What Is Market Share & How Do You Calculate It?
Published: December 07, 2022
In the marketing industry, you've likely heard the term "market share" from time to time, but what does it mean? Why is it necessary, and how is it calculated?

As marketers, it's important to understand market share so you know how your company ranks against competitors and can develop new marketing strategies to reach more potential customers. In this post, we’ll outline what market share is, how to calculate it, give real-life examples, and explain how you can increase yours.

What is market share?
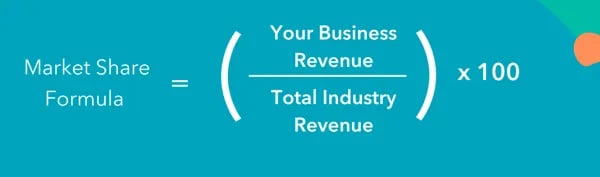
Market share formula.
Relative Market Share
Relative Market Share Formula
Market share examples.
How to Expand Your Market Share
Understand Your Market Share to Increase Business Success
![market share business model → Download Now: Market Research Templates [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/6ba52ce7-bb69-4b63-965b-4ea21ba905da.png)
Market share is the percentage of an industry's sales that a particular company owns. Essentially, it is the share of your business's total industry revenue from selling your products and services. Businesses with larger market shares are industry leaders and competition for smaller companies.
Suppose consumers buy 100 T-shirts, and 70 are from Company A, 25 from Company B, and 5 from Company C. In that case, Company A owns a market share of 70% and is the leading industry competitor .
Market share is typically calculated for a specific period, like yearly or quarterly sales, and is sometimes separated by region.
How to Calculate Market Share
Find your business’s total sales revenue for your preferred period and divide that number by your industry’s total revenue during the same period. Once you have this result, multiply the number by 100 to generate your market share percentage.
Calculating your market share will give you an overall understanding of your position in the industry, but it’s also helpful to understand how you measure up to your direct competitors. By understanding the basics of the stock market , you can easily understand how each company and their share make up the entire industry.
Relative Market Share
Relative market share compares your performance to industry leaders.
Rather than using total industry revenue, you’re dividing your market share by your top competitor's market share, multiplying the result by 100. The result will show you the portion of the market you own in relation to your most significant competitor. The image below shows the relative market share formula.

It may be easier to understand market share with real-life examples, so we’ll go over some below for businesses you may already be familiar with.
Nike Market Share
Nike is part of the athletic footwear and apparel industry, selling various sports equipment, casual shoes, and accessories.
Nike’s global market share in sportswear is estimated to be 43.7% . The brand is an industry competitor for Adidas and Under Armour.
Tesla Market Share
Tesla is part of the automotive industry and produces electric vehicles (EVs). Within the U.S. EV industry, Tesla holds an over 70% market share.
It's essential to recognize that the market for EVs worldwide is significantly smaller than standard vehicles. EV’s market share in the automobile industry is 2.8%, and Tesla’s is .8% . These differences are significant, so it is vital to analyze relative market share to compare your business to your direct competitors rather than just the market as a whole.
Spotify is a music-streaming platform and has the highest music-streaming market share with 31% of the market.
The second-highest market share belongs to Apple Music (15%), followed by Amazon Music (13), Tencent (13%), and YouTube (8%).
E-commerce company Amazon has a U.S. e-commerce market share of 37.8% and is the leading online retailer in the country. Second place belongs to Walmart with 6.3%, and third place goes to Apple with 3.9%.
Most recent statistics show Target is the largest department store retailer in the U.S. with a 38% market share. Walmart and Macy's both rank second with 13%.
Chew is an online pet product and food retailer with a market share of 40% in the U.S. The company plans to expand into the global market in 2024 and is expected to gain a 20% market share outside of the U.S. by 2030.
Google Market Share
Google has a market share of 92.37% , making it the most popular search engine in the world. It dominates the competition, as the second-largest industry leader is Bing with a market share of just 3.57%.
Once you’ve calculated your market share and understand how you relate to your industry competitors, you can begin strategizing how to increase your overall revenue.
How To Expand Your Market Share
Below are a few strategies your company can use to expand your market share .
1. Lower prices.
A great way to compete in your industry is to offer low prices. This is the low-hanging fruit of expanding your market share because consumers typically look for lower-cost products.
However, it's also important to note that the cheap option isn't right for every brand. You want to ensure that you’re pricing products appropriately to provide value to customers but not lose out on revenue opportunities to beat the competition.
2. Innovate new products and features.
Companies innovating and bringing new technology to the table often see their market share increase.
New products and features attract new customers, also known as acquisition , which is a driving factor for generating revenue. New customers make new purchases and, in turn, contribute to higher profit margins and larger contributions to overall industry revenue. More significant contributions directly translate to increased market share.
3. Delight your customers.
One of the best ways to grow your market share is to work on existing customer relationships.
You can inspire customer loyalty by delighting current customers by providing exceptional experiences and customer loyalty. Loyal customers are more likely to make repeat purchases, which increases your business revenue and contribution to total industry revenue. As mentioned above, higher revenue contributions equal a higher market share percentage.
4. Increase brand awareness.
Branding awareness and national marketing play a significant role in capturing market share. Getting your name out there is important, so customers know who you are. Becoming a household name and the preferred brand in an industry will help increase your market share.
Generally, larger companies have the highest market share because they can provide products and services more efficiently and effectively.
But why is this so important? Below, let's figure out what impact market share can have on your company.
Why is market share important?
Calculating market share lets companies know how competitive they are in their industry. Additionally, the more market share a company has, the more innovative, appealing, and marketable they are.
Market share is more important in industries that are based on discretionary income. Market share doesn't always have a significant impact in constantly growing industries. However, it's important to remember that a company can have too much market share — also known as a monopoly.
For example, with growing industries with a growing market share, companies can still increase their sales even if they lose market share.
On the other hand, with discretionary income industries, such as travel or non-essential goods like entertainment and leisure, the economy can significantly impact market share. Sales and margins can vary depending on the time of year, meaning that competition is always at an all-time high.
Higher competition often leads to risky strategies. For instance, companies might be willing to lose money temporarily to force competitors out of the industry and gain more market share. Once they have more market share, they can raise prices.
Lower market shares can let you know that you need to focus on customer acquisition, marketing to raise brand awareness, and overall strategies to increase revenue. Higher percentages indicate that your current plan is adequate and that you should focus on customer retention and product innovation.
Whether your company is well-established or just starting, it’s important to understand your industry standing as it will help you meet business objectives and achieve desired success.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

25 Tools & Resources for Conducting Market Research

What is a Competitive Analysis — and How Do You Conduct One?

Market Research: A How-To Guide and Template
![market share business model SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]

TAM SAM SOM: What Do They Mean & How Do You Calculate Them?
![market share business model How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Google%20Drive%20Integration/how%20to%20do%20a%20competitor%20analysis_122022.jpeg)
How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]
![market share business model 5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/challenges%20marketers%20face%20in%20understanding%20the%20customer%20.png)
5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]

Causal Research: The Complete Guide

Total Addressable Market (TAM): What It Is & How You Can Calculate It
![market share business model 3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-data-privacy-benefits-marketers_1.webp)
3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]
Free Guide & Templates to Help Your Market Research
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

Market Share: Business Model Canvas Explained
The term 'Market Share' within the context of the Business Model Canvas is a critical component that provides an understanding of a company's position within its industry. This article will delve into the intricacies of market share, its relevance to the Business Model Canvas, and how it influences revenue growth and innovation.
Market share is a measure of the proportion of a market that a company controls. It is calculated by dividing the company's total sales by the total sales of the industry. This measure is often used as an indicator of a company's competitiveness and its ability to grow revenue and innovate within its industry.
Understanding Market Share
Market share is a crucial metric in the business world as it provides a quantitative measure of a company's dominance in a particular market. It is a reflection of a company's competitive position and is often used to compare the performance of different companies within the same industry.
Increasing market share is a common business goal, as a larger market share often correlates with increased influence over market trends, higher customer loyalty, and the ability to leverage economies of scale. However, it's important to note that a high market share is not always indicative of profitability or success, as it may also reflect a company's reliance on price competition or other unsustainable practices.
Calculating Market Share
Market share is calculated by dividing a company's total sales by the total sales of the industry. This can be done on a unit basis (i.e., the number of items sold) or on a revenue basis (i.e., the total revenue generated). The result is then multiplied by 100 to get a percentage.
For example, if a company sells 100 units in a market where 1,000 units are sold in total, the company's unit market share would be 10%. Similarly, if a company generates $1 million in revenue in a market where the total revenue is $10 million, the company's revenue market share would be 10%.
Interpreting Market Share
Market share provides a snapshot of a company's competitive position within its industry. A high market share indicates that a company has a significant portion of the market, which can be a sign of strong customer loyalty, effective marketing strategies, or superior products or services.
However, a high market share can also be a sign of a lack of competition, which can lead to complacency and a lack of innovation. Conversely, a low market share can indicate a highly competitive market, but it can also be a sign of poor performance or ineffective strategies.
Market Share in the Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that allows companies to visualize and plan their business models. Market share plays a critical role in this tool as it provides a measure of the company's current position within its industry.
Understanding market share can help companies identify opportunities for growth and innovation. For example, a company with a low market share might see an opportunity to differentiate its products or services, target a new customer segment, or leverage new technologies to gain a competitive edge.
Market Share and Value Proposition
The Value Proposition is one of the key components of the Business Model Canvas. It describes the unique value that a company offers to its customers. A strong value proposition can help a company increase its market share by attracting more customers and retaining existing ones.
For example, a company that offers high-quality products at a lower price than its competitors has a strong value proposition. This can attract price-sensitive customers and lead to an increase in market share. Similarly, a company that offers innovative products or superior customer service can differentiate itself from its competitors and increase its market share.
Market Share and Customer Segments
Customer Segments are another key component of the Business Model Canvas. They represent the different groups of people or organizations that a company aims to reach and serve. Understanding market share can help a company identify which customer segments it is serving effectively and which ones it could target more effectively.
For example, a company with a high market share in a particular customer segment might see an opportunity to expand into a new segment. Conversely, a company with a low market share in a segment might need to reassess its strategies for serving that segment.
Market Share, Revenue Growth, and Innovation
Market share is closely linked to revenue growth and innovation. A company with a high market share has a larger customer base , which can lead to higher revenues. Moreover, a dominant position in the market can provide a company with the resources and confidence to invest in innovation.
However, it's important to note that a high market share is not a guarantee of revenue growth or innovation. A company must continually strive to improve its products or services, respond to changes in customer needs and preferences, and adapt to changes in the competitive landscape to maintain or increase its market share.
Market Share and Revenue Growth
Revenue growth is a key indicator of a company's financial health and success. A company with a high market share has a larger customer base, which can lead to higher revenues. However, a company must also focus on increasing its average revenue per customer to achieve sustainable revenue growth.
For example, a company can increase its average revenue per customer by upselling or cross-selling products or services, increasing prices, or introducing new products or services. These strategies can help a company increase its revenue even if its market share remains constant.
Market Share and Innovation
Innovation is a key driver of business success. A company with a high market share has the resources and confidence to invest in innovation. This can lead to the development of new products or services, improvements in operational efficiency, or the creation of new business models.
However, a high market share can also lead to complacency and a lack of innovation. Therefore, a company must continually strive to innovate and adapt to changes in the market to maintain or increase its market share.
Strategies for Increasing Market Share
There are several strategies that a company can use to increase its market share. These include differentiating its products or services, targeting new customer segments, leveraging new technologies, and improving customer service.
However, it's important to note that these strategies must be implemented in a sustainable manner. A company must not sacrifice profitability or long-term success for short-term gains in market share.
Differentiation
Differentiation involves creating unique products or services that are valued by customers. This can be achieved through superior quality, innovative features, or exceptional customer service. A differentiated offering can attract more customers and increase a company's market share.
However, differentiation requires a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences. A company must continually monitor changes in customer needs and preferences and adapt its products or services accordingly.
Targeting New Customer Segments
Targeting new customer segments involves identifying and serving new groups of customers. This can be achieved by expanding into new geographic markets, serving new demographic groups, or catering to new customer needs.
However, targeting new customer segments requires a deep understanding of these segments and the ability to serve them effectively. A company must invest in market research and customer insights to identify potential new segments and develop effective strategies for serving them.
Leveraging New Technologies
Leveraging new technologies involves using technology to improve products or services, enhance customer experiences, or increase operational efficiency. This can lead to improved product quality, faster service delivery, or lower costs, which can attract more customers and increase a company's market share.
However, leveraging new technologies requires a commitment to innovation and a willingness to take risks. A company must stay abreast of technological trends and be willing to invest in new technologies, even if the benefits are not immediately apparent.
Improving Customer Service
Improving customer service involves enhancing the quality of interactions between a company and its customers. This can be achieved by providing prompt and accurate responses to customer inquiries, resolving customer issues quickly and effectively, and going above and beyond to exceed customer expectations.
High-quality customer service can lead to increased customer loyalty and word-of-mouth referrals, which can increase a company's market share. However, improving customer service requires a commitment to customer satisfaction and a culture that values customer feedback.
Market share is a critical component of the Business Model Canvas and a key indicator of a company's competitive position within its industry. Understanding market share can help a company identify opportunities for growth and innovation, and develop effective strategies for increasing its market share in a sustainable manner.
However, a high market share is not a guarantee of success. A company must continually strive to improve its products or services, respond to changes in customer needs and preferences, and adapt to changes in the competitive landscape to maintain or increase its market share.
Whenever you are ready - here are a couple of ways how I can help you grow your business:
1. Business Free Training Design Sprint . Join Over 2,000 founders, creators and innovators in our FREE 7-day crash course on growth design. 7 emails delivered to your inbox giving you a flavour of the strategic planning, business growth systems and methods we use.
2. Builder OS - Online Course - If you're looking to grow your business, I share expertise, methods and step-by-step blueprints on finding growth opportunities, building lean offers and acquiring customers.
3. Venture Builder Newsletter - Sign up for the newsletter to receive 1 weekly email with practical tips on finding profitable niches, creating irresistible offers and traffic generating systems.out your business.

Helping designers and strategists turn their boldest ideas into market-leading ventures through Business, Design and Growth.
Whenever you are ready - here is how I can help:
1. Newsletter . Join over 2.000 founders, creators and innovators and get access to the business builder framework.
2. Business Builder OS - Masterclass on finding growth opportunities, building lean offers and acquiring customers - driven by A.I.
3. Builder Toolkit - 30 ideas on how to grow your revenue.
Actionable advice about spotting new opportunities, creating offers & growing revenue.
Find, build and grow new ventures, better and faster.
©2024 Untaylored. All Rights Reserved.
Plan Projections
ideas to numbers .. simple financial projections
Home > Business Plan > Market Share in a Business Plan

Market Share in a Business Plan
… so our market share should be …
To illustrate suppose the served available market (SAM) is 4.5 million and we expect to obtain 1% of this market. In this case the serviceable obtainable market (SOM) is calculated as follows.

The SOM is not normally calculated using a bottom up approach. However, it is a useful exercise to perform the calculation to see whether the business is able to operate at a level indicated by the estimated market share.
To illustrate suppose we have market size estimates for SAM of 4.5 million in year one rising to 7.59 million in year five. Additionally based on available resources (staff, equipment, funding etc.), the business estimates that it can deal with 300 customers in year one and 1600 customers in year five. Assuming an average value per customer of 150, we can calculate a bottom up market share as follows.
Using its available resources the business can support the market share calculated above. Consequently if the top down estimate of SOM is much larger than this the business need to rethink its plan to ensure compatibility with resources available.
Market Share Presentation

The investor will view the SOM as the short term target for the business. They will be looking for this to be achieved without too many problems to show that the business idea has potential. If the business can achieve the SOM then with further investment, it should be able to penetrate the SAM even further.
This is part of the financial projections and Contents of a Business Plan Guide . The guide is a series of posts on what each section of a simple business plan should include. The next post in this series sets out details of the marketing strategy which the business intends to use to win its share of the market.
About the Author
Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Plan Projections. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University.
You May Also Like
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A lot of preparation goes into starting a business before you can open your doors to the public or launch your online store. One of your first steps should be to write a business plan . A business plan will serve as your roadmap when building your business.
Within your business plan, there’s an important section you should pay careful attention to: your market analysis. Your market analysis helps you understand your target market and how you can thrive within it.
Simply put, your market analysis shows that you’ve done your research. It also contributes to your marketing strategy by defining your target customer and researching their buying habits. Overall, a market analysis will yield invaluable data if you have limited knowledge about your market, the market has fierce competition, and if you require a business loan. In this guide, we'll explore how to conduct your own market analysis.
How to conduct a market analysis: A step-by-step guide
In your market analysis, you can expect to cover the following:
Industry outlook
Target market
Market value
Competition
Barriers to entry
Let’s dive into an in-depth look into each section:
Step 1: Define your objective
Before you begin your market analysis, it’s important to define your objective for writing a market analysis. Are you writing it for internal purposes or for external purposes?
If you were doing a market analysis for internal purposes, you might be brainstorming new products to launch or adjusting your marketing tactics. An example of an external purpose might be that you need a market analysis to get approved for a business loan .
The comprehensiveness of your market analysis will depend on your objective. If you’re preparing for a new product launch, you might focus more heavily on researching the competition. A market analysis for a loan approval would require heavy data and research into market size and growth, share potential, and pricing.
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook
An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you’re targeting a growing industry or declining industry. For example, if you’re looking to sell VCRs in 2020, it’s unlikely that your business will succeed.
Starting your market analysis with an industry outlook offers a preliminary view of the market and what to expect in your market analysis. When writing this section, you'll want to include:
Market size
Are you chasing big markets or are you targeting very niche markets? If you’re targeting a niche market, are there enough customers to support your business and buy your product?
Product life cycle
If you develop a product, what will its life cycle look like? Lenders want an overview of how your product will come into fruition after it’s developed and launched. In this section, you can discuss your product’s:
Research and development
Projected growth
How do you see your company performing over time? Calculating your year-over-year growth will help you and lenders see how your business has grown thus far. Calculating your projected growth shows how your business will fare in future projected market conditions.
Step 3: Determine your target market
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential customer. Who is your ideal target customer? How can you cater your product to serve them specifically?
Don’t make the mistake of wanting to sell your product to everybody. Your target customer should be specific. For example, if you’re selling mittens, you wouldn’t want to market to warmer climates like Hawaii. You should target customers who live in colder regions. The more nuanced your target market is, the more information you’ll have to inform your business and marketing strategy.
With that in mind, your target market section should include the following points:
Demographics
This is where you leave nothing to mystery about your ideal customer. You want to know every aspect of your customer so you can best serve them. Dedicate time to researching the following demographics:
Income level
Create a customer persona
Creating a customer persona can help you better understand your customer. It can be easier to market to a person than data on paper. You can give this persona a name, background, and job. Mold this persona into your target customer.
What are your customer’s pain points? How do these pain points influence how they buy products? What matters most to them? Why do they choose one brand over another?
Research and supporting material
Information without data are just claims. To add credibility to your market analysis, you need to include data. Some methods for collecting data include:
Target group surveys
Focus groups
Reading reviews
Feedback surveys
You can also consult resources online. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau can help you find demographics in calculating your market share. The U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. Small Business Administration also offer general data that can help you research your target industry.
Step 4: Calculate market value
You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value.
A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the two. It requires for you to calculate the entire market and then estimate how much of a share you expect your business to get. For example, let’s assume your target market consists of 100,000 people. If you’re optimistic and manage to get 1% of that market, you can expect to make 1,000 sales.
A bottom-up analysis is more data-driven and requires more research. You calculate the individual factors of your business and then estimate how high you can scale them to arrive at a projected market share. Some factors to consider when doing a bottom-up analysis include:
Where products are sold
Who your competition is
The price per unit
How many consumers you expect to reach
The average amount a customer would buy over time
While a bottom-up analysis requires more data than a top-down analysis, you can usually arrive at a more accurate calculation.
Step 5: Get to know your competition
Before you start a business, you need to research the level of competition within your market. Are there certain companies getting the lion’s share of the market? How can you position yourself to stand out from the competition?
There are two types of competitors that you should be aware of: direct competitors and indirect competitors.
Direct competitors are other businesses who sell the same product as you. If you and the company across town both sell apples, you are direct competitors.
An indirect competitor sells a different but similar product to yours. If that company across town sells oranges instead, they are an indirect competitor. Apples and oranges are different but they still target a similar market: people who eat fruits.
Also, here are some questions you want to answer when writing this section of your market analysis:
What are your competitor’s strengths?
What are your competitor’s weaknesses?
How can you cover your competitor’s weaknesses in your own business?
How can you solve the same problems better or differently than your competitors?
How can you leverage technology to better serve your customers?
How big of a threat are your competitors if you open your business?
Step 6: Identify your barriers
Writing a market analysis can help you identify some glaring barriers to starting your business. Researching these barriers will help you avoid any costly legal or business mistakes down the line. Some entry barriers to address in your marketing analysis include:
Technology: How rapid is technology advancing and can it render your product obsolete within the next five years?
Branding: You need to establish your brand identity to stand out in a saturated market.
Cost of entry: Startup costs, like renting a space and hiring employees, are expensive. Also, specialty equipment often comes with hefty price tags. (Consider researching equipment financing to help finance these purchases.)
Location: You need to secure a prime location if you’re opening a physical store.
Competition: A market with fierce competition can be a steep uphill battle (like attempting to go toe-to-toe with Apple or Amazon).
Step 7: Know the regulations
When starting a business, it’s your responsibility to research governmental and state business regulations within your market. Some regulations to keep in mind include (but aren’t limited to):
Employment and labor laws
Advertising
Environmental regulations
If you’re a newer entrepreneur and this is your first business, this part can be daunting so you might want to consult with a business attorney. A legal professional will help you identify the legal requirements specific to your business. You can also check online legal help sites like LegalZoom or Rocket Lawyer.
Tips when writing your market analysis
We wouldn’t be surprised if you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information needed in a market analysis. Keep in mind, though, this research is key to launching a successful business. You don’t want to cut corners, but here are a few tips to help you out when writing your market analysis:
Use visual aids
Nobody likes 30 pages of nothing but text. Using visual aids can break up those text blocks, making your market analysis more visually appealing. When discussing statistics and metrics, charts and graphs will help you better communicate your data.
Include a summary
If you’ve ever read an article from an academic journal, you’ll notice that writers include an abstract that offers the reader a preview.
Use this same tactic when writing your market analysis. It will prime the reader of your market highlights before they dive into the hard data.
Get to the point
It’s better to keep your market analysis concise than to stuff it with fluff and repetition. You’ll want to present your data, analyze it, and then tie it back into how your business can thrive within your target market.
Revisit your market analysis regularly
Markets are always changing and it's important that your business changes with your target market. Revisiting your market analysis ensures that your business operations align with changing market conditions. The best businesses are the ones that can adapt.
Why should you write a market analysis?
Your market analysis helps you look at factors within your market to determine if it’s a good fit for your business model. A market analysis will help you:
1. Learn how to analyze the market need
Markets are always shifting and it’s a good idea to identify current and projected market conditions. These trends will help you understand the size of your market and whether there are paying customers waiting for you. Doing a market analysis helps you confirm that your target market is a lucrative market.
2. Learn about your customers
The best way to serve your customer is to understand them. A market analysis will examine your customer’s buying habits, pain points, and desires. This information will aid you in developing a business that addresses those points.
3. Get approved for a business loan
Starting a business, especially if it’s your first one, requires startup funding. A good first step is to apply for a business loan with your bank or other financial institution.
A thorough market analysis shows that you’re professional, prepared, and worth the investment from lenders. This preparation inspires confidence within the lender that you can build a business and repay the loan.
4. Beat the competition
Your research will offer valuable insight and certain advantages that the competition might not have. For example, thoroughly understanding your customer’s pain points and desires will help you develop a superior product or service than your competitors. If your business is already up and running, an updated market analysis can upgrade your marketing strategy or help you launch a new product.
Final thoughts
There is a saying that the first step to cutting down a tree is to sharpen an axe. In other words, preparation is the key to success. In business, preparation increases the chances that your business will succeed, even in a competitive market.
The market analysis section of your business plan separates the entrepreneurs who have done their homework from those who haven’t. Now that you’ve learned how to write a market analysis, it’s time for you to sharpen your axe and grow a successful business. And keep in mind, if you need help crafting your business plan, you can always turn to business plan software or a free template to help you stay organized.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- The Benefits of Market Share

How to Gain Market Share
- Market Share FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Fundamental Analysis
What Strategies Do Companies Employ to Increase Market Share?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/lesliecolor__leslie_kramer-5bfc262246e0fb0083bf8297.jpg)
Erika Rasure is globally-recognized as a leading consumer economics subject matter expert, researcher, and educator. She is a financial therapist and transformational coach, with a special interest in helping women learn how to invest.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/CSP_ER9-ErikaR.-dce5c7e19ef04426804e6b611fb1b1b4.jpg)
Katrina Ávila Munichiello is an experienced editor, writer, fact-checker, and proofreader with more than fourteen years of experience working with print and online publications.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KatrinaAvilaMunichiellophoto-9d116d50f0874b61887d2d214d440889.jpg)
A company’s market share is the percentage it controls of the total market for its products and services. Market share is an essential metric for businesses because it’s an indicator of a company’s profitability and success. It can signal dominance in an industry and how well a company’s revenue-generating efforts are working to achieve business goals.
Market share can affect operations, pricing of products and services, and, potentially stock market performance. A growing market share corresponds to growing revenue. That, in turn, means a business can scale up its operations and opportunity for greater profitability. To gain market share should be a serious business goal.
There are a number of strategies a company can put to work to increase market share. These include improving innovation, building and solidifying customer loyalty, employing a talented, dedicated workforce, acquiring other companies, deploying effective advertising, and pricing products and services efficiently.
Key Takeaways
- Market share is a company’s total sales in relation to total industry sales for the same period.
- Market share can highlight dominance over competitors.
- Market share helps a company measure the effectiveness of its strategies and strategic execution.
- Gaining market share should be one of management’s primary goals because of its effect on operations and profitability.
- The enormous benefits of market share underscore the importance of the strategies that can increase it.
Understanding the Benefits of Market Share
Market share is calculated by measuring the percentage of sales or percentage of units a company has in the overall market. Using the percentage of sales method, if a company has $1 million in annual sales and the total sales for the year in its industry are $100 million, the company’s market share is 1%. Under the percentage of units method, a company that sells 50,000 units annually in an industry where 5 million units are sold per year also has a market share of 1%.
A higher market share places companies at a competitive advantage :
- Companies with high market share often receive better prices from suppliers, as their larger order volumes increase their buying power .
- Increased market share and greater production go hand-in-hand, with the latter providing a company with the opportunity to decrease the cost to produce an individual unit due to economies of scale .
- Higher market share can help improve sales when existing, brand-loyal customers buy more of a company’s products.
- Market share may also widen a company’s overall customer base as potential new customers follow the lead of existing ones.
- Gaining market share can strengthen and spotlight a company’s reputation. In addition to boosting sales and increasing bargaining power, that can attract new, more talented employees.
Using sales, the formula to determine market share for a specific period of time is (total company revenue/total market revenue) x 100. Using units sold, the formula is (total number of units sold by company/total number of units sold in the industry)/100.
The importance of market share lies not simply in maintaining your company’s current share of the market. After all, as the industry grows, a company’s market share must grow as well to stay competitive and profitable. Increasing market share is crucial and involves gaining a bigger share than you have already. That would indicate that your growth is greater than average and you’re outperforming your competition.
Here are some areas a company can focus on to increase market share.
Innovation that attracts customers can come in different forms. One is useful, new technology that a company develops, introduces, and continues to improve before competitors gain a foothold. Consumers excited about the technology buy it, use it, and can become repeat customers. Innovative technology can build a company’s customer base with consumers new to the industry as well as consumers who leave another company for it.
A few other ideas for innovating to gain market share can include product innovation, production method improvements, and marketing strategies. The potential for high-value innovation exists throughout a company.
Customer Loyalty
Building and reinforcing relationships with existing customers by cultivating their loyalty is a smart strategy to gain market share. First of all, existing customer loyalty can help prevent customers from leaving a company for others when new products come to market. What’s more, a company can broaden its base with the word-of-mouth marketing so often provided by satisfied, happy customers.
Take advantage of chances to engage with customers who desire a closer connection and to deepen their positive experience. An added benefit is that this organic opportunity to welcome new customers and increase market share often can come without specifically related increases in a company’s marketing costs. Plus, loyal customers can sometimes share ideas for innovations to the products they love.
Skilled Workforce
A company that focuses on attracting and keeping talented employees is focused on increasing its market share. That’s because skilled employees can become dedicated employees. That, in turn, can cut expenses related to hiring and training. Plus, a skilled workforce that excels at its tasks can allow a company to maintain its focus on producing exceptional products and sales. Attracting the best requires competitive salaries and a strong selection of benefits, including options for flexible work schedules and relaxed office settings.
Acquisitions
To win market share and dominate an industry, a company can consider buying its competition. Such a move actually offers multiple strategies to increase market share in one action. With an acquisition , a company takes a competitor out of the market and assumes its market share. It captures its customer loyalty. Moreover, it can put products, services, and other strategic opportunities already developed by its acquisition to work immediately. If a company can’t buy another due to financial constraints, it can consider acquiring key employees to improve its own workforce and for the customer loyalty connected to those employees.
Advertising
Effective, frequent advertising offers a good opportunity to gain market share. Innovative branding and marketing through advertising can garner the attention of consumers, build connections with existing customers, and spur widespread desire for the products and services a company offers. High-impact advertising in different forms can help buyers understand and align with a company. No matter which advertising media is used, it’s wise to maintain continuity across design, voice, and message to ensure a strong, positive, and lasting impression. Companies should also make sure that their advertising actually targets the right market segment for their products and services.
Price Reductions
Lowering prices is a solid strategy to help a company win market share. Lower, more attractive prices can attract consumer attention and loyalty. That can increase the all-important sales that drive market share higher. In addition to decreasing the actual price for products, a company can consider promotions, coupons, bonus items, and other customer benefits. For instance, incentives such as referral programs and free shipping can generate extra interest and added sales.
How Can I Improve My Market Position?
One way a company can increase its market share is by improving the way its target market perceives it. This kind of positioning requires clear, sensible communications that impress upon existing and potential customers the identity, vision, and desirability of a company and its products. In addition, you must separate your company from the competition. As you plan such communications, consider these guidelines:
- Research as much as possible about your target audience so you can understand without a doubt what it wants. The more you know, the better you can reach and deliver exactly the message it desires.
- Establish your company’s credibility so customers know who you are, what you stand for, and that they can trust, not simply your products or services, but your brand.
- Explain in detail just how your company can better customers’ lives with its unique, high-value offerings. Then, deliver on that promise expertly so that the connection with customers can grow unimpeded and lead to new customers excited to join your base.
- Highlight the advantages that your company offers customers that competitors can’t match. Underscore your expertise in what you do and why that matters.
- Create messaging that is focused, personal to customers, meaningful for those who might become customers, and actionable in a way that can achieve results for both the target audience and company.
How Can I Attract New Customers?
One way to win market share is to win new customers. A company can increase its customer base in a variety of ways. Here are a few to consider:
- Improve marketing communications directed at potential new customers as well as existing customers.
- Refresh contact with customers not heard from lately with warm greetings, special offers, and discounts.
- Introduce existing customers to a referral program with appealing rewards as an incentive for providing the contact information of their friends and families. Or, if a program isn’t possible, ask for referrals from your most satisfied customers.
- Ask your most active customers to serve as brand ambassadors and actively spread the word about your company using their chosen medium.
- Review your website to be sure it has the look, feel, and message you wish to convey. A website review is a great opportunity to explain your company’s mission and goals as well as the goals developed to better the lives of customers and others.
- Monitor sites and platforms that promote business ratings and reviews. Respond to both complaints and compliments sincerely. Make every effort to help those whose posts require action. Consider linking positive reviews to the company site.
How Can I Prevent Loss of Market Share?
To avoid losing its market share, a company should monitor its market share metric, keep an eye on the performance of its competitors, and take steps to improve the aspects of its business that can affect its market share standing. These can include things like product and service quality and pricing, customer satisfaction, the growth of its customer base, marketing, and advertising, the quality of its staff, and the potential for the acquisition of competing companies.
Increasing market share can be vitally important to the financial health and continued success of a business. A company has a number of opportunities at hand to, not just maintain, but gain market share. Every company should understand the value a strong market share offers and commit to the ongoing effort that it can take to build it.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Market_Share_Final-a5f8b1b62e944765a3682cde4e569f06.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Why Business Models Matter
- Joan Magretta
A good business model begins with an insight into human motivations and ends in a rich stream of profits.
The Idea in Brief
The terms “business model” and “strategy” are among the most sloppily used in business. People use them interchangeably to refer to everything —so they mean nothing.
But no organization can afford fuzzy thinking about these fundamental concepts. A business model and a strategy are two different animals. One explains who your customers are and how you plan to make money by providing them with value; the other, how you’ll beat competitors by being different.
A well-thought-out business model also enables you to test and revise your assumptions about customers, think rigorously about your business, and align employees behind your company’s mission.
Sure, the business-model concept unraveled after flagrant misuse by dot bombs. But when you build a sound model that complements your strategy, you equip your company to beat even your toughest rivals.
The Idea in Practice
Powerful business models pass two tests:
1. The narrative test: The business model tells a logical story explaining who your customers are, what they value, and how you’ll make money providing them that value. The story’s plot may turn on one of two links in the generic business value chain:
- making something that satisfies an unmet need; e.g., American Express traveler’s checks gave travelers new peace of mind
- selling something in innovative ways; e.g., Eastern Exclusives distributes restaurant discount-coupon books in bulk to university housing departments, which distribute them free to dorms
2. The numbers test: A business model’s story holds up only if you tie assumptions about customers to sound economics—your P&L must add up. For example, on-line grocery models failed because customers declined to pay substantially more on-line than in stores. E-grocers couldn’t cover their marketing, technology, and delivery costs. Failing either test can prove fatal. Example:
When EuroDisney opened its Paris theme park, it assumed Europeans were like Americans. But instead of grazing all day at the park’s restaurants, Europeans wanted to eat meals at the same hour. Results? Overloaded restaurants, long lines, frustrated patrons. EuroDisney’s model failed the narrative test because it misunderstood customers’ motivations.
Models passing both tests clarify how your business’s various elements fit together. Example:
On-line auction giant eBay combined a compelling narrative with major profit potential. This on-line business “couldn’t be done offline” and still provide value to collectors, bargain hunters, and small-business people. Its narrow scope of activities creates a highly profitable cost structure. For example, sellers and buyers handle payment and shipping logistics—so eBay incurs no inventory or transportation costs and avoids credit risk.
A Strategy Complement
Having a solid business model isn’t enough. You also need a strategy, to plan how you’ll beat your rivals—by being different. Example:
Wal-Mart used Kmart’s business model—but implemented a unique strategy: Rather than trying to be just like its rivals, it promised different value to customers in different markets. It put big discount stores into “little one-horse towns” that competitors ignored. Founder Sam Walton bet—rightly—that if his stores beat city prices by offering name brands (not second-tier, private-label brands), townspeople would “shop [close to] home.”
“Business model” was one of the great buzzwords of the Internet boom, routinely invoked, as the writer Michael Lewis put it, “to glorify all manner of half-baked plans.” A company didn’t need a strategy, or a special competence, or even any customers—all it needed was a Web-based business model that promised wild profits in some distant, ill-defined future. Many people—investors, entrepreneurs, and executives alike—bought the fantasy and got burned. And as the inevitable counterreaction played out, the concept of the business model fell out of fashion nearly as quickly as the .com appendage itself.
- JM Joan Magretta is a senior associate at the Institute for Strategy and Competitiveness at Harvard Business School. She is the author of Understanding Michael Porter: The Essential Guide to Competition and Strategy .
Partner Center
- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.

Start this free course now. Just create an account and sign in. Enrol and complete the course for a free statement of participation or digital badge if available.
3.6 Market creator
Market creators offer platforms for developing transactions and exchanges, enabling buyers and sellers to meet in virtual places. The diffusion of the internet has favoured the separation of markets from physical spaces. Typical examples are eBay and Etsy.
Market creators make money by charging a fee for each transaction on their platform, or asking merchants to pay a fee to access the marketplace. Having the financial resources and the marketing capabilities to create an extensive base of users grants the success of this business model.

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
Nestle: Business Model, SWOT Analysis, and Competitors 2023
Inside This Article
In this blog article, we will dive into Nestle, one of the world's largest food and beverage companies, to explore its business model, conduct a SWOT analysis, and examine its competitors. Nestle's business model is centered around its diverse portfolio of brands, focusing on nutrition, health, and wellness. By analyzing the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, we can gain insights into its current and future prospects. Additionally, understanding Nestle's competitors will provide a comprehensive view of the industry landscape and the company's position within it.
What You Will Learn:
- Who owns Nestle: Discover the ownership structure of Nestle and understand the key stakeholders in the company.
- Mission statement of Nestle: Gain insight into Nestle's mission statement and understand their core values and objectives.
- How Nestle makes money: Explore the various revenue streams and business strategies employed by Nestle to generate profit and sustain growth.
- Nestle Business Model Canvas explained: Understand the key components of Nestle's business model and how they create and deliver value to their customers.
- Nestle's competitors: Identify the main competitors of Nestle in the industry and understand the competitive landscape.
- Nestle SWOT Analysis: Analyze the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing Nestle and gain a comprehensive understanding of their market position.
Who owns Nestle?
Ownership structure of nestle.
Nestle, one of the largest and most recognizable food and beverage companies globally, has a complex ownership structure. The ownership of Nestle is spread across a diverse set of shareholders, including institutional investors, individual shareholders, and Nestle itself. Let's delve deeper into the ownership structure of Nestle.
Institutional Investors
Institutional investors play a significant role in owning Nestle. These investors include pension funds, mutual funds, and other financial institutions. Some prominent institutional shareholders of Nestle include BlackRock, The Vanguard Group, and State Street Corporation. These institutions often hold a substantial number of shares due to their investment strategies and the size of their portfolios.
Individual Shareholders
Individual shareholders also own a considerable portion of Nestle. These individuals can range from small retail investors to wealthy individuals who have invested in the company. Nestle's shares are traded on stock exchanges, allowing anyone to become a shareholder by purchasing Nestle shares through a broker.
Nestle Treasury Shares
Nestle itself also owns a portion of its shares, referred to as treasury shares. These shares are typically repurchased by the company in the open market or through buyback programs. Nestle may hold treasury shares for various reasons, such as supporting employee stock option plans or using them for acquisitions or mergers.
Shareholder Activism
Shareholder activism has gained attention in recent years, with investors using their ownership stakes to influence companies' strategic decisions. While Nestle has faced some shareholder activism, it remains a robust and well-diversified company. The company's management and board of directors work to balance the interests of various shareholders while maintaining a focus on long-term growth and sustainability.
The Role of the Nestle Board of Directors
The Nestle Board of Directors, consisting of individuals with diverse backgrounds and expertise, plays a crucial role in the company's decision-making process. The board ensures that the interests of all shareholders are considered and promotes transparency and accountability in Nestle's operations. The board also appoints and oversees the executive management team responsible for day-to-day operations.
In conclusion, the ownership of Nestle is distributed among a broad range of shareholders, including institutional investors, individual shareholders, and the company itself. This diverse ownership structure helps ensure the stability and long-term growth of Nestle, while the board of directors oversees the interests of all shareholders.
What is the mission statement of Nestle?
Nestle's mission statement.
Nestle, one of the world's leading food and beverage companies, has a clear and concise mission statement that guides its business operations and strategic decisions. The company's mission statement is:
"Nestle is the world's leading nutrition, health, and wellness company. Our mission is to provide consumers with the best tasting, most nutritious choices in a wide range of food and beverage categories, and to promote a healthy lifestyle."
This mission statement reflects Nestle's commitment to not only providing high-quality and delicious products but also ensuring that these products contribute to the overall well-being of consumers. Nestle recognizes the importance of nutrition and aims to offer a diverse range of food and beverage options that cater to different dietary needs and preferences.
Furthermore, Nestle's mission statement emphasizes the company's dedication to promoting a healthy lifestyle. This goes beyond simply offering nutritious products; Nestle also actively encourages individuals to make informed choices and adopt healthier habits. By promoting health and wellness, Nestle aims to contribute to the overall improvement of global public health.
Nestle's mission statement also highlights the company's global presence and aspiration to be the leading player in the industry. As a multinational corporation, Nestle operates in numerous countries and serves a diverse customer base. By providing the best tasting and most nutritious choices in various food and beverage categories, Nestle aims to maintain its position as the preferred brand for consumers worldwide.
In conclusion, Nestle's mission statement encapsulates the company's commitment to nutrition, health, and wellness. By offering a wide range of high-quality products and promoting a healthy lifestyle, Nestle strives to provide consumers with the best choices for their well-being. This mission statement serves as a guiding principle for Nestle's business strategies and underscores its dedication to meeting the evolving needs of consumers in the food and beverage industry.
How does Nestle make money?
Revenue streams.
Nestle, one of the largest food and beverage companies in the world, generates revenue through a diverse range of sources. Here are the primary ways Nestle makes money:
1. Sales of Food and Beverages
The core of Nestle's business lies in the production and sale of various food and beverage products. From popular chocolate bars like KitKat and Crunch to bottled water brands like Perrier and San Pellegrino, Nestle offers a wide array of consumer goods. These products are sold globally through a vast distribution network, including supermarkets, convenience stores, and online platforms, contributing significantly to Nestle's revenue.
2. Nespresso and Coffee Systems
Nestle is known for its premium coffee brand, Nespresso, which has gained a strong following worldwide. Nespresso machines and coffee capsules are sold separately, providing a recurring revenue stream for Nestle. Additionally, Nestle's coffee systems, such as Dolce Gusto and Nescafe Dolce Gusto, offer a range of coffee-based beverages and machines, further diversifying their coffee-related revenue.
3. Pet Care Products
Nestle has also established a prominent presence in the pet care industry through its subsidiary, Purina PetCare. With an extensive portfolio of pet food brands like Purina ONE, Fancy Feast, and Friskies, Nestle caters to the nutritional needs of dogs, cats, and other pets. The revenue generated from the sales of pet care products contributes significantly to Nestle's overall financial performance.
4. Nutrition and Health Sciences
Nestle's commitment to nutrition and health sciences has led to the development of a range of specialized food and beverage products. These include infant formula, medical nutrition products, sports nutrition, and weight management solutions. With brands like NAN, Optifast, and PowerBar, Nestle targets specific dietary needs and health-conscious consumers, generating essential revenue from these segments.
5. Professional Services
Nestle also offers professional services to various sectors in the food industry, such as restaurants, hotels, and catering companies. Through its Nestle Professional division, the company provides culinary expertise, food solutions, and beverage systems tailored to meet the specific demands of these businesses. This segment contributes to Nestle's revenue stream by establishing long-term partnerships with key players in the foodservice industry.
6. Licensing and Partnerships
Furthermore, Nestle capitalizes on its strong brand recognition by engaging in licensing and partnerships. By granting licenses for the production of products bearing their brand names, Nestle expands its market reach while earning royalties from these collaborations. This strategy allows Nestle to leverage its reputation and generate additional revenue streams without significant investment.
In conclusion, Nestle's revenue streams encompass a wide range of products and services. From food and beverages to pet care and nutrition, Nestle strategically diversifies its offerings to cater to various consumer needs. Through its strong brand presence, global distribution network, and focus on innovation, Nestle continues to thrive in the highly competitive food and beverage industry.
Nestle Business Model Canvas Explained
What is the business model canvas.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that helps businesses visualize and analyze all the key components of their business in a single, concise framework. It was developed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur and has gained popularity for its simplicity and effectiveness in identifying and understanding a company's business model.
Understanding Nestle's Business Model Canvas
Nestle, one of the world's largest food and beverage companies, can be analyzed using the Business Model Canvas to gain insights into how the company creates, delivers, and captures value. Let's delve into the different elements of Nestle's Business Model Canvas:
Key Partnerships
Nestle has numerous key partnerships that contribute to its success. These partnerships include suppliers who provide raw materials for their products, distribution partners who help deliver their products to consumers, and strategic alliances with other companies to expand their product portfolio. By collaborating with various partners, Nestle is able to leverage their expertise, resources, and networks to enhance its overall value proposition.
Key Activities
Nestle's key activities encompass a range of operations that are vital to its business. These activities include research and development to innovate new products, production and manufacturing, marketing and advertising, and distribution. Nestle invests heavily in research and development to constantly improve its products and meet changing consumer demands. By conducting these key activities effectively, Nestle is able to create and deliver high-quality products to its customers.
Key Resources
Nestle possesses a wide array of key resources that enable its business operations. These resources include its extensive network of manufacturing facilities, a strong portfolio of brands, a talented workforce, and advanced technologies. Nestle's manufacturing facilities are strategically located worldwide, allowing the company to efficiently produce and distribute its products globally. Additionally, its strong portfolio of brands helps Nestle maintain a competitive edge in the market and cater to diverse consumer preferences.
Value Proposition
Nestle's value proposition lies in its ability to provide consumers with a wide range of high-quality food and beverage products that cater to different needs and preferences. The company focuses on offering nutritious and delicious products that meet the evolving tastes and lifestyles of consumers. Nestle's strong commitment to product quality, safety, and sustainability further enhances its value proposition, building trust and loyalty among its customers.
Customer Segments
Nestle serves a diverse range of customer segments across various demographics and geographies. The company targets individuals and families seeking convenient and nutritious food options, as well as professionals and athletes looking for performance-enhancing products. Nestle also caters to specific dietary needs, such as gluten-free or lactose-free products, to meet the requirements of niche market segments. By understanding and addressing the unique needs of different customer segments, Nestle can effectively capture market share and sustain customer loyalty.
Nestle utilizes multiple channels to distribute its products and reach its customers. These channels include retail stores, supermarkets, e-commerce platforms, and direct sales to institutions and businesses. Nestle's extensive distribution network ensures that its products are readily available to consumers worldwide, allowing the company to capitalize on market opportunities and maximize its reach.
Cost Structure
Nestle's cost structure is influenced by the complexity of its operations, including research and development, manufacturing, marketing, and distribution. The company invests significantly in research and development to innovate new products and improve existing ones. Manufacturing costs are also a substantial part of Nestle's cost structure due to its global production network. Additionally, marketing and advertising expenses play a crucial role in promoting Nestle's products and building brand awareness.
Nestle generates revenue from the sales of its food and beverage products across different categories, including powdered and liquid beverages, dairy products, cereals, confectionery, and pet care. The company's diversified product portfolio allows it to generate revenue from multiple sources, reducing its reliance on any single product category. Nestle's global presence and extensive distribution channels contribute to its consistent revenue streams.
Analyzing Nestle's Business Model Canvas provides valuable insights into how the company operates and creates value for its stakeholders. By understanding the key elements of Nestle's business model, it becomes apparent why the company has been able to maintain its position as a global leader in the food and beverage industry.
Which companies are the competitors of Nestle?
Introduction.
Nestle, a multinational food and beverage company, operates in a highly competitive industry. In this section, we will explore some of the key competitors of Nestle and the ways in which they challenge Nestle's market position.
Competitor 1: The Coca-Cola Company
One of the major competitors of Nestle is The Coca-Cola Company. Coca-Cola is a global leader in the non-alcoholic beverage industry, offering a wide range of carbonated and non-carbonated drinks. With iconic brands such as Coca-Cola, Sprite, Fanta, and Minute Maid, Coca-Cola has a strong presence in both developed and emerging markets.
Competitor 2: Unilever
Unilever is another significant competitor of Nestle, particularly in the consumer goods sector. Unilever is a multinational company that produces a diverse range of products, including food, beverages, cleaning agents, and personal care items. Some of Unilever's well-known brands include Dove, Lipton, Knorr, and Magnum. With a strong focus on sustainability and social responsibility, Unilever has gained a competitive edge in the market.
Competitor 3: Mondelez International
Mondelez International, a global snacking powerhouse, is another key competitor of Nestle. Mondelez owns a portfolio of popular brands such as Cadbury, Oreo, Toblerone, and Trident. With a strong presence in the confectionery and snack food industry, Mondelez competes directly with Nestle in various markets around the world.
Competitor 4: PepsiCo
PepsiCo is a multinational food and beverage company that poses a significant challenge to Nestle. With a diverse product portfolio that includes brands like Pepsi, Lay's, Gatorade, Tropicana, and Quaker Oats, PepsiCo competes with Nestle in several categories such as beverages, snacks, and breakfast cereals. PepsiCo's strong marketing strategies and global reach make it a formidable competitor for Nestle.
Competitor 5: Danone
Danone, a French multinational food-products corporation, is another key player in the market, competing directly with Nestle. Danone specializes in dairy products, bottled water, early life nutrition, and medical nutrition. With well-known brands like Activia, Evian, Aptamil, and Nutricia, Danone has a strong global presence and often challenges Nestle's market share in various product categories.
Nestle faces intense competition from several major players in the food and beverage industry. The Coca-Cola Company, Unilever, Mondelez International, PepsiCo, and Danone are just a few of the formidable competitors that constantly challenge Nestle's market position. This dynamic competition not only drives innovation but also ensures that consumers have a wide range of choices when it comes to their favorite food and beverage brands.
Nestle SWOT Analysis
Strong brand portfolio: Nestle has a wide range of well-known and reputable brands in its portfolio, such as Nescafe, KitKat, Maggi, and Nestea. This gives the company a competitive advantage and helps it to maintain its market share.
Global presence: Nestle operates in over 190 countries worldwide, which allows it to reach a large customer base and tap into different markets. This global presence also provides the company with economies of scale and the ability to adapt to local preferences.
Research and development capabilities: Nestle invests heavily in research and development to innovate and create new products. This enables the company to stay ahead of its competitors and cater to changing consumer trends and preferences.
Dependence on few markets: Despite its global presence, Nestle relies heavily on a few key markets for its revenue. This exposes the company to risks such as economic downturns, political instability, and changing regulations in those markets.
Controversies and ethical concerns: Nestle has faced several controversies and ethical concerns over the years, such as allegations of unethical marketing practices, exploitation of natural resources, and violation of labor rights. These issues can damage the company's reputation and affect consumer trust.
Product recalls: Like any food and beverage company, Nestle is not immune to product recalls. These incidents can have a negative impact on the company's reputation and consumer perception of its products.
Opportunities
Growing demand for healthier options: With increasing health consciousness among consumers, there is a growing demand for healthier food and beverage options. Nestle can capitalize on this trend by expanding its portfolio of nutritious and functional products.
Expansion into emerging markets: Emerging markets, such as India, China, and Brazil, offer significant growth opportunities for Nestle. These markets have a large population and a rising middle class, which creates a growing consumer base for the company's products.
Acquisitions and partnerships: Nestle can explore strategic acquisitions and partnerships to expand its product offerings and enter new markets. This can help the company gain a competitive edge and strengthen its position in the industry.
Intense competition: The food and beverage industry is highly competitive, with numerous global and local players vying for market share. Nestle faces intense competition from companies like Unilever, Coca-Cola, and PepsiCo, which can impact its market position and profitability.
Changing consumer preferences: Consumer preferences and trends can change rapidly, making it essential for Nestle to constantly innovate and adapt its products. Failure to do so may result in a decline in consumer demand and loss of market share.
Regulatory challenges: Nestle operates in multiple countries, each with its own set of regulations and standards. Compliance with these regulations can be challenging and may result in additional costs and restrictions on the company's operations.
In conclusion, Nestle has several strengths, such as a strong brand portfolio and global presence, which contribute to its market leadership. However, the company also faces weaknesses, such as dependence on few markets and controversies that can impact its reputation. Nestle has opportunities to capitalize on growing demand for healthier options and expansion into emerging markets. However, it also faces threats from intense competition, changing consumer preferences, and regulatory challenges.
Key Takeaways
- Nestle is a Swiss multinational conglomerate that is publicly traded, meaning it is owned by shareholders who hold its stock.
- The mission statement of Nestle is to enhance quality of life and contribute to a healthier future by offering a wide range of food and beverage products that are tasty, nutritious, and safe.
- Nestle makes money primarily through the sale of its food and beverage products, which are produced and sold all over the world.
- Nestle's business model canvas encompasses key elements such as key partners, key activities, value proposition, customer segments, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, resources, and cost structure.
- Some of Nestle's main competitors include companies like Unilever, Danone, PepsiCo, and Kraft Heinz. A SWOT analysis of Nestle reveals its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the competitive market.
In conclusion, Nestle is a multinational food and beverage company that has a strong presence in the global market. As for ownership, Nestle is a publicly traded company, with shares owned by various institutional and individual investors.
The mission statement of Nestle is to enhance the quality of life and contribute to a healthier future. This mission is evident in their commitment to providing nutritious and sustainable food and beverages to consumers worldwide.
Nestle generates its revenue through a diverse range of products, including bottled water, baby food, pet care, and confectionery. They have a strong focus on innovation and continuously introduce new products to cater to changing consumer demands.
The Nestle Business Model Canvas provides a comprehensive overview of how the company creates, delivers, and captures value. From key activities such as manufacturing and marketing to customer segments and revenue streams, the canvas helps understand the various components of Nestle's business operations.
Nestle faces competition from several companies in the food and beverage industry. Some of its main competitors include Unilever, Coca-Cola, PepsiCo, and Kraft Heinz. These companies also offer a wide range of products and strive to capture market share in the industry.
Lastly, conducting a SWOT analysis of Nestle reveals its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Nestle's strengths lie in its strong brand portfolio, global presence, and extensive distribution network. However, it faces challenges in terms of increasing competition, changing consumer preferences, and environmental concerns.
Overall, Nestle is a prominent player in the food and beverage industry, driven by its commitment to delivering high-quality products and contributing to a healthier future.
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
- Transportation & Logistics ›
Vehicles & Road Traffic
Tesla - statistics & facts
Financial performance boosted by the u.s. market, increased competition from chinese automakers, growing challenges influence tesla’s future, key insights.
Detailed statistics
Tesla's revenue 2008-2023
Tesla's vehicle sales by quarter YTD Q1 2024
Tesla's operating margin by quarter 2019-2023
Company Insights Top 100 transport & logistics companies
- United Parcel Service
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Current statistics on this topic.
Electric vehicle sales globally by model 2023
Plug-in electric vehicle market share by manufacturer 2023
Passenger Cars
Tesla's vehicle production by quarter Q1 2024
Related topics
- Electric vehicles worldwide
- Electric vehicles in the United States
- Electric vehicles in Europe
- Electric vehicle charging infrastructure in the United States
- Autonomous vehicles worldwide
- Connected cars worldwide
- Lithium-ion battery industry worldwide
Competitors
- Volkswagen Group
- General Motors Company
Recommended statistics
- Premium Statistic Most valuable automotive brands worldwide by brand value 2023
- Basic Statistic Plug-in electric light vehicle sales worldwide 2015-2022
- Premium Statistic Tesla's vehicle production by quarter Q1 2024
- Basic Statistic Tesla's vehicle sales by quarter YTD Q1 2024
- Premium Statistic Electric vehicle sales globally by model 2023
- Premium Statistic Range of selected electric vehicle models 2023
Most valuable automotive brands worldwide by brand value 2023
Most valuable brands within the automotive sector worldwide as of 2023, by brand value (in billion U.S. dollars)
Plug-in electric light vehicle sales worldwide 2015-2022
Estimated plug-in electric light vehicle sales worldwide from 2015 to 2022 (in million units)
Tesla's vehicle production by quarter Q1 2024
Number of Tesla vehicles produced worldwide from 1st quarter 2016 to 1st quarter 2024 (in units)
Tesla's vehicle sales by quarter YTD Q1 2024
Number of Tesla vehicles delivered worldwide from 1st quarter 2016 to 1st quarter 2024 (in 1,000 units)
Best-selling plug-in electric vehicle models worldwide in 2023 (in 1,000 units)
Range of selected electric vehicle models 2023
EV range of selected MY 2023 electric vehicles (in miles)
- Basic Statistic Tesla's revenue 2008-2023
- Basic Statistic Tesla's net income 2014-2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla's R&D spending 2010-2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla - SG&A expenditures 2008-2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla's free cash flow by quarter 2019-2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla's operating margin by quarter 2019-2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla's market capitalization 2023
Tesla's revenue 2008-2023
Tesla's revenue from FY 2008 to FY 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Tesla's net income 2014-2023
Tesla's net income/loss from FY 2014 to FY 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Tesla's R&D spending 2010-2023
Tesla's research and development expenses from FY 2010 to FY 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Tesla - SG&A expenditures 2008-2023
Tesla's selling, general and administrative expenses from FY 2008 to FY 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Tesla's free cash flow by quarter 2019-2023
Tesla's free cash flow from 1st quarter 2019 to 4th quarter 2023 (in million U.S. dollars)
Tesla's operating margin by quarter 2019-2023
Tesla's operating margin from 1st quarter 2019 to 4th quarter 2023
Tesla's market capitalization 2023
Tesla's market capitalization between March 31, 2020 and 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
- Premium Statistic Tesla's revenue by segment 2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla's gross margin by segment 2021-2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla's domestic and international revenue 2018-2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla: vehicle deliveries by main model and quarter 2024
- Premium Statistic Quarterly Tesla supercharger station and connector volume worldwide 2020-2023
Tesla's revenue by segment 2023
Tesla's revenue between FY 2022 and FY 2023, by segment (in millions U.S. dollars)
Tesla's gross margin by segment 2021-2023
Tesla's gross margin from FY 2021 to FY 2023, by key segment
Tesla's domestic and international revenue 2018-2023
Tesla's revenue in the United States, China, and other markets from FY 2018 to FY 2023 (in millions U.S. dollars)
Tesla: vehicle deliveries by main model and quarter 2024
Tesla vehicles delivered between 1st quarter 2020 and 1st quarter 2024, by main model (in 1,000 units)
Quarterly Tesla supercharger station and connector volume worldwide 2020-2023
Global quarterly volume of available Tesla supercharger stations and connectors between the 4th quarter of 2020 and the 4th quarter of 2023
Environmental impact
- Premium Statistic Average lifecycle emissions of Tesla Model 3/Y by selected countries and regions 2022
- Premium Statistic Volume of raw materials recovered by Tesla for recycling 2021-2022
- Premium Statistic Tesla's scope 1 emissions in 2021-2022, by sector
- Premium Statistic Scope 2 emissions of Tesla by sector 2021-2022
- Premium Statistic Scope 3 emissions of Tesla by category in 2022
- Premium Statistic Waste diverted from disposal by Tesla in global manufacturing by category 2021-2022
- Premium Statistic Waste diverted to disposal by Tesla in global manufacturing by category 2021-2022
- Premium Statistic Tesla's total freshwater withdrawal for manufacturing 2020-2022
Average lifecycle emissions of Tesla Model 3/Y by selected countries and regions 2022
Tesla Model 3/Y average lifecycle emissions for personal use in the United States, Europe, and China in 2022 (in grams of CO₂ equivalent emissions per mile)
Volume of raw materials recovered by Tesla for recycling 2021-2022
Total amount of recovered raw materials for recycling by Tesla between 2021 and 2022 by raw material (in metric tons)
Tesla's scope 1 emissions in 2021-2022, by sector
Scope 1 carbon emissions of Tesla from 2021 to 2022, by sector (in metric tons of CO₂ equivalent)
Scope 2 emissions of Tesla by sector 2021-2022
Amount of Scope 2 carbon emissions of Tesla from 2021 to 2022, by sector (in metric tons of CO₂ equivalent)
Scope 3 emissions of Tesla by category in 2022
Amount of Scope 3 emissions of Tesla in 2022, by category (in tons of CO₂ equivalent)
Waste diverted from disposal by Tesla in global manufacturing by category 2021-2022
Tesla's waste diverted from disposal in global manufacturing from 2021 to 2022, by category (in tons)
Waste diverted to disposal by Tesla in global manufacturing by category 2021-2022
Tesla's waste diverted to disposal in global manufacturing from 2021 to 2022, by category (in tons)
Tesla's total freshwater withdrawal for manufacturing 2020-2022
Overall amount of freshwater withdrawal for manufacturing by Tesla from 2020 to 2022 (in million cubic meters)
- Premium Statistic Plug-in electric vehicle sales worldwide by brand 2023
- Premium Statistic Plug-in electric vehicle market share by manufacturer 2023
- Premium Statistic BYD Group: revenue 2010-2023
- Premium Statistic BYD Group's total vehicle sales 2019-2022, by type
- Basic Statistic Volkswagen Group's sales revenue 2006-2023
- Premium Statistic Volkswagen Group BEV deliveries by brand 2022-2023
- Basic Statistic General Motors Company: revenue 2013-2023
- Premium Statistic Chevy Bolt EV sales in the United States 2017-2023
- Premium Statistic Global revenue of BMW Group 2007-2023
- Basic Statistic BMW i series: electric car deliveries 2014-2023
Plug-in electric vehicle sales worldwide by brand 2023
Estimated plug-in electric vehicle sales worldwide in 2023, by brand (in units)
Global plug-in electric vehicle market share in 2023, by main manufacturer
BYD Group: revenue 2010-2023
Revenue of BYD Group from 2010 to 2023 (in billion yuan)
BYD Group's total vehicle sales 2019-2022, by type
Total vehicle sales volume of BYD Group from FY 2019 to FY 2022, by type
Volkswagen Group's sales revenue 2006-2023
Volkswagen Group's sales revenue from FY 2006 to FY 2023 (in billion euros)
Volkswagen Group BEV deliveries by brand 2022-2023
Deliveries of battery electric vehicles by the Volkswagen Group between 2022 and 2023, by brand
General Motors Company: revenue 2013-2023
General Motors Company's sales and revenue streams between FY 2013 and FY 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Chevy Bolt EV sales in the United States 2017-2023
Number of Chevrolet Bolt electric vehicle sales in the United States between 2017 and 2023 (in units)
Global revenue of BMW Group 2007-2023
Global revenue of BMW Group from FY 2007 to FY 2023 (in million euros)
BMW i series: electric car deliveries 2014-2023
BMW Group's global BMW i series vehicle deliveries from FY 2014 to FY 2023 (in units)
Special focus on domestic market
- Premium Statistic Automotive manufacturers' estimated market share in the U.S. 2023
- Premium Statistic Tesla: Monthly U.S. market share 2023
- Premium Statistic Best-selling battery-electric cars in the United States 2023
- Premium Statistic Number of electric vehicle fast charging stations in the U.S. by connector 2024
Automotive manufacturers' estimated market share in the U.S. 2023
Estimated U.S. market share held by selected automotive manufacturers in 2023
Tesla: Monthly U.S. market share 2023
Tesla's estimated U.S. market share from January to December 2023
Best-selling battery-electric cars in the United States 2023
Best-selling battery-electric cars in the United States in 2023, based on new registrations (in units)
Number of electric vehicle fast charging stations in the U.S. by connector 2024
Number of electric vehicle fast charging stations in the United States as of April 2024, by connector type
Further reports Get the best reports to understand your industry
Get the best reports to understand your industry.
- Electric vehicle market in the Asia-Pacific region
- Electric vehicles in China
- Electric vehicles in Latin America
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
Tesla's China-made EV sales fall 18% in April; shares slip
- Medium Text
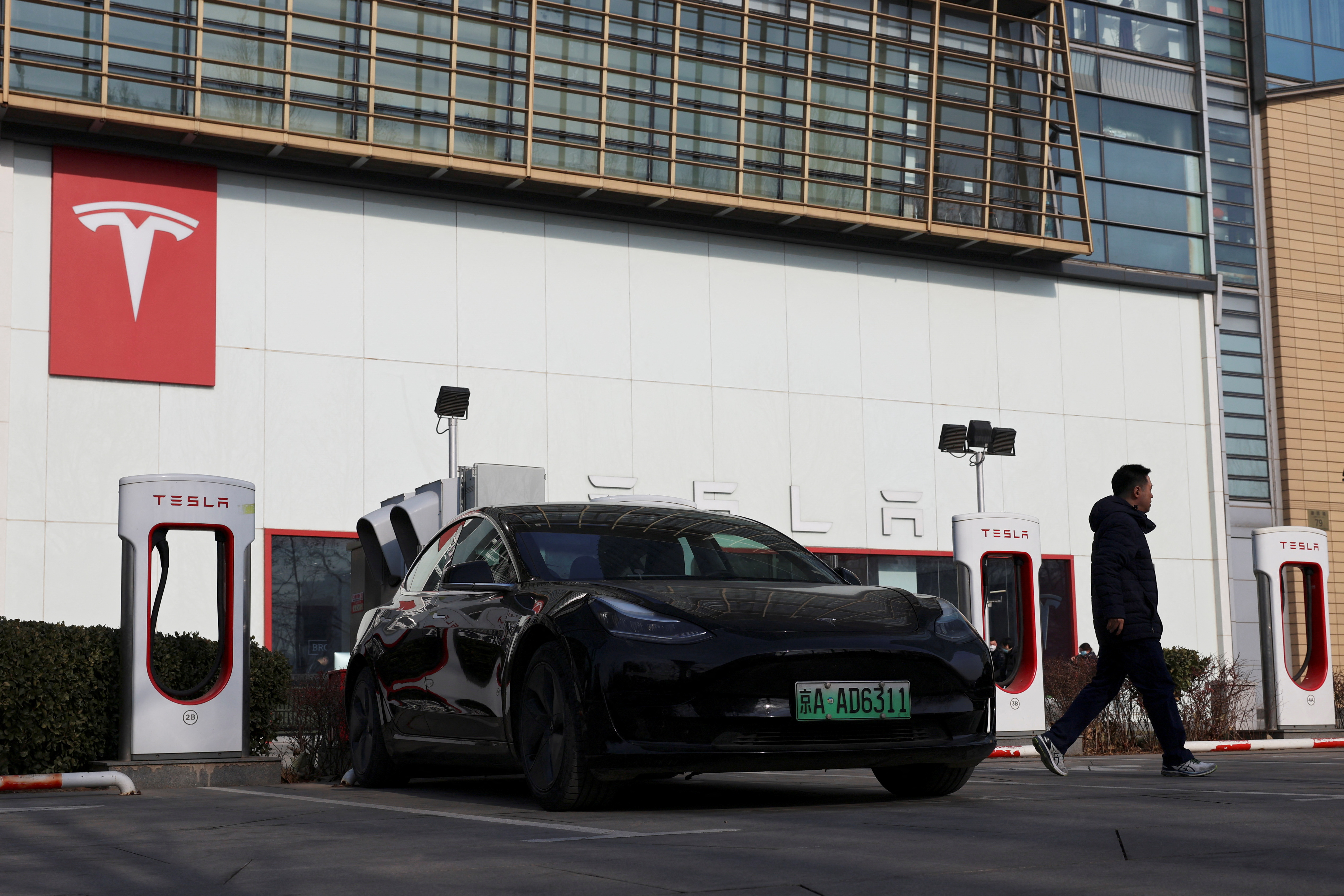

- Company Tesla Inc Follow
- Company BYD Co Ltd Follow
Sign up here.
Reporting by Qiaoyi Li, Brenda Goh, Miyoung Kim and Hyunjoo Jin in San Fracisco; Editing by Louise Heavens, Mark Potter and Daniel Wallis
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

China's consumer prices rise for third month, factory deflation persists
The numbers suggest resilient domestic demand despite a shaky economic recovery.

More From Forbes
Global top 10 best-selling smartphones: all from apple, samsung.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Global best-selling smartphones for Q1 2024
Every single one of the top ten best-selling smartphones globally is from one of just two companies: Apple and Samsung. Counterpoint Research just released its report on the top ten best-selling phones, and it’s a pretty familiar story from last year: Apple and Samsung cleaned up.
One change: people are spending more for iPhones, with Apple’s pricy Pro line growing to represent half of all iPhone sales so far this year, up from just 24% in 2023. It’s not just the Pro models that are doing well: Apple’s bigger Max models are also cleaning up, a sign that people increasingly want larger smartphones, says Counterpoint.
Here are the top 10 best-selling models of smartphones globally for Q1 2024, along with the percentage of total smartphone sales they captured:
- iPhone 15 Pro Max: 4.4%
- iPhone 15: 4.3%
- iPhone 15 Pro: 3.7%
- iPhone 14: 1.9%
- Galaxy S24 Ultra: 1.9%
- Galaxy A15 5G: 1.5%
- Galaxy A54: 1.4%
- iPhone 15 Plus: 1.3%
- Galaxy S24: 1.0%
- Galaxy A34: 1.0%
In the same quarter a year ago, Apple also captured the top four global best-selling spots.
Samsung’s high-end Galaxy S24 Ultra also did well, just as Samsung unseated Apple as the phone maker shipping the most units globally.
“The strong performance of the S24 series can be attributed to Samsung’s early refresh of the series, and its efforts in generative AI (GenAI) technology,” Counterpoint says . “The S24 series was the first to reach the market with GenAI features and capabilities, allowing users to create unique content and experience a new level of interaction with their smartphones.”
New FBI Warning As Hackers Strike Email Senders Must Do This 1 Thing
Baby reindeer real martha reveals identity in photo with piers morgan, 2 obvious signs of workplace gaslighting from a psychologist.
The downside of people choosing bigger, better, and more expensive phones: they’re also holding on to those phones for longer, and not upgrading as quickly. For Apple, Samsung, and other smartphone manufacturers, that means fewer sales per year even as cost per unit goes up.
That said, however, Q1 2024 also saw the highest smartphone revenue of any first quarter in history as the global smartphone market grew 6% to hit almost 300 million units shipped, Counterpoint reported just three days ago.
There’s clearly still a market for lower-end and less expensive phones: Apple’s iPhone 14 was the fourth-highest-selling model on the planet, and Samsung’s Galaxy A34 and A54, plus A15 5G, joined its S24 and S24 Ultra model in the top ten.
As selling smartphone units gets harder, Apple is transferring some of its focus to better and more valuable services, which people buy regardless of whether they have a new phone or not. In its recent quarterly earnings report, Apple beat forecasts of $23.1 billion in services revenue, hitting $23.9 billion to go along with a flat quarter of $46 billion of revenue from iPhone sales.
That flat quarter is somewhat concerning, especially given that Apple’s new sales in the U.S.—traditionally a strong market for the company—hit the lowest point in six years last quarter.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Tesla is headed for a new growth phase as Elon Musk is finally the 'adult in the room,' Wedbush says
- Tesla is back on track as Elon Musk is finally acting like the "adult in the room," Wedbush said.
- Dan Ives pointed to Tesla's latest earnings call, in which the firm issued firm guidance on its strategy.
- Rolling out a low-cost EV next year will be key to Tesla's growth, he said.

Tesla stock could be headed for better days, thanks to Elon Musk finally stepping up as the "adult in the room" to calm investors as the company battles an array of headwinds, according to Wedbush Securities analyst Dan Ives.
Ives pointed to Tesla's first-quarter earnings call on Tuesday , during which Musk issued firm guidance on the electric vehicle maker's strategy going forward.
In particular, the company reiterated its guidance on the Model 2, a lower-cost electric vehicle that's set to roll out next year and has been eagerly awaited by Wall Street to help juice sales as demand wanes. The cheapr model will be key to Tesla's success, which will be centered on sales volume over the near term, Ives said.
"Last night in a much needed conference call Elon Musk finally stepped up as the adult in the room and laid the foundation for Tesla's growth strategy with most importantly a lower cost vehicle now slated for 2025 production and delivery," Ives said in a note on Wednesday. "We believe the next wave of the Tesla growth story and autonomous vision is now forming and that is what we are focused on for our bullish investment thesis looking ahead."
Those bullish catalysts come amid a "dark" time for Tesla, with the company battling what Ives described as a "Category 5 storm" as it faces weak demand and growing competition, especially in China. Tesla's first-quarter results were a "disaster," Ives added, though investors were expecting that after the company reported its lowest sales in two years .
Despite near-term headwinds, Tesla is on a good track over the long run, Wedbush said. The company has a "golden vision" surrounding its full self-driving technology, which will be key to Tesla's strategy over the next decade, Ives added.
Wedbush maintained its outperform rating on the stock, but lowered the price target from $300 to $275 a share, implying a 90% upside from Tuesday's closing price.
Tesla stock surged in early trading on Wednesday, despite the company missing its revenue goal by nearly $1 billion over the last quarter. The stock was up 11% in early Wednesday trading.
- Main content
2 Chinese EV companies seem to be ganging up on Elon Musk's Tesla
- EV company Nio is launching a new affordable EV brand in China.
- Competitor BYD will reportedly supply batteries for the new range, which will compete with Tesla's Model Y.
- The alliance between the two companies will likely intensify pressure on Tesla in China.

Two of Tesla's biggest rivals in China are joining forces in yet another blow to Elon Musk .
Local EV giant Nio is launching a new affordable EV brand that will compete directly with the Model Y in China — and it has reportedly turned to Tesla rival BYD to provide batteries for one of these new EVs, according to a Reuters report .
Three sources with knowledge of the matter told Reuters that BYD has agreed to provide batteries for the new mass-market brand called Onvo, which Nio confirmeded to Reuters on Monday.
BYD will reportedly provide a small battery pack for one version of the Onvo EV, with Chinese battery maker CALB supplying a larger 85-kilowatt-hour battery pack.
Nio disputed the report, describing it as "inaccurate" in comments to Reuters.
Business Insider contacted BYD and Nio for comment but didn't immediately hear back.
Related stories
Nio, known for its battery-swapping technology , is set to unveil the first Onvo vehicle at the end of the month and is also planning a second smaller EV that will sell in Europe for under $30,000, per Reuters.
It marks a strategy shift for the EV startup, which has previously focused on the premium market , and it comes as it faces fierce competition in China.
The alliance between Nio and BYD will likely intensify pressure on Elon Musk in China, where Tesla sales have slumped amid brutal competition for EVs.
Deliveries from Tesla's Shanghai factory dropped 18% in April from a year ago, according to preliminary data from China's Passenger Car Association reported by Bloomberg .
The move poses a fresh challenge to Musk as he embarks on a shake-up at Tesla.
The automaker is simultaneously trying to secure EV dominance in China and expand its autonomous driving operations — all while slashing its workforce with ongoing job cuts .
Musk secured a big win in a surprise trip to Beijing last month, sealing a vital deal with Chinese tech giant Baidu that moved the automaker closer to rolling out its Full Self-Driving technology in the country.
The Tesla CEO is now reportedly eyeing up plans to deploy the company's forthcoming robotaxis, which the company plans to unveil in August , to China.
Once again, however, he is likely to face stiff competition from BYD and Nio, who are developing their own driving assistance software.
Watch: How did Tesla's bulletproof Cybertruck become so expensive and so delayed?
- Main content
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
China’s Electric Cars Keep Improving, a Worry for Rivals Elsewhere
More capable autonomous driving is just one way Chinese automakers are threatening to pull ahead — their E.V.s are also becoming bigger and roomier.

By Keith Bradsher
Reporting from Beijing
Automakers in China are building a new generation of bigger, more technologically advanced and competitive electric cars, threatening to leap further ahead of their global rivals as they step up exports around the world.
The dozens of car companies operating in China plan to put 71 new battery electric models on sale this year. Many new models have taller hoods for a bolder appearance and more storage space. The cars have bigger tires that improve braking. The seats are thicker and more comfortable. The batteries are ever smaller, more powerful and quicker to recharge.
The changes are aimed at making the cars even more appealing for customers in China and more competitive abroad. Along with plug-in hybrid cars, battery electric cars are taking sales away from gasoline-powered cars and their manufacturers.
China is also moving ahead with the technology and regulations for self-driving cars. The authorities approved data security arrangements this week for more capable autonomous vehicles. They approved cars from Tesla, the American electric vehicle company that also builds and sells cars in China, as well as five Chinese manufacturers, including BYD, Tesla’s principal global rival , and Nio, a longtime player in China’s auto sector .
The approvals show the Chinese government’s eagerness to push the development of self-driving vehicles, which are widely seen as central to future competitiveness in the car industry. The technology is more compatible with battery electric cars than with plug-in hybrids or gasoline-powered cars, and Chinese companies are trying to catch up with Tesla, the leader in these systems.
In the United States, Tesla’s so-called Autopilot feature has been the subject of a series of government safety investigations. But in China, regulators and the general public have tended to see the technology as safer than relying on human drivers.
Chinese automakers have been investing heavily in driver-assistance software. An electric car “is becoming a robot on wheels,” said Frank Wu, the vice president of design at Jiyue. The company is a joint venture of Zhejiang Geely, a Chinese automaker, and Baidu, one of China’s main artificial intelligence companies and Tesla’s partner in its self-driving efforts in China.
Better batteries and falling costs underpin China’s push in electric cars. CATL, based in southeastern China and the world’s largest manufacturer of electric car batteries , announced last week at the Beijing auto show that a 10-minute charge of its newest battery would give a range of 370 miles. A 30-minute full charge would give a range of 620 miles, the company said.
Achieving these distances involves extremely high-precision chemistry and engineering and “putting each nano-particle in the right place,” said Gao Huan, the chief technology officer of CATL’s electric car business.
The advances have meant automakers can use smaller batteries, freeing up space in cars’ interiors, or they can keep the battery the same size and achieve greater range.
Much of the extra space is going into larger back seats with more legroom.
“We’re going to put more focus on the backseat — we want to make it more appealing,” said Wang Tan, the general manager of design at XPeng Motors , a Chinese electric car manufacturer.
Manufacturers of electric vehicles used to put a priority on keeping cars as light as possible, because weight is what mostly matters for how far a car can go before needing a recharge. But more powerful batteries now allow electric vehicles to be taller and heavier.
Bigger front ends create a luxurious appearance that taps into many buyers’ admiration of sport utility vehicles, said Kris Tomasson, vice president of design at Nio.
“A higher front has that prestige,” he said.
Chinese automakers are also embracing designs with more edges, like a blue-green Denza Z9GT sedan displayed at the show by BYD. They are shifting away from lightweight but costly aluminum and building cars with a higher proportion of slightly heavier but cheaper steel alloys.
Aluminum body panels need to be more curved and do not allow for the sharper lines possible with a return to steel, said Stefan Sielaff, Geely’s vice president of global design. The effect is to make the cars more visually striking as automotive fashions shift away from the rounded shapes on previous electric cars.
Customers overseas as well as in China are getting pickier. Many are buying plug-in hybrids instead of cars powered only by batteries, although the markets for both are still growing in China.
Not all the electric cars at the Beijing show are bigger and roomier. Xiaomi, a Chinese producer of inexpensive smartphones, displayed its first electric car, the SU7 sports sedan. The tech company has made a move into the car market that Apple has mulled for many years without undertaking.
The SU7 looks almost identical from the outside to a Porsche Taycan electric car. But it costs less than a fifth of a Taycan, which ranges in China from $140,000 to $275,000.
Lei Jun, the chief executive of Xiaomi, was followed by a crowd of admirers as he walked around the auto show.
He exuded confidence in a speech at the SU7 introduction while still expressing worry about one rival. “Except Tesla, there seems to be hardly anyone better than us,” he said.
Chinese auto executives consistently express a mixture of respect and fear of Tesla, an automaker that did not introduce any new cars at the show. Last week, Tesla announced a 9 percent fall in sales and a 55 percent drop in profits in the first quarter of this year, and plans to lay off more than a tenth of its worldwide employees, or 14,000 people.
Long-established Western automakers, by contrast, lag in autonomous driving and are struggling to catch up in electric cars.
General Motors and Ford Motor have lost much of their market share in China over the past five years. Ford introduced the most-talked-about car at the Beijing auto show in 2020 , the Mustang Mach-E electric car. But administrative problems led to more than a year of production delays, and public interest evaporated.
Ford decided this year to emphasize very different Mustangs, equipped with hulking five-liter V-8 gasoline engines and four exhaust pipes.
Bill Russo, a former chief executive of Chrysler China who is now an electric car industry consultant in Shanghai, said Tesla had emerged as the sole strong global contender from the United States in the electric vehicle market.
“If they ever died, the whole E.V. market dies with it in the United States,” he said.
Established companies in Europe also face formidable challenges. China’s electric car exports to Europe are climbing, prompting a European Union investigation into whether they are unfairly subsidized.
Ralf Brandstätter, the chief executive of Volkswagen China, called for Chinese manufacturers to buy car parts in Europe and assemble them there using European workers.
“Then they have to handle a European labor force, European enterprises, and they have to compete in the same environment as we are competing,” he said. China has used steep tariffs and other measures to require that multinationals make cars in China for the Chinese market.
Chinese E.V.s are going next to the United States.
Geely is exporting its Polestar 2 to the United States from China, and paying a 27.5 percent tariff to do so. It is also beginning to export its new Polestar 3, before a planned shift of production to an assembly line being completed this summer in South Carolina.
Li You and Joy Dong contributed research.
Keith Bradsher is the Beijing bureau chief for The Times. He previously served as bureau chief in Shanghai, Hong Kong and Detroit and as a Washington correspondent. He has lived and reported in mainland China through the pandemic. More about Keith Bradsher
Steward files for bankruptcy, leaving its eight Massachusetts hospitals in limbo
Hospitals will stay open as company restructures debt under court supervision.
Steward Health Care, which once trumpeted its community hospital system as an accessible low-cost alternative to Boston’s medical goliaths, filed for bankruptcy protection early Monday morning.
Under Chapter 11 of the US bankruptcy code, Steward — which expanded nationally before falling into a deep financial crisis — will become a “debtor in possession,” continuing to operate its 31 hospitals in eight states while it seeks to restructure its debt under court supervision. Steward has eight hospitals in Eastern Massachusetts, though its Norwood Hospital remains closed following a flood.
“Steward does not expect any interruptions in its day-to-day operations, which will continue in the ordinary course throughout the [bankruptcy] process,” it said in a news release posted at 3:27 a.m. “Steward’s hospitals, medical centers and physician’s offices are open and continuing to serve patients and the broader community and our commitment to our employees will not change.”
Advertisement
As part of the bankruptcy process, Steward said it is “finalizing the terms” of $75 million in new financing from Medical Properties Trust, an Alabama real estate company that bought its Massachusetts hospital buildings in 2016. Steward said in a release it expects to receive $225 million more if it meets unspecified conditions acceptable to the hospital landlord, however on Monday evening, MPT said in a release it had not committed to any more financing beyond the $75 million.
The filing said Steward’s board named John Castellano, managing director of New York consulting firm AlixPartners, as chief restructuring officer, managing the company’s bankruptcy process. It said Steward had more than 100,000 creditors. It listed the company’s liabilities as between $1 billion and $10 billion, and its assets in the same range.
Steward filed in US Bankruptcy Court in Houston, after missing a payment deadline from a consortium of private credit firms that provided a loan of about $600 million last year, followed by a second “bridge” loan of $150 million in January.
The company said it was forced into bankruptcy because of a delay in a plan to sell its nationwide physicians group, called Stewardship Health, which would have brought additional capital to pay off its lenders.
It also blamed “insufficient reimbursement” from Medicare and Medicaid, the federal health insurance programs for seniors and low-income residents, and higher costs of labor and medical supplies. However a recent analysis showed that Steward hospitals are paid the same as if not better than many Massachusetts hospitals.
“Steward Health Care has done everything in its power to operate successfully in a highly challenging health care environment,” chief executive Ralph de la Torre said in a statement.
The fate of the hospitals’ hundreds of thousands of patients, and its nearly 16,000 employees in Massachusetts, will be determined by a process in which Steward’s lenders, deemed secured creditors, will hold an interest in the system as collateral. Some Steward hospitals have already seen employee departures and service cuts. Good Samaritan temporarily closed its Brockton cancer infusion center last month.
In a hastily called press conference Monday morning, Governor Maura Healey and other state officials stressed the continuity of hospital care while acknowledging there could be some “disruptions or inconveniences.” The governor said she hoped bankruptcy would clear the way for “getting Steward out of Massachusetts” while offering transparency about the company’s debts and liabilities.
“One of the good things about bankruptcy is that Steward and its CEO and its management team will no longer be able to lie,” Healey said, accusing them of “greed and mismanagement.”
State officials launched a public-facing Steward Health Care Resources website . The state also opened a patient hotline at 617-468-2189.
In bankruptcy court, a US trustee working for the Justice Department will appoint a panel of unsecured creditors, from staffing contractors to medical supply firms, who will negotiate with Steward and secured creditors on how to resolve its debts.
De la Torre, in a letter to Steward employees, took no responsibility for the hospital system’s financial problems, blaming inflation and a tough business environment for hospitals.
He acknowledged “the term ‘bankruptcy’ can raise some questions,” adding, “We fully expect that there will be some distracting local and media commentary as a result of this announcement.”
Independent bankruptcy experts said Steward will be required to come up with a plan that could involve raising new capital and replacing management, in addition to selling its hospitals.
The plan would have to be filed within 120 days and approved by the bankruptcy judge, they said. If that doesn’t happen, other parties — including the state of Massachusetts — could submit alternative plans to reorganize the hospital system and let it emerge from bankruptcy.
“Getting into bankruptcy is easy,” said D. Ethan Jeffery, an attorney for Boston law firm Murphy & King, who has represented debtors, trustees, and creditors in Chapter 11 cases. “Getting out is the trick.”
State Attorney General Andrea Campbell said she would ask the court to name an ombudsman to watch out for the interest of patients.
While the state has a clear interest in keeping the hospitals open, and preventing a patient influx to other resource-strained hospitals, its role in the bankruptcy process will initially be limited.
Last week, state officials activated a command center to manage the fallout on the Massachusetts health system from the anticipated breakup of Steward’s system.
In a statement, the Massachusetts Nurses Association and health care workers union 1199SEIU said that the state should use the bankruptcy process to protect health care assets.
“The bankruptcy declaration should only embolden the administration, the legislature, the healthcare industry, and all those who value the health of our communities to immediately take whatever steps are needed to ensure the preservation of these facilities and the safe transition to more stable and responsible not for profit ownership,” the unions said.
Steward operates two Boston hospitals, St. Elizabeth’s Medical Center in Brighton and Carney Hospital in Dorchester. It also runs Good Samaritan in Brockton, Holy Family in Methuen and Haverhill, Morton Hospital in Taunton, Nashoba Valley in Ayer, and Saint Anne’s in Fall River.
Steward-operated Norwood Hospital was temporarily shut down because of flooding in 2020. A rebuilding effort stalled earlier this year when contractors halted work, saying they hadn’t been paid.
Most of the hospitals were formerly part of the Caritas Christi Health Care, a Catholic system run for decades by the Boston Archdiocese. Steward, backed by private equity firm Cerberus Capital Management of New York, acquired the Caritas hospitals in 2010, converting them into for-profit institutions before launching a national expansion.
Under the bankruptcy procedure, Steward will likely be obliged to disclose far more detailed financial information than it has in the past. The company has not publicly filed financials since 2020, when Steward Health Care System reported a $407 million loss.
Court filings will also shine a spotlight on the multimillion-dollar rent obligations Steward hospitals have incurred to MPT, the real estate investment trust that bought the Massachusetts hospital buildings in 2016 for $1.2 billion. In 2021, Steward paid out a $111 million dividend to equity owners, including de la Torre , according to a lawsuit filed against the company by a California medical staffing firm.
Steward’s cash crunch came to light in January when MPT disclosed that the health system hadn’t been paying full rent for months. The company, which moved its headquarters from Boston to Dallas in 2018, has also been sued by at least two dozen vendors alleging they weren’t paid for supplies and services .
One big question hovering over the future of the hospitals is whether any new operators would inherit the rents Steward agreed to pay MPT, a major disincentive for would-be buyers of its hospitals.
Another question is how the bankruptcy will affect Steward’s plan to sell its doctors network, Stewardship Health, to the Optum unit of insurance giant UnitedHealth.
Before the bankruptcy, Steward had been counting on the transaction to help pay off lenders. But a state review process won’t formally begin until Steward and Optum finalize their purchase agreement and submit it to the Health Policy Commission, and it could take as long as nine months.
Regulators from other agencies, including the Massachusetts attorney general, the Federal Trade Commission, and the US Justice Department, were also expected to review the deal.
Robert Weisman can be reached at [email protected] . Jessica Bartlett can be reached at [email protected] . Follow her @ByJessBartlett .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Market share represents the percentage of an industry or market's total sales that is earned by a particular company over a specified time period. Market share is calculated by taking the company ...
Market share is the percentage of an industry's sales that a particular company owns. Essentially, it is the share of your business's total industry revenue from selling your products and services. Businesses with larger market shares are industry leaders and competition for smaller companies. Suppose consumers buy 100 T-shirts, and 70 are from ...
The market share is the proportion of the total sales in a specific industry attributable to a particular company. The formula to calculate market share divides a company's sales by the total sales of the industry across a given period. The relative market share compares a company's market share to its market leader, expressed as a percentage.
What is Market Share? Market share refers to the portion or percentage of a market earned by a company or an organization. In other words, a company's market share is its total sales in relation to the overall industry sales of the industry in which it operates.. Say, for example, the purchasing activity of consumers as a whole is 100 tubes of toothpaste, and a certain toothpaste maker sells ...
Market share is a critical component of the Business Model Canvas and a key indicator of a company's competitive position within its industry. Understanding market share can help a company identify opportunities for growth and innovation, and develop effective strategies for increasing its market share in a sustainable manner.
SOM = SAM x Market share %. SOM = 4,500,000 x 1% = 45,000. The obtainable market share forms the basis of the revenue projection in the business plan financial projection. It is therefore important that the estimate of the market share is supported and justified by the marketing plan. The SOM is not normally calculated using a bottom up approach.
Step 4: Calculate market value. You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value. A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the ...
Step 1: Combine top-down and bottom-up research. To build more focused and defensible total market opportunity estimates, combine aggregate competitor sales data and industry forecasts along with more specific, "bottom-up" data reflecting the customer base dynamics of the product or service. This approach enables product managers to create ...
A company's market share is the percentage it controls of the total market for its products and services. ... A business model is a company's profit-making plan which defines the products or ...
A look through HBR's archives shows that business thinkers use the concept of a "business model" in many different ways, potentially skewing the definition. Many people believe Peter Drucker ...
A good business model begins with an insight into human motivations and ends in a rich stream of profits. Subscribe Sign ... Earn badges to share on LinkedIn and your resume. Access more than 40 ...
CAPM. It is a model to predict a business's future and expansion or investment plans. It is a model used to calculate an investment's expected return. It is the primary model from which various other business models are designed. It is a market model used in corporate finance, also called the financial model.
Per Figure 5, Domino's grew its share of the global QSR market from 1.1% in 2012 to 1.6% in 2019. A strong business model positioned the company to benefit when other businesses were retreating ...
C] Revenue Outlook. For the full year, revenue is expected to increase by 9.3% from $31.9 billion in 2018 to $34.8 billion in 2019, and further by 4.7% to $36.5 billion in 2020. Higher revenue is ...
Let's get to know a little more about the Starbucks business model. Contents. A brief history of Starbucks ... on the stock market in mid-1992, with revenue of $73.5 mi and a market value of $271 mi. Four years after that, its first store outside North America was opened in Tokyo. ... Co-branding could increase its market share; Price ...
The global hotel industry comprises approximately 15.9 million rooms (o/w Marriott's market share is around 7%), broadly segmented into branded (multiple hotels under the same brand) and ...
Market creators offer platforms for developing transactions and exchanges, enabling buyers and sellers to meet in virtual places. The diffusion of the internet has favoured the separation of markets from physical spaces. Typical examples are eBay and Etsy. Market creators make money by charging a fee for each transaction on their platform, or ...
3. Stars: Products in high-growth markets with high market share. 4. Cash cows: Products in low growth markets with high market share; I find this isn't so applicable in the online marketing world for small and medium businesses - it's more of a Big Business corporate strategy model. See Annmarie's post on the BCG Matrix model for more details. 5.
The Target business model relies on a multilateral sales system, including retail, online, and leasing sales, as well as credit card fees. Regarded as the seventh-largest retailer in the United States of America, Target was established in 1962 with its headquarters in Minneapolis, Minnesota. The company is a big box department store in America ...
Some of its main competitors include Unilever, Coca-Cola, PepsiCo, and Kraft Heinz. These companies also offer a wide range of products and strive to capture market share in the industry. Lastly, conducting a SWOT analysis of Nestle reveals its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Oct 10, 2023. Financial technology has made its way into most aspects of the market. Redtail is the CRM software with the highest market share in all groups, beating out the others by a wide ...
Its Model 3 has become the world's best-selling all-electric vehicle model. ... Business information on 100m+ public and private companies ... Estimated U.S. market share held by selected ...
U.S. automaker Tesla sold 62,167 China-made electric vehicles in April, down 18% from a year earlier, lagging the broader market's surge, China Passenger Car Association (CPCA) data showed on Tuesday.
There's clearly still a market for lower-end and less expensive phones: Apple's iPhone 14 was the fourth-highest-selling model on the planet, and Samsung's Galaxy A34 and A54, plus A15 5G ...
Wedbush maintained its outperform rating on the stock, but lowered the price target from $300 to $275 a share, implying a 90% upside from Tuesday's closing price.
Two of Tesla's biggest rivals in China are joining forces in yet another blow to Elon Musk.. Local EV giant Nio is launching a new affordable EV brand that will compete directly with the Model Y ...
Tesla's stock gained more than 6% on Wall Street in pre-market trading, while Baidu's shares closed up 2.4% on Monday in Hong Kong. Tesla shares have fallen 32% so far this year. Competitive ...
General Motors and Ford Motor have lost much of their market share in China over the past five years. Ford introduced the most-talked-about car at the Beijing auto show in 2020 , the Mustang Mach ...
Steward trumpeted its model as a low-cost alternative to Boston's medical goliaths before expanding nationally and falling into a deep financial crisis.