- Contact sales
Start free trial

How to Write a Business Case (Template Included)

Table of Contents
What is a business case, how to write a business case, business case template, watch our business case training video, key elements of a business case, how projectmanager helps with your business case.
A business case is a project management document that explains how the benefits of a project overweigh its costs and why it should be executed. Business cases are prepared during the project initiation phase and their purpose is to include all the project’s objectives, costs and benefits to convince stakeholders of its value.
A business case is an important project document to prove to your client, customer or stakeholder that the project proposal you’re pitching is a sound investment. Below, we illustrate the steps to writing one that will sway them.
The need for a business case is that it collects the financial appraisal, proposal, strategy and marketing plan in one document and offers a full look at how the project will benefit the organization. Once your business case is approved by the project stakeholders, you can begin the project planning phase.
Projects fail without having a solid business case to rest on, as this project document is the base for the project charter and project plan. But if a project business case is not anchored to reality, and doesn’t address a need that aligns with the larger business objectives of the organization, then it is irrelevant.

Get your free
Use this free Business Case Template for Word to manage your projects better.
The research you’ll need to create a strong business case is the why, what, how and who of your project. This must be clearly communicated. The elements of your business case will address the why but in greater detail. Think of the business case as a document that is created during the project initiation phase but will be used as a reference throughout the project life cycle.
Whether you’re starting a new project or mid-way through one, take time to write up a business case to justify the project expenditure by identifying the business benefits your project will deliver and that your stakeholders are most interested in reaping from the work. The following four steps will show you how to write a business case.
Step 1: Identify the Business Problem
Projects aren’t created for projects’ sake. They should always be aligned with business goals . Usually, they’re initiated to solve a specific business problem or create a business opportunity.
You should “Lead with the need.” Your first job is to figure out what that problem or opportunity is, describe it, find out where it comes from and then address the time frame needed to deal with it.
This can be a simple statement but is best articulated with some research into the economic climate and the competitive landscape to justify the timing of the project.
Step 2: Identify the Alternative Solutions
How do you know whether the project you’re undertaking is the best possible solution to the problem defined above? Naturally, prioritizing projects is hard, and the path to success is not paved with unfounded assumptions.
One way to narrow down the focus to make the right solution clear is to follow these six steps (after the relevant research, of course):
- Note the alternative solutions.
- For each solution, quantify its benefits.
- Also, forecast the costs involved in each solution.
- Then figure out its feasibility .
- Discern the risks and issues associated with each solution.
- Finally, document all this in your business case.
Step 3: Recommend a Preferred Solution
You’ll next need to rank the solutions, but before doing that it’s best to set up criteria, maybe have a scoring mechanism such as a decision matrix to help you prioritize the solutions to best choose the right one.
Some methodologies you can apply include:
- Depending on the solution’s cost and benefit , give it a score of 1-10.
- Base your score on what’s important to you.
- Add more complexity to your ranking to cover all bases.
Regardless of your approach, once you’ve added up your numbers, the best solution to your problem will become evident. Again, you’ll want to have this process also documented in your business case.
Step 4: Describe the Implementation Approach
So, you’ve identified your business problem or opportunity and how to reach it, now you have to convince your stakeholders that you’re right and have the best way to implement a process to achieve your goals. That’s why documentation is so important; it offers a practical path to solve the core problem you identified.
Now, it’s not just an exercise to appease senior leadership. Who knows what you might uncover in the research you put into exploring the underlying problem and determining alternative solutions? You might save the organization millions with an alternate solution than the one initially proposed. When you put in the work on a strong business case, you’re able to get your sponsors or organizational leadership on board with you and have a clear vision as to how to ensure the delivery of the business benefits they expect.
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects.
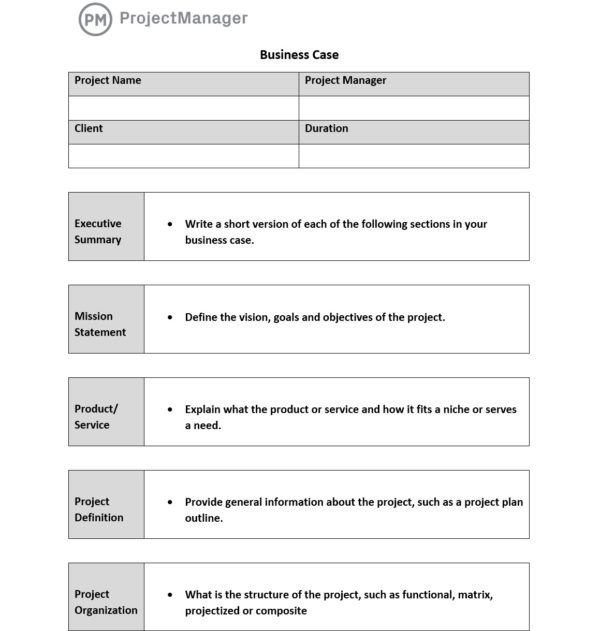
One of the key steps to starting a business case is to have a business case checklist. The following is a detailed outline to follow when developing your business case. You can choose which of these elements are the most relevant to your project stakeholders and add them to our business case template. Then once your business case is approved, start managing your projects with a robust project management software such as ProjectManager.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a short version of each section of your business case. It’s used to give stakeholders a quick overview of your project.
2. Project Definition
This section is meant to provide general information about your projects, such as the business objectives that will be achieved and the project plan outline.
3. Vision, Goals and Objectives
First, you have to figure out what you’re trying to do and what is the problem you want to solve. You’ll need to define your project vision, goals and objectives. This will help you shape your project scope and identify project deliverables.
4. Project Scope
The project scope determines all the tasks and deliverables that will be executed in your project to reach your business objectives.
5. Background Information
Here you can provide a context for your project, explaining the problem that it’s meant to solve, and how it aligns with your organization’s vision and strategic plan.
6. Success Criteria and Stakeholder Requirements
Depending on what kind of project you’re working on, the quality requirements will differ, but they are critical to the project’s success. Collect all of them, figure out what determines if you’ve successfully met them and report on the results .
7. Project Plan
It’s time to create the project plan. Figure out the tasks you’ll have to take to get the project done. You can use a work breakdown structure template to make sure you are through. Once you have all the tasks collected, estimate how long it will take to complete each one.
Project management software makes creating a project plan significantly easier. ProjectManager can upload your work breakdown structure template and all your tasks are populated in our tool. You can organize them according to your production cycle with our kanban board view, or use our Gantt chart view to create a project schedule.
8. Project Budget
Your budget is an estimate of everything in your project plan and what it will cost to complete the project over the scheduled time allotted.
9. Project Schedule
Make a timeline for the project by estimating how long it will take to get each task completed. For a more impactful project schedule , use a tool to make a Gantt chart, and print it out. This will provide that extra flourish of data visualization and skill that Excel sheets lack.
10. Project Governance
Project governance refers to all the project management rules and procedures that apply to your project. For example, it defines the roles and responsibilities of the project team members and the framework for decision-making.
11. Communication Plan
Have milestones for check-ins and status updates, as well as determine how stakeholders will stay aware of the progress over the project life cycle.
12. Progress Reports
Have a plan in place to monitor and track your progress during the project to compare planned to actual progress. There are project tracking tools that can help you monitor progress and performance.
Again, using a project management tool improves your ability to see what’s happening in your project. ProjectManager has tracking tools like dashboards and status reports that give you a high-level view and more detail, respectively. Unlike light-weight apps that make you set up a dashboard, ours is embedded in the tool. Better still, our cloud-based software gives you real-time data for more insightful decision-making. Also, get reports on more than just status updates, but timesheets, workload, portfolio status and much more, all with just one click. Then filter the reports and share them with stakeholders to keep them updated.

13. Financial Appraisal
This is a very important section of your business case because this is where you explain how the financial benefits outweigh the project costs . Compare the financial costs and benefits of your project. You can do this by doing a sensitivity analysis and a cost-benefit analysis.
14. Market Assessment
Research your market, competitors and industry, to find opportunities and threats
15. Competitor Analysis
Identify direct and indirect competitors and do an assessment of their products, strengths, competitive advantages and their business strategy.
16. SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis helps you identify your organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. The strengths and weaknesses are internal, while the opportunities and threats are external.
17. Marketing Strategy
Describe your product, distribution channels, pricing, target customers among other aspects of your marketing plan or strategy.
18. Risk Assessment
There are many risk categories that can impact your project. The first step to mitigating them is to identify and analyze the risks associated with your project activities.
ProjectManager , an award-winning project management software, can collect and assemble all the various data you’ll be collecting, and then easily share it both with your team and project sponsors.
Once you have a spreadsheet with all your tasks listed, you can import it into our software. Then it’s instantly populated into a Gantt chart . Simply set the duration for each of the tasks, add any dependencies, and your project is now spread across a timeline. You can set milestones, but there is so much more you can do.
You have a project plan now, and from the online Gantt chart, you can assign team members to tasks. Then they can comment directly on the tasks they’re working on, adding as many documents and images as needed, fostering a collaborative environment. You can track their progress and change task durations as needed by dragging and dropping the start and end dates.
But that’s only a taste of what ProjectManager offers. We have kanban boards that visualize your workflow and a real-time dashboard that tracks six project metrics for the most accurate view of your project possible.
Try ProjectManager and see for yourself with this 30-day free trial .
If you want more business case advice, take a moment to watch Jennifer Bridges, PMP, in this short training video. She explains the steps you have to take in order to write a good business case.
Here’s a screenshot for your reference.

Transcription:
Today we’re talking about how to write a business case. Well, over the past few years, we’ve seen the market, or maybe organizations, companies or even projects, move away from doing business cases. But, these days, companies, organizations, and those same projects are scrutinizing the investments and they’re really seeking a rate of return.
So now, think of the business case as your opportunity to package your project, your idea, your opportunity, and show what it means and what the benefits are and how other people can benefit.
We want to take a look today to see what’s in the business case and how to write one. I want to be clear that when you look for information on a business case, it’s not a briefcase.
Someone called the other day and they were confused because they were looking for something, and they kept pulling up briefcases. That’s not what we’re talking about today. What we’re talking about are business cases, and they include information about your strategies, about your goals. It is your business proposal. It has your business outline, your business strategy, and even your marketing plan.
Why Do You Need a Business Case?
And so, why is that so important today? Again, companies are seeking not only their project managers but their team members to have a better understanding of business and more of an idea business acumen. So this business case provides the justification for the proposed business change or plan. It outlines the allocation of capital that you may be seeking and the resources required to implement it. Then, it can be an action plan . It may just serve as a unified vision. And then it also provides the decision-makers with different options.
So let’s look more at the steps required to put these business cases together. There are four main steps. One, you want to research your market. Really look at what’s out there, where are the needs, where are the gaps that you can serve? Look at your competition. How are they approaching this, and how can you maybe provide some other alternatives?
You want to compare and finalize different approaches that you can use to go to market. Then you compile that data and you present strategies, your goals and other options to be considered.
And then you literally document it.
So what does the document look like? Well, there are templates out there today. The components vary, but these are the common ones. And then these are what I consider essential. So there’s the executive summary. This is just a summary of your company, what your management team may look like, a summary of your product and service and your market.
The business description gives a little bit more history about your company and the mission statement and really what your company is about and how this product or service fits in.
Then, you outline the details of the product or service that you’re looking to either expand or roll out or implement. You may even include in their patents may be that you have pending or other trademarks.
Then, you want to identify and lay out your marketing strategy. Like, how are you gonna take this to your customers? Are you going to have a brick-and-mortar store? Are you gonna do this online? And, what are your plans to take it to market?
You also want to include detailed information about your competitor analysis. How are they doing things? And, how are you planning on, I guess, beating your competition?
You also want to look at and identify your SWOT. And the SWOT is your strength. What are the strengths that you have in going to market? And where are the weaknesses? Maybe some of your gaps. And further, where are your opportunities and maybe threats that you need to plan for? Then the overview of the operation includes operational information like your production, even human resources, information about the day-to-day operations of your company.
And then, your financial plan includes your profit statement, your profit and loss, any of your financials, any collateral that you may have, and any kind of investments that you may be seeking.
So these are the components of your business case. This is why it’s so important. And if you need a tool that can help you manage and track this process, then sign up for our software now at ProjectManager .

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
- The beginner’s guide to writing an effe ...
The beginner’s guide to writing an effective business case

Nearly every project needs to be approved—whether that means getting the simple go-ahead from your team or gaining the support of an executive stakeholder. You may be familiar with using a project plan or project charter to propose a new initiative and get the green light for a project. But if your proposed project represents a significant business investment, you may need to build a business case.
If you’ve never written a business case, we’re here to help. With a few resources and a little planning, you can write a business case that will help you get the resources and support you need to manage a successful project.
What is a business case?
A business case is a document that explains the value or benefits your company will gain if you pursue a significant business investment or initiative. This initiative can be anything from the messaging for a new product or feature launch, a proposal to increase spend on a current initiative, or a significant investment with a new agency or contractor—to name a few. A compelling business case will outline the expected benefits of this significant investment decision. Key stakeholders will use the business case you provide to determine whether or not to move forward with an initiative.
If you’ve never created a business case, it may sound similar to other early project planning documentation. Here’s how it stacks up:
The difference between a business case and business plan
A business case is a proposal for a new strategy or large initiative. It should outline the business needs and benefits your company will receive from pursuing this opportunity.
A business plan , on the other hand, is an outline for a totally new business. Typically, you’d draft a business plan to map out your business strategy, your mission and vision statements, and how you’re planning on getting there. There may be a case where you create a business plan for an already-existing business, but you’d only do so if you’re trying to take your business in a significantly new direction.
Business case vs. executive summary
Business case vs. project charter.
If you need to create an elevator pitch for your project but you don’t quite need the full business case treatment, you might need a project charter. Much like a business case, a project charter outlines key details of an initiative. Specifically, a project charter will cover three main elements of your project: project objectives, project scope, and key project stakeholders. Your management team will then use the project charter to approve further project development.
Do you need a business case?
Not every project needs a business case—or even a project charter. Plan to build a business case only for initiatives or investments that will require significant business resources. If you’re working on a smaller initiative, consider creating a project charter to pitch your project idea to relevant stakeholders.
Even if you don’t need to pitch your project to any stakeholders, you should be ready to answer basic questions about your proposed project, like:
What is this project’s purpose?
Why are we working on this project?
How does this project connect to organizational goals and objectives?
Which metrics will we use to measure the success of the project ?
Who is working on this project?
When is this project going to be completed?
5 steps for creating and pitching a business case
Your business case shouldn’t just include key facts and figures—it should also tell a story of why pursuing a particular investment or initiative is a good idea for your business. When in doubt, avoid jargon and be brief—but always focus on communicating the value of the project. If this is your first time creating a business case, don’t worry. Follow these five steps to create a solid one.
1. Gather input
You don’t have to write a business case on your own. Instead, make sure appropriate team members and stakeholders are contributing to the relevant sections. For example, the IT team should be involved in any tooling and timeline decisions, while the finance team should review any budget and risk management sections. If you’re creating a business case to propose a new initiative, product line, or customer persona, make sure you also consult subject matter experts.
2. Plan to write your business case out of order
Some of the first things that appear in your business case—like your executive summary—should actually be drafted last, when you have all of the resources and information to make an informed suggestion. Your executive summary will present all of your findings and make a recommendation for the business based on a variety of factors. By gathering all of those details first—like project purpose, financial information, and project risk—you can ensure your executive summary has all of the relevant information.
3. Build your business case incrementally
A business case describes a significant investment for your company. Similarly, simply writing a business case is a significant investment of your time. Not every initiative is right for your business—so make sure you’re checking your work with stakeholders as you go. You don’t want to sink hours and weeks into this document only for it to be rejected by executive stakeholders right off the bat.
Consider doing a “soft launch” with an outline of your business case to your project sponsor or an executive stakeholder you have a good relationship with to confirm this initiative is something you should pursue. Then, as you build the different sections of your business case, check back in with your key stakeholders to confirm there are no deal-breakers.
4. Refine the document
As you create sections of your business case, you may need to go back and refine other sections. For example, once you’ve finished doing a cost-benefit analysis with your financial team, make sure you update any budget-related project risks.
Before presenting your business case, do a final read through with key stakeholders to look for any sections that can be further refined. At this stage, you’ll also want to write the executive summary that goes at the top of the document. Depending on the length of your business case, your executive summary should be one to two pages long.
5. Present the business case
The final step is to actually present your business case. Start with a quick elevator pitch that answers the what, why, and how of your proposal. Think of this presentation as your chance to explain the current business need, how your proposal addresses the need, and what the business benefits are. Make sure to address any risks or concerns you think your audience would have.
Don’t go through your business case page by page. Instead, share the document with stakeholders before the presentation so they have a chance to read through it ahead of time. Then, after your presentation, share the document again so stakeholders can dig into details.
A business case checklist
Start with the why.
The first section of the business case is your chance to make a compelling argument about the new project. Make sure you draft an argument that appeals to your audience’s interests and needs. Despite being the first section in your business case, this should be the last section you write. In addition to including the traditional elements of an executive summary , make sure you answer:
What business problem is your project solving? This is your chance to explain why your project is important and why executive stakeholders should consider pursuing this opportunity.
What is your business objective ? What happens at the end of a successful project? How will you measure success—and what does a successful project mean for your business?
How does this business case fit into your overall company business strategy plan? Make sure your proposed business case is connected to important company goals . The initiative proposed in your business case should move the needle towards your company's vision statement .
Outline financials and the return on investment
At this point in your business case, you should outline the project finance fundamentals. Don’t expect to create this section on your own—you should draft this in partnership with your company’s finance team. In particular, this section should answer:
How much will this project cost? Even if the initiative is completely new to your company, do some research to estimate the project costs.
What does each individual component of the project cost? In addition to estimating the total overall cost, break down the different project costs. For example, you might have project costs for new tools and resources, competitive intelligence resourcing, agency costs, etc.
What is the expected return on investment (ROI)? You’ve talked about the costs—now talk about how your company will benefit from this initiative. Make sure to explain how you calculated the ROI, too.
How will this project impact cash flow? Cash flow is the amount of money being transferred into and out of your business. Significant investments are going to cost a lot of money, so they’ll negatively impact cash flow—but you should also expect a high ROI, which will positively impact cash flow.
What is the sensitivity analysis? Sensitivity analysis is a summary of how uncertain your numbers are. There will be a variety of variables that impact your business case. Make sure to explain what those variables are, and how that could impact your projections.
Preview project details
Your business case is proposing a new initiative. In addition to the financial risks, take some time to preview project details. For example, your business case should include:
Your project objectives and key project deliverables . What will happen at the end of the project? What are you expecting to create or deliver once the project is over?
Your project plan . A project plan is a blueprint of the key elements your team needs to accomplish in order to successfully achieve your project goals.
The project scope . What are the boundaries of your project? What exact goals, deliverables, and deadlines will you be working towards?
A list of relevant project stakeholders . Who are the important project stakeholders and key decision makers for this work? This can include the members of the project team that would be working on this initiative, executive stakeholders who would sponsor the project, and any external stakeholders who might be involved.
A general project roadmap in a Gantt-chart like view. At this stage in the process, you don’t need to provide a detailed project timeline, but you should outline a general sense of when each project stage will happen in relation to the others. To do this, create a project roadmap in Gantt-chart like software . Make sure to include any important project milestones in your roadmap as well.
Any important project dependencies. Is there anything that would get in the way of this project getting started? Does this work rely on any other work that’s currently in flight?
Discuss project risks
Once you’ve outlined the financial impact and important project details, make sure you include any potential project risks. If you haven’t already, create a project risk management plan for your business case. Project risk management isn’t the process of eliminating risk—instead, it’s about identifying, analyzing, and proactively responding to any potential project risks. Clearly defining each project risk and how that risk might impact your project can best equip you and the project team to manage and avoid those risks.
In the risk section of your business case, include:
A risk analysis of any potential project risks. What is the risk? How likely is it to happen? What is the priority level of this risk?
What, if any, assumptions you are making. In project risk management, assumptions are anything you think will be true about the project, without those details being guaranteed facts. Basing project decisions around an assumption can open your project up to risk. Make sure you ratify every project assumption to avoid jeopardizing project success.
Any comparable alternatives in the market. If you’re writing a business case to pitch a new product or angle in the market, evaluate anything that already exists. Could the alternative impact your financial assessment or project success?
Develop an action plan
In the final section of your business case, outline how you will turn this business case into an actionable project. This section should answer questions like:
How will decisions be made? Who is responsible for the project? Who is the project sponsor? If you haven’t already, consider creating a RACI chart to outline project responsibilities.
How will progress be measured and reported? Not every project stakeholder needs to be notified of every project change. Outline key parts of your project communication plan , as well as how you’ll communicate project status updates .
What is the next course of action? If the management team ratifies this business case, what next steps will you take to put this into action?
Bring your business case to life
You’ve built a solid business case and it’s been ratified—congratulations! The next step is to bring your business case to life. It can be intimidating to initiate large-scale change , and implementing your business case is no exception.
If you haven’t already, make sure you have a project management tool in place to manage and organize your new initiative. With a central source of truth to track who’s doing what by when, share status updates, and keep project stakeholders in the loop, you can turn a great business case into a successful project.
Related resources
How to use a feasibility study in project management
How to track utilization rate and drive team profitability

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think
Project Charter vs Business Case (with Clear Differences)
Alessandro Maggio
- July 29, 2021
Share This Post
Project charter vs business case: what are the differences? What is a project charter, and what is a business case? Are these two documents interchangeable? In this guide, you will find all the explanation you need. If you are a project manager, this post is a must read.
In short, both the project charter and the business case are two documents that are essential to the existence of a project. Not all project requires them, but preparing them will ensure the projects are managed in a better way by setting the right expectations. In other words, preparing a project charter and a business case are a practice of solid, good management.
Project Charter vs Business Case
What is a project charter.
A project charter is a document that defines the scope of the project at a high level: it tells what needs to be done, what is the expected timeline, and what is the budget for the project. The project charter effectively authorizes the project, and appoints the project manager.
If the phrase “Let’s do it” would be a document, it would be a project charter. This is the first document you will create when the project is about to start, and it will set the tone and pace for any subsequent document and activity related to the project.

Who drafts the project charter? Often, it is directly the sponsor, which in project management terms is the person who commissions the project. That may be a paying customer, or an internal department. Of course, it does not have to be an individual, most likely it will be an organization or department (because in the end, analysis and consultants will draft such documents, and directors will sign them off).
Interestingly enough, the project charter comes after the business case . This is because the project charter is about getting the project started, while the business case is about deciding if the project is worth starting at all.
What is a Business Case?
Now that we know what a project charter is, we can introduce the business case to make our project charter vs business case comparison.
The business case is about understanding what the impacts on the business of a project will be. We call it business case because we “make a case”, we imagine a scenario when the project is complete, and we evaluate which results it would have.
Of course, not all projects are worth pursuing, so it is likely we will have to prepare many business cases and then start a project only for some of them, creating the project charter only for those.

So, how to structure a business case ? Giving a definitive answer to this question is beyond the scope of this post, but we still need to discuss the basics to better understand project charter vs business case.
To structure a business case, you need to estimate the cash flows of the project. How much will it cost to do it? When payment to suppliers will be expected? How will the project generate money? Will it produce cash by itself, or will it improve operations reducing costs in production, or maybe it will expand the customer base through some new marketing efforts?
Once you understand the basics, you need to estimate the actual amounts, and project them in a document or chart.
To give you an example, I personally worked on a project to install a Cisco Telepresence equipment to allow the senior management of a company to call their secondary headquarter after a Merger and Acquisition. The business case here was simple: if we do not buy the telepresence, senior management will have to travel a lot, at a cost to the company. Instead, with the Telepresence we buy the equipment once and have comparably small recurring costs. So, after how many trips saved will justify buying the telepresence equipment?
Project Charter vs Business Case and How They Interact
There is a caveat, which is crucial to compare project charter vs business case. The business case is not only about deciding if a project is worth investing or not. It is about setting the financial parameters for it being worth investing.
To make it even clearer: if the business case says the project makes sense if its costs are at half a million dollar, most likely it will not make sense if its costs end up at one full million instead.
So, the project charter draws from the business case for the financial parameters in which the project needs to operate. It also draws key assumptions from the business case as well, most likely about the scope and timeline. For example, if the project is creating an amazing ad for the Superbowl, it is clear the ad must be ready before the Superbowl, otherwise it will be worth nothing.
The project charter does not focus to explain why and how the project makes financial sense to the company. It just tells what needs to get done and what are the constraints, in a language that is easy to understand for the project manager. If the project manager follows the charter, then rest assured the project will turn out as expected and deliver the expected results (unless there were estimate errors in the business case).
Project Charter vs Business Case in Summary
In you were looking for a TL;DR, here’s a summary of our post on project charter vs business case.
The business case is the document that gets created first. It makes assumptions on a project in terms of its costs and expected revenue and based on that it determines if it makes sense financially. If it does, and if there are not better projects at the moment, then the project is pursued.
This is when we draft the project charter. This document is created by who commissions the project, sometimes appointing and involving the project manager. It tells at high level what needs to be done and what are the constraints in terms of budget, timeline, and scope. These constraints are important because they ensure the project will be able to realize what was defined in the business case.
So, project charter vs business case: these are not alternative document, rather documents with different purpose that we use at different stages of the project.
Where to Go Next?
If you found interesting this project charter vs business case article, you are probably considering how to best start and run a project. The best way to do so is to understand the concept of Net Present Value in depth. We have a wonderful article that assumes you know nothing and takes you well beyond the knowledge the average project manager has. This is something you absolutely need to not make bad estimates when creating your business case.
So, read now: The 1 Defintive Guide to NPV in Project Management .
Never Stop Learning...
The 7 most effective time management strategies, 6 amazing generative ai use cases for the real world.
Join the Newsletter to Get Ahead
Revolutionary tips to get ahead with technology directly in your inbox..
2021-07-29T16:30:00+00:00
Prime Opportunity
Project Management
Want Visibility from Tech Professionals?
If you feel like sharing your knowledge, we are open to guest posting - and it's free. find out more now..

Accessibility
Free courses.
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is a business case and how to write one (with template)

In this guide, we’ll define what a business case is, help you determine when you need one (and when you don’t), and walk you through a four-step process for creating a business case.

We’ll also outline what you should include in a business case and provide a free template you can use when writing a business case to secure stakeholder support for your next big project.
What is a business case?
Every project needs the support and approval of key stakeholders before it can launch. Many project and product leaders use a project plan or charter to communicate pertinent details to those involved.
Similarly, for large initiatives that require significant resources, potential investors are presented a business case outlining the costs, benefits, business need, and risks involved.
A business case is a document that defines the value it will deliver if executed and benefits the company over the costs involved. With a thorough understanding of the components to be included and necessary resources, it is possible to create a compelling business plan.
Why do you need a business case?
If a project is green-lit without a business case, it can lead to serious issues down the road. A project without clearly articulated expectations and goals can go on endlessly and aimlessly. This leads to wasted resources, money, and time with no outcome in the end.
A business case enables you to:
Align with strategy
Gain stakeholder support, prioritize projects, track outcomes.
A business case helps to showcase how a project is aligned with the overall strategy and goals of the organization. It clearly defines the problem or opportunity that the project is intended to address.
A business case also enables you to determine expected benefits and outcomes before you start a project or initiatives, thus projecting how the project contribute to achieving the organization’s goals.
A business case is a useful tool to provide a clear rationale for pursuing the project. A thorough business case can help key stakeholders decide whether to invest in the project by evaluating the feasibility, costs, risks and potential returns. A business case presentation gives stakeholders an opportunity to ask questions and address concerns.
A business case defines the value that the project is expected to deliver. Based on the value delivered by each project, business and product leaders can prioritize projects for budget cuts or further investments. Proper prioritization helps the organization achieve the goals aligned with the business strategy.
A business case provides a roadmap for the project, including the goals, milestones, and key deliverables. Once the project starts, a roadmap helps you keep track of your progress toward project goals, including what has already been achieved and what will be delivered at the end. Providing a timely update on the project to the key stakeholders is critical for setting expectations.
When you don’t need a business case
A business case is certainly helpful for large initiatives requiring support from key stakeholders, but there are some situations where creating a business case might be a waste of time.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
For instance, small or low-risk projects that would not impact the organization in any negative way do not require a business case because it would not make sense to spend that much effort on a low-scale project.
A business case might also be considered superfluous for a project that is already ongoing. It can be tempting to create a business case post-launch for the sole purpose of documenting decisions made and milestones achieved. However, it’s typically not worth the time investment because such a business case rarely adds any value or insights.
Before you take on the task of creating a business case, it’s important to carefully consider the need and to ensure that doing so would produce valuable insights to the decision-making process. It is in the best interest of everyone to forgo the business case creation process in situations where it does not provide any additional value and to focus instead on other activities that directly impact the project.
Business case vs. business plan
A business plan is not the same thing as a business case.
A business case outlines a proposed project and its potential benefits to convince key stakeholders to invest. It typically includes analysis of costs, value to be delivered, and associated risks, along with ROI.
A business plan, on the other hand, outlines the overall strategy and goals for an entire organization. It defines the what, why, and who for the business, covering the products and services offered, target segment, marketing and sales strategy, and operational and financial projections over a period of time. A business plan is designed to help potential outside investors make informed decisions about whether the business is worth investing in.
The table below breaks down the differences between a business plan and a business case:
How to write a business case
Before we dive into steps to create a business case, let’s review what we’ve learned so far:
- A business case is a document created during the initiation of the project but is referred throughout the project lifecycle
- A strong business case helps in building confidence and gaining support of key stakeholders
- A business case also helps you track a project’s progress over time
- A weak business case that is not aligned with strategy can lead to project failure
To write a business case, follow this four-step process:
- Identify the business need
- Explore all possible solutions
- Propose the best approach
- Outline the implementation process
1. Identify the business need
Projects are initiated to solve a business need and achieve a value or a benefit aligned to the goals of the organization.
The first step to create a business case is to identify the business problem and define it clearly. Market research and any available data to justify the business need is helpful to include in the business case.
2. Explore all possible solutions
Once the business problem has been identified, the next step is to explore all the possible solutions for that problem. You can do this systematically by listing out all the possible solutions along with other parameters, such as:
- The benefits of each approach
- Feasibility
- Time period
- Assumptions
A detailed analysis of each option predicting the cash flows, ROI, and value delivered would help key stakeholders understand each solution and cross-question the assumptions, feasibility, and other parameters.
3. Propose the best approach
Set a criteria to showcase how you evaluate each solution and then come up with the best out of the list.
To set the criteria, identify attributes that closely align to the organization’s strategy. For example, if the organization’s goal is to increase revenue in the next year, then an important criterion might be the solution with maximum revenue projection.
List the top three-to-five attributes to evaluate alternative solutions against and rank each solution 1–5. Once you rank all of them, total the ranks for all the attributes to indicate a clear winner.
Document this process and present it to stakeholders to ensure they are on the same page with the selection process of the best solution.
4. Outline the implementation process
Once the best solution has been proposed, the next step is to think about how it will be implemented.
When it comes to planning the implementation process, you need to define:
- Resources needed
- Timeline from initiation till the end
- Risks and how to mitigate
- Milestones and when they will be achieved
- Total cost involved and how much will be used by when
These four steps, when captured in detail, can help you win the support of key stakeholders and kick off your project with a solid foundation and a clear objective.
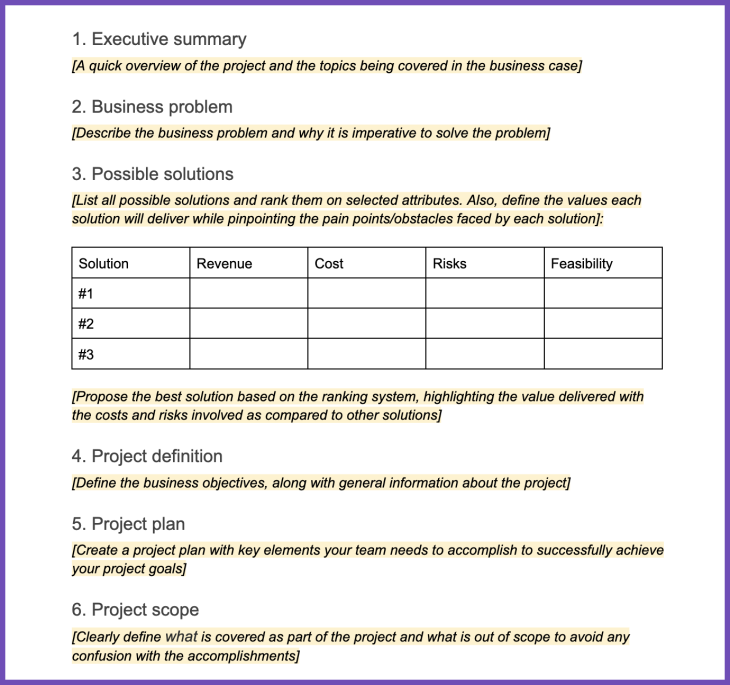
What is included in a business case?
Now that we’ve walked through the steps of how to create a business case, let us also take a look at what to include in the business case document to support the four steps outlined above.
Here’s what to include in a business case:
- Executive summary — A quick overview of the project and the topics being covered in the business case
- Business problem — A description of the business problem and why it is important to solve it
- Possible solutions — A list of possible solutions and how the best possible solution is identified
- Project definition — Define the business objectives to be achieved along with general information about the project
- Project plan — Create the project plan with key elements your team needs to accomplish to successfully achieve your project goals
- Project scope — Clearly define what would be covered as a part of the project and what is out of scope to avoid any confusion
- Project budget — Estimated cost involved to complete the project needs to be captured with a detailed breakdown
- Project roadmap — Projection of the estimated timeline for each stage of the project to be done. Be sure to include any important project milestones
- Project financials — Financial metrics depicting the cash flow, such as NPV, IRR, ROI, and payback period to help stakeholders understand the financial value the project can bring in over a period of time
- Risk assessment — Capture the risks involved and the steps planned to mitigate the risks
- Project stakeholders — A list of key stakeholders involved can help anyone looking at the document to reach out to them when needed. The list can include the project team, sponsoring executives, and any external stakeholders who might be involved
Business case template
To help you get started writing a business case for your next big project or initiative, we created a business case template that you can download and customize for free.
You can access this simple business case template by clicking here (be sure to select File > Make a copy from the main menu bar before editing the template).
Preparing the business case is only half the journey of initiating a project. The next step is to present the business plan to key stakeholders , answer their queries, and compel them to support the project.
Lastly, be sure to follow up with the attendees to make sure all the stakeholders are on the same page and aligned to support the project.
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #collaboration and communication
- #project management

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Leader Spotlight: Encouraging design thinking workshops, with Tamara Pluviose
Tamara Pluviose discusses her approach to design thinking workshops that promote problem-solving, brainstorming, and customer-centricity.

Crafting a successful product launch strategy: Key tips and steps
A launch strategy builds anticipation, maximizes initial sales, and establishes a strong market presence early on.
Leader Spotlight: Having a bias for action, with Anish Chadda
Anish Chadda discusses the importance of having a “bias for action” — iterating quickly instead of focusing on creating a perfect prototype.

DSDM: The dynamic systems development method
The dynamic system development method (DSDM) was first released in 1994 as a software development method to provide some discipline to RAD.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- ABOUT ELORUS
How to Write a Strong Business Case in Project Management

Ready to make your projects a hit every time? Whether you're in a traditional office or a fast-paced agile setting, knowing how to build a solid business case is your key to success. But what is a business case, really? How much does it really impact your project management, and what can go wrong if it's not well-crafted? Let’s take a closer look at the core concept of a business case and how project managers can write them effectively.
What is a business case in project management?
A business case is a document that outlines the reasons for a project, the expected benefits, and the risks involved. You should use a business case to convince decision-makers to approve the project and to provide guidance for the project team, all while enhancing stakeholder communication by clearly defining roles, responsibilities, expectations, and projected outcomes.
Many brands deploy project business cases to ensure that target objectives align with an agency’s business strategy. A business case can help you justify a project’s existence, and including these critical elements can also help ensure that an initiative will be strategically valuable.
What are the elements of a strong business case?
A well-written business case should include key sections, such as an executive summary, a risk analysis, and an implementation timeline. Let’s look at how each component can impact business case development .
The executive summary should provide a brief overview of the project, including the problem it addresses, the solution proposed, and the benefits you expect. Your project description will outline any existing problems that require attention, including their causes, results, and consequences, alongside the overall project scope and objectives.
A well-executed cost-benefit analysis can help you weigh projected expenses and the required work time of your team against potential returns. This analysis is a simple framework that you can apply to any number of projects to determine how financially viable they are. In addition, conduct a risk assessment beforehand to present this information alongside your cost-benefit analysis so you can develop a well-rounded view of the project for all involved parties.
Next, you’ll want to consider the project's key stakeholders . Who’s investing, who stands to benefit, and who needs to be involved in decision-making? The stakeholders section should list the people who must approve the project before it can proceed. Finally, you’ll have your implementation timeline that concludes your project business case. The timeline should provide a realistic view of expected project turnaround times and be thorough enough to include regular check-ins, milestones, and reviews.
Common business case development mistakes project managers should avoid
Of course, much of your success in building a business case depends on doing it correctly. With any business initiative, there’s a bit of a learning curve. Luckily, plenty of project managers have made common mistakes you can learn from. For starters, what happens when your business case doesn’t align with your strategic goals ? You could end up investing in a failed project, allocating resources to an ineffective process, or harming your brand image by promoting initiatives that seem out of touch with your strategy.
Beyond that, it’s all too easy to let a project business case become more burdensome and complicated than it needs to be. Be as concise as possible without omitting critical information. This includes any information that could benefit stakeholder communication and keep key members in the know.
Also, underestimating costs and poor risk assessment can both back you into a corner financially and creatively. Tighten up your cost-benefit analysis and use risk assessment to learn from past industry mistakes and your own brand’s missteps. Factor your brand’s current limitations into risk assessment to take a more holistic view of your business’s mitigation strategy.
Lastly, one of the biggest mistakes we see when developing a business case is a lack of flexibility . This includes applying a one-size-fits-all approach to different projects or failing to customize your business case for new initiatives. Be willing to listen to your data and respond to what it tells you.
What’s the role of the business case in agile project management?
Agile workflows are about adaptability and responding to data, market trends, or project needs. At a glance, this might seem different from a tightly structured business case in project management. However, applying a business case as an overarching vision and guidance tool can significantly benefit an agile environment.
On top of that, your business case development can identify the justification for project investment while simultaneously providing guidelines for task prioritization. Since Agile environments emphasize prioritization, collaboration, and communication, what better way to enhance all three than with a well-constructed business case?
Plus, since business cases should include rigorous risk assessment data, you can regularly revisit your strategy and adapt processes to mitigate emerging risks. Your business case can be a robust framework for any upcoming agile initiatives or agile-based project management when effectively issued.
Elorus can help you develop a more effective business case for project management
A business case is an essential tool for any project manager. It helps ensure that projects are well-planned and have a clear purpose with measurable benefits. Especially in service-based industries that thrive on new projects, processes, and initiatives, understanding how to deploy a business case can often mean the difference between brand growth and stagnation . For many businesses, understanding how to build a business case starts with the right tools and software platforms, like Elorus.
Elorus offers helpful business software so you can manage your projects more effectively. Our tools include cost monitoring and financial reporting features to make business case development a breeze. Get actionable insights into your project expenses, develop business cases that set your teams up for success, and use data-rich tools that help you grow your brand when you work with Elorus.
Grow your Business with Elorus
Invoicing, time tracking & expense management., table of contents, you might also like.

Project Cost Estimation: How to Do It Right and Stay on Budget

Project Management 101 part 1 - Project Management Definition And Use For Freelancers
Project Management 101 Part 2- How To Manage A Project Effectively From Start To Finish
- Twitter icon
- Facebook icon
- LinkedIn icon
How To Write a Business Case (and Get Your Project Approved) with free template
🎁 Bonus Material: Free Business Case Template

What is self management? How to take control of your personal productivity

Is your team “quiet quitting?” How to handle employee overload

A 4-Step Guide to Creating Powerful Team Rituals
Working with planio, see how our customers use planio.
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
How to Write a Business Case (With Example & Template)
May 19, 2022 - 10 min read
A business plan is a straightforward document. In it, you’ll include market research, your overall goals for the business , and your strategies for achieving those goals.
But what is a business case and why do you need one if a business plan outlines everything else?
A business case takes a closer look at a specific problem and how you can solve it. Think of a business case as the reason you create a project you’re going to manage in the first place.
The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to write a successful business case, including a checklist for identifying problems, researching solutions, and presenting to stakeholders. As a bonus, we’ll show you how to use Wrike to manage your product business cases with a requirements management template or implement them with a project scheduling template .
What is a business case?
A business case is a project you’ll assemble for identifying, addressing, and solving a specific business problem.
The key to a business case is the change it creates in your business. Developing a business case starts with identifying a problem that needs a permanent solution. Without that lasting change, a business case is only an observation about what’s going wrong. A complete business case addresses how a company can alter its strategy to fix that problem.
Front-to-back, a business case is a complete story. It has a beginning, a middle, and an end. It typically looks like this:
- Beginning: Someone identifies a problem within the business and presents the business case to the key decision-makers.
- Middle: With the project go-ahead, the company launches an internal team to address the business case and deliver results.
- End: The team delivers a presentation on the changes made and their long-term effects.
In short, a business case is the story of a problem that needs solving.

Examples of business cases
The problem for many companies is that they can turn a blind eye to challenges that are right in front of their faces. This is even the case when the company has a compelling product to sell.
Consider the example of Febreze . In the mid-1990s, a researcher at Procter & Gamble was working with hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin. His wife noticed that his clothes no longer smelled like cigarettes, which was a frequent complaint.
P&G had something of a miracle product on its hands. However, their approach was wrong. They initially marketed Febreze as a way to eliminate embarrassing smells. Predictably, the product flopped.
But P&G stuck at it. They had a potential business case on their hands: a highly marketable product proved difficult to market. What was going wrong? Working on the business case from beginning to end provided the answer.
After some focus group testing, P&G found out that few consumers recognized the nasty odors they were used to. Instead, they learned to use a different business case for Febreze: it was a cleaning product now, a way to make the house smell nice when the floors are vacuumed and the counters are wiped clean. They gave it its own pleasant smell and fashioned it into a cleaning product. And because it worked so well, so did the campaign.
That’s an example of a business case overall. But let’s get specific: developing a business case is easier when you have a template to look at. Let’s build an example using a made-up company, ABC Widgets, and a hypothetical business case. Let’s call our business case example “Operation Super Widgets”:
Business Case: ABC Widgets
Section 1: summary.
Briefly describe the problem and the opportunities.
ABC Widgets’ latest widget, the Super Widget, is suffering from supply issues, requiring higher shipping costs to procure the necessary resources, and eating into profits. We need to switch to a new supplier to restore the viability of the Super Widget.
Section 2: Project Scope
This section should include the following:
- Financial appraisal of the situation. Super Widgets are now 20% more expensive to produce than in the year prior, resulting in -1% profits with each Super Widget sold.
- Business objectives. To get revenues back up, we need to restore profit margins on Cost Per Unit Sold for every Super Widget back to 2020 levels. Benefits/limitations. Restoring Cost Per Unit Sold will restore 5% of sagging revenues. However, we are limited to three choices for new Super Widget suppliers.
- Scope and impact. We will need to involve supply chain managers and Super Widget project management teams, which may temporarily reduce the number of widgets we’re able to produce, potentially resulting in $25,000 in lost revenue.
- Plan . Project Management Teams A and B will take the next two weeks to get quotes from suppliers and select one while integrating an immediate plan to bring in new Super Widget parts for manufacturing within four weeks.
- Organization. Team Member Sarah will take the lead on Operation Super Widget Profit. Both teams will report to Sarah.
This is a bare-bones example of what a business case might look like, but it does hit on the key points: what’s the problem, how can you fix it, what’s the plan to fix it, and what will happen if you succeed?
How do you write and develop a business case?
When writing your own business case, the above example is a good guide to follow as you get started with the basics.
But, once you’re more familiar with the nuts and bolts, it’s also worth being prepared for some potential roadblocks you could face along the way.
Challenges of writing a good business case
Why don’t more companies create a business case? It might come down to a lack of good communication. Many people don’t even know how to write a business case, let alone present one.
“The idea may be great, but if it’s not communicated well, it won’t get any traction,” said Nancy Duarte , communication and author who wrote The HBR Guide to Persuasive Presentations.
The key challenge, notes Duarte, is taking abstract business concepts (like lagging numbers) and turning them into an immediately recognizable problem. After all, if a company already had perfect awareness that it was making a mistake, it likely would find a way to stop the error in its tracks.
A business case is challenging because it usually means you’ll have to persuade someone that change is needed. And change can be difficult. In a thriving business, it’s especially problematic because it’s easy to point to the bottom line and say that whatever the company is doing is already working.
How do you present a business case?
The tips and examples above give you some nice remedies for creating a business case without the typical problems. But you’ll still want to present a business case with the straightforward proposals and numbers you’d associate with any new project.
Essentially, it all comes down to how well your business case can persuade the decision-makers. That’s why you shouldn’t just build a case off of raw numbers. The bottom line might be a compelling argument, but it’s not always what “clicks.”
If you’re presenting a business case, you’re a salesperson. And not every sale is a matter of precise logic. It’s also about emotion—the story of why something’s gone wrong and what needs doing if you’re going to overcome it.
The art of a good business case is the art of persuasion. Keep these specific points in mind as you craft one of your own:
- Point to an example of a bad business case and liken it to the present case . No one likes the idea of watching themselves walk into a mistake. Presenting an example of a business that made the same mistake your company is making and then translating it into the present moment is a compelling way to craft a business case that makes ears perk up.
- Build a narrative. Nancy Duarte pointed out that in one business case, a client convinced a CEO to follow through with a project by using simple illustrations. It’s not that the idea of adding illustrations to the business case was so great. It’s that the illustrations were able to tell a compelling story about why the case needed to go through.
- Distill the idea into an elevator pitch. Try this exercise: get your business case down to one sentence. If you can’t explain it any more simply than that, your business case might not be as memorable as it needs to be to sway decision-makers.
- Use analogies to drive the point home. Let’s say you discovered a problem in a growing business. Overall, revenues are good — but you’ve noticed an associated cost that has the potential to explode in the future and tank the business. But it’s not compelling to use dollars and cents when the business is doing so well. Instead, consider introducing the business case with a simple analogy: “Without repair, every leaky boat eventually sinks.” You now have their attention. Use the numbers to drive the point home, but not to make the point.
If you’re presenting a business case to decision-makers, remember that it’s not only the logic of your argument that will convince people — it’s how persuasive you can be.
Business case checklist
Before you can check “learn how to write a business case” off your list, you have to know the essentials. Make sure you include the following elements in your business case checklist (and, of course, your business case itself):
- Reasons. This should be the most compelling part of your business case. You can tell a story here. And the most compelling stories start with a loss or a complication of some sort. What is the threat to the business that needs remedy? What are the reasons for moving forward?
- Potential courses of action. It’s not a complete story until we know the next chapter. A business case isn’t just about the problem — it’s about rectifying a problem through the solution. Recommend a few specific courses of action to help spur discussion about what to do next.
- Risks and benefits. Not every solution is going to be perfectly clean. There are going to be solutions with downsides. There are going to be costs along with the benefits. Make sure to include each of these to give a clear and complete picture. This is the time to manage expectations — but also the time to inspire action.
- Cost. What’s it going to cost to complete the project? The people making the decisions need to know the bottom line figure to assess which business cases to prioritize.
- Timeline. A good project isn’t only measured in dollars but in days, weeks, and months. What is the expected timeline for the business case? How quickly can the problem meet its solution?
With every business case, specificity is key. A vague timeline won’t help — a timeline with specific weekly milestones looks more achievable. To make your business case more compelling, always look for the specific details that tie your story together.

Business case template
A business case template is a document that outlines the key elements of a business case in a structured format. By using a standardized template, companies can ensure that all relevant information is captured and shared in a clear and consistent manner.
Depending on the size of your business and the scope of your project, your business case template can be as detailed or as simple as you like. For a smaller project, you can use a one-pager to get started, detailing the main points of your project, which include:
- Executive summary: An overview of your project, its goals, and the benefits of completing it for your business
- Team and stakeholders: A list of the relevant people involved in your project, and their contact information
- SWOT analysis : An analysis of how your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats weigh up against your competitors
- Risk analysis: An overview of the kind of risks that are involved with your project and how you may avoid them
- Budget and financial plan: Details of your budget and where you may secure financing for your project
- Project plan: A schedule of how you plan to implement your project and what tasks are involved
Let's see what that might look like.
How to write a business case with Wrike
Wrike’s project management software can step in and turn a business case from the seedling of an idea to a full-fledged initiative.
The requirements management pre-built template can help you document and track project requirements in a structured manner. The template includes sections for capturing stakeholder requirements and business cases, as well as any constraints that may affect the project’s success. By using this template, you can ensure that all necessary requirements are identified and that potential issues are addressed early in the project planning process.
If you want to move from the business case description to the actual implementation faster, consider using the project scheduling template . This template can help you create a detailed project timeline with milestones, identify task dependencies, and assign resources. By utilizing this template, you can ensure that the project is realistically achievable and meets all business needs, giving stakeholders confidence in the project’s success.
Kat Boogaard
Kat is a Midwest-based contributing writer. She covers topics related to careers, self-development, and the freelance life. She is also a columnist for Inc., writes for The Muse, is Career Editor for The Everygirl, and a contributor all over the web.
Related articles

What Is a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)?
A requirements traceability matrix is an integral part of an embedded system's life cycle. It helps organizations ensure that their products are safe and are meeting their intended standards. This is especially important for the medical, technology, and engineering industries. But any business that has a set of goals and standards to uphold can benefit from this proven requirements analysis tool. Here’s how to make an effective requirements traceability matrix and why you should start one today. What is a traceability matrix? A traceability matrix is a document that details the technical requirements for a given test scenario and its current state. It helps the testing team understand the level of testing that is done for a given product. The traceability process itself is used to review the test cases that were defined for any requirement. It helps users identify which requirements produced the most number of defects during a testing cycle. Not only does this show areas in need of improvement, but it also helps mitigate future roadblocks and identify process weaknesses. What is a requirements traceability matrix? A requirements traceability matrix (RTM) is a tool that helps identify and maintain the status of the project’s requirements and deliverables. It does so by establishing a thread for each component. It also manages the overall project requirements. This method is straightforward and can be easily done by anyone. There are many kinds of RTMs. For example, a test matrix is used to prove that tests were conducted. It can also be used to identify issues and requirements during the development of software. What are the benefits of a requirements traceability matrix? An RTM ensures that projects do everything they set out to do. This step-by-step process helps identify the requirements and the products that are required to be tested successfully. It also helps in determining the project's direction and timeline. First, it will support the identification of all requirements in a work product. Then, it will check to make sure there is coverage of all the requirements throughout the project’s lifetime. The RTM will show the requirements coverage in terms of the number of test cases, design status, and execution status. It will also show the UAT status for a specific test case. With all this information at your fingertips, your team will be able to analyze changes in requirements and make informed product development decisions on the fly. And because traceability links artifacts across the development lifecycle, it helps teams identify and resolve issues before they become problems. It can also help avoid the pressure of an audit. And if you do get audited, having an RTM will make it easier to demonstrate that you have complied with regulations which means you can avoid additional expenses or delays the audit may cause. You can even use it to track requirements from compliance regulations in a compliance matrix. That will help you understand what you need to test and develop before the work is finalized. In a nutshell: a requirements traceability matrix makes it easier to meet goals and manage projects. What do you include in a requirements traceability matrix? Create a simple chart with the following columns: Requirements: Add sub-columns for marketing requirements, product requirements, and system-level specifications (if applicable). Testing: Add a sub column for test cases and test runs. Deviation: Add a sub-column for any issues. Requirements traceability matrix example Here is a basic requirements traceability matrix example, including a description of the requirements, their business justification, and the status of the task. How to create a requirements traceability matrix in Wrike The matrix should be created early in the project life cycle to ensure it is up-to-date and incorporates all the details necessary for the project to be successful. A project management tool like Wrike is perfect for tracking, organizing, and assessing every last rule. First, gather your requirements list. Add them as individual projects in Wrike. Assign a due date, priority level, and set of corresponding tasks needed to achieve compliance to each one. Next, each requirement must have a unique and clearly defined purpose. Add these details to the project or corresponding task description so that the assignee fully understands what they are trying to achieve. Then, you can also use Wrike to securely plan for and store related materials. Supporting documents such as test scripts should be prepared ahead of the actual testing process. Simply create a task, set an approver, and add the final product to your Wrike files. Control who sees it with secure sharing. Finally, identify gaps in coverage. If any defects are found during the test cases, then they can be listed and mapped with business requirements and test scenarios. In Wrike, you can assign each one to an individual or team. You can also add an Approver who will sign off on the task once it’s complete. If there are any questions or comments, the collaborators can discuss them right within the task themselves, looping in colleagues using @mentions whenever another POV is needed. If a change request is made, you can view your existing project plans and give an informed evaluation of whether or not it can be done. If the answer is yes, you can then drag and drop project components for a new and accurate timeline. In Wrike, projects with tasks marked as dependent on one another will maintain these connections, so when you move them, you’ll still have all of your necessary components tied together, working uninterrupted. Once your RTM is complete, you can duplicate your processes and workflows in Wrike by creating a template for the ones you plan to repeat. This saves time and adds a layer of standardization that is crucial for meeting requirements. And because the testing process should be clearly defined to avoid any confusion, using Wrike to do so will ensure that it is carried out according to the requirements and time constraints. Wrike provides a secure collaborative workspace to organize, test, and bring all your projects up to speed with your RTM. Ready to streamline your product development compliance? Start today with a two-week free trial of Wrike.

Best Project Management Software for a Small Business: Ultimate Guide
What is the best project management software for small teams? Learn everything about project management software for small businesses with our guide.

What Is Cost Overrun? How to Prevent It
Struggling with project cost overrun? Find out how to prevent cost overrun in project management with actionable tips, tools, and strategies.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.

- Essential Business Writing
- Report Writing Courses
- Business Case Writing Courses
Proposal Writing
Presentation Skills
- Proposal / Bid Writer
- Business Plan Writer
- Business Case Writer
- Testimonials
- How to Write Highly Effective Business Cases
How To Write Business Plans and Business Cases

Setting the scene
“What’s the difference between a business case and a business plan?”
Few people can produce a ready answer to that question. After all, both business plans and business cases make predictions about future outcomes, but there is a big difference between the two.
Business plans
are based on the business model or business line of an organisation. They explain how the business will achieve its operational and financial goals by capitalising on the capability of the organisation.
Business plans may be written to explain how a business may meet its growth targets over one or more years.
Business cases
are based on a cost model. Business cases comprise an argument to convince a decision maker to approve a specific course of action over another.
A business case may be produced to justify the purchase of capital equipment.
1. What is a business plan?
2. how do i prepare, 3. how do i start, 4. how long should a business plan be, 5. how should i clarify my ideas, 6. what should a business plan contain, a) executive summary, b) management profiles, c) vision statement, d) mission statement.
e) Your proposition – company, product or service
f) Market description, analysis, segmentation, targeting and positioning
G) explanation of how the product, service or idea is different, h) outline marketing plan, i) outline sales plan and forecast, j) resources.
k) Financials (to include ROI and cash flow)
l) How to make it happen
7. should i use images and colour, 8. how should i present charts, 9. what is a business case, 10. what is the first stage, 11. how do i test my ideas, 12. defining options, 13. structure of a business case, 14. how do i encourage a decision, 15. any winning tips.
16. One last thing…
Business Plan
A business plan is a written document which describes your business, your goals and how you intend to achieve them over a given period. It is a forecast. It describes your starting point and the strategy you need to reach your proposed end point in one, two or three years.
It details your aims, describes your products and services, analyses market demand, and details the resources you need, the capability you have, and the income you anticipate to generate over a period of time.
In essence, your plan should provide sufficient information for the reader to calculate the credibility of your strategy, your chance of success, and in some cases, the risk people may take by investing in your business.

Ensure that you can answer questions about your plan with logic, completeness and clear thinking. You need to be able to describe three things:
- The situation – opportunity or problem
- Your plan to address the situation
- The payback
Creating an effective business plan means converting an exciting idea in your head into a compelling story on paper. It means applying logic and reasoning to your thoughts and creating a credible plan of action. Above all, it requires clarity of thought.
Clarity is the connection of your idea – your business proposition – to a coherent set of words, sentences, and numbers. It details what you wish to achieve – the business benefits – the why and who and when and where and how you are going to achieve them.
You must be able to answer why people should buy your business, product, service, or idea, in preference to someone else’s. Your answer should include the financial reasons why people should buy from you, which then means that your answer is essentially your value proposition.
A value proposition is a statement of value which you propose to deliver to potential buyers. This should be your starting point for developing your business plan.
Think of your value proposition as your elevator pitch. It should be clear, concise and compelling. It is about how you can deliver greater value or offer a better deal to potential customers than the current market can offer.
A value proposition details how your business, product or service can offer higher quality, lower cost, or something else desired by your customers, that your competitors can neither offer nor replicate easily. A value proposition should comprise a simple set of statements which:
- Describe how your business, product, service, or idea addresses the situation – problem or opportunity.
- Detail why the situation should be addressed or needs to be addressed in terms of opportunity, difficulty, or cost.
- Explain the benefits of your business plan – your business, product, service, or idea over alternatives.
- State the cost advantages of your business, product, service, or idea over competitive alternatives.
A business plan should contain essential information and no more than essential information necessary for the plan. The plan should be as short and as concise as possible. But it must contain everything necessary. In other words, it must be complete and leave no obvious questions unanswered.
A business plan can be as short as a couple of pages to many pages long depending on the product, service, market, and complexity of the proposition.
You need to have clarity about all aspects of your business plan and the influences upon it. SWOT may help you to distinguish between unimportant and important aspects which you need to consider. A SWOT analysis is a way of focusing on factors which may influence your success.

In particular, you need to be clear about threats to your plan. Readers need to see that you are knowledgeable about the environment in which you will be trading. That means you should never skip over areas of potential difficulty. Instead, define, analyse and conclude how and why you can overcome them. Realism is desirable in all business plans.
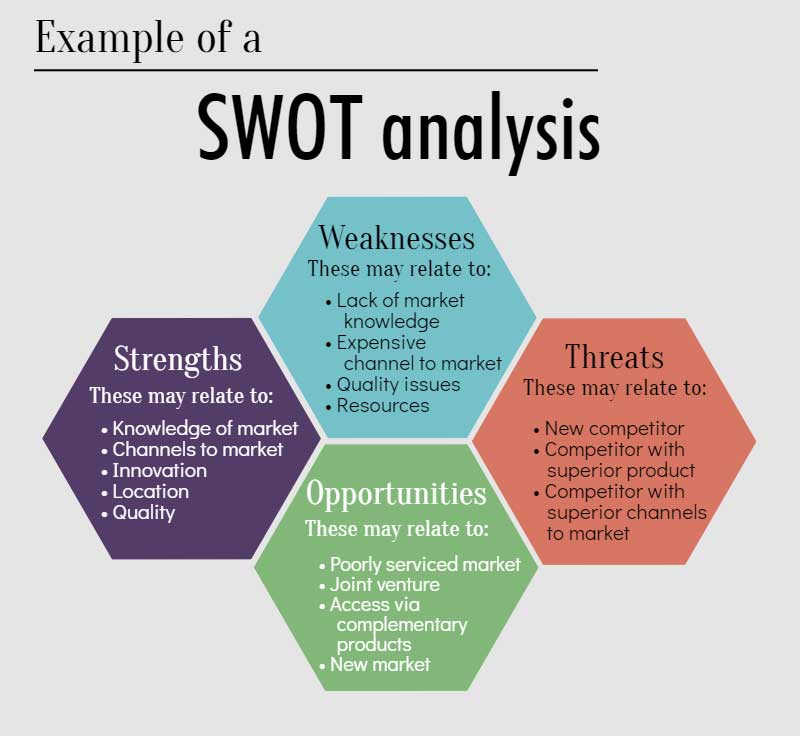
The number of sections your plan needs depends on the focus, technology or complexity of the proposed offering and may include:
b) Management profiles (if relevant)
The executive summary is the most important part of the document because it is likely to be read by all stakeholders. But don’t think of it as purely a summary of your business plan.
Think of it as an opportunity to “sell” your business idea. Think impact, engagement, and appeal. From your first word to your last, your executive summary requires high energy.
Your first sentence should be a benefit-focused entrée into an appealing, scene setting, first paragraph.
It should detail your vision, mission, the situation, proposal, and payback. It needs to mirror your document in the precise order of your document – from the proposition, market description, considerations, resources required and return on investment to cash flow. It needs to be well-structured, appealing, and highly credible.
Sketch out your executive summary in draft before starting your document. It should represent the skeleton of your document. Produce it in rough before writing your document and complete it after writing your whole document.
An executive summary – over one or perhaps two pages – should have seven parts:
- Proposition summary and how it meets the customer/market needs
- Situation definition - problem or opportunity
- Approach and proposition
- Financials/costings/payback
- Benefits/rationale to approach
- How to make it happen
If the business plan is to secure funding, investors will want to know the capability, experience, and track record of the people who will be driving the business. Short biographies of key people should be detailed.
State where you see your business in the future. A vision statement is a high-level overview of the business, the characteristics the business will display, and the goals that it will have achieved by a specific time.
Summarise your company’s purpose, means of operation, market, and scope of activity.
e) Your proposition - company, product or service
This section should start with an outline of why you have developed your offering – the need for it – and how it fits within the market, competitively. You should position your company, product or service in the mind of the reader.
The main focus of this section is on what you will offer the market in terms of business, product or service, technically and operationally. You should include charts, diagrams, and images as necessary to enable the reader to understand your offering and its comparative capability.
Ensure that the information you give is complete, that your narrative explains essential details, and that no questions are begged.
You should describe your product or service in terms of what marketers call a marketing mix. It’s a means of structuring an offering from a marketing perspective. It comprises: Product, Price, Placement, and Promotion, otherwise known as the 4 Ps.

This is about describing your product range or service, and how you will adapt it to support your customers’ needs and desires.
You should also include guarantees, support, and maintenance. Also include product variation, differentiation, and innovation.
This is the process of setting product prices. It may include discounts which relate to what you think customers are prepared to pay, and how they may wish to pay.
This might involve distribution channels, direct sales, indirect sales or e-commerce. In essence, you need to detail how you will get your product to market. Don’t go into detail here – instead, give detail at the section on sales plan and forecast.
This is about how you will promote your product, product line or company.
Markets are divided into groups of buyers – or segments. You should describe your market in segments.
Tailoring an approach to one or more groups – or one or more segments – over others is the only way to promote your offering. That’s why airlines promote first class services differently from economy class services.
One other thing you need to be aware of is that the segment or segments you propose are valid. Provided that a segment can be identified, is of reasonable size and can be reached economically, then it is a valid marketing target. Here are some variables:
These relate to age, gender, income, race, and ethnicity for the purpose of creating a clear and complete picture of the characteristics.
There are often regional differences. Customer preferences differ depending on which part of the country they may live.
Some customers are brand loyal. Others are heavy users while others are identified as light users.
This is based on activities, interests and opinions.
Segmentation
Segments which should be attractive are those which complement your business’s strengths and where demand, profitability, and growth are favourable.
Identify the variables, and then:
- Group potential customers into segments
- Group products into categories
- Produce Market/Product grid/s
You should also detail market influences. Markets are influenced by a number of factors such as technology, economics, politics, geography, social views, and so on. Refer to your SWOT analysis. You need to identify market factors which may influence your business plan and link them to justify your approach to achieving your proposition.
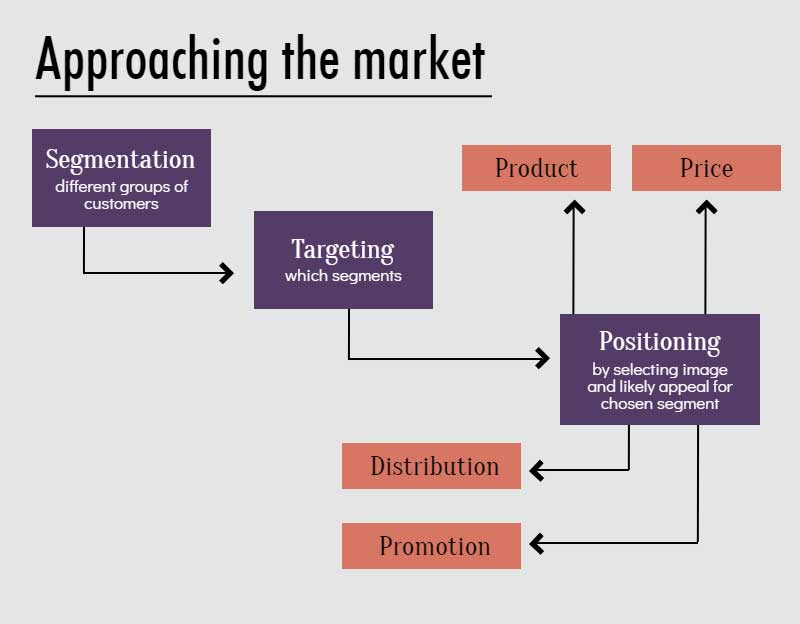
Link your marketing mix to your target segment. To do so, you need to answer these questions:
- How well is our target segment served by existing suppliers?
- What would be the cost of reaching that segment?
- How compatible with our strengths is this new target segment?
- What is our competitive position?
- What is the market growth potential?
Positioning
You need to think about how you compare with competitive products and services. You then need to decide how you wish to position your product or service in the eyes of your market.
Positioning is the process by which you create an image or identity in the minds of your target market. It is the “relative competitive comparison” your product or service occupies in a given market – as perceived by the market.
It is about identifying the differential advantage of your business to your target segments. For example, a Rolls Royce Dawn is positioned differently from a Ford Fiesta even though both products are classified as cars.
Your business plan may be focused on an existing product or service or developing something completely new. Alternatively, you may wish to compare what you are offering with a competitive product or service.
Differentiation is about a product, service or idea which is perceived by the market – not purely by you – as being different. Differentiation is the aim of most businesses.
It may relate to lower cost, faster delivery, higher quality, greater adaptability and so on. The aim of differentiation is to match your offering to customer needs, attract your market and generate market advantage. You need to be clear about how you are going to achieve this.
At this point, you should also detail the uniqueness of your offering – your unique selling proposition (USP) – which distinguishes you from the competition.
Think through each element of your offering and link it to the process of getting your offering to market.
Produce an outline marketing plan – summarising essential points. Leave full detail to the marketing plan. Digital marketing is likely to play a role in promoting your business, product or service, so you need to detail how it will achieve your goals.
A typical marketing plan includes the following:
Detail the income the plan is to generate.
- Environment – Focus on every external influence on getting your offering to market. It includes economics, social trends, political influences, legal and technological influences. Some factors may be advantageous to you, some not. Whatever they are, you need to detail them.
- Competitors – You need to detail the market positioning of all relevant competitors and their comparative strengths and weaknesses with specific reference to your market.
Based on the above analysis.
Segmentation, targeting, and positioning.
The four Ps – Product, Price, Promotion, and Placement.
Activity is likely to include search engine optimisation (SEO), content marketing, paid advertising (PPC) and social media marketing. Whatever it is that you decide to do, you need to detail it. Produce a chart of proposed activity against forecast return, over time.
Link these through to the financial section of your business plan.
The outline sales plan and forecast should include essential sales information from your full sales plan, and nothing more. It should detail the tactics you intend to use to reach your sales goals. If B2B, you should specify the market segments you intend to target and the companies and people you intend to approach.
You need to provide a chart which specifies sales resourcing needs and timescales of the complete sales lifecycle. It should be designed so that it is understood at a glance.
If you have prospects stating an intent to buy, these statements should be included here. The sales plan is the sharp end of your business plan.
The purpose of this section is to give readers confidence by demonstrating realism about your market and credibility about your forecast.
You should detail the resources you need to achieve your business goals – people, time, equipment and money. Specify lead times – recruitment times if relevant – and whatever else you deem essential. Demonstrate how you will achieve what you propose to achieve with the resources you propose to have.
k) Financials
The primary purpose of business, any business, is to make a profit. There is no other primary purpose. For that reason, the methods by which profit will be made needs to be detailed, clear and understandable at a glance
It should be complete and presented simply and clearly, and include:
- Funding requirements, envisaged return on investment, and cashflow.
- Clear description attached to numbers and lines as appropriate.
- Tables and charts with a consistent style.
- Key messages highlighted from each table or chart.
Include a timeline of who has to agree on what and by when.
The answer is yes. Images are a good way of getting points across. If colour makes your proposal look more attractive to read, then use it. Ensure, however, that images and colour support your message and don’t get in the way of it.
Give your chart a figure number and provide a summary underneath explaining the message your chart conveys. Provide narrative. Never leave it to the reader to interpret what your image or chart might mean.
Business Case
A business case is a justification for a proposed project or plan of action on the basis of its expected commercial benefit. It is a business argument.
It reveals a situation which is either a problem or an opportunity and details how the situation could be addressed in terms of benefits and risks.
It needs to show a compelling case for change, value for money, commercial viability, affordability, and achievability.

The first stage is to produce a rough justification for addressing a problem or opportunity. It may start with your belief that you can improve a situation, save cost, make money, or achieve competitive advantage.
Whatever it is, you are unlikely to have complete information straight away, but you should have a rough idea.
For instance, you should have an approximate idea of feasibility factors. These may include situation knowledge, market size, competition, income opportunity, costs, funding, resourcing, and risk.
What you should be clear about are the drivers for addressing the situation and why your idea, product or service may have commercial traction. While you might not have complete information, you should have sufficient data to list your anticipated business benefits.
The result of this information is called your value proposition and is the basis of your business case. Refer to section 3 to remind yourself of what a value proposition should contain.
At this stage and at every stage of writing your business case, you need to probe and test your ideas. Great business narrative doesn’t beg questions but answers them, so every one of your statements needs to be supported and credible.
All options need to be defined, and your analysis needs to be non-controversial. Your analysis should be written in such a way that interested parties would agree with your analysis – even those who are likely to oppose your recommendations.
You should deal with researched facts and not show bias, or reveal recommendations. All reasonable options need to be considered including that of doing nothing (provided that is a reasonable option).
Options need to be detailed in precisely the same way – proposed option, implications, and payback – so that they can be compared equally. Consideration may be:
This relates to business synergy and strategic fit. It answers the question whether the option will be good for the overall business.
This aspect relates to whether it is good value for money.
This relates to how the business case will be structured financially and whether it can be considered to be a good deal.
This is primarily focused on whether the proposal can be funded and is affordable.
This aspect is concerned with whether the preferred option can be delivered successfully as outlined in the business case.
It should have 7 sections comprising:
Executive summary
Problem or opportunity definition, proposed business case, market analysis.
This is the most important section of your business case as it is likely to be read by all stakeholders. Produce a benefit-focused first sentence as an entrée into an appealing, scene setting, first paragraph. Your complete summary should be written so that it can be understood at a glance. It should be credible and highly persuasive.
You should draft your executive summary after you have drafted your value proposition but before writing your document. The draft will be approximate and should be finalised after the document has been written.
This section should mirror your document in the precise order of your document – from the proposition, market description, considerations, resources required to the return on investment.
From your first word to your last, your writing requires high energy. It should detail the purpose of your business case, the situation which it addresses, and above all, the benefits of your business case.
- Summary of proposed solution.
- Summary of the situation - problem or opportunity.
- Expected outcomes.
- Summary of benefits of proposal solution.
Detail the problem or opportunity so that it can be understood at a glance. Your writing should be jargon-free and easily understood by anyone not associated with your business idea.
Your analysis should be non-contentious and utterly factual of the problem or opportunity. It should provide a background and context to your business case and include research data both favourable and unfavourable to your proposition.
Identify all sources of information which contribute towards your proposition. These may include:
This is the main body of your business case. Your proposition and your approach to the problem or market should be detailed stage by stage. Start with a description of your offering in terms of benefits, features and advantages in that order.
Above all you must explain why your proposition is well-placed to address the situation and precisely how your approach complements your current business strategy.
Three questions your proposition needs to answer at every stage are: How does your idea compare against competitive ideas? How will you reach the market? Where’s the proof that you are likely to succeed?
Anticipate reader questions and answer them within your business case. Provide credibility and proof if possible at every stage.
As a conclusion to this section, you should detail your prospects – or likely users of your proposition or offering – along with their job titles. Readers will be looking for assurance that you really do know your market, can reach it, and are able to generate your forecast financial return.
- Explanation of how the solution addresses the problem or opportunity
- Cost savings
- Non-economic (perhaps relating to regulatory compliance)
If your business case is opportunity focused, then market analysis, competitor analysis and factors related to the selling environment need to be evaluated.
Show complete understanding of the market, and provide a detailed explanation of how you will reach the market.
Identify which organisational objectives the business case supports and explain how it will support them. (These may include policy, regulatory requirements or commercial governance.)
- List assumptions which drive the business case.
- Detail the environment (financial, operational, political or other) on which the solution is dependent.
Summarise competitive practices or competitor positioning. If helpful, produce a SWOT analysis.
List alternative solutions including “do nothing” provided it’s a realistic alternative.
- Timescales for agreement stages.
- Invite questions.
- Summarise and conclude with strong benefit statement.
This section should provide a cost-benefit analysis detailing the pros and cons of your case. Use facts, figures, and charts to get your messages across and use captions to emphasise them.
Readers need to assimilate critical points from your data at a glance.
- Detail funding requirements, envisaged return on investment, and cash flow.
- Make sure description is attached to numbers and lines as appropriate.
- Ensure every table and chart has a consistent style.
- Highlight key messages from each table or chart.
List the benefits in order of importance. These should relate to all considerations from the financial to the strategic.
Specify the critical path – a timeline – of all stages of approval necessary to proceed. Include the names of the people who need to give their approval.
Once you’ve checked the coherence of your argument and the completeness of your document, it is time to cast a critical eye. In addition to being complete, your document needs to look highly readable.
Make sure that your proposition is business-appealing, logical, strong, well-written and with all essential facts and figures.
Ensure your document is clear, complete, and looks good. Appearance is important. Something which looks good is likely to be read. Masses of text is unappealing. Short paragraphs and clear structure is appealing. Ensure that essential information can be read at a glance.
16. One last thing...
Mistakes in spelling, punctuation or grammar not only distract but reduce the credibility of your document. Ask others to proofread. Then check and recheck before submitting what will become your highly effective business case.
This blog was written by Richard Walker, a director of Walkerstone Limited.
He can be contacted at: [email protected]
Walkerstone comprises business case writers, proposal writers and professional trainers.
We delivery scheduled courses, in-company training and executive coaching to people and organisations throughout Europe.
Courses include:
Business Case Writing
Essential Business Writing Skills
Report Writing
If you would like to know more, do contact us . We’d be delighted to hear from you.
Email : [email protected]
Telephone : 01252 792 270
- Explore courses
- Hire a business writer
- HTML Sitemap
01252 792 270

Walkerstone Limited, Registered office: Sheaves House, Birch Close, Boundstone, Farnham GU10 4TJ. Company number: 06514619. VAT number: 944 1865 05 By using this site, you agree we can set and use cookies. For details of these cookies and how to disable them, click to read our cookie policy | Terms Visit the Walkerstone blog for latest tips and guidance on business writing courses.
How to Write a Business Case (+Free Template)
.png)
Table of contents


Rochi Zalani
Does crafting a compelling business case make your palms sweaty? You’re not alone.
Creating a business case — a project management document enlisting the benefits vs. costs of executing a project — can feel daunting.
What should you include? What makes the document boring? How can you make your case convincing? Argh. It’s jaw-clenching. 😬
And yet, knowing how to present your argument well is critical to get buy-in from stakeholders. Instead of looking at it like a nuisance you don’t want to deal with, treat it like a holy grail that decides whether or not your project gets translated into action.
In this article, I’ll tell you exactly what a business case is and offer a step-by-step process to write one that gets the green light instantly.

Download our FREE business case template >
What is a business case?
A business case is a document you put together to highlight, address, and resolve a business problem.
Example : Let’s say you want to outsource your company’s marketing to an agency because they have more expertise, a larger team, and a freelance network.
A persuasive business case will highlight why the benefits outweigh the costs of this investment.
- Maybe you mention the problem — your marketing team is short-staffed, and you don’t have the budget to hire a full-time lead.
- Then, you highlight the proposed solutions — like hiring a freelance consultant, an agency, or an entry-level marketer.
- Lastly, you present your preferred option — working with an agency — and why it’s the most lucrative choice for the company.
Key stakeholders use this business case to decide whether or not to move forward with your initiative.
The crucial bit, especially for established enterprise companies, is shedding a spotlight on why the company should deviate from business-as-usual (BAU) and create a change instead. After all, if what the company is doing is already working, why disturb the harmony?
To continue our above example:
- When making a business case for hiring a marketing agency, call attention to why your current understaffed marketing department is unable to get results.
- Outsourcing to an agency will ensure you have the right-fit content marketing strategy that gets desired outcomes and takes some load off of your in-house team.
Your business case can take an advocacy slant — where you side with one preferred solution. Or you can also present all potential options and let the stakeholders decide for themselves based on your presentation — a more impartial approach.
A business case might sound just like creating a business plan or a project plan, but those three are different things.
AI Business case generator > AI Business case generator >

How is a business case different from a business plan and a project plan?
Business case vs. business plan :
- Specific VS broad - A business case zooms in and shows why the company should pursue a specific project. On the other hand, a business plan highlights why the company should go for a completely new business.
- Level of detail - A business plan includes overall market research, goals from the business as a whole, and how you plan to achieve those aims. You might prepare a business plan for an existing business if you’re aspiring to take a significantly new direction for the company.
Business case vs. project plan :
- The Why VS the How - A business case argues why a company should proceed with a project. A project plan, on the other hand, gets into the nitty-gritty of exactly how a company will tackle an approved project.
- Path to results - While a business case does include high-level steps on how you plan to achieve your desired results, it does so on a surface level without deep diving into the specifics of each step.
Every project needs a project plan. Every new business needs a business plan. But does every single project need a business case? No.
When would you need a business case?
If you are part of a multi-million dollar company, you may not need to present a well-crafted argument for buying a $5/month tool. But there are three conditions under which you definitely do need a business case:
- When you need to get a buy-in for significant investment from stakeholders.
- When you aim to provide all possible solutions for a problem.
- When you want to outline your vision for a project.
Having a business case in place ensures you’re taking a well-thought-out, strategic approach to implementing your project.
Your proposed solution might be a no-brainer inside your head. But how do you make stakeholders see eye to eye with you? It’s all about doing your homework right.
Preliminary checks: How to write a business case that gets the green light?
Here’s a five-step process you should follow before documenting your business case to ensure you get yeses all over.
Step 1: Engage the stakeholders
Ask the people what they want.
Before you even begin crafting your pitch, you should know the problems your target audience (AKA your stakeholders) are facing. Are they looking to cut costs? Is the business’ goal to boost employee retention this financial year? Do stakeholders want to increase profits?
- If your stakeholder is external investors, speak to several C-suite executives about what issues are causing the investors the most friction.
- If the stakeholders are your team members, schedule 1:1 catch-ups and chat about what’s a time-suck activity they want to eliminate.
- If it’s your manager, ask them what’s the biggest problem they’re looking to solve.
How much time should you devote to this step? It depends on your project. If it’s a high-stakes ask, demanding a wad of money, you must spend more time reading the room. Your aim is to sniff opportunities and get super specific about the problem you’re aiming to solve.
Andy Raskin, who helps CEOs align their leadership teams around a strategic narrative, showcased a deck by Uberflip that first highlighted the status quo with all the pain points of the target audience — followed by a teaser of the results stakeholders would get if they acted on their project.

Create something similar that shows the promise of your business case. You can also use a graph and data to show your proposition is profitable — especially if your stakeholders get numbers more than stories.
Dr. Mike Clayton , the founder of Online PM Courses , says this stakeholder pulse-check is a crucial no-brainer step for multifold reasons:
Think like a journalist on the ground. The more you understand your stakeholders, the better you can craft a business case that addresses their concerns.
Step 2: Research the market
You don’t want to lead a business case and have a stakeholder point out a better alternative you missed.
Don’t go into the research with assumptions. Have an open mind and study all possible solutions for your business problem.
Why? It’s simpler to course-correct now than find a better replacement during self-editing your business case — after you’ve already spent weeks preparing it.
For example, if your business case is about investing in an expensive software to hire better staff, dive deep and know about all possible other hiring tools out there. Hunt G2 , Capterra , TrustRadius , Reddit , and speak to other folks in the industry who might use these tools.
Airbnb’s pitch deck from 2008 is a good example of showing you’ve done your homework by highlighting why the rivals aren’t as big of a hit and then sharing your competitive advantage.

Marissa, Founder & President at M. Taffer Consulting , says not asking enough questions is the number one mistake you can make during research:
Step 3: Compare and shortlist various approaches you could take
Eliminate all the possible solutions that don’t fit your company. If you look at our last example, you can eliminate any tools that provide exclusively US-based folks if you’re looking to hire talent offshore. Once you have a list of solutions that make sense for you to consider, shortlist all of them and enlist their pros and cons. For each method, think:
- a) Why would this work well for the business?
- b) Does the cost of this method justify its benefits?
- c) What could go wrong if we moved ahead with this method?
Steve from Dreamit Ventures shares a “ Power Grid ” you can take inspiration from to make your own competition chart and why your preferred solution is better than the alternatives.

After running this fine-toothed comb, you’ll be able to cross off even more potential solutions. Now, only a handful of options worth considering remain.
Step 4: Compile data and finalize your preferred solution
The last step is pinpointing your preferred solution. If you’ve done step three right, the choice should be easy, or there’d be a tie between a couple options. The stakeholders should know you’ve done this homework. Compile all the data you’ve collected about the potential solutions to the business problem and convert it into a digestible form.
This could be as simple as converting your pros and cons list into a table or more complex, like presenting your data visually through graphs and pie charts.
For example, in the presentation Buffer used to raise half a million dollars , they presented a Business Model slide showing numbers with projected revenue, freemium model details, and user acquisition costs.

A business model is different from a business case, but you can use these same principles to highlight why stakeholders should move ahead with your preferred solution.
How much work you should crunch in this step depends on the specific business case, the problem you’re solving, and the size of your project.
- If it’s a small investment — like imbibing a no-meeting days policy in your company — don’t squander your hours making an aesthetic statistical representation.
- But if it’s a huge qualitative business case — such as hiring a high-ticket, successful freelance writer — schedule time in your calendar to present your case well.
You can also add a ranking criterion in your business case where you give a score between one to 10 to all possible solutions. Make the ranking system as nuanced as you wish, depending on your project.
Step 5: Document
With all the data in place and a preferred solution at hand, you’re ready to dive in and create your business case.
Is there a specific structure you should follow? Not really. Many organizations have a business case format that you can use for your project.
If there’s no such template at your company, and it’s your first rodeo at creating a business case, don’t worry. We have a handy template you can easily use and tweak to build your project business case.
What should you include in your business case? [Free template]
No two project business cases are made the same. You don’t need to provide a 50-page presentation for funding of $2,000 if your yearly revenue is in billions. The reverse is also true: You can’t write three slides if you’re trying to revamp the whole sales strategy.
Regardless, some things should be present in every business case — like an executive summary of the project, a predicted return on investment (ROI), and resources needed from the company.
I’ve listed these essentials below, along with a brief description of what you should include in each section. You can also tweak and create a personalized structure for each project. For example, if you think your risk assessment should precede the calculated ROI, feel free to make that change. There is no one ‘right’ way to make a business case.
At the end of this section, you can find a template you can copy and fill out for your own project.
Executive summary
An executive summary is the first section of your business case, but it’s the last thing you write. Why? Because it’s your written elevator pitch — it decides whether you pique your stakeholders’ interest or send them on a snooze fest.
If you think like a writer, this section is as important as writing a compelling introduction. In a short and snappy way, you have to present the summary of your project, its goals, and the benefits the business will derive from executing this project. Write it like an engaging hook that perks up the ears of your stakeholders.
Questions to answer :
- What is this project about?
- What are the goals for this project?
- What’s the business problem you’re tackling with this project?
Mission statement
Write a short section about the problem you’re trying to solve by implementing this project. The key thing to highlight here is how your project aligns with the overall business mission and fits into the company’s overarching goals.
- How does this business case fit into the company’s overall business goals?
- What specific problem are you trying to solve through this business case?
- What is the end goal of this project?
Problem analysis
Remember when you talked to stakeholders, researched solutions, compiled all the data, and finalized your proposed solution? This is the place to demonstrate all the work you’ve done and show you have a clear understanding of the problem at hand.
- Why is this an important problem for the business to address now?
- What are the competitors doing to fix this problem?
- What other solutions are present in the market?
Solution description
In this section, showcase why you recommend your preferred solution and how it's better than the alternatives in the market. The ‘solution description’ is also where you show exactly how you will bring your solution into execution and the operational resources needed for its implementation.
- What is your recommended solution?
- How is your preferred solution better than the alternatives?
- How will this solution be implemented operationally in the company?
SWOT and risk analysis of your preferred solution
Even your preferred method might have its weaknesses. Instead of curtailing them, bring them out in the open and show what you’ll do to eradicate the weaknesses and mitigate the risks. There’s also the option to split this section into two — SWOT analysis and risk assessment — if it’s a high-stakes business case.
Stephanie Walls , an NYC metro area-based project manager with almost ten years of experience, says omitting or underplaying the risks involved with a project is the biggest mistake you can make:
Questions to answer :
- What are the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with your proposed solution?
- How are you planning to double down on the strengths and opportunities?
- What’s the game plan for mitigating the risks, threats, and weaknesses?
Cost and benefits
Write the details of all the resources you need, whether funding or workforce, along with outlining how you plan to secure the necessary resources. Ask for help from an accountant if the balance sheet isn’t your forte. Next, deep dive into the benefits of implementing this solution and what ROI the business can hope to make from putting it into action.
- What are the resources you need to execute your solution?
- What is the expected return on investment if this project runs successfully?
- How do you plan on getting the financial and non-financial assets you need?
Overarching project plan and timelines
Without getting into the nitty-gritty, write the tasks involved with this project and how you plan on implementing them. Also include a timeline for when you'll be able to complete this project and when you can reach certain promised milestones.
- What are the tasks involved with implementing this project?
- How are the items to do divided and plan to be executed?
- When can the benefits of this project be realized?
Download your business case template
[Go to File > Make a copy > Fill in your project details].
These barebones formats will help provide a basic structure to your business case. But persuasion is more of an art than a math problem — and you don’t want to ramble and talk phooey while presenting your business case live with stakeholders staring down at you.
How can you inject some soul into a boring business case?
Best practices for creating a business case
Getting a lukewarm response to a business case you spent weeks (or even months) preparing, refining, and tightening is discouraging. Here are some handy best practices to add a little oomph to your argument:
#1: Craft a story around your business case
Data and figures are great. They prove your point is logical, well-thought, and supported by the math Gods. But they don’t “click” with people the same way stories do. Research has repeatedly proven stories to be more persuasive than statistics.
Change can be uncomfortable and fearful for stakeholders. A story tugs to the heart before it fancies the brain — helping people overcome their resistance to change.
The best part? When you become a great storyteller , you don’t just make your business case more convincing and engaging, but you also make your points more memorable. Only 5% of people remember statistics, while 63% of people remember stories, according to an experiment in Made to Stick by Chip Heath and Dan Heath.
Ideas for imbibing a story into your business case :
- Create a narrative around the problem your business case aims to solve.
- Show testimonials, dialogues, and feedback from real people.
- Use illustrations in your slide presentation to craft a story.
#2: Scrutinize each sentence
If you want to hold the attention of your stakeholders from the beginning to the end of your presentation, ensure each sentence you have adds value to your argument. Be ruthless in deleting fluff and presenting your case in as simple words as possible.
When you’ve spent so much sweat doing market research and collecting data, it can be hard to identify what’s relevant and what’s needless overwhelming information.
Even worse: Sentences that make sense to you might go over the head of your stakeholders. Use Wordtune to make your writing clearer, concise, and clean — no matter whether you want a casual tone, a business tone, or simply shorten your sentences. It’s your magic wand to translate hard-to-read sentences into legible ones with a single click.

Learn more : How To Write Better Sentences (And Develop Your Writing Skills)
Ideas for refining your business case so each sentence adds value :
- Ask an unbiased eye — your friend, spouse, or coworker — to point out what makes sense and what doesn’t.
- Develop some self-editing chops to ensure clarity and logic become your BFFs.
- Use tools like Wordtune to fine-tune your writing to be more accessible.
#3: Answer your audience’s questions in advance
A surefire way to get the stakeholders on your side is by predicting their questions and addressing their concerns before they get a chance to voice them.
For example, if the CFO might be worried about the finances, dig your hands into the accounting department and check your basics. Discuss expenses proactively and emphasize the benefits of betting on your business case.
If you have done your homework and spoken to stakeholders, this best practice is easy-peasy. You already know what’s on your audience’s mind and the issues they’re struggling with. But they aren’t the only ones who hold the reins.
While stakeholders are the primary decision-makers, there are also decision influencers — who have a high effect on what the stakeholders think of your business case. Similarly, the people who will do the day-to-day of the project — the implementers — might also raise some problems you might have missed.
Rhona Aylward , Deputy Everything Officer with a Project Management Office at Psoda , suggests dividing stakeholders into four camps depending on their relative importance to the project:
“A simple chart with influence on one axis and interest on the other works well. You then plot each stakeholder’s relative position and that shows you the level of engagement each one should get.

You then use this map to work out your engagement plan. Things to think about when planning are:
a) Are the stakeholders positive, negative, or neutral about your project?
b) Who are the biggest champions and who are the biggest detractors
c) Who is likely to be emotionally invested in the project’s outcome (positive or negative)?
d) Who is connected to who and how are they connected?”
Addressing your audience’s questions means predicting the problems of all these groups and tailoring your message for each. If your colleagues are the implementers, take their feedback on the first draft of your business case. If your manager is a decision influencer, run your business case idea by them before you start preparing it.
Ideas for addressing your audience’s concerns ahead of time :
- Interview stakeholders before you begin drafting your business case.
- Highlight how you’ll be resolving your stakeholder’s concern proactively in your presentation.
- Ask for insights into your business case from a few audience members ahead of time and include their recommendations while editing.
#4: Add visuals to splash some color to your business case
Facts and figures alone can be dry and tedious. But graphs and pie charts and video testimonials? They splash some much-needed color into your business case.
Data backs this up: When people hear or see information presented out loud, they remember 10% of it. But when the same info is armed with relevant images, people retain 65% of the data .
Ideas for adding visuals to your business case :
- Convert statistics into visual data formats — like tables and pie charts.
- Find elements where you can employ images and videos instead of text.
- Add a unique slant to your business case by taking an entertaining and/or casual approach.
#5: Treat your business case like a live document
As the project gets put into action, new information arises, or fresh roadblocks occur that weren’t accounted for in the business case. The competitive landscape might shift, leading to changes in your business strategy. The predicted finances become actual costs, which might be more or less than your estimates.
The business case should be up to date on all the changes happening during execution because it’s constantly referenced during a project.
Ideas for keeping your business case updated :
- Block time in your calendar every other week to update the business case.
- Assign responsibility among the team members to upgrade the business case.
- Reference the business case in every stage of the project and add any missing info as you move along.
Business case: The stepping stone to a project’s success
A business case isn’t just a theoretical document — it’s a breathing file that lays the groundwork for your action plan and helps you get tangible results.
Building a solid business case doesn’t just get stakeholders' buy-in, but also gives you a crystal clear vision for your project and makes execution less daunting.
Download the business case template to make your own easily and use Wordtune to make it tight as a drum. I hope you receive an overwhelming “yes” to your proposal!
Share This Article:
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)

How To Prepare For Studying Abroad (From Someone Who’s Done It)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
How to Write a Business Case (+ Free Template and Example)
Table of Contents
Let’s say you are a project manager — and you notice the communication tool your team is using is outdated and difficult to use.
It frequently causes issues in communication — team members don’t always receive meeting invites, messages get lost, you can’t save important information without writing it down somewhere separately, etc.
You discovered a new communication tool that you think would be great to switch to, but that would require the whole company to transition from one to the other. You can’t just suggest this to your superiors, without offering concrete evidence as to why the switch is necessary.
This is where a business case comes into play. It outlines why and how an endeavor or a project is worth undertaking. In this text, we will talk about:
- What a business case is,
- How it differs from similar documents,
- How to write and present a business case,
- The Five Case Model for preparing a business case, and
- The key elements of a business case.
We will also provide you with a business case template you can use, and an example you can reference.

What is a business case?
As per the PMBOK 7th Edition , “ a business case is a value proposition for a proposed project that may include financial and nonfinancial benefits. ”
On top of this, “ a business case can contain information about strategic alignment, assessment of risk exposure, economic feasibility study, return on investments, expected key performance measures, evaluations, and alternative approaches. ”
Basically, a business case is a document that acts as the summary of your project idea, providing the reasons it should be executed and focusing on the benefits it brings.
Writing one should be among the first steps to starting your project — as you will use it to gain the attention of the stakeholders and convince them to support your project.
We’ll get into detail on writing it, but first — let’s clear up the difference between a business case and some terms it’s often confused with.
Business case vs. business plan
A business case and business plan seem similar at first glance — they both outline a project and can be used for stakeholder propositions.
In reality, though, they are used for different things.
The main difference between the two is what they focus on.
Business cases are created for endeavors within a business — projects, acquisitions, events — while business plans are typically used when starting a new business.
A business plan will contain broader aspects of a business — like a mission statement or target market. Business cases are more specific, and they deal with an aspect of a business — be it an issue or an opportunity.
💡 Plaky Pro Tip
You can find examples of how to write a business plan in our guides on starting a business in different US states:
- How to start a business in Connecticut
- How to start a business in Arizona
- How to start a business in Alabama
- How to start a business in Arkansas
Business case vs. project plan
A business case can also be confused with a project plan . However, a business case should justify why a project should exist. Only after a project is approved, post business case review, a project plan is created.
Where a business case will speak on how a project should look, a project plan will determine how it will look. Meaning, business cases are broader and more theoretical. Project plans need to be exact, as they will serve as guidelines for all project team members .
Business case vs project charter
The main difference between a business case and a project charter lies in their similarities — a business case is used to justify a project’s existence, while a project charter is used to authorize its execution. Again, a business case is created before the project charter.
The second difference between the two is in how concrete they are. A business case suggests project managers, while the project charter authorizes them. Essentially, the project charter makes the final calls on how things should be done.
The same goes for the project scope — while a business case can suggest the schedule and budget of a project, the project charter will make the final decision.

Free project management software
Streamline your business — Improve planning, align teams, finish tasks with Plaky.

How to complete a business case in 3 steps
The business case is one of the most important documents to create for your project. Therefore, you should approach the process of making one with utmost care and attention.
For ease of reference, this process can be separated into the following steps:
- Do your research,
- Write incrementally, and
- Present your business case.
Step #1: Do your research
Rushing into things blindly will practically always result in failure. So, before you begin writing a business case, you must gather as much information as possible regarding the desired project.
It’s good to seek out information on matters you know little about. Consult experts in the fields required for your project.
For example, if you are creating an app to help tourists experience lesser-known landmarks, you want to consult both with IT experts and tourism experts for the appropriate locations.
Now, instead of relying on data you’re unsure of, you have concrete, confirmed information that you can create your project around.
Basically — you’re taking the guesswork out of the equation.
Step #2: Write incrementally
Now that you have all the information necessary for your project, it’s time to start writing your business case.
This is where you’ll determine where certain pieces of information you’ve gathered will fit — which piece of your project they are necessary for.
Knowing how to utilize what you’ve learned is essential for this step. For example, if you’ve gathered information on what it would take to create your app, you should know the:
- Employee skill sets required, and
- The number of employees needed for your project.
Once you have all the information, try to present it in a concise but compelling manner.
It’s good to check in with your project stakeholders for updated information and change the business case incrementally with their input. After all, the stakeholders have your project’s best interest at heart, so their advice is to the project’s benefit.
You want to save the executive summary for last since it will be a recap of all you’ve written in your business case.
Step #3: Present your business case
Now that you’ve completed your business case, it’s time to convince your stakeholders that it’s an endeavor worth pursuing.
Whether it’s external financiers or company seniors, you need to have important stakeholders on your side for the project to take off.
Your business case might be incredible, but if you cannot sell the idea you’re pushing, it will be difficult to get any backing. So, organize a presentation for your stakeholders or try an elevator pitch — a quick way of presenting your key points.
If you’re inexperienced with presenting your ideas, practicing an elevator pitch is a great way to realize what the main selling points of your project are.
An elevator pitch should last around 30 seconds — about as much as an elevator ride lasts — and include the main reasons someone should invest (be it their time, funds, or effort) into your project.
The Five Case Model for developing a business case
When writing your business case, you should not only be concerned with what the contents of your business case will look like but who will be reading that content as well.
There are many different kinds of stakeholders, and all of them will be looking for different appeals in your business case. To help you write one that can get positive remarks from all of them, you can use the Five Case model .
It suggests that a business case should be written from five different points of view, named:
- The strategic case,
- The economic case,
- The commercial case,
- The financial case, and
- The management case.
POV #1: The strategic case
The strategic case is written from the perspective of the business itself. It aims to show how a project will keep in line with the business objectives, goals, and vision — and benefit them.
The goal is to show how this project will positively impact the business — whether directly, through perhaps a product, or indirectly, through something like a PR stunt.
Check out the free strategic planning templates we offer in the post below:
- 14 Free Strategic Planning Templates (2024)
POV #2: The economic case
The economic case is written to show how the project brings social value, including environmental effects. The most important part of the economic case is the options analysis, which we will touch on in the next segment.
Not surprisingly, you want to focus on the economic case if you are making a project that will interact with the public.
POV #3: The commercial case
The commercial case is written to show the commercial strategy and cost-effective procurement of project resources . It shows that you have a good understanding of the marketplace by assessing supply options.
You’ll need to keep updated on costs, the resources you’ll need, as well as any risks that might come when acquiring them.
POV #4: The financial case
The financial case, in essence, wants to answer the question — can we afford it? It speaks on the funding of the project and the support of stakeholders and customers.
For the financial case, you need a thorough understanding of the capital, revenue, and whole-life costs of your project. You also need to address any possible gaps in funding that might arise during the course of the project.
POV #5: The management case
The management case is written to show the delivery, monitoring, and evaluation of the project. You need to assure your stakeholders that your project will be managed with the best practices and that all timelines are set with appropriate goals assigned to them.
It mostly covers the project governance and risk management elements of the business case, which we will talk about soon.
7 Key elements of a business case
A business case can have many elements — there can be over 50 elements in a detailed document.
However, we can divide and combine them into 7 key elements that should exist in every business case, namely:
- Executive summary
- Financial assessment
- Business objectives
- Project options analysis
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Project governance
- Risk management
Let’s dive further into them and see what you should look into when writing each of these elements in your business case.
Element #1: Executive summary
You could view the executive summary as a retelling of the essence of the business case. It gathers all the most important information from the rest of the document in one place.
An executive summary should start with an introduction and answer the following questions:
- What issue does the project solve or what opportunity does it take advantage of?
- What options exist to tackle this issue/opportunity?
- What option is the preferred solution?
Next, you want to present the research you went through to create this business case. Then, go through your recommended actions — the conclusion of your research. This is essentially where the bulk of your project expectancies go.
By the end, the reader of your executive summary should understand what they’re getting into for the rest of the document.
Element #2: Financial assessment
In the financial assessment, you want to predict the cash flows of your project. The first thing you want to show in this section is detailed cost estimates and risks.
You should produce cost estimates for different aspects of the project — for the app example, think UI design or marketing — and determine them at both the P50 and P90 levels of confidence.
P50 means a cost estimate with a 50% probability of not exceeding it, and P90 means a 90% chance of the same.
For example, you’re 50% sure that the UI design costs will not exceed $50k, but you’re 90% sure they won’t be over $70k.
Next, you want to present the following:
- Project funding analysis,
- Development analysis (the cost of scoping a project),
- Staffing impact summary, and
- Summary of costs for each project phase.
Element #3: Business objectives
The business objective answers a simple question — why are you doing the project?
Think back on what we described first in the executive summary. What opportunities or issues arose that require this project to exist?
How does this project relate to the current business strategy? You need to convince everyone reading that your project needs to happen.
What are your project goals? Once you determine project goals, you can determine:
- Project scope,
- Project constraints , and
- Project deliverables .
Element #4: Project options analysis
Now that you’ve justified the reason your project should exist, it’s time to take on different options for its execution.
This element is dedicated to analyzing the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of each option — basically, doing a SWOT analysis for each of them.
Then you want to shortlist the options by discarding the ones that don’t lead to the desired outcome. Finally, do a reassessment of the shortlisted options and discard options accordingly.
Take a look at the external stakeholder impact of each option. More specifically, you want to look at the nature and level of impacts, specify the negative ones, and propose how they should be managed and mitigated.
While this boils down to a risk analysis for each option, it’s broader and used to determine the overall risk of each option. A more detailed risk analysis, determining the weight of specific risks and building contingency plans, comes later.
The project that comes out of this will be the preferred option for tackling the issue or opportunity described, which will be used as a reference when the actual project is executed. Finally, determine target outcomes for the reference project, measured with project KPIs . The targets must be realistic and measurable, yet challenging.
Element #5: Cost-benefit analysis
A cost-benefit analysis is used to prove that your project is worth doing from a business point of view. It proves that the benefits of doing a project are greater than the costs, thus justifying the project.
The cost-benefit analysis is done in 4 steps:
- Establish a framework — in this step, ask yourself what the measurement of your project’s success is (hint — take a look at the KPIs you’ve determined) and make sure both costs and benefits are measurable.
- Analyze costs and benefits — measure the costs and benefits of your project separately. Some are obvious — material or employee costs — but some are more elusive. If you are using an owned facility to house the project in, you are not spending any money for rent, per se — but that facility’s worth is being directed towards your project, so it’s an indirect cost.
- Establish a value for the costs and benefits — to compare the costs and benefits, they must share an equal “value unit”. Traditionally, monetary currencies are used, but you can be more creative if the situation calls for it. Intangible costs and benefits can be difficult to place a specific value on, but not impossible to achieve still.
- Compare the value of the costs and benefits — compare the sums of both the costs and benefits of your project. If the benefits outweigh your costs, your business case is good to go. If it’s the opposite, maybe you should revise the option you chose in the previous element.
Element #6: Project governance
Who will do what in your project? This is the question you want to answer in the project governance element of your business case. A typical hierarchy is set as:
- Responsible minister,
- The project control group,
- Project sponsor, and lastly,
- Project team.
Next, you want to analyze communications. In essence, how and how frequently will you communicate with certain stakeholders?
You can use:
- Progress reports for superiors,
- Team meetings for team members as internal stakeholders, or
- Even social media for communication with customers as external stakeholders.
If you want to know more about the importance of communication in a project, check out this article:
- Why is communication important in project management?
Element #7: Risk management
Lastly, an element you mustn’t underestimate is risk management . Risk assessment is so vital to every project that it’s done while writing a business case, so even before the project is approved.
Risks are analyzed through 2 criteria — likelihood, and impact.
By likelihood, they can be:
- Almost certain,
- Possible, and
By impact, they can be:
- Major, and
- Catastrophic.
These criteria are used to create a risk matrix, determine the categories of risks, and make us aware of how urgent action is. Safe to say, if a risk is both catastrophic in impact and almost certain in likelihood, action on it is prioritized over any other.
You can vary these parameters of likelihood and severity to keep your analysis flexible, as seen here:

After all the risks have been identified, you want to construct a risk management plan , outlining all risks and their categories, as well as figuring out contingency plans for all of them.
If you want to learn more about managing risk in your projects, check out this guide:
- What is risk in project management?
Business case template + example
Knowing the steps to make a business case, however, does not properly explain what a business case looks like.
A business case can be very detailed — the sheer number of points in it could be as long as an academic paper.
But, we’ve created a business case template with 7 of the most important points it should have:
- Executive summary
- Cost benefit analysis

🔽 Get the free business case template here
A filled-out business plan template can be extensive, spanning many pages of documentation. So, to give you an idea of what you should be writing about in a specific situation — we have filled in a business case template with the thought process that will come into writing each element:
Project title: Poetry Night event
Start date: 10/5/2023
Project manager: William Cambridge
Contact info: [email protected]
Executive summary: Reasoning for a poetry night might come from doing a poll, showing that the local area has no such events, yet the populace shows a good number of aspiring writers and poets.
Financial assessment: Cost estimates for this project may vary — renting space may be mandatory, and you might want catering for the event. Both of these may vary in cost depending on the number of attendees, so for your P90 analysis you should take a look at the poll results to estimate the maximum number of guests.
Business objectives: This project is done for public benefit, but can also serve to boost the PR of an organization. The project goals might be viewed through the attendees’ satisfaction, a boost in your organization’s online presence, or a rise in the popularity of a poet you were trying to promote with the event.
Project options analysis: This section would be dedicated to analyzing the different kinds of executions of the poetry night. Should it be in public, or in a closed rented space? Should there be light music in the background, and would it be beneficial to the event if the music was live? If you’re unsure of the answer — consult with stakeholders. In this case, you could do another poll.
Cost benefit analysis: The benefits of this project will largely be intangible — the rise in your organization’s popularity or the satisfaction of attendees would be difficult to quantify with dollar signs. However, there might be tangible benefits to find — if your organization offers a product or service, is there an expected rise in procurement after the project’s completion?
Project governance: Who will be in charge of the organization of the project? Who will be the sponsor? Who will tend to the catering? Who will be the presenter, and whose poetry will be presented? Answering these questions gives us project governance in this example.
Risk management: Is there a possibility that very few people will show up? Is there a possibility that the vendor of the rented space or the catering cancels last minute? In that case, is there a backup you can use and how can you notify all attendees of the change effectively?
Conclusion: Use a business case to pitch your ideas correctly
By now, you should be aware that just having an idea usually isn’t enough to make someone want to support it. Analyzing it, justifying it, and creating a detailed business case around it are the essence of selling an idea to superiors or potential investors.
Always start with the idea itself — the best way to bring someone closer to it is to explain how you came up with it in the first place. Be sure to compare with alternatives, and show why your case is the one to go with.
A business case is a great tool to facilitate growth, whether it be small or large in scale.
✉️ Do you have experience with writing business cases and have additional advice on the subject? If yes, write to us at [email protected] and we may include your advice in this or future articles.

Luka Bogavac is a project management author and researcher who focuses on making project management topics approachable and informative. Experienced in entrepreneurial projects, education, and writing, he aims to make articles his younger self would appreciate. During free time, he enjoys hiking trips, or staying indoors with a good film.
What's on your to-do?
START MANAGING TASKS

Related posts
How to improve a remote workflow by centralizing tasks.
Task centralization platforms like Plaky help remote teams collaborate and communicate efficiently to achieve success….
Project Manager’s Guide to Surviving a Surge of New Projects
Simple tips for managing a sudden surge of new projects · 1. Assess the situation · 2. Manage all projects in one place · 3. Prioritize projects…
8 Gantt Chart Examples to Improve Your Project Management
Top 8 Gantt chart examples for project management: 1. Event planning Gantt chart, 2. Software engineering Gantt chart, 3. Business plan Gantt chart….
How to Make a Gantt Chart in PowerPoint (+ Free Templates)
Learn how to make a Gantt chart in PowerPoint step by step and get access to free Gantt chart PowerPoint templates….
How to Use Impact Effort Matrix for Improved Prioritization
The impact effort matrix is a prioritization tool that’s as simple to use as it is effective, requiring you to only assign impact and effort values …
How to Make a Gantt Chart in Excel (+ Free Template)
Wondering how to make a Gantt chart in Excel? Take a look at our step-by-step tutorial with pictures, or try our free Excel Gantt chart template….
Need a good project tracker?
Plaky is task management software for visual project planning. Manage tasks, collaborate, and get status reports. Unlimited projects, free forever.

Free Project Management Templates
How to Write a Business Case for Your Project
As a project manager, you may be asked to write a business case at some point. It is a detailed document with analysis, projections, and recommendations for a proposed project. A business case is used to seek approval from upper management or another decision-making body.
Preparing a business case can be daunting, especially if it’s your first experience. However, this article will help you get started. In addition to a step-by-step guide, we have a free business case template you can download.
TABLE OF CONTENTS:
As a project manager, you may be asked to write a business case at some point. It is a detailed document with analysis, projections, and recommendations for a proposed project. A business case is used to seek approval from upper management or another decision-making body.
Preparing a business case can be daunting, especially if it’s your first experience. However, this article will help you get started. In addition to a step-by-step guide, we have a free business case template you can download .
What Is a Business Case?
A business case is a thorough study used to seek approval for a new project or initiative. It typically includes a variety of information, such as a description of a problem or an opportunity the project will address. It also includes a list of the project’s goals and objectives, a description of the scope and boundaries of the work, a detailed analysis of the potential benefits and costs, and a list of any risks or challenges that may impact the project.
All of this information is used to evaluate the potential value of a project. If the project is determined to be viable, the report will be used to try to convince executives, investors, or board members to vote in its favor. Therefore, a business case is crucial for convincing stakeholders to move forward and to secure the necessary resources and support to be successful.
Why Is a Business Case Needed for a Project?
A business case provides the justification for starting a project. It provides a clear and concise assessment of the benefits, costs, and risks associated with a new endeavor. This in-depth look at a new project helps decision makers determine whether or not it is worth pursuing.
There are several reasons why a business case may be needed for a project:
- To obtain approval and funding: A business case is often used to obtain approval and funding for a project from upper management or external stakeholders.
- To allocate resources: A business case will detail the demand for resources if the project is accepted. By evaluating the pros and cons of a project, an organization can make better decisions about which projects to invest in and which ones to pass on.
- To track progress: A business case outlines the key milestones and deliverables to be achieved. It will help project managers track progress and measure the ongoing success of a project.
- To identify risks: Another use of the business case is to identify and assess potential risks associated with a project. Contingency plans can then be made to mitigate them and ensure success.
As you can see, a business case is an important tool for businesses and organizations. It not only helps them decide which projects best align with their goals and objectives, but it also helps them determine which projects they feel can be executed successfully based on the resources and support required.
Key Elements of a Business Case .
Each of the key elements in a business case serves a specific purpose in supporting the overall case for the project.
- Executive Summary: This includes an overview of the problem and the project or initiative proposed to solve it. It also includes anticipated outcomes, recommendations, and justification for the project.
- Business Case Analysis Team: Team members who worked on the business case will be listed here along with the role they played.
- Problem Definition: This section includes a problem statement, organizational impact, and technology migration.
- Project Overview: This overview includes a description of the project, goals and objectives, performance criteria, assumptions, constraints, and milestones.
- Strategic Alignment: Describes how the project aligns with the organization’s strategic plans and how the project supports them, as well as any value added.
- Cost Benefit Analysis: This section outlines the benefits including a potential return on investment, and the costs associated with the project.
- Alternative Analysis: This section outlines the alternative solutions that were considered and why the proposed project was selected instead.
- Approvals: The business case will elicit a definitive answer on the project with either a formal approval, or disapproval from the executive review board.
While the key elements listed above are a good place to start, not every business case has the same parameters. It will depend on your organization and its requirements. You should adapt your business case according to your unique environment.
How to Write a Business Case .
The first step is to be clear about what your project or initiative is. Are you trying to solve a problem or take advantage of a situation. What is the opportunity for the company? Is this a good time for the company to jump into this project? The proposed project must be clearly described and supported with research.
Next, list the alternative solutions. Explore their benefits versus costs. How feasible are they and what risks do they pose? Consider coming up with a ranking system and rank the options. Include this along with the ranking criteria in the business case so stakeholders can clearly see how you arrived at your recommendation.
Finally, describe in detail how your project will unfold. This will give decision makers the confidence you have done the research and have charted the best course for achieving the goal. The business case is created during the project initiation phase, but it will be used as a reference throughout the life cycle of the project.
Detailed Steps for Writing a Business Case:
- Identify the purpose. Determine the main goal of the business case. Is it to secure funding or to gain approval for a new initiative? Clearly defining the purpose will guide you as to what information is most important to include as you begin writing.
- Define the project. Clearly describe the project, including its scope, objectives, and deliverables. Explain how the project aligns with the company’s goals and objectives.
- List benefits. How will the project benefit the company? Include items such as cost savings, increased efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, or any other tangible or intangible benefits.
- Outline costs. What’s the bottom line when it comes to cost? Prepare a detailed accounting and don’t forget to include materials, labor, and other expenses.
- Develop Financial analysis. Use the information concerning the benefits and costs of the project to create a financial analysis that demonstrates the potential return on investment (ROI) of the project.
- Identify the risks and challenge. What are the potential risks and challenges of the project? How do you plan to mitigate or manage them?
- Review and Revise. You should plan to review the business case with key stakeholders. Come prepared to answer questions and be open to addressing concerns.
- Presentation. After you have made any necessary revisions, the business case can be finalized. All that is left it to present it.
We highly recommend that you use a template for writing your business case. A template provides a guide for organizing and presenting the information. It makes it easier for decision-makers to quickly see the key points and assess the potential value of the project—especially if you use the same format for all business cases in your organization.
A template is an easy way to make sure that decision makers have all the necessary information and that no important details have fallen through the cracks, strengthening your chances for approval.
What is a Simple Business Case?
A simple business case is one-page in length. For small projects, this is sufficient. Not every project requires pages and pages of analysis. Even though it is considered simple , it will still include the important components of a business case such as the executive summary, problem definition, project overview, strategic alignment, cost benefit analysis and approvals. However, each of these sections will be represented by only a few sentences that summarize the topic.
For example, let’s say the Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) wants to redesign the user interface on the company’s website. This is a relatively small project that won’t require a large amount of capital or company resources. But before the project can be approved, it’s important that the CMO presents a business case to upper management.
To get approval, management will need to know what the problem is, what the proposed solution is, whether the solution aligns with the company’s strategic goals, what benefits it will provide, and what the project will cost. This should provide enough information for the management to decide whether to approve or deny the project.
A simple project business case should include the following sections:
- Executive Summary: This gives the stakeholders a brief overview of the proposed project. In just a few sentences, it identifies the problem, the proposed solution, the expected outcomes, the recommendation for moving forward with the project, and the justification for implementing the project.
- Problem Definition: This section clearly defines the problem and the impact of the problem.
- Project Overview: This is a brief description of the project itself.
- Strategic Alignment: This section explains why you believe the project is compatible with the organization’s strategic plans, and thereby, why it’s valuable.
- Cost Benefit Analysis: This section presents the cost and benefits of the project.
- Approvals: This is a signature line where executive management can either approve or deny the project.
Project Business Case vs Project Charter .
A project business case and a project charter are both developed during the project initiation phase and are necessary for project approval, but they serve two distinct purposes.
In simple terms, a project business case looks at all facets of the pros and cons of a proposed project. The study presents detailed information and analysis to decision makers and walks them through the justification for moving forward. The goal is to provide enough evidence to get a green light and secure the funding and resources that are necessary.
A project charter, on the other hand, marks the formal start of the project. It defines in great detail the scope of the project, its objectives, names the project manager, as well as key stakeholders. It serves as a reference point throughout the project’s lifecycle.
While both documents are used to plan and execute a project, the business case focuses on gaining approval for the project, while the project charter focuses on the details of the executing the project.
Where to Download a Business Case Template .
If you’re feeling a bit overwhelmed at the prospect of creating a business case from scratch, relax. There is no need for that. Project Management Docs has a free business case template available for download that even includes sample answers to make your life easier.
This template provides a structured format for organizing and presenting the information in your business case, making it easier for decision-makers to understand and assess the potential value of the project.
The template will make sure you’ve covered all the bases. It includes everything the decision makers are looking for such as the project scope, objectives, benefits, costs, risks, and project plan—and it’s tailored to the needs of a wide range of industries and sectors.
By using this template, you can save time and effort in creating your business case, and you can be confident that you are including everything you should to make a strong case for your project.
Additionally, the examples included in the template can serve as a helpful guide in preparing your own business case. So, if you’re wondering what belongs in a certain section, the example will be there to give you an idea of what you need to write or include in that space. When you’re done, simply delete the example and move on to the next section.
Start Your Project Business Case Now .
Using our free template will help you hit the ground running. You won’t have to think about where to start, just follow its lead and start completing the sections. It’s a huge time saver, and you can feel confident it will be done correctly.
The Plain English Guide to Writing a Business Case
Published: April 01, 2021
Have you ever heard the age-old classic story of a company that got its start from a back-of-the-napkin idea? Or about the start-ups that started in someone's garage?

While all those stories are, of course, inspirational, a huge element that they leave out is that every business started because someone felt the project justified spending time and money on it.
That's why some projects require you to write a business case. Whether you want to start a company, pitch a new product, or perhaps you just want your business to use a new project management tool. Either way, a project that requires time and resources will also require justifying those expenses in the form of a business case.
Below, let's review what a business case is, plus an example and template to inspire your own business case.

What is a business case?
A business case is a document that evaluates whether a project or task makes sense to complete. It will present the reasoning for taking on a project, such as benefits, cost, risk, etc. Essentially, this document makes a case that a project makes business sense to do.
In a business case, you might include the background on a project, expected benefits, costs, risks, and opportunities. This document will justify taking on a certain project. So, how do you develop a business case? Let's dive in below.
Business Case Development
To develop a business case, you'll need to write several key components, including a proposal, strategy, budget, SWOT analysis, and project plan. With these documents, you should be able to prove that the project you're pitching is worth doing.
Let's dive into the steps for how you'll develop a business case below:
1. Research
Before you can write a business case, you need to do your research. First, you should have a goal in mind for your project, whether it's to create a new product, help drive more traffic/leads, or improve user experience.
Write down your goal and then conduct research to prove that your project is the way to achieve your goal.
You can begin by researching what competitors are doing and look for gaps that your project solves.
Start to brainstorm what this project's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats are. Additionally, you'll want to learn about your market -- whoever will be the consumer of the project, even if that's your own team.
Finally, you should start to look into what a budget would look like for your proposed solution.
2. Focus on one component at a time.
A business case will usually include several documents. Focus on one at a time, while keeping your notes organized.
Start with your proposal, then move on to your SWOT analysis, the competitive analysis, the project plan, overall strategy, and then the budget. It can be easy to get lost in just one of these tasks, so focus on one thing at a time to complete the bigger picture business case.
3. Write an implementation plan.
Once you've gathered your research and you're working through each component, it's time to start thinking about implementation.
How will you implement your project? Once you've made the business case that your project should be done, stakeholders will wonder how you'll execute it.
To do this, write an implementation plan that discusses how you'd complete the project and metrics that you'd track to measure success.
Once you're done writing your business case, look at the whole document and ask yourself whether it's comprehensive, measurable, and adaptable.
A business case doesn't need to be an entire business plan for a new product. Sometimes it will be less formal due to the size of the project. Either way, you want to make a strong case for your project, so it should be easy to understand and implement.
Now, let's look at an example of what a business case might look like.
Business Case Example
Now that you've seen what it takes to write a business case and what the process looks like, let's look at an example for inspiration.
In the example below, the project is about getting a new phone system to help the sales staff. Because this is a fairly small project, the business case isn't several pages long with exhaustive research.
However, it's important to keep in mind that while your business case might look something like this for a small scale project, it might include several pages of information if you're pitching something like a new product or a new UI to improve user experience.
The point in the business case is that it's adaptable to be whatever you need. However, the components of the business case will be the same regardless of how long it is. Every business case should include why a project should be done, the benefits, costs, risks, and budget.
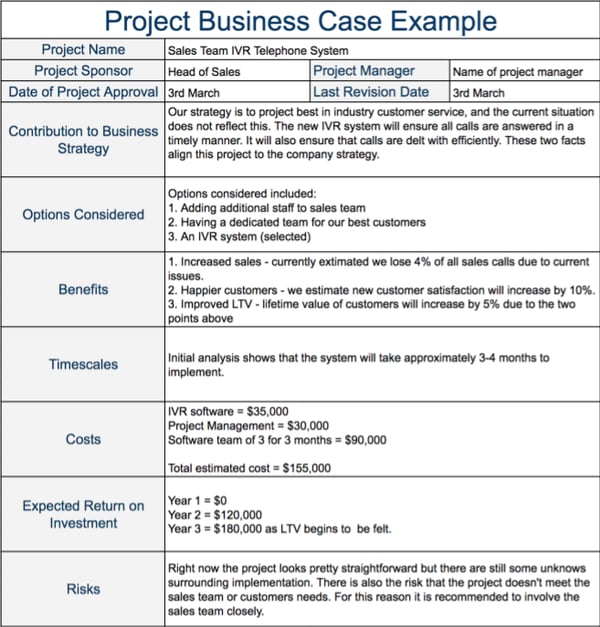
Don't forget to share this post!
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Learn center
- Project management
Everything you need to know to create a winning business case
Georgina Guthrie
March 28, 2021
Think of your business case as your sales pitch. It’s essentially a document (which is usually combined with a presentation) that explains how your proposed initiative aligns with your boss’s overall goals, the board, stakeholders, sponsors — or whoever else it is you’re trying to secure investment and/or support from.
In a nutshell, your business case should help decision-makers scrutinize their investments and ensure the proposed project will provide value compared to alternative options. Think of it as an opportunity for you to present your initiative and show off its benefits.
Business case vs. project proposal
The term ‘business case’ is often used interchangeably with ‘ project proposal .’ While they’re both tools for convincing stakeholders to invest time or resources, they are two subtly different things, each done at a different stage of the project.
A project proposal comes before the business case. It’s developed during the early stages of an initiative and focuses on your project’s vision, benefits, time and cost estimates, and impact on the organization. As with a business case, its initiation relies on the approval of stakeholders or board members.
A business case is the next stage of your sales pitch. It sets out, in more detail, the why, what, how, and whos of a project. A key difference is that, while a project proposal outlines budgets and return on investment, a business case explains financial requirements in more detail.
Some people like to do both, whereas others choose to combine them and present just one highly detailed project proposal instead. That’s absolutely fine. Your choice depends on time constraints, presenting opportunities, and the preferences of you and your investors. As with a project proposal, the initiative can’t progress until the stakeholders or investors have accepted or revised this.
Next comes a statement of work (SOW for short). This is a detailed, formal document that defines exactly what makes up a project to guarantee work is carried out according to expectations.
Finally, a project charter is a formal document setting out how the project will be managed, including assumptions, risks, scope, budgets, and timelines. It’s something you create after your business case and project proposal have been given the green light.
How to create a business case
Step 1: understand your problem and define your opportunity.
Many projects fail because there simply isn’t a need for the product or initiative. So before you begin, make sure your proposal is answering a real need. It sounds obvious, but millions of products, apps, business ventures, and projects have fallen flat because they didn’t get this first part right.
Step 2: Do your market research
Once you’ve defined a real need for your initiative, then do some market research. And do it thoroughly. Have any initiatives like yours existed before? If not, then you have a unique opportunity. If they have, then explain how yours is different. When you cite past similar-sounding ventures that failed, explain why and how yours will overcome their issues. When you cite the ones that succeeded, then, again, explain how your project will leverage their success while still differentiating itself.
Pro tip: Create a business SWOT chart to organize your thoughts and pinpoint your initiatives, strengths, and weaknesses.
And remember to research thoroughly. You don’t want to be standing up in the presentation explaining to the board that what the world really needs right now is bacon-flavored floss, only to be told it already exists . (Cue awkward silence…)
Step 3. Think of a plan B (and a plan C, D…)
Speaking of awkward silences, make sure you always, always, have a backup plan. You know those moments during a pitch or an interview when someone asks a really reasonable question, and the poor candidate doesn’t have an answer? It’s so uncomfortable. Make sure that doesn’t happen to you.
Choosing the right solution is tricky, and there are bound to be unanswered questions. It’s okay not to have a solution to every single question, but you’ll stand in better stead if you’ve shown you’ve considered these issues, rather than having the board highlight them, making you look unprepared.
The best thing to do is to have a series of alternative routes or solutions prepared, along with their respective benefits and risks, costs, and feasibility. The more you plan ahead, the more prepared you’ll look.
A good way to make sure you’ve considered every avenue is to run your proposal past your colleagues and non-work people. Your colleagues will address business-specific questions you perhaps hadn’t considered, and non-work people will ask those important questions that people working in the industry or business sometimes overlook.
Step 4: Show you’re the expert
Okay, so we told you to have backup plans and alternative routes. But that doesn’t mean you should throw them all at the board and see which one sticks. They want you to tell them what you think is best. So choose your preferred route, then rank the other options, being sure to explain why you think this is the best way to go.
Step 5: Describe your implementation plan
It’s not enough to talk the talk. Next, you’ll need to show off your practicality! This project is your baby, so if it gets the go-ahead, you’ll be the expert people turn to.
Show you’ve thought about how the initiative will look once it begins. This includes outlining your resource requests (backed up by reasons), and your plans for managing the project, including process improvement methodologies (if appropriate), and project management tools for tracking and automation.
You’ll need to show your stakeholders you’ve plotted out a clear path to achieving your goals. As we mentioned before, it’s a good idea to consider alternative routes to demonstrate your depth of understanding and diligence.
And remember, this isn’t an opportunity to look at the world through rose-tinted glasses (aka optimism bias ) and lead your stakeholders into a false sense of security. Practice due diligence and talk them through the risks, as well as the opportunities. That way, when you start your project, there’ll be no nasty surprises. A successful business case demonstrates a strong vision backed up by thorough research.
Step 6: Double-check you’ve included the key components
What should your business case include? Everyone’s different, but the following list contains the key elements.
- Executive summary (aka preface)
- Contents page/slide
- Business description/mission statement
- Product or service description
- Marketing strategy
- Competitors analysis
- SWOT diagram: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
- Implementation plan
- Operations overview (including drivers, scope, risks, benefits, and assumptions)
- Financial plan
- Conclusions and next steps
Step 7: Make it look professional
Finally, you’ll want your plan to look as neat, tidy, and professional as possible, so use the proper tools for all your data. Avoid having to mess around with weird Word formatting, and go straight for a quality app.
Document everything
We’ve mentioned a few times the different types of plans and files you should have put together before you’re done putting together your business case. Keeping track of everything you find is of the utmost importance. If you need to justify a decision to a stakeholder, or even a team member later on, it’s best if you have all of your research still on hand. You know the old adage “to see is to believe?” Well, have every visual that convinced you of the best plan of action to help you convince others.
You can thank us later.
Final thoughts
Make the details easy to understand at a glance so you can focus on wowing stakeholders with the benefits. And once you have buy-in? Invest in flexible project management software, such as Backlog , so you can track every piece of work, create a running history of every task, and make your project as smooth and successful as possible.
In fact, why keep it until the project kicks off? Use PM software to set reminders, track your tasks, and keep all your research, graphs, and plans in one cloud-based place to set your business case off on the right foot — before you’ve even stepped into the boardroom!
This post was originally published on March 21, 2019, and updated most recently on March 28, 2021.

How project managers design a change management process

Stop project failure in its tracks with a contingency plan
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Learn with Nulab to bring your best ideas to life
View or edit this activity in your CPD log.
What is a business case ?
A business case provides justification for undertaking a project, programme or portfolio.
It evaluates the benefit, cost and risk of alternative options and provides a rationale for the preferred solution.
Definition from APM Body of Knowledge 7th edition

Five elements of a business case
A common way of thinking about a business case is using these five elements:
- Strategic context : The compelling case for change.
- Economic analysis : Return on investment based on investment appraisal of options.
- Commercial approach : Derived from the sourcing strategy and procurement strategy.
- Financial case : Affordability to the organisation in the time frame.
- Management approach : Roles, governance structure, life cycle choice, etc.
The business case is reviewed and revised at decision gates as more mature estimates and information become available. The approved business case provides a record of the decisions made by governance about how to achieve the required return on investment from the work. It documents the options considered and it is normal practice to include the ‘do-nothing’ option as a reference. Through this approach, the business case becomes a record of the recommended option with rationale and evidence to support the decision.
The presentation of the business case, if approved, results in the formal startup of the project, programme or portfolio. The sponsor owns the business case.
It brings together the investment appraisal with evidence of how the investment is intended to lead to realisation of the intended benefits. All projects must have a business case that demonstrates the value of the work and it is outlined during the concept phase of the life cycle .
Contents of the business case

Source: Starting out in project management, 3rd edition
Starting out in project management
Your essential guide to the basics of project management. Written for anyone new to projects or wishing to progress their career as a project professional Starting Out charts the journey of the APM project life cycle, from concept through to delivery and handover.

APM Learning
The following business case resources are available on APM Learning. This is a member only resource.
- Information sheet - Business case
- Template - Business case
Find out more about APM Learning
Related reading
![project plan vs business case Liesdamnlies Resources [Whatispm Whatisabusinesscase] 1920X1080 (1) (1)](https://www.apm.org.uk/v2/media/fsndq5eu/liesdamnlies-resources-whatispm-whatisabusinesscase-1920x1080-1-1.jpg?anchor=center&mode=crop&width=340&height=204&rnd=133115152069400000)
APM Body of Knowledge 7 th edition
The APM Body of Knowledge 7 th edition is a foundational resource providing the concepts, functions and activities that make up professional project management. It reflects the developing profession, recognising project-based working at all levels, and across all sectors for influencers, decision makers, project professionals and their teams.

You may also be interested in

The APM Learning portal is an online resource which provides members with access to digital guides, modules and other digital learning resources as part of the membership benefit.

Project – APM's official journal – is circulated quarterly for members only, and online for regularly updated news, blogs, opinions and insights for those in the project community.


What Is a Business Case - Simply Explained
Have you ever wondered why a company or executive management decides to commit themselves to a particular project? After all, this type of investment isn't only about money, but time and effort. When making such a decision, many believe that a business plan determines overall objectives and strategies. But what's a business case, and how does it fit into this picture?
A business case zooms in on a specific problem and tells you how to solve it. This document is at the heart of any project and convinces key decision makers of the merits of a particular course of action by showing them the impacts, costs, and benefits. So, let's see how the business case works!
What Is a Business Case in Project Management?
At the beginning of every project, we face that infamous question, "why?"
Why should our organization start a new project? What do we expect to gain, and what are the costs involved? A business case is a document that tries to provide such answers. It identifies different aspects and argues why the project would be beneficial and the risks and costs involved.
In short, a business case will explain the benefits your company will gain if decision-makers decide to pursue a significant business investment. This project management document will show your stakeholders, customers, or clients that the project you pitch is a reasonable choice.
How Does the Business Case Relate to a Project?
You need a business case to convince decision-makers to accept the project idea. This document will also help your company prioritize projects that align with your business's overall goals.
Additionally, you can compare various ideas using the same criteria. This ensures transparency and an equal playing field for upcoming projects. If your organization chooses to proceed with the project, a project case will help you manage the scope during the initial stage .
When the project is completed, a business case can help you measure how well the company did the project planning and implementation.
Business Case vs. Business Plan
While these two terms are used interchangeably, they do have different concepts.
A business case examines a potential market opportunity at the product level. This market opportunity can be described as sizable, lasting, and lucrative. Business cases will assess whether an organization should make a product or offer a service that will try to solve a market problem.
Also, a business case proposes a comprehensive strategy or new initiative. It outlines the business benefits your company will receive by pursuing a business opportunity.
.png)
Business profitability Cheat Sheet
All Newsletter subscribers can download this (and other) ActiveCollab Project Management Guides.
*Enter your email address and subscribe to our newsletter to get your hands on this, as well as many other free project management guides.
Sorry, we could not subscribe you at this moment. please double check your email address. If issue still persist, please let us know by sending an email to [email protected]
On the other hand, a business plan examines a potential business opportunity at the company level. A business opportunity, in this case, is a void a company tries to fill by providing a specific product to the target market.
Moreover, a business plan can outline an entirely new business. Generally, you create a business plan to identify your vision statement, mission, business strategy, and how you will get there.
Business Case vs. Project Charter
A project charter is a document that clearly defines the project scope at a higher level. It explicitly states what needs to be done and establishes the project's schedule, time, and budget. The project charter is a document that appoints a project manager and authorizes the project.
It gives the project the green light, and it's the first document you will create when starting with the project.
The business case explains what effects the project will have on the business. We call it a business case for a reason. We imagine different scenarios: when the project will be finished and its results. Not all projects will be doable, so you will have to prepare numerous business cases and start a project only for some of them.
What Is the Purpose of a Business Case?
A business case's primary purpose is to justify an investment. It facilitates investment decisions at the project level. This document summarizes risks, benefits, and costs and helps an organization decide whether to fund or skip the project.
The organization will be able to make an informed decision based on real facts. Compared to PMP, a business case needs to be more detailed and written from a business point of view.
Components of a Business Case
A business case consists of four components:
- Costs: At this point, costs will be inevitably high, since you haven't completed the detailed work necessary to produce baseline costs. There is not enough information to make an effective investment decision.
- Benefits: They will define ROI, and this part is important because you will use it to evaluate costs and determine whether the business case is justified.
- Risks: Again, risks in the business case will be pretty high and will be linked to the project delivery. Nonetheless, risks will help you make the right decision.
- Timescales: These will define when the benefits will start and will be used as part of the cost-benefit for the project.
Don't forget that with the help of ActiveCollab project management software, you can successfully create a business case and turn an idea into reality.

Business Case Structure
A business case structure typically looks like this:
- Identify the problem: Projects are designed with a specific purpose, whether to solve a problem or create a business opportunity. Your first step is to figure out the problem, describe it, discover where it comes from, and then set a time frame to deal with it.
- Alternative solutions: How do you know the project you are undertaking is the best possible solution? Naturally, you don't; that's why you need an alternative for each solution and its benefits.
- Propose the best solution: Set criteria, and maybe decide on a scoring mechanism to help you choose the best solution. Whatever approach you apply, the best solution to your problem will be evident.
- Implementation approach: So, you've found the problem or opportunity; how will you reach it? Also, you need to convince your stakeholder that you are right and have found the best solution to achieve the company's goals.
Business Case Presentation
A business case presentation is a set of questions used to define all areas that need attention to make an informed decision: move forward or quit the project. Preferably, a business presentation should include costs and risks, which help decision-makers successfully make the right choice. Key stakeholders and sponsors are the ones who review business case presentations.

Business Case Evaluation
Business case evaluation is a process that evaluates a perceived need and determines the best ways to address this need while having in mind social, environmental, and financial impact. Its ultimate purpose is to help decision-makers make that business judgment: Do our customers require this project? Will this project solve real problems? How do you balance costs against expected benefits? What risks are involved, and how serious are they?
What Is a Business Case Analysis?
We use business case analysis to evaluate potential business decisions, mainly in the corporate world. A project manager is responsible for performing analysis and assessing the benefits, risks, and costs with the help of their specialist knowledge. Company stakeholders then review this analysis and decide whether to approve or not this decision.
Make Real Work Happen!
Start your trial today, free for 14 days! Onboard your team, plan, collaborate, organize your work, and get paid.
By signing up you are agreeing to the ActiveCollab Terms of Service & Privacy Policy .
Great, just a few seconds and you're in.
We detected that you already have an ActiveCollab account
You can log in to existing account or you may start a new one
Great, your account has been created!
You will be redirected to your new account in a couple of seconds.
Sorry, we could not create an account for you at this moment.
Please double check your email address. If the issue still persists, please let us know by sending an email to [email protected]
Sign up for ActiveCollab newsletter!
Choose your favorite topics and we'll send our stories from the tech front lines straight to your inbox.
Unsubscribe at any time * Privacy Policy
Just a second
Thank you for subscribing to our newsletter.
Oops, something went wrong! Please try again later.
Related Articles
Project Scope: Base for Successful Project Delivery

ActiveCollab Is a Wonderful Software Solution - Nerdfox Design

Tips for Creating a Project Plan
Start your free trial.
Enter your email to get 14 days of ActiveCollab absolutely free, without any limitations.
Mark as disposable account.
ActiveCollab Is Using Cookies
By accepting all cookies you are giving us permission to use our tracking technologies to personalize your content and provide you the best possible experience on our website. Essential cookies are always on as we need them to make sure our website is working properly.
Read more about our cookie policy.

Key Differences Between Business Case and Project Charter
- On May 7, 2023
- By David Usifo (PSM, MBCS, PMP®)
When you’re embarking on a new project, two essential documents that will come up during the project initiation are the business case and the project charter.
While both documents are necessary, they serve different purposes and contain different information.
Business case vs project charter. What are the differences? This blog post will discuss the differences between a business case and a project charter, their key elements, and when to use each document.
Table of Contents
What is a Business Case?
A business case is a document that justifies why a project is necessary. Any project that a business undertakes is bound to have an impact on the business.
The business case outlines the benefits, costs, and risks associated with the project to determine whether it’s worth pursuing and aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
Key Elements of a Business Case
- Executive Summary : A brief summary of the entire business case.
- Problem Statement : A description of the problem or opportunity the project aims to solve or exploit.
- Objectives : The goals and objectives of the project.
- Benefits : The expected benefits that the project will deliver.
- Costs : A detailed breakdown of the estimated costs of the project , including potential risks and contingencies.
- Stakeholder Analysis : An analysis of the project’s stakeholders and their needs and expectations.
- Risk Analysis : A comprehensive assessment of the risks associated with the project and how they will be managed.
When to Use a Business Case
The business case is used to evaluate the feasibility of a project before approving it. The document is presented to senior management or a project sponsor to secure funding and resources.
It can also be used during a project to assess whether the project should be continued or terminated.
What is a Project Charter?
A project charter is a document that officially initiates and authorizes a project. It outlines the project’s scope, objectives, and stakeholders.
Without a project charter, the project doesn’t officially exist. It designates the project manager , and gives the project manager the authority to utilize resources.
It also provides a high-level overview of the project and serves as a reference point throughout the project’s lifecycle .
The project charter’s purpose is to define the project scope , establish its objectives, and provide a roadmap for the project team.
The responsibility of drafting a project charter lies on the project sponsor although the sponsor may choose to delegate the drafting.
Key Elements of a Project Charter
- Project Title and Description : The project’s title and a brief description of its purpose.
- Project Objectives : The project’s specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound objectives.
- Scope : The project’s boundaries and what it will and will not deliver.
- Stakeholder Analysis : An analysis of the project stakeholders , their needs, and expectations.
- Assumptions : Any assumptions made about the project.
- Risks and Mitigation Strategies : A comprehensive assessment of the risks associated with the project and how they will be managed.
- Project Timeline : A high-level timeline of the project’s major milestones and deliverables.
When to Use a Project Charter
The project charter is used at the start of the project to initiate it formally and establish its objectives and scope.
The document is created by the project sponsor or manager and used as a reference point throughout the project’s lifecycle.
A project charter is typically created before the project plan and used to ensure that everyone involved in the project has a common understanding of its scope and objectives.
Business Case vs Project Charter: 5 Key Differences
A business case assesses the feasibility of a project idea in order to determine its feasibility, viability, and adherence to the business need, while a project charter formally initiates the project and establishes its scope and objectives.
A business case focuses on the benefits, costs, and risks associated with the project, while a project charter focuses on the project’s scope, objectives, and stakeholders.
A business case is created before a project is approved, while a project charter is created after a project is approved and is used to initiate the project formally.
4. Level of Detail
A business case requires a high level of detail as a comprehensive analysis of the project’s feasibility, while a project charter provides a high-level overview of the project’s scope and objectives.
5. Audience
While a business case is typically presented to senior management or a project sponsor to secure funding and resources, a project charter is shared with the project team and used as a reference point throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Using a Business Case and Project Charter Together
While a business case and a project charter serve different purposes, they are often used together to initiate and manage a project.
A business case provides the justification for the project, while a project charter establishes the project’s scope, objectives, and stakeholders.
Once a project is approved, the project team can use the project charter as a reference point throughout the project’s lifecycle to ensure that they are on track to deliver the project’s objectives.
So there you have it. A business case and a project charter are crucial documents in project management.
They both serve different purposes but are often used together to initiate and manage a project successfully.
By understanding the differences between them, you can ensure that you have the right documents in place for your project’s success.
Always remember to assess the feasibility of your project and provide a comprehensive analysis of its benefits, costs, and risks with a business case.
And, formally initiate your project and establish its scope, objectives, and stakeholders with a project charter.
Does a Business Case Come Before a Project Charter?
Yes, a business case usually comes before a project charter. The business case assesses the feasibility of a project and analyzes the benefits, costs, and risks associated with it.
Once the business case is approved, the project charter is created to formally initiate the project and establish its scope, objectives, and stakeholders.
Is Business Case Part of the Project Plan?
A business case is typically not considered a part of the project plan, but it’s an important document used to assess the feasibility of a project and provide an analysis of its benefits, costs, and risks.
The project plan, on the other hand, outlines the specific tasks, timelines, and resources required to execute the project.
While the business case can inform the project plan, they are distinct documents with different purposes in project management.
Who Writes the Business Case on a Project?
The business case is usually written by the project sponsor or a business analyst. However, depending on the organization’s structure, the project manager or a team of experts may also be involved in its development.
The business case should be a collaborative effort, with input from all relevant stakeholders, to ensure that it accurately reflects the project’s goals and aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Is a Business Case a Proposal?
A business case isn’t the same as a proposal. A proposal is a document that outlines a specific plan or solution, while a business case analyzes the feasibility and potential outcomes of a project. The business case provides a comprehensive analysis of the benefits, costs, and risks associated with a project and is used to determine whether a project is worth pursuing.
What are the Three Types of Business Case?
There are three types of business case: strategic, financial, and operational.
A strategic business case assesses the impact of a project on the overall business strategy. A financial business case evaluates the project’s costs and benefits in monetary terms. An operational business case looks at how the project will improve day-to-day operations.
Each type of business case provides a unique perspective on the project and helps stakeholders make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the project.
What Comes After a Business Case?
After a business case, the next step is usually the creation of a project charter. The project charter formally authorizes the project and outlines its scope, objectives, and stakeholders.
It serves as a high-level roadmap for the project and provides a foundation for its planning and execution.
David Usifo (PSM, MBCS, PMP®)
David Usifo is a certified project manager professional, professional Scrum Master, and a BCS certified Business Analyst with a background in product development and database management.
He enjoys using his knowledge and skills to share with aspiring and experienced project managers and product developers the core concept of value-creation through adaptive solutions.
Related Posts

A Guide to Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contracts in Project Procurement Management

A Guide to Fixed Price Incentive Fee Contracts in Project Procurement Management

Step-by-Step Guide to Enterprise Project Portfolio Management

A Guide on Cost of Conformance in Project Management
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Our business case template for Word is the perfect tool to start writing a business case. It has 9 key business case areas you can customize as needed. Download the template for free and follow the steps below to create a great business case for all your projects. ProjectManager's free business case template.
Business case vs. project charter. If you need to create an elevator pitch for your project but you don't quite need the full business case treatment, you might need a project charter. Much like a business case, a project charter outlines key details of an initiative. Specifically, a project charter will cover three main elements of your ...
There is a caveat, which is crucial to compare project charter vs business case. The business case is not only about deciding if a project is worth investing or not. It is about setting the financial parameters for it being worth investing. To make it even clearer: if the business case says the project makes sense if its costs are at half a ...
The business plan is based on a series of hypothesis, action plans, and a long-term calendar. Contrastingly, a business case is concrete - mainly because it's aimed at creating a short-term gain for the business with a well defined return on investment. To sum-up: a business plan is a strategic document, whereas a business plan is a tactical ...
A business case is a project management document that highlights the objectives, risks, benefits and costs of pursuing a project. ... Business Case vs Business Plan. A business case is an internal document used within an organization to justify a specific project or investment. It's created for stakeholders and decision-makers and focuses on ...
A business case is a useful tool to provide a clear rationale for pursuing the project. A thorough business case can help key stakeholders decide whether to invest in the project by evaluating the feasibility, costs, risks and potential returns. A business case presentation gives stakeholders an opportunity to ask questions and address concerns.
The Business Case is a reference point before, during, and after a project. As the project begins the Business Case establishes the ultimate goal of the project for all stakeholders—including the project manager and sponsor. There are invariably concepts in the minds of the key project participants of what they expect the project to accomplish.
A well-written business case should include key sections, such as an executive summary, a risk analysis, and an implementation timeline. Let's look at how each component can impact business case development. The executive summary should provide a brief overview of the project, including the problem it addresses, the solution proposed, and the ...
Business Case Project Plan; Provides a justification of why this project should be prioritized right now.: Provides a high-level outline of what is going to be made and how it will be made.: Business cases focus on outcomes and objectives.: Project plans focus on outputs and deliverables.: A business case is a strategic document used to consider an initiative in the context of the wider ...
Beginning: Someone identifies a problem within the business and presents the business case to the key decision-makers. Middle: With the project go-ahead, the company launches an internal team to address the business case and deliver results. End: The team delivers a presentation on the changes made and their long-term effects.
A business case is a justification for a proposed project or plan of action on the basis of its expected commercial benefit. It is a business argument. It is a business argument. It reveals a situation which is either a problem or an opportunity and details how the situation could be addressed in terms of benefits and risks.
A business case cannot be viewed as a business plan for a product. The reason is that the two documents differ by at least two primary dimensions: type of opportunity (market vs. business ...
Business case vs. project plan: The Why VS the How - A business case argues why a company should proceed with a project. A project plan, on the other hand, gets into the nitty-gritty of exactly how a company will tackle an approved project.
Business case vs. project plan. A business case can also be confused with a project plan. However, a business case should justify why a project should exist. Only after a project is approved, post business case review, a project plan is created. Where a business case will speak on how a project should look, a project plan will determine how it ...
While both documents are used to plan and execute a project, the business case focuses on gaining approval for the project, while the project charter focuses on the details of the executing the project. Where to Download a Business Case Template. If you're feeling a bit overwhelmed at the prospect of creating a business case from scratch, relax.
Let's dive into the steps for how you'll develop a business case below: 1. Research. Before you can write a business case, you need to do your research. First, you should have a goal in mind for your project, whether it's to create a new product, help drive more traffic/leads, or improve user experience. Write down your goal and then conduct ...
Business case vs. project proposal. The term 'business case' is often used interchangeably with 'project proposal.' While they're both tools for convincing stakeholders to invest time or resources, they are two subtly different things, each done at a different stage of the project. A project proposal comes before the business case. It ...
A business case provides justification for undertaking a project, programme or portfolio. It evaluates the benefit, cost and risk of alternative options and provides a rationale for the preferred solution. Definition from APM Body of Knowledge 7th edition. Buy APM Body of Knowledge.
John Spacey, updated on March 04, 2017. A business plan is a proposal for a new business or major change to an existing business. A business case is a proposal for a strategy or project. A business plan is typically targeted to investors. It may include a pitch, financial plan, business model, cost estimates, market analysis, competitive ...
Moreover, a business plan can outline an entirely new business. Generally, you create a business plan to identify your vision statement, mission, business strategy, and how you will get there. Business Case vs. Project Charter. A project charter is a document that clearly defines the project scope at a higher level. It explicitly states what ...
The purpose of a business case is to support business investment decisions. This paper examines the differences between developing business cases to facilitate decision making on projects--which are temporary--and on programs, which are often planned over extended timeframes. In doing so, it explores the literature on decision making, looking at how this function affects managerial performance ...
Business Case vs Project Charter: 5 Key Differences. 1. Purpose. A business case assesses the feasibility of a project idea in order to determine its feasibility, viability, and adherence to the business need, while a project charter formally initiates the project and establishes its scope and objectives. 2.