Business Plan Outline: The Essential Framework
By GGI Insights | April 8, 2024

Table of contents
This article explores the importance of business plan outlines, the choice between modular and linear approaches, the power of visual outlining techniques, the pros and cons of outline templates, and best practices for outlining.
By investing in a well-organized outline, entrepreneurs increase their chances of success in their entrepreneurial endeavors.
A well-structured business plan is the foundation of any successful venture. It provides a clear roadmap for entrepreneurs, helping them navigate the complexities of starting and growing a business. Understanding the right business plan format is one key aspect of a comprehensive business plan. The outline acts as a skeleton that organizes and guides the development of the plan, ensuring that all critical elements are addressed systematically and coherently.
Modular vs. Linear Approaches
When it comes to creating a business plan outline, entrepreneurs have two main options: a modular approach or a linear approach. Each approach has its own benefits and drawbacks, and understanding them can help business owners choose the most suitable method for their specific needs. Looking at various business plan examples can illustrate how some businesses might benefit more from a modular approach, while others find a linear approach more effective.
The modular approach involves dividing the business plan into separate sections or modules, each focusing on a specific aspect of the business. This approach allows for flexibility and customization, making it easier to update and modify individual modules without disrupting the overall structure of the plan. For example, if a company decides to change its marketing strategy, it can simply update the marketing module without having to rewrite the entire business plan. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for businesses operating in dynamic industries where changes are frequent.

Unlock growth potential and align your teams seamlessly with gardenpatch. Their growth strategists break down barriers and optimize your business for success. Click here to unlock business growth!
However, the modular approach may lack a cohesive flow and can make it challenging to maintain consistency across different sections. Without a clear narrative thread connecting the modules, the business plan may appear disjointed and confusing to readers. It requires careful planning and organization to ensure that each module seamlessly integrates with the others, creating a coherent and comprehensive business plan.
The linear approach involves creating a business plan in a step-by-step manner, following a predetermined sequence. This approach ensures a logical flow of information and makes it easier for readers to understand the interconnections between different sections , especially when detailing a comprehensive financial plan . By presenting information in a linear fashion, the business plan tells a story, guiding readers through the company's vision, mission, strategies, and financial projections in a structured and cohesive manner.
If new information or ideas arise during the business planning process, it may be more difficult to incorporate them into the existing linear structure. The need to maintain a strict sequence can limit the ability to accommodate unexpected developments or shifts in the business landscape. This approach is often favored by businesses operating in stable industries where changes are infrequent.
Adaptability Quotient
One key consideration when choosing between the modular and linear approaches is the adaptability quotient of the business. If a business operates in a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry, the modular approach may be more suitable as it allows for easier updates and adjustments. The ability to modify individual modules without disrupting the overall structure of the plan can be invaluable in industries where market conditions, technologies, or consumer preferences change frequently. In this case, a business roadmap that emphasizes flexibility and agility could be essential.
If a business operates in a stable industry with fewer changes, the linear approach may provide a more straightforward and efficient way of organizing the plan. In industries where the business model and strategies remain relatively constant, a linear approach can ensure a clear and logical presentation of information, making it easier for stakeholders to understand the business's direction and goals.
The choice between a modular and linear approach depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the business. It is essential for entrepreneurs to carefully evaluate their industry, market dynamics, and the level of adaptability required before deciding on the most suitable approach for their business plan outline.
The Power of Visual Outlining
Text-based business plan outlines are undoubtedly effective, but incorporating visual outlining techniques can enhance clarity and comprehension. Visual outlining employs graphic elements to represent the relationships and connections between different sections of the plan.
When it comes to presenting complex information in a concise and easily digestible format, visual outlining techniques are invaluable. They not only capture the attention of readers but also facilitate a deeper understanding of the business plan. Let's explore two popular visual outlining techniques that can take your business plan to the next level.
Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a popular visual outlining technique that uses diagrams to represent ideas and concepts. By linking different elements together and organizing them in a hierarchical structure, entrepreneurs can create a visual representation of their business plan. Mind maps provide a comprehensive overview while allowing for easy navigation and exploration of specific details.
Imagine having a bird's-eye view of your entire business plan, with all its components interconnected in a visually appealing and logical manner. Mind maps help entrepreneurs identify the core elements of their business, such as the mission statement, target market, and competitive analysis, and visually demonstrate how they are interrelated. This technique not only aids in organizing thoughts but also promotes creativity and innovative thinking.
Mind maps allow for flexibility and adaptability. As your business plan evolves, you can easily update and modify the mind map to reflect any changes. This dynamic nature of mind mapping ensures that your business plan remains relevant and up-to-date.
Flowcharts are another powerful tool for visual outlining in business plans. They use graphical symbols to represent the flow of processes or information. Flowcharts can help entrepreneurs visualize the step-by-step progression of their business operations, making it easier to identify bottlenecks or areas for improvement.
With a flowchart, you can visually map out the various stages of your business's workflow, from product development to customer acquisition and beyond. Each step is represented by a specific symbol, such as a rectangle for a process or a diamond for a decision point. By following the arrows that connect these symbols, readers can easily trace the flow of information or activities.
Flowcharts not only provide a clear overview of the business processes but also allow for a detailed analysis of each step. By examining the flowchart, entrepreneurs can identify any inefficiencies or potential roadblocks in their operations. This visual representation enables them to devise strategies for streamlining processes and improving overall efficiency.
Incorporating visual outlining techniques, such as mind mapping and flowcharts, into your business plan can greatly enhance its effectiveness. These techniques offer a visually engaging and comprehensive overview of your business, facilitating better understanding and analysis. So, why settle for a plain text outline when you can create a visually captivating business plan that leaves a lasting impression?
Outline Templates: Pros & Cons
Creating a business plan from scratch can be a time-consuming task. To streamline the process, entrepreneurs often use pre-designed outline templates that provide a structured framework for organizing their ideas. For instance, a coffee shop business plan might benefit from an industry-specific template that includes sections on customer demographics, café layout, and menu offerings. While these templates can be advantageous, it is essential to consider their pros and cons before opting for them.
Industry-Specific
Industry-specific outline templates are tailored to the unique requirements and nuances of particular sectors. They provide a starting point for entrepreneurs by including industry-specific sections and relevant key performance indicators. These templates can save time and ensure that critical information is not overlooked. For example, if you are starting a restaurant business, an industry-specific template may include sections on menu planning, kitchen layout, and customer service strategies.
Industry-specific templates can offer valuable insights and best practices specific to your field. They may include examples of successful business plans from similar businesses, giving you a better understanding of what works in your industry. This can be particularly helpful if you are new to the sector or looking for innovative ideas to differentiate your business.
It is important to note that industry-specific templates may lack flexibility. While they provide a solid foundation, they may not fully capture the unique aspects of a specific business. Each business has its own strengths, weaknesses, and competitive advantages that may not be adequately addressed in a template designed for a broader industry.
Universal Templates
Alternatively, entrepreneurs can opt for universal outline templates that are applicable to a wide range of industries. These templates provide a comprehensive framework that covers all essential elements of a business plan. Universal templates offer flexibility and can be easily customized to suit individual business needs. For example, they may include sections on market analysis, financial projections, and marketing strategies that can be adapted to any industry.
Universal templates also allow entrepreneurs to think outside the box and explore different business models. They encourage creativity and innovation by providing a structure that can be molded to fit various industries. This can be particularly beneficial for entrepreneurs who are looking to disrupt traditional business models or enter emerging markets.
It is important to consider that universal templates may require additional effort to adapt to specific industry requirements. While they provide a solid framework, entrepreneurs may need to invest more time and resources in customizing the template to accurately reflect their business. This can include conducting additional research, gathering industry-specific data, and tailoring the content to align with the unique needs of their target market.
Both industry-specific and universal outline templates offer advantages and disadvantages. Industry-specific templates provide a tailored approach and save time by including relevant sections and key performance indicators. On the other hand, universal templates offer flexibility and can be easily customized to suit individual business needs. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on the entrepreneur's specific requirements, industry, and level of customization desired.
Best Practices for Outlining
Creating a business plan outline is a crucial step in the process of writing a business plan . While there is no one-size-fits-all approach to outlining, following some best practices can greatly enhance the effectiveness and readability of the final document.
When outlining a business plan, one of the most important considerations is prioritizing the information presented. Starting with the most essential and impactful details and progressively guiding readers through supporting information can help ensure that they understand the key aspects of the business and its value proposition. By prioritizing information, you can provide a clear and concise overview of your business, setting the stage for a more in-depth exploration of the details.
Another critical factor to consider when creating a business plan outline is stakeholder alignment. It is essential to identify the key stakeholders and understand their specific interests and objectives. Tailoring the plan to meet their needs and expectations can significantly increase the chances of gaining support and buy-in from stakeholders. When stakeholders feel that their interests are being considered and addressed, they are more likely to actively participate in the implementation process, leading to a higher likelihood of success.
A well-aligned plan can help foster collaboration and cooperation among stakeholders. By clearly articulating the business's goals, strategies, and objectives, you can create a shared understanding and sense of purpose. This alignment can lead to more effective decision-making and a smoother implementation process.
When outlining a business plan, it is essential to consider the overall structure and flow of the document. Organizing the information in a logical and coherent manner can greatly enhance readability and comprehension. Consider using headings, subheadings, and bullet points to break down complex information into manageable sections. This approach can help readers navigate the document more easily and locate specific information quickly.
In addition to prioritizing information and ensuring stakeholder alignment, it is also beneficial to include relevant market research and analysis in the business plan outline. Providing data and insights about the industry, target market, and competitors can demonstrate a thorough understanding of the business's external environment. This information can also help support the business's value proposition and differentiate it from competitors.
When outlining a business plan, it is crucial to review and revise the document regularly. As the business evolves and new information becomes available, the outline should be updated to reflect these changes. Regularly reviewing and refining the outline can help ensure that the business plan remains current and relevant.
Creating a well-structured and comprehensive business plan outline is a critical step in the business planning process. By prioritizing information, aligning with stakeholders, considering the overall structure, including relevant research, and regularly reviewing and revising the outline, you can develop a document that effectively communicates your business's value proposition and increases the likelihood of successful implementation.
A well-structured business plan outline is a crucial component of any successful business venture. The choice between a modular or linear approach depends on the adaptability quotient of the business and the desired level of customization. Visual outlining techniques such as mind mapping and flowcharts can enhance clarity and comprehension. When using outline templates, entrepreneurs should consider industry-specific or universal options based on their specific requirements. Finally, following best practices such as prioritizing information and stakeholder alignment can further enhance the effectiveness of the business plan outline. By investing time and effort into creating a comprehensive and well-organized outline, entrepreneurs set themselves up for a greater chance of success in their entrepreneurial endeavors.
Popular Insights:
Shop with purpose at impact mart your purchase empowers positive change. thanks for being the difference.

Customer Onboarding: Proven Techniques for Seamless Client Integration
Customer journey: optimizing interactions for lasting customer loyalty, email open rates: enhancing the readership of your marketing emails, revenue: the fundamental pillar of business viability and growth, marketing strategies: craft dynamic approaches for business expansion, startup school: accelerating your path to entrepreneurial success, ecommerce marketing strategy: data-driven tactics for enhanced loyalty, hubspot crm review: a comprehensive look into what makes hubspot great, hubspot growth suite: catalyzing your company growth with integration, hubspot service hub: taking superb customer service to the next level.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Financial Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Taking Stock of Expenses
The income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet.
The financial section of your business plan determines whether or not your business idea is viable and will be the focus of any investors who may be attracted to your business idea. The financial section is composed of four financial statements: the income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet, and the statement of shareholders' equity. It also should include a brief explanation and analysis of these four statements.
Think of your business expenses as two cost categories: your start-up expenses and your operating expenses. All the costs of getting your business up and running should be considered start-up expenses. These may include:
- Business registration fees
- Business licensing and permits
- Starting inventory
- Rent deposits
- Down payments on a property
- Down payments on equipment
- Utility setup fees
Your own list will expand as soon as you start to itemize them.
Operating expenses are the costs of keeping your business running . Think of these as your monthly expenses. Your list of operating expenses may include:
- Salaries (including your own)
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Telecommunication expenses
- Raw materials
- Distribution
- Loan payments
- Office supplies
- Maintenance
Once you have listed all of your operating expenses, the total will reflect the monthly cost of operating your business. Multiply this number by six, and you have a six-month estimate of your operating expenses. Adding this amount to your total startup expenses list, and you have a ballpark figure for your complete start-up costs.
Now you can begin to put together your financial statements for your business plan starting with the income statement.
The income statement shows your revenues, expenses, and profit for a particular period—a snapshot of your business that shows whether or not your business is profitable. Subtract expenses from your revenue to determine your profit or loss.
While established businesses normally produce an income statement each fiscal quarter or once each fiscal year, for the purposes of the business plan, an income statement should be generated monthly for the first year.
Not all of the categories in this income statement will apply to your business. Eliminate those that do not apply, and add categories where necessary to adapt this template to your business.
If you have a product-based business, the revenue section of the income statement will look different. Revenue will be called sales, and you should account for any inventory.
The cash flow projection shows how cash is expected to flow in and out of your business. It is an important tool for cash flow management because it indicates when your expenditures are too high or if you might need a short-term investment to deal with a cash flow surplus. As part of your business plan, the cash flow projection will show how much capital investment your business idea needs.
For investors, the cash flow projection shows whether your business is a good credit risk and if there is enough cash on hand to make your business a good candidate for a line of credit, a short-term loan , or a longer-term investment. You should include cash flow projections for each month over one year in the financial section of your business plan.
Do not confuse the cash flow projection with the cash flow statement. The cash flow statement shows the flow of cash in and out of your business. In other words, it describes the cash flow that has occurred in the past. The cash flow projection shows the cash that is anticipated to be generated or expended over a chosen period in the future.
There are three parts to the cash flow projection:
- Cash revenues: Enter your estimated sales figures for each month. Only enter the sales that are collectible in cash during each month you are detailing.
- Cash disbursements: Take the various expense categories from your ledger and list the cash expenditures you actually expect to pay for each month.
- Reconciliation of cash revenues to cash disbursements: This section shows an opening balance, which is the carryover from the previous month's operations. The current month's revenues are added to this balance, the current month's disbursements are subtracted, and the adjusted cash flow balance is carried over to the next month.
The balance sheet reports your business's net worth at a particular point in time. It summarizes all the financial data about your business in three categories:
- Assets : Tangible objects of financial value that are owned by the company.
- Liabilities: Debt owed to a creditor of the company.
- Equity: The net difference when the total liabilities are subtracted from the total assets.
The relationship between these elements of financial data is expressed with the equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity .
For your business plan , you should create a pro forma balance sheet that summarizes the information in the income statement and cash flow projections. A business typically prepares a balance sheet once a year.
Once your balance sheet is complete, write a brief analysis for each of the three financial statements. The analysis should be short with highlights rather than in-depth analysis. The financial statements themselves should be placed in your business plan's appendices.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
5.6 The Business Plan
Learning objective.
- Discuss the importance of planning for your business, and identify the key sections of a business plan.
If you want to start a business, you must prepare a business plan. This essential document should tell the story of your business concept, provide an overview of the industry in which you will operate, describe the goods or services you will provide, identify your customers and proposed marketing activities, explain the qualifications of your management team, and state your projected income and borrowing needs.
Purpose of a Business Plan
The business plan is a plan or blueprint for the company, and it’s an indispensable tool in attracting investors, obtaining loans, or both. Remember, too, that the value of your business plan isn’t limited to the planning stages of your business and the process of finding start-up money. Once you’ve acquired start-up capital, don’t just stuff your plan in a drawer. Treat it as an ongoing guide to your business and its operations, as well as a yardstick by which you can measure your performance. Keep it handy, update it periodically, and use it to assess your progress.
In developing and writing your business plan, you must make strategic decisions in the areas of management, operations, marketing, accounting, and finance—in short, in all the functional areas of business that we described in Chapter 1 “The Foundations of Business” . Granted, preparing a business plan takes a lot of time and work, but it’s well worth the effort. A business plan forces you to think critically about your proposed business and reduces your risk of failure. It forces you to analyze your business concept and the industry in which you’ll be operating, and it helps you determine how you can grab a percentage of sales in that industry.
The most common use of a business plan is persuading investors, lenders, or both, to provide financing. These two groups look for different things. Investors are particularly interested in the quality of your business concept and the ability of management to make your venture successful. Bankers and other lenders are primarily concerned with your company’s ability to generate cash to repay loans. To persuade investors and lenders to support your business, you need a professional, well-written business plan that paints a clear picture of your proposed business.
Sections of the Business Plan
Though formats can vary, a business plan generally includes the following sections: executive summary, description of proposed business, industry analysis, mission statement and core values, management plan, goods or services and (if applicable) production processes, marketing, global issues, and financial plan. Let’s explore each of these sections in more detail. ( Note : More detailed documents and an Excel template are available for those classes in which the optional business plan project is assigned.)
Executive Summary
The executive summary is a one- to three-page overview of the business plan. It’s actually the most important part of the business plan: it’s what the reader looks at first, and if it doesn’t capture the reader’s attention, it might be the only thing that he or she looks at. It should therefore emphasize the key points of the plan and get the reader excited about the prospects of the business.
Even though the executive summary is the first thing read, it’s written after the other sections of the plan are completed. An effective approach in writing the executive summary is to paraphrase key sentences from each section of the business plan. This process will ensure that the key information of each section is included in the executive summary.
Description of Proposed Business
Here, you present a brief description of the company and tell the reader why you’re starting your business, what benefits it provides, and why it will be successful. Some of the questions to answer in this section include the following:
- What will your proposed company do? Will it be a manufacturer, a retailer, or a service provider?
- What goods or services will it provide?
- Why are your goods or services unique?
- Who will be your main customers?
- How will your goods or services be sold?
- Where will your business be located?
Because later parts of the plan will provide more detailed discussions of many of these issues, this section should provide only an overview of these topics.
Industry Analysis
This section provides a brief introduction to the industry in which you propose to operate. It describes both the current situation and the future possibilities, and it addresses such questions as the following:
- How large is the industry? What are total sales for the industry, in volume and dollars?
- Is the industry mature or are new companies successfully entering it?
- What opportunities exist in the industry? What threats exist?
- What factors will influence future expansion or contraction of the industry?
- What is the overall outlook for the industry?
- Who are your major competitors in the industry?
- How does your product differ from those of your competitors?
Mission Statement and Core Values
This portion of the business plan states the company’s mission statement and core values . The mission statement describes the purpose or mission of your organization—its reason for existence. It tells the reader what the organization is committed to doing. For example, one mission statement reads, “The mission of Southwest Airlines is dedication to the highest quality of customer service delivered with a sense of warmth, friendliness, individual pride, and company spirit” (Southwest Airline’s, 2011).
Core values are fundamental beliefs about what’s important and what is (and isn’t) appropriate in conducting company activities. Core values are not about profits, but rather about ideals. They should help guide the behavior of individuals in the organization. Coca-Cola, for example, intends that its core values—leadership, passion, integrity, collaboration, diversity, quality, and accountability—will let employees know what behaviors are (and aren’t) acceptable (The Coca-Cola Company, 2011).
Management Plan
Management makes the key decisions for the business, such as its legal form and organizational structure. This section of the business plan should outline these decisions and provide information about the qualifications of the key management personnel.
A. Legal Form of Organization
This section dentifies the chosen legal form of business ownership: sole proprietorship (personal ownership), partnership (ownership shared with one or more partners), or corporation (ownership through shares of stock).
B. Qualifications of Management Team and Compensation Package
It isn’t enough merely to have a good business idea: you need a talented management team that can turn your concept into a profitable venture. This part of the management plan section provides information about the qualifications of each member of the management team. Its purpose is to convince the reader that the company will be run by experienced, well-qualified managers. It describes each individual’s education, experience, and expertise, as well as each person’s responsibilities. It also indicates the estimated annual salary to be paid to each member of the management team.
C. Organizational Structure
This section of the management plan describes the relationships among individuals within the company, listing the major responsibilities of each member of the management team.
Goods, Services, and the Production Process
To succeed in attracting investors and lenders, you must be able to describe your goods or services clearly (and enthusiastically). Here, you describe all the goods and services that you will provide the marketplace. This section explains why your proposed offerings are better than those of competitors and indicates what market needs will be met by your goods or services. In other words, it addresses a key question: What competitive advantage will the company’s goods and services have over similar products on the market?
This section also indicates how you plan to obtain or make your products. Naturally, the write-up will vary, depending on whether you’re proposing a service company, a retailer, or a manufacturer. If it’s a service company, describe the process by which you’ll deliver your services. If it’s a retail company, tell the reader where you’ll purchase products for resale.
If you’re going to be a manufacturer, you must furnish information on product design, development, and production processes. You must address questions such as the following:
- How will products be designed?
- What technology will be needed to design and manufacture products?
- Will the company run its own production facilities, or will its products be manufactured by someone else?
- Where will production facilities be located?
- What type of equipment will be used?
- What are the design and layout of the facilities?
- How many workers will be employed in the production process?
- How many units will be produced?
- How will the company ensure that products are of high quality?
This critical section focuses on four marketing-related areas—target market, pricing, distribution, and promotion:
- Target market . Describe future customers and profile them according to age, gender, income, interests, and so forth. If your company will sell to other companies, describe your typical business customer.
- Pricing . State the proposed price for each product. Compare your pricing strategy to that of competitors.
- Distribution . Explain how your goods or services will be distributed to customers. Indicate whether they’ll be sold directly to customers or through retail outlets.
- Promotion . Explain your promotion strategy, indicating what types of advertising you’ll be using.
In addition, if you intend to use the Internet to promote or sell your products, also provide answers to these questions:
- Will your company have a Web site? Who will visit the site?
- What will the site look like? What information will it supply?
- Will you sell products over the Internet?
- How will you attract customers to your site and entice them to buy from your company?
Global Issues
In this section, indicate whether you’ll be involved in international markets, by either buying or selling in other countries. If you’re going to operate across borders, identify the challenges that you’ll face in your global environment, and explain how you’ll meet them. If you don’t plan initially to be involved in international markets, state what strategies, if any, you’ll use to move into international markets when the time comes.
Financial Plan
In preparing the financial section of your business plan, specify the company’s cash needs and explain how you’ll be able to repay debt. This information is vital in obtaining financing. It reports the amount of cash needed by the company for start-up and initial operations and provides an overview of proposed funding sources. It presents financial projections, including expected sales, costs, and profits (or losses). It refers to a set of financial statements included in an appendix to the business plan.
Here, you furnish supplemental information that may be of interest to the reader. In addition to a set of financial statements, for example, you might attach the résumés of your management team.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan tells the story of your business concept, provides an overview of the industry in which you will operate, describes the goods or services you will provide, identifies your customers and proposed marketing activities, explains the qualifications of your management team, and states your projected income and borrowing needs.
- In your business plan, you make strategic decisions in the areas of management, operations, marketing, accounting, and finance. Developing your business plan forces you to analyze your business concept and the industry in which you’ll be operating. Its most common use is persuading investors and lenders to provide financing.
A business plan generally includes the following sections:
- Executive summary . One- to three-page overview.
- Description of proposed business . Brief description of the company that answers such questions as what your proposed company will do, what goods or services it will provide, and who its main customers will be.
- Industry analysis . Short introduction to the industry in which you propose to operate.
- Mission statement and core values . Declaration of your mission statement , which are fundamental beliefs about what’s important and what is (and isn’t) appropriate in conducting company activities.
- Management plan . Information about management team qualifications and responsibilities, and designation of your proposed legal form of organization.
- Goods, services, and the production process . Description of the goods and services that you’ll provide in the marketplace; explanation of how you plan to obtain or make your products or of the process by which you’ll deliver your services.
- Marketing . Description of your plans in four marketing-related areas: target market, pricing, distribution, and promotion.
- Global issues . Description of your involvement, if any, in international markets.
- Financial plan . Report on the cash you’ll need for start-up and initial operations, proposed funding sources, and means of repaying your debt.
- Appendices . Supplemental information that may be of interest to the reader.
(AACSB) Analysis
Let’s start with three givens: (1) college students love chocolate chip cookies, (2) you have a special talent for baking cookies, and (3) you’re always broke. Given these three conditions, you’ve come up with the idea of starting an on-campus business—selling chocolate chip cookies to fellow students. As a business major, you want to do things right by preparing a business plan. First, you identified a number of specifics about your proposed business. Now, you need to put these various pieces of information into the relevant section of your business plan. Using the business plan format described in this chapter, indicate the section of the business plan into which you’d put each of the following:
- You’ll bake the cookies in the kitchen of a friend’s apartment.
- You’ll charge $1 each or $10 a dozen.
- Your purpose is to make the best cookies on campus and deliver them fresh. You value integrity, consideration of others, and quality.
- Each cookie will have ten chocolate chips and will be superior to those sold in nearby bakeries and other stores.
- You expect sales of $6,000 for the first year.
- Chocolate chip cookies are irresistible to college students. There’s a lot of competition from local bakeries, but your cookies will be superior and popular with college students. You’ll make them close to campus using only fresh ingredients and sell them for $1 each. Your management team is excellent. You expect first-year sales of $6,000 and net income of $1,500. You estimate start-up costs at $600.
- You’ll place ads for your product in the college newspaper.
- You’ll hire a vice president at a salary of $100 a week.
- You can ship cookies anywhere in the United States and in Canada.
- You need $600 in cash to start the business.
- There are six bakeries within walking distance of the college.
- You’ll bake nothing but cookies and sell them to college students. You’ll make them in an apartment near campus and deliver them fresh.
The Coca-Cola Company, “Workplace Culture,” The Coca-Cola Company, http://www.thecoca-colacompany.com/citizenship/workplace_culture.html (accessed August 31, 2011).
Southwest Airline’s company Web site, about SWA section, http://www.southwest.com/about_swa/mission.html (accessed August 31, 2011).
Exploring Business Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Search Product category Any value Sample Label 1 Sample Label 2 Sample Label 3
Business Plan vs. Financial Plan: What’s The Difference?
- December 16, 2022
- Fundraising

When preparing their business plan, entrepreneurs sometimes get confused between different terms, especially the difference between a business plan and a financial plan.
Whilst a business plan must include a financial plan, these 2 documents are very different and have separate objectives.
In this article we explain you what are a business plan and a financial plan, their objectives and what are the key differences between them.
What is a Business plan?

A business plan is a long document that contains a detailed description of your business and your strategy. Unlike a pitch deck, a business plan is a Word document and often includes 30 up to 100 pages.
We use business plans to communicate information about a business to third-parties. We often use it when a business needs funding. Debt investors (e.g. banks or venture debt investors ) almost always require a business plan as part of a loan application. Instead, equity investors usually ask for a pitch deck .
What should you include in a business plan?
Chances are you will find different definitions online for what you need to include in your business plan. Yet, most interested parties (investors or banks) agree on the different elements that a business plan must include, they are:
- Executive summary : usually a one-pager, this section outlines key information about the company such as a short business overview , operations, location and leadership
- Products and services : a detailed overview of the different products and/or services the company offers including features, benefits to customers and pricing. This section can also include, if relevant, information about the production and manufacturing elements (costs, materials and processes). Also, include here any proprietary technology (e.g. patents) your business might have
- Market analysis : a description of the market including its size and its growth. Here you should also include any information about your competitive environment, especially you position yourself vs. competitors
- Marketing strategy : this section explains how a business acquires and retains its customers. Your acquisition strategy ( inbound or outbound for example) as well as your conversion funnel must be clearly explained. If any, you should include here the different marketing campaigns you are running (e.g. paid ads, offline marketing), their goals and historical performance.
- Financial plan : every business plan must include a financial plan. As explained below, a financial plan is the projection in the future of the 3 financial statements . Usually, a financial plan is a 3- to 5-year forecast , depending on the objective of the business plan and the stage the business is in today.
What is a Financial plan?
As explained above, a financial plan is an element of every business plan.
A financial plan can take different forms (charts, tables) yet should always at least show the projection over a certain period ( 3- to 5-year usually) of the 3 financial statements.
A financial plan should also include some historical data (if any). If you have 3 years of historical financial data, include them in there as well. Indeed, investors will want to see how realistic are your projections .
Also, make it clear what are the key assumptions behind your financial forecasts: projecting the future isn’t easy and we often need to make some assumptions. Yet, the more available sources and data points you have to substantiate your projections, the better. Investors appreciate entrepreneurs who are realistic about their projections and understand the opportunities as well as the potentials risks involved. Whenever possible, use historical data and/or industry benchmarks .
Privacy Overview
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Transition to growth mode
with LivePlan Get 40% off now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

Does your business plan need a push?
Writting a business plan can be a springboard exercise for your business, and it's not as difficult as people think. All it takes is a bit of method, and some efficient tools. The good news our free articles and paid course have you covered!

Resources on Business Plan Writing :
An article of the Accelerated MBA written by:

Antoine Martin (Ph.D) | Business coach
Is this article relevant? Share it & help someone!
In this article:
Financial projections: how to write the financial plan in business plan.
So, you’ve decided to write a business plan? Good for you! It’s an important document that will help you outline your business goals, strategies, and tactics.
But it’s not just a document for you, as the business owner in charge of everything – it’s also important for potential investors and lenders.
In particular, one of the most important sections of your business plan should be your financial plan or, in other words, your overall financial projections for the next few years – understand, three to five years – distilled in a specific and highly codified format.
Why? Because the financial projections in a business plan are the numbers’ version of your pitch – if something doesn’t add-up, that’s where you see it.
Now, we know that numbers can be impressive (not to say daunting), so in this post, we’ll explain to you how to write a financial plan in your business plan.
We’ll also explain the logic you are supposed to follow to do things right (because financiers expect you to follow a very specific logic).
And we’ll explain what your business plan absolutely needs to include from a financial standpoint.
If that makes sense to you, then let’s get going!
By the way…
Before we dig into the financial projections’ discussion, let us give you a tiny bit of background!
We are professional business coaches, and our job is to push entrepreneurs and business owners to their next steps.
Business planning and business plans are part of that, obviously, therefore we have written a series of free articles on how to write a business plan – of which this page is a part.
We are on a mission to make entrepreneurship fun and accessible, so we provide about 80 percent of our content for free – including a free business plan template to be downloaded down this page.
Still, in case that’s not sufficient, we’ve also created our Business Plan Builder Module , which has been designed to make your life super easy.
Shameless plug: it gives you access to:
- a complete and solid business plan writing work-frame tool
- automated financial tables that take the hassle away (yayyy!)
- two designer-made templates (comprehensive + pitch deck)
- and two hours of tutorial videos recorded with a business coach to explain all the logic you’ll need to master if you plan on writing a business plan that converts.
There’s simply no way to make things easier!
Now, having said that, let’s get going.
As a reminder, what is a business plan about?
To start the discussion, remember that a business plan is about much more than just numbers. As we’ve explained in our article What are Business Plans For? , the role of such a document is to show that beyond a nice business plan pdf nobody really cares about, you have a real business and a plan to get it somewhere.
First, a business plan’s purpose is to help you explain what your project is about. In that sense, the document you need to write should be written as a storytelling instrument, designed, and formulated to tell people a story they will want to read AND remember.
Second, it should give you a way to showcase your main business objectives for the next few years, as well as the strategy you will put into place to get there and deliver on your promises.
Third, your business plan should also provide a market analysis, and a description of your main target segment. That gives the reader a better understanding of your ecosystem’s potential, but more importantly the exercise forces you to look around, open your eyes and do some meaningful research.
You wouldn’t want to drive blindfolded, would you?
Of course, your document should also have a financial component – which is the topic of this article – and there the challenge is to ensure that your financial projections make sense, that they are clear, accurate and easy to follow.
Long things short, investors and bankers expect you to match a very specific business plan outline and format (there’s a code!) and you don’t have much wiggle room there – so be careful in your approach!
What is a Financial Plan & what should it include?
Now, let’s get into the core of this article: financial plans and financial projections. What are they, why are they important – there is a lot to explore.
First things first, what is a financial plan? How important is it in a business plan? And what type of elements is it made of? What are the projected financial statements you need to provide? Oh, and what do we mean by ‘financial projections’ in the first place, by the way?
What is the role of a financial plan in business plan?
A financial plan is the financial part of your business plan. Its purpose is simple: explain to the reader what should be the ins and outs of your project from a financial perspective, and help them see if their own business projections are aligned with yours.
On the one hand, the idea is to put numbers on your project, to make it tangible and show that your vision includes the end and the means.
On the other, it is also to show that you are capable of defending your big idea as well as the projected financials that need to come with it – something that many wannabe entrepreneurs are actually unable to do…
As a side note, and as silly as that might sound, this means that your business plan should include a lot more than just a financial plan and a smart cash flow projection!
That point brings us back to the one we made earlier when we said that a business plan should follow a specific structure (go read that article!), but we mention it again because we want things to be very clear: your business plan should be a matter of storytelling, not just a matter of financial projections!
Typically, we often see accountants work on business plans, and what they produce is rarely enough because they only deliver financial estimates that make no real sense to non-accountants (even less to the entrepreneurs at stake) and leave aside the rest of the topics – particularly the storytelling!
Said differently? The numbers are one aspect of the story, but you still have to come up with the pitch – which is where the rest of the business plan comes in handy.
Make sure to deliver an easy-to-read mix!
Your financial plan must provide your financial projections
To get into the technical part of the discussion, the financial plan in your business plan should include your financial projections, organized in a very formal format.
That makes two distinct points to consider!
On the one hand, you should be able to show with clear numbers what money should come in and when (that’s the income forecasts), for this year but also for the next, the ones after that for three to five years.
On the other, you should also be able to show what money needs to go out to make the business roll. What are the production costs, the fixed and variable expenses, the salaries, and of course the various marketing expenses needed to generate the development you are planning on getting to.
On that point, remember that your cost of client acquisition should also be part of the formalized projections – otherwise your numbers will be flawed (and doomed).
Ultimately, you need to be very clear as to when your new business (or existing business) should break even, as to when should profits be expected, as to when lenders and investors will get their money back, so forth and so on.
It must include specific financial documents people will expect to see
From a very formal perspective, you shouldn’t be trying to make one single projection sheet. Nope! Your readers will expect to see three important financial documents in the financial section of the business plan you will introduce to them.
- A profit and loss statement – also known as your P&L statement, or as an income statement
- A cash flow statement
- And a balance sheet.
First, the P&L table or income statement should show what money is expected to come in or go out, but it should also show if and when the business will make a profit or a loss, year by year, for the next five years.
The sales forecast and the operating expenses should be easy to understand at that stage, and you should also be able to provide your estimated gross profit, your gross margin, as well as your net profit and net margin.
In case you are wondering, your gross profit corresponds to your sales minus your cost of production. Your net profit corresponds to the gross profit minus all the remaining costs.
It’s okay to read that twice…
Not being profitable is also okay, by the way. That’s the game. However, you must be able to explain why you won’t be profitable in a given year, and how you plan on filling the gap in the bank – otherwise your business dies, right?
Second, the cashflow statement should explain your cash flow management strategy and indicate when you will need to fill the bank account in, and why.
For instance, important account receivables could justify a temporary cashflow need, but the gaps left from the previous years should also be visible. Obviously, the funding needs should also be there and aligned with the financial situation of the business.
Third, the balance sheet is a summary of the previous two tables, except that it shows the various elements in terms of assets or liabilities. For instance, the account receivables we mentioned just before would be an asset (because some money is owed to the business) while account payables would be a liability (since the business owes money to someone else).
Does all this sound a little complex?
That’s because it is.
No need to worry, though. We have you covered and will provide all the templates and tools you need further below. For now, just keep reading.
So, what’s the financial plan in a business plan for?
To conclude, the financial plan in business plan should act as a financial cartography of what you have in mind for that business of yours.
- The financial plan should illustrate the plan you have for the business in terms of numbers
- It should include precise financial projections of what you think can be achieved
- It should clearly illustrate your cashflow management strategy
- And it should summarize the information clearly
- All of this through highly standardized tables financiers will understand very easily
What documents should a financial business plan contain?
Getting your financial business plan right is a lot simpler than it seems.
Now, when you’re pitching that business of yours to potential partners, investors or lenders, you’ll need to provide them with a series of financial statements.
Yet, how to produce those documents without jumping into a living nightmare? How to come up with cash flow projections that make sense instead of being purely random?
Word of caution: financial planning for businesses is typically complex.
The question is not only fair, but it is also super-duper common and literally blocks tons of entrepreneurs and small business owners on a daily basis.
Because financial planning for businesses is typically complex.
Because most people aren’t comfortable with numbers.
And because the vast majority of small business owners simply don’t know where to start.
That’s probably why you were looking for either a financial plan pdf template or an example of financial plan for small business owners a few minutes ago, isn’t it?
Typically, here is what happens.
Some try and do their best, but then they don’t feel confident with pitching and defending their financial analysis, so they keep delaying and nothing happens.
Others end up having recourse to external help, even though external business plan consultants usually aren’t a good idea at that stage.
And the rest gives up.
That’s a shame, especially if consider that financial planning for a small business and building a financial plan for a business plan are only a matter of having access to the right method and tools!
Yes, a big (big) part of the work is to guestimate, but the rest is about trusting the process with the right logic, method and tools – and there’s nothing you can’t manage here.
Especially with the right tools!
How to build your financial forecasts?
Now that you understand the different sections of a financial plan, let us talk about how to build financial forecasting.
In plain English, this part of the exercise is where you’ll estimate your company’s income and expenses for the next few years. Therefore, you should keep a few things in mind.
One, you need to have a good understanding of your business in order to create realistic forecasts.
Sounds silly? Maybe, but this is a mistake people make way too much, and when they fail at justifying their financial projections, everything else goes down.
Two, you absolutely want to make sure that your projections can explore various trends, i.e. your pessimistic, optimistic, and most likely scenarios.
- If everything goes extremely well, we’ll get there.
- If everything goes wrong, we’ll get there.
- But… we should reasonably expect to achieve this and that if we obtain the funding we need…
Can you see the idea?
Be sure to also factor in any potential changes or risks that could affect your business.
For example, if you’re expecting a new competitor to enter the market, you’ll need to account for that in your projections. By being realistic and accounting for as many variables as possible, you’ll give yourself the best chance of success so give it some thought!
Pragmatically, how do I come up with reasonable financial forecasts for my business plan?
It’s all a question of common sense, really.
- How much do you plan on selling?
- What are your short, medium and long term financial goals?
- What would be the cost of production?
- What margin does that leave you with?
- What fixed costs would you expect?
- How about variable costs?
- Have you included transaction fees and credit card fees in your costs?
- What is the cost of insurance premiums?
- Will there be any debt to repay?
- What type of budget do you need for marketing purposes?
- What is the cost of acquisition of the client?
- What operational margin does it leave before the taxman comes in?
- What kind of money do you need to meet your long term goals?
- Have you planned for any emergency fund at all?
Right, that’s a long list. But! Answering those questions should give you a strong basis to build financial projections that make sense, because that’s literally how you would read your income statement in the end.
If you were trying to translate boring numbers into a meaningful story, that’s exactly where you would start!
Again, we have you covered with all this.
If you are looking for a concrete and practical financial plan example, make sure to download our business plan template down the page. It will give you the basic pro forma financials you’ll need.
If you need to understand the logic behind the template and would rather use an automated spreadsheet to get everything done, however, then it’s time to stop struggling.
The Impactified Business Plan Builder will provide everything you need: the automated tables and two hours of business coaching videos designed to explain all the logic you’ll need – what are you waiting for?
Why Are Financial Projections so Important in the end?
So, overall, why is creating financial projections so important? Are there various types of financial projections anyway? There are several things to keep in mind here.
First, your financial projections are important because they give bankers and investors the numbers they need (to make an informed decision) in a format they expect to see.
Second, your projections show whether your strategy is aligned with the means at your disposal to achieve it and whether you are aware of the financial engineering required to make your business roll.
Third, and in a related way, forecasts will give you, as the entrepreneur in charge, an opportunity to show if you understand the business for real (or if someone else not present during the discussion wrote the plan for you).
All of these documents are important, but you (nobody else!) will need to be able to tell a story around them.
Investors aren’t just looking for numbers! They invest in teams and people before investing in projects, so they want to know that you understand your business and that you have a plan for the future!
So, make sure your financial projections are accurate and be prepared to answer any questions investors have about them.
Understanding the investment process
To understand how to handle the exercise properly, understanding the investment and funding process in general is important.
What do bankers and investors expect when they are looking at a business plan? How do they decide whether to invest or not? And how do the financial projections help them make that decision?
In short, investors are looking for a return on their investment. So, they want to know what they can expect to earn from their investment, and how that compares to the risks they’re taking.
Your projected income statement is important there, but so are your cashflow projections!
Your financial estimates should therefore show how your business will grow and what profits you’ll generate, both in the short-term and long-term. This information will help investors determine whether or not your business is a good investment.
In contrast, bankers have a much lower risk tolerance and are not interested in funding you – they lend money to those who have money to repay the debt (or some assets to engage as collateral in case something goes wrong). Hence, what they look for is not a high return on investment based on risk, but a repayment capacity based on predictability and wise financial management.
Said differently? You need to create financial projections that make sense and adapt your financial pitch to your audience accordingly.
Show investors that there is a great opportunity to make money at a later stage and show bankers you will be able to start repaying as soon as possible.
Again, if you need to explore the question of investors’ mindsets, we elaborate on that in our video module – it’s time to give it a try!
Business valuation and exit thinking
Last but not least, understanding the investment process means that you also need to start thinking in terms of valuation and exit.
Or, said differently, the financial plan in your business plan must lead you to think about what your business will be worth a few years from now, and about how you will be able to make money (for you and your investment partners) by selling it.
On the one hand, exit thinking relates to the idea that investors invest in a business with the expectation that the business will raise more money later on, at which stage a larger investor will come in and buy the existing investors out.
To make your investors some money, therefore, you have to start thinking in terms of exiting the business at some point – which means progressively turning the business into an asset that works on its own, for you and as much as possible without you.
This mindset is absolutely key – think about it!
On the other hand, the discussion leads us to think in terms of business valuation – understand, how much is the business worth, and how much could it be sold for.
That topic is probably getting too technical for this article’s discussion, so we’ll explore it in another post.
Meanwhile, make sure to listen to the exit & valuation video in The Business Plan Builder module . We explain all this and even go as far as giving you an automated valuation calculator in the financial tables part of the tool – again, you have no excuse!
Avoiding the typical mistakes small businesses make with financial planning
To finish with the discussion, what should you keep in mind if you wanted to turn your financial plan into an asset that generates money rather than frustration?
Like it or not, but small business financial planning isn’t an intuitive thing and people tend to make very typical mistakes you should avoid at all costs!
Know your business
First piece of advice, you really (really, really) want to know your business from every angle.
When you are writing the financial plan in your business plan, it’s important to remember that your projections should represent an estimate of future performance. That’s how investors and lenders will read your numbers anyway.
So, your financial projections and forecasts should be based on realistic assumptions and calculations that you should always be prepared to adjust as needed.
In order to make accurate projections, it is therefore extremely important to have a good understanding of your business and the industry it operates in. You should also consult with industry experts and other professionals who can help you make informed decisions about your business.
Do the exercise yourself!
When you’re writing your financial plan, it’s important to avoid making common mistakes. One of the most common errors is underestimating how much money your business will need to operate.
Another is to rely on business plan consultants to write your financial projections without being able to understand the numbers yourself. This can lead to mistakes if the numbers are incorrect, and it can lead to embarrassing ahem! moments if you can’t explain how this or that number ended up in the document.
The best way to ensure accuracy is to do the exercise yourself with the right tools in hand and the brainstorming support of someone you trust to challenge your thoughts and conclusions.
This can be done with your acting CFO or close financial advisor if you have one, or with a fellow entrepreneur if anyone around you has the right mindset to dig into the discussion with you.
Alternatively, hiring a business coach is another way to brainstorm and challenge yourself – follow the link to find out more about that.
Don’t be a tourist. That’s stupid.
Third piece of advice: don’t enter into a discussion with a potential partner as a tourist – this is stupid, and that could very well kill you.
We have seen countless entrepreneurs walk into a room (let alone into a large startup event) saying that they were raising money for their startup. Yet, more often than not, their financial targets are not set or beyond approximative, which means they can’t explain why they need money and how they are going to spend it.
When you do that, the only thing you do is be stupid and make sure everyone knows about it.
First, because they won’t take you seriously. Would you invest money into someone who can’t tell you how they’ll use it and with what return on investment expectations?
And second, because the people you talk to will most likely ask you to come back to them once you have more information to provide. Which either means “don’t come back before six months to a year” or “please don’t come back at all, I have better things to do with my time and more competent people to talk to”.
Don’t be a tourist or you’ll just burn yourself. That’s stupid.
Turn your numbers into a story
The fourth piece of advice is going to be a repeat from earlier, but it’s important so let’s be redundant.
Now that you’ve written your financial projections, it’s time to go beyond the numbers and start telling your business story. The financial plan in your business plan is a great place to start but remember that it’s just one part of your overall pitch.
You’ll also need to be ready to pitch your idea, product, or service, and be ready to defend your financial plan against questions from investors or lenders.
Think holistically and build a story people will want to listen to, remember and act on. Period!
TL;DR: Get your financial projections right!
Now that you understand the different components of a financial plan, it’s time to learn how to write it. The key to writing a good financial plan is to be realistic. Don’t make assumptions that are unrealistic or impossible to achieve.
Start by estimating your sales and expenses for the first year of business. Be as specific as possible, and remember to include both fixed and variable costs. From there, you can create a cash flow statement that shows how your business will generate and spend money over time.
The goal of a financial plan is to paint a realistic picture of your business’s financial future. So make sure to update your plan as your business changes and grows. With careful planning and accurate numbers, you can ensure that your business will be successful for years to come.
What should your business plan financial plan include?
- A profit and loss statement – also known as your P&L statement, or as an income statement
- A cash flow statement showing if your business plan financial projections are realistic
What is the purpose of your business plan’s financial projections?
- To how the plan you have for the business in terms of numbers
- To show a financial overview of what you think can be achieved, by when, with what means
- To show you have a cashflow management strategy that makes sense
- To show you understand the standardized expectations and know how to play by the book
- To show that, overall, your business proposal makes sense whatever the angle!
Need a reliable template and video tutorial to get your financial business plan & financial projections right?
It’s built around over 2 hours of explanatory videos and comes with everything you’ll need to:
- Figure out what you need to figure out – powerful, uh?
- Understand the business plan code!
- Write a top business plan – with just the right amount of words and pages!
- Build your financial estimates – with an automated financial projections template excel spreadsheet!
- Create a visually appealing pitch deck people will want to read thanks to our designer-made templates!
If you want to stop wasting your time, this is THE most simple business plan template, and you can’t afford to miss it!
Wanna’ start with something free? Our free business plan template is also here to help !
Psss! Share this Article!
Topics related to Financial Projections: How to write the financial plan in business plan:
- Financial plan in business plan coffee shop
- Financial plan in business plan template
Need help with building & scaling your business?
At Impactified , we are on a mission to make you build, grow, and scale businesses you can be proud of, and we do that by making our business coaching expertise available to you, in person and through kick-ass self-coaching modules. You will love the experience either way, the only question is, what makes the most sense to you?
More Insights on Business Plan Writing

Hey coach! I’m writing a business plan and I’m wondering how to build the financial projections part of the document. What’s the importance of financial projections exactly – I mean, isn’t it absolute BS? How do I write the financial plan in business plan, and even more importantly, how can I make sense of all those messy tables? Can you help me understand this? Thanks in advance!

Do I Need a Business Plan Consultant? No, You Don’t!
Hey there Coach! I’m a small business owner and I need to find some support with my business plan. People suggested that I find a business plan consultant near me, but that’s a big cost and I’m not too sure about what to expect from that. What’s your opinion about business plan consultants in general? Is there any alternative you would highly recommend? Thanks!

How Much Does a Business Plan Cost? Just Under $100!
Hey coach! I was wondering – how much does a business plan cost? I need one, and I’m thinking about having it written for me, so I’d love your insights. Also, I’ve heard business plan writers cost a lot of money, so I’m interested if you have tips for writing a low-cost business plan! Thanks!
The #1 Growth & Scale Facilitation Platform for Entrepreneurs
Building & scaling a business is tough, so we’ve built easy-to-use tools & programs you can leverage anytime to make your business rock. The rest is up to you!
Get Started
- Book a Call!
- Pitch Your Biz!
- Read our Entrepreneurs' blog!
Business Facilitation
- Why Hire a Facilitator?
- Entrepreneur Training
- Our Brochures
- Team performance Survey
- The FREE Coaching Newsletter
- Impactified News
- Get in touch
© 2019-Present - All Rights Reserved - Impactified.com
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
- United States (English)
- Australia (English)
- Belgium (English)
- Canada (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Hong Kong (English)
- Indonesia (English)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Malaysia (English)
- México (Español)
- Nederland (Nederlands)
- New Zealand (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Schweiz (Deutsch)
- Singapore (English)
- South Africa (English)
- Sweden (English)
- Taiwan (English)
- Thailand (English)
- United Kingdom (English)
How to Strengthen Collaboration Between Finance and the Business
Many companies suffer poor communication and collaboration between financial and non-financial groups. Learn how finance can engage operations in planning.

Many companies suffer from poor communication and collaboration between financial and nonfinancial managers. Operating managers don’t have sufficient input or buy-in to the financial planning process, and they aren’t educated about how their decisions can influence overall profitability. For its part, finance isn’t able to offer real performance insights that might truly help managers improve their results.
Instead of working closely together to plan and forecast, finance and business resort to negotiations that can involve high levels of conflict. Why is this, and how can it be changed to strengthen collaboration between finance and the business—and therefore transform FP&A?
Drowning in Metrics, Measurements, and Spreadsheets
First of all, companies sometimes flood managers with measurements and metrics, too few of which effectively help managers understand and improve their performance. Too much measuring can add cost and complexity to an organization.
Secondly, spreadsheets continue to dominate planning processes in most companies. While spreadsheets work well for individual productivity, they cause problems when it comes to sharing and aggregating. Finance gets bogged down in low-value-added work—such as formatting and troubleshooting spreadsheets—and can’t provide useful service to business managers.
Meanwhile, business managers waste time managing to budgets instead of managing their business. They often don’t get the information they need, when they need it, from finance. Instead, they’re deluged with data, metrics, and reports, much of which provides little value.
Furthermore, many planning systems are designed and implemented by finance and are seen as irrelevant by business managers. The result is lack of buy-in and enthusiasm.
Clearing the Decks for Useful Analysis and True Collaboration
Finance can make room for higher-value work for both themselves and managers by leading the way to less detail and complexity, simplifying internal systems, and reducing the amount of time managers spend producing counterproductive reports and analyzing too many measurements.
In so doing, finance can provide effective decision support and performance insight that can truly help managers improve their results, making finance a real partner rather than an adversary. Here are three best practices that will help you make these changes.
1. Continuous planning.
First, replace detailed annual planning cycles, which take too long and result in a budget that is already out of date as soon as it is complete. A more effective planning system is a continuous process, focused on rolling views that look 12 to 18 months ahead. These continuous plans should enable managers to respond more rapidly to emerging events and trends and to changing business environments.
Replacing the annual budget with a rolling forecast can save huge amounts of work, freeing all managers to spend more time on value-added work. It will also improve the relationship between finance and business managers, as finance will have more time to provide better service.
2. Move from monthly variance reporting to KPIs and dashboards.
Most companies manage through annual budgets and use monthly variance reporting as the primary feedback mechanism for managers. But monthly variance reporting is too slow and fails to reveal underlying causes of problems.
What is more effective is fast feedback of financial results, summarized and shown as trends and moving averages. KPIs should act as a management dashboard. They should provide managers with early warning signs when problems are brewing and action needs to be taken.
Defining measurements is just the first step. “The next step, and perhaps the hardest part, is to set in motion a cadence for the management team to know and really understand performance through KPIs so that they can use that knowledge to make the right decisions.
These KPIs should be few in number and appropriate to the level of management. A small number of key metrics should be reported daily and weekly. KPIs should provide a fast, high-level view of what is happening today and what is likely to happen in the short-term future. Moving to KPIs in this fashion will not only provide true value to managers but will also lighten the reporting load for the entire organization.
3. Deploy cloud technology that provides fast, relevant information, enabling collaboration.
Finance can use technology to provide a performance management system that delivers what managers need—fast, relevant information. Avoid investing in complex IT systems that consume valuable time and money without providing reasonable value.
Instead, implement a dedicated system that employs cloud-based technology to enable unlimited numbers of managers to work together on driver-based forecasts, which are automatically aggregated at every level. This system should also have tight integration with data from other enterprise systems, so that it serves as the primary performance management system.
By implementing these three best practices, your finance team can transform itself and your company’s performance management practices. Your finance team can move beyond simply being effective at financial management and scorekeeping, and instead become a trusted and integral member of the strategic management team. And finance can offer real performance insights that can truly help your managers improve their results.
Watch a demo , and see Workday Adaptive Planning in action.

More Reading

Shutterstock and Vancouver Coastal Health Move to Agile Planning for an Agile World
Faster, more confident decision-making starts with real-time access to data spanning the enterprise—so that finance can scenario plan in tune with a rapidly changing world. Shutterstock and Vancouver Coastal Health share their journeys to better planning.

Tech, Media, and Entertainment Industries Outlook: 4 Transformative Trends
Focus areas for leaders in the tech, media, and entertainment industries include upleveling their forecasting and planning capabilities, and using data-driven insights to gain a competitive advantage and meet consumer demand.

Donors, Dollars, and Data: Enhancing Nonprofit Financial Stewardship
More than 80% of nonprofits cite a lack of adequate technology as a barrier to gathering information on mission impact. In a new report, industry experts from CrossVue and Workday partnered to explain what this means for the future of the nonprofit industry.

Chief of Staff
Align strategy & operations across teams
Small business owner
Be released from the day-to-day
Startup founder
Find fit & grow your team
Board meetings
Run board meetings with ease.
Plans & roadmaps
Build organization or team plans.
Strategic alignment
Align leaders and teams.
Performance intelligence
AI powered performance intelligence.
Operating efficiency
Simplify, focus, and automate.
Business transformation
Run business improvement programs.

People development
Data driven people development.
Write plans, procedures, notes, or policies.
Use AI to build smart goals & OKRs.
Your vision masterplan.
Run projects, oragnize tasks across teams.
Align the operating rhythm, run effective meetings.
Diagnostics
Find growth gaps across the business.
Build scorecards, visualize performance.
Why partner?
Easier advisory with a demonstrable ROI
Become a partner
Become a fractal Chief of Staff.
ROI Calculator
See the ROI in our program.
GET CERTIFIED
Advisor Certifications
Be recognized as a strategic leader.
Platform specialist
Implement agile leadership practices.
CX Consultant
Lead sales, marketing, & service strategy.
EX Consultant
Lead people & culture strategy.
Business consultant
Lead business planning & strategy.
Leadership coach
Lead executive coaching.
Certified advisor
Fractal Chief of Staff, COO, or Strategic Advisor.
Help centre
Help and knowledge articles.
Waymaker Academy
Grow your skills.
Leadership articles.
Events & webinars
Join a masterclass.
Download resources.
Listen, learn, connect.
Product overview
3 Ways to build a better business.
Diagnose gaps, roadmap, goals & more
Watch a demo
Watch a detailed overview of Waymaker.io
For start ups & small business
Every essential step to grow
For scaling & enterprise business
Release your team to scale your business
For coaches & consultants
Become a high value advisor as a Waymaker partner
Playbooks for growth
On demand playbooks in Waymaker Academy
License types, prices and start a free trial
START MY FREE TRIAL
Lead and deliver
Get certified + free courses & playbooks
Waymaker's Leadership Curve
The framework overview
News & articles
Listen to leaders
eBooks & Webinars
Learn with our eBooks & Webinars
Get started, learn & find help
WATCH A DEMO
Build a better business with Waymaker partnership
How to partner
3 steps to a better coaching & consulting business
Get Certified
Become a Waymaker Certified Advisor
High Growth Advisor Program
Scale your advisory
Grow your partner business
Access free & paid services to grow your business
Model your partner ROI
Use our ROI calculator
SPEAK WITH OUR TEAM
About Waymaker
Join our team?
APPLY FOR A ROLE

Build a scaleable business & leadership advisory business.
Discover Waymaker partnership.
Become a Waymaker Partner
Scale your coaching & consulting.
Free courses and playbooks for Waymaker partners.
Be recognized for leadership.
Platform Specialist
For agile & business coaches.
For sales and marketing consultants.
For HR consultants and coaches.
Business Consultant
For strategic business coaches & consultants.
Leadership Coach
For executive and leadership coaches.
Certified Advisor
For recognized experts in leadership and strategy.

Bite sized brilliance to grow your business.
Leadership Blog
Podcast | leadership torque.
Helping you make business improvement, business as usual.
Learn with our downloadable eBooks.
Merch & Resources to help you achieve more by doing less.
Free courses and playbooks.
Leadership software
What is leadership software?
Waymaker Leadership Curve
A framework overview.
Get started, learn & find the help you need.

Platform features
Waymaker's intelligent platform includes goals (OKRs), roadmaps, meetings, tasks, and dashboards.
Diagnose growth gaps.
Create goals and OKRs.
Create roadmaps of goals.
Tasks, task automation, and task templates.
Automate meetings and minutes.
Build scorecards, view goal and task dashboards.
Professional services
Increase profits, reduce chaos.
Property & Development
Streamline & reduce risk.
Software & Technology
Align everyone, outperform growth
Small business
Work on your business, not in it.
WAYMAKER LEADERSHIP BLOG
- Effective Strategic Plans and Business Plans: Understanding the Difference Between
by Waymaker | Jul 25, 2023
Defining Strategic Plans and Business Plans
What is a strategic plan, what is a business plan, key components of strategic plans and business plans, elements of a strategic plan, elements of a business plan, the purpose and goals of the strategic plan and the business plan, the purpose of a strategic plan, the purpose of a business plan, the planning process: strategic plans vs. business plans, developing a strategic plan, developing a business plan, the role of stakeholders in each plan, stakeholder involvement in strategic plans, stakeholder involvement in business plans.
- You may also like...
Get started
In the world of business, the terms strategic plans and business plans are often used interchangeably. However, there are significant differences between these two types of plans that are important for entrepreneurs and business leaders to understand.

Before delving into the differences between strategic plans and business plans, it’s important to define each term.
A strategic plan is a long-term plan that outlines an organization’s goals and objectives and the actions needed to achieve them. It typically covers a three to five-year time period and focuses on broad, high-level initiatives that will position the organization for success in the future.
Strategic planning is a crucial process for any organization that wants to succeed in today’s competitive business environment. It allows organizations to identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and to develop a plan of action that will help them achieve their long-term goals.
During the strategic planning process, organizations typically conduct a thorough analysis of their internal and external environments. This includes an assessment of their current strengths and weaknesses, as well as an analysis of the market, competition, and other external factors that could impact their success.
Based on this analysis, organizations develop a set of strategic objectives and initiatives that will help them achieve their long-term goals. These initiatives may include expanding into new markets, developing new products or services, or investing in new technologies.
A business plan , on the other hand, is a detailed plan that outlines the steps a company will take to achieve its short-term goals and to operate on a daily basis. It typically covers a one to three-year time period and includes detailed financial projections, marketing plans, and operational strategies.
A business plan is a critical tool for any entrepreneur or small business owner who wants to succeed. It allows them to identify their target market, develop a marketing strategy, and create a roadmap for achieving their financial goals.
When developing a business plan, entrepreneurs typically begin by conducting market research to identify their target market and assess the competition. They then develop a marketing strategy that will help them reach their target market and differentiate themselves from the competition.
In addition to marketing, a business plan also includes detailed financial projections that outline the company’s revenue and expenses over the next one to three years. This allows entrepreneurs to identify potential financial challenges and develop strategies to overcome them.
Finally, a business plan includes operational strategies that outline how the company will operate on a day-to-day basis. This includes everything from hiring and training employees to managing inventory and fulfilling orders.
In conclusion, while both strategic plans and business plans are important tools for organizations and entrepreneurs, they serve different purposes. Strategic plans focus on long-term goals and broad initiatives, while business plans focus on short-term goals and daily operations.
Strategic plans and business plans are essential tools for any organization looking to achieve long-term success. While both plans share some common elements, they differ in their focus and level of detail.
A strategic plan is a comprehensive document that outlines an organization’s long-term goals and objectives. Key components of a strategic plan include:
- Mission Statement: This statement defines the organization’s purpose and values, and provides a framework for decision-making.
- Vision Statement: This statement describes the organization’s long-term aspirations and what it hopes to achieve in the future.
- Objectives: These are specific, measurable goals that the organization aims to achieve within a set timeframe.
- Strategies: These are the broad approaches that the organization will take to achieve its objectives.
- Tactics: These are the specific actions that the organization will take to implement its strategies.
By outlining these key components, a strategic plan provides a roadmap for the organization to follow as it works towards its long-term goals.
A business plan is a detailed document that outlines how a company will achieve its short-term and long-term goals. While it shares some elements with a strategic plan, a business plan is more focused on the day-to-day operations of the business. Key components of a business plan include:
- Executive Summary: This is a brief overview of the entire business plan, highlighting the key points and goals.
- Market Analysis: This section provides an in-depth look at the industry and market in which the company operates.
- Marketing and Sales Strategies: These are the specific tactics that the company will use to promote and sell its products or services.
- Operational Plans: This section outlines the day-to-day operations of the business, including staffing, production, and logistics.
- Financial Projections: This section provides detailed financial projections, including revenue, expenses, and profit margins.
- Funding Requirements: This section outlines the company’s funding needs and how it plans to secure financing.
By including these key components, a business plan provides a detailed roadmap for the company to follow as it seeks to achieve its goals and grow its operations.
Overall, both strategic plans and business plans are essential tools for any organization looking to achieve long-term success. By outlining clear goals and strategies, these plans provide a framework for decision-making and help ensure that the organization stays focused on its long-term objectives.
Strategic plans and business plans are both essential tools for any organization. They provide a clear roadmap for achieving goals and ensuring long-term success. While the two plans are similar in some ways, they serve different purposes and have different goals.
A strategic plan is a high-level document that outlines an organization’s long-term goals and objectives. It provides a roadmap for achieving those goals and helps to align the entire organization around a shared vision. The purpose of a strategic plan is to provide a framework for making strategic decisions that will move the organization closer to its desired future state.
Developing a strategic plan requires careful consideration of an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. It involves analyzing market trends, assessing the competition, and identifying potential risks and challenges. The end result is a comprehensive plan that outlines the steps necessary to achieve the organization’s long-term goals.
One of the key benefits of a strategic plan is that it helps to ensure that everyone in the organization is working towards the same goals. By creating a shared vision and providing a clear roadmap for achieving it, a strategic plan can help to align the efforts of all employees, departments, and stakeholders.
A business plan is a detailed document that outlines an organization’s short-term goals and objectives. It provides a roadmap for achieving those goals and helps to define the company’s market niche, outline its marketing and sales strategies, and determine the funding needed to cover startup costs and ongoing expenses.
The purpose of a business plan is to provide a clear and comprehensive plan for achieving the organization’s short-term goals. This includes identifying potential customers, outlining marketing and sales strategies, and determining the resources needed to launch and maintain the business.
Developing a business plan requires careful research and analysis. This includes assessing the market demand for the product or service, analyzing the competition, and identifying potential risks and challenges. The end result is a detailed plan that outlines the steps necessary to launch and grow the business.
One of the key benefits of a business plan is that it helps to ensure that the organization is well-prepared for the challenges of starting and growing a business. By providing a clear roadmap for achieving short-term goals, a business plan can help to minimize risks and increase the chances of success.
Strategic plans and business plans are both essential tools for any organization. While they serve different purposes and have different goals, they both provide a clear roadmap for achieving success. By developing a comprehensive strategic plan and a detailed business plan, organizations can ensure that they are well-prepared for both short-term and long-term success.
Planning is an essential part of any successful business, but the planning process can differ significantly depending on the type of plan being developed. Strategic plans and business plans have different goals, and therefore require different approaches to planning.
Use Waymaker Academy to learn how to build your business plan.

A strategic plan is a long-term plan that outlines an organization’s goals and objectives, and the strategies it will use to achieve them. Developing a strategic plan typically involves a lengthy planning process that includes input from a wide range of stakeholders, such as executives, employees, customers, and shareholders. The planning process may involve conducting research and analysis to identify opportunities and threats in the market, as well as the organization’s strengths and weaknesses.
The strategic plan should be reviewed and updated annually to ensure it remains relevant and aligned with the organization’s goals. This process may involve revisiting the organization’s mission and vision statements, as well as assessing the progress made towards achieving the goals outlined in the plan.
One of the key benefits of a strategic plan is that it provides a clear direction for the organization, helping to align everyone around a common set of goals and objectives. It also helps to ensure that resources are being allocated in the most effective way possible, and that the organization is able to adapt to changes in the market.
A business plan, on the other hand, is a shorter-term plan that outlines the company’s goals and objectives for the next one to three years. The process of developing a business plan typically involves a smaller team of stakeholders focused on executing the company’s short-term goals.
The business plan may also include input from investors, lenders, and other external stakeholders who have a vested interest in the company’s success. This may involve presenting financial projections, market analysis, and other data to demonstrate the viability of the business.
One of the key benefits of a business plan is that it provides a roadmap for the company’s short-term goals, helping to ensure that everyone is working towards the same objectives. It also helps to identify potential risks and challenges, and provides a framework for measuring progress and making adjustments as needed.
Overall, both strategic plans and business plans are important tools for any organization. By taking the time to develop a clear plan, companies can ensure that they are working towards their goals in the most effective way possible.
Stakeholder involvement plays a key role in both strategic plans and business plans, although the level and type of involvement can vary depending on the plan.
Stakeholder involvement is critical in the development of a strategic plan, as it ensures that all parties have a voice in shaping the organization’s future. This involvement also helps to build consensus around the organization’s goals and the strategies needed to achieve them.
Stakeholder involvement in a business plan may be more limited, as the focus is on executing short-term goals rather than shaping the organization’s long-term future. However, investors and lenders may play a significant role in the development of a business plan, as they provide funding and have a vested interest in the success of the company.
While strategic plans and business plans share some common elements, they serve very different purposes and are designed to achieve different goals. By understanding the differences between these two plans, entrepreneurs and business leaders can better plan for the future, execute their short-term goals, and position their organizations for long-term success.
You may also like…

Streamline Your Workflow with New Folder Functionality in Waymaker.io
We're excited to introduce folders, a new feature that will transform the way you organize your content across...

Introducing the People module: AI powered role descriptions, automated org charts, and powerful performance alignment.
The Waymaker People module makes it easy to plan roles, align performance metrics and build world class role...

Understanding the role of a company director as a small business leader
As a small business owner who also serves as a company director and an employee of your company, you hold a unique...
Performance intelligence software for holding plans, people, and performance accountable. Achieve up to 77% better goal performance with Waymaker.io
Business Plan vs Business Model Canvas Explained

6 min. read
Updated December 15, 2023
It might be stating the obvious, but planning and preparation are keys to success in business.
After all, entrepreneurs put in hard work to develop their product, understand the market they plan to serve, assess their competitive landscape and funding needs, and much more.
Successful business owners also take time to document their strategies for guiding the growth of their companies. They use these strategies to take advantage of new opportunities and pivot away from threats.
Two common frameworks for documenting strategies – the business model canvas and the business plan – are also among the easiest to get confused.
Though they can complement each other, a business model canvas and a business plan are different in ways worth understanding for any entrepreneur who’s refining their business concept and strategy.
Let’s start by digging deeper into what a business model canvas is.
- What is a business model canvas?
You may have heard the term “business model” before. Every company has one.
Your business model is just a description of how your business will generate revenue. In other words, it’s a snapshot of the ways your business will be profitable.
Writing a business plan is one way of explaining a company’s business model. The business model canvas takes a different approach.
A business model canvas is a one-page template that explains your business model and provides an overview of your:
- Relationships with key partners
- Financial structure
- And more…
While the business model is a statement of fact, the business model canvas is a strategic process—a method for either documenting or determining your business model.
It’s meant to be quickly and easily updated as a business better understands what it needs to be successful over time. This makes it especially useful for startups and newer businesses that are still trying to determine their business model.
You can think of a business model canvas as a condensed, summarized, and simplified version of a business plan. It’s a great way to quickly document an idea and get started on the planning process.
The business plan is a way to expand on the ideas from the canvas and flesh out more details on strategy and implementation.

Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Components of a Business Model Canvas
The simplest way to think about your business model canvas is to map it out visually. A business model canvas covers nine key areas:
- Value proposition : A company’s unique offering in the market and why it will be successful.
- Key activities: The actions that a company takes to achieve its value proposition.
- Customer segments : The types of people or businesses that are likely to want a company’s products or services.
- Channels : How a company reaches customers through marketing and distribution efforts.
- Customer relationships: How a company interacts with customers and maintains important relationships.
- Revenue streams: The ways in which a company makes money.
- Key resources: The assets such as property, equipment and staffing that a company needs to perform its key activities.
- Key partners: The relationships with suppliers, vendors, customers and other stakeholders a company must maintain in order to be successful.
- Cost structure: The major drivers of company expenses that will need to be tracked and managed.
[Want an even simpler alternative? Try downloading our free one-page plan template and start building your plan in less than 30 minutes.]
To get a better sense of how a business model canvas documents business strategy, consider a company like Netflix. The streaming company’s business model is based on generating subscription revenue through its content library and exclusive content.
If Netflix executives were to create a business model canvas, it would map out how the company leverages key resources, partnerships, and activities to achieve its value proposition and drive profitability. The business model is the destination.
The great thing about a business model canvas is that you can quickly document business ideas and see how a business might work at a high level. As you do more research, you’ll quickly refine your canvas until you have a business idea you think will work.
From there, you expand into a full business plan.
- What is a business plan?
If a business model canvas captures what a company looks like when it’s operating successfully, then a business plan is a more detailed version along with a company’s blueprint for getting there.
Think of your business plan as a process of laying out your goals and your strategies for achieving them.
The business plan is more detailed, and changes over time. It examines each aspect of your business, from operations to marketing and financials.
The plan often includes forward-looking forecasts of a company’s projected financial performance. These are always educated guesses. But these forecasts can also be used as a management tool for any growing business.
Comparing actual results to the forecast can be a valuable reality check, telling a business if they’re on track to meet their goals or if they need to adjust their plan.
A business plan is also a must for companies hoping to receive a bank loan , SBA loan , or other form of outside investment . Anyone putting up funds to help you grow will want to see you’ve done your homework.
So a business plan is how you not only prepare yourself, but also show your audience that you’re prepared.
Components of a business plan
While there are several different types of business plans meant for different uses, well-written plans will cover these common areas:
- Executive summary : A brief (1-2 pages) overview of your business.
- Products and services : Detailed descriptions of what you’re selling and how it fills a need in the market.
- Market analysis : Assessing the size of your market, and information about your customers such as demographics (age, income level) and psychographics (interests, values).
- Competitive analysis : Documenting existing businesses and solutions your target customers are finding in the market.
- Marketing and sales plan : Your strategies for positioning your product or service in the market, and developing a customer base.
- Operations plan : Describing how you will run the business from day to day, including how you will manage inventory, equipment, and staff.
- Organization and management team: Detailing the legal structure of the business, as well as key members, their backgrounds and qualifications.
- Financial Plans : Business financials that measure a company’s performance and health, including profit & loss statements, cash flow statements and balance sheets. Effective financial plans also include forward-looking sales forecasts and expense budgets.
How a business plan and business model canvas inform business strategy
Avoid the trap of using the two terms interchangeably. As we’ve shown, the two have different focuses and purposes.
The business model canvas (or our one-page plan template ) is a great starting point for mapping out your initial strategy. Both are easy to iterate on as you test ideas and determine what’s feasible.
Once you have a clearer sense of your idea, you can expand the canvas or one-page plan into a business plan that digs into details like your operations plan, marketing strategy, and financial forecast.
When you understand how – and when – to use each, you can speed up the entire planning process. That’s because the business model canvas lays out the foundation of your venture’s feasibility and potential, while the business plan provides a roadmap for getting there.
The work of business planning is about connecting the dots between the potential and the process.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- How both inform your strategy
Related Articles

10 Min. Read
Use This Simple Business Plan Outline to Organize Your Plan

5 Min. Read
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained

When Should You Write a Business Plan?

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Transform Tax Season into Growth Season
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.1.5: The Business Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 73816
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas, which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch, without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections (Figure 5.1.5.1). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.

Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap, that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the co-founder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew. “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse, and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
LINK TO LEARNING
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA). The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan
As the name implies, the executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions, requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. Its suggested sections are shown in Table 5.1.5.1.
ARE YOU READY?
Create a Brief Business Plan
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs, one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 5.1.5.2 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and ensure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 5.1.5.3 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM. This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 5.1.5.4 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 5.1.5.2 and Figure 5.1.5.3. A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.

Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 5.1.5.5 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 5.1.5.6 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture. Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements, a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing. Figure 5.1.5.4 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.

ENTREPRENEUR IN ACTION
Laughing Man Coffee
Hugh Jackman (Figure 5.1.5.5) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.

A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
WHAT CAN YOU DO?
Textbooks for Change
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
WORK IT OUT
Franchisee Set Out
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.

- Certifications
- Associate Business Strategy Professional
- Senior Business Strategy Professional
- Examination
- Partnership
- For Academic Affiliation
- For Training Companies
- For Corporates
- Help Center
- Associate Business Strategy Professional (ABSP™)
- Senior Business Strategy Professional (SBSP™)
- Certification Process
- TSI Certification Examination
- Get your Institution TSI Affiliated
- Become a Corporate Education Partner
- Become a Strategy Educator
- Frequently Asked Questions
Business plan vs Strategic Plan - What You Must Know

Like everything else in life, the nature of business needs a plan in place to follow and measure. Crafting a strategic roadmap isn't just a suggestion—it's a necessity.
This is one of the key elements of a startup or even a business division within an organization that is expanding or diversifying. It has every resource element and needs to be mapped out for the business, including projected milestones for the future.
However, every business strategist needs to know that there are some subtle differences between what constitutes a business plan, and the several differences it has with a strategic plan. Let’s walk through the different elements that comprise each and understand the outcome each aims to achieve.
Introducing The Business Plan
A business plan is exactly what the name suggests— a plan to start and run a business or a new entity of an existing business; usually either an expansion in a newer region or a diversification into a new market. Business plans are mainly created for internal reference purposes or external funding purposes, with the latter being the common usage. They form the basis of all business strategies and decisions made at the ownership level in an organization. The most essential components of a business plan include:
Organizational Plan - This is the core of a business plan, and it includes the mission and vision statement, along with the market in which the company plans to operate. This plan also encompasses thorough market research to gauge the potential of the business, crucial for securing funding or sponsorship. It articulates the rationale behind the business's growth trajectory, outlining clear timelines for achieving milestones along the way.
Financial Plan - A robust financial plan is the bedrock of any successful business venture, where cash flow reigns supreme, and a meticulously crafted balance sheet serves as the ultimate scorecard. A financial plan includes some of the most important elements of the entire business plan and includes elements like projected cash flow statements, capital requirements, a summary of projected overheads, a projected balance sheet including assets and liabilities, and income and expense statements.
Remember to regard this as the central nervous system, for it permeates and influences almost every aspiration the enterprise hopes to attain.
Sales and Marketing Plan - We mentioned “almost” everything above for this very reason. Sales and marketing form the other significant component of the business plan. These include sales forecasts and overheads, marketing and brand management summaries, and market share projections that the business hopes to achieve within a time frame.
Business plans are indeed comprehensive and all-encompassing. They form the basis of the business's existence or the rationale for investments in it. But what about translating these plans into action? How do we ensure that the sky-high goals set forth are actually achievable?
The Actionables- A Strategic Plan
Strategic plans constitute the basis of operations and responsibilities within the business. These plans lay the paths out for each member of the organization to follow and define the functional outline and the key outcomes for every project and process within the business. A strategic plan goes on to define the operations and their outcomes within the organization, its departments, and its employees. The single thread connecting strategic planning with the business plan is the vision of the organization, and for obvious reasons— vision serves as the guiding light for strategy formation, which, in turn, directs the day-to-day operations of the business.
Why A Strategic Plan is Crucial to The Organization
In a word— synchronization. A robust and well-laid-out strategic plan establishes the much-needed sync between teams and their objectives. Not only that, it also provides a guide for daily operations alongside the focus and direction that teams often need to get the job done, on time and within budget. When all these components are integrated into a cohesive network, the true value of a strategic plan emerges—a seamless and grand orchestration of departments, teams, and individuals using the resources allocated to them to achieve the key performance indicator that they are responsible for.
Elements to Consider in a Strategic Plan
When tasked with creating a strategic plan for your business, you will need to incorporate certain components that will ensure that the stakeholders are aligned completely with the organization’s goals and objectives. These include:
Vision and Values - The vision statement is the most important component of the strategic plan and the most overarching. It propels the organization towards established goals and the values that every employee and stakeholder must incorporate.
Goals - These are short, medium, or long-term, depending on the scope of the strategic plan. They provide the much-needed context for the organization to undertake initiatives that meet the vision while maintaining the values.
Guiding Principles - Often, organizations face crossroads where they must decide which steps to take next, to reach their vision. Principles are included in strategic plans to align teams towards the vision when faced with a dilemma and form a critical part of strategic planning.
Action Plans - A sum of key initiatives, processes, and projects that are required to be performed on a pre-determined periodic basis for the goal to be accomplished. These also include the time frames for each stakeholder responsible for each option. They usually follow the DACI format for each action (Driver, Approver, Contributor, Informed)
SWOT Analysis - The quintessential component, the Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats analysis of the strategic plan lends context to all business actions vis-a-vis the external environment. This includes competitors, market forces and conditions, identification of internal and external threats, and several other factors.
Read This - SWOT Analysis: How to Strengthen Your Business Plan
Here’s a table highlighting the main differences between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan with a focus on the key components of each—
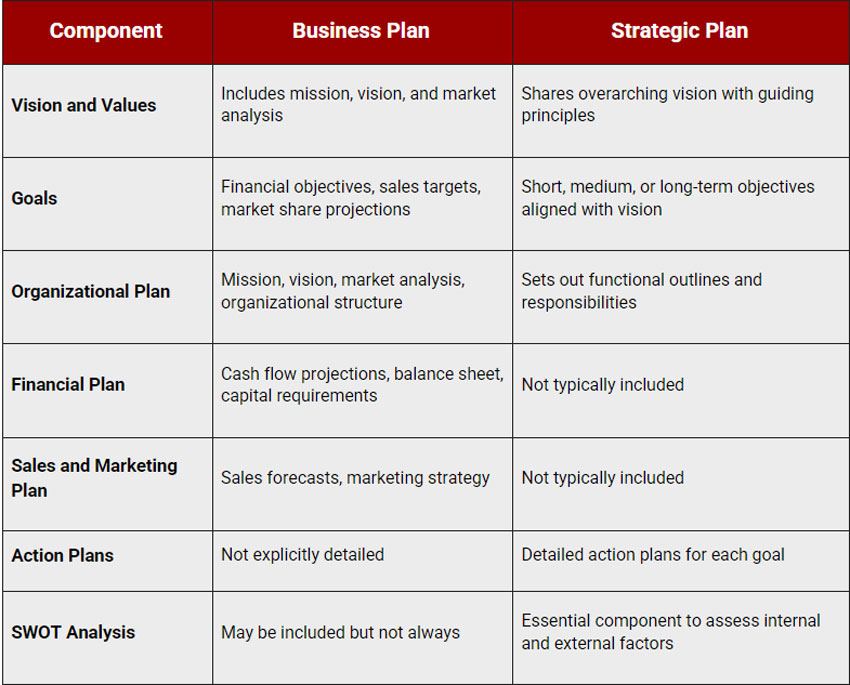
Learning All About Strategic Planning
In all businesses, a strategic plan serves as the foundational blueprint, akin to a meticulously drawn map for a general. It provides the essential guidance and direction needed for the entire organization to navigate toward success. It is crucial, therefore, to acquire the necessary skills and certifications for employment as a business strategist who would be entrusted with creating it. Know more about how to become a successful and sought-after business strategist today!

Recent Posts

How Data Analytics Can Revolutionize Your Business - A Strategist's Guide
Download this Strategist's Guide to empower yourself with resourceful insights:
- Roadblocks to Data Usage
- Advantages that Data Analytics offer for businesses
- Elements of a Data Analytics Strategy
- Top reasons why businesses must adopt a Data Analytics Strategy
- Case studies, Scenarios, and more

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Verify A Credential
Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TSI.
Stay Informed!
Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.
Start Your Journey with The Strategy Institute by Creating Your myTSI Account Today.
- Manage your professional profile conveniently.
- Manage your credentials anytime.
- Share your experiences and ideas with The Strategy Institute.
Account Login
- Remember Password
- Forgot Password?
Forgot Password
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Business Plan vs. Business Model
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 19, 2023 Updated on December 11, 2023

If you’re starting a business , you have a business model, whether you know it or not. A business model is the foundation of any business idea; it basically outlines how the concept offers value and potential for growth. Essentially, a solid business model ensures that the business will make money.
A business plan , on the other hand, is the business owner’s plan to put that model into action. It’s much more detailed and includes financial projections, objectives, management decisions and further steps.
Still unsure? Have no fear, this handy guide lays out the differences between a business plan and a business model so that you know exactly what you and your business need to succeed.
- Business Model
In simple terms, a business model is how the business will make money. Selling ice to eskimos, for instance, is a bad business model. Selling team jerseys to rabbit sports fans, on the other hand, is a solid business model.
The components of a business model are best illustrated by Swiss entrepreneur Alexander Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas, which is a visual representation with nine sections. Four sections represent internal elements of a business that enable it to function and are related to costs.
Four other sections represent external elements that enable the business to bring in revenue and are related to the customer. The ninth section is the business’ value proposition.
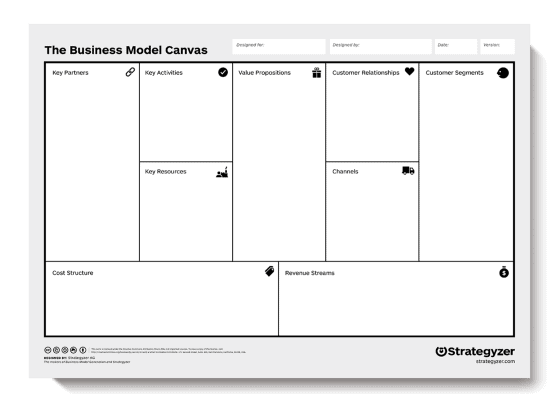
Value Proposition
The value proposition is at the heart of your business model. Your value proposition, which should be no more than two sentences long, needs to answer the following questions:
- What are you offering
- Whose problem does it solve
- What problem does it solve
- What benefits does it provide
- How is it better than competitor products
Key Activities
Key activities are all the activities required to run the business and create the proposed value. These can include product development and distribution and any other necessary activities.
Cost Structure
The cost structure is a sum of all you’ll need to spend to make the business function. It’s the costs you’ll incur to run the business and bring in revenue.
Key Partners
Key partners are external partners involved in delivering value, such as vendors and suppliers, or maybe a bank.
Key Resources
Key resources are any necessary practical elements that come with a cost. These might include your office space, employees, and equipment like computers.
Revenue Streams
Revenue streams are the ways in which you receive payment from customers. You may have more than one revenue stream, such as via direct sales and subscriptions.
Customer Segments
Customer segments are the groups of people to whom you provide goods or services. In other words, your target market. Maybe your products are aimed at younger women, for instance, or older men. Whatever your target segments, you should build customer personas of each group so that you know how and where to reach them with your marketing.
Customer Relationships
Customer relationships refer to how you interact with your customers to deliver value. Your interactions may be online only, by phone, in-person, or all of the above.
Channels refer to how you reach your customers, such as social media, internet search, direct sales calls, trade shows, and so on.
To Summarize
If you’re just starting a business, the Business Model Canvas is a great way to understand and examine your business model. One thing to remember is that the elements you put in your Canvas will be based on assumptions that will at some point be tested in the market and adapted as needed.
Another thing to remember is that you do not need to do a Business Model Canvas. It’s merely an exercise that can help provide insight into your business model.
- Business Plan
A business plan is a detailed document that describes how the business will function in all facets. The key is in the “plan” part of the name. It will specify how you’ll launch your business, gain customers, operate your company, and make money. A business plan, however, is not a static document .
The initial version will be based largely on assumptions, supported by research. As you run your business you’ll constantly learn what works and what does not and make endless tweaks to your plan.
Thus, creating a business plan is not a one-time action – it’s a dynamic and continuous process of crafting and adapting your vision and strategy.
You’ll present your business plan to potential backers, though in recent years some investors have begun to embrace the Business Model Canvas as a tool to assess a business’ potential.
A strong business plan includes eight essential components .
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the initial section of your business plan , written last, summarizing its key points. Crucial for capturing investors’ and lenders’ interest, it underscores your business’s uniqueness and potential for success. It’s vital to keep it concise, engaging, and no more than two pages.
2. Company Description/Overview
This section provides a history of your company, including its inception, milestones, and achievements. It features both mission (short-term goals and driving force) and vision statements (long-term growth aspirations). Objectives, such as product development timelines or hiring goals, outline specific, short-term targets for the business.
3. Products or Services Offered
Detail the product or service you’re offering, its uniqueness, and its solution to market problems. Explain its source or development process and your sales strategy, including pricing and distribution channels. Essentially, this section outlines what you’re selling and your revenue model.
4. Market Analysis
- Industry Analysis : Research your industry’s growth rate, market size, trends, and future predictions. Identify your company’s niche or sub-industry and discuss adapting to industry changes.
- Competitor Analysis : Examine main competitors , their unique selling points, and weaknesses. Highlight your competitive advantages and strategies for maintaining them.
- Target Market Analysis : Define your target market , their demographics, needs, and wants. Discuss how and where you’ll reach them and the potential for market shifts based on customer feedback.
- SWOT Analysis : Break down your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Detail your unique attributes, potential challenges, market opportunities, and external risks, along with strategies to address them.
5. Marketing and Sales Strategies
- Marketing and Advertising Plan : Use insights from your target market analysis to decide advertising channels, emphasizing platforms that best reach your audience, like TikTok over Instagram. Develop a concise value proposition to be central to all marketing, detailing how your product addresses specific needs.
- Sales Strategy and Tactics : Define where and how you’ll sell, such as online, in-store, or through direct sales calls. Sales tactics should highlight the customer’s needs, presenting your solution without overly aggressive promotion.
- Pricing Strategy : Decide on pricing based on market positioning, whether you aim to be a discount or luxury option. Ensure prices cover costs and yield profit, and position your product in a manner that aligns with the chosen price range. Justify your chosen pricing strategy in this section.
6. Operations and Management
- Operational Plan : Outline daily, weekly, and monthly operations, specifying roles, tasks, and quality assurance methods. Include supplier details and order schedules, ensuring clarity on key business functions and responsibilities.
- Technology Plan : For tech-based products, detail the development plan, milestones, and staffing. For non-tech companies, describe the technology tools and software you’ll employ for business efficiency.
- Management and Organizational Structure : Define who’s in charge, their roles, and their backgrounds. Discuss your management strategy and forecast the development of your organizational hierarchy.
- Personnel Plan : List current and future hires, specifying their roles and the qualifications necessary for each position. Highlight the significance of each role in the business’s operations.
7. Financial Plan
- Startup Costs : Clearly detail every anticipated cost before starting operations. This will be vital for understanding the initial investment required to get the business off the ground.
- Sales Projections : Estimate monthly sales for the first year, with an annual forecast for the next two years.
- Profit and Loss Statement : An overview of revenue minus costs, resulting in either a profit or loss.
- Cash Flow Statement : Provides clarity on the business’s liquidity by showing cash inflows and outflows over a specific period.
- Balance Sheet : Displays the company’s net worth by detailing its assets and liabilities.
- Break-even Analysis : Understand at which point revenues will cover costs, helping to predict when the business will start making a profit.
- Funding Requirements and Sources : Enumerate the required capital and the sources of this funding. This should also include the purpose for which these funds will be used at different stages.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) : Identify the metrics vital for measuring the company’s performance. Use these indicators to spot challenges, understand where improvements can be made, and pivot strategies as necessary. Ensure that each KPI aligns with the business’s objectives and offers actionable insights for growth.
Remember, although the financial section might seem daunting, it is pivotal for understanding the economic feasibility of your business. Proper financial planning helps in making informed decisions, attracting investors, and ensuring long-term sustainability. Don’t hesitate to engage financial experts or utilize tools and software to ensure accuracy and comprehensiveness in this section.
8. Appendices
The appendices section of a business plan is a repository for detailed information too extensive for the main document. This can include resumes of key personnel, full market research data, legal documents, and product designs or mockups. By placing this data in the appendices, it keeps the main plan concise while allowing stakeholders access to deeper insights when needed. Always ensure each item is clearly labeled and referenced at the relevant point in the main document.
As you can see, business models and business plans have some similarities, but in the main they are quite different. Your business model explains the foundational concept behind your business, while a business plan lays out how you’ll put that model into action and build a business.
When you’re starting a business, it’s best to have both, as the work of getting them done involves learning about your business from every angle. The knowledge you’ll gain is likely to be invaluable, and could even be the difference between success and failure.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
Relationship of Finance with Economics, Accounting, Management, and Marketing

Finance is an integrated part of overall management and is not a very independent area. It draws heavily on related disciplines and fields of study, such as economics, accounting, management, and marketing. Although these disciplines are interrelated, there are critical differences among them.
Relationship Between Finance and Economics
Finance and economics involve the allocation and use of resources, decision-making, the study of markets and economic systems , and the use of models and analysis.
Economics is the study of how men and society choose with or without the use of money to employ productive resources that could have alternative uses to produce various commodities and distribute them for consumption now or in the future among multiple people and groups in society.
While finance is specifically concerned with the allocation and use of financial resources, economics is more broadly concerned with the allocation and use of resources.
Relationship Between Finance and Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is concerned with the overall financial environment in which the firm operates.
Economics is also concerned with financial structure, money and banking system, money and capital market, financial intermediaries, and monetary and fiscal policies.
Financial managers recognize and understand how monetary policy affects the cost and availability of funds.
Financial managers beware of the various institutions and are versed in fiscal policy and its effects on the economy.
The financial manager should understand economic activity and the economic policy for decision-making.
Relationship Between Finance and Microeconomics
Finance is concerned explicitly with the allocation and use of financial resources. Microeconomics is concerned with allocating and using resources at the individual and firm.
Supply and demand relationships and profit maximization strategies . A mix of productive factors relates to optimum sales level and product pricing . Measurement of utility preference and risk determines the value. Rational depreciation will permit the achievement of the assets.
Financial decisions are made based on comparing marginal revenue and marginal cost, which increases the firm’s profit.
So, the field of finance is closely related to economics. Moreover, finance is the applied subject of economics.
Relationship Between Finance and Accounting
Accounting is an information system that identifies records and communicates the economic events of an organization to interested users.
Finance and accounting are closely related fields that both involve the management of financial resources, the use of financial statements , decision-making, financial planning, the analysis of financial data, the management of accounts payable and accounts receivable, the management of cash flow , compliance with laws and regulations, risk management, and communication.
There are three activities in accounting, such as;
- Identify economic events,
- record and provide financial activities, and
- Communicate to interested users.
Finance uses the data collected by accounting.
The purpose of accounting is the collection and presentation of financial data .
The financial manager uses accounting information for financial decision-making. The firm’s finance (treasurer) and accounting (controller) activities are closely related.
Accounting and finance are related to the emphasis on cash flows and the other to decision making.
Accounting is an essential input in financial decisions.
The accounting function is a necessary input into the finance function. Accounting generates information relating to the operations of the firms . The financial manager makes fund statements from income and financial statements .
Financial statement assists financial managers in evaluating past performance and future planning.
Accounting helps financial managers.
The Finance (treasurer) and accounting (controller) activities are typically within the control of the Chief Financial Officer (CFO)/ Vice President (Finance). Small firms’ controller (Accounts Manager) often performs the finance function.
The firm would be financially profitable in an accounting sense.
Relationship Between Finance and Management
Management is a set of activities directed at an organization’s resources to achieve organizational goals efficiently and effectively.
The relationships of finance with management are discussed below:
Financial Planning and Management Decisions
Financial policies will be devised to fit the management decisions of a firm in practice. The finance function of raising and using funds has a significant effect on other functions of management .
Management involves financial planning and analysis. The financial manager is the decision-maker of the firm. Finance uses planning , decision-making , control , and other management tools. Buying new machines or assets on an investment project affects the flow of funds .
Finance helps with day-to-day management operations.
Finance provides the funds that will be used in business . It requires payment of salaries and other benefits involving finance. Identifying the constraints of funds for the manager running the business is necessary.
- Financial advice and guidance: Finance professionals provide financial advice and guidance to management departments to help them make decisions about all business operations.
- Financial data and analysis: Financial data and analysis help management understand the business’s financial performance and make informed decisions about strategy and resource allocation.
- Developing budgets and forecasting financial performance: Finance can help develop budgets and forecast financial performance , which can help management make informed decisions about resource allocation and identify potential risks and opportunities.
Finance helps to maintain the day-to-day management operations by providing financial data and analysis, developing budgets, managing accounts payable and accounts receivable , managing cash flow, and providing financial advice and guidance.
Measuring The Performance of The Management
Finance provides financial data and analysis to support decision-making and resource allocation, while management is responsible for setting goals , making decisions, and allocating resources to achieve those goals.
Both finance and management monitor and measure the performance of an organization. Finance provides financial metrics such as profitability and returns on investment ( ROI ), and management is responsible for tracking and analyzing other performance indicators such as customer satisfaction and employee engagement.
Finance and management are closely related functions that work together to ensure the success and sustainability of an organization.
The decisions are made based on their financial effects on the firm’s overall value. Finally, the tools and techniques of management help analyze complex financial management problems.
Relationship Between Finance and Marketing
Finance and marketing are two different business areas, but they are closely related and often intersect.
Finance is concerned with managing a company’s financial resources, including the planning, acquiring, and managing financial assets such as cash, investments, and credit. Finance also involves creating and analyzing financial statements, budgeting, and forecasting.
On the other hand, marketing is concerned with promoting and selling products or services. It involves researching , understanding customer needs and preferences , developing marketing campaigns and strategies to reach and engage potential customers , and analyzing and tracking the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
Marketing is a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want by creating, offering, and exchanging value products with others .
Finance draws the decisions on supportive marketing methods.
Financial managers consider the impact of product development and cash flows from marketing.
Changes in the marketing process may necessitate capital expenditures, which the financial manager must evaluate and finance. There exists an inseparable relationship between the functions of finance and marketing.
Marketing activities directly or indirectly involve the use of finance.
The finance department provides the necessary funding for marketing campaigns through internal budget allocation or external funding sources. Marketing, advertising, and promotion activities affect financial resources.
Marketing and finance functions are made to maximize the profit and wealth of the firm.
Marketing and finance functions to maximize the profit and wealth of a firm .
When the marketing functions end, the finance functions begin. The financial policies will be devised to fit the firm’s marketing decisions.
Developing effective marketing strategies
Marketing can help identify target customers and develop strategies to reach them effectively, such as through advertising, social media, or content marketing. This can help increase sales and revenue, which can ultimately contribute to the profitability and wealth of the firm.
Managing expenses and maximizing the ROI of marketing strategies
Finance can help manage expenses and ensure that marketing campaigns are cost-effective, maximizing the return on investment (ROI). Carefully tracking and analyzing the results of marketing campaigns, finance identifies the campaigns that are the most effective in driving sales and revenue.
Both marketing and finance can work together to allocate resources effectively, ensuring that the right resources are used effectively to achieve the desired results.
Marketing and finance must collaborate to analyze market trends and identify opportunities for growth and expansion. This can involve identifying new customer segments or entering new markets, which can help increase sales and revenue.
Marketing and finance work together to manage risk , identify potential business threats, and develop contingency plans to address them. This can help protect the profitability and wealth of the firm.
Overall, marketing and finance can work together to maximize the profit and wealth of a firm by developing effective marketing strategies, managing expenses and maximizing ROI, allocating resources effectively, analyzing market trends, and managing risk.

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

What Is the Difference Between a Business Plan and an Operating Plan?
Related blogs.
- An overview of the business plan writing process
- The Benefits of Adapting to New Technology
- The Pros and Cons of Social Media Marketing
- Creating a Human Resources Plan
- Crafting a Compelling Executive Summary
Introduction
Starting a business requires careful planning and preparation. You need to create a plan to ensure successful operations in the future. Two key elements of your business plan are a business plan and an operating plan. Understanding the differences between the two is the key to creating an effective business plan.
A business plan is a written document that describes your business, its objectives, strategies, market analysis, and financial forecasts. It is created to provide a roadmap and set goals for the future. Business plans also outline potential risks, strategies, and key personnel to reach expected business goals.
An operating plan is focused on actions, priorities, guidelines, and logistics. It is a document that outlines the steps and processes the company must take to meet its objectives. An operating plan is often set in place to track progress, measure outcomes, and make adjustments where necessary.
This blog post will provide an overview of the differences between a business plan and an operating plan, as well as the key elements of each. It will discuss how to create an effective business plan using both documents.
Differences Between a Business Plan and an Operating Plan
When discussing business plans and operating plans, many people consider them to be one and the same. However, there are some distinct differences that separate these two kinds of plans. Understanding the purpose and differences of each is vital for any business proprietor to run their venture in a successful and timely manner.
Different Scope
A business plan typically looks at the big-picture goals of the company and examines where the company could be by a certain timeframe. It is often used for marketing purposes or for the synthesis of external and internal analysis to review the business and its goals. On the other hand, an operating plan focuses on much more immediate objectives and goals. Instead of discussing potential chances for the future, an operating plan looks at actions that need to be done within a few weeks or months.
Different Timeframe
A business plan often looks at upcoming opportunities over a 1-5 year span. This can be extremely beneficial to businesses in order to stay competitive in the market and compare their performance to previous years. Conversely, an operating plan focuses on what needs to happen within the next 1-3 months in order to be in compliance with those goals that have been set in the business plan. As a result, the timeframe for an operating plan is much shorter than that of a business plan.
Different Audience
The main purpose of a business plan is to attract investors who can provide the resources needed to start and sustain a business. As such, the business plan should be tailored to the investors who are being courted. An operating plan, however, is designed to keep internal teams on track to fulfill the goals and objectives of the business plan. The audience of an operating plan is generally the employees in the particular organization.
Overall, understanding the differences between a business plan and an operating plan is key for any business whether it is large or small. Each of these plans serves an important purpose and, when executed properly, can be the difference between success and failure for a business.
Components of a Business Plan
A business plan is a written document that defines a business’s goals, strategies and potential opportunities. It is comprised of several key components that provide direction and outline the action plan of a business. These components are essential for the success of a business and need to be structured in a logical and concise manner in order for a business to operate effectively.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is a concise overview of the key points in a business plan. It presents the major goals and objectives that a business hopes to achieve and the strategies it plans to implement in order to reach those goals. It should be brief, but comprehensive, so as to provide the reader with a clear and accurate understanding of the contents of the plan.
Business Overview and Mission Statement
The business overview and mission statement provide an insight into the purpose and the intentions of the business. It outlines what the business stands for, the values and ideals it follows, and the level of achievement it strives to achieve. It will usually elaborate on the type of customer service, quality of products, services, pricing and market values.
Market Analysis
The market analysis gives an insight into the industry and customer base. It will often include competitor analysis, customer profiles and estimated customer reach. The analysis results will influence product design, pricing tactics, advertising strategy, and overall marketing plans.
Products and Services
The products and services section will provide a detailed description of the range of products and services that a business offers. It should include information such as cost, target customer groups and brand positioning. It will also outline the various promotional methods and strategies that a business plans to use to increase visibility and customer awareness.
Management Team
The management team is responsible for the delivery of the plan. It will provide details about the individuals who are responsible for the running of the business. It includes information about their expertise, experience and their roles and responsibilities within the business.
Financial Projections
The financial projections will provide an estimation of the potential profitability and cash flow of the business. It will typically include income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements and a detailed breakdown of the expenditure structure. The financial projections should be based on realistic assumptions and be regularly monitored and updated.
The Components of an Operating Plan
An operating plan is an important document that outlines the strategy and goals of the organization. It evaluates the resources required, considers potential risks and includes a plan for long-term financial growth. It serves as a blueprint for accurate goal setting, financial and operational decisions and puts into motion the development of the company's products or services. In comparison, a business plan is an essential document used by organizations to attract capital and will present details about the company's background and its proposed products or services.
An operating plan is comprised of several components. Here's an overview of the key areas that it covers:
Organizational Strategy
The organizational strategy within an operating plan sets the direction and goals for the company. It explains how it plans to achieve those goals and involves defining the organization's vision, mission and core values. Additionally, it outlines different strategies for reaching the company’s goals that are based on the internal and external environment of the business.
Performance Goals
Performance goals laid out in an operating plan are specific, attainable and measurable. These should evaluate the performance of the organization on a regular basis to ensure that objectives are being met. The performance goals should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure they still fit with the organization’s strategy and vision.
Resource Plan
An operating plan should include the measures necessary to implement the organization’s strategy. This includes assessing what resources are required, such as capital, technology, personnel and buildings. The plan should also outline how these resources can be obtained and used to meet the organizational goals.
Financial Plan
A financial plan should be included in an operating plan to ensure that investments are made wisely and set the company up for long-term success. The financial plan should cover short-term plans, such as a budget, as well as long-term objectives, such as liquidity, sales, financial forecasting and cash flow. Capital requirements should also be outlined, such as how capital can be obtained from investors and lenders.
Risk Management Plan
An operating plan should include strategies for identifying and managing potential risks. This involves considering internal risks, such as employee changes, as well as external risks, such as economic, political and legal. The risk management plan should include a process for risk assessment and the steps that need to be taken to minimize or avoid identified risks.
How to Choose Between a Business Plan and an Operating Plan
Deciding whether to use a business or an operating plan (or both) ultimately depends on the nature of your business and the desired outcome. Below are some considerations for choosing between the two plans.
Consider the Stage of Your Business
When considering which plan to use, it’s important to think about where your business is in its life cycle. While both plans contain long term objectives, a business plan is typically used to launch or grow a new venture and includes projections for the future. An operating plan, on the other hand, is used for businesses that are already stable in order to maintain the current level of performance. So the choice between the two will depend on whether your business is just getting started or successfully operating.
Consider the Level of Granularity Needed for Objectives
When analyzing whether to go with a business or an operating plan, it is also important to consider the level of granularity needed to meet the desired objectives. A business plan generally outlines more abstract concepts such as the value proposition and competitive advantages of a business. An operating plan, however, is more prescriptive in that it seeks to define the specific steps needed to achieve success on the day to day. This could include tasks such as developing a sales strategy, marketing plan, and financial forecasting. Based on your desired outcome and the level of granularity needed, one of the plans may be a better fit for you.
Consider the Timeline for Each Plan
Another factor that should be taken into account is the timeline for each plan. A business plan typically has a longer horizon and contains more abstract goals that can span multiple years. An operating plan, however, is more short-term in nature, focusing on actions that need to be taken in order to achieve success over the next 12 months. Based on the timeline of your objectives, one of the plans may be more suitable than the other.
Ultimately, it is important to take the time to carefully consider the needs of your business when determining which plan to use. Considering factors such as the stage of the business, desired level of granularity, and timeline for goals will help you to make the best decision.
Key Takeaways
A business plan and an operating plan are two different types of plans for businesses. Understanding the differences between them is essential to achieving success in the business world.
A Business Plan
A business plan typically provides an overview of the overall strategy and goals of a business. It outlines the big-picture vision and strategy of the company and is targeted to potential investors or partners. Generally, a business plan is an in-depth look at a business’s background and goals, and includes information such as the executive summary, key strategies, marketing plans, and financial projections.
An Operating Plan
An operating plan differs from a business plan in that it focuses on the day-to-day operations of a business. It provides a detailed look into the day-to-day functioning and processes that are necessary for the company to operate. Operating plans are targeted more internally to management and the company’s employees. An operating plan can include tasks and deadlines, processes, staffing and resource plans, budgeting, and more.
Choosing Between a Business Plan and an Operating Plan
When deciding between which plan to use, consider the stage of your business, the level of granularity needed for objectives, and the timeline for each plan. For example, if your business is just starting out, it would make sense to focus on creating a business plan that outlines your overall strategy and goals. Conversely, if your business is established and running, an operating plan would be better for detailing the day-to-day operations of the business.
When starting or running a business, it is essential to be aware of the difference between a business plan and an operating plan. This blog post aimed to provide a comparison between the two plans, highlighting their importance in the context of businesses.
A business plan outlines the necessary steps to ensure the success of a company. It usually covers topics such as the company’s mission, target market, organizational structure, and competition. It can also feature a financial plan and projected income statements. In contrast, an operating plan is focused on the day-to-day operations of the business. It establishes the policies, procedures, and guidelines that the business should adhere to in order to reach the short and long-term goals set in the business plan. An operating plan can cover topics such as employee duties and responsibilities, budgeting, and marketing strategies.
In conclusion, business plans and operating plans are both important for the success of businesses. However, they serve different purposes, and it is important to understand the differences between the two in order to ensure the success of the company.

Fundrising Ready
MAC & PC Compatible
Immediate Download
Related Articles
The surprising truth about profitability in the appliance store industry: a deep dive into the numbers, why investing in an alcohol treatment center is more profitable than you think, counting the profits: a closer look at the profitability of accounting agencies, the art of boosting profits in your a la carte restaurant: a comprehensive guide, airbnb: unpacking the profitability of one of the world's most successful companies., the untold story of how car washes are making a fortune: discover the profit potential today, pedaling to profit: unveiling the lucrative world of bicycle couriers, thirsty for success discover the untapped profit potential of running a beer bar, the beauty within profits: discovering the lucrative world of beauty salons, unlocking the profit potential: how to make your beach hotel more profitable, leave a comment.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The linear approach involves creating a business plan in a step-by-step manner, following a predetermined sequence. This approach ensures a logical flow of information and makes it easier for readers to understand the interconnections between different sections, especially when detailing a comprehensive financial plan. By presenting information ...
The financial section of your business plan determines whether or not your business idea is viable and will be the focus of any investors who may be attracted to your business idea. The financial section is composed of four financial statements: the income statement, the cash flow projection, the balance sheet, and the statement of shareholders ...
6. Financials. The financial section of your business plan is critical, especially if you want to circulate the plan to investors or lenders. The purpose of this section is threefold: to 1) outline your business's financial plan, 2) demonstrate your profit potential, and 3) share your financing needs.
Sections of the Business Plan. Though formats can vary, a business plan generally includes the following sections: executive summary, description of proposed business, industry analysis, mission statement and core values, management plan, goods or services and (if applicable) production processes, marketing, global issues, and financial plan.
An example of a financial plan in Excel format. As explained above, a financial plan is an element of every business plan. A financial plan can take different forms (charts, tables) yet should always at least show the projection over a certain period (3- to 5-year usually) of the 3 financial statements.A financial plan should also include some historical data (if any).
Use the numbers that you put in your sales forecast, expense projections, and cash flow statement. "Sales, lest cost of sales, is gross margin," Berry says. "Gross margin, less expenses, interest ...
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
The financial plan should illustrate the plan you have for the business in terms of numbers. It should include precise financial projections of what you think can be achieved. It should clearly illustrate your cashflow management strategy. And it should summarize the information clearly.
An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
It will also improve the relationship between finance and business managers, as finance will have more time to provide better service. 2. Move from monthly variance reporting to KPIs and dashboards. Most companies manage through annual budgets and use monthly variance reporting as the primary feedback mechanism for managers.
The Purpose and Goals of the Strategic plan and the Business plan. Strategic plans and business plans are both essential tools for any organization. They provide a clear roadmap for achieving goals and ensuring long-term success. While the two plans are similar in some ways, they serve different purposes and have different goals.
First, let's look at the difference between a business and a strategic plan. For review: A business plan covers the "who" and "what" of the business. The strategic plan gives us long-term goals and explains "how" the business will get there, providing a long-term view. In broader terms, the business plan tells us who by showing us:
Your business model is just a description of how your business will generate revenue. In other words, it's a snapshot of the ways your business will be profitable. Writing a business plan is one way of explaining a company's business model. The business model canvas takes a different approach. A business model canvas is a one-page template ...
Business Plan Overview. Most business plans have several distinct sections (Figure 5.1.5.1). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we'll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan.
Strategic plans constitute the basis of operations and responsibilities within the business. These plans lay the paths out for each member of the organization to follow and define the functional outline and the key outcomes for every project and process within the business. A strategic plan goes on to define the operations and their outcomes ...
A business model is the foundation of any business idea; it basically outlines how the concept offers value and potential for growth. Essentially, a solid business model ensures that the business will make money. A business plan, on the other hand, is the business owner's plan to put that model into action. It's much more detailed and ...
The finance function monitors changes happening internally, within the business, and externally, outside the business. It then observes the impact of these changes on the finances of the business ...
Relationship Between Finance and Accounting. Accounting is an information system that identifies records and communicates the economic events of an organization to interested users.. Finance and accounting are closely related fields that both involve the management of financial resources, the use of financial statements, decision-making, financial planning, the analysis of financial data, the ...
An operating plan differs from a business plan in that it focuses on the day-to-day operations of a business. It provides a detailed look into the day-to-day functioning and processes that are necessary for the company to operate. Operating plans are targeted more internally to management and the company's employees.