Contents of a Business Plan: Everything You Need to Know
The contents of a business plan consist of a detailed description of what, when, why, where, and how the business's operations will be accomplished. 3 min read updated on January 01, 2024

Overview of a Business Plan
A business plan includes the cost of organizing the business, the anticipated sources of revenue, how the products and services are customer oriented, and anticipated profit margins. Business plans serve two main purposes. First, they are a guide business owners use to streamline management and planning/organization of the business. Second, they show potential venture capitalists, bankers, and other lenders a comprehensive plan to encourage them to invest in the business.
Sublevels of a business plan include:
- Marketing plan
- Financial plan
- Human resource plan
- Production plan
Elements of a Business Plan
A well-written business plan will include the following:
- Cover letter
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
- Mission statement
- Company background
- Products and services
- Competitive analysis
Marketing/Realization
- Location/Production/Administrative
- Management and international organization
- Risk analysis
- Financial planning
Summary/Conclusion
Cover Letter
The business plan's cover letter has the same purpose as a cover letter for a resume. The point is to engage prospective investors using the cover letter so they'll look at the entire plan. The cover letter should include the recipient's address, the date, and your address. Begin the cover letter with "Dear" followed by the person's name.
In the body of the cover letter, let the recipient know you're submitting a business plan with a short one-sentence description of the business and what the recipient can expect when reading the plan. In the next paragraph, indicate that you look forward to hearing from them and provide a phone number they can call at their convenience.
Thank them for their time. Sign off. Include your name in typewritten form along with your signature.
Keep this page short and to the point. Include your business logo, business name, if there is a founder, and the name. Add "Business Plan," an image (optional), and the date.
The table of contents is a roadmap to help the recipient peruse the list and easily find each section. Some people may choose to read sections one after the other while others may choose to skip around. Include every section and subsection that may be of interest to a potential investor.
This is an important section. Because you're targeting executives, the overview of your business should be top-quality information to entice them to read the complete plan. The focus should be a summary of the main facets of your business plan.
Mission Statement
This section is a short statement about your business's goal and what you plan to create through the enterprise.
Company Background
This is a short statement including the date the business was developed, its founders, stages of development, the date it was incorporated, and, for existing businesses, the level of success.
Also, include the key figures in the business and the ownership and legal structure.
Products and Services
Under this section, provide a detailed description of your customer needs, benefits to customers, marketing services, and advantages and disadvantages of any competitor services or products.
Marketing Plan
This will include an overview of the market in general with an emphasis on purchase incentives, market analysis, and customer structure. It will also include the position your business holds in the market using information from target customer groups, canvassed market segments, and sale channels.
Competitive Analysis
Provide information about your main competitors' names, locations, market positions, weaknesses, strengths, and target markets.
This section covers details about product range, services, and pricing strategies. Sales targets for the next five years should also be included.
Location/Production/Administration
Include the location of the business and the advantages and disadvantages of its location. The production should discuss in-house and/or outsourced production and material costs. The administration portion will discuss the office infrastructure, such as accounting and technical support.
Management and International Organization
This section could work written as an organizational chart outlining member functions and responsibilities, special skills, and salaries.
Risk Analysis
Provide information on anticipated internal risks such as marketing, production, management, and financing. External risks would include information on ecological, economic, social, and legal areas.
Financial Planning
Lay out your plan for short- and long-term financial planning.
This is a final wrap up of the business plan that binds the everything together.
If you need help with outlining the contents of a business plan, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Creating a Business Plan
- Business Plan Contents Page
- How to Make a Business Plan Format
- Business Description Outline
- Service Business Plan
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Business Plan for Existing Company
- Parts of Business Plan and Definition
- IT Company Business Plan
- Business Plan Format: Everything you Need to Know
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- 212 best farm names
How to Write a Business Plan (Plus Examples & Templates)
May 24, 2021

Have you ever wondered how to write a business plan step by step? Mike Andes, told us:
This guide will help you write a business plan to impress investors.
Throughout this process, we’ll get information from Mike Andes, who started Augusta Lawn Care Services when he was 12 and turned it into a franchise with over 90 locations. He has gone on to help others learn how to write business plans and start businesses. He knows a thing or two about writing business plans!
We’ll start by discussing the definition of a business plan. Then we’ll discuss how to come up with the idea, how to do the market research, and then the important elements in the business plan format. Keep reading to start your journey!
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is simply a road map of what you are trying to achieve with your business and how you will go about achieving it. It should cover all elements of your business including:
- Finding customers
- Plans for developing a team
- Competition
- Legal structures
- Key milestones you are pursuing
If you aren’t quite ready to create a business plan, consider starting by reading our business startup guide .
Get a Business Idea
Before you can write a business plan, you have to have a business idea. You may see a problem that needs to be solved and have an idea how to solve it, or you might start by evaluating your interests and skills.
Mike told us, “The three things I suggest asking yourself when thinking about starting a business are:
- What am I good at?
- What would I enjoy doing?
- What can I get paid for?”

If all three of these questions don’t lead to at least one common answer, it will probably be a much harder road to success. Either there is not much market for it, you won’t be good at it, or you won’t enjoy doing it.
As Mike told us, “There’s enough stress starting and running a business that if you don’t like it or aren’t good at it, it’s hard to succeed.”
If you’d like to hear more about Mike’s approach to starting a business, check out our YouTube video
Conduct Market Analysis
Market analysis is focused on establishing if there is a target market for your products and services, how large the target market is, and identifying the demographics of people or businesses that would be interested in the product or service. The goal here is to establish how much money your business concept can make.
Product and Service Demand

A search engine is your best friend when trying to figure out if there is demand for your products and services. Personally, I love using presearch.org because it lets you directly search on a ton of different platforms including Google, Youtube, Twitter, and more. Check out the screenshot for the full list of search options.
With quick web searches, you can find out how many competitors you have, look through their reviews, and see if there are common complaints about the competitors. Bad reviews are a great place to find opportunities to offer better products or services.
If there are no similar products or services, you may have stumbled upon something new, or there may just be no demand for it. To find out, go talk to your most honest friend about the idea and see what they think. If they tell you it’s dumb or stare at you vacantly, there’s probably no market for it.
You can also conduct a survey through social media to get public opinion on your idea. Using Facebook Business Manager , you could get a feel for who would be interested in your product or service.
I ran a quick test of how many people between 18-65 you could reach in the U.S. during a week. It returned an estimated 700-2,000 for the total number of leads, which is enough to do a fairly accurate statistical analysis.
Identify Demographics of Target Market
Depending on what type of business you want to run, your target market will be different. The narrower the demographic, the fewer potential customers you’ll have. If you did a survey, you’ll be able to use that data to help define your target audience. Some considerations you’ll want to consider are:
- Other Interests
- Marital Status
- Do they have kids?
Once you have this information, it can help you narrow down your options for location and help define your marketing further. One resource that Mike recommended using is the Census Bureau’s Quick Facts Map . He told us,
“It helps you quickly evaluate what the best areas are for your business to be located.”
How to Write a Business Plan

Now that you’ve developed your idea a little and established there is a market for it, you can begin writing a business plan. Getting started is easier with the business plan template we created for you to download. I strongly recommend using it as it is updated to make it easier to create an action plan.
Each of the following should be a section of your business plan:
- Business Plan Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Description of Products and Services
SWOT Analysis
- Competitor Data
- Competitive Analysis
- Marketing Expenses Strategy
Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Channel Assessment
- Operational Plan
- Management and Organizational Strategy
- Financial Statements and/or Financial Projections
We’ll look into each of these. Don’t forget to download our free business plan template (mentioned just above) so you can follow along as we go.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page
The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions.
A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
- Professionally designed logo
- Company name
- Mission or Vision Statement
- Contact Info
Basically, think of a cover page for your business plan like a giant business card. It is meant to capture people’s attention but be quickly processed.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 2. Create a Table of Contents
Most people are busy enough that they don’t have a lot of time. Providing a table of contents makes it easy for them to find the pages of your plan that are meaningful to them.
A table of contents will be immediately after the cover page, but you can include it after the executive summary. Including the table of contents immediately after the executive summary will help investors know what section of your business plan they want to review more thoroughly.
Check out Canva’s article about creating a table of contents . It has a ton of great information about creating easy access to each section of your business plan. Just remember that you’ll want to use different strategies for digital and hard copy business plans.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 3. Write an Executive Summary

An executive summary is where your business plan should catch the readers interest. It doesn’t need to be long, but should be quick and easy to read.
Mike told us,
How long should an executive summary bein an informal business plan?
For casual use, an executive summary should be similar to an elevator pitch, no more than 150-160 words, just enough to get them interested and wanting more. Indeed has a great article on elevator pitches . This can also be used for the content of emails to get readers’ attention.
It consists of three basic parts:
- An introduction to you and your business.
- What your business is about.
- A call to action
Example of an informal executive summary
One of the best elevator pitches I’ve used is:
So far that pitch has achieved a 100% success rate in getting partnerships for the business.
What should I include in an executive summary for investors?
Investors are going to need a more detailed executive summary if you want to secure financing or sell equity. The executive summary should be a brief overview of your entire business plan and include:
- Introduction of yourself and company.
- An origin story (Recognition of a problem and how you came to solution)
- An introduction to your products or services.
- Your unique value proposition. Make sure to include intellectual property.
- Where you are in the business life cycle
- Request and why you need it.
Successful business plan examples
The owner of Urbanity told us he spent 2 months writing a 75-page business plan and received a $250,000 loan from the bank when he was 23. Make your business plan as detailed as possible when looking for financing. We’ve provided a template to help you prepare the portions of a business plan that banks expect.
Here’s the interview with the owner of Urbanity:
When to write an executive summary?
Even though the summary is near the beginning of a business plan, you should write it after you complete the rest of a business plan. You can’t talk about revenue, profits, and expected expenditures if you haven’t done the market research and created a financial plan.
What mistakes do people make when writing an executive summary?
Business owners commonly go into too much detail about the following items in an executive summary:
- Marketing and sales processes
- Financial statements
- Organizational structure
- Market analysis
These are things that people will want to know later, but they don’t hook the reader. They won’t spark interest in your small business, but they’ll close the deal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 4. Company Description
Every business plan should include a company description. A great business plan will include the following elements while describing the company:
- Mission statement
- Philosophy and vision
- Company goals
Target market
- Legal structure
Let’s take a look at what each section includes in a good business plan.
Mission Statement
A mission statement is a brief explanation of why you started the company and what the company’s main focus is. It should be no more than one or two sentences. Check out HubSpot’s article 27 Inspiring Mission Statement for a great read on informative and inspiring mission and vision statements.
Company Philosophy and Vision

The company philosophy is what drives your company. You’ll normally hear them called core values. These are the building blocks that make your company different. You want to communicate your values to customers, business owners, and investors as often as possible to build a company culture, but make sure to back them up.
What makes your company different?
Each company is different. Your new business should rise above the standard company lines of honesty, integrity, fun, innovation, and community when communicating your business values. The standard answers are corporate jargon and lack authenticity.
Examples of core values
One of my clients decided to add a core values page to their website. As a tech company they emphasized the values:
- Prioritize communication.
- Never stop learning.
- Be transparent.
- Start small and grow incrementally.
These values communicate how the owner and the rest of the company operate. They also show a value proposition and competitive advantage because they specifically focus on delivering business value from the start. These values also genuinely show what the company is about and customers recognize the sincerity. Indeed has a great blog about how to identify your core values .
What is a vision statement?
A vision statement communicate the long lasting change a business pursues. The vision helps investors and customers understand what your company is trying to accomplish. The vision statement goes beyond a mission statement to provide something meaningful to the community, customer’s lives, or even the world.
Example vision statements
The Alzheimer’s Association is a great example of a vision statement:
A world without Alzheimer’s Disease and other dementia.
It clearly tells how they want to change the world. A world without Alzheimers might be unachievable, but that means they always have room for improvement.
Business Goals
You have to measure success against goals for a business plan to be meaningful. A business plan helps guide a company similar to how your GPS provides a road map to your favorite travel destination. A goal to make as much money as possible is not inspirational and sounds greedy.
Sure, business owners want to increase their profits and improve customer service, but they need to present an overview of what they consider success. The goals should help everyone prioritize their work.
How far in advance should a business plan?
Business planning should be done at least one year in advance, but many banks and investors prefer three to five year business plans. Longer plans show investors that the management team understands the market and knows the business is operating in a constantly shifting market. In addition, a plan helps businesses to adjust to changes because they have already considered how to handle them.
Example of great business goals
My all time-favorite long-term company goals are included in Tesla’s Master Plan, Part Deux . These goals were written in 2016 and drive the company’s decisions through 2026. They are the reason that investors are so forgiving when Elon Musk continually fails to meet his quarterly and annual goals.
If the progress aligns with the business plan investors are likely to continue to believe in the company. Just make sure the goals are reasonable or you’ll be discredited (unless you’re Elon Musk).

You did target market research before creating a business plan. Now it’s time to add it to the plan so others understand what your ideal customer looks like. As a new business owner, you may not be considered an expert in your field yet, so document everything. Make sure the references you use are from respectable sources.
Use information from the specific lender when you are applying for lending. Most lenders provide industry research reports and using their data can strengthen the position of your business plan.
A small business plan should include a section on the external environment. Understanding the industry is crucial because we don’t plan a business in a vacuum. Make sure to research the industry trends, competitors, and forecasts. I personally prefer IBIS World for my business research. Make sure to answer questions like:
- What is the industry outlook long-term and short-term?
- How will your business take advantage of projected industry changes and trends?
- What might happen to your competitors and how will your business successfully compete?
Industry resources
Some helpful resources to help you establish more about your industry are:
- Trade Associations
- Federal Reserve
- Bureau of Labor Statistics
Legal Structure
There are five basic types of legal structures that most people will utilize:
- Sole proprietorships
- Limited Liability Companies (LLC)
Partnerships
Corporations.
- Franchises.
Each business structure has their pros and cons. An LLC is the most common legal structure due to its protection of personal assets and ease of setting up. Make sure to specify how ownership is divided and what roles each owner plays when you have more than one business owner.
You’ll have to decide which structure is best for you, but we’ve gathered information on each to make it easier.
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the easiest legal structure to set up but doesn’t protect the owner’s personal assets from legal issues. That means if something goes wrong, you could lose both your company and your home.
To start a sole proprietorship, fill out a special tax form called a Schedule C . Sole proprietors can also join the American Independent Business Alliance .
Limited Liability Company (LLC)
An LLC is the most common business structure used in the United States because an LLC protects the owner’s personal assets. It’s similar to partnerships and corporations, but can be a single-member LLC in most states. An LLC requires a document called an operating agreement.
Each state has different requirements. Here’s a link to find your state’s requirements . Delaware and Nevada are common states to file an LLC because they are really business-friendly. Here’s a blog on the top 10 states to get an LLC.
Partnerships are typically for legal firms. If you choose to use a partnership choose a Limited Liability Partnership. Alternatively, you can just use an LLC.
Corporations are typically for massive organizations. Corporations have taxes on both corporate and income tax so unless you plan on selling stock, you are better off considering an LLC with S-Corp status . Investopedia has good information corporations here .

There are several opportunities to purchase successful franchises. TopFranchise.com has a list of companies in a variety of industries that offer franchise opportunities. This makes it where an entrepreneur can benefit from the reputation of an established business that has already worked out many of the kinks of starting from scratch.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 5. Products and Services
This section of the business plan should focus on what you sell, how you source it, and how you sell it. You should include:
- Unique features that differentiate your business products from competitors
- Intellectual property
- Your supply chain
- Cost and pricing structure
Questions to answer about your products and services
Mike gave us a list of the most important questions to answer about your product and services:
- How will you be selling the product? (in person, ecommerce, wholesale, direct to consumer)?
- How do you let them know they need a product?
- How do you communicate the message?
- How will you do transactions?
- How much will you be selling it for?
- How many do you think you’ll sell and why?
Make sure to use the worksheet on our business plan template .
How to Write a Business Plan Step 6. Sales and Marketing Plan
The marketing and sales plan is focused on the strategy to bring awareness to your company and guides how you will get the product to the consumer. It should contain the following sections:
SWOT Analysis stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Not only do you want to identify them, but you also want to document how the business plans to deal with them.
Business owners need to do a thorough job documenting how their service or product stacks up against the competition.
If proper research isn’t done, investors will be able to tell that the owner hasn’t researched the competition and is less likely to believe that the team can protect its service from threats by the more well-established competition. This is one of the most common parts of a presentation that trips up business owners presenting on Shark Tank .
SWOT Examples

Examples of strengths and weaknesses could be things like the lack of cash flow, intellectual property ownership, high costs of suppliers, and customers’ expectations on shipping times.
Opportunities could be ways to capitalize on your strengths or improve your weaknesses, but may also be gaps in the industry. This includes:
- Adding offerings that fit with your current small business
- Increase sales to current customers
- Reducing costs through bulk ordering
- Finding ways to reduce inventory
- And other areas you can improve
Threats will normally come from outside of the company but could also be things like losing a key member of the team. Threats normally come from competition, regulations, taxes, and unforeseen events.
The management team should use the SWOT analysis to guide other areas of business planning, but it absolutely has to be done before a business owner starts marketing.
Include Competitor Data in Your Business Plan
When you plan a business, taking into consideration the strengths and weaknesses of the competition is key to navigating the field. Providing an overview of your competition and where they are headed shows that you are invested in understanding the industry.
For smaller businesses, you’ll want to search both the company and the owners names to see what they are working on. For publicly held corporations, you can find their quarterly and annual reports on the SEC website .
What another business plans to do can impact your business. Make sure to include things that might make it attractive for bigger companies to outsource to a small business.
- Marketing Strategy
The marketing and sales part of business plans should be focused on how you are going to make potential customers aware of your business and then sell to them.
If you haven’t already included it, Mike recommends:
“They’ll want to know about Demographics, ages, and wealth of your target market.”
Make sure to include the Total addressable market . The term refers to the value if you captured 100% of the market.
Advertising Strategy
You’ll explain what formats of advertising you’ll be using. Some possibilities are:
- Online: Facebook and Google are the big names to work with here.
- Print : Print can be used to reach broad groups or targeted markets. Check out this for tips .
- Radio : iHeartMedia is one of the best ways to advertise on the radio
- Cable television : High priced, hard to measure ROI, but here’s an explanation of the process
- Billboards: Attracting customers with billboards can be beneficial in high traffic areas.
You’ll want to define how you’ll be using each including frequency, duration, and cost. If you have the materials already created, including pictures or links to the marketing to show creative assets.
Mike told us “Most businesses are marketing digitally now due to Covid, but that’s not always the right answer.”
Make sure the marketing strategy will help team members or external marketing agencies stay within the brand guidelines .

This section of a business plan should be focused on pricing. There are a ton of pricing strategies that may work for different business plans. Which one will work for you depends on what kind of a business you run.
Some common pricing strategies are:
- Value-based pricing – Commonly used with home buying and selling or other products that are status symbols.
- Skimming pricing – Commonly seen in video game consoles, price starts off high to recoup expenses quickly, then reduces over time.
- Competition-based pricing – Pricing based on competitors’ pricing is commonly seen at gas stations.
- Freemium services – Commonly used for software, where there is a free plan, then purchase options for more functionality.
HubSpot has a great calculator and blog on pricing strategies.
Beyond explaining what strategy your business plans to use, you should include references for how you came to this pricing strategy and how it will impact your cash flow.
Distribution Plan
This part of a business plan is focused on how the product or service is going to go through the supply chain. These may include multiple divisions or multiple companies. Make sure to include any parts of the workflow that are automated so investors can see where cost savings are expected and when.
Supply Chain Examples
For instance, lawn care companies would need to cover aspects such as:
- Suppliers for lawn care equipment and tools
- Any chemicals or treatments needed
- Repair parts for sprinkler systems
- Vehicles to transport equipment and employees
- Insurance to protect the company vehicles and people.
Examples of Supply Chains
These are fairly flat supply chains compared to something like a clothing designer where the clothes would go through multiple vendors. A clothing company might have the following supply chain:
- Raw materials
- Shipping of raw materials
- Converting of raw materials to thread
- Shipping thread to produce garments
- Garment producer
- Shipping to company
- Company storage
- Shipping to retail stores
There have been advances such as print on demand that eliminate many of these steps. If you are designing completely custom clothing, all of this would need to be planned to keep from having business disruptions.
The main thing to include in the business plan is the list of suppliers, the path the supply chain follows, the time from order to the customer’s home, and the costs associated with each step of the process.
According to BizPlanReview , a business plan without this information is likely to get rejected because they have failed to research the key elements necessary to make sales to the customer.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 7. Company Organization and Operational Plan
This part of the business plan is focused on how the business model will function while serving customers. The business plan should provide an overview of how the team will manage the following aspects:
Quality Control
- Legal environment
Let’s look at each for some insight.
Production has already been discussed in previous sections so I won’t go into it much. When writing a business plan for investors, try to avoid repetition as it creates a more simple business plan.
If the organizational plan will be used by the team as an overview of how to perform the best services for the customer, then redundancy makes more sense as it communicates what is important to the business.

Quality control policies help to keep the team focused on how to verify that the company adheres to the business plan and meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Quality control can be anything from a standard that says “all labels on shirts can be no more than 1/16″ off center” to a defined checklist of steps that should be performed and filled out for every customer.
There are a variety of organizations that help define quality control including:
- International Organization for Standardization – Quality standards for energy, technology, food, production environments, and cybersecurity
- AICPA – Standard defined for accounting.
- The Joint Commission – Healthcare
- ASHRAE – HVAC best practices
You can find lists of the organizations that contribute most to the government regulation of industries on Open Secrets . Research what the leaders in your field are doing. Follow their example and implement it in your quality control plan.
For location, you should use information from the market research to establish where the location will be. Make sure to include the following in the location documentation.
- The size of your location
- The type of building (retail, industrial, commercial, etc.)
- Zoning restrictions – Urban Wire has a good map on how zoning works in each state
- Accessibility – Does it meet ADA requirements?
- Costs including rent, maintenance, utilities, insurance and any buildout or remodeling costs
- Utilities – b.e.f. has a good energy calculator .
Legal Environment
The legal requirement section is focused on defining how to meet the legal requirements for your industry. A good business plan should include all of the following:
- Any licenses and/or permits that are needed and whether you’ve obtained them
- Any trademarks, copyrights, or patents that you have or are in the process of applying for
- The insurance coverage your business requires and how much it costs
- Any environmental, health, or workplace regulations affecting your business
- Any special regulations affecting your industry
- Bonding requirements, if applicable
Your local SBA office can help you establish requirements in your area. I strongly recommend using them. They are a great resource.
Your business plan should include a plan for company organization and hiring. While you may be the only person with the company right now, down the road you’ll need more people. Make sure to consider and document the answers to the following questions:
- What is the current leadership structure and what will it look like in the future?
- What types of employees will you have? Are there any licensing or educational requirements?
- How many employees will you need?
- Will you ever hire freelancers or independent contractors?
- What is each position’s job description?
- What is the pay structure (hourly, salaried, base plus commission, etc.)?
- How do you plan to find qualified employees and contractors?
One of the most crucial parts of a business plan is the organizational chart. This simply shows the positions the company will need, who is in charge of them and the relationship of each of them. It will look similar to this:

Our small business plan template has a much more in-depth organizational chart you can edit to include when you include the organizational chart in your business plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 8. Financial Statements
No business plan is complete without financial statements or financial projections. The business plan format will be different based on whether you are writing a business plan to expand a business or a startup business plan. Let’s dig deeper into each.
Provide All Financial Income from an Existing Business
An existing business should use their past financial documents including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to find trends to estimate the next 3-5 years.
You can create easy trendlines in excel to predict future revenue, profit and loss, cash flow, and other changes in year-over-year performance. This will show your expected performance assuming business continues as normal.
If you are seeking an investment, then the business is probably not going to continue as normal. Depending on the financial plan and the purpose of getting financing, adjustments may be needed to the following:
- Higher Revenue if expanding business
- Lower Cost of Goods Sold if purchasing inventory with bulk discounts
- Adding interest if utilizing financing (not equity deal)
- Changes in expenses
- Addition of financing information to the cash flow statement
- Changes in Earnings per Share on the balance sheet
Financial modeling is a challenging subject, but there are plenty of low-cost courses on the subject. If you need help planning your business financial documentation take some time to watch some of them.
Make it a point to document how you calculated all the changes to the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in your business plan so that key team members or investors can verify your research.
Financial Projections For A Startup Business Plan
Unlike an existing business, a startup doesn’t have previous success to model its future performance. In this scenario, you need to focus on how to make a business plan realistic through the use of industry research and averages.
Mike gave the following advice in his interview:
Financial Forecasting Mistakes
One of the things a lot of inexperienced people use is the argument, “If I get one percent of the market, it is worth $100 million.” If you use this, investors are likely to file the document under bad business plan examples.
Let’s use custom t-shirts as an example.
Credence Research estimated in 2018 there were 11,334,800,000 custom t-shirts sold for a total of $206.12 Billion, with a 6% compound annual growth rate.
With that data, you can calculate that the industry will grow to $270 Billion in 2023 and that the average shirt sold creates $18.18 in revenue.
Combine that with an IBIS World estimate of 11,094 custom screen printers and that means even if you become an average seller, you’ll get .009% of the market.
Here’s a table for easier viewing of that information.

The point here is to make sure your business proposal examples make sense.
You’ll need to know industry averages such as cost of customer acquisition, revenue per customer, the average cost of goods sold, and admin costs to be able to create accurate estimates.
Our simple business plan templates walk you through most of these processes. If you follow them you’ll have a good idea of how to write a business proposal.
How to Write a Business Plan Step 9. Business Plan Example of Funding Requests
What is a business plan without a plan on how to obtain funding?
The Small Business Administration has an example for a pizza restaurant that theoretically needed nearly $20k to make it through their first month.
In our video, How to Start a $500K/Year T-Shirt Business (Pt. 1 ), Sanford Booth told us he needed about $200,000 to start his franchise and broke even after 4 months.
Freshbooks estimates it takes on average 2-3 years for a business to be profitable, which means the fictitious pizza company from the SBA could need up to $330k to make it through that time and still pay their bills for their home and pizza shop.
Not every business needs that much to start, but realistically it’s a good idea to assume that you need a fairly large cushion.
Ways to get funding for a small business
There are a variety of ways to cover this. the most common are:
- Bootstrapping – Using your savings without external funding.
- Taking out debt – loans, credit cards
- Equity, Seed Funding – Ownership of a percentage of the company in exchange for current funds
- Crowdsourcing – Promising a good for funding to create the product
Keep reading for more tips on how to write a business plan.
How funding will be used
When asking for business financing make sure to include:
- How much to get started?
- What is the minimum viable product and how soon can you make money?
- How will the money be spent?
Mike emphasized two aspects that should be included in every plan,
How to Write a Business Plan Resources
Here are some links to a business plan sample and business plan outline.
- Sample plan
It’s also helpful to follow some of the leading influencers in the business plan writing community. Here’s a list:
- Wise Plans – Shares a lot of information on starting businesses and is a business plan writing company.
- Optimus Business Plans – Another business plan writing company.
- Venture Capital – A venture capital thread that can help give you ideas.
How to Write a Business Plan: What’s Next?
We hope this guide about how to write a simple business plan step by step has been helpful. We’ve covered:
- The definition of a business plan
- Coming up with a business idea
- Performing market research
- The critical components of a business plan
- An example business plan
In addition, we provided you with a simple business plan template to assist you in the process of writing your startup business plan. The startup business plan template also includes a business model template that will be the key to your success.
Don’t forget to check out the rest of our business hub .
Have you written a business plan before? How did it impact your ability to achieve your goals?
80% of businesses fail... Learn how not to.
Learn from business failures and successes in 5 min or less. The stories, frameworks, and tactics that will make you a 10x better founder.
Brandon Boushy
Related articles
How to Get a Business Loan (in 4 Easy Steps)
- Write a business plan.
- Evaluate your business eligibility.
- Look for the best business loans.
- Apply for a business loan .
How to Get a Business Loan: Write a Business Plan

Getting a Small Business Loan Requirements
- Age of the business
- Business credit score
- Personal credit score
- Business revenue
SIC or NAICS code
- Speed of approval
Age of Business

- Small Business Administration (SBA) 504 Loans : Requires at least two years based on tax returns .
- Startup Loans : Will normally require both collateral and personal guarantee, but are available for businesses that are just starting. SBA backed microloans are the lender of last resort.
- Shopify Loans : As little as four months based on our interview with a Shopify business owner who got her first Shopify loan in her fourth month in business.
Business Credit Score
Personal credit score.
- Payment Guaranty : You are responsible for paying the loan even if the business goes under.
- Performance Guaranty : You are responsible for completing the work that the loan was for even if the business goes under. This is common for construction projects.
Business Revenue

- Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) : Ten 1-digit Divisions, ninety-nine 2-digit Major Groups, and numerous 4-digit Industry Groups. View OSHA’s SIC manual . These are only for businesses formed before 1997. They are also only used in the U.S.
- North American Industrial Classification System (NAICS) : This system came out of NAFTA and is used in Mexico, Canada, and the U.S. The NAIC has 20 Sectors that are broken down into smaller parts based on the pic below. It is updated every five years. You can find your NAICS code on Census.gov .
- 48–49 : Transportation and Warehousing. Thin profit margins, high costs.
- 42 : Wholesale Trade. Susceptible to recessions.
- 44–45 : Retail Trade. High failure, likely to be hit by recessions.
- 56: Administrative, support, waste management, and remediation services. These have thin profit margins.
- 11 : Agriculture or forest products. These have lots of regulations.
- 812320 : Dry cleaners.
- 623110 : Healthcare (nursing homes, assisted living facilities, etc.). High regulations and costs impact the risks of business loans to this sector.
- 721110–721120: Hotels or motels (without casino ends in 10, with casino ends in 20). Recessions hit this sector hard.
- 561510 : Travel agencies. Seasonality and recessions both hit this sector hard.
- 485320: Limousine services w/ driver (except shuttle services) (except taxis). Highly discretionary purchase so recessions hit it harder than others.
- 485999: Airport limousine services (i.e., shuttle). Recessions hit it hard due to a small market.
- 532111 : Limousine rental without driver. Recessions hit it hard because of small market
- 722511 and 722513 : Restaurants. (Dine-in is 722511 and carryout is 722513.) They have high rates of failure.
- 492110 : Courier services. Recessions tend to hit them harder.
Speed of Approval
How hard is it to get a business loan.

- 48% of employers had lower revenue than the previous year.
- 33% of employers let employees go.
- 59% of businesses described themselves as in fair or poor financial conditions.
- 60% of employers are struggling with supply chain issues and retaining employees.
- 52% took out debt.
- 34% of small businesses sought funding, down from 40–45% pre-pandemic.
- 11% received all the funding they requested, while 59% have unmet financial needs or a shortfall of funding, and 31% didn’t need funding.
How to Get a Small Business Loan: Compare Options
- How much money you need .
- The loan options available.
- The lenders who provide each loan option.
How much of a business loan can I get?
- Amounts under $50K : Go for online lenders, merchant cash advances, business credit cards, or a microloan.
- $50K–$500K: Almost everywhere lends these values.
- $500K–$5M : You’ll want SBA 7(a) or SBA 504 loans
- $5M+ : Traditional bank loans are the most likely place to qualify.
What kind of business loans are there?
- Startup Business Loans
Unsecured Loans
Secured loans, traditional loans.
- Merchant Cash Advances
Term Loans
Lines of credit.
- Personal Loans
Home Refinance, Second Mortgages

- OnDeck : Offers term loans up to 24 months and lines of credit to businesses. Your business needs to be open for more than a year, make more than $100K revenue, and have a 600+ FICO credit score.
- Kabbage : Offers commercial credit lines if you have a 640 FICO credit score, over $3,000 per month in revenue, and more than a year in business.
- BlueVine : Offers commercial credit lines for business owners with 6+ months in business, and $10,000 monthly revenue.

- Bank of America Loans : Get a line of credit for businesses with more than $250K revenue and 2 years in business. This Bank of America Small Business loan runs a promotional offer occasionally that can be as much as six months reduced interest rate and 25% savings on fees.
- National Funding : With only 6 months in business, a 575 credit score, and an equipment quote from a vendor, you can get an equipment loan from National Funding for up to $150,000.
- Funding Circle : Get $ 25,000 to $500,000 term loans from Funding Circle with term lengths from 6 months to 7 years. The application process is quick and painless, with most approvals within three days.
- Bank account
- Credit cards
- Payment processing
- Corporate consulting
- Initial public offerings
- Mergers and acquisitions
Merchant Cash Advances (MCAs)

Invoice Factoring

Small Business Administration Loans
Sba 7a loans.


SBA 504 loans
- Increase jobs in an area both during and after construction.
- Reduce the affordable housing shortage.
- Increase economic activity.
- Reduce personal expenditures on gasoline in new neighborhoods.

SBA Disaster (SBAD) Loans
- Physical Damage Loans : These loans are for repairs and can be up to 20% more than the estimated repair after a disaster. Both homeowners and businesses can apply for these.
- Mitigation Assistance Loans : When you are repairing a first home or business property after a disaster, you can apply for mitigation assistance to prevent damage next time .
- Economic Injury Disaster Loans (EIDL) : If your business lost money because of a disaster, you may apply for an EIDL .
- Military Reservist Loans : For businesses that lose essential employees because they were called in to serve in the military or reserves, this can be a great help.
Personal Loans

How to Get a Startup Business Loan
- Gather personal and business bank statements.
- Maintain copies of your business licenses, EIN, and business formation.
- Find an SBA lender near you.
- Apply for an SBA microloan.
- Minimum credit score requirement : Assume a 650 FICO score
- Loan term : Three years or less (can be up to six years)
- Loan amount : $16,000 (Anything over $10,000 has a lower maximum interest rate, and $16,318 is the average approval.)

How to Get a Business Loan with Bad Credit
- Kiva : No interest crowdfunding loans of up to $15,000 that don’t ask for credit scores. Kiva requires between 5 and 35 people in your social network to contribute before they will allow you to list. Unfortunately, they aren’t available in Nevada and one other state.
- Portfolio backed line of credit: Also called security backed lines of credit (SBLOC), Pledge Loans, Insurance BLOC. These are basically backing your loans with assets that aren’t your house. They will be valued at lower than the market rate, but you can keep your assets and get funding this way.
- Self : Pay $25–$150 per month for 24 months. After the term is complete, you get back all but the $9 per month fee (rate may change). Self reports to all three agencies and offer additional services to help build your personal credit score.
How to Get a Loan to Start a Business
- SBA Microloans : Up to $50,000 through SBA approved lenders might be offered.
- Personal Loans : You can get a personal loan to start a business.
- Rollover Business Startup : Start a corporation, create a 401K, rollover 401K from another company, and buy your corporation’s stock with the 401K. Now you have funding.
- Friends and Family Loans : Borrow money from your family.
How to Get a Loan

- a DUNS number
- Six months of operations for an online lender and two years for SBA backed loans
- A business plan
- All your documents ready to go (Check each lender's requirements on their website.)
How to Apply for a Small Business Loan
- Gather the information in the previous section.
- Go to the website or bank to apply.
- Answer every question.
- Provide all documentation to the lender.
- Get a response if it is an instant approval or rejection.
- Be told you will be contacted if they need more information
- Wait for the lender to send the information to the SBA.
- Answer any follow up requests.
- Receive notice of approval or denial.
- Receive notification of approval and a funding date.
- Receive notice of rejection and how to request your business credit report.
Build Your Business
How to Start a Landscaping Business (And Make $100K+/Month)
Do you love being outside and working with your hands? How about the idea of being your own boss?
If your answer to these questions is a resounding “Yes!” then starting a landscaping business could be the perfect career for you. It certainly was for Mike Andes, the founder of Augusta Lawn Care .
Mike started Augusta Lawn Care as Andes Lawn Care to pay for college, but it became so successful that today it’s one of the fastest-growing franchises in the U.S. with over 93 landscaping business owners operating under his business model. The franchise office makes between $65K and $112K per month, and the average franchise makes approximately $37K per month.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"] We’re going to share everything you need to start a landscaping business, including:
What Is a Landscaper?
What does a landscaping business do, step 1: get landscaping experience, step 2: choose your niche and services, step 3. plan for landscaping services success, step 4: choose a landscaping business name, step 5: establish your company, step 6: purchase landscaping equipment, step 7: build your team, step 8: attract customers with marketing efforts, step 9: deliver quality work, start your own landscaping business.
Click on any of the links above to jump ahead to the information you want about how to start a landscaping business. [/su_note]
A landscaper is someone who uses their understanding of horticulture, building practices, and artistic design to beautify land. Landscape professionals perform tasks like:
- Leveling land
- Selecting plants and other materials that will thrive in the local climate
- Creating a layout that will create specific emotions, paths to follow, or lighting conditions
- Planting and caring for the landscape
What Is the Difference Between a Landscaping and Lawn Care Business?
A landscaping company is focused on the design and transformation of an outdoor area through planning, construction, arrangement, and planting of trees, shrubs, grass, and other decorative elements like paths and water features.
Lawn care services focus on mowing lawns, pest control, fertilizing land, and spreading seeds or sod.
Lawncare and landscaping are similar, and many companies provide both services.
Augusta Lawn Care is a lawn care company that provides landscaping services as well. Their list of landscaping services includes:
- Mowing: Cutting Grass
- Landscaping : Leveling services, design, planting new greenery
- Hardscaping : Creating pathways to encourage people to use when traveling through the lawn
- Lawn Care : Performing upkeep of customers’ lawns on a regular basis
- Property Cleanups : Removing weeds and leaves, plus trimming bushes
- Snow & Ice Removal: Removing snow and ice from pathways
Another landscaping services list might look like the list below.
- Garden and lawn maintenance (mowing, fertilizing, weeding, etc.)
- Maintaining and trimming trees and hedges
- Grooming golf courses
- Laying sod and lawn planting service
- Planting flowers, trees, and bushes
- Corporate/company landscaping
- Designing gardens to customer specifications
- Laying out and constructing walkways
- Installing retaining walls
- Building decks and patios
- Irrigation system design
Basically, anything involving the land around a home or business is the domain of a landscape professional. While larger landscaping companies will provide all of these services, others specialize in one area, like lawn maintenance or flower bed design.
Now that you know what landscapers do, let’s look at how to start a landscaping business.
How to Start a Landscaping Company
Starting a landscaping business is as simple as:
- Get Landscaping Experience
- Choose Your Niche and Services
- Plan for Landscaping Services Success
- Choose a Landscaping Business Name
- Establish Your Company
- Purchase Landscaping Equipment
- Build Your Team
- Attract Customers With Marketing Efforts
- Deliver Quality Work
Mike didn’t just wake up one day and decide to start Augusta Lawn Care. He grew up less than affluent and knew he would need to earn the money to pay for college. So he started mowing lawns at age 11 and kept doing it through his bachelor degree and MBA (He started college at 13!).
Eight years later, he was making over a million per year and started building out his landscaping business. He told us the biggest difference in his business now is:
[su_quote]As you grow your landscaping business, you’ll be less hands on. At first you’ll be mowing lawns and working with customers. Then you’ll start being the sales person, then you’ll literally just be supporting your employees.[/su_quote]
Check out our interview with Mike below.
Mike found podcasts and YouTube videos were one of the best ways to learn from other landscaping businesses. It gave him the knowledge and tips he needed to start his successful landscaping business.
You might want to start providing lawn maintenance services to learn more about the lifestyle and gain some experience. Lots of people like the idea of working outdoors, but the reality is often less than pleasant.
The workday usually starts between 6 and 7 AM, and the weather can be tough to adapt to. You never know whether you are built for starting a landscaping business until you’ve spent 4 hours moving rocks on a hot summer day.
Mike’s Courses and Franchises
Mike offers a business course to help you get into the landscaping industry. It provides lessons on:
- Starting a Business with $15,000
- Landscaping Business Basics
- Bookkeeping and Accounting
- Growing to $250,000 / Year
- Adding Retail Products
- Pay for Performance (P4P)
Plus, the course includes done-for-you templates and access to previous videos. It’s effectively providing you the same information he provides the franchisees, but you build your own brand. Check out what Mike has to say about the difference between his course and franchises.
Check out Mike’s Landscape Business Course !
As you saw above, landscaping covers a wide range of construction and lawn maintenance services. For a small landscaping business today, it’s often best to focus on just one specialty, like lawn care or landscape design, rather than trying to start off as a full service landscape company. Mike told us:
[su_quote]I tend to focus on the parts of the landscaping market that are easiest and most profitable.[/su_quote]
A new landscaping business will reduce startup costs and business expenses if they specialize. You’ll only be purchasing equipment that you need for the jobs you do. You’ll also need fewer skills, which means a smaller crew to get the job done.
Common niches in the landscaping industry include:
- Landscape maintenance: Rather than building or installing landscapes, you’ll be the one pruning hedges, mowing the lawn, and watering the flowers to keep them looking beautiful. Maintenance companies require the lowest initial investment because they require less equipment. On the other hand, you won’t be able to charge as much per hour as you could for more creative and labor-intensive services.
- Fertilization, weeding, and pest control: This is a specialized form of maintenance that focuses on keeping plants and lawns healthy. It requires expert knowledge of plant and grass care. You’ll also be working with potentially dangerous chemicals, so you may need to obtain extra permits or training.
- Sod and lawn installation: Businesses in this niche lay sod, spread grass seed, and install lawns for customers. This often means more one-time contracts than the recurring services offered by maintenance companies.
- Deck and patio construction: Those who have skills with building and construction can put them to great use in a landscaping business. Along with installing the deck and patio, you’ll beautify the area around it. Since this often involves new construction, you’ll need an intimate knowledge of your region’s building codes and other regulations.
- Landscape architecture and design: Businesses in this niche both design and install landscape features for clients. This can include labor-intensive projects like building retaining walls, building terraced gardens, or contouring the landscape. Designers work with customers, using their input to create attractive, livable outdoor spaces, so creativity and vision are key tools of the trade. You’ll also need to have some horticultural knowledge so you can arrange plantscapes that last and thrive.
Mike sticks mostly to the first three tasks, but he’ll occasionally do pathways and more detailed landscaping jobs.
Commercial vs. Residential Landscaping
Along with deciding which specific services you’ll offer, it’s also a good idea to consider what kind of customers you’ll work with. Mike focuses on residential landscaping for two key reasons:
- Lower up-front costs: Residential landscaping companies typically take a deposit at the start of the project that covers the cost of the materials. In commercial landscaping, you often don’t receive your pay until the job is finished, so you’ll have to pay for the materials out of your company’s funds.
- More creative freedom: In commercial landscaping, you’re typically working from a plan provided by the company. Even if this plan has flaws, you don’t get any freedom to make changes or improve it. With residential landscaping, you can work with the customer and make recommendations, giving you more control over the quality of the end result.
Commercial landscaping also has its advantages . You can have fewer clients, since commercial projects are often larger both in regard to the area and the client’s budget. It can also provide a more consistent revenue, especially in the maintenance and lawn care niche.
Create a Basic Lawn Care Price Sheet
One of the hardest things for new landscaping businesses is knowing how much to charge for services. Mike’s advice:
[su_quote]Do a lot of research.[/su_quote]
Different regions have standard price ranges for landscaping services, so that’s the first thing you should look up when you’re deciding on your prices. Each project is unique, though. Many new landscaping businesses have a tendency to under-bid for projects. They want all the work they can get and don’t want to be turned down by the client.
Another business owner, Brian Linson, told us:
[su_quote]Go out and get your numbers down when you’re bidding projects. Don’t be afraid to walk around and measure everything out. Just take your time when you’re bidding because the last thing you want to do is go back to a client and tell them you need more money to finish their project. That’s something no one wants to hear.[/su_quote]
Check out the rest of the interview with Brian below.
Check out Home Advisor’s list of costs for landscaping services :
- Lawn mowing/maintenance: $130
- Removing a tree stump: $349
- Leaf removal: $400
- Sealing asphalt: $527
- Tree and shrub maintenance: $800
- Deck sealing and waterproofing: $919
- Concrete removal: $1,081
- Patio or path repair: $1,454
- Deck repair: $1,987
- Installing sod: $1,997
- Driveway repair: $1,714
- Resloping/contouring: $2,116
- Fountain installation: $2,673
- Pond installation: $3,352
- Landscape installation: $3,300
- Patio and path installation: $3,900
- Landscape design: $4,569
- Installing a retaining wall: $5,933
- Building a deck: $7,650
A landscaping business owner needs to have a plan if they want their small business to be successful. It’s a seasonal business, so don’t forget to plan for reduced cash flow during the winter months.
How Much Does it Cost to Start a Landscaping Business?
Initial expenses for a landscaping company vary widely, depending on the size and scope of your operations. If you’re a one-person operation that only performs basic maintenance and mowing services, you can get started with as little as $1,000. Mike told us:
[su_quote]When we started, we started with $1,000 to buy a blower, a weed eater, and a lawn mower.[/su_quote]
That said, most landscaping businesses will require a larger investment. The average start-up cost is between $15,000 and $20,000 if you’re starting from scratch.
There are ways to lower these start-up costs, though. Buying used rather than new equipment can cut down significantly on your expenses. Mike specifically suggests buying your work vehicle used because they get damaged easily and the business asset will be devalued more if you buy it new.
You can also rent much of the equipment from home improvement stores, typically for around $100/day. While this is less cost-effective in the long term, it can be an excellent way to save on initial expenses if your financial resources are limited.
If you don’t want to start a business from the ground up, your other option is to buy a franchise. While this often takes more money up-front, it can be a good option for a first-time entrepreneur since you won’t need to do as much leg work to get it off the ground.
How Much Does a Landscape Business Owner Make Per Year?
The short answer, again, is “it depends.” According to Lawn & Landscape Magazine ’s State of the Industry Report , the average annual salary of a landscape company owner ranges from around $31,000-$69,000 per year.
Mike hasn’t shared his salary, but with $699 to $1200 monthly franchise fees from 93 franchises, it’s fair to say he’s making decent money.
Writing a Landscaping Business Plan
A business plan is a living document that plans for the future of your company. You’ll definitely need one if you plan to apply for small business loans or other financing, since both bankers and investors will ask to see it.
Even if you’re opening the business with your own savings, a business plan is a helpful document. It’s where you’ll outline your company’s mission statement and long-term goals, along with detailing your initial and ongoing expenses.
If you’ve never written a business plan before, take a look through a sample business plan to get more guidance on what to include and how to write it. Among the things, your business plan should include:
- The business’s mission and objectives
- A description of the company
- The services you’ll offer
- An analysis of the market
- A summary of your sales and marketing strategy
- The business’s organizational and management structure
- Initial budget figures and financial projections
Mike even recorded a whole video about planning your own company. Check it out below.
[su_youtube url="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Seac5PbUZXk"]
It’s important to put some thought into choosing the name of your company. Your landscape business name is the first impression customers will get, so make sure the name explains what you do.
Once you’ve picked business names for a landscaping business, it’s a pain to change them, so that’s more motivation to get it right the first time. If you’re having trouble coming up with landscaping business names, a business name generator can help you get started.
The best landscape business names are short, simple, and tell people exactly what your business does. It should be easy to remember but also unique enough to stand out from the competition.
Keep in mind that much of a business’s presence in the modern day is online. Check to see if the business names you’re considering are available as domain names so you can get one that matches. You can use the WhoIs LookUp to see if a domain is available with the business name you want.
Once you’ve determined what kind of services you’re going to offer, you’ll be better able to do the logistical work of establishing a company. This includes:
- Creating a Business Structure
- Getting a Landscaping Business License
- Opening a Business Bank Account
- Getting Landscaping Insurance
Keep reading for more information on how to start a small landscaping business.
Create a Business Structure
Creating a separate business entity for your landscaping company separates your business assets and your personal assets. Most local landscaping companies choose to use a limited liability company (LLC), but there are other business models that will protect your assets. To create a business entity, just go to your Secretary of State business portal.
Find out more about business entities .
Landscaping Business License Requirements
Every new business has to be registered before they can legally operate. First, obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN). This is your business’ federal tax ID, which you’ll need to open a bank account, hire employees, or apply for local permits. You can apply for an EIN through the IRS website .
You’ll also need to register with the county clerk’s office for local business licenses. Depending on your state’s laws, you may also need to apply for a sales tax permit. Each state is different, so check with your local SBA.
The specific licenses and permits required for a landscaping business vary depending on your state. Check with your state’s business licensing association to find out what’s required in your area.
Get a Business Bank Account
Go to a local bank and open an account. That way when your clients pay an invoice, it goes straight into your bank. Then you can pay yourself, your business expenses, and your employees. Learn more about business bank accounts .
Get Business Insurance
Potential customers expect landscaping companies to be insured to cover job sites if they damage something while on the job. That means you need to have at least property damage and general liability insurance. Commercial clients might have other requirements.
If you’re using your personal vehicle, don’t forget to get commercial driver’s insurance.
The types of landscape services you’re going to provide will determine which specific equipment you’ll need. After you’ve decided on a niche, create a landscaping tools list.
If your start-up budget isn’t enough to cover everything on your list, you don’t need to fret. Start by renting more expensive tools, then buy them as you go. This was Brian’s approach when BL Landscapes was first starting. Even now, he says,
[su_quote]We buy the tools we need for the job, and when you sign another job you take some of that money and buy the tool you need for that job, and that way you just keep building up.[/su_quote]
This can cut into your profits, of course. If you spend $500 on equipment for a $1,000 job, you’re not going to have much left over at the end. It’s worth it in the long run, though, because the next time a job calls for that tool, it’ll be pure profit.
Generally speaking, it’s better to buy fewer pieces of high-quality equipment than try to buy a full range of tools right off the bat. All tools wear out over time, but a well-made shovel with a fiberglass handle will serve you well for longer than the cheapest option on the shelf.
Craigslist can be a good place to find used equipment if you want to save some money. For new tools, you can check hardware stores like Home Depot and Lowes, as well as nurseries and farm supply stores.
Landscape Tools List
Here is some of the equipment you’re likely to need as a landscaping business, along with each tool’s approximate cost:
- Manual gardening tools (shovels, rakes, shears, trowels, etc.): $10-$50 each
- Push mower: $200-$1,000
- Riding lawn mower: $1,000-$5,000
- Leaf blower: $100-$500
- Lawn spreader: $100-$500
- Sprayer (for fertilizer, pesticides, etc.): $50-$200
- Trimmer: $50-$300
- Edger: $80-$350
- Water saw: $500-$4,000
- Plate compactor: $300-$5,000
- Trailer: $1,500-$5,000
- Heavy-duty truck: $10,000-$50,000
- Portable generator: $500-$2,000
Check out this blog by Spyker to learn more about each tool.
Other landscaping companies might be one-man operations, but for larger jobs you’ll need some help. Hiring employees is one of the most difficult aspects of owning a business, and while you can find plenty of advice on the topic, there’s no substitute for experience.
Offering competitive pay is a good way to attract top talent to your company. There are a few approaches you can take:
- Mike uses Pay for Performance, which means the more effective the employee is, the more money they make.
- BL Landscapes pays $25 per hour.
- You can combine the two and give a minimum hourly wage plus commission.
You can find quality employees at a variety of places:
- Job marketplaces like LinkedIn and Monster
- Trade Schools and Colleges
Sometimes, you’ll even meet them at lunch. We talked to a recruiter to find out how to hire.
You’ve started your own business, but how do you find potential customers?
You’ll want to create a marketing plan that identifies your target market and how you’re going to communicate with them.
You’ll also want to make sure you have:
- A Business Website
- Landscaping Business Cards
- Truck Decals
- Social Media
Mike told us:
[su_quote]Paid media allows you to control your lead flow. Just spend 1-2% of revenue for paid media when you’re slowing down. Painting trucks, uniforms, and brochures are also marketing. Everything we do is a form of marketing.[/su_quote]
The first thing Brian did when he started BL Landscapes was reach out to local real estate agents. He also built relationships with his local suppliers, like nurseries and home improvement stores. As a low-cost marketing option, Brian says,
[su_quote]When we started, we had some cheap landscape business cards made. Go put them [out in your community], and start telling people and throwing your name out there. Really that’s the biggest thing, is just to get your name out there to anyone you can. Make yourself a Facebook business page and start going at it.[/su_quote]
Mike encourages landscapes to share as much about their existing business as possible. The more you share what landscapers do, the more capable you are of benefiting from word-of-mouth marketing.
The absolute best advertising for a landscaping company is a well-completed project. If you consistently deliver long-lasting, beautiful landscapes, that will secure repeat business and bring in new clients when those happy customers tell their friends.
Make sure to make it easy for clients to recommend you. Give them some business cards, and provide the link to your Google reviews on your invoice. Don’t be afraid to ask. You can book clients for routine maintenance, too.
About 50% of BL Landscapes’s business comes from repeat customers. Continuing service and after-installation coverage is a huge part of this. They cover their work with a warranty, and will often help fix issues for customers even after this period has expired.
As Brian says:
[su_quote]Whether it’s a mistake we made or a product that failed, we try to go back and make it right.[/su_quote]
This approach has paid off for him. In their six years of business, BL Landscapes has a 100% customer satisfaction rate. His customers know they can count on him to use high-quality materials that will stay beautiful for years to come.
We’ve answered your questions about landscaping companies, including:
- What do landscapers do?
- How much do landscapers make?
- How much to start a landscaping business?
- How to start a landscaping business with no money
- How to find what landscaping license you need
- How to come up with business names for landscaping
It doesn’t take a huge investment to start a lawn care company, and the revenue potential is high. As you can see from Mike’s success, the best way to financial success is to plan ahead and provide your company with a strong foundation.
Whether you start your own company or buy one that’s already up and running, the ultimate key to long-term success is to provide quality services. Starting a new business is never easy, but the effort you put in can yield fantastic results if you follow Mike’s advice about how to start a lawn mowing business.
What’s keeping you from getting started?
How to Buy a Business With No Money (2024)
There are plenty of ways to buy a business with no money. One of the most common strategies is called seller financing—and nearly 80% of business purchases include at least some of it.
We’re going to share some options for buying a business without money, or with very little money, up front. You’ll learn what to look for during a business acquisition and how to negotiate the deal.
[su_note note_color="#dbeafc"]If you’re looking to start buying businesses without money, click on one of the links below—or simply read on—to learn more.
Use seller financing
Get a small business administration (sba) loan, bring on investors or partners, work with business brokers, identify goals before you buy an existing business, find the right business for sale, value the business, negotiate your deal, close the deal and transition into ownership.
- Why start new businesses when you can buy businesses with no money? [/su_note]
How can I buy a business without money?

There are multiple ways to buy an existing business from the current business owners. Using a combination of these strategies can help you buy a business with no money of your own. Some of the most common funding options include:
- Using seller financing
- Getting a Small Business Administration loan
- Bringing on investors or partners
Let’s look into each.
Seller financing, also called owner financing, is one of the most common ways of transferring ownership from a current owner to a new business owner. According to the mergers and acquisitions firm Morgan & Westfield , 80% of all small business purchases use at least some seller financing.
In deals that use seller financing, sellers fund a portion of the small business purchase in exchange for a percentage of the cash flow for a specific period after the new business owner takes over. The buyer often pays the remaining balance with a down payment and periodic installments.
The terms of the deal may look something like below:
• Percent seller finances: 10% to 20% • Your down payment: 30% to 80%, but 50% is fairly standard • Interest rates: 6.6% to 16.5%, comparable to the Small Business Administration's current rates • Note duration: Three to seven years
When you propose seller financing, you’ll likely have to create and sign a promissory note and agree to a Uniform Commercial Code lien . Most sellers may require you to maintain specific financial benchmarks as well.
The SBA offers small business loans to people buying a small business. 7(a) loans are easier to get when buying an existing business because there is a record of profitability that new ventures do not have.
When applying for a 7(a) loan, apply for enough financing to purchase the existing business and cover expenses for ongoing operations.
You can also bring on investors or partners when you want to buy a business without money up front. Investors can be a friends-and-family business loan, venture capitalists, or crowdfunding.
How to buy a business with no money

Buying a business with no money is as simple as following the six-step process below:
- Identify goals before you buy an existing business.
- Work with business brokers.
- Find the right business for sale.
- Value the business.
- Negotiate the deal.
- Close the deal and transition into ownership.
Before you start looking for business acquisitions, you’ll want to think about what you are trying to achieve by buying an established business. You might buy a business to:
- Hedge risk: Investing in an established, income-generating business can limit risk and provide reliable income, as it has already gone through most of the struggles that upstart companies experience.
- Accelerate your retirement: A leveraged buyout allows you to keep your current financial investments and grow your income, which gets you closer to retirement.
- Finance your growth: Using leverage helps small business owners build their businesses quickly.
- Improve liquidity: Taking out a business loan for a business acquisition will help small business owners increase their cash on hand, which makes it easier to cover business expenses.
In addition to the goals listed above, you may be interested in a specific business model, like an online business or making money with passive income plays.
Buying an existing business is a complex task, and you need an experienced broker to help you enter your next business venture correctly. You’ll want a business broker because they:
- Have experience completing deals
- Have tools to help them find and evaluate businesses
- Routinely deal with business acquisition paperwork
- Help you through the process
Next, you’ll establish your business acquisition goals.
Buying a business has never been easier. There are several business listing sites, like:
When buying a business, you want to find businesses that can provide a win-win deal. Look for small businesses that have certain qualities. We’ll discuss the essential qualities of a business for sale next.
Look for an owner who is ready to get out

Buying a business is easier when the seller is looking for potential buyers and wants to sell the business quickly. You’ll have to find out the seller’s motivations for selling the business, which may include:
- Reaching retirement age
- Moving to care for a family member
- Equipment issues
- Lack of automation
- High churn rates
- Lack of marketing
- Revenue problems
- Employee turnover
Ultimately, each of these is a potential opportunity for a new business owner to get a deal on the small business and dramatically improve the cash flow and profitability. Some may also lower the purchase price or make it easier to receive seller financing.
Look for businesses with growth opportunities
Some businesses provide clear opportunities for growth if purchased. Look for qualities such as:
- Outdated technology: Just by implementing new tech, business buyers can dramatically improve operating costs. SBA lenders have loans specifically meant to help a business’s success through improving technology.
- Lack of competition: Business buyers can really benefit when the competition can’t keep up with the improvements you make once it’s your own business.
Look for businesses you’re familiar with

While it’s possible to purchase a business you (or consumers) don’t know much about, searching for the following qualities can help ensure a seamless transition:
- Age: Old, reputable businesses can provide financial security and provide a brand to build upon.
- Known business models: Own businesses you understand. Spending money on a business model you must learn adds risk and time to learn the business.
Next, you’ll want to dig into the financial statements and other business aspects to decide on a fair business price.
You’ll want to visit the business to check it out. There, you’ll be able to see how it operates, determine where it can improve, and make other observations that can’t be made from afar.
If you like what you see so far, it’s time to send a letter of intent to the business owner so you can start the due diligence process.
You’ll want to understand their financial statements, especially areas like cash flow, operating expenses, accounts receivable, and outstanding debt.
You’ll also want to understand the age of the equipment to determine if you’ll need equipment financing. You may also be able to use the equipment as collateral to secure alternative funding options.
You might want to prepare a list of questions before buying businesses . Then, you’ll want to calculate business valuation , which will guide how much money you’re prepared to spend.

Buying a business will require negotiating a price that’s fair to both business owners. You can negotiate both the purchase price and the sale terms, but you need to decide which is more important to you and which is more important to the seller.
When you have multiple financing options lined up or are using your own money up front, you might find it most beneficial to negotiate the price. But when you seek seller financing, you might just give them their asking price in exchange for more favorable financing options.
Offer a higher interest rate

Seller financing can be made more attractive by bumping up the interest rates.
For instance, let’s assume the buyer wants $500K and you want to pay over seven years. That’s not an attractive deal if you offered to pay $75K annually. To get more favorable payment terms, you can raise the interest rate.
Which offer would you take?
- $500K up front
- $100K up front and $478K over 2 annual payments
- $100K up front and $504K over 3 annual payments
- $100K up front and $528K over 4 annual payments
- $100K up front and $550K over 5 annual payments
- $100K up front and $575K over 6 annual payments
- $100K up front and $630K over 7 annual payments
All except for the last one are paying 10% interest. The last option has a higher interest rate, pays the seller an extra $4K per year, but still allows you to keep more cash on hand each year.
Bring on a silent partner
You can always bring in a silent partner if you don’t have the cash up front. Silent partners contribute monetarily and often benefit from the sale, but they don’t take an active role otherwise.
You might also be able to secure venture capital, though venture capitalists tend to want more involvement. Make sure you negotiate for the venture capitalist to be a silent partner because many actively help investments grow.
Find a secondary source of financing

Seller loans don’t normally cover all the financing when buying a business. Loans like SBA financing or traditional bank loans may be secured by using equipment or accounts receivable (meaning the money you are set to make) as collateral.
Learn about in our article about business loans .
Raise the capital through crowdfunding
Crowdfunding uses alternative financing options to get the money you need. With crowdfunding, you can offer donors incentives (like products or equity) in exchange for contributions, or you can offer to pay them back with just like if you were given a loan.
There are tons of options for crowdfunding. Learn more below:
Use your cash flow
A great way to get a loan to buy a business is using your cash flow or accounts receivable to secure a loan. They’ll want to take a specific amount out each week, but it’s another to purchase a business with no money up front.
Learn more about cash flow loans through National Business Credit .
Finance growth

While deciding how to get financing for a business, don’t forget to give yourself some wiggle room for improvements and operational expenses. You might need to write a business plan to show how the money will be spent. Learn more in our guide to writing a business plan .
Take your time to show you have a plan to turn the funds into new revenue and prove you can pay the loan back.
Once you’ve secured professional advice, chosen the business you want to buy, done your due diligence, secured a loan, paid the down payment, and signed the contract, you’ll still have to transfer ownership. This step includes:
- Building an operational transition timeline
- Building relationships with employees
- Transferring all authorization, contracts, bank accounts, and other legalities
- Hiring an operator if you plan to be a passive investor
Why start new businesses when you can buy businesses with no money?

Starting a new business can be a real challenge if you don’t have money. You have to learn a lot as you go and may not be able to afford new freelancers or employees until you start earning revenue.
But buying an existing business without money is something that happens all the time. You’ll start with the business’s existing revenue and systems, then turn your focus to fixing areas that you’ve identified as problematic.
Have you ever bought a business without money? How did it go? We want to know.
nice work https://binarychemist.com/
My Name is PRETTY NGOMANE. A south African female. Aspiring to do farming. And finding a home away from home for the differently abled persons in their daily needs.
Become a business owner in less than 90 days
Start your 10-day free trial of the UpFlip Academy and learn how to start your own business from scratch.
Get business advice straight to your Inbox

- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business


How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 6 min read
The Content of Business Plans
Here we look at the key ingredients required to produce an effective business plan.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
The precise form and content of a business plan will vary from organization to organization, to reflect the different economic, market and other environmental contexts within which each organization operates. In addition to this, the form and content of the business plan will depend to an extent, on the process that was used to produce it.
Business plans need to be set in a context . For most organizations, this will be the corporate or strategic plan that describes the key components of the strategic environment in which the organization will be operating.

Departments will have a specific and identifiable part to play in the overall aim and objectives. That role should be described in a statement of purpose : the equivalent of the mission or vision statement that would exist in most commercial forms of organization. The statement of purpose should set out clearly and concisely the essential, distinctive role that the department will play in helping the organization to achieve its aim and objectives.
Business plans are statements of intent relating to some future period of time . The choice of that period of time may be imposed, in that the corporate plan requires that business plans cover a set time period. If this is not the case then the time period should be chosen carefully: there may well be a natural cycle of activity that helps to dictate what is an appropriate period over which to plan.
Associated with the statement of purpose there should be clear and measurable objectives that are SMART :
- M easurable
- A chievable
- T ime-limited
It should be possible to determine whether or not any particular objective has been achieved. The means by which this is done may be either through some unambiguous measure or by using an indicator , perhaps some surrogate measure that is almost certainly associated with the achievement of the main objective.
Objectives may relate to programs , a set of related activities designed to achieve some objective and often with an identifiable funding stream associated with it, or they may be related to organizational divisions of the department. Each objective should be the responsibility of a named individual. In some cases, it will be necessary to attribute responsibility for the achievement of an objective to more than one individual or, in exceptional cases, to a team or group. There are difficulties associated with this approach however. Objectives held by many are often effectively held by none, and it is all too easy for managers to assume that another individual is taking some action when in fact he/she is not. Where objectives are to be jointly held then, if at all possible, the respective contribution of each individual should be made clear.
All departments operate within an environment that is characterized by variety and uncertainty. The external environment contains the client groups that the department seeks to serve, the other organizations with which it competes to do so, and the general sociological, technological, environmental and political factors that are likely to affect the organization in its mission to meet the needs of its clients.
The business plan should describe the key components of this external environment clearly and concisely, in a way that illustrates easily the likely future development of each component and what this means for the plans of the department. In the most general of terms, future developments in the external environment are likely to result in the appearance of threats to the achievement of the aims and objectives of the department or opportunities that the department might seek to exploit.
Determining the boundary of the department will define the external environment from the internal environment. The internal environment is likely to contain many of the resources that the department will need to achieve its objectives. Analysis of these resources and how they are likely to develop over the period of the business plan ought to result in the identification of strengths that the department will be able to use to help it achieve its objectives, and weaknesses that, if not dealt with, might compromise its ability to do so.
Many organizations produce a summary of the threats and opportunities existing or likely to develop in the external environment, and the strengths and weaknesses associated with the internal environment in the form of a SWOT statement. Good practice in this area would seek to match up the components of the statement, identifying explicitly where strengths allow the exploitation of some opportunity or the countering of some threat: and where weaknesses leave the department vulnerable to an identified threat or unable to exploit some opportunity.
Such a tactic also helps to identify those ‘strengths’ that are not intended to be put to some use in exploiting an opportunity or countering a threat and therefore encourages the department to assess the extent to which they truly are strengths. In a similar vein, weaknesses that do not lead to vulnerability in terms of exposure to threats or inability to exploit opportunities, if correctly diagnosed, might safely be left unmanaged.
Business plans contain at their hearts a description of the range of products and services that the department will produce or deliver and the client groups that it will seek to serve. In appropriate circumstances, these products and services and client groups might each be classified as ‘existing’ and ‘new’, and programs of activity devised accordingly. Given that, in time, all existing products and services are likely to become unwanted and irrelevant and that new client groups are likely to emerge, then it is good practice to plan to direct at least some activity in the department towards identifying and meeting these developments.
Business plans are achieved through the deployment of resources . In this context, the term resources is used to refer to anything that can be used to help achieve an objective or aim. Some obvious and common resources are:
Less obvious (although often at least as important) resources are:
- specialist knowledge
Where possible, the cost of resources consumed in the achievement of an objective should be quantified. In practice, this is most easily done for tangible resources and can, in practice, be quite difficult for those resources that have no physical existence, such as expertise.
A business plan should therefore contain a statement of the resources required to achieve the objectives with the cost of acquiring, maintaining or retaining them.
Where the resources to be deployed in the execution of a business plan are other than the most simple and straightforward, managers should consider the production of a resource management plan . This would set out:
- the key resources that are required for effective and efficient implementation of the business plan
- for resources not currently held by the department, an indication of how they are to be acquired and the cost, or the cost of maintaining or retaining those that are already held
- any likely future development of resources held that is necessary for the achievement of the plan and the costs of doing so. In this regard and with specific reference to human resources, the cost of ensuring the appropriate development of knowledge, skills and behaviors should be included here
- the identification of any resources that might be regarded as surplus to requirements, with a statement of what is proposed by way of disposing of such resources, including how much this is likely to cost
Where the deployment of resources is anything other than the most trivial of tasks then a plan for their deployment would be considered good practice.
Plans are statements of intent with regard to future actions . Given that the future is inherently unpredictable, it is possible that some significant future event will not materialize or a necessary condition may not come about. A robust business plan must therefore deal with the issue of risk .
All business plans depend to some extent or other on assumptions. Managers of departments should take care, therefore, to bring to the surface their own assumptions and those of the other individuals involved in helping them to produce the business plan. Documenting the key assumptions that underpin the plan is also good practice, as is testing each for consistency with assumptions made elsewhere.
Given that it is unlikely that all assumptions and forecasts will come about exactly as predicted in the plan, good practice mandates the use of sensitivity analysis . This essentially asks: “What would happen if the key variables affecting the achievement of objectives changed?”. For example, if the plan contained an assumption about future rates of price increase then you might test out the impact of rates that were slightly less and slightly more than you had assumed. If changing this assumption by, say, 5%, results in a 10% change in performance then you might reasonably conclude that that results are sensitive to changes in this key variable.
Sensitivity analysis might cause you, as the manager of the department, to revisit the plan, perhaps seeking to augment the risk management strategy or to change an objective because it is inherently and unacceptably risky.
Nowadays, most organizations have implemented programs of continuous improvement , however they might be designated in practice. As someone who manages others, you will wish to ensure that as well as having such programs in place for all key client-related and other activities, the same treatment is afforded to the process of business planning itself. You should be continuously striving to find ways to make the process of producing the business plan more effective and efficient each time you do it.
Join Mind Tools and get access to exclusive content.
This resource is only available to Mind Tools members.
Already a member? Please Login here

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Tips for Dealing with Customers Effectively

Pain Points Podcast - Procrastination
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - starting a new job.
How to Hit the Ground Running!
Ten Dos and Don'ts of Career Conversations
How to talk to team members about their career aspirations.
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Communication skills - start here.
Discover Our Top 100 Business Communication Tools
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
Business Plan Table of Contents

Free Problem Statement Templates
- May 10, 2024
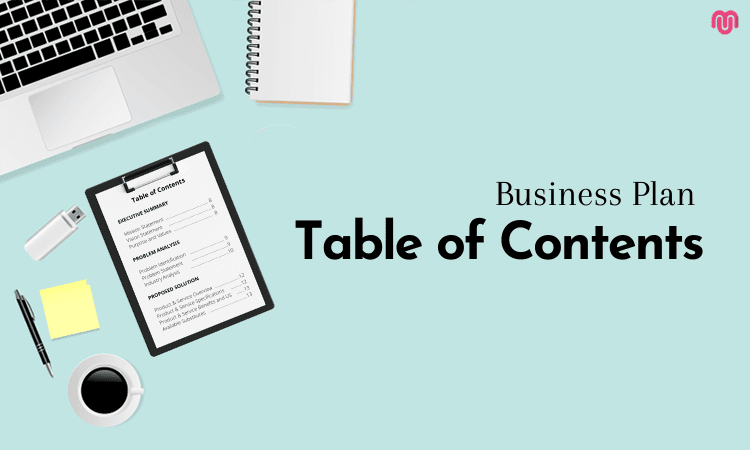
Looking for how & why to write a business plan table of contents ? Well, a nicely written TOC is essential for guiding readers through your plan and highlighting key sections.
It also enhances the overall professionalism and readability by setting the tone for the whole plan later. Let’s explore the sample table of contents along with the pros of adding TOC to the plan.
Why include a Business Plan Table of Contents?
A table of contents serves as the outline of a business plan. It assists the reader in navigating through the document and is placed at the beginning of a business plan. This helps the reader effortlessly find and browse through the topics that interest them.
It includes all the major sections and subcategories of a business plan. The sections are arranged logically with page numbers. And it usually precedes the executive summary.
Sample Business Plan Table of Contents
Presenting the sample business plan table of contents—your perfect partner in creating a well-organized plan. It is necessary to highlight all the necessary areas of the plan.
From below, you can even use the business plan template! It is ready for you to customize according to your needs along with the TOC!
- EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- Mission Statement
- Vision Statement
- Purpose and Values
- Problem Identification
- Problem Statement
- Industry Analysis
- Product & Service Overview
- Product & Service Specifications
- Product & Service Benefits and USPs
- Available Substitutes
- Competitive Overview
- Direct and Indirect Competitors
- SWOT Analysis
- Competitive Position
- Market Share Analysis
- Barriers to Entry
- Market Overview
- Market Size
- Market Segmentation
- Ideal Customer Profile
- Sales & Marketing Objectives
- Pricing Strategies
- Promotion Strategies
- Site Location
- Staffing and Training
- Resource Allocation
- Purchasing Process
- Production Process
- Quality Control Metrics
- Customer Service
- Key Management
- Board of Directors
- Board of Advisors
- Financial Overview
- Business Model
- Financial Projections
- Marketing and Personnel Expenses
- Funding Requirements
- Terms of Investment
- Exit Strategy
Benefits of Adding a Business Plan Table of Contents
A table of contents is an extremely important part of any formal document, let alone a business plan. It is the most commonly found aspect in every large format document, from books to magazines to business plans. Let’s see the benefits of a business plan table of contents:
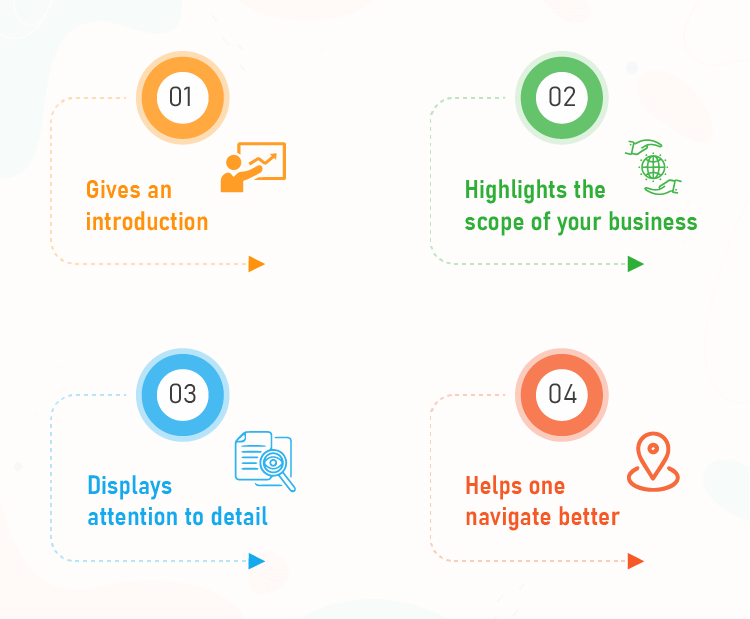
1. Acts as an introduction
The table of contents is placed before all the sections of a business plan. This will help the reader get a good look at the contents before diving into the details. Primarily, it introduces the reader to your business plan. This can get readers interested and excited to read more.
2. Gives an overview of the scope
A table of contents further enables the reader to judge the scope of your business idea. To mirror the exact essence of your business plan, the table of contents should be crafted carefully.
Whether it’s an investor or another company you wish to partner with, any formal entity interested in your business skims through your table of contents. Hence, it is wise to convey exactly what you intend to.
3. Displays attention to detail
While creating a table of contents, you include not only the major sections of your business plan but also the subsections. These subsections will convey that you have paid attention to the smallest of things while drafting your business. This indirectly sends a message that you are serious about your business ventures.
4. Provides easier navigation
This is an obvious but very significant advantage of a table of contents. Incorporating it into your business plan will add a navigational aspect to your document. Regardless if it’s a physical document or an e-document, a table of contents will help the reader go to any specific section they want.
In the case of an e-document, you can include links to the pages. So the reader can go to a particular section by clicking on the page numbers.
Create visual appealing business plans with our
Plans starting from $7/month

Build Trust in your Business with a Table of Contents
Writing a table of contents for your business plan is a subtle yet powerful way to captivate your potential investors or business partners. It is essentially a summary of the document that acts as a roadmap for your business activities.
So, whether you’re a new business seeking funding or an established business looking to refine your strategy, investing time in creating a thoughtful table of contents is a wise choice.
You can smoothen the process with the help of business planning software and get guidance for each step. So, all the very best!
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Related Articles
Write a Mission Statement For Your Business Plan: Explained with Examples

How to Write a Vision Statement for Your Business

Business Problem Statement Explained with Examples
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
Watch CBS News
Social Security projected to cut benefits in 2035 barring a fix
By Aimee Picchi
Edited By Alain Sherter
Updated on: May 7, 2024 / 11:28 AM EDT / CBS News
The timeline to replenish Social Security is being extended. The federal retirement program said Monday it may not need to cut benefits until 2035, one year later than previously forecast, because of stronger performance by the U.S.
The new projection, from the Social Security Board of Trustees' annual report, amounts to "good news" for the program's 70 million beneficiaries, said Martin O'Malley, Commissioner of Social Security, in a statement. Even so, he urged Congress to take steps to shore up the program to ensure it can pay full benefits "into the foreseeable future."
Social Security relies on its trust funds to provide monthly checks to beneficiaries, with the funds primarily financed through the payroll taxes that workers and businesses provide with each paycheck. But the funds' reserves are drawing down because spending is outpacing income, partly due to the wave of baby boomer retirements and an aging U.S. population.
Experts underscore that if the trust funds are depleted, benefits won't suddenly disappear. Instead, Social Security beneficiaries will face a cut to their monthly checks, with the agency on Monday projecting that recipients would lose 17% of their current benefits.
That would be painful for millions of retired and disabled Americans, but it represents a modest improvement from last year, when the Social Security Administration projected that benefits could be slashed by 23% if the trust funds reached the point of depletion.
Advocates for older Americans praised the improved outlook, while pressing Congress to take action on shoring up the program.
"Congress owes it to the American people to reach a bipartisan solution, ensuring people's hard-earned Social Security benefits will be there in full for the decades ahead," AARP CEO Jo Ann Jenkins said in a statement. "The stakes are simply too high to do nothing."
Lawmakers have yet to take action despite being aware of the looming funding crisis, noted Maya MacGuineas, president of the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, a think tank that focuses on the federal fiscal policies, in a statement.
"Every year we get closer to the deadline, we seem to get further away from the solutions," she said. Without a fix, "Social Security's retirement trust fund will be insolvent when today's 58-year-olds reach the normal retirement age and today's youngest retirees turn 71."
Economic boost
O'Malley attributed the improved Social Security forecast to the stronger economy, pointing to what he called "impressive wage growth, historic job creation, and a steady, low unemployment rate." In other words, a healthy job market is resulting in more Social Security taxes going into the funds' coffers.
The report comes as Social Security's financial outlook has become a political lightning rod, with Republicans proposing that the retirement age be raised — effectively cutting benefits for millions of current workers — and former President Donald Trump indicating he would be open to cuts to Social Security and Medicare.
Democrats argue that there are other ways to fix the program without cutting benefits, such as raising the cap on payroll taxes. Currently, individual income over $168,600 is exempt from the Social Security payroll tax.
Medicare's "go broke" date
Meanwhile, Medicare's go-broke date for its hospital insurance trust fund was pushed back five years to 2036 in the latest report, thanks in part to higher payroll tax income and lower-than-projected expenses. Medicare is the federal government's health insurance program that covers people age 65 and older and those with severe disabilities or illnesses. It covered more than 66 million people last year, with most being 65 and older.
Once the fund's reserves become depleted, Medicare would be able to cover only 89% of costs for patients' hospital visits, hospice care and nursing home stays or home health care that follow hospital visits.
In a statement on Monday, President Joe Biden credited his administration's economic policies for Social Security and Medicare's stronger outlook.
"Since I took office, my economic plan and strong recovery from the pandemic have helped extend Medicare solvency by a decade, with today's report showing a full five years of additional solvency," he said. "I am committed to extending Social Security solvency by asking the highest-income Americans to pay their fair share without cutting benefits or privatizing Social Security."
—With reporting by the Associated Press.
- Social Security
Aimee Picchi is the associate managing editor for CBS MoneyWatch, where she covers business and personal finance. She previously worked at Bloomberg News and has written for national news outlets including USA Today and Consumer Reports.
More from CBS News

As a Social Security cut looms, should seniors buy long-term care insurance now?

3 great ways seniors can grow their cash now

3 times to buy long-term care insurance at 65 (and 3 times not to)

Do seniors need home warranties?
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Settlement could cost NCAA nearly $3 billion; plan to pay athletes would need federal protection
FILE - Boston College play SMU during the first half of the Fenway Bowl NCAA football game at Fenway Park Thursday, Dec. 28, 2023, in Boston. With the expanded College Football Playoff locked in through 2031, questions still remain about what the rest of the postseason will look like. One thing is certain, there will still be bowl games. (AP Photo/Winslow Townson, File)
- Copy Link copied
SCOTTSDALE, Ariz. (AP) — The NCAA and major college conferences are considering a possible settlement of an antitrust lawsuit that could cost them billions in damages and force schools to share athletics-related revenue with their athletes.
But even if college sports leaders create a new, more professional model for collegiate athletics they likely would need help from Congress if athletes are not classified as employees.
Two people familiar with settlement discussions related to House vs. the NCAA told the AP on Friday the association could pay out $2.9 billion in damages over 10 years to resolve the class-action lawsuit — which is set to go to trial in January. Schools in the Big Ten, Big 12, Atlantic Coast Conference and Southeastern Conference could be on the hook for about $30 million per year, which would include about $20 million annually directed to their athletes.
The people spoke on condition of anonymity because settlement negotiations were not being made public, and emphasized a deal is far from finalized. Conditions of an agreement still must be approved by the NCAA board of governors and the presidential boards of each of the four conferences.
Yahoo Sports and ESPN first reported details of the potential settlement agreement.
U.S. District Judge Claudia Wilken, who already has ruled on several high-profile antitrust cases against the NCAA in the Northern District of California, ordered the sides to attempt to settle the case months ago. A more developed plan emerged from a meeting of NCAA and conference officials in Dallas last week.
Earlier this week, Big 12 Commissioner Brett Yormark declined to discuss anything related to a possible settlement or the gathering in Dallas while speaking with reporters after his conference meetings in Arizona wrapped up.
There is quiet acknowledgement among many college sports administrators that a settlement of House is the best course of action. The case, brought by former Arizona State swimmer Grant House, contends college athletes should receive a cut of the billions of dollars in media rights fees that go to the power conferences and the NCAA, dating to 2016.
The NCAA is facing several other antitrust challenges to compensation and transfer rules, but House has become a catalyst for action.
In a previous filing, attorneys for the NCAA and the conferences contend damages in House will be $1.4 billion, though in successful antitrust cases damages are tripled.
The NCAA and college sports leaders have been seeking help from Congress in the form of a federal law to regulate NIL compensation for several years, but there has been little movement on that front.
More recently the emphasis from NCAA President Charlie Baker and others has shifted to trying to prevent college athletes from being deemed employees.
Even with a settlement in House and a revenue-sharing plan, the NCAA and major conferences could still need a federal law or antitrust protection to prevent more challenges.
A separate antitrust lawsuit in Pennsylvania dealing with the employment status is also active.
“In terms of their legal options one is to go to Congress, two is to recognize the athletes as employees and enter collective bargaining agreements, the other one is to try to operate in a way that is more defensible under the law,” Tulane sports law professor Gabe Feldman said. “The door is still open to re-invent itself to either withstand litigation or gain more support for congressional intervention.”
Feldman said a federal law that denies college athletes employment status could face a court challenge without the NCAA and conferences being granted an antitrust exemption by Congress.
“It’s hard to ask Congress to protect something that so many see as exploitative,” Feldman said.
A recent ruling from an National Labor Relations Board regional director paved the way for members of the Dartmouth men’s basketball team to vote to join a union. The school is fighting that decision.
Some type of revenue-sharing agreement or substantially increased payments to college athletes on top of scholarships seems inevitable.
Baker himself proposed in December creating a new tier of Division I in which schools would be required to pay at least half their athletes $30,000 per year in trust funds. Baker also encouraged schools to bring NIL activities for athletes in-house instead of solely allowing them to work with third-party entities.
Baker’s D-I project proposal has mostly been tabled, but allowing — though not requiring — schools to pay their athletes seems closer than ever to becoming a reality.
Follow Ralph D. Russo at https://twitter.com/ralphDrussoAP and listen at http://www.appodcasts.com
AP college football: https://apnews.com/hub/college-football
Undergraduate Admissions

- Quantitative Business Economics (QBE)
Purdue University in West Lafayette
Quantitative Business Economics (QBE) combines the principles of economics, business, and quantitative methods to analyze trends. While Economics is the study of choices people make, Quantitative Business Economics is more focused on the specific parts of systems in order to predict future outcomes.
Companies rely heavily on data to make decisions. Students in the QBE major will develop skills to identify problems and the tools to fix them. It is a great major for students interested in careers in Public Policy, Consulting, and Data Analytics.
Courses in the QBE major include econometrics, game theory, and advanced statistical methods. QBE is the only major in the Daniels School that requires a capstone project senior year. Students will get hands-on experience working with Economics professors to solve real-world problems with data.
Maximize your experience in QBE by joining organizations such as the Purdue Economic Association, Boilermaker Consulting Group, or work with professors in the Purdue University Research Center in Economics.
Plan of Study
Quantitative Business Economics , BS
Transfer to Quantitative Business Economics (QBE)
Purdue admits to individual majors. Transfer students must meet Purdue's overall transfer criteria , as well as any major-specific requirements. Before you apply, check the closed programs page to confirm this major is open to transfer students. If it is, refer to the information below for major-specific transfer criteria.
Minimum GPA: 3.0
Additional Requirements: Must have a grade of B or better in any college-level calculus course.
Contact Information
A.J. Frigo (765) 496-0264 [email protected]
Careers in Quantitative Business Economics (QBE)
- Business Analyst
- Data Scientist
- Financial Analyst
- Marketing Research Analyst
- Policy Analyst
- Business / Management
- Mathematics
- Public Service or Social Sciences
- Science and Research
- Business Analytics and Information Management
- Economics (Daniels School of Business)
- Integrated Business and Engineering
- Management (General)
- Supply Chain and Operations Management
- College of Business

COMMENTS
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
A business plan includes the cost of organizing the business, the anticipated sources of revenue, how the products and services are customer oriented, and anticipated profit margins. Business plans serve two main purposes. First, they are a guide business owners use to streamline management and planning/organization of the business.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Above all, the numbers should help answer why your business can do it better. 4. Competitive Analysis. A good business plan will present a clear comparison of your business vs your direct and indirect competitors. This is where you prove your knowledge of the industry by breaking down their strengths and weaknesses.
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
How to Write a Business Plan Step 1. Create a Cover Page. The first thing investors will see is the cover page for your business plan. Make sure it looks professional. A great cover page shows that you think about first impressions. A good business plan should have the following elements on a cover page:
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
13 Key Business Plan Components. We've built a comprehensive guide to the major parts of a business plan for you. From elements like the executive summary to product descriptions, traction, and financials, we'll guide you on all of the key sections you should include in your business plan. December 14th, 2022 | By: The Startups Team | Tags ...
The Content of Business Plans. The precise form and content of a business plan will vary from organization to organization, to reflect the different economic, market and other environmental contexts within which each organization operates. In addition to this, the form and content of the business plan will depend to an extent, on the process ...
Sample Business Plan Table of Contents. Presenting the sample business plan table of contents—your perfect partner in creating a well-organized plan. It is necessary to highlight all the necessary areas of the plan. From below, you can even use the business plan template! It is ready for you to customize according to your needs along with the ...
For a thorough explanation of how to write a business plan, refer to Shopify's guide. 12 components of a business plan. Business plans vary depending on the product or service. Some entrepreneurs choose to use diagrams and charts, while others rely on text alone. Regardless of how you go about it, good business plans tend to include the ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
A business plan is a formal document (about 15-25 pages in length) that precisely defines a company's objectives in fine detail. It also describes how the company plans to achieve its goals. All companies — including startups and established institutions — create and use business plans.
A business plan can take many forms, depending on the venture. A four-person management consulting firm may produce a leaner plan focused on service expertise and industry experience compared to a 20-employee widget maker, which would also have to describe products, manufacturing techniques, competitive forces and marketing needs, among other details.
Creating a good business plan is one of the most important tasks when starting a small business. A business plan that defines and identifies goals helps business owners focus. It also provides direction and focus for their employees. Potential investors and lenders want to see your business plan and business model forecasts.
How do you write a business plan? It can seem overwhelming, but your plan is an important step in helping your company launch and grow. Parts of a Business Plan: 7 Essential Sections
Here are 10 sections of a business plan that you may wish to include: 1. Executive summary. This is an essential part of a successful business plan that often takes the most time to complete. It's also one that you may consider completing last, even though it's usually the first thing that the reader sees. An executive summary is the definitive ...
The Associated Press is an independent global news organization dedicated to factual reporting. Founded in 1846, AP today remains the most trusted source of fast, accurate, unbiased news in all formats and the essential provider of the technology and services vital to the news business.
The approval is a major step in the city's goal to reconnect the major road between Lake Street and the Midtown Greenway. The Kmart building in the way was finally demolished in late 2023 after a ...
Economic boost. O'Malley attributed the improved Social Security forecast to the stronger economy, pointing to what he called "impressive wage growth, historic job creation, and a steady, low ...
A cyberattack has disrupted "clinical operations" at major health care nonprofit Ascension, forcing it to take steps to minimize any impact to patient care, an Ascension spokesperson told CNN ...
The league is in advanced stages of a new round of media-rights deals. Disney's payments would increase under a proposed deal.
The NCAA and major college conferences are considering a possible settlement of an antitrust lawsuit that could cost them billions in damages and force schools to share athletics-related revenue with their athletes. ... Even with a settlement in House and a revenue-sharing plan, the NCAA and major conferences could still need a federal law or ...
Quantitative Business Economics (QBE) Webpage Transfer to Quantitative Business Economics (QBE) Purdue admits to individual majors. Transfer students must meet Purdue's overall transfer criteria, as well as any major-specific requirements.Before you apply, check the closed programs page to confirm this major is open to transfer students. If it is, refer to the information below for major ...
Content from the May 13, 2024 of the Hartford Business Journal. ... CT Dept. of Public Health inks major East Hartford lease to store PPE, other emergency supplies ...