Essay on World Trade Organization (WTO)
Read this essay to learn about World Trade Organization (WTO). After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Introduction to World Trade Organization for International Business 2. Reasons to Join WTO for International Business 3. Functions 4. Decision Making 5. Organizational Structure 6. Principles of the Multilateral Trading System 7. The Deadlock 8. Ministerial Conferences and Other Details.
Essay on World Trade Organization Contents:
- Essay on GATT/WTO System and Developing Countries

Essay # 1. Introduction to World Trade Organization for International Business:
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the only international organization that deals with global rules of trade between nations. It provides a framework for conduct of international trade in goods and services. It lays down the rights and obligations of governments in the set of multilateral agreements.
In addition to goods and services, it also covers a wide range of issues related to international trade, such as protection of intellectual property rights and dispute settlement, and prescribes disciplines for governments in formulation of rules, procedures, and practices in these areas. Moreover, it also imposes discipline at the firm level in certain areas, such as export pricing at unusually low prices.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The basic objective of the rule-based system of international trade under the WTO is to ensure that international markets remain open and their access is not disrupted by the sudden and arbitrary imposition of import restrictions.
Under the Uruguay Round, the national governments of all the member countries have negotiated improved access to the markets of the member countries so as to enable business enterprises to convert trade concessions into new business opportunities.
The emerging legal systems not only confer benefits on manufacturing industries and business enterprises but also create rights in their favour. The WTO also covers areas of interest to international business firms, such as customs valuation, pre-shipment inspection services, and import licensing procedures, wherein the emphasis has been laid on transparency of the procedures so as to restrain their use as non-tariff barriers.
The agreements also stipulate rights of exporters and domestic procedures to initiate actions against dumping of foreign goods. An international business manager needs to develop a thorough understanding of the new opportunities and challenges of the multilateral trading system under the WTO.
The WTO came into existence on 1 January 1995 as a successor to the General Agreements on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). Its genesis goes back to the post-Second- World-War period in the late 1940s when economies of most European countries and the US were greatly disrupted following the war and the great depression of the 1930s.
Consequently a United Nations Conference on Trade and Employment was convened at Havana in November 1947.
It led to an international agreement called Havana Charter to create an International Trade Organization (ITO), a specialized agency of the United Nations to handle the trade side of international economic cooperation.
The draft ITO charter was ambitious and extended beyond world trade discipline to rules on employment, commodity agreements, restrictive business practices, international investment, and services. However, the attempt to create the ITO was aborted as the US did not ratify it and other countries found it difficult to make it operational without US support.
The combined package of trade rules and tariff concessions negotiated and agreed by 23 countries out of 50 participating countries became known as General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT): an effort to salvage from the aborted attempt to create the ITO.
India was also a founder member of GATT, a multilateral treaty aimed at trade liberalization. GATT provided a multilateral forum during 1948-94 to discuss the trade problems and reduction of trade barriers.
World Trade Organization membership increased from 23 countries in 1947 to 123 countries by 1994. GATT remained a provisional agreement and organization throughout these 47 years and facilitated considerably, tariff reduction. During its existence from 1948 to 1994, average tariffs on manufactured goods in developed countries declined from about 40 per cent to a mere 4 per cent.
It was only during the Kennedy round of negotiations in 1964-67, that an anti-dumping agreement and a section of development under the GATT were introduced. The first major attempt to tackle non-tariff barriers was made during the Tokyo round. The eighth round of negotiations known as the Uruguay Round of 1986-94 was the most comprehensive of all and led to the creation of the WTO with a new set up of agreements.
Essay # 2. Reasons to Join WTO for International Business:
Despite the disciplinary framework for conduct of international trade under the WTO, countries across the world including the developing countries were in a rush to join the pack. The WTO has nearly 153 members, accounting for over 97 per cent of world trade. Presently, 34 governments hold observer status, out of which 31 are actively seeking accession, including large trading nations, such as Russia and Taiwan.
The major reasons for a country to join the WTO are :
i. Since each country needs to export its goods and services to receive foreign exchange for essential imports, such as capital goods, technology, fuel, and sometimes even food, it requires access to foreign markets. But countries require permission for making their goods and services enter foreign countries.
Thus countries need to have bilateral agreements with each other. By joining a multilateral framework like the WTO, the need to have individual bilateral agreements is obviated as the member countries are allowed to export and import goods and services among themselves.
ii. An individual country is unlikely to get a better deal in bilateral agreements than what it gets in a multilateral framework. It has been observed that developing countries had to commit to a greater degree to developed countries in bilateral agreements than what is required under the WTO.
iii. A country can learn from the experiences of other countries, being part of the community of countries and influence the decision-making process in the WTO.
iv. The WTO provides some protection against subjective actions of other countries by way of its dispute settlement system that works as an in-built mechanism for enforcement of rights and obligations of member countries.
v. It would be odd to remain out of WTO framework for conducting international trade that has been in existence for about six decades and accounts for over 97 per cent of world trade. It may even be viewed as suspicious by others.
Essay # 3. Functions of WTO:
The major function of the WTO is to ensure the flow of international trade as smoothly, predictably, and freely as possible. This is a multilateral trade organization aimed at evolving a liberalized trade regime under a rule-based system.
The basic functions of WTO are:
i. To facilitate the implementation, administration, and operation of trade agreements.
ii. To provide a forum for further negotiations among member countries on matters covered by the agreements as well as on new issues falling within its mandate.
iii. Settlement of differences and disputes among its member countries.
iv. To carry out periodic reviews of the trade policies of its member countries.
v. To assist developing countries in trade policy issues, through technical assistance and training programmes.
vi. To cooperate with other international organizations.
Essay # 4. Decision Making of WTO :
WTO is a member-driven consensus-based organization. All major decisions in the WTO are made by its members as a whole, either by ministers who meet at least once every two years or by their ambassadors who meet regularly in Geneva.
A majority vote is also possible but it has never been used in the WTO and was extremely rare in the WTO’s predecessor, GATT. The WTO’s agreements have been ratified in all members’ parliaments. Unlike other international organizations, such as the World Bank and the IMF, in WTO, the power is not delegated to the board of directors or the organization’s head.
In view of the complexities involved in multilateral negotiations among 150 member countries with diverse resource capabilities, areas of special interest, and geo-political powers, decision-making through consensus is highly challenging.
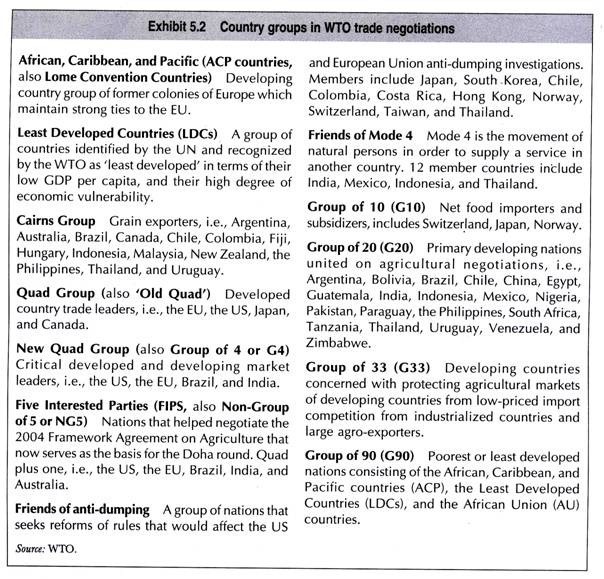
Developed countries with much greater economic and political strengths often employ pressure tactics over developing and least developed countries in building up a consensus. This has led to considerable networking among the member countries and evolving of several country groups as shown in Exhibit 5.2.

(v) Cancun Ministerial Conference :
The fifth MC was held in Cancun (Mexico) during 10-14 September 2003 under heightened strain between the major developed and developing countries. Developing countries believed that heavy subsidies on production and exports of agriculture in developed countries had been grievously harming their agriculture which is means of livelihood of their major population unlike in developed countries.
There was hardly any significant action perceived on the part of the developed countries in the areas of implementation of issues and Special and Differential Treatment. On the other hand, developed countries insisted upon starting the negotiations on the Singapore issues.
Under this atmosphere of complete apprehension, anger, and mistrust, no agreement could be reached and the MC terminated without any comprehensive declaration.
(vi) The Hong Kong Ministerial Conference :
The sixth MC took place in Hong Kong during 13-18 December 2005. It called for conclusions in 2006 of negotiations launched at Doha in 2001 and establishment of targets and time frames in specific areas.
The key outcomes of the Hong Kong Ministerial Conference included:
i. Amendment to TRIPS agreement reaffirmed to address public health concerns of developing countries.
ii. Duty free, quota free market access for all LDC products by all developed countries.
iii. Resolved complete Doha work programme and finalized negotiations in 2006.
iv. Elimination of export subsidies in cotton by developed countries in 2006; reduction of trade distorting domestic subsidies more ambitiously and over a shorter period.
v. Elimination of export subsidies in agriculture by 2013 with substantial part in the first half of the implementation period. Developing countries, such as India will continue to have right to provide marketing and transport subsidies on agricultural exports for five years after the end date for elimination of all forms of export subsidies.
vi. The agreement that the three heaviest subsidizers, i.e., the European Union, the US, and Japan, were to attract the highest cut in their trade distortion domestic support.
Developing countries like India with no Aggregate Measurement of Support (AMS) will be exempt from any cut on de minimus (entitlement to provide subsidies annually on product-specific as well as non-product specific basis each up to 10 per cent of the agricultural production value) as well as on overall levels of domestic trade distortion support (consists of the AMS, the Blue Box, and de minimus).
vii. Establishment of modalities in agriculture and Non-Agriculture Market Access (NAMA).
viii. The agreement that developing countries were to have flexibility to self-designate appropriate number of tariff lines as special products. In order to address situations of surge in imports and fall in international prices, both import quantity and price triggers have been agreed under the Special Safeguard Mechanism for developing countries.
ix. The agreement that in NAMA and Special and Differential Treatment (S&DT), elements such as flexibility and less-than-fall reciprocity in reduction commitments for developing countries reassured.
x. No sub-categorization of developing countries when addressing concerns of small, vulnerable economies.
Subsequently, at the General Council meeting held at Geneva on 31 July 2006, an agreement was reached on the framework in order to conduct the negotiations. Preliminary agreements were reached on broad approaches, especially in the areas of agriculture and industrial tariffs.
It was decided to drop the three Singapore issues on investment, competition policy, and government procurement whereas negotiations on trade facilitation were to follow.
Essay # 9. GATT/WTO System and Developing Countries:
Over the years, the divide between the developed and developing countries in the WTO has widened, leading to deadlocks in the process of multilateral negotiations. It has also triggered widespread demonstrations (Fig. 5.5) across the world due to conflicting interests of member countries.

Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
What Is the World Trade Organization (WTO)?
Created in 1995, the World Trade Organization (WTO) is an international institution that oversees the rules for global trade among nations. It superseded the 1947 General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) created in the wake of World War II.
The WTO is based on agreements signed by a majority of the world’s trading nations. The main function of the organization is to help producers of goods and services, as well as exporters and importers, protect and manage their businesses.
As of 2021, the WTO has 164 member countries, with Liberia and Afghanistan the most recent members, having joined in July 2016, and 25 “observer” countries and governments.
Key Takeaways
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) oversees global trade rules among nations and mediates disputes.
- The WTO has been a force for globalization, with both positive and negative effects.
- Big businesses tend to support the WTO for its positive impact on international economic growth.
- Skeptics see it as increasing the wealth gap and hurting local workers and communities.
Understanding the World Trade Organization (WTO)
The WTO is essentially an alternative dispute or mediation entity that upholds the international rules of trade among nations. The organization provides a platform that allows member governments to negotiate and resolve trade issues with other members. The WTO’s main focus is to provide open lines of communication concerning trade among its members.
The WTO has lowered trade barriers and increased trade among member countries. It also has also maintained trade barriers when it makes sense to do so in the global context. The WTO attempts to mediate between nations in order to benefit the global economy.
Once negotiations are complete and an agreement is in place, the WTO offers to interpret the agreement in case of a future dispute. All WTO agreements include a settlement process that allows it to conduct neutral conflict resolution.
WTO Leadership
On Feb. 15, 2021, the WTO’s General Council selected two-time Nigerian finance minister Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala as its director-general. She is the first woman and the first African to be selected for the position. She took office on March 1, 2021, for a four-year term.
No negotiation, mediation, or resolution would be possible without the foundational WTO agreements. These agreements set the legal ground-rules for international commerce that the WTO oversees. They bind a country’s government to a set of constraints that must be observed when setting future trade policies.
The agreements protect producers, importers, and exporters while encouraging world governments to meet specific social and environmental standards.
In recent years, the U.S. relationship with the WTO has been cool. The feeling is that the WTO is not doing enough to counteract China's unfair trade practices.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the WTO
The history of international trade has been a battle between protectionism and free trade, and the WTO has fueled globalization, with both positive and adverse effects. The organization’s efforts have increased global trade expansion. There are side effects to globalization, including a negative impact on local communities and human rights.
Proponents of the WTO, particularly multinational corporations, believe that the organization is beneficial to business, seeing the stimulation of free trade and a decline in trade disputes as beneficial to the global economy.
Skeptics believe that the WTO undermines the principles of organic democracy and widens the international wealth gap. They point to the decline in domestic industries and increasing foreign influence as negative impacts on the world economy.
As part of his broader attempts to renegotiate U.S. international trade deals, when he was in office, then-President Donald Trump threatened to withdraw from the WTO, calling it a “disaster.” A U.S. withdrawal from the WTO could have disrupted trillions of dollars in global trade. However, he didn’t withdraw the U.S. from the WTO during his time in office.
Why Is the World Trade Organization Important?
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the body that keeps global trade running smoothly. It oversees the rules and mediates disputes among its member nations. It now has 164 member nations and 25 observer nations (out of a total 195 nations in the world).
What Are the Main Functions of the World Trade Organization?
The World Trade Organization (WTO) administers the trade agreements made among its member nations. It also mediates any trade disputes that arise.
Is the U.S. a Member of the World Trade Organization (WTO)
The U.S. has been a member of the WTO since 1995 and signed its General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in 1948.
In 1999, then-President Bill Clinton facilitated the acceptance of China into the WTO. The impact on China and on the world continues to be debated to this day.
World Trade Organization. “ Who We Are .”
World Trade Organization. " WTO In Brief ."
KRQE. “ New WTO chief pushes for vaccine access, fisheries deal .”
NPR. “ Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala Makes History As WTO’s First African And Female Leader .”
Politico. "'All talk and no walk': America ain't back at the WTO."
National Geographic. " Effects of Economic Globalization ."
Foreign Policy. “ U.S. Effort to Depart WTO Gathers Momentum .”
Canadian Politics and Public Policy. " The Tragic Legacy of Bill Clinton's China Doctrine ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wto.asp-final-ce09db65daba4777826ee2c1f032996d.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
81 World Trade Organization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best wto topic ideas & essay examples, 📌 simple & easy world trade organization essay titles, 👍 good essay topics on world trade organization.
- The Importance of WTO The opportunity the developing countries enjoy in the world trade with the developed countries also gives them the opportunity to see how the developed countries carry out their trade.
- China’s Accession to the World Trade Organization Compared to the decade before the accession to the WTO, the share of labor-intensive agricultural products in China’s total agricultural exports in the period of 2002 to 2005 increased by 4.
- WTO Impacts on the Economy of Saudi Arabia The World Trade Organisation is the platform established by the victorious nations of the World War II as a long bargained outcome of GATT to ensure the open opportunity of free market entry for the […]
- The Problem of Developing Countries Access to the WTO Dispute Settlement In his article, Najah Hassan Salamah has reviewed the state of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in the WTO and whether the decision to join the organization was right for the economy of the state.
- Origin, Purpose and Important Aspects of the WTO It ensures that trade between countries is governed by a number of agreements that helps the WTO in its advocacy for fairness of the terms of international trade.
- Should World Trade Organization Be Reformed? But as Oxfam noted, “…despite its youth, the WTO is dangerously insensitive to the needs of the global trading system in the early twenty-first century”.
- WTO’s Role of Ensuring Smooth, Predictable and Free Flow of Trade Trade barriers refer to the different actions undertaken by the government in its effort to limit free flow of goods into and out of a respective country.
- Problem With the Imposed Plan of WTO All the members of the WTO are agreed on the point that they would reduce the tariffs but the rates under and after the negotiation were the bound tariff rates of the country rather than […]
- Suggestions on How the World Trade Organization Could Rule in the Issue of Geographical Indications These nations feel that rich, developed nations like the United States and the members of the European Union are the only ones that have advantage from the organization.
- Banana Dispute: World Trade Organization vs. European Union One of the main factors that led to emergence of the dispute between EU and Latin American countries is the tariffs that were imposed on banana imports by EU.
- WTO Membership for China: Opportunities and Challenges One of the major opportunities that WTO membership provides for China is the possibility of transformation of the heavily regulated economy to the rules-based one adapted to market requirements.
- Nexavar Compulsory License and WTO Agreement According to the legal provisions on Patents Act in section 84 of the Indian laws, the price of the drug was too high and beyond the reach of most Indians.
- Russia as a World Trade Organization Member The biggest reason why the West has been trying to incorporate Russia into the W.T.O.has been to ensure that they control the country’s trade as stipulated in the organization’s articles of association.
- WTO and Its Success in Jordan Despite the success and opportunities that entering the WTO is bound to bring to Jordan entrepreneurs, the state is obviously going to suffer a crisis caused by the necessity to comply with the standards of […]
- The World Trade Organization (WTO) Despite being required to represent the rich and the poor equally, the rules of WTO have been written by and for corporations with vested interests.
- World Trade Organization: Achieving Objectives in Jordan The organization also ensures that the countries involved in world trade adhere or follow the rules of trade treaties that the members of the World Trade Organization sign.
- Identifying and Assessing the Economic Costs and Benefits of WTO Negotiations Failure It is important to note that, the major cause for the collapse was the United States and the European Union, who completely declined the request to lower down tariffs and subsidies just to pave way […]
- World Trade Organization vs. USA on the Byrd Amendment The implication of this Act is that the non-US companies that sell their products below the cost price in the United States are subjected to fines, and the funds given to the United States firms […]
- Russia Joins the World Trade Organization In the 2000s, some of the political figures that were in charge of the process either left the team or had too many responsibilities to handle.
- WTO: Serving the Wealthy, Not the Poor Bello argues that the WTO is only serving the interests of the wealthy countries and not the poor. The article demonstrates the nature of exploitation the wealthy nations exert on the poor nations by adopting […]
- The World Trade Organization Role in the World of Trade Regional trade agreements are a segment of the international trade and a key feature of multilateral trading systems that presents the members of the world trade organization with opportunities and challenges.
- Russia’s Entry into the World Trade Organization It is the aim of this paper to critically discuss the opportunities and obstacles resulting from Russia’s entry into the WTO, not only for the country but also for the rest of the world.
- Theoretical Analysis – The World Trade Organization Additionally, the operation of the WTO is also hindered by the fact the process of making international trading rules and regulation is influenced by the developed countries.
- World Trade Organization: Regulations and Contracts between Countries The General Agreement for Trade in Services as a binding contract is used to enhance and support business of services which are never well developed in developing countries.
- World Trade Organization Trade Agreements The reason for this is apparent – the manner, in which the WTO settles trade-disputes between country-members and provides the sets of recommendations, with respect to what should be the essence of economic reforms in […]
- World Trade Organization: Tariffs and Trade Effect of a tariff on import market Where: SSm = domestic supply of solar panels DDm = Domestic demand for solar panels Pw=c= is the world price It is clear that any tariff will cause […]
- World Trade Organization and Globalization The key purpose of the WTO is the creation of codes of conduct for member governments, from the exchange of trade policy commitments during the negotiations; whereby it acts as a forum for international cooperation […]
- Why Do Critics Argue That the WTO Is Suffering From a Crisis of Legitimacy? Another accusation of the World Trade Organization in regard to its legitimacy position is that it has been involved in the widening of the gap that prevails between the poor and the rich.
- Relationship Between WTO and the Regional Trade Organizations They are also affecting the decisions of the elected leaders in the many economies and make them subject to the interest of the people.
- CME on WTO Negotiation Issues When the Canadian market is opened to foreign competition, this shall help to boost the living standards and productivity of the Canadians in a number of ways.
- World Trade Organization Regulations Unless it is accepted, the poor nationals will continue to suffer at the expense of the rich nations which have developed economies and comparative advantage in terms of trade.
- The Achievements of World Trade Organization The defending country is not able to influence the formation of the panel or prolong the duration of the case, because WTO has a time frame within which to determine any dispute.
- Understanding of the World Trade Organization The world body mandated with the duty of overseeing peaceful operations of international businesses in the world is the World Trade Organization.
- The World Trade Organization Global Rules and Function All member countries must inform the WTO of new laws and trade policies in use so that the WTO can scrutinize and ensure their implementation. This has led the WTO to focus on trade opportunities […]
- The Role of Charismatic World Trade Organization and the Expansion of Free International Trade
- Should the U.S. Participate in the International Criminal Court and the World Trade Organization
- Free Trade, Sovereignty, Democracy: The Future of the World Trade Organization
- What the Public Should Know about Globalization and the World Trade Organization
- Global Administrative Law and the World Trade Organization’s Legitimacy Crisis
- US Commerce Secretary Stresses Urgency of Winning Support for China in World Trade Organization
- World Trade Organization and Regional Trade Agreements
- Russian Federation and Its Entry in the World Trade Organization
- World Trade Organization’s Function and Structure
- The Economic Impact of World Trade Organization (WTO) Membership on China
- Russian Agriculture: the First Year within the World Trade Organization
- The World Trade Organization Deals with Trade Between Nations
- The Admission of China into the World Trade Organization
- Plurilateral Agreements: A Viable Alternative to the World Trade Organization
- What Might a Trump Withdrawal from the World Trade Organization Mean for US Tariffs
- Role of World Trade Organization in Facilitating International Trade
- The Anti-World Trade Organization Protest in Seattle
- The Founding of and Debate Over the World Trade Organization
- Electronic Trade in the World Trade Organization – Difficulties in Negotiating an Agreement
- Antidumping and the World Trade Organization in the Nineties
- Market Structure and the Environmental Implications of Trade Liberalization: Russia’s Accession to the World Trade Organization
- General Equilibrium Analysis of Croatia’s Accession to the World Trade Organization
- The World Trade Organization and The Theory of Absolute
- Trade, Intellectual Property Rights, and the World Trade Organization
- Financial Services Liberalization in the World Trade Organization
- Beliefs About the World Trade Organization
- Trade Wars and the World Trade Organization: Causes, Consequences, and Change
- The Constitutionalization of the World Trade Organization: Legitimacy, Democracy, and Community in the International Trading System
- Role of the World Trade Organization in Multilateral International Trade
- The Economic Structure of Renegotiation and Dispute Resolution in the World Trade Organization
- The Benefits of the Free Trade and Fair Trade Policies of North America and the World Trade Organization
- World Trade Organization and General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade Origins and Objectives
- Tracking Distortions in Agriculture: China and Its Accession to the World Trade Organization
- The World Trade Organization and Environmental Protection
- International Trade and the Impact of China’s World Trade Organization Membership
- What Do Trade Negotiators Negotiate About? Empirical Evidence from the World Trade Organization
- The Effect of China Joining the World Trade Organization on Its Economy
- Merits and Demerits of World Trade Organization for Russia
- World Trade Organization Conference in Seattle and Its Failure Implications
- The Role of World Trade Organization and Its Impact on Globalization
- World Trade Organization and Its Role in Promoting Trade
- The Dispute Settlement Crisis in the World Trade Organization: Causes and Cures
- The World Trade Organization Exigences Concerning the International Trade Liberalization
- Intellectual Property Rights And Dispute Settlement In The World Trade Organization
- The Effects of the Decision of China to Join the World Trade Organization on the Country’s Economy
- The European Unions Effect On World Trade Organization
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, January 24). 81 World Trade Organization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/world-trade-organization-essay-topics/
"81 World Trade Organization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 24 Jan. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/world-trade-organization-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '81 World Trade Organization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 24 January.
IvyPanda . 2023. "81 World Trade Organization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." January 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/world-trade-organization-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "81 World Trade Organization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." January 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/world-trade-organization-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "81 World Trade Organization Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." January 24, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/world-trade-organization-essay-topics/.
- Economic Topics
- Walmart Topics
- Manufacturing Essay Topics
- Globalization Essay Topics
- Antitrust Law Research Topics
- Consumer Protection Questions
- Intercultural Communication Questions
- Government Regulation Titles
WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION
Home | About WTO | News & events | Trade topics | WTO membership | Documents & resources | External relations
Contact us | Site map | A-Z | Search
español français
Ambassador Alparslan Acarsoy of Türkiye, the Chair of the WTO agriculture negotiations, facilitated the discussion on the trade aspects of cotton, while Deputy Director-General Jean-Marie Paugam, acting on behalf of Director-General Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala, chaired the meeting on the development dimension of cotton.
Chair: “Solid basis” for cotton negotiations to build upon
WTO members regret the absence of a negotiating outcome at MC13 on agriculture, including cotton, Ambassador Acarsoy said, especially as the text on cotton was considered largely stabilized.
He noted that Brazil has introduced a draft decision on agriculture which will be discussed at the next meeting of the General Council on 21-22 May.
The Chair also said he believed that members have a solid basis on which to restart the negotiations on cotton. “Our goal should be to engage as soon as possible in results-oriented, intensive discussions based on the work done thus far, with a view to achieving a substantive outcome at MC14, taking into account the singularity of cotton,” he told the meeting.
Some members exchanged views on how to resume the negotiations on agriculture and cotton. Many said that existing texts could form a basis for the continuation of discussions, including proposals made before MC13 and the text that was under negotiation at the ministerial conference, as well as the recent Brazilian proposal. Some WTO members also underscored the importance of reducing trade-distorting domestic support and enhancing market access for cotton.
The C-4+ recalled the mandate of the Hong Kong Ministerial Declaration , and urged members to address cotton “ambitiously, expeditiously, and specifically” within the agriculture negotiations. They said they were encouraged to see the evolution of WTO members' positions, and expressed optimism about making progress on agricultural issues, especially cotton, by the next Ministerial Conference (MC14), which is due to be held in Cameroon.
Market trends and transparency
The International Cotton Advisory Committee (ICAC) highlighted that global cotton production increased slightly, by 1%, while cotton prices dropped by 7% in the 2023/24 season. ICAC noted that the downward trend in commodity prices, including for cotton, makes it challenging for farmers to decide which crops to plant, impacting future global agricultural production and market dynamics. ICAC also presented details of ongoing projects in Africa that aim to help farmers respond better to market challenges.
The International Trade Centre (ITC) introduced the updated Cotton Portal , in partnership with the WTO, highlighting new features and enhanced functions for market research and learning.
The WTO Secretariat introduced its updated “background paper” ( TN/AG/GEN/34/Rev.20 and two addenda) compiling the latest information on cotton policies in domestic support, market access and export competition.
“Partenariat pour le Coton”, World Cotton Day 2024
Summarizing the results of the WTO-FIFA high-level event in Abu Dhabi , DDG Paugam stated that the “ Partenariat pour le Coton ” marks a new stage of WTO-FIFA cooperation and gives a clear visual identity to future activities and products that will emerge from this platform.
The FIFA representative briefed participants on the extensive media coverage of the Abu Dhabi event and reiterated the organization's commitment to delivering concrete action with partners for the C-4 and African countries at large.
Reviewing advances linked to the WTO-FIFA cotton project, DDG Paugam said: “Following the launch of the “Partenariat pour le Coton” brand, five studies are being prepared on investment conditions in cotton-to-textile manufacturing in the C-4+ countries (C-4 and Côte d’Ivoire), focusing on products such as t-shirts and hoodies. The results will be released in June at the Global Review of Aid for Trade.”
Regarding the next steps of the project, the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) and ITC — two partners of the “Partenariat pour le Coton” — presented the preliminary results of the five baseline analyses on the current situation of the entire cotton-to-textile/apparel value chain in C-4+ countries mentioned by DDG Paugam. These analyses highlight challenges and opportunities for these countries to move up the value chain.
The C-4+ countries welcomed the solid progress made on the WTO-FIFA initiative and stressed the importance of enhancing investment in infrastructure in the long run. Some participants suggested the need to build synergies among different projects.
Benin announced that it will host the 2024 World Cotton Day event on 7 October in collaboration with ICAC, marking the first celebration of this day on African soil. Several organizations expressed their full support for Benin and emphasized the importance of bringing to the centre of the stage African plans to develop the cotton sector. DDG Paugam confirmed that Director-General Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala will participate in the event in person.
Other ongoing projects on cotton development
The WTO Secretariat presented the latest edition of the “Evolving Table on Cotton Development Assistance” ( WT/CFMC/6/Rev.36 ), which provides updates on the implementation and disbursement of development assistance for cotton.
The table shows an increase in the number of active projects in cotton-specific development assistance, totalling 42 projects amounting to USD 362 million in commitments. The table also indicates a constant decline in agriculture and infrastructure-related development assistance over the last five reviews.
The C-4 again expressed their concerns about the decreasing level of support for agriculture and infrastructure-related projects. They reiterated the importance of funding the regional cotton projects outlined in their “Route du Coton” documents ( WT/CFMC/W/72 and WT/CFMC/W/73 ). They thanked African Export-Import Bank (Afreximbank) for its contribution and said that a total of USD 25 million is needed to invest in these projects so that C-4+ countries can improve the entire cotton value chain.
Participants also welcomed the other concrete technical work conducted by the WTO Secretariat, including the 26 March webinar on the severe impact of the cotton leafhopper pest in Western and Central Africa ( WT/CFMC/W/98 ), organized in partnership with the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The webinar explored innovative ways to combat pests without depleting soils and examined how to improve cotton production and quality.
Climate change, COVID-19
Higher temperatures will lower cotton yields and quality, ICAC warned, in a presentation highlighting the challenges that the sector faces due to climate change. ICAC also noted that the African cotton sector could positively contribute to storing carbon in the soil – potentially surpassing “net zero” targets for greenhouse gas emissions.
Participants commended ICAC for taking the initiative on this important topic, while some also shared details of ongoing national programmes aimed at helping the agriculture sector adapt to the changing climate.
Following a proposal put forward by the C-4+ , WTO members agreed to change the agenda item on “COVID and Cotton” to “Crises Affecting the Cotton Industry”, so as to include all events that affect the sector, including geopolitical tensions, price volatility and climate change.
Side events
Two side events took place on the margins of the Cotton Day event. First, on 6 May, ICAC and the Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States (OACPS) organized a seminar focused on empowering sustainable cotton development across ACP countries.
Secondly, on 8 May, the WTO Secretariat, ITC and ICAC organized a seminar to promote the updated WTO Cotton Portal — a platform which provides producers and traders with comprehensive market information related to cotton.

Problems viewing this page? If so, please contact [email protected] giving details of the operating system and web browser you are using.

COMMENTS
Essay # 3. Functions of WTO: ADVERTISEMENTS: The major function of the WTO is to ensure the flow of international trade as smoothly, predictably, and freely as possible. This is a multilateral trade organization aimed at evolving a liberalized trade regime under a rule-based system. The basic functions of WTO are: i.
Introduction. The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an international organization whose main responsibility is to facilitate smooth trade between. The organization was established in 1995 and has greatly evolved over the years to replace the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
In brief, the World Trade Organization (WTO) is the only international organization dealing with the global rules of trade. Its main function is to ensure that trade flows as smoothly, predictably and freely as possible. "The past 75 years have seen an exceptional growth in world trade. Merchandise exports have grown on average by 6% annually.
World Trade Organization (WTO), international organization established to supervise and liberalize world trade. The WTO is the successor to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which was created in 1947 in the expectation that it would soon be replaced by a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) to be called the International Trade Organization (ITO).
The WTO has issued a call for young economists to submit papers for the 2024 WTO Essay Award. The aim of the award is to promote high-quality research on trade policy and international trade cooperation and to reinforce the relationship between the WTO and the academic community. Essays must be submitted by 3 June 2024.
The WTO has issued a call for young economists to submit papers for the 2023 WTO Essay Award. The aim of the award is to promote high-quality research on trade policy and international trade cooperation and to reinforce the relationship between the WTO and the academic community. Essays must be submitted by 2 June 2023. Last year's winner ...
ments, viewed from the vantage point of history, look more inevitable than. they seemed when they began.1 This brief essay examines the formation of the World Trade Organization (WTO) twenty years after its creation, explores the contributions it has made in its first two decades, and assesses how well it has.
Chad P. Bown (PIIE) Working Papers 23-15. December 2023. Photo Credit: REUTERS/Denis Balibouse. This paper surveys the economics of industrial policy as it relates to the World Trade Organization (WTO). Motivated by concern that the modern use of industrial policy is emerging in ways that threaten cooperation in the international trading system ...
Introduction. The WTO (World Trade Organization) is the only organization in the world dealing with trade agreements between countries and it is characterized by a number of trading rules. The chief goal of the WTO is to oversee the production, exportation and importation of goods and services. It ensures that trade between countries is ...
The Importance of WTO Essay. Exclusively available on IvyPanda. According to Schorkopf and Stoll (200), WTO is an abbreviation for the international body, World Trade Organization. This body is responsible for being the facilitator of trade around the globe, and entails creating multilateral forums in which agreements are made and disputes ...
The WTO has issued a call for young economists to submit papers for the 2024 WTO Essay Award. The aim of the award is to promote high-quality research on trade policy and international trade cooperation and to reinforce the relationship between the WTO and the academic community. Essays must be submitted by 3 June 2024.
When China joined the World Trade Organization in 2001, the event was hailed as a pivotal development for the global economic system and a bold marker of the country's commitment to reform. It took 15 long years of negotiation to reach the deal, a reflection of the challenge of reconciling China's communist command economy with global ...
World Trade Organization - WTO: The World Trade Organization (WTO) is the only international organization that deals with the global rules of trade between nations. The WTO is built on WTO ...
The WTO has issued a call for young economists to submit papers for the 2023 Essay Award for Young Economists. The aim of the award is to promote high-quality research on trade policy and ...
Despite the huge contribution the GATT has made to the world economy since 1948, substantial scope remains for further contributions from and adaptations by its successor since 1995, the World Trade Organization. After first reviewing why the world needs the WTO, this paper examines the main challenges confronting the organization as we approach the new millennium, and assesses the WTO's ...
The World Trade Organization is an international trade organization that was established in 1995 to administer trade agreements, as agreed upon by member countries. The WTO was formed after countries realized that the initial agreements of trade had loopholes, and a standardized forum was essential for fair trade among different countries.
The WTO is primarily a negotiating forum and treaty law whereby member governments take part to solve trade issues and give consent to be bound by procedural rules. Established on 1st January 1995 and based in Geneva, the WTO is the only international organisation dealing with legal rules for international trade and trade policy.
Hence, in this respect, the second section of this essay will evaluate whether the WTO meets the goals that it was created for, which is to increase trade liberalisation and enhance global economic welfare. Further, in international organisations such as the WTO where power considerations are important, political effectiveness is crucial. ...
Started in 1995 as the successor to the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, the now‐ 164‐ member World Trade Organization (WTO) consists of a baseline set of trade rules (agreements), a ...
The WTO has issued a call for young economists to submit papers for the 2022 WTO Essay Award. The aim of the award is to promote high-quality research on trade policy and international trade cooperation and to reinforce the relationship between the WTO and the academic community. Essays must be submitted by 6 June 2022. Last year's winners ...
The WTO has issued a call for young economists to submit papers for the 2021 WTO Essay Award. The award aims to promote high-quality research on trade policy and international trade co-operation and to reinforce the relationship between the WTO and the academic community. Essays must be submitted by 7 June 2021. The essay award, now in its 13th ...
The WTO established the annual WTO Essay Award for Young Economists in 2009. The award, which carries a prize of CHF 5,000, aims to promote high-quality economic research on the WTO and WTO-related issues and to reinforce the relationship between the WTO and the academic community.
Intellectual Property Rights And Dispute Settlement In The World Trade Organization. The Effects of the Decision of China to Join the World Trade Organization on the Country's Economy. The European Unions Effect On World Trade Organization. 69 World Bank Essay Topic Ideas & Examples 102 Yoga Topics to Write about.
Abstract. Anti-dumping (AD) and countervailing duties (CVD) are discriminatory forms of trade protection, (sometimes) allowable by the WTO. The typical rationale behind such discretionary duties is unfair foreign pricing and government subsidies on exports, Material injury to domestic businesses etc.
WTO working papers. The papers listed below are working papers, and hence they usually represent research in progress. Such research may be conducted in the preparation of Secretariat reports, studies or informational material for WTO members. These papers are circulated for discussion and comment because critical review of professional ...
At the WTO's Cotton Day on 7 May, the Cotton-4+ countries (Benin, Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali and Côte d'Ivoire), and other cotton-producing developing economies reviewed the progress made in implementing the WTO-FIFA Memorandum of Understanding on Cotton, notably the launch of the "Partenariat pour le Coton" in the margins of the 13th Ministerial Conference (MC13) in February. Participants ...