A free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature
- Linda B. Buck
- Social Structure

New & Improved API for Developers
Introducing semantic reader in beta.
Stay Connected With Semantic Scholar Sign Up What Is Semantic Scholar? Semantic Scholar is a free, AI-powered research tool for scientific literature, based at the Allen Institute for AI.

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.

28 Best Academic Search Engines That make your research easier
This post may contain affiliate links that allow us to earn a commission at no expense to you. Learn more

If you’re a researcher or scholar, you know that conducting effective online research is a critical part of your job. And if you’re like most people, you’re always on the lookout for new and better ways to do it.
I’m sure you are familiar with some research databases. But, top researchers keep an open mind and are always looking for inspiration in unexpected places.
This article aims to give you an edge over researchers that rely mainly on Google for their entire research process.
Our list of 28 academic search engines will start with the more familiar to less.
Table of Contents
#1. Google Scholar
Google Scholar is an academic search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines.
Great for academic research, you can use Google Scholar to find articles from academic journals, conference proceedings, theses, and dissertations. The results returned by Google Scholar are typically more relevant and reliable than those from regular search engines like Google.
Tip: You can restrict your results to peer-reviewed articles only by clicking on the “Scholarly”
- Scholarly results are typically more relevant and reliable than those from regular search engines like Google.
- You can restrict your results to peer-reviewed articles only by clicking on the “Scholarly” tab.
- Google Scholar database Coverage is extensive, with approx. 200 million articles indexed.
- Abstracts are available for most articles.
- Related articles are shown, as well as the number of times an article has been cited.
- Links to full text are available for many articles.
- Abstracts are only a snippet of the full article, so you might need to do additional searching to get the full information you need.
- Not all articles are available in full text.
Google Scholar is completely free.
#2. ERIC (Education Resources Information Center)
ERIC (short for educational resources information center) is a great academic search engine that focuses on education-related literature. It is sponsored by the U.S. Department of Education and produced by the Institute of Education Sciences.
ERIC indexes over a million articles, reports, conference papers, and other resources on all aspects of education from early childhood to higher education. So, search results are more relevant to Education on ERIC.
- Extensive coverage: ERIC indexes over a million articles, reports, and other resources on all aspects of education from early childhood to higher education.
- You can limit your results to peer-reviewed journals by clicking on the “Peer-Reviewed” tab.
- Great search engine for educators, as abstracts are available for most articles.
ERIC is a free online database of education-related literature.
You might also like:
- SCI Journal: Science Journal Impact Factor
- 15 Best Websites to Download Research Papers for Free
- 11 Best Academic Writing Tools For Researchers 2024
- 10 Best Reference Management Software for Research 2024
- Academic Tools
#3. Wolfram Alpha

Wolfram Alpha is a “computational knowledge engine” that can answer factual questions posed in natural language. It can be a useful search tool.
Type in a question like “What is the square root of 64?” or “What is the boiling point of water?” and Wolfram Alpha will give you an answer.
Wolfram Alpha can also be used to find academic articles. Just type in your keywords and Wolfram Alpha will generate a list of academic articles that match your query.
Tip: You can restrict your results to peer-reviewed journals by clicking on the “Scholarly” tab.
- Can answer factual questions posed in natural language.
- Can be used to find academic articles.
- Results are ranked by relevance.
- Results can be overwhelming, so it’s important to narrow down your search criteria as much as possible.
- The experience feels a bit more structured but it could also be a bit restrictive
Wolfram Alpha offers a few pricing options, including a “Pro” subscription that gives you access to additional features, such as the ability to create custom reports. You can also purchase individual articles or download them for offline use.
Pro costs $5.49 and Pro Premium costs $9.99
#4. iSEEK Education
- 15 Best Websites To Download Research Papers For Free
- 30+ Essential Software For Researchers
- 15 Best Academic Research Trend Prediction Platforms
- 15 Best Academic Networking And Collaboration Platforms
iSEEK is a search engine targeting students, teachers, administrators, and caregiver. It’s designed to be safe with editor-reviewed content.
iSEEK Education also includes a “Cited by” feature which shows you how often an article has been cited by other researchers.
- Editor-reviewed content.
- “Cited by” feature shows how often an article has been cited by other researchers.
- Limited to academic content.
- Doesn’t have the breadth of coverage that some of the other academic search engines have.
iSEEK Education is free to use.
#5. BASE (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine)

BASE is hosted at Bielefeld University in Germany and that’s where it name stems from (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine).
Known as “one of the most comprehensive academic web search engines,” it contains over 100 million documents from 4,000 different sources.
Users can narrow their search using the advanced search option, so regardless of whether you need a book, a review, a lecture, a video or a thesis, BASE has what you need.
BASE indexes academic articles from a variety of disciplines, including the arts, humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences.
- One of the world’s most voluminous search engines,
- Indexes academic articles from a variety of disciplines, especially for academic web resources
- Includes an “Advanced Search” feature that lets you restrict your results to peer-reviewed journals.
- Doesn’t include abstracts for most articles.
- Doesn’t have related articles, references, cited by
BASE is free to use.
- 10 Best Reference Management Software for Research 2023
- 15 Best Academic Networking and Collaboration Platforms
- 30+ Essential Software for Researchers
- 15 Best Academic Blogging and Content Management
- 11 Best Academic Writing Tools For Researchers
CORE is an academic search engine that focuses on open access research papers. A link to the full text PDF or complete text web page is supplied for each search result. It’s academic search engine dedicated to open access research papers.
- Focused on open access research papers.
- Links to full text PDF or complete text web page are supplied for each search result.
- Export formats include BibTeX, Endnote, RefWorks, Zotero.
- Coverage is limited to open access research papers.
- No abstracts are available for most articles.
- No related articles, references, or cited by features.
CORE is free to use.
- Best Plagiarism Checkers for Research Papers in 2024
#7. Science.gov

Science.gov is a search engine developed and managed by the United States government. It includes results from a variety of scientific databases, including NASA, EPA, USGS, and NIST.
US students are more likely to have early exposure to this tool for scholarly research.
- Coverage from a variety of scientific databases (200 million articles and reports).
- Links to full text are available for some articles.
Science.gov is free to use.
- 15 Best Academic Journal Discovery Platforms
- Sci Hub Review
#8. Semantic Scholar

Semantic Scholar is a recent entrant to the field. Its goal is to provide more relevant and effective search results via artificial intelligence-powered methods that detect hidden relationships and connections between research topics.
- Powered by artificial intelligence, which enhances search results.
- Covers a large number of academic articles (approx. 40 million).
- Related articles, references, and cited by features are all included.
- Links to full text are available for most articles.
Semantic Scholar is free to use.
- 11 Best Academic Writing Tools For Researchers
- 10 Best Reference Management Software for Research
- 15 Best Academic Journal Discovery Platforms
#9. RefSeek
RefSeek searches more than five billion documents, including web pages, books, encyclopedias, journals, and newspapers.
This is one of the free search engines that feels like Yahoo with a massive directory. It could be good when you are just looking for research ideas from unexpected angles. It could lead you to some other database that you might not know such as the CIA The World Factbook, which is a great reference tool.
- Searches more than five billion documents.
- The Documents tab is very focused on research papers and easy to use.
- Results can be filtered by date, type of document, and language.
- Good source for free academic articles, open access journals, and technical reports.
- The navigation and user experience is very dated even to millenials…
- It requires more than 3 clicks to dig up interesting references (which is how it could lead to you something beyond the 1st page of Google)
- The top part of the results are ALL ads (well… it’s free to use)
RefSeek is free to use.
#10. ResearchGate

A mixture of social networking site + forum + content databases where researchers can build their profile, share research papers, and interact with one another.
Although it is not an academic search engine that goes outside of its site, ResearchGate ‘s library of works offers an excellent choice for any curious scholar.
There are more than 100 million publications available on the site from over 11 million researchers. It is possible to search by publication, data, and author, as well as to ask the researchers questions.
- A great place to find research papers and researchers.
- Can follow other researchers and get updates when they share new papers or make changes to their profile.
- The network effect can be helpful in finding people who have expertise in a particular topic.
- Interface is not as user friendly
- Can be overwhelming when trying to find relevant papers.
- Some papers are behind a paywall.
ResearchGate is free to use.
- 15 Best Academic Research Trend Prediction Platforms
- 25 Best Tools for Tracking Research Impact and Citations
#11. DataONE Search (formerly CiteULike)
A social networking site for academics who want to share and discover academic articles and papers.
- A great place to find academic papers that have been shared by other academics.
- Some papers are behind a paywall
CiteULike is free to use.
#12. DataElixir
DataElixir is deigned to help you find, understand and use data. It includes a curated list of the best open datasets, tools and resources for data science.
- Dedicated resource for finding open data sets, tools, and resources for data science.
- The website is easy to navigate.
- The content is updated regularly
- The resources are grouped by category.
- Not all of the resources are applicable to academic research.
- Some of the content is outdated.
DataElixir is free to use.
#13. LazyScholar – browser extension
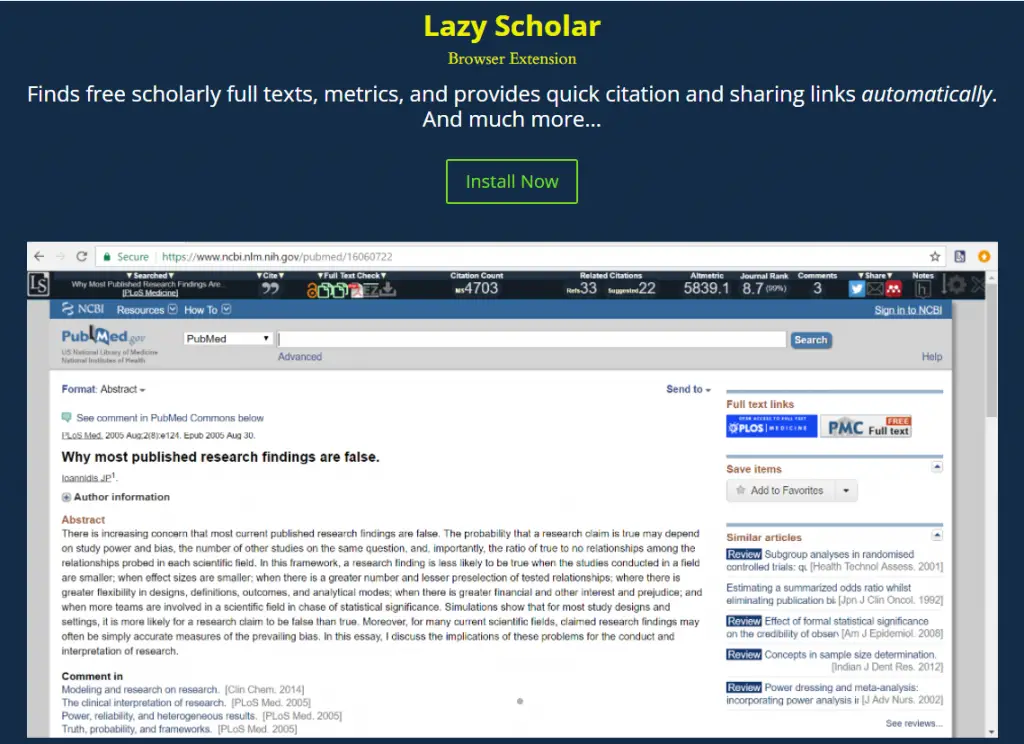
LazyScholar is a free browser plugin that helps you discover free academic full texts, metrics, and instant citation and sharing links. Lazy Scholar is created Colby Vorland, a postdoctoral fellow at Indiana University.
- It can integrate with your library to find full texts even when you’re off-campus.
- Saves your history and provides an interface to find it.
- A pre-formed citation is availlable in over 900 citation styles.
- Can recommend you topics and scans new PubMed listings to suggest new papers
- Results can be a bit hit or miss
LazyScholar is free to use.
#14. CiteseerX – digital library from PenState

CiteseerX is a digital library stores and indexes research articles in Computer Science and related fields. The site has a robust search engine that allows you to filter results by date, author.
- Searches a large number of academic papers.
- Results can be filtered by date, author, and topic.
- The website is easy to use.
- You can create an account and save your searches for future reference.
CiteseerX is free to use.
- Surfer Review: Is It Worth It?
- 25 Best Tools For Tracking Research Impact And Citations
#15. The Lens – patents search
The Lens or the Patent Lens is an online patent and scholarly literature search facility, provided by Cambia, an Australia-based non-profit organization.
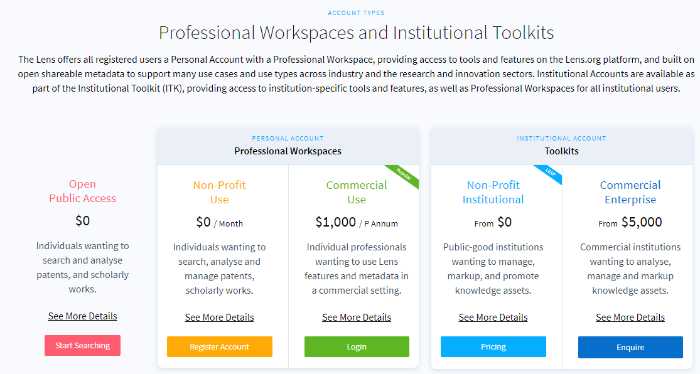
- Searches for a large number of academic papers.
The price range can be free for non-profit use to $5,000 for commercial enterprise.
#16. Fatcat – wiki for bibliographic catalog
Fatcat is an open bibliographic catalog of written works. The scope of works is somewhat flexible, with a focus on published research outputs like journal articles, pre-prints, and conference proceedings. Records are collaboratively editable, versioned, available in bulk form, and include URL-agnostic file-level metadata.
- Open source and collaborative
- You can be part of the community that is very focused on its mission
- The archival file-level metadata (verified digests and long-term copies) is a great feature.
- Could prove to be another rabbit hole
- People either love or hate the text-only interface
#17. Lexis Web – Legal database
Are you researching legal topics? You can turn to Lexis Web for any law-related questions you may have. The results are drawn from legal sites and can be filtered based on criteria such as news, blogs, government, and commercial. Additionally, users can filter results by jurisdiction, practice area, source and file format.
- Results are drawn from legal sites.
- Filters are available based on criteria such as news, blogs, government, and commercial.
- Users can filter results by jurisdiction, practice area, source and file format.
- Not all law-related questions will be answered by this search engine.
- Coverage is limited to legal sites only.
Lexis Web is free for up to three searches per day. After that, a subscription is required.
#18. Infotopia – part of the VLRC family
Infotopia touts itself as an “alternative to Google safe search.” Scholarly book results are curated by librarians, teachers, and other educational workers. Users can select from a range of topics such as art, health, and science and technology, and then see a list of resources pertaining to the topic.
Consequently, if you aren’t able to find what you are looking for within Infotopia’s pages, you will probably find it on one of its many suggested websites.
#19. Virtual Learning Resources Center

Virtual Learning Resources Center (VLRC) is an academic search engine that features thousands of academic sites chosen by educators and librarians worldwide. Using an index generated from a research portal, university, and library internet subject guides, students and instructors can find current, authoritative information for school.
- Thousands of academic information websites indexed by it. You will also be able to get more refined results with custom Google search, which will speed up your research.
- Many people consider VLRC as one of the best free search engines to start looking for research material.
- TeachThought rated the Virtual LRC #3 in it’s list of 100 Search Engines For Academic Research
- More relevant to education
- More relevant to students
Powered by Google Custom Search Engine (CSE), Jurn is a free online search engine for accessing and downloading free full-text scholarly papers. It was created by David Haden in a public open beta version in February 2009, initially for locating open access electronic journal articles in the arts and humanities.
After the indexing process was completed, a website containing additional public directories of web links to indexed publications was introduced in mid-2009. The Jurn search service and directory has been regularly modified and cleaned since then.
- A great resource for finding academic papers that are behind paywalls.
- The content is updated regularly.uren
Jurn is free to use.
#21. WorldWideScience
The Office of Scientific and Technical Information—a branch of the Office of Science within the U.S. Department of Energy—hosts the portal WorldWideScience , which has dubbed itself “The Global Science Gateway.”
Over 70 countries’ databases are used on the website. When a user enters a query, it contacts databases from all across the world and shows results in both English and translated journals and academic resources.
- Results can be filtered by language and type of resource
- Interface is easy to use
- Contains both academic journal articles and translated academic resources
- The website can be difficult to navigate.
WorldWideScience is free to use.
#22. Google Books
A user can browse thousands of books on Google Books, from popular titles to old titles, to find pages that include their search terms. You can look through pages, read online reviews, and find out where to buy a hard copy once you find the book you are interested in.
#23. DOAJ (Directory of Open Access Journals)
DOAJ is a free search engine for scientific and scholarly materials. It is a searchable database with over 8,000 peer-reviewed research papers organized by subject. It’s one of the most comprehensive libraries of scientific and scholarly resources, with over 8,000 journals available on a variety of themes.
#24. Baidu Scholar
Baidu Xueshu (Academic) is the Chinese version for Google Scholar. IDU Scholar indexes academic papers from a variety of disciplines in both Chinese and English.
- Articles are available in full text PDF.
- Covers a variety of academic disciplines.
- No abstracts are available for most articles, but summaries are provided for some.
- A great portal that takes you to different specialized research platform
- You need to be able to read Chinese to use the site
- Since 2021 there is a rise of focus on China and the Chinese Communist Party
Baidu Scholar is free to use.
#25. PubMed Central
PubMed is a free search engine that provides references and abstracts for medical, life sciences, and biomedical topics.
If you’re studying anything related to healthcare or science, this site is perfect. PublicMed Central is operated by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, a division of the U.S. National Library of Medicine. It contains more than 3 million full-text journal articles.
It’s similar to PubMed Health, which focuses on health-related research and includes abstracts and citations to over 26 million articles.
#26. MEDLINE®
MEDLINE® is a paid subscription database for life sciences and biomedicine that includes more than 28 million citations to journal articles. For finding reliable, carefully chosen health information, Medline Plus provides a powerful search tool and even a dictionary.
- A great database for life sciences and biomedicine.
- Contains more than 28 million references to journal articles.
- References can be filtered by date, type of document, and language.
- The database is expensive to access.
- Some people find it difficult to navigate and find what they are looking for.
MEDLINE is not free to use ( pricing information ).
Defunct Academic Search Engines
#27. microsoft academic .
Microsoft Academic
Microsoft Academic Search seemed to be a failure from the beginning. It ended in 2012, then re-launched in 2016 as Microsoft Academic. It provides the researcher with the opportunity to search academic publications,
Microsoft Academic used to be the second-largest academic search engine after Google Scholar. Microsoft Academic provides a wealth of data for free, but Microsoft has announced that it will shut Microsoft Academic down in by 2022.
#28. Scizzle
Designed to help researchers stay on top of the literature by setting up email alerts, based on key terms, for newspapers.
Unfortunately, academic search engines come and go. These are two that are no longer available.
Final Thoughts
There are many academic search engines that can help researchers and scholars find the information they need. This list provides a variety of options, starting with more familiar engines and moving on to less well-known ones.
Keeping an open mind and exploring different sources is essential for conducting effective online research. With so much information at our fingertips, it’s important to make sure we’re using the best tools available to us.
Tell us in the comment below which academic search engine have you not heard of? Which database do you think we should add? What database do your professional societies use? What are the most useful academic websites for research in your opinion?
There is more.
Check out our other articles on the Best Academic Tools Series for Research below.
- Learn how to get more done with these Academic Writing Tools
- Learn how to proofread your work with these Proofreading Tools
- Learn how to broaden your research landscape with these Academic Search Engines
- Learn how to manage multiple research projects with these Project Management Tools
- Learn how to run effective survey research with these Survey Tools for Research
- Learn how get more insights from important conversations and interviews with Transcription Tools
- Learn how to manage the ever-growing list of references with these Reference Management Software
- Learn how to double your productivity with literature reviews with these AI-Based Summary Generators
- Learn how to build and develop your audience with these Academic Social Network Sites
- Learn how to make sure your content is original and trustworthy with these Plagiarism Checkers
- Learn how to talk about your work effectively with these Science Communication Tools
10 thoughts on “28 Best Academic Search Engines That make your research easier”
Thank you so much Joannah..I have found this information useful to me as librarian in an academic library
You are welcome! We are happy to hear that!
Thank You Team, for providing a comprehensive list of academic search engines that can help make research easier for students and scholars. The variety of search engines included offers a range of options for finding scholarly articles, journals, and other academic resources. The article also provides a brief summary of each search engine’s features, which helps in determining which one is the best fit for a specific research topic. Overall, this article is a valuable resource for anyone looking for a quick and easy way to access a wealth of academic information.
Thank you for taking the time to share your feedback with us. We are delighted to hear that you found our list of academic search engines helpful in making research easier for students and scholars. We understand the importance of having a variety of options when it comes to finding scholarly articles, journals, and other academic resources, and we strive to provide a comprehensive list of resources to meet those needs.
We are glad that you found the brief summary of each search engine’s features helpful in determining which one is the best fit for a specific research topic. Our goal is to make it easy for our readers to access valuable academic information and we’re glad that we were able to achieve that for you.
We appreciate your support and thank you for your kind words. We will continue to provide valuable resources for students and researchers in the future. Please let us know if you have any further questions or suggestions.
No more questions Thank You
I cannot thank you enough!!! thanks alot 🙂
Typography animation is a technique that combines text and motion to create visually engaging and dynamic animations. It involves animating individual letters, words, or phrases in various ways to convey a message, evoke emotions, or enhance the visual impact of a design or video. – Typography Animation Techniques Tools and Online Software {43}
Hi Joannah! Here’s another one you may want to add! Expontum ( https://www.expontum.com/ ) – Helps researchers quickly find knowledge gaps and identify what research projects have been completed before. Thanks!
Expontum – Helps researchers quickly find knowledge gaps and identify what research projects have been completed before. Expontum is free, open access, and available to all globally with no paid versions of the site. Automated processes scan research article information 24/7 so this website is constantly updating. By looking at over 35 million research publications (240 million by the end of 2023), the site has 146 million tagged research subjects and 122 million tagged research attributes. Learn more about methodology and sources on the Expontum About Page ( https://www.expontum.com/about.php )
Hey Ryan, I clicked and checked your site and thought it was very relevant to our reader. Thank you for sharing. And, we will be reviewing your site soon.
Sounds good! Thanks, Joannah!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We maintain and update science journals and scientific metrics. Scientific metrics data are aggregated from publicly available sources. Please note that we do NOT publish research papers on this platform. We do NOT accept any manuscript.
2012-2024 © scijournal.org
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Google Scholar: the ultimate guide

What is Google Scholar?
Why is google scholar better than google for finding research papers, the google scholar search results page, the first two lines: core bibliographic information, quick full text-access options, "cited by" count and other useful links, tips for searching google scholar, 1. google scholar searches are not case sensitive, 2. use keywords instead of full sentences, 3. use quotes to search for an exact match, 3. add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year, 4. use the side bar controls to adjust your search result, 5. use boolean operator to better control your searches, google scholar advanced search interface, customizing search preferences and options, using the "my library" feature in google scholar, the scope and limitations of google scholar, alternatives to google scholar, country-specific google scholar sites, frequently asked questions about google scholar, related articles.
Google Scholar (GS) is a free academic search engine that can be thought of as the academic version of Google. Rather than searching all of the indexed information on the web, it searches repositories of:
- universities
- scholarly websites
This is generally a smaller subset of the pool that Google searches. It's all done automatically, but most of the search results tend to be reliable scholarly sources.
However, Google is typically less careful about what it includes in search results than more curated, subscription-based academic databases like Scopus and Web of Science . As a result, it is important to take some time to assess the credibility of the resources linked through Google Scholar.
➡️ Take a look at our guide on the best academic databases .
One advantage of using Google Scholar is that the interface is comforting and familiar to anyone who uses Google. This lowers the learning curve of finding scholarly information .
There are a number of useful differences from a regular Google search. Google Scholar allows you to:
- copy a formatted citation in different styles including MLA and APA
- export bibliographic data (BibTeX, RIS) to use with reference management software
- explore other works have cited the listed work
- easily find full text versions of the article
Although it is free to search in Google Scholar, most of the content is not freely available. Google does its best to find copies of restricted articles in public repositories. If you are at an academic or research institution, you can also set up a library connection that allows you to see items that are available through your institution.
The Google Scholar results page differs from the Google results page in a few key ways. The search result page is, however, different and it is worth being familiar with the different pieces of information that are shown. Let's have a look at the results for the search term "machine learning.”
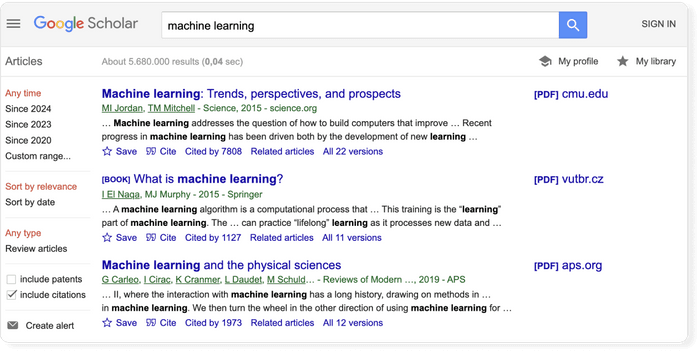
- The first line of each result provides the title of the document (e.g. of an article, book, chapter, or report).
- The second line provides the bibliographic information about the document, in order: the author(s), the journal or book it appears in, the year of publication, and the publisher.
Clicking on the title link will bring you to the publisher’s page where you may be able to access more information about the document. This includes the abstract and options to download the PDF.

To the far right of the entry are more direct options for obtaining the full text of the document. In this example, Google has also located a publicly available PDF of the document hosted at umich.edu . Note, that it's not guaranteed that it is the version of the article that was finally published in the journal.
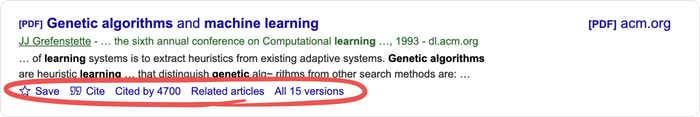
Below the text snippet/abstract you can find a number of useful links.
- Cited by : the cited by link will show other articles that have cited this resource. That is a super useful feature that can help you in many ways. First, it is a good way to track the more recent research that has referenced this article, and second the fact that other researches cited this document lends greater credibility to it. But be aware that there is a lag in publication type. Therefore, an article published in 2017 will not have an extensive number of cited by results. It takes a minimum of 6 months for most articles to get published, so even if an article was using the source, the more recent article has not been published yet.
- Versions : this link will display other versions of the article or other databases where the article may be found, some of which may offer free access to the article.
- Quotation mark icon : this will display a popup with commonly used citation formats such as MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and Vancouver that may be copied and pasted. Note, however, that the Google Scholar citation data is sometimes incomplete and so it is often a good idea to check this data at the source. The "cite" popup also includes links for exporting the citation data as BibTeX or RIS files that any major reference manager can import.
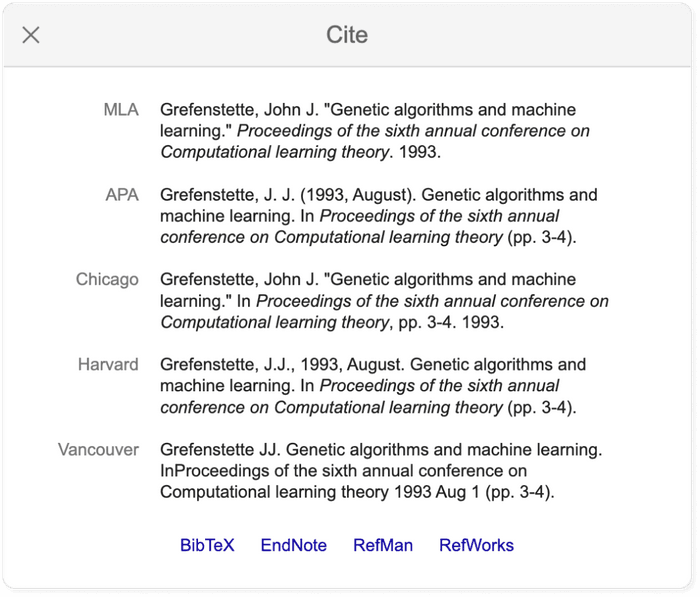
Pro tip: Use a reference manager like Paperpile to keep track of all your sources. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular academic research engines and databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons and later cite them in thousands of citation styles:
Although Google Scholar limits each search to a maximum of 1,000 results , it's still too much to explore, and you need an effective way of locating the relevant articles. Here’s a list of pro tips that will help you save time and search more effectively.
You don’t need to worry about case sensitivity when you’re using Google scholar. In other words, a search for "Machine Learning" will produce the same results as a search for "machine learning.”
Let's say your research topic is about self driving cars. For a regular Google search we might enter something like " what is the current state of the technology used for self driving cars ". In Google Scholar, you will see less than ideal results for this query .
The trick is to build a list of keywords and perform searches for them like self-driving cars, autonomous vehicles, or driverless cars. Google Scholar will assist you on that: if you start typing in the search field you will see related queries suggested by Scholar!
If you put your search phrase into quotes you can search for exact matches of that phrase in the title and the body text of the document. Without quotes, Google Scholar will treat each word separately.
This means that if you search national parks , the words will not necessarily appear together. Grouped words and exact phrases should be enclosed in quotation marks.
A search using “self-driving cars 2015,” for example, will return articles or books published in 2015.
Using the options in the left hand panel you can further restrict the search results by limiting the years covered by the search, the inclusion or exclude of patents, and you can sort the results by relevance or by date.
Searches are not case sensitive, however, there are a number of Boolean operators you can use to control the search and these must be capitalized.
- AND requires both of the words or phrases on either side to be somewhere in the record.
- NOT can be placed in front of a word or phrases to exclude results which include them.
- OR will give equal weight to results which match just one of the words or phrases on either side.
➡️ Read more about how to efficiently search online databases for academic research .
In case you got overwhelmed by the above options, here’s some illustrative examples:
Tip: Use the advanced search features in Google Scholar to narrow down your search results.
You can gain even more fine-grained control over your search by using the advanced search feature. This feature is available by clicking on the hamburger menu in the upper left and selecting the "Advanced search" menu item.

Adjusting the Google Scholar settings is not necessary for getting good results, but offers some additional customization, including the ability to enable the above-mentioned library integrations.
The settings menu is found in the hamburger menu located in the top left of the Google Scholar page. The settings are divided into five sections:
- Collections to search: by default Google scholar searches articles and includes patents, but this default can be changed if you are not interested in patents or if you wish to search case law instead.
- Bibliographic manager: you can export relevant citation data via the “Bibliography manager” subsection.
- Languages: if you wish for results to return only articles written in a specific subset of languages, you can define that here.
- Library links: as noted, Google Scholar allows you to get the Full Text of articles through your institution’s subscriptions, where available. Search for, and add, your institution here to have the relevant link included in your search results.
- Button: the Scholar Button is a Chrome extension which adds a dropdown search box to your toolbar. This allows you to search Google Scholar from any website. Moreover, if you have any text selected on the page and then click the button it will display results from a search on those words when clicked.
When signed in, Google Scholar adds some simple tools for keeping track of and organizing the articles you find. These can be useful if you are not using a full academic reference manager.
All the search results include a “save” button at the end of the bottom row of links, clicking this will add it to your "My Library".
To help you provide some structure, you can create and apply labels to the items in your library. Appended labels will appear at the end of the article titles. For example, the following article has been assigned a “RNA” label:
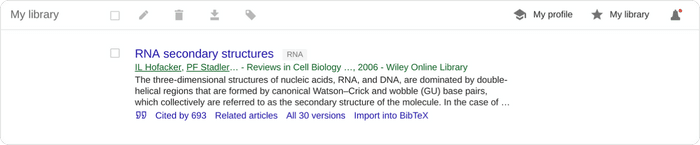
Within your Google Scholar library, you can also edit the metadata associated with titles. This will often be necessary as Google Scholar citation data is often faulty.
There is no official statement about how big the Scholar search index is, but unofficial estimates are in the range of about 160 million , and it is supposed to continue to grow by several million each year.
Yet, Google Scholar does not return all resources that you may get in search at you local library catalog. For example, a library database could return podcasts, videos, articles, statistics, or special collections. For now, Google Scholar has only the following publication types:
- Journal articles : articles published in journals. It's a mixture of articles from peer reviewed journals, predatory journals and pre-print archives.
- Books : links to the Google limited version of the text, when possible.
- Book chapters : chapters within a book, sometimes they are also electronically available.
- Book reviews : reviews of books, but it is not always apparent that it is a review from the search result.
- Conference proceedings : papers written as part of a conference, typically used as part of presentation at the conference.
- Court opinions .
- Patents : Google Scholar only searches patents if the option is selected in the search settings described above.
The information in Google Scholar is not cataloged by professionals. The quality of the metadata will depend heavily on the source that Google Scholar is pulling the information from. This is a much different process to how information is collected and indexed in scholarly databases such as Scopus or Web of Science .
➡️ Visit our list of the best academic databases .
Google Scholar is by far the most frequently used academic search engine , but it is not the only one. Other academic search engines include:
- Science.gov
- Semantic Scholar
- scholar.google.fr : Sur les épaules d'un géant
- scholar.google.es (Google Académico): A hombros de gigantes
- scholar.google.pt (Google Académico): Sobre os ombros de gigantes
- scholar.google.de : Auf den Schultern von Riesen
➡️ Once you’ve found some research, it’s time to read it. Take a look at our guide on how to read a scientific paper .
No. Google Scholar is a bibliographic search engine rather than a bibliographic database. In order to qualify as a database Google Scholar would need to have stable identifiers for its records.
No. Google Scholar is an academic search engine, but the records found in Google Scholar are scholarly sources.
No. Google Scholar collects research papers from all over the web, including grey literature and non-peer reviewed papers and reports.
Google Scholar does not provide any full text content itself, but links to the full text article on the publisher page, which can either be open access or paywalled content. Google Scholar tries to provide links to free versions, when possible.
The easiest way to access Google scholar is by using The Google Scholar Button. This is a browser extension that allows you easily access Google Scholar from any web page. You can install it from the Chrome Webstore .

- Corrections
Search Help
Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more.
Finding recent papers
Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar:
- click "Since Year" to show only recently published papers, sorted by relevance;
- click "Sort by date" to show just the new additions, sorted by date;
- click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Locating the full text of an article
Abstracts are freely available for most of the articles. Alas, reading the entire article may require a subscription. Here're a few things to try:
- click a library link, e.g., "FindIt@Harvard", to the right of the search result;
- click a link labeled [PDF] to the right of the search result;
- click "All versions" under the search result and check out the alternative sources;
- click "Related articles" or "Cited by" under the search result to explore similar articles.
If you're affiliated with a university, but don't see links such as "FindIt@Harvard", please check with your local library about the best way to access their online subscriptions. You may need to do search from a computer on campus, or to configure your browser to use a library proxy.
Getting better answers
If you're new to the subject, it may be helpful to pick up the terminology from secondary sources. E.g., a Wikipedia article for "overweight" might suggest a Scholar search for "pediatric hyperalimentation".
If the search results are too specific for your needs, check out what they're citing in their "References" sections. Referenced works are often more general in nature.
Similarly, if the search results are too basic for you, click "Cited by" to see newer papers that referenced them. These newer papers will often be more specific.
Explore! There's rarely a single answer to a research question. Click "Related articles" or "Cited by" to see closely related work, or search for author's name and see what else they have written.
Searching Google Scholar
Use the "author:" operator, e.g., author:"d knuth" or author:"donald e knuth".
Put the paper's title in quotations: "A History of the China Sea".
You'll often get better results if you search only recent articles, but still sort them by relevance, not by date. E.g., click "Since 2018" in the left sidebar of the search results page.
To see the absolutely newest articles first, click "Sort by date" in the sidebar. If you use this feature a lot, you may also find it useful to setup email alerts to have new results automatically sent to you.
Note: On smaller screens that don't show the sidebar, these options are available in the dropdown menu labelled "Year" right below the search button.
Select the "Case law" option on the homepage or in the side drawer on the search results page.
It finds documents similar to the given search result.
It's in the side drawer. The advanced search window lets you search in the author, title, and publication fields, as well as limit your search results by date.
Select the "Case law" option and do a keyword search over all jurisdictions. Then, click the "Select courts" link in the left sidebar on the search results page.
Tip: To quickly search a frequently used selection of courts, bookmark a search results page with the desired selection.
Access to articles
For each Scholar search result, we try to find a version of the article that you can read. These access links are labelled [PDF] or [HTML] and appear to the right of the search result. For example:
A paper that you need to read
Access links cover a wide variety of ways in which articles may be available to you - articles that your library subscribes to, open access articles, free-to-read articles from publishers, preprints, articles in repositories, etc.
When you are on a campus network, access links automatically include your library subscriptions and direct you to subscribed versions of articles. On-campus access links cover subscriptions from primary publishers as well as aggregators.
Off-campus access
Off-campus access links let you take your library subscriptions with you when you are at home or traveling. You can read subscribed articles when you are off-campus just as easily as when you are on-campus. Off-campus access links work by recording your subscriptions when you visit Scholar while on-campus, and looking up the recorded subscriptions later when you are off-campus.
We use the recorded subscriptions to provide you with the same subscribed access links as you see on campus. We also indicate your subscription access to participating publishers so that they can allow you to read the full-text of these articles without logging in or using a proxy. The recorded subscription information expires after 30 days and is automatically deleted.
In addition to Google Scholar search results, off-campus access links can also appear on articles from publishers participating in the off-campus subscription access program. Look for links labeled [PDF] or [HTML] on the right hand side of article pages.
Anne Author , John Doe , Jane Smith , Someone Else
In this fascinating paper, we investigate various topics that would be of interest to you. We also describe new methods relevant to your project, and attempt to address several questions which you would also like to know the answer to. Lastly, we analyze …
You can disable off-campus access links on the Scholar settings page . Disabling off-campus access links will turn off recording of your library subscriptions. It will also turn off indicating subscription access to participating publishers. Once off-campus access links are disabled, you may need to identify and configure an alternate mechanism (e.g., an institutional proxy or VPN) to access your library subscriptions while off-campus.
Email Alerts
Do a search for the topic of interest, e.g., "M Theory"; click the envelope icon in the sidebar of the search results page; enter your email address, and click "Create alert". We'll then periodically email you newly published papers that match your search criteria.
No, you can enter any email address of your choice. If the email address isn't a Google account or doesn't match your Google account, then we'll email you a verification link, which you'll need to click to start receiving alerts.
This works best if you create a public profile , which is free and quick to do. Once you get to the homepage with your photo, click "Follow" next to your name, select "New citations to my articles", and click "Done". We will then email you when we find new articles that cite yours.
Search for the title of your paper, e.g., "Anti de Sitter space and holography"; click on the "Cited by" link at the bottom of the search result; and then click on the envelope icon in the left sidebar of the search results page.
First, do a search for your colleague's name, and see if they have a Scholar profile. If they do, click on it, click the "Follow" button next to their name, select "New articles by this author", and click "Done".
If they don't have a profile, do a search by author, e.g., [author:s-hawking], and click on the mighty envelope in the left sidebar of the search results page. If you find that several different people share the same name, you may need to add co-author names or topical keywords to limit results to the author you wish to follow.
We send the alerts right after we add new papers to Google Scholar. This usually happens several times a week, except that our search robots meticulously observe holidays.
There's a link to cancel the alert at the bottom of every notification email.
If you created alerts using a Google account, you can manage them all here . If you're not using a Google account, you'll need to unsubscribe from the individual alerts and subscribe to the new ones.
Google Scholar library
Google Scholar library is your personal collection of articles. You can save articles right off the search page, organize them by adding labels, and use the power of Scholar search to quickly find just the one you want - at any time and from anywhere. You decide what goes into your library, and we’ll keep the links up to date.
You get all the goodies that come with Scholar search results - links to PDF and to your university's subscriptions, formatted citations, citing articles, and more!
Library help
Find the article you want to add in Google Scholar and click the “Save” button under the search result.
Click “My library” at the top of the page or in the side drawer to view all articles in your library. To search the full text of these articles, enter your query as usual in the search box.
Find the article you want to remove, and then click the “Delete” button under it.
- To add a label to an article, find the article in your library, click the “Label” button under it, select the label you want to apply, and click “Done”.
- To view all the articles with a specific label, click the label name in the left sidebar of your library page.
- To remove a label from an article, click the “Label” button under it, deselect the label you want to remove, and click “Done”.
- To add, edit, or delete labels, click “Manage labels” in the left column of your library page.
Only you can see the articles in your library. If you create a Scholar profile and make it public, then the articles in your public profile (and only those articles) will be visible to everyone.
Your profile contains all the articles you have written yourself. It’s a way to present your work to others, as well as to keep track of citations to it. Your library is a way to organize the articles that you’d like to read or cite, not necessarily the ones you’ve written.
Citation Export
Click the "Cite" button under the search result and then select your bibliography manager at the bottom of the popup. We currently support BibTeX, EndNote, RefMan, and RefWorks.
Err, no, please respect our robots.txt when you access Google Scholar using automated software. As the wearers of crawler's shoes and webmaster's hat, we cannot recommend adherence to web standards highly enough.
Sorry, we're unable to provide bulk access. You'll need to make an arrangement directly with the source of the data you're interested in. Keep in mind that a lot of the records in Google Scholar come from commercial subscription services.
Sorry, we can only show up to 1,000 results for any particular search query. Try a different query to get more results.
Content Coverage
Google Scholar includes journal and conference papers, theses and dissertations, academic books, pre-prints, abstracts, technical reports and other scholarly literature from all broad areas of research. You'll find works from a wide variety of academic publishers, professional societies and university repositories, as well as scholarly articles available anywhere across the web. Google Scholar also includes court opinions and patents.
We index research articles and abstracts from most major academic publishers and repositories worldwide, including both free and subscription sources. To check current coverage of a specific source in Google Scholar, search for a sample of their article titles in quotes.
While we try to be comprehensive, it isn't possible to guarantee uninterrupted coverage of any particular source. We index articles from sources all over the web and link to these websites in our search results. If one of these websites becomes unavailable to our search robots or to a large number of web users, we have to remove it from Google Scholar until it becomes available again.
Our meticulous search robots generally try to index every paper from every website they visit, including most major sources and also many lesser known ones.
That said, Google Scholar is primarily a search of academic papers. Shorter articles, such as book reviews, news sections, editorials, announcements and letters, may or may not be included. Untitled documents and documents without authors are usually not included. Website URLs that aren't available to our search robots or to the majority of web users are, obviously, not included either. Nor do we include websites that require you to sign up for an account, install a browser plugin, watch four colorful ads, and turn around three times and say coo-coo before you can read the listing of titles scanned at 10 DPI... You get the idea, we cover academic papers from sensible websites.
That's usually because we index many of these papers from other websites, such as the websites of their primary publishers. The "site:" operator currently only searches the primary version of each paper.
It could also be that the papers are located on examplejournals.gov, not on example.gov. Please make sure you're searching for the "right" website.
That said, the best way to check coverage of a specific source is to search for a sample of their papers using the title of the paper.
Ahem, we index papers, not journals. You should also ask about our coverage of universities, research groups, proteins, seminal breakthroughs, and other dimensions that are of interest to users. All such questions are best answered by searching for a statistical sample of papers that has the property of interest - journal, author, protein, etc. Many coverage comparisons are available if you search for [allintitle:"google scholar"], but some of them are more statistically valid than others.
Currently, Google Scholar allows you to search and read published opinions of US state appellate and supreme court cases since 1950, US federal district, appellate, tax and bankruptcy courts since 1923 and US Supreme Court cases since 1791. In addition, it includes citations for cases cited by indexed opinions or journal articles which allows you to find influential cases (usually older or international) which are not yet online or publicly available.
Legal opinions in Google Scholar are provided for informational purposes only and should not be relied on as a substitute for legal advice from a licensed lawyer. Google does not warrant that the information is complete or accurate.
We normally add new papers several times a week. However, updates to existing records take 6-9 months to a year or longer, because in order to update our records, we need to first recrawl them from the source website. For many larger websites, the speed at which we can update their records is limited by the crawl rate that they allow.
Inclusion and Corrections
We apologize, and we assure you the error was unintentional. Automated extraction of information from articles in diverse fields can be tricky, so an error sometimes sneaks through.
Please write to the owner of the website where the erroneous search result is coming from, and encourage them to provide correct bibliographic data to us, as described in the technical guidelines . Once the data is corrected on their website, it usually takes 6-9 months to a year or longer for it to be updated in Google Scholar. We appreciate your help and your patience.
If you can't find your papers when you search for them by title and by author, please refer your publisher to our technical guidelines .
You can also deposit your papers into your institutional repository or put their PDF versions on your personal website, but please follow your publisher's requirements when you do so. See our technical guidelines for more details on the inclusion process.
We normally add new papers several times a week; however, it might take us some time to crawl larger websites, and corrections to already included papers can take 6-9 months to a year or longer.
Google Scholar generally reflects the state of the web as it is currently visible to our search robots and to the majority of users. When you're searching for relevant papers to read, you wouldn't want it any other way!
If your citation counts have gone down, chances are that either your paper or papers that cite it have either disappeared from the web entirely, or have become unavailable to our search robots, or, perhaps, have been reformatted in a way that made it difficult for our automated software to identify their bibliographic data and references. If you wish to correct this, you'll need to identify the specific documents with indexing problems and ask your publisher to fix them. Please refer to the technical guidelines .
Please do let us know . Please include the URL for the opinion, the corrected information and a source where we can verify the correction.
We're only able to make corrections to court opinions that are hosted on our own website. For corrections to academic papers, books, dissertations and other third-party material, click on the search result in question and contact the owner of the website where the document came from. For corrections to books from Google Book Search, click on the book's title and locate the link to provide feedback at the bottom of the book's page.
General Questions
These are articles which other scholarly articles have referred to, but which we haven't found online. To exclude them from your search results, uncheck the "include citations" box on the left sidebar.
First, click on links labeled [PDF] or [HTML] to the right of the search result's title. Also, check out the "All versions" link at the bottom of the search result.
Second, if you're affiliated with a university, using a computer on campus will often let you access your library's online subscriptions. Look for links labeled with your library's name to the right of the search result's title. Also, see if there's a link to the full text on the publisher's page with the abstract.
Keep in mind that final published versions are often only available to subscribers, and that some articles are not available online at all. Good luck!
Technically, your web browser remembers your settings in a "cookie" on your computer's disk, and sends this cookie to our website along with every search. Check that your browser isn't configured to discard our cookies. Also, check if disabling various proxies or overly helpful privacy settings does the trick. Either way, your settings are stored on your computer, not on our servers, so a long hard look at your browser's preferences or internet options should help cure the machine's forgetfulness.
Not even close. That phrase is our acknowledgement that much of scholarly research involves building on what others have already discovered. It's taken from Sir Isaac Newton's famous quote, "If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants."
- Privacy & Terms
Google Scholar
Using Google Scholar with your HarvardKey allows you to make the most of provided links, granting access to full text available through Harvard Library subscriptions.
Google Scholar can quickly surface highly cited peer-reviewed articles, abstracts, books, patents, scholarly web pages, and more.
Explore Google Scholar

Connect Google Scholar To Your Library Access
Connecting Google Scholar to your Harvard Library access is a good way to make sure you get access to articles that Harvard Library subscribes to.
Here's how:
- Go to Google Scholar and sign in to your Google account
- Look for the menu options
- Go into the settings and select "Library links"
- Type in Harvard and select: Harvard University - Try Harvard Library
- Deselect the box for WorldCat if shown
- Save your preferences
- Search your topic and look for the "Try Harvard Library" links to the right of the articles. This link should take you to Harvard's access to that item
Google Scholar Tips
- Like Google, Google Scholar allows searching of metadata terms, but unlike Google, it also indexes full text.
- Choose the default search or select “Advanced search” to search by title, author, journal, and date.
- For more advanced researchers, it is possible to specify phrases in quotation marks, enter Boolean queries, or search within fields.
- You may also create an account to set up your author profile or sign up for alerts.
- In settings, you may elect to limit your search by language and show citation import links.
- Results are returned in relevance-ranked order, generally favoring entries when search terms appear in document titles and prioritizing documents with larger citation counts.
🇺🇦 make metadata, not war
A comprehensive bibliographic database of the world’s scholarly literature
The world’s largest collection of open access research papers, machine access to our vast unique full text corpus, core features, indexing the world’s repositories.
We serve the global network of repositories and journals
Comprehensive data coverage
We provide both metadata and full text access to our comprehensive collection through our APIs and Datasets
Powerful services
We create powerful services for researchers, universities, and industry
Cutting-edge solutions
We research and develop innovative data-driven and AI solutions
Committed to the POSI
Cost-free PIDs for your repository
OAI identifiers are unique identifiers minted cost-free by repositories. Ensure that your repository is correctly configured, enabling the CORE OAI Resolver to redirect your identifiers to your repository landing pages.
OAI IDs provide a cost-free option for assigning Persistent Identifiers (PIDs) to your repository records. Learn more.
Who we serve?
Enabling others to create new tools and innovate using a global comprehensive collection of research papers.

“ Our partnership with CORE will provide Turnitin with vast amounts of metadata and full texts that we can ... ” Show more
Gareth Malcolm, Content Partner Manager at Turnitin
Academic institutions.
Making research more discoverable, improving metadata quality, helping to meet and monitor open access compliance.

“ CORE’s role in providing a unified search of repository content is a great tool for the researcher and ex... ” Show more
Nicola Dowson, Library Services Manager at Open University
Researchers & general public.
Tools to find, discover and explore the wealth of open access research. Free for everyone, forever.

“ With millions of research papers available across thousands of different systems, CORE provides an invalu... ” Show more
Jon Tennant, Rogue Paleontologist and Founder of the Open Science MOOC
Helping funders to analyse, audit and monitor open research and accelerate towards open science.

“ Aggregation plays an increasingly essential role in maximising the long-term benefits of open access, hel... ” Show more
Ben Johnson, Research Policy Adviser at Research England
Our services, access to raw data.
Create new and innovative solutions.
Content discovery
Find relevant research and make your research more visible.
Managing content
Manage how your research content is exposed to the world.
Companies using CORE

Gareth Malcolm
Content Partner Manager at Turnitin
Our partnership with CORE will provide Turnitin with vast amounts of metadata and full texts that we can utilise in our plagiarism detection software.
Academic institution using CORE
Kathleen Shearer
Executive Director of the Confederation of Open Access Repositories (COAR)
CORE has significantly assisted the academic institutions participating in our global network with their key mission, which is their scientific content exposure. In addition, CORE has helped our content administrators to showcase the real benefits of repositories via its added value services.
Partner projects

Ben Johnson
Research Policy Adviser
Aggregation plays an increasingly essential role in maximising the long-term benefits of open access, helping to turn the promise of a 'research commons' into a reality. The aggregation services that CORE provides therefore make a very valuable contribution to the evolving open access environment in the UK.

- Skip to search
- Skip to main navigation
- Skip to footer navigation
- Login Logged in as Username Log Out
- Français
- Español
- Ελληνικά
Basic Search

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Download 55 million PDFs for free
Explore our top research interests.

Engineering

Anthropology

- Earth Sciences

- Computer Science

- Mathematics

- Health Sciences

Join 261 million academics and researchers
Track your impact.
Share your work with other academics, grow your audience and track your impact on your field with our robust analytics
Discover new research
Get access to millions of research papers and stay informed with the important topics around the world
Publish your work
Publish your research with fast and rigorous service through Academia.edu Publishing. Get instant worldwide dissemination of your work
Unlock the most powerful tools with Academia Premium

Work faster and smarter with advanced research discovery tools
Search the full text and citations of our millions of papers. Download groups of related papers to jumpstart your research. Save time with detailed summaries and search alerts.
- Advanced Search
- PDF Packages of 37 papers
- Summaries and Search Alerts

Share your work, track your impact, and grow your audience
Get notified when other academics mention you or cite your papers. Track your impact with in-depth analytics and network with members of your field.
- Mentions and Citations Tracking
- Advanced Analytics
- Publishing Tools
Real stories from real people

Used by academics at over 15,000 universities

Get started and find the best quality research
- Academia.edu Publishing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Cognitive Science
- Academia ©2024
- Discover Data
- Open Access Search
- Access Journals
- Open Access Journal
- Citation Context
- Cheaper Access to Publications
- Research Analytics
Microsoft Research
Did you create this tool? Get in touch!

4 Alternative Search Engines for Better Research Results
Madison McCollum
May 13, 2024
Google is kind of awful.
I mean, don’t get me wrong, I use Google for everything, but it is a mess, especially when I consider the God-Tier search engine it used to be in my teens. When I was young, we trusted google to deliver the best results and even learned tricks to narrow down searches effectively. Now, Google has become a minefield of advertisements, optimized (affiliate) content, and SEO tactics that push genuine websites, businesses, and services further down the results page.
Getting on the first page of Google now often means you’ve mastered the art of ‘website optimization,’ which means you essentially know how to craft your site with the right words and links to please Google’s ever-hungry algorithms.
Research even shows that Google, and other search engines, are getting worse at delivering quality results. While I don’t have the answer to how we fix this, I do have some hope for those who rely on Google for research—students, scientists, or even the average-curious-George often have to sift through countless pages of content to find reputable information.
Thankfully, there are several alternative search engines that can make the research process easier:
Refseek.com
This academic resource search is great for students, researchers, or people wanting to research specific topics. It aims to make academic information easily accessible by tossing out sponsored links and commercial results.
Base-search.net [Bielefeld Academic Search Engine]
This search engine pulls from more than 11,000 content providers, 60% of which are open access (free). It’s ran by Bielefeld University Library, who all have been checked and approved by qualified personnel of the library staff.
link.springer.com/
You can access more than 10 million scientific documents. From books to articles to research journals on various subjects. There are even open source text books on 10+ subjects: like Earth and Environmental Sciences and Statistics!
Science.gov
Run by CENDI, a volunteer-powered organization, this search engine aims to increase the impact of federally funded science and technology research. Science.gov helps connect researchers to millions of research articles and is partnered with 12 Federal Agency Members.
Plus, a bonus:
Swisscows.com/en .
Most search engines take a little bit of your information with them. Maybe it’s just your location or IP address, maybe it’s your search results themselves— having information on you (as general as it may be) helps keep the lights on.
Swisscow’s services are based in Switzerland, which has some of the most strict privacy policies in the world, and provides fully encrypted searches. It doesn’t keep any personal data, IP addresses, or search queries, and has a built-in filter for pornography and violence that can’t be overridden, making it a safer choice for kids.
These alternatives can help streamline your research process and offer a break from the cluttered search results on Google, so give them a try the next time you're looking for something special!
May 19, 2021
Related Articles
Fetch rewards: the app that sounds too good to be true, acting on principle: pioneer and oec forge community bonds in cooperative clean-up, connect what matters: join us for our 2024 annual meeting, related articles.
Fetch Rewards is an app that rewards shoppers for receipt they turn in.
Pioneer and OEC forge community bonds through service
The role cooperative members play in rural Oklahoma

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Get 30 days free. 1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
Semantic Reader is an augmented reader with the potential to revolutionize scientific reading by making it more accessible and richly contextual. Try it for select papers. Semantic Scholar uses groundbreaking AI and engineering to understand the semantics of scientific literature to help Scholars discover relevant research.
JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals, books, and primary sources. Explore the world's knowledge, ... Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016) Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 ... Search for images Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. ...
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
15 Best Academic Journal Discovery Platforms. 15 Best Academic Research Trend Prediction Platforms. 15 Best Websites To Download Research Papers For Free. #20. Jurn. Powered by Google Custom Search Engine (CSE), Jurn is a free online search engine for accessing and downloading free full-text scholarly papers.
Google Scholar is a freely accessible web search engine that indexes the full text or metadata of scholarly literature across an array of publishing formats and disciplines. Released in beta in November 2004, the Google Scholar index includes peer-reviewed online academic journals and books, conference papers, theses and dissertations, preprints, abstracts, technical reports, and other ...
You can explore all of them here. 2. Google Scholar. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is undoubtedly one of the popular search engines. With its vast database of scholarly literature, Google Scholar allows users to search for articles, theses, books, and conference papers across multiple academic disciplines.
Google Scholar searches are not case sensitive. 2. Use keywords instead of full sentences. 3. Use quotes to search for an exact match. 3. Add the year to the search phrase to get articles published in a particular year. 4. Use the side bar controls to adjust your search result.
For corrections to academic papers, books, dissertations and other third-party material, click on the search result in question and contact the owner of the website where the document came from. For corrections to books from Google Book Search, click on the book's title and locate the link to provide feedback at the bottom of the book's page.
Connecting Google Scholar to your Harvard Library access is a good way to make sure you get access to articles that Harvard Library subscribes to. Here's how: Go to Google Scholar and sign in to your Google account. Look for the menu options. Go into the settings and select "Library links". Type in Harvard and select: Harvard University - Try ...
Search Advanced search. See personal stories from the global research community on misinformation, public exposure, online abuse and other key issues. Explore stories. Elsevier journals offer the latest peer-reviewed research papers on climate change, biodiversity, renewable energy and other topics addressing our planet's climate emergency. ...
Research Policy Adviser. Aggregation plays an increasingly essential role in maximising the long-term benefits of open access, helping to turn the promise of a 'research commons' into a reality. The aggregation services that CORE provides therefore make a very valuable contribution to the evolving open access environment in the UK.
The main academic full-text databases are open archives or link-resolution services, although others operate under different models such as mirroring or hybrid publishers. Such services typically provide access to full text and full-text search, but also metadata about items for which no full text is available.
RefSeek - Academic Search Engine. Web. Documents. Type 2 or more characters for results. Learn about: Flowers, Chocolate. Browse the Reference Site Directory. Academic search engine for students and researchers. Locates relevant academic search results from web pages, books, encyclopedias, and journals.
Help you achieve your academic goals. Whether we're proofreading and editing, checking for plagiarism or AI content, generating citations, or writing useful Knowledge Base articles, our aim is to support students on their journey to become better academic writers. We believe that every student should have the right tools for academic success.
One of the largest and most authoritative collections of online journals, books, and research resources, covering life, health, social, and physical sciences.
Sage empowers researchers, librarians and readers through: Gold and Green Open Access publishing options. Open access agreements. Author support and information. LEARN MORE. Explore the content of our microsites focusing on various topics from across all Sage journals. Subscription and open access journals from Sage, the world's leading ...
More than 340 mio. scientific documents from more than 11.000 content providers. BASE is one of the world's most voluminous search engines for academic web resources.
Work faster and smarter with advanced research discovery tools. Search the full text and citations of our millions of papers. Download groups of related papers to jumpstart your research. Save time with detailed summaries and search alerts. Advanced Search. PDF Packages of 37 papers.
A service to help the academic community find academic content, researchers, and more. A search engine that provides many innovative ways to explore academic publications, authors, conferences, journals, organizations, and keywords; connecting millions of scholars, students, librarians, and other users.
Academic Researcher. Field trends, graphs and much more information. Product Tour. Not sure where to start? Research Intelligence. Get Academic Field Trends. Expert Finder. Discover Expert Researchers. Scinapse Trends. Specific Target Trends. Paper Search. Find a Specific Paper. Release Notes. April 22, 2024. Scinapse 2.2. Main page ...
Swisscow's services are based in Switzerland, which has some of the most strict privacy policies in the world, and provides fully encrypted searches. It doesn't keep any personal data, IP addresses, or search queries, and has a built-in filter for pornography and violence that can't be overridden, making it a safer choice for kids.