
- C Programming Tutorial
- Basics of C
- C - Overview
- C - Features
- C - History
- C - Environment Setup
- C - Program Structure
- C - Hello World
- C - Compilation Process
- C - Comments
- C - Keywords
- C - Identifiers
- C - User Input
- C - Basic Syntax
- C - Data Types
- C - Variables
- C - Integer Promotions
- C - Type Conversion
- C - Type Casting
- C - Booleans
- Constants and Literals in C
- C - Constants
- C - Literals
- C - Escape sequences
- C - Format Specifiers
- Operators in C
- C - Operators
- C - Arithmetic Operators
- C - Relational Operators
- C - Logical Operators
- C - Bitwise Operators
- C - Assignment Operators
- C - Unary Operators
- C - Increment and Decrement Operators
- C - Ternary Operator
- C - sizeof Operator
- C - Operator Precedence
- C - Misc Operators
- Decision Making in C
- C - Decision Making
- C - if statement
- C - if...else statement
- C - nested if statements
- C - switch statement
- C - nested switch statements
- C - While loop
- C - For loop
- C - Do...while loop
- C - Nested loop
- C - Infinite loop
- C - Break Statement
- C - Continue Statement
- C - goto Statement
- Functions in C
- C - Functions
- C - Main Functions
- C - Function call by Value
- C - Function call by reference
- C - Nested Functions
- C - Variadic Functions
- C - User-Defined Functions
- C - Callback Function
- C - Return Statement
- C - Recursion
- Scope Rules in C
- C - Scope Rules
- C - Static Variables
- C - Global Variables
- Arrays in C
- C - Properties of Array
- C - Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- C - Passing Arrays to Function
- C - Return Array from Function
- C - Variable Length Arrays
- Pointers in C
- C - Pointers
- C - Pointers and Arrays
- C - Applications of Pointers
- C - Pointer Arithmetics
- C - Array of Pointers
- C - Pointer to Pointer
- C - Passing Pointers to Functions
- C - Return Pointer from Functions
- C - Function Pointers
- C - Pointer to an Array
- C - Pointers to Structures
- C - Chain of Pointers
- C - Pointer vs Array
- C - Character Pointers and Functions
- C - NULL Pointer
- C - void Pointer
- C - Dangling Pointers
- C - Dereference Pointer
- C - Near, Far and Huge Pointers
- C - Initialization of Pointer Arrays
- C - Pointers vs. Multi-dimensional Arrays
- Strings in C
- C - Strings
- C - Array of Strings
- C - Special Characters
- C Structures and Unions
- C - Structures
- C - Structures and Functions
- C - Arrays of Structures
- C - Self-Referential Structures
- C - Lookup Tables
- C - Dot (.) Operator
- C - Enumeration (or enum)
- C - Structure Padding and Packing
- C - Nested Structures
- C - Anonymous Structure and Union
- C - Bit Fields
- C - Typedef
- File Handling in C
- C - Input & Output
- C - File I/O (File Handling)
- C Preprocessors
- C - Preprocessors
- C - Pragmas
- C - Preprocessor Operators
- C - Header Files
- Memory Management in C
- C - Memory Management
- C - Memory Address
- C - Storage Classes
- Miscellaneous Topics
- C - Error Handling
- C - Variable Arguments
- C - Command Execution
- C - Math Functions
- C - Static Keyword
- C - Random Number Generation
- C - Command Line Arguments
- C Programming Resources
- C - Questions & Answers
- C - Quick Guide
- C - Useful Resources
- C - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary

Assignment Operators in C
In C language, the assignment operator stores a certain value in an already declared variable. A variable in C can be assigned the value in the form of a literal, another variable, or an expression.
The value to be assigned forms the right-hand operand, whereas the variable to be assigned should be the operand to the left of the " = " symbol, which is defined as a simple assignment operator in C.
In addition, C has several augmented assignment operators.
The following table lists the assignment operators supported by the C language −
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Simple assignment operator. Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand | C = A + B will assign the value of A + B to C |
| += | Add AND assignment operator. It adds the right operand to the left operand and assign the result to the left operand. | C += A is equivalent to C = C + A |
| -= | Subtract AND assignment operator. It subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C -= A is equivalent to C = C - A |
| *= | Multiply AND assignment operator. It multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C *= A is equivalent to C = C * A |
| /= | Divide AND assignment operator. It divides the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand. | C /= A is equivalent to C = C / A |
| %= | Modulus AND assignment operator. It takes modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand. | C %= A is equivalent to C = C % A |
| <<= | Left shift AND assignment operator. | C <<= 2 is same as C = C << 2 |
| >>= | Right shift AND assignment operator. | C >>= 2 is same as C = C >> 2 |
| &= | Bitwise AND assignment operator. | C &= 2 is same as C = C & 2 |
| ^= | Bitwise exclusive OR and assignment operator. | C ^= 2 is same as C = C ^ 2 |
| |= | Bitwise inclusive OR and assignment operator. | C |= 2 is same as C = C | 2 |
Simple Assignment Operator (=)
The = operator is one of the most frequently used operators in C. As per the ANSI C standard, all the variables must be declared in the beginning. Variable declaration after the first processing statement is not allowed.
You can declare a variable to be assigned a value later in the code, or you can initialize it at the time of declaration.
You can use a literal, another variable, or an expression in the assignment statement.
Once a variable of a certain type is declared, it cannot be assigned a value of any other type. In such a case the C compiler reports a type mismatch error.
In C, the expressions that refer to a memory location are called "lvalue" expressions. A lvalue may appear as either the left-hand or right-hand side of an assignment.
On the other hand, the term rvalue refers to a data value that is stored at some address in memory. A rvalue is an expression that cannot have a value assigned to it which means an rvalue may appear on the right-hand side but not on the left-hand side of an assignment.
Variables are lvalues and so they may appear on the left-hand side of an assignment. Numeric literals are rvalues and so they may not be assigned and cannot appear on the left-hand side. Take a look at the following valid and invalid statements −
Augmented Assignment Operators
In addition to the = operator, C allows you to combine arithmetic and bitwise operators with the = symbol to form augmented or compound assignment operator. The augmented operators offer a convenient shortcut for combining arithmetic or bitwise operation with assignment.
For example, the expression "a += b" has the same effect of performing "a + b" first and then assigning the result back to the variable "a".
Run the code and check its output −
Similarly, the expression "a <<= b" has the same effect of performing "a << b" first and then assigning the result back to the variable "a".
Here is a C program that demonstrates the use of assignment operators in C −
When you compile and execute the above program, it will produce the following result −

01 Career Opportunities
- Top 50 Mostly Asked C Interview Questions and Answers
02 Beginner
- Understanding do...while loop in C
- If...else statement in C Programming
- If Statement in C
- Understanding realloc() function in C
- Understanding While loop in C
- Why C is called middle level language?
- Arithmetic Operators in C Programming
- Relational Operators in C Programming
C Programming Assignment Operators
- Logical Operators in C Programming
- Understanding for loop in C
- if else if statements in C Programming
- Beginner's Guide to C Programming
- First C program and Its Syntax
- Escape Sequences and Comments in C
- Keywords in C: List of Keywords
- Identifiers in C: Types of Identifiers
- Data Types in C Programming - A Beginner Guide with examples
- Variables in C Programming - Types of Variables in C ( With Examples )
- 10 Reasons Why You Should Learn C
- Boolean and Static in C Programming With Examples ( Full Guide )
- Operators in C: Types of Operators
- Bitwise Operators in C: AND, OR, XOR, Shift & Complement
- Expressions in C Programming - Types of Expressions in C ( With Examples )
- Conditional Statements in C: if, if..else, Nested if
- Switch Statement in C: Syntax and Examples
- Ternary Operator in C: Ternary Operator vs. if...else Statement
- Loop in C with Examples: For, While, Do..While Loops
- Nested Loops in C - Types of Expressions in C ( With Examples )
- Infinite Loops in C: Types of Infinite Loops
- Jump Statements in C: break, continue, goto, return
- Continue Statement in C: What is Break & Continue Statement in C with Example
03 Intermediate
- Getting Started with Data Structures in C
- Constants in C language
- Functions in C Programming
- Call by Value and Call by Reference in C
- Recursion in C: Types, its Working and Examples
- Storage Classes in C: Auto, Extern, Static, Register
- Arrays in C Programming: Operations on Arrays
- Strings in C with Examples: String Functions
04 Advanced
- How to Dynamically Allocate Memory using calloc() in C?
- How to Dynamically Allocate Memory using malloc() in C?
- Pointers in C: Types of Pointers
- Multidimensional Arrays in C: 2D and 3D Arrays
- Dynamic Memory Allocation in C: Malloc(), Calloc(), Realloc(), Free()
05 Training Programs
- Java Programming Course
- C++ Programming Course
- C Programming Course
- Data Structures and Algorithms Training
- C Programming Assignment ..

C Programming For Beginners Free Course
What is an assignment operator in c.
Assignment Operators in C are used to assign values to the variables. They come under the category of binary operators as they require two operands to operate upon. The left side operand is called a variable and the right side operand is the value. The value on the right side of the "=" is assigned to the variable on the left side of "=". The value on the right side must be of the same data type as the variable on the left side. Hence, the associativity is from right to left.
In this C tutorial , we'll understand the types of C programming assignment operators with examples. To delve deeper you can enroll in our C Programming Course .
Before going in-depth about assignment operators you must know about operators in C. If you haven't visited the Operators in C tutorial, refer to Operators in C: Types of Operators .
Types of Assignment Operators in C
There are two types of assignment operators in C:
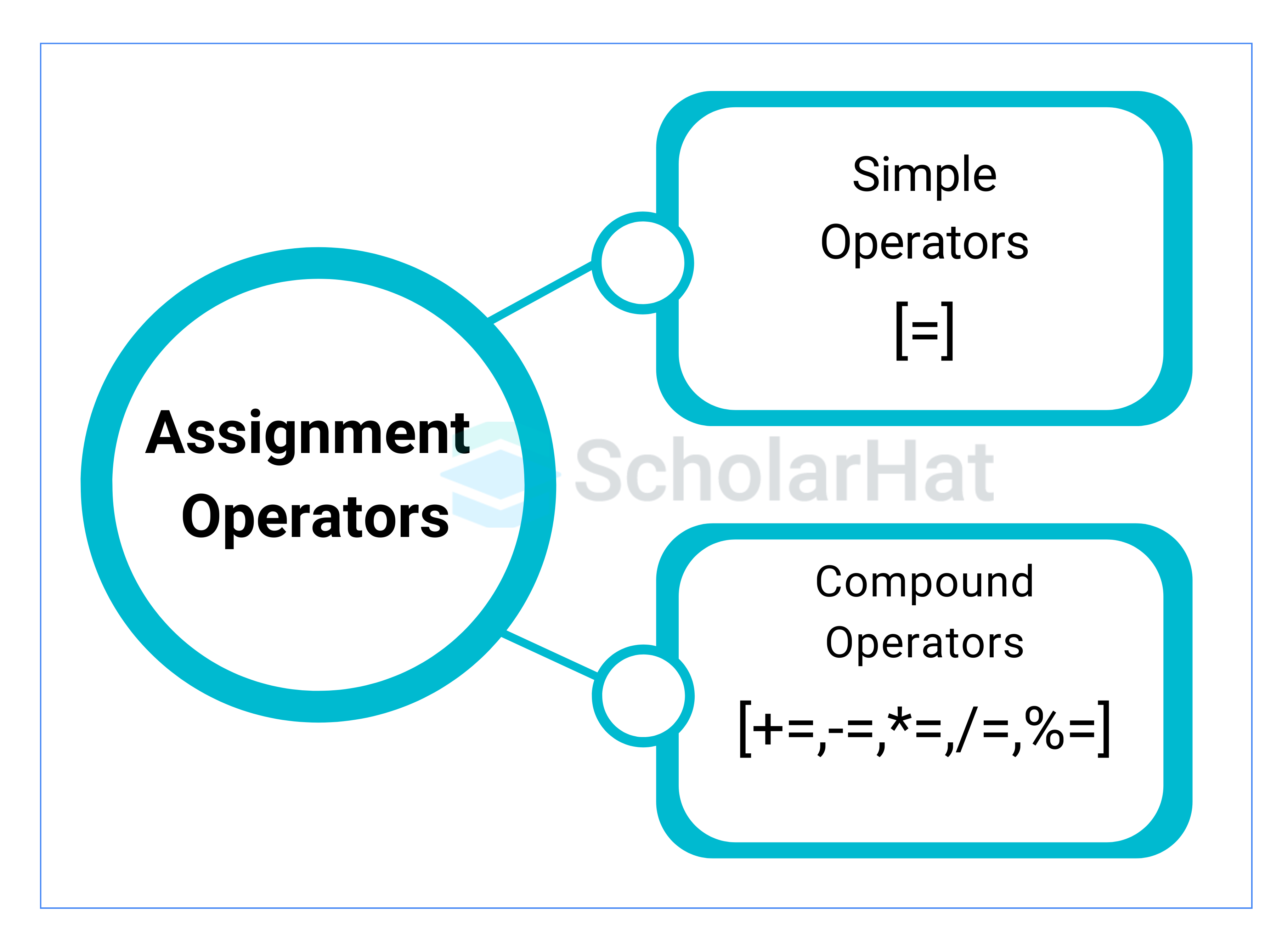
| += | addition assignment | It adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| -= | subtraction assignment | It subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| *= | multiplication assignment | It multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand |
| /= | division assignment | It divides the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand. |
| %= | modulo assignment | It takes modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand. |
Example of Augmented Arithmetic and Assignment Operators
There can be five combinations of bitwise operators with the assignment operator, "=". Let's look at them one by one.
| &= | bitwise AND assignment | It performs the bitwise AND operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| |= | bitwise OR assignment | It performs the bitwise OR operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| ^= | bitwise XOR assignment | It performs the bitwise XOR operation on the variable with the value on the right |
| <<= | bitwise left shift assignment | Shifts the bits of the variable to the left by the value on the right |
| >>= | bitwise right shift assignment | Shifts the bits of the variable to the right by the value on the right |
Example of Augmented Bitwise and Assignment Operators
Practice problems on assignment operators in c, 1. what will the value of "x" be after the execution of the following code.
The correct answer is 52. x starts at 50, increases by 5 to 55, then decreases by 3 to 52.
2. After executing the following code, what is the value of the number variable?
The correct answer is 144. After right-shifting 73 (binary 1001001) by one and then left-shifting the result by two, the value becomes 144 (binary 10010000).
Benefits of Using Assignment Operators
- Simplifies Code: For example, x += 1 is shorter and clearer than x = x + 1.
- Reduces Errors: They break complex expressions into simpler, more manageable parts thus reducing errors.
- Improves Readability: They make the code easier to read and understand by succinctly expressing common operations.
- Enhances Performance: They often operate in place, potentially reducing the need for additional memory or temporary variables.
Best Practices and Tips for Using the Assignment Operator
While performing arithmetic operations with the same variable, use compound assignment operators
- Initialize Variables When Declaring int count = 0 ; // Initialization
- Avoid Complex Expressions in Assignments a = (b + c) * (d - e); // Consider breaking it down: int temp = b + c; a = temp * (d - e);
- Avoid Multiple Assignments in a Single Statement // Instead of this a = b = c = 0 ; // Do this a = 0 ; b = 0 ; c = 0 ;
- Consistent Formatting int result = 0 ; result += 10 ;
When mixing assignments with other operations, use parentheses to ensure the correct order of evaluation.
Live Classes Schedule
| ASP.NET Core Certification Training | Jul 06 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| Advanced Full-Stack .NET Developer Certification Training | Jul 06 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| Full Stack .NET | Jul 06 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| React JS Certification Training | Best React Training Course | Jul 06 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| Generative AI For Software Developers | Jul 14 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| Angular Certification Course | Jul 14 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| ASP.NET Core Certification Training | Jul 15 | MON, WED, FRI | Filling Fast | ||
| Advanced Full-Stack .NET Developer Certification Training | Jul 15 | MON, WED, FRI | Filling Fast | ||
| Azure Master Class | Jul 20 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| Azure Developer Certification Training | Jul 21 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| Software Architecture and Design Training | Jul 28 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast | ||
| .NET Solution Architect Certification Training | Jul 28 | SAT, SUN | Filling Fast |
Can't find convenient schedule? Let us know
About Author

- 22+ Video Courses
- 800+ Hands-On Labs
- 400+ Quick Notes
- 55+ Skill Tests
- 45+ Interview Q&A Courses
- 10+ Real-world Projects
- Career Coaching Sessions
- Email Support
We use cookies to make interactions with our websites and services easy and meaningful. Please read our Privacy Policy for more details.
Next: Execution Control Expressions , Previous: Arithmetic , Up: Top [ Contents ][ Index ]
7 Assignment Expressions
As a general concept in programming, an assignment is a construct that stores a new value into a place where values can be stored—for instance, in a variable. Such places are called lvalues (see Lvalues ) because they are locations that hold a value.
An assignment in C is an expression because it has a value; we call it an assignment expression . A simple assignment looks like
We say it assigns the value of the expression value-to-store to the location lvalue , or that it stores value-to-store there. You can think of the “l” in “lvalue” as standing for “left,” since that’s what you put on the left side of the assignment operator.
However, that’s not the only way to use an lvalue, and not all lvalues can be assigned to. To use the lvalue in the left side of an assignment, it has to be modifiable . In C, that means it was not declared with the type qualifier const (see const ).
The value of the assignment expression is that of lvalue after the new value is stored in it. This means you can use an assignment inside other expressions. Assignment operators are right-associative so that
is equivalent to
This is the only useful way for them to associate; the other way,
would be invalid since an assignment expression such as x = y is not valid as an lvalue.
Warning: Write parentheses around an assignment if you nest it inside another expression, unless that is a conditional expression, or comma-separated series, or another assignment.
| • | The basics of storing a value. | |
| • | Expressions into which a value can be stored. | |
| • | Shorthand for changing an lvalue’s contents. | |
| • | Shorthand for incrementing and decrementing an lvalue’s contents. | |
| • | Accessing then incrementing or decrementing. | |
| • | How to avoid ambiguity. | |
| • | Write assignments as separate statements. |
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
C Assignment Operators
- 6 contributors
An assignment operation assigns the value of the right-hand operand to the storage location named by the left-hand operand. Therefore, the left-hand operand of an assignment operation must be a modifiable l-value. After the assignment, an assignment expression has the value of the left operand but isn't an l-value.
assignment-expression : conditional-expression unary-expression assignment-operator assignment-expression
assignment-operator : one of = *= /= %= += -= <<= >>= &= ^= |=
The assignment operators in C can both transform and assign values in a single operation. C provides the following assignment operators:
| Operator | Operation Performed |
|---|---|
| Simple assignment | |
| Multiplication assignment | |
| Division assignment | |
| Remainder assignment | |
| Addition assignment | |
| Subtraction assignment | |
| Left-shift assignment | |
| Right-shift assignment | |
| Bitwise-AND assignment | |
| Bitwise-exclusive-OR assignment | |
| Bitwise-inclusive-OR assignment |
In assignment, the type of the right-hand value is converted to the type of the left-hand value, and the value is stored in the left operand after the assignment has taken place. The left operand must not be an array, a function, or a constant. The specific conversion path, which depends on the two types, is outlined in detail in Type Conversions .
- Assignment Operators
Was this page helpful?
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources

Assignment Operators In C [ Full Information With Examples ]
![Assignment Operators In C [ Full Information With Examples ] Assignment Operators In C](https://cstutorialpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Assignment-Operators-in-C-.png)
Assignment Operators In C
Assignment operators is a binary operator which is used to assign values in a variable , with its right and left sides being a one-one operand. The operand on the left side is variable in which the value is assigned and the right side operands can contain any of the constant, variable, and expression.
The Assignment operator is a lower priority operator. its priority has much lower than the rest of the other operators. Its priority is more than just the comma operator. The priority of all other operators is more than the assignment operator.
We can assign the same value to multiple variables simultaneously by the assignment operator.
x = y = z = 100
Here x, y, and z are initialized to 100.
In C language, the assignment operator can be divided into two categories.
- Simple assignment operator
- Compound assignment operators
1. Simple Assignment Operator In C
This operator is used to assign left-side values to the right-side operands, simple assignment operators are represented by (=).
2. Compound Assignment Operators In C
Compound Assignment Operators use the old value of a variable to calculate its new value and reassign the value obtained from the calculation to the same variable.
Examples of compound assignment operators are: (Example: + =, – =, * =, / =,% =, & =, ^ =)
Look at these two statements:
Here in this example, adding 5 to the x variable in the second statement is again being assigned to the x variable.
Compound Assignment Operators provide us with the C language to perform such operation even more effecient and in less time.
Syntax of Compound Assignment Operators
Here op can be any arithmetic operators (+, -, *, /,%).
The above statement is equivalent to the following depending on the function:
Let us now know about some important compound assignment operators one by one.
“+ =” -: This operator adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the output to the left operand.
“- =” -: This operator subtracts the right operand from the left operand and returns the result to the left operand.
“* =” -: This operator multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
“/ =” -: This operator splits the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
“% =” -: This operator takes the modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand.
There are many other assignment operators such as left shift and (<< =) operator, right shift and operator (>> =), bitwise and assignment operator (& =), bitwise OR assignment operator (^ =)
List of Assignment Operators In C
| = | sum = 101;101 is assigned to variable sum |
| += | sum += 101; This is same as sum = sum + 101 |
| -= | sum -= 101; This is same as sum = sum – 101 |
| *= | sum *= 101; This is same as sum = sum * 101 |
| /= | sum /= 101; This is same as sum = sum/101 |
| %= | sum %= 101; This is same as sum = sum % 101 |
| &= | sum&=101; This is same as sum = sum & 101 |
| ^= | sum ^= 101; This is same as sum = sum ^ 101 |
Read More -:
- What is Operators In C
- Relational Operators In C
- Logical Operators In C
- Bitwise Operators In C
- Arithmetic Operators In C
- Conditional Operator in C
- Download C Language Notes Pdf
- C Language Tutorial For Beginners
- C Programming Examples With Output
- 250+ C Programs for Practice PDF Free Download
Friends, I hope you have found the answer of your question and you will not have to search about the Assignment operators in C Language
However, if you want any information related to this post or related to programming language, computer science, then comment below I will clear your all doubts.
If you want a complete tutorial of C language, then see here C Language Tutorial . Here you will get all the topics of C Programming Tutorial step by step.
Friends, if you liked this post, then definitely share this post with your friends so that they can get information about the Assignment operators in C Language
To get the information related to Programming Language, Coding, C, C ++, subscribe to our website newsletter. So that you will get information about our upcoming new posts soon.
Jeetu Sahu is A Web Developer | Computer Engineer | Passionate about Coding, Competitive Programming, and Blogging
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
PrepBytes Blog
ONE-STOP RESOURCE FOR EVERYTHING RELATED TO CODING
Sign in to your account
Forgot your password?
Login via OTP
We will send you an one time password on your mobile number
An OTP has been sent to your mobile number please verify it below
Register with PrepBytes
Assignment operator in c.
Last Updated on June 23, 2023 by Prepbytes

This type of operator is employed for transforming and assigning values to variables within an operation. In an assignment operation, the right side represents a value, while the left side corresponds to a variable. It is essential that the value on the right side has the same data type as the variable on the left side. If this requirement is not fulfilled, the compiler will issue an error.
What is Assignment Operator in C language?
In C, the assignment operator serves the purpose of assigning a value to a variable. It is denoted by the equals sign (=) and plays a vital role in storing data within variables for further utilization in code. When using the assignment operator, the value present on the right-hand side is assigned to the variable on the left-hand side. This fundamental operation allows developers to store and manipulate data effectively throughout their programs.
Example of Assignment Operator in C
For example, consider the following line of code:
Types of Assignment Operators in C
Here is a list of the assignment operators that you can find in the C language:
Simple assignment operator (=): This is the basic assignment operator, which assigns the value on the right-hand side to the variable on the left-hand side.
Addition assignment operator (+=): This operator adds the value on the right-hand side to the variable on the left-hand side and assigns the result back to the variable.
x += 3; // Equivalent to x = x + 3; (adds 3 to the current value of "x" and assigns the result back to "x")
Subtraction assignment operator (-=): This operator subtracts the value on the right-hand side from the variable on the left-hand side and assigns the result back to the variable.
x -= 4; // Equivalent to x = x – 4; (subtracts 4 from the current value of "x" and assigns the result back to "x")
* Multiplication assignment operator ( =):** This operator multiplies the value on the right-hand side with the variable on the left-hand side and assigns the result back to the variable.
x = 2; // Equivalent to x = x 2; (multiplies the current value of "x" by 2 and assigns the result back to "x")
Division assignment operator (/=): This operator divides the variable on the left-hand side by the value on the right-hand side and assigns the result back to the variable.
x /= 2; // Equivalent to x = x / 2; (divides the current value of "x" by 2 and assigns the result back to "x")
Bitwise AND assignment (&=): The bitwise AND assignment operator "&=" performs a bitwise AND operation between the value on the left-hand side and the value on the right-hand side. It then assigns the result back to the left-hand side variable.
x &= 3; // Binary: 0011 // After bitwise AND assignment: x = 1 (Binary: 0001)
Bitwise OR assignment (|=): The bitwise OR assignment operator "|=" performs a bitwise OR operation between the value on the left-hand side and the value on the right-hand side. It then assigns the result back to the left-hand side variable.
x |= 3; // Binary: 0011 // After bitwise OR assignment: x = 7 (Binary: 0111)
Bitwise XOR assignment (^=): The bitwise XOR assignment operator "^=" performs a bitwise XOR operation between the value on the left-hand side and the value on the right-hand side. It then assigns the result back to the left-hand side variable.
x ^= 3; // Binary: 0011 // After bitwise XOR assignment: x = 6 (Binary: 0110)
Left shift assignment (<<=): The left shift assignment operator "<<=" shifts the bits of the value on the left-hand side to the left by the number of positions specified by the value on the right-hand side. It then assigns the result back to the left-hand side variable.
x <<= 2; // Binary: 010100 (Shifted left by 2 positions) // After left shift assignment: x = 20 (Binary: 10100)
Right shift assignment (>>=): The right shift assignment operator ">>=" shifts the bits of the value on the left-hand side to the right by the number of positions specified by the value on the right-hand side. It then assigns the result back to the left-hand side variable.
x >>= 2; // Binary: 101 (Shifted right by 2 positions) // After right shift assignment: x = 5 (Binary: 101)
Conclusion The assignment operator in C, denoted by the equals sign (=), is used to assign a value to a variable. It is a fundamental operation that allows programmers to store data in variables for further use in their code. In addition to the simple assignment operator, C provides compound assignment operators that combine arithmetic or bitwise operations with assignment, allowing for concise and efficient code.
FAQs related to Assignment Operator in C
Q1. Can I assign a value of one data type to a variable of another data type? In most cases, assigning a value of one data type to a variable of another data type will result in a warning or error from the compiler. It is generally recommended to assign values of compatible data types to variables.
Q2. What is the difference between the assignment operator (=) and the comparison operator (==)? The assignment operator (=) is used to assign a value to a variable, while the comparison operator (==) is used to check if two values are equal. It is important not to confuse these two operators.
Q3. Can I use multiple assignment operators in a single statement? No, it is not possible to use multiple assignment operators in a single statement. Each assignment operator should be used separately for assigning values to different variables.
Q4. Are there any limitations on the right-hand side value of the assignment operator? The right-hand side value of the assignment operator should be compatible with the data type of the left-hand side variable. If the data types are not compatible, it may lead to unexpected behavior or compiler errors.
Q5. Can I assign the result of an expression to a variable using the assignment operator? Yes, it is possible to assign the result of an expression to a variable using the assignment operator. For example, x = y + z; assigns the sum of y and z to the variable x.
Q6. What happens if I assign a value to an uninitialized variable? Assigning a value to an uninitialized variable will initialize it with the assigned value. However, it is considered good practice to explicitly initialize variables before using them to avoid potential bugs or unintended behavior.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Linked List
- Segment Tree
- Backtracking
- Dynamic Programming
- Greedy Algorithm
- Operating System
- Company Placement
- Interview Tips
- General Interview Questions
- Data Structure
- Other Topics
- Computational Geometry
- Game Theory
Related Post
Null character in c, ackermann function in c, median of two sorted arrays of different size in c, number is palindrome or not in c, implementation of queue using linked list in c, c program to replace a substring in a string.
Home » Learn C Programming from Scratch » C Assignment Operators
C Assignment Operators
Summary : in this tutorial, you’ll learn about the C assignment operators and how to use them effectively.
Introduction to the C assignment operators
An assignment operator assigns the vale of the right-hand operand to the left-hand operand. The following example uses the assignment operator (=) to assign 1 to the counter variable:
After the assignmment, the counter variable holds the number 1.
The following example adds 1 to the counter and assign the result to the counter:
The = assignment operator is called a simple assignment operator. It assigns the value of the left operand to the right operand.
Besides the simple assignment operator, C supports compound assignment operators. A compound assignment operator performs the operation specified by the additional operator and then assigns the result to the left operand.
The following example uses a compound-assignment operator (+=):
The expression:
is equivalent to the following expression:
The following table illustrates the compound-assignment operators in C:
| Operator | Operation Performed | Example | Equivalent expression |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiplication assignment | x *= y | x = x * y | |
| Division assignment | x /= y | x = x / y | |
| Remainder assignment | x %= y | x = x % y | |
| Addition assignment | x += y | x = x + y | |
| Subtraction assignment | x -= y | x = x – y | |
| Left-shift assignment | x <<= y | x = x <<=y | |
| Right-shift assignment | x >>=y | x = x >>= y | |
| Bitwise-AND assignment | x &= y | x = x & y | |
| Bitwise-exclusive-OR assignment | x ^= y | x = x ^ y | |
| Bitwise-inclusive-OR assignment | x |= y | x = x | y |
- A simple assignment operator assigns the value of the left operand to the right operand.
- A compound assignment operator performs the operation specified by the additional operator and then assigns the result to the left operand.

Assignment Operators in C

Updated June 21, 2023

Introduction to Assignment Operators in C
Assignment operators are used for assigning value to the variable. Like any other operator, C also supports Assignment Operator which is a binary operator that operates on any two operands. It has two values such as the right value and the left value. It has lower precedence than all available operators but has higher precedence than the comma operator.
Start Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Different List of Assignment Operators in C
Below is the list of Assignment operators in C
- The simple assignment operator (=) : This operator Assigns values from the right operands to the left operand.
- Add AND operator (+=): This operator adds the right operand to the left operand and assigns the output to the left operand.
- Subtract AND operator (-=): This operator subtracts the right operand from the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- Multiply AND operator (*=): This operator multiplies the right operand with the left operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- Divide AND operator (/=): This operator divides the left operand with the right operand and assigns the result to the left operand.
- Modulus AND operator (%=): This operator takes modulus using two operands and assigns the result to the left operand.
There are many other assignment operators such as the Left shift AND (<<=) operator, Right shift AND operator (>>=), Bitwise AND assignment operator (&= ), Bitwise exclusive OR and assignment operator (^=), Bitwise inclusive OR and assignment operator(|=)
Examples of Assignment Operators in C
Examples of Assignment Operators are given below:
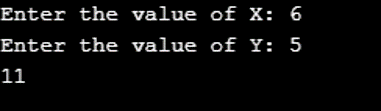
Program to implement the use of = operator:
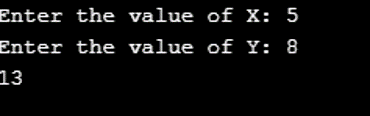
Program to implement the use of Add AND operator (+=) in C:
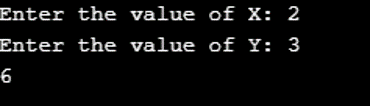
Program to use Subtract AND operator (- =) in C:

Program to use Multiply AND operator (*=) in C:
Program to use Divide AND operator (/=) in C:
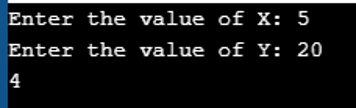
Program to use Modulus AND operator (%=) in C
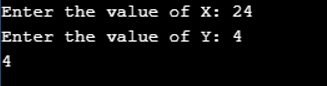
Program to use Left shift AND (<<=) operator in C
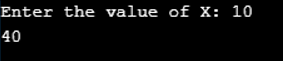
Program to use Right shift AND (>>=) operator in C
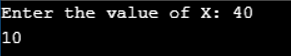
Program to use Bitwise AND assignment operator (&= ) in C
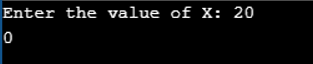
Example #10
Program to use Bitwise exclusive OR and assignment operator (^=)
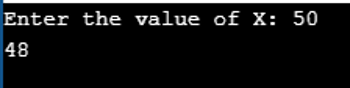
Example #11
Program to use Bitwise inclusive OR and assignment operator (|=) in C
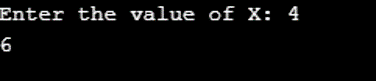
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Assignment Operators in C” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
- Logical Operators in C
- Logical Operators in C#
- Arithmetic Operators in Java
- JavaScript Assignment Operators

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW
C Functions
C structures, c reference, c operators.
Operators are used to perform operations on variables and values.
In the example below, we use the + operator to add together two values:
Although the + operator is often used to add together two values, like in the example above, it can also be used to add together a variable and a value, or a variable and another variable:
C divides the operators into the following groups:
- Arithmetic operators
- Assignment operators
- Comparison operators
- Logical operators
- Bitwise operators
Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform common mathematical operations.
| Operator | Name | Description | Example | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | Adds together two values | x + y | |
| - | Subtraction | Subtracts one value from another | x - y | |
| * | Multiplication | Multiplies two values | x * y | |
| / | Division | Divides one value by another | x / y | |
| % | Modulus | Returns the division remainder | x % y | |
| ++ | Increment | Increases the value of a variable by 1 | ++x | |
| -- | Decrement | Decreases the value of a variable by 1 | --x |
Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables.
In the example below, we use the assignment operator ( = ) to assign the value 10 to a variable called x :
The addition assignment operator ( += ) adds a value to a variable:
A list of all assignment operators:
| Operator | Example | Same As | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | x = 5 | x = 5 | |
| += | x += 3 | x = x + 3 | |
| -= | x -= 3 | x = x - 3 | |
| *= | x *= 3 | x = x * 3 | |
| /= | x /= 3 | x = x / 3 | |
| %= | x %= 3 | x = x % 3 | |
| &= | x &= 3 | x = x & 3 | |
| |= | x |= 3 | x = x | 3 | |
| ^= | x ^= 3 | x = x ^ 3 | |
| >>= | x >>= 3 | x = x >> 3 | |
| <<= | x <<= 3 | x = x << 3 |
Comparison Operators
Comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). This is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions.
The return value of a comparison is either 1 or 0 , which means true ( 1 ) or false ( 0 ). These values are known as Boolean values , and you will learn more about them in the Booleans and If..Else chapter.
Comparison operators are used to compare two values.
Note: The return value of a comparison is either true ( 1 ) or false ( 0 ).
In the following example, we use the greater than operator ( > ) to find out if 5 is greater than 3:
A list of all comparison operators:
| Operator | Name | Example | Description | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equal to | x == y | Returns 1 if the values are equal | |
| != | Not equal | x != y | Returns 1 if the values are not equal | |
| > | Greater than | x > y | Returns 1 if the first value is greater than the second value | |
| < | Less than | x < y | Returns 1 if the first value is less than the second value | |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | x >= y | Returns 1 if the first value is greater than, or equal to, the second value | |
| <= | Less than or equal to | x <= y | Returns 1 if the first value is less than, or equal to, the second value |
Logical Operators
You can also test for true or false values with logical operators.
Logical operators are used to determine the logic between variables or values, by combining multiple conditions:
| Operator | Name | Example | Description | Try it |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| && | AND | x < 5 && x < 10 | Returns 1 if both statements are true | |
| || | OR | x < 5 || x < 4 | Returns 1 if one of the statements is true | |
| ! | NOT | !(x < 5 && x < 10) | Reverse the result, returns 0 if the result is 1 |
C Exercises
Test yourself with exercises.
Fill in the blanks to multiply 10 with 5 , and print the result:
Start the Exercise

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
- Assignment Statement
An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program .
Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted by a variable name.

The symbol used in an assignment statement is called as an operator . The symbol is ‘=’ .
Note: The Assignment Operator should never be used for Equality purpose which is double equal sign ‘==’.
The Basic Syntax of Assignment Statement in a programming language is :
variable = expression ;
variable = variable name
expression = it could be either a direct value or a math expression/formula or a function call
Few programming languages such as Java, C, C++ require data type to be specified for the variable, so that it is easy to allocate memory space and store those values during program execution.
data_type variable_name = value ;
In the above-given examples, Variable ‘a’ is assigned a value in the same statement as per its defined data type. A data type is only declared for Variable ‘b’. In the 3 rd line of code, Variable ‘a’ is reassigned the value 25. The 4 th line of code assigns the value for Variable ‘b’.
Assignment Statement Forms
This is one of the most common forms of Assignment Statements. Here the Variable name is defined, initialized, and assigned a value in the same statement. This form is generally used when we want to use the Variable quite a few times and we do not want to change its value very frequently.
Tuple Assignment
Generally, we use this form when we want to define and assign values for more than 1 variable at the same time. This saves time and is an easy method. Note that here every individual variable has a different value assigned to it.
(Code In Python)
Sequence Assignment
(Code in Python)
Multiple-target Assignment or Chain Assignment
In this format, a single value is assigned to two or more variables.
Augmented Assignment
In this format, we use the combination of mathematical expressions and values for the Variable. Other augmented Assignment forms are: &=, -=, **=, etc.
Browse more Topics Under Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Concept of Data types
- Built-in Data Types
- Constants in Programing Language
- Access Modifier
- Variables of Built-in-Datatypes
- Declaration/Initialization of Variables
- Type Modifier
Few Rules for Assignment Statement
Few Rules to be followed while writing the Assignment Statements are:
- Variable names must begin with a letter, underscore, non-number character. Each language has its own conventions.
- The Data type defined and the variable value must match.
- A variable name once defined can only be used once in the program. You cannot define it again to store other types of value.
- If you assign a new value to an existing variable, it will overwrite the previous value and assign the new value.
FAQs on Assignment Statement
Q1. Which of the following shows the syntax of an assignment statement ?
- variablename = expression ;
- expression = variable ;
- datatype = variablename ;
- expression = datatype variable ;
Answer – Option A.
Q2. What is an expression ?
- Same as statement
- List of statements that make up a program
- Combination of literals, operators, variables, math formulas used to calculate a value
- Numbers expressed in digits
Answer – Option C.
Q3. What are the two steps that take place when an assignment statement is executed?
- Evaluate the expression, store the value in the variable
- Reserve memory, fill it with value
- Evaluate variable, store the result
- Store the value in the variable, evaluate the expression.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Variables in Programming Language
- Concept of Data Types
- Declaration of Variables
- Type Modifiers
- Access Modifiers
- Constants in Programming Language
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Video Walkthrough
You will work on the assignments for CS107 on the myth machines, which you access remotely. You'll initially make a copy of the starter project to modify, use command-line tools to edit and debug your code, and use some 107-specific tools like Sanity Check and Submit to test and submit your work. See below for the common steps you'll use to work on assignments.
Logging Into Myth
You will work on your programs in CS107 remotely on the myth machines, which are pre-installed with all the necessary development tools. Check out the getting started guide for how to log in remotely.
Starting An Assignment
For each assignment, you will first "clone" a copy of the assignment starter files into your own directory so you will be able to modify files. Some assignments will have randomized or user-specific data, and each student will have their own copy of the assignment to copy. The assignments are managed using a "version control system" called git ; we will not be focusing on git in CS107, but you can feel free to look into how git works if you're interested.
Note: Do not put any CS107 assignments online publicly on GitHub or any other publicly available website . This is a violation of the Stanford Honor Code.
To clone a copy of the assignment, first navigate to the directory where you would like to store the copy of the assignment. You may wish to create a CS107 folder, for instance, in your personal AFS space, using the mkdir command. Then, use the git clone command as follows:
This will make a folder named assign0 that you can then go into to start working on the assignment. You should type the above commands exactly as shown, including the odd-looking $USER at the end, but replacing assign0 with assign1 , assign2 , etc., depending on the assignment you are cloning. Now you can start working on the assignment!
Working On The Assignment
You'll use a variety of tools to work on the assignment, such as gdb (debugger) and make (compiling), that we'll introduce this quarter.
Using Sanity Check For Testing
As part of each assignment, we provide a testing program called "sanity check" that ensures you have worked on certain required files, and compares the output of your program to that of the provided sample executable and reports on discrepancies, allowing you to detect and address any issues before you submit. It also allows you to add your own custom tests.
To run the sanity check tool for a given assignment with our provided tests, first navigate to the directory containing the assignment you would like to test. Then, execute the tools/sanitycheck command as follows:
In the output, if a test fails, it will indicate either "MISMATCH" or "NOT OK". MISMATCH indicates that your program successfully ran to completion but the output it produced did not match the output produced by the sample. NOT OK reports that your program did not successfully complete (exited due to a fatal error or timed out) and its output was not compared to the sample.
- Passing sanity check suggests the autotester won't have problems interpreting your output, and that's good. If it doesn't match, you should fix your output to meet the required format so that your output is not misjudged in grading. To earn proper credit, your program must conform to the output specification given in the assignment writeup and match the behavior of our sample executable. Minor variations like different amounts of whitespace can usually be ignored, but changing the format, reordering output, or leaving behind extraneous print debugging statements will thwart the autotester and cause your program to be marked wrong. If sanitycheck fails when you run it on the final version you submit, you will lose points when we re-run that test when we grade the assignment. Just because sanitycheck passes does not mean that your assignment is correct, but failing a test means that it is not correct.
- There are a few situations, such as allowed latitude in the spec or equivalent re-wording of error messages, where a mismatch is not actually an error--- i.e. the program's behavior is a valid alternative to the sample, but sanity check doesn't know that. The autotester defers these cases to the judgment of the grading CA to identify whether such mismatches are true failures or harmless variation.
- You can run sanity check as many times as you need. Our submit tool will even encourage one final run before you submit.
- An additional benefit of running sanitycheck early and often is that it makes a snapshot of your code as a safety precaution. This backup replaces the original starter code generated for you, so you can re-clone the assignment using the same git clone command and get the last code you backed up.
Using Sanity Check With Your Own Custom Tests
The default tests supplied for sanity check may not be particularly rigorous nor comprehensive, so you will want to supplement with additional tests. You can create inputs of your own and write them into custom tests to be used by the sanitycheck tool. Create a text file using this format:
To run your custom tests, invoke sanitycheck with its optional argument, which is the name of the custom test file
When invoked with an argument, sanity check will use the test cases from the named file instead of the standard ones. For each custom test listed in the file, sanity check runs the sample solution with the given command-line arguments and captures its output, then runs your program with the same arguments to capture its output, and finally compares the two results and reports any mismatches.
Submitting An Assignment
Once you've finished working on an assignment, it's time to submit! The tools/submit command lets you submit your work right from myth . The submit tool verifies your project's readiness for submission. It will make the project to ensure there is no build failure and will offer you the option to run sanity check. If any part of verification fails, the submission is rejected and you must fix the issues and try submit again. Here's an example of using this command.
- If verification passes and submissions are being accepted, the project is submitted and a confirmation message indicates success. If the deadline has passed and grace period expired, the submission is rejected.
- To submit an updated version, just repeat the same steps. Only your most recent submission is graded.
- submitting performs the same backup process as sanity check.
- If you run into a submit failure that you cannot resolve, please seek help from the course staff. We recommend that you make a test submit well in advance of the deadline to confirm things will roll smoothly when the time comes.
Submission deadlines are firm. Cutting it too close runs the risk of landing on the wrong side -- don't let this happen to you! Submit early to give yourself a safety cushion and avoid the last-minute stress.
Assignment Tips
Be cautious with C: C is designed for high efficiency and unrestricted programmer control, with no emphasis on safety and little support for high-level abstractions. A C compiler won't complain about such things as uninitialized variables, narrowing conversions, or functions that fail to return a needed value. C has no runtime error support, which means no helpful messages when your code accesses an array out of bounds or dereferences an invalid pointer; such errors compile and execute with surprising results. Keep an eye out for problems that you may have previously depended on the language to detect for you.
Memory and pointers: Bugs related to memory and/or pointers can be tricky to resolve. Make sure you understand every part of your code that you write or change. Also keep in mind that the observable effects of a memory error can come at a place and time far removed from the root cause (i.e. running off the end of a array may "work fine" until you later read the contents of a supposedly unrelated variable). gdb and Valgrind can be extremely helpful in resolving these kinds of bugs. In particular, Valgrind is useful throughout the programming process, not just at the end. Valgrind reports on two types of memory issues: errors and leaks. Memory errors are toxic and should be found and fixed without delay. Memory leaks are of less concern and can be ignored early in development. Given that the wrong deallocation can wreak havoc, we recommend you write the initial code with all free() calls commented out. Much later, after having finished with the correct functionality and turning your attention to polishing, add in the free calls one at a time, run under Valgrind, and iterate until you verify complete and proper deallocation.
Use good style from the start : Always start with good decomposition, rather than adding it later. Sketch each function's role and have a rough idea of its inputs and outputs. A function should be designed to complete one well-defined task. If you can't describe the function's role in a sentence or two then maybe your function is doing too much and should be decomposed further. Commenting the function before you write the code may help you clarify your design (what the function does, what inputs it takes, and what outputs it produces, how it will be used). Start by using good variable names, rather than going through and changing them later. Using good style the first time makes your code better designed, easier to understand, and easier to debug.
Understand your code : At every step, you want to ensure that you understand the code you are writing, what it does, and how it works. Don't make changes without understanding why you are making them, and what the result will be.
Test : use our recommended testing techniques to incrementally develop your program, test at each step, and always have a working program.
Get help if you need it! : 107 has a lot of helpful resources, including written materials on the web site, textbook readings, lectures, labs, the online discussion forum, helper hours, and more. We are happy to help or answer your questions!
Frequently Asked Questions
How can i reproduce/debug a problem that appears during sanity check.
Look through the sanity check output to find the command being executed:
Run that same command (in shell, gdb, or Valgrind) to replicate the situation being tested. You can also view the file contents (such as the hymn file in the above command) to better understand what is being tested.

Is it possible to write a custom test to verify Valgrind correctness or memory/time efficiency?
Unfortunately not; custom sanity check tests compare on output only. You will need to supplement with other forms of testing to verify those additional requirements.
Can I submit a program that doesn't pass sanity check?
We strongly recommend that you resolve any sanity check failures before submitting, but the submit tool will not force you to do so. To submit a project doesn't pass sanity check, respond no when asked if you want to run sanity check, and the project will be submitted without that check.
How can I verify that my submission was successful?
Your gradebook page (accessible from the navigation bar at the top) lists the timestamp of the most recent submission we have received.
Although it is not necessary, if you would like to triple-check, you can view the contents of your submission by re-cloning your class repo. For example, navigate to your home directory and git clone /afs/ir/class/cs107/repos/assignN/$USER mysubmission . This will create a mysubmission directory that contains the files you submitted for assignN (be sure to replace N with the assignment number). If you're satisfied that everything is as intended in mysubmission , then you're done and you can delete the mysubmission directory. If not, figure out what's not right, fix it, and submit again.
cppreference.com
Assignment operators.
| (C11) | ||||
| Miscellaneous | ||||
| General | ||||
| (C11) | ||||
| (C99) | ||||
Assignment and compound assignment operators are binary operators that modify the variable to their left using the value to their right.
| Operator | Operator name | Example | Description | Equivalent of |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| = | basic assignment | a = b | becomes equal to | |
| += | addition assignment | a += b | becomes equal to the addition of and | a = a + b |
| -= | subtraction assignment | a -= b | becomes equal to the subtraction of from | a = a - b |
| *= | multiplication assignment | a *= b | becomes equal to the product of and | a = a * b |
| /= | division assignment | a /= b | becomes equal to the division of by | a = a / b |
| %= | modulo assignment | a %= b | becomes equal to the remainder of divided by | a = a % b |
| &= | bitwise AND assignment | a &= b | becomes equal to the bitwise AND of and | a = a & b |
| |= | bitwise OR assignment | a |= b | becomes equal to the bitwise OR of and | a = a | b |
| ^= | bitwise XOR assignment | a ^= b | becomes equal to the bitwise XOR of and | a = a ^ b |
| <<= | bitwise left shift assignment | a <<= b | becomes equal to left shifted by | a = a << b |
| >>= | bitwise right shift assignment | a >>= b | becomes equal to right shifted by | a = a >> b |
| Simple assignment Notes Compound assignment References See Also See also |
[ edit ] Simple assignment
The simple assignment operator expressions have the form
| lhs rhs | |||||||||
| lhs | - | expression of any complete object type |
| rhs | - | expression of any type to lhs or with lhs |
Assignment performs implicit conversion from the value of rhs to the type of lhs and then replaces the value in the object designated by lhs with the converted value of rhs .
Assignment also returns the same value as what was stored in lhs (so that expressions such as a = b = c are possible). The value category of the assignment operator is non-lvalue (so that expressions such as ( a = b ) = c are invalid).
rhs and lhs must satisfy one of the following:
- both lhs and rhs have compatible struct or union type, or..
- rhs must be implicitly convertible to lhs , which implies
- both lhs and rhs have arithmetic types , in which case lhs may be volatile -qualified or atomic (since C11)
- both lhs and rhs have pointer to compatible (ignoring qualifiers) types, or one of the pointers is a pointer to void, and the conversion would not add qualifiers to the pointed-to type. lhs may be volatile or restrict (since C99) -qualified or atomic (since C11) .
- lhs is a (possibly qualified or atomic (since C11) ) pointer and rhs is a null pointer constant such as NULL or a nullptr_t value (since C23)
| has type (possibly qualified or atomic(since C11)) _Bool and rhs is a pointer or a value(since C23) | (since C99) |
| has type (possibly qualified or atomic) and rhs has type | (since C23) |
[ edit ] Notes
If rhs and lhs overlap in memory (e.g. they are members of the same union), the behavior is undefined unless the overlap is exact and the types are compatible .
Although arrays are not assignable, an array wrapped in a struct is assignable to another object of the same (or compatible) struct type.
The side effect of updating lhs is sequenced after the value computations, but not the side effects of lhs and rhs themselves and the evaluations of the operands are, as usual, unsequenced relative to each other (so the expressions such as i = ++ i ; are undefined)
Assignment strips extra range and precision from floating-point expressions (see FLT_EVAL_METHOD ).
In C++, assignment operators are lvalue expressions, not so in C.
[ edit ] Compound assignment
The compound assignment operator expressions have the form
| lhs op rhs | |||||||||
| op | - | one of *=, /= %=, += -=, <<=, >>=, &=, ^=, |= |
| lhs, rhs | - | expressions with (where lhs may be qualified or atomic), except when op is += or -=, which also accept pointer types with the same restrictions as + and - |
The expression lhs @= rhs is exactly the same as lhs = lhs @ ( rhs ) , except that lhs is evaluated only once.
| If lhs has type, the operation behaves as a single atomic read-modify-write operation with memory order . For integer atomic types, the compound assignment @= is equivalent to: addr = &lhs; T2 val = rhs; T1 old = *addr; T1 new; do { new = old @ val } while (! (addr, &old, new); | (since C11) |
[ edit ] References
- C17 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2018):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 72-73)
- C11 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2011):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 101-104)
- C99 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:1999):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 91-93)
- C89/C90 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:1990):
- 3.3.16 Assignment operators
[ edit ] See Also
Operator precedence
| Common operators | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a = b | ++a | +a | !a | a == b | a[b] | a(...) |
[ edit ] See also
| for Assignment operators |
- Recent changes
- Offline version
- What links here
- Related changes
- Upload file
- Special pages
- Printable version
- Permanent link
- Page information
- In other languages
- This page was last modified on 19 August 2022, at 09:36.
- This page has been accessed 58,085 times.
- Privacy policy
- About cppreference.com
- Disclaimers
Assignment Statement in C
How to assign values to the variables? C provides an assignment operator for this purpose, assigning the value to a variable using assignment operator is known as an assignment statement in C.
The function of this operator is to assign the values or values in variables on right hand side of an expression to variables on the left hand side.
The syntax of the assignment expression
Variable = constant / variable/ expression;
The data type of the variable on left hand side should match the data type of constant/variable/expression on right hand side with a few exceptions where automatic type conversions are possible.
Examples of assignment statements,
b = c ; /* b is assigned the value of c */ a = 9 ; /* a is assigned the value 9*/ b = c+5; /* b is assigned the value of expr c+5 */
The expression on the right hand side of the assignment statement can be:
An arithmetic expression; A relational expression; A logical expression; A mixed expression.
The above mentioned expressions are different in terms of the type of operators connecting the variables and constants on the right hand side of the variable. Arithmetic operators, relational
Arithmetic operators, relational operators and logical operators are discussed in the following sections.
For example, int a; float b,c ,avg, t; avg = (b+c) / 2; /*arithmetic expression */ a = b && c; /*logical expression*/ a = (b+c) && (b<c); /* mixed expression*/
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Related Posts
- #define to implement constants
- Preprocessor in C Language
- Pointers and Strings
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- C All Exercises & Assignments
Write a C program to check whether a number is even or odd
Description:
Write a C program to check whether a number is even or odd.
Note: Even number is divided by 2 and give the remainder 0 but odd number is not divisible by 2 for eg. 4 is divisible by 2 and 9 is not divisible by 2.
Conditions:
- Create a variable with name of number.
- Take value from user for number variable.
Enter the Number=9 Number is Odd.
Write a C program to swap value of two variables using the third variable.
You need to create a C program to swap values of two variables using the third variable.
You can use a temp variable as a blank variable to swap the value of x and y.
- Take three variables for eg. x, y and temp.
- Swap the value of x and y variable.
Write a C program to check whether a user is eligible to vote or not.
You need to create a C program to check whether a user is eligible to vote or not.
- Minimum age required for voting is 18.
- You can use decision making statement.
Enter your age=28 User is eligible to vote
Write a C program to check whether an alphabet is Vowel or Consonant
You need to create a C program to check whether an alphabet is Vowel or Consonant.
- Create a character type variable with name of alphabet and take the value from the user.
- You can use conditional statements.
Enter an alphabet: O O is a vowel.
Write a C program to find the maximum number between three numbers
You need to write a C program to find the maximum number between three numbers.
- Create three variables in c with name of number1, number2 and number3
- Find out the maximum number using the nested if-else statement
Enter three numbers: 10 20 30 Number3 is max with value of 30
Write a C program to check whether number is positive, negative or zero
You need to write a C program to check whether number is positive, negative or zero
- Create variable with name of number and the value will taken by user or console
- Create this c program code using else if ladder statement
Enter a number : 10 10 is positive
Write a C program to calculate Electricity bill.
You need to write a C program to calculate electricity bill using if-else statements.
- For first 50 units – Rs. 3.50/unit
- For next 100 units – Rs. 4.00/unit
- For next 100 units – Rs. 5.20/unit
- For units above 250 – Rs. 6.50/unit
- You can use conditional statements.
Enter the units consumed=278.90 Electricity Bill=1282.84 Rupees
Write a C program to print 1 to 10 numbers using the while loop
You need to create a C program to print 1 to 10 numbers using the while loop
- Create a variable for the loop iteration
- Use increment operator in while loop
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
- C Exercises Categories
- C Top Exercises
- C Decision Making
Class of 2028!
Are you getting excited for Fall 2024?
Read our Move-In Guide and check out our Summer Orientation Presentation for everything you need to know leading up to move-in!
Move-In Guide
Orientation Resources & Presentation

Essential Tips for Carolina Housing Assignments
By: Jordan Cady, with Matt Bertram
Welcome to Carolina Housing! Whether you’re a transfer student, an incoming first-year, or a returning student, understanding the housing assignment process is crucial for a smooth experience. My name is Jordan Cady, the Assistant Director for Assignments with Carolina Housing, and I’m here to guide you through the key points you need to know.
Priority Deadlines
One of the most important things to keep in mind is your priority deadlines. Carolina Housing runs various housing processes throughout the year, including returning room selection, first-year assignments, summer housing, and sometimes even winter break housing. Each of these processes comes with its own priority deadline.
• First-year students: The priority deadline is typically in May.
• Returning students: The priority deadline for the next academic year usually falls between October and November.
Make sure you know your specific deadline to maximize your chances of securing your preferred housing.
Communication Through UNC Email
We communicate all housing-related information via your UNC email. This includes move-in and move-out details, opportunities for room reassignment, and closure notices. It’s essential to regularly check your UNC email to stay informed and avoid missing important updates. While we do offer a newsletter for parents, all official communications are directed to your UNC email.
Understanding Your Housing Contract
Every housing application concludes with signing a housing contract. This contract includes critical information such as:
• Bill proration
• Cancellation penalties
• Rights and responsibilities of both you and Carolina Housing
Reviewing the contract thoroughly before signing is a good practice to ensure you understand all terms and conditions.
Resources and Support
Our processes vary depending on whether you’re a first-year student applying in the summer or a returning student applying in the fall. For detailed information tailored to your specific situation, explore our website, call us, or stop by our office. The assignments team is dedicated to making your housing experience as easy and comfortable as possible. We’re here to help with any questions regarding billing, room changes, room contents, and move-in procedures.
We’re excited to have you with us and look forward to meeting you. Welcome back or welcome to Carolina Housing!

Assignments in Viva Learning
Assignments in Viva Learning refer to courses that your organization marks as mandatory for learners.
Note: Assignments are shown only to users with Viva learning premium license.
Where to find your assignments
The card on the home page
Assigned to section in My Learning
Assignment details are also shown on the details page of a Learning object
Progress tracking in Viva Learning Personalize your learning with Viva Learning Discover Viva Learning content

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Understanding the assignment: For Pirates' veterans, rehab a chance to pay it forward

Kevin Gorman is a TribLive reporter covering the Pirates. A Baldwin native and Penn State graduate, he joined the Trib in 1999 and has covered high school sports, Pitt football and basketball and was a sports columnist for 10 years. He can be reached at [email protected] .
Remove the ads from your TribLIVE reading experience but still support the journalists who create the content with TribLIVE Ad-Free.
Get Ad-Free >
Sign Up for Notifications
Stay up-to-date on important news from TribLIVE
TribLIVE's Daily and Weekly email newsletters deliver the news you want and information you need, right to your inbox.
News Spotlight
- How to Select the Best Commercial Cleaning Service for Your Business BergTown Family Cleaning Partner News
- Pressure and Soft Washing in Westmoreland & Allegheny, PA Keystone Pressure Washing & Roof Cleaning, LLC Partner News
- David McCullough, Pulitzer-winning historian and Pittsburgh native, dies at 89 TribLive
- How to Maintain and Care for Your Granite and Natural Stone Countertops Vangura Partner News
- Nicholas Castellanos vs. Cubs Preview, Player Prop Bets - July 3 TribLive
- Brian Boyle grateful for another chance at the NHL with the Penguins TribLive
- What is a Live Podcast Theater? Poduty Live's Podcast Theater Partner News
- Cody Bellinger vs. Phillies Preview, Player Prop Bets - July 3 TribLive
- Riley Greene vs. Twins Preview, Player Prop Bets - July 3 TribLive
- How to Choose the Right Arborist for Your Tree Care Needs BeaverJack Tree Service, LLC Partner News
Everywhere Assignments: What You Need to Know About Assigning Construction Contracts and and Claims
Karly A. Houchin
ARTICLE 1 July 2024
This paper provides a foundation for construction lawyers navigating their way through assignments and pass-through claims. Readers will gain clarity on which claims can and cannot be assigned, the types of pass-through claims allowed in Texas, and the statutory schemes and equitable doctrines crucial for advising clients effectively.
Download Assigning Claims and Contracts in Texas at https://www.allensworthlaw.com/legal-updates/sign-sign-everywhere-assignments-what-you-need-to-know-about-assigning-construction-contracts-and-claims/
C Data Types
C operators.
- C Input and Output
- C Control Flow
- C Functions
- C Preprocessors
C File Handling
- C Cheatsheet
C Interview Questions
- C Programming Language Tutorial
C Language Introduction
- Features of C Programming Language
- C Programming Language Standard
- C Hello World Program
- Compiling a C Program: Behind the Scenes
- Tokens in C
- Keywords in C
C Variables and Constants
- C Variables
- Constants in C
- Const Qualifier in C
- Different ways to declare variable as constant in C
- Scope rules in C
- Internal Linkage and External Linkage in C
- Global Variables in C
- Data Types in C
- Literals in C
- Escape Sequence in C
- Integer Promotions in C
- Character Arithmetic in C
- Type Conversion in C
C Input/Output
- Basic Input and Output in C
- Format Specifiers in C
- printf in C
- Scansets in C
- Formatted and Unformatted Input/Output functions in C with Examples
- Operators in C
- Arithmetic Operators in C
- Unary operators in C
- Relational Operators in C
- Bitwise Operators in C
- C Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators in C
- Increment and Decrement Operators in C
- Conditional or Ternary Operator (?:) in C
- sizeof operator in C
- Operator Precedence and Associativity in C
C Control Statements Decision-Making
- Decision Making in C (if , if..else, Nested if, if-else-if )
- C - if Statement
- C if...else Statement
- C if else if ladder
- Switch Statement in C
- Using Range in switch Case in C
- while loop in C
- do...while Loop in C
- For Versus While
- Continue Statement in C
- Break Statement in C
- goto Statement in C
- User-Defined Function in C
- Parameter Passing Techniques in C
- Function Prototype in C
- How can I return multiple values from a function?
- main Function in C
- Implicit return type int in C
- Callbacks in C
- Nested functions in C
- Variadic functions in C
- _Noreturn function specifier in C
- Predefined Identifier __func__ in C
- C Library math.h Functions
C Arrays & Strings
- Properties of Array in C
- Multidimensional Arrays in C
- Initialization of Multidimensional Array in C
- Pass Array to Functions in C
- How to pass a 2D array as a parameter in C?
- What are the data types for which it is not possible to create an array?
- How to pass an array by value in C ?
- Strings in C
- Array of Strings in C
- What is the difference between single quoted and double quoted declaration of char array?
- C String Functions
- Pointer Arithmetics in C with Examples
- C - Pointer to Pointer (Double Pointer)
- Function Pointer in C
- How to declare a pointer to a function?
- Pointer to an Array | Array Pointer
- Difference between constant pointer, pointers to constant, and constant pointers to constants
- Pointer vs Array in C
- Dangling, Void , Null and Wild Pointers in C
- Near, Far and Huge Pointers in C
- restrict keyword in C
C User-Defined Data Types
- C Structures
- dot (.) Operator in C
- Structure Member Alignment, Padding and Data Packing
- Flexible Array Members in a structure in C
- Bit Fields in C
- Difference Between Structure and Union in C
- Anonymous Union and Structure in C
- Enumeration (or enum) in C
C Storage Classes
- Storage Classes in C
- extern Keyword in C
- Static Variables in C
- Initialization of static variables in C
- Static functions in C
- Understanding "volatile" qualifier in C | Set 2 (Examples)
- Understanding "register" keyword in C
C Memory Management
- Memory Layout of C Programs
- Dynamic Memory Allocation in C using malloc(), calloc(), free() and realloc()
- Difference Between malloc() and calloc() with Examples
- What is Memory Leak? How can we avoid?
- Dynamic Array in C
- How to dynamically allocate a 2D array in C?
- Dynamically Growing Array in C
C Preprocessor
- C Preprocessor Directives
- How a Preprocessor works in C?
- Header Files in C
- What’s difference between header files "stdio.h" and "stdlib.h" ?
- How to write your own header file in C?
- Macros and its types in C
- Interesting Facts about Macros and Preprocessors in C
- # and ## Operators in C
- How to print a variable name in C?
- Multiline macros in C
- Variable length arguments for Macros
- Branch prediction macros in GCC
- typedef versus #define in C
- Difference between #define and const in C?
- Basics of File Handling in C
- C fopen() function with Examples
- EOF, getc() and feof() in C
- fgets() and gets() in C language
- fseek() vs rewind() in C
- What is return type of getchar(), fgetc() and getc() ?
- Read/Write Structure From/to a File in C
- C Program to print contents of file
- C program to delete a file
- C Program to merge contents of two files into a third file
- What is the difference between printf, sprintf and fprintf?
- Difference between getc(), getchar(), getch() and getche()
Miscellaneous
- time.h header file in C with Examples
- Input-output system calls in C | Create, Open, Close, Read, Write
- Signals in C language
- Program error signals
- Socket Programming in C
- _Generics Keyword in C
- Multithreading in C
- C Programming Interview Questions (2024)
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 1
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 2
- Commonly Asked C Programming Interview Questions | Set 3
C is a procedural programming language initially developed by Dennis Ritchie in the year 1972 at Bell Laboratories of AT&T Labs. It was mainly developed as a system programming language to write the UNIX operating system.
The main features of the C language include:
- General Purpose and Portable
- Low-level Memory Access
- Clean Syntax
These features make the C language suitable for system programming like an operating system or compiler development.
Why Should We Learn C?
Many later languages have borrowed syntax/features directly or indirectly from the C language. Like syntax of Java, PHP, JavaScript, and many other languages are mainly based on the C language. C++ is nearly a superset of C language (Only a few programs may compile in C, but not in C++).
So, if a person learns C programming first, it will help him to learn any modern programming language as well. As learning C help to understand a lot of the underlying architecture of the operating system. Like pointers, working with memory locations, etc.
Get Started with C Learn C fundamentals and advanced concepts, then solve practical problems right in your browser window with Educative’s interactive skill path Become a C Programmer. Sign up at Educative.io with the code GEEKS10 to save 10% on your subscription.
Difference Between C and C++
C++ was created to add the OOPs concept into C language so they both have very similar syntax but both are a bit different from each other. Following are some main differences between C and C++ Programming language.
- C++ supports OOPs paradigm while C only have procedural concept of programming.
- C++ have exception handling capablities. In C, we have to resolve manually.
- There are no references in C.
There are many more differences between C and C++ which are discussed here: Difference between C and C++
Beginning with C Programming
Writing the first program in c.
The following code is one of the simplest C programs that will help us the basic syntax structure of a C program.
Let us analyze the structure of our program line by line.
Structure of the C program
After the above discussion, we can formally assess the structure of a C program. By structure, it is meant that any program can be written in this structure only. Writing a C program in any other structure will hence lead to a Compilation Error. The structure of a C program is as follows:
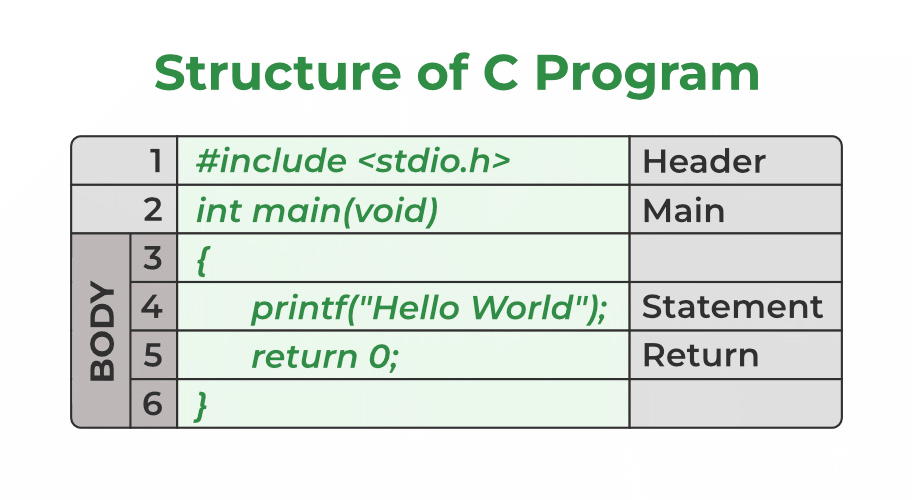
Components of a C Program:
1. header files inclusion – line 1 [#include <stdio.h>].
The first and foremost component is the inclusion of the Header files in a C program. A header file is a file with extension .h which contains C function declarations and macro definitions to be shared between several source files. All lines that start with # are processed by a preprocessor which is a program invoked by the compiler. In the above example, the preprocessor copies the preprocessed code of stdio.h to our file. The .h files are called header files in C. Some of the C Header files:
- stddef.h – Defines several useful types and macros.
- stdint.h – Defines exact width integer types.
- stdio.h – Defines core input and output functions
- stdlib.h – Defines numeric conversion functions, pseudo-random number generator, and memory allocation
- string.h – Defines string handling functions
- math.h – Defines common mathematical functions.
2. Main Method Declaration – Line 2 [int main()]
The next part of a C program is to declare the main() function. It is the entry point of a C program and the execution typically begins with the first line of the main(). The empty brackets indicate that the main doesn’t take any parameter (See this for more details). The int that was written before the main indicates the return type of main(). The value returned by the main indicates the status of program termination. See this post for more details on the return type.
3. Body of Main Method – Line 3 to Line 6 [enclosed in {}]
The body of a function in the C program refers to statements that are a part of that function. It can be anything like manipulations, searching, sorting, printing, etc. A pair of curly brackets define the body of a function. All functions must start and end with curly brackets.
4. Statement – Line 4 [printf(“Hello World”);]
Statements are the instructions given to the compiler. In C, a statement is always terminated by a semicolon (;). In this particular case, we use printf() function to instruct the compiler to display “Hello World” text on the screen.
5. Return Statement – Line 5 [return 0;]
The last part of any C function is the return statement. The return statement refers to the return values from a function. This return statement and return value depend upon the return type of the function. The return statement in our program returns the value from main(). The returned value may be used by an operating system to know the termination status of your program. The value 0 typically means successful termination.
How to Execute the Above Program?
In order to execute the above program, we need to first compile it using a compiler and then we can run the generated executable. There are online IDEs available for free like GeeksforGeeksIDE , that can be used to start development in C without installing a compiler.
- Windows: There are many free IDEs available for developing programs in C like Code Blocks and Dev-CPP . IDEs provide us with an environment to develop code, compile it and finally execute it. We strongly recommend Code Blocks.
- Linux: GCC compiler comes bundled with Linux which compiles C programs and generates executables for us to run. Code Blocks can also be used with Linux.
- macOS: macOS already has a built-in text editor where you can just simply write the code and save it with a “.c” extension.
Application of C
- Operating systems: C is widely used for developing operating systems such as Unix, Linux, and Windows.
- Embedded systems: C is a popular language for developing embedded systems such as microcontrollers, microprocessors, and other electronic devices.
- System software: C is used for developing system software such as device drivers, compilers, and assemblers.
- Networking: C is widely used for developing networking applications such as web servers, network protocols, and network drivers.
- Database systems: C is used for developing database systems such as Oracle, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
- Gaming: C is often used for developing computer games due to its ability to handle low-level hardware interactions.
- Artificial Intelligence: C is used for developing artificial intelligence and machine learning applications such as neural networks and deep learning algorithms.
- Scientific applications: C is used for developing scientific applications such as simulation software and numerical analysis tools.
- Financial applications: C is used for developing financial applications such as stock market analysis and trading systems.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads, improve your coding skills with practice.
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
C assignments in an 'if' statement
I came across this line of code written in C that confuses me coming from a JavaScript background.
Is this assigning s to data[q] , and if it equals true/1, return s?
- 3 Yes, you are right. This has been discussed here – byxor Commented Sep 2, 2016 at 10:14
- basically it returns s as long as data[q] is != 0. In C, everything except 0 is true. (of course s is assigned data[q]). – Nidhoegger Commented Sep 2, 2016 at 10:15
3 Answers 3
Yes, an assignment...well assigns...but it's also an expression. Any value not equalling zero will be evaluated as true and zero as false.
it would be the same as
- 2 "Evaluated as 1" is really confusing, it's more like "any non-zero value will be considered to be true". – unwind Commented Sep 2, 2016 at 10:18
Your code is assigning data[q] to s and then returns s to the if statement. In the case when s is not equal to 0 your code returns s otherwise it goes to the next instruction.
Or better said it would expand to the following:
- Oh that's interesting. So any other value than 0? Because what I learned from JavaScript is if (true) return something. – cocacrave Commented Sep 2, 2016 at 15:36
- Every value which is not 0 is considered true in C. – Adrian Jałoszewski Commented Sep 2, 2016 at 15:37
Basically C evaluates expressions. In
The value of data[q] is the the value of expression here and the condition is evaluated based on that.
The assignment
is just a side-effect .
Read this [ article ] on sequence points and side-effects
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged c or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Community Products Roadmap Update, July 2024
- Featured on Meta
- We spent a sprint addressing your requests — here’s how it went
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network...
- Policy: Generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT) is banned
- The [lib] tag is being burninated
- What makes a homepage useful for logged-in users
Hot Network Questions
- How does the temperature of the condenser impact an air conditioner's energy usage?
- When do you know things are actually going poorly in graduate school?
- Guessing whether the revealed number is higher
- In-Place Reordering of Doubly Linked List Nodes to Ensure Memory Contiguity
- How does the common pins on rotary DIP switches work
- Naming - Lists - All elements except the last
- Why danach instead of darüber?
- Why do we use real numbers for (for example) masses in physics and how do we verify product axioms?
- Is intuitionistic mathematics situated in time?
- Align 3 tables neatly
- Sitting on a desk or at a desk? What's the diffrence?
- Can someone please translate this commentary by Malbim on Psalm 86:12
- Filling holes with original geometry patches after heavy alterations
- what does たし mean here?
- Making a node in TikZ occupy the vertical space of one line - at least as far as positioning a "pin" is concerned
- Why didn't Jimmy Neutron realize immediately when he read the note on the refrigerator that the note is phony, as the note says "son or daughter..."?
- Where is the pentagon in the Fibonacci sequence?
- Is it possible to "label" Segwit spendable output ScriptPubKeys with arbitrary bytes?
- How do I close a phantom window that is leftover from compiz (I think?)
- I want to leave my current job during probation but I don't want to tell the next interviewer I am currently working
- Hourly pay rate calculation between Recruiting and Payroll Systems
- My previously healthy avocado plant was pruned bare and has since been turning brown on top
- What does a D&D Beyond Digital Code do and is it worth it?
- If a lambda is declared as a default argument, is it different for each call site?
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Veteran shortstop, former AL batting champ Tim Anderson designated for assignment by Marlins
Philadelphia Phillies’ Nick Castellanos, right, steals second past Miami Marlins shortstop Tim Anderson during the seventh inning of a baseball game, Friday, June 28, 2024, in Philadelphia. (AP Photo/Matt Slocum)
- Copy Link copied
MIAMI (AP) — Veteran shortstop and former AL batting champ Tim Anderson was designated for assignment by the Miami Marlins on Tuesday.
Anderson struggled offensively throughout his 65-game stint in Miami, hitting .214 in 234 at-bats with three extra-base hits.
“It’s never an easy day when you have to DFA one of your everyday players,” Marlins manager Skip Schumaker said before a series-opening game against Boston. “Tim was awesome in the clubhouse. I didn’t know him before this year and he was one of the harder workers I’ve ever been around.”
Anderson didn’t fulfill the offensive expectations the Marlins anticipated when he signed a one-year free agent deal. The 31-year-old Anderson played his first eight seasons with the Chicago White Sox and batted over .300 four consecutive years. In 2019, Anderson hit .335 and won the AL batting title.
Injuries and a drop-off in production affected Anderson’s final season in Chicago. The White Sox declined the $14 million club option on Anderson’s contract and he became a free agent.
First-year Marlins president Peter Bendix made Anderson his first notable free agent addition, signing him to a one-year $5 million deal in February.
“It’s one thing if the guy’s not putting in the work and that’s an easy move. This was not one of those cases,” Schumaker said. “Tough day for us and I hope he lands on his feet somewhere because he’s still young and still has a lot to give to the game.”
The Marlins recalled infielder Xavier Edwards from Triple-A Jacksonville to take Anderson’s spot on the roster.
AP MLB: https://apnews.com/hub/mlb
Los Angeles Angels | Angels’ Rendon could be ready before All-Star…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- High School
Los Angeles Angels
Los angeles angels | angels’ rendon could be ready before all-star break after more than 2 months out, the oft-injured third baseman is not expected to take a minor league rehab assignment, although manager ron washington says he would like him to.

As the team plays at Oakland and Chicago to face the Cubs over the next week, Rendon will put the finishing touches on his rehab from a partial tear in his hamstring that has kept him out for more than two months.
The major step will come next weekend when Rendon faces live pitching in a controlled setting at Angel Stadium either Thursday and Friday, or Friday and Saturday, according to Manager Ron Washington. As recently as last week, the Angels hoped Rendon could face live pitching this weekend, but that plan was adjusted to have him stay home during the road trip when he could see pitchers on consecutive days.
“When we come back, hopefully, he’ll be ready to go right before the All-Star break,” Washington said.
As of now, it does not appear as if Rendon will go out on a minor league rehab assignment.
“They’re still trying to decide; trying to talk him into it,” Washington said. “Now, it’s the player’s decision. And you can talk to them all you want. If they decide they don’t want to go. … I’m not going to beat a dead horse. I’m not going to make that an issue because he doesn’t want to go on a rehab assignment. You got the right to decide if you want to go or not.”
Three-time American League MVP Mike Trout has similarly avoided going on minor league rehab assignments in recent seasons, last playing in an official minor league game in 2017 when he was on the mend from thumb surgery.
Washington, who has brought an old-school culture back to the Angels this season, admitted to a preference for injury rehab assignments for hitters.
“I’m not gonna make that an issue,” Washington said. “Yeah, inside of me, it’s bothering me, but I’m not gonna make that an issue because there is nothing I can do about it. It’s the law. So I’m going to go with the law.
“You would hope that he would go … but if he doesn’t want to go, that’s not going to be an issue for me. I have enough stuff (going on) to be worried about something like that.”
ALMOST THERE
Infielder Brandon Drury, who has been out for nearly two weeks with an upper respiratory illness, could be in the starting lineup as early as Tuesday at Oakland. Washington said Drury was available off the bench Saturday and gave him a pinch-hit appearance on Sunday. Drury struck out to end the sixth inning.
Drury last played in a game June 18, and while he has been struggling this season, with a .173 batting average and .233 on-base percentage, he did have a hit in three of his last four games.
Even with Drury’s return, and the plan to activate Rendon soon, Washington still intends to get as much playing time as possible for Luis Rengifo, including at designated hitter if it warrants.
Rengifo entered Sunday’s game batting .329 since June 9, a span of 18 games, with home runs in the first two games of the series against the Tigers.
NEW FRIENDS
The Anaheim Ducks’ two first-round draft picks participated in a dual first-pitch ceremony with forward Beckett Sennecke and defenseman Stian Solberg each having the honor. Sennecke, a native of Canada, was the No. 3 overall selection Friday, while Solberg, a native of Norway was selected with the No. 23 pick.
Both players wore the team’s new primarily orange jersey with the menacing duck-billed retro goalie mask.
Also throwing out a separate first pitch was Galaxy defender Eriq Zavaleta, who was participating in the Angels’ El Salvadorian heritage celebration.
Angels are off Monday.
Angels (RHP Jose Soriano, 4-5, 3.48 ERA) at Oakland (RHP Mitch Spence, 4-4, 4.35 ERA), Tuesday, 6:40 p.m., Bally Sports West, 830 AM
- Newsroom Guidelines
- Report an Error
More in Los Angeles Angels

SUBSCRIBER ONLY
Los angeles angels | angels done in by sloppy defense and anemic hitting in loss to a’s.

Los Angeles Angels | Angels first baseman Nolan Schanuel’s confidence soars with recent hot streak

Los Angeles Angels | Angels’ José Soriano allows 4 runs in his return from injured list

Los Angeles Angels | Demoted Angels starter Reid Detmers making strides toward a return

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Different types of assignment operators are shown below: 1. "=": This is the simplest assignment operator. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. Example: a = 10; b = 20; ch = 'y'; 2. "+=": This operator is combination of '+' and '=' operators. This operator first adds the current ...
Simple assignment operator. Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand. C = A + B will assign the value of A + B to C. +=. Add AND assignment operator. It adds the right operand to the left operand and assign the result to the left operand. C += A is equivalent to C = C + A. -=.
Assignment Operators in C are used to assign values to the variables. They come under the category of binary operators as they require two operands to operate upon. The left side operand is called a variable and the right side operand is the value. The value on the right side of the "=" is assigned to the variable on the left side of "=".
7 Assignment Expressions. As a general concept in programming, an assignment is a construct that stores a new value into a place where values can be stored—for instance, in a variable. Such places are called lvalues (see Lvalues) because they are locations that hold a value. An assignment in C is an expression because it has a value; we call it an assignment expression.
An assignment expression has the value of the left operand after the assignment. It's to allow things like this: a = b = c; (although there's some debate as to whether code like that is a good thing or not.) Incidentally, this behaviour is replicated in Java (and I would bet that it's the same in C# too). edited Feb 20, 2017 at 8:59.
The assignment operators in C can both transform and assign values in a single operation. C provides the following assignment operators: | =. In assignment, the type of the right-hand value is converted to the type of the left-hand value, and the value is stored in the left operand after the assignment has taken place.
Assignment Operators In C. Assignment operators is a binary operator which is used to assign values in a variable, with its right and left sides being a one-one operand. The operand on the left side is variable in which the value is assigned and the right side operands can contain any of the constant, variable, and expression. Example -: x = 18 ...
The assignment operator in C, denoted by the equals sign (=), is used to assign a value to a variable. It is a fundamental operation that allows programmers to store data in variables for further use in their code. In addition to the simple assignment operator, C provides compound assignment operators that combine arithmetic or bitwise ...
Code language:C++(cpp) The = assignment operator is called a simple assignment operator. It assigns the value of the left operand to the right operand. Besides the simple assignment operator, C supports compound assignment operators. A compound assignment operator performs the operation specified by the additional operator and then assigns the ...
Introduction to Assignment Operators in C. Assignment operators are used for assigning value to the variable. Like any other operator, C also supports Assignment Operator which is a binary operator that operates on any two operands. It has two values such as the right value and the left value. It has lower precedence than all available ...
Comparison operators are used to compare two values (or variables). This is important in programming, because it helps us to find answers and make decisions. The return value of a comparison is either 1 or 0, which means true ( 1) or false ( 0 ). These values are known as Boolean values, and you will learn more about them in the Booleans and If ...
Assignment Statement. An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program. Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted.
5. Assignment Operators in C. Assignment operators are used to assign value to a variable. The left side operand of the assignment operator is a variable and the right side operand of the assignment operator is a value. The value on the right side must be of the same data type as the variable on the left side otherwise the compiler will raise ...
Shorthand assignment operator combines one of the arithmetic or bitwise operators with assignment operator. For example, consider following C statements. int a = 5; a = a + 2; The above expression a = a + 2 is equivalent to a += 2. Similarly, there are many shorthand assignment operators. Below is a list of shorthand assignment operators in C.
Assignment Tips. Be cautious with C: C is designed for high efficiency and unrestricted programmer control, with no emphasis on safety and little support for high-level abstractions. A C compiler won't complain about such things as uninitialized variables, narrowing conversions, or functions that fail to return a needed value. ...
Assignment operators are used in programming to assign values to variables. We use an assignment operator to store and update data within a program. They enable programmers to store data in variables and manipulate that data. The most common assignment operator is the equals sign (=), which assigns the value on the right side of the operator to ...
Assignment performs implicit conversion from the value of rhs to the type of lhs and then replaces the value in the object designated by lhs with the converted value of rhs . Assignment also returns the same value as what was stored in lhs (so that expressions such as a = b = c are possible). The value category of the assignment operator is non ...
C provides an assignment operator for this purpose, assigning the value to a variable using assignment operator is known as an assignment statement in C. The function of this operator is to assign the values or values in variables on right hand side of an expression to variables on the left hand side.
Write a C program to check whether number is positive, negative or zero . Description: You need to write a C program to check whether number is positive, negative or zero. Conditions: Create variable with name of number and the value will taken by user or console; Create this c program code using else if ladder statement
Welcome to Carolina Housing! Whether you're a transfer student, an incoming first-year, or a returning student, understanding the housing assignment process is crucial for a smooth experience. My name is Jordan Cady, the Assistant Director for Assignments with Carolina Housing, and I'm here to guide you through the key points you need to know.
Assignments in Viva Learning refer to courses that your organization marks as mandatory for learners. Note: Assignments are shown only to users with Viva learning premium license. Where to find your assignments
There are two very closely related concepts in play here. An initializer is a specific syntactic construct. In the declaration. int n = 42; the 42 is an initializer.In the statement. n = 42; the 42 is not an initializer; n = 42 is syntactically an assignment-expression.. On the other hand, the standard also uses the word "initialized" to refer to things other than initializers.
The rehab assignment is an important step in the process for players who have spent long stretches on the injured list to return to the major leagues. For four Pirates 30-somethings, it serves as ...
This paper provides a foundation for construction lawyers navigating their way through assignments and pass-through claims. Readers will gain clarity on which claims can and cannot be assigned, the types of pass-through claims allowed in Texas, and the statutory schemes and equitable doctrines crucial for advising clients effectively.
C Language: C is the procedural Programming language. It was designed to be compiled using a compiler. The Language has small and fixed number of keywords like if/else, for, while,.. etc. We can use more than one assignment that may be used in one statement in this language. Functions are also used here, it can return values that can be ignored, wh
Basically C evaluates expressions. In. s = data[q] The value of data[q] is the the value of expression here and the condition is evaluated based on that. The assignment. s <- data[q] is just a side-effect.
MIAMI (AP) — Veteran shortstop and former AL batting champ Tim Anderson was designated for assignment by the Miami Marlins on Tuesday. Anderson struggled offensively throughout his 65-game stint in Miami, hitting .214 in 234 at-bats with three extra-base hits.
Washington, who has brought an old-school culture back to the Angels this season, admitted to a preference for injury rehab assignments for hitters. "I'm not gonna make that an issue ...