- Class 12 Commerce
- Class 12 Commerce Projects
- Class 12 Business Studies Projects

Class 12 Business Studies Project
Class 12 Business Studies project in the principle of management is one of the important topics for business studies. However, a few students would be apprehensive about how and what to prepare a project. This dilemma of how to accomplish the project work drives to an issue of copying projects from peers. It is a general issue where students weigh project work as a burden and do not pay attention to how to prepare it. If you are confronting a similar obstacle at the beginning of given project work. The best thing, to begin with, is a sample project work.
Download Free PDFs of Business Studies Projects for Class 12:
The project for Business Studies Class 12 will undoubtedly assist all those students who really want to have a summary of what a project for class 12 looks like. It will completely answer all your questions on what are the different things we should contemplate while preparing a Business Studies project. The whole project work is of 20 marks. To be well aware of the entire Business Studies syllabus for class 12, click here for the Business Studies Syllabus Class 12.
Additionally few tricks and tips to prepare Business Studies Project Class 12 are given below.
1. Handwritten TOC (Table of Content).
It is important for any students to understand that the table of content for Business Studies Project for Class 12 should be written by hand and not typed or printed.
2. Distinct Handwriting
Content written by hand must be clear and neat, so the examiner can read the content properly. A neat project can secure students excellent marks.
3. Submit in Spiral Bound
Make sure that the project is submitted neatly attached in a spiral-bound book.
4. Project Format
The formatting of a project should be in a file set up.
5. Size of the paper
The overall project has to be hand-written and the size of the paper should be A4.
6. Check Notes Alignment
Project notes have to be written only on the science project paper, on the ruled side and not on the blank pages.
7. Headers
Leave the same portion margin on the Bottom, Top, left, and right of the project page.
8. Number each Pages
The entire project needs to have numbers.
9. Tables and Numbers
- The entire mentioned tables and numbers must be arranged in the middle of the page, categorized with the numbers, titles, and required labels.
10. Classification of the Project
The outer and the first cover of the project should have the title/heading, along with student information including school name and the year.
- Acknowledgement
- Certificate (if you have any)
- Table of contents
- Topic and Introduction with a suitable heading
- Newspaper cuttings (If Any)
- Summary/Conclusion of the project
- Bibliography
- Teachers Remarks and Observation.
Learning Outcomes of Business Studies Project for Class 12
The learning results recognise the important areas of Class 12 Business Studies Projects’ learning of the subject. Four (4) learning outcomes are clearly explained: knowledge application, communication, collaboration and independent learning.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S for more project work for Class 12, Business Studies Important Questions , question papers, sample papers, syllabus and Commerce notifications.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Udaan Programs
- Udaan Webinar
- IBPS SO LAW
- Civil Judge (Pre+Mains)
- Hotel Management
- CAT & OMETs
- Jaipur [Bapu Nagar]
- Jaipur [Vaishali Nagar]
- Jaipur [JLN Marg]
- Delhi (South Extension)
- Delhi (Pitampura)
- Delhi (CP Center)
- Delhi (Dwarka)
- Gurugram (Sector 27)
- Gurugram (Sector 50)
- Mumbai (Andheri)
- Mumbai (Navi Mumbai)
- Mumbai (Thane)
- Chandigarh Sector 36D
- Chandigarh Sector 8C
- Lucknow Hazratganj
- Lucknow Aliganj
- Jaipur (Bapu Nagar)
- Jaipur (Vaishali Nagar)
- Gurugram (Sector 14)
- Chandigarh 36D Sector
- Chandigarh 8C Sector
- Jaipur[Vaishali Nagar]
- Navi Mumbai
- Lucknow [Aliganj]
- Lucknow [Hazratganj]
- CUET Law 2024
- IPMAT Indore
- IPMAT Rohtak
- Christ University
- St. Xaviers
- Judiciary Study Material
- Chhattisgarh (CGPSC)
- Haryana (HJS)
- Uttar Pradesh (UP PCSJ)
- Rajasthan (RJS)
- Madhya Pradesh [MP]
- Delhi [DJS]
- Bihar [BPSC]
- Uttarakhand [UKPSC]
- Jharkhand [JKPSC]
- Himachal Pradesh [HPPSC]
- LegalEdge AISAT
- LegalEdge IST
- Judiciary Gold AIJSAT
- Judiciary Gold IST
- SuperGrads IPM AISAT
- SuperGrads IPM IST
- Supergrads CUET AISAT
- SuperGrads CUET IST
- SuperGrads CAT
- Creative Edge
- LegalEdge AIOM
- SuperGrads AICUET
- Judiciary AIOMC
- Supergrads IPM AIOM
- CreativEdge AIOM
Free Videos
- CLAT Free Videos
- UGC NET LAW
- RBI Grade B
- Uttarakhand
- Judiciary Notes
- Judiciary Videos
- KAUN BANEGA JUDGE
- Daily Current Affairs
- Weekly Current Affairs
- Monthly Current Affairs
- LegalEdge UG
- SuperGrads Webinar
- SuperGrads CUET Webinar
- Creative Edge Webinar
- Judiciary (Beginners)
- UDAAN Webinar
- Law School Blogs
- LAW Entrances
- Management Entrances
- CUET Exam [UG & PG]
- Design & Architecture
- LAW & Judiciary
- Management Exams
- CUET Exams [UG & PG]
- Design & Architecture Exams
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics 2024
Author : Palak Khanna
Updated On : March 22, 2024
Why Read This Article: Gain insights into the marking scheme, potential Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics CBSE, and best practices for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies projects to ensure optimal learning and good scores in project work.
As part of the holistic learning approach, the CBSE Class 12 Business Studies curriculum includes project wor k.
These projects enable students to apply theoretical concepts to real-world situations, fostering a practical understanding of business and commerce.
The board suggests a couple of Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics CBSE you can choose to work on your project that carries 20 marks in the final exam.
Let’s check the Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics CBSE suggested by the board of CBSE.
Download Free Study Material for CBSE 2024 by SuperGrads
Objective of CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics 2024
Following their completion of the Business Studies project work, students will be able to:
- Gain exposure to the operational environment in the field of business management and related services.
- Develop a practical approach by utilizing modern technologies.
- Inculcate critical abilities such as teamwork, problem-solving, time management, and the collection, processing, analysis, and synthesis of relevant data to arrive at insightful conclusions.
- Become actively involved in the study process and show off their independence-working skills.
- Make learning entertaining so you will remember it.
1689744675.webp)
Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics CBSE 2024
In order to give pupils a solid understanding of the concepts and procedures pertaining to business (trade and industry), as well as their interaction with society, the course in business studies is introduced at the senior school level.
Business is a dynamic process that combines human initiative, natural resources, and technology in a continually shifting international environment.
Project Work has been added to the Business Studies Syllabus for Classes XI and XII by the CBSE in order to help students better grasp the context in which a business functions and how it interacts with the social, economic, technological, and legal environment.
Choosing a relevant and engaging topic is essential for a successful project. Here are some potential topics for consideration:
CBSE business studies project class 12 on marketing management topics are as follows -
- CBSE business studies project for class 12 topics - Project One: Elements of Business Environment
- Topics for business studies project for class 12 CBSE- Project Two: Principles of Management
- Business studies marketing project topics for class 12 CBSE Project Three: Stock Exchange
- CBSE class 12 business studies project on business environment topics Project Four: Marketing
Check: Courses after 12th Commerce
Presentation and Submission of Project Report
At the end of the stipulated term, each student will prepare and submit his/her project report.
The following essentials are required to be fulfilled for its preparation and submission.
1. The total length of the project will be 25 to 30 pages.
2. The project should be handwritten.
3. The project should be presented in a neat folder.
4. The project report should be developed in the following sequence-
- The cover page should include the title of the Project, student information, school and year.
- List of contents
- Acknowledgements and preface (acknowledging the institution, the places visited and the persons who have helped).
- Introduction.
- Topic with a suitable heading.
- Planning and activities are done during the project, if any.
- Observations and findings of the visit.
- Conclusions (summarized suggestions or findings, the future scope of the study).
- Photographs (if any).
- Appendix
- Teacher’s observation.
- Signatures of the teachers.
- At the completion of the evaluation of the project, it should be punched in the centre so that the report may not be reused but is available for reference only.
- The project will be returned after evaluation. The school may keep the best projects.
Check: CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Syllabus
How to prepare for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Project 2024?
Preparing for the Class 12 Business Studies project involves a combination of research, organization, and presentation. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you effectively navigate this task:
Choose Your Topic Wisely
Select a topic that genuinely interests you. This will make the research process engaging rather than tedious.
Ensure the topic is relevant and aligns with the CBSE curriculum.
Understand the Project Objectives
Clearly define what you aim to achieve with the project. This will act as a roadmap throughout your work.
Check: Class 12 Business Studies Important Questions
Research Thoroughly
Use textbooks, online resources, libraries, and newspapers for your research.
When sourcing information from the internet, ensure the websites are credible.
If your topic requires, conduct surveys, interviews, or visit businesses.
Plan Your Structure
Begin with an introduction that outlines the purpose and significance of your study.
Clearly segment your project with headings and subheadings, such as objectives, research methodology, data analysis, conclusions, and recommendations.
Check: CUET Business Studies Syllabus
Data Collection and Analysis
Depending on the nature of your project, collect primary data (through surveys or interviews) and/or secondary data (from existing resources).
Use graphs, charts, and tables for a visual representation of your findings. This enhances clarity and makes the project visually appealing.
Drafting and Writing
Start by creating a rough draft. This helps you organize your thoughts and findings.
Keep your language clear and concise. Remember, the aim is to communicate your findings effectively.
Check: Class 12 Business Studies Sample Papers
Cite Your Sources
Always give credit to your sources of information. This avoids issues of plagiarism and showcases the authenticity of your work.
Practice Your Presentation
You'll likely need to present your project and undergo a viva. Familiarize yourself thoroughly with your content.
Prepare for potential questions that teachers might ask during the viva.

Review and Proofread
Before finalizing, review your work. Check for grammatical errors, ensure data accuracy, and see if the project flows logically.
Feedback Loop
It's always a good idea to have a peer, teacher, or mentor review your project. They might offer a fresh perspective or catch errors you missed.
Check: How to study Business Studies Class 12
Final Presentation
Use tools like PowerPoint for your presentation, if required.
Ensure that your written report is neatly bound and presented. First impressions do matter.
Check: Class 11 Business Studies Sample Papers
Be Ready for Feedback
After presenting, be open to feedback. This helps in learning and improving.
Tips:
Start early. Don't leave your project for the last minute. Spacing out your work will lead to better quality research and less stress.
Engage with the topic. A genuine interest will reflect in the quality of your work.
Business Studies equips individuals with skills that are applicable in a wide range of sectors and roles. The knowledge acquired often forms the foundation for successful careers in the dynamic world of business.
Marking Scheme of CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics 2024
The allocation of Marks for the CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Project is 20 Marks.
The marks will be allocated under the following heads:
Check: CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Viva Questions
Conclusion
The CBSE Class 12 Business Studies project is an opportunity for students to dive deep into the business realm and understand its nuances. Selecting a compelling topic and following the marking scheme not only secures good marks but also provides knowledge and insights into the world of commerce.
Download Your Free CBSE Prep Material
Fill your details
Recently Published
St Xaviers Application Form 2024: Check the steps for Registration Process
Updated On : May 16, 2024
IPMAT Answer Key 2024: Check your Answers
CUET Jamia Millia Islamia Eligibility Criteria 2024
Updated On : May 15, 2024
CUET DU Eligibility Criteria 2025
How to Ace Reading Comprehension for CUET 2024
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I choose a topic not listed in the CBSE guidelines?

Is it necessary to have primary data for the project?
Are group projects allowed?
Can I use digital tools for my project?
How do I prepare for the viva?
March 22, 2024
Online Coaching
Test Series
Trending Exams
- Architecture
- Career Counselling
Scholarship Tests
- Judiciary Gold
- Supergrads IPM
- SuperGrads CUET
- LegalEdge After College
Mentor Tips
- CLAT Prep Tips
- AILET Prep Tips
- IPMAT Prep Tips
- NATA Prep Tips
- NID Prep Tips
- Judiciary Prep Tips
- CAT Prep Tips
ABOUT TOP RANKERS
Toprankers, launched in 2016, is India’s most preferred digital counselling & preparation platform for careers beyond engineering & medicine. We envision to build awareness and increase the success rate for lucrative career options after 12th. We offer best learning practices and end-to-end support to every student preparing for management, humanities, law, judiciary & design entrances.
: +91-7676564400
Social Channels

- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Study Mumbai
ICSE, CBSE study notes & home schooling, management notes, solved assignments
Business Studies Projects: Class 12 CBSE
April 4, 2022 by studymumbai Leave a Comment

CBSE Class 12 students have to make a Business Project as part of their Class 12 Business Studies (BST) wherein they have to do literature review, gather data, make inferences and give conclusions.
Here’s how to create a Business Studies class 12 project (BST project) on various topics such as principles of management, elements of business environment, marketing management, principels of management, stock exchange, consumer protection, and more.
GET INSTANT HELP FROM EXPERTS!
Hire us as project guide/assistant . Contact us for more information
Marketing Management
Students can make projects Marketing Management, wherein they can choose any product on which they have to to conduct research about the various marketing aspects of the product.
You may choose products such as : Adhesives, Bathing Soap, Bread, Butter, Chocolate, Cheese, Coffee, Cosmetics, Cutlery, Eraser, Hair Oil, Handbags, Hair Dye, Inverters, Jeans, Jewellery, Lipstick, Microwave, Mobile Phones, Moisturizer, Music System, Newspaper, Noodles, Pencil, Sauces, Toys, Wallet, Washing Machine.
Elements of Business Environment
In case you intend to make a project on Elements of the business environment, here’s what you should inlcude:
- Changes in packaging for products like fruits and vegetables, plastic/wooden furniture, milk, reuse of packages, packages as a means of advertisement, etc.
- Changes in the patterns of export and import of different products.
- Effect of changes in the technological environment on employee behaviour.
- Impact due to anti-plastic campaigns.
- Social factors affecting acceptance and rejection of certain products (atta maker, dishwasher)
Principles of Management Project in Business Studies
For this Business Studies class 12 project, students should visit a departmental store, industrial unit, fast food outlet and see how Fayol’s General Principles of Management or F.W. Taylor’s Scientific Management Techniques applies to that busines sunit.
Stock Exchange
For this topic, students must inlcude various aspects of the stock market such as stock market trends, profit or loss calculation, talk about capital market, sources of business finance, along with other concepts used in stock market. Business Studies class 12 project should inlcude the following:
- Provide brief history of stock exchanges in India.
- Prepare a hypothetical portfolio with a sum of INR 100,000 in any 5 top companies over a period of 20 working days.
- Provide reasons for price fluctuations. For example, wars, strikes and accidents, political environment, spread of an epidemic, change of seasons, international events, etc.
- Find the value of the investments and update the portfolio (shown through various graphical representations).
Consumer Protection
Include the following:
- Define consumer protection
- Caveat Emptor to Consumer Protection
- Various ways for conumers to seek redressal
- Mention about Consumer protection act in India, Rights of consumers
Guidelines for Class 12 Business Studies project:
Here are the official CBSE guidelines for the Class 12 Business Studies project:
The Project must 25 to 30 pages long (handwritten).
Follow this specified format:
- Cover Page: Student information, School name and year
- Index (List of Contents)
- Acknowledgement and Preface
- Introduction
- Topic with a Unique Title/Heading
- List of activities and planning done to gather information about the project (If any)
- Observations from the places of visit
- Conclusions
- Photographs (if any)
- Teacher’s remarks
- Signature of the teachers
StudyMumbai.com is an educational resource for students, parents, and teachers, with special focus on Mumbai. Our staff includes educators with several years of experience. Our mission is to simplify learning and to provide free education. Read more about us .
Related Posts:
- Class 12 (CBSE): English Projects
- Digital Marketing: Case Studies, Strategies, Projects
- CBSE Class-10 Social Science
- CBSE Class-8 Social Science
- Class 6 German: CBSE / ICSE / IGCSE / IB
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
ICSE CLASS NOTES
- ICSE Class 10 . ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Class 8 . ICSE Class 7
- ICSE Class 6 . ICSE Class 5
- ICSE Class 4 . ICSE Class 2
- ICSE Class 2 . ICSE Class 1
ACADEMIC HELP
- Essay Writing
- Assignment Writing
- Dissertation Writing
- Thesis Writing
- Homework Help for Parents
- M.Com Project
- BMM Projects
- Engineering Writing
- Capstone Projects
- BBA Projects
- MBA Projects / Assignments
- Writing Services
- Book Review
- Ghost Writing
- Make Resume/CV
- Create Website
- Digital Marketing
STUDY GUIDES
Useful links.
- Referencing Guides
- Best Academic Websites
- FREE Public Domain Books
myCBSEguide
- Marketing Management class 12...
- Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE class 12 Business Studies Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE board exams and school based annual examinations. Class 12 Business Studies notes on chapter 11 Marketing Management are also available for download in CBSE Guide website.
CBSE Guide Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
CBSE guide notes are the comprehensive notes which covers the latest syllabus of CBSE and NCERT. It includes all the topics given in NCERT class 12 Business Studies text book. Users can download CBSE guide quick revision notes from myCBSEguide mobile app and my CBSE guide website.
12 Business Studies notes Chapter 11 Marketing Management
Download CBSE class 12th revision notes for chapter 11 Marketing Management in PDF format for free. Download revision notes for Marketing Management class 12 Notes and score high in exams. These are the Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter 11 in minutes. Revision notes in exam days is one of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days.
Download Revision Notes as PDF
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes CHAPTER – 11 Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
MEANING OF SOME IMPORTANT TERMS:
• Needs = basic human requirements. Essential items necessary or fundamental to human existence.
• Wants= desire for a particular product. Tend to be “satisfier specific”.
• Demand- willingness to buy is backed by purchasing power
• Utility – want satisfying power of a product.
• What can be marketed:
• A product = • bundle of utility not confined to physical products but can refer to other things of value such as services, ideas, place. It refers to anything that satisfies a need or want.
• may be tangible or intangible(i.e. goods and services)
• even people can be marketed • Customers= people or organizations that seek satisfaction of their wants. • “Marketers‟ = • Anyone taking a more active role in the process of exchange is called a marketer. Normally it is the seller. But in certain situations, it may also be the buyer. This may be in the situation of rare supply.
• Sellers as marketer are the deliverers or providers of satisfaction. They makes available products or services and offers them to customers with an intention of satisfying customer needs and wants. They can be divided into:
• Goods marketers (such as Hindustan Lever)
• Services marketers (such as Indian Airlines)
• Others marketing experiences (such as Walt Disney) or places (like tourist destinations). • Marketing activities =activities carried on by the marketers to facilitate exchange of goods and services between the producers and the users of such products. • Market is:
• Place where buyers and sellers meet and conduct buying and selling activities. It does not necessarily mean a geographical place(e.g. conduct of business thro telephone, mail or internet)
• The other ways in which this term is being used is in the context of a product market (cotton market, gold or share market), geographic market (national and international market), type of buyers (consumer market and industrial market) and the quantity of goods transacted (retail market and wholesale market).
• In the modern marketing sense, it refers to a set of actual or potential buyers of a product or service i.e. all customers who share a particular need or want and are able to buy the product (also referred to as target markets)
Important Features of Marketing
1. Needs and wants: Satisfaction of the needs and wants of individuals and organizations.
2. Creating a market offering: Complete offer for a product of service.
3. Customer value: greatest benefit or value for the money.
4 . Exchange mechanism: Exchange of products/services for money/for something of value to them.
Meaning and concept of Marketing Management
Marketing management means management of the marketing functions. It is the process of organizing, directing and controlling the activities related to marketing of goods and services to satisfy customers’ needs & achieve organizational goals.
The process of Marketing involves:
i. Choosing a target market
ii. Getting, keeping as well as growing the customer
• that is, ensure that the target customers purchase the firm‘s product, ensure that they keep their customers satisfied with the products and attract new customers so that the firm can grow.
iii. Create, develop and communicate superior values to the customers.
Functions of Marketing/Marketing activities
Gathering And Analyzing Market Information:
• systematic investigation of facts
• SWOT analysis
• Necessary to identify needs
• Decisions can be wrt. Identifying customer needs and wants, identifying buying motives, choice of a brand name, packaging and media used for promotion.
• Data is available both from primary as well as secondary sources.
Marketing planning : • Aim = to develop a complete marketing plan so that the marketing objectives can be achieved. • It also must specify the action programs . • E.g if a marketer aims at enhancing his market share in the country in the next three years, then his marketing plan should include various important aspects like plan for increasing level of production, promotion of products etc.
Product designing and development: • Involves decisions regarding the product to be manufactured and it‘s attributes such as its quality considerations, packaging, models and variations to be introduced etc.. • Done by anticipating customer needs and developing new products or improving existing products to satisfy these needs.
Standardization and grading: • Standardization = Process of setting certain standards for a product on the basis of its desired qualities. E.g. ISI mark for electrical goods. • Grading = Division of products into classes made up of units possessing similar features such as for agricultural products
Packaging and labeling: • Packaging‘ refers to designing a package (that is a wrapper or a container) for a product. • Packaging protects the products from damage , risks of spoilage, breakage and leakage. It also makes buying convenient for customers and serves as a promotional tool. • Labeling = designing a label to be put on the package. It may vary from a simple tag to complex graphics.
Branding • Whether to sell the product in its generic name or in a Brand name. • Helps in differentiation, builds customer loyalty and promote its sale. • Decision = whether each product will have a separate brand name or the same brand name to be used for all products.
Concepts & Philosophies of Marketing
1. PRODUCTION CONCEPT = In the earlier days of the industrial revolution, the number of producers were limited, → limited supply of industrial products → not able to match demand . So, anyone who was able to produce goods could easily find buyers for the same.
2. PRODUCT CONCEPT= With passage of time, the supply improved→ customers started looking for products that were superior in performance, quality and features.
3. SELLING CONCEPT= increase in scale of production→ competition among the sellers → Product quality and availability alone did not ensure survival as a large number of firms were now selling products of similar quality.
4. MARKETING CONCEPT : Implies that a firm can achieve its goals by identifying needs of the customer and satisfying them better than the competitors. Customer satisfaction is the precondition for realizing the firm’s goal and objectives,
5. SOCIAL MARKETING CONCEPT : Under this concept customer satisfaction is supplemented by social welfare. Some products bring harmful effect on environment so these should not be supplied. It pays attention to the social, ethical and ecological aspects of marketing. Raman, Joginder, John, Iqbal and Shreya are friends. They are operating different business. Each one has his/her own concept regarding operating their business. Raman believes in producing products at a large scale. Thereby decreasing the average cost of the products and selling it’s at a reasonable price.
Meaning and Concept of Marketing and Selling
Marketing is a wide term. It refers to a large set of activities of which selling is just one part. A marketer before making the sale does a lot of other activities such as planning the type, design of the product, the price and selecting the distribution outlets at which the same would be available.
Selling: refers to the sale of goods or service through publicity, promotion and salesmanship. The title of the product is transferred from seller to buyer. The entire focus in selling is to covert the product into cash.
Difference between Selling & Marketing
Marketing Mix
There are a large number of factors that affect marketing decisions. They can be classified as:
• Non-controllable factors and Controllable factors: To be successful, a firm needs to take sound decisions wrt controllable factors while keeping the environmental factors in mind.
To develop marketing tools, marketing managers use the above mentioned controllable factors and the set of marketing tools that a firm uses to pursue its marketing objectives in the target market is described as Marketing Mix. Success of a market offer will depend upon how well these ingredients are mixed to create superior value for customers and simultaneously achieve their sales and profit objective. Thus, an ideal marketing mix would need: • Producing satisfying products • Offered to buyers at a reasonable price • Conveniently available • About which communication is offered
Marketing mix refers to ingredients or the tools or the variables which the marketeer mixes in order to interact with a particular market.
11.8.1 Elements of Marketing Mix
The four main elements of marketing mix as classified by MCcarthy are:
A. Product B. Price C. Place/Physical Distribution D. Promotion
Elements/4 Ps of Marketing Mix
4. Place Mix: Physical distribution: Various decisions regarding distribution of products.
• Channels of distribution: Whether wholesalers, retailers are to be used or not.
• Physical movement of the products from producer to consumers.
• Storage, transportation, managing inventory (stock) etc.
i) Branding:
The process used to create a distinct identity of a product. It is the process of using a name, term, symbol or design individually or in some combination to identify a product.
Brand : Name, term, sign, design or some combination of the above used to identify the products of the seller and to differentiate them from those of competitors .
Qualities of a Good Brand Name
1. Short, easy to pronounce, spell and remember(Rin, Vim, Ponds)
2. Suggest product benefits and quality (Genteel, Boost)
3. Distinctive (Zodiac, Safari)
4. adaptable to packing or labeling requirements, to different advertising media and to different languages.
5. Versatile to accommodate new products(Maggi)
6. Capable of being registered and protected legally
7. Have staying power(should not get outdated easily.
Advantages of Branding-
Advantages to the marketers:
1. Enables product differentiation:.
• Distinguishes the firms products from that of its competitors, thus secures and controls its markets.
2. Helps in advertising and display programmes:
• Without a brand, the advertiser can only create an awareness about the generic product and not be sure of the sale of his brand.
3. Differential pricing:
• As when customers like and become used to a brand, they would agree to pay a little more for it than the competing product
4. Ease in introduction of a new product
minimizes selling costs – enjoys the reflected glory of the brand.
Advantages to Customers:
1. Helps in product identification:
• If customer is satisfied with a brand, he will not make a close inspection every time.
2. Ensures quality:
• deviation in quality, customers can have a recourse to the manufacturer/marketer. ↑ confidence and level of satisfaction of customers
3. Status symbol:
• Because of their quality, customers feel proud of suing them and so ↑ level of satisfaction of customers
2. (ii) Packaging: Act of designing and producing the container or wrapper of a product. Good packaging often helps in selling the product so it is called a silent salesman.
Levels of Packaging
1. Primary Package: refers to the product’s immediate container e.g. toffee in a wrapper, a match box.
2. Secondary Package : refers to additional layers of protection that are kept till the product is ready for use e.g. a Colgate toothpaste usually comes in a card board box.
Functions of Packaging
1. Product Identification : Packaging helps in identification of the product.
2. Product Protection: The main function of the packing is to provide protection to the product from dirt, insects and breakage.
3. Convenience: It provides convenience in carriage, stocking and in consumption.
4. Product Promotion: Packaging simplifies the work of sales promotion.
Advantages of Packaging
• Rising Standards Of Health And Sanitation – As chances of adulteration in such goods are minimized
• Self-Service Outlets – so some of the traditional role assigned to personal selling w.r.t promotion has gone to packaging.
• Innovational Opportunities – innovation on packaging used to market products e.g. tetra packs for milk.
• Product differentiation – colour, size, material etc of packaging makes a difference in perception of customers about the quality of the product.
3 . Labelling :
Labelling means putting identification marks on the package. Label is a carrier of information & provides information like – name of the product, name of the manufacturer, contents of the product, expiry and manufacturing date, general information for use, weight etc. Labels perform following functions:
1. Identify the product: It helps the customers to identify the product from the various types available. For example: We can easily identify a Cadbury chocolate from the various chocolates by purple colour of its label.
2. Describe the product and specify its contents:
5. Providing information required by law: There is legal compulsion to print batch no., contents, max retail price, weight/volume on all the products and statutory warning on the packet of cigarettes, “Smoking is injuries of health”: In case of hazard on/poisonous material appropriate safety warnings need to be put.
II P-PRICE MIX:
Meaning and concept of Price: Sum of values that consumers exchange for the benefit of having or using the product Price may therefore be defined as the amount of money paid by a buyer (or received by a seller) in consideration of the purchase of a product or a service
Normally expressed in monetary terms. Decisions include decisions wrt basic price, discounts to be offered etc
Factors determining price determination:
1. Pricing Objectives
(a) to maximise profits in the short term-tend to charge maximum price.
(b) Obtain large share of the market i.e., by maximising sales it will charge lower price.
(c) Firm is operating in the competitive market it may charge low price for it.
2. Product cost:
• Price should include all costs and also include a fair return for undertaking the marketing effort and risk.
• Includes costs of producing, distributing and selling the product.
• Costs sets the floor price – the minimum level / lower limit at which the product may be sold. • Price should recover Total costs (Fixed costs/overheads + Variable costs+ Semi-variable costs) in the long run, but in certain circumstances(introduction of a new product/entry into a new market) product price may not cover all the costs for a short while.
3. Utility and demand:
• Utility provided by the product and the demand of a product set the upper limit of price that a buyer would be willing to pay for a product.
• Buyers pay to the point where the utility of the demand is more than or eequal to the utility derived from it.
• Law of demand = consumers purchase more at a lesser price.
• Elasticity of demand = responsiveness of demand to change in prices of a product. Demand = elastic if a small change in price results in a large change in quantity demanded.
• If demand is inelastic, firm can fix higher prices.
4. Competition in Market : Prices of competitors need to be considered before fixing prices.
5. Government Policies: Products regulated by government pricing regulations need to be priced as per government policies.
III. P-Place Mix/Physical Distribution Mix
A set of decisions needs to be taken to make the product available to customers for purchase and consumption.
• The marketer needs to make sure that the product is available at the right quantity, at the right time and at the right place.
• It requires development of:
• Channels of distribution
• Physical distribution of products.
Components of physical distribution-
1. Order Processing: Accurate & speedy order processing leads to profit & goodwill & vice versa.
2. Transportation: Add value of the goods by moving them to the place where they are required.
3. Inventory control: Additional demand can be met in less time, the need for inventory will also be low.
4. Ware housing: Need arises to fill the gap between the time when the product is produced & time when it is required for consumption.
Channels of Distribution
• Includes a series of firms/ individuals/ people/institutions/merchants and functionaries who form a network which helps in the transfer of title to a product from the producer to the end consumer.
• They help to overcome time, place and possession gaps that separate the goods and services from those who need/want them from those who want them
Types of Channels:
Direct Channel — Manufacturer-Customer. Eg. mail order, internet, door to door selling.
Indirect Channel —
1. Manufacturer-Retailer-Customer.
Usually used for specialty goods like expensive watches, appliances, Cars( Maruti Udyog) etc.
2. Manufacture-wholesaler-Retailer-customer.
Usually used for consumer goods like soaps , salt etc.
3. Manufacture → Agent → Wholesaler → Retailer → Customer
Factors Determining Choice of Channels of Distribution
IV. P-Promotion Mix
Tools/Elements of Promotion Mix
1. Advertising: Most commonly used tool of promotion. It is an impersonal form to communication, which is paid by the marketers (sponsors) to promote goods and services. Common mediums are newspaper, magazine, television & radio.
Role or Importance of Advertising
1. Paid Form –sponsorer has to bear the costs of communicating with the prospective buyer.
2. Impersonality – no direct face to face contact between prospects and advertisers. Creates a monologue and not a dialogue.
3. Identified Sponsor –undertaken by an identified individual who makes the advertising effort and bears the costs of it.
4. Mass Reach – large number of people over a large geographical area can be reached.
5. Enhancing Customer Satisfaction And Confidence – creates confidence and prospective buyers feel more comfortable and assured about the product quality
6. Expressiveness – due to development in art, computer designs and graphics, special effect can be created that makes simple products and messages look attractive.
7. Economy- because of its wide reach, overall cost of advertising gets spread over a wide audience and per unit cost of reach ↓.
Objections against Advertising: Though advertising is one of the most frequently used medium of promotion of goods & services but it attracts a lot of criticism/objections against it, which are as follows: 1. Increased Product Price: Which is ultimately added to product cost, manufacturers pass this cost to ultimate customers. 2. Confusion to Customers: The number of advertisements shown for a single product having different brands confuse the customers and it becomes very difficult for them to make choice. 3. Encouraging sale of Inferior Products: In many cases some product features are over emphasized. 4. Advertisement of Bad Tastes: Events, models degrade the human dignity. 5. Undermines Social Values and Promotes Materialism: It induces the customers to buy more and more products. Because of emphasis on materialism, social relationships are distorted which brings social disorder. In the changed economic environment of globalisation, advertising is considered as an important tool of marketing. It helps a firm in effectively communicating with its target market, increasing the sale and thereby reducing the per unit cost of production. It is not a social waste rather it adds value to the social cause by giving a boost to production and generating employment.
2. Personal Selling Personal selling consists of contacting prospective buyers of product personally i.e face to face interaction between seller and buyer for the purpose of sale.
Features of the Personal Selling
1. Personal contact is established under personal selling.
2. Oral conversation.
3. Quick solution of queries.
4. Receipt of additional information.
1. Physical qualities: Tidy appearance, good posture, cheerful smile etc
2. Psychological qualities: good nature with Empathy and ego drive,
3. Technical quality: Full technical knowledge about the product,
4. Good communication skills – Polite, tactful, having good manners etc
5. Honesty,
6. Courtesy,
7. Persistent- must not give up as one additional argument can close a sale.
Merits of Sales Promotion:
1. Attention Value: Attract attention of people through use of incentives. 2. Useful In New Product Launch: Sales promotion tools induce people to break away from their regular buying behavior and try new products. 3. Synergy in Total Promotional Efforts: Sales promotion activities add to the overall effectiveness of the promotional efforts (advertising and personal selling) of a firm.
• Limitations Of Sales Promotion – if used frequently: a. Reflects Crisis: A firm that frequently relies on sales promotion activities may give the impression that it is unable to manage its sales and there are no takers for its products. b. Spoils Product Image: Consumers may feel that the products are not of good quality or are not appropriately priced.
1. Product Combination: Offering another product as gift along with the purchase of a product.
2. Istant draws and assigned gift: Scratch a card and instantly win a prize with the purchase of a TV, T. Shirt, Refrigerator etc.
3. Q uantity Gift: Offering extra quantity of the product e.g., Buy three LUX soaps and get one free.
4. Refunds: Refunding a part of price paid by customer on production of some proof of purchase. e.g Rs 2 off on presentation of empty pack of Ruffle lays
5. Sampling : Offer of free samples of the product to potential customers. Generally used at the time of introduction of a product.
Public Relations
“The Chartered Institute of Public Relations” defines Public Relations as a strategic management function that adds value to an organization by helping it to manage its reputation Public relations covers a wide range of tactics, usually involve providing
information to independent media sources in the hope of gaining favorable coverage. It also involves a mix of promoting specific products, services and events and promoting the overall brand of an organization, which is an ongoing tact. Public Relation tools include:
1. Press Release: A press release is an announcement of an event, performance, or other newsworthy item that is issued to the press by a public relations professional of an organization. It is written in the form of a story with an attractive heading so that the media quickly grasp and circulates the message through newspaper/radio/television/internet.
2. Press Kits: It is a comprehensive package of information outlining a company’s products and services most frequently sent to members of the press. It includes
• A brief company biography.
• Information of senior management.
• Comments from customers.
• Reprints of newspaper and magazine articles.
• Photos of products.
3. Brochures: It is a booklet published by the organization which contains the organization’s background, its ethics, vision, mission, its past, present and future projects, its CISP, etc. E.g.: brochure given to new employees to give them a gist of the organization.
4. Newsletter: It is a printed publication produced at regular intervals focusing on a particular set of people. The content of a newsletter is presented in a writing style that is less formal and letter-like. For example, a newsletter published by a college consists of information about activities conducted during a particular period, special achievements by students or teachers, etc.
5. Events and Press support: Special events are acts of news development. The ingredients are time, place, people, activities, drama, showmanship; one special event may have many subsidiary events, such as luncheons, banquets, contests, speeches, and many others as part of the buildup.
6. Conferences and Seminars: Conferences and seminars are conducted for making people aware about the organization. For example travel companies generally call prospective clients and offer travel packages. The members are contacted through telephones and asked to attend seminar.
7. Websites: A website acts as a window for the outside world to know an organization. So it is designed not just to serve as a resource for members, but also to present a positive message to non-members who are browsing through.
ROLE OF ‘PR’ IN AN ORIGINATION
(i) Smooth functioning of business and achievement of objectives. (ii) Building corporate image that affects favorably on its products. Up keep of parks, gardens, sponsoring sports activities etc.
- CBSE Revision notes (PDF Download) Free
- CBSE Revision notes for Class 12 Business Studies PDF
- CBSE Revision notes Class 12 Business Studies – CBSE
- CBSE Revisions notes and Key Points Class 12 Business Studies
- Summary of the NCERT books all chapters in Business Studies class 12
- Short notes for CBSE class 12th Business Studies
- Key notes and chapter summary of Business Studies class 12
- Quick revision notes for CBSE board exams
CBSE Class-12 Revision Notes and Key Points
Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies. CBSE quick revision note for class-12 Business Studies, Chemistry, Math’s, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter. Even if you wish to have an overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to do if for you. These notes will certainly save your time during stressful exam days.
- Revision Notes for class-12 Physics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Chemistry
- Revision Notes for class-12 Mathematics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Biology
- Revision Notes for class-12 Accountancy
- Revision Notes for class-12 Economics
- Revision Notes for class-12 Business Studies
- Revision Notes for class-12 Computer Science
- Revision Notes for class-12 Informatics Practices
- Revision Notes for class-12 English Core
- Revision Notes for class-12 History
- Revision Notes for class-12 Physical Education
To download Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies, sample paper for class 12 Physics, Chemistry, Biology, History, Political Science, Economics, Geography, Computer Science, Home Science, Accountancy, Business Studies and Home Science; do check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
- Nature and Significance of Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Principles of Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Business Environment class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Planning class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Organizing class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Staffing class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Directing class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Controlling class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Financial Management class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Financial Markets class 12 Notes Business Studies
- Consumer Protection class 12 Notes Business Studies
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
Leave a comment.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Class 12th /
Marketing Management Class 12 Notes
- Updated on
- Jan 28, 2022

Business Studies is an integral subject of the class 12 commerce syllabus and marketing management is one of the most scoring chapters of the class 12 business studies syllabus. If you are thorough with your notes and prepare well, it can be easy as well. . Here in this blog, we shall discuss in brief about this chapter. If you are preparing for your class 12 board exams then it would be of great help to you. Read on to know more about m arketing management class 12.
Important Definitions in Marketing Management Class 12
Market : Set of potential and actual buyers of a product or service’.
Customer : People or organisations that seek satisfaction of their needs and wants.
Marketer or Seller : The marketer is a person or organisation who offers products or services to the customer with an intention of satisfying the customer.
Marketing: It is a social process by which individuals acquire what they need and want through creating, offering and freely exchanging products and services of value with others.
JF Pyle says, “Marketing is that phase of business activity through which the human wants are satisfied by the exchange of goods and services.”
Essential Features of Marketing
Here are the important features of marketing:
- Need and want
- Creating a market offering
- Customer value
- Exchange Mechanism
Marketing Management
P lanning, organising, directing and controlling the activities in exchange of goods and services. Marketing management involves:
- Identifying the target market
- Growing customers in target market
Difference between Selling and Marketing
One can differentiate between marketing and selling on the basis of
- Scope
- Objective
- Start and end
- Efforts
- Approach
Marketing Management Philosophies
Listed below are few of the marketing management philosophies:
- Production concept
- Product concept
- Selling concept
- Marketing concept
- Societal concept
Objectives of Marketing Management
- Creates demand
- Market share
- Profitable sales volume through customer satisfaction
Functions of Marketing
- Gathering and analysing market information
- Market planning
- Product designing and development
- Standardisation and grading
- Packaging and Labelling
- Customer support services
- Pricing of products
- Promotion and selling
- Physical distribution
- Transportation
- Storage and warehousing
Marketing Mix
Refers to the ingredients or the tools or the variables mixed by the marketeer to interact with a particular market.
Philip Kotler defines marketing mix as, “Marketing mix are the set of – marketing tools that firm uses to pursue its marketing objectives in the target market.”
Elements of Marketing Mix
- Product : the tangible or intangible products that are offered to the customer.
Classification of Product
Products can be classified in two categories
- Consumer goods
- Industrial goods
Consumer Goods
One of the important sections of Marketing Management Class 12 is Consumer Goods. These are defined on the basis of certain characteristics. Here are the some of the categories and their examples as Consumer Goods:
- Durable products
- Non-durable products
- Convenient goods
- Shopping goods
- Speciality goods
Industrial Product
In Marketing Management Class 12, Industrial products are used as an input or raw material in the production of consumer goods, e.g., tools, machinery etc. Features of industrial products are a number of buyers, the channel of distribution, geographical concentration, derived demand, technical consideration, reciprocal buying and leasing.
Industrial goods are classified as
- Material and Parts
- Capital Item
- Supplies and Business Services
Product Mix
It refers to important decisions that are related to the product such as quality of product, product packing etc.
- Branding : A brand is the identification of a product. It can be in the form of a name, symbol or design etc.
- Various Terms Related to Brand- Brand, Brand Name, Brand Mark and Trade Mark.
- Helps in product differentiation
- Helps in advertising
- Differential pricing
- Easy introduction of new product
- Helps in identification of product
- Ensures quality
- Status symbol
A set of tasks or activities that involve designing, production of an appropriate wrapper, container for the product.
- There are three levels of packaging
- Primary packaging
- Secondary packaging
- Transportation packaging
- The rising standard of health and sanitation
- Self-service outlets
- Product differentiation
- Innovational opportunities
- Functions of Packaging
- Identification
- Convenience
Labelling
The process of labelling involves putting identification marks on the package. Functions of labels are:
- Describe the product and specify its contents
- Identify the product
- Helps in grading
- Promotes sale
- Providing information required by law/legal requirement
It is the value for which a product or service is provided to the customer by the seller.
This involves taking important decisions related to fixing the price of any commodity. The factors that must be kept in mind while fixing the price of a commodity:
- Pricing objectives
- Product cost
- Extent of competition in the market
- Customer’s demand and utility
- Government and legal regulation
- Marketing methods used
Pricing Strategies
There are two pricing strategies – Price skimming and Penetration pricing.
It refers to important decisions that involve physical distribution of goods and services. These decisions include deciding the channel of distribution, market for distribution.
Functions of Distribution Channels
- Sorting/Granding
- Accumulation
- Negotiation
- Risk taking
Factors Determining Choice of a Channel
The factors that are essential in determining choice of a channel are give below:
- Product related factors
- Competitive factors
- Company related factors
- Market related factors
- Environmental factors
Promotion Mix
It refers to all the important decisions that are related to promotion of sales of products and services.
Given below are the important tools or elements of promotion, are also called elements of promotion mix:
Advertising
- Sales promotion
- Personal selling
It is defined as the paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of ideas, goods or services and by identified sponsor. The advantages of advertisement are listed below:
- Expressiveness
- Enhancing customer satisfaction
Apart from the advantages, there are certain Disadvantages of Advertisement as well, listed below:
- Less forceful
- Less effective
- Difficulty in media choice
- Inflexibility
- Lack of feedback
- Adds to cost
- Undermines social values
- Confuses the buyers
- Encourages sale of inferior products
- Some advertisements are not appealing
Different Platforms Available for Advertising
Sales promotion.
It is the short term use of certain promotional activities that stimulate the customer to buy the product.
Sales Promotion Techniques for Customers
- Rebate and Discount
- Refunds and Product combination
- Quantity gift and Instant draws and assigned gift
- Lucky draw and Usable benefit
- Full finance @ 0%
- Sampling and Contents
Merits of Sales Promotion
- Attention attract
- Useful in new product launch
- Synergy in total promotion efforts
- Aid to other promotion tools
Demerits of Sales Promotion
- Reflects Crisis
- Spoils Product Image
Personal Selling
As the name suggests personal selling means selling personally and involves one on one interaction between the seller and the customer for the purpose of sale.
So, this was all about Marketing Management class 12l. We hope it helps you prepare for your exams and also aids you in revising. If you are confused about which career path to choose after class 12th commerce then get in touch with our experts at Leverage Edu. They will help you choose a stream that suits you perfectly and help you carve a niche for yourself. Sign up for a free session today!
So, this was all about Marketing Management class 12l. We hope it helps you prepare for your exams and also aids you in revising. If you are confused about which career path to choose after class 12th commerce then get in touch with our experts at Leverage Edu . They will help you choose a stream that suits you perfectly and help you carve a niche for yourself. Sign up for a free session today!
Sonal is a creative, enthusiastic writer and editor who has worked extensively for the Study Abroad domain. She splits her time between shooting fun insta reels and learning new tools for content marketing. If she is missing from her desk, you can find her with a group of people cracking silly jokes or petting neighbourhood dogs.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?

8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
- Top Colleges
- Top Courses
- Entrance Exams
- Admission 2024
- Study Abroad
- Study in Canada
- Study in UK
- Study in USA
- Study in Australia
- Study in Germany
- IELTS Material
- Scholarships
- Sarkari Exam
- Visual Stories
- College Compare
- Write a review
- Login/ Register
- Login / Register
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics 2024

Manali Ganguly ,
Mar 4, 2024
Share it on:
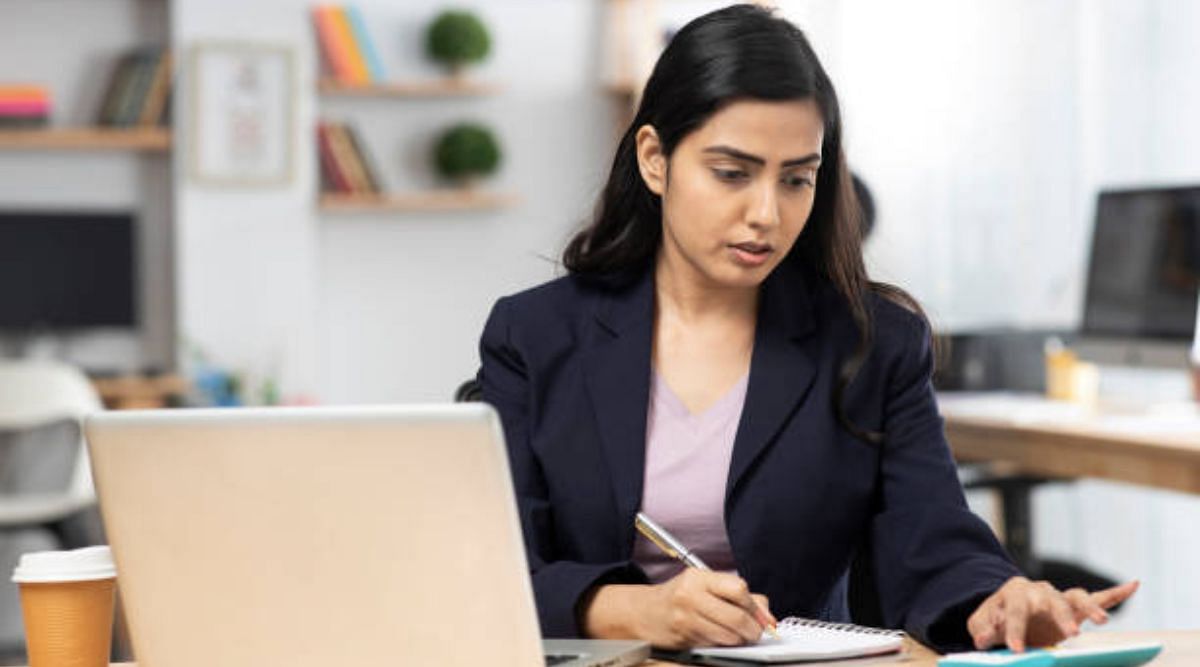
CBSE Class 12 Business Studies project topics 2024 are Elements of Business Environment, Stock Exchange,Principles of Business Management, and Marketing. A viva is conducted on the project report. The report including the viva carries 20 marks.
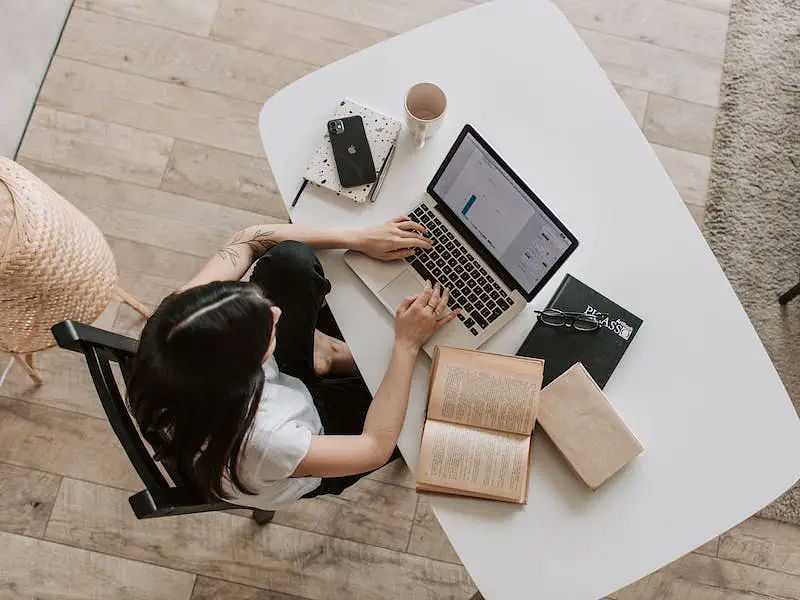

CBSE Class 12 Business Studies project topics 2024 includes the Elements of Business Environment, Principles of Business Management, Stock Exchange, and Marketing. The project report for CBSE 12th board exams carries 20 marks. The students are helped by the teachers in the selection of the project topics.
The project report is included in the CBSE curriculum to give a practical knowledge of what the students read throughout the year. The students are supposed to visit the fields and organisations while creating the report which exposes them to the professional market as well, apart from increasing their knowledge on the topic.
Table of Contents
Project 1: Elements of Business Environment
Project 2: principles of business management, project 3: stock exchange, project 4: marketing, project report: presentation, submission, cbse class 12 business studies project: marks distribution, how to choose cbse class 12 business studies project topics 2024.
The students must work on the following topics as suggested by the Central Board of Secondary Education:
The students must choose one of the topics given below, under the supervision of teachers.
- The alterations that the system of packaging has undergone in recent years. How has this impacted the economy?
- Why did Coca Cola and Fanta change to Thums up and Campa Cola in the 70s and then Pepsi and Coke in the 80s?
- How has there been a change in the role of women in the last 25 years, with respect to joint family, nuclear family, and women being the bread winners for the family.
- The change in the pattern of export and import.
- The rate of change of interest rates and an effect of the same on the savings.
- Child labour laws.
- The laws regulating the establishment of industries and the licences necessary for setting up the business.
- The anti plastic campaign
- What are the social factors that contribute to the acceptance or rejection of a particular product?
- How can an environmental change affect the services in a particular place?
Also Read: CBSE Class 12th Business Studies Syllabus 2023-24: Download PDF
The students must visit any of the below mentioned places to complete the project:
- Industrial Unit
- Departmental Store
- Fast Food Outlet
- Any place suggested by the teacher
This project must contain the following components:
- Graphical representation for the share prices for different companies or organisations on varying dates.
- How factors like festivals, seasons, and human and natural disasters affect a share’s market value?
- How does the market value of a share undergo change with change in the policies and the political environment?
- Identify the top 10 out of 25 companies based on the market value of shares, irrespective of profit and loss.
Also Read: Business Studies Class 12th Notes
The students can create take any product or service and create a report keeping in mind the following points:
- The product or service type and the process involved.
- Brand name.
- Product range.
- Logo or identification mark.
- Packaging and labelling.
- Product price and the factors that are considered while fixing the price.
- Channels of distribution and reason for selection of the same.
- Warehousing and transportation of the product.
- Promotional techniques applied.
- Grading of the product and standardisation.
Also Read: CBSE Class 12 Books 2024: Download NCERT PDFs for All Subjects
The students must submit the project report at the end of the term. The project report report must essentially be made keeping in mind the following points:
- The project must be written in hand.
- The project must be neat and give a clear flow of information.
- The cover page must include the information about the student such as the name, school, and year of submission.
- A page must be dedicated to ‘Contents’.
- The project report must contain an acknowledgement and a preface.
- A page must contain the ‘Introduction’.
- The topic must be written with a beautiful and catchy heading.
- The plan and activities implemented in the project must also be written in the project report.
- The observations must be listed down.
- The project must have a page dedicated to ‘Conclusion’.
- The appendix to the project must be included in the report.
Also Read: CBSE Class 12th Accountancy Syllabus 2023-24: Download PDF
The marks distribution for the project report is done considering a few elements. The scheme of distribution of marks has been shared below:
The CBSE class 12 students can consider the below mentioned points while selecting the topic of the project:
- Wise Selection of Topic: The selection of the topic must be done very carefully. A topic must be chosen that the student finds interesting to work on. This will enhance their effort and outcome of the project.
- Understand the Objective of the Project: In order to work on a project, it is crucial to understand the aims and objectives of the same. This will give a dimension to the project.
- Structural Planning: Planning the structure of the project is crucial as this keeps the flow and connectivity between the different sections of the project.
- Thorough Research Work: It is crucial to carry out a good research on the project-topic from reliable and authentic resources.
- Creating a Rough Draft: Without investing much time in this part, a rough draft must be created prior to starting the project report. This will give directions to the project.
- Collection and Analysis of Data: Data must be collected methodically and an analysis of the data must be done through graphs.
- Citing the Resources: This is a very crucial part of the project. Proper citation and referencing is mandatory.
- Proofreading and Reviewing: The project report must be revised thoroughly and proofread before final submission.
Also Read: CBSE Subject Codes for Class 12: Check Subject-Wise Code List
What is the total marks allotted to the Business Studies project in CBSE class 12?
How much marks is allotted to viva in CBSE class 12 Business Studies project?
What are the project topics for Business Studies in CBSE class 12?
POST YOUR COMMENT
Related articles.

What does RT mean in CBSE marksheet?

CBSE Admit Card ID Finder 2024 - Online & Offline Method

How to Convert CBSE CGPA to Percentage?

What is Essential Repeat in CBSE Class 12 2024?
CBSE Roll Number Finder 2024 for Class 10th & 12th

How to Calculate CBSE Class 12 Score Percentage?

CBSE Revaluation 2024: How to Apply for Class 10 & 12?
Get Free Scholarship worth 25000 INR

Project On Marketing Strategies For Skin Care Products For Class 12
Table of Contents
Acknowledgments
Completing this project has been a journey filled with exploration, research, and insights, and it would not have been possible without the support and contributions of several individuals and resources.
First and foremost, I express my gratitude to [Supervisor/Project Mentor’s Name], whose guidance and expertise have been invaluable throughout this undertaking. Their constructive feedback, encouragement, and wealth of knowledge have significantly enriched the depth and quality of this project.
I would like to extend my appreciation to the authors and researchers whose works provided the foundation for the literature review and formed the basis for a comprehensive understanding of the skincare industry. The wealth of information gleaned from their studies has been instrumental in shaping the insights presented in this project.
I am deeply thankful to [Name of Organization/Institution], which provided access to resources, databases, and a conducive environment for academic and professional growth. The support from the institution has been a cornerstone in the successful completion of this project.
Furthermore, I would like to acknowledge the participants and interviewees who generously shared their experiences and insights during the data collection phase. Their perspectives have added a real-world dimension to this project, enhancing its relevance and applicability.
Lastly, I extend my appreciation to friends and family who provided unwavering support, understanding, and encouragement throughout this academic endeavor. Their belief in the importance of this research fueled my motivation and determination to deliver a project that meets the highest standards.
This project stands as a collaborative effort, and I am grateful to each individual and entity that played a role, no matter how small, in its realization
Introduction
The skincare industry has undergone a transformative journey in recent years, evolving from a conventional hygiene practice to a dynamic realm that occupies a significant space in the tapestry of self-care. With changing consumer lifestyles and an escalating awareness of the vital role skincare plays in personal well-being, the industry has witnessed unprecedented growth and innovation.
This project endeavors to delve into the intricate landscape of marketing strategies employed by manufacturers in the skincare domain. As the market becomes increasingly dynamic and competitive, understanding the nuances of how brands navigate this terrain becomes crucial for both industry players and observers alike.
The global skincare market, estimated at a staggering USD X billion in 20XX, reflects not only the sheer scale of consumer engagement but also the diverse array of products catering to an ever-expanding demographic. This analysis will scrutinize the industry from various angles, from market size and segmentation to product analysis, competitor strategies, and the intricate web of consumer behavior that underpins purchasing decisions.
As we embark on this exploration, we aim to uncover the driving forces behind the industry’s growth, the challenges that shape its landscape, and the strategic moves manufacturers employ to stand out in an environment teeming with choices. By dissecting the marketing mix and unveiling the layers of consumer behavior, this project seeks to provide insights into the mechanisms that propel the skincare industry forward.
In the pages that follow, we will journey through the industry’s intricacies, unraveling the tales of innovation, consumer preferences, and marketing prowess that collectively shape the fascinating narrative of skincare in the contemporary world.
Industry Analysis
- Market Size and Growth : In the ever-expanding realm of skincare, the global market boasts robust growth, clocking in at a staggering USD X billion in 20XX, with a projected annual growth rate of Y%. This surge is ascribed to an escalating emphasis on personal appearance, the uptick in disposable incomes, and a burgeoning health consciousness among consumers.
Market Segmentation :
- Demographic Segmentation: Skincare offerings extend their reach across a diverse demographic spectrum, from teens to the elderly. Tailoring products to specific age brackets stands out as a prevalent strategy.
- Psychographic Segmentation: The key lies in comprehending consumers’ lifestyles and personalities, a foundation for crafting products that seamlessly align with their inclinations.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Scrutinizing purchasing patterns and product usage unravels insights essential for fine-tuning marketing tactics aimed at distinct consumer segments.

Product Analysis
- Types of Skin Care Products : The skincare panorama sprawls across a myriad of products, ranging from cleansers, moisturizers, toners, serums, sunscreens, to specialized treatments. Each category assumes a distinct role in the tapestry of a comprehensive skincare regimen.
- Popular Ingredients : Hyaluronic acid, retinol, and vitamin C emerge as stalwarts in the skincare arena. Responding to the clamor for clean beauty products, manufacturers are progressively infusing natural and sustainable ingredients into their formulations.

Competitor Analysis
Identification of Key Competitors : Pivotal players in the skincare arena encompass the likes of [Company A], [Company B], and [Company C], each wielding unique strengths and navigating through individual weaknesses in the market.
Comparative Analysis :
- Pricing Strategies: [Company A] positions itself as a luxury brand with a premium pricing strategy, while [Company B] opts for affordability, casting a wider net over the consumer base.
- Product Positioning: [Company C] carves its niche by accentuating dermatologist-approved formulations, fostering trust and credibility among consumers.
- Marketing Communication Strategies: [Company A] banks on influencer partnerships for promotion, a stark contrast to [Company B], which channels its efforts through traditional advertising conduits.
Buying Decision Process
- Problem Recognition: Identifying skincare needs and concerns, catalyzing the decision-making journey.
- Information Search: Navigating through a sea of information, exploring skincare solutions through online reviews, expert opinions, and brand websites.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: Weighing the pros and cons of different skincare products, considering factors like ingredients, brand reputation, and user testimonials.
- Purchase Decision: Committing to a skincare product based on the gathered information and personal preferences.
- Post-Purchase Behavior: Reflecting on the efficacy of the purchased product, sharing experiences through reviews, and potentially becoming a loyal customer.
Factors Influencing Purchases:
- Social Factors (family, reference groups): Seeking input from social circles, family, and trusted friends for skincare recommendations.
- Cultural Factors (cultural values, subcultures): Aligning skincare choices with cultural values and subcultural influences.
- Personal Factors (lifestyle, personality): Tailoring skincare choices to individual lifestyles and personalities.
- Psychological Factors (motivation, perception): Motivated by the desire for healthier skin, influenced by perceptions of beauty and self-care.
Marketing Mix (4Ps)
1. Product:
- Unique Selling Propositions (USPs): Highlighting innovative formulations, sustainable practices, and ongoing research into effective skincare ingredients.
- Innovative formulations and packaging: Delivering skincare products with cutting-edge formulations and visually appealing packaging.
- Continuous research on effective skincare ingredients: Staying ahead through constant exploration and incorporation of the latest in skincare research.
- Premium Pricing for luxury brands: Positioning luxury brands at a premium price point, reflecting exclusivity and quality.
- Competitive Pricing for mass-market products: Ensuring affordability for mass-market products to capture a broader consumer base.
- Discounts and promotions during festive seasons: Leveraging seasonal promotions to drive sales and enhance brand loyalty.
- Online and Offline Distribution Channels: Maximizing reach through both digital platforms and physical retail outlets.
- Strategic partnerships with beauty retailers: Collaborating with established beauty retailers to expand product accessibility.
- Availability in dermatology clinics and spas: Establishing a presence in professional skincare settings to enhance credibility.
4. Promotion:
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC): Ensuring a cohesive brand message across various communication channels.
- Social Media Campaigns (Instagram, YouTube): Engaging consumers through visually appealing content on popular social media platforms.
- Influencer Marketing with beauty influencers: Tapping into influencer networks to amplify brand reach and credibility.
- Educational content about skincare routines: Providing informative content to empower consumers and foster trust.
Marketing Strategies
1. Target Market:
- Demographic Segmentation (age, gender): Tailoring products for specific age groups and gender preferences.
- Psychographic Segmentation (lifestyle, values): Crafting products aligned with diverse lifestyles and values.
- Positioning as a solution to specific skincare concerns: Emphasizing the role of products in addressing specific skincare issues.
2. Branding:
- Strong Brand Image and Recognition: Cultivating a distinct and recognizable brand identity in the skincare landscape.
- Consistent Brand Messaging: Maintaining coherence in communication to reinforce brand values.
- Building Emotional Connections with Consumers: Creating emotional resonance to foster a deeper connection with the audience.
3. Digital Marketing:
- Social Media Campaigns (Facebook, Twitter): Utilizing popular social platforms for targeted marketing campaigns.
- Influencer Collaborations on TikTok: Leveraging the influence of TikTok personalities to connect with a younger demographic.
- E-commerce Platforms for Direct-to-Consumer Sales: Capitalizing on the digital marketplace for direct consumer engagement.
4. Product Launch Strategies:
- Research-backed product development: Ensuring new products are grounded in thorough research and development.
- Limited edition launches to create buzz: Generating excitement through exclusive and limited product releases.
- Collaborations with influencers for launch events: Partnering with influencers to amplify the impact of product launches.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges :
- Intense competition and market saturation: Navigating a crowded market with differentiation strategies and innovation.
- Regulatory hurdles and compliance: Adhering to stringent regulations while staying agile in product development.
- Consumer skepticism towards product claims: Building trust through transparent communication and verified results.
Opportunities :
- Rising demand for natural and sustainable products: Meeting the evolving consumer preference for eco-friendly and sustainable skincare options.
- Emerging markets and untapped consumer segments: Exploring new geographical markets and demographic segments for growth.
- Technological advancements in skincare formulations: Embracing and showcasing technological innovations to stay at the forefront of the industry.
In conclusion, the skincare industry’s meteoric rise is intricately tied to dynamic shifts in consumer behavior and a heightened awareness of skincare’s role in self-care. As explored in this analysis, manufacturers navigate this competitive landscape through strategic marketing initiatives that span product innovation, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotion. The consumer decision-making process, influenced by various factors, shapes the industry’s trajectory, making it imperative for brands to understand and cater to diverse preferences.
The marketing mix (4Ps) elucidates the nuanced strategies adopted by skincare brands, emphasizing the importance of product differentiation, pricing strategies, accessible distribution, and impactful promotion. Targeted marketing strategies, robust branding efforts, and a strong digital presence further solidify a brand’s position in the market.
While challenges such as market saturation and regulatory hurdles persist, opportunities abound in the form of rising demand for sustainable products, unexplored consumer segments, and continuous technological advancements. To thrive in this ever-evolving landscape, skincare brands must remain agile, responsive to consumer needs, and committed to innovation.
In essence, the skincare industry’s success hinges on a delicate balance between understanding consumer behavior, implementing effective marketing strategies, and adapting to the dynamic market forces at play. As the industry continues to evolve, those brands that can navigate these intricacies stand poised for sustained growth and success in this flourishing sector.
Bibliography
- Smith, J. (20XX). “The State of the Global Skincare Market.” Journal of Beauty Trends , link .
- Johnson, M. (20XX). “Consumer Behavior in the Beauty Industry: A Comprehensive Analysis.” International Journal of Marketing Research , link .
- Brown, A. et al. (20XX). “Marketing Mix Strategies in the Skincare Industry.” Journal of Business and Marketing , link .
- Davis, C. (20XX). “Innovations in Skincare: A Case Study of Successful Product Launches.” Journal of Product Development , link .
- Robinson, S. et al. (20XX). “The Impact of Influencer Marketing on Consumer Purchasing Behavior in the Beauty Sector.” Social Media Studies , link .
Certificate of Completion
This is to certify that I, [Student’s Name], a [Class/Grade Level] student, have successfully completed the “Project on marketing strategies for skin care products for class 12.” The project explores the fundamental principles and key aspects of the chosen topic, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance and implications.
In this project, I delved into in-depth research and analysis, investigating various facets and relevant theories related to the chosen topic. I demonstrated dedication, diligence, and a high level of sincerity throughout the project’s completion.
Key Achievements:
Thoroughly researched and analyzed Project on Project on marketing strategies for skin care products for class 12. Examined the historical background and evolution of the subject matter. Explored the contributions of notable figures in the field. Investigated the key theories and principles associated with the topic. Discussed practical applications and real-world implications. Considered critical viewpoints and alternative theories, fostering a well-rounded understanding. This project has significantly enhanced my knowledge and critical thinking skills in the chosen field of study. It reflects my commitment to academic excellence and the pursuit of knowledge.
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Subscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Project On Marketing Strategies For Skin Care Products For Class 12 PDF
Related articles.

EVS Project On Electricity Consumption for Class 11th And 12th

Geography Project On Agriculture In India For Class 10 ICSE

English Project on The Portrait of a Lady For Class 11th CBSE

Geography Project On Meteorological Instruments and Their Uses For Class 9th
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.

Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Marketing Class 12 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 11 (Free PDF Download)
- Revision Notes

Revision Notes for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 - Free PDF Download
The Class 12 Business Studies revision notes Chapter 11 includes and summarises all of the key concepts such as the definition of marketing, features of marketing, functions of marketing, marketing mix, marketing mix ingredients, and so on. The NCERT Class 12 Revision Notes Business Studies Chapter 11 assist students in understanding all of the important ideas discussed in this chapter. The revision notes PDF are written in a straightforward manner to provide students with a better learning experience prepared and curated by the subject-matter experts at Vedantu and this PDF can be downloaded for free from Vedantu app and official website.
Topics Covered in Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing
Introduction to Marketing
Features of Marketing
Marketing Management
Marketing Management Philosophies (The Production Concept, Product Concept, The Marketing Concept, The Selling Concept, The Societal Marketing Concept)
Differences in the Marketing Management Philosophies
Functions of Marketing
Role of Marketing
Marketing Mix Elements (Product, Price, Place, And Promotion)
Advertising
Physical Distribution
Personal Selling
Download CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 12 Business studies revision notes for other chapters:

Related Chapters
Access Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 11 Marketing
Meaning of market .
The term "market" refers to the gathering place of buyers and sellers to conduct transactions involving the exchange of goods and services. The term "market" comes from the Latin word "Marcatus," which means "to trade."
Marketing
Marketing is defined as "a human activity aimed at satisfying needs and desires through an exchange process."
Philip Kotler
Marketing concept is a key to determining the needs, desires of target markets, delivering the desired satisfactions more efficiently and effectively by competitors is critical to achieving organizational goals.
Features of Marketing
1. Needs and Wants:
The marketing process assists consumers in obtaining what they require and desire.
A need is said to be known as a state of deprivation or the feeling that one is depriving oneself of something.
Needs are fundamental to human beings and are unrelated to a specific product.
2. Creating a Market Offering:
Market offering is the process of offering and introducing a product or service with specific features such as size, quality, taste, and so on for the purpose of selling.
3. Customer Value:
Marketing used to facilitate the exchange of goods as well as services between buyers and sellers.
4. Exchange Mechanism:
The exchange mechanism is used in the marketing process.
Exchange refers to the process where two or more parties used to come together in order to get the desired goods or service from someone while in exchange for something. For example, money is the medium of exchange used to purchase or sell a product or service.
The following conditions needs to be met in order for an exchange to take place:
a. There must be at least two parties.
b. providing something of value to the other party
c. communication
d. freedom to accept or reject offer
e. willingness of the parties to enter into a transaction
What can be Marketed?
1. Physical product
2. Services
3. Ideas
4. Person
5. Palace
6. Experience
7. Properties
8. Events
9. Information
10. Organisation
Marketer
A marketer is anyone who makes an extra effort to identify the needs of the consumers and offer the product or service as well as persuade them in order to buy in the process of exchange. .
Sellers, as marketers, are the ones who provide satisfaction. They make products/services available and sell them to customers in order to meet their needs and desires.
They are classified as follows:
a. goods marketers (such as Hindustan Lever)
b. services marketers (such as Indian Airlines)
c. others marketing experiences or places (such as Walt Disney) (like tourist destinations).
Marketing activities are those undertaken by marketers in order to facilitate the exchange of goods and services between producers and consumers.
Marketing Management
Marketing management is the administration of marketing functions.
It is considered as the process of organizing, directing as well as controlling the activities associated with marketing goods and services in order to meet the needs of customers and achieve organizational goals.
“Marketing management is defined as the art and science of selecting target markets and acquiring, retaining, and growing customers by creating, delivering, and communicating superior customer service.”
Philip Kotler
The Process of Management of Marketing Involves:
a. Identifying a target market
b. Creating demand by producing products that meet the needs and interests of customers.
c. Create, develop, and communicate superior customer values: To provide superior value products/services to prospective customers, and to communicate these values to other potential buyers in order to persuade them to purchase the product/service.
Marketing and Selling
Marketing: It refers to a broad range of activities, of which selling is only one component. Before making a sale, a marketer must plan the type, design, and price of the product, as well as select the distribution channels and the appropriate promotional mix for the target market.
Selling: refers to the sale of a product or service through advertising, promotion, and salesmanship. The product's title is transferred from seller to buyer. The primary goal of selling is to turn a product into cash.
Difference Between Marketing and Selling
Marketing Management Philosophies
Marketing Concepts/Philosophies usually refers to determining the needs as well as wants of the target markets & then delivering the desired satisfactions more efficiently and effectively by competitors is critical to achieving organizational goals.
1. Production Concept:
Because the number of producers was limited in the early days of the industrial revolution, industrialists assumed that consumers were only interested in easily and widely available goods at an affordable price.
2. Product Concept:
As time passed, supply improved, and customers began to prefer products that were superior in performance, quality, and features.
As a result, product improvement has become the key to a company's profit maximization.
3. Selling Concept:
Increased production scale resulted in increased competition among sellers. Because there were so many companies selling similar products, product quality and availability were insufficient to ensure survival.
Consumers will not buy products unless the company engages in aggressive sales and promotional activities.
4. Marketing Concept :
Marketing begins with determining what consumers want in order to satisfy consumers and profit.
Customer satisfaction is a prerequisite for achieving the firm's goals and objectives.
5. Social Marketing Concept:
Customer satisfaction is supplemented by social welfare in this concept.
A company that adopts the societal concept must balance the company's profits, consumer satisfaction, and societal interests.
Functions of Marketing
1. Gathering and Analyzing Market Information:
Systematic fact-gathering and information-analysis
Examining a business environment's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Identifying customer needs and desires, determining purchasing motivations, selecting a brand name, packaging, and promotional media, and so on.
Data is available from both primary and secondary sources.
2. Marketing Planning :
Create an appropriate marketing plan in order to meet marketing objectives.
It should specify the action plans to achieve these goals.
For example, if a marketer wants to increase his country's market share in the next three years, his marketing plan should include various important aspects such as a plan for increasing production levels, product promotion, and so on.
3. Product Designing and Development:
Involves decisions about the product to be manufactured and its attributes, such as quality considerations, packaging, new models and variations, and so on.
A good design can improve the performance of the product while also giving it a competitive advantage in the market.
Anticipate customer needs and create new products or improve existing ones to meet those needs.
4. Standardization and Grading:
Standardisation refers to the production of goods that meet predetermined specifications, which aids in the production of uniformity and consistency (e.g., ISI Mark).
Grading is said to be the process of categorizing different products into different groups based on important characteristics such as quality, size, and so on.
5. Packaging and Labeling:
Packaging is called as the process of designing as well as developing a package for a product that protects it from damage, spoilage, breakage, and leakage. It also makes purchasing easier for customers and serves as a marketing tool.
Labeling is the process of designing a label to be placed on a package. It can range from a simple tag to intricate graphics. For example, colgate, lays, and so on.
6. Branding:
It aids in product differentiation, builds customer loyalty, and promotes sales.
An important decision area is branding strategy, which determines whether each product will have a separate brand name or the same brand name will be used for all products.
7. Customer Support Services:
Customer support services are extremely effective at increasing prospective customer sales and developing brand loyalty for a product.
It aims to provide maximum customer satisfaction while also building brand loyalty.
Examples include sales services, customer complaints and adjustments, credit services, maintenance services, technical services, and consumer information.
8. Pricing of Product:
Product price refers to the amount of money that customers must pay in order to obtain a product.
It is an important factor in a product's success or failure.
Because the price of a product/service is related to its demand, the price should be set after considering all of the factors that influence the price of the product.
9. Promotion:
Product and service promotion entails informing customers about the firm's product, its features, and so on, and persuading them to purchase the products.
Promotional methods include advertising, personal selling, public relations, and sales promotion.
10. Physical Distribution:
The two major decision areas under this function are
(a) the channels of distribution or marketing intermediaries to be used (e.g. wholesalers, retailers); and the marketing intermediaries to be used.
(b) Physical movement of the product from the point of manufacture to the point of consumption.
11. Transportation:
Transportation refers to the physical movement of goods from one location to another.
When selecting a mode of transportation, various factors such as the nature of the product, cost, location of the target market, and so on should be considered.
12. Storage or Warehousing:
Proper storage of products is required to maintain a smooth flow of products in the market.
Storage and warehousing are used to protect against unavoidable delays in delivery or to meet contingencies in demand.
Marketing Mix
A large number of factors influence marketing decisions; these are classified as ‘non-controllable factors' and ‘controllable factors.'
Controllable factors are those that can be influenced at the firm level.
Environmental variables are factors that influence a decision but are not controllable at the firm level.
In order to be successful, a company must make sound decisions after analyzing controllable factors and keeping environmental factors in mind.
Marketing Mix refers to the set of marketing tools that a company employs to achieve its marketing objectives in the target market.
The success of a market offer is determined by how well these ingredients are combined to provide superior value to customers while also meeting sales and profit goals.
Elements of Marketing Mix
The marketing mix consists of four main elements
A. Product
B. Price
C. Place/Physical Distribution
D. Promotion
These elements are used to popularly known as 4 P’s of the marketing.
1. Product: A product is defined as "anything of value" that is offered for sale in the market. Colgate, Dove, and so on.
2. Price: the sum of money that a customer must pay in order to obtain a product or service.
3. Place: Physical product distribution, i.e. making the product available to customers at the point of sale.
4. Promotion: Informing customers about the products and convincing them to purchase them.
Product
A product, in the eyes of the customer, is a collection of utilities that is purchased because of its ability to meet a specific need.
Classification of Products

Products can be classified into two categories:
(i) Consumers ‘products,
(ii) Industrial products.
A. Shopping Efforts Involved
On the basis of the buyers' time and effort.
1. Convenience Products: Convenience goods are consumer products that are frequently purchased for immediate use. Medicines, newspapers, stationery, toothpaste, and so on.
2. Shopping Products: Shopping products are those in which buyers spend a significant amount of time comparing the quality, price, style, suitability, and so on at various stores before making a final purchase. For example, electronic goods, automobiles, and so on.
3. Specialty Products: Specialty products are goods that have unique characteristics that compel customers to go out of their way to purchase them. For example, art, antiques, and so on.
B. Durability of Products
1. Non-durable Products: These are consumer goods that are consumed in a short period of time. For example, milk, soap, stationery, and so on.
2. Durable Products: Tangible items that can withstand repeated use, such as a refrigerator, radio, bicycle, and so on.
3. Services: Intangible services are those activities, benefits, or satisfactions that are sold, such as dry cleaning, watch repairs, hair cutting, postal services, doctor services, and so on.
Industrial Products
Industrial products are those that are used as inputs in the manufacturing process.

Characteristics
Number of Buyers
Channel Levels
Geographic Concentration
Derived Demand
Role of Technical Considerations
Reciprocal Buying
Leasing Out
Classification
Materials and Parts: items that are completely incorporated into the manufacturer's products.
Capital Items: the manufacture of finished goods, such as installations and equipment.
Supplies and Business Services: short-term goods and services that aid in the development or management of the final product. Repairs and maintenance, for example.
Branding:
Branding is the process of creating a corporate brand identity for consumers and imprinting that brand identity on their minds, which necessitates brand positioning and brand management.
Amazon's Jeff Bezos
The process of developing a product's distinct identity. It is the process of identifying a product by using a name, term, symbol, or design alone or in some combination.
Brand: A name, term, sign, design, or some combination of the above used to identify and differentiate the seller's products from those of competitors.
Advantages to the Marketers
Enables Product Differentiation Through Marking: It aids in distinguishing its product from that of its competitors.
Aids in the development of advertising and display programs
Differential Pricing: It allows a company to charge different prices for different products.
Ease of New Product Introduction
Advantages to the Customers
Aids in Product Identification: Assists customers in identifying products.
Ensures Quality: Ensures product quality
Status Symbol: Brands become status symbols due to their quality As an example, consider Benz automobiles.
Characteristics of Good Brand Name
Short, simple to say, spell, recognize, and remember
Suggest the product's advantages and characteristics.
Different from other products
Adaptable to packing or labeling requirements, as well as different advertising media and languages.
Versatile enough to accommodate new products;
Legally registered and protected
Packaging
Packaging: The act of designing and developing a product's container or wrapper. Because good packaging often aids in the sale of a product, it is referred to as a silent salesman.
Levels of Packaging
1. Primary Package: This is the product's immediate container/covering, such as toffee in a wrapper, a match box, a soap wrapper, and so on.
2. Secondary Package: It's all about additional layers of protection that are kept until the product is ready for use, such as a red cardboard box for Colgate toothpaste.
3. Transportation Package: refers to additional packaging components required for storage, identification, and transportation, such as putting a package of toffees into cardboard boxes for storage at a manufacturer's warehouse and transportation.
Functions of Packaging
Product Identification: Packaging aids in product identification.
Product Protection: The primary function of the packaging is to protect the product.
Facilitating Product Usage: It makes transportation, stocking, and consumption easier.
Product Promotion: Packaging makes sales promotion easier.
Rising Health and Sanitation Standards: It is believed that there is minimal adulteration in packaged goods.
Self-Service Outlets: Good and appealing packaging can help to promote a product.
Opportunities for Innovation: Packaging innovation has increased the shelf life of products.
For example, tetra packs for milk.
Product Differentiation: The color, size, material, and other characteristics of packaging influence customers' perceptions of the product's quality.
Labelling
Labeling is the process of affixing identification marks to a package. Labels are information carriers that provide information such as the name of the product, the name of the manufacturer, the contents of the product, the expiry and manufacturing date, general information for use, weight, and so on.
Labels Perform Following Functions:
1. Identify the product: It assists customers in identifying the product among the various types of products available. For example, the purple color of a Cadbury chocolate label easily distinguishes it from other chocolates.
2. Describe and specify the product's contents: The manufacturer provides all information regarding the product's contents, etc.
3. Product grading: With the help of labels, products can be classified into different categories based on quality, nature, and so on, for example: Brooke Bond Red Label, Brooke Bond Yellow Label, Brooke Bond Green Label, and so on.
4. Aids in product promotion: Attractive and colorful labels excite customers and entice them to purchase the products. For example, 40 percent extra free, as stated on detergent, buy two get one free, and so on.
5. Providing legal information: There is a legal requirement to print the batch number, maximum retail price, weight/volume on all products, and a statutory warning on the packet of cigarettes, “Smoking is harmful to one's health”: In the event of a hazard on/poisonous material, appropriate safety warnings should be posted.
ii. Pricing
Meaning of Price:
It is considered as the sum of the values that customers exchange in exchange for the benefit of owning or using the product. Price can thus be defined as the sum of money paid by a buyer (or received by a seller) in exchange for the purchase of a product or service.
Factors Determining Price Determination:
1. Pricing Objectives
The marketing firm's goal is to maximize profits. Pricing objectives can be determined in both the short and long run. If the company wants to maximize profits in the short run, it will charge the highest price for its products. However, in order to maximize its total profit in the long run, it would choose a lower per unit price in order to capture a larger share of the market and earn higher profits through increased sales.
2. Product Cost:
Price should cover all costs and aim to earn a reasonable profit above and beyond the cost.
It takes into account the costs of manufacturing, distribution, and sale of the product.
Costs establish the floor price, or the lowest price at which the product can be sold.
The price should rise. Total costs (Fixed costs/overheads + Variable costs + Semi-variable costs) in the long run, but in certain circumstances (introduction of a new product or entry into a new market), the product price may not cover all costs for a short period of time.
3. Utility and Demand:
The utility provided by the product, as well as the demand for the product, determine the maximum price that a buyer will be willing to pay for that particular product.
Buyers would be willing to pay until the utility of the demand exceeded or equaled the utility derived from it.
According to the law of demand, consumers buy more at a lower price.
Demand elasticity is the responsiveness of demand to changes in product prices. If a small change in price leads to a larger change in quantity demanded, demand is elastic. Firms can set higher prices if demand is inelastic.
4. Extent of Competition in Market:
Before setting prices, competitors' prices and anticipated actions must be considered.
5. Government Policies:
In the public interest, the government can intervene to regulate product prices.
6. Marketing Methods Used:
Other marketing elements such as distribution system, sales promotion efforts, packaging type, product differentiation, credit facility, and so on all have an impact on the price fixing process.
iii. Physical Distribution
A series of decisions must be made in order to make the product available for purchase and consumption by customers.
The marketer must ensure that the product is available in sufficient quantities, at the appropriate time, and in the appropriate location.
A channel of distribution is a group of companies and individuals who take title, or assist in the transfer of title, to specific goods or services as they move from producers to consumers.
Choosing an appropriate channel of distribution is a critical marketing decision that affects an organization's performance. It is a strategic decision whether the firm will use direct marketing channels or long channels involving a number of intermediaries.
1. Order Processing: Provide accurate and timely order processing, without which orders would arrive late or in the wrong quantity. As a result, customers will be dissatisfied, with the risk of losing business and goodwill.
2. Transportation: It transports goods from manufacturers to consumers, making the product available at the point of sale.
3. Inventory control: Choosing the level of inventory is an important inventory decision. Additional demand can be met in less time, and inventory requirements will be minimal.
4. Warehousing: The act of storing and sorting products in order to create time utility in them is referred to as warehousing. It is required to bridge the gap between the time the product is manufactured and the time it is distributed for consumption.
Components of Physical Distribution:
Functions of Distribution Channels
1. Sorting: Middlemen obtain supplies of goods from a variety of sources, which are not always of the same quality.
2. Accumulation: the accumulation of goods into larger homogeneous stocks that aid in the maintenance of a continuous flow of supply.
3. Allocation entails dividing homogeneous stock into smaller, more marketable lots.
4. Assorting: the collection of products for resale.
5. Product Promotion: Middlemen take part in activities such as demonstrations, special displays, and so on.
6. Bargaining: Manufacturers, intermediaries, and customers bargain over price, quality, and other issues.
7. Risk Taking: Merchant middlemen take title to the goods, assuming risks such as price and demand fluctuations, spoilage, destruction, and so on.
Channels of Distribution
Consists of a network of firms, individuals, merchants, and functionaries who assist in the transfer of title to a product from the producer to the end consumer.
Intermediaries help to cover a large geographical area and increase distribution efficiency, including transportation, storage, and negotiation. They also provide customers with convenience by having a variety of items available in one location, as well as serving as an authentic source of market information because they are in direct contact with the customer.
Types of Channels:
Direct Channel ( Zero Level)
The manufacturer and the customer establish a direct relationship. Manufacturer-Customer. For example, mail order, internet, and door-to-door sales.
Indirect Channel
The distribution network is referred to as indirect when a producer uses one or more intermediaries to move goods from the point of production to the point of sale.
1. Manufacturer-Retailer-Customer (One Level Channel)
Between the manufacturers and the customers, one intermediary, namely retailers, is used. Typically used for high-end items such as watches, appliances, automobiles (Maruti Udyog), and so on.
2. Manufacturer-wholesaler-Retailer-customer (Two Level Channel):
This channel is primarily used for consumer goods distribution. Typically used for consumer goods such as soaps, salt, and so on.
3. Manufacturer → Agent → Wholesaler → Retailer → Customer (Three Level Channel):
Manufacturers use their own selling agents or brokers in this case, who connect them with wholesalers, then retailers, and finally consumers.
Factors Determining Choice of Channels of Distribution
The selection of an appropriate channel of distribution is a critical marketing decision.
1. Product Related Factors: The nature of the product, whether it is industrial or consumer goods, perishable or nonperishable, etc., determines the distribution channels used.
2. Company Characteristics: The company's financial strength and the level of control it wishes to exert over other channel members. Short channels are used to exert more control over intermediaries and vice versa.
3. Competitive Factors: Companies may copy the channels used by their competitors.
4. Market Factors: The size of the market as well as the geographical concentration of potential buyers influence channel selection.
5. Environmental Factors: Legal constraints and a country's economic situation. In a down economy, marketers use shorter distribution channels.
iv. Promotion
Promotion is the use of communication with the dual goal of informing potential customers about a product or a service as well as persuading them to purchase it.
Promotion is a critical component of the marketing mix in which marketers use various communication tools to encourage the exchange of goods and services in the market.
It is a set of promotional tools/techniques used by a company to entice and persuade customers to buy its products.
Promotion Mix
A promotion mix is considered as a combination of promotional tools used by a company to achieve its communication goals.
Promotion mix tools:
(i) Advertising,
(ii) Personal Selling,
(iii) Sales Promotion,
(iv) Publicity.
1. Advertising
Advertising, as defined by a specific sponsor, is a paid form of nonpersonal presentation and promotion of goods, services, or ideas.
The most widely used promotional tool. It is a cold, impersonal form of communication that is paid for by marketers (sponsors) to promote their products and services. Newspapers, magazines, television, and radio are all common mediums.
Features
Paid Form: The sponsor must bear the cost of communicating with customers.
Lack of Personalization: There is no direct face-to-face contact between the prospect and the advertiser.
Identified Sponsor: Advertising is done by a specific person or company.
Merits
Mass Reach: a large number of people can be reached across a large geographical area.
Increasing customer satisfaction and trust.
Expressiveness: It is a powerful medium of communication.
Economy: Because of its wide reach, is a very cost-effective mode of communication.
Limitations
Less Forceful: There is no pressure on the prospects to listen to the message.
Feedback Deficit:
Inflexibility: It is less flexible because the message is standardised and not tailored to the individual.
Low Efficacy: It is difficult to get advertising messages heard by the intended prospects.
Objections to Advertising
Some critics argue that advertising is a social waste because it raises costs, multiplies people's needs, and undermines social values.
1. Adds to Cost: Unnecessary advertising raises the cost of the product, which is then passed on to the buyer in the form of high prices.
2. Undermines Social Values: It undermines social values while encouraging materialism.
3. Confuses the Buyers: A similar product of the same nature/quality confuses the buyer.
4. Encourages Sale of Inferior Products: It makes no distinction between superior and inferior goods.
5. Some Advertisements are in Bad Taste: These depict something that some people do not agree with.
2. Personal Selling
Personal selling entails personally contacting prospective buyers of a product, i.e. engaging in a face-to-face interaction between seller as well as the buyer for the purpose of sale.
Features of the Personal Selling
1. Under personal selling, personal contact is established.
2. Establishing relationships with prospective customers, which are critical in closing sales.
3. Oral communication
4. Quick response to queries.
Merits of Personal Selling
1. Flexibility
2. Direct Feedback
3. Minimum wastage
Role of Personal Selling
Importance to Business Organisation
(i) Effective Promotional Tool
(ii) Versatile Tool
(iii) Reduces Effort Wastage
(iv) Consumer Attention
(v) Long-Term Relationship
(vi) Personal Relationship
(vii) Role in the Introduction Stage
(viii) Customer Relationship
Importance to Customers
(i)Assist in the Identification of Needs
(ii) Up-to-date market information
(iii) Expert advice
(iv) Customers are enticed
Importance to Society
(i)Converts the most recent demand
(ii) Employment Possibilities
(iii) Job Opportunities
(iv) Salesperson Mobility
(v) Standardization of Products
3. Sales Promotion
Short-term incentives or other promotional activities that aim to pique a customer's interest in purchasing a product are referred to as sales promotion.
Merits of Sales Promotion
Attention Value: Using incentives, attract people's attention.
Useful in New Product Launch: Sales promotion tools persuade people to abandon their usual purchasing habits and try new products.
Synergy in Total Promotional Efforts: Sales promotion activities contribute to the overall effectiveness of a company's promotional efforts.
Limitations of Sales Promotion
Reflects Crisis: A company that frequently relies on sales promotion activities may give the impression that it is unable to manage its sales and that its products are unpopular.
Damages Product Image: Customers may believe that the products are of poor quality or are overpriced.
Commonly Used Sales Promotion Activities
Product Combination: Including another product as a free gift with the purchase of one.
Rebate: Providing products at reduced prices.
Instant draws and assigned gifts: Scratch a card and instantly win a prize with the purchase of a TV, Tea, or Refrigerator, for example.
Lucky Draw: a lucky draw coupon for free gasoline when a certain amount is purchased, and so on.
Useful Benefit: 'Purchase goods worth Rs 3000 and get a holiday package worth Rs 3000 free,' and so on.
Full finance at 0%: Many marketers of consumer durables such as electronics, automobiles, and so on offer simple financing schemes such as "24 easy instalments" and so on.
Contests: Holding competitive events that require the use of skills or luck, etc.
Quantity Gift: Providing an extra quantity of the product, for example, "Buy three, get one free."
Refunds: Refunding a portion of the price paid by the customer upon presentation of proof of purchase.
Discount: Selling products at a lower price than the list price.
Sampling: Provide free product samples to potential customers. Typically used at the time of a product's introduction.
4. Publicity
Publicity occurs when favorable news about a product or service is broadcast in the mass media. For example, if a manufacturer makes a breakthrough in the development of a car engine and this news is covered by television, radio, or newspapers as a news item.
Features of Publicity are:
I. Publicity is a form of communication that is not compensated.
II. There is no identified sponsor
5. Public Relations
Public relations encompasses a wide range of tactics and is typically concerned with providing information to independent media outlets in the hope of obtaining favorable coverage. It also includes a mix of promoting specific products, services, and events as well as promoting an organization's overall brand, which is an ongoing tactic.
Role of Public Relations:
1. Press Relations: A press release is an announcement of an event, performance, or other newsworthy item issued to the press by an organization's public relations professional. It is written in the form of a positive story with an appealing heading in order for the media to quickly grasp and spread the message.
2. Product promotion: The company tries to draw attention to new products by organizing sporting and cultural events such as news conferences, seminars, and exhibitions, among other things.
3. Corporate Communication: The image of the organization is promoted through newsletters, annual reports, brochures, and other means.
4. Lobbying: The organization maintains cordial relations with government officials and ministers in charge of corporate affairs, industry, and finance in regard to business and economic policies.
5. Counseling: The public relations department advises management on general issues affecting the public and the company's position.
Maintaining Good Public Relations also Helps in Achieving the Following Marketing Objectives:
(a) Building awareness
(b) Building credibility
(c) Stimulates sales force
(d) Lowers promotion costs
Difference Between Advertising and Personal Selling
Advertising
An impersonal mode of communication
The transmission of standardised messages
An inflexible mode of communication
Broad reach
Low cost per person reached
Cover the market in a short period of time.
Makes use of mass media
Lacks direct feedback
Effective in generating and maintaining interest
Consumers are the primary target market
Personal Selling
Personal form of communication
Non-standardised messages
Flexibility
Limited reach
High cost per person
Extensive efforts to cover the entire market
Makes use of sales personnel.
Immediate and direct feedback
Plays an important role in the awareness stage
The Target market is comprised of industrial buyers
Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 Revision Notes
Introduction to class 12 business studies marketing revision notes.
By following the Chapter 11 Class 12 Business Studies Revision Notes, students will get the meaning of the term ‘marketing’ and will be able to understand the distinction between ‘marketing’ and ‘selling’. The Class 12 Marketing Notes enlist the functions of marketing, its role in the development of an economy in terms of society, firms, and consumers.
The Class 12 Revision Notes Chapter 11 comprise explanations of the different elements of the marketing mix, its classification into different categories, the factors that affect price determination, the types of distribution channels, and the tools of promotion mix like sales promotion, personal selling, publicity, and advertising.
Meaning of Marketing
The market is commonly referred to as a place where sellers and buyers carry out transactions for the involvement of the exchange of services and goods. Marketing is widely defined as the performance of the business activities that direct the flow of services and goods from producers and consumers.
(Image to be added soon)
There are four significant and crucial features of Marketing.
Customer Value - Customer value is the process of marketing that facilitates the exchange of the services and products between the buyers and sellers.
Needs and Wants - Needs and wants is another vital process of marketing that helps groups or individuals to obtain what they need and what they want.
Exchange Mechanism - The exchange mechanism is the process of marketing that involves the exchange of services and products for money or some other products.
Creating a Market Offering - The creation of market offerings like taste, size, or quality that are available at a given location or outlet.
A few functions of marketing that helps in the exchange of goods and services are as follows.
Product Development and Designing:- Product design plays a vital role in the selling of a product. A company whose product is designed better sells more products than the companies whose products are weakly designed.
Labelling and Packaging:- Packaging refers to the development and design of packages for the products, while labelling refers to the development and design of labels to be put on the package.
Customer Support Services:- This refers to the services provided to consumers such as adjustments, sales services, and handling customer complaints. All the services aim to present maximum consumer satisfaction.
Analyzing and Gathering Market Information:- This is a crucial function of marketing that quickly identifies the consumer’s needs and helps to facilitate
Warehousing or Storage:- A proper storage maintains the smooth flow of products and services in the market. The need for storage is essential to ensure the adequate stock of goods or products against unavoidable delays or to cover up the contingencies in demand. Retailers and wholesalers play a vital role.
Key Benefits of Referring to Revision Notes for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing
Referring to Revision Notes for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing, it will help you to:
Solve any type of questions asked from this particular chapter in the exam confidently.
Strengthen your chapter concepts
Minimise your exam stress and anxiety
To keep track of all the important topics covered in the chapter.
Enhance your conceptual clarity
The CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing revision Notes supplied in this article provide an overview of the chapter and assist you in preparing the chapter so that every idea is addressed in accordance with the syllabus standards. CBSE Quick Notes Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing are excellent for last-minute rapid revision. Download the CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Chapter 11 Marketing revision Notes to successfully try all chapter questions in the test.

FAQs on Marketing Class 12 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 11 (Free PDF Download)
1. Define Marketing Mix and enlist its elements.
The marketing mix is the total of policies formulated with a view of the successful completion of the multiple marketing activities. The main goal is to attract all types of consumers.
Elements of Marketing Mix:- There are four primary elements-
Product – refers to the decisions relating to the product
Price – Price mix refers to the decisions related to price fixation of product or service.
Place – refers to activities that make a firm’s products available to the target customers.
Promotion – refers to the combination of promotional tools used by the business to inform customers about the products.
2. State the difference between marketing and selling.
The difference between Marketing and Selling are as follows-
Marketing starts before the goods or services are produced while selling starts after the production has taken place.
Marketing entails a variety of marketing operations, whereas selling is accomplished through advertising, sales promotion, and personal selling strategies.
Marketing maximises profits via customer happiness, whereas selling maximises profits by number of sales.
The primary goal of marketing is to satisfy customers, whereas the primary goal of selling is to attract customers.
3. What does Chapter 11 “Marketing” teach students?
Chapter 11 "Marketing" teaches pupils about crucial components of company marketing. Students will understand the definition of marketing, the distinction between marketing and selling, marketing functions, and key aspects of the marketing mix. Students will also comprehend the classification of various product categories, distinct product distribution methods, and significant promotional tactics. Students may utilise Vedantu's Revision Notes Chapter 11 to better comprehend the material. Kids can also utilise these notes to study for exams.
4. Where can I find Revision Notes for Chapter 11 Class 12 Business Studies?
In today's society, Business Studies is a fascinating and vital topic. Students will certainly appreciate it as they learn about many areas of business. When studying for this topic, students may be expected to study a considerable quantity of knowledge. They don't need to be concerned since Vedantu is always eager to assist. Simple revision notes for Class 11 Business Studies will be available to students. These notes are very valuable for students, especially for last-minute study before exams.
5. Is Chapter 11 of Class 12 Business Studies easy?
Business studies is a fascinating topic. People with a natural aptitude for business can undoubtedly benefit from understanding the various business fundamentals. Yet, like with any topic, if you do not attempt to comprehend the fundamental principles of Chapter 11, it may look frightening to you. Chapter 11 of Class 12 Business Studies will be a breeze if you study the ideas and problem diagrams well and recall the key definitions.
6. What do you mean by “Branding”?
Branding is the process of developing a company's distinctive identity via the creation of a distinct brand for the business. This include developing a company's name, image, and logo. This is regarded as a key part of decision-making in any company's marketing. To sell their business, successful organisations employ effective branding techniques. Effective branding leads to more customers and more successful product marketing.
7. How are products classified?
Products of a company are classified into two major categories:
Consumer products: These are products directly purchased by the consumers for their personal use. Such consumer products comprise three types
Convenience products
Shopping products
Speciality products
Industrial products: These are products used for producing other products. These include materials and parts, capital items, and supplies, and business services.
Vedantu provides useful notes for this topic on their website. You can access these revision notes from the Vedantu app.
Study Materials for Class 12

Class 12 Mathematics Project Ideas for Summer Vacation (2024)
img src="https://img.jagranjosh.com/images/2024/May/1452024/class-12-maths-project-ideas.jpg" width="1200" height="675" />
Mathematics Project Topics and Ideas for Class 12: The summer holidays of 2024 are about to begin for school students. Teachers might be wondering about the vacation homework. Since students have a lot of leisure time during their summer break, this time can be best utilised to ensure practical learning. Here, we have brought you the list of Class 12 Maths project topics and ideas that can be easily made by students with minimum resources and at their homes. The below-listed Class 12 Maths project ideas for summer vacation can be chosen by students as per their own convenience and interest.
Projects are the best method of learning while having fun, especially when you are on your vacation. Working model projects also involve the development of various skills in students such as decision-making, problem-solving, creation, and innovation, paying attention to detail, and most importantly ensuring a positive outcome of the work done.
Class 12 Mathematics Project Ideas & Topics for Summer Vacation
The list of Class 12 Maths project ideas and topics has been listed below. Students can opt for the best alternative and utilise their leisure time to gain some extra internal marks, while also ensuring the grasping of knowledge.
- Determinants
- Graphs of Inverse trigonometric functions
- Defining Matrices and its types
- Direction cosines and direction ratios in three-dimensional geometry
- Real-life applications of integrals and derivatives
- Vectors and scalars quantities in real life
- History of Mathematics including great Mathematicians and their contributions
- Formula chart for differentiation and integration
- Probability
- The Random Fibonacci Sequence
Class 12 Maths Project: Things to Include in Project File
Here’s the complete list of details that must be a part of your Class 12 Maths project. Check what you should include in the project to ensure full marks.
- Certificate
- Acknowledgement
- Introduction
- Bibliography
Students must choose the topic of project wisely, since a lot of research, dedication, and patience will be required to complete the project and most importantly ensure that the project is good. Also, research is the key to any assignment that you do. The project should be objective-oriented, detailed, informative, unique, and understandable.
Also Check:
CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus 2024-2025
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
Revision Notes for Class 12 Maths
Class 12 Maths Formula Pages

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Its a Business Studies Class XII Project based on CBSE guidelines. The selected product is Fruit Juice named DELISH. Its my original idea. Education. 1 of 61. Download now. Download to read offline. Business Studies Class 12th Marketing management Project- Fruit Juice - Download as a PDF or view online for free.
For this BST project class 12 on Marketing Management, The students can consider the following products and conduct research to gather information about the various aspects concerning the marketing of the product. Some of the most prominent and sought-after products are mentioned in the table below: Adhesives: Mobile Phones: Inverters:
The Marketing Management project for class 12 on water bottles aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the marketing practices and strategies employed by water bottle companies to effectively position their products, create brand awareness, and gain a competitive advantage in the market. Through comprehensive research and study, we will delve ...
Key Achievements: Thoroughly researched and analyzed Marketing Management Project On Cars Manufacturing For Class 12 CBSE. Examined the historical background and evolution of the subject matter. Explored the contributions of notable figures in the field. Investigated the key theories and principles associated with the topic.
Marketing. Marketing is a social process of identifying needs and wants and satisfying them through created market offering by giving something of value to the customer with the help of an exchange mechanism. Important Features of Marketing. Needs and wants. The needs and wants of the target market should be identified. Creating a market offering.
This is the class 12 Business studies project on Marketing Management. I've selected "shoes" as my product here. You can take ideas or reference from the vi...
This is to certify that I, [Student's Name], a [Class/Grade Level] student, have successfully completed the "Marketing management project on perfumes for class 12 CBSE.". The project explores the fundamental principles and key aspects of the chosen topic, providing a comprehensive understanding of its significance and implications.
The project for Business Studies Class 12 will undoubtedly assist all those students who really want to have a summary of what a project for class 12 looks like. It will completely answer all your questions on what are the different things we should contemplate while preparing a Business Studies project. The whole project work is of 20 marks.
Marketing Management File (Business Studies Project) for class 12 as per the guidelines of CBSE.Unit: Marketing ManagementTopic: Marketing Management of Sare...
💯ECONOMICS PROJECT💯👇👇https://youtu.be/zOtk9qKLUaEBST PROJECT ON PRINCIPLES OF MANAGEMENT👇👇https://youtu.be/icr-VY0DcTgTHIS Video...👇Topic ...
Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics CBSE 2024. In order to give pupils a solid understanding of the concepts and procedures pertaining to business (trade and industry), as well as their interaction with society, the course in business studies is introduced at the senior school level. Business is a dynamic process that combines human ...
Business Studies class 12 project should inlcude the following: Provide brief history of stock exchanges in India. Prepare a hypothetical portfolio with a sum of INR 100,000 in any 5 top companies over a period of 20 working days. Provide reasons for price fluctuations. For example, wars, strikes and accidents, political environment, spread of ...
CBSE Class-12 Revision Notes and Key Points. Marketing Management class 12 Notes Business Studies. CBSE quick revision note for class-12 Business Studies, Chemistry, Math's, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter.
Industrial Product. In Marketing Management Class 12, Industrial products are used as an input or raw material in the production of consumer goods, e.g., tools, machinery etc. Features of industrial products are a number of buyers, the channel of distribution, geographical concentration, derived demand, technical consideration, reciprocal ...
Table of Contents. CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Project Topics 2024. Project 1: Elements of Business Environment. Project 2: Principles of Business Management. Project 3: Stock Exchange. Project 4: Marketing. Project Report: Presentation, Submission. CBSE Class 12 Business Studies Project: Marks Distribution.
Presenting the class 12th Business Studies Project on MARKETING - Milk.Hope you like the project. Don't forget to like and share the video with your friends ...
Business studies project class 12 on marketing management.docx - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site. ...
Marketing Strategies. 1. Target Market: Demographic Segmentation (age, gender): Tailoring products for specific age groups and gender preferences. Psychographic Segmentation (lifestyle, values): Crafting products aligned with diverse lifestyles and values. Positioning as a solution to specific skincare concerns: Emphasizing the role of products ...
FAQs on Marketing Class 12 Notes CBSE Business Studies Chapter 11 (Free PDF Download) 1. Define Marketing Mix and enlist its elements. The marketing mix is the total of policies formulated with a view of the successful completion of the multiple marketing activities. The main goal is to attract all types of consumers.
BUSINESS PROJECT MARKETING MANAGEMENT - SOAP - CLASS 12 - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document provides details about marketing a bathing soap product called TruEssence. It includes sections on selecting the product, competitive brands, required licenses, product details for TruEssence soap, logo, label design ...
MARKETING class 12 bst project on chocolate - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. cbse class 12 bst project on chocolate hope it helps you all:)
Mathematics Project Topics and Ideas for Class 12: The summer holidays of 2024 are about to begin for school students. Teachers might be wondering about the vacation homework. Since students have ...
Business Studies Project: Class 12 Marketing Management (Jeans) | PDF | Jeans | Brand. Marketing Management - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online.