Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures.
How to write a research question
Last updated
7 February 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
In this article, we take an in-depth look at what a research question is, the different types of research questions, and how to write one (with examples). Read on to get started with your thesis, dissertation, or research paper .
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is a research question?
A research question articulates exactly what you want to learn from your research. It stems directly from your research objectives, and you will arrive at an answer through data analysis and interpretation.
However, it is not that simple to write a research question—even when you know the question you intend to answer with your study. The main characteristics of a good research question are:
Feasible. You need to have the resources and abilities to examine the question, collect the data, and give answers.
Interesting. Create research questions that offer fascinating insights into your industry.
Novel. Research questions have to offer something new within your field of study.
Ethical. The research question topic should be approved by the relevant authorities and review boards.
Relevant. Your research question should lead to visible changes in society or your industry.
Usually, you write one single research question to guide your entire research paper. The answer becomes the thesis statement—the central position of your argument. A dissertation or thesis, on the other hand, may require multiple problem statements and research questions. However, they should be connected and focused on a specific problem.
- Importance of the research question
A research question acts as a guide for your entire study. It serves two vital purposes:
to determine the specific issue your research paper addresses
to identify clear objectives
Therefore, it helps split your research into small steps that you need to complete to provide answers.
Your research question will also provide boundaries for your study, which help set limits and ensure cohesion.
Finally, it acts as a frame of reference for assessing your work. Bear in mind that research questions can evolve, shift, and change during the early stages of your study or project.
- Types of research questions
The type of research you are conducting will dictate the type of research question to use. Primarily, research questions are grouped into three distinct categories of study:
qualitative
quantitative
mixed-method
Let’s look at each of these in turn:
Quantitative research questions
The number-one rule of quantitative research questions is that they are precise. They mainly include:
independent and dependent variables
the exact population being studied
the research design to be used
Therefore, you must frame and finalize quantitative research questions before starting the study.
Equally, a quantitative research question creates a link between itself and the research design. These questions cannot be answered with simple 'yes' or' no' responses, so they begin with words like 'does', 'do', 'are', and 'is'.
Quantitative research questions can be divided into three categories:
Relationship research questions usually leverage words such as 'trends' and 'association' because they include independent and dependent variables. They seek to define or explore trends and interactions between multiple variables.
Comparative research questions tend to analyze the differences between different groups to find an outcome variable. For instance, you may decide to compare two distinct groups where a specific variable is present in one and absent in the other.
Descriptive research questions usually start with the word 'what' and aim to measure how a population will respond to one or more variables.
Qualitative research questions
Like quantitative research questions, these questions are linked to the research design. However, qualitative research questions may deal with a specific or broad study area. This makes them more flexible, very adaptable, and usually non-directional.
Use qualitative research questions when your primary aim is to explain, discover, or explore.
There are seven types of qualitative research questions:
Explanatory research questions investigate particular topic areas that aren't well known.
Contextual research questions describe the workings of what is already in existence.
Evaluative research questions examine the effectiveness of specific paradigms or methods.
Ideological research questions aim to advance existing ideologies.
Descriptive research questions describe an event.
Generative research questions help develop actions and theories by providing new ideas.
Emancipatory research questions increase social action engagement, usually to benefit disadvantaged people.
Mixed-methods studies
With mixed-methods studies, you combine qualitative and quantitative research elements to get answers to your research question. This approach is ideal when you need a more complete picture. through a blend of the two approaches.
Mixed-methods research is excellent in multidisciplinary settings, societal analysis, and complex situations. Consider the following research question examples, which would be ideal candidates for a mixed-methods approach
How can non-voter and voter beliefs about democracy (qualitative) help explain Town X election turnout patterns (quantitative)?
How does students’ perception of their study environment (quantitative) relate to their test score differences (qualitative)?
- Developing a strong research question—a step-by-step guide
Research questions help break up your study into simple steps so you can quickly achieve your objectives and find answers. However, how do you develop a good research question? Here is our step-by-step guide:
1. Choose a topic
The first step is to select a broad research topic for your study. Pick something within your expertise and field that interests you. After all, the research itself will stem from the initial research question.
2. Conduct preliminary research
Once you have a broad topic, dig deeper into the problem by researching past studies in the field and gathering requirements from stakeholders if you work in a business setting.
Through this process, you will discover articles that mention areas not explored in that field or products that didn’t resonate with people’s expectations in a particular industry. For instance, you could explore specific topics that earlier research failed to study or products that failed to meet user needs.
3. Keep your audience in mind
Is your audience interested in the particular field you want to study? Are the research questions in your mind appealing and interesting to the audience? Defining your audience will help you refine your research question and ensure you pick a question that is relatable to your audience.
4. Generate a list of potential questions
Ask yourself numerous open-ended questions on the topic to create a potential list of research questions. You could start with broader questions and narrow them down to more specific ones. Don’t forget that you can challenge existing assumptions or use personal experiences to redefine research issues.
5. Review the questions
Evaluate your list of potential questions to determine which seems most effective. Ensure you consider the finer details of every question and possible outcomes. Doing this helps you determine if the questions meet the requirements of a research question.
6. Construct and evaluate your research question
Consider these two frameworks when constructing a good research question: PICOT and PEO.
PICOT stands for:
P: Problem or population
I: Indicator or intervention to be studied
C: Comparison groups
O: Outcome of interest
T: Time frame
PEO stands for:
P: Population being studied
E: Exposure to any preexisting conditions
To evaluate your research question once you’ve constructed it, ask yourself the following questions:
Is it clear?
Your study should produce precise data and observations. For qualitative studies, the observations need to be delineable across categories. Quantitative studies must have measurable and empirical data.
Is it specific and focused?
An excellent research question must be specific enough to ensure your testing yields objective results. General or open-ended research questions are often ambiguous and subject to different kinds of interpretation.
Is it sufficiently complex?
Your research needs to yield substantial and consequential results to warrant the study. Merely supporting or reinforcing an existing paper is not good enough.
- Examples of good research questions
A robust research question actively contributes to a specific body of knowledge; it is a question that hasn’t been answered before within your research field.
Here are some examples of good and bad research questions :
Good: How effective are A and B policies at reducing the rates of Z?
Bad: Is A or B a better policy?
The first is more focused and researchable because it isn't based on value judgment. The second fails to give clear criteria for answering the question.
Good: What is the effect of daily Twitter use on the attention span of college students?
Bad: What is the effect of social media use on people's minds?
The first includes specific and well-defined concepts, which the second lacks.
Ensure all terms within your research question have precise meanings. Avoid vague or general language that makes the topic too broad.
- The bottom line
The success of any research starts with formulating the right questions that ensure you collect the most insightful data. A good research question will showcase the objectives of your systematic investigation and emphasize specific contexts.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Questions
Definition:
Research questions are the specific questions that guide a research study or inquiry. These questions help to define the scope of the research and provide a clear focus for the study. Research questions are usually developed at the beginning of a research project and are designed to address a particular research problem or objective.
Types of Research Questions
Types of Research Questions are as follows:
Descriptive Research Questions
These aim to describe a particular phenomenon, group, or situation. For example:
- What are the characteristics of the target population?
- What is the prevalence of a particular disease in a specific region?
Exploratory Research Questions
These aim to explore a new area of research or generate new ideas or hypotheses. For example:
- What are the potential causes of a particular phenomenon?
- What are the possible outcomes of a specific intervention?
Explanatory Research Questions
These aim to understand the relationship between two or more variables or to explain why a particular phenomenon occurs. For example:
- What is the effect of a specific drug on the symptoms of a particular disease?
- What are the factors that contribute to employee turnover in a particular industry?
Predictive Research Questions
These aim to predict a future outcome or trend based on existing data or trends. For example :
- What will be the future demand for a particular product or service?
- What will be the future prevalence of a particular disease?
Evaluative Research Questions
These aim to evaluate the effectiveness of a particular intervention or program. For example:
- What is the impact of a specific educational program on student learning outcomes?
- What is the effectiveness of a particular policy or program in achieving its intended goals?
How to Choose Research Questions
Choosing research questions is an essential part of the research process and involves careful consideration of the research problem, objectives, and design. Here are some steps to consider when choosing research questions:
- Identify the research problem: Start by identifying the problem or issue that you want to study. This could be a gap in the literature, a social or economic issue, or a practical problem that needs to be addressed.
- Conduct a literature review: Conducting a literature review can help you identify existing research in your area of interest and can help you formulate research questions that address gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Define the research objectives : Clearly define the objectives of your research. What do you want to achieve with your study? What specific questions do you want to answer?
- Consider the research design : Consider the research design that you plan to use. This will help you determine the appropriate types of research questions to ask. For example, if you plan to use a qualitative approach, you may want to focus on exploratory or descriptive research questions.
- Ensure that the research questions are clear and answerable: Your research questions should be clear and specific, and should be answerable with the data that you plan to collect. Avoid asking questions that are too broad or vague.
- Get feedback : Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, feasible, and meaningful.
How to Write Research Questions
Guide for Writing Research Questions:
- Start with a clear statement of the research problem: Begin by stating the problem or issue that your research aims to address. This will help you to formulate focused research questions.
- Use clear language : Write your research questions in clear and concise language that is easy to understand. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that may be unfamiliar to your readers.
- Be specific: Your research questions should be specific and focused. Avoid broad questions that are difficult to answer. For example, instead of asking “What is the impact of climate change on the environment?” ask “What are the effects of rising sea levels on coastal ecosystems?”
- Use appropriate question types: Choose the appropriate question types based on the research design and objectives. For example, if you are conducting a qualitative study, you may want to use open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed responses.
- Consider the feasibility of your questions : Ensure that your research questions are feasible and can be answered with the resources available. Consider the data sources and methods of data collection when writing your questions.
- Seek feedback: Get feedback from your supervisor, colleagues, or peers to ensure that your research questions are relevant, appropriate, and meaningful.
Examples of Research Questions
Some Examples of Research Questions with Research Titles:
Research Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
- Research Question : What is the relationship between social media use and mental health, and how does this impact individuals’ well-being?
Research Title: Factors Influencing Academic Success in High School
- Research Question: What are the primary factors that influence academic success in high school, and how do they contribute to student achievement?
Research Title: The Effects of Exercise on Physical and Mental Health
- Research Question: What is the relationship between exercise and physical and mental health, and how can exercise be used as a tool to improve overall well-being?
Research Title: Understanding the Factors that Influence Consumer Purchasing Decisions
- Research Question : What are the key factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions, and how do these factors vary across different demographics and products?
Research Title: The Impact of Technology on Communication
- Research Question : How has technology impacted communication patterns, and what are the effects of these changes on interpersonal relationships and society as a whole?
Research Title: Investigating the Relationship between Parenting Styles and Child Development
- Research Question: What is the relationship between different parenting styles and child development outcomes, and how do these outcomes vary across different ages and developmental stages?
Research Title: The Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy in Treating Anxiety Disorders
- Research Question: How effective is cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders, and what factors contribute to its success or failure in different patients?
Research Title: The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Research Question : How is climate change affecting global biodiversity, and what can be done to mitigate the negative effects on natural ecosystems?
Research Title: Exploring the Relationship between Cultural Diversity and Workplace Productivity
- Research Question : How does cultural diversity impact workplace productivity, and what strategies can be employed to maximize the benefits of a diverse workforce?
Research Title: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Research Question: How can artificial intelligence be leveraged to improve healthcare outcomes, and what are the potential risks and ethical concerns associated with its use?
Applications of Research Questions
Here are some of the key applications of research questions:
- Defining the scope of the study : Research questions help researchers to narrow down the scope of their study and identify the specific issues they want to investigate.
- Developing hypotheses: Research questions often lead to the development of hypotheses, which are testable predictions about the relationship between variables. Hypotheses provide a clear and focused direction for the study.
- Designing the study : Research questions guide the design of the study, including the selection of participants, the collection of data, and the analysis of results.
- Collecting data : Research questions inform the selection of appropriate methods for collecting data, such as surveys, interviews, or experiments.
- Analyzing data : Research questions guide the analysis of data, including the selection of appropriate statistical tests and the interpretation of results.
- Communicating results : Research questions help researchers to communicate the results of their study in a clear and concise manner. The research questions provide a framework for discussing the findings and drawing conclusions.
Characteristics of Research Questions
Characteristics of Research Questions are as follows:
- Clear and Specific : A good research question should be clear and specific. It should clearly state what the research is trying to investigate and what kind of data is required.
- Relevant : The research question should be relevant to the study and should address a current issue or problem in the field of research.
- Testable : The research question should be testable through empirical evidence. It should be possible to collect data to answer the research question.
- Concise : The research question should be concise and focused. It should not be too broad or too narrow.
- Feasible : The research question should be feasible to answer within the constraints of the research design, time frame, and available resources.
- Original : The research question should be original and should contribute to the existing knowledge in the field of research.
- Significant : The research question should have significance and importance to the field of research. It should have the potential to provide new insights and knowledge to the field.
- Ethical : The research question should be ethical and should not cause harm to any individuals or groups involved in the study.
Purpose of Research Questions
Research questions are the foundation of any research study as they guide the research process and provide a clear direction to the researcher. The purpose of research questions is to identify the scope and boundaries of the study, and to establish the goals and objectives of the research.
The main purpose of research questions is to help the researcher to focus on the specific area or problem that needs to be investigated. They enable the researcher to develop a research design, select the appropriate methods and tools for data collection and analysis, and to organize the results in a meaningful way.
Research questions also help to establish the relevance and significance of the study. They define the research problem, and determine the research methodology that will be used to address the problem. Research questions also help to determine the type of data that will be collected, and how it will be analyzed and interpreted.
Finally, research questions provide a framework for evaluating the results of the research. They help to establish the validity and reliability of the data, and provide a basis for drawing conclusions and making recommendations based on the findings of the study.
Advantages of Research Questions
There are several advantages of research questions in the research process, including:
- Focus : Research questions help to focus the research by providing a clear direction for the study. They define the specific area of investigation and provide a framework for the research design.
- Clarity : Research questions help to clarify the purpose and objectives of the study, which can make it easier for the researcher to communicate the research aims to others.
- Relevance : Research questions help to ensure that the study is relevant and meaningful. By asking relevant and important questions, the researcher can ensure that the study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge and address important issues.
- Consistency : Research questions help to ensure consistency in the research process by providing a framework for the development of the research design, data collection, and analysis.
- Measurability : Research questions help to ensure that the study is measurable by defining the specific variables and outcomes that will be measured.
- Replication : Research questions help to ensure that the study can be replicated by providing a clear and detailed description of the research aims, methods, and outcomes. This makes it easier for other researchers to replicate the study and verify the results.
Limitations of Research Questions
Limitations of Research Questions are as follows:
- Subjectivity : Research questions are often subjective and can be influenced by personal biases and perspectives of the researcher. This can lead to a limited understanding of the research problem and may affect the validity and reliability of the study.
- Inadequate scope : Research questions that are too narrow in scope may limit the breadth of the study, while questions that are too broad may make it difficult to focus on specific research objectives.
- Unanswerable questions : Some research questions may not be answerable due to the lack of available data or limitations in research methods. In such cases, the research question may need to be rephrased or modified to make it more answerable.
- Lack of clarity : Research questions that are poorly worded or ambiguous can lead to confusion and misinterpretation. This can result in incomplete or inaccurate data, which may compromise the validity of the study.
- Difficulty in measuring variables : Some research questions may involve variables that are difficult to measure or quantify, making it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions from the data.
- Lack of generalizability: Research questions that are too specific or limited in scope may not be generalizable to other contexts or populations. This can limit the applicability of the study’s findings and restrict its broader implications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- News & Highlights
- Publications and Documents
- Postgraduate Education
- Browse Our Courses
- C/T Research Academy
- K12 Investigator Training
- Harvard Catalyst On-Demand
- Translational Innovator
- SMART IRB Reliance Request
- Biostatistics Consulting
- Regulatory Support
- Pilot Funding
- Informatics Program
- Community Engagement
- Diversity Inclusion
- Research Enrollment and Diversity
- Harvard Catalyst Profiles

Creating a Good Research Question
- Advice & Growth
- Process in Practice
Successful translation of research begins with a strong question. How do you get started? How do good research questions evolve? And where do you find inspiration to generate good questions in the first place? It’s helpful to understand existing frameworks, guidelines, and standards, as well as hear from researchers who utilize these strategies in their own work.
In the fall and winter of 2020, Naomi Fisher, MD, conducted 10 interviews with clinical and translational researchers at Harvard University and affiliated academic healthcare centers, with the purpose of capturing their experiences developing good research questions. The researchers featured in this project represent various specialties, drawn from every stage of their careers. Below you will find clips from their interviews and additional resources that highlight how to get started, as well as helpful frameworks and factors to consider. Additionally, visit the Advice & Growth section to hear candid advice and explore the Process in Practice section to hear how researchers have applied these recommendations to their published research.
- Naomi Fisher, MD , is associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School (HMS), and clinical staff at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH). Fisher is founder and director of Hypertension Services and the Hypertension Specialty Clinic at the BWH, where she is a renowned endocrinologist. She serves as a faculty director for communication-related Boundary-Crossing Skills for Research Careers webinar sessions and the Writing and Communication Center .
- Christopher Gibbons, MD , is associate professor of neurology at HMS, and clinical staff at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Joslin Diabetes Center. Gibbons’ research focus is on peripheral and autonomic neuropathies.
- Clare Tempany-Afdhal, MD , is professor of radiology at HMS and the Ferenc Jolesz Chair of Research, Radiology at BWH. Her major areas of research are MR imaging of the pelvis and image- guided therapy.
- David Sykes, MD, PhD , is assistant professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), he is also principal investigator at the Sykes Lab at MGH. His special interest area is rare hematologic conditions.
- Elliot Israel, MD , is professor of medicine at HMS, director of the Respiratory Therapy Department, the director of clinical research in the Pulmonary and Critical Care Medical Division and associate physician at BWH. Israel’s research interests include therapeutic interventions to alter asthmatic airway hyperactivity and the role of arachidonic acid metabolites in airway narrowing.
- Jonathan Williams, MD, MMSc , is assistant professor of medicine at HMS, and associate physician at BWH. He focuses on endocrinology, specifically unravelling the intricate relationship between genetics and environment with respect to susceptibility to cardiometabolic disease.
- Junichi Tokuda, PhD , is associate professor of radiology at HMS, and is a research scientist at the Department of Radiology, BWH. Tokuda is particularly interested in technologies to support image-guided “closed-loop” interventions. He also serves as a principal investigator leading several projects funded by the National Institutes of Health and industry.
- Osama Rahma, MD , is assistant professor of medicine at HMS and clinical staff member in medical oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI). Rhama is currently a principal investigator at the Center for Immuno-Oncology and Gastroenterology Cancer Center at DFCI. His research focus is on drug development of combinational immune therapeutics.
- Sharmila Dorbala, MD, MPH , is professor of radiology at HMS and clinical staff at BWH in cardiovascular medicine and radiology. She is also the president of the American Society of Nuclear Medicine. Dorbala’s specialty is using nuclear medicine for cardiovascular discoveries.
- Subha Ramani, PhD, MBBS, MMed , is associate professor of medicine at HMS, as well as associate physician in the Division of General Internal Medicine and Primary Care at BWH. Ramani’s scholarly interests focus on innovative approaches to teaching, learning and assessment of clinical trainees, faculty development in teaching, and qualitative research methods in medical education.
- Ursula Kaiser, MD , is professor at HMS and chief of the Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension, and senior physician at BWH. Kaiser’s research focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms by which pulsatile gonadotropin-releasing hormone regulates the expression of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone genes.
Insights on Creating a Good Research Question

Play Junichi Tokuda video

Play Ursula Kaiser video
Start Successfully: Build the Foundation of a Good Research Question

Start Successfully Resources
Ideation in Device Development: Finding Clinical Need Josh Tolkoff, MS A lecture explaining the critical importance of identifying a compelling clinical need before embarking on a research project. Play Ideation in Device Development video .
Radical Innovation Jeff Karp, PhD This ThinkResearch podcast episode focuses on one researcher’s approach using radical simplicity to break down big problems and questions. Play Radical Innovation .
Using Healthcare Data: How can Researchers Come up with Interesting Questions? Anupam Jena, MD, PhD Another ThinkResearch podcast episode addresses how to discover good research questions by using a backward design approach which involves analyzing big data and allowing the research question to unfold from findings. Play Using Healthcare Data .
Important Factors: Consider Feasibility and Novelty

Refining Your Research Question
Play video of Clare Tempany-Afdhal

Play Elliott Israel video
Frameworks and Structure: Evaluate Research Questions Using Tools and Techniques
Frameworks and Structure Resources
Designing Clinical Research Hulley et al. A comprehensive and practical guide to clinical research, including the FINER framework for evaluating research questions. Learn more about the book .
Translational Medicine Library Guide Queens University Library An introduction to popular frameworks for research questions, including FINER and PICO. Review translational medicine guide .
Asking a Good T3/T4 Question Niteesh K. Choudhry, MD, PhD This video explains the PICO framework in practice as participants in a workshop propose research questions that compare interventions. Play Asking a Good T3/T4 Question video
Introduction to Designing & Conducting Mixed Methods Research An online course that provides a deeper dive into mixed methods’ research questions and methodologies. Learn more about the course
Network and Support: Find the Collaborators and Stakeholders to Help Evaluate Research Questions

Network & Support Resource
Bench-to-bedside, Bedside-to-bench Christopher Gibbons, MD In this lecture, Gibbons shares his experience of bringing research from bench to bedside, and from bedside to bench. His talk highlights the formation and evolution of research questions based on clinical need. Play Bench-to-bedside.
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A research question is the main query that researchers seek to answer in their study. It serves as the basis for a scholarly project such as research paper, thesis or dissertation. A good research question should be clear, relevant and specific enough to guide the research process. It should also be open-ended, meaning that it allows for multiple possible answers or interpretations.
If you have located your general subject and main sources but still aren’t quite sure about the exact research questions for your paper, this guide will help you out. First, we will explore the concept of it together, so you could answer it in your work. Then some simple steps on composing your inquiry will be suggested. In the end, we will draw your attention to some specific details which can make your work good or bad. Sometimes it’s just easier to delegate all challenging tasks to a reliable research paper service . StudyCrumb is a trustable network of qualified writers ready to efficiently solve students’ challenges.
What Is a Good Research Question: Full Definition
Good research questions provide a concise definition of a problem. As a scholar, your main goal at the beginning is to select the main focus. It should be narrow enough so you could examine it within your deadline. Your work should be focused on something specific. Otherwise, it will require too much work and might not produce clear answers. At the same time your answer should be arguable and supported by data you’ve collected. Take a look at this example:

How to Write a Research Question: Step-By-Step Guide
In this section we will examine the process of developing a research question. We will guide you through it, step by step. Keep in mind that your subject should be important for your audience. So it requires some preliminary study and brainstorming. Let’s take a closer look at the main steps.
Step 1. Choose a Broad Topic for Your Research Paper Question
First, you need to decide on your general direction. When trying to identify your research paper questions, it is better to choose an area you are really interested in. You should be able to obtain enough data to write something about this topic. Therefore, do not choose something out of your reach. At the same time, your broad topic should not be too simple. Research paper questions that can be answered without any study would hardly make any sense for your project.
Step 2. Do Preliminary Reading Before Starting Your Research Question
Next, it is time we explore the context of the selected topic. You wouldn’t want to choose research questions that have already been examined and answered in detail. On the other hand, choosing a topic that is a complete ‘terra incognita’ might be a bridge too far for your project. Browse through available sources that are related to this topic. You should try and find out what has been discovered about it before. Do you see a gap that you can fill with your study? You can proceed with developing your exact inquiry! Have no time for in-depth topic exploration? Leave this task to professionals. Entrust your “ write my research paper ” order to StudyCrumb and get a top-notch work.
Step 3. Consider an Audience for Your Research Question
It is good to know your reader well to be able to convey your ideas and results to them in the best possible way. Before writing research questions for your projects, you might need to perform a brief analysis of your audience. That's how you'll be able to understand what is interesting for them and what is not. This will allow you to make better decisions when narrowing your broad topic down. Select a topic that is interesting for your reader! This would contribute much to the success for writing a research paper .
Step 4. Start Asking a Good Research Question
After you have considered your options, go ahead and compose the primary subject of your paper. What makes a good research question? It should highlight some problematic and relevant aspects of the general topic. So, after it is answered, you should have obtained some new valuable knowledge about the subject. Typically scholars start narrowing down their general topic by asking ‘how’, ‘why’ or ‘what’s next’ questions. This approach might help you come up with a great idea quickly.
Step 5. Evaluate Your Research Question
Finally, after you have composed a research paper question, you should take a second look at it and see if it is good enough for your paper. It would be useful to analyze it from the following sides:
- Is it clear for your audience?
- Is it complex enough to require significant study?
- Is it focused on a certain aspect of your general topic?
You might use the help of your peers or your friends at this step. You can also show it to your tutor and ask for their opinion.
Types of Research Questions: Which to Choose
A number of research questions types are available for use in a paper. They are divided into two main groups:
Qualitative questions:
- Explanatory
- Ethnographic
Quantitative questions:
- Descriptive
- Comparative
- Relationship based.
Selecting a certain type would impact the course of your study. We suggest you think about it carefully. Below you can find a few words about each type. Also, you can seek proficient help from academic experts. Buy a research paper from real pros and forget about stress once and for all.
Qualitative Research Questions: Definition With Example
When doing qualitative research, you are expected to aim to understand the different aspects and qualities of your target problem. Therefore, your thesis should focus on analyzing people’s experience, ideas and reflections rather than on obtaining some statistical data and calculating trends. Thus, this inquiry typically requires observing people’s behavior, interacting with them and learning how they interpret your target problem. Let’s illustrate this with an example:

What Is Contextual Research Questions
Contextual research revolves around examining your subject in its natural, everyday environment. It may be watching animals living in their usual habitats or people doing their normal activities in their familiar surroundings (at home, at school or at office). This academic approach helps to understand the role of the context. You'll be able to better explain connections between your problem, its environment and outcomes. This type of inquiry ought to be narrow enough. You shouldn’t have to examine each and every aspect of the selected problem in your paper. Consider this example:

Definition and Sample of Evaluative Research Questions
Evaluative research is performed in order to carefully assess the qualities of a selected object, individual, group, system or concept. It typically serves the purpose of collecting evidence that supports or contradicts solutions for a problem. This type of inquiry should focus on how useful a certain quality is for solving the problem. To conduct such study, you need to examine selected qualities in detail. Then, you should assume whether they match necessary criteria. It might include some quantitative methods such as collecting statistics. Although, the most important part is analyzing the qualities. If you need some examples, here’s one for you:

Explanatory Research Questions: Definition With Example
Your paper can be dedicated to explaining a certain phenomenon, finding its reasons and important relationships between it and other important things. Your explanatory research question should aim to highlight issues, uncertainties and problematic aspects of your subject. So, your study should bring clarity about these qualities. It should show how and why they have developed this way. An explanation may include showing causes and effects of issues in question, comparing the selected phenomenon to other similar types and showing whether the selected qualities match some predefined criteria. If you need some examples, check this one:

Generative Research Questions
This type of research is conducted in order to better understand the subject. With its help, you can find some new solutions or opportunities for improvement. Therefore, its main purpose is to develop a theoretical basis for further actions. You need to compose your generative research questions in a way that facilitates obtaining new ideas. It would help to begin with asking ‘why’, ‘what is the relationship between the subject and the problems X, Y, and Z’, ‘what can be improved here’, ‘how we can prevent it’ and so on. Need relevant examples? We’ve got one for you:

Ethnographic Research Question
Ethnography research is focused on a particular group of people. The aim is to study their behavior, typical reactions to certain events or information, needs, preferences or habits. Important parameters of this group which are most relevant to your general subject are taken into consideration. These are age, sex, language, religion, ethnicity, social status and so on. Main method in this case is first-hand observation of people from the selected group during an extended period of time. If you need strong examples, here’s one:

Quantitative Research Questions: Full Definition With Examples
Quantitative research deals with data – first of all, it is numeric data. It involves mathematical calculations and statistical analysis. It helps to obtain knowledge which is mostly expressed in numbers, graphs and tables. Unlike the qualitative type, the purpose of quantitative research is finding patterns, calculating probabilities, testing causal relationships and making predictions. It is focused on testing theories and hypotheses. (We have the whole blog on what is a hypothesis .) It is mostly used in natural and social sciences. These are: chemistry, biology, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc. Here are a couple of examples:

Descriptive Research Questions: Definition With Example
This is probably the most widespread type of quantitative research question. Such inquiries seek to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred. They describe it accurately and systematically. These inquiries typically start with ‘what’. You are expected to use various methods to investigate one or more variables and determine their dependencies. Note, however, that you cannot control or manipulate any of these variables. You can only observe and measure them. Looking for some interesting examples? Here is one:

Definition of Comparative Research Questions
Comparative research question is used to highlight different variables and provide numerical evidence. This type is based on comparing one object, parameter or issue with another one of a similar kind. It can help to discover the differences between two or more groups by examining their outcome variables. Take a look at these two examples:

Relationship Research Questions
We conduct this type of research when we need to make it clear whether one parameter of a selected object causes another one. A relationship based quantitative research question should help us to explore and define trends and interactions between two or more variables. Are these two things mutually dependent? What kind of dependence is it? How has it developed? And what are possible outcomes of this connection? Here is an example of relationship-based quantitative research questions:

Research Questions Examples: Free
This section contains a number of helpful examples of research questions. Feel free to use them as inspiration to create your own questions and conduct productive study. Let’s start with two simple ones:

Are you interested in well written and inspiring questions? Do you want to learn what to avoid in your study? Just stay with us – there will be more of them below.
Examples of Good and Bad Research Questions
Everyone is interested in getting the best possible appraisal for their study. Choosing a topic which doesn't suit your specific situation may be discouraging. Thus, the quality of your paper might get affected by a poor choice. We have put together some good and bad examples so that you could avoid such mistakes.
Good Research Questions Examples
It is important to include clear terms into your questions. Otherwise, it would be difficult for you to plan your investigation properly. Also, they must be focused on a certain subject, not multiple ones. And finally, it should be possible to answer them. Let’s review several good examples:

Examples of Bad Research Questions
It is difficult to evaluate qualities of objects, individuals or groups if your purpose is not clear. This is why you shouldn’t create unclear research questions or try to focus on many problems at once. Some preliminary study might help to understand what you should focus on. Here are several bad examples:

In case you may need some information about the discussion section of a research paper example , find it in our blog.
Final Thoughts on Research Questions
In this article we have made a detailed review of the most popular types of research questions. We described peculiarities. We also provided some tips on conducting various kinds of study. Besides, a number of useful examples have been given for each category of questions.
Feel free to check out essay writing services. We have experienced writers who can help you compose your paper in time. They will absolutely ensure the high quality of your text.
Frequently Asked Questions About Research Questions
1. what is an example of a weak research question.
Here is an example of the weakest research question:
An answer would be simply making a list of species that inhabit the country. This subject does not require any actual study to be conducted. There is nothing to calculate or analyze here.
2. What is the most effective type of research question?
Most effective type of research question is the one that doesn't have a single correct answer. However, you should also pay close attention to your audience. If you need to create a strong effect, better choose a topic which is relevant for them.
3. What is a good nursing research question?
If you need an idea for a nursing research question, here are a few helpful examples you could use as a reference:
4. What are some sociological research questions?
Sociological questions are the ones that examine the social patterns or a meaning of a social phenomenon. They could be qualitative or quantitative. They should target groups of people with certain parameters, such as age or income level. Keep in mind that type of study usually requires collecting numerous data about your target groups.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

39 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.63(8); 2019 Aug
Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls
Wilson fandino.
Guys' and St Thomas' Hospital National Health Service Foundation Trust, London, United Kingdom
The process of formulating a good research question can be challenging and frustrating. While a comprehensive literature review is compulsory, the researcher usually encounters methodological difficulties in the conduct of the study, particularly if the primary study question has not been adequately selected in accordance with the clinical dilemma that needs to be addressed. Therefore, optimising time and resources before embarking in the design of a clinical protocol can make an impact on the final results of the research project. Researchers have developed effective ways to convey the message of how to build a good research question that can be easily recalled under the acronyms of PICOT (population, intervention, comparator, outcome, and time frame) and FINER (feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant). In line with these concepts, this article highlights the main issues faced by clinicians, when developing a research question.
INTRODUCTION
What is your research question? This is very often one of the first queries made by statisticians, when researchers come up with an interesting idea. In fact, the findings of a study may only acquire relevance if they provide an accurate and unbiased answer to a specific question,[ 1 , 2 ] and it has been suggested that up to one-third of the time spent in the whole process—from the conception of an idea to the publication of the manuscript—could be invested in finding the right primary study question.[ 3 ] Furthermore, selecting a good research question can be a time-consuming and challenging task: in one retrospective study, Mayo et al . reported that 3 out of 10 articles published would have needed a major rewording of the question.[ 1 ] This paper explores some recommendations to consider before starting any research project, and outlines the main difficulties faced by young and experienced clinicians, when it comes time to turn an exciting idea into a valuable and feasible research question.
OPTIMISATION OF TIME AND RESOURCES
Focusing on the primary research question.
The process of developing a new idea usually stems from a dilemma inherent to the clinical practice.[ 2 , 3 , 4 ] However, once the problem has been identified, it is tempting to formulate multiple research questions. Conducting a clinical trial with more than one primary study question would not be feasible. First, because each question may require a different research design, and second, because the necessary statistical power of the study would demand unaffordable sample sizes. It is the duty of editors and reviewers to make sure that authors clearly identify the primary research question, and as a consequence, studies approaching more than one primary research question may not be suitable for publication.
Working in the right environment
Teamwork is essential to find the appropriate research question. Working in the right environment will enable the investigator to interact with colleagues with different backgrounds, and create opportunities to exchange experiences in a collaborative way between clinicians and researchers. Likewise, it is of paramount importance to get involved colleagues with expertise in the field (lead clinicians, education supervisors, research mentors, department chairs, epidemiologists, biostatisticians, and ethical consultants, among others), and ask for their guidance.[ 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]
Evaluating the pertinence of the study
The researcher should wonder if, on the basis of the research question formulated, there is a need for a study to address the problem, as clinical research usually entails a large investment of resources and workforce involvement. Thus, if the answer to the posed clinical question seems to be evident before starting the study, investing in research to address the problem would become superfluous. For example, in a clinical trial, Herzog-Niescery et al . compared laryngeal masks with cuffed and uncuffed tracheal tubes, in the context of surgeons' exposure to sevoflurane, in infants undergoing adenoidectomy. However, it appears obvious that cuffed tracheal tubes are preferred to minimise surgeons' exposure to volatile gases, as authors concluded after recruiting 60 patients.[ 9 ]
Conducting a thorough literature review
Any research project requires the identification of at least one of three problems: the evidence is scarce, the existing literature yields conflicting results, or the results could be improved. Hence, a comprehensive review of the topic is imperative, as it allows the researcher to identify this gap in the literature, formulate a hypothesis and develop a research question.[ 2 ] To this end, it is crucial to be attentive to new ideas, keep the imagination roaming with reflective attitude, and remain sceptical to the new-gained information.[ 4 , 7 ]
Narrowing the research question
A broad research question may encompass an unaffordable extensive topic. For instance, do supraglottic devices provide similar conditions for the visualization of the glottis aperture in a German hospital? Such a general research question usually needs to be narrowed, not only by cutting away unnecessary components (a German hospital is irrelevant in this context), but also by defining a target population, a specific intervention, an alternative treatment or procedure to be compared with the intervention, a measurable primary outcome, and a time frame of the study. In contrast, an example of a good research question would be: among children younger than 1 year of age undergoing elective minor procedures, to what extent the insertion times are different, comparing the Supreme™ laryngeal mask airway (LMA) to Proseal™ LMA, when placed after reaching a BIS index <60?[ 10 ] In this example, the core ingredients of the research question can be easily identified as: children <1 year of age undergoing minor elective procedures, Supreme™ LMA, Proseal™ LMA and insertion times at anaesthetic induction when reaching a BIS index <60. These components are usually gathered in the literature under the acronym of PICOT (population, intervention, comparator, outcome and time frame, respectively).[ 1 , 3 , 5 ]
PICOT FRAMEWORK
Table 1 summarises the foremost questions likely to be addressed when working on PICOT frame.[ 1 , 6 , 8 ] These components are also applicable to observational studies, where the exposure takes place of the intervention.[ 1 , 11 ] Remarkably, if after browsing the title and the abstract of a paper, the reader is not able to clearly identify the PICOT parameters, and elucidate the question posed by the authors, there should be reasonable scepticism regarding the scientific rigor of the work.[ 12 , 13 ] All these elements are crucial in the design and methodology of a clinical trial, as they can affect the feasibility and reliability of results. Having formulated the primary study question in the context of the PICOT framework [ Table 1 ],[ 1 , 6 , 8 ] the researcher should be able to elucidate which design is most suitable for their work, determine what type of data needs to be collected, and write a structured introduction tailored to what they want to know, explicitly mentioning the primary study hypothesis, which should lead to formulate the main research question.[ 1 , 2 , 6 , 8 ]
Key questions to be answered when working with the PICOT framework (population, intervention, comparator, outcome, and time frame) in a clinical research design
Occasionally, the intended population of the study needs to be modified, in order to overcome any potential ethical issues, and/or for the sake of convenience and feasibility of the project. Yet, the researcher must be aware that the external validity of the results may be compromised. As an illustration, in a randomised clinical trial, authors compared the ease of tracheal tube insertion between C-MAC video laryngoscope and direct laryngoscopy, in patients presenting to the emergency department with an indication of rapid sequence intubation. However, owing to the existence of ethical concerns, a substantial amount of patients requiring emergency tracheal intubation, including patients with major maxillofacial trauma and ongoing cardiopulmonary resuscitation, had to be excluded from the trial.[ 14 ] In fact, the design of prospective studies to explore this subset of patients can be challenging, not only because of ethical considerations, but because of the low incidence of these cases. In another study, Metterlein et al . compared the glottis visualisation among five different supraglottic airway devices, using fibreroptic-guided tracheal intubation in an adult population. Despite that the study was aimed to explore the ease of intubation in patients with anticipated difficult airway (thus requiring fibreoptic tracheal intubation), authors decided to enrol patients undergoing elective laser treatment for genital condylomas, as a strategy to hasten the recruitment process and optimise resources.[ 15 ]
Intervention
Anaesthetic interventions can be classified into pharmacological (experimental treatment) and nonpharmacological. Among nonpharmacological interventions, the most common include anaesthetic techniques, monitoring instruments and airway devices. For example, it would be appropriate to examine the ease of insertion of Supreme™ LMA, when compared with ProSeal™ LMA. Notwithstanding, a common mistake is the tendency to be focused on the data aimed to be collected (the “stated” objective), rather than the question that needs to be answered (the “latent” objective).[ 1 , 4 ] In one clinical trial, authors stated: “we compared the Supreme™ and ProSeal™ LMAs in infants by measuring their performance characteristics, including insertion features, ventilation parameters, induced changes in haemodynamics, and rates of postoperative complications”.[ 10 ] Here, the research question has been centered on the measurements (insertion characteristics, haemodynamic variables, LMA insertion characteristics, ventilation parameters) rather than the clinical problem that needs to be addressed (is Supreme™ LMA easier to insert than ProSeal™ LMA?).
Comparators in clinical research can also be pharmacological (e.g., gold standard or placebo) or nonpharmacological. Typically, not more than two comparator groups are included in a clinical trial. Multiple comparisons should be generally avoided, unless there is enough statistical power to address the end points of interest, and statistical analyses have been adjusted for multiple testing. For instance, in the aforementioned study of Metterlein et al .,[ 15 ] authors compared five supraglottic airway devices by recruiting only 10--12 participants per group. In spite of the authors' recommendation of using two supraglottic devices based on the results of the study, there was no mention of statistical adjustments for multiple comparisons, and given the small sample size, larger clinical trials will undoubtedly be needed to confirm or refute these findings.[ 15 ]
A clear formulation of the primary outcome results of vital importance in clinical research, as the primary statistical analyses, including the sample size calculation (and therefore, the estimation of the effect size and statistical power), will be derived from the main outcome of interest. While it is clear that using more than one primary outcome would not be appropriate, it would be equally inadequate to include multiple point measurements of the same variable as the primary outcome (e.g., visual analogue scale for pain at 1, 2, 6, and 12 h postoperatively).
Composite outcomes, in which multiple primary endpoints are combined, may make it difficult to draw any conclusions based on the study findings. For example, in a clinical trial, 200 children undergoing ophthalmic surgery were recruited to explore the incidence of respiratory adverse events, when comparing desflurane with sevoflurane, following the removal of flexible LMA during the emergence of the anaesthesia. The primary outcome was the number of respiratory events, including breath holding, coughing, secretions requiring suction, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, and mild desaturation.[ 16 ] Should authors had claimed a significant difference between these anaesthetic volatiles, it would have been important to elucidate whether those differences were due to serious adverse events, like laryngospasm or bronchospasm, or the results were explained by any of the other events (e.g., secretions requiring suction). While it is true that clinical trials evaluating the occurrence of adverse events like laryngospasm/bronchospasm,[ 16 , 17 ] or life-threating complications following a tracheal intubation (e.g., inadvertent oesophageal placement, dental damage or injury of the larynx/pharynx)[ 14 ] are almost invariably underpowered, because the incidence of such events is expected to be low, subjective outcomes like coughing or secretions requiring suction should be avoided, as they are highly dependent on the examiner's criteria.[ 16 ]
Secondary outcomes are useful to document potential side effects (e.g., gastric insufflation after placing a supraglottic device), and evaluate the adherence (say, airway leak pressure) and safety of the intervention (for instance, occurrence, or laryngospasm/bronchospasm).[ 17 ] Nevertheless, the problem of addressing multiple secondary outcomes without the adequate statistical power is habitual in medical literature. A good illustration of this issue can be found in a study evaluating the performance of two supraglottic devices in 50 anaesthetised infants and neonates, whereby authors could not draw any conclusions in regard to potential differences in the occurrence of complications, because the sample size calculated made the study underpowered to explore those differences.[ 17 ]
Among PICOT components, the time frame is the most likely to be omitted or inappropriate.[ 1 , 12 ] There are two key aspects of the time component that need to be clearly specified in the research question: the time of measuring the outcome variables (e.g. visual analogue scale for pain at 1, 2, 6, and 12 h postoperatively), and the duration of each measurement (when indicated). The omission of these details in the study protocol might lead to substantial differences in the methodology used. For instance, if a study is designed to compare the insertion times of three different supraglottic devices, and researchers do not specify the exact moment of LMA insertion in the clinical trial protocol (i.e., at the anaesthetic induction after reaching a BIS index < 60), placing an LMA with insufficient depth of anaesthesia would have compromised the internal validity of the results, because inserting a supraglottic device in those patients would have resulted in failed attempts and longer insertion times.[ 10 ]

FINER CRITERIA
A well-elaborated research question may not necessarily be a good question. The proposed study also requires being achievable from both ethical and realistic perspectives, interesting and useful to the clinical practice, and capable to formulate new hypotheses, that may contribute to the generation of knowledge. Researchers have developed an effective way to convey the message of how to build a good research question, that is usually recalled under the acronym of FINER (feasible, interesting, novel, ethical and relevant).[ 5 , 6 , 7 ] Table 2 highlights the main characteristics of FINER criteria.[ 7 ]
Main features of FINER criteria (Feasibility, interest, novelty, ethics, and relevance) to formulate a good research question. Adapted from Cummings et al .[ 7 ]
Novelty and relevance
Although it is clear that any research project should commence with an accurate literature interpretation, in many instances it represents the start and the end of the research: the reader will soon realise that the answer to several questions can be easily found in the published literature.[ 5 ] When the question overcomes the test of a thorough literature review, the project may become novel (there is a gap in the knowledge, and therefore, there is a need for new evidence on the topic) and relevant (the paper may contribute to change the clinical practice). In this context, it is important to distinguish the difference between statistical significance and clinical relevance: in the aforementioned study of Oba et al .,[ 10 ] despite the means of insertion times were reported as significant for the Supreme™ LMA, as compared with ProSeal™ LMA, the difference found in the insertion times (528 vs. 486 sec, respectively), although reported as significant, had little or no clinical relevance.[ 10 ] Conversely, a statistically significant difference of 12 sec might be of clinical relevance in neonates weighing <5 kg.[ 17 ] Thus, statistical tests must be interpreted in the context of a clinically meaningful effect size, which should be previously defined by the researcher.
Feasibility and ethical aspects
Among FINER criteria, there are two potential barriers that may prevent the successful conduct of the project and publication of the manuscript: feasibility and ethical aspects. These obstacles are usually related to the target population, as discussed above. Feasibility refers not only to the budget but also to the complexity of the design, recruitment strategy, blinding, adequacy of the sample size, measurement of the outcome, time of follow-up of participants, and commitment of clinicians, among others.[ 3 , 7 ] Funding, as a component of feasibility, may also be implicated in the ethical principles of clinical research, because the choice of the primary study question may be markedly influenced by the specific criteria demanded in the interest of potential funders.
Discussing ethical issues with local committees is compulsory, as rules applied might vary among countries.[ 18 ] Potential risks and benefits need to be carefully weighed, based upon the four principles of respect for autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice.[ 19 ] Although many of these issues may be related to the population target (e.g., conducting a clinical trial in patients with ongoing cardiopulmonary resuscitation would be inappropriate, as would be anaesthetising patients undergoing elective LASER treatment for condylomas, to examine the performance of supraglottic airway devices),[ 14 , 15 ] ethical conflicts may also arise from the intervention (particularly those involving the occurrence of side effects or complications, and their potential for reversibility), comparison (e.g., use of placebo or sham procedures),[ 19 ] outcome (surrogate outcomes should be considered in lieu of long term outcomes), or time frame (e.g., unnecessary longer exposition to an intervention). Thus, FINER criteria should not be conceived without a concomitant examination of the PICOT checklist, and consequently, PICOT framework and FINER criteria should not be seen as separated components, but rather complementary ingredients of a good research question.
Undoubtedly, no research project can be conducted if it is deemed unfeasible, and most institutional review boards would not be in a position to approve a work with major ethical problems. Nonetheless, whether or not the findings are interesting, is a subjective matter. Engaging the attention of readers also depends upon a number of factors, including the manner of presenting the problem, the background of the topic, the intended audience, and the reader's expectations. Furthermore, the interest is usually linked to the novelty and relevance of the topic, and it is worth nothing that editors and peer reviewers of high-impact medical journals are usually reluctant to accept any publication, if there is no novelty inherent to the research hypothesis, or there is a lack of relevance in the results.[ 11 ] Nevertheless, a considerable number of papers have been published without any novelty or relevance in the topic addressed. This is probably reflected in a recent survey, according to which only a third of respondents declared to have read thoroughly the most recent papers downloaded, and at least half of those manuscripts remained unread.[ 20 ] The same study reported that up to one-third of papers examined remained uncited after 5 years of publication, and only 20% of papers accounted for 80% of the citations.[ 20 ]
Formulating a good research question can be fascinating, albeit challenging, even for experienced investigators. While it is clear that clinical experience in combination with the accurate interpretation of literature and teamwork are essential to develop new ideas, the formulation of a clinical problem usually requires the compliance with PICOT framework in conjunction with FINER criteria, in order to translate a clinical dilemma into a researchable question. Working in the right environment with the adequate support of experienced researchers, will certainly make a difference in the generation of knowledge. By doing this, a lot of time will be saved in the search of the primary study question, and undoubtedly, there will be more chances to become a successful researcher.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 December 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
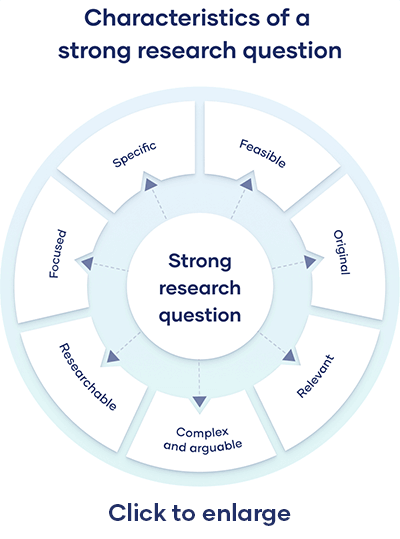
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, research questions quiz, frequently asked questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarised in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, December 12). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-question/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Sign Up Free
Do you want a free Survey Software?
We have the #1 Online Survey Maker Software to get actionable user insights.
How To Write a Good Research Question: Guide with Definition, Tips & Examples

Sameer Bhatia
Founder and CEO - ProProfs
Review Board Member
Sameer Bhatia is the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of ProProfs.com. He believes that software should make you happy and is driven to create a 100-year company that delivers delightfully ... Read more
Sameer Bhatia is the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of ProProfs.com. He believes that software should make you happy and is driven to create a 100-year company that delivers delightfully smart software with awesome support. His favorite word is 'delight,' and he dislikes the term 'customer satisfaction,' as he believes that 'satisfaction' is a low bar and users must get nothing less than a delightful experience at ProProfs. Sameer holds a Masters in Computer Science from the University of Southern California (USC). He lives in Santa Monica with his wife & two daughters. Read less

Market Research Specialist
Emma David, a seasoned market research professional, specializes in employee engagement, survey administration, and data management. Her expertise in leveraging data for informed decisions has positively impacted several brands, enhancing their market position.

Research questions form the backbone of any study, guiding researchers in their search for knowledge and understanding. Framing relevant research questions is the first essential step for ensuring the research is effective and produces valuable insights.
In this blog, we’ll explore what research questions are, tips for crafting them, and a variety of research question examples across different fields to help you formulate a well-balanced research questionnaire.
Let’s begin.
What Is a Research Question?
A research question is a specific inquiry or problem statement guiding a research study, outlining the researcher’s intention to investigate. Think of it as a roadmap for your paper or thesis – it tells you exactly what you want to explore, giving your work a clear purpose.
A good research question not only helps you focus your writing but also guides your readers. It gives them a clear idea of what your research is about and what you aim to achieve. Before you start drafting your paper and even before you conduct your study, it’s important to write a concise statement of what you want to accomplish or discover.
This sets the stage for your research and ensures your work is focused and purposeful.
Why Are Research Questions Important?
Research questions are the cornerstone of any academic or scientific inquiry. They serve as a guide for the research process, helping to focus the study, define its goals, and structure its methodology.
Below are some of its most significant impacts, along with hypothetical examples to help you understand them better:
1. Guidance and Focus
Research questions provide a clear direction for the study, enabling researchers to narrow down the scope of their investigation to a manageable size. Research efforts can become scattered and unfocused without a well-defined question without a well-defined question, leading to wasted time and resources.
For example, consider a researcher interested in studying the effects of technology on education. A broad interest in technology and education could lead to an overwhelming range of topics to cover. However, by formulating a specific research question such as, “ How does the use of interactive digital textbooks in high school science classes affect students’ learning outcomes?” the researcher can focus their study on a specific aspect of technology in education, making the research more manageable and directed.
2. Defining the Research Objectives
A well-crafted research question helps to clearly define what the researcher aims to discover, examine, or analyze. This clarity is crucial for determining the study’s objectives and ensures that every step of the research process contributes toward achieving these goals.
For example, in a study aimed at understanding the impact of remote work on employee productivity, a research question such as “ Does remote work increase productivity among information technology professionals? ” directly sets the objective of the study to measure productivity levels among a specific group when working remotely.
3. Determining the Research Methodology
The research question influences the choice of methodology, including the design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques. It dictates whether the study should be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods and guides the selection of tools and procedures for conducting the research.
For example, in a research question like “ What are the lived experiences of first-generation college students? ” a qualitative approach using interviews or focus groups might be chosen to gather deep, nuanced insights into students’ experiences. In contrast, a question such as “ What percentage of first-generation college students graduate within four years?” would require a quantitative approach, possibly utilizing existing educational data sets for analysis.
4. Enhancing Relevance and Contribution
A well-thought-out research question ensures that the study addresses a gap in the existing literature or solves a real-world problem. This relevance is crucial for the contribution of the research to the field, as it helps to advance knowledge, inform policy, or offer practical solutions.
For example, in a scenario where existing research has largely overlooked the environmental impacts of single-use plastics in urban waterways, a question like “ What are the effects of single-use plastic pollution on the biodiversity of urban waterways?” can fill this gap, contributing valuable new insights to environmental science and potentially influencing urban environmental policies.
5. Facilitating Data Interpretation and Analysis
Clear research questions help in structuring the analysis, guiding the interpretation of data, and framing the discussion of results. They ensure that the data collected is directly relevant to the questions posed, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
For example, in a study asking, “ How do social media algorithms influence political polarization among users? ” the data analysis would specifically focus on the mechanisms of algorithmic content delivery and its effects on user behavior and political views. This focus makes it straightforward to interpret how algorithm-induced echo chambers might contribute to polarization.
Types of Research Questions
Understanding the different types of research questions is essential for researchers to effectively design and conduct studies that align with their research objectives and methodologies
These questions can be broadly categorized into three main types: quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method research questions.
Let’s explore each type in-depth, along with some examples.
Type A: Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to answer specific research questions or hypotheses. It focuses on quantifying relationships, patterns, and phenomena, often using statistical methods for analysis. Quantitative research questions are typically structured and aim to explore relationships between variables or assess the impact of interventions.
Quantitative research questions can again be subcategorized into three distinct types:
1. Descriptive Questions :
Descriptive questions aim to describe characteristics, behaviors, or phenomena within a population. These questions often start with words like “ how much ,” “ how many ,” or “ what is the frequency of .” They provide a snapshot of a particular situation or phenomenon.
Example: “ What is the average age of first-time homebuyers in the United States?”
2. Comparative Questions :
Comparative questions seek to compare two or more groups, conditions, or variables to identify differences or similarities. They often involve the use of statistical tests to determine the significance of observed differences or associations.
Example: “Is there a significant difference in academic performance between students who receive tutoring and those who do not?”
3. Relationship Questions:
Relationship questions explore the associations or correlations between variables. They aim to determine the strength and direction of relationships, allowing researchers to assess the predictive power of one variable on another.
Example: “What is the relationship between exercise frequency and levels of anxiety among adults?”
Type B: Qualitative Research Questions
Qualitative research involves the exploring and understanding of complex phenomena through an in-depth examination of individuals’ experiences, behaviors, and perspectives. It aims to uncover meaning, patterns, and underlying processes within a specific context, often through techniques such as interviews, observations, and content analysis.
Types of qualitative research questions:
1. Exploratory Questions:
Exploratory questions seek to understand a particular phenomenon or issue in depth. They aim to uncover new insights, perspectives, or dimensions that may not have been previously considered.
Example: “What are the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in accessing healthcare services in rural communities?”
2. Descriptive Questions:
Descriptive questions aim to provide a detailed description or portrayal of a phenomenon or social context. They focus on capturing the intricacies and nuances of a particular situation or setting.
Example: “What are the communication patterns within multicultural teams in a corporate setting?”
3. Explanatory Questions:
Explanatory questions delve into the underlying reasons, mechanisms, or processes that influence a phenomenon or behavior. They aim to uncover the ‘why’ behind observed patterns or relationships.
Example: “What factors contribute to employee turnover in the hospitality industry?”
Type C: Mixed-Methods Research Questions
Mixed-methods research integrates both quantitative and qualitative approaches within a single study, allowing researchers to gain a comprehensive understanding of a research problem. Mixed-method research questions are designed to address complex phenomena from multiple perspectives, combining the strengths of both quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
Types of Mixed-Methods Research Questions:
1. Sequential Questions:
Sequential questions involve the collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data in separate phases or stages. The findings from one phase inform the design and implementation of the subsequent phase.
Example: “Quantitatively, what are the prevalence rates of mental health disorders among adolescents? Qualitatively, what are the factors influencing help-seeking behaviors among adolescents with mental health concerns?”
2. Concurrent Questions:
Concurrent questions involve the simultaneous collection and analysis of quantitative and qualitative data. Researchers triangulate findings from both methods to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem.
Example: “How do students’ academic performance (quantitative) correlate with their perceptions of school climate (qualitative)?”
3. Transformative Questions:
Transformative questions aim to use mixed-methods research to bring about social change or inform policy decisions. They seek to address complex societal issues by combining quantitative data on prevalence rates or trends with qualitative insights into lived experiences and perspectives.
Example: “What are the barriers to accessing healthcare services for underserved communities, and how can healthcare policies be redesigned to address these barriers effectively?”
Steps to Developing a Good Research Question
Developing a good research question is a crucial first step in any research endeavor. A well-crafted research question serves as the foundation for the entire study, guiding the researcher in formulating hypotheses, selecting appropriate methodologies, and conducting meaningful analyses.
Here are the steps to developing a good research question:
Identify a Broad Topic
Begin by identifying a broad area of interest or a topic that you would like to explore. This could stem from your academic discipline, professional interests, or personal curiosity. However, make sure to choose a topic that is both relevant and feasible for research within the constraints of your resources and expertise.
Conduct Preliminary Research
Before refining your research question, conduct preliminary research to familiarize yourself with existing literature and identify gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions within your chosen topic. This step will help you narrow down your focus and ensure that your research question contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
Narrow Down Your Focus
Based on your preliminary research, narrow down your focus to a specific aspect, problem, or issue within your chosen topic. Consider the scope of your study, the availability of resources, and the feasibility of addressing your research question within a reasonable timeframe. Narrowing down your focus will help you formulate a more precise and manageable research question.
Define Key Concepts and Variables
Clearly define the key concepts, variables, or constructs that are central to your research question. This includes identifying the main variables you will be investigating, as well as any relevant theoretical or conceptual frameworks that will guide your study. Clarifying these aspects will ensure that your research question is clear, specific, and focused.
Formulate Your Research Question
Based on your narrowed focus and defined key concepts, formulate your research question. A good research question is concise, specific, and clearly articulated. It should be phrased in a way that is open-ended and leads to further inquiry. Avoid vague or overly broad questions that are difficult to answer or lack clarity.
Consider the Type of Research
Consider whether your research question is best suited for quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods research. The type of research question will influence your choice of methodologies, data collection techniques, and analytical approaches. Tailor your research question to align with the goals and requirements of your chosen research paradigm.
Evaluate the Significance and Relevance
Evaluate the significance and relevance of your research question within the context of your academic discipline, field of study, or practical implications. Consider how your research question fills gaps in knowledge, addresses practical problems, or advances theoretical understanding. A good research question should be meaningful and contribute to the broader scholarly conversation.
Refine and Revise
Finally, refine and revise your research question based on feedback from colleagues, advisors, or peers. Consider whether the question is clear, feasible, and likely to yield meaningful results. Be open to making revisions as needed to ensure that your research question is well-constructed and aligned with the goals of your study.
Examples of Research Questions
Below are some example research questions from various fields to provide a glimpse into the diverse array of inquiries within each field.
1. Psychology Research Questions:
- How does childhood trauma influence the development of personality disorders in adulthood?
- What are the effects of mindfulness meditation on reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression?
- How does social media usage impact self-esteem among adolescents?
- What factors contribute to the formation and maintenance of romantic relationships in young adults?
- What are the cognitive mechanisms underlying decision-making processes in individuals with addiction?
- How does parenting style affect the development of resilience in children?
- What are the long-term effects of early childhood attachment patterns on adult romantic relationships?
- What role does genetics play in the predisposition to mental health disorders such as schizophrenia?
- How does exposure to violent media influence aggressive behavior in children?
- What are the psychological effects of social isolation on mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic?
2. Business Research Questions:
- What are the key factors influencing consumer purchasing behavior in the e-commerce industry?
- How does organizational culture impact employee job satisfaction and retention?
- What are the strategies for successful international market entry for small businesses?
- What are the effects of corporate social responsibility initiatives on brand reputation and consumer loyalty?
- How do leadership styles influence organizational innovation and performance?
- What are the challenges and opportunities for implementing sustainable business practices in emerging markets?
- What factors contribute to the success of startups in the technology sector?
- How do economic fluctuations affect consumer confidence and spending behavior?
- What are the impacts of globalization on supply chain management practices?
- What are the determinants of successful mergers and acquisitions in the corporate sector?
3. Education Research Questions:
- What teaching strategies are most effective for promoting student engagement in online learning environments?
- How does socioeconomic status impact academic achievement and educational attainment?
- What are the barriers to inclusive education for students with disabilities?
- What factors influence teacher job satisfaction and retention in urban schools?
- How does parental involvement affect student academic performance and school outcomes?
- What are the effects of early childhood education programs on later academic success?
- How do culturally responsive teaching practices impact student learning outcomes in diverse classrooms?
- What are the best practices for implementing technology integration in K-12 education?
- How do school leadership practices influence school climate and student outcomes?
- What interventions are most effective for addressing the achievement gap in STEM education?
4. Healthcare Research Questions:
- What are the factors influencing healthcare-seeking behavior among underserved populations?
- How does patient-provider communication affect patient satisfaction and treatment adherence?
- What are the barriers to implementing telemedicine services in rural communities?
- What interventions are effective for reducing hospital readmissions among elderly patients?
- How does access to healthcare services impact health disparities among marginalized communities?
- What are the effects of nurse staffing levels on patient outcomes in acute care settings?
- How do socioeconomic factors influence access to mental healthcare services?
- What are the best practices for managing chronic disease patients in primary care settings?
- What are the impacts of healthcare reform policies on healthcare delivery and patient outcomes?
- How does cultural competence training for healthcare providers affect patient trust and satisfaction?
5. Computer Science Research Questions:
- What are the security vulnerabilities of blockchain technology, and how can they be mitigated?
- How can machine learning algorithms be used to detect and prevent cyber-attacks?
- What are the privacy implications of data mining techniques in social media platforms?
- How can artificial intelligence be used to improve medical diagnosis and treatment?
- What are the challenges and opportunities for implementing edge computing in IoT systems?
- How can natural language processing techniques be applied to improve human-computer interaction?
- What are the impacts of algorithmic bias on fairness and equity in decision-making systems?
- How can quantum computing algorithms be optimized for solving complex computational problems?
- What are the ethical considerations surrounding the use of autonomous vehicles in transportation systems?
- How does the design of user interfaces influence user experience and usability in mobile applications?
Create a Compelling Research Question With the Given Examples
Understanding research questions is essential for any successful research endeavor. We’ve explored the various research questions – quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-methods – each with unique characteristics and purposes.
Through various examples, tips, and strategies, we’ve seen how research questions can be tailored to specific fields of study.
By following these guidelines, we are confident that your research questions will be well-designed, focused, and capable of yielding valuable insights.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some good research question examples.
Good research questions are clear, specific, relevant, and feasible. For example, “How does childhood trauma influence the development of personality disorders in adulthood?”
What are some examples of good and bad research questions?
Good research questions are focused and relevant, such as “What factors influence employee job satisfaction in the hospitality industry?” Bad research questions are vague or trivial, like “What is the favorite color of employees in the hospitality industry?”
Watch: How to Create a Survey Using ProProfs Survey Maker

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Popular Posts in This Category

What’s the Best Time to Send a Survey

Conducting Gap Analysis: Steps, Tools and Examples
Employee Surveys is Still the Best Way to Measure Engagement

25 Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion (DEI) Survey Questions to Ask

11 Best Wufoo Alternatives and Competitors

Employee Engagement Survey Questions You Should Ask
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research Questions
Try Qualtrics for free
How to write qualitative research questions.
11 min read Here’s how to write effective qualitative research questions for your projects, and why getting it right matters so much.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a blanket term covering a wide range of research methods and theoretical framing approaches. The unifying factor in all these types of qualitative study is that they deal with data that cannot be counted. Typically this means things like people’s stories, feelings, opinions and emotions , and the meanings they ascribe to their experiences.
Qualitative study is one of two main categories of research, the other being quantitative research. Quantitative research deals with numerical data – that which can be counted and quantified, and which is mostly concerned with trends and patterns in large-scale datasets.
What are research questions?
Research questions are questions you are trying to answer with your research. To put it another way, your research question is the reason for your study, and the beginning point for your research design. There is normally only one research question per study, although if your project is very complex, you may have multiple research questions that are closely linked to one central question.
A good qualitative research question sums up your research objective. It’s a way of expressing the central question of your research, identifying your particular topic and the central issue you are examining.
Research questions are quite different from survey questions, questions used in focus groups or interview questions. A long list of questions is used in these types of study, as opposed to one central question. Additionally, interview or survey questions are asked of participants, whereas research questions are only for the researcher to maintain a clear understanding of the research design.
Research questions are used in both qualitative and quantitative research , although what makes a good research question might vary between the two.
In fact, the type of research questions you are asking can help you decide whether you need to take a quantitative or qualitative approach to your research project.
Discover the fundamentals of qualitative research
Quantitative vs. qualitative research questions
Writing research questions is very important in both qualitative and quantitative research, but the research questions that perform best in the two types of studies are quite different.
Quantitative research questions
Quantitative research questions usually relate to quantities, similarities and differences.
It might reflect the researchers’ interest in determining whether relationships between variables exist, and if so whether they are statistically significant. Or it may focus on establishing differences between things through comparison, and using statistical analysis to determine whether those differences are meaningful or due to chance.
- How much? This kind of research question is one of the simplest. It focuses on quantifying something. For example:
How many Yoruba speakers are there in the state of Maine?
- What is the connection?
This type of quantitative research question examines how one variable affects another.
For example:
How does a low level of sunlight affect the mood scores (1-10) of Antarctic explorers during winter?
- What is the difference? Quantitative research questions in this category identify two categories and measure the difference between them using numerical data.
Do white cats stay cooler than tabby cats in hot weather?
If your research question fits into one of the above categories, you’re probably going to be doing a quantitative study.
Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions focus on exploring phenomena, meanings and experiences.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research isn’t about finding causal relationships between variables. So although qualitative research questions might touch on topics that involve one variable influencing another, or looking at the difference between things, finding and quantifying those relationships isn’t the primary objective.
In fact, you as a qualitative researcher might end up studying a very similar topic to your colleague who is doing a quantitative study, but your areas of focus will be quite different. Your research methods will also be different – they might include focus groups, ethnography studies, and other kinds of qualitative study.
A few example qualitative research questions:
- What is it like being an Antarctic explorer during winter?
- What are the experiences of Yoruba speakers in the USA?
- How do white cat owners describe their pets?
Qualitative research question types
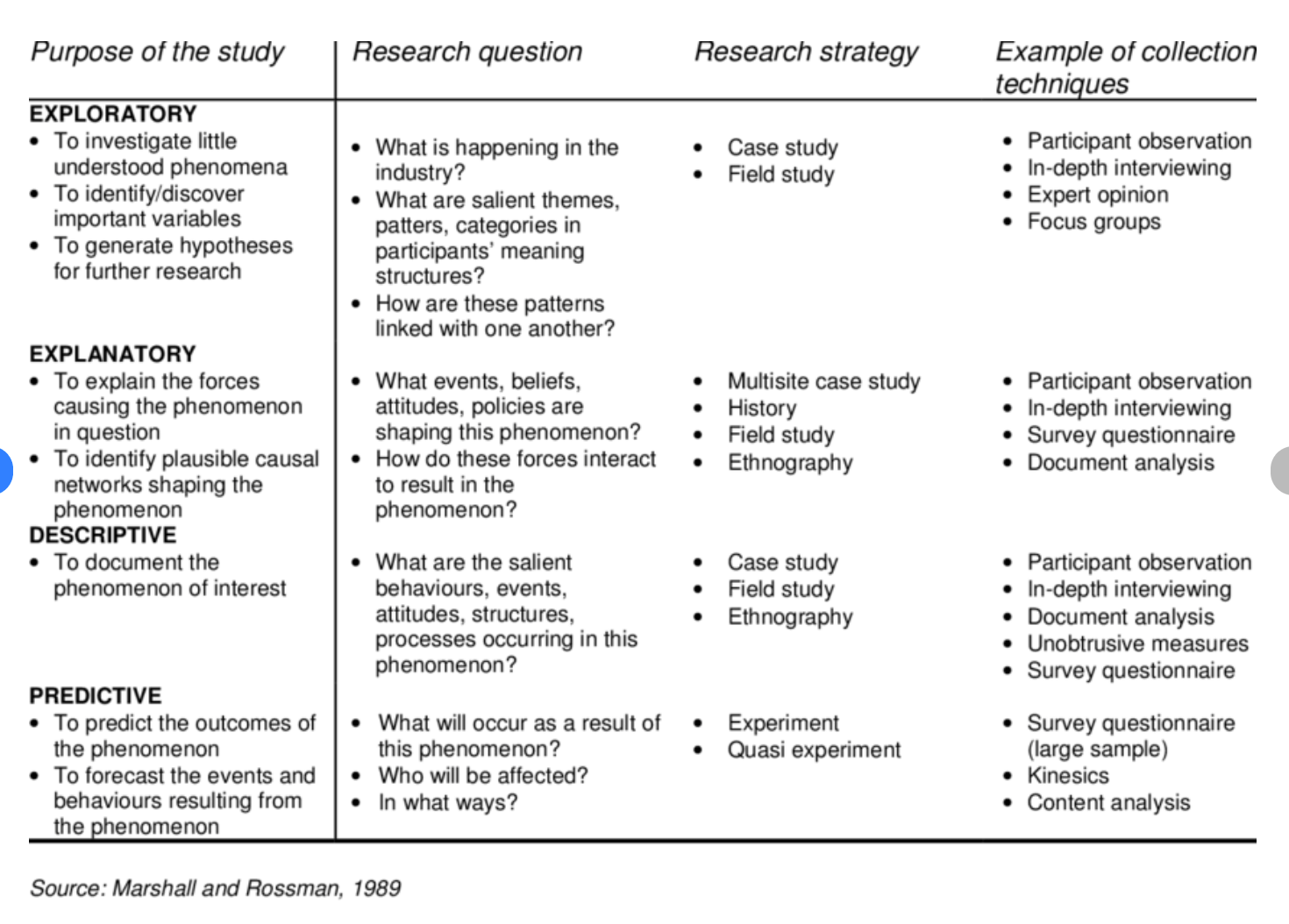
Marshall and Rossman (1989) identified 4 qualitative research question types, each with its own typical research strategy and methods.
- Exploratory questions
Exploratory questions are used when relatively little is known about the research topic. The process researchers follow when pursuing exploratory questions might involve interviewing participants, holding focus groups, or diving deep with a case study.
- Explanatory questions
With explanatory questions, the research topic is approached with a view to understanding the causes that lie behind phenomena. However, unlike a quantitative project, the focus of explanatory questions is on qualitative analysis of multiple interconnected factors that have influenced a particular group or area, rather than a provable causal link between dependent and independent variables.
- Descriptive questions
As the name suggests, descriptive questions aim to document and record what is happening. In answering descriptive questions , researchers might interact directly with participants with surveys or interviews, as well as using observational studies and ethnography studies that collect data on how participants interact with their wider environment.
- Predictive questions
Predictive questions start from the phenomena of interest and investigate what ramifications it might have in the future. Answering predictive questions may involve looking back as well as forward, with content analysis, questionnaires and studies of non-verbal communication (kinesics).
Why are good qualitative research questions important?
We know research questions are very important. But what makes them so essential? (And is that question a qualitative or quantitative one?)
Getting your qualitative research questions right has a number of benefits.
- It defines your qualitative research project Qualitative research questions definitively nail down the research population, the thing you’re examining, and what the nature of your answer will be.This means you can explain your research project to other people both inside and outside your business or organization. That could be critical when it comes to securing funding for your project, recruiting participants and members of your research team, and ultimately for publishing your results. It can also help you assess right the ethical considerations for your population of study.
- It maintains focus Good qualitative research questions help researchers to stick to the area of focus as they carry out their research. Keeping the research question in mind will help them steer away from tangents during their research or while they are carrying out qualitative research interviews. This holds true whatever the qualitative methods are, whether it’s a focus group, survey, thematic analysis or other type of inquiry.That doesn’t mean the research project can’t morph and change during its execution – sometimes this is acceptable and even welcome – but having a research question helps demarcate the starting point for the research. It can be referred back to if the scope and focus of the project does change.
- It helps make sure your outcomes are achievable
Because qualitative research questions help determine the kind of results you’re going to get, it helps make sure those results are achievable. By formulating good qualitative research questions in advance, you can make sure the things you want to know and the way you’re going to investigate them are grounded in practical reality. Otherwise, you may be at risk of taking on a research project that can’t be satisfactorily completed.
Developing good qualitative research questions
All researchers use research questions to define their parameters, keep their study on track and maintain focus on the research topic. This is especially important with qualitative questions, where there may be exploratory or inductive methods in use that introduce researchers to new and interesting areas of inquiry. Here are some tips for writing good qualitative research questions.
1. Keep it specific
Broader research questions are difficult to act on. They may also be open to interpretation, or leave some parameters undefined.
Strong example: How do Baby Boomers in the USA feel about their gender identity?
Weak example: Do people feel different about gender now?
2. Be original
Look for research questions that haven’t been widely addressed by others already.
Strong example: What are the effects of video calling on women’s experiences of work?
Weak example: Are women given less respect than men at work?
3. Make it research-worthy
Don’t ask a question that can be answered with a ‘yes’ or ‘no’, or with a quick Google search.
Strong example: What do people like and dislike about living in a highly multi-lingual country?
Weak example: What languages are spoken in India?
4. Focus your question
Don’t roll multiple topics or questions into one. Qualitative data may involve multiple topics, but your qualitative questions should be focused.
Strong example: What is the experience of disabled children and their families when using social services?
Weak example: How can we improve social services for children affected by poverty and disability?
4. Focus on your own discipline, not someone else’s
Avoid asking questions that are for the politicians, police or others to address.
Strong example: What does it feel like to be the victim of a hate crime?
Weak example: How can hate crimes be prevented?
5. Ask something researchable
Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
Strong example: How do perceptions of physical beauty vary between today’s youth and their parents’ generation?
Weak example: Which country has the most beautiful people in it?
Related resources
Qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, business research methods 12 min read, qualitative research interviews 11 min read, market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
How to…write a good research question
Affiliations.
- 1 Centre for Research in Professional Learning, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK.
- 2 School of Medicine, Dentistry and Biomedical Sciences, Queen's University Belfast, Belfast, Northern Ireland, UK.
- 3 LEARN! Academy, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
- 4 VUmc School of Medical Sciences, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
- PMID: 29575667
- DOI: 10.1111/tct.12776
This paper, on writing research questions, is the first in a series that aims to support novice researchers within clinical education, particularly those undertaking their first qualitative study. Put simply, a research question is a question that a research project sets out to answer. Most research questions will lead to a project that aims to generate new insights, but the target audience and the methodology will vary widely. The term 'evaluation question' is used less commonly, but the same principles apply. The key difference is that evaluation questions are typically more focused on the immediate context: for example, the effectiveness of an educational intervention in a particular setting. Whether your ambition is for research or evaluation, we hope that you will find this paper helpful for designing your own educational projects. A research question is a question that a research project sets out to answer.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd and The Association for the Study of Medical Education.
- Guidelines as Topic
- Qualitative Research*

Literature Reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- Getting started
- Types of reviews
Define topic
Brainstorming, limit scope, how ai can help, helpful resources.
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
Mission animated icons created by Freepik - Flaticon
For example, the following research question is too broad.
Does social media affect mental health in college students?
A more focused research question could be:
Does social media play a role in the number of eating disorder diagnoses in college-aged women?
Need some guidance? Contact your subject librarian for a research consultation or reach out to [email protected] .
Start the brainstorming process:
- Begin by identifying a broad topic of research interest (the more you're personally interested in it, the better!). Write it down to clarify your focus.
- Narrow down your scope by considering specific areas within this topic that you want to explore.
- Identify key themes and elements related to these specific areas. These will be the building blocks of your investigation.
- Finally, integrate these key areas and elements into a well-crafted research question.
One way to brainstorm is to use a flowchart.

The scope of a topic encompasses the boundaries and constraints you set for your research. The more precise your research question, the smoother the research process becomes.
Feeling stuck? Here are some ways you can narrow down your topic:
- geographic location
- time period
- discipline/field of study
- age group, etc.

You: I need to conduct a literature review about social media, mental health, and college students. What are some example research questions within this topic?
ChatGPT:
- How does the frequency and nature of social media use impact the mental health of college students?
- What role do specific social media platforms play in influencing the mental well-being of college students?
- How do online social interactions on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, or Twitter relate to the mental health outcomes of college students?
- Are there differences in the association between social media use and mental health outcomes based on demographic factors such as gender, age, or academic major among college students?
- What strategies do college students employ to cope with negative mental health effects associated with social media use?
- How does the perception of social support through online platforms affect the mental health of college students?
- To what extent does the comparison of oneself to others on social media contribute to mental health challenges among college students?
- What interventions or educational programs are effective in promoting positive mental health behaviors in the context of social media use for college students?
- How do social media literacy and awareness programs impact the mental health attitudes and behaviors of college students?
- What is the relationship between the use of social media for academic and social purposes and the mental health outcomes of college students?
Generative AI tools : ChatGPT , Google Gemini (formerly Bard) , Claude , Microsoft Copilot
For more information on how to incorporate AI tools into your research, check out the section on AI Tools .
- Developing Your Research Question
- Developing a Researchable Question
- Brainstorming tips from UNC Writing Center
- << Previous: Types of reviews
- Next: 2. Plan your search >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries


Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Jump to DSE Guide
Purpose statement overview.
The purpose statement succinctly explains (on no more than 1 page) the objectives of the research study. These objectives must directly address the problem and help close the stated gap. Expressed as a formula:

Good purpose statements:
- Flow from the problem statement and actually address the proposed problem
- Are concise and clear
- Answer the question ‘Why are you doing this research?’
- Match the methodology (similar to research questions)
- Have a ‘hook’ to get the reader’s attention
- Set the stage by clearly stating, “The purpose of this (qualitative or quantitative) study is to ...
In PhD studies, the purpose usually involves applying a theory to solve the problem. In other words, the purpose tells the reader what the goal of the study is, and what your study will accomplish, through which theoretical lens. The purpose statement also includes brief information about direction, scope, and where the data will come from.
A problem and gap in combination can lead to different research objectives, and hence, different purpose statements. In the example from above where the problem was severe underrepresentation of female CEOs in Fortune 500 companies and the identified gap related to lack of research of male-dominated boards; one purpose might be to explore implicit biases in male-dominated boards through the lens of feminist theory. Another purpose may be to determine how board members rated female and male candidates on scales of competency, professionalism, and experience to predict which candidate will be selected for the CEO position. The first purpose may involve a qualitative ethnographic study in which the researcher observes board meetings and hiring interviews; the second may involve a quantitative regression analysis. The outcomes will be very different, so it’s important that you find out exactly how you want to address a problem and help close a gap!
The purpose of the study must not only align with the problem and address a gap; it must also align with the chosen research method. In fact, the DP/DM template requires you to name the research method at the very beginning of the purpose statement. The research verb must match the chosen method. In general, quantitative studies involve “closed-ended” research verbs such as determine , measure , correlate , explain , compare , validate , identify , or examine ; whereas qualitative studies involve “open-ended” research verbs such as explore , understand , narrate , articulate [meanings], discover , or develop .
A qualitative purpose statement following the color-coded problem statement (assumed here to be low well-being among financial sector employees) + gap (lack of research on followers of mid-level managers), might start like this:
In response to declining levels of employee well-being, the purpose of the qualitative phenomenology was to explore and understand the lived experiences related to the well-being of the followers of novice mid-level managers in the financial services industry. The levels of follower well-being have been shown to correlate to employee morale, turnover intention, and customer orientation (Eren et al., 2013). A combined framework of Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) Theory and the employee well-being concept informed the research questions and supported the inquiry, analysis, and interpretation of the experiences of followers of novice managers in the financial services industry.
A quantitative purpose statement for the same problem and gap might start like this:
In response to declining levels of employee well-being, the purpose of the quantitative correlational study was to determine which leadership factors predict employee well-being of the followers of novice mid-level managers in the financial services industry. Leadership factors were measured by the Leader-Member Exchange (LMX) assessment framework by Mantlekow (2015), and employee well-being was conceptualized as a compound variable consisting of self-reported turnover-intent and psychological test scores from the Mental Health Survey (MHS) developed by Johns Hopkins University researchers.
Both of these purpose statements reflect viable research strategies and both align with the problem and gap so it’s up to the researcher to design a study in a manner that reflects personal preferences and desired study outcomes. Note that the quantitative research purpose incorporates operationalized concepts or variables ; that reflect the way the researcher intends to measure the key concepts under study; whereas the qualitative purpose statement isn’t about translating the concepts under study as variables but instead aim to explore and understand the core research phenomenon.
Best Practices for Writing your Purpose Statement
Always keep in mind that the dissertation process is iterative, and your writing, over time, will be refined as clarity is gradually achieved. Most of the time, greater clarity for the purpose statement and other components of the Dissertation is the result of a growing understanding of the literature in the field. As you increasingly master the literature you will also increasingly clarify the purpose of your study.
The purpose statement should flow directly from the problem statement. There should be clear and obvious alignment between the two and that alignment will get tighter and more pronounced as your work progresses.
The purpose statement should specifically address the reason for conducting the study, with emphasis on the word specifically. There should not be any doubt in your readers’ minds as to the purpose of your study. To achieve this level of clarity you will need to also insure there is no doubt in your mind as to the purpose of your study.
Many researchers benefit from stopping your work during the research process when insight strikes you and write about it while it is still fresh in your mind. This can help you clarify all aspects of a dissertation, including clarifying its purpose.
Your Chair and your committee members can help you to clarify your study’s purpose so carefully attend to any feedback they offer.
The purpose statement should reflect the research questions and vice versa. The chain of alignment that began with the research problem description and continues on to the research purpose, research questions, and methodology must be respected at all times during dissertation development. You are to succinctly describe the overarching goal of the study that reflects the research questions. Each research question narrows and focuses the purpose statement. Conversely, the purpose statement encompasses all of the research questions.
Identify in the purpose statement the research method as quantitative, qualitative or mixed (i.e., “The purpose of this [qualitative/quantitative/mixed] study is to ...)
Avoid the use of the phrase “research study” since the two words together are redundant.
Follow the initial declaration of purpose with a brief overview of how, with what instruments/data, with whom and where (as applicable) the study will be conducted. Identify variables/constructs and/or phenomenon/concept/idea. Since this section is to be a concise paragraph, emphasis must be placed on the word brief. However, adding these details will give your readers a very clear picture of the purpose of your research.
Developing the purpose section of your dissertation is usually not achieved in a single flash of insight. The process involves a great deal of reading to find out what other scholars have done to address the research topic and problem you have identified. The purpose section of your dissertation could well be the most important paragraph you write during your academic career, and every word should be carefully selected. Think of it as the DNA of your dissertation. Everything else you write should emerge directly and clearly from your purpose statement. In turn, your purpose statement should emerge directly and clearly from your research problem description. It is good practice to print out your problem statement and purpose statement and keep them in front of you as you work on each part of your dissertation in order to insure alignment.
It is helpful to collect several dissertations similar to the one you envision creating. Extract the problem descriptions and purpose statements of other dissertation authors and compare them in order to sharpen your thinking about your own work. Comparing how other dissertation authors have handled the many challenges you are facing can be an invaluable exercise. Keep in mind that individual universities use their own tailored protocols for presenting key components of the dissertation so your review of these purpose statements should focus on content rather than form.
Once your purpose statement is set it must be consistently presented throughout the dissertation. This may require some recursive editing because the way you articulate your purpose may evolve as you work on various aspects of your dissertation. Whenever you make an adjustment to your purpose statement you should carefully follow up on the editing and conceptual ramifications throughout the entire document.
In establishing your purpose you should NOT advocate for a particular outcome. Research should be done to answer questions not prove a point. As a researcher, you are to inquire with an open mind, and even when you come to the work with clear assumptions, your job is to prove the validity of the conclusions reached. For example, you would not say the purpose of your research project is to demonstrate that there is a relationship between two variables. Such a statement presupposes you know the answer before your research is conducted and promotes or supports (advocates on behalf of) a particular outcome. A more appropriate purpose statement would be to examine or explore the relationship between two variables.
Your purpose statement should not imply that you are going to prove something. You may be surprised to learn that we cannot prove anything in scholarly research for two reasons. First, in quantitative analyses, statistical tests calculate the probability that something is true rather than establishing it as true. Second, in qualitative research, the study can only purport to describe what is occurring from the perspective of the participants. Whether or not the phenomenon they are describing is true in a larger context is not knowable. We cannot observe the phenomenon in all settings and in all circumstances.
Writing your Purpose Statement
It is important to distinguish in your mind the differences between the Problem Statement and Purpose Statement.
The Problem Statement is why I am doing the research
The Purpose Statement is what type of research I am doing to fit or address the problem
The Purpose Statement includes:
- Method of Study
- Specific Population
Remember, as you are contemplating what to include in your purpose statement and then when you are writing it, the purpose statement is a concise paragraph that describes the intent of the study, and it should flow directly from the problem statement. It should specifically address the reason for conducting the study, and reflect the research questions. Further, it should identify the research method as qualitative, quantitative, or mixed. Then provide a brief overview of how the study will be conducted, with what instruments/data collection methods, and with whom (subjects) and where (as applicable). Finally, you should identify variables/constructs and/or phenomenon/concept/idea.
Qualitative Purpose Statement
Creswell (2002) suggested for writing purpose statements in qualitative research include using deliberate phrasing to alert the reader to the purpose statement. Verbs that indicate what will take place in the research and the use of non-directional language that do not suggest an outcome are key. A purpose statement should focus on a single idea or concept, with a broad definition of the idea or concept. How the concept was investigated should also be included, as well as participants in the study and locations for the research to give the reader a sense of with whom and where the study took place.
Creswell (2003) advised the following script for purpose statements in qualitative research:
“The purpose of this qualitative_________________ (strategy of inquiry, such as ethnography, case study, or other type) study is (was? will be?) to ________________ (understand? describe? develop? discover?) the _________________(central phenomenon being studied) for ______________ (the participants, such as the individual, groups, organization) at __________(research site). At this stage in the research, the __________ (central phenomenon being studied) will be generally defined as ___________________ (provide a general definition)” (pg. 90).
Quantitative Purpose Statement
Creswell (2003) offers vast differences between the purpose statements written for qualitative research and those written for quantitative research, particularly with respect to language and the inclusion of variables. The comparison of variables is often a focus of quantitative research, with the variables distinguishable by either the temporal order or how they are measured. As with qualitative research purpose statements, Creswell (2003) recommends the use of deliberate language to alert the reader to the purpose of the study, but quantitative purpose statements also include the theory or conceptual framework guiding the study and the variables that are being studied and how they are related.
Creswell (2003) suggests the following script for drafting purpose statements in quantitative research:
“The purpose of this _____________________ (experiment? survey?) study is (was? will be?) to test the theory of _________________that _________________ (compares? relates?) the ___________(independent variable) to _________________________(dependent variable), controlling for _______________________ (control variables) for ___________________ (participants) at _________________________ (the research site). The independent variable(s) _____________________ will be generally defined as _______________________ (provide a general definition). The dependent variable(s) will be generally defined as _____________________ (provide a general definition), and the control and intervening variables(s), _________________ (identify the control and intervening variables) will be statistically controlled in this study” (pg. 97).
Sample Purpose Statements
- The purpose of this qualitative study was to determine how participation in service-learning in an alternative school impacted students academically, civically, and personally. There is ample evidence demonstrating the failure of schools for students at-risk; however, there is still a need to demonstrate why these students are successful in non-traditional educational programs like the service-learning model used at TDS. This study was unique in that it examined one alternative school’s approach to service-learning in a setting where students not only serve, but faculty serve as volunteer teachers. The use of a constructivist approach in service-learning in an alternative school setting was examined in an effort to determine whether service-learning participation contributes positively to academic, personal, and civic gain for students, and to examine student and teacher views regarding the overall outcomes of service-learning. This study was completed using an ethnographic approach that included observations, content analysis, and interviews with teachers at The David School.
- The purpose of this quantitative non-experimental cross-sectional linear multiple regression design was to investigate the relationship among early childhood teachers’ self-reported assessment of multicultural awareness as measured by responses from the Teacher Multicultural Attitude Survey (TMAS) and supervisors’ observed assessment of teachers’ multicultural competency skills as measured by the Multicultural Teaching Competency Scale (MTCS) survey. Demographic data such as number of multicultural training hours, years teaching in Dubai, curriculum program at current school, and age were also examined and their relationship to multicultural teaching competency. The study took place in the emirate of Dubai where there were 14,333 expatriate teachers employed in private schools (KHDA, 2013b).
- The purpose of this quantitative, non-experimental study is to examine the degree to which stages of change, gender, acculturation level and trauma types predicts the reluctance of Arab refugees, aged 18 and over, in the Dearborn, MI area, to seek professional help for their mental health needs. This study will utilize four instruments to measure these variables: University of Rhode Island Change Assessment (URICA: DiClemente & Hughes, 1990); Cumulative Trauma Scale (Kira, 2012); Acculturation Rating Scale for Arabic Americans-II Arabic and English (ARSAA-IIA, ARSAA-IIE: Jadalla & Lee, 2013), and a demographic survey. This study will examine 1) the relationship between stages of change, gender, acculturation levels, and trauma types and Arab refugees’ help-seeking behavior, 2) the degree to which any of these variables can predict Arab refugee help-seeking behavior. Additionally, the outcome of this study could provide researchers and clinicians with a stage-based model, TTM, for measuring Arab refugees’ help-seeking behavior and lay a foundation for how TTM can help target the clinical needs of Arab refugees. Lastly, this attempt to apply the TTM model to Arab refugees’ condition could lay the foundation for future research to investigate the application of TTM to clinical work among refugee populations.
- The purpose of this qualitative, phenomenological study is to describe the lived experiences of LLM for 10 EFL learners in rural Guatemala and to utilize that data to determine how it conforms to, or possibly challenges, current theoretical conceptions of LLM. In accordance with Morse’s (1994) suggestion that a phenomenological study should utilize at least six participants, this study utilized semi-structured interviews with 10 EFL learners to explore why and how they have experienced the motivation to learn English throughout their lives. The methodology of horizontalization was used to break the interview protocols into individual units of meaning before analyzing these units to extract the overarching themes (Moustakas, 1994). These themes were then interpreted into a detailed description of LLM as experienced by EFL students in this context. Finally, the resulting description was analyzed to discover how these learners’ lived experiences with LLM conformed with and/or diverged from current theories of LLM.
- The purpose of this qualitative, embedded, multiple case study was to examine how both parent-child attachment relationships are impacted by the quality of the paternal and maternal caregiver-child interactions that occur throughout a maternal deployment, within the context of dual-military couples. In order to examine this phenomenon, an embedded, multiple case study was conducted, utilizing an attachment systems metatheory perspective. The study included four dual-military couples who experienced a maternal deployment to Operation Iraqi Freedom (OIF) or Operation Enduring Freedom (OEF) when they had at least one child between 8 weeks-old to 5 years-old. Each member of the couple participated in an individual, semi-structured interview with the researcher and completed the Parenting Relationship Questionnaire (PRQ). “The PRQ is designed to capture a parent’s perspective on the parent-child relationship” (Pearson, 2012, para. 1) and was used within the proposed study for this purpose. The PRQ was utilized to triangulate the data (Bekhet & Zauszniewski, 2012) as well as to provide some additional information on the parents’ perspective of the quality of the parent-child attachment relationship in regards to communication, discipline, parenting confidence, relationship satisfaction, and time spent together (Pearson, 2012). The researcher utilized the semi-structured interview to collect information regarding the parents' perspectives of the quality of their parental caregiver behaviors during the deployment cycle, the mother's parent-child interactions while deployed, the behavior of the child or children at time of reunification, and the strategies or behaviors the parents believe may have contributed to their child's behavior at the time of reunification. The results of this study may be utilized by the military, and by civilian providers, to develop proactive and preventive measures that both providers and parents can implement, to address any potential adverse effects on the parent-child attachment relationship, identified through the proposed study. The results of this study may also be utilized to further refine and understand the integration of attachment theory and systems theory, in both clinical and research settings, within the field of marriage and family therapy.
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Problem Statement
- Next: Conceptual Framework >>
- Last Updated: May 16, 2024 8:25 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting
Money blog: Popular music magazine closes months after online relaunch – but 90s lad mag is back
Q magazine has abruptly closed just months after its relaunch due to "business reasons" - but Loaded is back. Read this and the rest of today's consumer and personal finance news - and leave a comment - below.
Monday 20 May 2024 12:17, UK
- August interest rate cut on cards - economists
- Virgin Trains could return to West Coast route
- Popular music magazine closes months after online relaunch – but 90s lad mag is back
- Two big moments this week - here's what's happening
Essential reads
- Money Problem : 'My second-hand Ford is being written off with a known issue - but no one is taking responsibility'
- How to sell your home without an estate agent
- Tourist taxes to watch out for in popular holiday destinations
- Basically... What is PIP - and what could government changes mean?
- Best of the Money blog - an archive
Ask a question or make a comment
A popular music magazine has been closed down just months after being relaunched online.
Q, which originally closed after 34 years in 2020, was revived as an online publication nearly six months ago after a licensing deal was struck by New-York based Empire Media Group.
But its surprise closure, which came to light on Friday, means a team of six full-time staff have lost their jobs.
Writer Will Harris is one of them, saying he'd lost his "first full-time employment in a dozen years".
Writing on Substack , he said the move had been a "business decision" but that staff had been working long hours to "make it the best publication" possible.
"We worked our shifts, worked before and after our shifts, and delivered consistently top-shelf content that was, to our way of thinking, exactly the sort of thing that a new incarnation of Q Magazine should offer," he wrote.
Editor-in-chief Andrew Barker said the decision to shut the magazine down "came with no advance warning, and no indication that anything was wrong".
"To say that we were shocked and devastated would be a colossal understatement."
Sky News has contacted Empire Media Group for comment.
Separately, last week saw the return of a 90s lads mag Loaded.
The magazine relaunched its website after disappearing nine years ago, offering a £9 monthly membership.
As part of its revival, it has changed its tagline from "for men who should know better" to "for men who know better".
"The relaunch of the platform is a digital rebellion for the modern man who refuses to fit into a stereotype, from the finest in music, sports, film, and anything else that is of interest," it said in a statement.
"Loaded is about building a space where men challenge each other, celebrate wins, and tackle all that matters to them."
Virgin Trains has applied for a licence that could see it return to running rail services on the West Coast route between London and Glasgow, five years after losing its contract.
The company had operated the service, which runs from London Euston via Birmingham and Manchester to Scotland, for 22 years before Avanti West Coast took over in 2019.
The company has now applied to the regulator - the Office of Rail and Road - for an Open Access licence. If granted, it means Virgin Trains receives no subsidy and runs services alongside the franchise, at its own risk.
A spokesperson for Virgin Group told Sky News: "While this application is just the first step towards exploring what might be possible, we think Open Access is the way forward.
"Open Access increases consumer choice and competition both of which Virgin has always supported."
By Sarah Taaffe-Maguire , business reporter
After four weeks of rises the Financial Times Stock Exchange (FTSE) 250 index of the 101st to 350th most valuable companies on the London Stock Exchange has begun a fifth week in positive territory - up 0.54%.
If it ends this week higher than now it'll be the best run it has had since before the pandemic, in December 2019.
The most valuable companies on the London Stock Exchange - the FTSE 100 index - also started the week on a high, up 0.22%. Mexican mining company Fresnillo is the best performing company of the day so far with shares up 3.17% as copper hit an all-time peak.
The oil price is staying lower than all of April and most of March at $84.24 for a barrel of Brent crude oil - the benchmark price.
A pound is equal to $1.2696 or €1.1675.
The average salary advertised on job sites increased by 0.45% to £38,810 in April, according to vacancies website Adzuna.
Only two sectors - legal and travel - experienced a fall in the average salary being offered.
"[This] demonstrates rising business confidence throughout the UK and that companies are keen to hire specialist staff," said Andrew Hunter, co-founder of Adzuna.
"They are willing to pay well for new team members too."
He said the East Midlands continued to see the largest annual increases for the fifth month in a row - helped by roles in science, tech and professional services.
Every Monday we get an expert to answer your money problems or consumer disputes. Find out how to submit yours at the bottom of this post. Today's question is...
We bought a Ford C-Max second hand four years ago. It's less than eight years old now with 77,000 miles. Our garage says the car is a write-off due to a known issue with EcoBoost engines. Ford refuses to pay for repairs. Anything I can do? Rory Raftery
Rory did not leave his contact details so we haven't been able to talk to the dealership - but we had some luck with Ford. First though, Scott Dixon, from The Complaints Resolver , lays out your basic rights...
Your contract is always with the trader who sold you the goods (in this case the garage), not the manufacturer.
Any reference to warranties is irrelevant, as the Consumer Rights Act 2015 overrides this and gives you an implied statutory warranty for free for up to six years in England and Wales and five years in Scotland.
The act states that goods ought to be:
- Fit for purpose
- As described
- Satisfactory quality
- Last a reasonable length of time
As we are past six months since you bought the car, the onus is on you to prove it had inherent faults when it was sold.
I would seek an independent report to reinforce your case and dispute. Given that this has been a well-known issue with EcoBoost engines for quite some time, the trader who sold you the vehicle should have carried out additional checks.
A cursory Google search reveals that a loss of engine power and serious valve damage is commonplace on higher mileage EcoBoost engines.
I would check to see if this vehicle has been subject to a recall. Also check the MOT history to see if any advisory notices were flagged and not remedied before you bought the vehicle.
Is the garage a member of The Motor Ombudsman? You can check that too here .
How did you pay for it?
You should always pay at least a deposit by credit card if possible, as it gives you additional free protection and joint liability under S75 Consumer Credit Act 1974 for purchases over £100.
If you paid a deposit by credit card, contact your credit card provider and say you want to raise a S75 dispute and claim for a faulty car.
They will ask for more details – say the supplier is in "breach of contract" under the Consumer Rights Act 2015 and has supplied a defective/faulty car. You have exhausted all options with the retailer and cannot resolve your dispute.
If the car is on finance, they bought the defective vehicle from the dealer and own it. You can go down the same route and raise a S75 claim against them for a breach of contract under the Consumer Rights Act 2015.
If you reach a stalemate with the credit card provider or finance company, ask for a deadlock letter setting out their final position so you can submit a formal complaint (with the final response/deadlock letter) to the Financial Ombudsman Service (FOS).
They do not like cases being referred to the FOS as it costs them money. The FOS will examine documents given to you as the customer at the point of sale. The dealership is responsible for any representations made in those documents. You are seeking to reject the car, so make this clear.
Offers made will be calculated on the anticipated lifespan of the goods – time of use and depreciation. Ask for any offers made to be evidenced with calculations to ascertain how the amount has been arrived at.
Car dealerships will often cite that they are entitled to deduct 45p a mile for use on refund calculations when you try to reject a faulty vehicle. This is a scam. The FOS has ruled that 25p a mile is fair and acceptable, so keep that in mind when any offers are made.
Statutory limitations on any consumer dispute is six years in England and Wales and five years in Scotland from the date the goods were received.
This does not detract from the expected lifespan of the goods – it is simply a limit on the time you have to resolve the dispute under the Consumer Rights Act 2015.
Options and next steps
If all else fails, you could take your case to the small claims court if it was England, or follow simple procedure in Scotland .
Ford response
A Ford spokesperson told the Money team: "Ford is confident in the robustness and reliability of its EcoBoost engine technology when the stated guidelines for maintenance and service are followed.
"Ford UK is happy to investigate service support and/or compensation measures for any customer who believes they have had an EcoBoost engine issue and is happy to review cases with a full-service history for vehicles up to 10 years old with less than 150,000 miles.
"For any customers in the UK whose vehicle meets these parameters, you can speak to our customer relationship team and contact details can be found on our website here ."
Ford offered to look at this specific case - but sadly Rory didn't leave contact details for us to pass on.
This feature is not intended as financial advice - the aim is to give an overview of the things you should think about. Submit your dilemma or consumer dispute via:
- The form above - make sure you leave a phone number or email address
- Email [email protected] with the subject line "Money blog"
- WhatsApp us here
A tiny Mexican taco stand has won a Michelin star.
El Califa de Leon in Mexico City offers just four types of tacos, with McDonald's prices, no reservations and plates served in plastic bags.
"The secret is the simplicity of our taco. It has only a tortilla, red or green sauce, and that's it. That, and the quality of the meat," chef Arturo Rivera Martinez told AP.
He's also probably the only Michelin-starred chef who, when asked what beverage should accompany his food, answers: "I like a Coke."
Thousands of time a day, he grabs a fresh, thinly sliced fillet of beef from a stack and slaps it on the grill, tosses a pinch of salt over it, squeezes half a lime on top, and grabs a soft round of freshly rolled tortilla dough onto the solid metal slab to puff up.
After less than a minute - he won't say exactly how long because "that's a secret" - he flips the beef over with a spatula, flips the tortilla, and very quickly scoops it onto a plate - then calls out the customer's name who ordered it.
Asked how it felt to get a Michelin star, he said in Mexico City slang, "esta chido ... esta padre," or "it's neat, it's cool".
El Califa de Leon, which was founded in 1968, is the only taco stand among the 16 Mexican restaurants given one star, as well as two eateries that have got two stars.
Other than perhaps one street food stand in Bangkok, it is probably the smallest restaurant ever to get a star
Half of the 100 square-foot (9.29 square-metre) space is taken up by a solid steel plate grill.
The other half is packed with standing customers, and an assistant who rolls out the rounds of tortilla dough constantly.
The prices are quite high by Mexican standards: the tacos range in price from 53 Mexican pesos to 82 Mexican pesos - that works out at around £2.50 to £4.
Waitrose's new Ottolenghi range has proved popular with customers, with sales reportedly 97% higher than predicted.
The nine products created in partnership with restaurateur Yotam Ottlenghi launched in 275 stores last month.
It marked the supermarket's first major deal with a celebrity chef since it ended its tie-up with Heston Blumenthal last year.
According to The Grocer, demand has been "unprecedented", with five of the nine lines unavailable online last week.
We checked and it seems stocks have since been replenished.
Waitrose told the news outlet performance of the range had "exceeded expectations", with sales 97% higher than anticipated.
The Pomegranate Harissa Paste has proved to be the top seller for the first two weeks.
The products have a 20% launch discount until 18 June.
A slim majority of economists believe the Bank of England will start cutting interest rates in August.
Thirty-eight of 71 polled by Reuters expect a cut to 5% in August - compared with 31 opting for June and two for September.
BoE governor Andrew Bailey said earlier this month that once they start falling, rates could dip lower than markets had been forecasting - prompting hope that mortgage holders could see rates closer to 3% next year.
The base rate has sat at 5.25%, a 16-year high, since August.
The aim was to reduce inflation by encouraging saving rather than spending, which tends to slow price rises.
Inflation has fallen dramatically from 11.1% in October to 3.2% in March - and April's figure, to be announced at 7am on Wednesday, is likely to put it closer to the target of 2%.
The next base rate decision is on 20 June.
"The reason I'm currently leaning a little bit more towards August rather than June is that with signs the economy is doing okay, the BoE is unlikely to feel the need to rush into cutting interest rates," said Dean Turner, chief eurozone and UK economist at UBS Global Wealth Management.
"They have time to ensure further progress on services inflation and wage pressures."
We're back for another week of consumer news, personal finance tips and all the latest on the economy - with two big moments playing out this week.
This is how the week in the Money blog is shaping up...
Today : Every week we ask industry experts to answer your Money Problems . Today, a reader's car has been written off with a known fault but they say no one is taking responsibility.
Tuesday : This week's Basically... explains everything you need to know about the FTSE.
Wednesday : It's inflation day - an announcement at 7am is expected to reveal that inflation returned to around the target level of 2% in April. But forecasters have been consistently off in the past year or two. We'll also have another Michelin chef picking their best Cheap Eats .
Thursday : Savings Champion founder Anna Bowes will be back with her weekly insight into the savings market.
Friday : The energy price cap for July-September will be announced - with a drop predicted. We'll also have everything you need to know about the mortgage market this week with the guys from Moneyfacts.
Running every weekday, Money features a morning markets round-up from the Sky News business team and regular updates and analysis from our business, City and economic correspondents, editors and presenters - Ed Conway , Mark Kleinman , Ian King , Paul Kelso and Adele Robinson .
You'll also be able to stream Business Live with Ian King on weekdays at 11.30am and 4.30pm.
Bookmark news.sky.com/money and check back from 8am, and through the day, each weekday.
The Money team is Emily Mee, Bhvishya Patel, Jess Sharp, Katie Williams, Brad Young and Ollie Cooper, with sub-editing by Isobel Souster. The blog is edited by Jimmy Rice.
By Ollie Cooper , Money team
Estate agent fees are one of the big expenses in selling a house - but rule changes and the rise of private sale websites have made it more common for people to go it alone.
But how easy is it - and what do you need to know? We spoke to industry experts to find out.
Firstly, what do estate agents do for their money?
An estate agent will typically charge in the range of 1%-3.5% of the sale price.
That means for the average house price (£284,691 from December) you could pay anywhere from £2,846 to £9,964 in commission fees.
"When you use an estate agent, their fee includes taking professional photographs, advertising your home, conducting property viewings, and negotiating a price on your behalf," says Jack Smithson from the home ownership site Better.co.uk .
In addition, an estate agent will compile comprehensive details of your house, including room sizes and descriptions of fixtures and fittings.
"They will also provide a concise write-up about the local area, highlighting amenities, schools, and transportation links," Jack adds.
And they'll conduct checks on buyers for you (more on this later).
It sounds like a lot, but...
"Selling your home yourself can be a manageable process with a few key steps," Jack says.
Preparation
You should begin by thoroughly researching house prices in your area, using websites like Rightmove and Zoopla - but seek free valuations from local estate agents to ensure you have a realistic asking price in mind.
Next, you want to take high-quality photos of your house.
Jack advises using tutorials on YouTube to learn new shooting and editing techniques that can take you to the next level.
You then want to write down what makes your home unique.
"While browsing other listings for inspiration, take it a step further by emphasising what you love about living in your home and the surrounding area," Jack suggests.
"Whether it's the refreshing scent of the coastline or the tranquil sounds of village life, incorporating these details can help potential buyers visualise living there," he advises.
Like using YouTube for photography tips, you can use free tools such as ChatGPT and Grammarly if you need help with your writing, Jack says.
Advertising
This is probably the biggest perk of going through an established estate agent - your home is much more likely to be viewed because they will have an established audience and a market. But it's very possible to do it alone.
"When it comes to advertising your home, explore a variety of avenues including local newspapers and social media," Jack says.
"Consider using websites like Strike, which allow individuals to list their properties for free on platforms like Rightmove," he suggests.
Viewings
Once you've secured some viewings, you've got the opportunity to make it a bit more personal than estate agents ever could - a real advantage.
"Explain the reasons behind your decision to purchase the property, highlight its unique features, and share the aspects of your neighbourhood that make it a desirable place to live," Jack says.
The small things matter when showing people round - so try to take an objective look around before you bring anyone in.
Do the things you'd do normally - make sure it smells nice and it's clean and tidy.
"Lastly, it's worth knowing that you must legally provide potential buyers with a free Energy Performance Certificate (EPC)."
The sale itself
Perhaps the most daunting aspect is the physical exchange of contracts and money.
An estate agent would typically oversee the process of the initial offer acceptance to the transfer of keys to the new owner.
However, if you go it alone, you'll need to become the central point of contact - bridging the gap between your solicitor or conveyancer and the buyer and their legal representative.
"Once you've accepted an offer on your property, your first task is to draft what's called a memorandum of sale," Jack says.
This document is a written confirmation of your acceptance of the offer and details the agreed price along with any specific conditions you've both agreed to.
"It's then recommended to engage the services of a solicitor or conveyancer to ensure all legal obligations are met," Jack says (of course, you'll need to do this even if you have an estate agent).
The cost of hiring one typically ranges from a few hundred to over £1,000, depending on factors such as fixed fees, hourly rates, the complexity of the sale and additional costs like property searches or land registry fees.
"In the absence of an estate agent, you'll be responsible for keeping your buyer informed about the progress of the sale. This involves regular updates on the status of legal procedures and any relevant developments," Jack says, before adding that this can actually be a good thing.
"By taking on these responsibilities independently, you'll have greater control over the sale process. However, it will require you to be exceptionally organised, and you'll need to be very good at communicating too."
Any risks to be aware of?
Rita Patel, legal director at law firm Browne Jacobson , tells us the biggest risk for people selling their properties without an estate agent is the lack of a vetting and verification process of the potential buyer.
Estate agents will verify the buyer's identity and check the buyer's proof and source of funds - without this, there's no way to assess the buyer is legitimate and can afford to buy.
"Whilst this process is something lawyers can help with, this is often at an additional cost, and you'll need to start from square one if there is an issue with a potential buyer's identification and/or financial eligibility," Rita says.
More generally, selling without an agent can extend the time it takes to sell.
"Zoopla suggests this timeframe is normally around 17-34 weeks, but with no one on hand to consistently promote and drive the property sale at all stages, going solo drags this process out," Rita says.
"Agents can also help mediate any potential breakdowns in communication between the buyer and seller - reducing the likelihood of having to go back to market and start again."
The advantages
Laura Owen-Brown, a PR manager from Gloucestershire, tells us she is set to sell her house without an estate agent in the near future.
"My disappointment with estate agents stems from their lack of familiarity with the properties they attempted to sell me when I was buying my current house," she says.
"They couldn't tell me about the details that truly matter, like the optimal times for sunlight in the garden, how much council tax I'd pay, what the roof was made of, the places I could walk my dog off lead or the impact of post-football match traffic on Sundays.
"These types of details can shape the experience of living in a house for years and are just as important as the square footage, EPC rating or how many bedrooms a property has," she adds.
She says the current "transactional" approach to selling houses feels "impersonal and outdated" to her.
"Yes, I'll have to handle more admin, but the savings in both money and time will make it worthwhile. Liaising with buyers and solicitors directly without a third party slowing everything down will mean I can be in control and have transparency throughout the process, especially during negotiations," she says.
All in all...
As Laura says, it's very much a case of whether you can stomach the admin and are happy to take the risks on background financial checks.
If you are aware of all the above and willing to take on the organisational burden, you could save yourself a serious chunk of cash.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


Research Specialist
- Madison, Wisconsin
- SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND PUBLIC HEALTH/RADIOLOGY-GEN
- Partially Remote
- Staff-Full Time
- Staff-Part Time
- Opening at: May 15 2024 at 16:30 CDT
- Closing at: May 29 2024 at 23:55 CDT
Job Summary:
The successful candidate will work with Dr. Vivek Prabhakaran's Neuroimaging research program on projects ranging from normal aging to dementia. (S)he/they will be actively engaged in cutting-edge neuroimaging and biomarker research studies in normal aging as well as stroke, epilepsy, and dementia. This position requires analytic thinking, good interpersonal skills, excellent writing skills, the flexibility to work independently and collaboratively, and the ability to communicate effectively with colleagues and study participants. Primary areas of responsibility include data processing, regulatory work which involves working with the IRB liaison, helping team members with scientific writing and preparation of scientific abstracts, posters, papers, and grants.
Responsibilities:
- 10% Conducts research experiments according to established research protocols with moderate impact to the project(s). Collects data and monitors test results
- 20% Operates, cleans, and maintains organization of research equipment and research area. Tracks inventory levels and places replenishment orders
- 20% Reviews, analyzes, and interprets data and/or documents results for presentations and/or reporting to internal and external audiences
- 15% Participates in the development, interpretation, and implementation of research methodology and materials
- 10% Provides operational guidance on day-to-day activities of unit or program staff and/or student workers
- 5% Performs literature reviews and writes reports
- 10% Assist in scheduling meetings. Attend lab meetings, interact with lab investigators/staff, and execute other research-related tasks as determined by the supervising principal investigator or scientific staff.
- 10% Assist with study visits, maintain IRB and other regulatory approvals.
Institutional Statement on Diversity:
Diversity is a source of strength, creativity, and innovation for UW-Madison. We value the contributions of each person and respect the profound ways their identity, culture, background, experience, status, abilities, and opinion enrich the university community. We commit ourselves to the pursuit of excellence in teaching, research, outreach, and diversity as inextricably linked goals. The University of Wisconsin-Madison fulfills its public mission by creating a welcoming and inclusive community for people from every background - people who as students, faculty, and staff serve Wisconsin and the world. For more information on diversity and inclusion on campus, please visit: Diversity and Inclusion
Required Bachelor's Degree in neurobiology, psychology, neuroscience, biomedical engineering, kinesiology, life sciences, or related area.
Qualifications:
Preferred: - Minimum one year of lab experience - Experience with neuroimaging packages/analyses - Experience with neuropsych testing
Full or Part Time: 50% - 100% This position may require some work to be performed in-person, onsite, at a designated campus work location. Some work may be performed remotely, at an offsite, non-campus work location.
Appointment Type, Duration:
Ongoing/Renewable
Minimum $54,120 ANNUAL (12 months) Depending on Qualifications
Additional Information:
University sponsorship is not available for this position, including transfers of sponsorship. The selected applicant will be responsible for ensuring their continuous eligibility to work in the United States (i.e. a citizen or national of the United States, a lawful permanent resident, a foreign national authorized to work in the United States without the need of an employer sponsorship) on or before the effective date of appointment. This position is an ongoing position that will require continuous work eligibility. UW-Madison is not an E-Verify employer, and therefore, is not eligible to employ F1-OPT STEM Extension participants. If you are selected for this position you must provide proof of work authorization and eligibility to work.
How to Apply:
To apply for this position, please click on the "Apply Now" button. You will be asked to upload a current resume/CV and a cover letter briefly describing your qualifications and experience. You will also be asked to provide contact information for three (3) references, including your current/most recent supervisor during the application process. References will not be contacted without prior notice.
Gabriella Fisk [email protected] 608-890-0034 Relay Access (WTRS): 7-1-1. See RELAY_SERVICE for further information.
Official Title:
Research Specialist(RE047)
Department(s):
A53-MEDICAL SCHOOL/RADIOLOGY/RADIOLOGY
Employment Class:
Academic Staff-Renewable
Job Number:
The university of wisconsin-madison is an equal opportunity and affirmative action employer..
You will be redirected to the application to launch your career momentarily. Thank you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Applicant Tutorial
Disability Accommodations
Pay Transparency Policy Statement
Refer a Friend
You've sent this job to a friend!
Website feedback, questions or accessibility issues: [email protected] .
Learn more about accessibility at UW–Madison .
© 2016–2024 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System • Privacy Statement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Based on the research question definition provided, formulate your query. If you are looking for criteria for a good research question, Stone (2002) says that a good research question should be relevant, decided, and meaningful. Creating a research question can be a tricky process, but there is a specific method you can follow to ease the process.
A well-crafted research question (or set of questions) sets the stage for a robust study and meaningful insights. But, if you're new to research, it's not always clear what exactly constitutes a good research question. In this post, we'll provide you with clear examples of quality research questions across various disciplines, so that you can approach your research project with confidence!
A good research question should: Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose. Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper. Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. Preliminary research. The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles.
Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be "Slavery in the American South" or "Films of the 1930s.". Do some preliminary research on your general topic.
Steps to Write Research Questions. You can focus on the issue or research gaps you're attempting to solve by using the research questions as a direction. If you're unsure how to go about writing a good research question, these are the steps to follow in the process: Select an interesting topic Always choose a topic that interests you.
5. Review the questions. Evaluate your list of potential questions to determine which seems most effective. Ensure you consider the finer details of every question and possible outcomes. Doing this helps you determine if the questions meet the requirements of a research question. 6.
The research questions provide a framework for discussing the findings and drawing conclusions. Characteristics of Research Questions. Characteristics of Research Questions are as follows: Clear and Specific: A good research question should be clear and specific. It should clearly state what the research is trying to investigate and what kind ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, project, or thesis. It pinpoints exactly what you want to find out and gives your work a ...
As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables. Here, an example could be something like "What is the relationship between X and Y" or "Does A have an impact on B". As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables ...
Insights on Creating a Good Research Question. Junichi Tokuda, PhD, focuses on how to start successfully, and divulges the unique approach he has as a basic scientist when developing a good research question. Play Junichi Tokuda video. Ursula Kaiser, MD, encourages drawing on an already established interest in your subject matter to showcase ...
A good research question should be clear, relevant and specific enough to guide the research process. It should also be open-ended, meaning that it allows for multiple possible answers or interpretations. ... How to Write a Research Question: Step-By-Step Guide. In this section we will examine the process of developing a research question. We ...
Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1. Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (collectively called the "golden thread") are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you're crafting a research proposal, dissertation or thesis.We receive questions almost every day about this "holy trinity" of research and there's certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we've crafted this post to help ...
The process of formulating a good research question can be challenging and frustrating. While a comprehensive literature review is compulsory, the researcher usually encounters methodological difficulties in the conduct of the study, particularly if the primary study question has not been adequately selected in accordance with the clinical dilemma that needs to be addressed.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
5. Facilitating Data Interpretation and Analysis. Clear research questions help in structuring the analysis, guiding the interpretation of data, and framing the discussion of results. They ensure that the data collected is directly relevant to the questions posed, making it easier to draw meaningful conclusions.
In essence, the research question that guides the sciences and social sciences should do the following three things:2. 1) Post a problem. 2) Shape the problem into a testable hypothesis. 3) Report the results of the tested hypothesis. There are two types of data that can help shape research questions in the sciences and social sciences ...
This paper, on writing research questions, is the first in a series that aims to support novice researchers within clinical education, particularly those undertaking their first qualitative study ...
This is especially important with qualitative questions, where there may be exploratory or inductive methods in use that introduce researchers to new and interesting areas of inquiry. Here are some tips for writing good qualitative research questions. 1. Keep it specific. Broader research questions are difficult to act on.
This paper, on writing research questions, is the first in a series that aims to support novice researchers within clinical education, particularly those undertaking their first qualitative study. Put simply, a research question is a question that a research project sets out to answer. Most research questions will lead to a project that aims to ...
Start the brainstorming process: Begin by identifying a broad topic of research interest (the more you're personally interested in it, the better!).Write it down to clarify your focus. Narrow down your scope by considering specific areas within this topic that you want to explore.; Identify key themes and elements related to these specific areas.These will be the building blocks of your ...
The chain of alignment that began with the research problem description and continues on to the research purpose, research questions, and methodology must be respected at all times during dissertation development. You are to succinctly describe the overarching goal of the study that reflects the research questions.
Researchers are learning that handwriting engages the brain in ways typing can't match, raising questions about the costs of ditching this age-old practice, especially for kids.
Teacher Notes. Ask pupils as a group to come up with arguments 'for' and 'against' wearing a school uniform. They can then watch this short film and check if they predicted the same ...
We speak to a consumer dispute expert and Ford about a reader's car, which is being written off with a known issue. Read this and the rest of today's consumer and personal finance news - and leave ...
Job Summary: The successful candidate will work with Dr. Vivek Prabhakaran's Neuroimaging research program on projects ranging from normal aging to dementia. (S)he/they will be actively engaged in cutting-edge neuroimaging and biomarker research studies in normal aging as well as stroke, epilepsy, and dementia. This position requires analytic thinking, good interpersonal skills, excellent ...