Need a business plan? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB1 Business Plan
- EB2 Visa Business Plan
- EB5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- UK Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- UK Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Planning
- Landlord Business Plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- eCommerce business plan
- Online Boutique Business Plan
- Mobile Application Business Plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food Delivery Business Plan
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples

State Farm Agent Business Plan Template
Nov.11, 2021
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
State Farm Agent business plan for starting your own business
A thoughtful business plan is required to build a successful insurance agency. Are you planning to start your insurance agency? For that, you need a well written and well-thought business plan.
The insurance agents, also known as insurance sales agents are involved in a variety of things. These include life insurance, property insurance, health insurance, long-term care insurance and disability insurance.
If you are interested to start a business in this industry and to know how to start a state farm agency, continue to read this state farm agent business plan. Just like our previous business plan for ecommerce , we have mention all the required steps to start your business.
No matter if you want to write indoor shrimp farm business plan , business plan for farmers market , oyster farming business plan , landscaping business plan , pig farming business plan or mushroom growing business plan , you can use this template for all kinds of purposes.
Executive Summary
2.1 the business.
Lifeline Insurance Company will be a registered general insurance company in New York. It was incorporated under the law of the US as a private Limited Liability Company.
We plan to transform into a Public Limited Liability Company in the future. So that we can get listed on the Stock Exchange of New York.
When starting a state farm agent business, you should be aware of becoming a state farm agent pros and cons. Also, similar to the landlord business plan , it is important to mention the management, customers and target of the business.
2.2 Management of State Farm Agent Business
When writing a state farm business proposal, it is necessary to plan everything before starting the business.
Lifeline Insurance Company will work on making its management strong that can support the growth of the company. We will make sure that we hire highly qualified and experienced people to help us in building the dream company.
The management body of our company mainly comprises the CEO, head of claims and premium collection, marketing executive, HR manager, accountant and customer care representatives.
2.3 Customers of State Farm Agent Business
The Lifeline insurance company will target small businesses and medium-sized businesses in and around the heart of the US – New York City. We will also make efforts to grow and sell our insurance policies in the other cities of the US as well.
Our customers will be from the US and other countries from the world. We have listed down the customers that we have designed our services and products for
- Entrepreneurs
- Corporate organizations
- Real Estate owners
- Blue Chips Companies
- The Government
- Sports Organizations
In state farm agent business plan example available online, you can find many other customers that an insurance company has.
2.4 Business Target
We plan to make the most out of state farm agent signing bonus. We are optimistic to become one of the most popular insurance companies in New York in the next 5 years.
Our primary goal is to cover all the investment in the next 3 years of our launch. Our secondary goal is to ensure that our customers are satisfied with our services and they get their claims when due without unnecessary delays.
We want to get included in the list of companies who are generating large revenue and are most trusted by people.
Company Summary
3.1 company owner.
Neil Fred will be the CEO of Lifeline Insurance Company. He will be responsible for providing direction to the business. Neil completed his degree from the University of London in Insurance and then decided to start his agency instead of doing a job. Neil knew that this industry is global and wide and he can make a lot out of it.
Keeping in view all these points, he decided to start a state farm agency program. He worked on all the things required for opening a state farm agency. He got the personnel and financial plan required in starting a state farm agency.
3.2 Why the State Farm Agent Business is being started?
Neil made research on the insurance market and got an idea of the profit he can make from starting a general insurance company. This business is a kind of business that never goes into loss. He first thought to start an insurance company in a specialized area.
Later when he realized that he can excel in the general market, he decided to open a general insurance company. Remember, in any state farm business plan sample, it is necessary to mention why and how the business is started.
3.3 How the State Farm Business will be started?
Starting an insurance company can be challenging. It is never easy to break into the industry. The insurance business is a business venture that is recession-proof and can stand the test of time. We have listed down the important steps you need to take to open your insurance business.
Make a research
If you do not have experience working as an insurance agent, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the insurance industry. Before you step into the world of insurance, make sure that you understand the necessary terms and concepts. When you completely understand the insurance products, terms, management skills, and sales savvy, you will be able to run this business successfully.
A business plan is required
Before starting any kind of business, a strong and well-thought business plan is required. Your business plan will decide how you are going to get the clients and how will you differentiate yourself from other insurance companies. When you write a business plan for your business, you will get a direction and vision for your business.
Get a license
To start an insurance company, you need to get a license. If you are planning to open an insurance company in the US, you need to get a license from the Association of Insurance Commissioners. This step is time-consuming but without it, you cannot start an insurance company.
Secure Financing
Certain factors decide how much investment you need to start an insurance business. These factors include your location, business model and more. People who are working independently with no or few staff members will have minimum expenses to cover. While larger agencies need more money to start and run their businesses.
Access to Insurance Carriers
To sell insurance, you need to get in contact with the insurance carriers. The insurance carriers affiliate themselves with the insurance companies that want to sell their products.
Promote the business
After you have made a strong business plan, got a license, secured your financing and affiliate yourself with the insurance carriers, the last but not the least step is to promote your business.
In the state farm agent business plan, it is necessary to mention all the services that your insurance company will provide.
When you open a state farm agency, you list down all the services you want to offer to your clients. When Neil was planning to start a state farm agency, he decided to provide the following services:
- Life & Health Insurance
- Property & Vehicle Insurance
- Disability & Group Insurance
- Agriculture & Travel Insurance
These services vary from state farm business to business.
Marketing Analysis of State Farm Agent Business
In the state farm business plan for new agents, the marketing analysis is necessary to mention. Neil wanted to get through this step smoothly so he got the services of marketing experts.
Business plan for investors
To start and run a successful business, solid state farm agent business plans are required. In all the state farm business plan examples, you will find this important part of the marketing analysis of a business.
No one can deny the importance of marketing analysis because whether the business is going to fail or succeed heavily depends on it. Marketing analysis forms the basis of many important decisions and steps in running a business. The state farm marketing plan include market trends, market segmentation, business target and product pricing.
5.1 Market Trends
The US has the largest number of insurance companies in the world. In a research made in 2013, the total gross premium on a global scale was 4.640 trillion US dollars, out of which 1.274 trillion was only written in the US. This figure shows how big the insurance market is in the US.
One common trend in the insurance industry is the existence of small insurers as single corporations. They partner up with holding companies. It has a lot of benefits because the survival of single insurance companies after turbulence is pretty low.
5.2 Marketing Segmentation
In the insurance industry, markets are segmented into different groups. The products or services offered by an insurance company are tailored to match the needs of the client. The advantage of marketing segmentation is to help the insurance organization identify the needs of their customers.
The marketing segmentation for our insurance company will be following:
Household sector
The household sector will include retired and self-employees and salaried staff.
Corporate sector
This sector will include big and small businesses.
Industrial sector
The industrial sector will include industries and manufacturers.
Organizations
This sector includes all kinds of organizations and institutions.
5.3 Business Target
The state farm mission statement includes the business target that a company aims to achieve. The business target of Lifeline General Insurance Company is to become one of the top companies in the US.
excellent work
excellent work, competent advice. Alex is very friendly, great communication. 100% I recommend CGS capital. Thank you so much for your hard work!
We aim to expand our state farm insurance franchise to other cities of the US as well. We are optimistic to cover all of our investment in the next 5 years of our launch.
5.4 Product Pricing
In the insurance industry, there is an established trend in pricing the products. Pricing the products and services depends upon the risk involved in the insurance policy covers. This calculation is done by the experts who keep in view all the aspects and then give the pricing.
The Lifeline Insurance Company will sell its insurance products and services at a low rate as compared to other insurance companies in town to increase our sales and customers.
Marketing Strategy for State Farm Agent Business
In every state farm agent business plan sample, you will find the marketing strategy because it is an important component in every state farm agent business proposal.
To make your insurance business run successfully, aggressive marketing is extremely important. It is why there are always men and women selling their insurance cover to people.
To survive in this industry, you need to be prepared to spend a lot of money on marketing and advertising your business to promote your products. There should be a strong marketing team that come up with unique and innovative ideas that can catch the attention of potential clients.
6.1 Competitive Analysis
The insurance market has become much more competitive over the last ten years. To survive in this industry, you have to be highly proactive, creative and customer-centric. Neil was aware of this high competition and he was prepared to compete among the leading insurance companies in the US.
From marketing managers to social media managers, a strong team is required to run an insurance business successfully.
6.2 Sales Strategy
- We will introduce our business to other small and medium-sized businesses by sending them letters, brochures and our policy.
- We will advertise our business using social media platforms to reach out to millions of people.
- We will attend seminars, expos and business fares to enhance our network and customers.
- We will hire sales agents and marketing executives to carry out direct marketing of our services and products.
6.3 Sales Monthly
6.4 sales yearly, 6.5 sales forecast, personnel plan.
In state farm agent business plans, an important part is the personnel plan. To open state farm agency, it is crucial to plan everything before the launch. Like in every state farm business plan proposal example, the personnel plan is an important step as it affects the decisions and success of any business.
The success and reputation of any business depend mainly on the staff and management of that company. The more loyal management, the more successful the business is. The personnel plan contains detailed information about the number and types of people who will work in a company. The advice of HR experts is vital to take at this step to make important decisions.
7.1 Company Staff
Neil Fred will be the owner and CEO of Lifeline Insurance business. The following people will be needed to run our company
- 1 Legal Secretary
- 2 general insurance managers
- 1 Head of Premium Collections
- 1 Head of Claims
- 3 customer representatives
- 2 client service executives
7.2 Average Salary of Employees
Financial plan.
The next step in state farm business plan is the financial plan. Like a personnel plan, it is also a crucial step in making any business plan. Like in all state farm business plan example, the financial plan covers all the points regarding the company expenses. It also includes the cost to start a business.
- The cost required for license, permits and policies
- The cost for buying computers, furniture, printers, telephones, and fax machines
- The salary of the employees
- The cost of making a website
- The rent of the office
8.1 Important Assumptions
8.2 break-even analysis, 8.3 projected profit and loss, 8.3.1 profit monthly, 8.3.2 profit yearly, 8.3.3 gross margin monthly, 8.3.4 gross margin yearly, 8.4 projected cash flow, 8.5 projected balance sheet, 8.6 business ratios.
- How do you make money as a State Farm agent?
The state farm agents get the clients. They come up with innovative and unique strategies to attract new clients and are paid based on successful sales and commissions. When you know how to start a state farm agency, you can make more money from your business.
- How much do State Farm agents make per policy?
The insurance agents get a commission of 40% in their sales for the first year. From the second year, the commission on the same sales become 2 to 5 percent. The commissions are pre-defined in the state farm agency program.
- Is a State Farm agent a sole proprietor?
Yes, state farm agents work as independent contractors and they are solely responsible for making decisions regarding the management and staff employed by them. The detail is given in the state farm agent business plan.
Download State Farm Agent Business Plan Sample in pdf
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Vegetable Farming Business Plan

Trading Business Plan

How To Write A Textile Manufacturing Business Plan

Start a Vending Machine Business in 2024: A Detailed Guide

Oil and Gas Business Plan

What Is Strategic Planning: Definition and Process

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:
An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know
- Translated Resources |
- Service Centers |
- Local Dashboard
Farmers.gov is not optimized for this browser. Please use the latest versions of Chrome, Edge, or Safari for the best experience. Dismiss
Find your state/county's agriculture data and USDA resources on your farmers.gov Local Dashboard !
How to Start a Farm: Plan Your Operation
Think about your operation from the ground up and start planning for your business. A good farm business plan is your roadmap to start-up, profitability, and growth, and provides the foundation for your conversation with USDA about how our programs can complement your operation.
Keep reading about planning your business below, get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey , or jump to a different section of the farmer's journey.
On This Page
Why you need a farm business plan.
A comprehensive business plan is an important first step for any size business, no matter how simple or complex. You should create a strong business plan because it:
- Will help you get organized . It will help you to remember all of the details and make sure you are taking all of the necessary steps.
- Will act as your guide . It will help you to think carefully about why you want to farm or ranch and what you want to achieve in the future. Over time, you can look back at your business plan and determine whether you are achieving your goals.
- Is required to get a loan . In order to get an FSA loan, a guarantee on a loan made by a commercial lender, or a land contract, you need to create a detailed business plan . Lenders look closely at business plans to determine if you can afford to repay the loan.
How USDA Can Help
Whether you need a good get-started guide, have a plan that you would like to verify, or have a plan you’re looking to update for your next growth phase, USDA can help connect you to resources to help your decisions.
Your state's beginning farmer and rancher coordinator can connect you to local resources in your community to help you establish a successful business plan. Reach out to your state's coordinator for one-on-one technical assistance and guidance. They can also connect you with organizations that specifically serve beginning farmers and ranchers.
It is important to know that no single solution fits everyone, and you should research, seek guidance, and make the best decision for your operation according to your own individual priorities.
Build a Farm Business Plan
There are many different styles of business plans. Some are written documents; others may be a set of worksheets that you complete. No matter what format you choose, several key aspects of your operation are important to consider.
Use the guidelines below to draft your business plan. Answering these kinds of questions in detail will help you create and develop your final business plan. Once you have a business plan for your operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center. During your visit, we can help you with the necessary steps to register your business and get access to key USDA programs.
Business History
Are you starting a new farm or ranch, or are you already in business? If you are already in business:
- What products do you produce?
- What is the size of your operation?
- What agricultural production and financial management training or experience do you, your family members, or your business partners have?
- How long have you been in business?
Mission, Vision, and Goals
This is your business. Defining your mission, vision and goals is crucial to the success of your business. These questions will help provide a basis for developing other aspects of your business plan.
- What values are important to you and the operation as a whole?
- What short- and long-term goals do you have for your operation?
- How do you plan to start, expand, or change your operation?
- What plans do you have to make your operation efficient or more profitable ?
- What type of farm or ranch model (conventional, sustainable, organic, or alternative agricultural practices) do you plan to use?
Organization and Management
Starting your own business is no small feat. You will need to determine how your business will be structured and organized, and who will manage (or help manage) your business. You will need to be able to convey this to others who are involved as well.
- What is the legal structure of your business? Will it be a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, trust, limited liability company, or other type of entity?
- What help will you need in operating and managing your farm or ranch?
- What other resources, such as a mentor or community-based organization , do you plan to use?
Marketing is a valuable tool for businesses. It can help your businesses increase brand awareness, engagement and sales. It is important to narrow down your target audience and think about what you are providing that others cannot.
- What are you going to produce ?
- Who is your target consumer ?
- Is there demand for what you are planning to produce?
- What is the cost of production?
- How much will you sell it for and when do you expect to see profit ?
- How will you get your product to consumers ? What are the transportation costs and requirements?
- How will you market your products?
- Do you know the relevant federal, state, and local food safety regulations? What licensing do you need for your operation?
Today there are many types of land, tools, and resources to choose from. You will need to think about what you currently have and what you will need to obtain to achieve your goals.
- What resources do you have or will you need for your business?
- Do you already have access to farmland ? If not, do you plan to lease, rent, or purchase land?
- What equipment do you need?
- Is the equipment and real estate that you own or rent adequate to conduct your operation? If not, how do you plan to address those needs?
- Will you be implementing any conservation practices to sustain your operation?
- What types of workers will you need to operate the farm?
- What additional resources do you need?
Now that you have an idea of what you are going to provide and what you will need to run your operation you will need to consider the finances of your operation.
- How will you finance the business?
- What are your current assets (property or investments you own) and liabilities (debts, loans, or payments you owe)?
- Will the income you generate be sufficient to pay your operating expenses, living expenses, and loan payments?
- What other sources of income are available to supplement your business income?
- What business expenses will you incur?
- What family living expenses do you pay?
- What are some potential risks or challenges you foresee for your operation? How will you manage those risks?
- How will you measure the success of your business?
Farm Business Plan Worksheets
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan.
Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans.
- FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet
- FSA-2037 Instructions
Planning for Conservation and Risk Management
Another key tool is a conservation plan, which determines how you want to improve the health of your land. A conservation plan can help you lay out your plan to address resource needs, costs and schedules.
USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) staff are available at your local USDA Service Center to help you develop a conservation plan for your land based on your goals. NRCS staff can also help you explore conservation programs and initiatives, such as the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) .
Conservation in Agriculture
Crop insurance, whole farm revenue protection and other resources can help you prepare for unforeseen challenges like natural disasters.
Disaster Recovery

Special Considerations
Special considerations for businesses.
There are different types of farm businesses each with their own unique considerations. Determine what applies to your operation.
- Organic Farming has unique considerations. Learn about organic agriculture , organic certification , and the Organic Certification Cost Share Program to see if an organic business is an option for you. NRCS also has resources for organic producers and offers assistance to develop a conservation plan.
- Urban Farming has special opportunities and restrictions. Learn how USDA can help farmers in urban spaces .
- Value-Added Products . The Agricultural Marketing Resource Center (AgMRC) is a national virtual resource center for value-added agricultural groups.
- Cooperative. If you are interested in starting a cooperative, USDA’s Rural Development Agency (RD) has helpful resources to help you begin . State-based Cooperative Development Centers , partially funded by RD, provide technical assistance and education on starting a cooperative.
Special Considerations for Individuals
Historically Underserved Farmers and Ranchers: We offer help for the unique concerns of producers who meet the USDA definition of "historically underserved," which includes farmers who are:
- socially disadvantaged
- limited resource
- military veterans
Women: Learn about specific incentives, priorities, and set asides for women in agriculture within USDA programs.
Heirs' Property Landowners: If you inherited land without a clear title or documented legal ownership, learn how USDA can help Heirs’ Property Landowners gain access to a variety of programs and services
Business Planning
Creating a good business plan takes time and effort. The following are some key resources for planning your business.
- Farm Answers from the University of Minnesota features a library of how-to resources and guidance, a directory of beginning farmer training programs, and other sources of information in agriculture. The library includes business planning guides such as a Guide to Developing a Business Plan for Farms and Rural Businesses and an Example Business Plan .
- The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers information about starting, managing, and transitioning a business.
SCORE is a nonprofit organization with a network of volunteers who have experience in running and managing businesses. The Score Mentorship Program partners with USDA to provide:
- Free, local support and resources, including business planning help, financial guidance, growth strategies.
- Mentorship through one-on-one business coaching -- in-person, online, and by phone.
- Training from subject matter experts with agribusiness experience.
- Online resources and step-by-step outlines for business strategies.
- Learn more about the program through the Score FAQ .
Training Opportunities
Attend field days, workshops, courses, or formal education programs to build necessary skills to ensure you can successfully produce your selected farm products and/or services. Many local and regional agricultural organizations, including USDA and Cooperative Extension, offer training to beginning farmers.
- Cooperative Extension offices address common issues faced by agricultural producers, and conduct workshops and educational events for the agricultural community.
- extension.org is an online community for the Cooperative Extension program where you can find publications and ask experts for advice.
Now that you have a basic plan for your farm operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center.
2. Visit Your USDA Service Center
How to Start a Farm with USDA
Get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey or jump to a specific page below.
Find Your Local Service Center
USDA Service Centers are locations where you can connect with Farm Service Agency, Natural Resources Conservation Service, or Rural Development employees for your business needs. Enter your state and county below to find your local service center and agency offices. If this locator does not work in your browser, please visit offices.usda.gov.
Learn more about our Urban Service Centers . Visit the Risk Management Agency website to find a regional or compliance office or to find an insurance agent near you.

12: Business Plans
What is a business plan.
A business plan is a document that helps you to organize and succinctly summarize the vision you have for your business. The plan contains the operational and financial objectives of a business, the detailed plans and budgets showing how the objectives are to be realized.
A good business plan will contain the following:
- Your business vision, mission statement, key values, and goals
- Description of the product(s) you intend to produce
- Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats the business may experience are described
- Production plans
- Marketing plans
- Estimated start-up costs
- Information on your legal structure and management team
- Current financial statements or projected financial statements.
- Resume or brief explanation of your background and relevant experience
- Less than 10 total pages so that people actually read it
Helpful Publications for Writing a Business Plan
General Business Resource Publications:
- Starting an Ag-Business? A Pre-Planning Guide http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2004/Cornell_AEM_eb0408.pdf
- Business Transfer Guide: Junior Generation http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2016/Cornell-Dyson-eb1605.pdf
- Producing a Business Plan for Value-Added Agriculture http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2007/Cornell_AEM_eb0708.pdf
- Business Planning for the Agriculture Sector: A Guide to Business Plan Development for Start-up to Mid-size Operations http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2010/Cornell_ pdf
- Building a Sustainable Business (Sustainable Agricultural Research Education (SARE)Publications) sare.org/publications/business.htm 280 pages of education and practical exercises to guide you through the financial, management, and interpersonal skills needed to start a successful farm business. Order hard copy for $17 or download PDF online for free.
Cornell Cooperative Extension Publications for Specific Commodities:
- Landscape Business Planning Guide http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2003/Cornell_AEM_eb0313.pdf
- Writing a Business Plan: A Guide for Small Premium Wineries http://publications.dyson.cornell.edu/outreach/extensionpdf/2002/Cornell_AEM_eb0206.pdf
- Writing a Business Plan: An Example for a Small Premium Winery https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/122203/2/Cornell_AEM_eb0207.pdf
Getting Help Writing a Business Plan
Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Business Plan Outline
- Farm Business Plan Home
- 1. Executive Summary
- 2. Company Overview
- 3. Industry Analysis
- 4. Customer Analysis
- 5. Competitive Analysis
- 6. Marketing Plan
- 7. Operations Plan
- 8. Management Team
- 9. Financial Plan
Farm Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your farm business plan.
We have helped over 5,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their farms.
Below are links to each section of a small farm business plan template. It can be used to create a vegetable farm business plan, fruit farm business plan, agriculture farm business plans or many other types of rural businesses.
Sample Business Plan For Farms & Agricultural Businesses
- Executive Summary – The Executive Summary is the most important part of your business plan. It is a brief description of your farm, its products and services, potential market opportunity, and competitive advantage.
- Company Overview – Also called the Company Analysis, here, you will provide a detailed description of your agriculture business history, its products and other services, and business structure.
- Industry Analysis – In the Industry Analysis, you will provide an in-depth analysis of the industry in which your farm operates including industry trends, market size and growth, and government regulations.
- Customer Analysis – In the Customer Analysis, you will identify your target market and provide insights into their purchasing habits. You will also create customer segments and discuss your marketing strategy for reaching them.
- Competitive Analysis – In the Competitive Analysis, you will identify your direct competition and provide insights into their strengths and weaknesses. You will also discuss your competitive advantage and how you plan to stay ahead of the competition.
- Marketing Plan – The Marketing Plan includes a discussion of your marketing strategy and tactics along with your pricing strategy. You will also provide a budget for your marketing activities including attending farmers’ markets or advertising a farm stand.
- Operations Plan – In the Operations Plan, you will discuss your farm’s day-to-day operations. You will also provide your business goals that you plan to achieve and a budget for your operating expenses.
- Management Team – In this section, you will provide a brief overview of the farm owners and farm management team, their experience in the agricultural industry, and the organizational chart.
- Financial Plan – In this section, you will provide three-year financial statements for your farm. This will include your income statements, projected balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
Next Section: Executive Summary >
Farm Business Plan FAQs
What is a farm business plan.
A farm business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your farm business. Among other things, a good agriculture farm business plan outlines your business concept, identifies your target audience , presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your farm business plan using our Farm Business Plan Template here .
What Are the Main Types of Farms?
There are many types of farms. Some have commercial farms that produce crops and agricultural products for sale. Others have cooperative farms owned by people who pool their resources together and share profits among themselves. There are also vegetable farms, dairy, micro, organic, poultry, subsistence, or urban farms.
What Are the Main Sources of Revenues and Expenses for a Farm?
The primary source of revenue for a farm is the sale of its farmed goods such as rice, corn, milk, beef, chicken, depending on the kind of farm a business is.
Some key expenses for a farm are labor expenses, production costs like irrigation, fertilizer, water, and machinery maintenance.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Agriculture Business?
Farm business plans often receive funding from bank loans. Financing is also typically available from grants offered by local and state governments. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are other funding options. This is true for starting any agricultural business.
What are the Steps To Start a Farm Business?
Starting a farming business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
- Develop An Agricultural Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed agriculture business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast. It should also include your business goals and mission statement. You can quickly complete your farm business plan using our Farm Business Plan Template here .
- Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your farm business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your farm business is in compliance with local laws.
- Register Your Agriculture Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your farm business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
- Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your farm business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
- Choose a Business Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
- Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
- Acquire Necessary Farm Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your agricultural business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
- Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your farm business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful farm business and agribusiness planning:
- How to Start a Farm Business
Where Can I Get a Farm Business Plan PDF?
You can download our free farm business plan template PDF here . This is a good farm business plan template you can use in PDF format.

Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 3,500 farmers create business plans to start and grow their farm businesses. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a farm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Farm Business Plan Template here >
What is a Farm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your farm business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Farm
If you’re looking to start a farm business or grow your existing farm business you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your farm business in order to improve your chances of success. Your farm business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes. It can be used to create a vegetable farm business plan, or a dairy farm, produce farm, fruit farm, agriculture farm and more.
Source of Funding for Farm Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a farm business are personal savings, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable. But they will want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business.
The second most common form of funding for a farm business is angel investors. Angel investors are wealthy individuals who will write you a check. They will either take equity in return for their funding, or, like a bank, they will give you a loan.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
Your business plan should include 10 sections as follows:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of farm business you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have a farm business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of farm businesses.
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the farm business industry. Discuss the type of farm business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of farm business you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types among others:
- Vegetable Farm : this type of farm grows a wide variety of vegetables (but not grains or soybeans) and melons in open fields and in greenhouses.
- Dairy Farm : this type of farm primarily raises cattle for milk. Typically, this type of farm does not process the milk into cheeses or butter, etc.
- Fruit Farm : this type of farm primarily grows fruits.
- Hay and Crop Farm : More than half of these types of farms grow hay, while a small number grow sugar beets. A variety of other crops, such as hops and herbs, are included in the industry. Some operators also gather agave, spices, tea and maple sap.
- Industrial Hemp Farm : this type of farm grows and harvests cannabis plants with a tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content of less than 0.3% by weight.
- Plant & Flower Farm : this type of farm grows nursery plants, such as trees and shrubs; flowering plants, such as foliage plants, cut flowers, flower seeds and ornamentals; and short rotation woody trees, such as Christmas trees and cottonwoods.
- Vertical Farming : This type of farm involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often using controlled environment agriculture (CEA) technologies. This method dramatically reduces the amount of land space needed for farming and can increase crop yields.
In addition to explaining the type of farm business you operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include sales goals you’ve reached, acquisition of additional acreage, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the farm business.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the farm business industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy particularly if your research identifies market trends. For example, if there was a trend towards decaffeinated farm business consumption, it would be helpful to ensure your plan calls for plenty of decaffeinated options.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your farm business plan:
- How big is the farm business (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your farm business. You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your farm business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: food manufacturers, grocery wholesalers, retail grocers, restaurants, individual consumers, etc.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of farm business you operate. Clearly food manufacturers would want different pricing and product options, and would respond to different marketing promotions than retail grocers.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Farm Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Farm Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other farm businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes processed foods, imported goods, and growing produce themselves. You need to mention such competition to show you understand the true nature of the market.
With regards to direct competition, you want to detail the other farm businesses with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be farm businesses located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What products do they offer?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide superior products?
- Will you provide products that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you make it easier or faster for customers to acquire your products?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a farm business plan, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : in the product section you should reiterate the type of farm business that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to wholesale crops, will you also offer subscriptions to individuals?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the products you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your farm. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your farm centrally located near gourmet restaurants and specialty grocers, etc. Discuss how your location might provide a steady stream of customers. Also, if you operate or plan to operate farm stands, detail the locations where the stands will be placed.
Promotions : the final part of your farm business marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Making your farm stand extra appealing to attract passing customers
- Distributing produce samples from the farm stand or at farmers markets
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local bloggers and websites
- Local radio advertising
- Banner ads at local venues
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your farm business such as serving customers, delivering produce, harvesting, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to serve your 1,000th customer, or when you hope to reach $X in sales. It could also be when you expect to hire your Xth employee or acquire more arable land.
Management Team
To demonstrate your farm business’s ability to succeed as a business, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in farming. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in farming and/or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you serve 100 customers per week or 200? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : While balance sheets include much information, to simplify them to the key items you need to know about, balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. For instance, if you spend $100,000 on building out your farm, that will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $100.000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt. For example, let’s say a company approached you with a massive $100,000 supplier contract, that would cost you $50,000 to fulfill. Well, in most cases, you would have to pay that $50,000 now for seed, equipment, employee salaries, etc. But let’s say the company didn’t pay you for 180 days. During that 180 day period, you could run out of money.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a farm business:
- Location build-out including barn construction, land preparation, etc.
- Cost of equipment like tractors and attachments, silos, barns, etc.
- Cost of nutrients and maintaining machinery
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Your new farm’s business plan must include a detailed financial plan based on reasonable assumptions of your costs and revenues. To determine if the results you show in this plan will be attractive to investors, look at industry standard financial metrics to see how you measure up against the farming industry, or your sector of the industry, on average. These are some basic measures and ratios to study.
Value of Production
The value of production is equal to your farm’s cash receipts plus the changes in value of product inventory and accounts receivable, less your livestock purchases. This is a measure of the value of the commodities you have produced in the period.
Net Farm Income
The NFI or net farm income, represents the value of production less direct and capital costs in the time period. This is a dollar figure, and not a ratio relating the income to the investment made, so it cannot be used to compare the farm against other farms.
Gross Margin
This represents the NFI less depreciation. The gross margin shows how much money is available in the year to cover the unallocated fixed costs, and dividends to owners and unpaid operators.
Return on Farm Assets
This is a ratio that can be used to compare the farm with others. This is calculated as NFI plus interest expense less unpaid operator labor, all divided by the total assets of the farm.
Asset Turnover Ratio
This ratio is equal to the value or production over the total farm assets. Combined with the operating profit margin ratio, this shows the efficiency of the farm in generating revenues.
Operating Profit Margin Ratio
This ratio is similar to Return on Farm Assets, but divides the same numerator (NFI plus interest expense less unpaid operator labor) by the value of production figure. This shows the percentage of each revenue dollar that becomes profit. If it is low, a higher turnover can compensate, and if it is high, a lower turnover ratio is required.
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your store design blueprint or location lease.
Farm Business Plan Summary
Putting together a business plan for your farm business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. It can be used for a small farm business plan template or any other type of farm. You will really understand the farm business, your competition and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful farm business.
Download Our Farm Business Plan PDF
You can download our farm business plan PDF here . This is a small farm business plan example pdf you can use in PDF format.
Farm Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my farm business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Farm Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Farm Business Plan.
Where Can I Download a Free Farm Business Plan Example PDF?
You can download our farm business plan PDF template here . This is an example business plan template you can use in PDF format.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Farm business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates


Farm Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
Farm Business Plan
If you want to start a successful farm or expand your current farming business, you need a business plan.
Fortunately, you’re in the right place. Our team has helped develop over 100,000 business plans over the past 20 years, including thousands of farm business plans.
The following farm business plan template and example gives you the key elements you must include in your plan. In our experience speaking with lenders and investors, the template is organized in the precise format they want.
You can download our Farm Business Plan Template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Example Business Plan For Farm Businesses
I. executive summary, business overview.
[Company Name], located at [insert location here] is a new, 500 acre organic dairy, beef, and wheat farm providing food products to regional distributors. [Company Name] is headed by [Founder’s Name], an experienced farm manager.
[Company Name]will sell high-quality beef cuts, wheat by the bushel, and whole milk. The products will be certified organic as growth hormones, fertilizers and pesticides will not be used in production.
Customer Focus
[Company Name] will primarily serve regional distributors of dairy, beef, and wheat products. Some products may be sold directly to manufacturers in the local area for the production of other products from these ingredients.
These businesses typically gross $5 million to $50 million in annual revenues and source their supplies from farms within a 100 mile radius of their facilities.
Distributors and manufacturers of food products in the region see growth in interest in organic products and are in need of organic ingredients for suppliers. Consumers show increased demand for these organic products at stores.
Management Team
[Company Name]’s most valuable asset is the expertise and experience of its founder, [Founder’s Name]. [First name] has been a farm operations manager for the past 15 years. He has spent much of his career working with Blue Ridge Farms, where he oversaw dairy, meat, and grain production.
[Company name] will also employ an experienced salesmanager to sell to distributors and manufacturers. This will be a skilled salesperson trained in farm sales by [Founder’s Name]. An assistant manager will manage day-to-day operations of the farm.
Success Factors
[Company Name] is uniquely qualified to succeed due to the following reasons:
- [Company Name] will fill a specific market niche in organic foods. In addition, we have surveyed the regional distributors and received extremely positive feedback saying that they explicitly want to buy our products when launched.
- Our location is within 100 miles of numerous potential distributors and contains hundreds of acres of arable land.
- The management team has a track record of success in the farming business.
Financial Highlights
[Company Name] is seeking a total funding of $683,200 of debt capital to open its farm. The capital will be used for funding capital expenditures and location build-out, hiring initial employees, marketing expenses and working capital.
Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
II. Company Overview
You can download our Farm Business Plan Template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.

Who is [Company Name]?
[Company Name], located at [insert location here] is a new 500 acredairy, beef, and wheat farm providing food products to regional distributors. [Company Name] is headed by [Founder’s Name], an experienced farm manager. 300 acres of its land will be devoted to growing wheat and the remainder will be for dairy, beef, and office facilities.
While [Founder’s Name] has been in the farming business for some time, it was in [month, year] that he decided to launch [Company Name]. Specifically, during this time, [Founder] met with a former friend and fellow independent organic farm owner in South Dakota who has had tremendous success. After discussing the business at length, [Founder’s Name] clearly understood that a similar farm would enjoy significant success in his hometown.
Specifically, the customer demographics and competitive situations in the South Dakota area of his friend and in his hometown were so similar that he knew the business would work. After surveying the local market, [Founder’s name] went ahead and founded [Company Name].
[Company Name]’s History
Upon returning from South Dakota, surveying the local customer base, and finding potential land to start the farm, [Founder’s Name] incorporated [Company Name] as an S-Corporation on [date of incorporation].
The business is currently being run out of [Founder’s Name] home office, but once the land is purchased and [Company Name]’s facilities are finalized, all operations will be run from there.
Since incorporation, the Company has achieved the following milestones:
- Found land and negotiated rate
- Developed the company’s name, logo and website located at [website]
- Determined building, equipment and fixture requirements
- Begun recruiting key employees
[Company Name]’s Products
[Founder’s Name] will be able to provide customers with the following products:
- High-quality organic beef cuts
- Organically-grown wheat by the bushel
- Organic whole milk
III. Industry Analysis
The American commercial farming industry continues to be subsidized by the government to bolster low food prices. This is a volatile and difficult industry in the United States, with small and medium-sized farms increasingly being bought by large farms or struggling to survive on their own.
However, for organic foods, trends are positive. Organic foods sales are projected to increase 18% per year over the next three years and were estimated at $23 billion last year, according to the Organic Trade Association Market Survey. This sector is said to represent 3% of overall food and beverage sales. Global demand for organic foods increases by over $5 billion per year.
The farming industry includes multiple segments including poultry meat, beef, dairy, grain crops, vegetables, fruits, and more. Many businesses focus on only one specific segment, while some produce multiple types of crops in order to hedge against price changes in any one segment.
Recently, Horizon, the largest US organic food brand, dropped the term “organic” from its dairy products choosing instead to use the term “natural”. Critics noted that the term “natural” has no regulatory meaning and shows Horizon’s attempt to lower the cost of production by not meeting the requirements for the organic label. This shows a concern in the market about the meaning behind labels and highlights the importance of regulation to create common definitions.
Organic.org published the following list of reasons to support organic foods and beverages:
- Reduce the toxic load: Keep chemicals out of the air, water, soil and our bodies
- Reduce if not eliminate farm pollution
- Protect future generations
- Build healthy soil
- Taste better and truer flavor
- Assist family farmers of all sizes
- Avoid hasty and poor science in your food
- Eating with a sense of place
- Promote biodiversity
- Celebrate the culture of agriculture
Trends in the industry include the following:
- Meat and fish that are organically produced are becoming more popular
- Organic dairy, bread, and grain are becoming more popular
- Organic-only supermarkets are becoming more popular
- Traditional supermarkets are increasing organic purchases to keep up with these competitors.
IV. Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
[Company Name]will primarily serve regional distributors of dairy, beef, and wheat products. Some products may be sold directly to manufacturers in the local area for the production of other products from these ingredients.
These businesses typically gross from $5 million to $50 million in annual revenues and source their supplies from within a 100 mile radius of their facilities.
Customer Segmentation
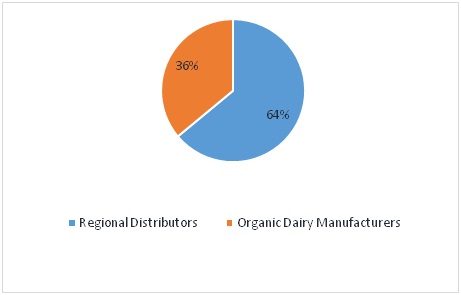
The Company will primarily target the following two customer segments:
- Regional Organic Distributors: Organic food distributors source organic meat, dairy, and grains from medium and large farms, and sell them to food manufacturers who process, package and sell the products.
- Organic Dairy Manufacturers: Small manufacturers that process organic dairy products, such as butter, cream, and cheese work directly with local farms to keep costs low whenever possible.
V.Competitive Analysis
Direct & indirect competitors.
The following twoorganic farms operate within a 100 mileradius of [Company Name]. These, and other smaller organic farms like them, are the direct competitors of the business. Indirect competitors include non-organic dairy, beef, and grain farms.
Nature’s Bounty Farm
Nature’s Bounty Farm is a five-year old farm which produces vegetables and grains for organic distributors. They operate a 1000 acre farm, producing a high volume of goods.
However, Nature’s Bounty Farm does not offer organic dairy and meat, which are up-and-coming products.
Thompson Organics
Thompson Organics is a small, 300 acre, ten-year old farm which produces organic grains and bakes organic breads. They sell all of their products at farmer’s markets and directly at retail stores. This distribution strategy requires Thompson to have skilled customer service and sales employees, as well as facilities for baking and packaging.
Because Thompson avoids selling through to distributors, its brand is known directly by consumers who look for organic foods and it can command a premium. However, they, like Nature’s Bounty Farm, do not offer organic dairy and meat. They also have a high cost structure because of their small scale and operations.
Competitive Advantage
[Company Name] enjoys several advantages over its competitors. These advantages include:
- Client-oriented service: [Company Name] will have a full-time sales manager to keep in contact with customers and answer their everyday questions. [Founder’s Name] realizes the importance of accessibility to customers and will instruct the sales manager to proactively solicit feedback from customers.
- Management: [Founder’s Name] has been extremely successful working in the farming business and will be able to use his previous experience to assure clients of the care that [Company Name] will take to create the best organic products. His unique qualifications will serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than [Company Name’s] competitors.
- Transparency: To continue to assure customers and the government of the organic quality of [Company Name]’s products, operations can be inspected by customers at a moments notice, and a guide to the operations will be created to detail all of the steps in the production process for each crop.
- Product Line: By offering wheat, dairy, and meat, [Company Name] will seek to hedge against price volatility in any one of these commodities.
VI. Marketing Plan
[Company Name] will use several strategies to promote its name and develop its brand. By using an integrated marketing strategy, [Company Name] will win customers and develop consistent revenue streams.
The [Company Name] Brand
The [Company name] brand will focus on the Company’s unique value proposition:
- High-quality, organic milk, beef, and grains
- Service built on long-term relationships
- Transparency of operations to achieve customer assurance of organic quality
Promotions Strategy
Targeted Cold Calls
[Company Name] will initially invest significant time and energy into contacting potential customers via telephone and then by visiting their facilities. In order to improve the effectiveness of this phase of the marketing strategy, a highly-focused call list will be used; targeting distributors and manufacturers with an expressed interest in organic products. As this is a very time-consuming process, it will primarily be used during the startup phase to build an initial customer base.
Industry Events
By attending regional farming conferences, association meetings, and symposia, [Company Name] will network with industry leaders, and seek referrals to potential customers. [Founder’s Name] will often attend with the company sales manager, but both may attend separately in the future as they gain experience in this networking.
[Company Name] will invest resources in two forms of geographically-focused internet promotion—organic search engine optimization and pay-per-click advertising. The Company will develop its website in such a manner as to direct as much traffic from search engines as possible. Additionally, it will use highly-focused, specific keywords to draw traffic to its website, where potential clients will find a content-rich site that presents [Company Name] as the trustworthy, high quality producer of organic foods that it is.
Pricing Strategy
[Company Name]’s pricing will be competitive compared with Nature’s Bounty Farm. Pricing will be about 50% lower than retail prices to allow for wholesalers and retailers to earn their margins.
VII. Operations
[Company Name] will carry out its sales operations through phone calls and visits to customer offices. The sales manager will increasingly direct sales activities, although [Founder’s Name] will be heavily involved at first.
The assistant manager will run the day-to-day operations of the farm, including scheduling and assigning the work of farm hands, sourcing and purchasing supplies and basic equipment, keeping the company’s books, maintaining legal licenses, handling insurance and insuring that the company meets government regulations. He will contact specialists for equipment repairs when needed and veterinarians to care for the cows when they require medical attention.
Field work by the farm hands will be from sunrise to sunset, with indoor work during the hottest parts of the day and after dark. Field work will include preparing fields for planting, the planting process, tending to planted fields, harvesting, and packaging grain into bushels. Work with the cows will include feeding, taking them in and out of the pasture, and running the milking equipment. It will also include slaughtering and dressing the cows for beef when directed.
[Company Name]’s long term goal is to become the highest quality farmer in the [city] area. We seek to do this by ensuring customer satisfaction and developing a loyal and successful clientele.
The following are a series of steps that will lead to this long-term success. [Company Name] expects to achieve the following milestones in the following [xyz] months:
VIII. Management Team
[First name] is intimately familiar with the operations requirements for a farm producing the same products as [Company Name]. He has received organic training certification to become an organic food producer.
[Company name] will also employ an assistant manager to manage operations. This will be an experienced operations manager who will be trained in farm operations by [Founder’s Name]. Furthermore, a sales manager will be hired to focus on marketing, sales, and customer service to distributors as manufacturers for [Company Name] products. These two individualswill either have undergraduate business degrees or years of relevant operations or sales experience.
Hiring Plan
In order to launch the business we will also hire the following additional employee:
- Farm Hand: (1 full-time to start) Additional farm hands will be hired if capacity increases or if another farm is started.
The hiring process will be managed by the assistant manager who will be directly responsible for the farm hand, with oversight and approval by [Founder’s Name]. This individual must be in top physical condition, have experience in physical labor, and have great mechanical facility and care for the quality of his work and products.
The assistant manager and [Founder’s Name] will provide back-up support for the farm hand in the busiest times and when he is out sick or on vacation.
IX. Financial Plan
Revenue & pricing.
[Company Name]’s revenues will come primarily fromsale in three product areas.
The price of beef is only an average per cow, and individual cuts are sold at market rates depending on the quality of the cut of meat.
Prices are expected to fluctuate with market volatility on the rise, although they are expected to rise consistently, on average.
Key Cost Drivers
As with most services, labor expenses are the key cost drivers. The staff of four will earn competitive salaries allowing [Company Name] to hireexperienced workers. Furthermore, the costs of the mortgage and its interest for the land will be significant.
The major cost drivers for the company’s operation will consist of:
- Marketing expenses (associations, events, internet marketing).
Capital Requirements and Use of Funds
- Build-out of farm and equipment purchases: $273,200
- Initial marketing expenditure: $10,000
- Property down payment: $100,000
- Working capital: $300,000 to pay for marketing, salaries, and lease costs until [Company Name] reaches break-even
Key Assumptions & Forecasts
The following table reflects the key revenue and cost assumptions made in the financial model.
5 Year Annual Balance Sheet
5 Year Annual Cash Flow Statement
Comments are closed.


Apply MyCAS
- In the News
- Upcoming Events
- Online Classes
- Agricultural Tourism
- Beginning Farmers
- Dry Farming
- OSU Organic Agriculture
- Olive Research for Oregon
- Whole Farm Management
- Start Your Business Plan
- Refine Your Business Plan
- Business Planning Resources
Sample Business Plans
- Berries & Grapes
- Biodiversity & Pest Management
- Harvest & Handling
- Herbs & Flowers
- Nursery Crops & Greenhouses
- Tree Fruits & Nuts
- Winter Farming
- Drought, Fire, Flood, Disaster Relief and Resiliency Programs
- Dry Farming Research
- Community Support Agriculture
- Marketing Your Farm
- Meat & Eggs
- Raw Agricultural Products
- Value Added
- Farmers' Markets
- Organic Fertilizer and Cover Crop Calculators
- Hay Production
- Irrigation & Fencing
- Mud & Manure Management
- Nutrient Management
- Pasture and Grazing Management
- Weeds, Poisonous Plants, & Other Pests
- Soil Testing
- Soil Surveys
- Improving Soil Quality & Cover Crops
- Agricultural Composting and Water Quality
- Water & Irrigation
- Business Planning

Below are examples of different farm business plans and a loan application:
Oregon Flower Farm Business Plan Example
Interval Farm Business Plan Sample
Peach Farm Business Plan Sample
USDA FSA Sample Microloan Application
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Small Business Tools
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
- Sample Business Plans
- Retail, Consumers & E-commerce
Small Farming Business Plan
Want to transform your small land into a farming business? Indeed, a brilliant business venture to undertake. After all, all sorts of farming businesses enjoy a vast market.
Anyone can start a farming business. However, a detailed business plan is essential to drive this business to its desired potential and secure funding if required.
Need help writing a business plan for your small farm? You’re at the right place. Our small farming business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write A Small Farming Business Plan?
Writing a small farming business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
Introduce your Business:
- This section may include the name of your small farming business, its location, when it was founded, the type of small farming business (E.g., vegetable farming, bee farming, aquaculture, organic farming), etc.
Market Opportunity:
- For instance, you may include fruits, vegetables, herbs, and spices as products and mention organic produce, exotic fruits, and local produce as some of your USPs.
Marketing & Sales Strategies:
Financial highlights:, call to action:.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your company. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
Business Description:
- Vegetable farming
- Bee farming
- Aquaculture
- Organic farming
- Describe the legal structure of your small farm, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
Mission Statement:
Business history:.
- Additionally, If you have received any awards or recognition for excellent work, describe them.
Future Goals
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
Target market:
- For instance, farmers’ markets, specialty retailers, and local customers would be an ideal target audience for smart farming businesses.
Market size and growth potential:
- For instance, the global smart farming market is expected to reach 53 billion dollars by 2032, so it is crucial to define the segment of your target market and its growth potential.
Competitive Analysis:
Market trends:.
- For instance, agrotech and automation have a booming market; explain how you plan on dealing with this potential growth opportunity.
Regulatory Environment:
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your small farming business plan:
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products And Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
Describe your farm products:
Describe the type of products your small farming business will offer. A vegetable farming business may include a detailed description of crops and their varieties here.
Mention products:
Provide a list of products that will be available at your small farm. This list may include,
Value-added services:
Quality measures:.
- This may include quality control processes, clear service standards, regular maintenance, and training.
Additional Services
In short, this section of your small farming plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
Unique Selling Proposition (USP):
- For example, organic and sustainable practices, fresh local produce, and exotic products could be some of the great USPs for a vegetable and fruit small farm.
Pricing Strategy:
Marketing strategies:, sales strategies:, customer retention:.
Overall, this section of your small farming business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your small farming business, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
Staffing & Training:
Operational process:, equipment & machinery:.
- Explain how these technologies help you maintain quality standards and improve the efficiency of your business operations.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your small farming business’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
Founders/CEO:
Key managers:.
- It should include, key executives(e.g. COO, CMO.), senior management, and other department managers (e.g. farm manager, sales manager.) involved in the small farming business operations, including their education, professional background, and any relevant experience in the farming industry.
Organizational structure:
Compensation plan:, advisors/consultants:.
- So, if you have any advisors or consultants, include them with their names and brief information consisting of roles and years of experience.
This section should describe the key personnel for your small farming services, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
Profit & loss statement:
Cash flow statement:, balance sheet:, break-even point:.
- This exercise will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to sustain or be profitable.
Financing Needs:
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the small farming industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your small farming business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample small farming business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful small farming plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our small farming business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Farming Business Plan
Organic Farm Business Plan
Guide to Effective Customer Analysis
Business Plan Outline Crafting Guide
Business Plan Table of Contents Example
Business Plan Example Template
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a small farming business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful small farming business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your small farm.
How to get funding for your small farming business?
There are several ways to get funding for your small farming business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
How do I write a good market analysis in a small farming business plan?
Market analysis is one of the key components of your business plan that requires deep research and a thorough understanding of your industry. We can categorize the process of writing a good market analysis section into the following steps:
- Stating the objective of your market analysis—e.g., investor funding.
- Industry study—market size, growth potential, market trends, etc.
- Identifying target market—based on user behavior and demographics.
- Analyzing direct and indirect competitors.
- Calculating market share—understanding TAM, SAM, and SOM.
- Knowing regulations and restrictions
- Organizing data and writing the first draft.
Writing a marketing analysis section can be overwhelming, but using ChatGPT for market research can make things easier.
How detailed should the financial projections be in my small farming business plan?
The level of detail of the financial projections of your small farming business may vary considering various business aspects like direct and indirect competition, pricing, and operational efficiency. However, your financial projections must be comprehensive enough to demonstrate a complete view of your financial performance.
Generally, the statements included in a business plan offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
What key components should a small farming business plan include?
The following are the key components your small farming business plan must include:
- Executive summary
- Business Overview
- Market Analysis
- Products and services
- Sales and marketing strategies
- Operations plan
- Management team
- Financial plan
Can a good small farming business plan help me secure funding?
Indeed. A well-crafted small farming business plan will help your investors better understand your business domain, market trends, strategies, business financials, and growth potential—helping them make better financial decisions.
So, if you have a profitable and investable business, a comprehensive business plan can certainly help you secure your business funding.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .


- Free Business Plan Template
- Free Online Education to Start Your Own Business
Download: MOBI Business Plan Template
Enroll now: MOBI's FREE Starting a Business course
MOBI Business Plan Template
The primary value of your business plan is to create a written resource that evaluates most aspects of your new business including a description of your target customers and markets, profitability, organization, operations and more. The very process of writing your business plan helps you put your ideas on paper so you can evaluate what resources you have and what you need to be successful.
Your business plan is your blueprint for starting your business, your script to tell the story of your business to others, and your comprehensive analysis of the opportunity for your business. Business plans help you plan your roadmap, state your goals, share your vision, and analyze your strategy. A business plan is an important and valuable tool for new as well as existing businesses.
This MOBI Business Plan Template consists of sections that relate to the content included in the MOBI Starting a Business course . You can also use this template as a guide independently. We have created this template with the input of key stakeholders such as economic development agencies, lenders, mentors and successful entrepreneurs. You can complete sections of the business plan as you go through the course, to apply what you are learning along the way, or you can wait until you have completed the course. This business plan template is a universal model suitable for most types of business, which you can customize to fit your circumstances. MOBI provides leading topics, questions, and suggestions in each section to guide you. Here are some instructions to help you get started:
- On the cover page replace the MOBI spark with your own logo and provide your business name, personal name, contact information, and date.
- Complete each section leaving the main title, such as “Executive Summary,” and using the subtitles and questions as a guideline. Replace those subtitles and questions with the needed and relevant information. If some of the subtitles work with your format, you can keep them. You can type directly over the provided content or delete it as you complete it.
- You might want to start each section on a new page, which can also be helpful if you decide to include a Table of Contents.
Once you complete your business plan, be sure that key stakeholders review it. Business plans are not static; they will change as your business and the business environment change around you. It’s important to continually review and update your business plan to adjust for these changes.
BUSINESS PLAN
Enter Your Business Name
Enter Your Name
Enter Date
Contact Information
Executive Summary Provide a summary of your business by addressing these key areas.
Name and Description of Business State the name of your business and describe your product or service.
Targeted Market and Customers Describe your target markets and customers and why they want or need your product or service.
Trends in this Industry What are the current trends in the industry that make this a good time for your product or service? For example, is the market for your product growing, and why? Have others failed to address a particular need that your product or service will address?
Value Proposition Provide a brief statement of the unique benefits and value your business will deliver to your customers. Describe the unique qualities of your product or service that will enable you to be profitable.
The Vision Describe the vision of your business and why you are committed to pursuing this vision and making it successful.
Founder Background: Work/life experience related to the intended business Describe your work/life experience, educational credentials, and how they are related to the business you plan to start. Include a list of your skills and knowledge, which will be required in your business.
Your Team If you plan to hire full- or part-time employees or seek business partners, describe your plan for engaging with these other members of your team. If you already have employees or partners, describe key personnel and their roles here.
Goals for business: Outline your key goals for your business. (Explain your plans for growing the business and what you can realistically accomplish in a defined period of time.)
Financing and Financial Projections ( Many business owners require the assistance of a bookkeeper or accountant when completing this section.)
Startup Capital Provide a table or spreadsheet showing the sources of your startup capital including what you or other investors will contribute and what you intend to borrow. Create a list of what the startup capital will be used for and how much will be left over for working capital ( SCORE Startup Expenses Template ).
Accounting Statements Prepare your starting balance sheet and projected profit and loss (income) statements for the first three years. (By month for the first year and then by year for years two and three.) Forecast your month-to-month cash flow requirements for the first year.
Analysis of Costs List and explain the key costs and profit margins that are important for your business. Classify your costs as fixed, variable, product, delivery, etc.
Break-Even Analysis Based on your costs and pricing strategy, prepare a break-even analysis.
Internal Controls Explain your internal and cash controls. For instance, check signing policy, strategy for controlling shrinkage, and control of incoming merchandise or supplies.
Business Organization
Business Organization Explain the form of business organization you intend to use and why it is best for your business (sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, etc.).
Professional Consultants List the names of your key advisors: bookkeeper/accountant, consultants, lawyer, insurance agent, and any other professionals.
Business Location
If you need a physical location other than your home to operate your business, identify your business space needs considering all phases of your workflow (production, storage, shipping, potential employees, customer meetings, and future requirements). Explain why the location you picked meets your workflow needs.
Marketing and Sales
Market Research: Your Customers and Competition Describe your ideal customer (who will be purchasing your product/service, key characteristics).
- Include any research that has helped you identify and characterize your target customer.
Describe your position in the market, your strongest competitors, and how you intend to compete.
Marketing Strategy and Tools Describe your overall marketing strategy, how you will find, engage, and build customers, including:
- Traditional marketing tools (signage, storefront, collateral, advertising, promotion, uniforms, mail, etc.).
- Online marketing (website, social media, email marketing, text marketing, others).
- Ecommerce (if applicable).
- Describe in detail how you plan to sell your products or services online.
- Describe how your best competitors utilize ecommerce and your strategy to improve on their practices.
- Research and identify the different channels where you will sell your product or services. What is your expectation of sales?
- Detail how will you take orders, process payments, and fulfill requests?
- Provide a detailed breakdown of the costs involved in creating, operating, and maintaining your ecommerce activities.
Sales Strategy Describe your sales process, activities you will conduct, obstacles you expect, how you will overcome them, and any customer service strategies to retain and expand your customer base.
Include k ey details about how you will operate your business.
- Outline the workflow of your business and the processes and procedures you will put into place.
- If applicable, provide details about how you will procure supplies, manufacture your product, and deliver your product or service to your customer. Include any equipment and facilities that you need.
- Describe how you will measure the success of your operations for quality, efficiency, cost control, or other measures of performance. Include any testing.
- Order fulfillment: describe your order fulfillment process, software to be used, and quality control methods.
- Supply chain: describe products/materials you need to purchase in order to make your product, include primary and secondary sources for these. products/materials, lead times, purchasing methods, and tools.
- Staffing: skill requirements, training program, supervision, outsourced functions, and hiring timeline.
Addendum: Licenses and Permits *Addendums can include but are not limited to License and Permits*
Make a comprehensive list of all licenses and permits you will need to do business in your area.
Your list should include the following: (For US-based businesses; requirements differ by country and region.)
- Name under which you intend to do business
- Permissions and/or limitations on the use of your property or facilities
- Federal, state, and local licenses (city/county), permits, and certifications needed to do business in your area (e.g. business tax license, seller's permit, safety certifications, employer identification number, etc.)
- Industry licenses needed for your particular area of business (contractor, electrician, daycare, beauty, etc.)
- International and national intellectual property protection through trademarks, copyright, and patents.
Download: MOBI Business Plan Template
Follow mobi on social media.
Certificate Courses Login


500+ business plans and financial models
Executive Summary of a Steakhouse: Template & Example
- May 6, 2024
- Business Plan , Executive Summary

A steakhouse business plan needs a straightforward executive summary . This part of your plan is the first thing investors and partners see, and it should clearly outline what your steakhouse is all about. It’s where you explain what makes your steakhouse different and worth investing in.
We recommend using a two-slide PowerPoint format for this summary. The first slide should cover the basics of your business and the market you’re entering. Here, you detail your steakhouse’s products, location, and what sets you apart from others. The second slide focuses on your management team and your financial plans, highlighting the people behind the business and how you expect the steakhouse to grow financially.
This simple, two-slide approach ensures that your executive summary is easy to follow and covers all the essential points about your steakhouse business.

Steakhouse Business Plan

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
Steakhouse Executive Summary: Page 1

Business Overview
When detailing the business overview in your executive summary, it’s crucial to provide clear and concise information. This includes the name of your steakhouse, its location, and an overview of daily operations.
These details not only introduce your business but also set the stage for its unique qualities. Indeed, a unique selling proposition (USP) is what sets your steakhouse apart from the competition. Whether it’s your focus on dry-aged steaks, locally sourced ingredients, or your commitment to providing a memorable dining experience, your USP should be a focal point of your executive summary. It’s what captures the interest of your audience and showcases the unique value your steakhouse brings to the market.
Example: “Prime Cuts Grill,” nestled in the heart of [specific area or neighborhood], caters to discerning diners seeking an elevated culinary experience. Spanning [total square footage] sq ft, our steakhouse boasts a main dining area exuding sophistication, complemented by a private dining room for intimate gatherings. Our strategic location in [description of location, e.g., bustling downtown area, affluent neighborhood] ensures accessibility and visibility, attracting a diverse clientele ranging from families to business executives.
Market Overview
Understanding and presenting the market size , growth trends, and industry dynamics are integral parts of the market analysis .
This section should highlight the potential of the steakhouse market, backed by relevant data like market value and growth rates. Discussing industry trends, such as the increasing demand for high-quality dining experiences or the popularity of farm-to-table concepts, provides insight into the evolving landscape and where your steakhouse fits within it.
Equally important is the competitive landscape. Your executive summary should identify key competitors and explain how your steakhouse positions itself in this environment. Whether you focus on offering unique cuts of beef, exceptional service, or a distinctive ambiance, this is your opportunity to showcase how your steakhouse is poised to stand out in a competitive market.
Example: Committed to quality and sustainability, Prime Cuts Grill meticulously sources prime beef cuts from renowned ranches celebrated for their ethical standards. Our menu showcases expertly cooked steaks paired with premium sides and an extensive selection of fine wines and spirits, offering a distinctive dining experience in a [casual/fine dining] ambiance.
Steakhouse Executive Summary: Page 2

Management Team
The management team’s background and expertise are significant assets to your steakhouse business. In your executive summary, highlight the key qualifications and experiences of your team members.
This might include your co-founder’s extensive experience in restaurant management or your head chef’s culinary accolades. Demonstrating the team’s expertise not only builds credibility but also assures potential investors and partners of your steakhouse’s capability to succeed.
Example: [Name], Co-Founder, and Executive Chef, spearheads Prime Cuts Grill’s culinary vision, leveraging [number] years of culinary expertise to curate a menu that harmonizes innovation with tradition. With a keen focus on operational excellence, [Name] oversees staff management, customer service, and financial stewardship, ensuring a seamless dining experience for patrons.
Financial Plan
The financial plan overview should succinctly summarize your steakhouse’s financial goals and projections, including revenue targets and profit margins, to provide a clear picture of its financial trajectory.
Example: Prime Cuts Grill aims to achieve $[2.7] million in annual revenue by 2028, with a targeted [11]% profit margin ( EBITDA ). Our financial strategy encompasses prudent resource allocation, strategic marketing initiatives , and a relentless commitment to delivering unparalleled culinary experiences, positioning Prime Cuts Grill as a formidable player in the competitive steakhouse landscape.
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
COMMENTS
This is the order of topics in a traditional business plan: Step 1: Executive summary: The executive summary is the most important part of your plan - a one-page summary of the entire business plan. And it will probably be the part of the business plan that you circle back to and write last. Step 2: Description: The why — your company's ...
In generating the Profit and Loss, the sales forecast was based on the $1.8 million book of business. revenue and raw new sales commission paid to the agency. As mentioned, the goal for the business. is to increase its sales incrementally year by year in order of 3%, 2.5%, 2%, 1.5%, and 1%.
Services. In the state farm agent business plan, it is necessary to mention all the services that your insurance company will provide. When you open a state farm agency, you list down all the services you want to offer to your clients. When Neil was planning to start a state farm agency, he decided to provide the following services:
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan. Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans. FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet. FSA-2037 Instructions.
A farm business plan is an essential document for new farm start-ups or farms seeking funding. Farm business plans give an overview of the business, including company history, owner/operator backgrounds, products/services, projections, and more. Use this template to quickly create your farm business plan.
Cornell Small Farms Program Online Course BF 202: Business Planning. The Cornell Small Farms Program offers 20+ online courses every year on many topics related to the production and business sides of farming. Most are taught by Cornell Cooperative Extension educators. BF 202 is a 6-week course that will guide you through the process of writing ...
Commercial liability umbrella policies. Provides extra financial protection against costly lawsuits that may exceed your policy limits. Commercial liability umbrella policies. Get small business insurance to help meet your unique needs, including business owner policies, commercial auto insurance, and professional liability.
2. Validate your small business idea by conducting market research. You should feel confident that your product or service will have a hungry audience and that you can offer it in a better way than your competitors. 3. Write your business plan. When thinking about the process of running a small business, a business plan will help you organize ...
Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts. Example traditional business plans. Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners.
Insurance Agency Business Plan Template. Written by Dave Lavinsky. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 3,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their insurance agencies. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning.
They have operated the farm on leased land in central Vermont for the past three years. This business plan will serve as an operating guide for Down in the Dirt Farm as they purchase a new farm and grow their farm business. In this document Taylor and Phoebe will address the following goals: Purchasing the new farm property in January 2019.
e-Farm Management Training. The introduction video covers important components that should be included in a business plan. The Strategic Planning video discusses in more detail the process of a strategic planning that should be part of a business plan including vision statements, mission statements, goals and objectives.
AgPlan (Center for Farm Financial Management, UMN) AgPlan is an easy business plan app that anyone can use. The AgPlan financial spreadsheet is an Excel-based set of financial spreadsheets that includes a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow tool. Income Statements (also called a Profit and Loss Statement, and is similar to an ...
Sample Business Plan For Farms & Agricultural Businesses. Executive Summary - The Executive Summary is the most important part of your business plan. It is a brief description of your farm, its products and services, potential market opportunity, and competitive advantage. Company Overview - Also called the Company Analysis, here, you will ...
Farm Business Plan Template. Your business plan should include 10 sections as follows: Executive Summary. Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan. The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the ...
Our team has helped develop over 100,000 business plans over the past 20 years, including thousands of farm business plans. The following farm business plan template and example gives you the key elements you must include in your plan. In our experience speaking with lenders and investors, the template is organized in the precise format they want.
Oregon Flower Farm Business Plan Example. Interval Farm Business Plan Sample. Peach Farm Business Plan Sample. USDA FSA Sample Microloan Application. Small Farms Program Oregon State University Send E-mail Phone: 541-713-5009. OSU College of Agricultural Sciences 430 Strand Agriculture Hall Corvallis, Oregon 97331.
Open a separate small business checking account. Many banks offer special small business accounts (with perks!) that can help you keep your business expenses separate from your personal ones. With a separate account, and a separate credit or debit card connected, you'll have a log of all your business's costs. Just be sure to use the right card ...
Writing a small farming business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and ...
MOBI Business Plan Template. The primary value of your business plan is to create a written resource that evaluates most aspects of your new business including a description of your target customers and markets, profitability, organization, operations and more. The very process of writing your business plan helps you put your ideas on paper so ...
Storage of any hazardous materials at or above State-defined thresholds makes a facility subject to the HMBP program. The general thresholds are 55 gallons of a liquid, 200 cubic feet of a gas, and 500 pounds of a solid. There are some exemptions to these thresholds. The Hazardous Materials Compliance Division (HMCD) is responsible for the HMBP ...
What is a Hazardous Materials Business Plan? ... California State Regulations: California Code of Regulations, Title 19, Division 5, Chapter 1, Sections 5010.1 to 5040.2. If you have any questions regarding the HMBP program, please contact the program at [email protected].
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template. Buy for $75. Download example. Steakhouse Executive Summary: Page 1 ... such as the increasing demand for high-quality dining experiences or the popularity of farm-to-table concepts, provides insight into the evolving landscape and where your steakhouse fits within it ...
California has some of the lowest minimum insurance requirements in the country. California drivers must have at least: Bodily injury liability: $15,000 per person / $30,000 per accident. Property damage liability: $5,000 per accident. Don't worry; we have coverage options and plans that can help protect you while you're on the road.