Home Blog Business How To Craft & Deliver an Effective Business Plan Presentation (Quick Guide)

How To Craft & Deliver an Effective Business Plan Presentation (Quick Guide)
A vital element in today’s highly competitive business landscape is the ability to craft and deliver a business plan presentation. This applies to both entrepreneurs and corporate leaders.
This guide describes essential aspects required to build a business plan presentation and deliver it to stakeholders.
Table of Contents
What is a Business Plan Presentation?
Is a business plan presentation the same as a business presentation, executive summary, justification of the business proposal, swot analysis, the niche of the proposal & actors in the industry, competitors, competitive intensity, trend analysis and critical variables, value chain, market analysis, jobs-to-be-done, value proposition, revenue streams, cost structure, distribution channels, key partnerships for the business model, organizational structure & management, go to market and marketing plan, development plan, qa, and continuous improvement model, distribution plan, inventory management, initial funding and financing structure, projection of income and costs.
- Evaluation of Projected Return vs. Required
Risk Evaluation
Sensitivity to critical variables, how to present bibliographical information in a business plan presentation, how to deliver a business plan presentation.
A business plan presentation is the medium we use to communicate a business plan to an audience.
Presenters commonly ask what is the target length of a business plan presentation in terms of slides. Our expertise in this field tells us it’s advisable to work between 13-20 slides, remaining as concise as possible and using the help of visual aids. Let the graphics speak rather than fill your slides with text blocks.
No. A business plan presentation is used to communicate an identified business opportunity and how it is planned to be served in a way that generates profit. A business presentation is a more generic term, explained in our article about business presentation examples .
How to Create a Business Plan Presentation
This section will list our recommended content for a successful business plan presentation. We broke it down into four stages which help the presenter build the story backing the business: a-. The opportunity and the competitive landscape analyzed, b- the business model designed and tested to serve the opportunity, c- the implementation plan of the business model, and finally, d- the financial and economic projections estimated that show the profitability of the opportunity.
For the purpose of this guide, the slides will refer to a case study of photo editing software. To replicate this slide deck creation process, you can speed up design decisions by working with the SlideModel AI Presentation Maker and tailoring it to your project.
So, how to make a business plan presentation? Let’s see a step by step guide.
Stage 1 – Identifying the Opportunity
After the title slide that defines how to start a presentation , any business plan should proceed by introducing the executive summary in a concise but impactful format.
The purpose of the executive summary is to inform the audience what to expect from the presentation and its conclusion.
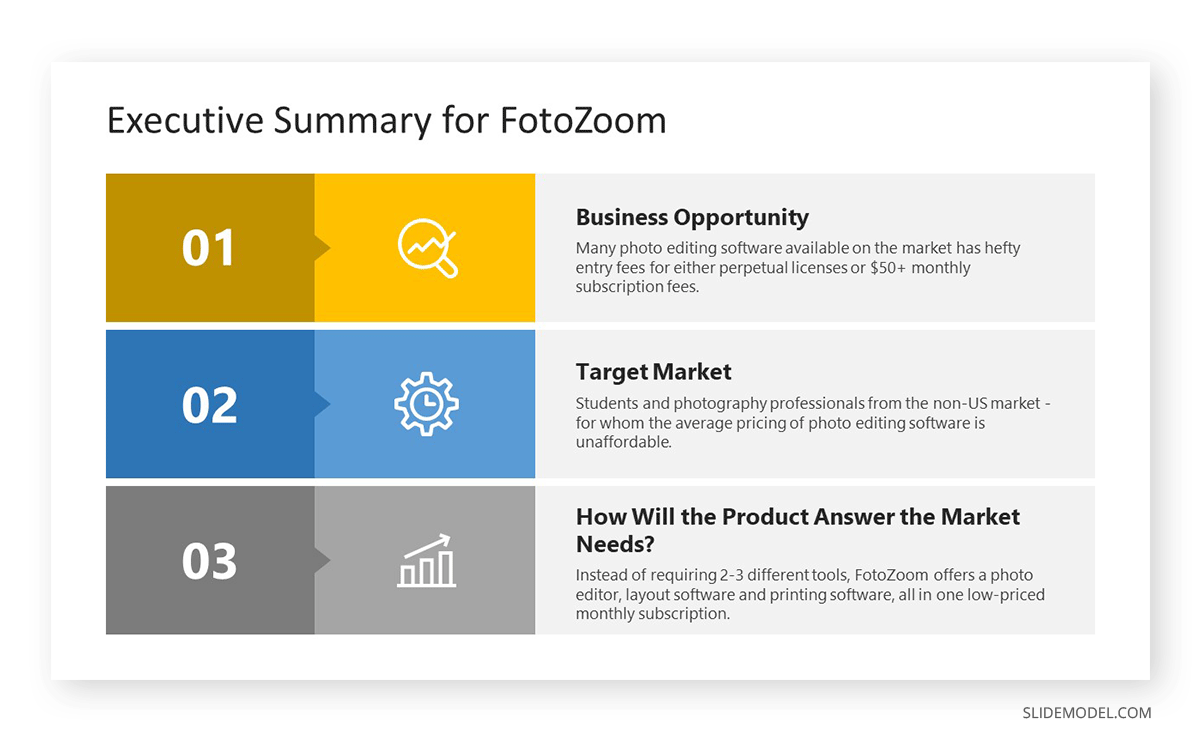
Work with a maximum of two slides for this section, highlighting the key elements through visual cues. Check our guide on how to present an executive summary .
The next slide should disclose all the reasoning behind the business plan proposal, why this plan is being presented at this present moment, and projections of how the plan aligns with the current market trends.
Presenters can share the analysis done by the Market research team as long as it’s made clear which problem is relevant to the current market trends that this business plan aims to solve.
Mention all the references used to arrive at the conclusions expressed so data is backed with meaningful sources.
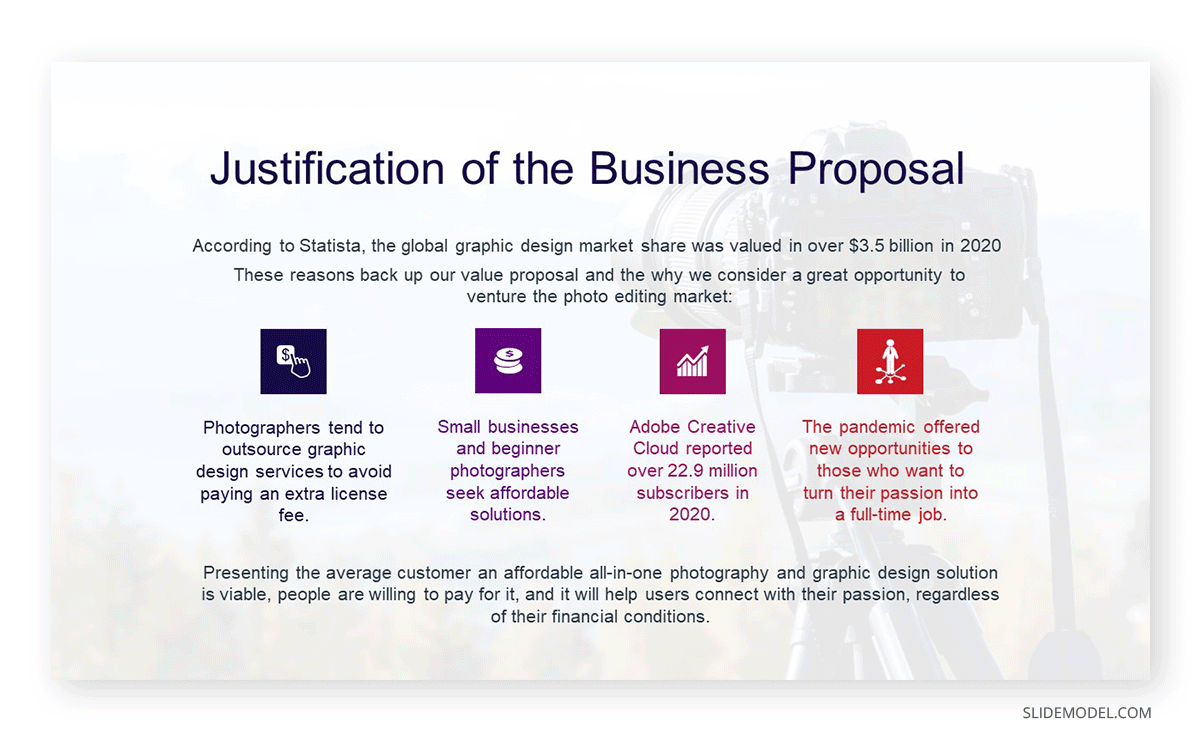
Any corporate PPT template can help you craft this slide, but presenters can also boost their performance through the use of infographics . If your solution for the selected problem involves a complex process, consider using a process flow template to expose the step-by-step justification of this proposal.
Use a SWOT template to showcase the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats of this business opportunity.
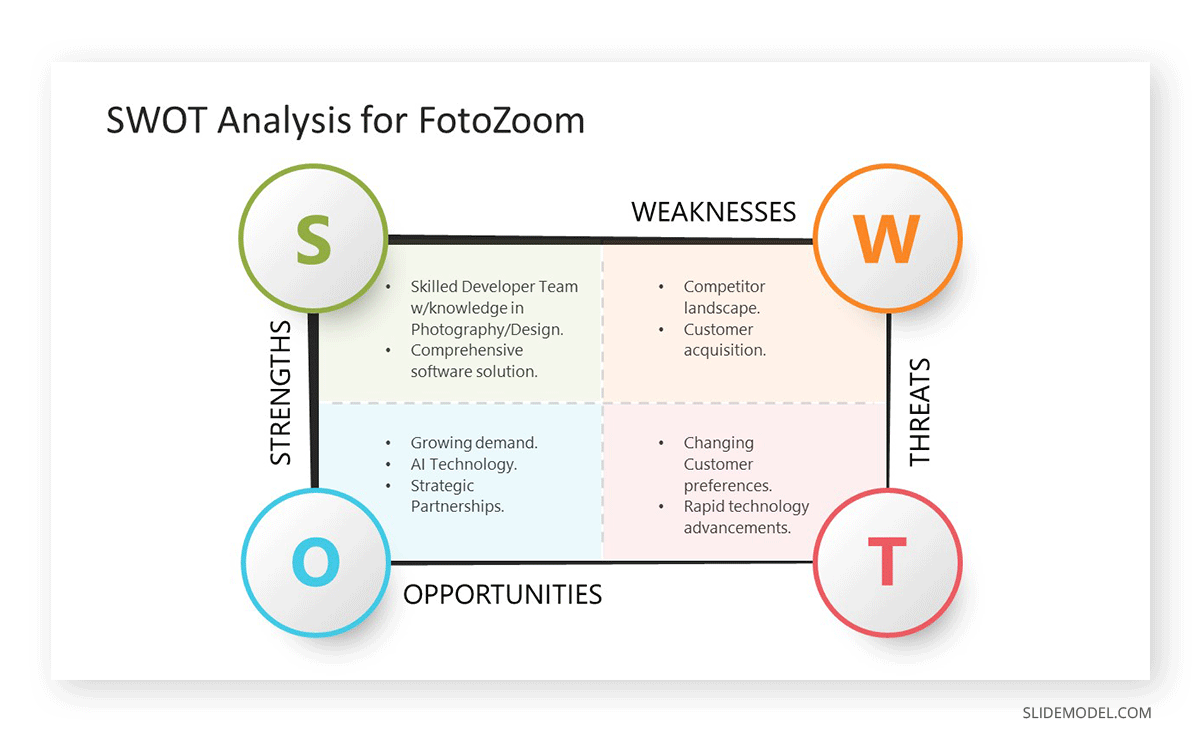
Make sure the SWOT diagram is legible. Work your way to meet the same aesthetic style despite speeding up the process with templates. Mention the tools used for gathering the information for this SWOT Analysis in the footnote and ensure the audience understands which information elements help you reach conclusions in each quadrant. Check our guide on how to create a SWOT analysis and see if your business plan requires a SWOT or SOAR analysis .
Every business plan is scoped under a niche or industry sector. With this slide, describe the sector in which the proposal is immersed. Communicate its value, list the actors involved, and describe their high-level relationships.
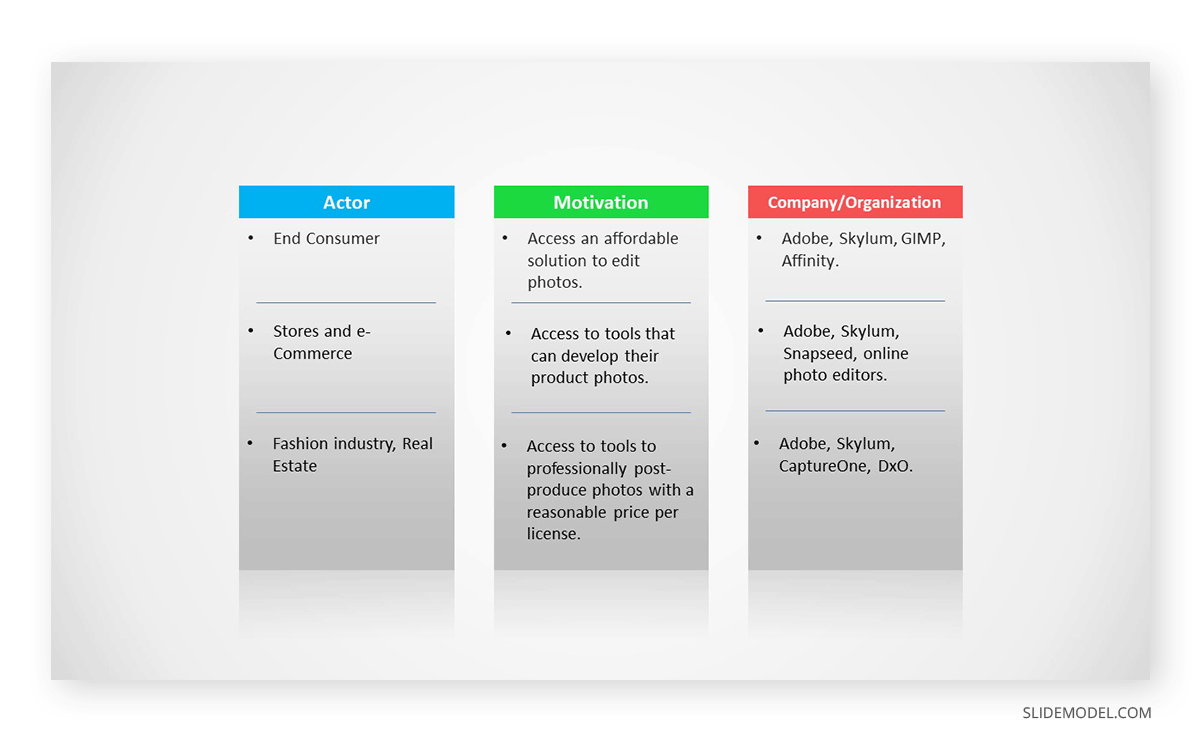
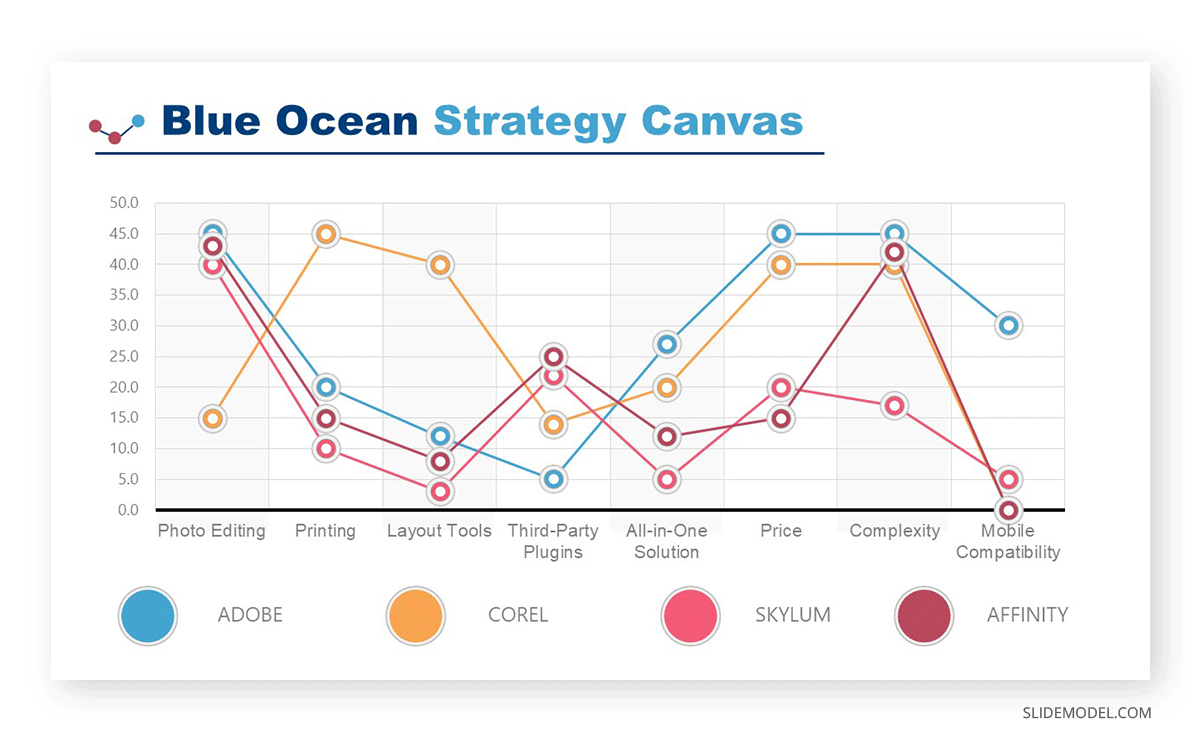
List the analyzed competitors. Communicate their attributes. The competitors’ comparison in business plan presentation can be visually explained using tools from the Blue Ocean Strategy framework, like the Strategy Canvas .
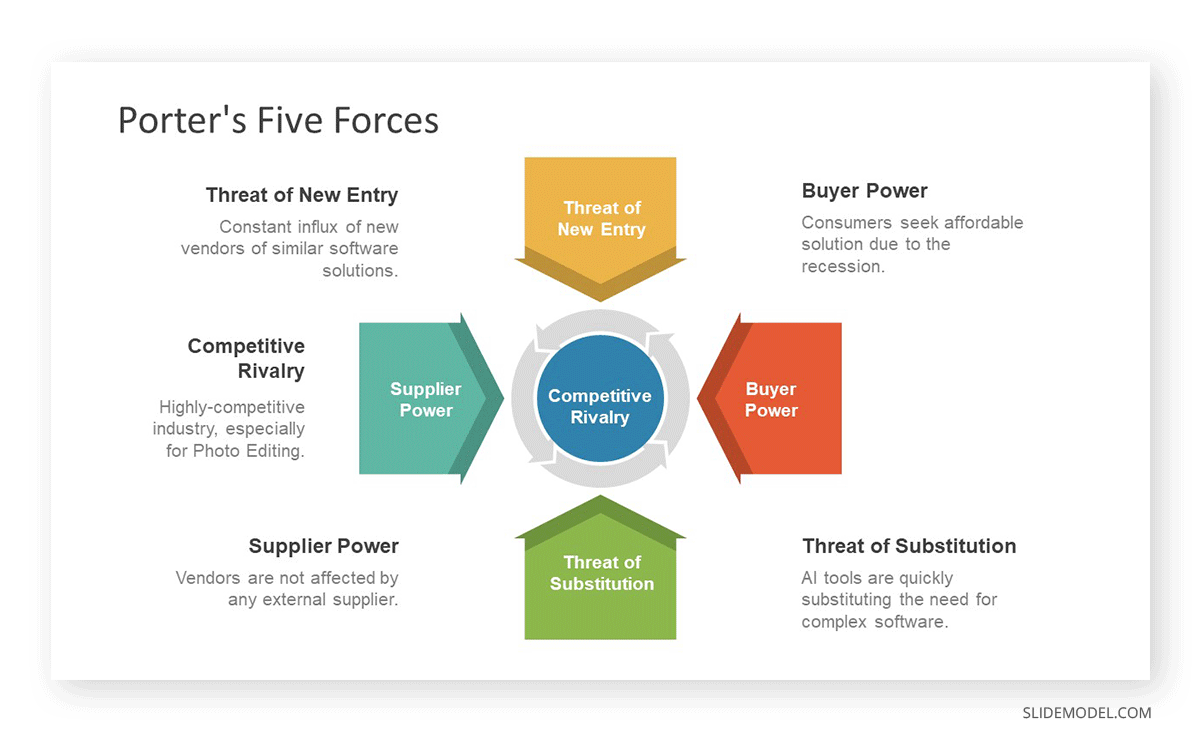
The competitive intensity of an industry sector is studied through the Porter’s 5 Forces model. This intensity expresses how attractive the industry is. Explain the conclusion in each force showcasing the model.
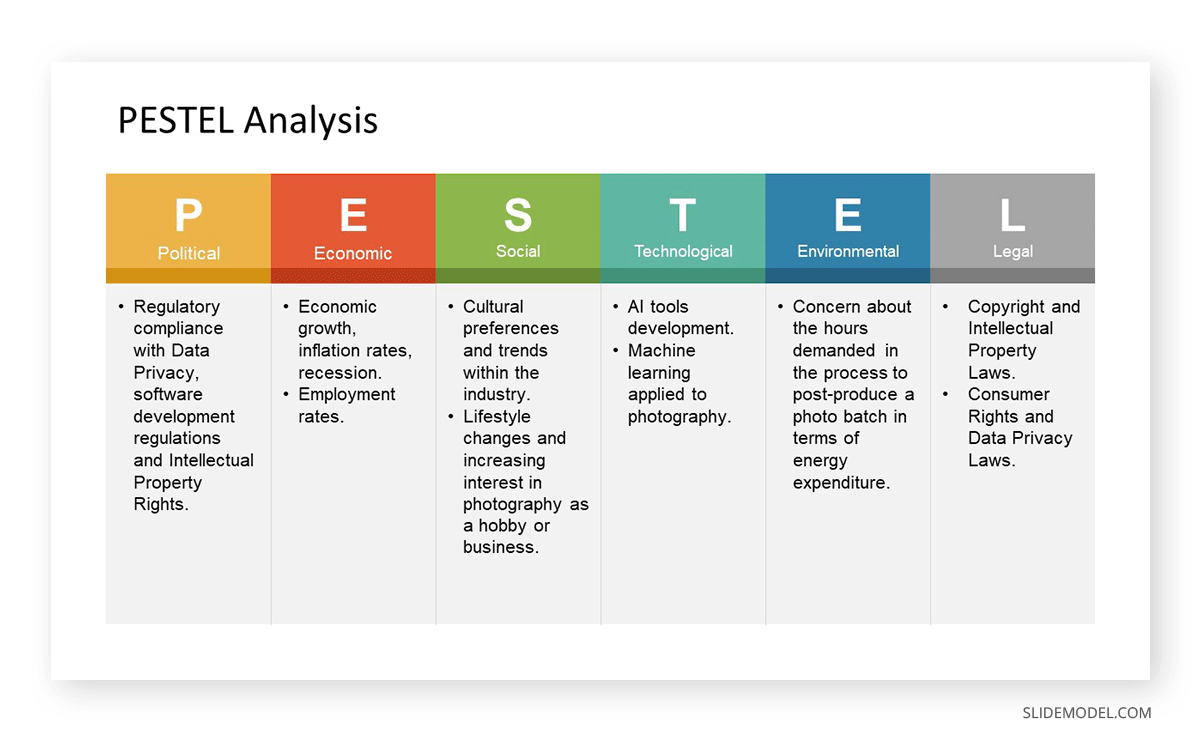
First, introduce the variables identified as important for the industry sector, citing the insight’s source. Secondly, drill down each variable and break down the different trend dimensions ( PESTEL )
- Use a highly visual slide, like a dashboard template , to introduce factual data regarding the trends over a specific time period. Growth rates must be represented in time frames of over 180 days to evaluate the trend accurately.
- List the critical variables (consumers, product, production capability, and financing) briefly.
- Disclose how each variable can affect pricing and your position within the niche for that trend. Presenters can refer to case studies from successful competitor stories on how they responded to trend changes in the niche.
When presenting the value chain, we ought to articulate the sequence of activities the company handles to create value within the business plan. Start by breaking down the value chain into its key components, briefly explaining the stages from inbound logistics all the way through customer service. It is important to highlight the linking point between each stage and express the value of coordinating team activities to enhance overall efficiency.
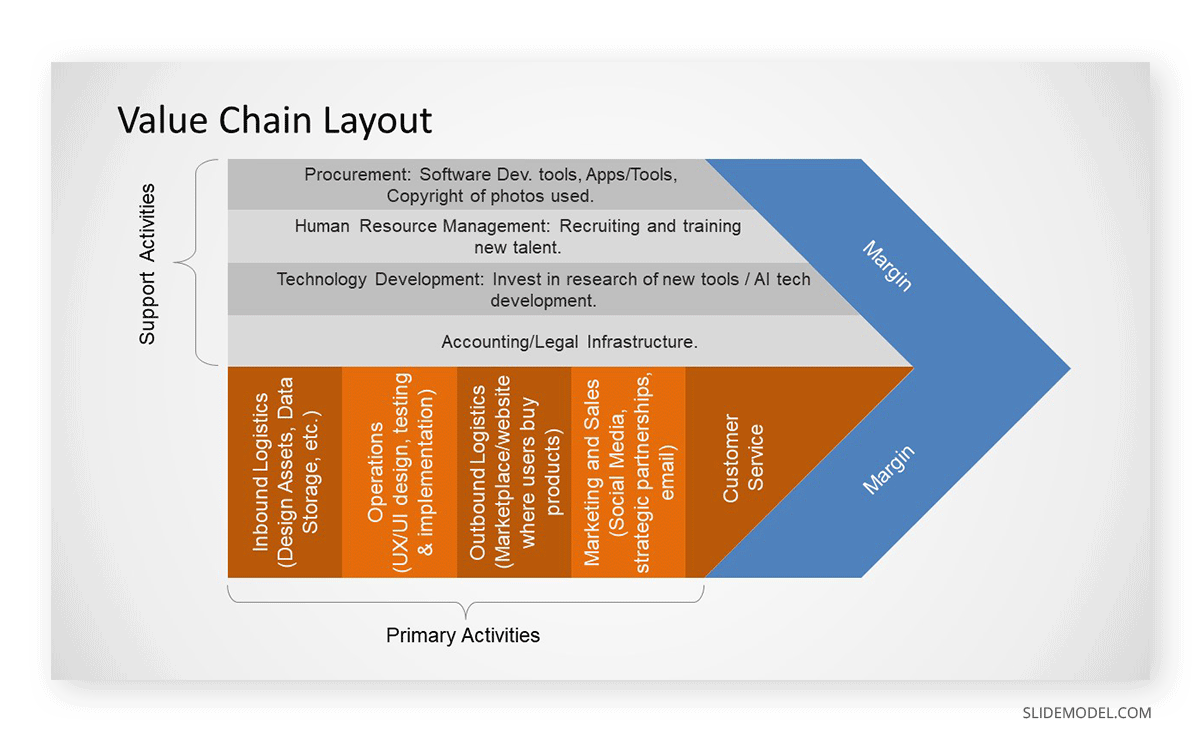
We can use flowchart diagram templates as visual aids for the audience so they can understand the process sequence. Check our guide on how to make a flowchart .
Present the identified Market and its Segments. Continue explaining how conclusions were driven through the analysis and sizing of the market.
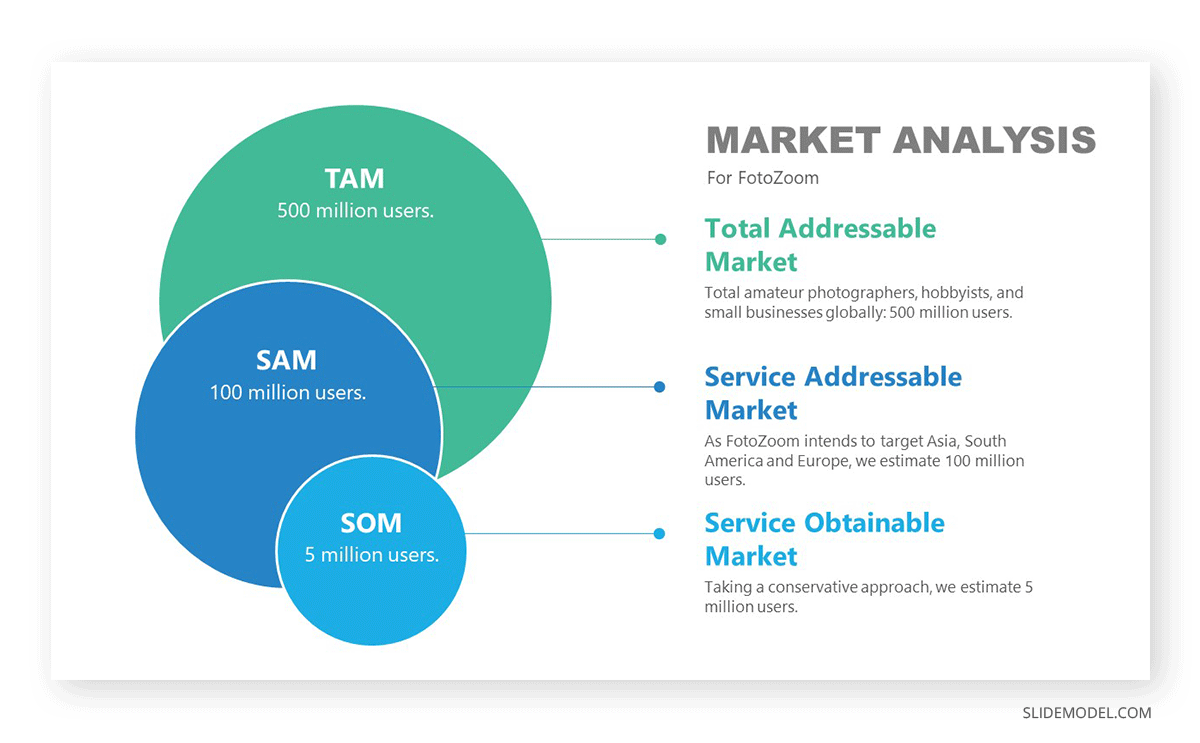
Presenters can use target market analysis templates , market segmentation templates , or TAM SAM SOM templates to compare their target market with the total available market.
We recommend you check our guide on market segmentation for this process.
Then drill down with a Persona definition.
This study can be made by creating ideal customers, describing their demographics and psychological factors that make them prospective candidates to purchase the product or service this business plan presentation refers to.
Here is our guide on creating buyer personas .
The Jobs-to-be-Done theory explains why certain customers are attracted to products and services and how those elements solve core problems in the consumers’ lives.
A Perceptual Map is a tool we can use to measure the consumer perception of different products/services in the same market. This can be particularly useful if our value proposal is to brand ourselves as cheaper alternatives to already existing solutions. Check our guide on perceptual maps for further information.
Check our guide on the Jobs-to-be-Done framework and add suggestions to the business plan presentation.
Stage 2 – Business Model
To describe the Business Model in your Business Plan Presentation, use the business model canvas analysis tool. Display your design in one slide.
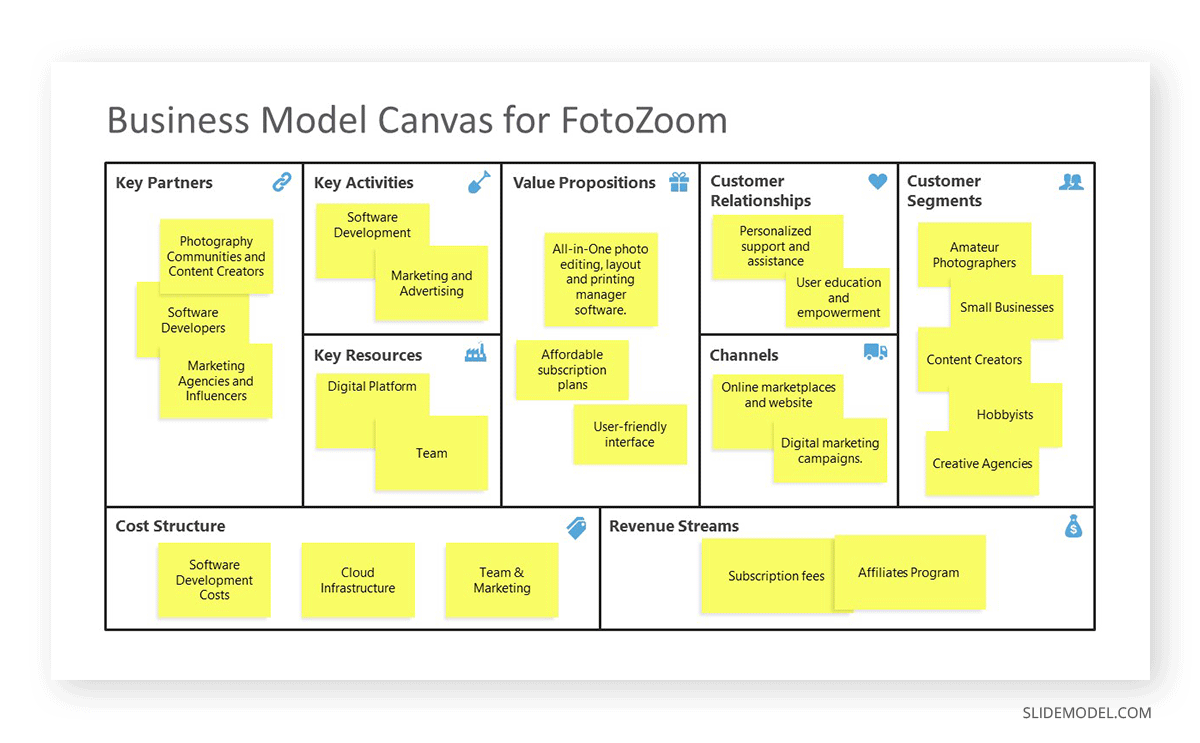
For specific sections of the BMC, you can add slides if you need to drill down for further details. In our experience, the following sections require a deeper level of explanation.
List the Segments targeted in your Business Model. You can include a slide with additional information and segment size. Reference the Market analysis explained earlier to justify the selection or which were the pivots applied.
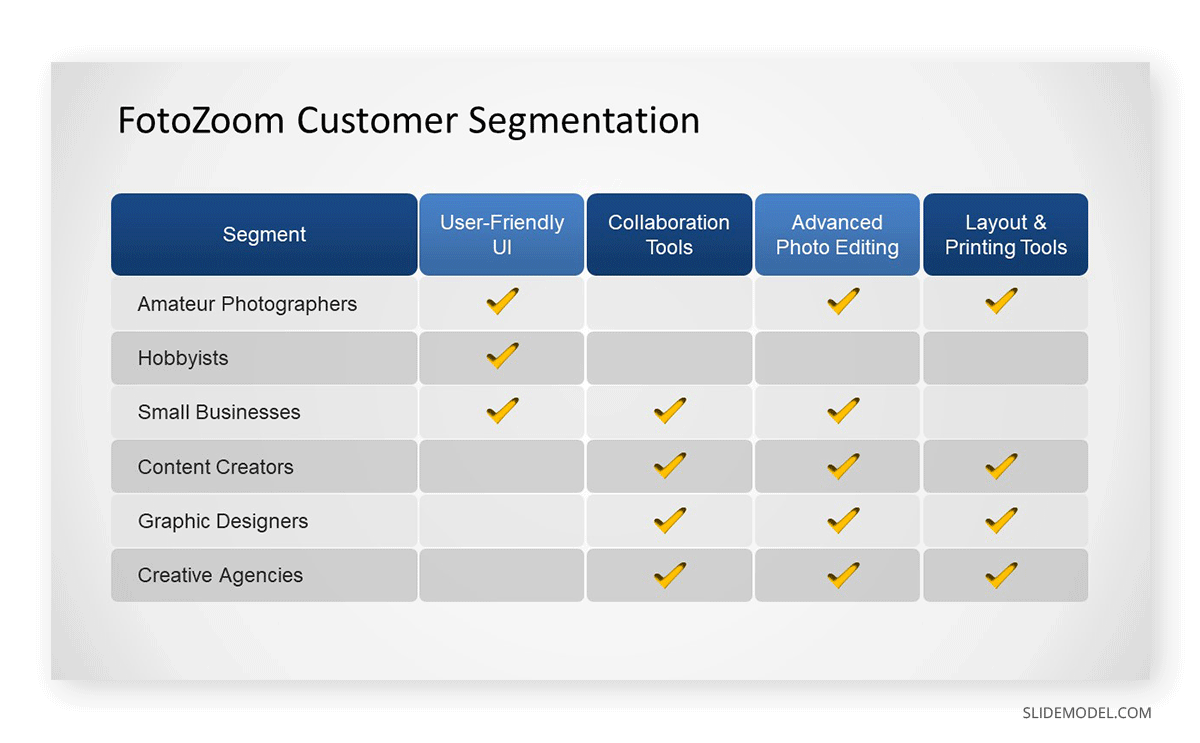
In order to explain the reasoning behind the Value Proposition and how it serves the segments selected, you can use the Value Proposition Canvas tool to explain the logic behind this selection.
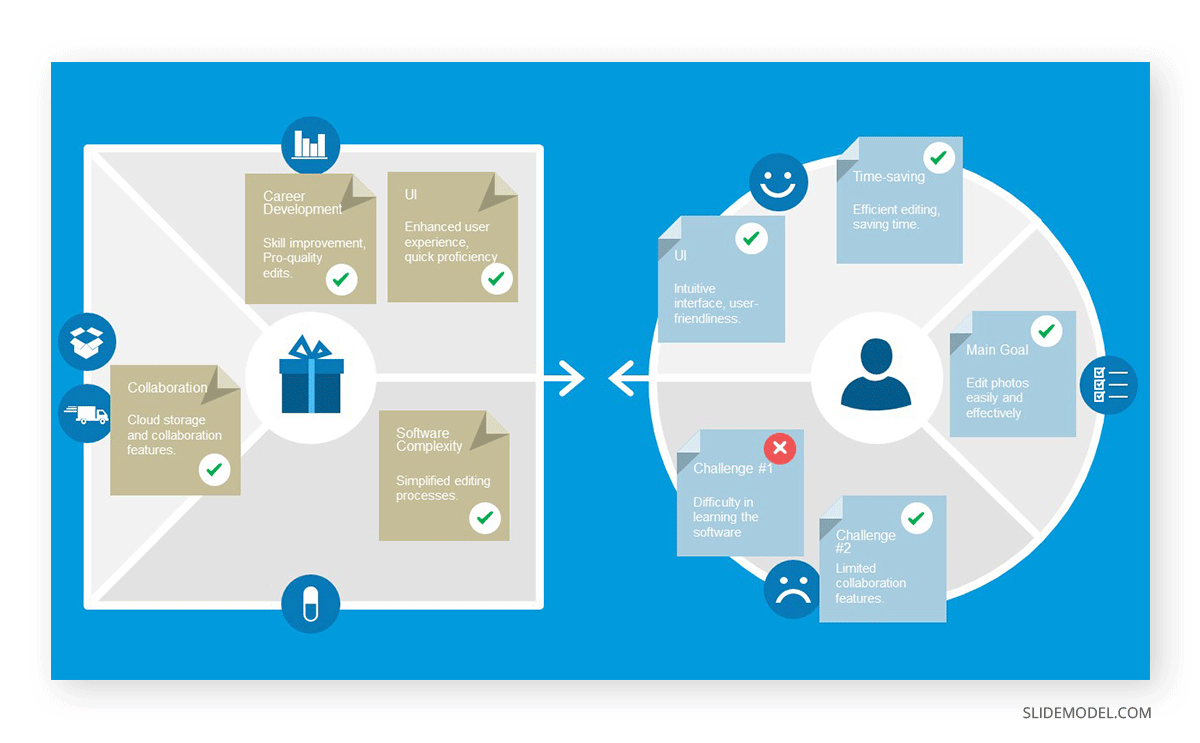
The Value Proposition outlines the unique benefit our product or service offers the market and why customers should choose our offer over potential alternatives. Since we have already analyzed the potential buyers and presented the market, it’s time to deliver that value proposition using our best assets: customer testimonials, report data, surveys, etc.
As testimonials often weigh the most in established brands, be sure to present this information through a narrative that showcases why your product or service had a positive impact on the life of that customer. You can use customer testimonial templates to give an extra boost through visual aids.

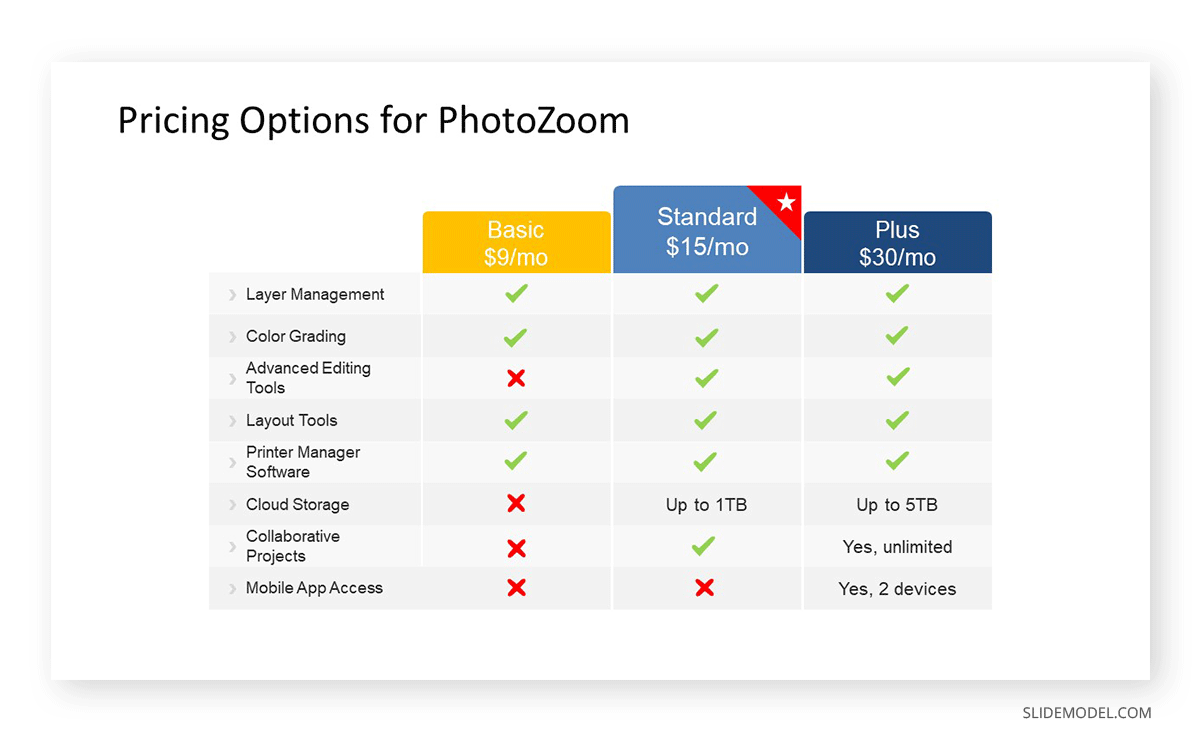
Explaining how much the customers will pay for the product/services is critical to understanding the viability and profitability of the business. Showcase for each segment the pricing model and the engagement terms.
The Income Model expresses the sources of revenue for our business plan. This has to be in relationship with the pricing strategy for established businesses. Lean startups can work concerning their minimum viable product (MVP) and then elaborate with projections for future releases or changes in their income stream structure.
At this point, companies need to present the sources of revenue depending on their origin:
- Product Sales
- Subscription Model
- Freemium Model
- Partnerships with other brands in different niches
- Advertising and Sponsorships
- Monetization
Check our guide on pricing strategy models for more information about how to present this point. You can use revenue stream templates to represent this data in style.
Drill down the cost structure categories and relate them to the Value Chain explained earlier. Show a cost breakdown chart to make it easier for the audience to understand their weight in the total costs.
As this step can be a bit complex to articulate, we recommend you check our guide on Cost Structure to see how you can resume all that information in one slide.
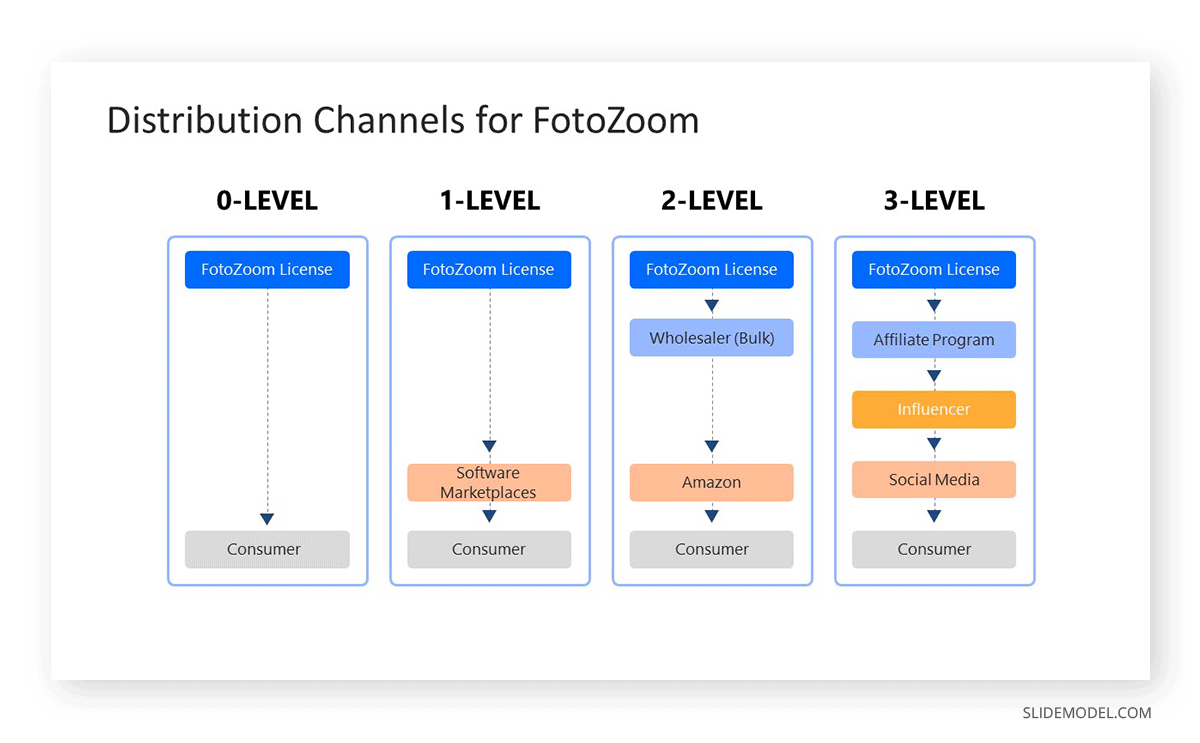
At the business model stage, distribution channels should be briefly introduced since they will be mentioned again in the Distribution Plan . In some industries, it is important to highlight which channels are chosen over others for the sake of revenue and faster operation.
Our Distribution Channels PowerPoint Template is a perfect resource for this.
Presenting the strategic partnerships for the business plan is a way to prove the plan’s potential reach and success factor. On this behalf, companies must list which resources they are sharing with their business partners regarding expertise, technology, distribution channels, or capital, as these elements will impact the cost structure.
You can use the Business Partnership PowerPoint Template to present this information in a professional-looking format.
Stage 3 – Implementation
The business plan is designed to offer a product, deliver a service, or combine both. At this stage, the business plan presentation drills down on how the organization will build/deliver the product/service implementing the business model outlined earlier.
Describe how the company operates regarding human capital and its roles. Presenters must describe to the audience the hierarchical structure, responsibilities, and how they play a role within the value chain.
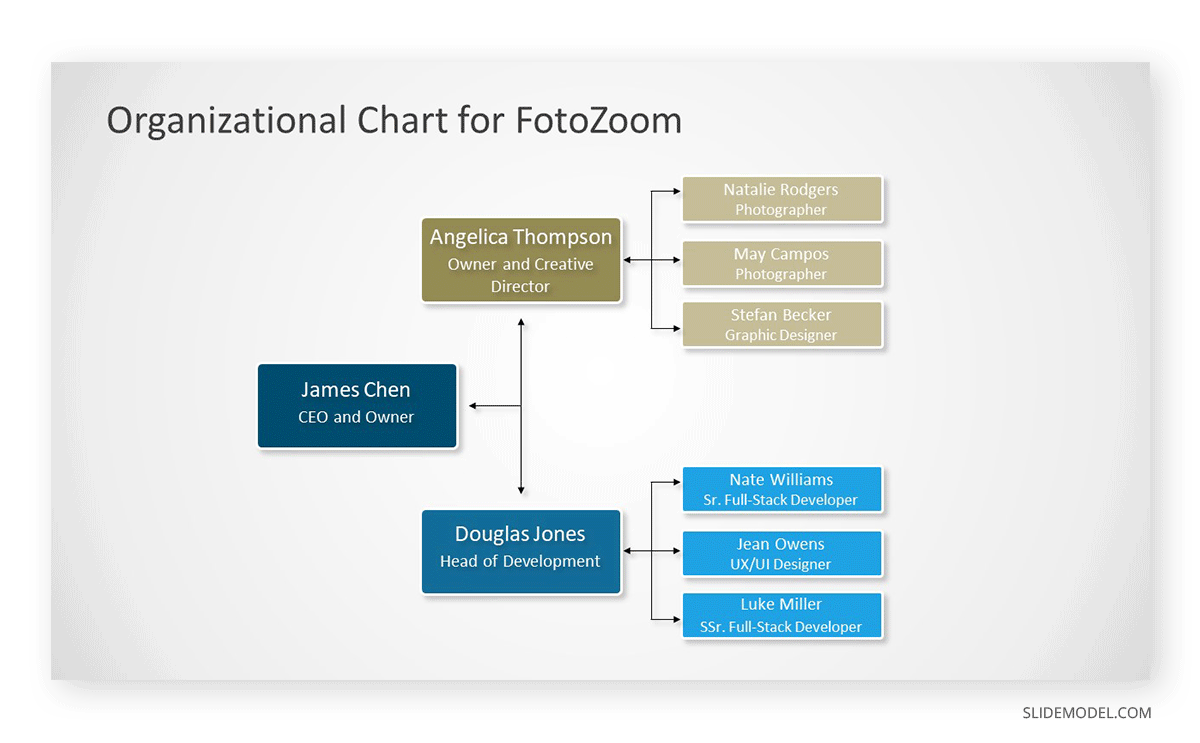
You can use Org Charts to represent the roles and responsibilities in the organization visually. It is also advisable to highlight the expertise and experience of the management team, as it helps to build trust.
The Human Resource Plan must refer to your planned recruitment, training, and employee onboarding. Which talent will be required, and how is it planned to build the different teams of the structure.
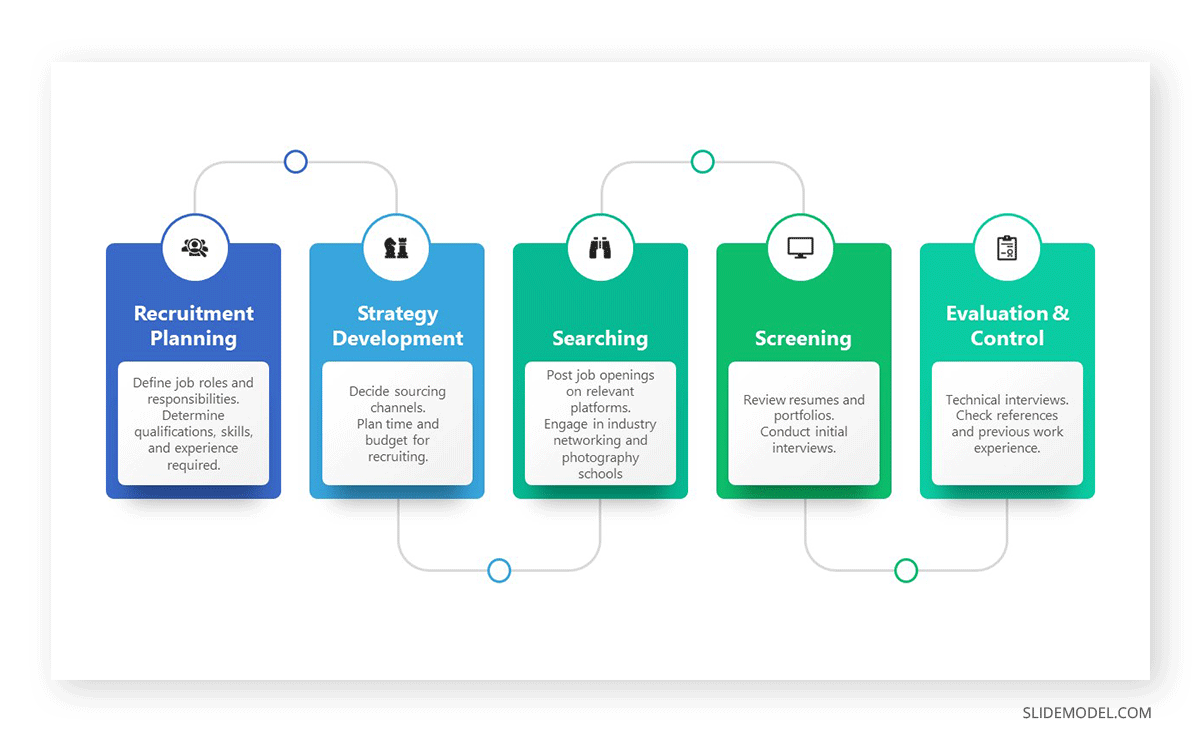
Check the Go To Market Strategy guide and describe how the Business Plan will enter the market and overcome the initial barriers. Continue with the Marketing Plan limited to 1-2 slides resuming the plan’s tactics to increase brand awareness and the selected channels for this strategy.
You can use the Marketing Plan Templates help to speed up the process by focusing on the content to fill rather than the design or creating complex charts from scratch.
Present the sales plan describing the full sales process, lead generation, nurturing customers, and conversion strategies.
Use Sales PowerPoint Templates to visually illustrate your sales process, like the Sales Pipeline Slide Template for PowerPoint , which depicts the process from lead acquisition to a closed deal.
Check our guide on Sales Plan for further information on this topic.
This step refers to presenting the product/service development plan, the Quality Assurance processes behind its validation, and your company’s commitment to a continuous improvement process based on surveyed data or customer feedback.
We can refer to testimonials, user case experiences our team successfully troubleshot, or experiences we learned from competitors in the same niche.
Presenting the distribution plan involves addressing logistics topics, supply chain , and sharing fulfillment strategies. Although we already presented the potential distribution channels, this is the step in which you detail how each will interact and their impact on the estimated revenue.
Present one slide mentioning your company’s approach to these channels, if applicable:
- Direct Sales (either physical store or e-commerce)
- Retail Partnerships
- Wholesalers or Distributors
- E-Commerce marketplaces
This step involves two different approaches depending on the kind of industry we’re in. For traditional business, inventory management in a business plan presentation must highlight how the inventory will be handled to minimize transportation costs or overproduction. Projections must be shown per quarterly period and take into account seasonality if it has a significant impact on the required storage capacity.
On the other hand, e-commerce companies have to present their online infrastructure to secure the product’s availability 24/7, how customer tickets are handled when the customer cannot access the product, server costs, and how we prevent online leaks.
Stage 4 – ROI and Risk Evaluation
This section will outline the Financial Plan of your Business.
Showcase the financial structure, including equity, debt, and potential investors, at the moment of kick-starting this business. It is a good practice to consider the initial funding slide to be a brief summary of those points, with particular emphasis on the funding needs.
Cash Flow Diagrams , Comparison Chart templates , and Timeline templates to showcase when funds help to meet each of the plan’s milestones are good ideas to represent the elements on this slide.
Income and expense projections must be presented over a defined time period by using graphs or charts to clearly visualize the trends supporting each change.
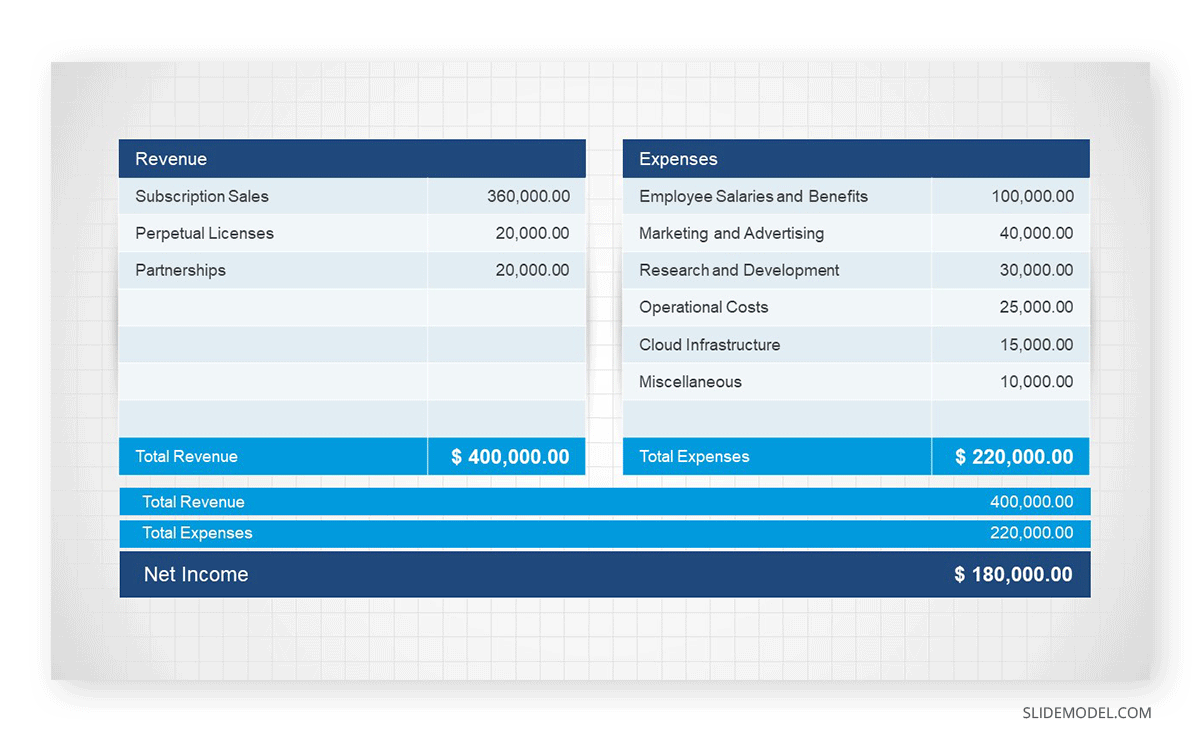
Break down the revenue sources with clear, identifiable icons to showcase: product sales, subscription fees, advertisement, affiliates, etc. Sales estimations have to be realistic and conservative, as they will be contrasted with the production, marketing, administrative, and personnel costs to leave a gross profit margin calculation.
Evaluation of Projected Return vs. Required
Demonstrate the feasibility of your business plan. Start by presenting the profit margins in relation to the projection of income and expenses, then introduce the break-even analysis .
Presenters can make their message more relevant by presenting an ROI calculation and contrasting it with industry benchmarks in the same niche. By following this approach, presenters prove how the ROI offered by this business plan aligns with the investment’s risk projection.
Presenting a risk evaluation analysis in a business plan presentation involves introducing both risks and their mitigation strategies.
Risk Management templates , like the ROAM framework, can help organize potential risk sources by their severity and impact on the organization. A pyramid diagram can be used to demonstrate how risk management can be delegated across the organization to completely eradicate the risk factor depending on its severity.
The elements you should consider presenting are mainly regulatory changes, market changes, competitors (new or existing), and financial crises.
The final point in our business plan presentation involves summarizing how key variables can influence the projected returns in our plan. Examples of these variables can be sudden increases in raw materials (affecting production costs and sales prices), a new pandemic (affecting workforce capacity and shortage of raw materials), geopolitical situations like war, etc.
We highly recommend presenting these critical variables using scenario analysis techniques according to measured data. Introduce best-case, worst-case, and most likely-case to give a full panorama of how your organization is prepared against any contingency.
An often overlooked point in a business plan presentation comes when listing the bibliographical information used to craft the business plan. Follow these steps to ensure a professional outcome for this slide or document.
- Use a title like: “Bibliography,” “Source Credits,” or “References.” If your business plan presentation cites examples from other companies, use a “Works Cited” section.
- References are usually shown in the APA style, but the MLE or Chicago style can be requested depending on your location or situation.
- Maintain a consistent style in terms of reference style used, font, text size, and formatting options across the entire slide deck. Footnotes or in-text citations can be used for important data.
- Verbally acknowledge your sources when required throughout the course of your presentation. This helps to establish credibility and respect for other people’s work rather than just dropping a slide with chunks of text.
This section will cover the most commonly asked questions on delivering a business plan presentation.
How many slides should my business plan presentation list?
This will depend entirely on your niche and the complexity of the business plan. Generally, work with at least 15 slides and no more than 30. It is best to use an extra slide rather than overcrowd an existing slide with tons of information.
What is the best format to present a business plan?
There are different options to present any business plan, so the selected option will mostly consist of the presenter’s preferred style and the audience’s age and interests.
- PowerPoint Presentation : You can start from a blank slide and go all the way through a professionally designed PPT template . PowerPoint documents allow you to present images, text, audio, videos, and any kind of graphic to help you convey the core ideas behind the business plan. They can work with any PC or Mac device, as well as mobile devices.
- PDF Documents: This can be a choice made in a hurry or by preference. Sharing a PDF document can work, but you must include the fonts used in the original document, as some compatibility issues can be present.
- Pitch Deck : Rather than doing a lengthy business plan presentation, a pitch deck consists of a maximum of 15 slides to deliver your proposal concisely. This is the typical approach we can see in TV shows like Shark Tank.
- Video Presentation : In some cases, using a video in a business plan presentation is relevant, especially if we are to introduce an innovative product in the market. You can use videos to showcase features, present services in a live format, introduce your team, and plenty of other options.
Are printables required in business plan presentations?
Although they are not required, using supplementary material in business plan presentations can be useful. You can prepare reference material for investors, especially involving complex data like graphs in an amplified format (and reference the slide in which they appear and vice versa).
Providing a printable to accompany your business plan presentation helps to give an image of professionalism and respect to your proposal.
What are the don’ts of writing a business plan?
The main purpose of this article is to craft and deliver a business plan presentation. Still, we would like to clarify some common errors seen in business plans that typically affect the performance of the presentation.
- Using overcomplicated language : Jargon or unnecessary acronyms may confuse spectators who are not in touch with all the details relevant to a particular industry.
- Ignoring the audience : Not considering the variety of interests among investors, partners, and team members can hinder your presentation.
- Neglecting/underestimating competitors : Any realistic business plan considers the existing competitors in their niche and perhaps potential newcomers. Not doing so will leave you unprepared to present a doable business plan.
- Ignoring Risk Assessment : Omitting the Risk Assessment analysis and mitigation strategies does not respect the value investors and your team have.
How long should the business plan presentation be?
As a general guideline, try to fit your business plan presentation between 20-30 minutes. Some complex plans may require additional time to be presented.
Does the presentation need to be tailored to different audiences?
Using this tactic can be a winning factor for both investors and your team, as you prioritize effective communication for the roles they are relevant. Take these items into consideration for tailoring the presentation for specific needs.
In-Company Presentation
The focus should be on goal accomplishment and the strategies targeted to the team’s roles. Emphasize how teamwork is the pathway to success and how each individual contributes to the bigger picture.
If new technologies or knowledge are required as part of the business plan implementation, then this is the moment to disclose that information and inform the process to coach the team into it.
Board Meeting
Whenever delivering the business plan presentation to a board of directors, focus on the strategic goals, financial projections, and KPIs.
Showcase how this business plan aligns with the company’s core values, mission, vision, and long-term strategy.
Potential Investors
Presenting your unique value proposition, potential ROI, and highlighting the market opportunity is extremely important. Focus on selling your business model and vision with accurate financial projections and growth strategy.
Dedicate some minutes to present your industry’s competitive landscape and answer why your product or service is a better offering than what competitors produce.
As we can see, creating a business plan presentation is a process that can be time-consuming if we lack the required business plan presentation tools to turn data into visually appealing formats.
Remember to work concisely without losing the big picture of what you intend to explain. Your presentation is the entry point into the heart of your business; therefore, by adopting a structured approach, you can deliver an experience that engages, inspires, and builds confidence.
Finally, let’s see some business plan PowerPoint presentation examples & business plan templates that you can use to speed up the presentation design process and save time.
1. Coffee Shop Illustration Business Plan Slides

Create your new business plan presentation with quality vector illustrations for Coffee Shops. Ideal for cafeterias, coffee bars, barista giftshop stores, bookshops and more.
Use This Template
2. Real Estate Business Plan PowerPoint Template

Realtors looking to start their own agencies should take a look at this attractive selection of slides with tailored real estate vector illustrations. These presentation plan slides show the different stages that a prospective buyer may incur, from hiring the services of a Real Estate agent, checking different properties, to finally buying a home. Graphs and charts are included in vivid colors that are fully editable to meet the required branding.
3. Restaurant Business Model PowerPoint Template

As we’ve seen with the previous cases, these vector images depicting typical restaurant activities can help us build a business plan presentation sample to discuss with our team prior to an important meeting. Save time and money by introducing these professional designs into your presentation.
4. One Pager Business Plan PowerPoint

To briefly summarize the objectives of your business plan, work in-team with this one-pager business plan slide. Ideal to take notes, give a general picture of the current status of the business plan and key growth opportunities.
5. Business Plan PowerPoint Templates
If you want to create the best business plan presentation, this slide deck can make that task 100% easier. Containing all the elements described in this guide, introduce your data and prepare to deliver a powerful speech.
6. Flat Bold Business Plan PowerPoint Template
Another slide deck intended for those looking at how to make a business plan presentation that delivers a memorable experience. With a minimalistic design approach, it perfectly balances formal elements and impactful visual cues to help increase your audience’s retention rate.
7. Car Sharing Business Plan PowerPoint Template

Create the next Uber-like car-sharing service with the help of these carpooling vector illustrations perfectly arranged in a cohesive business plan slide deck. Presenters can explain the ins and outs of their business model with highly detailed graphics that grab the attention of potential investors. Check it out now!
8. Beauty Salon Business Plan PowerPoint Template
Business plan presentations don’t have to look formal or boring. This slide deck is geared towards beauty salon businesses, especially for those targeted to women. Chic design, bold color scheme, and extremely useful tools like a pricing list to present an idea like a subscription-based model where consumers see the total value of their investment.
9. CrossFit Business Plan PowerPoint Template

Finally, we list an option filled with tools and gym vector illustrations for those looking to start a gym business or CrossFit academy. These illustrations were crafted with care to express the core idea on every single slide, such as human-shaped graphs to present relevant KPIs.

Like this article? Please share
Business Planning, Business Presentations Filed under Business
Related Articles
Filed under Business • May 17th, 2024
How to Make a Transition Plan Presentation
Make change procedures in your company a successful experience by implementing transition plan presentations. A detailed guide with PPT templates.

Filed under Business • May 8th, 2024
Value Chain Analysis: A Guide for Presenters
Discover how to construct an actionable value chain analysis presentation to showcase to stakeholders with this detailed guide + templates.
Filed under Business • April 22nd, 2024
Setting SMART Goals – A Complete Guide (with Examples + Free Templates)
This guide on SMART goals introduces the concept, explains the definition and its meaning, along the main benefits of using the criteria for a business.
Leave a Reply
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![business strategic planning slideshare [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources

Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

How to find alignment on AI

What is content marketing? A complete guide
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide

Aspect Ratio:
File Size: 28.4 MB
Number of Slides: 200
Terms of Usage
Training Presentation/Powerpoint:
Strategic planning:, eight steps to implementation.
Description
In a constantly evolving world, organizations need strategic planning to adapt and stay ahead of the competition. However, despite being a basic business practice, many organizations struggle to make it work, resulting in disappointing outcomes. Our research and experience show that most strategic planning processes are poorly executed and rarely impact day-to-day decisions. To be successful, a strategic planning process should provide a framework against which all decisions can be evaluated.
What sets this model apart is that it includes a pre-planning step for assessing the organization's readiness and making the necessary preparations for a successful planning process. Additionally, the model incorporates steps for values scanning and shaping the organizational culture, which can greatly impact both the process of planning and the resultant strategic plan. The framework also facilitates the envisioning of the future state and creating the strategic business model before conducting the performance assessment, enabling the planning team to be creative and innovative before becoming analytical and critical. Lastly, the framework includes both traditional and newer frameworks/tools focusing on value creation.
The Eight Steps of Strategic Planning are presented in a sequential manner to guide organizational leaders and key stakeholders in planning and creating the organization's future.
The Eight Steps of Strategic Planning include:
Step 1: Plan the Planning Process
Step 2: Define Shared Values and Mission
Step 3: Analyze the Current Organizational Profile
Step 4: Create an Inspiring Vision
Step 5: Compare Current to Envisioned Organization
Step 6: Develop Strategies, Objectives and Plans
Step 7: Execute Action Plans
Step 8: Monitor Results and Make Improvements
Using this model for strategic planning will provide new direction and energy to the organization. The steps and sub-steps can be adapted to suit the specific needs and desires of the organization.
This comprehensive Strategic Planning PPT training presentation is most suited for the organization's internal planning team, strategy deployment professionals, and independent consultants. It can be used during annual planning cycles or when important real-time strategy decisions need to be made.
Note: This training presentation package includes:
Strategic Planning PPT training presentation (PowerPoint format, 16:9 widescreen)
Strategic Planning poster (PDF format, in color and monochrome, printable in A3/A4 size)
Learning Objectives
Acquire knowledge on the key concepts and principles of strategic planning
Describe the eight-step strategic planning process and the key frameworks and tools
Define the key factors for successful strategic planning
Key Concepts and Principles of Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning Process: The Eight-step Strategic Planning Model
Key Strategy Frameworks and Tools
Strategic Planning Best Practices
Included are the key strategy frameworks and tools such as: Power/Interest Grid for Stakeholder Analysis; VRIO Framework; Porter's Value Chain; PESTLE Analysis; BCG Growth/Share Matrix; McKinsey-GE Matrix; Porter's Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Profile Matrix; SWOT Analysis; Porter's Generic Strategies; BCG Strategy Palette; Ansoff's Matrix; Blue Ocean Strategy; Impact-Probability Matrix; Strategyzer's Value Proposition Canvas; Strategyzer's Business Model Canvas; McKinsey 7-S Model; and Balanced Scorecard.
You may also be interested in the following related documents (sold separately):
Strategic Planning: Eight Steps to Implementation
Hoshin Kanri
A3 Hoshin Planning
Design Thinking Workshop Guide
Customer Journey Mapping
Value Proposition Canvas
Business Model Canvas
Service Design
Digital Transformation: People, Organization & Change
Digital Transformation: Step-by-step Implementation Guide
Digital Customer Service
Lean Daily Management System
Lean Start-up

Search form

- Table of Contents
- Troubleshooting Guide
- A Model for Getting Started
- Justice Action Toolkit
- Best Change Processes
- Databases of Best Practices
- Online Courses
- Ask an Advisor
- Subscribe to eNewsletter
- Community Stories
- YouTube Channel
- About the Tool Box
- How to Use the Tool Box
- Privacy Statement
- Workstation/Check Box Sign-In
- Online Training Courses
- Capacity Building Training
- Training Curriculum - Order Now
- Community Check Box Evaluation System
- Build Your Toolbox
- Facilitation of Community Processes
- Community Health Assessment and Planning
- Section 1. An Overview of Strategic Planning or "VMOSA" (Vision, Mission, Objectives, Strategies, and Action Plans)
Chapter 8 Sections
- Section 2. Proclaiming Your Dream: Developing Vision and Mission Statements
- Section 3. Creating Objectives
- Section 4. Developing Successful Strategies
- Section 5. Developing an Action Plan
- Section 6. Obtaining Feedback from Constituents: What Changes are Important and Feasible?
- Section 7. Identifying Action Steps in Bringing About Community and System Change
- Main Section
A PowerPoint presentation summarizing the major points in the section.
Strategic Planning Powerpoint Templates and Google Slides Themes
Unlock the potential of your strategic planning with our professionally designed templates that will help you visualize and communicate your ideas effectively.
Explore Free Strategic Planning Presentation Templates

Elegant Strategic Roadmap Infographics
Looking for a sleek way to showcase your next big plan? Our PowerPoint and Google Slides template is perfect for ... Read more

College Engineer Resume Slides
Experience the seamless blend of professionalism and personality with this Powerpoint and Google Slides template. Specifically designed for aspiring engineers ... Read more

Animated Meeting Plan Blue Illustrative Minimal Business Slides
Tired of pointless meetings? Guarantee clarity and inspiration with these animated meeting plan slides, easy to use as a Google ... Read more

Curved Timeline Slides
Stay on top of your game with this curved timeline, ready to go as a Google Slides template, PowerPoint theme, ... Read more

Blue Marketing Slides
Download this free template to showcase your content like a professional. This design has isometric illustrations on business, marketing and technology topics. Use it in a working environment to present your marketing plan, media strategy or to pitch your next idea. ... Read more

Green Marketing Slides
Create a deck that grabs everyone’s attention with this multipurpose free template. Thanks to the teamwork illustrations this template will fit a keynote on business planning, your next marketing strategy or a new project proposal. Face your presentation like a pro with this illustrated theme! ... Read more
Professional designs for your presentations
SlidesCarnival templates have all the elements you need to effectively communicate your message and impress your audience.
Suitable for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Download your presentation as a PowerPoint template or use it online as a Google Slides theme. 100% free, no registration or download limits.
- Google Slides
- Editor’s Choice
- All Templates
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Google Slides Help
- PowerPoint help
- Who makes SlidesCarnival?

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Appendix 1: Mastering Strategic Management Powerpoints
Chapter 1 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 2 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 3 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 4 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 5 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 6 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 7 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 8 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 9 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 10 – Part 1 [PowerPoint]
Chapter 10 – Part 2 [PowerPoint]
Mastering Strategic Management - 1st Canadian Edition Copyright © 2014 by Janice Edwards is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Business Strategic Planning
Business Strategic Planning Read less

Recommended
More related content, what's hot, what's hot ( 20 ), similar to business strategic planning, similar to business strategic planning ( 20 ), recently uploaded, recently uploaded ( 20 ).
- 1. KHWAJA YUNUS ALI UNIVERSITY Welcome to our Presentation
- 2. 1. Ahasanul Hasan ID: 2016202010019 BBA 8th Batch, Department of Business Administration Khwaja Yunus Ali University Enayetpur, Sirajganj
- 3. Business Strategic Planning Presentation Topic;
- 4. Strategic planning is a process in which organizational leaders determine their vision for the future as well as identify their goals and objectives for the organization. Strategic planning is a process of decisions made by an organization to set goals and to outline a course of action to achieve those goals, to grow the business and to help the be profitable. What is Strategic Planning
- 5. What is not Strategic Planning 1. Strategic Planning does not attempt to make future decision. Decision can be made only in Present. 2. Strategic Planning is not forecasting Product Sales & then determining what should be done to assume the fulfillment of the forecasts with respect to such things as material purchases, facilities, manpower etc. Strategic Planning goes beyond present forecasts of much more fundamentals such as: - Are we in the right business? - What are our basic objectives? - When will our present become obsolete? - Are our markets accelerating or eroding? Gap Analysis from present to future. 3. Strategic Planning is not necessarily the preparation of massive, detailed, interrelated sets of plans. 4. Strategic Planning is not an effort to replace managerial intuition & judgment. 5. Strategic Planning is not a simple aggregation of functional plans or an extrapolation of current budgets. It is a systems approach to maneuvering an enterprise over time through the uncertain waters of its changing environment prescribed aims.
- 6. Benefits of Strategic Planning Strategic planning is an organizational management activity that is used to set priorities, focus energy and resources, strengthen operations, ensure that employees and other stakeholders are working toward common goals, establish agreement around intended outcomes/results, and assess and adjust the organization's direction in response to a changing environment. The benefits of strategic planning are below:
- 7. 1. Able to set more realistic objectives that are demanding, yet attainable. 2. A need for better information for decision-making may be recognized. 3.Growth can be accelerated and improved. 4.Poor performing areas can be identified and eliminated 5.Gain control of operational problems. 6.Develop better communications with those both inside and outside of the company. 7.Provides a road map to show where the company is going and how to get there. 8.Develops better internal coordination of activities. 9.Develops a frame of reference for budgets and short – range operating plans 10. Gives a sense of security among employees that comes from better understanding of the changing environment and the company’s ability to adapt.
- 8. FOURTEEN PROCESSES OF STRATEGIC PLANNING The strategic planning process includes establishing the sequence in which those goals should fall so that the organization is enabled to reach its stated vision.
- 9. 1. Developing A Company philosophy : Establishing the beliefs ,values, attitude and unwritten guidelines that add up to “the way we do things here” 2. Planning Strategy : Development of Concepts, ideas & plans to achieve objectives 3. Establishing Goals: Deciding achievement targets shooter in time range or narrower in scope than objective 4. Setting Objectives : An objective is typically enduring and timeless 5. Establishing Policies : Deciding on plans of action to guide the performance of all major activities in carrying out strategy in accordance with company Philosophy 6. Planning the Organization structure: The “harness” that helps people pull together in performing activities in accordance with strategy ,Philosophy & Policies. 7. Providing Personnel : Selection, Recruitment & Training
- 10. 8. Establishing Procedure : For Important & recurring activities 9. Providing Facilities : Plant Equipment & other facilities 10. Providing Capital : Making sure that business has money & credit needed to provide facilities & working Capital 11. Setting Standards : Establish measures of performance that will enable the business to achieve its long term objective 12. Establishing Management Programs & Operational Plans: There are phases of total planning process that include strategic Planning 13. To Provide Control Information : Supply of facts and figures to help people, follow strategy, policies, procedures, programs: to keep alert to forces at work inside & outside the business and to own performance against established plans & standards. 14. Activating People: Commanding and Motivating people up and down the line in accordance with Philosophy, Policies, Procedures and Standards in carrying out plans of the Company.
- 11. Why Some Firms Do No Strategic Planning Some firms do not engage in strategic planning, and some firms do strategic planning but receive no support from managers and employees. Some reasons for poor or no strategic planning are as follows:
- 12. • Lack of knowledge or experience in strategic planning— No training in strategic planning. • Poor reward structures— When an organization assumes success, it often fails to reward success. When failure occurs, then the firm may punish. • Firefighting— An organization can be so deeply embroiled in resolving crises and firefighting that it reserves no time for planning. • Waste of time— Some firms see planning as a waste of time because no marketable product is produced. Time spent on planning is an investment. • Too expensive— Some organizations see planning as too expensive in time and money. • Laziness— People may not want to put forth the effort needed to formulate a plan. • Content with success— Particularly if a firm is successful, individuals may feel there is no need to plan because things are fine as they stand. But success today does not guarantee success tomorrow. • Fear of failure— By not taking action, there is little risk of failure unless a problem is urgent and pressing. Whenever something worthwhile is attempted, there is some risk of failure. • Overconfidence— As managers a mass experience, they may rely less on formalized planning. Rarely, however, is this appropriate. Being overconfident or overestimating experience can bring demise. Forethought is rarely wasted and is often the mark of professionalism.
- 13. • Prior bad experience— People may have had a previous bad experience with planning, that is, cases in which plans have been long, cumbersome, impractical, or inflexible. Planning, like anything else, can be done badly. • Self-interest— When someone has achieved status, privilege, or self-esteem through effectively using an old system, he or she often sees a new plan as a threat. • Fear of the unknown— People may be uncertain of their abilities to learn new skills, of their aptitude with new systems, or of their ability to take on new roles. • Honest difference of opinion— People may sincerely believe the plan is wrong. They may view the situation from a different viewpoint, or they may have aspirations for themselves or the organization that are different from the plan. Different people in different jobs have different perceptions of a situation. • Suspicion— Employees may not trust management.
- 14. Seventeen Guidelines for the Strategic-Planning Process to Be Effective 1. It should be a people process more than a paper process. 2. It should be a learning process for all managers and employees. 3. It should be words supported by numbers rather than numbers supported by words. 4. It should be simple and non routine. 5. It should vary assignments, team memberships, meeting formats, and even the planning calendar. 6. It should challenge the assumptions underlying the current corporate strategy. 7. It should welcome bad news. 8. It should welcome open-mindness and a spirit of inquiry and learning. 9. It should not be a bureaucratic mechanism. 10. It should not become ritualistic, stilted, or orchestrated. 11. It should not be too formal, predictable, or rigid. 12. It should not contain jargon or arcane planning language. 13. It should not be a formal system for control. 14. It should not disregard qualitative information. 15. It should not be controlled by “technicians.” 16. Do not pursue too many strategies at once. 17. Continually strengthen the “good ethics is good business” policy.
- 15. Thank you all That’s all our presentation

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Strategic Leadership PPT Templates with Examples and Samples

Sapna Singh
Strategic leadership is envisioning, articulating, deeply holding, and relentlessly pursuing goals. Toyota Motor Corporation, a Japanese multinational automaker, is a prime example of strategic leadership. Realizing that the US auto industry was more developed and effective than the Japanese, Toyota adopted a policy of deeply researching its rivals and imitating their best practices. Toyota’s strong leadership supported this organizational strategy of identifying its flaws, emphasizing efficiency, and fostering high-caliber design and innovation. They spent years studying the production lines of American automakers before combining their processes with American ones to produce something superior.
SlideTeam’s pre-designed PPT Templates on Leadership Skills can help you unleash your leadership potential and take on the challenge of becoming the change you wish to see in the world.
In another example, the extraordinary rise in the value of Amazon shares, which rose 225% during the first half of the previous decade and eventually 650%, can be credited to the astute leadership and strategic management of Jeff Bezos, the company’s founder and CEO. The leadership of Steve Jobs, co-founder of Apple Inc., and Elon Musk, co-founder of PayPal and SpaceX, has guaranteed that their companies maintain a competitive advantage with fresh insight and outlook.
Organizations that want to accomplish their objectives and stay ahead of the competition must practice good strategic management . Use SlideTeam’s PPT Templates to ensure your presentation is consistent with your company’s unique strategy and messaging.
Strategic leadership: A fantastic edge to your organization.
Strategic leadership is essential for a company to survive tumultuous times. It facilitates simplification of the process, boosts output, encourages innovation, and cultivates a culture of initiative and creativity among employees.
This blog is a valuable tool for company executives looking to improve their management and leadership skills. Use SlideTeam’s Top 10 Strategic Leadership PPT Templates to convey your organization’s strategic vision to the staff in a way that inspires them to realize it. These templates will support you in managing employees every day to increase output and boost morale. The 100% customizable nature of the templates allows you to edit your presentations. The content-ready slides give you the much-needed structure.
Use SlideTeam’s top-notch PPT Templates to embrace a shared vision for your organization’s success.
Give your team a clear sense of purpose and encourage cooperation to achieve a common objective.
Template 1: Strategic Leadership PPT
This PPT Deck covers the fundamentals of the leadership development process, helping you lead individuals, teams, and organizations and develop tools for understanding business difficulties. Use this template to practice strategic leadership and incorporate high-level strategic plans into your organization. The complete deck covers strategic leadership and a value-based framework to build emotional intelligence. It also includes topics, such as enterprise management processes, training processes and workplace problems. Employ this presentation to give your team a sense of direction and collaboration as they work toward a common goal. Download it now!

Download this template
Template 2: Strategic Leadership Guide PPT
Strategic leadership helps companies continuously plan, observe, and assess their needs to achieve long-term objectives. Use this PowerPoint Presentation to help you with systematic business planning, strategy formulation, and implementation. It is an excellent manual to cover all aspects of strategic management. This deck includes tools, models, frameworks, and leadership styles to help you become a more effective strategic leader. It depicts the step-by-step approach to developing a successful strategic plan, along with examples of how to implement that plan to accomplish goals. This PPT is an excellent resource for gaining practical insights into strategic leadership and achieving long-term corporate objectives. Get it right away!

Template 3: Organizational Strategic Leadership Development Framework PPT
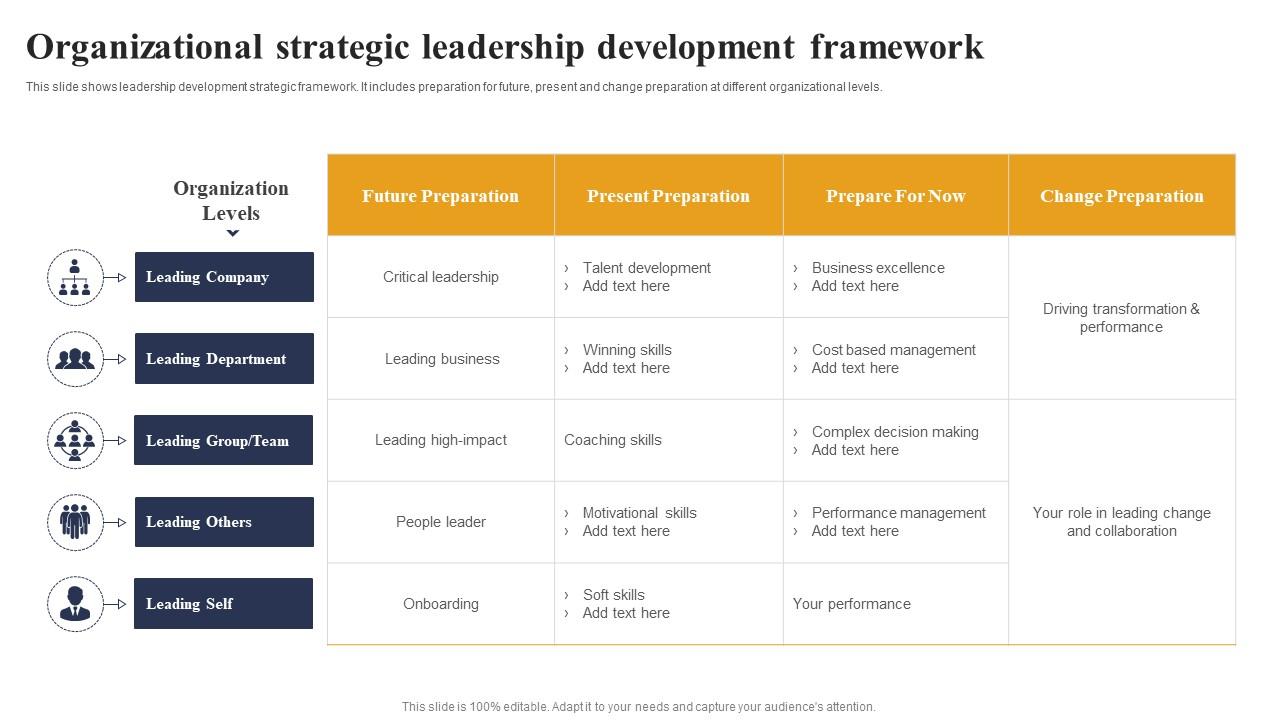
The leadership development process is critical for a company aiming to improve systemic business planning. This leadership development strategic framework slide helps create a cohesive vision of what leadership looks like in your organization. It encompasses future, present, and change preparation at organizational levels. Use this presentation to establish standards for executives, allowing them to manage day-to-day difficulties and meet organization's expectations. Save it now!
Template 4: Strategic Leader- Overview and Ways for Becoming Effective Leader PPT
Professionals in leadership roles should take the time to polish their strategic leadership abilities and change their style to meet demands of teams to improve the success rate of strategic plans. Use this PPT Template to demonstrate skills required to become a strategic leader at work. This slide discusses the characteristics of a successful strategic leader and how to become one. These also lay the groundwork for strategy creation and implementation by establishing organizational structure, allocating resources, and expressing strategic vision. Employ this download to emphasize the characteristics of great strategic leaders and provide helpful tips for building and honing these vital talents. Get it now!

Template 5: Principles to Unlock Potential Strategic Leadership in an Organization
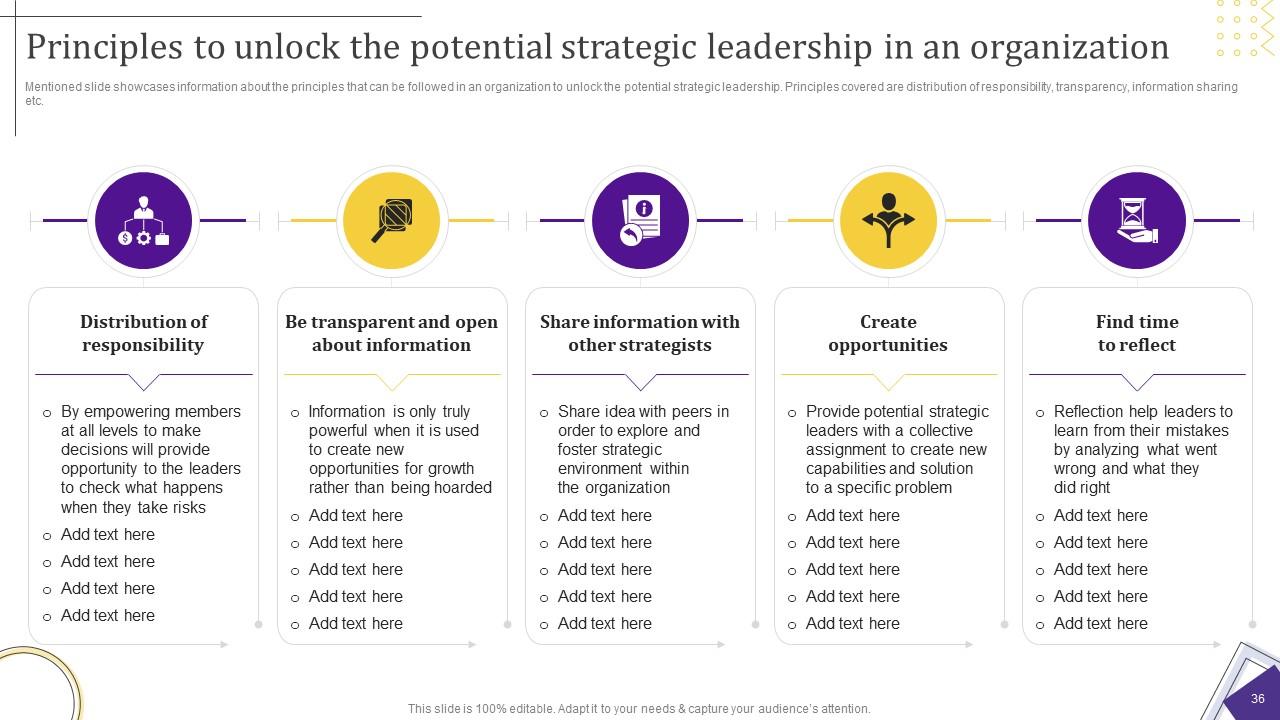
Strategic leadership is the capacity to anticipate change and create results under challenging conditions. This PPT Slide demonstrates the principles for unlocking strategic leadership potential and addressing leadership challenges inside a company. The principles mentioned include responsibility distribution, transparency, information exchange, etc. The idea is to combine organizational systems and individual characteristics to help organizations succeed. Use this resource to get insights into each of these principles and practical recommendations on how leaders can put these into practice. Get it now!
Template 6: Strategic Leadership Dashboard to Track Employee Performance
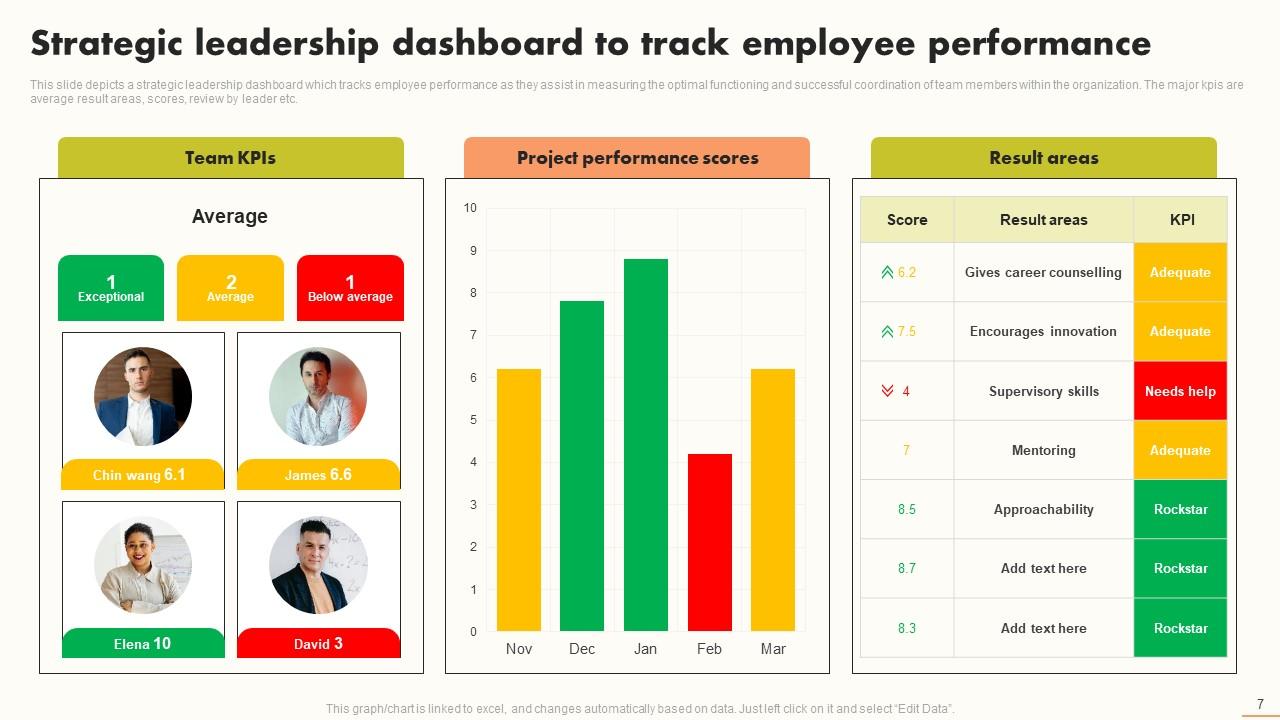
This interactive strategic dashboard is the ideal data visualization analytics tool for displaying employees’ performance on a high-level scale over a specific period. Use this PPT Layout to assess team members’ optimal functioning and successful coordination inside the organization under strategic leadership. The crucial KPIs include average result areas, scores, leader reviews, etc. This helps the team stick to the core activities or tasks to flourish. Use this resource to delve deeper into team performance across domains, and design focused plans for ongoing development. Get it today!
Template 7: Overcoming Strategic Leadership Challenges at Workplace PPT
Strategic leadership aids in developing a thorough awareness of the issues at hand. This pre-designed PPT Template depicts the leadership challenges a manager or leader experiences and overcomes to keep teams and enterprises on track. This slide contains a leadership strategy for overcoming workplace obstacles to improve procedures and foster a sense of community. It comprises team alignment, offering projects and understanding employee perspectives, to help leaders handle contradiction or uncertainty. This guide is ideal for understanding leadership challenges and methods to solve them. Grab it now!

Template 8: Developing Strong Strategic Leadership in Organization PPT
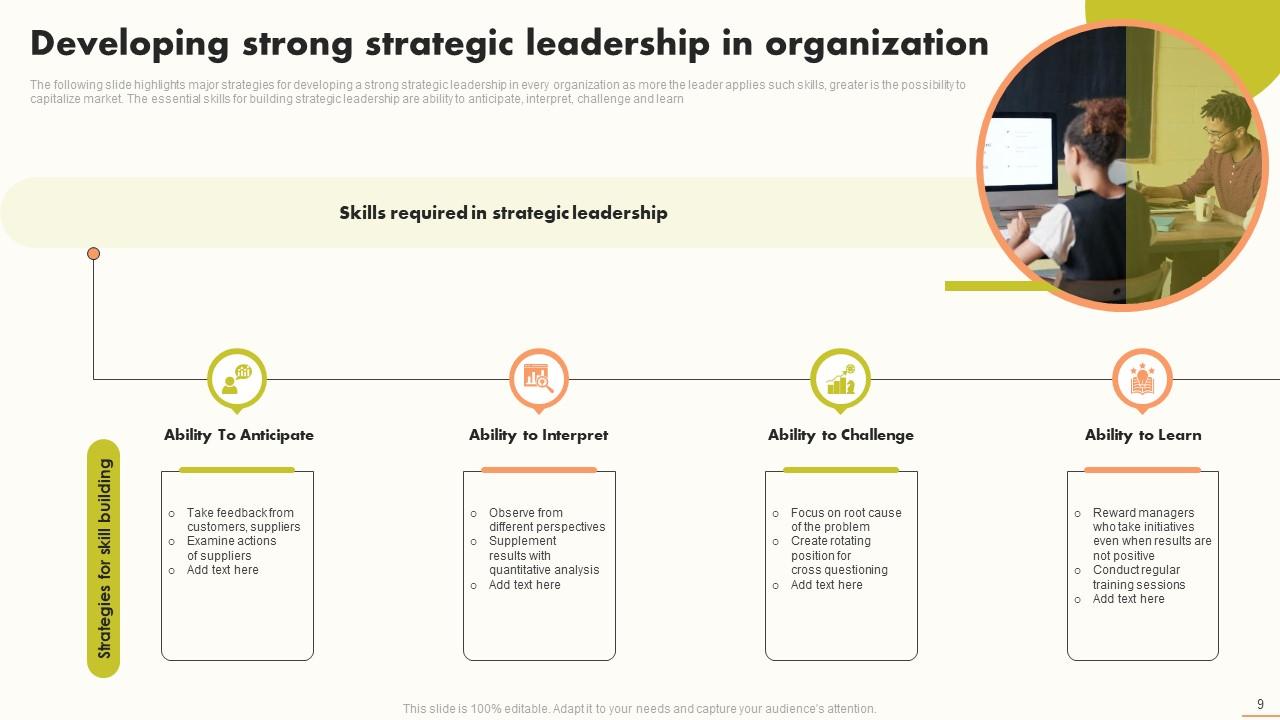
This PPT Slide covers fundamental strategies for creating good strategic leadership in an organization. This component of the leadership development process supports a leader in capitalizing on market opportunities and cultivating a high-performance culture. The ability to anticipate, understand, challenge, and learn are critical to developing strategic leadership. This will help leaders improve their emotional intelligence and make more informed and sensible judgments. Use this download to create a thorough leadership strategy for your company's success. Grab it now!
Template 9: Strategic Leadership Initiatives for High-Performing Organizations
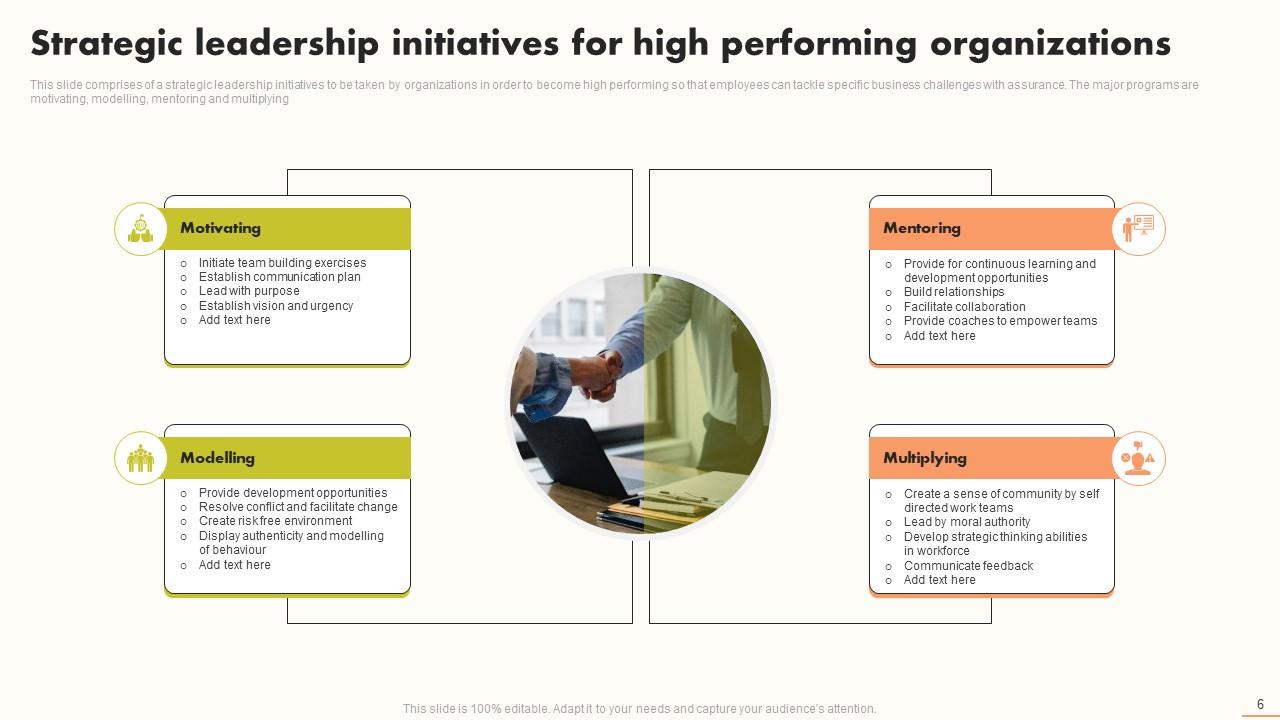
This PPT Template demonstrates strategic leadership measures that firms can implement to improve performance. This helps develop an effective team environment and inspires your staff to achieve excellence. The primary programs are motivating, modeling, mentoring, and multiplying to establish and lead a high-performance team. Use this slide to invest in staff development by training and rotating them through positions and responsibilities. Get it now!
Template 10: Example of Strategic Leadership
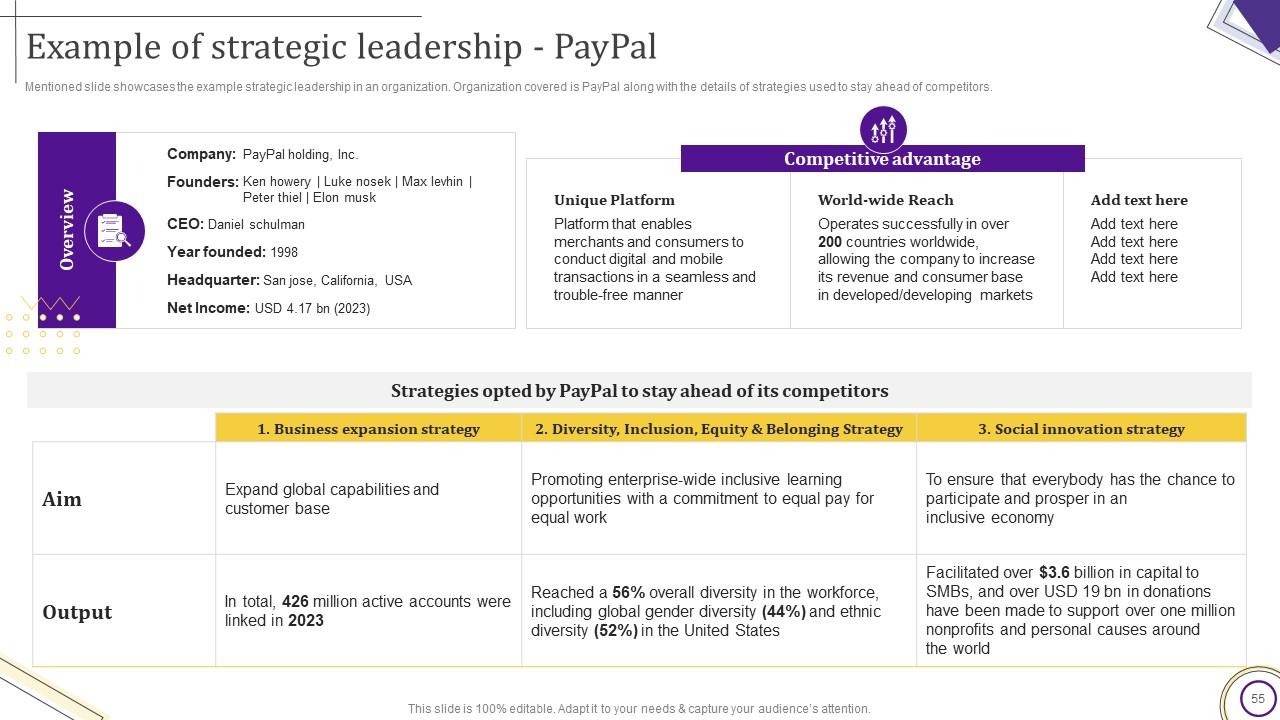
This slide exemplifies strategic leadership in an organization. It uses PayPal as an example and outlines its techniques on staying ahead of the competition. It helps dissect the systematic and strategic decisions that have driven PayPal’s extraordinary success. Use this presentation to learn how this company has established trust, provided unquestionable value, and cultivated strong relationships. Get it right away!
Anticipate, conceive, and plan.
Strategic leadership fosters an integrated view of the corporate environment, both locally and globally. Use SlideTeam’s PPT Templates to help you plan, lead, and maximize available resources as you implement initiatives.
PS Explore SlideTeam’s Leadership PPT Templates to ensure that leadership evolves as a culture. It addresses topics like inclusive leadership, strategic leadership manuals, leadership development programs, and succession planning to prepare staff members for leadership positions.
Related posts:
- One-Page Strategic Plan: Your Roadmap to Stellar Business Performance
- Top 17 Strategic Planning PowerPoint Templates For Your Business
- How to Build Brand Perception ? Samples and Examples Included
- Must-have Strategic Planning Goals and Objectives Examples Templates with Samples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Strategic Management PPT Templates with Samples and Examples

Top 10 Leadership Skills Presentation Templates with Examples and Samples

Top 10 Leadership Presentation Templates with Examples and Samples
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

11 templates

21 templates

holy spirit
35 templates

memorial day
12 templates

17 templates

art portfolio
81 templates
Action Plan for Business Strategy
It seems that you like this template, action plan for business strategy presentation, premium google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Download the Action Plan for Business Strategy presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. The world of business encompasses a lot of things! From reports to customer profiles, from brainstorming sessions to sales—there's always something to do or something to analyze. This customizable design, available for Google Slides and PowerPoint, is what you were looking for all this time. Use the slides to give your presentation a more professional approach and have everything under control.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
What are the benefits of having a Premium account?
What Premium plans do you have?
What can I do to have unlimited downloads?
Don’t want to attribute Slidesgo?
Gain access to over 24500 templates & presentations with premium from 1.67€/month.
Are you already Premium? Log in
Related posts on our blog

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Corporate and Division Strategic Planning
Feb 11, 2013
300 likes | 826 Views
Corporate and Division Strategic Planning. Figure 4-4: The Business Strategic-Planning Process. Industry scope (needs-defined) Products and applications scope (direct/indirect competition) Competence scope (technology and/or marketing competencies). Vertical scope (vertical integration)
Share Presentation
- business strategic planning
- scorecard analysis
- profitability efficiency strategic responsibility
- strategic controls
- performance analysis tools financial

Presentation Transcript
Corporate and Division Strategic Planning Figure 4-4:The Business Strategic-Planning Process To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Industry scope (needs-defined) Products and applications scope (direct/indirect competition) Competence scope (technology and/or marketing competencies) Vertical scope (vertical integration) Market-segment scope (target market) Geographical scope (#cities, #countries, large vs small cities) Corporate and Division Strategic Planning Mission statements define the company’s major competitive scopes To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
SWOT Analysis Opportunities and threats stemming from the external environment Internal strengths and weaknesses Monitor key forces for trends For each trend, conduct an MOA - Marketing Opportunity Analysis Business Strategic Planning To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
SWOT Analysis Opportunities and threats stemming from the external environment Internal strengths and weaknesses Brand awareness, image, reputation Distribution, pricing, customer loyalty, product benefits Finance, R&D, manufacturing Business Strategic Planning To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Business Strategic Planning • Overall orientation with respect to product, price, promotion, and price To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Corporate and Division Strategic Planning • Product-Market Expansion Matrix (Growth Strategies) To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Corporate and Division Strategic Planning Figure 4-2:The Boston Consulting Group’s Growth-Share Matrix To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Program Formulation and Implementation • Specific manipulations of the 4Ps. • “Tactics” To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Business Strategic Planning Effective Goals (quant and qual): Must be Realistic Must be Consistent Must be Hierarchical Must be Stated Quantitatively To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Corporate and Division Strategic Planning • Strategic business units (SBUs) share three characteristics: • Single business or collection of businesses which can be managed separately • Has own set of competitors • Has manager responsible for strategic planning and profits To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
The Marketing Process Figure 4-6:Factors Influencing Company Marketing Strategy To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Managing The Marketing Process Methods of Organizing the Marketing Department Function Global Aspects Geographic Area Products or Brands Corporate Divisions Customers or Markets To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Types of Control Annual plan Profitability Efficiency Strategic Responsibility of top and middle management Examines whether planned results are achieved Managing The Marketing Process To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
The Marketing Process Figure 4-7:Financial Model of Return on Net Worth To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
The Marketing Process Evaluating Annual Performance: Marketing expense-to-sales analysis Market share analysis Performance Analysis Tools Financial analysis Market-based scorecard analysis Sales analysis To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Types of Control Annual plan Profitability Efficiency Strategic Responsibility of marketing controller Examines where the company is making and losing money Managing The Marketing Process To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Business Strategic Planning Differentiation Porter’s GenericStrategies Focus Overall cost leadership To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Types of Control Annual plan Profitability Efficiency Strategic Responsibility of line & staff and / or marketing controller Evaluates and attempts to improve spending efficiency of marketing expenditures Managing The Marketing Process To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Types of Control Annual plan Profitability Efficiency Strategic Responsibility of top management and marketing auditor Examines whether company is pursuing its best opportunities Managing The Marketing Process To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
Managing The Marketing Process • Strategic controls should be conducted periodically via: • Marketing-effectiveness reviews • Marketing audits • Additional reviews to consider: • Marketing excellence review • Ethical and social responsibility review To accompany A Framework for Marketing Management, 2nd Edition
- More by User

Strategic Planning and Control
Strategic Planning and Control. Planning. Planning Involves: Determining an organization’s primary objectives and Developing courses of action to attain them The Planning PROCESS is:. Planning. This is because it facilitates: Plans often do and should change
1.36k views • 43 slides

Strategic Planning
Strategic Planning. Agenda. Icebreaker Welcome and Introductions Agenda Review What is Strategic Planning Types of Strategic Planning Planning to Plan Strategic Planning Process Strategic Planning Tools and Techniques Parking Lot Discussion/Evaluation. Learning Objectives.
979 views • 35 slides

STRATEGIC PLANNING
STRATEGIC PLANNING. YOUR LOGO. COMPLETED BY: [ NAME ] DATE COMPLETED: [ DATE ]. STRATEGIC PLANNING. Executive Summary Your Company Product / Service Development Marketing Plan Market Research Measurable Marketing Goals Situational Analysis (SWOT) Financial Plan
545 views • 15 slides

Corporate Strategic Planning
Corporate Strategic Planning. Asia-Pacific Marketing Federation Certified Professional Marketer Copyright Marketing Institute of Singapore. Outline. Introduction Meaning & Role of Strategic Planning Corporate Mission Strategic Business Units (SBU) Marketing Audit. Strategic Fit.
1.94k views • 24 slides

STRATEGIC PLANNING AND ASSESSMENT PLANNING
STRATEGIC PLANNING AND ASSESSMENT PLANNING. Presentation to CLAS Unit Heads Nov. 16, 2005. Maria Cimitile Julie Guevara Carol Griffin. ASSESSMENT AND STRATEGIC PLANNING. Assessment is a component of Strategic Planning Assessment Plans will follow the University Assessment Committee format
782 views • 21 slides

Strategic Planning CS Division
209 views • 13 slides

Kerri Woehler Rail Planning and Strategic Assessment Manager Rail Division
Amtrak Cascades Pacific Northwest High-Speed Rail Corridor Transportation Border Working Group. Kerri Woehler Rail Planning and Strategic Assessment Manager Rail Division. Lynn Peterson Secretary of Transportation. Ron Pate Rail Division Director. Katy Taylor Chief of Staff.
397 views • 13 slides

Corporate Strategic Planning. Presented by: Mike Monar. Strategic Planning: Course Objectives. Strategic Planning: Course Objectives. Session One . Introduction to Strategic Planning & Preparation . Session Objectives. This session will prepare you to:.
2.09k views • 179 slides

Strategic Planning and Marketing
Strategic Planning and Marketing. Introduction to Marketing. Your chief marketing officer comes to you and says: “We really should start making smartphones that use Google android or Windows software (instead of Apple). We could sell a lot more phones.” What would you say?.
267 views • 12 slides

STRATEGIC PLANNING. STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT IN HEALTH CARE 10 MARCH 2008. POLICY AND PROCEDURE. POLICY OFFICIALLY EXPRESSED GUIDELINES AND SYSTEMS GOVERNING BEHAVIOR AND/OR DECISION MAKING PROCEDURE GUIDES ACTIONS IN CARRYING OUT POLICY. GOOD POLICY. WELL THOUGHT OUT FLEXIBLE
512 views • 21 slides

Parks and Recreation Division Strategic Planning Update
Parks and Recreation Division Strategic Planning Update. Presented by: Paul N. Curtis. Timetable. Step 1 – Analysis/Assessment of the Vision 2020 Plan and the Waterways Commission Strategic Plan (2000-2005) – November, 2007
742 views • 58 slides

Strategic Planning. Strategic planning is the managerial decision process that matches the organization’s resources and capabilities to its market opportunities for long-term growth Firms may become multi-product companies with self-contained divisions Strategic Business Units (SBUs)
891 views • 13 slides

Strategic Planning. Concepts and Considerations for Criminal Justice Integrators Implementing Criminal Justice Technologies in the 21 st Century Seminar. Stratagem – a cunning method of achieving something, a piece of trickery Strategic – giving an advantage, a strategic position
508 views • 31 slides

Strategic Challenges Project and Strategic Planning
Faculty & Staff Days January 9, 2013 Jim Luke, Project Champion. Strategic Challenges Project and Strategic Planning. Card Checkup. Remember a year ago?. Two AQIP Projects. Systems Portfolio : Where We Are. Getting to A Strategy. Mission & Vision: What We Want To Be
598 views • 32 slides

STRATEGIC PLANNING AND ASSESSMENT PLANNING. Presentation to CoIS Dec. 14, 2005. Julie Guevara, Accreditation and Assessment Officer (Carol Griffin, General Education, Director; Maria Cimitile, Associate Dean, CLAS). ASSESSMENT AND STRATEGIC PLANNING.
441 views • 26 slides

Strategic Roadmaps and Planning within the Universe Division
Strategic Roadmaps and Planning within the Universe Division. Briefing to the Astronomy and Astrophysics Advisory Committee 15 February 2005 Michael Salamon Universe Division, Science Mission Directorate NASA Headquarters. Two Roadmap Processes within the Universe Division.
391 views • 24 slides

Division of Student Affairs Strategic Planning Summary
Division of Student Affairs Strategic Planning Summary. September 2007. Mission. The Division of Student Affairs provides student learning and leadership opportunities that enhance overall academic, professional and personal success. Vision.
349 views • 18 slides

Planning Division
Monthly Report December, 2012. Planning Division. Ken Hung 28 Dec. 2012. Review and Prospect of Market. Agenda. 2012 Main Project of Planning Div. Target & Strategy of 2013. Review of 2012. Performance of the Competitors. 2012 Q1~Q3 FYP. Group 1 Prudential 25% (906B)
371 views • 21 slides

Strategic planning
Strategic planning. Scouting Slovakia Kristián Šeffer International Commisioner. Strategic thinking First strategic plan od Scouting Slovakia: period 2005-2009 MESSAGE Scouting is a lifestyle; Scouting teaches life skills; Scouting makes the quality of life better
586 views • 19 slides

Strategic Planning and Strategic Management
MANAGEMENT Meeting and Exceeding Customer Expectations EIGHTH EDITION. Strategic Planning and Strategic Management. Prepared by Deborah Baker Texas Christian University. learning objectives. Describe the nature of strategic planning and strategic management
666 views • 44 slides

Strategic Planning and Execution
Strategic Planning and Execution. Present to Future… Dimple Grover [email protected]. Strategic Planning. Strategic Planning.
180 views • 13 slides
Artificial intelligence in strategy
Can machines automate strategy development? The short answer is no. However, there are numerous aspects of strategists’ work where AI and advanced analytics tools can already bring enormous value. Yuval Atsmon is a senior partner who leads the new McKinsey Center for Strategy Innovation, which studies ways new technologies can augment the timeless principles of strategy. In this episode of the Inside the Strategy Room podcast, he explains how artificial intelligence is already transforming strategy and what’s on the horizon. This is an edited transcript of the discussion. For more conversations on the strategy issues that matter, follow the series on your preferred podcast platform .
Joanna Pachner: What does artificial intelligence mean in the context of strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: When people talk about artificial intelligence, they include everything to do with analytics, automation, and data analysis. Marvin Minsky, the pioneer of artificial intelligence research in the 1960s, talked about AI as a “suitcase word”—a term into which you can stuff whatever you want—and that still seems to be the case. We are comfortable with that because we think companies should use all the capabilities of more traditional analysis while increasing automation in strategy that can free up management or analyst time and, gradually, introducing tools that can augment human thinking.
Joanna Pachner: AI has been embraced by many business functions, but strategy seems to be largely immune to its charms. Why do you think that is?
Subscribe to the Inside the Strategy Room podcast
Yuval Atsmon: You’re right about the limited adoption. Only 7 percent of respondents to our survey about the use of AI say they use it in strategy or even financial planning, whereas in areas like marketing, supply chain, and service operations, it’s 25 or 30 percent. One reason adoption is lagging is that strategy is one of the most integrative conceptual practices. When executives think about strategy automation, many are looking too far ahead—at AI capabilities that would decide, in place of the business leader, what the right strategy is. They are missing opportunities to use AI in the building blocks of strategy that could significantly improve outcomes.
I like to use the analogy to virtual assistants. Many of us use Alexa or Siri but very few people use these tools to do more than dictate a text message or shut off the lights. We don’t feel comfortable with the technology’s ability to understand the context in more sophisticated applications. AI in strategy is similar: it’s hard for AI to know everything an executive knows, but it can help executives with certain tasks.
When executives think about strategy automation, many are looking too far ahead—at AI deciding the right strategy. They are missing opportunities to use AI in the building blocks of strategy.
Joanna Pachner: What kind of tasks can AI help strategists execute today?
Yuval Atsmon: We talk about six stages of AI development. The earliest is simple analytics, which we refer to as descriptive intelligence. Companies use dashboards for competitive analysis or to study performance in different parts of the business that are automatically updated. Some have interactive capabilities for refinement and testing.
The second level is diagnostic intelligence, which is the ability to look backward at the business and understand root causes and drivers of performance. The level after that is predictive intelligence: being able to anticipate certain scenarios or options and the value of things in the future based on momentum from the past as well as signals picked in the market. Both diagnostics and prediction are areas that AI can greatly improve today. The tools can augment executives’ analysis and become areas where you develop capabilities. For example, on diagnostic intelligence, you can organize your portfolio into segments to understand granularly where performance is coming from and do it in a much more continuous way than analysts could. You can try 20 different ways in an hour versus deploying one hundred analysts to tackle the problem.
Predictive AI is both more difficult and more risky. Executives shouldn’t fully rely on predictive AI, but it provides another systematic viewpoint in the room. Because strategic decisions have significant consequences, a key consideration is to use AI transparently in the sense of understanding why it is making a certain prediction and what extrapolations it is making from which information. You can then assess if you trust the prediction or not. You can even use AI to track the evolution of the assumptions for that prediction.
Those are the levels available today. The next three levels will take time to develop. There are some early examples of AI advising actions for executives’ consideration that would be value-creating based on the analysis. From there, you go to delegating certain decision authority to AI, with constraints and supervision. Eventually, there is the point where fully autonomous AI analyzes and decides with no human interaction.
Because strategic decisions have significant consequences, you need to understand why AI is making a certain prediction and what extrapolations it’s making from which information.
Joanna Pachner: What kind of businesses or industries could gain the greatest benefits from embracing AI at its current level of sophistication?
Yuval Atsmon: Every business probably has some opportunity to use AI more than it does today. The first thing to look at is the availability of data. Do you have performance data that can be organized in a systematic way? Companies that have deep data on their portfolios down to business line, SKU, inventory, and raw ingredients have the biggest opportunities to use machines to gain granular insights that humans could not.
Companies whose strategies rely on a few big decisions with limited data would get less from AI. Likewise, those facing a lot of volatility and vulnerability to external events would benefit less than companies with controlled and systematic portfolios, although they could deploy AI to better predict those external events and identify what they can and cannot control.
Third, the velocity of decisions matters. Most companies develop strategies every three to five years, which then become annual budgets. If you think about strategy in that way, the role of AI is relatively limited other than potentially accelerating analyses that are inputs into the strategy. However, some companies regularly revisit big decisions they made based on assumptions about the world that may have since changed, affecting the projected ROI of initiatives. Such shifts would affect how you deploy talent and executive time, how you spend money and focus sales efforts, and AI can be valuable in guiding that. The value of AI is even bigger when you can make decisions close to the time of deploying resources, because AI can signal that your previous assumptions have changed from when you made your plan.
Joanna Pachner: Can you provide any examples of companies employing AI to address specific strategic challenges?
Yuval Atsmon: Some of the most innovative users of AI, not coincidentally, are AI- and digital-native companies. Some of these companies have seen massive benefits from AI and have increased its usage in other areas of the business. One mobility player adjusts its financial planning based on pricing patterns it observes in the market. Its business has relatively high flexibility to demand but less so to supply, so the company uses AI to continuously signal back when pricing dynamics are trending in a way that would affect profitability or where demand is rising. This allows the company to quickly react to create more capacity because its profitability is highly sensitive to keeping demand and supply in equilibrium.
Joanna Pachner: Given how quickly things change today, doesn’t AI seem to be more a tactical than a strategic tool, providing time-sensitive input on isolated elements of strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: It’s interesting that you make the distinction between strategic and tactical. Of course, every decision can be broken down into smaller ones, and where AI can be affordably used in strategy today is for building blocks of the strategy. It might feel tactical, but it can make a massive difference. One of the world’s leading investment firms, for example, has started to use AI to scan for certain patterns rather than scanning individual companies directly. AI looks for consumer mobile usage that suggests a company’s technology is catching on quickly, giving the firm an opportunity to invest in that company before others do. That created a significant strategic edge for them, even though the tool itself may be relatively tactical.
Joanna Pachner: McKinsey has written a lot about cognitive biases and social dynamics that can skew decision making. Can AI help with these challenges?
Yuval Atsmon: When we talk to executives about using AI in strategy development, the first reaction we get is, “Those are really big decisions; what if AI gets them wrong?” The first answer is that humans also get them wrong—a lot. [Amos] Tversky, [Daniel] Kahneman, and others have proven that some of those errors are systemic, observable, and predictable. The first thing AI can do is spot situations likely to give rise to biases. For example, imagine that AI is listening in on a strategy session where the CEO proposes something and everyone says “Aye” without debate and discussion. AI could inform the room, “We might have a sunflower bias here,” which could trigger more conversation and remind the CEO that it’s in their own interest to encourage some devil’s advocacy.
We also often see confirmation bias, where people focus their analysis on proving the wisdom of what they already want to do, as opposed to looking for a fact-based reality. Just having AI perform a default analysis that doesn’t aim to satisfy the boss is useful, and the team can then try to understand why that is different than the management hypothesis, triggering a much richer debate.
In terms of social dynamics, agency problems can create conflicts of interest. Every business unit [BU] leader thinks that their BU should get the most resources and will deliver the most value, or at least they feel they should advocate for their business. AI provides a neutral way based on systematic data to manage those debates. It’s also useful for executives with decision authority, since we all know that short-term pressures and the need to make the quarterly and annual numbers lead people to make different decisions on the 31st of December than they do on January 1st or October 1st. Like the story of Ulysses and the sirens, you can use AI to remind you that you wanted something different three months earlier. The CEO still decides; AI can just provide that extra nudge.
Joanna Pachner: It’s like you have Spock next to you, who is dispassionate and purely analytical.
Yuval Atsmon: That is not a bad analogy—for Star Trek fans anyway.
Joanna Pachner: Do you have a favorite application of AI in strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: I have worked a lot on resource allocation, and one of the challenges, which we call the hockey stick phenomenon, is that executives are always overly optimistic about what will happen. They know that resource allocation will inevitably be defined by what you believe about the future, not necessarily by past performance. AI can provide an objective prediction of performance starting from a default momentum case: based on everything that happened in the past and some indicators about the future, what is the forecast of performance if we do nothing? This is before we say, “But I will hire these people and develop this new product and improve my marketing”— things that every executive thinks will help them overdeliver relative to the past. The neutral momentum case, which AI can calculate in a cold, Spock-like manner, can change the dynamics of the resource allocation discussion. It’s a form of predictive intelligence accessible today and while it’s not meant to be definitive, it provides a basis for better decisions.
Joanna Pachner: Do you see access to technology talent as one of the obstacles to the adoption of AI in strategy, especially at large companies?
Yuval Atsmon: I would make a distinction. If you mean machine-learning and data science talent or software engineers who build the digital tools, they are definitely not easy to get. However, companies can increasingly use platforms that provide access to AI tools and require less from individual companies. Also, this domain of strategy is exciting—it’s cutting-edge, so it’s probably easier to get technology talent for that than it might be for manufacturing work.
The bigger challenge, ironically, is finding strategists or people with business expertise to contribute to the effort. You will not solve strategy problems with AI without the involvement of people who understand the customer experience and what you are trying to achieve. Those who know best, like senior executives, don’t have time to be product managers for the AI team. An even bigger constraint is that, in some cases, you are asking people to get involved in an initiative that may make their jobs less important. There could be plenty of opportunities for incorporating AI into existing jobs, but it’s something companies need to reflect on. The best approach may be to create a digital factory where a different team tests and builds AI applications, with oversight from senior stakeholders.
The big challenge is finding strategists to contribute to the AI effort. You are asking people to get involved in an initiative that may make their jobs less important.
Joanna Pachner: Do you think this worry about job security and the potential that AI will automate strategy is realistic?
Yuval Atsmon: The question of whether AI will replace human judgment and put humanity out of its job is a big one that I would leave for other experts.
The pertinent question is shorter-term automation. Because of its complexity, strategy would be one of the later domains to be affected by automation, but we are seeing it in many other domains. However, the trend for more than two hundred years has been that automation creates new jobs, although ones requiring different skills. That doesn’t take away the fear some people have of a machine exposing their mistakes or doing their job better than they do it.
Joanna Pachner: We recently published an article about strategic courage in an age of volatility that talked about three types of edge business leaders need to develop. One of them is an edge in insights. Do you think AI has a role to play in furnishing a proprietary insight edge?
Yuval Atsmon: One of the challenges most strategists face is the overwhelming complexity of the world we operate in—the number of unknowns, the information overload. At one level, it may seem that AI will provide another layer of complexity. In reality, it can be a sharp knife that cuts through some of the clutter. The question to ask is, Can AI simplify my life by giving me sharper, more timely insights more easily?
Joanna Pachner: You have been working in strategy for a long time. What sparked your interest in exploring this intersection of strategy and new technology?
Yuval Atsmon: I have always been intrigued by things at the boundaries of what seems possible. Science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke’s second law is that to discover the limits of the possible, you have to venture a little past them into the impossible, and I find that particularly alluring in this arena.
AI in strategy is in very nascent stages but could be very consequential for companies and for the profession. For a top executive, strategic decisions are the biggest way to influence the business, other than maybe building the top team, and it is amazing how little technology is leveraged in that process today. It’s conceivable that competitive advantage will increasingly rest in having executives who know how to apply AI well. In some domains, like investment, that is already happening, and the difference in returns can be staggering. I find helping companies be part of that evolution very exciting.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategic courage in an age of volatility

Bias Busters Collection
11 min read
The success of any organization relies on its ability to attract, retain and develop top talent. Talent acquisition refers to the ongoing strategy and process an organization and its HR department uses to source, attract, evaluate, hire and retain the highly qualified new employees it needs to grow.
A well-crafted talent acquisition strategy has become a critical component for organizations seeking to secure a competitive edge. Beyond simply filling open roles, a comprehensive talent acquisition strategy encompasses a holistic approach to talent management , from identifying organizational needs to nurturing relationships with potential candidates.
By recognizing the importance of a strategic and proactive talent acquisition approach, companies can position themselves as employers of choice. This approach can foster a culture that not only attracts the right candidates but also cultivates long-term success and sustainability.
A talent acquisition strategy is a comprehensive plan that an organization develops to optimize its talent acquisition—the identification, attraction and retention of the right talent. It includes a series of interconnected processes and initiatives designed to align the organization’s talent needs with its business objectives. The strategy outlines the methods and processes for sourcing, screening and selecting candidates, while also focusing on employee retention and long-term development.
Talent acquisition strategy involves the use of various recruitment methods, technologies and practices. It enables HR professionals and the organization to build a strong employer brand, create a positive candidate experience and foster an effective, diverse and inclusive workforce. An effective talent acquisition strategy continually adapts to changes in industry trends and candidate preferences. It ensures that the organization’s talent acquisition efforts remain competitive and resilient.
An effective talent acquisition strategy includes elements designed to effectively attract, asses, identify and retain the best talent for the organization’s current and future hiring needs. The creation of a successful strategy should include these steps:
A compelling employer brand can set an organization apart, making it an attractive destination for skilled professionals. Many steps can be taken to build and enhance an employer brand, including:
- Define the employer value proposition (EVP): Clearly articulate what sets the company apart as an employer—what it stands for and the kind of working environment it offers. Highlight the unique benefits, opportunities and culture.
- Create a compelling careers page: Build an organized and informative careers page on the company website. Describe the application process. Use engaging content, images and videos to showcase the work environment.
- Collect and share employee success stories: Let employees describe their experiences working at the company, including career growth, work-life balance and company culture.
- Use social media: Promote the employer brand on social media by sharing company news, employee stories and industry insights. Engage with potential candidates and encourage a sense of community.
- Offer competitive compensation and benefits: Meet or exceed industry standards for pay and benefits packages and clearly communicate these offerings to potential candidates.
- Foster employee engagement and growth: Create a supportive work environment that encourages employee engagement, professional development and career advancement.
- Initiate employee advocacy: Encourage employees to become brand advocates. Provide them with tools to share positive experiences on their personal social media accounts and professional networks.
- Promote diversity and inclusion: Widen the pool of top candidates by highlighting initiatives that demonstrate the organization’s commitment to creating a diverse and inclusive workplace.
- Provide a positive candidate experience: Streamline the recruitment process to ensure a seamless and positive experience for all candidates. Communicate with transparency.
- Highlight work-life balance: Showcase any flexible work arrangements, wellness programs or other initiatives that prioritize the health and happiness of employees.
- Attend industry events: Participate in conferences, webinars, speaking engagements, award competitions and other events to establish a presence and engage with potential candidates.
- Monitor online reviews: Respond to reviews, whether positive or negative, to demonstrate a commitment to improving and addressing concerns.
- Measure impact: Use analytics and metrics to assess the effectiveness of branding efforts. Monitor website traffic, application rates and employee referrals to gauge their success.
- Seek feedback and continuously improve: A positive candidate experience can contribute to a favorable employer brand. Gather feedback from candidates who go through the hiring process.
Conduct a thorough assessment of current and future talent that the organization requires to achieve its business objectives.
- Conduct an organizational analysis: Identify key areas where new talent is needed to support the company’s current and projected business goals and growth plans.
- Determine short- and long-term talent needs: Distinguish between immediate hiring needs and future requirements. Prioritize roles that require immediate attention.
- Develop candidate profiles: Create personas for ideal candidates and write detailed job descriptions for each role based on the skills and qualifications necessary for success.
- Evaluate internal talent: Encourage employee retention by identifying suitable internal candidates for open positions and evaluate existing employees to determine if they can be upskilled or reassigned to fulfill upcoming roles.
A diverse range of sourcing channels can effectively connect with a wider pool of potential candidates. Key sourcing channels include:
- Company website: Maintain an updated careers page on the company website that provides comprehensive information about the organization, job openings and the application process.
- Job boards: Post openings on popular job boards and career websites such as Indeed, LinkedIn, Glassdoor and Monster to reach active job seekers.
- Recruitment agencies: Collaborate with reputable recruitment agencies and staffing firms that specialize in the same industry to gain access to their talent pool and sourcing expertise.
- Social media platforms: Use LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram and TikTok to promote job openings, share company culture and engage with potential candidates.
- Employee referrals: Encourage current employees to refer potential candidates from their professional networks. Implement an employee referral program to incentivize employees to recommend qualified candidates.
- Networking events: Attend industry-specific networking events and job fairs to establish connections with potential candidates and build relationships within the industry.
- Professional associations: Engage with relevant professional associations and groups to reach candidates who are actively involved in the same field.
- Employee alumni networks: Reconnect with former employees who may be interested in returning or referring other qualified candidates.
- Online forums and communities: Participate in online communities and industry-specific groups where professionals discuss relevant topics and raise awareness about job opportunities.
- Talent marketplaces: Explore online talent marketplaces and freelance platforms to connect with freelancers and independent contractors for short-term vacancies or special project roles.
- Direct outreach: Reach out to potential candidates through emails, messages on professional networking platforms or phone calls to introduce the company and discuss relevant opportunities.
Implementing a structured and comprehensive screening process can help assess candidates’ skill sets, qualifications and cultural fit. To develop an effective screening process:
- Review resumes and cover letters: Assess their qualifications, relevant experience and alignment with the job requirements. Look for key achievements, skills and career progression that match the position.
- Conduct phone screenings: Assess candidates’ communication skills, professional demeanor and overall fit for the role.
- Administer skills assessments: Administer tests or assignments to evaluate candidates’ technical skills, problem-solving abilities and job-related competencies.
- Conduct multiple or panel interviews: Gather diverse perspectives on each candidate’s fit for the role by arranging separate or panel interviews with key stakeholders.
- Include behavioral interviews: Use behavioral interviews to understand candidates past behavior and assess how they might respond to specific situations in the workplace.
- Assess cultural fit : During the interview process, evaluate candidates’ alignment with the company’s culture and values. Ask questions that assess their work style and preferred work environment.
- Check references: Reach out to the provided references to verify the accuracy of candidates’ work history, skills and achievements.
- Conduct background checks: Include employment verification, education verification and criminal record checks. This validation of candidates’ qualifications ensures they meet the necessary requirements.
- Assess soft skills: Evaluate candidates’ soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, adaptability and leadership potential, during the interview process.
Here are some effective ways to improve the candidate experience:
- Provide clear communication: Ensure that candidates are informed about the next steps and the expected timeline throughout the hiring process.
- Streamline the application process: Minimize the number of steps required and optimize the application platform for user-friendliness.
- Create transparent job descriptions: Include the role’s responsibilities, qualifications and expectations and provide insights into the company culture and values.
- Conduct engaging and respectful interviews: Ensure that interviews are well-organized, respectful and engaging, with interviewers who are well-prepared, ask relevant questions.
- Personalize candidate engagement: Tailor candidate interactions to create a personalized and meaningful experience.
- Offer constructive feedback: Provide specific insights into their strengths and areas for development to help them understand how they can improve and grow professionally.
- Ensure consistent employer branding: Ensure that the candidate experience aligns with the employer brand. Maintain consistency in messaging, communication style and overall candidate engagement.
- Provide responsive and accessible support: Make it easy for candidates to contact the hiring team or recruitment professionals for guidance and support.
- Follow up: Express appreciation and provide closure on their application status, whether they are selected or not. Encourage them to stay connected with the company for future opportunities.
- Gather feedback: Implement satisfaction surveys to gather feedback on the overall hiring process. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement in the candidate experience.
By leveraging data-driven insights, organizations can make informed decisions, optimize the recruitment processes and improve the overall quality of hires. Here are several ways in which data and analytics can be used in a talent acquisition strategy:
- Forecast talent demand: Analyze historical data and job market trends to forecast future talent demands. This helps anticipate hiring needs and proactively source and attract the best candidates in advance.
- Sourcing channel performance analysis: Track and study the performance of different sourcing channels such as job boards, social media and recruitment agencies.
- Candidate journey assessment: Identify potential bottlenecks or areas for improvement at each stage of the recruitment process. This helps create a smoother and more efficient experience.
- Application and hiring metrics: Use metrics such as application completion rates, time-to-hire, cost-per-hire and quality of hire to measure the effectiveness of the recruitment strategy.
- Candidate assessment and selection: Implement data-driven assessment tools and techniques to objectively evaluate candidates based on skills, competencies and cultural fit.
- Employer brand perception analysis: Monitor and analyze online reviews, social media mentions and candidate feedback to gauge the perception of the employer brand.
- Diversity and inclusion: Analyze data on candidate demographics, hiring outcomes and employee retention to identify opportunities for fostering a more inclusive environment.
- Return on investment (ROI) analysis: Evaluate the ROI of different recruitment initiatives and strategies to assess their effectiveness in attracting and retaining top talent. Analyze the cost and benefits associated with each.
- Predictive analytics for talent management: Use predictive analytics to identify potential high-performing candidates, forecast employee retention rates and develop talent management strategies .
Technology can play a pivotal role in enhancing various aspects of a talent acquisition strategy. It can enable organizations to streamline recruitment processes, improve candidate experience and make data-driven hiring decisions. Here are several ways technology can be leveraged as part of a comprehensive talent acquisition strategy:
- Applicant tracking systems (ATS): Implementing an ATS can help automate and streamline the recruitment process, from job postings to managing candidate applications. ATS platforms enable recruiters to track candidate progress, schedule interviews and communicate with applicants efficiently, creating a more organized and efficient hiring process.
- AI-powered sourcing and screening: AI can help analyze resumes, assess candidate fit and even conduct initial screenings, allowing recruiters to identify top talent more effectively.
- Video interviews: Save time and resources and get a more comprehensive understanding of candidates’ communication skills and demeanor by using video interviewing platforms.
- Employee referral software: Enable employees to refer potential candidates and track the status of their referrals. This technology can streamline the employee referral process.
- Virtual events and career fairs: Host virtual career fairs and events using online platforms to connect with a broader pool of candidates and showcase the employer brand.
- Data analytics and reporting tools: Data-driven insights can help recruiters make informed decisions, identify bottlenecks in the recruitment process and optimize hiring strategies.
- Mobile recruitment applications: Develop mobile-friendly recruitment applications and platforms that allow candidates to conveniently apply for jobs, submit resumes and engage with recruiters.
- Candidate relationship management (CRM) systems: CRM systems help recruiters maintain a database of potential candidates, nurture relationships over time and provide a personalized and engaging experience for each candidate.
Incorporating diversity and inclusion initiatives into recruitment can yield numerous benefits: improved innovation, enhanced employee morale and a positive employer brand. Here are more reasons why diversity and inclusion are essential to a talent acquisition strategy:
- Enhanced innovation and creativity: A diverse workforce brings together individuals with unique perspectives, experiences and backgrounds. This diversity fosters innovation, creativity and new ideas.
- Improved employee performance: Inclusive workplaces that value diversity often experience improved employee morale, engagement and overall job satisfaction.
- Broader talent pool: A commitment to diversity and inclusion in the talent acquisition process expands the candidate pool, allowing organizations to attract and retain an array of top talent.
- Better understanding of customer needs: Employees from different backgrounds can enable organizations to develop products and services that better meet the demands of a diverse market.
- Positive employer branding: Companies that prioritize diversity and inclusion are often viewed as progressive, inclusive and socially responsible, making them more attractive to job seekers.
- Legal and ethical compliance: Emphasizing diversity and inclusion ensures that organizations comply with antidiscrimination laws and promote fairness and equity in the workplace.
- Adaptability to changing demographics: Diverse and inclusive work environments are better equipped to navigate cultural differences, adapt to changing demographics and effectively engage with a diverse customer base.
Integrating diversity and inclusion into the talent acquisition strategy requires a comprehensive approach. It involves creating inclusive job descriptions, implementing bias-free recruitment practices, providing diversity training and fostering an inclusive workplace culture. By prioritizing diversity and inclusion, organizations build a more dynamic, innovative and resilient workforce reflective of the diverse society in which they operate.
Building a talent pipeline involves proactively identifying and nurturing relationships with potential candidates even if there are no immediate job openings. Here’s why building a talent pipeline is an important part of a talent acquisition strategy:
- Proactive recruitment: By cultivating relationships with potential candidates in advance, companies can reduce the time and resources required to fill future job openings when they arise.
- Shortened time-to-hire: With a prequalified pool of candidates readily available, organizations can quickly engage and evaluate, leading to faster decision-making and onboarding processes.
- Strategic succession planning: A well-developed talent pipeline enables organizations to identify and groom internal talent for future leadership roles and key positions.
- Reduced recruitment costs: By continuously engaging with potential candidates over time, organizations can reduce their reliance on external recruiters, job boards and other sourcing channels.
- Enhanced candidate quality: Nurturing relationships with candidates over time allows organizations to gain a deeper understanding of their skills, experiences and cultural fit.
- Improved employer branding: Maintaining a talent pipeline demonstrates an organization’s commitment to talent development and recruitment, enhancing the employer brand.
- Increased agility and flexibility: Having access to a pool of qualified candidates enables organizations to adapt swiftly to emerging opportunities and challenges.
- Long-term relationship building: Regular engagement with these candidates creates a positive candidate experience, even if they are not immediately selected for a role.
Regular evaluation allows organizations to identify areas for improvement, make necessary adjustments and align the talent acquisition strategy with the changing needs of the business. Here are several ways that an organization can assess its talent acquisition strategy:
- Key performance indicators (KPIs): Establish and monitor specific KPIs related to the talent acquisition process such as time-to-fill, cost-per-hire, quality of hire and candidate satisfaction. Regularly tracking these metrics provides insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of the recruitment process and helps identify areas for improvement.
- Candidate feedback and surveys: Gather feedback from candidates who have gone through the recruitment process to understand their experience, perception of the brand and overall satisfaction, as well as to identify opportunities for enhancing the candidate experience.
- Data analysis and reporting: Assess the performance of different sourcing channels, the quality of candidates sourced and the success rates of various recruitment initiatives.
- Continuous process improvement: Solicit feedback from recruiters, hiring managers and other stakeholders involved in the talent acquisition process to identify bottlenecks, streamline workflows and implement best practices.
- Talent market analysis: Conduct regular analyses of the talent market to understand emerging skill requirements, industry trends, shifts in the labor market and adjust the talent acquisition strategy accordingly.
- Internal stakeholder engagement: Engage with internal stakeholders, including senior leadership, human resource management and hiring managers, to gather insights into the effectiveness of the talent acquisition strategy.
While attracting top talent is essential, retaining and developing existing employees is equally crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of an organization. Investing in employee development and creating growth opportunities within the organization can increase employee satisfaction and reduce turnover rates. This saves the organization time and resources associated with recruiting and training new hires.
Enhanced employee engagement, employee experience, succession planning and the cultivation of a learning culture provides several benefits, including: clear career paths for employees help avoid leadership gaps, and contribute to the organization’s overall growth and competitiveness. All of this attracts job seekers drawn to companies that prioritize employee growth, learning and career advancement.
Still, the cornerstone of organizational success remains a forward-thinking talent acquisition strategy—driving growth, fostering resilience and positioning companies for sustained excellence in the years to come.
As a leading talent acquisition and skills development consultancy, IBM Consulting® works closely with clients to tailor solutions specific to their recruiting and skilling needs. Whether you are looking to address high turnover, enhance the recruiting technology stack, improve work force productivity, address skills shortages, or create an effective learning experience for a diverse workforce, IBM can provide customized strategies and tools across consulting, technology and managed services.
Get our newsletters and topic updates that deliver the latest thought leadership and insights on emerging trends.
Watch on demand: Modernize your workforce with generative AI skills
Explore talent acquisition and skills development with IBM Consulting
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
4 Common Types of Team Conflict — and How to Resolve Them
- Randall S. Peterson,
- Priti Pradhan Shah,
- Amanda J. Ferguson,
- Stephen L. Jones

Advice backed by three decades of research into thousands of team conflicts around the world.
Managers spend 20% of their time on average managing team conflict. Over the past three decades, the authors have studied thousands of team conflicts around the world and have identified four common patterns of team conflict. The first occurs when conflict revolves around a single member of a team (20-25% of team conflicts). The second is when two members of a team disagree (the most common team conflict at 35%). The third is when two subgroups in a team are at odds (20-25%). The fourth is when all members of a team are disagreeing in a whole-team conflict (less than 15%). The authors suggest strategies to tailor a conflict resolution approach for each type, so that managers can address conflict as close to its origin as possible.
If you have ever managed a team or worked on one, you know that conflict within a team is as inevitable as it is distracting. Many managers avoid dealing with conflict in their team where possible, hoping reasonable people can work it out. Despite this, research shows that managers spend upwards of 20% of their time on average managing conflict.
- Randall S. Peterson is the academic director of the Leadership Institute and a professor of organizational behavior at London Business School. He teaches leadership on the School’s Senior Executive and Accelerated Development Program.
- PS Priti Pradhan Shah is a professor in the Department of Work and Organization at the Carlson School of Management at the University of Minnesota. She teaches negotiation in the School’s Executive Education and MBA Programs.
- AF Amanda J. Ferguson is an associate professor of Management at Northern Illinois University. She teaches Organizational Behavior and Leading Teams in the School’s MBA programs.
- SJ Stephen L. Jones is an associate professor of Management at the University of Washington Bothell. He teaches Organizational and Strategic Management at the MBA level.
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business strategic planning involves developing a set of actions to gain a competitive advantage. A business strategy should craft goals aligned with the overall strategy and cascaded throughout the company. Competitive advantage is created when a company's profitability is greater than competitors by outperforming them. A business model ...
Vision and Strategy. 5. Sun Tze on Strategy "Know your enemy, know yourself, and your victory will not be threatened. Know the terrain, know the weather, and your victory will be complete.". 6. Strategic Marketing ―Marketing Strategy is a series of integrated actions leading to a sustainable competitive advantage.".
Strategic planning powerpoint. Apr 23, 2012 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 154 likes • 237,447 views. R. robdude9626. Business Technology. 1 of 20. Download now. Strategic planning powerpoint - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
Business Strategic Planning - Download as a PDF or view online for free
A strategic plan is a document that reflects how a company plans to function and grow over a significant period of time, usually three-to-five years. It is based on a mission/vision statement, stated core values, and goals. A strategic plan also includes all the steps an organization needs to take in order to get where it needs to be.
Feb 27, 2014 •. 27 likes • 13,202 views. Dr. J. Jayapradha Varma Follow. Business. 1 of 15. Download Now. Download to read offline. Business strategic planning and corporate strategic planning - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
12. CONCLUSION ⦿ The toy company has the potential to restructure their policy and develop effective planning for successful establishment of the business. ⦿ The company is efficient to manage their performance in long run due to strong employee base, but it is necessary to develop proper strategy to handle the diverse workforce and influence them successfully for enhancing the overall ...
Business • February 2nd, 2024. A vital element in today's highly competitive business landscape is the ability to craft and deliver a business plan presentation. This applies to both entrepreneurs and corporate leaders. This guide describes essential aspects required to build a business plan presentation and deliver it to stakeholders.
Pick a color that contrasts with those used in your business branding. Then use this color to present the problem. If you're struggling to pick the right contrast, take a look at the color wheel. Find your primary brand color. Then pick a contrast in the other half of the wheel, avoiding the one directly opposite.
Slide 1: This slide introduces Strategic Planning.State Your Company Name and begin. Slide 2: This slide states Agenda of the presentation. Slide 3: This slide presents Table of Content for the presentation. Slide 4: This slide highlights title for topics that are to be covered next in the template. Slide 5: This slide showcases Company's Competitive Advantage.
At its core, strategic planning is the process through which an organization defines its objectives, evaluates its resources, and charts a course of action to achieve its long-term goals. It's like the roadmap that guides a business toward its desired future. . Strategic planning is crucial for several reasons.
Template 5: Strategic Planning Proposal Template. Elevate your proposals with our Strategic Planning Proposal template. Craft a compelling cover letter and set the proposal context in motion. Seamlessly outline your action plan, bridge gaps with insightful gap analysis, and present a clear project timeline.
This business strategy PowerPoint slideshow will help you develop plans and techniques and execute plans as well to accomplish those business goals. Follow a set of competitive moves to have your business attract customers. ... Template 7: Financial Projections for Strategic Planning. Financial projections for strategic planning comprise ...
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
Strategic Goals PPT Slide. Your strategic plan should state a clear direction for the company. Establish where your business is going and translate your vision into realistic long-term goals. Use this white-and-teal corporate slide to share up to four strategic goals and set the expected results for the next period.
Rise to the Challenge With Free Business Plan Slide Templates. Roll up your sleeves and dive into your next project with these business plan PowerPoint templates. Browse a wide range of themes, including clean minimal, elegant black, neon startup, travel agency, corporate leadership training, finance, business career advice, hotel management ...
The Eight Steps of Strategic Planning include: Step 1: Plan the Planning Process. Step 2: Define Shared Values and Mission. Step 3: Analyze the Current Organizational Profile. Step 4: Create an Inspiring Vision. Step 5: Compare Current to Envisioned Organization. Step 6: Develop Strategies, Objectives and Plans. Step 7: Execute Action Plans.
Section 1. An Overview of Strategic Planning or "VMOSA" (Vision, Mission, Objectives, Strategies, and Action Plans) Section 2. Proclaiming Your Dream: Developing Vision and Mission Statements; Section 3. Creating Objectives; Section 4. Developing Successful Strategies; Section 5. Developing an Action Plan; Section 6.
Free Strategic Planning Slide Templates for an Effective Slideshow. Take your strategic planning presentations to the next level with a powerful strategic planning PowerPoint template. Whether you're a business executive, consultant, or student, these templates will help you communicate your strategic ideas with clarity and impact.
Slide 1: This slide introduces Strategic Business Plan.State Your Company Name and begin. Slide 2: This slide presents Agenda.Add your agenda and use it. Slide 3: This slide presents Content which further showcases Executive Summary, Vision & Mission, Goals & Objectives, Operational Highlights, Milestone Achieved, Key Performance Indicator, Financial Summary, Operational Challenges, Operating ...
Chapter 6: Supporting the Business-Level Strategy: Competitive and Cooperative Moves. ... Portfolio Planning and Corporate-Level Strategy. Conclusion. Chapter 9: Executing Strategy through Organizational Design ... Appendix 1: Mastering Strategic Management Powerpoints Chapter 1 [PowerPoint] Chapter 2 [PowerPoint]
Download the Steel Mill Business Plan presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Conveying your business plan accurately and effectively is the cornerstone of any successful venture. This template allows you to pinpoint essential elements of your operation while your audience will appreciate the clear and concise presentation, eliminating ...
Business Strategic Planning - Download as a PDF or view online for free
The strategic framework template simplifies the process by allowing you to define precise objectives and track the progress of three key results associated with each objective. Using this strategic plan template, you can streamline goal management and enhance productivity. 6. General Strategic Plan Template.
Template 2: Strategic Leadership Guide PPT. Strategic leadership helps companies continuously plan, observe, and assess their needs to achieve long-term objectives. Use this PowerPoint Presentation to help you with systematic business planning, strategy formulation, and implementation.
Premium Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Download the Action Plan for Business Strategy presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. The world of business encompasses a lot of things! From reports to customer profiles, from brainstorming sessions to sales—there's always something to do or something to analyze. This customizable ...
Feb 11, 2013. 300 likes | 808 Views. Corporate and Division Strategic Planning. Figure 4-4: The Business Strategic-Planning Process. Industry scope (needs-defined) Products and applications scope (direct/indirect competition) Competence scope (technology and/or marketing competencies). Vertical scope (vertical integration) Download Presentation.
We look at how new AI tools can help executives develop a business strategy that uses data insights to avoid biases and make crucial decisions more quickly. ... Only 7 percent of respondents to our survey about the use of AI say they use it in strategy or even financial planning, whereas in areas like marketing, supply chain, and service ...
An effective talent acquisition strategy includes elements designed to effectively attract, asses, identify and retain the best talent for the organization's current and future hiring needs. The creation of a successful strategy should include these steps: Develop a strong employer brand. A compelling employer brand can set an organization ...
The first occurs when conflict revolves around a single member of a team (20-25% of team conflicts). The second is when two members of a team disagree (the most common team conflict at 35%). The ...