
.

Assignment of Lease
Jump to Section
What is an assignment of lease.
The assignment of lease is a title document that transfers all rights possessed by a lessee or tenant to a property to another party. The assignee takes the assignor’s place in the landlord-tenant relationship.
You can view an example of a lease assignment here .
How Lease Assignment Works
In cases where a tenant wants to or needs to get out of their lease before it expires, lease assignment provides a legal option to assign or transfer rights of the lease to someone else. For instance, if in a commercial lease a business leases a place for 12 months but the business moves or shuts down after 10 months, the person can transfer the lease to someone else through an assignment of the lease. In this case, they will not have to pay rent for the last two months as the new assigned tenant will be responsible for that.
However, before the original tenant can be released of any responsibilities associated with the lease, other requirements need to be satisfied. The landlord needs to consent to the lease transfer through a “License to Assign” document. It is crucial to complete this document before moving on to the assignment of lease as the landlord may refuse to approve the assignment.
Difference Between Assignment of Lease and Subletting
A transfer of the remaining interest in a lease, also known as assignment, is possible when implied rights to assign exist. Some leases do not allow assignment or sharing of possessions or property under a lease. An assignment ensures the complete transfer of the rights to the property from one tenant to another.
The assignor is no longer responsible for rent or utilities and other costs that they might have had under the lease. Here, the assignee becomes the tenant and takes over all responsibilities such as rent. However, unless the assignee is released of all liabilities by the landlord, they remain responsible if the new tenant defaults.
A sublease is a new lease agreement between the tenant (or the sublessor) and a third-party (or the sublessee) for a portion of the lease. The original lease agreement between the landlord and the sublessor (or original tenant) still remains in place. The original tenant still remains responsible for all duties set under the lease.
Here are some key differences between subletting and assigning a lease:
- Under a sublease, the original lease agreement still remains in place.
- The original tenant retains all responsibilities under a sublease agreement.
- A sublease can be for less than all of the property, such as for a room, general area, portion of the leased premises, etc.
- Subleasing can be for a portion of the lease term. For instance, a tenant can sublease the property for a month and then retain it after the third-party completes their month-long sublet.
- Since the sublease agreement is between the tenant and the third-party, rent is often negotiable, based on the term of the sublease and other circumstances.
- The third-party in a sublease agreement does not have a direct relationship with the landlord.
- The subtenant will need to seek consent of both the tenant and the landlord to make any repairs or changes to the property during their sublease.
Here is more on an assignment of lease here .
Parties Involved in Lease Assignment
There are three parties involved in a lease assignment – the landlord or owner of the property, the assignor and the assignee. The original lease agreement is between the landlord and the tenant, or the assignor. The lease agreement outlines the duties and responsibilities of both parties when it comes to renting the property. Now, when the tenant decides to assign the lease to a third-party, the third-party is known as the assignee. The assignee takes on the responsibilities laid under the original lease agreement between the assignor and the landlord. The landlord must consent to the assignment of the lease prior to the assignment.
For example, Jake is renting a commercial property for his business from Paul for two years beginning January 2013 up until January 2015. In January 2014, Jake suffers a financial crisis and has to close down his business to move to a different city. Jake doesn’t want to continue paying rent on the property as he will not be using it for a year left of the lease. Jake’s friend, John would soon be turning his digital business into a brick-and-mortar store. John has been looking for a space to kick start his venture. Jake can assign his space for the rest of the lease term to John through an assignment of lease. Jake will need to seek the approval of his landlord and then begin the assignment process. Here, Jake will be the assignor who transfers all his lease related duties and responsibilities to John, who will be the assignee.
You can read more on lease agreements here .

Image via Pexels by RODNAE
Assignment of Lease From Seller to Buyer
In case of a residential property, a landlord can assign his leases to the new buyer of the building. The landlord will assign the right to collect rent to the buyer. This will allow the buyer to collect any and all rent from existing tenants in that property. This assignment can also include the assignment of security deposits, if the parties agree to it. This type of assignment provides protection to the buyer so they can collect rent on the property.
The assignment of a lease from the seller to a buyer also requires that all tenants are made aware of the sale of the property. The buyer-seller should give proper notice to the tenants along with a notice of assignment of lease signed by both the buyer and the seller. Tenants should also be informed about the contact information of the new landlord and the payment methods to be used to pay rent to the new landlord.
You can read more on buyer-seller lease assignments here .
Get Help with an Assignment of Lease
Do you have any questions about a lease assignment and want to speak to an expert? Post a project today on ContractsCounsel and receive bids from real estate lawyers who specialize in lease assignment.
ContractsCounsel is not a law firm, and this post should not be considered and does not contain legal advice. To ensure the information and advice in this post are correct, sufficient, and appropriate for your situation, please consult a licensed attorney. Also, using or accessing ContractsCounsel's site does not create an attorney-client relationship between you and ContractsCounsel.
Meet some of our Assignment of Lease Lawyers
Kerbis' practice includes business and real estate transactions, estate planning, and limited scope litigation consulting. Mathew has negotiated deals involving multinational corporate franchises and has collectively helped hundreds of clients with their transactional, civil litigation, and appellate legal needs. Throughout his tenure as an American Bar Association leader, Mathew has advocated for legal education reform, interviewed ABA Presidents and State Appellate and Supreme Court Justices, and lobbied Congress on behalf of the legal profession. As a law student, Mathew served as an extern for the Honorable Justice Robert E. Gordon of the Illinois Appellate Court, First District.
Craig E. Yaris is a Managing Partner at Holon Law Partners, with the experience and drive to handle all your Franchise, General Business Practice, and Mediation needs. As a former small business owner and Chief Operating Officer of a franchisor himself, Mr. Yaris is passionate about promoting business growth. He has experience handling daily operations, employee disputes, and negotiations of pertinent contracts for a franchise company with 100 locations in five states, where he organized and conducted semi- annual meetings to educate and inform franchisees of best practices for improved growth. In addition, Mr. Yaris was responsible for the preparation and filing of the UFOC (Uniform Franchise Offering Circular) in several states and is well-versed in business formation. Between his time as Franchisor and Conflict Resolution Specialist, Mr. Yaris was the Co-Founder and Chief Operating Officer of an online company whose goal was to help inform marketers and business owners of the fast-paced and ongoing changes within their specific verticals. This experience helped him hone his research and writing skills and prepared him for the cloud-based aspects of Holon Law Partners. Mr. Yaris also has extensive experience in public speaking, as he has planned and delivered several keynote addresses and educational seminars for many New York-based organizations, and as a Continuing Education Instructor for Hofstra University. Prior to joining Parlatore Law Group, Mr. Yaris worked as a Patient Advocate, and more recently, a Conflict Resolution Specialist, where he mediated and resolved disputes on behalf of patients with insurance companies. In this role, he negotiated for coverage of previously denied medications and medical procedures as well as successfully mediated disputes between individuals and business partners which would have otherwise resulted in protracted litigation. In addition, he has experience mediating employer and employee disputes as well as helping resolve family conflict. He has also studied and attended many Non-Violent Communication (NVC) workshops and strives to bring these tools and methods to all of his mediations. His variety of experiences speak to his ability to handle small business needs at all stages of business growth and development. Mr. Yaris also has experience with business growth and development, as he has worked with several small business on creating and implementing strategies for steady growth. In addition, to spending time with family, Mr. Yaris volunteers his time helping spread the message of the ACLU and he supports many local charities focused on families and children. He is admitted to practice in New York.
15 years for legal experience; expertise in contracts, healthcare, ERISA, physicians, financial services, commercial contracts, employment agreements, etc. I am adept at all contracts and can provide you with efficient and quality services. I have worked at a law firm, financial services company, consulting ,and non-profit.
In his firm, Talented Tenth Law, Antoine focuses on helping people maximize their protection and prosperity in the courtroom and the boardroom. His firm’s services include representing people in lawsuits involving breach of contract, many types of civil lawsuits and helping business owners win government contracts among other things.
Tom is a former chief legal officer of public and private companies. He has extensive experience in mergers & acquisitions, commercial transactions, joint ventures, finance, securities laws and general corporate law across a broad range of industries, including construction, consumer products, e-commerce, energy and healthcare. As an attorney who practiced at two different Top 50 international law firms, he can deliver "Big Law" service at a competitive price. Prior to becoming a lawyer, Tom served as an officer in the U.S. Army and attained the rank of Captain. He served a tour in Iraq where he led a reconnaissance platoon and was awarded the Bronze Star Medal.
Amy has served as outside general counsel and litigator to established businesses throughout western Washington since 2010. Her passion and focus is providing the best possible representation for clients in the construction, transportation and hospitality industries.
I am bar certified in the lovely state of Missouri. I received my J.D. from The University of Iowa College of Law (2019) and my B.A. in Political Science from BYU-Idaho (2015).
Find the best lawyer for your project
Contract to lease land from a church.
I’m planning on leasing land from a church. Putting a gym on the property. And leasing it back to the school.
Ok; first step is that you will need a leasing contract with the church. Ask them to prepare one for you so you would just need an attorney to review the agreement and that should cost less than if you had to be the party to pay a lawyer to draft it from scratch. You need to ensure that the purpose of the lease is clearly stated - that you plan to put a gym on the land so that there are no issues if the church leadership changes. Step 2 - you will need a lease agreement with the school that your leasing it do (hopefully one that is similar to the original one your received from the church). Again, please ensure that all the terms that you discuss and agree to are in the document; including length of time, price and how to resolve disputes if you have one. I hope this is helpful. If you would like me to assist you further, you can contact me on Contracts Counsel and we can discuss a fee for my services. Regards, Donya Ramsay (Gordon)

Quick, user friendly and one of the better ways I've come across to get ahold of lawyers willing to take new clients.
How It Works
Post Your Project
Get Free Bids to Compare
Hire Your Lawyer
Real Estate lawyers by top cities
- Austin Real Estate Lawyers
- Boston Real Estate Lawyers
- Chicago Real Estate Lawyers
- Dallas Real Estate Lawyers
- Denver Real Estate Lawyers
- Houston Real Estate Lawyers
- Los Angeles Real Estate Lawyers
- New York Real Estate Lawyers
- Phoenix Real Estate Lawyers
- San Diego Real Estate Lawyers
- Tampa Real Estate Lawyers
Assignment of Lease lawyers by city
- Austin Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- Boston Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- Chicago Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- Dallas Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- Denver Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- Houston Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- Los Angeles Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- New York Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- Phoenix Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- San Diego Assignment of Lease Lawyers
- Tampa Assignment of Lease Lawyers
Contracts Counsel was incredibly helpful and easy to use. I submitted a project for a lawyer's help within a day I had received over 6 proposals from qualified lawyers. I submitted a bid that works best for my business and we went forward with the project.
I never knew how difficult it was to obtain representation or a lawyer, and ContractsCounsel was EXACTLY the type of service I was hoping for when I was in a pinch. Working with their service was efficient, effective and made me feel in control. Thank you so much and should I ever need attorney services down the road, I'll certainly be a repeat customer.
I got 5 bids within 24h of posting my project. I choose the person who provided the most detailed and relevant intro letter, highlighting their experience relevant to my project. I am very satisfied with the outcome and quality of the two agreements that were produced, they actually far exceed my expectations.
Want to speak to someone?
Get in touch below and we will schedule a time to connect!
Find lawyers and attorneys by city
- About Office News
- Office Help
- Offices.net Scholarships
- Offices.Net Home
A Full Guide to Commercial Lease Assignment (Lease Transfer)

Dealing with a fixed-term lease agreement and looking to move offices or downsize? The topic of commercial lease transfer can be confusing to navigate, particularly when you are unsure of your rights and obligations under the lease.
If you’re renting a commercial property, you signed a contract at the beginning of your tenancy called a lease agreement , which contains all the details of your rights and obligations while occupying and conducting business operations at the commercial property. Your agent is required by law to give you a copy of the lease agreement if you don’t already have one.
The following article will serve as a full guide to commercial lease assignment, providing business owners with an overview of the legal considerations and elements required for an assignment of lease.
- 1 What is a Commercial Lease Assignment?
- 2 Current Market Conditions Boosting Lease Transfers and Flexible Arrangements
- 3 What is the Difference Between Commercial Lease Assignment and Subleasing?
- 4 Why Would You Want to Transfer a Lease?
- 5 How to Go About Transferring Your Commercial Lease
- 6.1 Goals and obligations of the original lessee and new tenant
- 6.2 Starting date of lease assignment
- 6.3 Pitfalls and consequences
- 7.0.1 Further Insights
What is a Commercial Lease Assignment?
Also known as a lease transfer, a commercial lease assignment involves a tenant transferring all of their interests and rights in a lease to a new party. This new tenant will take on the responsibilities of the existing lease, including rent and any other obligations, leaving the original tenant free to exit the agreement.
Commercial lease assignment often occurs when tenants want to leave their commercial property prior to the end of a fixed-term agreement. This often happens when a business quickly needs to upsize or downsize their space, move to a new city, or go out of business.
State law dictates whether tenants require their landlord’s consent prior to transferring a lease or subletting a part of their space. However, most lease agreements will clearly outline full transfer provisions prior to being signed and, whilst it is possible for lease assignment to be forbidden, the vast majority of agreements allow for transfers.

Current Market Conditions Boosting Lease Transfers and Flexible Arrangements
There has been a marked increase in the number of lease transfers and sublets of commercial properties in recent years, largely as a result of increased instances of remote work and downsizing seen across multiple industries. This reduced need for workspace has persisted, as many workers have continued to show a preference for remote and hybrid work arrangements if and when suitable.
Changing employee priorities have forced many businesses to reconsider their existing lease agreements, resulting in an increase in both commercial lease assignments and sublease agreements .
Landlords have adapted their offerings in the face of this changed market demand. Many are now offering flexible, month-to-month leases, allowing tenants to rest easy knowing that they won’t be stuck in a long-term lease agreement if their situation changes.
However, in the case of premium office spaces in highly sought-after locations or warehousing facilities close to major transport links, traditional leases are still very much the norm. In these cases, landlords may have realized that fully reconfiguring their offerings for flexible-usage is financially unrealistic. This may be due to a number of factors, including high-levels of existing demand for traditional leases, the saturation of the flexible workspace market, and the requirements of their typical target tenants.
So, if you’re leasing long-term commercial property and need out of the agreement, or at least to downsize, a lease transfer is a great solution that can leave all contracted parties satisfied.

What is the Difference Between Commercial Lease Assignment and Subleasing?
A commercial sublease, which is a type of lease transfer, occurs when a tenant who currently leases property agrees to let another tenant use the space concurrently. The agreement involves all three parties: the original tenant, the new tenant, and the property owner.
When you sublease your space, you become the sub-lessor (or sub-landlord), and your new tenant is now the sublessee (or subtenant). Your agreement with them will normally allow them to reside in your space – or a specified portion of it – for either the remaining term of your lease or some other pre-determined length of time.
It’s important to keep in mind that, as the original lessee, you’re still liable and responsible for making monthly lease payments on a sublet agreement. Therefore, you must collect rent from your subtenant each month while continuing to make rental payments directly to your landlord.

Why Would You Want to Transfer a Lease?
Lease transfers can be done to adjust the leased property size and monthly rent. A business owner may decide that they need to upsize or downsize their leased premises prior to the end of their original lease term.
Also, a lease transfer may be sought because the current tenant wants to vacate the rental property entirely, with no plans to lease elsewhere. This may be due to outside factors (e.g. a global pandemic) or the forced closure of a business.
A lease transfer, or a sublease arrangement, may also be desired so that two businesses with complementary strengths can share a workspace and mutually benefit from their operational proximity. No matter how complementary the proposed new tenant is to the existing tenant, this new business relationship will require the landlord’s permission (unless they have been given prior written consent providing them with sole discretion over subletting)
How to Go About Transferring Your Commercial Lease
The only necessary requirement for lease transfer is to identify a new lessee. In the vast majority of cases, your landlord cannot deny your request for a lease transfer unreasonably , yet it’s still in your best interest to find a new tenant with an established rental history and who can financially afford the rent on time. The only situation in which a commercial landlord can instantly deny a lease transfer request is if this provision was established in the initial lease agreement, however, this type of provision will often scare off prospective tenants.
If you’re looking to transfer your lease, most agents will request that the new tenant apply as if they were renting any other property as a primary lessee. Be sure that, in addition to their application , the prospective tenant provides documentation like company financials and past rental receipts to support your transfer request. This way, there’s no doubt of their ability to be a reliable tenant.
If you wish to transfer your lease, you must have written consent from your landlord – mere verbal agreement will not suffice. Without your landlords’ express permission in writing, any attempted transfer of lease will be considered null and void. You will then need to fill out a lease assignment agreement, outlining the proposed assignee, current tenant, landlord, and existing lease term.

Important Things to Keep in Mind
To avoid any unnecessary stress or surprises, it helps to understand your rights and responsibilities before beginning the commercial lease transfer process.
Goals and obligations of the original lessee and new tenant
When considering a lease transfer, it is crucial to first identify the goal you hope to achieve through this deal. Most commercial leases have restrictions on transferring the lease, so before beginning any negotiations, all rights and obligations of the involved parties must be closely analyzed. If everyone’s interests are clear from the start, then agreement upon terms should run much more smoothly.
Starting date of lease assignment
In most cases , tenants need to pay their rent a month before move-in date. Confirm that the party being assigned the lease understands when they are responsible for making their first rent payment, so there are no delayed payments. This is also important for sublease agreements, because existing tenants are often liable for any missed rental payments made by the sublessee.
Pitfalls and consequences
Depending on the terms of the lease transfer and the legal documentation, the original lessee may find themselves responsible for any actions or defaults of the new leaseholder.
As commercial leases often last several years, this could result in a heavy financial burden and significant legal consequences. Careful negotiation at the outset will always lead to a more positive outcome, so it’s important to tick all appropriate procedural and legal boxes when pursuing a commercial lease assignment.

Wrapping up
Before you begin subletting or transferring/assigning a lease, be sure that you understand the objectives of both parties and identify the correct method of altering the lease. Both lessors and lessees should also review all clauses in the lease and negotiate based on everyone’s incentives and interests. If there is any confusion about preparing or reviewing documents related to this process, it’s important to consult with legal advisors for the sake of all parties concerned.
Further Insights
Looking for more articles about the US office market and general office matters? You can find a number of recent posts below! Alternatively, if you’re a business or freelancer looking for flexible workspace in the US, we can help to connect you to a wide range of serviced offices and coworking spaces in highly sought-after locations such as New York City , Los Angeles , Houston , Atlanta , Miami , Chicago , and Dallas . You can also call us to have a discussion about your requirements on 972-913-2742 .
Miami Office Market Report | Q2-Q3 2022 Mid-2022 Las Vegas Office Market Report The Impact of Proptech on Commercial Real Estate 15 In-Person Employee Recognition Ideas for the New World of Work Mid-2022 Houston Commercial Real Estate Market Report Coworking Space for Students on U.S. College Campuses How the Decentralization of Cities Has Changed the U.S. Office Space Market US Office Market Trends 2022 – Statistics, Challenges and Outlook January 2022 – U.S. National Office Market Report The Great Resignation or the Great Retention? How Employers Yield the Power Heading into 2022 5 Ways to Create a Great Office Culture
Tags: 2022 , commercial lease assignment , commercial property , guides , landlords , lease transfer , Office Space , subleasing , tenants This entry was posted on Tuesday, November 8th, 2022 at 8:46 am and is filed under 2022 , Business Advice , Leases , Office Talk .
A little something about you, the author. Nothing lengthy, just an overview.
Top Business Locations
- Atlanta, GA
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- Manhattan, NY
- San Francisco, CA
Recent News
- Commercial Real Estate Depreciation – How Does It Work?
- NYC Office Space Rental: A Cost Analysis
- Cost of Office Space in San Francisco vs LA Office Rental Prices
- Mixed-Use Commercial Property: What You Need to Know
- 8 Benefits of In-Person Meetings: Meeting in Person vs Online
- September 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- February 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- August 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- October 2019
- February 2017
- January 2017
- November 2016
- October 2016
- February 2016
- January 2016
- November 2015
- October 2015
- August 2015
- February 2015
- January 2015
- November 2014
- October 2014
- September 2014
- August 2014
- December 2013
- February 2013
- October 2012
- September 2012
- August 2012
- February 2012
- November 2010
- February 2010
- December 2009
- October 2009
- September 2009
- August 2009
- February 2009
- January 2009
- November 2008
- October 2008
- September 2008
- Atlanta (4)
- Best Cities for Business in the USA (15)
- Brooklyn (1)
- Business Advice (50)
- Business Districts (11)
- Business Spotlights (15)
- Business Start Ups (18)
- California (12)
- CBD's (5)
- Chicago (5)
- Christmas (2)
- Cities & States (24)
- Companies (3)
- Company Relocation (4)
- Conferences (2)
- Corporate Entertainment (3)
- Corporate Retreats (1)
- Coworking Space (2)
- Eco Matters (2)
- Employee Recognition (1)
- Employee Rights (6)
- Employment and Worklife (11)
- Employment Regulations (7)
- Entrepreneurs (5)
- Environment (1)
- Famous People (1)
- Finance & Tax (2)
- Florida (3)
- Georgia (2)
- Houston (4)
- Illinois (3)
- Landmarks (2)
- Las Vegas (2)
- Los Angeles (7)
- Manhattan (6)
- Market Overviews (6)
- Meetings (7)
- Mixed Use Property (1)
- Mixed-Use Office Space (1)
- National Market Reports (1)
- New York (12)
- North Carolina (1)
- Office Amenities (1)
- Office Etiquette (14)
- Office Health (9)
- Office Organization (18)
- Office Planning (3)
- Office Relations (21)
- Office Renovation (3)
- Office Rental (3)
- Office Space Forecasts and Trends (18)
- Office Space Options Series (8)
- Office Talk (35)
- Office-code-of-conduct (3)
- Orlando (1)
- Philadelphia (1)
- Presentations (3)
- Real Estate (8)
- Remote Workers (3)
- Salary Expectations (1)
- San Francisco (5)
- Seattle (2)
- Skyscrapers (1)
- Subleasing (1)
- Technology (3)
- Tourism (3)
- Trends and Statistics (21)
- Uncategorized (4)
- Virtual Offices (2)
- Washington (4)
Copyright © 2000 - 2024. All Rights Reserved. About Offices.net Privacy Policy Contact Us Commercial Real Estate

Subletting vs. Assigning a Commercial Lease
Your step-by-step guide to subleasing and assigning commercial real estate.
- Commercial real estate laws vary by state, so it's crucial to understand your legal entitlements and the terms of your Commercial Lease Agreement.
- When assigning a lease, a business tenant may still be liable for the property unless they obtain a formal release.
- Subleasing provides flexibility, but it also adds responsibilities such as managing the subtenant.
Table of Contents
Subleasing commercial property, steps to subleasing commercial property, assigning a commercial lease, steps to assigning a commercial lease, should you sublet or assign a commercial lease, related documents.
- COMMERCIAL LEASE AGREEMENT
- COMMERCIAL SUBLEASE AGREEMENT
- LEASE ASSIGNMENT
- You are able to quickly transfer partial rights of a commercial property to save money on rent expenses. This will prevent you from breaking a lease term, or having to pay out the remainder of the lease.
- You get to be flexible in your sublease contract.
- If you are sharing a space, you may benefit from shared resources or customers, networking, reduced carbon footprint, and workplace diversity.
- You may be adding to your workload by managing a tenant, in addition to your own landlord-tenant relationship.
- You are liable to the landlord for damages or lease violations that occur from the sublease.
- If you need to relocate or downsize your business, or you're simply unable to pay your rent, assignment can relieve you of your lease obligations.
- You do not have to manage a subtenant, as they will be in direct contact with the landlord.
- If released, you incur no liability for the assignee.
- You assign all lease rights to another tenant, which means you may no longer return to the space.
- If you have not been released by the landlord, you may still be liable for the new tenant.
Related Legal Documents, Forms, and Contracts
Commercial lease agreement, commercial sublease agreement, lease assignment, related articles.

- Find a Lawyer
- Legal Topics
- Real Estate Law
- Commercial Real Estate
Assigning a Commercial Lease
(This may not be the same place you live)
What Is an Assignment of a Commercial Lease?
A commercial lease is a written contract that is used when a commercial tenant rents space from a landlord. Commercial real estate law is the area of law that governs commercial leases and commercial tenant and landlord rights.
Similar to other types of leases, a commercial lease gives a commercial tenant the right to occupy the space and conduct business activities for a specified period of time. These commercial tenant rights are in exchange for the commercial tenant making monthly rent payments to the landlord.
A commercial lease also guides both parties regarding their legal rights and responsibilities associated with the commercial real estate transaction.
The most common example of a commercial lease would be when a tenant leases business property, such as:
- An office space;
- A standalone retail space;
- A restaurant;
- A retail store located in a mall or other similar shopping center.
Depending on the specific type of commercial lease that the parties enter into, the lease agreement will provide instructions, such as which party is responsible for making repairs and which party is liable for paying real property taxes on the space.
An assignment of a commercial lease refers to when one commercial party of the lease transfers all the interest and obligations of their lease to another third party. Generally, in a commercial setting, a commercial tenant will assign their interest in their commercial lease to another commercial tenant. Similarly, a landlord to a commercial lease may also assign their interest in the lease to another landlord.
It is important to note that many commercial leases will include restrictions on the ability of a commercial tenant to assign their lease. As such, it is important that commercial tenants review their lease in order to determine if assigning their lease is possible. A commercial lease will note all of the rights that the commercial tenant maintains over the commercial property, including assignability of the lease.
Additionally, it is also important to note that most consumer protection laws that apply to residential leases do not apply to commercial leases. However, depending on the state laws in which the commercial lease was entered into, restrictions on assignment of commercial leases may be valid if such restrictions are deemed “reasonable.”
What Is a Sublease of a Commercial Lease?
Can a commercial lease be assigned or subleased, what happens if i breach the lease through subletting or assignment, do i need a lawyer for my commercial sublease or assignment issue.
A sublease of a commercial lease occurs when a commercial tenant transfers a portion of their lease rights to a third party for a temporary period. A commercial tenant may either sublet a portion of their commercial space while they continue to work in the same space or sublet the entire commercial location until the end of the lease or a period of time.
For example, suppose that a company is a seasonal commercial business, such as a Halloween or firework store. If such a company has signed a year-long fixed lease term, they may seek to sublet their commercial property for the 8 months in which their store is not operational in order to generate income to pay rent on the commercial space.
It is important to note that when subletting, the original commercial tenant, known as the “sublessor,” is still obligated to the landlord for the original terms of the commercial lease. This means the sublessor maintains “privity of estate” and “privity of contract” with the landlord. The sublessee, or the person that intends to utilize the lease for a temporary period of time, is only liable to the original commercial tenant for the lease, not the landlord.
In other words, the original lease between the original commercial tenant and the landlord remains in full effect throughout the sublease period. Additionally, the original commercial tenant is now responsible for the new tenant. This means that the sublessee would go to the original tenant with any concerns they had regarding the rental property, as well as pay rent directly to them.
Subleases have become increasingly popular for big box retail stores that seek to lease corners of their commercial space to smaller retail stores. They are also popular for startups that do not have enough capital to lease an entire commercial space and prefer to cut costs by sharing a commercial space with other companies.
For instance, in grocery stores or shopping centers , you may see nail salons, ophthalmology services, cell phone repair shops, banks, or even food vendors that are subleasing from the main big box store.
Other common reasons a company may seek out a sublease include:
- Lower Rental Rates: Rates for commercial subleases, especially short-term subleases, are typically less than standard commercial lease rates;
- Flat Rental Payment Structure: Commercial subleases often have a flat rental payment structure with no unusual surprises;
- Fewer Obligations: In a commercial sublease, the sublessee usually has limited obligations to repair and maintain common areas;
- Less Complex Lease: Commercial subleases are usually not as complex as original commercial leases; or
- Additional Income: As noted above, the most common reason for subleasing is for the original commercial tenant to gain an additional source of rental income in order to make or lessen their lease payments.
As mentioned above, whether a commercial tenant may sublease or assign a commercial lease will be governed by the original commercial lease that was entered into by the commercial tenant and the landlord. Once again, the terms of the commercial lease may expressly prohibit the commercial tenant from subletting or assigning their lease entirely.
The lease terms may also allow the tenant to sublease or assign their commercial lease only with the landlord’s consent or if certain conditions have been met. Many states and local jurisdictions prohibit a landlord from withholding consent to assign or sublease a property if the reason is unreasonable.
In the absence of a provision in the executed commercial lease stating otherwise, a commercial lease can generally be assigned or subleased. As such, the ability of a commercial tenant to sublease or assign a commercial lease should always be discussed and negotiated prior to signing or renewing a commercial lease.
Similar to a commercial tenant’s ability to assign or sublet their lease, the penalties for breaching the lease will typically be governed by the terms of the commercial lease that was entered into by the tenant and landlord.
In addition to any legal remedies for breaching the lease, the landlord or tenant may also recover any contractual damages caused by the other party’s breach of the original lease terms. The non-breaching party may also seek to terminate the lease agreement altogether.
As can be seen, assigning or subletting a commercial lease may be a great option for companies seeking to move away from their commercial location permanently or to generate income.
However, commercial lease agreements and contracts can be very complex. As such, it may be in your best interests to consult with an experienced real estate lawyer to help you understand your legal options for assigning or subletting a lease. An experienced real estate lawyer will be able to guide you through the process of assigning or subletting your commercial lease and ensure that your legal position is protected.
Finally, an attorney will also be able to represent you in court, as necessary, should a dispute arise regarding assigning a commercial lease.
Save Time and Money - Speak With a Lawyer Right Away
- Buy one 30-minute consultation call or subscribe for unlimited calls
- Subscription includes access to unlimited consultation calls at a reduced price
- Receive quick expert feedback or review your DIY legal documents
- Have peace of mind without a long wait or industry standard retainer
- Get the right guidance - Schedule a call with a lawyer today!
Need a Real Estate Lawyer in your Area?
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia

Travis Peeler
LegalMatch Legal Writer
Updating Author
Travis earned his J.D. in 2017 from the University of Houston Law Center and his B.A. with honors from the University of Texas in 2014. Travis has written about numerous legal topics ranging from articles tracking every Supreme Court decision in Texas to the law of virtual reality. In his spare time off from the legal world and quest for knowledge, this 3rd degree black belt and certified instructor aspires to work with various charities geared towards bringing access to entertainment and gaming to all persons. Read More

Ken LaMance
Senior Editor
Original Author

Jose Rivera
Managing Editor
Related Articles
- Real Property Management
- Commercial Property for Sale Lawyers
- Commercial Landlord Rights
- What Is a Real Estate Business Plan?
- Negotiating a Commercial Lease
- Commercial Leases: Assignment vs. Sublet
- What is a Commercial Lease Agreement?
- Commercial Property Legal Issues
- Commercial Lease Disputes
- Commercial Real-Estate Law From the Tenant's Perspective
- Commercial Lease Security Deposit
- The Law of Commercial Subleases
- Commercial Landlord
- Holdover: Commercial Lease
- Eviction of Medical Marijuana Dispensaries
- Evicting a Commercial Tenant: Medical Marijuana Dispensaries
- Evicting a Commercial Tenant in Illinois
- Commercial Tenant Eviction in New York
- Commercial Eviction Process in Florida
- Commercial Tenant Rights and Eviction Process in California
- Right of Assignee or Sub-lessee to Enforce a Purchase Option
- Commercial Landlord Refuses to Allow Sublease or Assignment
- Implied Warranty of Suitability In Commercial Leases
- Subletting or Assigning Commercial Leases: New York
- Commercial Lease Trade Fixture Laws
- Commercial Landlord's Reasonable Consent to Sublease or Assign
- Pros and Cons in Buying or Leasing a Commercial Real Estate
- Laws Regarding Shopping Center Lease
- Percentage Lease Lawyers
- Net Lease Law
Discover the Trustworthy LegalMatch Advantage
- No fee to present your case
- Choose from lawyers in your area
- A 100% confidential service
How does LegalMatch work?
Law Library Disclaimer

16 people have successfully posted their cases
- Business Breakups in Virginia
- Contract Management
- Minority Shareholder Protections
- Emerging Companies
- Entity Formation
- Foreign Companies Entering U.S. Market
- Real Estate and Leases
- Starting a Business, Licensing & Compliance
- Registered Agent Services
- Succession Planning for Business Owners
- Tax Law Matters
- Charitable Solicitation Practice Group
- Trade Secrets
- Building Your Cornerstone
- Employee Document Vault
- Employee Handbook Tuneup Services
- Guidelines for Hiring or Firing Employees
- Separation Agreements
- Drug Testing Your Workforce – Best Practices
- Laws Affecting Drug Testing Policies
- VA, MD, DC, Rights & Obligations
- Age Discrimination
- Americans with Disabilities Act
- At-Will Employment
- Fair Labor Standards Act
- Family Medical Leave Act
- Pregnancy Discrimination Act
- District of Columbia
- For Employers of Uniformed Services Members
- Employer Considerations For Government Contractors
- For Non-Profits
- Collaborative Divorce
- Fourth Level Menu Sample
- High Net Divorce
- Same Sex Divorce
- Military Divorce
- Uncontested Divorce
- Litigation vs. Alternative Dispute Resolution in Divorce
- Post-Divorce Enforcement and Appeals
- Alimony and Spousal Support
- Child Custody
- Child Support
- Filing for Divorce in Virginia
- Divorce Security Clearance
- Property Division
- Child Custody and Visitation
- Marital Agreements
- International Family Law
- Domestic Violence and Protective Orders
- Co-Parenting in Virginia
- Bid Protests
- Government Contract Claims and Appeals
- 8(a) Small Business
- HUBZone Small Business
- SDVOSB Program
- Veteran-Owned Small Business
- Women-Owned Small Business
- Arbitration, Mediation & Alternative Dispute Resolution Attorneys
- Commercial & Business Litigation
- Employment Disputes
- Government Contracting Disputes
- Intellectual Property Disputes
- Local Counsel
- Pre-Litigation
- Estate Planning FAQs
- Families With Children
- Business Succession Planning
- Asset Protection Planning
- Celebrity Estate Planning Mistakes
- Legal Business Contingency Plans
- Become a Referral Partner
- Probate is Complex – FAQ and Answers
- Trust & Estate Litigation
- Andrew “Andy” Baxter
- Heba K. Carter
- Grace Clagett
- Joanna Foard
- Erika Gnazzo
- Merritt Green
- Elizabeth Hart
- Erin E. Masin
- Evan St. John
- Robert Wolfson
- How We Help
- Practical Counsel Blog
- Bid Protest Weekly
- Video Library
- Quotes in The News
- GCPC First Generation Law Student Scholarship
- Testimonials
- Make Payments

Assignments & Subleases in Commercial Real Estate Leases
Assignments and Subleases
For many businesses, entering into a lease is an essential and important part of their businesses. Other than payroll, lease payments are often a business’s largest expense. However, given the complexity and sheer length of a typical commercial lease, it is a daunting proposition to review and negotiate a lease on your own. This is the third in a series of articles discussing the major issues to be considered in a typical commercial lease.
This week, we’ll explore assignments and subleases. While assignments and subleases will have varying terms and conditions on a case-by-case basis, we’ll discuss generally about the issues involved in most assignments and subleases.
An assignment of a lease occurs when an existing tenant (“Assignor”) assigns its rights and obligations under the lease to a new tenant (“Assignee”). Another form of assignment occurs when a landlord sells the property and a new landlord takes over the lease. A sublease is often used when the existing tenant (often referred to as “Sublandlord” or “Sublessor”) rents a portion of, or the entire leased premises to another tenant (“Sublessee”), typically for a limited term. Some leases provide landlords the right to terminate the lease if an existing tenant requests an assignment or lease.
Assignment clauses may also be triggered unwittingly by change of ownership, or equity transfers, in a corporate or LLC tenant. Leases frequently state that a transfer of a certain percentage of the shares or membership interest in a corporate or LLC tenant shall be construed an assignment. A tenant should always check its lease for such provisions prior to entering into an equity transfer transaction.
PRACTICAL COUNSEL: In both assignments and subleases, the rights and obligations of the existing and incoming tenants are delineated in the underlying lease document. A prospective tenant should take care when reviewing a proposed lease to ensure that they understand the implications of an assignment or sublease, as they may be faced with unfavorable consequences. Whether a business needs to move out of a leased space due to growth, sell itself, or has space that is not being used, the assignment and sublease clauses will come into play and it is imperative to understand their implications. The actual assignment of lease or sublease agreements should also be drafted and negotiated carefully to conform to the underlying lease, as well as protect the best interests of the Assignor, Assignee, Sublessor or Sublessee.
This commercial lease assignment is between , an individual a(n) (the " Original Tenant ") and , an individual a(n) (the " New Tenant ").
On or about , the Original Tenant and (the " Landlord ") entered into a lease agreement (the " Lease ").
The Lease covers the commercial property located at , , and more particularly described as follows: (the " Premises "). The Premises contains feet of interior floor space.
Under section of the Lease, the Original Tenant is permitted to assign its interest in the Lease, with the consent of the Landlord.
The Original Tenant wishes to assign to the New Tenant its rights in, and delegate all of its obligations under, the Lease, and the New Tenant wishes to accept this assignment.
The parties therefore agree as follows:
1. ASSIGNMENT.
The Original Tenant assigns to the New Tenant of all its rights in, and delegates to the New Tenant all of its obligations under, the Lease. This transfer will become effective as of (the " Effective Date "), and will continue until the present term of the Lease ends.
2. ASSUMPTION OF RIGHTS AND DUTIES.
After the Effective Date, the New Tenant shall assume all rights and duties under the Lease, including the obligation to pay rent under the Lease when it is due. The Original Tenant will have no further obligations under the Lease The Original Tenant will remain bound to the Landlord under the Lease, notwithstanding the assignment . However, the Original Tenant remains responsible for obligations accruing before the Effective Date.
3. REIMBURSEMENT.
On or before the Effective Date, the New Tenant shall pay $ to the Original Tenant, which is the sum of:
- (a) The security deposit held by the Landlord under the Lease; and
- (b) The rent or other deposits paid in advance by the Original Tenant for any period after the effective date of this assignment.
4. INDEMNIFICATION.
- (a) The Original Tenant shall indemnify the New Tenant against any award, charge, claim, compensatory damages, cost, damages, exemplary damages, diminution in value, expense, fee, fine, interest, judgment, liability, settlement payment, penalty, or other loss (a " Loss ") or any attorney's or other professional's fee and disbursement, court filing fee, court cost, arbitration fee, arbitration cost, witness fee, and each other fee and cost of investigating and defending or asserting a claim for indemnification (a " Litigation Expense ") arising out of the Original Tenant's breach of its obligations under the Lease before the Effective Date.
- (b) The New Tenant shall indemnify the Original Tenant against all Losses or Litigation Expenses relating to the Lease, except if those Losses or Litigation Expenses arise from the Original Tenant's failure to perform its obligations under the Lease before the Effective Date.
- (c) The New Tenant shall indemnify the Original Tenant against all Losses or Litigation Expenses attributable to the acts or omissions of the New Tenant or its agents, contractors, or employees with respect to the Premises or any activities on the Premises. This indemnification will survive the termination of the Lease and this assignment.
5. CONTINUING EFFECTIVENESS OF LEASE.
This assignment is made on the understanding that all other terms of the Lease remain in full effect, including the prohibition against further assignments and subleases without the Landlord's express written consent.
6. ORIGINAL TENANT'S REPRESENTATIONS.
The Original Tenant represents that it:
- (a) has the power and authority to enter into and carry out this assignment;
- (b) has not previously assigned its rights under the Lease;
- (c) is the lawful and sole owner of the interests assigned under this assignment;
- (d) the interests assigned under this assignment are free from all encumbrances;
- (e) except for the Landlord and the Original Tenant, there are no parties in possession or occupancy of the Premises or any part of them, and there are no parties with possessory rights on the Premises or any part of them; and
- (f) has performed all obligations and made all required payments under the Lease.
7. CONDITION OF PREMISES.
The New Tenant has examined and inspected the Premises and accepts them "as is" and in their present condition with all faults. Except as provided in this assignment, the Original Tenant makes no representations, covenants, or guaranties about the status, nature, or condition of the Lease or the Premises.
8. INTERPRETATION.
In interpreting the language of this assignment, the parties shall be treated as having drafted this assignment after meaningful negotiations. The language in this assignment will be construed as to its fair meaning and not strictly for or against either party.
9. GOVERNING LAW.
- (a) Choice of Law. The laws of the state of govern this assignment (without giving effect to its conflicts of law principles).
- (b) Choice of Forum. Both parties consent to the personal jurisdiction of the state and federal courts in , .
10. AMENDMENTS .
No amendment to this assignment will be effective unless it is in writing and signed by a party or its authorized representative.
11. COUNTERPARTS; ELECTRONIC SIGNATURES.
- (a) Counterparts. The parties may execute this agreement in any number of counterparts, each of which is an original but all of which constitute one and the same instrument.
- (b) Electronic Signatures. This agreement, agreements ancillary to this agreement, and related documents entered into in connection with this agreement are signed when a party's signature is delivered by facsimile, email, or other electronic medium. These signatures must be treated in all respects as having the same force and effect as original signatures.
12. SEVERABILITY.
If any one or more of the provisions contained in this assignment is, for any reason, held to be invalid, illegal, or unenforceable in any respect, that invalidity, illegality, or unenforceability will not affect any other provisions of this assignment, but this assignment will be construed as if those invalid, illegal, or unenforceable provisions had never been contained in it, unless the deletion of those provisions would result in such a material change so as to cause completion of the transactions contemplated by this assignment to be unreasonable.
13. NOTICES.
- (a) Writing; Permitted Delivery Methods. Each party giving or making any notice, request, demand, or other communication required or permitted by this assignment shall give that notice in writing and use one of the following types of delivery, each of which is a writing for purposes of this assignment: personal delivery, mail (registered or certified mail, postage prepaid, return-receipt requested), nationally recognized overnight courier (fees prepaid), facsimile, or email.
- (b) Addresses. A party shall address notices under this section to a party at the following addresses:
- If to the Original Tenant:
- If to the New Tenant:
- (c) Effectiveness. A notice is effective only if the party giving notice complies with subsections (a) and (b) and if the recipient receives the notice.
14. WAIVER.
No waiver of a breach, failure of any condition, or any right or remedy contained in or granted by the provisions of this assignment will be effective unless it is in writing and signed by the party waiving the breach, failure, right, or remedy. No waiver of any breach, failure, right, or remedy will be deemed a waiver of any other breach, failure, right, or remedy, whether or not similar, and no waiver will constitute a continuing waiver, unless the writing so specifies.
15. ENTIRE AGREEMENT.
This agreement constitutes the final agreement of the parties. It is the complete and exclusive expression of the parties' agreement about the subject matter of this agreement. All prior and contemporaneous communications, negotiations, and agreements between the parties relating to the subject matter of this agreement are expressly merged into and superseded by this agreement. The provisions of this agreement may not be explained, supplemented, or qualified by evidence of trade usage or a prior course of dealings. Neither party was induced to enter this agreement by, and neither party is relying on, any statement, representation, warranty, or agreement of the other party except those set forth expressly in this agreement. Except as set forth expressly in this agreement, there are no conditions precedent to this agreement's effectiveness.
16. HEADINGS.
The descriptive headings of the sections and subsections of this assignment are for convenience only, and do not affect this agreement's construction or interpretation.
17. EFFECTIVENESS.
This assignment will become effective when all parties have signed it.The date this assignment is signed by the last party to sign it (as indicated by the date associated with that party's signature) will be deemed the date of this assignment.
18. NECESSARY ACTS; FURTHER ASSURANCES.
Each party shall use all reasonable efforts to take, or cause to be taken, all actions necessary or desirable to consummate and make effective the transactions this assignment contemplates or to evidence or carry out the intent and purposes of this assignment.
[SIGNATURE PAGE FOLLOWS]
Each party is signing this agreement on the date stated opposite that party's signature.
[PAGE BREAK HERE]
LANDLORD'S CONSENT AND RELEASE
As Landlord under the Lease, I hereby consent to this assignment of the Lease, and to the New Tenant's assumption of the Original Tenant's obligations under the Lease, including the obligation to pay rent when it is due. As of the Effective Date, I release the Original Tenant from all liability for obligations (including rent payments) under the Lease However, the Original Tenant remains primarily obligated as tenant under the Lease and I do not waive or relinquish any rights under the Lease against either the Original Tenant or the New Tenant.
EXHIBIT A Attach copy of Lease
Free Assignment of Commercial Lease Template
Transfer your commercial lease to a new tenant smoothly. create an assignment of a commercial lease to clearly articulate the new tenant's rights, responsibilities, and obligations..
Complete your document with ease
How-to guides, articles, and any other content appearing on this page are for informational purposes only, do not constitute legal advice, and are no substitute for the advice of an attorney.
Assignment of commercial lease: How-to guide
Occasionally, tenants wish to leave a rental property before the end of their lease. Individuals may take new jobs in new cities, and companies may go out of business or sell their enterprises to a third party.
Whatever the reason, tenants can transfer their original commercial lease to new parties by completing an assignment of the lease.
An assignment transfers one party's interest and obligations under a lease to another party.
During these tenant transfers, the new tenant takes on the lease responsibilities, including paying rent and property maintenance of the leased premises, and the original tenant is released from most of their duties.
Successful property management begins with good documentation and a properly drafted, executed assignment:
Ensures that all parties involved understand the obligations being transferred
Defines the responsibilities that each party will have under the new arrangement
Lays the foundation for a long-lasting landlord and new tenant relationship
Important aspects to consider when drafting commercial leases
Laws about the original commercial lease agreement.
State laws governing real estate, renting, leasing, and assignments vary widely and can tremendously affect your arrangement.
Since the tenant is legally responsible for this document, they must include specific information like financial statements in the commercial lease assignment. Consider your state and local laws for additional information required in your area.
Criteria for commercial landlords in providing consents
A landlord may consider only proper factors when deciding whether or not to consent to an assignment.
Some criteria will be regarded as impermissible by courts, such as refusal based on race or sex of the proposed new tenant. If your landlord does not consent to your attempted assignment, ensure they give you clear written reasons for the decision. Failure to provide such reasons can itself be deemed unreasonable.
Consequences of not providing consent
It is essential to seek the landlord’s permission for the proposed transfer of the duties.
Depending on your jurisdiction or the terms of your original lease, a landlord’s failure to respond to your request for consent to assignment within a specific time may be deemed consent. Sometimes, it may give the assigning tenant grounds to terminate the lease. Review the original lease and your state’s laws for additional details.
Although a landlord is not required to consent to a lease assignment agreement, in some cases, your lease will state that a landlord’s consent will not be “unreasonably” withheld. This is more common in commercial leases than in a residential lease. What is considered unreasonable varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, and you should review the laws in your area (and the assignment clause in your original lease agreement) for additional information. On the other hand, if the lease states that the landlord may use their “sole discretion” to evaluate the new tenant, they can veto this assignment without any reason.
Rights of the original tenant
The original tenant cannot assign more rights than the original lease. For example, if the lease term is one year, the assignment term cannot be two years.
Review the lease assignments before signing
Most leases require the landlord’s written consent before an assignment becomes effective. Review the assignment provisions and the original lease agreement for additional information and see if other requirements must be met to make the lease assignment agreement valid.
Get the assignment signed
Sign three copies of the assignment, one for you, the other party, and the landlord. Depending on the nature of its terms, you may decide to have the document witnessed or notarized. This will limit later challenges to the validity of a party’s signature.
Be sure the assignee gets a copy of the original lease by attaching it to the assignment. Its terms will bind them, and they should know their new obligations and rights.
If your agreement is complicated, contact an attorney to help draft a document that meets your needs.
Key components of a commercial lease assignment
The following instructions will help you understand the terms of your assignment.
Introduction
In this section, identify the parties and, if applicable, what type of organization(s) they are. Write down how the document identifies each party. For example, the current tenant can be addressed as the “original tenant” or “assignor” as they assign the lease to the new tenant, and the new tenant can be called the “new tenant” or “assignee.”
Furthermore, add the date on which the assignment will become effective – when it is signed.
The “whereas” clauses, referred to as recitals, define the world of the agreement and offer essential background information about the parties.
In this assignment, the recitals include a simple statement of the parties’ intent to assign the original tenant’s interest in the lease and the new tenant’s intent to assume it. Provide a brief description of the rented property and the landlord’s name under the lease.
You don't need to include a complete legal description for the property description, but provide enough information to identify it. For individual houses, the address will usually be sufficient. If the property has a specific name (e.g., “Lincoln Towers”), include that as well. If only a section of the premises is assigned, clarify that in this description.
This section mentions the assignor’s assignment of their right and interest in the lease to the assignee. This assignment clause allows you to determine whether all of the assignor’s interest in the lease is being assigned or only part of it. For example, if interest in only one-half of the premises is being assigned, the document should note this.
Assumption of rights and duties
This section clarifies the assignor’s responsibilities for the duties listed under the lease (e.g., rent, maintenance of property, etc.). For example, whether:
The assignor is ultimately released from any liability they had under the lease. For example, if the assignee defaults, the landlord cannot seek payment from the assignor.
The assignor will be liable to the landlord if the assignee defaults.
In any event, the assignor will remain responsible for any obligations that occurred before the assignment. In other words, if the damage happened to the apartment before the transfer or the assignor did not fulfill another obligation under the lease, the assignor remains responsible for the building occupied.
Reimbursement
In many rental relationships, amounts are paid in advance or deposited as security for the landlord.
At the end of the lease, this security deposit (with deductions subtracted or interest added) is returned to the tenant. If an entire interest is assigned, the lease does not end, and the assigning party cannot get this money back. This paragraph requires the assignee to pay those amounts to the assignor, and any later return of that money by the landlord will be made to the assignee.
Indemnification
In such clauses, the assignee promises to bear the financial cost of any injury the assignor suffers due to its assignment and any lawsuits arising from its activities on the premises. Note that there is an exception for things done by the assignor before the effective date of the assignment — the assignor remains responsible for those actions.
Continuing effectiveness of lease
Here, emphasize that the original lease terms are still effective to the assignee, except for the assignment.
Assignor’s representations and warranties
List the assignor’s promises under the assignment. Note that this is not a detailed list of services to be provided. Instead, this is the assignor’s assurance that the lease and the rental interest it’s providing are helpful (i.e., no one else lives or has an interest in the place, the lease is still in effect, the assignor is not behind in rental payments, etc.). If there are additional representations the assignor should be making, feel free to include those here.
Condition of premises
Here, mention that the premises are not warranted to be perfect or valuable in a particular way. Instead, the assignee is taking the rented property for what it is and is accepting it in that state.
Additional terms of assignment
This optional provision allows the assignor and the assignee to include any representations, warranties, or other provisions particular to their situation.
Interpretation
This section provides information that both parties were on equal footing in negotiating the consent to assignment. In many cases, a contract is interpreted favorably by the individual who did not draft it. This clause clarifies that both parties were involved in the drafting, so the document should not be read in favor of (or against) either.
Here, list the addresses to which all official or legal correspondence should be delivered. This can be the tenant’s business address or the mailing address for both the assignor and the assignee.
Modification
This section indicates that any changes to the document are only effective if they are made in writing and signed by both parties.
Governing law
This section allows the parties to choose the state laws used to interpret the document.
Counterparts; electronic signatures
This section explains that even if the parties sign the assignment in different locations or use electronic devices to transmit signatures (e.g., fax machines or computers), the separate pieces will be considered part of the same agreement. In a modern world where signing parties are often not in the same city—much less the same room — this provision ensures that business can be transacted efficiently without sacrificing the validity of the agreement as a whole.
Entire agreement
This clause mentions that the document parties are signing is “the agreement” about the issues involved. Unfortunately, the inclusion of this provision will not prevent a party from arguing that other enforceable promises exist, but it can provide you some protection from these claims.
Landlord’s consent and release
Review the terms of the original lease agreement to determine whether or not the landlord’s consent is required to make the assignment effective. This is usually the case. If so, have the landlord sign the document.
Frequently asked questions
What is the purpose of an assignment of lease.
Whether it's because it's time to move to a new space or city, business isn't booming, a company gets sold, or otherwise, sometimes commercial tenants must leave a lease before it ends. And sometimes, they may want to transfer the responsibilities of their lease to someone new. A lease assignment occurs in this case.
Here's the information you'll need to have handy to complete your assignment of commercial lease:
Who the old tenant is : Have their name and contact information ready
Who the new tenant is : Have their information available
What is the difference between an assignment and a sublease?
An assignment transfers one party's interest in an agreement to a third party. In this case, the original tenant gives all their interest to a new tenant. That new tenant steps into the shoes of the old tenant and the old tenant is released from most of their obligations under the lease (although this can be changed by agreement).
This is not the same as a sublease. Under a sublease , a third party is granted only those specific rights provided in the sublease. The original tenant remains ultimately liable for residual obligations under the lease or any failures of the new tenant to meet their obligations. This means that the original tenant will be responsible (in equal measure with the new tenant) for any skipped rent payments or damage to the property.
Related templates

Assignment of Agreement
Transfer work responsibilities efficiently with an assignment of agreement. Facilitate a smooth transition from one party to another.

Assignment of Residential Lease
Simplify lease transfers with an assignment of residential lease agreement. With the landlord's approval, smoothly transfer your lease responsibilities to a new tenant while documenting the arrangement comprehensively.

Landlord Consent to Assignment
Facilitate lease transfers with a landlord consent to assignment form. Provide tenant and landlord information, along with the rental property address, and grant permission for the lease transfer easily.

How does it work?
1. choose this template.
Start by clicking on "Fill out the template"
2. Complete the document
Answer a few questions and your document is created automatically.
3. Save - Print
Your document is ready! You will receive it in Word and PDF formats. You will be able to modify it.
Lease Assignment Agreement
Rating: 4.9 - 137 votes
A Lease Assignment Agreement is a short document that allows for the transfer of interest in a residential or commercial lease from one tenant to another. In other words, a Lease Assignment Agreement is used when the original tenant wants to get out of a lease and has someone lined up to take their place.
Within a Lease Assignment Agreement, there is not that much information included, except the basics: names and identifying information of the parties, assignment start date, name of landlord, etc. The reason these documents are not more robust is because the original lease is incorporated by reference , all the time. What this means is that all of the terms in the original lease are deemed to be included in the Lease Assignment Agreement.
A Lease Assignment Agreement is different than a Sublease Agreement because the entirety of the lease interest is being transferred in an assignment. With a sublease, the original tenant is still liable for everything, and the sublease may be made for less than the entire property interest. A Lease Assignment transfers the whole interest and puts the new tenant in place of the old one.
The one major thing to be aware of with a Lease Assignment Agreement is that in most situations, the lease will require a landlord's explicit consent for an assignment. The parties should, therefore, be sure the landlord agrees to an assignment before filling out this document.
How to use this document
This Lease Assignment Agreement will help set forth all the required facts and obligations for a valid lease assignment . This essentially means one party (called the Assignor ) will be transferring their rights and obligations as a tenant (including paying rent and living in the space) to another party (called the Assignee ).
In this document, basic information is listed , such as old and new tenant names, the landlord's name, the address of the property, the dates of the lease, and the date of the assignment.
Information about whether or not the Assignor will still be liable in case the Assignee doesn't fulfill the required obligations is also included.
Applicable law
Lease Agreements in the United States are generally subject to the laws of the individual state and therefore, so are Lease Assignment Agreements.
The Environmental Protection Agency governs the disclosure of lead-based paint warnings in all rentals in the States. If a lead-based paint disclosure has not been included in the lease, it must be included in the assignment. Distinct from that, however, required disclosures and lease terms will be based on the laws of the state, and sometimes county, where the property is located.
How to modify the template
You fill out a form. The document is created before your eyes as you respond to the questions.
At the end, you receive it in Word and PDF formats. You can modify it and reuse it.
A guide to help you: Tenants and Subtenants Obligations under a Sublease Agreement
Other names for the document:
Assignment Agreement for Commercial Lease, Assignment of Commercial Lease, Assignment of Lease, Assignment of Residential Lease, Assignment Agreement for Lease
Country: United States
Housing and Real Estate - Other downloadable templates of legal documents
- Security Deposit Return Letter
- Rent Payment Plan Letter
- Residential Lease Agreement
- Sublease Agreement
- Tenant Maintenance Request Letter
- Rent Receipt
- Late Rent Notice
- Notice of Intent to Vacate
- Roommate Agreement
- Quitclaim Deed
- Parking Space Lease Agreement
- Short-Term Lease Agreement
- Tenant Security Deposit Return Request
- Termination of Tenancy Letter
- Change of Rent Notice
- Complaint Letter to Landlord
- Lease Amendment Agreement
- Notice of Lease Violation
- Consent to Sublease
- Eviction Notice
- Other downloadable templates of legal documents
Commercial Lease Assignment and Sublet Provisions
A balancing act for landlords and tenants, july 2020 by adam f. aldrich.

This article identifies common problems involved in commercial lease transfers through assignments and subleases. It offers both landlords and tenants tips for solving these problems when negotiating assignment and sublease provisions in leases.
The modern commercial lease is a complex, integrated document that attempts to balance the competing interests of the landlord and tenant. As a result, commercial leases are the subject of much negotiation and are never “one size fits all.” In fact, commercial leases are one of the least standardized documents in real estate practice.
When any commercial lease is to be transferred in part through a sublet or in its entirety through an assignment, the issues multiply. The transfer provisions, which once seemed moot, become operative to determine whether the lease can be transferred and, if so, under what conditions. If, during lease negotiations, the parties overlooked the lease transfer provisions or gave them cursory consideration, they may be unpleasantly surprised by the result. While landlords and tenants have divergent economic interests with respect to transferring the lease, their legitimate concerns can be appropriately addressed through thoughtfully crafted transfer provisions.
This article explores common problems, issues, and solutions encountered in commercial lease transfers through assignments and subleases. It is intended to be useful both to the lawyer who infrequently encounters lease transfer problems and the seasoned practitioner who deals with lease transfer issues every day.
Distinguishing Between an Assignment and Sublease
Assignments and subleases have fundamental differences that are frequently misunderstood. A lease is both a conveyance of an interest in property and a contract. 1 After executing the lease, the landlord and tenant are bound to one another by privity of contract and by privity of estate. As a result, they may each enforce the provisions of the written lease through privity of contract and the promises that arise from privity of estate. 2 Privity of contract allows enforcement of the lease provisions, while privity of estate allows enforcement of only those promises that run with the land. 3
Whether the landlord, tenant/assignor, and subtenant/assignee call their arrangement an assignment or a sublease, courts typically look at the substance of the transaction. In an assignment, a tenant transfers its entire interest in the lease. 4 After assigning its interest in the lease, the assignee has privity of estate with the landlord, but the assignee and the landlord are not in privity of contract unless the assignee assumes the tenant’s obligations under the lease. 5 Assignment of the lease ends the original tenant’s rights to possession, but absent an express release under the lease terms, its liability under the lease continues. 6 This means the original tenant remains secondarily liable for the assignee’s obligations under the lease. Thus, the tenant/assignor may find itself liable at a future date if the assignee fails to perform its obligations under the lease.
In a sublease, however, the tenant transfers less than the remaining term or less than the tenant’s entire interest in the lease, leaving the original tenant with a reversionary interest in the lease. 7 The relationship between the original landlord and the original tenant, including both privity of contract and privity of estate, remains intact, thereby creating the relationship of landlord and tenant between the original tenant (sublandlord) and the new tenant (subtenant). The original landlord and the subtenant have no privity of estate or privity of contract with one another, so the original tenant remains liable for the actions and omissions of the subtenant. 8 However, the subtenant’s rights will terminate with the original lease or when the landlord declares a forfeiture of the tenant’s lease term. 9
A third, less common type of transfer is a partial assignment of a lease. Such assignments are called assignments “pro tanto,” not subleases, because they grant possession of a portion of the leased premises to the new tenant for the balance of the lease term. 10 The landlord now has two tenants and, in effect, two leases. There is little guiding case law on this hybrid lease transfer, so it is not entirely clear whether the assignee has a contractual relationship with the landlord. 11 Due to the vagaries and uncertainties that can result when a transfer of possession encompasses less than all of the space, partial assignments should be avoided. To avoid assignments pro tanto, landlords should consider prohibiting assignments of less than the original tenant’s entire interest in the lease. If a landlord proceeds with a partial assignment, it should clearly document the arrangement, including the rights and remedies of the landlord, original tenant, and new tenant, and acknowledge the transaction as a partial assignment and not a sublease. 12
The accompanying table illustrates the many differences between an assignment, sublease, and partial assignment. 13
Restrictions on Assignments and Subleases
Colorado law favors the free transferability of rights. 14 As a result, landlords frequently attempt to limit the tenant’s right to transfer the lease by including lease provisions specifically restricting the tenant’s right to assign or sublet. Under Colorado law, outright prohibitions against assignments are permissible and are not considered invalid restraints on alienation. 15 Even if outright prohibitions on assignments or subletting are enforced, such provisions “are construed against the restriction.” 16 This means a court generally will construe such stipulations “against the party invoking them.” 17 A breach of the restriction against transfer does not terminate the lease, 18 but may give rise to a claim for default. 19 Generally, tenants in commercial leases negotiate exceptions to strict prohibitions against assignments or subletting because transfer provisions may be their only viable exit strategy if they find they can no longer afford the space or no longer need it.
Consent to Assignments and Subleases
Recognizing that absolute prohibitions are neither favored by the courts nor acceptable to most tenants, some landlords include modified prohibitions in their leases that limit the tenant’s rights to transfer the lease and, if a transfer is permitted, allow the landlord to enforce the lease against both the original tenant and the new tenant to the maximum extent possible. Such provisions may reserve to the landlord, either in its sole discretion or without unreasonably withholding its consent, the right to approve a proposed lease transfer. Although the reservation of the landlord’s right to approve a proposed assignment or sublease is for the landlord’s benefit, 20 the landlord is bound to the standards set out in the lease for consents to an assignment or sublease. 21 Accordingly, once the landlord has established the standards for its consent in the lease, it cannot object to a proposed assignment or sublease if the tenant has met the appropriate requirements.
It is well established in Colorado law that “without a freely negotiated provision in the lease giving the landlord an absolute right to withhold consent, a landlord’s decision to withhold consent must be reasonable.” 22 Thus, if a lease contains a provision against subletting or assignment, but is silent on a landlord’s right to withhold consent, Colorado law forbids the landlord from withholding its consent unreasonably if the tenant tenders a suitable subtenant or assignee to the landlord. 23
Disputes often arise as to what is a ‘‘reasonable” withholding of the landlord’s consent. This debate has led to the enunciation of specific standards of reasonableness. If a lease provision “requires that consent to an assignment will not be unreasonably or arbitrarily withheld, a landlord is held to the standard of conduct of a reasonably prudent person.” 24 Therefore, a landlord must only consider “those factors that relate to a landlord’s interest in preserving the value of the property,” 25 which do not include “[a]rbitrary considerations of personal taste, convenience, or sensibility . . . .” 26 Whether a landlord has acted reasonably is a fact-specific inquiry. 27 Most courts have held that the tenant bears the burden of proving that the landlord acted unreasonably in withholding consent, 28 but some courts have required the landlord to prove it acted reasonably. 29 Courts have been divided on a tenant’s right to terminate a lease where the landlord has been found to have unreasonably withheld consent. 30
There are several reliable rules that courts follow in determining whether a landlord acted reasonably. First, a landlord cannot refuse consent for racial or other discriminatory reasons. 31
Second, a landlord may not deny consent to improve its general economic position or to receive increased rent. 32 However, a landlord may deny consent to protect its interest in the value, condition, and operation of the property or the performance of lease covenants. 33 For example, in Cafeteria Operators L.P. v. AMCAP/Denver Limited Partnership , the tenant leased the premises to run a cafeteria-style restaurant. 34 After several failed attempts to operate the restaurant, the tenant marketed the space to prospective subtenants, including non-cafeteria restaurant owners. 35 When a non-cafeteria restaurant owner expressed interest in subleasing the premises, the tenant sought the landlord’s approval to the proposed sublease, but the landlord refused. The Court found that the landlord reasonably withheld consent because the proposed sublessee would have changed the “character” of the shopping center by operating “the largest restaurant of its kind, raising concerns about lighting, maintenance, traffic, and parking.” 36 Moreover, the subtenant would sell alcohol and stay open late, and its proposed occupancy raised “concerns about security, safety of patrons, and parking requirements.” 37 Similarly, the Court in List v. Dahnke found that the landlord reasonably withheld consent where the landlord determined that a Thai-American restaurant operated by the assignee would not be successful at that location, but the Court did not identify the facts that led the landlord to such conclusion. 38
Third, a court may make a finding of unreasonableness if a landlord refuses consent to a proposed transfer without obtaining relevant information to make its decision. 39 Before making the decision, the landlord should obtain sufficient information on the transferee’s financial condition; the transferee’s experience in operating its business; how the premises are to be used; projected sales, gross income, and income per square foot; and, in the case of a sublease, the size of the subleased space. 40
Fourth, courts may consider how long it takes the landlord to make the decision on the requested assignment. If the landlord instantly refuses consent or waits too long to make a decision, the court could make a finding of unreasonableness. 41 Conversely, if the tenant fails to allow the landlord a reasonable amount of time to issue a decision, the withholding of consent can be found reasonable. 42 In Parr v. Triple L&J Corp. , the Court found that the landlord unreasonably withheld consent when it deferred making a decision on the proposed assignment, thereby delaying the sale of the tenant’s business until the prospective buyer withdrew his offer. 43 The tenant sought approval from the landlord for an assignment of the lease as part of the sale of its business. The landlord requested all personal and financial information on the proposed assignee and the assignee’s business plan, and the tenant provided prompt responses that demonstrated the assignee’s experience in restaurant management and “perfect credit score.” 44 Because the landlord unreasonably withheld consent, the landlord was held liable to the tenant under a breach of contract theory, as well as for lost profits on the sale of its business. 45
Similarly, the Court in Bert Bidwell Investors Corp. v. LaSalle and Schiffer, P.C. addressed whether the landlord unreasonably withheld consent to the tenant’s request to transfer the lease where the assignee was “ready, willing, and able to assume the lease as written, and to use the premises for the same business as that of the tenants.” 46 The landlord ultimately refused consent because it “didn’t like” the proposed assignee. 47 Based on the lease, which required the landlord’s consent to assign, the landlord argued that it “had the right to relet the premises as it saw fit and to be arbitrary in doing so.” 48 Relying on List , the Court found that the landlord acted unreasonably in refusing to accept the proposed new tenant. 49 Nevertheless, parties may create their own standards and definition of reasonableness, and if they do, courts will enforce and apply such standards. 50
As these cases illustrate, if a landlord wishes to withhold consent absent a sole and unconditional contractual right to do so, it must have fact-based reasons for doing so and cannot arbitrarily withhold or delay its consent. The landlord should communicate its decision in writing to the tenant and enumerate all fact-based reasons to preserve all arguments for reasonableness. 51 Before making the request to assign or sublet the premises, the tenant should gather information about the proposed assignee’s or subtenant’s financial status, business acumen, and proposed operations, and then submit this information to the landlord, along with an assignment or sublease document signed by the tenant and assignee or subtenant. While the landlord must still consent to the transaction, 52 such documentation places the tenant in a stronger position to rebut any superficial or arbitrary reasons the landlord may proffer for denying consent. And if litigation ensues, it will be critical for the tenant’s case to show that it supplied the landlord with as much information as possible concerning the assignee’s or subtenant’s financial status and operations, to avoid having the trier of fact determine that the landlord acted reasonably in denying consent due to a lack of information from the tenant.
Recapture, Termination, and Renewal Rights
Leases may grant the landlord the right to terminate the lease and to retake the tenant’s space if the tenant wishes to assign its lease or sublet its space, or if the tenant transfers the lease without the landlord’s consent. Replacing the tenant by recapturing the premises can benefit both the landlord and the tenant, but each party will want to weigh the pros and cons of such an agreement.
Terminating the lease allows the landlord to eliminate existing lease weaknesses and to enter into a new lease with a potentially better tenant on a clean slate. Moreover, recapturing the premises and directly leasing it to the proposed assignee can save the landlord substantial dollars in tenant improvements that can be passed on to the new tenant through reduced or free rent for a portion of the lease term. But the landlord must pay close attention to market conditions before terminating the lease. Terminating the lease in a strong market when space is at a premium and rents are high allows the landlord to enter into a new lease with a new tenant at a higher rate, but the landlord may take a loss on its investment in the premises in a down market when rates are depressed and there is an oversupply of space.
The tenant, on the other hand, risks losing its investment in its business and the leased premises. Before requesting a transfer, the tenant should closely scrutinize the lease to determine the potential outcome. Under some leases, the act of notifying the landlord of an intent to assign or sublet can trigger the recapture provision. 53 Similarly, if the lease is assigned without the landlord’s consent, it may trigger the recapture right if that right is expressly provided in the lease. 54 Landlords should closely review the recapture language before terminating the lease because restraints on alienation and lease forfeitures are disfavored. 55
When a tenant violates the transfer provisions by transferring the lease without the landlord’s consent, the landlord should send a notice of default to the tenant and demand that the default be cured by nullifying the transfer, 56 unless the lease provides that transferring the lease is an automatic termination. If the tenant is unable to nullify the transfer when it receives the notice, it could be liable for default damages incurred by the landlord. 57 If the tenant does not cure the default and the landlord will not approve (and has the right not to approve) the assignee or subtenant, the landlord may terminate the lease (or the tenant’s right to possession) if the lease so permits. 58 If the landlord fails to terminate the lease 59 or accepts rent after breach of the anti-assignment clause, 60 it may be deemed to have waived the right to terminate. Once the lease is terminated as a result of the default, the landlord must consider its duty to mitigate damages. 61
If the space is recaptured and the lease terminated, the tenant’s lease obligations will be terminated with respect to all recaptured space, including the payment of rent. 62 Moreover, the tenant will no longer have privity of contract or estate with the landlord, assignee, or subtenant because the lease will be terminated as to the tenant. 63 If the landlord recaptures the premises, the tenant is spared the rent expense while it finds a transferee. But if the landlord does not recapture, the tenant can make a transfer without fear that the landlord will then exercise its recapture rights.
Another important issue is whether an option to renew contained in a lease assigned or subleased to a third party remains exercisable following the transfer. If the assigned lease gives the original tenant a renewal option, the assignee can extend the term unless the renewal option is reserved from the assignment. 64 If a tenant/sublandlord grants its subtenant an option to renew based on the tenant’s option in the prime lease, the subtenant is dependent on the tenant/sublandlord for a lease extension because it does not have contractual privity with the landlord. 65 If the tenant/sublandlord refuses to exercise its renewal option so as to enable the subtenant to take advantage of the rights that were granted to it, the tenant may be liable to the subtenant. 66 To protect its option to renew, the subtenant should request or require a recognition agreement from the landlord when negotiating a sublease, whereby the landlord agrees to recognize the sublease if the prime lease terminates due to the tenant/sublandlord’s default. 67
The Impact of Bankruptcy Proceedings on Assignments and Subleases
Bankruptcy laws can have a significant impact on commercial leases when the tenant files for bankruptcy protection. Generally, a trustee is appointed to administer the bankruptcy estate, except in Chapter 11 cases where the debtor-in-possession is the tenant. 68 For debtors with executory contracts and/or unexpired leases, 11 USC § 365 contains a series of rules that govern those documents. Section 365 of the bankruptcy code provides the tenant/debtor with the statutory right to assume or reject executory contracts and unexpired leases to which it is a party, subject to objections by creditors and other parties-in-interest, and ultimately the court’s approval. 69 The debtor may, in turn, assign the lease if the assignee provides “adequate assurance of future performance.” 70 During the period between filing the bankruptcy petition and the date on which the lease is assumed or rejected, the tenant must continue to pay rent and perform the material terms of the lease. 71 It should be noted that written waivers of § 362’s automatic stay have been found to be unenforceable unless they are part of a previous bankruptcy proceeding. 72 Thus, landlords should not assume that a waiver in the lease is enforceable if the tenant files for bankruptcy.
From the debtor’s perspective, the right to reject the lease is “vital to the basic purpose of Chapter 11” because it can free the tenant from the obligation to pay all future rent under the lease. 73 If a lease is rejected with bankruptcy court approval, the debtor has no legal interest in the lease or the leased premises, and it must vacate the leased premises. If, however, the debtor fails to vacate the premises, the landlord can file a motion to lift the automatic stay so it can file or continue an eviction action in state court. If the debtor rejects the lease, the landlord may have a claim for “rejection damages” pursuant to 11 USC § 502(b)(6), subject to the mitigation-of-damages duty. 74
As a condition to assuming the lease, the debtor must cure all monetary defaults and provide adequate assurances of future performance under the lease. 75 A debtor who assumes the lease may be able to assign the lease free of restrictions on transfer set forth in the lease and over the landlord’s objection, 76 which may turn out to be a significant right for the debtor if it holds a below-market lease with sufficient time remaining on the lease term. However, a bankruptcy court has discretion to reject an assignment if it finds, for example, that the assignment would disrupt the tenant mix by changing the image of a shopping center or violating the use restriction in the lease. 77 A landlord may favorably view the debtor’s assumption because it assures continuation of the lease and the cure of existing defaults. But if the tenant is holding a below-market lease, the landlord may favor rejection to enable it to negotiate a new lease. A landlord may object to the debtor’s attempted lease assumption if the landlord disagrees with the debtor’s plan to cure the default or believes the debtor has not provided adequate assurance that the default will be cured or the debtor will perform in the future.
Section 365(b)(3)(C) of the bankruptcy code provides specific protections for “a lease of real property in a shopping center” by providing that no assignment can occur without assurances that use clauses and other provisions vital to the operation of the shopping center will continue to be performed, “including (but not limited to) provisions such as a radius, location, use, or exclusivity provision, and will not breach any such provision contained in any other lease, financing agreement, or master agreement relating to such shopping center.” The purpose of § 365(b)(3)(C) “is to preserve the landlord’s bargained-for protections with respect to premises use and other matters that are spelled out in the lease with the debtor-tenant.” 78 Moreover, § 365(b)(3)(D) requires adequate assurance “that assumption or assignment of such lease will not disrupt any tenant mix or balance in such shopping center.” Despite the bankruptcy code’s language protecting shopping centers, some bankruptcy courts have found lease provisions that limit the use of the shopping center premises to be per se restraints on alienation. 79 To avoid an adverse ruling if a shopping center tenant files for bankruptcy, a landlord should arm itself with as much evidence and expert testimony as possible to show a disruption in tenant mix or a real potential for violating other tenants’ rights if an assignment is allowed. 80
While a tenant’s bankruptcy filing places the lease in limbo, a landlord can be proactive by approaching the tenant to determine whether it intends to reject or assume the lease. Landlords and tenants should not treat the existing lease as a static document that presents the tenant with a “take it or leave it” proposition for assumption. If the tenant voices concerns about the current lease, the landlord can renegotiate the lease to entice the tenant to assume a modified lease (subject to court approval) that keeps the tenant in the premises and paying rent.

Negotiating Lease Transfer Provisions
Negotiating lease transfer provisions is an important process for both the landlord and the tenant because, at some time in the future, the landlord or the tenant may be forced to accept a previously unknown or undesirable counterparty to the lease. It is critical that attorneys impress upon their respective clients the short-term and long-term ramifications that could result from their negotiations of the lease transfer provisions. Landlords and tenants should consider the following issues when negotiating assignment and subletting provisions.
The Landlord’s Perspective
- The landlord’s primary objective in negotiating assignment and subleasing provisions is control , including control over the mix of tenants and control over the use of the leased premises. Thus, the landlord will use the transfer provisions to protect its interests in the premises.
- A landlord’s foremost concern is almost always the tenant’s ability to pay rent, in full, on a timely basis. A landlord should negotiate requirements that a prospective assignee or subtenant must meet, such as minimum net worth and minimum gross sales.
- The landlord can protect itself by including a right to recapture the premises if a tenant seeks to assign its lease or to sublet its premises. However, landlords should carefully consider whether to include language that terminates the lease automatically upon receipt of an assignment request because it could constitute a restraint on alienation, which is disfavored, and the landlord may prefer the leasehold to continue. 81
- The landlord should keep the original tenant on the hook. Landlords should oppose any transfer provision that relieves the original tenant of its obligations under the lease upon an assignment. Having a tenant with a vested interest in the assignee’s ability to perform the lease is helpful to ensure that a lease is transferred to a worthy transferee. Additionally, in the event the assignee does default, if the original tenant’s liability has been preserved, the landlord’s chances of recovery are improved.
- The landlord should limit the use rights of a subsequent assignee or subtenant. A landlord should seek to protect its right to control the mix of tenants, particularly in retail settings, so as not to violate exclusive use provisions. 82 Moreover, exclusives and use restrictions held by other tenants at a shopping center must be considered in conjunction with a potential change in use that may occur upon assignment or subletting.
- The landlord should seek to share in excess rent. 83 For example, where a tenant assigns its lease or subleases its premises, it may be paid more than the amount the tenant is obligated to pay the landlord under the lease. If the assignment or sublease had not been entered into, those same financial accommodations would theoretically have been available to the landlord if it had leased directly to the assignee or subtenant. Accordingly, a landlord should seek the right to share in this excess financial consideration along with the tenant, or if it has the leverage, to obtain 100% of such excess.
The Tenant’s Perspective
- The tenant’s goal is maintaining flexibility. The tenant’s ability to maintain flexibility through the lease largely depends on its leverage to negotiate favorable lease terms. A new business seeking space in a desirable retail shopping center may have little or no leverage to negotiate the transfer provisions, but a large corporation leasing significant space may have considerable negotiating strength. Thus, it is imperative that the tenant’s leasing broker and attorney understand the market forces at play in any lease negotiation.
- The tenant should seek flexibility to share the leased premises or certain portions of it (i.e., floor space, utilities, and parking) with its related entities and affiliates with which it has a business relationship, without having to seek the landlord’s consent in each instance. This issue is particularly important for large companies with divisions that operate under different business names.
- The tenant should also seek flexibility to restructure its organization without the landlord and the lease acting as an impediment to such alteration, by negotiating into the lease specific language permitting such changes. The tenant’s ability to reorganize its business, either through a merger, consolidation, or sale, could be delayed or impeded by the landlord under the transfer provisions if these provisions are not properly negotiated at the letter of intent stage or before the lease is executed.
- The tenant should maintain an exit strategy if the premises no longer satisfy its business needs because it has outgrown the space or needs less space. This is particularly important in the era of COVID-19. For example, start-up companies can quickly outgrow their leased premises, but if the landlord does not have more space available, the company must seek out new or additional space, frequently at a higher rate. Conversely, a change in economic forces can cause the tenant’s business to quickly retract. Thus, prospective tenants should be mindful to negotiate termination and rights of first refusal options for newly available space in the same building, with the end goal of ensuring that the size of their leased space does not impair their business objectives. 84
- The tenant should insist that the landlord’s right to approve a lease transfer not be unreasonably withheld, if the landlord insists on reserving such right. The lease should detail the specific standards the tenant must meet to obtain approval, such as the transferee’s minimum net worth and minimum business experience.
- Counsel for the tenant should attempt to include a provision for automatically releasing the tenant and any guarantor from further liability at the time of the lease transfer or after the transfer occurs if the assignee or sublessee can meet or exceed certain financial marks, such as net worth, sales, or revenue.
- The tenant should negotiate (1) the right to revoke a transfer request during a defined period after the landlord issues a notice to terminate and recapture the premises, and (2) a reasonable period to vacate the premises before the tenant will be subject to eviction proceedings if the tenant does not revoke the transfer request. Where the landlord insists on a termination and recapture provision, this rescission right provides a tenant the flexibility to stop the recapture process according to the tenant’s particular circumstances and commercial exigencies.
The relationships established between the parties to a lease, sublease, or assignment can be complicated. While the ability to transfer the lease can be a valuable tool for the tenant, the landlord’s interest in protecting its investment by choosing its occupants is equally compelling. However, a balance can be struck that provides the tenant the flexibility it needs while preserving the landlord’s control and minimizing its risk. During lease negotiations, both parties should recognize that changing circumstances during the lease term could trigger the need to assign the lease or sublet the premises. If thoughtful attention is given to negotiating the transfer provisions, the parties can assure themselves that, if the need arises to transfer the lease, their respective interests will be reasonably protected.
Thank you for your interest in Colorado Lawyer!
You have reached your maximum number of free articles.
For unlimited access to Colorado Lawyer articles, log in to your CBA account or join the Colorado Bar Association. For technical support, email [email protected] .
Adam F. Aldrich is the founder of Aldrich Legal, LLC, a Denver-based law firm focused on real estate and business transactions and litigation—(303) 325-5683. Coordinating Editor: Christopher D. Bryan .
Explore This Issue

Resources for Pro Se Litigation in the US District Court for the District of Colorado
Access to justice by kristen l. mix.

The Colorado Appellate Courts’ Commitment to Diversity and Inclusion
Judges’ corner by gilbert m. román and lino lipinsky de orlov.

The Perpetual Discussion
The sidebar by mark levy, related topics.
1 . Schneiker v. Gordon , 732 P.2d 603, 606 (Colo. 1987) (recognizing the “dual nature of a lease” as both a contract and a conveyance of an interest in land).
2 . Id. at 606–07.
3 . Shaffer v. George , 171 P. 881, 882 (Colo. 1917).
4 . Gordon Inv. Co. v. Jones , 227 P.2d 336, 340 (Colo. 1951).
5 . Shaffer , 171 P. at 882.
6 . Roget v. Grand Pontiac, Inc. , 5 P.3d 341, 345 (Colo.App. 1999) (“after the assignment, the assignee becomes primarily liable for the obligations under the contract, while the assignor remains secondarily liable”).
7 . Gordon Inv. Co. , 227 P.2d at 340.
8 . J.E. Martin, Inc. v. Interstate 8th St. , 585 P.2d 299, 301 (Colo.App. 1978) (“the delegation of duties under a lease and their assumption by a third person do not absolve the original lessee, absent the lessor’s knowledge and consent, simply by virtue of the conduct of the lessee and third party”). See also 1 Friedman and Randolph Jr., Friedman on Leases § 7:7.2 (Practising Law Institute 5th ed. 2013).
9 . V.O.B. Co. v. Hang It Up, Inc. , 691 P.2d 1157, 1159 (Colo.App. 1984).
10 . Friedman and Randolph Jr. , supra note 8 at § 7:4.2.
11 . Barbuti, “Assignments Pro Tanto And Why To Avoid Them,” 22 The Practical Real Estate Lawyer 24, 24–25 (Sept. 2006).
12 . Id. at 24.
13 . Id. at 23 (reprinted in part).
14 . Parrish Chiropractic Ctrs., P.C. v. Progressive Cas. Ins. Co. , 874 P.2d 1049, 1052 (Colo. 1994) (“Contract rights generally are assignable, except where assignment is prohibited by contract or by operation of law or where the contract involves a matter of personal trust or confidence”).
15 . Union Oil Co. of Cal. v. Lindauer , 280 P.2d 444, 447 (Colo. 1955). See also Malouff v. Midland Fed. Sav. and Loan Ass’n , 509 P.2d 1240, 1243 (Colo. 1973) (recognizing that “[t]he common law doctrine of restraints on alienation is a part of the law in Colorado”).
16 . Friedman and Randolph Jr., supra note 8 at § 7:3.3. See also Malouff , 509 P.2d at 1243 (holding “that the question of the invalidity of a restraint depends upon its reasonableness in view of the justifiable interests of the parties”).
17 . Beck v. Giordano , 356 P.2d 264, 265 (Colo. 1960).
18 . Lindauer , 280 P.2d at 447.
19 . Fink v. Montgomery Elevator Co. of Colo. , 421 P.2d 735, 738 (Colo. 1966).
20 . Routt Cty. Mining Co. v Stutheit , 72 P.2d 692, 693 (Colo. 1937).
21 . Parr v. Triple L & J Corp. , 107 P.3d 1104 (Colo.App. 2004).
22 . Cafeteria Operators L.P. v. AMCAP/Denver Ltd. P’ship , 972 P.2d 276, 278 (Colo.App. 1998).
23 . Id. See also Basnett v. Vista Vill. Mobile Home Park , 699 P.2d 1343, 1346 (Colo.App. 1984) (holding that a landlord may not unreasonably refuse consent under a silent consent clause because that result “incorporates the principles of fair-dealing and reasonableness and also preserves freedom of contract”), rev’d on other grounds , 731 P.2d 700 (Colo. 1987).
24 . List v. Dahnke , 638 P.2d 824, 825 (Colo.App. 1981).
25 . Cafeteria Operators L.P. , 972 P.2d at 279.
26 . List , 638 P.2d at 825.
28 . Ring v. Mpath Interactive, Inc. , 302 F.Supp.2d 301, 305 (S.D.N.Y. 2004); Toys “R” Us, Inc., No. 88 C 10349, 1995 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 14878 at *111 (N.D.Ill. Sept. 29, 1995); Restatement (Second) of Prop.—Landlord and Tenant § 15.2 cmt. g (American Law Inst. 1976).
29 . E.g., Campbell v. Westdahl , 715 P.2d 288, 293 (Ariz.Ct.App. 1985).
30 . Friedman and Randolph Jr., supra note 8 at § 7:3.4 (citing cases).
31 . Cent. Bus. Coll. v. Rutherford , 107 P. 279, 280 (Colo. 1910); List , 638 P.2d at 825 (dictum).
32 . Kendall v. Ernest Pestana, Inc. , 709 P.2d 837, 845 (Cal. 1985).
33 . Id. at 845. See also Econ. Rentals, Inc. v. Garcia , 819 P.2d 1306, 1317 (N.M. 1991).
34 . Cafeteria Operators L.P. , 972 P.2d at 277.
36 . Id. at 279.
38 . List , 638 P.2d at 825.
39 . Toys “R” Us, Inc. , U.S. Dist. LEXIS 14878 at *124 (landlord’s refusal before it has relevant information that should be obtained in making the consent decision may be unreasonable).
40 . Shaffer, The Sublease and Assignment Deskbook at 80–81 (American Bar Ass’n 2d ed. 2016).
41 . Compare Parr , 107 P.3d at 1107 (affirming trial court’s ruling that the landlord unreasonably withheld consent where the landlord delayed consent, which caused the proposed assignees to withdraw their offer to purchase the business) with Toys “R” Us, Inc. , 1995 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 14878 at *124 (landlord’s refusal before it has relevant information that should be obtained in making the consent decision may be unreasonable).
42 . Fahrenwald v. LaBonte , 653 P.2d 806, 811 (Idaho Ct.App. 1982).
43 . Parr , 107 P.3d at 1106.
45 . Id. at 1107.
46 . Bert Bidwell Inv. Corp. v. LaSalle and Schiffer , P.C., 797 P.2d 811 (Colo.App. 1990).
47 . Id. at 811.
48 . Id. at 812.
50 . Toys “R” Us, Inc. , 1995 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 14878 at *115 (citations omitted) (“where a lease contains provisions giving further meaning to a reasonableness clause, the standard of reasonableness varies”); Shaffer, supra note 40 at 80–81.
51 . Golden Eye, LTC v. Fame Co. , No. 0603166/2007, 2008 N.Y. Misc 8571 at *16 (N.Y. Gen Term Jan. 16, 2008) (“the Court may not determine reasonableness if withholding consent is based on grounds that were not included in the letter refusing consent”).
52 . Shaffer, supra note 40 at 74–75.
53 . Carma Developers (Cal.), Inc. v. Marathon Dev. Cal., Inc. , 826 P.2d 710 (Cal. 1992).
54 . Lindauer , 280 P.2d at 447.
55 . Murphy v. Traynor , 135 P.2d 230, 231 (Colo. 1943).
56 . Shoemaker v. Shaug , 490 P.2d 439, 441 (Wash.Ct.App. 1971) (finding that the tenant was not in default of the anti-assignment provision because it could reassign the lease back to itself).
57 . La Casa Nino, Inc. v. Plaza Esteban , 762 P.2d 669, 672 (Colo. 1988) (citing Schneiker v. Gordon , 732 P.2d 603 (Colo. 1987)).
58 . Gordon Inv. Co. , 227 P.2d at 260–61 (tenant’s subletting was held a breach that permitted landlord to terminate the lease).
59 . Shakey’s Inc. v. Caple , 855 F.Supp. 1035, 1043–44 (E.D.Ark. 1994) (holding that the landlord was estopped from terminating a lease on account of an unapproved sublease because the landlord did not act promptly).
60 . Merkowitz v. Mahoney , 121 Colo. 38, 42 (Colo. 1949) (“It is the general rule that any act done by a landlord, with knowledge of an existing right of forfeiture, which recognizes the existence of the lease is a waiver of the right to enforce the forfeiture”); Werner v. Baker , 693 P.2d 385, 387 (Colo.App. 1984) (“the lessor’s acceptance of rent accruing after the breach of an anti-assignment clause, with knowledge of the breach, constitutes a waiver of the right to terminate the lease for breach of that clause”). Cf. Nouri v. Wester & Co. , 833 P.2d 848, 851 (Colo.App. 1992) (holding that waiver of conditions against assignment by accepting rent did not carry over to other provisions in the lease).
61 . La Casa Nino, Inc. , 762 P.2d at 672.
62 . Carma Developers (Cal.), Inc. , 826 P.2d 710.
63 . Schneiker , 732 P.2d at 611.
64 . Friedman and Randolph Jr., supra note 8 at §§ 7:5.1 and 7:7.1.
65 . Tiger Crane Martial Arts Inc. v. Franchise Stores Realty Corp. , 235 A.D.2d 994, 995 (N.Y.App.Div. 1997) (“It is well settled that where, as here, a sublease is expressly made subject to the terms of a master lease, the subtenant has no legal right to compel the tenant to exercise an option for renewal of the entire demised premises in order to permit the subtenant to exercise an option for renewal of its subleased premises, absent proof of an agreement on the part of the tenant to exercise its option to renew for the benefit of the subtenant or evidence of special circumstances entitling the subtenant to such relief”).
66 . Burgess Pic-Pac, Inc. v. Fleming Cos. , 190 W. Va. 169, 175 (W.Va. 1993) (discussing liability of sublandlord to subtenant for failure to exercise renewal option after request from subtenant).
67 . Senn, Commercial Real Estate Leases: Preparation, Negotiation, and Forms , § 13.14 (Wolters Kluwer 6th ed. 2019).
68 . 11 USC § 1107.
69 . 11 USC § 365(a).
70 . 11 USC § 365(f)(2)(B).
71 . 11 USC § 365(d)(3).
72 . In re DB Capital Holdings, LLC , 454 B.R. 804, 816 (Bankr. D.Colo. 2011) (“waivers, unless they were part of a previous bankruptcy proceeding . . . should not be enforced”).
73 . NLRB v. Bildisco & Bildisco , 465 U.S. 513, 528 (1984); 11 USC § 502(b)(6).
74 . In re Shane Co. , 464 B.R. 32, 38–41 (Bankr. D.Colo. 2012) (discussing damages claim under 11 USC § 502(b)(6)).
75 . 11 USC § 365(b)(1).
76 . 11 USC § 365(f); In re Bricker Systems, Inc. , 44 B.R. 952 (Bankr. E.D. Wis. 1984) (recognizing that § 365(f) invalidates restrictions on assignment of contracts or leases by a debtor or trustee and allows assignment of assumed contracts at a later date).
77 . In re Federated Dep’t Stores, Inc. , 135 B.R. 941 (Bankr. S.D. Ohio 1991); In re Martin Paint Stores , 199 B.R. 258 (Bankr. S.D.N.Y. 1996), aff’d , S. Blvd., Inc. v. Martin Paint Stores , 207 B.R. 57 (S.D.N.Y. 1997).
78 . In re Trak Auto Corp. , 367 F.3d 237, 244 (4th Cir. 2004) (internal citation omitted).
79 . In re Bradlee Stores, Inc. , No. 00-16033, 2001 U.S. Dist. LEXIS 14755 (S.D.N.Y. Sept. 20, 2001) (holding that restriction on assignment violated the anti-assignment provisions of § 365(f)); In re Rickel Home Ctrs., Inc. , 240 B.R. 826, 832 (D.Del. 1998) (striking restrictive use provision).
80 . In re Trak Auto Group , 367 F.3d at 242 (enforcing use provision concerning the sale of automobile parts and accessories in shopping center lease); In re J. Peterman Co. , 232 B.R. 366 (Bankr. E.D.Ky. 1999) (rejecting assignment of shopping center lease where proposed assignment would violate radius restriction in lease and assignee did not sell similar merchandise as the original tenant). But see In re Toys “R” Us, Inc. , 587 B.R. 304, 307 (Bankr. E.D.Va. 2018) (overruling landlord’s objection to the debtor’s assignment on the grounds that it would violate the exclusivity provision of another lease in the shopping center and would disrupt the shopping center’s tenant mix and balance).
81 . Friedman and Randolph Jr., supra note 8 at § 7:1.1.
82 . In re Ames Dept. Stores, Inc. , 127 B.R. 744, 752–54 (Bankr. S.D.N.Y. 1991) (discussing rights of landlord to protect the tenant mix at the shopping center in the context of the lease and a subsequent bankruptcy filing of the tenant).
83 . Carma Developers (Cal.), Inc. , 826 P.2d 710 (upholding the landlord’s contractual right to capture excess rent).
84 . For an interesting discussion on the assignability of rights of first refusal, see Mitchell, “Can a Right of First Refusal Be Assigned?” 985 U. Chi. L. Rev. (2001).
As these cases illustrate, if a landlord wishes to withhold consent absent a sole and unconditional contractual right to do so, it must have fact-based reasons for doing so and cannot arbitrarily withhold or delay consent.
Assignment and Assumption of Leases (Commercial Real Estate Purchase and Sale) (CA) | Practical Law

Assignment and Assumption of Leases (Commercial Real Estate Purchase and Sale) (CA)
Practical law standard document w-003-5114 (approx. 17 pages).
How Do I Assign a Commercial Lease in the UK?

By Clare Farmer
Updated on 27 June 2023 Reading time: 5 minutes
This article meets our strict editorial principles. Our lawyers, experienced writers and legally trained editorial team put every effort into ensuring the information published on our website is accurate. We encourage you to seek independent legal advice. Learn more .
Deed of Assignment
What happens after the lease is assigned, other ways to end your lease agreement, key takeaways, frequently asked questions.
As a commercial tenant, you may not be able to honour your commercial lease for the entire lease term. The lease term refers to the time period in which you occupy the property. This property may be your business’ HQ, warehouse or distribution centre. There are various reasons as to why you may want to terminate your lease early and assign the lease. This article will explain the three critical instructions for assigning a UK commercial lease.
Assignment is a property transfer by the ‘assignor’ (the holder of the property) to the ‘assignee’ (the person receiving the property). As the commercial tenant, you are also the ‘assignor’ and, as such, may effectively assign your lease to another business owner. At this point, they become the new commercial tenant. This means that the new tenant is liable for the lease obligations in the commercial lease, such as rent payments and repair obligations.
The effect of an assignment is that you are now no longer a party to the lease. However, you will still be liable for the lease obligations if your landlord requires you to guarantee the new tenant’s lease obligations. This will be where an Authorised Guarantee Agreement (AGA) is put in place.
Whilst some commercial leases may not allow lease assignment, those which do will generally have conditions attached for the assignment to be valid. The assignment provision may detail whether there are conditions you must satisfy.
If you want to assign your commercial lease, you must know how to do so. Below, we detail three essential instructions to assign a UK commercial lease.
1. Find an Assignee
If you wish to assign your commercial lease, the first step will be to find a suitable business owner. They will be the assignee. A potential assignee will want first to inspect the lease terms in your commercial lease agreement before they agree to take on the lease. One term they will specifically look for is the permitted use of the commercial premises. This is because they will need to ensure that their business activities can occur on the commercial premises.
They may also want to carry out checks on, for example:
- the local authority;
- utility companies; and
- environmental issues.
It is not just your prospective assignee who will carry out checks when you assign the lease. You also will want to carry out checks on your prospective assignee, as will your commercial landlord. It is best to pre-empt the checks your landlord will carry out to ensure you select an assignee who can meet them satisfactorily. For example, you will need to check your assignee’s:
- financial status; and
- previous lease references.
2. Landlord Consent
Once you are satisfied you have found a suitable assignee for your lease assignment, you will likely need to get your commercial landlord’s consent before you assign your commercial lease. You should do this as soon as possible. UK law states that your landlord must respond to your request without unreasonable delay and should not unreasonably refuse to give consent for the lease assignment. It is advisable to get a solicitor to assist you with this.
Other Consent Considerations
Before you assign the lease to a specific business owner, you will also have to get your landlord’s consent that you may indeed assign the lease to this person. A landlord may include conditions in the commercial lease agreement as to who the assignee can be to ensure that the prospective tenant:
- can pay the rent;
- will look after the landlord’s commercial property; and
- will behave well on the commercial premises to avoid disturbing other businesses and tainting the landlord’s name.
Your landlord has the right to ask you to provide documents and information about the assignee. Your landlord may require information about your assignee’s position, such as their financial status, which you should have previously checked.
Once your landlord agrees to assign the lease, they will give you a document which is a licence to assign. They may also require you to sign an Authorised Guarantee Agreement. Your solicitor will typically review both documents before the documents are finalised and thereafter become binding.
If your commercial lease details no conditions surrounding the assignment of a lease, such as the need to get your landlord’s consent, you will not need a licence to assign the lease.
3. Assign the Lease
Once you have found a business owner to be the assignee for your commercial lease and your landlord consents to them being the new commercial tenant, you can start the lease transfer process and assign the lease.
As the tenant, you are responsible for assigning the lease. The process might vary depending on the lease term. If the lease is for seven years or more, you should use a Land Registry form which is a TR1. This method involves a simple transfer of the lease and is suitable where your lease is a registered lease. Where your commercial lease is less than seven years, you can assign it with a deed of assignment. This method is suitable where the commercial lease is unregistered.
Once the landlord consents to the proposed new tenant, the landlord and the new tenant will enter into a deed of assignment. This is the formal document that transfers your lease to the new tenant. It ends your duties concerning the lease, which the new tenant then takes over and agrees to be bound by. Since this is a legal document that all parties will need legal advice on, you and the new tenant must decide who will pay for the landlord’s legal fees.
Provided you did not enter into an authorised guarantee agreement with your now ex-landlord, you are released from any responsibility concerning the commercial premises you leased. The new tenant takes those responsibilities on. If you had to enter into an authorised guarantee agreement to secure the landlord’s agreement to the new tenant, that new tenant is still responsible for abiding by the terms of the original commercial lease. However, you are still potentially liable for the new tenant’s breach of that lease.
Before you ask your landlord if you can assign your lease to someone else, note that there are other ways to end your lease agreement early. These include:
- taking advantage of a ‘break clause’ (also known as an early termination clause ) in your lease agreement;
- asking your landlord to agree to let you terminate your lease early; and
- asking your landlord if you can find a subtenant for the property you rent.

This cheat sheet outlines what you should be aware of in your lease agreement.
Assigning a lease allows a tenant to terminate a commercial lease before it comes to an end. It allows you to end your lease obligations and pass these on to another business owner. If you wish to assign your lease, there are three key instructions on how to assign your commercial lease. The first is to find a suitable assignee (a new tenant) for your commercial premises. The new tenant will need, for example, to carry on a business similar to yours. The second is to gain consent to assign your lease from your commercial landlord, which may require you to obtain a licence to assign. Your landlord must also agree to the new commercial tenant you propose as the assignee. It is likely your landlord will carry out financial checks to confirm the proposed commercial tenant’s financial health. Finally, you can assign the lease with a land registry form or deed of assignment.
If you need help understanding the key instructions to assign a commercial lease in the UK, contact our experienced leasing lawyers as part of our LegalVision membership. For a low monthly fee, you will have unlimited access to lawyers to answer your questions and draft and review your documents. Call us today on 0808 196 8584 or visit our membership page .
Lease assignment is when a commercial tenant transfers their lease to a third party. The third party will then take on the lease obligations and be the new tenant in a commercial lease.
The first key instruction when you want to assign a commercial lease is to find a suitable assignee; this is a third party that becomes the new tenant and is bound by the commercial lease.
We appreciate your feedback – your submission has been successfully received.
Register for our free webinars
Understanding your business’ new employment law obligations, a roadmap to business success: how to franchise in the uk, contact us now.
Fill out the form and we will contact you within one business day
Related articles

4 Ways to End Your Commercial Lease Early in the UK

5 Tips When Purchasing a Business in England and Wales

Can My Landlord Terminate My Commercial Lease in the UK?

Commercial Rent Reviews in England and Wales
We’re an award-winning law firm

2023 Economic Innovator of the Year Finalist - The Spectator

2023 Law Company of the Year Finalist - The Lawyer Awards

2023 Future of Legal Services Innovation - Legal Innovation Awards

2021 Fastest Growing Law Firm in APAC - Financial Times
Jordan Law Group
Real Estate Attorney Los Angeles for Evictions, Fraud & Nondisclosure and HOA Disputes
Commercial Leases and Properties – CA Rules on Assignments & Subleases
Starting with Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.010, California has codified the rules with respect to a tenant’s transfer of interest in a commercial lease, i.e., an assignment or sublease. For purposes of the rules regarding assignments and subleases of commercial property, a “lease” would include a lease or sublease of real property for other than residential purposes, and includes modifications and other agreements affecting a lease. A “tenant” includes a subtenant or assignee. A “transfer” of a tenant’s interest includes an assignment, sublease, or other voluntary or involuntary transfer or encumbrance of all or part of a tenant’s interest in the lease, and a “restriction on transfers includes a provision in a lease that restricts the right of transfer of the tenant’s interest in the lease. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.020. These rules apply to all commercial leases except to leases with restrictions on transfers executed before September 23, 1983 wherein the lease does not provide a standard for a landlord giving or withholding consent. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.270.
Legislative Findings and Declarations:
Until the case of Kendall v. Ernest Pestana, Inc., 40 Cal.3d 488 (1985), and its predecessor, Cohen v. Ratinoff, 147 Cal.App.3d 321 (1983), the parties to commercial real property leases could reasonably rely on the law of the state to provide that if a lease restriction requires the landlord’s consent for transfer of the tenant’s interest in the lease but provides no standard for giving or withholding consent, the landlord’s consent may be unreasonably withheld. (Emphasis added.)
The California Legislature found that the Kendall and Cohen decisions reversed the law on which parties to commercial real property leases executed before September 23, 1983, the date of the Cohen decision, could reasonably rely, thereby frustrating the expectations of the parties, with the result of impairing commerce and economic development.
Restrictions on Transfers in a Commercial Lease:
Most commercial leases contain restrictions on the tenant’s ability to freely transfer or assign his/her/its interest in the lease. If the lease does not include a restriction on the tenant’s ability to transfer, then the tenant retains an unrestricted right to transfer the interest in the lease. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.210. Any ambiguity in a restriction on transfer of a tenant’s interest in a lease shall be construed in favor of transferability. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.220. A landlord may restrict a tenant’s right to transfer by absolutely prohibiting transfers. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.230.
Standards, Conditions and Consent:
A restriction on transfer of a tenant’s interest in a lease may provide that the transfer is subject to any express standard or condition, including, but not limited to, a provision that the landlord is entitled to some or all of any consideration the tenant receives from a transferee in excess of the rent under the lease. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.240.
A restriction on transfer of a tenant’s interest in a lease may require the landlord’s consent for transfer subject to any express standard or condition for giving or withholding consent, including, but not limited to, either of the following: (a) The landlord’s consent may not be unreasonably withheld. (b) The landlord’s consent may be withheld subject to express standards or conditions. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.250.
Tenant’s Burden Of Proof For Unreasonably Withholding Consent:
If a restriction on transfer of the tenant’s interest in a lease requires the landlord’s consent for transfer but provides no standard for giving or withholding consent, the restriction on transfer shall be construed to include an implied standard that the landlord’s consent may not be unreasonably withheld. Whether the landlord’s consent has been unreasonably withheld in a particular case is a question of fact on which the tenant has the burden of proof. The tenant may satisfy the burden of proof by showing that, in response to the tenant’s written request for a statement of reasons for withholding consent, the landlord has failed, within a reasonable time, to state in writing a reasonable objection to the transfer. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.260.
Tenant Remedies For Unreasonable Withholding Of Consent:
Restrictions – A remedy provided by law for violation of the rights of the tenant or of the landlord concerning transfer of a tenant’s interest in a lease, including a remedy provided in this article, is (a) subject to an express provision in the lease that affects the remedy and (b) subject to any applicable defense, whether legal or equitable, including, but not limited to, waiver and estoppel. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.300.
Remedies – If a restriction on transfer of a tenant’s interest in a lease requires the landlord’s consent for transfer subject to an express or implied standard that the landlord’s consent may not be unreasonably withheld, and the landlord unreasonably withholds consent to a transfer in violation of the tenant’s rights under the lease, in addition to any other remedies provided by law for breach of a lease, the tenant has all the remedies provided for breach of contract, including, but not limited to, either or both of the following: (a) The right to contract damages caused by the landlord’s breach; and (b) The right to terminate the lease. See Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.310.
If you have questions regarding your Commercial Lease, contact one of our Los Angeles Commercial Lease Attorneys for a free consultation and case evaluation.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Commercial lease assignments: A guide for businesses

Business owners often consider commercial lease assignments to enhance flexibility, mitigate financial burdens, or adapt to evolving operational requirements.
The work landscape, particularly in cities like London, is also evolving with the widespread adoption of remote and hybrid models, with many tenants seeking to streamline their footprints and reduce overhead costs.
Whether your business is looking for a more suitable space or navigating market fluctuations, this article will give you an overview of the lease assignment process and the essential legal aspects to consider.
What is the assignment of a lease?
The assignment of a lease refers to the legal process through which a tenant transfers their lease obligations and rights to another party, known as the assignee. This strategic move allows businesses to exit their premises before the lease term ends, with the assignee assuming responsibility for complying with the lease terms and obligations.
Businesses may consider lease assignment for various reasons, such as relocation, financial constraints, or changes in business needs. For instance, a company experiencing rapid growth may seek more extensive premises, making lease assignment an attractive option to exit the current arrangement.
What role does a solicitor play?
Understanding the legal complexities is vital when considering the assignment of a commercial lease. In this process, solicitors offer expert advice and can negotiate with the landlord to secure favourable terms within the assignment agreement, safeguarding the client's interests.
Their pivotal role extends to drafting and finalising essential legal documents associated with lease assignments, such as:
- Licence to assign: A solicitor can assist in drafting this document, ensuring that it covers all necessary conditions and terms for the assignment, meets legal requirements, and protects the interests of both parties.
- Rent deposit deed: Solicitors can draft the rent deposit deed, specifying the details of the deposit arrangement, its purpose, and the conditions under which the landlord can use the deposit, providing legal clarity for both parties.
- Authorised guarantee agreement (AGA): Solicitors are instrumental in creating an AGA, outlining the legal commitment by the outgoing tenant to guarantee the new tenant's performance. They ensure that the agreement is comprehensive and legally sound, protecting the interests of the landlord and the outgoing tenant.
Avoiding the legal pitfalls of lease assignments
While every commercial lease assignment is unique, several legal aspects require careful consideration.
1. Leasehold covenants: Ensuring compliance
Understanding leasehold covenants is essential in the lease assignment process as it involves recognising and complying with the agreed-upon obligations and restrictions outlined in the lease agreement. These covenants dictate how the property can be used, any alterations or improvements allowed, and other conditions the current and potential tenants must adhere to.
For example, if a leasehold covenant stipulates that the premises can only be used for office purposes, you cannot assign the lease to a manufacturing company.
Failure to understand and meet these covenants could lead to complications, including the landlord's refusal to consent to the assignment or potential legal issues. Comprehending these covenants is essential for a smooth and legally compliant lease assignment.
2. Securing the landlord's consent: A prerequisite
Before proceeding with a lease assignment, obtaining the landlord's consent is paramount. This process involves submitting a formal request providing details about the proposed assignee and their financial stability.
While landlords cannot unreasonably withhold consent, specific lease terms may give them grounds to do so. Understanding the particular conditions for refusal is crucial, so it is important to seek legal advice as soon as possible.
3. Liabilities when assigning a commercial lease
Understanding liabilities when assigning a lease is crucial for business owners as it directly impacts their ongoing responsibilities and potential financial obligations. Transferring a lease doesn't automatically absolve the original tenant of all liabilities; they may still be held accountable if the new tenant defaults on payments or breaches lease terms.
An authorised guarantee agreement (AGA) is a legal commitment often used in the context of commercial lease assignments. When a tenant assigns its lease to a new tenant, the outgoing tenant (assignor) may be required to provide an AGA. This agreement serves as a guarantee by the original tenant to the landlord, ensuring that the obligations of the new tenant (assignee) under the lease will be fulfilled.
The AGA means that if the new tenant defaults on the lease obligations, the outgoing tenant remains liable, guaranteeing the landlord a level of financial security. The original tenant can be pursued for any unpaid rent or other breaches of the lease terms by the new tenant. The AGA provides a legal mechanism for the landlord to seek redress from the outgoing tenant if issues arise with the assigned lease.
Clear comprehension of these liabilities ensures informed decision-making and risk mitigation during the lease assignment process.
4. Navigating regulatory changes
The evolving regulatory landscape, particularly factors like Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs), can add additional challenges to lease assignments. For example, if you took on a lease before Minimum Energy Efficiency Standards (MEES) came into effect on April 1, 2018, the regulations did not apply at the time of the lease's inception. However, if you are now considering assigning the lease, MEES regulations would be applicable.
A landlord may be less willing to agree to the lease assignment if it becomes essential to ensure that the property meets the required EPC standards to comply with the current regulations.
5. Formalising with Land Registry: A vital step
Registering an assignment with the Land Registry is an important step in the lease assignment process. If a lease is granted with a term of over seven years, it must be registered to record the change of tenant officially.
Failure to complete this registration can have significant consequences, including potential challenges to the validity and enforceability of the assignment.
What are the alternatives to assigning a commercial lease?
When considering an exit from a commercial lease, it's crucial to recognise that assignment is just one of several options. Exploring these options is vital, and seeking guidance from a solicitor ensures a comprehensive understanding of the available choices.
- Assignment vs. subletting: Assignment involves permanently transferring your lease obligations to a new tenant. On the other hand, subletting a commercial property allows you to lease a part of your space to another party, retaining your responsibility for the entire lease.
- Taking advantage of a 'break clause': A break clause is a provision in the lease allowing either party to terminate the agreement early, typically at predefined intervals. It provides a strategic exit, but conditions and notice periods must align with the lease terms.
- Early termination with landlord's consent: Seeking your landlord's agreement to terminate the lease prematurely can be challenging. It requires negotiations and may involve financial considerations. Legal advice is essential to navigate this complex process and safeguard your interests.
Business owners can make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives by understanding the intricacies, exploring alternatives, and leveraging legal expertise.
Commercial lease expertise
Our team of experienced commercial property solicitors is dedicated to guiding you through the lease assignment process. Every business has unique needs, so we offer tailored advice that aligns with your objectives.
In addition to lease assignments, we can provide guidance on alternative options for ending a commercial lease, such as subletting, break clauses, and lease termination.
With solicitors in London, Brighton, East Sussex, and Cumbria, we assist commercial landlords and tenants nationwide.
Looking to assign a commercial lease?
You might also like to read:
Subletting strategies: maximising flexibility in commercial leases, how to surrender a commercial lease: a guide for landlords and tenants.

How to end a commercial lease early: A quick guide
Repair clauses in commercial leases: what tenants need to know.
- Make an Enquiry
- 020 8290 0440
- Wealth Planning
- Probate & Administration of Estates
- Older and Vulnerable Client services
- Contentious Probate FAQs
- Divorce Applications
- Civil Partnerships
- Domestic Abuse & Injunctions
- Prenuptial Agreements & Asset Protection
- Landlord and Tenant Disputes
- Consumer Disputes
- Contract Disputes
- Property Disputes
- Probates, Wills, and Estates Disputes
- Debt collection
- Professional Negligence
- Discrimination, bullying & harassment
- Redundancy & Settlement Agreements
- Whistleblowing
- Contractual Disputes & Post-Termination Restrictions
- Contracts, Incentive & Remuneration
- Sale & Purchase (Conveyancing)
- Equity Release
- Joint Ownership & Loan Agreements
- Mortgages & Remortgages
- Pre-Auction Advice
- Right to Buy & Shared Ownership
- Transfer of Equity
- New Build Purchases
- Leasehold and Freehold Advice
- Mergers, Acquisitions and Disposals
- Shareholder & Partnership Agreements
- Finance & Growth Funding
- Joint Ventures
- Insolvency and Restructuring
- Commercial Contracts
- Intellectual Property & Data Protection
- Terms and Conditions
- Franchise Agreements
- Business Start-ups
- Commercial Landlord and Tenant Disputes
- Boardroom & Shareholder Disputes
- Contractual Disputes
- Debt Collection
- Redundancy & Business Restructuring
- Employers' HR & Retainer Services
- Defending Tribunal Claims
- Employment Contracts & Staff Handbook
- Managing Exits & Settlement Agreements
- Commercial Conveyancing
- Landlord & Tenant
- Land Development
- Secured Lending
- Agricultural Land & Estates
- Real Estate
- Retail, Hospitality & Leisure
- Financial & Professional Services
- Education & Independent Schools
Elliot Lewis
- 020 8461 6199
- Contact details
Jane MacLeod
- 020 8461 6152
Stuart Ruff
- 01732 496 460
David Hacker
- 020 8461 6151
Emma Thompson
- 020 8461 6110
Vikki Herbert
- 020 8461 6211
- 01732 496 468
Yildiz Betez
- 020 8461 6214
To contact us with any enquiry, please fill in the following form so that a relevant legal advisor can contact you as soon as possible.
Commercial lease assignment: when can consent reasonably be refused?
Advice | 25 June 2018
In this article, he delves a little deeper and considers when consent to such requests can reasonably be refused.
In a previous article , David Hacker, commercial property expert with Thackray Williams provided an overview of the rules governing requests from tenants for permission to assign a commercial lease. In this article, he delves a little deeper and considers when consent to such requests can reasonably be refused.
‘The law governing lease assignment is clear: consent to assign must be granted unless circumstances exist which make it reasonable for permission to be refused’, says David. ‘but what is not so clear is what sort of circumstances need to exist to meet the reasonableness requirement.’
The burden of proving that the refusal of consent is reasonable in any given case will always rest with the landlord, which makes taking legal advice at an early stage crucial.

Stipulations in the lease
Leases granted after 1 January 1996 will usually set out the circumstances in which consent to an assignment may be refused. These may include where, in the landlord’s reasonable opinion, it appears that the proposed new tenant will not be able to meet their liabilities under the terms of the lease, including where there is evidence to suggest that the new tenant will not be able to pay the rent.
It is also possible that the lease will stipulate the conditions that may be imposed where consent is given, such as the need for the outgoing tenant to enter an authorised guarantee agreement to secure the new tenant’s performance of the lease obligations, or a requirement that the new tenant pays a rent deposit.
A landlord who relies on the provisions of a lease in this way to justify the refusal of consent, or who is only willing to provide consent subject to the specified conditions, will not be in breach of the statutory duty to give consent. This is because the provisions relied on will have been agreed in advance and therefore the existing tenant will have known from the moment they signed up to the lease the hurdles they would have to overcome if they wish to assign.
Considerations outside of the lease
In addition to stipulations as to consent and conditions in the lease itself, a landlord may also be able to refuse consent on other grounds, or to impose other conditions, if in the circumstances it is reasonable to do so.
For leases entered before 1996, relying on considerations outside of the lease is the only way in which a refusal of consent, or the imposition of conditions, can be justified. This is because, prior to 1996, it was not possible for stipulations regarding these matters to be included within the lease itself. This makes it more difficult to be sure whether or not the reasonableness test is satisfied.
The main rule when seeking to rely on considerations not stipulated within the lease is that you cannot refuse consent, or seek to impose conditions, unless the reason for this has something to do with the relationship between you and the tenant and to things you expect may happen because of the proposed assignment. Examples of when this may be the case are detailed below.
In no circumstances can you use a request for consent as leverage to get any sort of advantage, for example by trying to get the existing tenant to agree to vary some aspect of the lease.
Examples of common scenarios
If the financial information provided by the proposed new tenant does not convince you that they will pay the rent due under the lease reliably, it should be reasonable to withhold consent. However, if, as part of the arrangements for assignment, provision has been made for the performance of the lease obligations by the new tenant to be guaranteed, then this is something which must be taken into account when assessing the request.
Before deciding what to do, you may want to inspect the property to check what sort of condition it is in. In a previous case which came before the courts, a landlord was held to be reasonable in refusing consent where the leased property was already in serious disrepair and they were not confident that the new tenant had the resources to deal with it. You should, however, be wary of relying on a breach of covenant as a reason for refusing consent because you will retain the right to pursue the existing tenant for this after the assignment has taken place. Minor breaches of the terms of the lease, in particular, will not be a reasonable ground for refusal.
You may be justified in taking the proposed new tenant’s intended use of the leased property into account. If you believe the intended use will breach the terms of the lease, then this should be a reasonable ground for refusing consent. Likewise, if you own a parade of shops, or the leased property is in a shopping centre, and there is a tenant mix policy in place to ensure a good range of uses, it will usually be reasonable to refuse consent to a tenant whose intended use does not fit with that policy.
Wherever reasonableness is involved, there are no hard and fast rules, which is why landlords faced with a request for consent to assignment need sound legal advice at the earliest possible opportunity. With the help of your solicitor you can ensure that you have access to all the information you need to make an informed decision and, where justifiable reasons for refusal exist, you can frame your objections appropriately and within a reasonable period.
For further advice about the assignment of a commercial lease, or for any other commercial property matter, please contact David Hacker.
How Do You Assign or Transfer a Commercial Lease?

By Jessica Dinh Lawyer
Updated on December 15, 2023 Reading time: 5 minutes
This article meets our strict editorial principles. Our lawyers, experienced writers and legally trained editorial team put every effort into ensuring the information published on our website is accurate. We encourage you to seek independent legal advice. Learn more .
- 1. Seek Your Landlord’s Consent
2. Deed of Assignment
3. transferring a retail lease, key takeaways.
If you lease a commercial property to operate your business, there may be situations where you need to transfer the lease. There are usually two situations when a tenant will transfer (also known as an assignment ) a commercial lease to another party (the assignee) before the end of a lease term. Namely, where the tenant is:
- selling their business, and the purchaser agrees to accept the existing lease rather than enter into a new lease with the landlord; or
- is proposing to exit the lease and has found a party who will take on the existing lease.
This article explains how the transfer of a commercial lease works. It also explains the critical terms of the deed of assignment from the perspective of the landlord, tenant and assignee.
1. Seek Your Landlord’s Consent
As soon as you propose an assignment as a tenant, you should:
- review the existing lease to identify if the lease can be assigned;
- identify the requirements of landlord’s consent upon assignment; and
- correspond with the landlord or agent as to consent and approval of the proposed assignee under the lease.
When seeking your landlord’s consent for the assignment, the proposed new tenant must usually provide their financial and business references to the landlord.
Can a Landlord Refuse to Assign a Retail Lease?
If the lease is a retail lease, the landlord will not be able to withhold consent to an assignment unreasonably. The retail legislation (different in each state) provides the grounds on which the landlord can withhold their consent. These generally include the:
- assignee proposes to change the permitted use;
- assignee has financial resources or retailing skills that are inferior to the assignor, and
- assignor has not complied with the relevant steps, per the retail legislation in that particular state, including providing a disclosure statement.
Ensure that you check the retail legislation in that particular state when carrying out an assignment.
After obtaining the landlord’s consent, a deed of consent to assignment is prepared (deed of consent).
A deed of consent is a legal document that outlines that the:
- landlord confirms their consent to the transfer of lease;
- tenant agrees to transfer their entire interest in the lease to the assignee from a specific date (the assignment date); and
- assignee, or new tenant, agrees to assume the rights and obligations of the lease as if they were the original tenant (such as repairs, security and payment of rent and outgoings) from the assignment date. This will continue until the end of the lease term and during any option or renewal terms.
The Landlord
Generally, the landlord’s key concern is that the transfer does not affect their rights under the lease. The landlord can address this concern by ensuring that the original tenant (assignor) has complied with all of their obligations under the lease until the assignment date. The landlord will have the right to take action against the tenant after the assignment date for any existing breach of the lease.
Additionally, the landlord will want to make sure that the assignee can comply with the lease obligations. This will often involve an assessment of the assignee as a tenant. The landlord will thoroughly examine the information before confirming their consent to the transfer. This might include:
- financial statements;
- business history; and
- professional references.
Finally, there is usually an agreement about who is liable for the costs of the deed of assignment. The landlord’s lawyer usually prepares the agreement. However, the outgoing tenant or the incoming tenant pays these costs, not the landlord.
The deed of assignment usually requires the assignee to give the relevant security and guarantees.
The Outgoing Tenant
As the outgoing tenant, your key concern is to be released from your obligations under the lease from the assignment date. The deed of assignment can address this concern by specifying that:
- the tenant is released from any claims or liabilities under the lease from the assignment date (provided that there is not an existing breach of the lease); and
- if the tenant has provided any security, it is to be returned or refunded.
It is important for you to remember that you are bound to the terms of the lease until the transfer of the commercial lease is formalised through the deed of assignment. Accordingly, you should continue to comply with your obligations under the lease until the assignment date.
On that note, a landlord might not agree to release you entirely from your obligations if the retail legislation in your state does not prevent this. This means that if the new tenant defaults, you could be responsible for fulfilling the lease obligations. In that case, you would need guarantees or an indemnity from the new tenant.
If the transfer of deed has to be registered, typically with retail leases, you (the assignor) usually organise the registration of the transfer, whose costs are divided with the new tenant (the assignee).
The Assignee
The new tenant’s, or the assignee’s, key concern is for the landlord to accept the transfer of the commercial lease from the assignment date. The deed of assignment can address this concern by providing that:
- the landlord accepts the assignee as tenant from the assignment date;
- the landlord will observe their obligations specified in the lease in favour of the assignee; and
- if required in the relevant state, the parties sign a transfer of lease form and register the transfer at the land titles office.
The assignee should ensure that they have reviewed the contents of the commercial lease (including the disclosure statement if it is a retail lease). Then, they must review the lease before signing the deed of assignment. This is because the assignee will need to comply with the obligations of the tenant from the assignment date. These obligations may include the provision of security and a personal guarantee.
A personal guarantee is taken on by an individual to guarantee the obligations of another individual or entity. For example, the assignee providing may provide a personal guarantee where a particular party becomes a guarantor. If you cannot meet your obligations (such as to pay the lease), then the guarantor will have to meet that obligation themselves.
Before finalising the deed of assignment, it is important that the landlord, assignor and assignee agree on who bears the costs of preparing, negotiating and registering the deed of assignment. Generally, you, as the assignee, will bear the costs. However, you may choose to add a cap or exclude negotiation costs.
If the lease you are transferring is a retail lease, the tenant will typically need to give the assignee a disclosure statement. This statement also includes details of any changes to the disclosure statement that the landlord provided when the lease was first entered into.
The disclosure statement outlines the vital information that the assignee needs to know, including the:
- current annual rent under the lease;
- current estimated outgoings payable under the lease;
- term of the lease and any options to renew; and
- details of the premises.
Generally, the tenant may request an updated disclosure statement from the landlord before the transfer of the commercial lease. The landlord has an obligation to provide the updated disclosure statement, usually within 14 days from the date of the request.
The disclosure statement requirements differ between the states and territories. For example, in:
- New South Wales, the assignee must receive the disclosure statement at least seven days before the date of the transfer; and
- Victoria and Queensland, the assignee must receive the disclosure statement at least seven days before the assignor requests the landlord’s consent.
The consequences of failing to provide a disclosure statement also differ between the states and territories. For example, the assignee may:
- withhold payment of rent;
- seek compensation from the landlord; or
- terminate the lease within a specific timeframe.
It is essential for all parties to be aware of the requirements and consequences of the disclosure statement provisions in their particular state or territory.
Additionally, transferring a lease may also lead to stamp duty implications . Stamp duty is a tax imposed on the purchase of assets and transactions of property. Therefore, if you are transferring a lease, you will commonly have to pay stamp duty. It is important that you are aware of the circumstances where you, as a tenant, will be required to pay stamp duty.

A factsheet that sets out the three ways to end a commercial lease in Australia: surrendering your lease, assigning it or subletting it.
Whether you are a landlord, tenant or assignee, it is crucial that you understand your rights and obligations when transferring a commercial lease. Further, the transfer of a retail lease leads to additional requirements and consequences related to the disclosure statement. Finally, you need to be aware of the steps you should take to ensure a smooth assignment.
If you need assistance with drafting or reviewing the terms of a deed of assignment, our experienced leasing lawyers can assist as part of our LegalVision membership. For a low monthly fee, you will have unlimited access to lawyers to answer your questions and draft and review your documents. Call us today on 1300 544 755 or visit our membership page .
We appreciate your feedback – your submission has been successfully received.
Register for our free webinars
Sponsoring overseas workers for your hospitality business, safeguarding vulnerable clients: mandatory ndis & in-home aged care reporting, tips for sponsoring overseas workers for ndis and aged care, engaging contractors: latest employment law changes, contact us now.
Fill out the form and we will contact you within one business day
Related articles

Deadlines for the Option to Renew a Lease in NSW

10 Things a Tenant Should Know Before Signing a Lease

How Will the Changes to the Retail Leases Act 1994 (NSW) Affect My Business?

I’m Selling a Business. How Do I Transfer the Lease?
We’re an award-winning law firm

2023 Fast Firms - Australasian Lawyer

2022 Law Firm of the Year - Australasian Law Awards

2021 Law Firm of the Year - Australasian Law Awards

2020 Excellence in Technology & Innovation Finalist - Australasian Law Awards

2020 Employer of Choice Winner - Australasian Lawyer
Subleases vs. Assignments in Commercial Tenancies
A commercial lessee may bring a third party into the lease agreement one of two ways: by sublease or by assignment. The distinguishing factor between the two concepts is the relationship between the original, or head lessee (tenant) and the head lessor (landlord). In the context of a sublease, the head lessee maintains the role of tenant with the head lessor as landlord, while in an assignment, the head lessee is removed from the relationship and the sublessee becomes the tenant of the head lessor in its place.
Historically speaking, the common law in Ontario has maintained that in order for a commercial lease to be considered a sublease rather than an assignment, the head lessee must retain a reversionary interest in the original lease by ending the sublease at least one day before the expiry of the head lease. This serves to guarantee the head lessee’s rights and interests in the property under the head lease. Failure to retain this interest has generally been interpreted to mean that the head lessee has indeed assigned the head lease to the sublessee.
However, a recent decision of the Ontario Court of Appeal (ONCA) has set a new standard for the interpretation of a sublease vs. an assignment, which could have a significant impact for commercial lessors and lessees going forward in Ontario.
Head Lease and Sublease Set to Expire on the Same Day
In this case, the head lessor (Smile Dental) entered into a seven-year commercial lease with the head lessee (Hazelton) in 2010 for a retail property in Toronto. In the lease, Hazelton retained the right to renew the lease for an additional five-year term upon six months’ notice to Smile Dental. In 2013, Hazelton completed extensive renovations to the property, including the removal of a bathroom. In 2016, Hazelton subleased the premises to a third-party clothing retailer (Outhere). Both the head lease and the sublease were set to expire on the same date, September 30, 2017, meaning that Hazelton did not reserve a reversionary right to the property. However, the terms of the sublease expressly stated that Hazelton did not have an obligation to renew or extend the sublease in favour of Outhere.
Six months before the end of the lease term, Hazelton notified Smile Dental that it wished to renew the head lease for a five-year term. The parties began negotiations with respect to the rent amount for the renewal, however, they were not able to come to terms. Two days before the lease was set to expire, Smile Dental notified Hazelton that it had no right to renew, asserting that Hazelton was in default of the lease due to the removal of the bathroom, which had been completed without Smile Dental’s authorization. The lease ended on the 30 th , and Smile Dental entered into a direct landlord/tenant relationship with Outhere, allowing it to remain in the space.
Hazelton brought an application seeking the following relief:
- A declaration that it had rightfully exercised its option to a five-year renewal of its lease starting October 1, 2017;
- An order that Smile Dental and Outhere deliver vacant possession of the premises; and
- An order that, in accordance with the terms of the head lease, an arbitrator be appointed to determine the rent payable during the five-year renewal period.
At Trial, Dispute Settled Under Principles of Contract Law
The applications judge acknowledged that Smile Dental had raised the “ancient common law” that stands for the concept that by not reserving the last day of the head lease for itself, a sublessor (in this case, Hazelton) in effect creates an assignment rather than a sublease. The judge also looked at case law standing for the proposition that when a head lease contains rights not granted in a subsequent sublease, those rights are reserved for the tenant under the head lease. However, the judge did not undertake any efforts to reconcile the two concepts. Instead, the court decided the matter on the basis of contract law. The applications judge found that Smile Dental had, in fact, breached its contractual duty to negotiate the renewal with Hazelton in good faith. However, the court found that no actual financial loss or damages had resulted and therefore dismissed Hazelton’s application.
Intent is Key in Determining Sublease vs. Assignment
The ONCA decision delved deeper into the conflicting case law and the issue of assignment vs. sublease, ultimately basing its finding on s. 3 of the Commercial Tenancies Act (the “ Act ”). The section states:
The relation of landlord and tenant does not depend on tenure, and a reversion in the lessor is not necessary in order to create the relation of landlord and tenant, or to make applicable the incidents by law belonging to that relation; nor is it necessary, in order to give a landlord the right of distress, that there is an agreement for that purpose between the parties.
The ONCA noted that s. 3 specifies that a reversion to the head lessor is not necessary to create a landlord and tenant relationship, indicating that a sublessor need not reserve a day for itself at the end of a sublease. However, the court did not want to create the result that any sublease would remain a sublease, thereby losing the distinction between an assignment and sublease. The ONCA held that regardless of whether there was a reversion to the sublessor, courts should look to the actions of the parties to determine their intent. In the case at hand, Hazelton had specifically retained a right to renew the head lease but had not extended the same right in the sublease to Outhere. This clearly demonstrated an intention to retain the role of lessee under the head lease, and not create an assignment to Outhere.
The ONCA further held that Smile Dental knew of the renovations prior to entering into initial negotiations with Hazelton respecting the renewal of the lease. Since Smile Dental had indicated a willingness to renew after discovering the removal of the bathroom, the ONCA found that it was simply using the renovations as a basis to justify the decision to deal directly with Outhere instead of Hazelton.
The ONCA found that the applications judge erred in undertaking a damages analysis when Hazelton had claimed no damages, but rather injunctive and declaratory relief. Noting that courts should limit analysis to the relief sought by the applicant, the appeals court set this determination aside.
Ultimately, the ONCA found that Hazelton had not in fact assigned its lease to Outhere, as demonstrated by the contents of the sublease and the notification to Smile Dental that it wished to renew the head lease. The court awarded Hazelton the relief it sought and ordered the parties to enter into arbitration to settle the matter of the rental amount to be paid under the renewal.
Takeaways for Commercial Landlords and Tenants
This case serves to add certainty and clarity to the notion that a commercial tenant must retain the last day of a head lease in its own name in order to avoid creating an assignment rather than a sublease. Rather than relying on the right of reversion, courts should look instead to the actions and intentions of the parties when making such a determination. However, best practices still dictate that nothing is better than a clear and carefully set out lease agreement, which expressly sets out the intentions of each party. This can help both landlords and tenants to avoid potential litigation down the road.
Contact GLG LLP in downtown Toronto for assistance with finalizing or renewing a commercial lease agreement. Their real estate and business lawyers have extensive experience drafting and reviewing commercial lease agreements of various sizes and across multiple industries. The firm also represents clients in litigation should that become necessary. To schedule a confidential consultation, call NUMBER or fill out the online form.
Please provide us with as much detail as you can about your case. A lawyer will be in touch as soon as possible.

- Asia Pacific
- Hong Kong SAR, China
- New Zealand
- Philippines
- Taiwan, China
- Czech Republic
- Netherlands
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- El Salvador
- United States
- Investor Relations
Colliers Helps Shaheen & Gordon Expand Presence in Downtown Manchester with Lease at 1155 Elm Street
Colliers, a global leader in commercial real estate services, is pleased to announce the expansion of Shaheen & Gordon, which has secured a long-term lease at 1155 Elm Street in Manchester, NH.
Represented by Bob Rohrer, Managing Director at Colliers in Manchester, NH, Shaheen & Gordon found its ideal office space in the heart of downtown Manchester. Denis Dancoes of Cushman & Wakefield represented the Landlord, Farley White.
Situated at the corner of Bridge and Elm Streets, 1155 Elm stands as a prominent downtown office building, serving as a gateway to the central business district.
“Shaheen & Gordon selected 1155 Elm after carefully considering several downtown Manchester options. They chose 1155 because it is a premiere office building that is well located and professionally managed. Working with our client, we secured a long-term lease, providing ample space for growth, while strengthening their presence in the downtown community.”
Bob Rohrer Managing Director | Colliers
Shaheen & Gordon anticipates relocating to its new 11,000 SF premises at 1155 Elm Street by July. Concurrently, its current 4,200 SF standalone office building at 180 Bridge Street in Manchester is listed for sale and for lease.
Related Experts

Robert Rohrer
Managing Director | New Hampshire
Manchester, NH
As Managing Director and Principal of Colliers’ New Hampshire offices, my responsibilities include managing the day-to-day operations of our firm and its continued growth and position within our marketplace. In this role, my primary goal is to provide a working environment that allows our brokers and staff to deliver to our clients the highest level of service available in our industry. One way to meet the above goal is to “practice what I preach” by advocating for my clients to the best of my ability. That means putting my 25+ years of experience - including my understanding of the business, the people, and the market - to work on every assignment I undertake. One of the great things about the commercial real estate industry is that no two deals are the same. I enjoy the challenge of being involved with complex, multi-layered projects that require me to continually build upon my understanding of the business. Strategizing and solving a real “game-changer” for a client is my favorite part of what I do. I am particularly interested in working on investment opportunities, development and redevelopment projects, and with assisting industrial and office users in finding the perfect real estate solutions for their business plan. I am fortunate to work with a group of professionals who complement my knowledge of commercial real estate so that, working collaboratively, we are able to provide informed and innovative real estate solutions. This team approach means we work quickly and efficiently on a variety of assignments at any given time. Prior to my commercial real estate career, I worked in sales for Xerox Corp. and was an attorney (still licensed, but not practicing).
Lake Zurich Commercial Property for Lease
Looking to rent commercial real estate in Lake Zurich, Illinois? Search for office space, warehouses, retail properties, and mo...

LAKE ZURICH SQUARE
199 s rand rd lake zurich, il 60047.

635 Oakwood Dr
635 oakwood dr lake zurich, il 60047.

444 S Rand Road
444 s rand rd lake zurich, il 60047.

Lake Zurich Building
330 il-22 lake zurich, il 60047.

Landmark Corporate Center
3880 salem lake dr long grove, il 60047.

Deertrail Court
884 s rand rd lake zurich, il 60047.

225 S Rand Rd
225 s rand rd lake zurich, il 60047.

950 W Main Street
950 w main street lake zurich, il 60047.
350 Surryse Road, Suite 300
350 surryse rd lake zurich, il 60047.

Oakwood Road Flex
61 - 95 oakwood rd lake zurich, il 60047.

20338-20350 Rand Rd., Deer Park, IL
20350 n rand rd lake zurich, il 60047.

Lake Zurich Shopping Center
Rand rd, route 22 & ela rd lake zurich, il 60047.

572 W Il Route 22
572 w il route 22 lake zurich, il 60047.

Lakeview Plaza - Lake Zurich
41-193 s rand rd lake zurich, il 60047.

715 Ela Professional Building
715 ela rd lake zurich, il 60047.

North Lake Commons
345 s rand rd lake zurich, il 60047.

Based off of your search, you may also like
Dunham's Sports Outlots
4450 24th ave fort gratiot twp, mi 48059.

6314 Odana Rd Madison, WI 53719

Kettering Crossing
2801 wilmington pike kettering, oh 45429.

Midtowne Shopping Center
201 n university ave little rock, ar 72205.

Weatherford Medical Plaza
1105 santa fe dr weatherford, tx 76086.

1005 Woodland Office
1005 court st woodland, ca 95695.

The Village at Riverstone
University blvd & l j pkwy sugar land, tx 77479.

4008 S. Pine Street - Unit 1
4008 s pine st tacoma, wa 98409.

World Equestrian Center Retail Campus
Nw 80th ct ocala, florida, fl 34482.

14,000 SF = (all 9 classrooms)
1021 pierce st trinidad, co 81082.

1179 Dekalb Pifke
1179 dekalb pike blue bell, pa 19422.

111 Division Street East
111 division st e buffalo, mn 55313.
7846 Dixie Highway
7846 dixie hwy louisville, ky 40258.

Sienna Grande Shops
Sienna pkwy & waters lake blvd missouri, tx 77459.

Five Cities
Senate dr monroe, oh 45050.

Quaker City Supply
1909 e westmoreland st philadelphia, pa 19134.
11th St Los Angeles, CA 90038

2460 E Rosedale S
2460 e rosedale st fort worth, tx 76105.
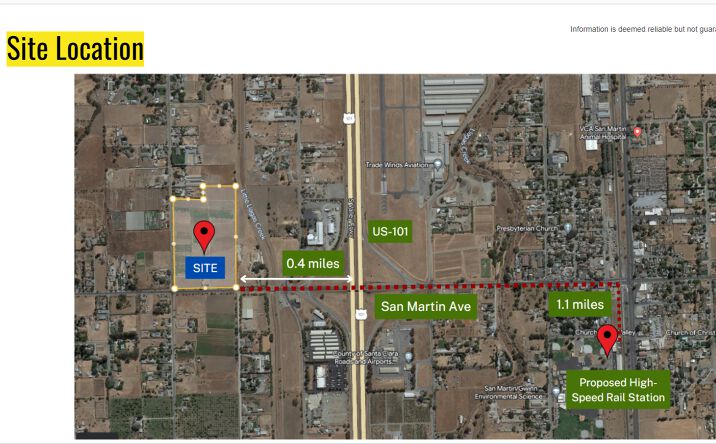
San Martin Lots
1020 e san martin ave san martin, ca 95046.

Pinewood Shopping Center
1306 fm 1960 rd w houston, tx 77090.
- Lake Zurich
Nearby Spaces
- Barrington 19 spaces
- Palatine 91 spaces
- Deer Park 7 spaces
- Schaumburg 255 spaces
- Mundelein 47 spaces
- Hoffman Estates 105 spaces
- Buffalo Grove 112 spaces
- Arlington Heights 183 spaces
- Rolling Meadows 111 spaces
- Vernon Hills 62 spaces
- Cary 22 spaces
- Libertyville 83 spaces
- Fox River Grove 9 spaces
- Grayslake 26 spaces
- Wheeling 57 spaces
- Elgin 133 spaces
- Island Lake 7 spaces
- Round Lake Beach 41 spaces
- Lake Barrington 10 spaces
- Mount Prospect 65 spaces
- Long Grove 3 spaces
- Naperville Park District 254 spaces
- Naperville 265 spaces
- West Dundee 14 spaces
- Elk Grove Village 46 spaces
- Itasca 21 spaces
- Algonquin 49 spaces
- Crystal Lake 64 spaces
- Deerfield 51 spaces
- Lincolnshire 75 spaces
- McHenry 41 spaces
- Gurnee 86 spaces
- Bloomingdale 53 spaces
- Bartlett 24 spaces
- Downtown 27 spaces
- Wood Dale 26 spaces
- West Town 177 spaces
- Des Plaines 201 spaces
- Chicago 3169 spaces
- East Dundee 6 spaces
Lake Zurich Space Types
- Retail 14 spaces
- Office 15 spaces
- Restaurant 4 spaces
- Land 2 spaces
- Industrial 4 spaces
- Special Purpose 3 spaces
- New Listings
- Start my search
- Work with a lender
- List for free
- Lead Connect
- Feature your listing
- Broker Dashboard
- Account Settings
- Office/Retail Mixed
- Multi-Family
- Medical Office
- Special Purpose
Search Type
Space details.
- Space Size: any 100 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 2,500 3,000 3,500 4,000 5,000 7,500 10,000 15,000 20,000 30,000 50,000 75,000 100,000 to any 100 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 2,500 3,000 3,500 4,000 5,000 7,500 10,000 15,000 20,000 30,000 50,000 75,000 100,000
- Acres: any 1 5 10 25 50 100 500 1,000 to any 1 5 10 25 50 100 500 1,000
- Lease Rate: any $1,000 / month $1,500 / month $2,000 / month $2,500 / month $3,000 / month $4,000 / month $5,000 / month $7,500 / month $10,000 / month $20,000 / month $50,000 / month $100,000 / month to any $1,000 / month $1,500 / month $2,000 / month $2,500 / month $3,000 / month $4,000 / month $5,000 / month $7,500 / month $10,000 / month $20,000 / month $50,000 / month $100,000 / month
- Sale Price any $100,000 $250,000 $500,000 $1,000,000 $2,000,000 $5,000,000 $10,000,000 $25,000,000 to any $100,000 $250,000 $500,000 $1,000,000 $2,000,000 $5,000,000 $10,000,000 $25,000,000
- Building Size: any 100 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 7,500 10,000 15,000 20,000 30,000 50,000 75,000 100,000 to any 100 500 1,000 1,500 2,000 3,000 4,000 5,000 7,500 10,000 15,000 20,000 30,000 50,000 75,000 100,000
- # of Floors: any 1 2 3 4 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 to any 1 2 3 4 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90
- Year Built: any 2020 2015 2010 2005 2000 1995 1990 1985 1980 1975 1970 1965 1960 1955 1950 1945 1940 1935 1930 to any 2020 2015 2010 2005 2000 1995 1990 1985 1980 1975 1970 1965 1960 1955 1950 1945 1940 1935 1930
- Class Rating: any A+ A B C
- LEED: any Certified Silver Gold Platinum
- Modified: any 3 days 7 days 30 days 90 days 180 days
Lake Zurich, IL Commercial Real Estate For Lease

No results found
Try zooming out to search a larger region or try broadening your limits on size, price, etc.
Market Stats
Lake Zurich has 89 commercial real estate spaces for lease, representing 616,168 sqft space. 58 buildings are available for sale. In the past 30 days, Lake Zurich has had 4 spaces leased.
Metropolitan areas near Lake Zurich, IL
- Chicago-Naperville-Elgin, IL-IN-WI
Counties near Lake Zurich, IL
Search specific use types.

- Edit SEO copy
Net-Lease Investment Volume Falls at a Slower Pace in Q1
U.s. net-lease investment | q1 2024.
May 17, 2024 2 Minute Read
Looking for a PDF of this content?
Executive summary.
- Net-lease investment volume fell by 26% year-over-year in Q1 to $7.4 billion, compared with a 21% decline in total commercial real estate investment volume.
- For the year ending Q1 2024, net-lease investment volume decreased by 44% from the comparable period in 2023 to $36.3 billion. Total commercial real estate volume over the same period fell by 43%.
- Industrial & logistics remained the largest sector for net-lease investment, although its share of total volume fell to 51% from 55% a year earlier. The retail sector’s share decreased to 27% from 31%, while the office share increased to 22% from 13%.
- The average net-lease cap rate increased by 70 basis points (bps) year-over-year to 6.6%. High inflation and 10-year Treasury yields, combined with tight credit conditions, pushed up average cap rates in Q1. CBRE expects that net-lease cap rates will stabilize in the second half of this year once the interest rate outlook improves.
- The average U.S. 10-year Treasury yield fell by 20 bps quarter-over-quarter to 4.2% but was 50 bps higher than a year ago. Spreads between the average net-lease cap rate and 10-year Treasury yield increased to 241 bps in Q1 2024 from 218 bps in Q1 2023.
- Account Details
- Email Preferences
- Member FAQs
© 2024 Observer Media · Terms · Privacy
ICSC Las Vegas: What to Expect Day by Day at the Big Retail Convention
By mark hallum may 16, 2024 2:08 pm.
ICSC ’s annual retail convention is back this month at the Las Vegas Convention Center with a full schedule bound to render all but the most vigorous attendees dead on their feet.
Here’s everything you need to know about the largest retail real estate conference in North America.
ICSC is a trade organization that promotes retail marketplaces where people (as its mission statement says) “shop, dine, work, play and gather.” The initials once stood for International Council of Shopping Centers, but these days it’s just ICSC.
Officially starting May 19, ICSC will get the ball rolling with a Retail Real Estate Case Competition with students from university real estate programs across the country presenting their solutions to real problems experienced by real companies.
The winners who impress the judges the most could get up to $20,000 in prize money, as has been the case in previous years.
This will take place May 19 between 8 a.m. and 2 p.m. Vegas time at the Wynn Las Vegas ’ Mouton section of the casino.
From 1 p.m. to 4:15 p.m., you can pick your poison with a whole bunch of workshops that cover topics such as capital stack management, learning about search engine optimization and leveraging artificial intelligence, as well as a dealmaking master class.
These can be found in the Wynn’s Lafite section.
Then close out the day with a reception that will see sportscaster and former professional and college football coach Nick Saban give a keynote speech at the Cristal section of the Wynn, followed by an opening reception in the event pavilion and garden. ICSC’s Global Awards ceremony at Margaux then caps the day.
“Ninety to 120 days out, my team will start to focus on the meetings we want to schedule and think about how we want to spend that social networking time, because if you go there without a very defined agenda it’s really difficult to have the kind of interactions and meetings that you want to have,” Michael O’Neill of Cushman & Wakefield (CWK) told Commercial Observer.
ICSC’s first day will wrap up at 8 p.m. on Sunday — it’s a school night — but that doesn’t mean there won’t be opportunities to mingle. After-parties, however, may be invitation-only.
Nevertheless, Newmark will have a celebration on Sunday from 4:30 to 6:30 p.m. at Intrigue Nightclub at the Wynn and Marcus & Millichap will be hosting The Retail Party from 7 to 10 p.m. at XS Nightclub .
Shake off that hangover and do it fast because Day Two waits for no one.
If you get to the convention center by 7:15 a.m., you’ll be just in time to catch breakfast and a forum called “Women Dealmakers: Empowering Women to Do Business Their Way.” Moderated by ICSC COO Valerie Richardson , panelists will include Amy Fingerhut of CBRE (CBRE) , Tanya Ragan of Wildcat Management , Tabassum Zalotrawala of McDonald’s USA and Robin Zeigler of Mural Real Estate Partners .
For those who hit the snooze button, another opportunity to digest food and insights will come in the form of “Building Retail Bridges: How Cities Can Align With National Retailers for Economic Development.” Starting at 7:30 a.m., the forum will be moderated by David Barilla of Orlando’s Downtown Development Board and include Pat Barber of Grocery Outlet and Meredith LeNoir of McDonald’s as speakers.
At 10 a.m., Naveen Jaggi of JLL will moderate the forum “The Marketplaces Industry: Innovative Perspectives to Transformative Insights.” The discussion will include Angele Robinson-Gaylord of Starbucks , Barrie Scardina of Cushman & Wakefield and Zalotrawala of McDonald’s.
At 10:45, Ken McIntyre of the Real Estate Executive Council , a trade association seeking to boost industry diversity, will moderate “Deal or No Deal: Key Considerations for Future Investing” with Karly Iacono of CBRE, Bryant “Bo” Okoroji of Steerpoint Capital and Vince Tibone of Green Street .
“Transforming Tradition: Reimagining Mall Design to Meet Consumers’ Needs” will begin at 1 p.m. and will be led by Stephanie Cegielski of ICSC. The forum will include Mark Hunter of CBRE, Annmarie Plenge of Pacific Retail Capital Partners and Greg Whitney of Poag Development Group speaking on the topic.
“The Breaking Ground Series: Women-Led Retail Concepts Transforming Shopping Spaces and Places” will start at 1:45 p.m. and will be a chance to hear from Open Realty Advisors ’ Carren Coston on her successes and future prospects.
At 2:30 p.m., retail coach Caroline Harrelson will moderate “Urban and Suburban Renewal Strategies — Lessons From Successful Revitalization Projects” with panelists Kevin Kramer from Village of Hoffman Estates , Arturo Sneider of Primestor Development and D. Lynn Spruill , the mayor of Starkville, Miss.
Meghann Martindale of Avison Young will moderate “The Office: The Effect of Flexible Work Models on Foot Traffic” at 3:15 p.m. with panelists Ethan Chernofsky of Placer.ai and Brandon Isner of CBRE.
“Retailtainment Concepts – An Experience Worth Shopping” begins at 4 p.m. and will include Alanna Joy Loeffler of Cushman & Wakefield as moderator and David Hochberg of Jaguar Bolera , Christine Nebiar of Brand Urban , Holly Rome of JLL and Eric Taylor of Sky Zone as panelists.
From 5:30 to 7 p.m. ICSC’s diversity reception will take place in the Margaux section of the Wynn.
“We’re focusing on meeting with all the child care operators. We actually have a private event that we were invited to by a broker on Sunday, and we’ll meet with child care operators there and outside of the ICSC event itself,” Pablo Barreiro , chairman of Fortec , told CO. “I think that it is good to have a conversation off site because it is a big event, things go fast and you don’t have a lot of time to talk.”
On Monday night, NY Developers are hosting an invite-only party at LIV Beach in Fontainebleau Las Vegas from 7:30 to 10:30 p.m.
Thus Day Two will end.
Day Three will start at 10 a.m. with panels much like the day prior. “The Social Shopper: Influencer Marketing’s Impact on Consumer Buying Habits” will be moderated by Najla Kayyem of Pacific Retail Capital Partners and paneled by Ashlyn Booth of JLL, Liz Glosson of The Dealey Group , Kyle Inserra of Zelnick & Company and Christine Mastandrea of Whitestone REIT .
Learn about “Shifting Store Formats: The Impact on Tenant Mixes, Leases and Portfolio” at 10:45 with moderator Anjee Solanki of Colliers (CIGI) leading the discussion with Michael Moran of CBRE, Scott Schnuckel of Kohl’s Department Stores and Caroline Wu of Placer.ai.
The last panel of the day will be “Tech-Driven Retail Experiences: From Augmented Reality to Contactless Payments,” which will be moderated by Amanda Metcalf of ICSC and include James Cook of JLL, Darren Mann of The ARIA Network and Deborah Weinswig of Coresight Research .
Mark Hallum can be reached at [email protected] .
Developer Legion Files Permits to Demolish Office Building It Just Bought for $58M
Desantis beefs up live local act to boost construction of multifamily dev, jp morgan chase inks office deal in west palm, deutsche bank, ksl partners provide $185m refi for miami hotel.

New York City Office Owners and Brokers Tout Recovery
By brian pascus.

MCB to Lead Massive Mixed-Use Development in Silver Spring
By jacob gardenswartz.

Global Cities Post-Pandemic Have a Blueprint in London’s Recent Success
By jace tyrrell.

COMMENTS
Landlord's assignment of a commercial lease. Sometimes a commercial landlord needs to sell his property. After the new owner, or assignee-buyer, buys the property subject to existing leases, the assignor-landlord assigns the leases to the new owner, who can then collect rent. The assignor-landlord notifies tenants by sending a notice of sale, a ...
Lease Assignment 101. In basic terms, a lease assignment occurs when the current tenant to an existing lease agreement (known as the "assignor") assigns the lease rights and obligations to a third party (known as the "assignee"). A lease assignment should not be confused with a sublease, in which the existing tenant transfers by a ...
An assignment of lease agreement is a contract to effectuate a transfer ... Assignments and Collateral Assignments Of Commercial Leases Terrence M. Dunn, a member of this news-letter's Board of Editors, is a founding partner of Einbinder & Dunn, in charge of the firm's business, real estate, trusts & estates and fash-ion law practices. ...
An assignment ensures the complete transfer of the rights to the property from one tenant to another. The assignor is no longer responsible for rent or utilities and other costs that they might have had under the lease. Here, the assignee becomes the tenant and takes over all responsibilities such as rent.
A commercial sublease, which is a type of lease transfer, occurs when a tenant who currently leases property agrees to let another tenant use the space concurrently. The agreement involves all three parties: the original tenant, the new tenant, and the property owner. When you sublease your space, you become the sub-lessor (or sub-landlord ...
Commercial real estate laws vary by state, so it's crucial to understand your legal entitlements and the terms of your Commercial Lease Agreement. ... A Lease Assignment Agreement is used when a tenant who is renting property from a landlord wants to transfer the entire interest that the tenant has in the property to a third party. The third ...
What Is an Assignment of a Commercial Lease? A commercial lease is a written contract that is used when a commercial tenant rents space from a landlord. Commercial real estate law is the area of law that governs commercial leases and commercial tenant and landlord rights. Similar to other types of leases, a commercial lease gives a commercial ...
An assignment of a lease occurs when an existing tenant ("Assignor") assigns its rights and obligations under the lease to a new tenant ("Assignee"). Another form of assignment occurs when a landlord sells the property and a new landlord takes over the lease. A sublease is often used when the existing tenant (often referred to as ...
Laws about the original commercial lease agreement. State laws governing real estate, renting, leasing, and assignments vary widely and can tremendously affect your arrangement. Since the tenant is legally responsible for this document, they must include specific information like financial statements in the commercial lease assignment.
Lease Assignment Agreement. Last revision 02/19/2024. Formats Word and PDF. Size 3 to 4 pages. 4.9 - 137 votes. Fill out the template. A Lease Assignment Agreement is a short document that allows for the transfer of interest in a residential or commercial lease from one tenant to another. In other words, a Lease Assignment Agreement is used ...
The modern commercial lease is a complex, integrated document that attempts to balance the competing interests of the landlord and tenant. As a result, commercial leases are the subject of much negotiation and are never "one size fits all." In fact, commercial leases are one of the least standardized documents in real estate practice.
An assignment and assumption of leases used in transactions for the purchase and sale of California commercial real estate where the seller assigns and the purchaser assumes the seller's interests and obligations, as the landlord, under the leases encumbering the real property. This Standard Document has integrated notes with important explanations and drafting and negotiating tips for both ...
1. Find an Assignee. If you wish to assign your commercial lease, the first step will be to find a suitable business owner. They will be the assignee. A potential assignee will want first to inspect the lease terms in your commercial lease agreement before they agree to take on the lease.
Lease. 3. Assignment. The Assignor assigns, transfers and sets over unto the Assignee all of the Assignor's right, title and interest in and to the Lease, including, without limitation, any and ... without the benefit of any inspection or investigation, and reserves any rights with re spect to any default that would be revealed by such an ...
Commercial Leases and Properties - CA Rules on Assignments & Subleases. Starting with Cal. Civ. Code § 1995.010, California has codified the rules with respect to a tenant's transfer of interest in a commercial lease, i.e., an assignment or sublease. For purposes of the rules regarding assignments and subleases of commercial property, a ...
While every commercial lease assignment is unique, several legal aspects require careful consideration. 1. Leasehold covenants: Ensuring compliance . Understanding leasehold covenants is essential in the lease assignment process as it involves recognising and complying with the agreed-upon obligations and restrictions outlined in the lease ...
In a previous article, David Hacker, commercial property expert with Thackray Williams provided an overview of the rules governing requests from tenants for permission to assign a commercial lease.In this article, he delves a little deeper and considers when consent to such requests can reasonably be refused. 'The law governing lease assignment is clear: consent to assign must be granted ...
creation or assignment of a lease. The creation or assignment of real estate leases is not subject to any national or local taxes. This is in contrast to the transfer of title in real estate, which triggers cantonal and communal transfer taxes. When leasing real estate, the tenant is not subject to any particular taxes payable on the rent.
is proposing to exit the lease and has found a party who will take on the existing lease. This article explains how the transfer of a commercial lease works. It also explains the critical terms of the deed of assignment from the perspective of the landlord, tenant and assignee. 1. Seek Your Landlord's Consent.
A commercial lessee may bring a third party into the lease agreement one of two ways: by sublease or by assignment. The distinguishing factor between the two concepts is the relationship between the original, or head lessee (tenant) and the head lessor (landlord). In the context of a sublease, the head lessee maintains the role of tenant with ...
Real Estate and Leasing Services . Lease Agreement . CAM/REALS - FORM 2501 (04/16) Page 2 of 3 ... commercial and residential quality kitchen equipment, vending and ice machines, and purchasing products certified by the U.S. EPA's Water Sense program. ... Any monies collected for the assignment or sublease shall be paid directly to the ...
Colliers, a global leader in commercial real estate services, is pleased to announce the expansion of Shaheen & Gordon, which has secured a long-term lease at 1155 Elm Street in Manchester, NH. Represented by Bob Rohrer, Managing Director at Colliers in Manchester, NH, Shaheen & Gordon found its ideal office space in the heart of downtown ...
136 Madison Avenue 5th & 6th Floors New York, NY 10016. Request Info. Crexi. For Lease. IL. Lake Zurich. Office. Search Office properties for lease in Lake Zurich. Review property details, see photos & contact leasing agents without leaving your desk.
Search commercial real estate for lease in Lake Zurich, including offices, warehouses & retail space. See photos, get details & contact leasing agents.
Amazon (AMZN) signed a new lease for nearly 1.2 million square feet of Class A industrial space in the Inland Empire with CapRock Partners, according to a mid-quarter report released Friday by Cushman & Wakefield. The property spans over 60 acres at 3945 Lytle Creek Road in Fontana, Calif., according to leasing marketing materials.
Find your next Lake Zurich, Il commercial space for lease. Search 71 spaces in 92 buildings for office, retail, or industrial spaces. Tenants. Start my search; Work with a lender; Education; ... Lake Zurich has 89 commercial real estate spaces for lease, representing 616,168 sqft space. 58 buildings are available for sale.
Net-lease investment volume fell by 26% year-over-year in Q1 to $7.4 billion, compared with a 21% decline in total commercial real estate investment volume. For the year ending Q1 2024, net-lease investment volume decreased by 44% from the comparable period in 2023 to $36.3 billion. Total commercial real estate volume over the same period fell ...
ICSC's first day will wrap up at 8 p.m. on Sunday — it's a school night — but that doesn't mean there won't be opportunities to mingle. After-parties, however, may be invitation-only. Nevertheless, Newmark will have a celebration on Sunday from 4:30 to 6:30 p.m. at Intrigue Nightclub at the Wynn and Marcus & Millichap will be ...