CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Class 6 Mathematics Worksheets
We have provided below free printable Class 6 Mathematics Worksheets for Download in PDF. The worksheets have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 6 Mathematics . These Worksheets for Grade 6 Mathematics cover all important topics which can come in your standard 6 tests and examinations. Free printable worksheets for CBSE Class 6 Mathematics , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 6 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable worksheets for Mathematics Class 6 with solutions and answers. All worksheets and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Mathematics Class 6. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf worksheets for Mathematics class 6 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 6 Mathematics Worksheets with Answers and test papers are given below.
Mathematics Class 6 Worksheets Pdf Download
Here we have the biggest database of free CBSE NCERT KVS Worksheets for Class 6 Mathematics . You can download all free Mathematics worksheets in Pdf for standard 6th. Our teachers have covered Class 6 important questions and answers for Mathematics as per the latest curriculum for the current academic year. All test sheets question banks for Class 6 Mathematics and CBSE Worksheets for Mathematics Class 6 will be really useful for Class 6 students to properly prepare for the upcoming tests and examinations. Class 6th students are advised to free download in Pdf all printable workbooks given below.
Topicwise Worksheets for Class 6 Mathematics Download in Pdf
More worksheets for class 6 mathematics, advantages of solving class 6 mathematics worksheets.
- As we have the best collection of Mathematics worksheets for Grade 6, you will be able to find important questions which will come in your class tests and examinations.
- You will be able to revise all important and difficult topics given in your CBSE Mathematics textbooks for Class 6 .
- All Mathematics worksheets for standard 6 have been provided with solutions. You will be able to solve them yourself and them compare with the answers provided by our teachers.
- Class 6 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Mathematics chapter wise assgnments and worksheets for free in Pdf
- Class 6 Mathematics Workbook will help to enhance and improve subject knowledge which will help to get more marks in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 6 Mathematics students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free worksheets for Mathematics Class 6 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 6 Mathematics chapter-wise worksheets which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get worksheets for Mathematics in Grade 6, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here subject-wise Mathematics Grade 6 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best quality question bank for Class 6 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 6 Urdu Worksheets

Class 6 Mathematics Knowing our Numbers Worksheets

Class 6 Tamil Worksheets
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers
The NCERT solutions for class 6 maths chapter 2 Whole Numbers are curated by experts from IIT and Cambridge University. These solutions are the perfect study material for the students as they will help them revise important concepts like natural numbers , predecessor, successor, whole numbers, and many more. NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers will further introduce the number line, performing mathematical operations on it and the properties of whole numbers.
Class 6 maths NCERT solutions chapter 2 Whole Numbers has detailed and precise solutions for all the questions. All the solutions are structured in a stepwise manner. These questions will test the logical and reasoning skills of a student. With the help of this article, let us take a look at the in-depth analysis of this chapter, and also you can find some of these in the exercises given below.
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.3
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 PDF
NCERT solutions class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers is a comprehensive study material for students who want to excel in exams. This chapter discusses the various properties of whole numbers like closure, commutative, associative, and distributive properties. These properties make the calculation easy and simple for the students. Given below are the links for each exercise of the NCERT Solutions .
☛ Download Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 Whole Numbers
NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Download PDF

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 will enable students to understand whole numbers by studying different properties such as the commutative property of addition and subtraction , closure property, associative property of addition and multiplication , and many more. Let us do an exercise-wise analysis of NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers.
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1 - 8 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2 - 7 Questions
- Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.3 - 5 Question
☛ Download Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 NCERT Book
Topics Covered: Some of the important topics covered in Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 are Number lines, properties of whole numbers , and patterns in whole numbers. Each of the properties is discussed with relevant examples. Students will also find proof of each of these properties explained in a precise manner.
Total Questions: Class 6 maths chapter 2 Whole Numbers consists of a total of 20 questions, out of which 15 sums are subdivided such that they range from easy to medium level problems. At the same time, the remaining 5 are complex problems that require brainstorming.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2
NCERT solutions class 6 maths chapter 2 does not have any mathematical formulas ; however, there are certain important concepts like the properties of whole numbers and performing mathematical operations on a number line that we will cover in this section. These properties will help students understand the nature of numbers . Let us go through these concepts one by one:
- Two whole numbers can be added or multiplied in any order. For whole numbers, we claim that addition and multiplication are commutative.
- Moving to the right on the number line refers to addition while moving to the left relates to subtraction. Multiplication entails making equal-distance hops from a starting point of zero.
- When two whole numbers are added together, the result is always a whole number. Multiplying two whole numbers yields a whole number as well. When it comes to addition and multiplication, we say that the entire numbers are closed. Whole numbers, on the other hand, are not closed.
Important Questions for Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2
Faqs on ncert solutions for class 6 maths chapter 2, why are ncert solutions class 6 maths chapter 2 important.
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 is an important resource for class 6 students. This chapter will introduce the students to new concepts like number lines and the properties of whole numbers. These concepts will eventually help students form a solid base for the mathematical learnings of higher classes.
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Provided in NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers?
All the questions in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers are handpicked by the subject experts and cover a range of topics such as the concept of predecessor and successor, properties of whole numbers, and its representation on a number line. Each of the problems requires a different approach and covers a variety of topics giving an extra advantage to the students.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2?
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 is based on the concept of whole numbers. The properties of whole numbers are discussed in detail here. The explanations presented in this chapter also help the students perform various mathematical operations like addition, subtraction on a number line.
How Many Questions are there in Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 Whole Numbers?
There are a total of 20 questions in NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers. All these questions are divided into 3 exercises. By solving each of these questions, students can score good marks in examinations and explore the concept in detail.
How CBSE Students can utilize NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 effectively?
To effectively utilize the NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2, students must solve problems based on the properties of whole numbers. They should study the theory well in order to understand the difference between whole and natural numbers. Regularly practicing the concepts that involve the number line by drawing accurate figures will also help the students gain the necessary expertise in the topic.
Why Should I Practice Class 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Whole Numbers Chapter 2?
Most of the questions asked in exams are inspired by the NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers. These solutions cover the entire syllabus; thus by just practicing questions in the NCERT Solutions, students will be able to get fluent with the topics such as addition and subtraction on a number line, different properties of whole numbers like distributive, commutative, and patterns in whole numbers.

Worksheet for class 6 Maths
Cbse class 6 maths questions (worksheets) .
Worksheet for class 6 Maths is prepared by the subject matter experts of Home-tution.com having years of teaching experience. It consists of all types of questions starting with easy and slowly moving to difficult questions ensuring coverage of the entire syllabus. The worksheet for class 6 Maths is prepared with subjective questions and MCQ-based questions with detailed explanations of each question asked in the Worksheet for class 6 Maths. All the chapters asked in the CBSE class 6 Maths are covered in chapter wise Worksheet for class 6 Maths. Find More worksheets for class 6 before solving do solve NCERT questions with the help of NCERT Solutions for class 6 Maths .
Download chapter wise worksheet for class 6 Maths
Types of questions covered in worksheets for class 6 maths.
Worksheets for class 6 Maths consist of questions uploaded in pdf form for easy download and pdf are uploaded chapter-wise. We have uploaded all the chapters of CBSE class 6 and all the questions are solved with the right set of details. Questions added in the worksheet for class 6 maths are MCQ based having one choice is correct.
Worksheets questions for chapter 1 Maths
1. States having the highest population is
(a) 867305.
(b) 867301.
(c) 008673.
(d) 086730.
Answer: (a) Explanation: Numbers of digits are more.
2. Correct descending order is
(a) 307731 > 045011 > 037631 > 093671 > 036731.
(b) 307731 > 093671 > 045011 > 037631 > 036731.
(c) 307731 > 045011 > 093671 > 037631 > 036731.
(d) 307731 > 093671 > 037631 > 036731 > 045011.
Answer: (b) Explanation: Look at the number of digits, further look at digits at lakh, thousands, and hundred. etc place. The number with the greatest digit is the greatest.
3. The greatest number is
(a) 7528411.
(b) 7500400.
(c) 7501411.
(d) 7528471.
Answer: (d) Explanation: Look at the number of digits, further look digits at lakh, thousands, hundreds…..etc place. The number with the greatest digit is the greatest.
4. Without repetition the greatest 4 – digit number from 3, 7, 0, and 4 is
(a) 3704.
(b) 4073.
(c) 4370.
(d) 7430.
Answer: (d) Explanation: Greatest digit is at the greatest place.
5. The smallest 4 – digit number (Repetition of the digit is allowed) from 7, 3, 4, 9 is
Answer: (a) Explanation: Since repetition is allowed smallest digit will give the smallest number.
Worksheet questions for chapter 2 Maths
Q1: The numbers, which we use for counting, are known as
(a) natural numbers.
(b) whole numbers.
(c) integers.
(d) fractions.
Explanation:
Natural number as well as counting starts with 1.
Q2: The number, which has no predecessor in the whole number, is
Explanation:The number 0 does not have any predecessor in the whole number. This is because the predecessor of 0 is = 0 – 1 = which is not a whole number.
Q3: On the number line, the distance between any two points is called a
(b) number.
(c) unit distance.
(d) distance.
Ans. (c) Explanation: The distance between any two points is known as unit distance.
For example, a distance between 1 and 4 is a 3-unit distance, and, a distance between 0 and 6 is a 6-unit distance.
Q4: Additive element of 12 is
Explanation-Additive element of 12 is –12 which gives the result: 12 + (-12) = 0
Q5: The school canteen charges Rs 20 for lunch and Rs 5 for milk each day. The total cost of both the things to spend in six days is
(b) Rs 100.
(c) Rs 150.
(d) Rs 200.
Ans. (c) Explanation: Cost of both the things (lunch and milk) = Rs (20 + 5) = Rs 25 Total cost of both the things in six days = Rs 25 x 6 = Rs 150
Worksheet questions for chapter 3 Maths
1. The Number which is a factor of every number
(a) 0 (b) 1
(c) itself (d) both 1 & 0
1. (b) For example
4 = 4 × 1
7 = 7 × 1
2. Which number is not a factor of 18?
(a) 5 (b) 3
(c) 2 (d) 6
2. (a) factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6 and 9
3. Which of the following numbers is not a multiple of 8?
(a) 64 (b) 4
(c) 16 (d) 80
3. (b) 4 is a factor of 8
4. How many Prime Numbers are in between 10 to 20?
(a) 5 (b) 7
(c) 4 (d) 3
4. (c) Prime Numbers between 10 to 20 are 11, 13, 17, and 19
5. The two numbers which have only 1 as their common factor are called
(a) Co-primes (b) Twin prime
(c) Composite (d) None of these
5. (a) Co-primes do have not any factor except 1.
6. The number which is not a multiple of 2 is called
(a) Even (b) Odd
(c) Prime (d) Composite
6. (b) We cannot divide odd number exactly by 2
Worksheet questions for chapter 4 Maths
Q1: The part of a straight line having two endpoints is known as
(b) line segment.
(d) surface.
Explanation: A line segment is a part of a straight line. It has two endpoints.
Q2: If two lines have one common point, they are called
(a) intersecting lines.
(b) parallel lines.
(c) line segment.
(d) concurrent lines.
Explanation: Lines intersect each other at a particular point is known as a common point and the lines are known as intersecting lines.
Q3: If three or more points lie on the same straight line, then the points are called
(a) end-points.
(b) common points.
(c) collinear points.
(d) non-collinear points.
Explanation: The above figure shows collinear points A, B C and D, as these points lie on the same line.
Q4: A straight line that starts from a given fixed point and moves in the same direction is known as
(c) perpendicular.
(d) curved line.
Ans. (a) Explanation: The above figure shows a straight line that starts from a fixed point A and moves through point B in the same direction. Thus, line AB is a ray.
Q5: A point determines a location and is usually denoted by
(a) small letter.
(b) capital letter.
(d) symbol.
Explanation: A point is represented by a dot and denoted by a capital letter like A, B, X, etc.
NCERT Solutions All Classes
- Maths Formula
- NCERT Solutions
- Home tuition for Maths
- Home tuition Near me
- JEE classes online
- NEET Classes Online
- Dance classes near me
- Important Questions
- Home tuition for class 10 near me
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 6 Maths Questions (Worksheets)
. how to download the worksheet for class 6 maths.
Worksheet for class 6 Maths can be downloaded chapter-wise from Home-tution.com and the pdf version is printable. Our experts uploaded all the chapter-wise worksheets for class 6 Maths on this page just click on the maths chapter for which you need worksheets.
. What are the chapters covered in the worksheet for class 6 Maths?
worksheet for class 6 Maths covers all the chapters in the syllabus of CBSE and we have uploaded chapter-wise worksheets for class 6 Maths. The chapters covered in these pages are 1 - Knowing Our Numbers, 2 - Whole Numbers, 3 - Playing with Numbers, 4 - Basic Geometrical Ideas,5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes,6 – Integers,7 – Fractions,8 – Decimals, 9 - Data Handling, 10 – Mensuration,11 – Algebra, 12 - Ratio and Proportion, 13 – Symmetry, 14 - Practical Geometry.
. Do the worksheets for class 6 Maths covers the entire syllabus?
Yes, all the chapters asked in class 6 Maths are covered and apart from this each chapter of maths we have added questions from all sections.
LetsPlayMaths.Com
Class vi math, class 6 - set worksheet 2.
P = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} Q = {a, e, i, o, u} R = {10, 12, 14, 16, 18}
1. 3 ∈ R, mark True / False. a) True b) False
2. e ∈ Q, mark True / False. a) True b) False
3. 14 ____ R a) = b) ≠ c) ∈ d) ∉
4. 5 ____ R a) = b) ≠ c) ∈ d) ∉
5. 7 ∉ P, mark True / False. a) True b) False
6. Write the below mentioned set in Roster form. The set of prime numbers less than 15. a) {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 12, 13} b) {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17} c) {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13} d) None of these
7. Write the below mentioned set in Roster form. The set of multiples of 4 less than 25. a) {4, 8, 12, 20, 24} b) {4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28} c) {4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24} d) None of these
8. Rewrite the following set in Roster form. A = {x | x is an even number greater than 10 and less than 20} a) {12, 14, 16, 18, 19} b) {12, 14, 16, 18} c) {12, 16, 18, 20} d) {10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20}
9. Write a set whose members are perfect square natural numbers and each element is less than 40. a) P = {1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36} b) P = {1, 3, 9, 16, 25, 36} c) P = {4, 9, 16, 25, 36} d) P = {1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49}
10. A set of A of all 2-digit numbers, the sum of whose digits is 8. a) A = {17, 26, 44, 53, 62, 71, 80} b) A = {17, 26, 35, 44, 53, 62, 71, 80} c) A = {17, 26, 35, 44, 53, 62, 71} d) None of these
11. Write the following set in the set builder form. P = {a, e, i, o, u} a) P = {x | x is a vowel of English alphabet} b) P = {x | x is a letter of English alphabet} c) P = {x | x is a consonant of English alphabet} d) None of these
12. Write the following set in the set builder form. A = {January, March, May, July, August, October, December} a) A = {x | x is a month of the year having 30 days} b) A = {x | x is a month of the year having 31 days} c) A = {x | x is a month of the year having 28 days} d) None of these
13. Write the following set in the set builder form. R = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} a) R = {x | x is a natural number less than 10} b) R = {x | x is a natural number less than 9} c) R = {x | x is a whole number less than 10} d) none of these
14. Write the following sets in a Roster form. P = {x | x is number of dots on a dice} a) P = {1, 2, 3, 5, 6} b) P = {1, 2, 4, 5, 6} c) P = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} d) None of these
15. Write the following sets in a Roster form. Q = {x | x is prime factor of 30} a) Q = {1, 2, 3, 10, 15, 30} b) Q = {1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30} c) Q = {2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15} d) None of these
If you want to download the above worksheet, please click below link.
Set-2 Download the pdf
Set Worksheet - 1
Set Worksheet - 2
Set Worksheet - 3
Answer Sheet
Set-Answer Download the pdf
Copyright © 2024 LetsPlayMaths.com. All Rights Reserved. Email: [email protected]
Class 6 Maths WS - 2
Loading ad...
Clunysalem1
prime numbers
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF
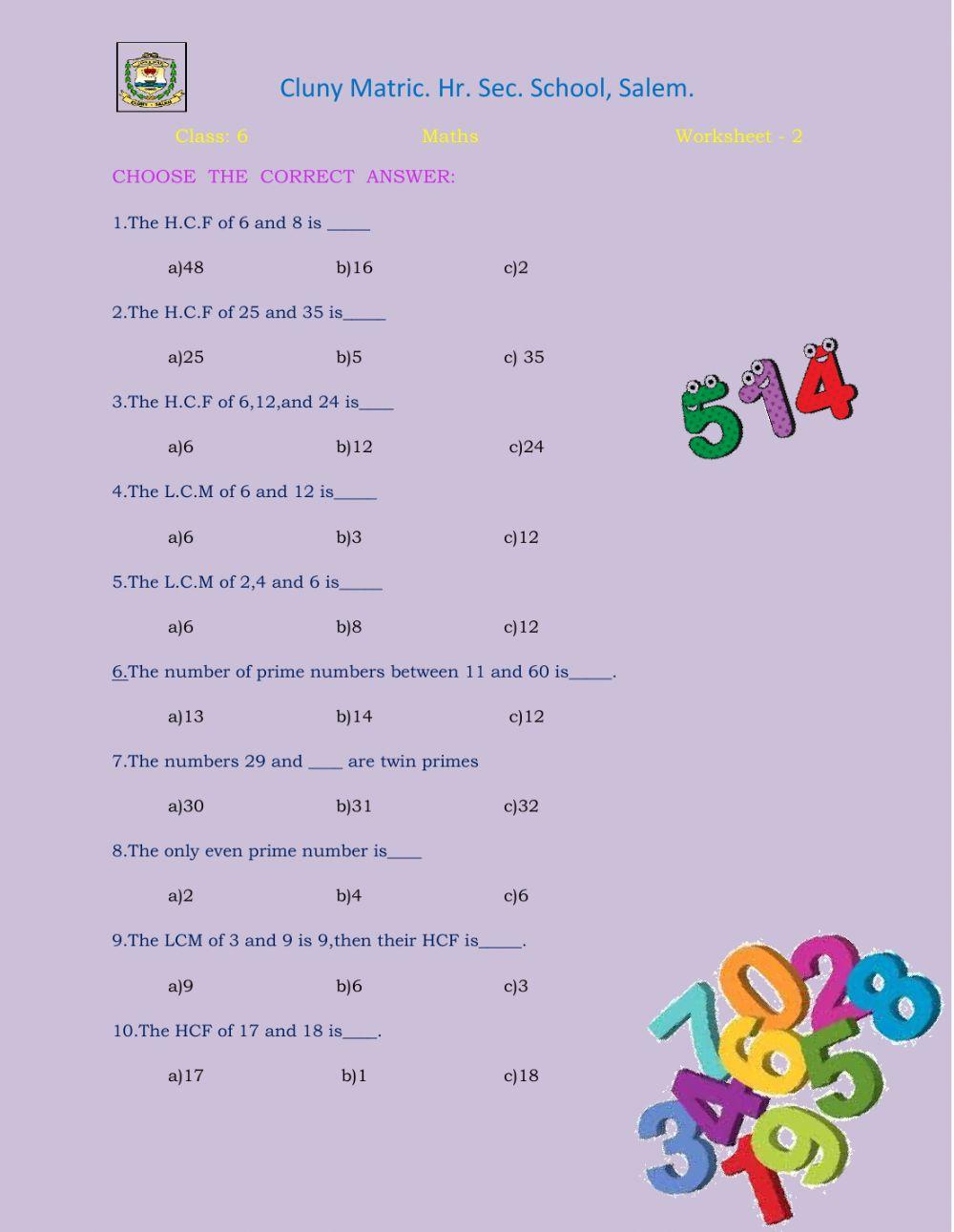

Worksheets for Class 6 Maths
Chapter-2 whole numbers worksheet-2 class 6 maths.
- Active page
Sep 29, 2022, 16:45 IST
Whole numbers are a set of natural numbers that include zero. 0 is the smallest number. Whole numbers are 0, 1, 2, 3, ……… Natural numbers are whole numbers, but not all whole numbers are natural numbers.

Solved Examples
Q1. The numbers which we use for counting are known as.
- Natural numbers
- Prime numbers
- Composite numbers
- Rational numbers
Ans. Correct option is 1
The numbers 1, 2, 3, which we use for counting are known as natural numbers.
Q2. The product of a whole number and zero is?
- Natural number
- Whole number
- Composite number
- Whole number, natural number
Ans. Correct option is 2
If x is whole number
Then, x x 0=0
Q3. The sum of two natural numbers is?
- Whole number and natural number
- Irrational number
Ans. Correct option is 3
Since 1+2=3 ,1+1=2,2+2=4
3, 2, 4 are whole number and natural number.
Q4. The whole number between 0 to 5 are ?
- 0,1,2,3,4,5
ie., 1,2,3,4
Q5. The number with which when 10 is multiplied product remains the same
Since, 10 x 1 = 10
Q6. The multiplicative identity element of 20 is
Since, n x 1 = n
Q7. 2 x 3 = 3 x 2 is an example of
- Closure property
- Commutative property
- Associative property
- Distributive property
Since a x b = b x a is a general form of commutative property
Q8. Product of two even numbers is
- None of them
Since 2 x 2 = 4 is an even number
Q9. The quotient of 25 /1 is
if a is any whole number ,then a/1 = a
Here 25 is a whole number.
Q10. 4 x (5-3) = (4 x 5) - (4 x 3) is an example of
- Distributive property of multiplication over addition
- Distributive property of multiplication over subtraction
Ans. Correct option is 4
Since a x (b - c)=(a x b) - (a x c) is a general form of distributive property of mulplication over subtraction
Download worksheet-2 of class 9 maths chapter Whole Numbers and start solving the questions for reference use the solutions . Before solving the worksheet of Physics Wallah it is highly recommend reading the theory of chapter and solve the questions given in your textbook. Do follow NCERT Solutions for class 6 Maths prepared by expert faculty of Physics Wallah.
Below link consist of class 6 Maths Chapter - 2 Whole Numbers download your free pdf copy from the below mentioned link of chapter Whole Numbers.
Related Link
- chapter - 2 Whole Numbers worksheet - 1
- chapter - 2 Whole Numbers worksheet - 2
- chapter - 2 Whole Numbers worksheet - 3
Talk to Our counsellor


Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
Subtraction
Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs

Download & Print Only $2.50
Second Grade Math Worksheets
Free grade 2 math worksheets.
Our grade 2 math worksheets emphasize numeracy as well as a conceptual understanding of math concepts . All worksheets are printable pdf documents.
Grade 2 math topics:
Skip Counting
Place Value & Rounding
Counting Money
Telling Time
Data & Graphing
Word Problems

Sample Grade 2 Math Worksheet
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.

Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
- Forgot Password?
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 - Whole Numbers
- NCERT Solutions

NCERT Class 6 Maths Chapter 2: Complete Resource for Whole Numbers
NCERT Solutions of Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 wants to offer more knowledge on numbers, which is an extension to the first chapter for grade 6 students. NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 offered by Vedantu provides well-disciplined, verified, structured material for the student Victor to solve several solved problems. These materials are used for competitive exams also. Every NCERT Solution is provided to make the study simple and interesting on Vedantu. Subjects like Science, Maths, English, and Hindi will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 6 Science , Maths solutions, and solutions of other subjects.
Important Topics Covered in This Chapter
The following list has been provided so that students can get an idea of the topics that are covered in this chapter before diving into the solution to the NCERT textbook questions.
Introduction
Whole Numbers
Number Line
Properties of Whole Numbers
Patterns in Whole Numbers
Access NCERT Solutions for Maths Chapter 2 – Whole Numbers
Exercise (2.1).
1. Write the Next Three Natural Numbers After
Natural numbers are those numbers which start from positive integers and go on till infinity.
To find the next three natural numbers, just add
1 to every preceding integer.
10,999+1=11,000
11,000+1=11,001
11,001+1=11,002
Thus the three natural numbers after
11000,11001,11002 .
2. Write the Three Whole Numbers Occurring Just Before
Whole numbers are those numbers which start from zero and go on till infinity.
To find the three whole numbers occurring before the number, just subtract
1 from every preceding integer.
10,001−1=10,000
10,000−1=9,999
9,999−1=9,998
Thus the three whole numbers occurring before
10000,9999,9998 .
3. Which is the Smallest Whole Number?
Since the whole numbers start with zero, the smallest whole number is zero.
0 is the smallest number.
4. How Many Whole Numbers are There Between
32 and 53 ?
To find the number of whole numbers between two numbers, we have to list out the numbers between
32 and 53 .
The numbers are
33,34,35,...,52 .
Numbers between
32=(53−32)−1
So there are
20 whole numbers between
5. Write the Successor of
The successor is the number that comes after the given number.
It can be found by adding
1 to the given number.
2440701+1=2440702
So the successor of
100199+1=100200
1099999+1=1100000
2345670+1=2345671
6. Write the Predecessor of
The predecessor is the number that comes before the number.
It can be found by subtracting
1 from the given number.
So the predecessor of
2,08,090−1=2,08,089
2,08,090 is
76,54,321−1=76,54,320
76,54,321 is
7. In Each of the Following Pairs of Numbers, State Which Whole Number is on the Left of the Other Number on the Number Line. Also,Write Them with the Appropriate Sign
(>,<)
(>,<) between them.
Numbers in the number line always increase from left to right.
Here the smaller number is
503 lies on the left of
530 on the number line and
530>503.
307 lies on the left of
370 on the number line and
370>307.
98765,56789
56789 lies on the left of
98765>56789
98765on the number line and
98765>56789.
9830415,10023001
9830415 lies on the left of
9830415<10023001
10023001 on the number line and
9830415<10023001.
8. Which of the Following Statements are True (T) and Which are False (F):
(a) Zero is the Smallest Natural Number.
So the smallest natural number is
1and not zero.
So the given statement “Zero is the smallest natural number” is false.
400 is the Predecessor of
So the given statement “
400 is the predecessor of
399” is false.
(c) Zero is the Smallest Whole Number.
So the smallest whole number is zero.
So the given statement “Zero is the smallest whole number” is true.
600 is the successor of
599:” is true.
(e) All Natural Numbers are Whole Numbers.
Natural numbers are those which start from positive integers to infinity.
So natural numbers will also come under whole numbers.
So all natural numbers are whole numbers.
So the given statement “All natural numbers are whole numbers” is true.
(f) All Whole Numbers are Natural Numbers.
So all natural numbers are whole numbers but not all whole numbers are natural numbers since natural will miss zero from whole numbers.
So the given statement “All whole numbers are natural numbers” is false.
(g) The Predecessor of a Two Digit Number is Never a Single Digit Number.
Let us consider a two digit number.
Thus the predecessor of a two digit number is a single digit number in this case.
So the given statement “The predecessor of a two digit number is never a single digit number’ is false.
1 is the Smallest Whole Number.
So the smallest whole number is
1 is the smallest whole number” is false.
(i) The Natural number
1 has no predecessor.
Natural numbers are those which start from positive integers and go on till infinity.
1and it has no predecessor.
So the given statement “The natural number
1 has no predecessor” is true.
(j) The Whole Number
1 has no Predecessor.
0 which is a whole number.
Thus the given statement “The whole number
1 has no predecessor” is false.
(k) The Whole Number
13 Lies Between
0,1,2,3,...,11,12,13,...
The whole number
13 lies after
12 and not between them.
So the given statement “The whole number
13 lies between
12 “ is false.
(l) The whole Number
0 has no Predecessor.
So the smallest number in the whole number is zero and it has no predecessor.
0 has no predecessor” is true.
(m) The Successor of Two Digit Number is Always a Two Digit Number”
The successor is the number that comes after the given number.
Thus the successor of a two digit number is a three digit number in this case.
So the given statement “The successor of a two digit number is always a two digit number’ is false.
Exercise (2.2)
1. Find the Sum by Suitable Rearrangement:
837+208+363
Add unit places of a two digit number and check if we get an easier number.
And then add those numbers and simplify them like this to get the final answer.
837+208+363=(837+363)+208
So the sum of the numbers
837+208+363 by suitable arrangement is
1962+453+1538+647
1962+453+1538+647=(1962+1538)+(453+647)
1962+453+1538+647 by suitable arrangement is
2. Find the Product by Suitable Arrangement:
Arrange the numbers in such a way that we get easier numbers while multiplying them.
And multiply them again to get the final answer.
2×1768×50=(2×50)×1768
=(100×1768)
So the product of
2×1768×50 by suitable arrangement is
4×166×25=(4×25)×166
4×166×25 by suitable arrangement is
8×291×125=(125×8)×291
=(1000×291)
8×291×125 by suitable arrangement is
625×279×16=(625×16)×279
=(10000×279)
625×279×16 by suitable arrangement is
285×5×60=285×(5×60)
285×5×60 by suitable arrangement is
125×40×8×25
125×40×8×25=(125×8)×(40×25)
=(1000×1000)
125×40×8×25 by suitable arrangement is
3. Find the Value of the Following:
297×17+297×3
It is in the form of
So we can use distributive property over addition, that is,
a(b+c)=ab+ac
297×17+297×3=297(17+3)
So the value of
297×17+297×3 is
54279×92+8×54279
54279×92+8×54279=54279(92+8)
54279×92+8×54279 is
81265×169−81265×69
So we can use distributive property over subtraction, that is,
a(b−c)=ab−ac
81265×169−81265×69=81265(169−69)
81265×169−81265×69 is
3845×5×782+769×25×218
The equation can be reduced as,
3845×5×782+769×25×218=3845×5×782+769×5×5×218
=3845×5×782+3845×5×218
3845×5×782+769×25×218=3845×5(782+218)
=3845×5×1000
3845×5×782+769×25×218 is
4. Find the Product Using Suitable Properties:
Write the given number
738×103=738×(100+3)
Use the distributive law over addition, that is,
738×103=(738×100)+(738×3)
=73800+2214
The product of
738×103 by using proper identity is
854×102=854×(100+2)
854×102=(854×100)+(854×2)
=85400+1708
854×102 by using proper identity is
258×1008=258×(1000+8)
258×1008=(258×1000)+(258×8)
=258000+2064
258×1008 by using proper identity is
1005×168=(1000+5)×168
1005×168=(1000×168)+(5×168)
=168000+840
1005×168 by using proper identity is
5. A taxi Driver Filled his Car's Petrol Tank with
40 Litres of Petrol on Monday. The Next day, He Filled the Tank with
50 Litres of Petrol. If the Petrol Costs
Rs.44 Per Litre, How Much did he Spend on Petrol?
Amount of Petrol filled on Monday
Amount of petrol filled on next day
Total amount of petrol filled
Cost of one litre petrol
90 litre petrol
Thus the taxi driver spent
Rs.3960 on petrol.
6. A Vendor Supplies
32 litres of milk to a hotel in the morning and
68 litres of milk in the evening. If the milk costs
Rs.15 per litre, how much money is due to the vendor per day?
Amount of milk supply in the morning
Amount of milk supply in the evening
Total amount of milk supply
=100 litres
Cost of one litre milk
100 litre milk
Amount of money due to the vendor per day is
7. Match the Following:
425×136=425×(6+30+100)
This is in the form of
a(b+c)=ab+ac which is a distributivity multiplication under addition which is in the option (c).
2×48×50=2×50×48
a×b×c=a×c×b which is commutative under multiplication which is in the option (a).
80+2005+20=(80+20+2005)
a+b+c=a+c+b which is commutative under addition which is in the option (b).
Exercise (2.3)
1. Which of the Following will not Represent Zero:
The given numbers represent the sum the numbers,
So it gives an answer which is a non-zero number.
1+0 does not represent zero.
The given numbers represent the multiplication of the numbers,
0×0represents zero.
The given numbers represent the division of the numbers,
02 represents zero.
The given numbers represent the difference of the numbers followed by division.
10−102 represents zero.
2. If the Product of Two Whole Numbers is Zero, Can We Say That One or Both of Them Will Be Zero? Justify Your Examples.
Let us consider two numbers as
4,0in which one of them is zero.
Product of these numbers is
If we consider both the numbers to be zero, then
0×0=0.
Yes, we can say that one or both of the whole numbers will be zero.
3. If the Product of Two Whole Numbers is
1 , Can We Say That One or Both of the Numbers will be
1 ? Justify Through Examples.
Let us consider both the whole number to be
Consider either of the numbers to be any other whole number, let it be
So the product of both the whole number will not always be equal to
No, we cannot say that the product of one or both the numbers will be
4. Find Using Distributive Property:
101=(100+1)
728×(100+1)
728×(100+1)=728×100+728×1
1001=(1000+1)
5437×(1000+1)
5437×(1000+1)=5437×1000+5437×1
=5437000+5437
5437×1001 is
824×(20+5)=(824×20)+(824×5)
=16480+4120
125=(100+20+5)
4275×(100+20+5)
4275×(100+20+5)=(4275×100)+(4275×20)+(4275×5)
=427500+85500+21375
4275×125 is
504=(500+4)
(500+4)×35=500×35+4×35
5.Study the pattern:
123×8+3=987
1234×8+4=9876
12345×8+5=98765
Since it was like
12...n×8+n=n...1
The next two terms are
123456×8+6=987654
1234567×8+7=9876543
And the pattern will be like:
987654,9876543.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 - Whole Numbers Free PDF
NCERT Solutions of Maths book for Class 6 are available in PDF format for free to download. It helps the students to practise whenever they want. Additionally, the book can be stored for future purposes like academic exams or competitive exams or olympiads etc. Students also need not bother about the uninterrupted internet connection. The free PDF is available to practise more examples in their leisure Time and also can verify or recall the sums during the time of examination. It also benefits the students to work together so they can share their knowledge with them.
2.1 Introduction
At the beginning of the chapter, the Whole Numbers of Class 6 by the NCERT Solutions are recalling the numbers and explaining the concepts of successor and predecessor. Students can easily understand because these are similar to before and after numbers. As the level of the student increases, the terminology also changes at times. So the student should be aware of all the terms because several students may lose their marks without knowing the terms even though they knew the concept very well.
2.2 Whole Numbers
After attaining the knowledge of the successor and predecessor, the students may get a doubt, what is the predecessor of one. So, in order to clarify this, Aryabhatta discovered the numeral called zero. All the natural numbers, including zero, are nothing but Whole Numbers. NCERT Solutions of the Maths book of Chapter 2 has explained it in detail. So we can say that the national numbers are a subset of Whole Numbers.
2.3 Number Line
The NCERT solutions of Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers PDF has introduced A New concept to the students, which is called the number line. Students can understand it as simple as the numbers because it is representing the numbers on your straight line. The number line can be used to represent additions, subtractions, and multiplications too. The experience of teachers of NCERT solutions has been verified thoroughly and explained the concept with several examples. Also, students can assess themselves by using the exercises and practice questions.
2.4 Properties of Whole Numbers
As of now, the students got knowledge of ‘what are the Whole Numbers?’. So the NCERT Solutions of Vedantu wants to give more on each topic. For that purpose, students are about to learn about the properties of Whole Numbers. The Whole Numbers may satisfy different properties. They are as follows:
Closure Property: The Whole Numbers can hold the closure property for both the addition and multiplication.
Associative Property: The Whole Numbers also satisfy the associated property for both the addition and multiplication.
Distributive of Multiplication Over Addition: It means that the Whole Numbers can satisfy the distributivity of multiplication only on additions but not on multiplications.
2.5 Patterns in Whole Numbers
NCERT Solutions of Chapter 2 Mathematics Class 6 taught the students in an understandable way about the patterns available in the Whole Numbers. The pattern means the way of representing or the appearance of that particular number. Students can learn it very enthusiastically. Because here the numbers can appear in different shapes like a straight line, square, rectangle, or a triangle or any other. So the students can enjoy more and more numbers to represent their favourite shapes.
Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Exercises
Key takeaways of the ncert solutions of class 6 maths chapter 2: whole numbers .
Students can take many things from NCERT Solutions on the official website of Vedantu. It is like an assorted back which consists of all types of requirements. The benefits of the NCERT solutions are:
The explanation will be understandable and liberally according to the level of the student.
It provides a test purpose and unsolved questions more than enough to become strong in that particular subject for every chapter.
The free PDF benefits the students in several ways and there will not be any further issues of the affordability of the parents.
The doubts of the students can be clarified through the live session available on the official website.
Along with this, students can also view additional study materials provided by Vedantu, for Class 6 Maths Chapter 1 - Knowing Our Numbers.
NCERT Books Class 6
CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Revision Notes
CBSE Class 6 Maths Syllabus
Related Questions
1. Write the given number in expanded form: 74836.
2. Find the HCF and LCM of 42 and 72 by the prime factorization method i.e., by the fundamental theorem of arithmetic.
3. Raju is 22 years old and Ramu is 19 years old. Write the difference between their ages in the Roman system.
4. The sum of the two-digit number is 132. If their HCF is 11, the numbers are:
55, 77
5. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
Whole numbers are closed under addition
Whole numbers are closed under multiplication
Whole numbers are closed under subtraction
Whole numbers are not closed under subtraction
6. State true or false:
Every natural number is a whole number.
7. For the following pairs of numbers, verify the property:
Product of the number = Product of their H.C.F. and L.C.M.
8. Give one example each to the following statements.
A whole number which is not a natural number.
How many whole numbers are there between 1032 and 1209?
Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 - Whole Numbers offer an exceptional resource for students to grasp fundamental mathematical concepts effectively. The platform's well-structured and comprehensive approach ensures that learners can build a strong foundation in this crucial topic. By providing step-by-step explanations, examples, and practice exercises, Vedantu empowers students to enhance their problem-solving skills and gain confidence in dealing with whole numbers. The user-friendly interface and accessibility make learning engaging and convenient. With Vedantu's NCERT Solutions, students can bridge the gap between theory and application, making mathematics an enjoyable and rewarding experience, ultimately fostering academic excellence.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 - Whole Numbers
1. Explain the Closure Property on Addition and Multiplication with an example.
The closure property of addition and multiplication states that when you add or multiply any two numbers from a set, the result will also be a number from the same set.
For example, if you add two whole numbers, the result will always be a whole number. Similarly, if you multiply two whole numbers, the result will always be a whole number.
For addition, a + b = b + a
3000 + 5000 = 8000
5000 + 3000 = 8000
For multiplication, a x b = b x a
25 x 50 = 1250
50 x 25 = 1250
2. Explain the Associative Property on Addition and Multiplication with an example.
The Whole Numbers can satisfy the associated property on both additions and multiplications similar to the closure property. Let's see an example of this.
For addition, a+(b+c) = (a+b)+c
2+ (4+6) = (2+4)+6 = 12
For multiplication, a x (b x c )= (a x b) x c
2 x (4 x 6) = (2 x 4) x 6 = 48
3. What are the properties available in Mathematics for numbers?
Generally, we have six properties for the numbers. However, there will not be any compulsion that all members should satisfy all the properties. Some of the properties were satisfied and some may not. The basic properties available are -
Closure property
Associative property
Commutative property
Distributive property
Identity property
Inverse property etc.
4. Where can I access the solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2?
Class 6 Chapter 2 is an easy chapter if practised regularly. To make it easier, you can easily avail the solutions on Vedantu. The solutions can easily be accessed free of cost via the link given. There are a variety of modules and example papers available on the Vedantu website and the Vedantu mobile app for those who are interested and want to do well in their exams.
5. What is the whole number in Class 6 Maths Chapter 2?
Whole numbers are basic counting numbers in mathematics: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,... These include 55, 88, 69856555 etc. Natural numbers beginning with 1 are included in the definition of whole numbers. Positive integers and 0 are included in whole numbers. For more information and guidance you can visit the Vedantu Site (vedantu.com) or the Vedantu app. The problems of this chapter can be tricky sometimes and hence it is advisable to practice them carefully even if you find them simple. Practice well for your exams!
6. Do I need to practice all the questions provided in Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 NCERT Solutions?
Indeed. It is very important that you practice and answer all questions since they cover a variety of subjects and concepts and will give you a good understanding of the kind of questions that might be set from those areas and the framework of the question paper. These questions also help you learn how different questions from the same topic may be set. Each exercise should be thoroughly revised. The Vedantu website and Vedantu mobile app both provide a variety of modules as well as example papers on these subjects if you're so inclined.
7. What is the number 0?
Zero is a number that can be classified as a whole number, a real number, and a non-negative integer. It is not classified as undercounting, odd, positive natural or negative whole numbers and neither a complex number. It is quite tricky to classify zero into different categories. It can be included in multiple equations involving complex numbers though. Practice all the problems related to these topics and other topics of this chapter as well in order to score well in them.
8. Can zero be classified as a natural number?
Zero is a number that is a whole number, a real number, and a non-negative integer. It is neither a counting, odd, positive natural, or negative whole number, nor is it a complex number. It is difficult to categorise zero in numerous ways. It can, however, be used in numerous equations involving complex values. If you are interested in obtaining various modules and example papers relating to these areas, you can simply get them through the Vedantu website as well as the Vedantu mobile app.
- ICSE Class 6
- ICSE Class 6 Selina Solution
- Class 6 Maths Concise Selina Solutions
- Class 6 Chapter 2 Estimation
Selina Solutions Concise Mathematics Class 6 Chapter 2 Estimation
Step by step Selina Solutions are given here for students of Class 6. These Selina Solutions help students to understand thoroughly the difficult questions while solving them. Subject experts have designed the solutions in order to help students in improving their performance in academics. Students who want to score high marks are advised to follow these solutions and practice them continuously during exam preparation.
Estimation means to make an idea about quantities, to judge approximate size, cost, population, etc. The problems of this chapter will improve students’ skills in solving in an effective way. Students can make use of the PDF of Selina Solutions Concise Mathematics Class 6 and download from the links available here.
Selina Solutions Concise Mathematics Class 6 Chapter 2: Estimation Download PDF

Exercises of Selina Solutions Concise Mathematics Class 6 Chapter 2: Estimation
Exercise 2(A) Solutions
Exercise 2(B) Solutions
Access Selina Solutions Concise Mathematics Class 6 Chapter 2: Estimation
Exercise 2(a) page no: 11.
1. Round off each of the following to the nearest ten:
If the ones place digit is less than 5, replace ones digit by 0, and keep the other digit as the same
And if the digit at ones place is 5 or more than 5, increase tens digit by 1 and replace ones digit by 0
(i) 62 to the nearest ten is 60
(ii) 265 to the nearest ten is 270
(iii) 543 to the nearest ten is 540
(iv) 8261 to the nearest ten is 8260
(v) 6294 to the nearest ten is 6290
2. Round off each of the following to the nearest hundred:
If the digit at tens place is less than 5, replace each one of tens and ones digits by 0 and keep the other digits as the same
If the tens digit is 5 or more than 5, increase the hundreds digit by 1 and replace each of tens and ones digit by 0
(i) 748 to the nearest hundred is 700
(ii) 784 to the nearest hundred is 800
(iii) 2667 to the nearest hundred is 2700
(iv) 5432 to the nearest hundred is 5400
(v) 6388 to the nearest hundred is 6400
3. Round off each of the following to the nearest thousand: (i) 6475 (ii) 6732 (iii) 25352 (iv) 32568 (v) 9248
Observe the hundreds digit of the given number
If the hundreds digit is less than 5, replace each one of hundreds, tens, and ones digits by 0 and keep the other digits as same
If hundreds digit is 5 or more than 5 in the given number, increase thousand digit by 1 and replace each other digit on its right by 0
(i) 6475 to the nearest thousand is 6000
(ii) 6732 to the nearest thousand is 7000
(iii) 25352 to the nearest thousand is 25000
(iv) 32568 to the nearest thousand is 33000
(v) 9248 to the nearest thousand is 9000
4.Round off (i) 578 to the nearest ten. (ii) 578 to the nearest hundred. (iii) 4327 to the nearest thousand. (iv) 32974 to the nearest ten-thousand. (v) 27487 to the nearest ten-thousand.
(i) 578 to the nearest ten is 580
(ii) 578 to the nearest hundred is 600
(iii) 4327 to the nearest thousand is 4000
(iv) 32974 to the nearest ten-thousand is 30000
(v) 27487 to the nearest ten- thousand is 30000
5. Round off each of the following to the nearest ten, nearest hundred and nearest thousand. (i) 864 (ii) 1249 (iii) 54, 547 (iv) 68, 076 (v) 56, 293
(i) 864 to the nearest ten is 860
864 to the nearest hundred is 900
864 to the nearest thousand is 1000
(ii) 1249 to the nearest ten is 1250
1249 to the nearest hundred is 1200
1249 to the nearest thousand is 1000
(iii) 54547 to the nearest ten is 54550
54547 to the nearest hundred is 54500
54547 to the nearest thousand is 55000
(iv) 68076 to the nearest ten is 68080
68076 to the nearest hundred is 68100
68076 to the nearest thousand is 68000
(v) 56293 to the nearest ten is 56290
56293 to the nearest hundred is 56300
56293 to the nearest thousand is 56000
6. Round off the following to the nearest tens ; (i) ₹ 562 (ii) 837 m (iii) 545 cm (iv) ₹ 27
(i) ₹ 562 to the nearest ten is ₹ 560
(ii) 837 m to the nearest ten is 840 m
(iii) 545 cm to the nearest ten is 550 cm
(iv) ₹ 27 to the nearest ten is ₹ 30
7.List all the numbers which can be round off to 30.
26, 27, 28, 29,31, 32, 33, 34 are the numbers that can be rounded off to 30
8.List all the numbers which can be rounded off to 50. Solution:
46, 47, 48, 49, 51, 52, 53, 54 are the numbers that can be rounded off to 50
9. Write the smallest and the largest numbers which are rounded off to 80.
75 is the smallest number which is rounded off to 80 and 84 is the largest number which is rounded off to 80
10.Write the smallest and the largest numbers which are rounded off to 130.
125 is the smallest number which is rounded off to 130 and 134 is the largest number which is rounded off to 130
Exercise 2(b) page no: 17
1.Estimate the sum of each pair of numbers to the nearest ten : (i) 67 and 44 (ii) 34 and 87 (iii) 23 and 66 (iv) 78 and 18 (v) 96 and 55
(i) 67 to the nearest ten is 70
44 to the nearest ten is 40
Sum of these numbers = 70 + 40
∴Required sum = 110
(ii) 34 to the nearest ten is 30
87 to the nearest ten is 90
Sum of these numbers = 30 + 90
∴Required sum = 120
(iii) 23 to the nearest ten is 20
66 to the nearest ten is 70
Sum of these numbers = 20 + 70
∴Required sum = 90
(iv) 78 to the nearest ten is 80
18 to the nearest ten is 20
Sum of these numbers = 80 + 20
∴Required sum = 100
(v) 96 to the nearest ten is 100
55 to the nearest ten is 60
Sum of these numbers = 100 + 60
∴Required sum = 160
2.Estimate the sum of each pair of numbers to the nearest hundred: (i) 336 and 782 (ii) 546 and 342 (iii) 270 and 495 (iv) 4280 and 5295
(v) 4230 and 2410
(i) 336 to the nearest hundred is 300 and 782 to the nearest hundred is 800
Sum of these numbers = (300 + 800)
∴Required sum = 1100
(ii) 546 to the nearest hundred is 500 and 342 to the nearest hundred is 300
Sum of these numbers = (500 + 300)
∴Required sum = 800
(iii) 270 to the nearest hundred is 300 and 495 to the nearest hundred is 500
Sum of these numbers = (300 + 500)
(iv) 4280 to the nearest hundred is 4300 and 5295 to the nearest hundred is 5300
Sum of these numbers = (4300 + 5300)
∴Required sum = 9600
(v) 4230 to the nearest hundred is 4200 and 2410 to the nearest hundred is 2400
Sum of these numbers = (4200 + 2400)
∴Required sum = 6600
3.Estimate the sum of the following pair of numbers to the nearest thousand: (i) 53826 and 36455 (ii) 56802 and 22475
(i) 53826 to the nearest thousand is 54000
36455 to the nearest thousand is 36000
∴Required sum = 54000 + 36000
(ii) 56802 to the nearest thousand is 57000
22475 to the nearest thousand is 22000
∴Required sum = 57000 + 22000
4. Estimate the following differences correct to nearest ten : (i) 82 – 27 (ii) 96 – 36 (iii) 508 – 248
(i) 82 to the nearest ten is 80 and 27 to the nearest ten is 30
∴Required difference = (80 – 30)
(ii) 96 to the nearest ten is 100 and 36 to the nearest ten is 40
∴Required difference = (100 – 40)
(iii) 508 to the nearest ten is 510 and 248 to the nearest ten is 250
∴Required difference = (510 – 250)
5.Estimate each difference to the nearest hundred: (i) 769 – 314 (ii) 856 – 687 (iii) 6352 – 2086
(i) 769 to the nearest hundred = 800 and
314 to the nearest hundred = 300
∴Required difference = (800 – 300)
(ii) 856 to the nearest hundred = 900 and
687 to the nearest hundred = 700
∴Required difference = (900 – 700)
(iii) 6352 to the nearest hundred = 6400 and
2086 to the nearest hundred = 2100
∴Required difference = (6400 – 2100)
6.Estimate each difference to the nearest thousand: (i) 45974 – 38766 (ii) 76003 – 48399
(i) 45974 to the nearest thousand = 46000
38766 to the nearest thousand = 39000
∴Required difference = (46000 – 39000)
(ii) 76003 to the nearest thousand = 76000
48399 to the nearest thousand = 48000
∴Required difference = (76000 – 48000)
7. Estimate each of the following products by rounding off each number to the nearest ten : (i) 49 x 52 (ii) 63 x 38 (iii) 27 x 54 (iv) 53 x 85 (v) 74 x 67
(i) 49 to the nearest ten = 50 and
52 to the nearest ten = 50
∴Required product = (50 × 50)
(ii) 63 to the nearest ten = 60 and
38 to the nearest ten = 40
∴Required product = (60 × 40)
(iii) 27 to the nearest ten = 30 and
54 to the nearest ten = 50
∴Required product = (30 × 50)
(iv) 53 to the nearest ten = 50 and
85 to the nearest ten = 90
∴Required product = (50 × 90)
(v) 74 to the nearest ten = 70 and
67 to the nearest ten = 70
∴Required product = (70 × 70)
8. Estimate each of the following products by rounding off each number to the nearest hundred : (i) 477 x 213 (ii) 624 x 236 (iii) 333 x 247 (iv) 537 x 283
(v) 382 x 127
(i) 477 x 213
477 to the nearest hundred = 500 and
213 to the nearest hundred = 200
∴Required product = (500 × 200)
(ii) 624 x 236
624 to the nearest hundred = 600 and
236 to the nearest hundred = 200
∴Required product = (600 × 200)
(iii) 333 x 247
333 to the nearest hundred = 300 and
247 to the nearest hundred = 200
∴Required product = (300 × 200)
(iv) 537 x 283
537 to the nearest hundred = 500 and
283 to the nearest hundred = 300
∴Required product = (500 × 300)
382 to the nearest hundred = 400 and
127 to the nearest hundred = 100
∴Required product = (400 × 100)
9. Estimate each of the following products by rounding off the first number correct to nearest ten and the other number correct to nearest hundred : (i) 28 x 287 (ii) 432 x 128 (iii) 48 x 165 (iv) 72 x 258 (v) 83 x 664
(i) 28 x 287
28 to the nearest ten = 30 and
287 to the nearest hundred = 300
∴Required product = (30 × 300)
(ii) 432 x 128
432 to the nearest ten = 430 and
128 to the nearest hundred = 100
∴Required product = (430 × 100)
(iii) 48 x 165
48 to the nearest ten = 50 and
165 to the nearest hundred = 200
∴Required product = (50 × 200)
(iv) 72 x 258
72 to the nearest ten = 70 and
258 to the nearest hundred = 300
∴Required product = (70 × 300)
(v) 83 x 664
83 to the nearest ten = 80 and
664 to the nearest hundred = 700
∴Required product = (80 × 700)
10. Estimate each of the following quotients by converting each number to the nearest ten: (i) 87 ÷ 28 (ii) 84 ÷ 23 (iii) 77 ÷ 22 (iv) 198 ÷ 24 (v) 355 ÷ 26
(i) 87 ÷ 28
87 ÷ 28 is approximately (to the nearest 10) equal to
90 ÷ 30 = 3
(ii) 84 ÷ 23
84 ÷ 23 is approximately (to the nearest 10) equal to
80 ÷ 20 = 4
(iii) 77 ÷ 22
77 ÷ 22 is approximately (to the nearest 10) equal to
(iv) 198 ÷ 24
198 ÷ 24 is approximately (to the nearest 10) equal to
200 ÷ 20 = 10
(v) 355 ÷ 26
355 ÷ 26 is approximately (to the nearest 10) equal to
360 ÷ 30 = 12
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

WorkSheets Buddy
Download Math, Science, English and Many More WorkSheets

Grade 6 Whole Numbers Worksheets
Grade 6 maths whole numbers multiple choice questions (mcqs).
1. Write the successor of 1997. (a) 1996 (b) 1997 (c) 1998 (d) none of these
2. Which is the smallest whole number? (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) 2 (d) -1
3. Find value of 297 × 17 + 297 × 3 (a) 5940 (b) 5980 (c) 5942 (d) 5970
4. Fill in the blanks to make the statement true. 6245 + (631 + 751) = (631 + …………) + 751 (a) 6245 (b) 751 (c) 200 (d) 231
5. 5 divided by 0 is: (a) 5 (b) 0 (c) 1 (d) not defined
6. 0 divided by 6 is: (a) 6 (b) 0 (c) 1 (d) 60
7. The sum of a number with a whole number is always: (a) 0 (b) 100 (c) even number (d) a natural number
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 1
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 2
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 3
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 4
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 5
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 6
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 7
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 8
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 9
- CBSE Worksheets for Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Assignment 10
8. The sum of two whole numbers is always: (a) zero (b) 100 (c) a whole number (d) odd number
9. Smallest natural number is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) -1
10. The natural numbers along with zero form the collection of: (a) Whole numbers (b) Integers (c) Rational numbers (d) Real numbers
11. Which natural number has no predecessor? (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 10 (d) 100
12. Whole numbers are closed under which operation? (a) Addition (b) Subtraction (c) Division (d) None of these
13. Which number is identity for addition of whole number? (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 10 (d) 100
14. Which number is identity for multiplication of whole numbers? (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 10 (d) 100
15. Smallest whole number is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) -1
16. Predecessor of which two digit number has a two digit? (a) 99 (b) 100 (c) 101 (d) 111
17. How many natural numbers are there? (a) 100 (b) 1000 (c) infinitly many (d) 10
18. The product or multiplication of a number with zero is always: (a) zero (b) one (c) the number itself (d) none of these
19. The line on which we represent the natural number is known as: (a) counting line (b) number line (c) digit line (d) 1760
20. Predecessor of which two digit number has a single digit? (a) 9 (b) 10 (c) 0 (d) 11
Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers True (T) or False (F)
1. Zero is the smallest natural number. 2. Zero is the smallest whole number. 3. All natural numbers are whole numbers. 4. All whole numbers are natural numbers. 5. The predecessor of a two digit number is never a single digit number. 6. The natural number 1 has no predecessor. 7. The whole number 1 has no predecessor. 8. The whole number 13 lies between 11 and 12. 9. The whole number 0 has no predecessor. 10. The successor of a two digit number is always a two digit number.
Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Very Short Answer Type Questions
1. Write the predecessor and successor of (a) 1997 (b) 12000 2. Find 8 × 1769 × 25. 3. Find 12 × 35 using distributivity. 4, What is the difference between the largest number of 5 digits and the smallest 6 digit? 5. The product of two whole numbers is zero. What do you conclude? 6. Find 7 + 18 + 13.
Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Short Answer Type Questions
1. Study the pattern: 1 × 8 + 1 =9 1234 × 8 + 4 = 9876 12 × 8 + 2 = 98 12345 × 8 + 5 = 98765 123 × 8 + 3 = 987 Write the next two steps? 2. The school canteen charges ₹ 20 for lunch and ₹ 4 for milk for each day. How much money do you spend in 5 days on these things? 3. Simplify 126 × 55 + 126 × 45. 4. Find using distributive property. (a) 5437 × 10001 (b) 824 × 25
Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Long Answer Type Questions
1. In each of the following pairs of numbers, state which whole number is on the left of the other number on the number line. Also write them with the appropriate sign (>, <) between them. (a) 530, 503 (b) 98765, 56789 (c) 9830415, 10023001 2. A taxi driver filled his car petrol tank with 40 litre of petrol on Monday. The next day he filled the tank with 50 litres of petrol. If the petrol costs ₹ 44 per litre, how much did he spend in all on petrol? 3. A vendor supplies 32 litres of milk’ to a hotel in the morning and 68 litres of milk in the evening. If the milk costs ₹ 15 per litre, how much money is due to the vendor per day?
Worksheets for Class 6 Maths
Share this:.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Class 6 Mathematics Worksheets. We have provided below free printable Class 6 Mathematics Worksheets for Download in PDF. The worksheets have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 6 Mathematics. These Worksheets for Grade 6 Mathematics cover all important topics which can come in your standard 6 tests and examinations.
If you are a CBSE Class 6 stu dent, you may be looking for the CBSE Class 6 Maths Worksheets to practice. Yes, we have provided CBSE Class 6 Maths Worksheets Free PDF with Answers on this page to download and practice.. CBSE Class 6 Maths is an important subject, as it lays the foundation for understanding more complex concepts in later classes. On top of that, many real-world problems can be ...
CBSE Class 6 Maths Worksheet for students has been used by teachers & students to develop logical, lingual, analytical, and problem-solving capabilities. So in order to help you with that, we at WorksheetsBuddy have come up with Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 6 Maths Worksheets for the students of Class 6. All our CBSE NCERT Class 6 Maths practice ...
Class 6 maths worksheet consists of visual simulations to help your child visualize concepts being taught. These class 6 maths worksheets equip students with the skills required to excel, not only in their school maths but in other subjects like science. Comprehension of new concepts like integers and algebra are crucial for later ages and ...
Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Important Questions will help students gain a comprehensive understanding and acquire fundamentals of the formulas, concepts, topics, and theories under the chapter- Whole Numbers. Regular and continuous practice of the essential questions on class 6 Mathematics Chapter 2 will help you solve the numerical, identify the ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers are a comprehensive study material for students preparing for the Class 6 Mathematics exam. These NCERT Solutions are prepared by the subject-matter experts at BYJU'S to provide a proper understanding of the basic concepts included in this chapter. It includes exercise-wise solved ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers. NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 will enable students to understand whole numbers by studying different properties such as the commutative property of addition and subtraction, closure property, associative property of addition and multiplication, and many more.Let us do an exercise-wise analysis of NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths ...
worksheet for class 6 Maths covers all the chapters in the syllabus of CBSE and we have uploaded chapter-wise worksheets for class 6 Maths. The chapters covered in these pages are 1 - Knowing Our Numbers, 2 - Whole Numbers, 3 - Playing with Numbers, 4 - Basic Geometrical Ideas,5 - Understanding Elementary Shapes,6 - Integers,7 - Fractions,8 ...
Whole Numbers Class 6 Extra Questions Short Answer Type. Question 11. Using the properties, find the values of each of the following: (a) 736 x 102. (b) 8165 x 169 - 8165 x 69. Solution: (a) 736 x 102 = 736 x (100 + 2) = 736 x 100 + 736 x 2 [Using distributive property] = 73600 + 1472 = 75072.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Exercise 2.2 Whole Numbers Ex 2.1 Whole Numbers Ex 2.3 NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Ex 2.2 Exercise 2.2 Ex 2.2 Class 6 Maths Question 1. Find the sum by suitable arrangement: (a) 837 + 208 + 363 (b) 1962 + […]
Class 6 Maths Worksheets consists of 14 chapters. All 14 chapters are necessary and important for the foundation of Mathematics. Class 6 Maths required conceptual clarity and practice. Academic team of Physics Wallah having experts in penal prepared 400 plus worksheets. Each worksheet having 100 questions with step-by-step solutions.
Class 6 - Set Worksheet 2. P = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} Q = {a, e, i, o, u} R = {10, 12, 14, 16, 18} 1. 3 ∈ R, mark True / False. a) True b) False
NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Ex 2.2 can be checked from here. Students can also download the solutions in PDF format for free. Login. Study Materials. ... Access NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 2: Whole Numbers Exercise 2.2. 1. Find the sum by suitable rearrangement: (a) 837 + 208 + 363 (b) 1962 + 453 + 1538 + 647 ...
This worksheet will help all the Class 6 kids in learning integers by referring to well-explained examples of integers. Examples of Questions of Integers for Class 6. Here are some integers questions for Class 6 with answers. 1. Write the integer numbers using the number line: 4 more than 6. 2 more than -7. 7 less than -4. 4 less than - Solution:
Class 6 Maths WS - 2. Loading ad... Clunysalem1 Member for 3 years 10 months Age: 12-15. Level: Grade 6. Language: English (en) ... Math (1061955) Main content: Hcf and lcm (2000987) prime numbers. Loading ad... Share / Print Worksheet. Google Classroom Microsoft Teams Facebook Pinterest Twitter Whatsapp Download PDF
Download worksheet-2 of class 9 maths chapter Whole Numbers and start solving the questions for reference use the solutions . Before solving the worksheet of Physics Wallah it is highly recommend reading the theory of chapter and solve the questions given in your textbook.
K5 Learning offers free worksheets, flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads. Free grade 2 math worksheets, organized by grade and topic. Skip counting, addition, subtraction, place value, multiplication, division, fractions, rounding, telling time ...
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 2 - Whole Numbers. 1. Explain the Closure Property on Addition and Multiplication with an example. The closure property of addition and multiplication states that when you add or multiply any two numbers from a set, the result will also be a number from the same set.
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Chapter 2: Whole Numbers Exercise 2.1. 1. Write the next three natural numbers after 10999. Solutions: The next three natural numbers after 10999 are 11000, 11001 and 11002. 2. Write the three whole numbers occurring just before 10001. Solutions:
2.Estimate the sum of each pair of numbers to the nearest hundred: (i) 336 and 782. (ii) 546 and 342. (iii) 270 and 495. (iv) 4280 and 5295. (v) 4230 and 2410. Solution: (i) 336 to the nearest hundred is 300 and 782 to the nearest hundred is 800. Sum of these numbers = (300 + 800)
Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers Long Answer Type Questions. 1. In each of the following pairs of numbers, state which whole number is on the left of the other number on the number line. Also write them with the appropriate sign (>, <) between them. (a) 530, 503.