the collected data were analyzed through identification of the statistical tests that were used and the P value threshold for statistical significance. A clinical trial that evaluated the effect of endotracheal tube scraping during mechanical ventilation reported that categorical variables were analyzed with the chi-square or Fisher exact test, and continuous variables were presented as mean ± SD or median (interquartile range) based on distribution and analyzed with t test or Mann-Whitney test. 31 P < .05 was considered significant. The statistical analysis section of this paper distinctly identified the tests used to analyze specific data points and provided an explanation for when mean or median was reported.
The statistical analysis should also describe how the power analysis was conducted to determine the appropriate sample size. Justification for the approach should be provided when needed. For example, the study that evaluated the effect of endotracheal tube scraping calculated sample size for each treatment group based on previous institutional data for the mean duration of mechanical ventilation and determined that each group needed 136 subjects with an alpha of 0.05 and power of 0.80. 31 Citing references for the rationale and justification for the selected statistical tests is also an approach to support the choice of test. The previously noted evaluation of methacholine reactivity used a reference to support the use of partition analysis. 30 The software package and version used for data analysis should also be specified in the data analysis portion of the methods section. 16
- A Methods Model
Several publications were used throughout this paper to demonstrate the different elements of the methods section of a research paper. A summary of each of those elements and the individual components comprised within each subsection adapted from the endotracheal tube scraping clinical trial are included in Table 2 . 31 It is important to note how some items were further described in the text, such as the technique for airway suctioning, the definition of a successful spontaneous breathing trial, an explanation for extubation outcome, the elements of the ventilator-associated event prevention bundle, and how ventilator-associated events were defined. These specifics provide additional information to help determine validity and generalizability, and highlight the importance of including enough detail to duplicate the study.
Summary of Methods Elements and Details from a Published Paper
The methods section is an important part of a manuscript because it provides information on the validity of the study. One of the main reasons for manuscript rejection is an inadequate description of the methods. Enough detail must be provided so others could repeat the study and reproduce the results, similar to following a recipe. The methods section should be structured for logical and chronological flow, and be written in past tense. There are multiple components of the methods section that must be adequately described and thoroughly detailed to provide an understanding of how the results were obtained to interpret the findings. Subheadings can be helpful for organizing the methods section into subsections when there is a considerable amount of information to report, but subheadings should be used judiciously. A well-written methods section will guide the reader through the research process and provide adequate information to evaluate study validity and credibility of the results as well as reproduce the work.
- Correspondence: Denise Willis MSc RRT RRT-NPS AE-C FAARC, Respiratory Care Services, Arkansas Children’s Hospital, 1 Children’s Way, Slot 303, Little Rock, AR 72202. E-mail: WillisLD{at}archildrens.org
Ms Willis is a Section Editor for R espiratory C are .
Ms Willis presented a version of this paper at the symposium Research in Respiratory Care at AARC Congress 2022 held November 8, 2022, in New Orleans, Louisiana.
- Copyright © 2023 by Daedalus Enterprises
- Stenson JF ,
- Lendner M ,
- Annesley TM
- Ghasemi A ,
- Bahadoran Z ,
- Zadeh-Vakili A ,
- Montazeri SA ,
- Hosseinpanah F
- Azevedo LF ,
- Canário-Almeida F ,
- Almeida Fonseca J ,
- Costa-Pereira A ,
- Hespanhol V
- 16. ↵ International Committee of Medical Journal Editors . Recommendations for the conduct, reporting, editing, and publication of scholarly work in medical journals . Updated May 2022 . https://www.icmje.org/recommendations/ . Accessed July 6, 2023
- Zaccagnini M ,
- 20. ↵ United States Department of Health and Human Services . 45 Code of Federal Regulations Part 46 . https://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/regulations-and-policy/regulations/45-cfr-46/index.html . Accessed July 6, 2023
- 21. ↵ National Institutes of Health Office of Laboratory and Animal Welfare . Public Health Service Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals . https://olawnihgov/policies-laws/phs-policyhtm 2015 . Accessed July 6, 2023.
- Truumees M ,
- Tonzola D ,
- Cerrone F ,
- Zimmerman D ,
- Goodfellow LT
- Pestana K ,
- Sombatsaphay V ,
- Morais CCA ,
- Mueller AL ,
- Al-Subu AM ,
- Friestrom E ,
- Langkamp MR ,
- Yngsdal-Krenz RA ,
- Martinez-Alejos R ,
- Marti J-D ,
- Li Bassi G ,
- Gonzalez-Anton D ,
- Pilar-Diaz X ,
- Reginault T ,
- Hunninghake JC ,
- McCullough SB ,
- McCann ET ,
- Charlton ME ,
- Villanueva KA ,
In this issue

- Table of Contents
- Table of Contents (PDF)
- Cover (PDF)
- Index by author
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word on American Association for Respiratory Care.
NOTE: We only request your email address so that the person you are recommending the page to knows that you wanted them to see it, and that it is not junk mail. We do not capture any email address.
Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager

- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
Jump to section
Related articles, cited by....
Advertisement
Frozen human brain tissue can now be revived without damage
Using a new approach, scientists have successfully frozen and thawed brain organoids and cubes of brain tissue from someone with epilepsy, which could enable better research into neurological conditions
By Christa Lesté-Lasserre
15 May 2024
Thawed brain organoids shown via an imaging technique called immunofluorescence staining
Weiwei Xue et al.
A new technique has allowed scientists to freeze human brain tissue so that it regains normal function after thawing, potentially opening the door to improved ways of studying neurological conditions.
Brain tissue doesn’t usually survive freezing and thawing, a problem that has significantly hindered medical research. In an effort to overcome this, Zhicheng Shao at Fudan University in Shanghai, China, and his colleagues used human embryonic stem cells to grow self-organising brain samples, known as organoids, for three weeks — long enough for the development of neurons and neural stem cells that can become different kinds of functional brain cells.
The researchers then placed these organoids — which measured 4 millimetres across on average — in different chemical compounds, such as sugars and antifreeze, that they suspected might help keep the brain cells alive while frozen and able to grow after being thawed.
Restoring the brain’s mitochondria could slow ageing and end dementia
After storing these organoids in liquid nitrogen for at least 24 hours, the team thawed them and looked for cell death or the growth of neurites — the “branches” of nerve cells — over the following two weeks.
Based on the rates of cell death and growth associated with each compound, the researchers chose their top compound candidates, trying different combinations during freezing and thawing tests on a new set of organoids.
Sign up to our Health Check newsletter
Get the most essential health and fitness news in your inbox every Saturday.
The combination that led to the least cell death and most growth was a blend of chemical compounds called methylcellulose, ethylene glycol, DMSO and Y27632 — which the scientists named “MEDY”. They suspect MEDY interferes with a pathway that otherwise programs cellular death.
Shao and his colleagues tested MEDY through a series of experiments involving brain organoids ranging from 28 days old to more than 100 days old. The team placed the organoids in MEDY, before freezing — usually for 48 hours — and thawing them. The researchers then observed their growth in the laboratory for up to 150 days post-thawing.
They found that the thawed organoids’ appearance, growth and function were highly similar to those of organoids of the same age that had never been frozen, even among those that had been frozen in MEDY for 18 months. The team also observed similar results for organoids representing different regions of the brain.
Finally, the researchers took 3-millimetre cubes of brain tissue from a 9-month-old girl with epilepsy and placed them in MEDY, before freezing and thawing them. The tissue maintained its pre-freezing structure and continued to remain active in a laboratory culture for at least two weeks after thawing.
We are finally starting to understand brain fog and how to treat it
Being able to freeze human brain tissues could lead to better investigations of brain development in the lab for health research, says Roman Bauer at the University of Surrey in the UK.
João Pedro Magalhães at the University of Birmingham in the UK says he is impressed that the team’s method successfully prevented cell death and preserved function. “We know brain cells are very fragile and sensitive to stress,” he says.
With significantly more research and the use of larger tissues, the work could one day lead to freezing entire brains, says Magalhães. “Thinking decades or centuries ahead, we can imagine patients being cryopreserved when they have a terminal condition or astronauts being cryopreserved in order to travel to other star systems,” he says. MEDY may represent “one small step” towards that goal, says Magalhães.
Journal reference:
Cell Reports Methods DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100777
Sign up to our weekly newsletter
Receive a weekly dose of discovery in your inbox! We'll also keep you up to date with New Scientist events and special offers.
More from New Scientist
Explore the latest news, articles and features
Brain activity seems to be more complex in baby girls than boys
Subscriber-only
Light and sound therapy for Alzheimer’s may also prevent 'chemo brain'
Human brains have been mysteriously preserved for thousands of years, new evidence finally reveals how male and female brains really differ, popular articles.
Trending New Scientist articles
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 18 May 2024
Research on trajectory control technology for L-shaped horizontal exploration wells in coalbed methane
- Xiugang Liu 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Zaibing Jiang 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Yi Wang 3 ,
- Haitao Mo 3 ,
- Haozhe Li 3 &
- Jianlei Guo 3
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 11343 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Energy science and technology
- Engineering
Horizontal wells have significant advantages in coal bed methane exploration and development blocks. However, its application in new exploration and development blocks could be challenging. Limited geological data, uncertain geological conditions, and the emergence of micro-faults in pre-drilled target coal seams make it hard to accurately control the well trajectory. The well trajectory prior to drilling needs to be optimized to ensure that the drilling trajectory is within the target coal seam and to prevent any reduction in drilling ratio (defined here as the percentage of the drilling trajectory in the entire horizontal section of the well located in the target coal seam) caused by faults. In this study, the well trajectory optimization is achieved by implementing the following process to drill pilot hole, acquire 2D resonance, and azimuthal gamma logging while drilling. The pilot hole drilling can obtain the characteristic parameters of the target coal seam and the top and bottom rock layers in advance, which can provide judgment values for the landing site design and real-time monitoring of whether the wellbore trajectory extends along the target coal seam; 2D resonance exploration can obtain the construction of set orientation before drilling and the development of small faults and formation fluctuations in the horizontal section, which can optimize the well trajectory in advance; the azimuth gamma logging while drilling technology can monitor the layers drilled by the current drill bit in real time, and can provide timely and accurate well trajectory adjustment methods.The horizontal well-Q in the Block-W of the Qinshui Basin was taken as a case study and underwent technical mechanism research and applicability analysis. The implementation of this new innovative process resulted in a successful drilling of a 711 m horizontal section, with a target coal seam drilling rate of 80%. Compared to previous L-type wells, the drilling rate increased by about 20%, and the drilling cycle shortened by 25%. The technical experience gained from this successful case provides valuable insight for low-cost exploration and development of new coalbed methane blocks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Study on optimization of layout parameters of high-level boreholes in Pingdingshan coal mine
Study on parameter optimization of deep hole cumulative blasting in low permeability coal seams
A new mathematical modeling approach for thermal exploration efficiency under different geothermal well layout conditions
Introduction.
Coal Bed Methane (CBM) is found in many parts of the world, and is considered as a clean and abundant source of energy 1 , 2 , 3 . In general, CBM wells mainly include three types; vertical, cluster and horizontal wells. The cluster and horizontal wells belong to directional wells. Moreover, horizontal wells could be further classified into; V-, U- and L-shaped wells. Which in turn could also be divided according to their radius, and branches. Figure 1 below provide an illustration for some of these wells.
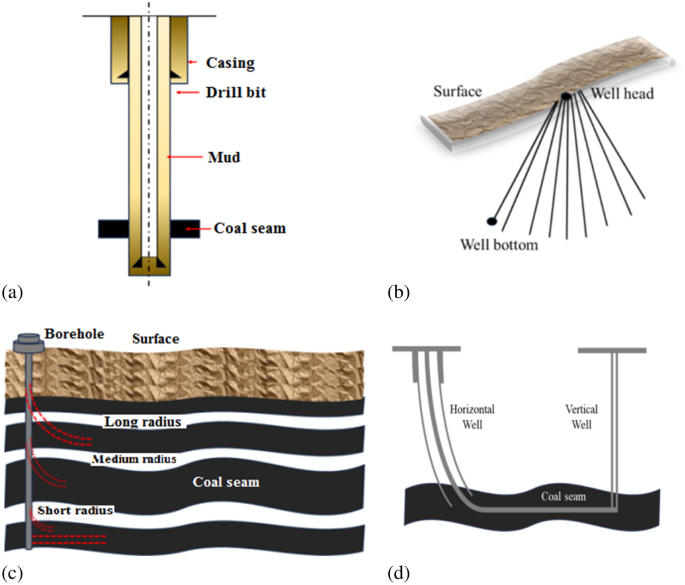
Illustration of well types; ( a ) Vertical well, ( b ) Cluster well, ( c ) Horizontal Well, and ( d ) Horizontal L-Shaped well with a vertical well forming a U-Shaped well.
In the development of CBM wells, L-shaped, U-shaped and multi-branch horizontal wells are usually used for new exploration and development blocks (defined here as new fields or area blocks in the oil and gas industry) 4 , 5 , 6 . However, complex formation structure, and small faults development have made it an extremely challenging task to achieve high output from newly developed CBM wells 7 . For instance, U-shaped wells (a well type in which a vertical well and a horizontal well are connected in the same target layer) face huge difficulties in accurate docking along the coal seam and have limited benefits in the presence of multiple faults in the horizontal Section 8 . Similarly, the applicability of multi-branch horizontal wells is poor, especially in complex stratigraphic structures and fault development of the block 9 .
On the other hand, L‑shaped horizontal wells are often adopted as the main type of wells for exploring and developing CBM in new blocks. The L-shaped horizontal wells exhibit uncomplicated drilling prerequisites, demonstrate a low probability of wellbore collapse or obstruction, and facilitate subsequent access for maintenance of the initial wellbore 10 . However, the drilling process of these wells are not free of challenges. L-shaped wells have a high requirement for wellbore trajectory control, and they are usually difficult to achieve one-time “soft landing” and ultra-long horizontal segment footage 10 . In addition, drainage equipment and method are another key restriction for the promotion and application of this type of well 11 . For example, reported completion data from several exploration wells indicated that the drilling ratio along the coal seam of the actual trajectory is less than 60%. The drilling cycle is nearly two months, and gas production is low 11 . Table 1 illustrates a tabulated analysis of the applicability and challenges associated with different well types in exploration blocks characterized by complex geological formations and the presence of micro-faults.
Various methods have been used to improve the drilling ratio, by improving the trajectory control. These methods, shown in Table 2 , include: geological guidance technology of adjacent well data, electromagnetic waves, natural gamma measurement, and three-dimensional seismic exploration technology. However, each method has its own limitations, such as high costs, difficulty in obtaining gamma values in specific directions, and signal loss when applied to drilling in complex formations 12 , 13 .
This study delves into trajectory control methods for Horizontal wells within Coalbed Methane (CBM) exploration and development blocks. The approach involves the utilization of pilot holes to determine the characteristics of the target coal seam and the surrounding upper and lower rock layers based on the magnitude of gamma values. This information serves as a predictive identification of marker layers, allowing real-time control and adjustment of the drilling trajectory within the target coal seam. This methodology enables the identification of whether the drilling trajectory is presently positioned within the target coal seam, the roof rock layer, or the floor rock layer. Additionally, a two-dimensional resonance exploration technology is employed for geological structure and fault detection prior to drilling, enabling pre-drilling trajectory optimization. Furthermore, azimuth gamma logging technology is utilized for real-time monitoring and correction of the drilling trajectory's horizontal positioning during the drilling process. Using L-shaped Short-Radius Well-Q in Block-W of the Qinshui Basin as a case study, a comprehensive assessment of the combined effectiveness of these three methods is conducted. Simultaneously, the research delves into the technical mechanisms and applicability analysis. This exploration of the technical mechanisms aims to enhance the understanding of the functions of these methods, their application conditions, and the analysis and utilization of their technical effects.
Trajectory control methodology
Pilot hole drilling, construction background and reasons.
The area formation structure and faults nature could be obtained by two-dimensional seismic data. Seismic surveys and exploratory drilling in the area could provide a good indication on the coal seam actual depth, coal seam distribution, layers, belts and interbeds. For the geological conditions of developing new blocks, such as less drilling data, less seismic exploration data, complex formation structure and micro-fault development, etc., before drilling, it is imperative to obtain the key parameters of the target coal seam, including its lithology, gas-bearing capacity, gamma value, etc., along with those of the rock layers above and below it. This will allow for the determination of the precise horizon of the coal seam and provide technical support for real-time monitoring and well trajectory control along the target coal seam. To achieve this, it is necessary to design and implement a pilot hole drilling program to obtain the characteristic parameters of the target coal seam and the surrounding strata 14 , 15 .
Pilot hole construction design
Once the goal of layer identification is achieved, the next step is to backfill and sidetrack the pilot hole to open branches and land according to the actual occurrence of the coal seam. To ensure the effectiveness of the pilot hole guidance in subsequent construction, it is advisable to minimize the distance between the coal-seem top point (the point where the drilling trajectory first drills into the target coal seam) and the landing point by increasing the well angle of inclination. Conversely, in order to enhance the construction efficiency of the pilot hole, it is preferable to keep the depth of the pilot hole to a minimum, which is indicated by a small well angle of inclination (70 degrees). Figure 2 illustrates this concept.
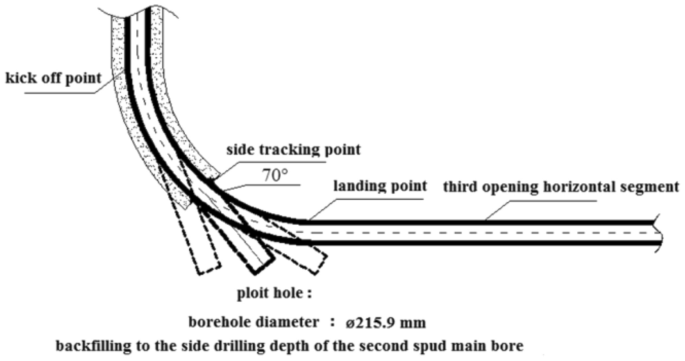
Optimization of pilot hole scheme.
Taking into account the underlying reasons and background for constructing a pilot hole, as well as the difficulty of side-tracking and the efficiency of construction, a comprehensive plan has been developed. The plan involves drilling the pilot hole at a steady angle of approximately 70° until the bottom of the target coal seam is reached.
- Two-dimensional resonance exploration
Resonance exploration mechanism
The seismic wave frequency resonance exploration technology is a novel geophysical exploration method that utilizes the frequency resonance principle prevalent in nature to investigate underground geological formations 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 . This technique enables the acquisition of geometric attributes of subsurface structures, such as fractures and faults. Figure 3 illustrates a typical resonance diagram of a seismic wave.
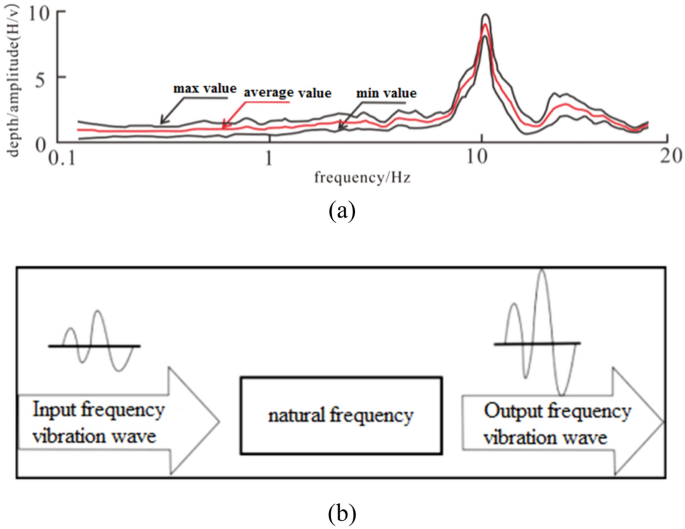
( a ) Typical resonance curve of seismic wave ( b ) self-excite resonance to vibration.
Resonance exploration technology boasts numerous advantages, including high sensitivity to density changes, exceptional vertical and horizontal resolution, and an exploration depth of up to 5000 m. Additionally, this technology can be acquired and processed passively, making it an economical and straightforward exploration method 20 .
Analysis of technical applicability
At this stage, the analysis of the existing two-dimensional seismic data in the exploration block would indicate the geological structure of the target coal seam in the block. In addition, it will reveal fault’s locations beside faults development status. The pilot hole drilling can accurately obtain the actual depth of the target coal seam and the characteristic parameter values of the target layer, as well as the roof and floor, but conventional means cannot predict structural conditions such as the development of micro faults in the horizontal section of the drilling along the designated direction. This increases the difficulty of well trajectory control and makes it challenging to ensure the coal seam drilling ratio. However, the two-dimensional resonance exploration technology can be used to infer the development of small faults in the horizontal section drilled along the specified direction by interpreting the resonance image. This enables the optimization of the well trajectory in advance to control the actual drilling trajectory and improve the drilling rate of the target coal seam.
Azimuth gamma control technology
Working principle of azimuth gamma.
The azimuth gamma logging tool is utilized to measure the width of gamma ray energy level 21 , 22 , 23 . The scintillation counter captures gamma rays from the stratum, and azimuth gamma logging while drilling offers unique advantages 24 , 25 . Firstly, it enables real-time calculation of the strata's apparent dip angle. It is convenient to calculate the apparent dip angle of the strata by utilizing the azimuth gamma data. The apparent dip angle at the current position can be obtained as long as it is required to cross an interface. The formula for calculating the apparent dip angle using the azimuth gamma 26 is as follows:
where α is the apparent strata dip; D is the well diameter; Δd is the distance between the upper and lower gamma value change points; β is the well deviation angle.
Second, measuring the natural gamma value in a specific direction. By transmitting up and down gamma data in real-time, it becomes possible to accurately determine the positions of different formation interfaces 27 , 28 . This information can then be used to ensure that the trajectory of the control well is precisely aligned with the target coal seam after drilling is complete. The specific process involved is illustrated in Fig. 4 .
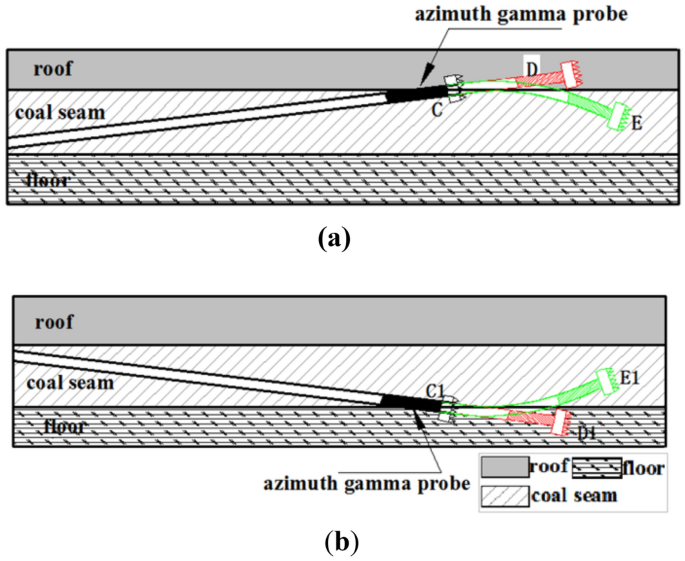
Trajectory control based on azimuth-while-drilling gamma logging. ( a ) Coal seam drilled out from the roof. ( b ) Coal seam drilled out from the floor.
The drilling process in the horizontal section along the coal seam is susceptible to deviate from the target due to increased drilling pressure or the impact of the formation structure. The strata above and below the coal seam are usually mudstone or carbonaceous mudstone. When using azimuth gamma logging during drilling, the upper gamma value first increases, followed by the lower gamma value, indicating that the drilling has exited the coal seam roof at point C in Fig. 4 a. When the upper and lower gamma values become similar, it suggests that the drilling has left the layer, as shown at point D in Fig. 4 a. To correct the inclined drilling control track deviation, the trajectory correction process is initiated when drilling to point C using azimuth gamma measurement, as demonstrated at point E in Fig. 4 a. Similarly, when the lower gamma value increases first and the upper gamma value increases later, it indicates that the drilling trajectory is exiting the coal seam floor at point C1 in Fig. 4 b. When the upper and lower gamma values become similar, the drilling has left the layer, as shown at point D1 in Fig. 4 b. To correct the incremental drilling control track deviation, the trajectory correction process is initiated when drilling to point C1, as illustrated at point E1 in Fig. 4 b.
In terms of technical applicability, conventional natural single gamma logging technology cannot accurately determine the bit's position once it leaves the coal seam, making it challenging to provide precise corrective measures. This issue is particularly problematic wherever the geological structure of the target coal seam is complex, micro faults are developed, and the coal seam is thin. To ensure the penetration ratio of the target coal seam and ensure the safety of underground construction, azimuth gamma logging while drilling technology can be utilized. This technology allows for the real-time monitoring of the current drilling horizon and provides effective guidance during construction. As a result, the drill bit can efficiently drill into the coal seam, maximizing the penetration ratio of the target coal seam.
Technical applicability analysis
In the second drilling operation, if the targeted coal seam is complex due to its thinness or the presence of micro-faults, it will be very challenging to accurately determine the position of the drilling bit after it exits the coal seam. Therefore, it will be necessary to use azimuth gamma logging while drilling. This technology enables the real-time monitoring of the drilling bit's current horizon, guiding the construction process and ensuring that the bit drills to the maximum extent possible within the coal seam.
Trajectory control technology and case study
Geological setting.
In this study, the short radius, well-Q in Block-W of the Qinshui Basin is taken as an example. Based on the most recent exploration wells drilled in Block-W of Qinshui Basin, the geological horizons have been revealed. The strata in the block, from bottom to top, consist of Paleozoic Ordovician, Carboniferous, Permian, Mesozoic Triassic, Jurassic, and Cenozoic Quaternary. The stratum near Well-Q has a general inclination from northeast to northwest, and Coal Seam no.15 is the development target stratum. The coal seam is located in the lower part of the Taiyuan Formation and has a simple structure. It is a thick coal seam that is stable and easy to drill throughout the area and generally contains 0–2 layers of dirt shale. The effective thickness of the coal seam ranges from 0 to 5.30 m, with an average of 3.39 m. It is thicker in the east and thinner in the west. However, there is one exploration well in the block that did not drill into Coal Seam no.15, possibly due to fault interference resulting in the loss of the coal seam. The coal seam deposit depth ranges from 728 to 2002 m, with an average of 1479 m. The depth is shallow in the southeast of the block and gradually deepens towards the northwest. Due to the influence of the stratum tendency (Stratum dip), the depth of the coal seam reaches over 1500 m in the west 14 . The roof lithology of the coal seam mostly consists of sandy mudstone, mudstone, siltstone, and fine sandstone, while the floor is mostly sandy mudstone, mudstone, and siltstone.
Wellbore structure
Designing an optimized wellbore structure can greatly improve drilling efficiency and safety by reducing annular pressure loss and back pressure (the drilling tool back pressure phenomenon), especially for long well sections. In the case of Well-Q, the wellbore structure was designed with a three-opening sections to ensure gas production of the coal seam during subsequent fracturing development. The first section seals the formation prone to collapse and leakage in the upper part of the primary casing, creating a safe drilling environment for the second well section. The second section seals sandstone, mudstone, and sandy mudstone intervals at the upper part of the coal seam, with the second well section casing obliquely drilled to a depth of no less than 3 m from the target coal seam no.15.
The third section extends along coal seam no.15 and runs casing to form a stable gas production channel to prevent coal seam collapse in the horizontal section due to the influence of multiple factors such as fracturing in the later stage. Prior to drilling the second well section of the main borehole, pilot hole drilling was carried out to obtain relevant geological parameter information of the target coal seam and the adjacent marker bed. Specific design parameters and requirements are as follows:
In the first well section, a ø 346.1 mm drill bit was used to drill into the stable bedrock for 30 m. J55 grade steel ø 273.1 mm surface casing was then lowered and cementing cement slurry returned to the surface.
In the second well section, a ø 241.3 mm drill bit was used to drill to the roof of the target no.15 coal seam and then the drilling was stopped. The landing point was determined based on the lithology of the roof of the coal seam and the actual drilling process. N80 grade steel ø 193.7 mm technical casing was run to 3–5 m above the roof of the coal seam. Through variable density cementing process, high-density cement slurry was used to return to 300 m above the roof of Coal Seam no.15, while low-density cement slurry returned to the surface.
The third well section was drilled with a ø 171.5 mm drill bit. After entering the target coal seam no.15, the drilling followed the coal seam. Upon reaching the designed well depth, P110 grade steel ø 139.7 mm production casing was run, and the well was completed without cementing.
The pilot hole was drilled with a ø215.9 mm bit, and the inclination angle stabilizing drilling crossed the floor of the target coal seam for tens of meters. Subsequently, the bit was backfilled with pure cement slurry to the side drilling depth of the second well section. The specific wellbore structure is shown in Fig. 5 .

Well structure.
Case study: well-Q design optimization
Using Well-Q as a case study, the pilot hole trajectory design included the following: straight well section, kicking-off section, and stabilizing section. The stabilizing drilling passes through the floor of Coal Seam no.15 for approximately 30 m at an inclination angle of 70° to ensure accurate measurement of the gamma value, gas measurement value, and other characteristic parameters of the target coal seam bottom and floor using a simple gesturing instrument. The pilot hole is sealed by backfilling it with 42.5 grade Portland cement up to the well section with an inclination of about 25°, and the cement slurry has a specific gravity of 1.6–1.7 g/cm3. As the well deviation angle increases, the azimuth angle of directional and composite drilling becomes more stable, particularly when the well deviation angle exceeds 25°, resulting in a smaller azimuth drift 29 . This stability is beneficial for the subsequent inclined side-tracking in the main wellbore's second well section. The pilot hole and main borehole design trajectories are shown in Fig. 6 .
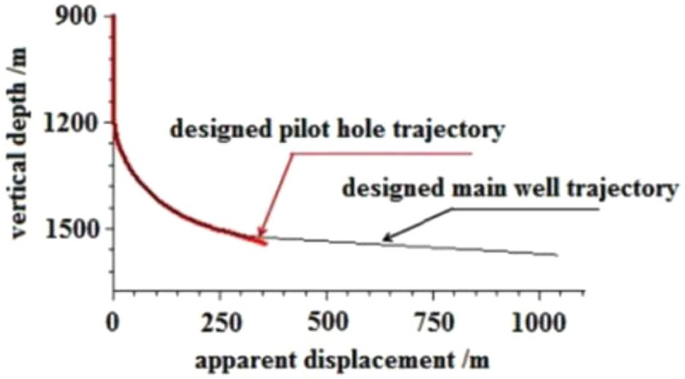
Design trajectory of pilot hole and main hole.
Significant data has been obtained through the pilot hole design and the actual drilling of Well-Q. This dataset is pivotal for precise trajectory control in Coalbed Methane (CBM) exploration. The acquisition process relies on several methods, including real-time drilling natural gamma logging for gamma values of marker layers, and downhole gas logging for coal seam gas characteristics. The examination of cuttings recorded in real-time during drilling operations further aids in the identification and differentiation of these marker layers.
The critical information gleaned encompasses the identification of the K2 marker bed, the longitudinal stratification of the target no.15 coal seam, as well as the lithological composition, gamma values, and gas-bearing attributes of the upper and lower rock layers. These specific parameters are thoughtfully presented in Fig. 7 , establishing a robust foundation for the meticulous control of trajectory and the rational design of the landing point within the target coal seam. This dataset also serves as a valuable point of reference, ensuring the seamless execution of the horizontal drilling phase within the coal seam. Consequently, these findings play a pivotal role in enhancing drilling efficiency, ultimately culminating in the realization of efficient drilling objectives.
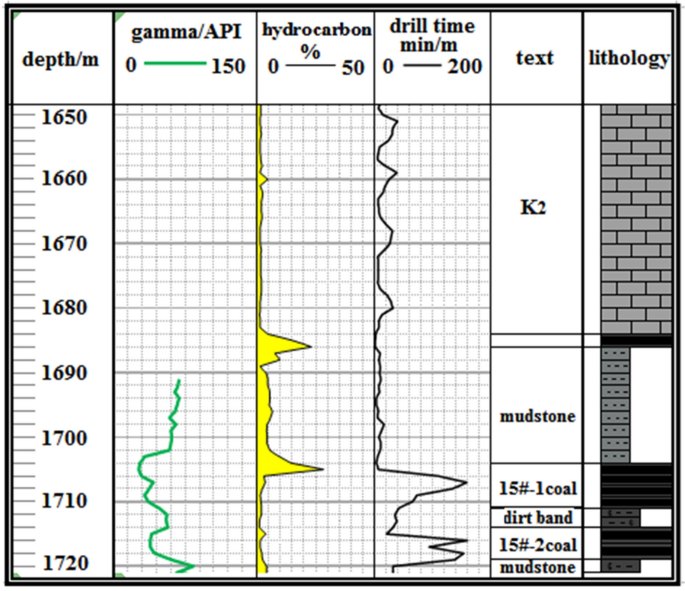
Characteristic parameters and lithology map of the marker layer, target, top, bottom layer.
The effect of two-dimensional resonance method
The horizontal section's overall drilling azimuth in the target coal seam is 200°. To identify minor faults in the coal seam azimuth direction, measurement points are arranged every 10 m from the landing point A to the final target point B along the 200° azimuth direction. Additionally, one exploration point is set every 20 m across the azimuth line perpendicular to the landing point A and 200° azimuth direction. Furthermore, exploration points are arranged 300 m along both sides of the landing point. Figure 8 shows the specific layout of the exploration points, where Line (L1) represents the 711 m long horizontal well section of the target coal seam in the 200° azimuth direction. Meanwhile, Line (L2) represents the 600 m long vertical section between the landing point A and L1. The obtained data from these exploration points are crucial in detecting potential faults and ensuring smooth drilling of the horizontal section of the coal seam. ultimately leading to improved drilling ratios and more efficient drilling.
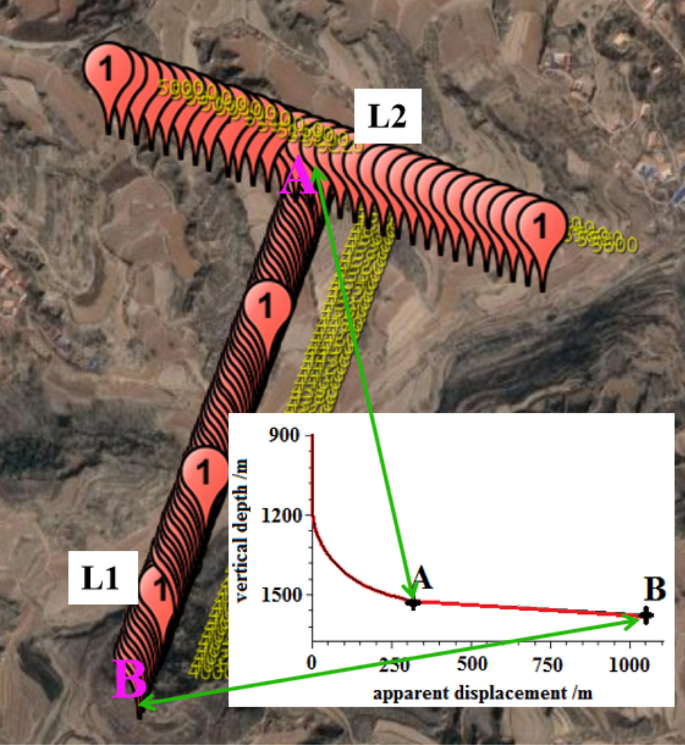
Two-dimensional resonance exploration layout points.
Figure 9 shows the seismic frequency resonance inversion profile. The trajectory of the designed horizontal section coincides with the ground position of L1, with the no.4700 measuring point located at the ground projection position of the A target point, and the no.4000 measuring point located at the ground projection position of the B target point. Based on the interpretation of seismic frequency resonance line L1 profile, it is observed that the burial depth of the coal seam on the horizontal well section from target A to target B of the no.15 coal seam in the direction of 200° azimuth is shallow in the northeast and deep in the southwest. The overall trend of the burial depth of the coal seam indicates a shallow-to-deep trend. Furthermore, three small faults are expected to be encountered while drilling along this azimuth direction, located at no.4700, no.4280 and no.4096 measuring points, respectively, with a fault distance of approximately 5–10 m.
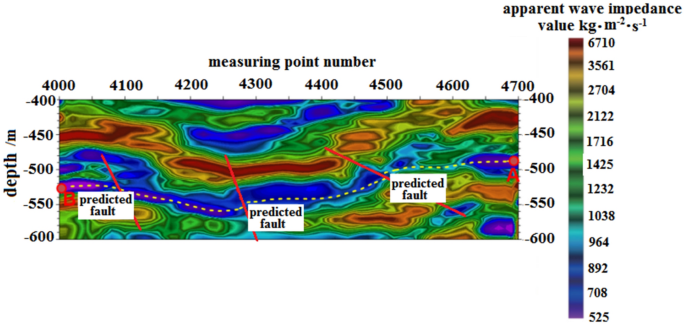
Design of horizontal section trajectory resonance exploration inversion profile.
The contour map of fault points found in the horizontal section is displayed in Fig. 10 . This map serves as a useful tool in guiding the vertical depth control of the horizontal section track.
Contour map of fault points in the horizontal section.
To ensure that the drilling trajectory is within the target coal seam and to prevent any reduction in drilling ratio caused by the faults, it is necessary to optimize the well trajectory prior to drilling. Each fault point must be considered as a target point and their relative coordinate positions are presented in Table 3 .
Resonance exploration data is utilized to adjust the trajectory parameters every 10 to 20 m during the actual drilling process. This is before exploring the coal seam behind the fault following reasonable adjustment of the parameters. This method is simple and minimizes the length of the non-coal section during the coal chasing process after drilling through the fault. Based on the coordinate position of each target point, the design of the directional trajectory for the third well section is optimized, as shown in Fig. 11 .
optimized well trajectory for drilling reservoir section. ( a ) vertical section, ( b ) horizontal projection section.
The optimized design trajectory should be followed during actual drilling, ensuring that the dogleg degree ≤ 4°/30 m required by the management method for safe operations. Across the fault points F1, F2, and F3, the length of the non-coal section for coal tracking drilling was 56 m, 53 m, and 35 m, respectively. The total non-coal section for actual drilling was approximately 144 m, while achieving a drilling ratio of 80% for the target coal seam with an average thickness of 2.06 m. The entire drilling cycle takes approximately 45 days.
Azimuth gamma application
By analyzing the azimuth gamma data obtained during the drilling of the pilot hole and using the basic parameters of the pilot hole and formula ( 1 ), the apparent dip angle of the stratum near the designed landing point is determined to be α = 6.5°. The parameters of the landing point are shown in Fig. 12 , and the deviation angle of the actual main borehole trajectory of the second well section at the landing point β should be controlled at around 83.5° to ensure that the drilling ratio along the coal seam of the third well section is achieved and to reduce the frequency of directional trajectory adjustment.
Parameters of the landing site.
During the drilling of the third horizontal section of Well-Q, a combination of Two-dimensional resonance exploration results and azimuth gamma logging while drilling technology was used to guide rapid coal tracking during the drilling of three faults. The process for each fault was as follows:
F1 Fault: The logging curve in Fig. 13 indicates that the F1 fault caused the drilling track of the 1920–1976 m well section to be drilled out from the coal seam roof. Geological logging revealed that the rock debris returning out of the hole bottom contained a large amount of mudstone. Based on the Two-dimensional resonance exploration inversion (Fig. 9 ) and fault contour (Fig. 10 ), the coal seam was traced by drilling with deviation correction through the lowering of well deviation. The actual drilling track during the pursuit of coal process is shown in Fig. 14 .
Non-coal seam section azimuth gamma logging curve crossing fault F 1 .
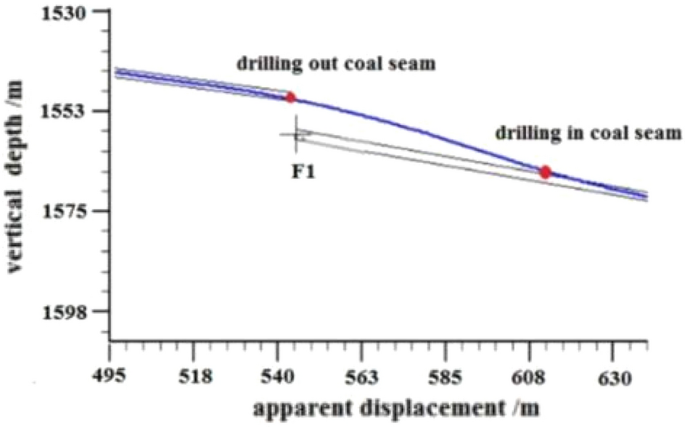
Actual drilling trajectory of fault F 1 in pursuit coal.
F2 Fault: The logging curve in Fig. 15 shows that the F2 fault caused the drilling trajectory of the 2130–2183 m well section to be drilled out from the coal seam roof. Geological logging revealed that the rock debris returning out of the hole bottom contained a large amount of mudstone. Based on the Two-dimensional resonance exploration inversion (Fig. 9 ), the back fault block of F2 fault in the direction of drilling trajectory of F2 fault shows a tendency of coal seam incline, so directly using lowering deviation correction drilling to trace the coal seam is not feasible and increases the length of the non-coal seam section. Therefore, the coal seam was pursued by increasing well deviation and rectifying drilling. The actual drilling track during the pursuit of coal process is shown in Fig. 16 .
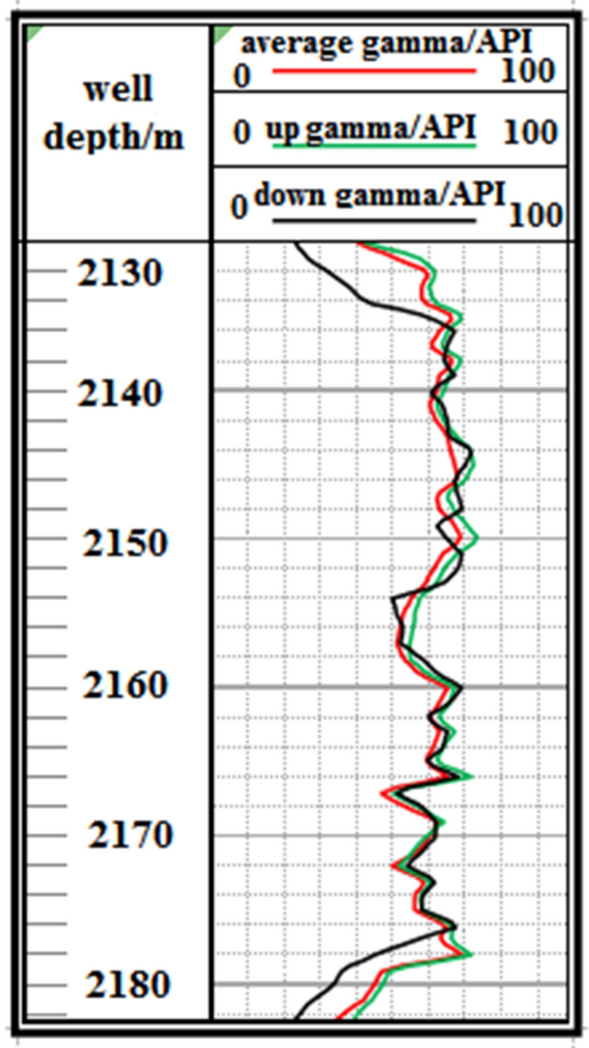
Non-coal seam section azimuth gamma logging curve crossing fault F 2 .
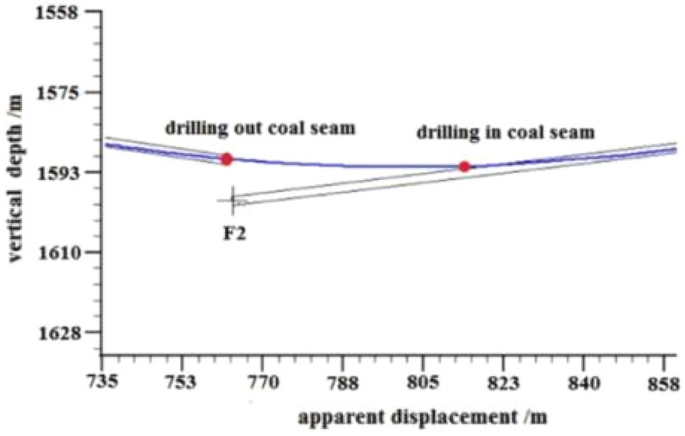
Actual drilling trajectory of fault F 2 in pursuit coal.
F3 Fault: The logging curve in Fig. 17 shows that the F3 fault caused the drilling trajectory of the 2315–2350 m well section to be drilled out from the coal seam roof floor. Geological logging revealed that the rock debris returning out of the hole bottom contained a large amount of carbonaceous mudstone. Using formula ( 1 ), the coal point well inclination angle was calculated as 96°. Based on the Two-dimensional resonance exploration inversion (Fig. 9 ) and fault contour (Fig. 10 ), the coal seam was pursued by slowly lowering the well inclination and correcting the deviation. The actual drilling track during the pursuit of coal process is shown in Fig. 18 . The well inclination angle was 91° upon returning back to the coal seam, after which drilling along the coal seam was continued normally.
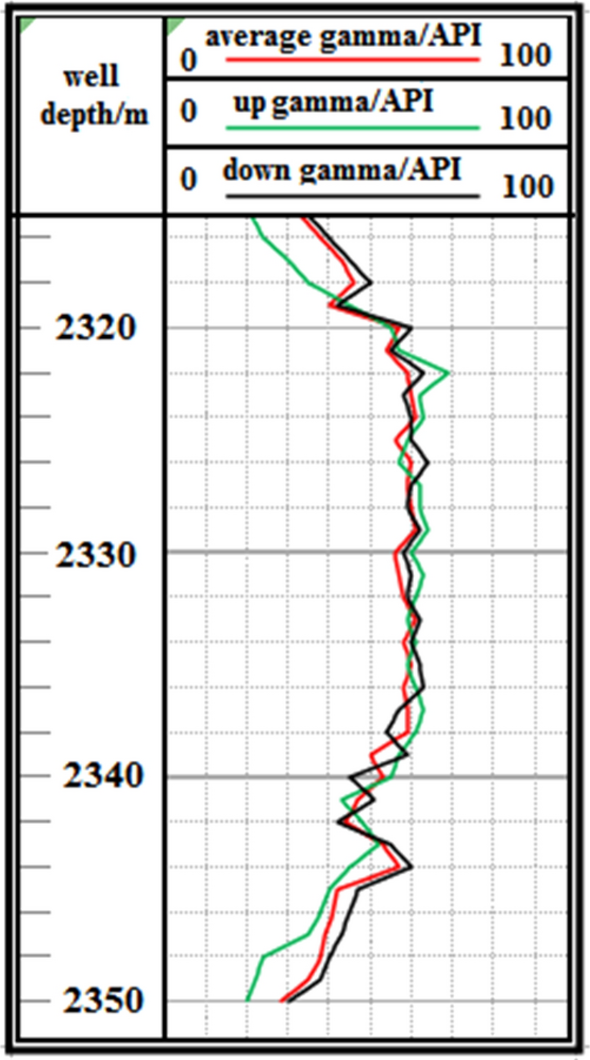
Non-coal seam section azimuth gamma logging curve crossing fault F 3 .
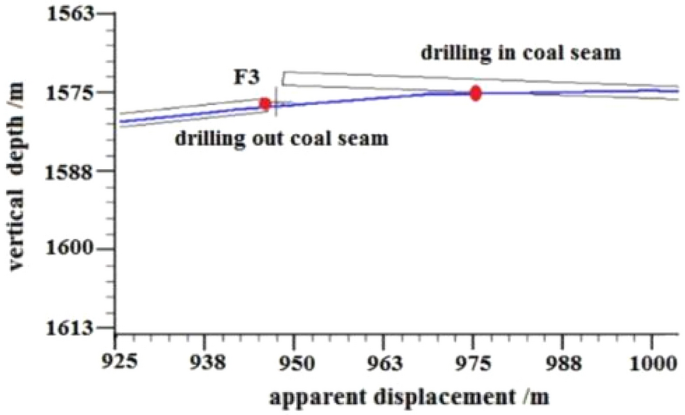
Actual drilling trajectory of fault F 3 in pursuit coal.
In conclusion, for the exploration block of CBM, the combined use of pilot hole drilling, two-dimensional resonance exploration technology, and azimuth gamma logging technology has proven effective in controlling the drilling of short-radius horizontal sections along the seam and ensuring the coal seam drilling ratio. Two major points can be drawn from this:
The two-dimensional resonance exploration technology detected the development of micro faults in the horizontal section of the drilling, enabling trajectory optimization before drilling. The azimuth gamma logging while drilling technology monitored the current drill bit drilling horizon in real-time, ensuring timely and accurate well trajectory adjustment.
The comprehensive use of these technologies has led to a 20% improvement in the coal seam drilling ratio and a 25% reduction in drilling cycle time in tested short-radius wells in the new exploration and development block-W in Qinshui Basin. This provides technical experience for low-cost exploration and development of CBM in new blocks.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Sun, W. L., Chen, Z. Y., Chen, X., Wang, S. H. & Fu, X. Y. Geological features and resource potentials of coalbed methane basins in China. Oil Gas Geol. 26 (2), 141–146 (2005).
Google Scholar
Qin, Y. Evaluation and production technology of coalbed methane reservoir. China University of Mining and Technology Press, (1996).
Men, X. Y., Han, Z., Gong, H. J. & Wang, X. Y. Challenges and opportunities of CBM exploration and development in China under new situations. Nat. Gas. Ind. 38 (09), 10–16 (2018).
Zhang, P. Y., Sun, J. M. & Cheng, Z. G. Application of azimuthal gamma ray imaging logging while drilling to geosteering in horizontal wells of H area, Ordos Basin. Sci. Technol. Eng. 21 (23), 9713–9724 (2021).
Dai, Y. J., Li, S. Q., Xia, L. Y., Li, J. X. & Lv, Y. A CBM development well type optimization method based on the long-run marginal cost. Nat. Gas. Ind. 38 (07), 113–119 (2018).
CAS Google Scholar
Liu, Y. K., Wang, F. J., Tang, H. M. & Liang, S. Well type and pattern optimization method based on fine numerical simulation in coalbed methane reservoir. Environ. Earth Sci. 73 (10), 5877–5890 (2015).
Article ADS CAS Google Scholar
Jia, H. M., Hu, Q. J., Fan, B., Mao, C. H. & Zhang, Q. Causes for low CBM production of vertical wells and efficient development technology in northern Zhengzhuang Block in Qinshui Basin. Coal Geol. Explor. 49 (2), 34–42 (2021).
Liu, C. C., Jia, H. M., Mao, S. F., Cui, X. R. & Peng, H. The development characteristics and main control factors of the open-hole multi-branch CBM horizontal wells. Coal Geol. Explor. 46 (5), 140–145 (2018).
Huang, W. et al. Construction technologies and stimulation of U-shape well for CBM development—with 2014ZX-U-05V/H well of coal 15 in SiHe mine as an example. Coal Geol. Explor. 43 (6), 133–136 (2015).
Hu, Q. J. et al. Discussion of the geological adaptability of coal-bed methane horizontal wells of high-rank coal formation in southern Qinshui Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 44 (4), 1178–1187 (2019).
Liu, C. C., Jia, H. M. & Mao, S. F. The development characteristics and main control factors of the open-hole multi-branch CBM horizontal wells. Coal Geol. Explor. 46 (5), 140–145 (2018).
Wang, L., Li, L., Sheng, L. M., Dou, X. R. & Zhang, L. C. Electromagnetic wave DREMWD system and its field test. Oil Drill Prod. Technol. 35 (02), 20–23 (2013).
Pang, Q., Feng, Q. H., Ma, Y., Zhang, Y. Y. & Peng, X. H. The application of three-dimensional geological modeling technology in horizontal well geologic steering: A case from X3–8 horizontal well development zone. Nat. Gas Geosci. 28 (3), 473–478 (2017).
Song, H. B. et al. Controlling geological factors and coalbed methane enrichment areas in Southern Wuxiang Block, Qinshui Basin. J. China Coal Soc. 46 (12), 3974–3987 (2019).
Liu, C. H., Liu, S. C., Yan, S., Liu, Y. & Su, L. Application of integrated geophysical exploration techniques to detecting shallow coal gob. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 8 (1), 51–54 (2021).
Zhang, Q. Key technologies for drilling and completion of No.15 coal L-shaped horizontal well in Zhengzhuang block. Qinshui Basin. Coal Eng. 53 (11), 61–66 (2021).
Xue, A. M., Li, D., Song, H. X. & Zhang, A. J. Image the earth with the frequency resonance effect of vibration noise. Geol. Rev. 65 (supplement1), 47–48 (2021).
Li, H. et al. Application of shallow seismic exploration combining mixed source surface waves and three-component frequency resonance method in fine detection of urban shallow geological structure. Prog. Geophys. 35 (3), 1149–1155 (2020).
Liu, X. G., Li, J. F., Zhang, Q. & Zhang, J. Practice of accurate control technology for multi-branch horizontal grouting well trajectory of coal seam floor limestone reinforcement in Zhaogu No.1 Mine. Saf. Coal Mines 52 (11), 100–103 (2021).
Zhu, C. C. & Li, H. Application of seismic frequency resonance technique in goaf detection of heavy-cover coal seams. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. 18 (5), 774–779 (2021).
Du, Z. Q., Hao, Y. L., Zhang, G. L., Yang, Z. B. & Lu, D. The application of the azimuth gamma logging while drilling for the geosteering in the horizontal wells in Jidong Oil field. Mud. Logging Eng. 19 (1), 18–21 (2008).
Tang, H. Q. Image processing method of LWD azimuthal gamma data. Lithol. Reserv. 29 (1), 110–115 (2017).
Zheng, Y. T., Fang, F., Wu, J. P., Li, J. B. & Zhang, W. Development and application of near-bit gamma-ray imaging system during drilling. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 44 (3), 70–76 (2020).
Liu, X. P., Fang, J. & Jin, Y. H. Application status and prospect of LWD data transmission technology. Well Logging Technol. 32 (3), 249–253 (2008).
Sun, D. J. & Sun, L. Application of geosteering technology in construction of CBM horizontal well. Coal Geol. Explor. 43 (02), 106–108 (2015).
Zhang, J. Q. et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting method in detecting goaf of thick overburden coal mine. Geol. Rev. 65 (supplement1), 52–54 (2021).
Wu, C. L. Application of azimuth gamma in coal bed methane horizontal wells. J. Drill. Eng. 48 (5), 69–75 (2021).
Chen, G., Wang, K. B., Jiang, B. C. & Wang, X. L. Comparison and application of LWD lithology identification method. Coal Geol. Explor. 46 (01), 165–169 (2018).
Liu, H. B., Fan, Z. X. & Gao, M. Study on decreasing the azimuth drift in the directional well. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field. 2 (10), 80–82 (2003).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The financial support by the Found of the National Key Research and Development Program and Key Special Fund Project (No.2018YFC0808202) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, 100083, China
Xiugang Liu & Zaibing Jiang
China Coal Research Institute, Beijing, 100013, China
Xi’an Research Institute Co. Ltd., China Coal Technology and Engineering Group Corp., Xi’an, 710077, China
Xiugang Liu, Zaibing Jiang, Yi Wang, Haitao Mo, Haozhe Li & Jianlei Guo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
X.L. conceived the study and, together with Z.J., Y.W., and H.M. did the literature search, selected the studies. X.L. and H.L. extracted the relevant information. X.L. synthesised the data. J.G. drawed pictures. X.L.and Z.J.wrote the first drafts of the paper.Y.W.and H.M.critically revised successive drafs of the paper. All authors approved the final drafts of the manuscript. X.L. is the guarantor of the study.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xiugang Liu .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Liu, X., Jiang, Z., Wang, Y. et al. Research on trajectory control technology for L-shaped horizontal exploration wells in coalbed methane. Sci Rep 14 , 11343 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60550-4
Download citation
Received : 17 January 2024
Accepted : 24 April 2024
Published : 18 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60550-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Coalbed methane (CBM)
- Short-radius wells
- Trajectory control
- Azimuth gamma logging while drilling (LWD)
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

Collaborative Action Research in a Northern Early Childhood Educator Program: Professional Learning of Instructors and Interns
- Erica McDonald Aurora College
- Charlene Simpson Aurora College
- Sarah McGregor Aurora College
- Shelley Stagg Peterson Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, University of Toronto
- Nazila Eisazadeh Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, University of Toronto
This collaborative action research, carried out by early childhood education interns, with the support of their instructor and two university researchers, shows the empowerment of postsecondary students that occurs when they are responsible for designing and implementing research projects tailored to their placement contexts. The early childhood educator interns took up a stance as reflective practitioners who developed professional skills and knowledge in an area that was meaningful to them—teaching young children their Indigenous language. The interns shared responsibility for their learning with their instructor, who was also conducting research into her practice, gathering data to identify the impact of her new teaching approach on interns’ learning. The simultaneous use of collaborative action research methods at the instructor and intern levels provides research-based information for the larger professional field. Additionally, the college instructor and the student interns are positioned as research-practitioners who use action research to support their professional growth.
Author Biographies
Erica mcdonald, aurora college.
Erica McDonald, an educator for over 20 years, is an instructor in Aurora College’s Early Learning and Childcare Program.
Charlene Simpson, Aurora College
Charlene Simpson, a Tłichǫ diploma graduate of Aurora College’s Early Learning and Child Care program, is an early childhood educator at the daycare in Whati, Northwest Territories.
Sarah McGregor, Aurora College
Sarah McGregor, a diploma graduate of Aurora College's Early Learning and Child Care Program, is an educational assistant in Yellowknife Education District No. 1.
Shelley Stagg Peterson, Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, University of Toronto
Shelley Stagg Peterson, a former elementary teacher in rural Alberta, is a professor of literacy education in the Department of Curriculum, Teaching and Learning at OISE/University of Toronto.
Nazila Eisazadeh, Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, University of Toronto
Nazila Eisazadeh, a registered early childhood educator in Ontario, is a Postdoctoral Fellow on the NOW Play project.

Copyrighted material allows the author to quote briefly (up to 100 words) for scholarly purposes from most published materials, providing the source is correctly cited within the manuscript. If the author wishes to use figures, tables, or longer quotations, written permission must be obtained from the writer or publisher to reprint the material. Under such circumstances, the author needs to provide a permission summary with their manuscript submission. Written permissions must also be provided by subjects in any photographs or audio or video segments. If the subjects are children, a signed release from a parent or guardian must be provided for each child visible in the photograph or video segment, or heard on an audio clip. In addition, although linking to another site does not require permission, replication (such as "screen shots") or description of a site within the manuscript requires permission to be sought from originator of web site, including those created by students, teachers, or schools.
Information
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians
Make a Submission

Bibliometric Analysis of Edible Insects from Entomology Category Based on Web of Science
- Published: 16 May 2024
Cite this article

- Bao-Zhong Yuan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2353-3873 1 &
- Jie Sun 2
11 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Based on Web of Science database and using the bibliometric analysis method, the 3591 papers were analyzed in the field of edible insects topic research from Entomology category during of 1942 to December 18, 2022. All papers written most in English (98.134%), were from 11,742 authors, 2841 affiliation and 132 countries or territories, and published in 127 journals and book series. The top five journals are Insects (290, 8.076%), Journal of Insects as Food and Feed (285, 7.853%), Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata (194, 5.402%), Journal of Economic Entomology (172, 4.79%) and Journal of Stored Products Research (159, 4.428%), each journal published more than 159 papers. Top five countries were USA, Peoples R China, Brazil, Germany, England. Top four organizations were United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), State University System of Florida, Wageningen University Research, Kansas State University, each with more than 73 papers. The top five authors were Arthur FH, Athanassiou CG, Phillips TW, Campbell JF, Subramanyam B, each published more than 18 papers. All keywords were separated into seven clusters for different research topics. Based on ESI database, there were twenty-eight top papers both twenty-eight highly cited paper and two front papers. Visualizations offer exploratory information on the current state in a scientific field or discipline as well as indicate possible developments in the future.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
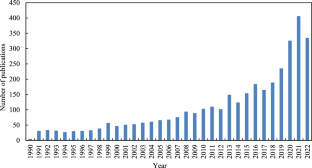
Similar content being viewed by others
When is it biological control? A framework of definitions, mechanisms, and classifications

The environmental sustainability of insects as food and feed. A review
Nanotechnology in pest management: advantages, applications, and challenges
Aguilar-Toalá JE, Cruz-Monterrosa RG, Liceaga AM (2022) Beyond human nutrition of edible insects: health benefits and safety aspects. Insects 13(11):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13111007
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Alarcon-Elbal PM, Suarez-Balseiro C, Holguino-Borda J, Riggio-Olivares G (2022) Research on medical and veterinary entomology in the insular Caribbean: a bibliometric analysis. Int J Trop Insect Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-022-00929-w
Article Google Scholar
Behmer ST (2009) Insect herbivore nutrient regulation. Annu Rev Entomol 54:165–187. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.54.110807.090537
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Clarivate, 2022: Journal Citation Reports ™ 2021 https://jcr.clarivate.com/jcr/browse-journals .
Douglas AE (2015) Multiorganismal insects: diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu Rev Entomol 60:17–34. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-010814-020822
Giora D, Marchetti G, Cappellozza S, Assirelli A, Saviane A, Sartori L, Marinello F (2022) Bibliometric analysis of trends in mulberry and silkworm research on the production of silk and its by-products. Insects 13(7):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13070568
Hahn DA, Denlinger DL (2011) Energetics of insect diapause. Annu Rev Entomol 56:103–121. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-112408-085436
Isman MB (2006) Botanical insecticides, deterrents, and repellents in modern agriculture and an increasingly regulated world. Annu Rev Entomol 51:45–66. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.51.110104.151146
Kavle RR, Pritchard ETM, Bekhit AEDA, Carne A, Agyei D (2022) Edible insects: a bibliometric analysis and current trends of published studies (1953–2021). Int J Trop Insect Sci 42(5):3335–3355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-022-00814-6
Lacey LA, Frutos R, Kaya HK, Vail P (2001) Insect pathogens as biological control agents: do they have a future? Biol Control 21(3):230–248. https://doi.org/10.1006/bcon.2001.0938
Lehane MJ (1997) Peritrophic matrix structure and function. Annu Rev Entomol 42:525–550. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.42.1.525
Linsley EG (1942) Insect food caches as reservoirs and original sources of some stored products pests. J Econ Entomol 35(3):434–439
Lumanlan JC, Williams M, Jayasena V (2022) Edible insects: environmentally friendly sustainable future food source. Int J Food Sci Technol 57(10):6317–6325. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.16006
Article CAS Google Scholar
Mabelebele M, Kolobe SD, Malematja E, Sebola NA, Manyelo TG (2022) A comprehensive review of the importance of selected trace elements present in edible insects. Biol Trace Elem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03423-z
Matandirotya NR, Filho WL, Mahed G, Maseko B, Murandu CV (2022) Edible insects consumption in Africa towards environmental health and sustainable food systems: a bibliometric study. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(22):14823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214823
Moshobane MC, Khoza TT, Niassy S (2022) The period of insect research in the tropics: a bibliometric analysis. Int J Trop Insect Sci 42(1):989–998. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-021-00616-2
Piña-Domínguez IA, Ruiz-May E, Hernández-Rodríguez D, Zepeda RC, Melgar-Lalanne G (2022) Environmental effects of harvesting some Mexican wild edible insects: an overview. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems 6:1021861. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2022.1021861
Rajendran S, Sriranjini V (2008) Plant products as fumigants for stored-product insect control. J Stored Prod Res 44(2):126–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspr.2007.08.003
Schulz AN, Lucardi RD, Marsico TD (2021) Strengthening the ties that bind: an evaluation of cross-disciplinary communication between invasion ecologists and biological control researchers in entomology. Ann Entomol Soc Am 114(2):163–174. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/saaa052
Shelton AM, Zhao JZ, Roush RT (2002) Economic, ecological, food safety, and social consequences of the deployment of Bt transgenic plants. Annu Rev Entomol 47:845–881. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.47.091201.145309
Stopar K, Trdan S, Bartol T, Arthur FH, Athanassiou CG (2022) Research on stored products: a bibliometric analysis of the leading journal of the field for the years 1965–2020. J Stored Prod Res 98:101980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jspr.2022.101980
Struelens Q, Silvie P (2020) Orienting insecticide research in the tropics to meet the sustainable development goals. Curr Opin Insect Sci 1(40):24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2020.05.015
Valente-Neto F, Piovezan-Borges AC, Urbieta GL, Samways MJ, Roque FD (2022) Research networks should improve connectivity for halting freshwater insect extinctions. Ecol Entomol 47(1):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/een.13091
van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2022) Manual for VOSviewer version 1.6.18. Leiden University, Leiden
Google Scholar
van Huis A (2013) Potential of insects as food and feed in assuring food security. Annu Rev Entomol 58:563–583. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-120811-153704
VOSviewer (version 1.6.18, 2022, Leiden University, Leiden, the Netherlands)
Wallace JB, Webster JR (1996) The role of macroinvertebrates in stream ecosystem function. Annu Rev Entomol 41:115–139. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.41.010196.000555
Yuan BZ, Sun J (2022) Bibliometric analysis of rice and climate change publications based on Web of Science. Theoret Appl Climatol 150(1–2):347–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-022-04169-3
Yuan BZ, Sun J (2023) Research trend of rice and greenhouse gases based on Web of Science: a bibliometric analysis. All Earth 35(1):16–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/27669645.2022.2164412
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Plant Science and Technology, Huazhong Agricultural University, Shizishan Street, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei Province, 430070, China
Bao-Zhong Yuan
Library, Huazhong Agricultural University, Shizishan Street, Hongshan District, Wuhan, Hubei Province, 430070, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bao-Zhong Yuan .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The present study reports the bibliometric analysis of edible insects from entomology category based on web of science during of 1942 to December 18, 2022. All papers written most in English (98.134 %), were from 11,742 authors, 2841 affiliation and 132 countries or territories, and published in 127 journals and book series. All keywords were separated into seven clusters for different research topics. The recent or front research topic were edible insects. Visualizations offer exploratory information on the current state in a scientific field or discipline as well as indicate possible developments in the future. We expect the results of this study to help researchers and communities better align their present and future work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yuan, BZ., Sun, J. Bibliometric Analysis of Edible Insects from Entomology Category Based on Web of Science. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-024-01570-y
Download citation
Received : 14 February 2023
Revised : 15 May 2023
Accepted : 08 March 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-024-01570-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometric analysis
- Edible insects
- Web of science (WoS)
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Data and Statistics on ADHD
- Free Materials on ADHD
- Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder Articles
- Clinical Care and Treatment
Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)

About Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)

Is it ADHD?

Symptoms of ADHD
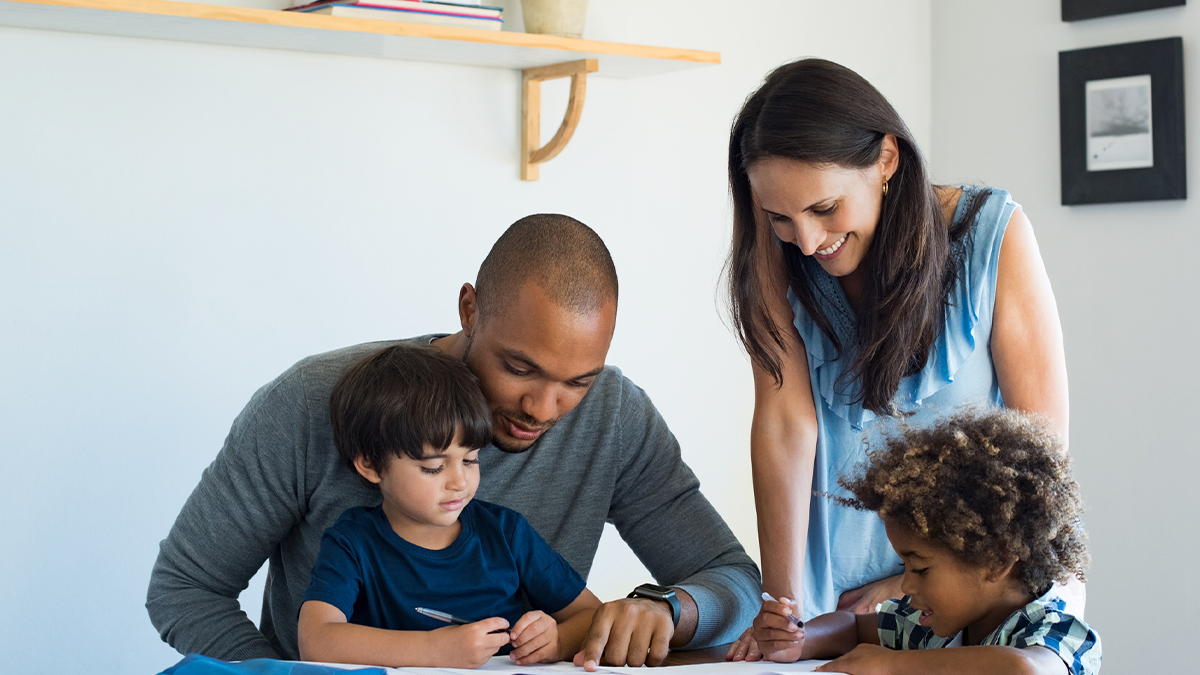

Treatment of ADHD

ADHD Information and Resources for States

School Changes — Helping Children with ADHD

CDC's Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) site includes information on symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, data, research, and free resources.
For Everyone
Health care providers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research papers in the social and natural sciences often follow APA style. This article focuses on reporting quantitative research methods. In your APA methods section, you should report enough information to understand and replicate your study, including detailed information on the sample, measures, and procedures used.
The methods section should describe what was done to answer the research question, describe how it was done, justify the experimental design, and explain how the results were analyzed. Scientific writing is direct and orderly. Therefore, the methods section structure should: describe the materials used in the study, explain how the materials ...
The methods section is a fundamental section of any paper since it typically discusses the 'what', 'how', 'which', and 'why' of the study, which is necessary to arrive at the final conclusions. In a research article, the introduction, which serves to set the foundation for comprehending the background and results is usually ...
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail ...
The Methods section of a research article is like a roadmap leading to the core of the research, guiding the readers through the actual journey the authors took to reach their destination. In the manuscript, this section contains the essential details for other scientists to replicate the experiments of the study and help the common readers to understand the study better.
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded ...
The Methods section of a research article includes an explanation of the procedures used to conduct the experiment. For authors of scientific research papers, the objective is to present their findings clearly and concisely and to provide enough information so that the experiment can be duplicated. Research articles contain very specific ...
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study's overall validity and reliability.
Methods section is the easiest part of the scientific paper and you can start writing it down even when the research is unfinished. It has to be written in the past tense because you have already written the proposal and either you have started or have conducted the study. The basic elements of the methods section are study design, setting and ...
The methods section of a research paper provides the information by which a study's validity is judged. Therefore, it requires a clear and precise description of how an experiment was done, and the rationale for why specific experimental procedures were chosen. The methods section should describe what was done to answer the research question, describe how it was done, justify the experimental ...
Writing* / standards. The methods section of a research paper provides the information by which a study's validity is judged. Therefore, it requires a clear and precise description of how an experiment was done, and the rationale for why specific experimental procedures were chosen. The methods section should describe wh ….
Passive voice is often considered the standard for research papers, but it is completely fine to mix passive and active voice, even in the method section, to make your text as clear and concise as possible. Use the simple past tense to describe what you did, and the present tense when you refer to diagrams or tables.
The methodology section or methods section tells you how the author (s) went about doing their research. It should let you know a) what method they used to gather data (survey, interviews, experiments, etc.), why they chose this method, and what the limitations are to this method. The methodology section should be detailed enough that another ...
This chapter describes the method section of the article where the sample, measures, and research design are detailed. The method section of one's article is the place where one describes how they carried out their study. Cast broadly, these are the most important questions to answer as one writes their method section: What information will readers need to evaluate the validity of one's study ...
The Methods section is a fundamental component of any research paper, playing a crucial role in establishing the validity and reliability of your study. It serves as a detailed roadmap of the research process that you undertook, providing sufficient information for the replication of the study. An effectively written Methods section can enhance the impact and credibility of your research ...
Abstract. The methods section of a research paper provides the information by which a study's validity is judged. Therefore, it requires a clear and precise description of how an experiment was ...
Keep it brief. The methods section should be succinct but include all the noteworthy information. This can be a difficult balance to achieve. A useful strategy is to aim for a brief description that signposts the reader to a separate section or sections of supporting information. This could include datasets, a flowchart to show what happened to ...
In writing this section, study design describing the type of the article, study subjects to be investigated, methods, and procedures of measurements should be provided under four main headings. [ 1 , 2 ] Accordingly, in brief, we can emphasize the importance of providing clear-cut, adequate, and detailed information in the 'Materials and ...
The methods section should explain how subjects were identified and should state inclusion and exclusion criteria. All materials used to complete the study should be described in detail, including equipment, drugs, gases, chemicals, treatments, interventions, or other items. Study procedures should outline all steps taken to obtain the results ...
The Methods section is the part of a scientific paper that describes how the study was carried out. This section describes each technique that was used in the study and any relevant details about the materials, subjects, and so on. Some journals refer to this as the 'Materials and Methods' section, and some clinically-focused journals will ...
The methods section of a manuscript is one of the most important parts of a research paper because it provides information on the validity of the study and credibility of the results. Inadequate description of the methods has been reported as one of the main reasons for manuscript rejection. The methods section must include sufficient detail so that others could repeat the study and reproduce ...
Being able to freeze human brain tissues could lead to better investigations of brain development in the lab for health research, says Roman Bauer at the University of Surrey in the UK.. João ...
Various methods have been used to improve the drilling ratio, by improving the trajectory control. These methods, shown in Table 2, include: geological guidance technology of adjacent well data ...
This collaborative action research, carried out by early childhood education interns, with the support of their instructor and two university researchers, shows the empowerment of postsecondary students that occurs when they are responsible for designing and implementing research projects tailored to their placement contexts. The early childhood educator interns took up a stance as reflective ...
Based on Web of Science database and using the bibliometric analysis method, the 3591 papers were analyzed in the field of edible insects topic research from Entomology category during of 1942 to December 18, 2022. All papers written most in English (98.134%), were from 11,742 authors, 2841 affiliation and 132 countries or territories, and published in 127 journals and book series. The top ...
Human experience is imbued by the sense of being an embodied agent. The investigation of such basic self-consciousness has been hampered by the difficulty of comprehensively modulating it in the laboratory while reliably capturing ensuing subjective changes. The present preregistered study fills this gap by combining advanced meditative states with principled phenomenological interviews: Forty ...
The Methods section of a research article includes an explanation of the procedures used to conduct the experiment. For authors of scientific research papers, the objective is to present their findings clearly and concisely and to provide enough information so that the experiment can be duplicated. Research articles contain very specific ...
Find information on symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, data, research, and free resources. Find information on symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, data, research, and free resources. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. An official website of the United States government.