Verilog Ports
Verilog 1995, verilog 2001 onwards.
Ports are a set of signals that act as inputs and outputs to a particular module and are the primary way of communicating with it. Think of a module as a fabricated chip placed on a PCB and it becomes quite obvious that the only way to communicate with the chip is through its pins. Ports are like pins and are used by the design to send and receive signals from the outside world.


Types of Ports
Ports are by default considered as nets of type wire .
Ports declared as inout can act as both input and output.
In the code shown below, there are three input ports, one output port and one inout port.
It is illegal to use the same name for multiple ports.
Signed ports
The signed attribute can be attached to a port declaration or a net/reg declaration or both. Implicit nets are by default unsigned .
If either the net/reg declaration has a signed attribute, then the other shall also be considered signed.
Port Variations
Verilog has undergone a few revisions and the original IEEE version in 1995 had the following way for port declaration. Here, module declaration had to first list the names of ports within the brackets and then direction of those ports defined later within the body of the module.
ANSI-C style port naming was introduced in 2001 and allowed the type to be specified inside the port list.
If a port declaration includes a net or variable type, then that port is considered to be completely declared. It is illegal to redeclare the same port in a net or variable type declaration.
If the port declaration does not include a net or variable type, then the port can be declared in a net or variable type declaration again.

- The Verilog-AMS Language
Ports, also referred to as pins or terminals, are used when wiring the module to other modules. As such, ports are wires. Ports declarations for simple wire are wire declarations with the keyword wire replaced by one of the following direction specifiers: input , output , or inout . For example:
For other types of wires, or for registers (registers may only be declared as outputs), the declaration is simply preceded by the direction specifier:
By default the content of multi-bit ports are interpreted as unsigned numbers (the values are interpreted as positive binary numbers). It is possible to explicitly specify whether the number is to be interpreted as a signed or unsigned number as follows:
In this case, gain is unsigned and offset is signed, which means it is interpreted as a twos-complement signed number. So, if gain = 4’bF, its value is interpreted as 15, and if offset = 7’b7FF, then its value is interpreted as -1.
If it is necessary to apply a discipline to a port, the port declaration should be repeated with direction specifier replaced by the discipline. For example:
Verilog also supports buses of continuous signals and wreals (you must declare these as buses rather than arrays):
The Cadence simulator does not seem to follow the standard when it comes to declaring buses of wreals. With the Cadence simulator you should declare buses of wreals as arrays rather than as buses:
Modules and Ports in Verilog
A Module is a basic building design block in Verilog and it can be an element that implements necessary functionality. It can also be a collection of lower-level design blocks. As a part of defining a module, it has a module name, port interface, and parameters (optional). The port interface i.e. inputs and outputs is used to connect the high-level module with the lower one and hides internal implementation.
Declaration
The module is declared using a keyword ‘module’ with an optional port list and followed by its implementation. In the end, it is enclosed with the keyword ‘endmodule’.
A module consists of variable declaration, dataflow statements, behavioral blocks, instantiation of lower hierarchical modules, tasks, and functions. All of these are optional depending on the requirement statements or blocks that can be used, but module, endmodule, and module name are mandatory. It is not allowed to have nested modules; instead, it allows instantiating sub-module to have the module connections.
An interface to communicate with other modules or a testbench environment is called a port. In simple words, the input/ output pins of digital design are known as ports. This interface is termed a port interface or port list. Since the port list is available for connection, internal design implementation can be hidden from other modules or an environment.
Verilog keywords used for port declaration are as follows:
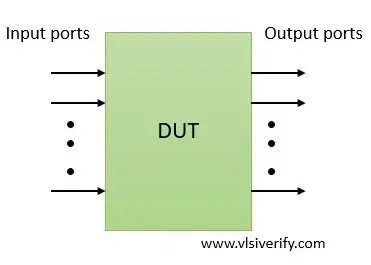
Ports in Verilog
- Ports are of wire data type by default.
- If output ports hold their value, then they must be declared as reg data type.
- The input and inout ports can not be reg as they can not store values. Input ports pass signals from externally connected signals.
Connection rules in Verilog port
While writing a module, the designer needs to make sure what type of signals have to be connected to the module’s inputs and outputs and follow the below rules.
For understanding port connecting rules, consider the current design module as an internal world and outside of the module to be an external world.
Module instantiation
While designing complex digital circuits, usually it is split into various modules that connect to have a top-level block. Thus, Verilog supports a hierarchical design methodology. When a module is instantiated, a unique object is created and it has a unique name. Similarly, a top-level design can also be instantiated while creating a testbench.
Following the hierarchical approach, a particular signal can be reached out following hierarchy and each identifier is separated using a dot.
A mechanism for connecting the port to the external signals
When a module is instantiated in the top-level hierarchy or top-level design in a testbench, any one of the following methods can be used.
Method A: Connecting a port list in an ordered manner
An ordered manner connection is feasible when a port list has minimum signals as the user has to follow the same order in which design level signals are declared.
Design declaration:
Design instantiation in testbench:
Observe that the port list in design mux_2_1 and its instantiation in testbench mux_tb follow the same order.
Note: It is not mandatory to use different names at the design and testbench level.
Method B: Connecting a port list by name
For complex designs having more ports, remembering and writing in the same order while instantiating the design is error-prone. In this method, the order of port list connection does not matter based on the port name, the connection is established.
For an above example,
Verilog Tutorials
- Verilog Ports
01 Sep 2021
While declaring a Verilog module, port list needs to be also declared if we want our module to connect with another modules. The port list consists of various nets and variables, along with the direction.
Components of port
Each port consists of 3 main components:
- Port direction
- Port data type
- Port signal name
Port Direction
There are 3 directions which can be used in the port list:
- Input – This is used for the input ports and input is the keyword used to make an input port.
- Output – This is used for output port.
- InOut – This is used if the port is bidirectional, i.e., it can act as both input and output. inout is the keyword used for this.
Port Data type
Not all data types can be used as a port . Some of the data types like, real , event cannot be used with the port. Ports can be made signed or unsigned using signed keyword before the data type.
In the above example, the port declaration for a and b is invalid.
Port name can be any valid identifier in Verilog.

Port List Declaration
There are 2 ways in which port list can be declared.
Method One (Verilog 1996)
This method is more popular in old versions of Verilog, but in newer versions Verilog introduced a new way to declare a port list based on ANSCI C style. But the old way of declaration is still supported in recent versions and thus can also be used.
In this method, only the port name is used in the port list. The data type and the direction of the ports can be declared later in the body of the module. Also, in this method, the input ports cannot be declared as reg , it can only have a net data type.
Method two (Verilog 2001)
This method is based on ANSCI C, i.e., the way in which we declare the function arguments in C language. In this method, the port direction and data types are mentioned with the port name. If the direction and data type is not mentioned, the direction and data type of previous port is used for this port also. The ports declared using this method, cannot be redeclared in the module body.
Keys points to remember while declaring Verilog port list:
- input ports can only have net data type.
- In newer ANSCI C style port list declaration ports cannot be redeclared again inside module.
- New and old style of port declaration cannot be mixed
- Default data type of any port is net .
Referencing ports (Port Connection)
When we instantiate, a module having ports, we need to connect it to other modules or the top modules using the ports. There are 2 ways to connect the ports with the signals:
Port connection by Order
- Port connection by name
In this connection, the signals which is declared inside the parent module should match the ports according to the position of the port in port list. This type of connection is prone to error, as signal can be easily connected to the wrong port.
Port connection by Name
In this connection, the name of the ports is used to connect the signal with the specific port. This type of connection is not prone to error as order of the ports are important in this case. .port_name(signal_name) is the syntax to use port connection by name.
- Introduction to Verilog
- Verilog Event Semantics
- Basics of Verilog
- Verilog Syntax
- Data Types in Verilog
- Verilog Vectors
- Verilog Arrays
- Verilog Modules
- Verilog Operators
- Verilog Procedural Blocks
- Verilog Assignments
- Different types of loops in Verilog
- Conditional Statements in Verilog
- Verilog functions and tasks
- Compiler Directives in Verilog
- Verilog System Functions
- Delays in Verilog

- Interview Q
Verilog Tutorial
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Interview Questions

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Computer Network
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Control System
Data Mining
Data Warehouse


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Verilog 2001 onwards. Ports are a set of signals that act as inputs and outputs to a particular module and are the primary way of communicating with it. Think of a module as a fabricated chip placed on a PCB and it becomes quite obvious that the only way to communicate with the chip is through its pins. Ports are like pins and are used by the ...
If you must use any port as inout, Here are few things to remember: You can't read and write inout port simultaneously, hence kept highZ for reading. inout port can NEVER be of type reg. There should be a condition at which it should be written. (data in mem should be written when Write = 1 and should be able to read when Write = 0). For e.g.
Ports, also referred to as pins or terminals, are used when wiring the module to other modules. As such, ports are wires. Ports declarations for simple wire are wire declarations with the keyword wire replaced by one of the following direction specifiers: input, output, or inout. For example: output out; input in;
3. In Verilog, you can only do a constant assignment to a net type. A reg type is used in an always block to assign something based on a sensitivity list (it can be synchronous, e.g. flip-flop, or asynchronous, e.g. latch, or gate). A net type is used for assignments using the assign keyword or when connecting ports.
But assign connection2 = connection1; is only uni-directional. Thus between bi-directional ports should use direct connections or you should only use bi-directional Verilog constructs between them. The assign ... is not one of them. But in you case the signal is uni-directional so it does not matter.
Modules, ports, instantiation The module is the basic unit of hierarchy in Verilog I Modules describe: I boundaries [module, endmodule] I inputs and outputs [ports] I how it works [behavioral or RTL code] I Can be a single element or collection of lower level modules I Module can describe a hierarchical design (a module of modules) I A module should be contained within one le
The above Figure shows an example for module instantiation. Figure shows module "SYNCHRO" which consists of 2 'D' flip-flops and are connected in serial fashion. Module "SYNCHRO" has 2 input ports "ASYNC" and "CLOCK" and 1 output port "SYNC". Verilog Programming for DFF instantiated in the SYNCHRO module: module DFF (Q ...
Modules. A Module is a basic building design block in Verilog and it can be an element that implements necessary functionality. It can also be a collection of lower-level design blocks. As a part of defining a module, it has a module name, port interface, and parameters (optional). The port interface i.e. inputs and outputs is used to connect ...
Port Name. In the last part of the port declaration, we assign a name to the port. It is a recommended practice to have a meaningful name for the signal which depends upon its functionality. So continuing the example of AND design using Verilog, we can now define the ports for it. It has two 1-bit inputs and a 1-bit output.
Port Direction. There are 3 directions which can be used in the port list: Input - This is used for the input ports and input is the keyword used to make an input port. Output - This is used for output port. InOut - This is used if the port is bidirectional, i.e., it can act as both input and output. inout is the keyword used for this.
there is no way in verilog to declare different directions to different bits of a single vector port. The direction works on the whole declaration of a port. The only way to do it is to split the single port into multiple ports with different names, e.g. module main( output wire tx, input wire rx, output wire out, input wire in );
The keyword "module" is followed by the module name and the port list. The port specifies all port signals as inputs, outputs, or inout (bi-directional). Local signals are declared immediately following the module/port statement using the keyword "wire". Combinational assignments are made using the assign statement.
assign y = ce ? d : q; endmodule Example 1 - Verilog-1995 version of the muxff module A Verilog-1995 version of this model requires that the q-port be declared three times: once in the module header, once as an output port and once as a reg-variable data type. The d, clk, ce and rst_n ports must all be declared twice: once in the module header ...
port connections, and (4) using new SystemVerilog .* implicit port connections. The styles are compared for coding effort and efficiency. 2.1 Verilog positional port connections Verilog has always permitted positional port connections. The Verilog code for the positional port connections for the CALU block diagram is shown in Example 1.
Verilog Ports. Port is an essential component of the Verilog module. Ports are used to communicate for a module with the external world through input and output. It communicates with the chip through its pins because of a module as a fabricated chip placed on a PCB. Every port in the port list must be declared as input, output or inout.
Verilog rule of thmb 2: drive a Verilog wire with assign statement or port output, and drive a Verilog reg from an always block. If you want to drive a physical connection with combinatorial logic inside an always@(*) block, then you have to declare the physical connection as Verilog reg.
If you don't connect an input/inout port of a submodule it will be connected to some default value by the synthesis tool. This is usually 'b0 for an input, or 'bz for an inout port, but could be anything. Leaving inputs unterminated is not ideal. If you don't connect an output port of a submodule, it will be unused.
I'm new to Verilog and still learning it, but the first think I get about that language is that it's all about ports interconnections. ... Though, this is probably more work just so you can organize your port assignments a different way. Share. Improve this answer. Follow answered Oct 12, 2016 at 17:15. dave_59 dave_59. 41.1k 3 3 gold badges 25 ...
This paper presents the relative motion dynamics of a two-satellite EMFF in the port-Hamiltonian framework and constructs an accurate nonlinear model of the dynamics. Utilizing the concept of Interconnection and Damping Assignment and nonlinear disturbance observer, a composite disturbance-rejection passivity-based controller is designed ...
The SystemVerilog LRM (IEEE 1800-2017) describes ports in interfaces as follows: One limitation of simple interfaces is that the nets and variables declared within the interface are only used to connect to a port with the same nets and variables. To share an external net or variable, one that makes a connection from outside the interface as ...
Verilog Module not updating as expected 1 Variable size and number of port/array port in module which are parameter dependent in Verilog System verilog