- Dedicated team
- Machine Learning
- Enterprise software
- Marketplace
- Travel, Health and Lifestyle
- Corporate Websites

What is a SaaS Business Model and How Does it Work
Dmytro umen.
Few innovations have been as disruptive, impactful, and recent as the SaaS business model. Whether a startup pivots to embrace this dynamic approach or emerges expressly to leverage its potential, the allure of SaaS revenue in today's bustling market is undeniable. With the aggregated industry value projected to soar past $25 billion annually, seizing the opportunity to delve into the SaaS presents an enticing prospect for organizations of all sizes. Yet, to thrive in this competitive arena, it's imperative to grasp the essence of successful SaaS business model excellence — the strategies, organizational frameworks, and pivotal metrics that underpin business success.
Key takeaways
- SaaS, short for Software as a Service, is a business model where software is hosted on the cloud, enabling users to access its features through monthly or annual subscriptions.
- The SaaS model benefits vendors with predictable revenue, lower upfront costs, and reduced maintenance expenses, alongside scalability, flexibility, and a strategic approach to combat software piracy. It attracts significant investor interest due to its growth potential and high retention rates.
- B2B and B2C SaaS models, while sharing core service and business metrics, differ in focus and strategies. Successful SaaS companies often blend these models, leveraging a dual-funnel strategy to cater to both business clients and individual consumers, enhancing their market reach and profitability.
- There exist six potential pricing options for monetizing your SaaS product: freemium, flat, usage-based, per-user, tiered, and hybrid pricing.
- SaaS founders face challenges such as ensuring data security, managing multi-tenancy complexity, and maintaining regulatory compliance, which are pivotal for sustaining user trust and competitive advantage.
- When bringing your SaaS business model to fruition, you have three primary options: either initiate the project independently and seek software development consulting when needed, assemble an internal team with further augmentation, or opt to outsource the product development process to a third-party service provider.
Why is SaaS taking over the world?
SaaS, or Software as a Service, has swiftly become the preferred choice for both customers and businesses alike. The allure of SaaS lies in its seamless functionality; it simply "just works", without the hassle of installations or the fear of data loss due to hardware failures.
From a business perspective, the economics of SaaS are irresistible, with recurring revenue streams enabling predictable cash flows that fuel rapid expansion. The meteoric rise of SaaS companies, boasting impressive growth rates and a collective industry worth of nearly $197 billion in 2023 , underscores their dominance.
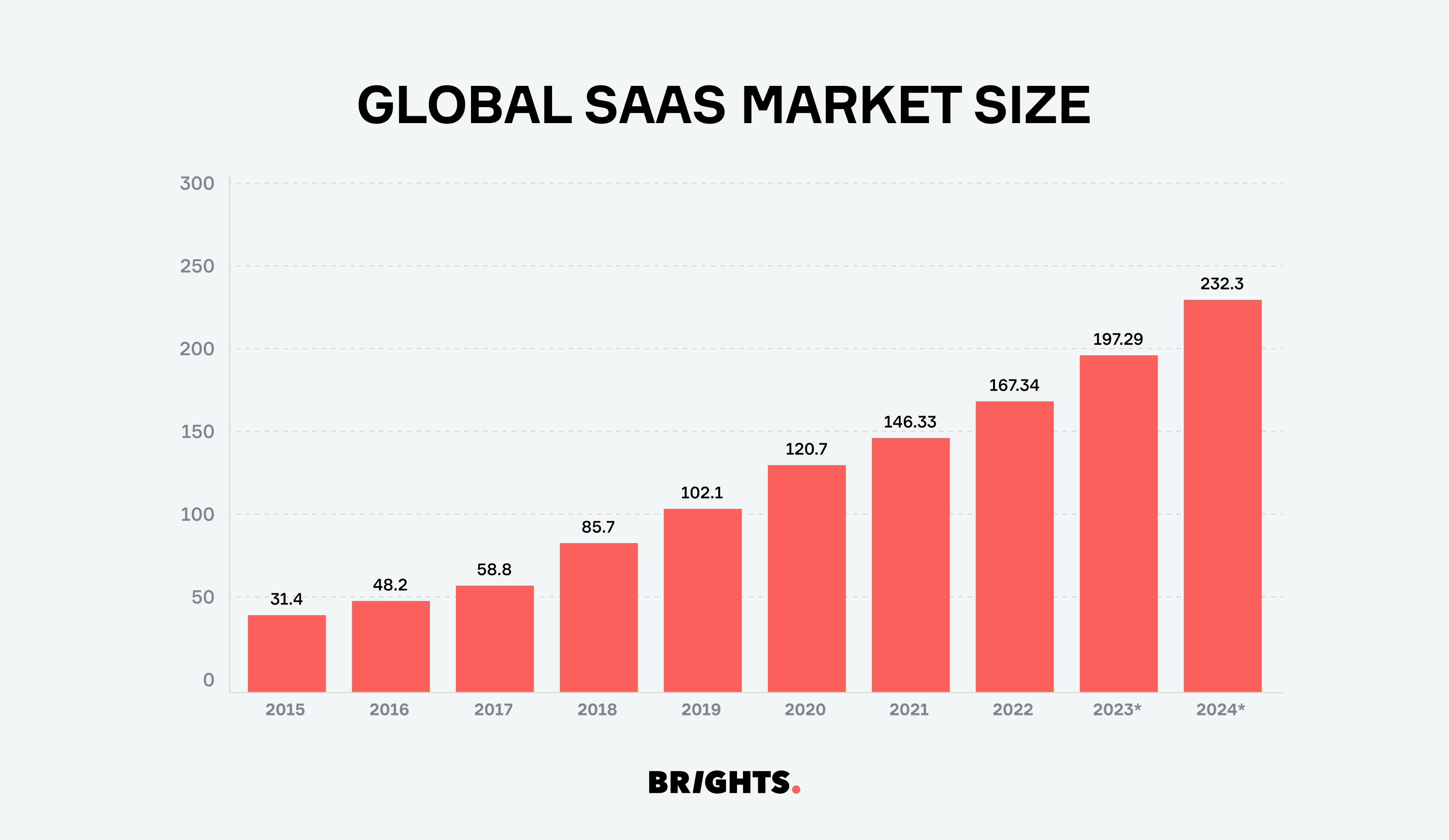
SaaS business model in a nutshell
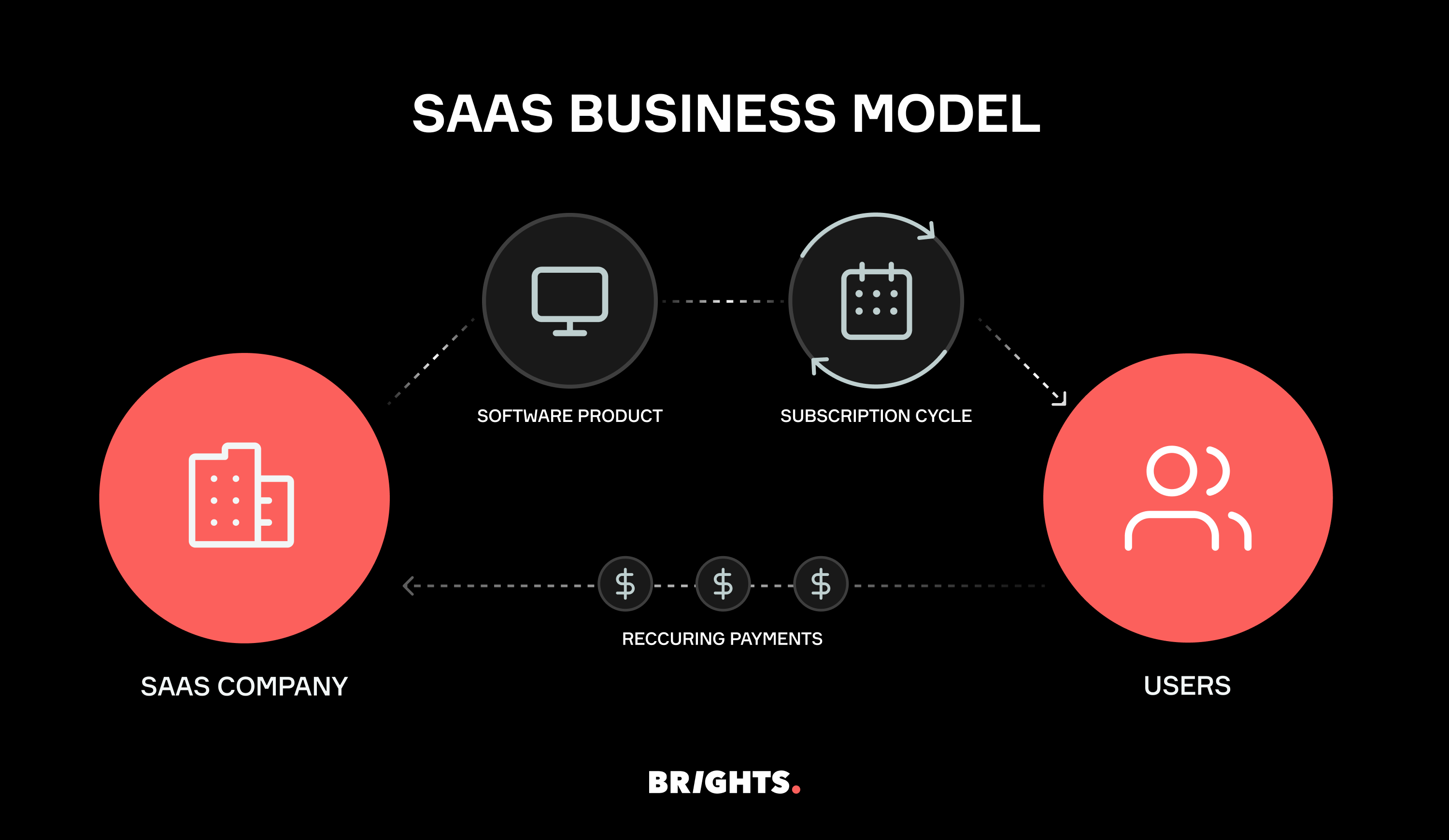
SaaS stands as one of the primary trio of cloud computing service models, sharing the stage with Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
In essence, the Software as a Service business model revolves around financializing software, transforming it from a product with a static price tag into a dynamic, forecastable cash flow instrument. At its core lies a straightforward equation that encapsulates the key metrics driving a SaaS venture's revenue:
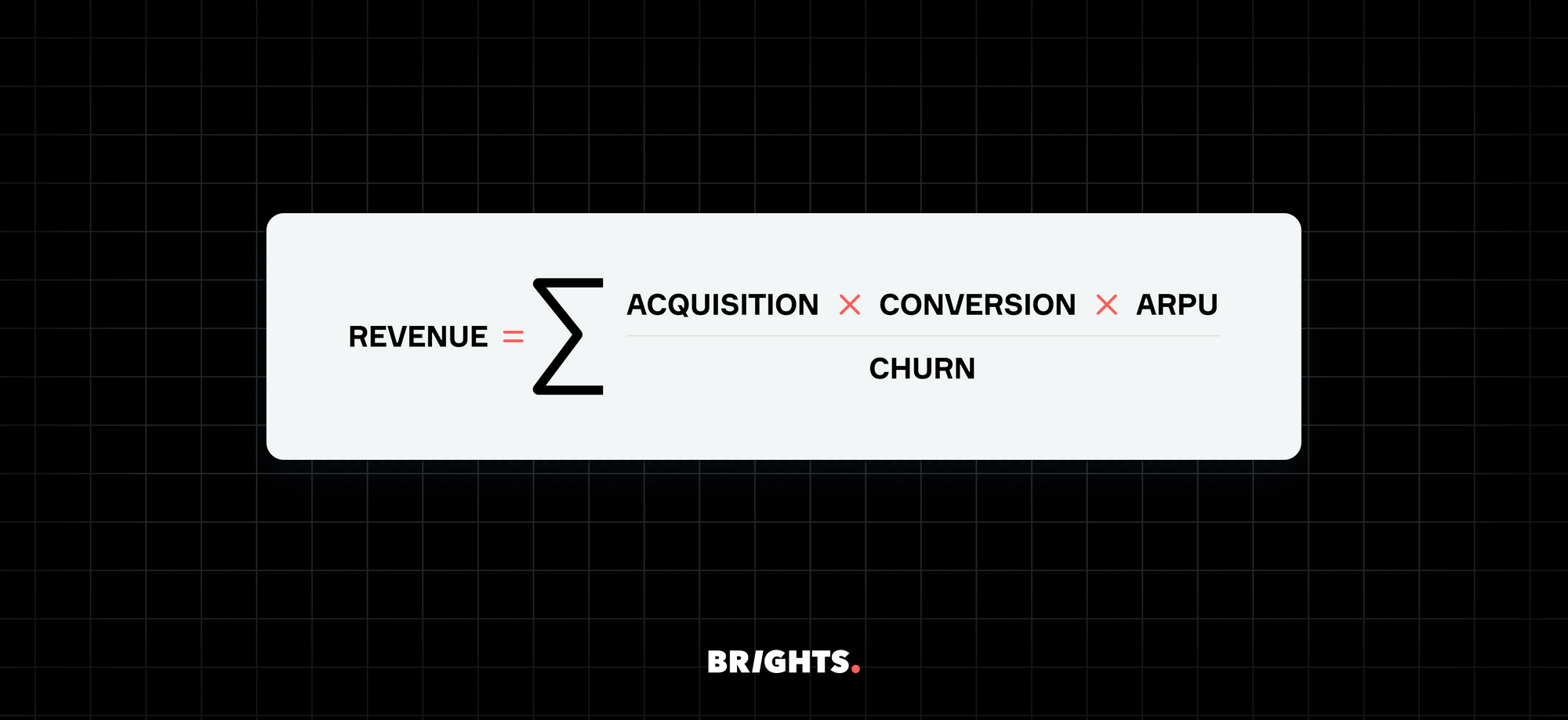
Acquisition represents the effectiveness in attracting and converting prospects into paying customers, while ARPU denotes the average revenue generated per account. Churn, on the other hand, signifies the percentage of customers who discontinue their subscriptions over a given period. By understanding these components and their interplay, businesses can project their long-term revenue and customer lifetime value (LTV) with relative simplicity, facilitating strategic planning and growth.
For instance, imagine a SaaS product with a monthly churn rate of 3%. In this scenario, each customer's expected lifetime would extend to approximately 33 months (1 / 0.03), assuming a steady subscription fee of $50 per month. Consequently, the anticipated lifetime revenue per new customer would total $1,650 ($50 * 33 months).
Furthermore, because SaaS has high profit margins, even small improvements in how many people sign up can lead to immediate increases in revenue and, over time, increase enterprise valuation. While working on getting more customers, keeping them, and reducing the number who unsubscribe might require a lot of effort, changing pricing strategies is a relatively simple way to grow. However, it's important to understand that SaaS companies will approach revenue plateaus, dictated by the interplay of acquisition, conversion, and churn dynamics. If these areas do not improve, growth can stop, putting the company at risk. Especially considering the capital-intensive nature of SaaS expansion, with substantial upfront investments in marketing and sales driving customer acquisition and revenue growth.
Types of software business model
In the software business, various models shape how companies operate and generate revenue. These can be broadly categorized into three main types:
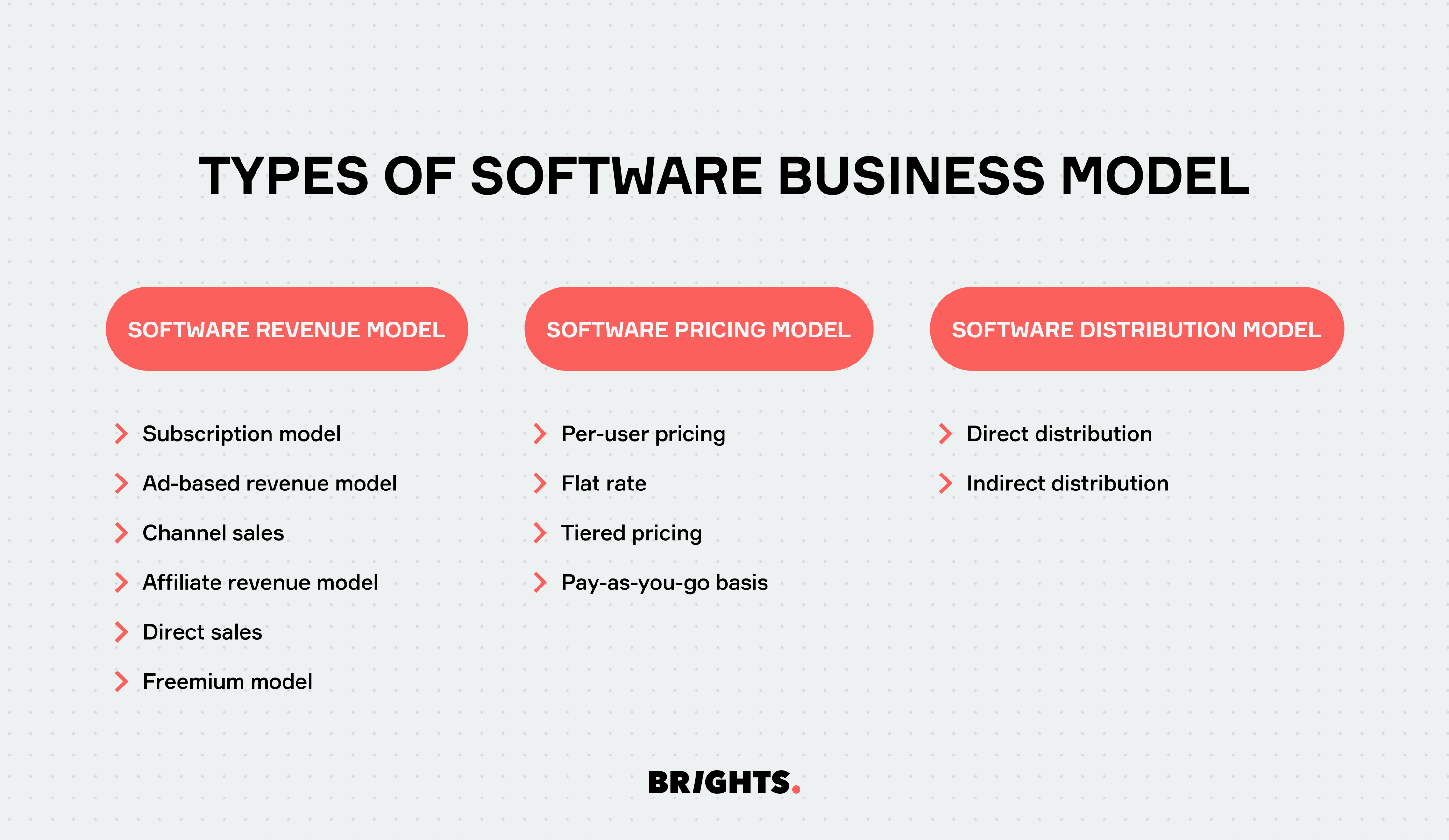
Software revenue model
The software revenue model is pivotal for understanding how a SaaS business generates profit and monetizes its offerings. It not only determines the pricing strategy but also sheds light on the target audience and effective marketing strategies. The following are common types of software revenue models:
- Subscription model
- Ad-based revenue model
- Channel sales
- Affiliate revenue model
- Direct sales
- Freemium model
Software pricing model
In the software pricing model, crucial decisions are made regarding the cost of the service or product. Researching competitors' pricing can offer a competitive edge. Key software pricing models include:
- Per-user pricing
- Tiered pricing
- Pay-as-you-go basis
Software distribution model
The software distribution model concerns how services or products are disseminated to customers, considering who sells them and the methodologies employed. Common distribution models include:
- Direct distribution
- Indirect distribution
Ultimately, the choice of software distribution model hinges on business requirements, budget constraints, and overarching objectives.
B2B and B2C SaaS models
B2B SaaS and B2C SaaS may share similarities in service provision, business models, and performance metrics, such as churn rate and conversion rate. However, the distinctions between the two are stark, particularly in terms of various departments critical to their operation and success.
Many new founders make the mistake of believing they must choose between developing a B2B or B2C SaaS product. However, contrary to this belief, numerous highly profitable SaaS companies successfully operate within both realms simultaneously. They adopt a dual-funnel approach, akin to the strategy exemplified by Dropbox.
Take, for instance, companies like Dropbox, Trello, Canva, Castos, and Squadcast. While primarily categorized as B2B SaaS, they also maintain a substantial consumer or prosumer tier.
Embracing a hybrid model offers significant advantages, including:
- Stable growth curve
By catering to a diverse clientele, you balance smaller customers with higher churn rates alongside businesses at higher price points with lower churn, resulting in a more stable growth trajectory.
- Enhanced brand presence
Engaging with consumers amplifies your brand's reach. A sizable consumer base fosters a strong brand following, facilitating organic word-of-mouth marketing on a larger scale.
- Increased Average Revenue Per User (ARPU)
The varied customer mix typically yields higher ARPU figures compared to traditional B2C SaaS models. Consequently, you can allocate more resources towards sales and marketing initiatives.
Ultimately, there's no definitive answer regarding whether to pursue a B2B or B2C SaaS approach. However, from an economic standpoint, B2B ventures tend to be more advantageous for bootstrapped or predominantly bootstrapped enterprises.
In addition, B2B SaaS solutions typically boast greater complexity and a wider array of features compared to their B2C counterparts. This complexity arises from the distinct requirements of B2B customers, who demand advanced functionalities and customization options tailored to their specific business needs. Moreover, B2B solutions often excel in integration capabilities, security features, and reporting functionalities, among other advanced attributes.
In contrast, B2C SaaS solutions prioritize simplicity and user-friendliness. These solutions emphasize intuitive interfaces and streamlined features to deliver a seamless user experience. While B2C offerings may lack the extensive customization and advanced functionalities of B2B solutions, they excel in accessibility and ease of use, catering to a broader audience.
In essence, success in the SaaS realm hinges on acquiring numerous customers and retaining them, rather than solely focusing on securing large deals.
Examples of successful SaaS platforms
Let's explore a few examples of successful SaaS platforms and delve into how they have transformed their respective industries, catering to both business and consumer needs alike.
LinkedIn stands as a cornerstone in professional networking, revolutionizing the way individuals connect, share insights, and advance their careers. As a B2B SaaS platform, it provides a digital space where professionals can access a suite of services, including job searching, talent recruitment, and professional networking tools. LinkedIn has become an indispensable resource for both professionals and businesses, facilitating meaningful connections and opportunities in the professional landscape.
As a B2B SaaS communication platform, Slack has redefined workplace collaboration and communication dynamics. Offering features such as instant messaging, file sharing, and seamless integrations with various productivity tools, Slack enables teams to work more efficiently and effectively. Its user-friendly interface and robust functionality have made it a staple in modern workplaces across industries, empowering teams to streamline communication and collaboration processes.
Spotify stands out as a transformative force in the realm of music consumption, offering a personalized and immersive music streaming experience. Operating as a B2C SaaS platform, Spotify provides users with access to an extensive library of songs, playlists, and podcasts on-demand through its subscription-based model. With personalized recommendations and curated playlists tailored to individual preferences, Spotify has become the go-to destination for music enthusiasts worldwide, reshaping how people discover, enjoy, and share music.
If you're seeking inspiration, dive into our article highlighting the top SaaS startups to watch in 2024.
SaaS product stages
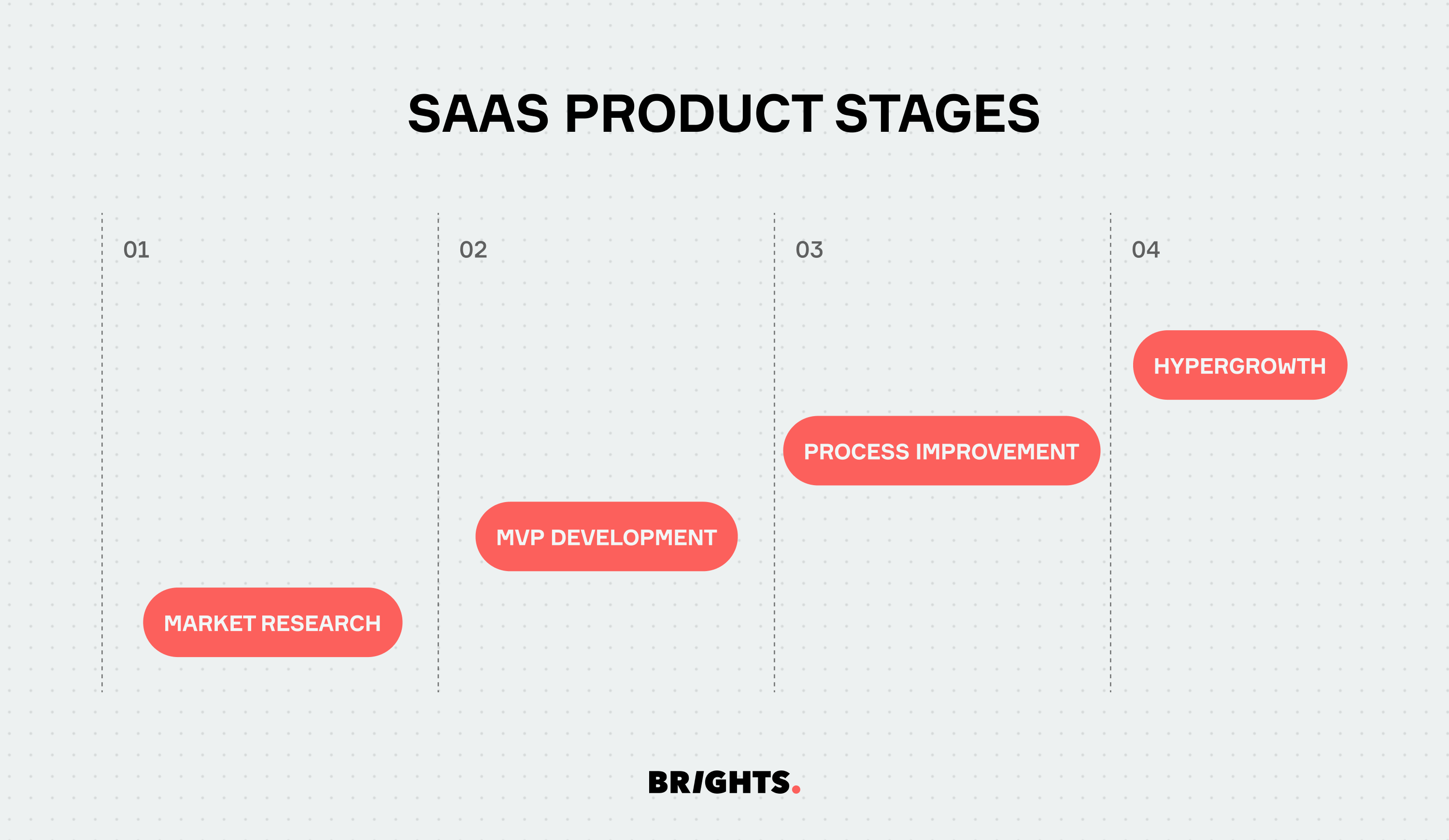
Market research
Market research enables you to understand customer needs, market trends, and competitor landscapes. At Brights, we leverage industry expertise and data-driven insights to identify market opportunities and validate product concepts. With a detailed discovery phase, you gain valuable market intelligence sans development cost, guiding strategic decision-making and maximizing the potential for product success.
MVP development
The development of a Minimum Viable Product is a crucial stage in the SaaS product lifecycle, allowing businesses to validate their ideas and gather feedback from early adopters. Brights specializes in MVP development , leveraging agile methodologies and rapid prototyping to bring concepts to life efficiently and cost-effectively. With our expertise, you can launch MVP quickly and iteratively, minimizing time to market and maximizing resource efficiency in development cost.
Process improvement
Continuous process improvement is essential for optimizing SaaS product performance and enhancing customer satisfaction. We offer process improvement consulting services, conducting thorough assessments and implementing tailored strategies to streamline workflows, enhance scalability, and drive operational excellence.
Hypergrowth
Hypergrowth signifies a phase of rapid expansion and scaling for SaaS businesses, driven by increasing market demand and customer adoption. Brights team provides technical expertise with team extension to support businesses during hypergrowth phases, offering cloud infrastructure management, performance optimization, and scalability planning services. By leveraging Brights' capabilities, businesses can scale their operations seamlessly and sustainably, enabling them to capitalize on growth opportunities and achieve long-term success.
Read also: How much does it cost to develop a SaaS product?
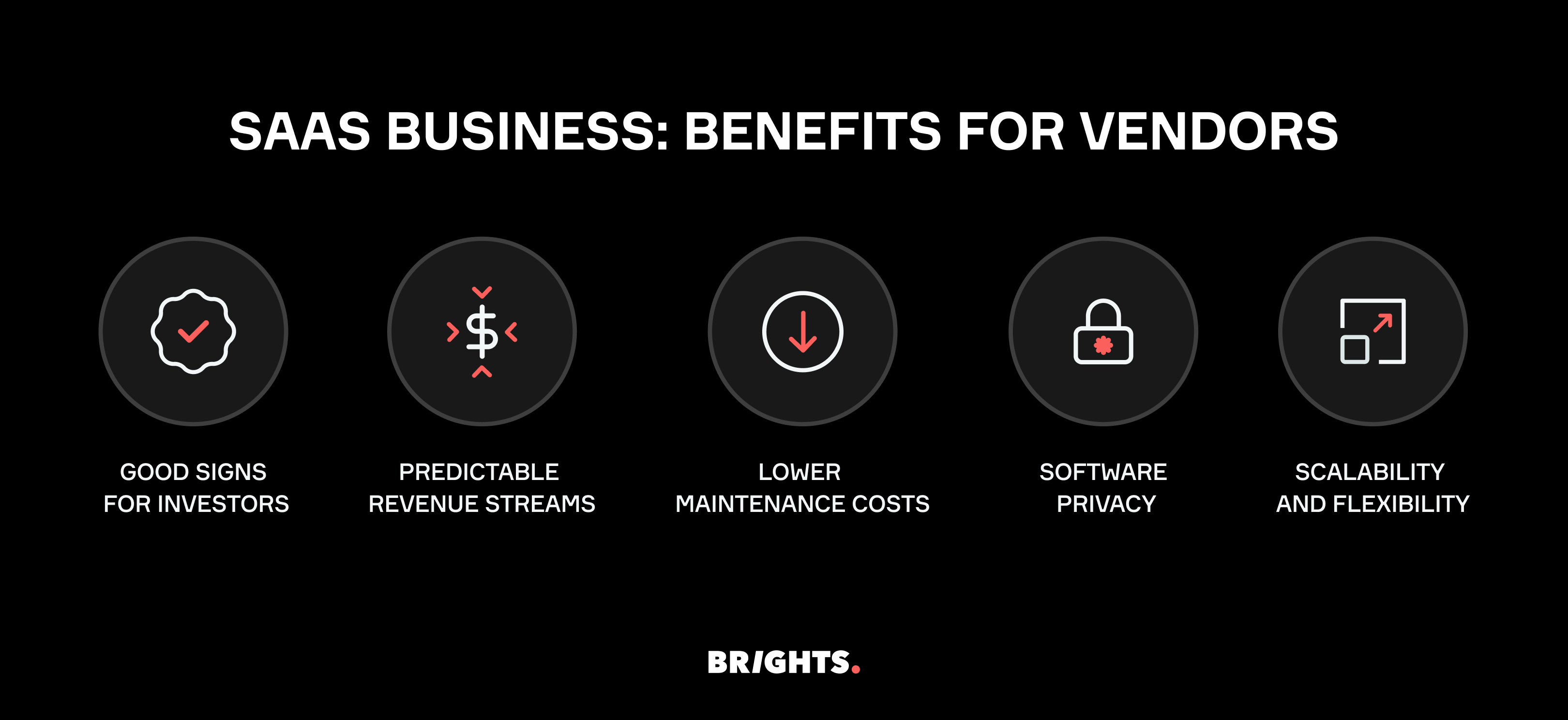
SaaS business: benefits for vendors
Good signs for investors.
The subscription-based revenue model, coupled with low customer acquisition costs and high customer retention rates, can lead to exponential revenue growth over time. This growth trajectory is particularly appealing to venture capitalists and private equity firms seeking high returns on investment. According to Dealroom, 47% of VC was invested in startups with a SaaS business model in 2023, a trend that has been on the rise over the past decade. Additionally, the relatively low upfront costs associated with SaaS startups compared to traditional software companies reduce the barrier to entry for investors, allowing for diversification within investment portfolios.
Predictable revenue streams
Advantages of the SaaS business model include vendors' predictable revenue streams, with subscription-based pricing contributing to stable income. According to a report by Gartner, by 2025, SaaS is expected to account for 60% of all public cloud services revenue, highlighting its growing significance as a revenue driver for vendors.
Lower maintenance costs
By leveraging cloud-based infrastructure, SaaS vendors can significantly reduce upfront investment in hardware and IT infrastructure. Research by IDC forecasts that spending on public cloud services will reach $1.35 trillion by 2027, with SaaS accounting for a significant portion of this expenditure, underscoring the cost-saving benefits of cloud-based solutions for vendors.
Software privacy
One effective strategy in combating software piracy involves leveraging the inherent difficulty associated with pirating cloud-based software. Unlike traditional software installations, cloud-based solutions operate on remote servers accessible via the Internet, making unauthorized copying and distribution far more challenging. By adopting cloud-based models, software providers can significantly reduce the prevalence of piracy, safeguarding their intellectual property and revenue streams.
Scalability and flexibility
SaaS platforms provide vendors with scalability and flexibility, allowing them to adapt to changing market demands and user needs. A survey conducted by Flexera found that 93% of organizations reported using SaaS applications, indicating the widespread adoption of SaaS solutions among businesses of all sizes.
Challenges and risks of the SaaS model
Navigating the risks of the SaaS business model poses various challenges that require careful consideration and strategic management.
Multi-tenancy complexity
Multi-tenancy architecture poses intricate challenges in SaaS development, requiring a delicate balance between resource sharing and data privacy, security, and customization. Various models, including isolated, shared, and hybrid tenancy, each present unique complexities that must be navigated effectively to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction.
Data security and privacy
Data security and privacy are paramount concerns for SaaS development, necessitating robust measures to safeguard sensitive information while maintaining user accessibility and experience. Balancing convenience with comprehensive protection requires careful planning and implementation throughout the SaaS development lifecycle, from design and testing to deployment.
Scalability and performance
Scalability and performance are fundamental considerations in SaaS development, demanding strategies to accommodate growing user bases and maintain seamless operation under varying workloads. Achieving zero downtime deployment, addressing integration challenges, and optimizing system performance are critical for sustaining competitiveness and meeting user expectations.
Integration issues and third-party options
Integration challenges, including third-party integration and data consistency, present significant hurdles for SaaS developers seeking to streamline operations across diverse platforms and applications. Seamless integration of cloud-based SaaS products with other SaaS apps meticulous planning and execution to minimize disruptions and ensure seamless functionality.
Regulatory compliance
Maintaining regulatory compliance is a complex challenge in SaaS development, as companies must navigate a landscape of laws and regulations governing data security, privacy, and financial transactions. Adhering to evolving legal requirements demands ongoing diligence and expertise, ensuring that SaaS solutions meet compliance standards across diverse industries and regions.

Brights SaaS expertise
Our proficiency in SaaS development is exemplified by our involvement in groundbreaking projects such as a creative-focused project management platform aimed at streamlining the production process of creative assets.
In this project we focused on making it easy for users to work with videos and large files. This means they can quickly turn their ideas into real work, and it's also easy to chat and give feedback in real-time now. We also worked on making it simpler to get approval for the work. We designed a system where users can decide how to get things approved. This makes the whole process faster and easier for everyone.
Security was another area where we made a big difference. We added an extra layer of protection, kind of like a secret code, to keep the work safe and make the platform intuitive.
Lastly, we made sharing and getting notifications better. Now, users can share the work with others and get notified instantly. This means they don't have to wait, and can see their work right from the email.
Our partnership has transformed it into a more user-friendly and secure platform, ideal for managing creative projects and working with the team and partners. Brights' contributions underscore the power of successful collaboration in delivering valuable tools for creative teams.
The future of SaaS
In conclusion, the future of SaaS is poised for unprecedented expansion and transformation. As technology evolves and consumer expectations evolve alongside it, the SaaS landscape will continue to evolve rapidly, offering novel solutions to address emerging challenges across industries. With advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics, the potential for SaaS to revolutionize business operations, streamline workflows, and drive innovation is immense.
Moreover, the rise of edge computing, 5G technology, and the IoT will further propel the growth of SaaS by enabling seamless connectivity and unlocking new use cases. As such, entrepreneurs, developers, and investors alike stand poised to capitalize on the vast opportunities presented by the dynamic and ever-expanding field of SaaS. With the right vision, strategy, and execution, the possibilities are truly limitless in shaping the future of SaaS and redefining the way we work, collaborate, and interact with technology.
Request a quote
Mail us [email protected] or call +380 (44) 227-42-62
- 86 Hoza street, office 410, Warsaw, Poland, 00-682
- 50-b Simyi Prakhovykh str., Kyiv, Ukraine, 01033
- 276 Fifth Ave Ste 704 PMB 80, New York, NY, United States, 10001
This website uses cookies. For more information please see Privacy Policy .
- Product Launch
- Scaling Impact
- B2B SaaS Course
Product-Market Fit
- AI Strategy
Unlocking The Power of the SaaS Business Model: Everything You Need to Know

- October 24, 2023

The world of software has experienced a radical shift with the rise of the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) business model . As more businesses and consumers embrace the convenience and flexibility of cloud-based software, understanding the intricacies of the SaaS business model becomes increasingly critical. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the essence of the SaaS business model, its key components, various types, and the challenges it faces. We’ll also dive into developing the ideal SaaS business model, examine successful examples, and provide essential metrics and tools for SaaS executives.
Key Takeaways
- The SaaS business model combines subscription-based pricing and cloud-based delivery into a software solution
- Clear target market, product-market fit, customer acquisition strategies, testimonials & social proof are essential components for a successful SaaS business.
- Data driven decision making is key to track performance metrics and optimize operations while leveraging tools & resources available to reach scale.
The Essence of the SaaS Business Model
Cloud-based software offered on a subscription basis forms the foundation of a SaaS business. The business model deployed by a SaaS company is related to how it provides value and generates revenue. In this article, we explain the SaaS business model which is the combination of subscription-based pricing and cloud-based delivery. SaaS software eliminates the need for end-user licenses and infrastructure to host the software, as it’s hosted in the cloud. This unique business model offers compelling advantages such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use, making it an attractive choice for businesses and consumers alike.

The fundamental equation of the SaaS revenue model is Revenue = ARPU (Average Revenue Per User) x Customer Lifetime. This equation highlights the importance of acquiring and retaining paying customers while optimizing revenue streams. Recurring membership revenue, either in the form of monthly recurring revenue (MRR) or annual recurring revenue (ARR), forms the traditional main revenue stream for a SaaS business. The SaaS model’s success lies in its ability to provide a competitive advantage and adapt to the ever-changing needs of businesses and consumers.
Different Types of SaaS Business Models
A variety of SaaS business models, each bearing its unique benefits and challenges, are available. These include different pricing model options such as:
- Subscription pricing
- Tiered pricing
- Pay-per-usage
- One-time fee
- Monthly vs. annual subscription models
- Freemium model
Understanding the intricacies of each model can help SaaS businesses choose the most suitable option for their specific needs.
The subsequent sections present a detailed exploration of these different business models.
Subscription Pricing
Subscription pricing is a popular SaaS business model where customers pay a recurring fee to access the software. This model provides businesses with predictable recurring revenue and fosters customer loyalty by allowing them to access the software for a fixed fee rather than incurring large upfront costs or unpredictable variable costs.

Subscription pricing also enables SaaS businesses to scale their offerings easily, as customers can upgrade or downgrade their plans at their convenience and based on their needs.
Tiered Pricing
Tiered pricing is a SaaS business model that offers different pricing tiers with varying features and benefits. This model allows businesses to cater to a diverse range of customer segments and needs, from small businesses to large enterprises. By offering multiple pricing plans with different combinations of features, SaaS businesses can appeal to a wider audience and maximize their revenue potential.
Examples of SaaS companies that leverage tiered pricing include Zendesk , Mailchimp , Canva , and Microsoft 365 Business .
Pay Per Usage
Pay-per-usage is a SaaS business model where customers pay based on their usage of the software. This model offers flexibility for customers who may not require continuous access to the software or prefer to pay only for what they use.
Pay-per-usage pricing can be beneficial for businesses that want to provide cost-effective solutions for their customers, while still generating revenue based on the actual usage of their product.
One-Time Fee
The one-time fee model is a SaaS business model that requires customers to pay a one-time fee for lifetime access to the software. This model can be advantageous for customers who prefer not to commit to long-term subscriptions and for businesses that wish to generate immediate revenue. However, it may present challenges in terms of predicting and sustaining consistent revenue streams, as there are no recurring payments from customers so this model doesn’t work well for SaaS businesses with variable costs based on usage.
Monthly vs Annual
Monthly and annual subscription models each have their own advantages and disadvantages for SaaS businesses. A monthly subscription provides predictable recurring revenue and steady income but may be more susceptible to customer churn and higher customer acquisition costs.

Annual subscriptions, on the other hand, offer cost savings to customers and more predictable cash flow for businesses but may require more significant upfront commitments from customers.
SaaS businesses can maximize their revenue potential by offering both subscription options and allowing customers to choose the plan that best suits their needs.
Freemium Model
One way to try and add a much larger volume of users on your platform is to leverage what’s referred to as the freemium model. This is where your SaaS business offers users a free tier that is limited by feature set or capacity. The idea is that overtime there will be opportunities to upsell users to a higher tier or paid subscription.
The freemium model works very well for SaaS companies like Hubspot , but it isn’t for everyone. You need to be VERY certain about your activation points because if you aren’t, your costs could scale while your revenue shrinks.
Key Components of a Successful SaaS Business Model
To achieve success in the SaaS industry, businesses must focus on several critical components, including:
- Identifying the target market
- Ensuring product-market fit
- Implementing customer acquisition strategies
- Leveraging customer testimonials and social proof
- Pricing in a competitive manner
In the successive subsections, a more detailed exploration of these components and their contributions to the success of a SaaS business is provided.
Clear Target Market
A clearly defined target market within a SaaS business brings multiple advantages, such as:
- Optimizing marketing and sales initiatives
- Maximizing the number of paid conversions
- Strengthening credibility and trust
- Streamlining resource allocation
- Optimizing product development

This landing page from Hubspot makes it very clear that their software is for sales teams. Being more specific with your targeting and marketing will make it MUCH easier for you to connect with your buyer.
Ensuring that the product meets the needs of the intended customer base is crucial for a SaaS business to achieve product-market fit. To attain product-market fit, SaaS companies must go beyond merely responding to feature requests and instead focus on the commonalities among their most successful customers.
Products that are able to fit into the right markets often observe an exponential growth in their sales. Conversion rates tend to be much higher compared to other software products and working on can be considerably more enjoyable. By prioritizing product-market fit, SaaS businesses can effectively address their customers’ needs and drive long-term success.
Customer Acquisition Strategies
Customer acquisition strategies, including:
- Content marketing and outreach
- Referral programs
- Pricing adjustments
- Providing incentives and discounts
- Utilizing social media
These strategies are vital for the growth of a SaaS business. One successful example of a SaaS business leveraging customer acquisition strategies is HubSpot, which employed a “Freemium” model, offering a free version of their product and upselling customers to paid plans. By providing value upfront and reducing customer acquisition costs, HubSpot managed to exponentially grow its customer base.

Pro Tip: The freemium model can be a great way to gain a lot of users quickly. However, you need to be careful that you aren’t giving too much away. If you do, conversions will be low which means low revenue and high costs.
Also essential is the monitoring of customer acquisition cost (CAC) to ensure that the lifetime value (LTV) of customers surpasses the cost of acquiring them by a significant margin.
Pro Tip: A common ratio often used to determine the financial health of a SaaS business is a ratio of these two metrics LTV / CAC. The optimal threshold you should hope to achieve is 3/1 for this metric. Too low and you’re either not charging enough or spending too much to acquire customers. Too high and you could probably be growing faster.
Customer Testimonials and Social Proof
Customer testimonials and social proof are powerful tools that can help SaaS businesses build trust and credibility with potential customers. By showcasing real-life examples of satisfied customers and the benefits they’ve experienced from using the product, SaaS businesses can instill confidence in potential customers and persuade them to give the software a try.

Companies like Hubspot, Mailchimp and Slack have successfully leveraged customer testimonials to provide social proof and establish trust with prospective customers. Collecting customer testimonials can be done through personalized emails or messages, requesting feedback on the user’s experience with the software, and even offering incentives such as discounts or freebies in exchange for testimonials.
Pricing Competitively
Setting competitive pricing for a SaaS business can be challenging, as companies must balance profitability with customer acquisition. Some strategies for pricing SaaS products competitively include:
- Gaining insight into the target market’s willingness to pay
- Evaluating the pricing of direct competitors
- Adjusting accordingly based on the platform’s additional features, market saturation, and other factors
- Calculating the ROI or return on investment for their customers
By analyzing competitor prices and constructing pricing tiers that reflect users’ varying needs, SaaS businesses can ensure they remain competitive while maximizing profitability.
Challenges of a SaaS Business Model
Several challenges and obstacles including high churn rates, scaling, competitive pricing, and matching user expectations confront SaaS businesses.
The subsequent subsections contain detailed discussions about these challenges and potential solutions to overcome them through the design of your SaaS business model.
High Churn Rates
High churn rates are a common challenge faced by SaaS businesses, as customer retention is crucial for maintaining growth and profitability. To reduce churn rates, businesses can:
- Analyze the reasons behind customer churn
- Implement strategies to address them
- Offer competitive pricing
- Provide exceptional customer support
- Continuously update and improve the product to meet evolving customer needs
A great strategy related to a SaaS business model to reduce churn is to offer discounts along the cancellation workflow for customers. For example, if your customer wishes to cancel, you might offer them a 50% discount on the next month to remain a customer. This strategy is valuable because it’s often cheaper to keep an existing customer than to find a new one. The key here is to keep your discount below your CAC or customer acquisition cost.
Scaling and Growth
Scaling a SaaS business can be challenging due to the need for continuous investment in product development and customer support. To manage growth and scaling effectively while preserving service quality, businesses can:
- Align their product, marketing, and sales teams
- Incentivize referrals and affiliates
- Enhance integration capabilities
- Optimize their sales strategy
- Perform a competitive analysis
A key to keep in mind as you attempt to scale your SaaS business related to your business model is to keep your profitability and LTV / CAC ratio in mind. Focus on LTGP or lifetime gross profit and the performance of key SaaS economic metrics.

Get our awesome product content delivered daily-ish to your inbox

Related Material: For more information on LTGP or lifetime gross profit and the most important SaaS economic metrics read my related articles.
Setting competitive pricing can be difficult for SaaS businesses, as they must balance profitability with the cost of customer acquisition. To price their products competitively, businesses can:
- Gain insight into their target market’s willingness to pay
- Evaluate the pricing of their direct competitors
- Adjust their pricing based on market saturation and their platform’s most valuable features
This is a key area of differentiation for your SaaS business model. The most effective SaaS business model’s aren’t just priced competitively, they are priced perfectly. They know EXACTLY what to monetize and WHEN. This should be an intense area of focus for your experimentation efforts as you learn about activation points and track return on investment for your customers.
Matching User Expectations
SaaS businesses must continuously adapt and improve their offerings to meet the evolving expectations of their users. This can be achieved by investing in product development, listening to customer feedback, and staying up-to-date with industry trends.

By focusing on matching user expectations, SaaS businesses can ensure their products remain relevant and valuable, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The key to innovation here through your SaaS business model is to focus on the MOST valuable functionality you can provide to your users. If you know their top problem worth solving then your core functionality should be based around it.
Additional Reading: To learn more about problems worth solving see my articles here and here .
Developing the Ideal SaaS Business Model
Creating the optimal SaaS business model requires a deep understanding of the target market, building ROI into the experience, and making data-driven decisions.
The succeeding subsections will guide on achieving these objectives and developing a successful SaaS business model.
Understanding Your Target Market
Gaining a deep understanding of your target market is essential for developing a successful SaaS business model. By understanding the needs and preferences of your target audience, you can:
- Tailor your product development and marketing efforts to cater to their specific requirements
- Create a product that effectively addresses their problems and provides maximum value
- Increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.

Building a ROI Into the Experience
Ensuring a strong return on investment (ROI) for customers is crucial for a SaaS business to maximize your products LTV or lifetime value. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
- Offer competitive pricing to attract customers and provide them with a cost-effective solution.
- Provide customer testimonials and social proof to showcase the success and satisfaction of existing customers.
- Focus on product-market fit by understanding the needs and pain points of your target audience and tailoring your product to meet those needs.
By implementing these strategies, SaaS businesses can ensure their customers receive maximum value for their investment, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and retention.

The objective is to provide your customers with a strong ROI. For example, if your software costs $1 and you give them back $2 in value that’s great, but if you can give them back $5 or $10 your product would be AMAZING.
Not Leaving Money on the Table
SaaS businesses must ensure they are maximizing revenue opportunities by:
- Offering a range of pricing options
- Providing flexible pricing plans
- Exploring new ways to monetize their product
By doing so, SaaS businesses can attract a wider audience and maximize their revenue potential.
The best way to balance generating revenue and providing value is to track the customer’s ROI or return on investment. The greater the value they get back from their investment into your software the more likely they are to become raving fans that will stay with you a long time.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Utilizing data to make informed decisions is key for a SaaS business to optimize its offerings and strategies. By collecting and analyzing data on customer behavior, preferences, and needs, businesses can identify trends and opportunities for growth and expansion. This allows them to make data-driven decisions that will ultimately lead to improved performance and success in the SaaS industry.

You should be continually investing in research and discovery with your users and customers. Build momentum by solving their top problem then go find their next biggest problem. This activity and what you do with your software should be continuously driven by data. Review my guide on identifying problems worth solving to learn more.
Case Studies: 5 SaaS Business Model Examples
To illustrate the various SaaS business models and strategies, we present five case studies of successful SaaS businesses:
Hubspot is a CRM or customer relationship management platform for businesses. They leverage a freemium business model for their B2B SaaS product. This means you can join for free and only pay when you want to upgrade in either capacity or unlocking advanced functionality that they pub behind their paywall.
Mailchimp provides email marketing software for businesses. Mailchimp also leverages a freemium business model which allows their customers to send a certain number of emails to a certain number of contacts before they need to upgrade their account.
Apollo is a cold outreach sales and marketing platform for businesses. Apollo leverages a freemium model and tiered approach for their B2B SaaS business model. With Apollo you will pay for additional capacity or functionality that isn’t included in their free tier.
Slack is a workplace communication and productivity platform for businesses. Slack leverages a freemium model then has a few paid tiers based on primarily advanced functionality and the extensibility of their platform. If you want to integrate Slack further into your workplace software stack, then you will likely begin paying for Slack for the privilege.
Atlassian primarily offers workplace productivity software for technical teams of businesses across many industries. Atlassian has a fantastically effective business model. The team at Atlassian does an exceptional job of making it super cost effective to hop onto their platform when your operation is small, but charging you more as you grow. This is great example of how NOT to leave money on the table. Atlassian also primarily does this by leveraging a freemium model then offers various paid tiers for accessing advanced functionality.
These examples demonstrate how different SaaS businesses have leveraged their unique business models and strategies to achieve success in the industry. It’s obvious to see that each of these highly successful B2B SaaS products has effectively leveraged the freemium and tiered pricing business models. Study each to learn more about how to design yours.
Essential Metrics for SaaS Businesses
Tracking critical metrics is crucial to measure the success of a SaaS business and make informed decisions. By monitoring these metrics, SaaS businesses can gain insights into their performance and identify areas for improvement. You should be tracking:
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
- Customer lifetime value (LTV)
- Customer churn
- Monthly recurring revenue (MRR)
This will enable them to optimize their business strategies and ultimately achieve greater success in the industry.

For a deeper dive on SaaS metrics read my guide here .
Tools and Resources for SaaS Entrepreneurs
SaaS entrepreneurs can benefit from a range of tools and resources to optimize their business operations and strategies. Some popular tools for SaaS businesses include:
- Example: Stripe
- Example: Hubspot
- Example: Hotjar and Google Analytics
- Example: Asana and Atlassian
- Example: Mailchimp and Apollo
By leveraging these tools and resources, SaaS entrepreneurs can streamline their processes, make data-driven decisions, and ultimately achieve greater success in their businesses.
In conclusion, the SaaS business model offers numerous advantages and opportunities for growth in today’s competitive software market. By understanding the key components of a successful SaaS business, exploring different business models, and overcoming common challenges, SaaS entrepreneurs can optimize their businesses for success. By leveraging essential metrics, tools, and resources, they can make data-driven decisions and build a strong foundation for long-term success. With dedication, innovation, and a customer-centric approach, the possibilities for SaaS businesses are virtually endless.
For more help developing the optimal business model for your SaaS business, schedule a free strategy session with me .
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of a saas business model.
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a type of cloud computing that delivers applications over the Internet. Popular SaaS examples include Dropbox, Salesforce, Google Workspace and Zoom. Services are typically priced on a subscription or pay-as-you-use model instead of purchasing all features upfront.
What is the 3 3 2 2 rule for SaaS?
The 3 3 2 2 rule for SaaS indicates that a successful SaaS company managed for aggressive growth should triple their annual revenues for two consecutive years, followed by doubling them for the next two years. This should be starting from a material baseline of over $1 million in annual recurring revenue (ARR).
How does a SaaS company make money?
A SaaS company typically earns money from recurring membership revenue which is most often set up in the form of ARR or MRR. The software product is distributed at a fixed price, with customers paying regularly on either a monthly or annual subscription basis.
What is a SaaS business model?
The SaaS business model is based on the premise of centrally hosted software being licensed to customers via subscription plans. Customers can access the software through a cloud infrastructure, operated through a web browser, and pay a monthly fee for it.
What are the key components of a successful SaaS business model?
Successful SaaS businesses identify their target market, ensure product-market fit, implement customer acquisition strategies, leverage customer testimonials and social proof, and price competitively to develop a successful SaaS business model.
Related posts
Maximizing Impact: The Power of Generative AI for Nonprofits

The Ultimate Guide to Effective SaaS Google Ads: Tips, Tricks, and Examples

The Ultimate Guide to Software Advertising: Boost Your Marketing Strategy

Unleashing the Power of Fintech: How Financial Technology Is Revolutionizing Our Lives
An In-Depth Guide to the Product Development Process

Find the Right SaaS Consultant for Your Business
- 250 Main Street, 2nd Floor, USA
- [email protected]
Mastering the SaaS Business Model: A Comprehensive Guide
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the Software as a Service (SaaS) business model has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing how software solutions are delivered, consumed, and monetized. As businesses increasingly seek flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions, the SaaS model has become a driving force, disrupting traditional software licensing and delivery methods. This thorough book explores the nuances of the Software as a Service (SaaS) business model, including its significance, different varieties, underlying theories, and useful applications in various industries.
What is the SaaS Business Model?
The SaaS (Software as a Service) business model involves delivering software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis. Instead of purchasing and installing software on individual devices, users access SaaS applications through web browsers or dedicated client interfaces. This model eliminates the need for upfront software licensing fees and hardware investments, offering businesses a more cost-effective and scalable solution. SaaS providers manage the software’s infrastructure, maintenance, updates, and security, while users benefit from easy access, regular updates, and flexible payment options.
The SaaS business model typically includes features such as:
Scalability: .
SaaS applications are designed to scale effortlessly to accommodate growing user bases and evolving business needs. Users can easily adjust their subscription plans to access additional features or accommodate increased usage without disruption.
Accessibility:
SaaS applications can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, enabling users to work remotely and collaborate seamlessly across different locations. This accessibility fosters productivity and flexibility in today’s distributed work environments.
Regular Updates and Maintenance:
SaaS providers are responsible for maintaining and updating the software to ensure optimal performance, security, and compliance with industry standards. Users benefit from continuous improvements and enhancements without the hassle of manual updates or upgrades.
Integration Capabilities:
SaaS applications often integrate with other software systems and platforms, allowing seamless data exchange and workflow automation. This interoperability enhances efficiency and enables organizations to leverage investments in complementary tools and technologies.
Pay-Per-Use Options:
Some SaaS providers offer pay-per-use or pay-as-you-go pricing models, allowing users to pay only for the resources or features they consume. This flexible pricing structure enables cost optimization and aligns expenses with actual usage, which is particularly beneficial for businesses with fluctuating demand.
Data Security and Compliance:
SaaS providers implement robust security measures to protect user data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. These measures include encryption, access controls, regular audits, and adherence to industry-specific standards such as GDPR or HIPAA, instilling user confidence and trust.
Why is it important to follow the SaaS Business Model?
Adopting the SaaS business model offers numerous advantages for both software providers and customers, making it an increasingly important approach in today’s digital landscape:
Recurring Revenue Streams:
For software providers, the SaaS model enables predictable and recurring revenue streams through subscription-based pricing, fostering long-term customer relationships and a more sustainable business model.
Lower Upfront Costs:
Customers benefit from lower upfront costs than traditional software licensing, paying a subscription fee instead of a large one-time purchase price.
Scalability and Flexibility:
Because SaaS solutions are so easily scalable, they encourage agility and adaptation by enabling firms to quickly modify their expenses and use them in response to changing needs.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
Software vendors handle all maintenance, security patches, and updates, guaranteeing that users never have to worry about manual updates or additional IT work to stay up to speed.
Accessibility and Collaboration:
With SaaS applications accessible from any internet-connected device, users can work remotely and collaborate seamlessly, enhancing productivity and enabling a distributed workforce.
SaaS Model Types
While the core concept of the SaaS business model revolves around delivering software over the Internet on a subscription basis, there are various types and approaches within this model. Here are some common SaaS model types:
Freemium Model:
- Offers a basic version of the software for free, with optional upgrades to premium, paid plans for enhanced features.
- This model attracts users with a low barrier to entry while monetizing through premium offerings.
Subscription-Based Model:
- Users pay recurring subscription fees (monthly, quarterly, or annually) for continued access to the software.
- Pricing structures may vary based on user count, feature sets, or usage levels.
Usage-Based Model:
- Charge customers based on usage metrics, such as data storage, bandwidth utilization, or API calls.
- This model aligns costs with actual usage, providing flexibility for customers with fluctuating needs.
Tiered Pricing Model:
- Offers the software at multiple price levels, each tier providing a distinct set of features and functionalities.
- Customers can choose a tier matching their requirements and budget, allowing customization and scalability.
Enterprise Model:
- This model is tailored for large enterprises and includes dedicated support, specialized pricing, and deployment options.
- They are designed to meet enterprise-level clients’ unique needs and demands, often involving customizations and integrations.
The Fundamental Equation of SaaS
At the core of the SaaS business model lies a fundamental equation that determines the success and profitability of a SaaS company:
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) > Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
This formula emphasizes the crucial need to maximize client lifetime value while obtaining and keeping clients at a reasonable cost. SaaS companies must work hard to ensure that the money they get from each customer throughout their lifetime is greater than the money they spend finding and keeping them.
How would the SaaS business model apply to Businesses/Industries?
Numerous advantages and opportunities are provided by the SaaS business model, which can be implemented in a variety of industries and business types:
Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs):
SaaS solutions offer SMBs affordable access to enterprise-grade software, enabling them to leverage powerful tools and capabilities without significant upfront investments.
Startups and Entrepreneurs:
The SaaS model allows startups to launch and scale their software offerings quickly, minimizing infrastructure costs and enabling rapid iteration and customer feedback loops.
Large Enterprises:
Enterprise-level SaaS solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and reduced IT overhead, allowing large organizations to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and adapt to changing business needs.
Vertical Industries:
SaaS solutions can be tailored to specific industries, such as healthcare, finance, retail, or manufacturing, providing specialized functionality and compliance with industry-specific regulations.
Horizontal Applications:
SaaS offerings like customer relationship management (CRM), project management , and productivity tools can be utilized across various industries and businesses, enabling broad adoption and scalability.
How does the SaaS business model work?
To access and utilize the software, users of the SaaS business model must pay a recurring cost. This revenue model is based on subscriptions. This is how it usually operates:
Acquisition:
Software providers attract potential customers through various marketing and sales channels, often offering free trials or freemium versions to showcase their products.
Onboarding:
Customers sign up for the SaaS service, providing billing and user information, and are granted access to the software.
Subscription Management:
Customers are billed regularly (monthly, quarterly, or annually) based on their chosen subscription plan and usage.
Delivery and Support:
The software supplier hosts and maintains the application, guaranteeing its security, performance, and availability. The service includes constant updates and customer support.
Retention and Expansion:
SaaS providers focus on retaining existing customers by delivering value, addressing their evolving needs, and offering opportunities for expansion through additional features, users, or integrations.
Recurring Revenue:
Successful SaaS businesses generate predictable and recurring revenue streams from their customer base, fostering long-term growth and profitability.
SaaS Business Stages
SaaS businesses typically go through several stages as they grow and evolve, each with its challenges and opportunities:
Startup Stage:
This initial stage focuses on developing a minimum viable product (MVP), validating the market, and acquiring early adopters.
Growth Stage:
As the customer base expands, the emphasis shifts to scaling operations, optimizing customer acquisition and retention, and securing funding for further growth.
Maturity Stage:
Established SaaS businesses focus on maintaining market leadership, enhancing product offerings, and exploring new revenue streams or expansion opportunities.
Renewal/Expansion Stage:
Existing customers are approached for subscription renewals, upsells, or cross-sells, leveraging their familiarity with the product and the value it provides.
Potential Exit Stage:
Successful SaaS companies may consider exit strategies, such as acquisitions or initial public offerings (IPOs), providing liquidity for investors and founders.
Tools that Help to Grow SaaS Businesses
To support and enhance the growth of SaaS businesses, various tools and platforms can be leveraged:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Tools like Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM help manage customer interactions, sales pipelines, and customer data.
Marketing Automation:
Platforms such as Marketo, HubSpot, and Pardot enable automated marketing campaigns, lead nurturing, and customer engagement.
Analytics and Business Intelligence:
Products and services such as Looker, Mixpanel, and Google Analytics offer important insights into consumer behavior, usage trends, and business success.
Customer Success and Support:
Tools like Intercom, Zendesk, and Freshdesk facilitate customer support, feedback management, and proactive customer success initiatives.
Billing and Subscription Management:
Platforms like Recurly, Chargify, and Zuora help manage subscription billing, payment processing, and revenue recognition.
Development and Deployment:
Tools like GitHub, CircleCI, and AWS enable efficient software development, version control, and deployment processes for SaaS applications.
The Pros of the SaaS Business Model
The SaaS business model offers numerous advantages for both software providers and customers:
Software providers benefit from predictable and recurring revenue streams, enabling better forecasting and long-term growth planning.
Customers enjoy lower upfront costs and easy access to enterprise-grade software without significant upfront investments.
Reduced IT Overhead:
Customers benefit from reduced IT overhead, as the software provider is responsible for hosting, maintaining, and securing the application and its associated infrastructure.
Rapid Time-to-Value:
SaaS solutions can be deployed and accessed quickly, enabling businesses to realize value and productivity gains faster than traditional software implementations.
The Cons of the SaaS Model
While the SaaS business model offers numerous advantages, it also has certain limitations and challenges:
Internet Dependency:
SaaS solutions require a stable internet connection, which can be challenging in areas with poor connectivity or during outages.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
Even with SaaS providers’ security precautions, some companies could still be worried about data privacy and the dangers of keeping confidential data on external servers.
Integration Challenges:
Integrating different SaaS solutions with preexisting on-premises or cloud apps can be challenging and require more resources or customization.
Vendor Lock-In:
Switching from one SaaS provider to another can be difficult due to data migration challenges and compatibility issues, potentially leading to vendor lock-in.
Limited Customization:
Large-scale customization to satisfy particular business requirements may be limited because SaaS solutions are usually made to cater to a wide range of users.
Ongoing Costs:
Although SaaS removes the need for upfront expenses, companies still need to account for regular subscription fees, which can add up over time and possibly surpass the price of a conventional software license.
Software/Applications using the SaaS business model:
Salesforce:.
- Salesforce offers a cloud-based CRM (Customer Relationship Management) platform that helps businesses manage sales, marketing, customer service, and more.
- It provides a comprehensive suite of tools for lead management, pipeline tracking, customer engagement, and analytics, accessible via subscription-based pricing.
Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365):
- Microsoft 365 is a suite of productivity and collaboration tools delivered as a cloud-based service, including Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, Teams, and more.
- Users can access these applications from any device with an internet connection, enabling seamless collaboration, document sharing, and real-time communication.
Google Workspace (formerly G Suite):
- Google Workspace offers cloud-based productivity tools, including Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, and Meet.
- It enables users to create, edit, and collaborate on documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and more, securely stored in the cloud and accessible from anywhere.
- Zoom is a cloud-based video conferencing and collaboration platform that allows users to host online meetings, webinars, and virtual events.
- With features such as HD video and audio, screen sharing, and chat, Zoom has become popular for remote work, distance learning, and social gatherings.

- Slack is a cloud-based messaging and collaboration platform designed to streamline organizational communication and teamwork.
- It offers channels for team discussions, direct messaging, file sharing, and integration with third-party tools, enhancing productivity and fostering a connected workplace culture.
Who Best Fits a SaaS Business Model?
Although the SaaS business model can be used by many other types of companies and sectors, the following may be especially good fits:
SMBs can benefit from the affordability, scalability, and reduced IT overhead offered by SaaS solutions, enabling them to access enterprise-grade software without significant upfront investments.
Startups and Rapidly Growing Companies:
SaaS solutions allow startups and rapidly growing companies to quickly deploy and scale software solutions without requiring extensive infrastructure investments, enabling agility and responsiveness to changing business needs.
Businesses with Distributed or Remote Workforces:
Organizations with employees or teams distributed across multiple locations can leverage the accessibility and collaboration capabilities of SaaS applications to enhance productivity and seamless collaboration.
Companies Seeking Cost Optimization:
Businesses looking to optimize their IT costs and shift from capital expenditures (CapEx) to operating expenses (OpEx) can benefit from SaaS solutions’ subscription-based pricing model.
Industries with Strict Compliance and Security Requirements:
SaaS providers often invest heavily in security and compliance measures, making SaaS solutions viable for industries with stringent regulations, such as healthcare, finance, and government.
How does the SaaS business model differ from traditional software licensing?
Conventional software licensing usually entails paying an upfront amount for a perpetual license and recurring maintenance fees. The SaaS model, in contrast, charges a recurring fee for users to access and utilize the software hosted by the provider.
What are the benefits of the SaaS model for customers?
Key customer benefits include lower upfront costs, scalability and flexibility, automatic updates and maintenance, accessibility from any internet-connected device, and reduced IT overhead.
How do SaaS providers generate revenue?
SaaS providers generate revenue through recurring subscription fees customers pay to access their software solutions. Revenue streams can be based on pricing models, such as flat-rate subscriptions, tiered pricing, usage-based billing, or freemium models.
What is the freemium model in SaaS?
A basic program version is free under the freemium model, with the option to upgrade to premium, paid plans with more features and capabilities. With time, this strategy hopes to turn free users into paying clients by drawing them in with an offer.
How does the SaaS model impact software updates and maintenance?
The software provider is responsible for hosting, maintaining, and updating the program under the SaaS model. Without manual installation or additional IT work, users immediately receive updates and security fixes, guaranteeing they always have access to the newest features and functionalities.
What are some challenges associated with the SaaS business model?
Challenges may include customer acquisition and retention, managing churn rates, ensuring data security and compliance, seamless integration with other systems, scalability, performance as user bases grow, and potential vendor lock-in for customers.
The SaaS business model has revolutionized how software solutions are delivered, consumed, and monetized. By embracing this innovative approach, software providers can tap into recurring revenue streams, foster long-term customer relationships, and deliver a superior user experience. In contrast, customers benefit from cost-effective, scalable, and constantly updated solutions. As businesses prioritize agility, cost-efficiency, and digital transformation, the SaaS business model is poised to become increasingly prevalent across industries. Software providers that adapt to this model and effectively navigate its nuances will be well-positioned to succeed in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
- Share This Post:
Add a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
Client management software: boost efficiency with powerful tools, financial planning software solutions for better budgeting, unlock your language potential with language learning software.
Benefits of SaaS: Should you choose a SaaS business model?
SaaS has many advantages: it’s easy to adopt and low-cost upfront. But there can be disadvantages too. Is SaaS right for you?
What is SaaS?
- SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS vs. on-premise
- 4 advantages of choosing SaaS
- 4 disadvantages of SaaS
- Are you ready for a SaaS model?
Join our newsletter for the latest in SaaS
By subscribing you agree to receive the Paddle newsletter. Unsubscribe at any time.
The SaaS model continues to gain traction. It seems as though more and more companies are jumping on the cloud bandwagon…and for good reason. If you haven’t transitioned to SaaS yet, I promise moving to a cloud-based computing system sounds more complicated than it actually is. There are many different cloud-based models for storing data, but this article is focused directly on SaaS.
I’ll walk you through what SaaS is, how it compares to other cloud services, and the pros/cons of SaaS.

SaaS stands for “software as a service.” SaaS is when a provider hosts an application and makes it available to subscribers over the internet. Simply, any company that sells software via a central, cloud-based system can be considered SaaS. SaaS is typically a downloadable application that users can use as long as they have an internet connection.
SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS vs. on-premise: What’s the difference?
There are two other cloud service models to be aware of: PaaS and IaaS. PaaS stands for ‘platform as a service,’ providing developers with a complete environment for developing and deploying apps over the internet. IaaS stands for ‘infrastructure as a service’ and provides the hardware to perform various tasks.
Some common examples of SaaS solutions are of course ProfitWell, SalesForce, Microsoft Office, Zoom, Dropbox—the list goes on.
Cloud infrastructure services , aka IaaS, are highly scalable and automated computer, network, and storage resources. IaaS is made up of a collection of physical and virtualized resources. Customers typically don’t interact with the physical data centers, but it is provided as a service to them. Google Compute Engine (GCE), Digital Ocean, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) are all good examples of IaaS.
Platform as a service, PaaS , is also a cloud computing but service providers deliver platforms to clients, allowing them to develop, run, and manage business applications without the need to build and maintain the infrastructure. PaaS’s delivery model is similar to SaaS, however instead of delivering the software over the internet, PaaS is a platform for software creation. Some PaaS examples include Windows Azure, Google App Engine, and Force.com .
4 benefits & advantages of choosing SaaS
Moving everything to the cloud, in general, has numerous benefits. For Saas, specifically, the benefits all boil down to cost and ease of use. Let’s get right into each direct benefit you’ll definitely appreciate once you transition to SaaS.
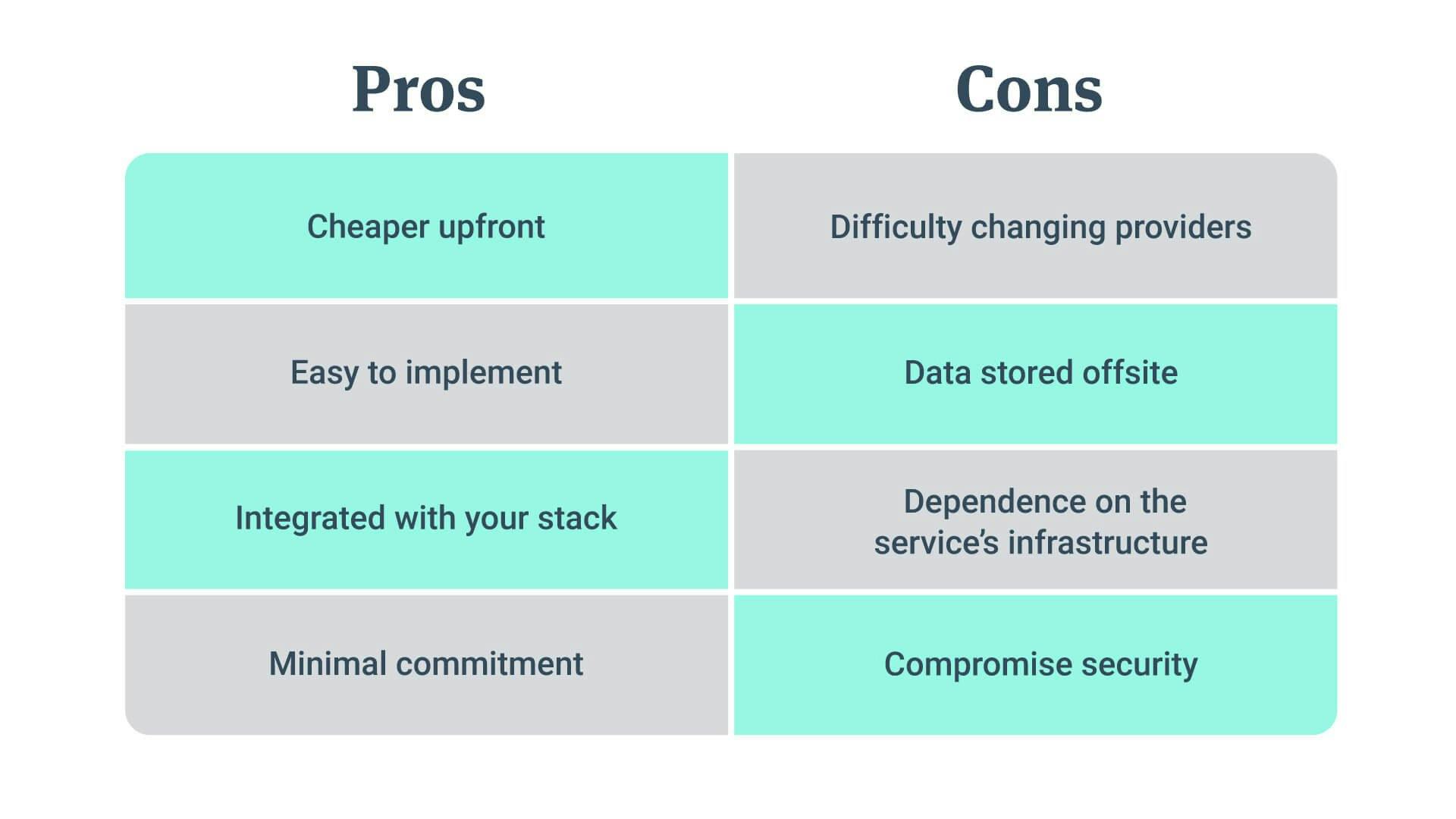
Cheaper upfront
Since SaaS is typically subscription-based (aka, no licensing fees) there are lower costs upfront. SaaS exists in the cloud, meaning hardware installation costs are completely eliminated. Without hardware—you don’t have to continuously pay for hardware maintenance. This makes SaaS advantageous for startups.
Easy to implement
SaaS is already installed and configured in a cloud, so you don’t have to worry about setting up the infrastructure (which can get complicated). Implementation typically only involves registering and either downloading a web browser extension or the application to your computer.
Adopting SaaS means you don’t have to build out your own infrastructure and software. Beyond the implementation stage, SaaS is easy for updates. SaaS providers manage hardware and software updates, leaving you with a more seamless experience.
Integrated with your stack
The SaaS model is extremely customizable as most SaaS applications are geared toward integrations. Take ProfitWell for example. We understand that you need additional software to maximize your business. We integrate with a variety of different platforms. With ProfitWell, you can easily use our products to manage your pricing while also managing your billing through a service like Stripe.
Minimal commitment
Annual contracts are the best in terms of reducing churn. However, the subscription model is flexible. Offering month-to-month payments makes customers feel more at ease signing on with your product, knowing they can back out if they are unhappy. Most SaaS companies also offer different plans that include various pricing options and service features. Having a wide variety of software allows customers to switch things up if need be.
4 potential downsides & disadvantages of SaaS
While I tend to think the pros outweigh the cons when it comes to SaaS, I’ll mention the cons regardless. The few points I’m about to break down are things to consider if you are planning on transitioning to SaaS.
Difficulty of changing providers
If your SaaS provider goes bust or you want to make a change, transferring your data may be difficult. Have the conversation with your SaaS provider in advance about how you can easily access data or transfer it in case you want to change plans or the provider goes south.
Storing your data offsite
Depending on how sensitive your data is, storing it offsite with a SaaS service may present problems with compliance. SaaS is definitely gaining fraction, but there are limited options because a lot of applications have yet to develop SaaS versions. Before purchasing a software subscription, research the capabilities you need and ensure they are present.
Dependence on the service’s infrastructure
With a SaaS product, you're dependent on their infrastructure and software: if it goes down, so do you. Most SaaS vendors do promise reliability, however you should still do your research on the reliability of a certain vendor before moving forward. You also need to decide if your company can handle the potential of an outage, that’s completely out of your control. I’m not saying an outage is definitely going to happen, but there is always the risk and you need to be aware that this could happen when using SaaS.
Compromised security
Security is the biggest concern for companies hesitant about transitioning to the SaaS model. Data is stored locally with conventional software, but with SaaS, your data is likely stored offsite by the vendor. You must rely on the vendor to properly secure and backup all of your data. Another security risk is when employees access the software on potentially insecure outside connections. This increases the risk for hackers and people stealing your information. To maximize security protection, research your vendor thoroughly. As for your employees, require them to enable two-factor authentication when using the software on their own computers.

Take the headache out of growing your software business
We handle your payments, tax, subscription management and more, so you can focus on growing your software and subscription business.
Is your business ready for a SaaS model?
Not all businesses are meant to be a SaaS business, but if you have a great software, an existing customer base, and a recurring payment processor, you’re on your way there. When implemented correctly, SaaS is a better business model for not only clients but also software providers. It gives your customers an easy-to-use system while giving your business a simple way to upgrade your product and push those changes out to customers easily.
If you want to take your business to the next level and are ready to experience even more growth, transition to SaaS.
Related reading

What Is SaaS? How Software-as-a-Service Can Boost Your Business

Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a software distribution model in which a cloud provider hosts applications and makes them available to end-users over the internet. It’s an acronym that stands for software as a service and describes any software that isn’t run at your premises, never resides on a local machine, and is a full-blown app on its ow n.
A few examples of SaaS companies include Zoom, Slack, Canva, Microsoft, and HubSpot.
How Does SaaS Work?
Now that we’ve answered what SaaS is and understand what a SaaS platform looks like, we can spend a little more time discussing how it works.
With 99% of companies reporting that they use at least one SaaS-based application an d SaaS spending projected to hit $500 billion by 2023, you may even find you’re already relying on SaaS without realizing it.
SaaS applications are delivered using the cloud delivery model. You only need your web browser to access them.
There's no need to host the app on your server and worry about allocating the necessary resources or conducting database management. You also don't need to download anything to your local system to manage and work in these business applications. Instead, you can access them online, in the cloud, and complete whatever tasks that need completing that way.
Accessing and using cloud-based software works as follows:
- In most cases, you have to purchase a subscription to a product or service.
- Then, you have to log in to your account via your preferred web browser to gain access to the applications or tools you wish to use.
- You don’t have administrative control over the app — all of that is handled by the provider.
- The provider handles updates and system changes — you merely have a user-based account.
That may sound limiting on the surface. But an estimated 25,000 SaaS products are currently available, according to Statista , with countless satisfied users and customers who find this arrangement appealing.
And that takes us directly to our next topic — the benefits.
Software as a Service Benefits
SaaS has its benefits, with the most significant advantage being that you don’t have to install and maintain your applications. It makes it so end-users and large enterprise-level companies can run software applications without downloading anything.
You don’t have to invest in a server or hardware to sustain the software. Instead, a standard computer is often all you need to use SaaS products.
Other benefits worth noting include:
Reduced Costs and Flexible Payments
Most SaaS products are delivered at a monthly or yearly subscription fee with affordable costs. That often makes complex software with high upfront costs much more accessible to people from all industries and company sizes.
Although there are enterprise resource planning ( ERP ) SaaS vendors, you’ll often find these products provide tiered plans offering a range of services that scale up in price as demand within your organization increases.
Additionally, there are no costs associated with maintaining your on-premise application. There’s no need to shell out a lot of money for expensive hardware or a server to support your team’s needs.
Maintenance on server setups can be pricey, too. With SaaS, you don’t have to worry about that at all. Instead, you can focus on usual business management tasks rather than technical setup, configuration, and maintenance.
Scalability
As we mentioned above, you can scale up your plan in most SaaS solutions based on your needs, company size, and other requirements.
And here's the good news: That also translates to how you can increase or decrease the number of features you have on-demand access to.
With cloud services designe d for all types of businesses, you'll undoubtedly find something suitable for your company without overwhelming you or your team with unnecessary functionality. Take HubSpot's plans, for example.
You can get started with the complete HubSpot CRM for free and upgrade to a premium plan later. Or, you can opt-in for just the features you need with the Marketing Hub, Sales Hub, Service Hub, CMS Hub, or the Operations Hub.
Automatic Updates
SaaS model products are updated automatically, so you don’t have to worry about purchasing new app versions or upgrades. All of that is taken care of for you in the cloud. You don’t even have to click an “update” button sometimes — you’ll just get to enjoy new features.
Administrative teams maintain these systems. The structure of the software delivery model is out of your hands. But the tools within are there for you to use.
Accessibility
Another fantastic benefit of SaaS providers is that they are delivered through an Internet connection within your web browser, so the operating system you use doesn't matter. The Mac or Windows compatibility issues often associated with traditional software vendors just don't apply here.
Plus, you can access your software from anywhere at any time. You're not limited to just your work laptop or iPad. And you also don't need to use a dedicated machine with the software installed on it.
Instead, you access the SaaS from any computer or mobile device with a web browser installed. So long as you have your login information, you can access and use the tools you need in real-time, wherever you happen to be.
Customization
Another benefit of relying on SaaS is you can customize which features you want and integrate your SaaS platforms with other tools and apps. One of the best things about SaaS is how different platforms play together.
For instance, HubSpot has integrations available for over 100 different SaaS apps, including services like Kissmetrics and Zapier. Cloud-based service providers can wor k together much more seamlessly than remote tools ever could.
It truly opens businesses up for untold levels of collaboration.
Are There Any Disadvantages to SaaS?
As with anything else, SaaS also comes with its own set of challenges. However, many find them not to be a deal-breaker. And to most, the pros outweigh the cons.
Let’s explore these potential drawbacks.
Issues Beyond Your Control
If a SaaS provider experiences a service disruption, you might be unable to use the platform for the interruption duration. Yes, on-premises software can have issues too.
But if a cloud service provider h as outages, there’s nothing you can tangibly do to fix the problem. You just have to sit tight and wait for it to be resolved.
The same applies if the service changes its offer. For instance, if the company changes its pricing plans, feature availability, or other factors.
And if a service shuts down completely, you might have to find a different SaaS solution altogether. The overall lack of control can be an issue for some.
Security Breaches
With an increase in cyber security threats in general, there is a possibility that a security breach might happen within the SaaS solution you’ve chosen. Cloud security relies heavily on individual user security, too. Selecting good passwords with two- factor authentication helps.
However, the platform itself also needs to have robust security.
No Control Over Versioning
Lastly, if the provider releases or adopts a new version of the cloud application, it ’ll typically do so in a uniform fashion. That means the update or new revision will be rolled out to all customers whether or not they want it.
That may result in accounting for extra time and resources for training your team and/or clients and customers.
Streamline Your Business With HubSpot’s SaaS Solutions
Now that we've answered your pressing questions about what SaaS is, consider reaping the benefits of SaaS with HubSpot.
Our solutions are free to get started. You can explore our many SaaS options , including our CRM's forever-free plan, or upgrade to a premium plan for added features once it’s time to scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some examples of saas.
SaaS or software-as-a-service can take many forms. You’ll find that just about any online service or cloud application has a SaaS component. That means messaging apps like Slack, webinar apps like Zoom, backup and storage apps like Dropbox, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools like HubSpot qualify. Other SaaS companies worth noting include Salesforce, GoToMeeting, Atlassian, and collaboration tools like Google Workspace. Even image editing tools like Canva qualify as SaaS tools.
Is SaaS the same as the cloud?
SaaS and the Cloud are closely connected, but they are not the same. SaaS describes a full software application that isn't run on a local machine but instead hosted and operated from the cloud. As the end-user, you never have to download any software or app to use the service, and your work within it can be conducted from anywhere with access to a web browser.
On the other hand, cloud computing services describe a virtual environment in which software, networks, data, and infrastructure are housed for software development or other server-side tasks — without ever interacting with a physical server.
The two are closely related, but you can think of it this way: All SaaS applications are cloud-based but not everything having to do with the cloud is SaaS.
What’s the difference between SaaS and PaaS?
SaaS, or Software-as-a-Service, describes the software application the end-user can access via a web browser. According to IBM , PaaS, which stands for Platform-as-a-Service , describes a cloud-hosted platform ready for software development, data processing, communications, app management, and other platform-based tasks.
It’s important to note another acronym you should know in this context: IaaS. IaaS or Infrastructure-as-a-Service is another cloud-based service.
But rather than delivering an application or a platform, it instead provides the infrastructure or resources to companies via the cloud to build and manage servers or networks, configure operating systems, and set up and manage data storage — all without needing to purchase and house expensive servers.
Can I customize SaaS?
Standard SaaS options often aren’t customizable outside of basic settings. However, enterprise-level companies can request customizations to SaaS solutions, as they’re paying a premium for expanded services.
Sometimes, that results in changes to interfaces or the customer experience. In others, it refers to the addition (or omission) of various features.
What is a SaaS Business Model and How Does It Work?

Tech Researcher and Writer
Table of content
- The Software as a Service business model charges users to access and use an application hosted on external cloud servers.
- The Software as a Service model offers a lot of benefits for users, including reduced costs, scalability, and accessibility. Due to its popularity, software creators who choose the SaaS model have a high chance to succeed with their product.
- There are six possible SaaS business model pricing options to monetize your SaaS product: freemium, flat, usage-based, per-user, tiered, and hybrid pricing. Your choice should be based on your product’s specifics.
- There are three options on how you can bring your SaaS business idea to life: start working on the idea on your own and get software development consulting if needed, hire an internal team and a chief technology officer, or outsource product development to a third party.
If you are looking for information about the SaaS business model, you are probably thinking about creating your own subscription-based startup. Knowing the fundamentals before you start planning your startup is extremely important to understand how the SaaS model can power your business and how you can benefit from it.
Stories of such successful SaaS companies as Salesforce , Shopify , and Zoom prove that the SaaS business model works and will continue to stay indispensable for a long time to come.
So, what is a SaaS business model? Why SaaS is the best business model for most startups (including those that are only starting and those with an established user base)? What are SaaS business model benefits and revenue streams? In this article, we will give comprehensive answers to these questions.
Introduction to SaaS
The emergence of SaaS as we know it today started to take shape in the late 1990s, when the idea of Application Service Providers (ASPs) started to gain popularity. ASPs provided services like hosting, managing, and delivering business applications and services to customers over the internet. However, at that time, this concept faced serious challenges associated with security concerns and limited internet infrastructure.
In the early 2000s, when internet bandwidth improved, the ASP model evolved into what we now call Software as a Service (SaaS) — a delivery model that makes software accessible online via subscription. Salesforce and NetSuite were among the first companies to offer SaaS solutions.
At that point, SaaS started to become a mainstream delivery model. Companies that offered their software products with a traditional, on-premises model started migrating to SaaS, appreciating its cost-effectiveness, scalability, and accessibility. Now, SaaS has almost completely replaced the traditional on-premises software delivery model.
What is the SaaS business model?
The SaaS business model involves selling software products as a service instead of selling licenses for on-premises software instances.
In short, the distinctive features of SaaS are:
- hosting on cloud infrastructure
- subscription-based pricing
- regular updates and maintenance from the provider's side
SaaS revolutionized software delivery, offering various benefits for both users and providers. However, what can SaaS offer as a business model?
There are two major types of SaaS business models: the B2B SaaS business model and B2C SaaS business model. You should learn more about these types when deciding on the target audience for your SaaS startup.
B2B SaaS business model
B2B SaaS, or the business-to-business model, involves SaaS companies selling software products to other businesses on a subscription basis. Companies use B2B SaaS products to optimize their internal processes and effectively achieve business goals. For example, many businesses use software like Slack or Zoom for communication, services like Mailchimp for email marketing process automation, etc.
The story of B2B SaaS apps often starts when companies decide to build custom software to solve their internal needs. When the primary goal is achieved, businesses realize their problems are not unique and that many other companies around the world strive for a similar solution. That’s the point when they decide to turn their internal software into a SaaS product to sell it to a wider audience.
For example, one of our clients, the owner of a marketing agency, asked us to build a custom all-in-one SMM platform for managing the agency’s everyday tasks. We had to build a tool to meet the internal needs of our client’s team (such as an improved content approval process) and provide integrations with social media services like X (previously Twitter), LinkedIn, Instagram, and Facebook. Then, our client decided to create a SaaS product that would help other marketing agencies solve similar problems. When we successfully completed the project, our client managed to attract investors to fund further development of a platform version developed by the Clockwise team.
B2C SaaS business model
B2C SaaS, or the business-to-customer SaaS business model, refers to SaaS products that target individual, non-business consumers. These are products we use in our everyday lives: cloud storage services like Dropbox, music streaming services like Spotify, meditation apps like Headspace , and so on.
If you want to launch a B2C product, your startup will need to closely interact with users. While in the case of a B2B service, the requirements of your target audience are somewhat obvious, catering to the needs of each individual user of a B2C service requires more attention. You need to constantly monitor customers’ feedback and be ready to upgrade your product accordingly.
Let’s consider Spotify as an example. This music streaming service is used by casual listeners, fitness enthusiasts, podcast lovers, DJs, and music explorers. It would be impossible to make Spotify equally convenient for such a diverse group of users without listening to their feedback.
Peculiarities of SaaS products
To give you a better understanding of what the SaaS business model is, we will describe five features inherent to the vast majority of modern SaaS products.
Pay-as-you-go pricing model
The most widely known feature of SaaS is the pay-as-you-go model (or subscription-based model). Basically, this is what SaaS business model is all about: users pay for your software product as a service instead of buying a perpetual license for it.
In most scenarios, this consumption-based model is more convenient than other pricing models, allowing users to align expenses with operational needs. You can establish the value for features and resources used and bill users accordingly.
Cloud infrastructure
SaaS applications are typically hosted in the cloud. Basically, this means that the data is stored on remote servers maintained by a cloud provider. This eliminates the need for users to install, manage, and maintain the software on their own.
The terms “cloud application” and “SaaS application” are frequently used interchangeably, but there's a key distinction. A cloud application simply hosts in the cloud, while a SaaS application is not just in the cloud; it's delivered to users via a subscription-based pricing model. If you want to find out more on this topic, proceed to reading our SaaS vs cloud article.
You as the product owner can choose a reliable cloud provider for your application instead of having to invest in your own hardware and infrastructure. This will allow you to pay only for resources used and scale up and down with ease. In addition, cloud hosting is widely available nowadays, and you are free to choose from dozens of providers. The most popular cloud service providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS) , Microsoft Azure , and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) .
Integrations
SaaS products can be used as a suite of services rather than one separate service, since they are designed to be integrated with other applications. You can integrate your SaaS application with third-party services with the help of an API (application programming interface) —intermediary software that allows applications to communicate with each other.
Consider HubSpot — a world-known SaaS platform for inbound marketing, sales, and customer service. HubSpot integrates with hundreds of services including CRM systems, email marketing tools, analytics tools, e-commerce platforms, and social media apps.
Users can seamlessly transfer data between their existing applications and a new SaaS service when they adopt the latter. This involves integrating the new service with their established tools, allowing for smooth and efficient data exchange. Moreover, as a SaaS provider, you can enhance and enrich your app’s functionality by connecting it to other software without the need to develop features from scratch.
Multi-tenant and single-tenant architecture
Applications built according to the SaaS business model often use a multi-tenant architecture , where multiple users share common infrastructure but are isolated from each other, or a single-tenant architecture where users get dedicated resources and greater customization possibilities. These architectures are considered particular to SaaS products, as they are designed to meet users’ specific requirements.

Email services like Gmail, for example, are used by many users, but each has their own email account. Accounts use the same infrastructure while still being separate. For Gmail, a multi-tenant architecture allows for efficient use of resources: instead of dedicating separate infrastructure to each user, resources are shared dynamically, making the system scalable and cost-effective. On the other hand, for an enterprise CRM system, for example, a single-tenant architecture makes more sense. In this case, each user has their own isolated instance of the application, with dedicated resources and customization options.
SaaS business model examples
To help you understand what we mean when talking about SaaS businesses, we’ve compiled a list of the most successful Software as a Service products. You likely use some of them almost every day.
Google Apps
Everything from the good old Gmail system to scheduling events on your calendar is hosted on a cloud service. For example, you can easily access your Google Photos or check your email from wherever you are.
If you are not a member of Team Google, Dropbox is a good SaaS alternative for storing files and images. Once you add a new photo to your Dropbox account, it can be accessed by any desktop or web-based application with a Dropbox integration.
Slack Slack is a great tool for team communication offered as a cloud-based software product. Slack messages are secured and the entire system is built on a cloud service.
Amazon Web Services Amazon Web Services is now a pack of more than 70 cloud-based apps that cover analytics, app integration, cost management, development needs, etc.
Zendesk If you strive to provide clients with flawless service, you have probably employed Zendesk for your support needs. Would it be surprising if we said it uses the SaaS business model too?
If you are looking for some inspiration, check out our article about the top fast-growing SaaS startups .
Advantages of the SaaS business model
Not sure whether you should create your own application following the SaaS business model? In this part, we tell you about the advantages that it can bring to you as a business owner and how it can be beneficial in terms of meeting the needs of your potential customers.
SaaS business model benefits for vendors
Let’s take a look at them:
Recurring income
SaaS business model is probably the most suitable one for those who dream of stable profit from their startup. With a SaaS product, you attract a new user once and can count on a number of recurring payments from them. Working on retention and satisfaction of the existing customer base is challenging, but in this case, you can focus on building long-term relationships. In addition, the recurring SaaS revenue model promotes better returns on investment due to a predictable and stable cash flow.
Cost-efficiency and easy scaling
Since most SaaS products are hosted in the cloud, you use the provider’s infrastructure resources without the need to buy and configure your own hardware. Also, scaling (adding new features or handling an increased flow of users) is effortless and doesn’t require you to invest a significant amount of money for upgrading your own infrastructure.
Bigger market share
With a product built according to the SaaS business model, you can cover a major market segment. You can do this by providing various pricing plans to cover moderate needs of individual users and the needs of businesses of different sizes.
You can also grow along with your customers: an entrepreneur who uses the first basic version of your app to start their own small business may eventually become the CEO of an enterprise, while your startup may turn into a platform with a comprehensive suite of services for businesses of all sizes.
Customer loyalty
SaaS products gain a loyal user base because of their quality, features, and regular updates they provide to please customers. But these aren’t the only reasons why customers stay committed to SaaS products.
When a SaaS product serves business needs and responds in a timely manner to new industry challenges, it usually becomes an integral part of companies’ internal processes. Thus, even when a better analog of the product appears on the market, companies are not likely to spend time and resources on replacing what they already have.
This will allow you as a SaaS vendor to build a loyal customer base and retain relationships with customers that are ready to invest in your service for years and years, receiving predictable and stable revenue.
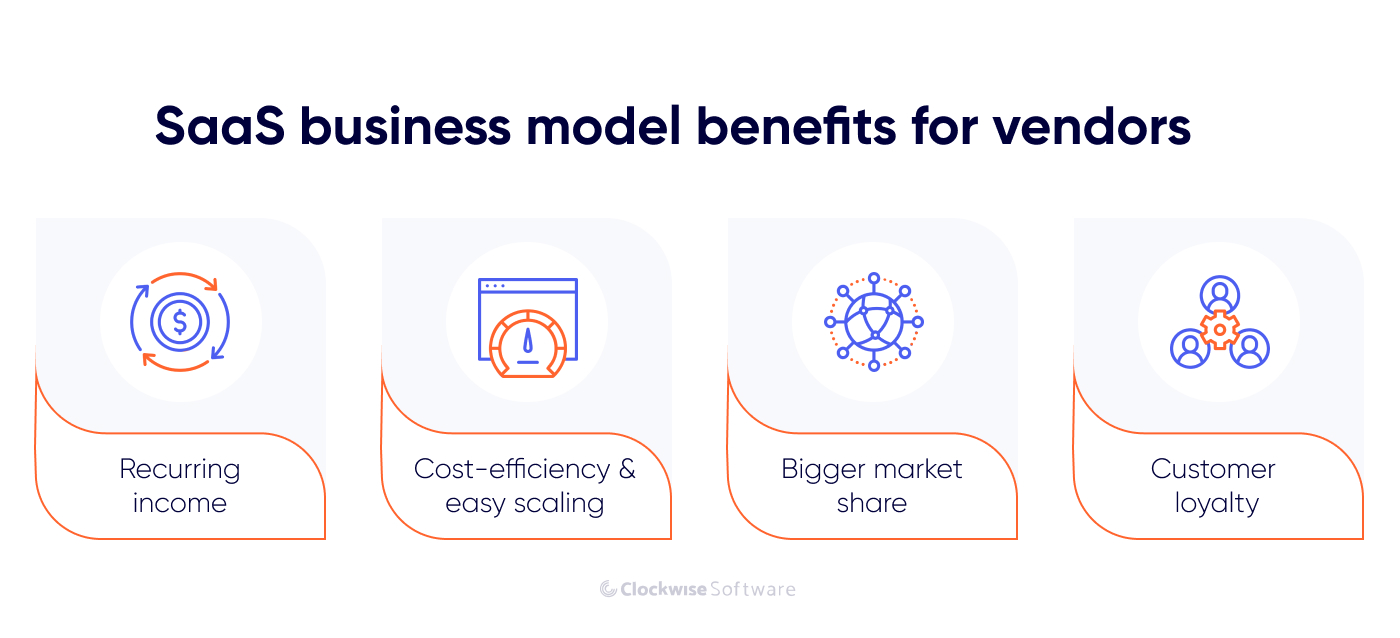
SaaS business model benefits for users
Understanding SaaS business model benefits for users is important if you want to create a user-oriented product. Moreover, benefits for users directly influence the success of this business model and therefore the revenue from such projects.
Here’s how benefits for users become benefits for SaaS developers:
Price flexibility
Users often choose SaaS products for their affordability. You can find a SaaS solution for any need and budget. Some SaaS products appear to be expensive even for very successful businesses (for example, the licensing cost of SAP S4HANA, a cloud-based ERP system , can reach $100,000 per year), but it’s always a matter of scale. However, the price flexibility offered by the SaaS business model is what will allow you to attract more customers by covering the needs of different user groups.
Customers can use a free trial or pay for a one-month subscription to assess the benefits of your product, or they can choose from different pricing plans, ranging from basic to advanced, before fully committing to your service. All this will allow you to expand the boundaries of your potential user base.
Choosing the right way to provide price flexibility for your customers is one of the keys to success. Later in the article, we talk about how to do so in detail.
Easy adoption
Since products built according to the SaaS business model are available via a browser or can be installed in a few clicks, user onboarding is mostly hassle-free. If a user is a business owner who needs a particular app to enhance business processes within the company, they normally won’t need to dedicate a lot of time to educating team members. The majority of SaaS apps are built to be as user-friendly and intuitive as possible, providing manuals and tutorials to reduce the time required for users’ onboarding.
SaaS services don’t require complex setup and education, allowing you as a product owner to attract and retain more customers.
Accessibility
SaaS products can be accessed from any device that has a web browser and an internet connection, unlike on-premises software whose accessibility is limited to certain devices. The accessibility of SaaS products becomes vital for remote work scenarios, where multiple workers need to access the same document or project and make changes to it in real time.
Thanks to SaaS accessibility, you as a product owner can provide clients with flexibility so they can access software from any device.
Thanks to seamless integrations with other services, users can benefit from smooth and efficient work. For example, let’s say you use Trello to organize your tasks and Slack to communicate with your team. Integration between Trello and Slack means that you can receive notifications in your Slack channel whenever a task is completed in Trello, making it easier for you to stay updated without having to switch between applications.
Third-party integrations in your SaaS product will contribute to increased user satisfaction. The main concern here is to understand the true needs of your target audience and provide users with useful integrations: this way, your users won’t have any reason to look for alternatives.
SaaS business model challenges
With all of its benefits, SaaS also comes with some challenges that you can’t ignore if you want to create a successful startup.
Investment challenges
Desiring to start a SaaS startup from scratch, most founders search for ways to minimize resources and investments needed for the initial product version. From our experience, developing a solid SaaS product MVP requires $100,000 at minimum. Considering all the risks associated with startup creation, investing this amount in development can be challenging, especially if you don't have experience launching startups.
Moreover, no SaaS product can be considered a cash cow that brings stable passive income by default. In order to keep growing — and just to operate day to day — a startup requires significant capital. And here is another challenge associated with investments: even if the first version of your startup gains some success, it may still not be enough to attract investment for refining your app.
Our company has broad experience in SaaS product development . When a client approaches us with the intention to create a SaaS product (or turn an existing app into a SaaS product), we start from a project discovery phase , which includes market research, idea validation, risk identification , and many other processes. Thanks to this, our clients are able to see how viable their ideas are, the main risks associated with their projects and ways to overcome them, and how to properly allocate their resources. Investing in discovery means increasing your chances to release a successful product. Once a product has proven value, it becomes much less risky to invest in its scaling. Also, a properly executed project discovery phase may help you attract potential investors, as they will be able to evaluate the project’s prospects as well as your determination to bring your project to life.

Competition
When you sell your software product on a subscription basis, you have to provide nearly flawless service. Otherwise, your users may start comparing your product with alternatives. In addition, you should pay attention to competitors that can lure your audience — both existing competitors and those that may appear in the future.
You should consider launching an app as only your first step in launching a SaaS business. The next step is to maintain it. For this, you will need a long-term development and support team that will take care of fixing bugs, keeping users’ data safe, adding new features in accordance with users’ demands, and providing necessary system upgrades.
In order to deal with competition challenges, you need to build your development process in an adaptive way, being ready to respond to changing market conditions and user needs. At Clockwise Software, we organize development according to an Agile methodology that is focused on iterative and incremental practices, adaptive planning, continuous improvements, and early delivery. The last item is achieved by building an MVP : a basic app version that has a minimal set of features — just enough to be evaluated by the first users.
Thanks to such an approach, we can make sure that further development (after the MVP launch) will be based on real users’ feedback, not assumptions or predictions. If you deliver a service your users truly need, they won’t have any reasons to look for alternative SaaS products. This way, we minimize risks associated with market acceptance and high competition.
SaaS revenue model: How to monetize your startup?
In this section, we explain how to choose the proper SaaS revenue model to monetize your product.
Freemium is a SaaS revenue model that allows users to access a certain set of features for free. This model works because it allows every potential user who is interested in a product to get hooked on it and have a positive experience with it. Freemium can be considered the best way to prove product–market fit and “buy” customers.
Some startups, like Flickr (an image and video hosting service), implement an ad-supported strategy and charge users only for an ad-free package with more features. Advertising allows you to monetize an application even when users use it for free.
Other startups may allow everyone to try out their basic tier with certain limitations that can be removed for a fee. For example, Slack lets free users access the most recent 10,000 messages in their archives. However, users with paid plans have unlimited access to their message history. This way, Slack allows small teams to use the service for free. They get used to the service, know all its benefits, and don’t want to give up Slack as they grow and hit the limit. At that point, they are ready to pay to keep using the same convenient work environment.
Using this model and providing your basic services for free will allow you to gain a solid user base and expand your market presence. However, you should also consider the nature of the SaaS product you are planning to create before deciding that this monetization strategy will work for you.
Products like communication tools that benefit from a large number of users can take advantage of the freemium model. At the same time, for complex SaaS startups whose products have a steep learning curve, as well as for those that require high support and maintenance costs, freemium isn’t the most suitable model.
Why is freemium attractive for users?
- Free access. Users can assess an app’s benefits using a basic version without any upfront payment. If they are satisfied, they will be ready to pay for advanced features or upgrade to the ad-free version.
- Risk-free. For users, freemium is the most risk-free option. They can use an app for free for as long as they need without fear of wasting money.
Flat pricing
This SaaS revenue model users have to pay a flat fee to use an app for a certain period of time. That is, for a fixed price, users can get unlimited access to all of the app’s functionality without additional charges. This model provides predictability for both the user and the provider.
Flat pricing is popular among many companies, as it’s simple, transparent, and reliable. For example, Basecamp , a project management and team collaboration tool, offers all features in a single Pro Unlimited subscription that is equally suitable for growing businesses and established companies. Thus, Basecamp subscribers don’t have to worry about additional charges or subscription scaling.
Nonetheless, flat pricing is not one-size-fits-all. While it offers stable and predictable revenue, which is crucial for accurate financial forecasting and business growth, products with unique features won’t benefit from the simplicity offered by flat pricing. Moreover, services with variable usage patterns and resource consumption, like cloud storage services or complex CRM software , may lose out on potential revenue if they opt for flat pricing.
Why is flat pricing attractive to users?
- Simplicity and predictability. Flat pricing allows users to easily plan their budget, as there are no hidden fees and there’s no need to upgrade.
- Value. Thanks to straightforward pricing, users can fully assess the app’s value.
Usage-based pricing
In a usage-based pricing model, the provider charges the customer according to the resources used. Usage-based pricing can be considered the most convenient for users: it caters to their changing needs and allows them to use resources wisely without exceeding limits.
With a usage-based pricing model, your startup can benefit from increased customer satisfaction, value–price alignment, and the ability to capture a larger market share by catering to diverse user needs.
One of the best examples of how both a user and provider can benefit from a usage-based pricing model is Twilio . This software allows users to perform communication activities such as sending and receiving messages or making phone calls through a web service API. Twilio charges users depending on the selected type and volume of communication. For example, Twilio charges per SMS.
Usage-based pricing is best when software use can be directly attributed to resource use. However, it’s not the most appropriate model for software whose value is determined by its complexity, such as specific features or types of data analysis.
Why is usage-based pricing attractive to users?
- Cost efficiency. Users pay only for the actual resources they consume. This way, the service’s cost and value are perfectly aligned.
- Flexibility. Users can easily scale the app’s usage up and down as their needs vary, all without having to overpay for features they won’t use.
Per-user pricing
As the name suggests, per-user pricing depends on the number of users that access the software.
This model is flexible and provides a predictable and scalable revenue stream. For example, the Asana work management platform has three pricing plans: Personal for up to 10 users, and Starter and Advanced for up to 500 users. These plans are targeted at different types of companies: small, midsized, and enterprise-level.
The per-user pricing model is the best choice for software that is tied to teamwork: project management tools, communication platforms, and collaborative software. This will allow you to grow revenue proportionally alongside the number of users. However, you are not likely to benefit from this model if you’re planning to create utility-based software or highly specific software that requires a more customized pricing structure.
Why is per-user pricing attractive to users?
- Cost control. Users can easily adjust the number of users per subscription as their team size increases or decreases, ensuring fair cost control.
- Simplicity. Thanks to simplified billing, per-user pricing allows users to pay only for value received.
Tiered pricing
The core of this SaaS revenue model lies in charging users for a specific set of features or resources that one subscriber can use for a certain monthly fee. Typically, pricing plans are organized according to different levels, ranging from a basic set of features to all features provided by the service (unlimited). All plans that fall between these two may gravitate toward the basic or unlimited plan to a greater or lesser degree.
For users, tiered pricing offers a wide variety of choices. For a provider, it allows for covering a broader audience and attracting more attention thanks to its flexibility. By implementing a tiered pricing model, Dropbox was able to cover both the B2B and B2C market segments, offering six different pricing plans: for individuals, for friends and family, for freelancers, for smaller teams, for larger teams, and for organizations. All of these plans have different sets of features, different types of security, and so on.
Software products that have different features that cater to different users’ needs and budgets can benefit from a tiered monetization strategy. However, apps that don’t have significant variability in features may fail to attract users by offering different packages for different prices and will benefit more from billing users on an all-in-one basis.
Why is tiered pricing attractive to users?
- Customization. Thanks to different plans, users can choose the features that are suited to their needs.
- Affordability. Tiered pricing allows users with different budgets to use the same product, ensuring affordability.
Hybrid pricing
When choosing a pricing strategy for your SaaS startup, you don’t have to stick to one strategy. You’re free to vary your strategy along with changing the functionality of your app and your business goals. In addition, you can combine strategies, implementing a hybrid pricing model. For example, you can offer a free subscription with basic features, like in the freemium model, and at the same time provide several pricing plans with different feature packs, like in the tiered pricing model.

Key SaaS business model metrics
What can help you make the most of the SaaS business model? For sure, following SaaS trends and implementing user-oriented approaches during the SaaS product life cycle are important tasks on your way to success, but you shouldn’t forget about important SaaS business model metrics that can help you analyze and monitor your startup’s performance. Let’s consider the most important metrics in detail:
- Customer churn rate will help you evaluate which percentage of subscribers canceled or didn’t renew their subscriptions over a specific period. It should be tracked on a monthly or quarterly basis. User surveys and feedback analysis help identify reasons for a high churn rate.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV) helps in assessing the long-term value of acquiring a customer. It’s the predicted average amount of money a customer is expected to generate throughout their entire relationship with the company. This metric allows for understanding the value of your company.
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC) is the cost of acquiring a new customer. It includes marketing, sales, and other expenses. Ideally, this metric should be lower than CLV.
- Recurring revenue represents the total revenue generated on a monthly (MRR) or annual (ARR) basis. It helps analyze the performance of your business.
- Expansion revenue measures the additional revenue generated by existing customers. This is any revenue you get in excess of the user’s initial purchasing price. It helps in estimating overall growth of your business.
These metrics help you evaluate the success and health of your SaaS business, stimulate further growth, and track issues.
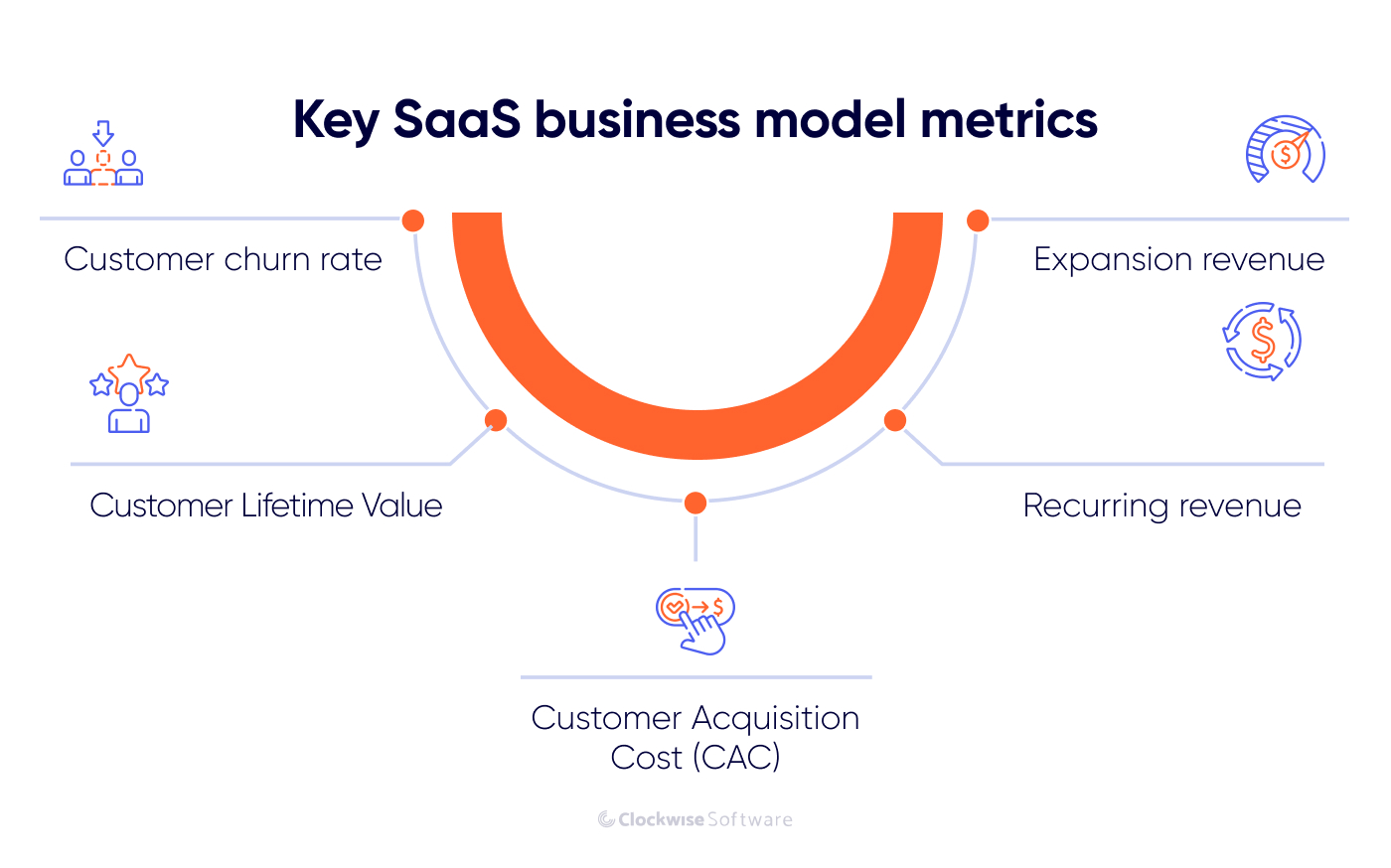
How to bring your SaaS business idea to life?
If you want to start a business based on SaaS business model, you need a team consisting of developers experienced in cloud computing, designers that can turn complex functionality into a user-friendly interface, a business analyst (BA) who can bridge the gap between technical and business requirements, QA engineers that can ensure flawless app performance, and a project manager (PM) who will lead the entire project.
Depending on your needs and the resources you currently possess, there are three possible ways to start bringing your SaaS business idea to life:
If an idea is all you have, make use of a software development consulting service. This option will work best if you need to prove your idea’s viability and find out how to move on with your project. In this scenario, you get access to expertise from a team of specialists that have broad SaaS experience. For example, in our company, you can consult with a team of SaaS development experts that are typically involved in the development process itself: backend and frontend developers, UI/UX designer, QA engineers, business analysts, and project managers.
As the outcome of software development consulting, your idea will be validated and you’ll receive a detailed development plan aligned with your goals, a reliable estimate of risks associated with your project, as well as a detailed custom app development cost estimation .
If you have a development team but lack technical leadership to properly build your SaaS app, get a Chief Technology Officer (CTO) as a Service . If you can’t deal with the technical side of your project, you may consider hiring a CTO as a service — a tech specialist or a team of tech specialists that will consult you on all tech-related questions and work for you on an on-demand (project) basis. Which type of architecture (multi-tenant or single-tenant) to choose for your app, what cloud provider to choose, how to select a technology stack, how to establish a software engineering team structure — you can answer all these questions with CTO as a Service. You can consult with your CTO before and during the development process.
You also can work with a company that provides IT staff augmentation services to hire dedicated developers for your SaaS project that will work alongside your team on a project basis. They will provide the necessary tech expertise your developers lack.
If you want to focus on the business side and not dive into technical processes, outsource the development process . If the two services we mentioned above aren’t enough and you prefer to focus on the business side of the project, you can outsource your project to a software development company. An experienced development team will take over the work on your product, from planning and software requirements documentation right to the product launch. You, in turn, will only be involved as a key decision-maker and keep in touch with the PM to track the project's progress.
You may choose outsourcing software development to Ukraine or another Eastern European country where you can choose from a wide pool of highly qualified professionals and established software development companies with proven experience in various industries.
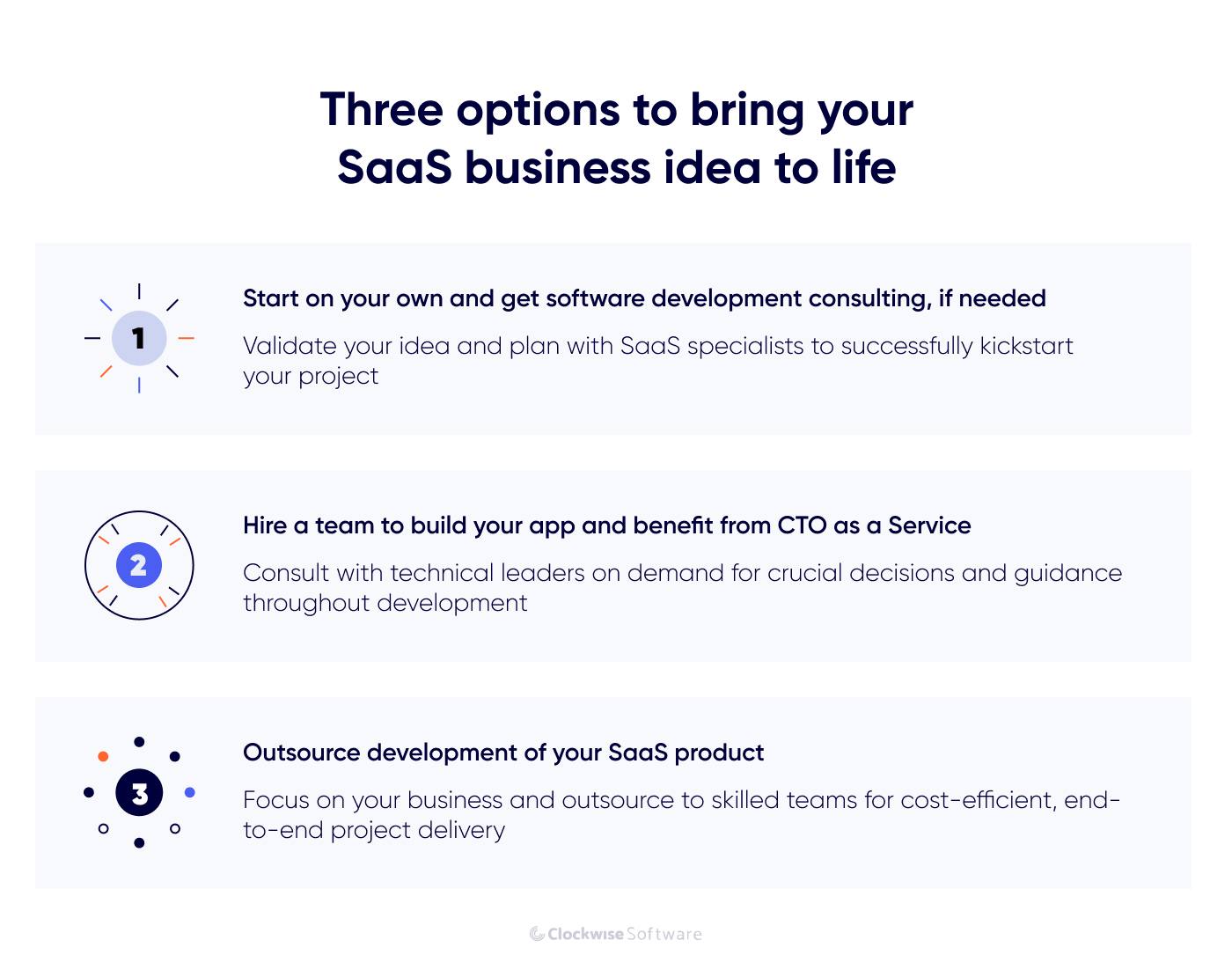
Implementing a SaaS business model: Clockwise Software’s experience
Clockwise Software has broad experience in SaaS product development. During more than eight years in the business, we have successfully completed dozens of SaaS projects, so we have a lot of stories to tell.
One of our most notable projects that shows the benefits of SaaS business model implementation is Whitelance .
Our client approached us with a functioning and successful freelancer marketplace platform. The client’s team discovered that there were a lot of founders willing to pay for using the platform’s functionality to start their own marketplaces.
The Clockwise Software team had to rewrite the web-based application ’s architecture from scratch to enable it to serve multiple clients. For this, we implemented a multi-tenant architecture so each tenant (client) has access to a customized front end, unified back end, dedicated database, default set of features, and large library of advanced functionality. Thus, each Whitelance subscriber can have their own marketplace, choosing from ready marketing and brand materials to customize the app’s front end.
Now, Whitelance is a white-label freelance marketplace that lets people run their own Upwork-style platform. It offers services for companies, freelancers, and marketplace admins.
By partnering with Clockwise Software, Whitelance was able to turn their existing functionality with proven value into a new revenue stream by implementing a SaaS business model.
The SaaS business model offers plenty of benefits. Thanks to flexible and transparent pricing, accessibility and scalability, and automatic and regular updates, users are encouraged to stay loyal to your app and pay money for it on a regular basis.
To build a successful product following the SaaS business model, you need to pay attention to challenges associated with investments and market competition, choose the most beneficial monetization strategy for your product (freemium, usage-based, per-user, flat, or tiered), and opt for the most suitable way to bring your idea to life.
Want to know more about the project cost?

- Growth Audit
- User Onboarding Review
- User Onboarding Build
- User Onboarding Optimize
- Case Studies & Resources

A Complete Guide to the SaaS Business Model
14 billion customers use at least one SaaS product to optimize their business operations. Even individuals use Saas products (think Spotify, or Netflix) for daily activities, or entertainment. It may seem that if you've built a Saas product, success is guaranteed.
In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of SaaS business and see how to build a Saas business that works, sustains, and grows.
What is the SaaS Business Model?
SaaS or software as a service is a business model that deploys its software on the cloud and allows users to access the product features with monthly or annual subscriptions. Users don’t have to download and install anything on their physical devices and can log in through the internet from any location.
As opposed to conventional business models, SaaS doesn’t run on one-time transactions and uses recurring payments to maintain the revenue stream.
SaaS is designed to serve big corporations and individuals alike. When software is built to cater to other business requirements, it’s a B2B (business-to-business) SaaS product. And if it directly targets the end customer, it’s called a B2C (business-to-customer) SaaS product.
Example– Freshbooks is accounting software with an ideal customer base of businesses and entrepreneurs. It’s an example of a B2B SaaS business model, whereas Netflix is a B2C online video streaming platform with millions of customers having their accounts in its system.
What are its Advantages Over Traditional Business Models?
1. Flexibility to Scale
Since the resources are deployed over the cloud instead of physical apparatus, it becomes much easier for SaaS businesses to scale for the sudden surges in demand. Even new features can be added without disrupting the rest of the active services.
2. Higher Adoption
Onboarding a user on the cloud platform is hassle-free and quick since no complex installations are required. Also, users can access the account anytime and anywhere, boosting the product's stickiness.
3. Revenue Predictability
Since users log into the server to access their accounts, tracking their activity and usage becomes easy. It provides the required visibility for businesses to spot healthy and about-to-churn accounts. These metrics allow accurate revenue forecasting and time to compensate for any possible losses.
4. Limiting Product Piracy
The SaaS products are delivered through the web or mobile applications. It restricts the illegal distribution of the product to unauthentic users.
What are its Disadvantages Over Traditional Models?
1. Longer Conversion Cycles
The market is flooded with SaaS products, and this cut-throat competition makes it difficult for businesses to convince customers to choose them over others.
It leads to more money spent on marketing the product and acquiring customers.
2. Demands Heavy Capital
Businesses need to be closest to the best option in the market if they want to dominate it. It requires more than just a good idea. A skilled tech team, aggressive marketing, proactive sales, and much more needs money.
So if you don’t have a runway to persist for at least the initial days, it would be difficult for you to excel.
What are the Revenue Streams For a SaaS Business?
1. Monthly or Annual Subscriptions
It’s the most reliable form of revenue where users engage in subscription billing by paying a recurring fee to avail the benefits of the product.
The subscription amount can vary for users depending on which plan and how many features they want to consume.
2. In-app Purchases
The add-ons that the user can buy after subscribing to the product are in-app purchases.
For example, an online editor, Canva, provides its users with free templates, but they can also buy a paid one from the platform.
3. Custom Solutions
Mainly enterprises come up with custom requirements to solve their unique use cases. In such scenarios, B2B SaaS companies develop on-demand solutions for clients at an additional cost. This cost can be one-time or recurring depending on the resources expended by you for them.
4. Dedicated Support
A SaaS solution is incomplete without a compatible service team. Clients understand the importance of 24/7 support to make the most of the product and are willing to pay extra for it.
For businesses, it can be an opportunity to boost revenue by adding dedicated multi-channel support to clients. Ensure that even your basic plan has some extent of customer support. Otherwise, it can work against you.
5. Reports & Analytics
Data is the new currency. So you can leverage your data processing capabilities to charge the customers for advanced analytics and reports.
How to Optimize Your Revenue?
Your revenue balances on how much you spend acquiring the customers and what returns you get from them.
So, to optimize your cash flow, let’s fix these two metrics.
1. Lower Customer Acquisition Cost
CAC is what it costs you to get a new customer to your business. Start with a solid system that can make lead generation a self-running cycle.
- Identify your niche market and ideal customer
- Research their needs and the channels they are most active on
- Deploy conventional and uncommon channels for marketing your brand. Instagram and Quora are great places to start from.
- Plan your pricing strategy considering your target audience in mind.
- Develop a freemium SaaS model to attract potential customers.
- Invest in excellent service and support to boost customer loyalty for more referrals.
2.Boost Customer Lifetime Value
Customer Lifetime Value, or LTV, is the forecasted revenue a customer can bring in their expected partnership with you.
Though it’s a prediction, it should be based on data-driven analysis rather than assumptions.
- Streamline the onboarding process with proper training and self-help documents.
- Conduct regular customer surveys to understand their feedback and expectations.
- Include highly requested features to your product to enhance product stickiness.
- Schedule monthly or quarterly review calls to explore more opportunities in an account.
- Engage with all departments of a business you are serving to boost product adoption across the organization.
For more information on how to optimize your lead conversions and grow your revenue, check out The Ultimate Guide to Optimize B2B SaaS Lead Conversions and Grow Your Revenue.
What’s the Way Forward?
There is no doubt that SaaS is the new buzzword. Customers, whether businesses or the general public, both appreciate the ease of convenience and value for money.
And if you can’t fulfill the market needs, someone else will. That’s why it’s crucial to stay on your feet and aim to improvise every day. SaaS solutions are perfect for eCommerce platforms as they allow company owners to scale up their businesses.
The simplest way to do this is by introducing the right team and tools to your endeavor. Bring onboard the top talent who can help you market your product cost-effectively. Since straight away hiring top guns for your team might not be pocket-friendly, you can always squeeze out the best through outsourced talent or consider help from MVP development companies .
SaaS marketing agencies are the best bet here because they come pre-equipped with the latest industry trends and resources to guide a budding business to success.
And most importantly, keep an eye on the metrics that matter so you can objectively evaluate your progress.
Some SaaS Business Model FAQs
1. What are the pros and cons of a SaaS business model?
- Easy to scale and enhance
- Flexible to allow the pivot and product modifications
- Promises better returns on the investment with recurring revenue
- Caters to a broader market and audience
- Better product adoption
- Highly competitive space
- More risks for customer churn
- Demands capital to set up and sustain the business
2.What are the stages of a SaaS business?
- Pre-startup: Where you are just brainstorming the business idea and basic organizational structure
- Start-up: When you bring together teams and tools to start the business on the ground
- Growth: The stage when you start acquiring clients and scaling your team
- Maturity: When you have a stable product, you can grow by adding more features or go bigger with IPO
3. What are the most relevant metrics for a SaaS business?
- CAC : Customer Acquisition Cost is the amount spent on getting a new client.
- LTV : Customer Lifetime Value is the predicted revenue a client can bring to your business throughout your partnership.
- Monthly Recurring Revenue : It is the recurring payment done by clients monthly.
- Churn Rate : The number of clients who discontinued your services out of the total client base.
- Net Promoter Score : The score your clients give your product on a scale of 1 to 10.
SaaS or software as a service is a business model that deploys its software on the cloud and allows users to access the product features with monthly or annual subscriptions.
Here are the main things that give a SaaS business model an edge over traditional business models:
- Flexibility to scale
- Higher adoption
- Predictability of revenue
- Limiting product piracy.
There are five main revenue streams for a SaaS business:
- Monthly or annual subscriptions
- In-app purchases
- Custom solutions
- Dedicated multi-channel support

RELATED ARTICLES

The SaaS Business Model: How and Why it Works


What is the SaaS Business Model?
The typical business model for a SaaS business is a unique and exciting one to dive into. Software as a Service (SaaS) companies are not going away anytime soon and there is much more innovation that will continue to come from SaaS businesses. Looking at companies like Salesforce, Slack, and Zoom (just to name a few), it’s clear that the business model works. But how and why does it work? Read on for a complete breakdown and understanding of the SaaS business model.
SaaS or “Software as a Service” is a delivery model for software where a centrally located, cloud-based software is licensed to its customers via a subscription model. This might be annual, monthly, per user, or by package level but a company can be consider a SaaS company if they are hosting their software on the cloud and licensing it out.
At the core through all of these stages, the business model is based on a subscription payment set-up. This is core to the business and the building block of the model. A SaaS company may offer various types of subscriptions for different products or various end-users, but the subscription model is key to the foundation of the business. Due to the fact that SaaS companies are hosted on a centrally located cloud, they are in a unique position to constantly be updating the software and pushing those updates to users. This update and growth process for SaaS products is much quicker then in-house hardware that used to require very manual processes for the end-user. The subscription model combined with the consistent updates typically present with SaaS products leads to a higher customer retention than other business models. SaaS companies aid this by baking in very high-touch customer success teams to their sales cycle, continuing to work with and serve the customer even after an annual or monthly subscription is committed to.
A SaaS company follows a business model typically goes through 3 phases: early stage, growth stage, and mature stage. All stages involve different levels of funding. For a deeper dive on that specific component, read more here .
Related Resource: 20 Best SaaS Tools for Startups
The early stage of a SaaS company is focused on building out a product-market fit and securing some early, loyal customers. The team is typically bootstrapped or operating on a very small seed or friends and family round. The team typically stays small at this stage as well.
The growth stage in the SaaS business model is focused on scaling extremely quickly by taking on funding via Venture Capital or Angel investors and pushing the limits of your product’s success by taking some risks, scaling the team, entering into incubators, taking on more strategic advisors, and selling up-market. This stage is all about establishing metrics to track success and working to go above and beyond those in order to keep growing the business.
Related Resource: Who Funds SaaS Startups?
The mature stage kicks in when success is proven, the audience is present and hungry for the product, and the focus is now on growing and retaining customers vs. proving out the concept. The focus now can shift to continuing to fine-tune the business via pricing updates, continued product growth and development, and brand building.
Stages of a SaaS Business Model
As we mentioned in our Startup Funding Stages Guide , “There are multiple stages of startup funding: Seed, Series A, Series B, Series C, and so forth. Startups should be conscientious about the funding rounds that they will go through, which are generally based on the current maturity and development of the company.”
The same idea holds true with respects to a SaaS company. A SaaS business model is one of the most attractive to a venture capitalist. The lifecycle and funding stages likely look something like this:
Related Resource: 23 Top VC Investors Actively Funding SaaS Startups
Related Resource: How to Start and Operate a Successful SaaS Company
Seed Funding
Seed funding is a startup’s earliest funding stage. Often, seed funding comes from angel investors, friends and family members, and the original company founders.
Series A Funding
“When a company is first founded, stock options are generally sold to the company’s founders, those close to them, and angel investors. After this, a preferred stock can be sold to investors in the form of a Series A. Series A allows investors to get in early with a business that they truly believe in. It’s a mutually beneficial relationship for both the company and the future stock holders.”
Series B+ Funding
“Once a business has been launched and established, it may need to acquire Series B (and beyond) funding. A business will only acquire Series B funding after it has started its operations and proven its business model. Series B funding is generally less risky than Series A funding, and consequently there are usually more interested investors.”
Important SaaS Business Model Metrics
While diving deeper into the SaaS business model, it’s important to understand the key SaaS metrics that will inevitably pop-up along the way. These key SaaS Metrics are critical to track in order to understand the health of a SaaS business.
MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue)
Not to be confused with ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue), MRR is how much money your company can be expected to bring in every month. Going beyond the basic meaning, MRR is a functional metric through which you can gauge your company’s income and success. MRR growth equals business growth – the same goes for shrinking MRR most likely equaling a negative impact on the business. MRR trends are incredibly important to subscription-based businesses, because they compound over time.
CAC (Customer Acquisition Cost)
The sum total it takes for your team to acquire a customer. This includes the time of the sales reps but also the marketing dollars spent. Tracking your customer acquisition cost tells you a lot about how your company is operating. If the dollars and time spent to acquire a single customer is higher than the MRR or ARR that customer brings in, that can be a huge red flag for the business. Over time, your customer acquisition cost will also tell you whether it’s getting more difficult or easier to acquire new customers. You’ll be able to look at trends to see when acquiring customers becomes more affordable, and if there are specific seasons during which customer acquisition is more expensive.

LTV (Lifetime Value)
Here at Visible, we consider LTV of a customer to be the most important metric you can track. LTV is the average customer revenue multiplied by the gross margin percentage divided by customer churn rate. Another way to think about it is MRR or ARR X Customer Lifetime. Understanding LTV is important in assessing the overall health of your company as well as justifying CAC costs to your investors. Some good news as you’re starting your business – you can track CAC and LTV right in Visible .
Essentially, churn is loss. You can have customer churn – the number of customers that cancel their subscription to your business annually or monthly. You can also have revenue churn – how much money is lost annually or monthly. Churn is expected in most businesses but maintaining an acceptable rate in comparison with the growth of your business is a key metric to understand, measure, and track. You can accept about three to five percent of your small to medium sized businesses portfolio every month or less than 10 percent annually. As enterprise level businesses go, aim for a churn rate less than one percent. Your churn rate should continue to decline in subsequent years until you reach negative churn.
Customer Retention
This SaaS metric refers to how long you are able to maintain a customer per your subscription model. This could be annually or monthly. Healthy retention can also be customer growth. If a software is user-based or has multiple product components, upsell and expansion can be possible leading to annual retention exceeding 100%. Healthy customer retention may not mean you maintain every customer every year, but you ultimately are seeing growth in the business through a balance of renewals, upsells, and contract expansions.
Successful SaaS Business Model Examples
There are thousands of SaaS businesses in the world today with more growing every year. Despite the model being a popular and growing business practice, 93% of SaaS startups fail within the first 3 years due to a lack of product market fit, run into cash flow problems, or experience more churn than growth. Diving into a few examples of successful SaaS businesses can be a helpful way to better understand the business model.

Salesforce is one of the most recognizable SaaS companies and was a true Trailblazer in the space. You can read a brief history of the business here. Salesforce has been so successful because it was one of the first companies to truly implement the SaaS Business Model successfully and has intelligently scaled by continuing to not only update it’s products, but by acquiring products where they see new opportunity effectively retaining customers and upselling them into new products as well as constantly expanding out into serving new industries. They are a mature company now with roughly 30,000 employees globally and a heavy focus on customer story-telling and partnership as a way to stay top of mind in the SaaS world.
An extension of the SaaS model that has emerged and has proven to be successful is the “Freemium” model. This pricing structure allows a portion of the product to be used for free by a user or team with full features being available through a subscription. This model works because it allows users and teams to get hooked on a product, have a positive experience with it, and share it internally and externally. This model is a good way to prove product-market fit and keep CAC down by having the product and its use take on a viral aspect with customers being bought in to a point that when the ask comes in to purchase the full software, the education that typically happens around a sale has a lot less friction associated with this.
Two companies with extremely successful Freemium models are Slack and Zoom . Both tools can be used for free by individuals, teams, and even larger organizations but have limits on things like storage, meeting times, and seat #s that are only available when an enterprise package is purchased.
Pros & Cons of a SaaS Business Model
Like any business model, there are of course pros and cons to diving down any particular path.
Pros of a SaaS Model
- Rapid growth – if you find product-market fit early and are able to secure funding, the possibility of growing your company to a Billion dollar valuation is very real and can happen extremely quickly.
- Ease of deployment – because SaaS lives in the cloud, it can be easy to make quick fixes to your product and sell to and serve customers from virtually anywhere.
- Predictable revenue – the subscription model affords you the ability to fairly consistently understand how much money you can expect to make. There is no seasonality in a subscription model and annual or monthly contracts provide security that many other business models cannot guarantee.
Cons of a SaaS Model
- Upfront costs – If you aren’t able to secure funding right away, it can be tough to maintain the capital and manpower needed to grow your company quickly enough to be successful. It’s common to not see profitability in the first few years, so it can be a hard business model to follow by truly bootstrapping. Specifically the cost of a team, CAC, and cost to build out the infrastructure to host your cloud software are major factors to consider.
- High risk – growing fast also means you can fail fast. Taking on a lot of capital and scaling quickly can bring reward but if something changes in the market, your business could crash and burn overnight.
- Churn – although revenue may be predictable, if the wrong combination of events takes place in a year (major competitor comes to market, market needs change, economic changes occur), you may see a huge bout of churn in a renewal cycle. This extreme shift could be almost impossible to bounce back from.
SaaS Business Model Growth Strategies
In addition to the “Freemium” model shared above, there are many other growth strategies that can be implemented in a SaaS Business model. A few popular ones include:
Customer Stories and Referrals
If your SaaS is integral to the way a company does business, you may be lucky enough to have customers who are super fans and love advocating for the value you bring to their day, their work, and their business. Capitalizing on these success stories through marketing content, speaking events, or even referrals can be a smart way to grow your business in an authentic way. These customer stories are good proof points to why you work. Referrals can often lead to better conversations earlier on with prospective customers or even help your sales team break into accounts that have been historically tricky to sell to. Here is an example from one of our customers:

Thought Leadership
If your company is selling into a specific space, a common strategy is to try and become the “expert” in that space. If your company blog or community group can provide value to your end-user outside of your product, that credibility will spread. Lattice does a great job of this. They have built a free 10k plus HR community group for any HR leader. They keep this space completely focused on their ultimate end-user but never focus on the product, simply provide a space for that community to meet. From there they are able to source content and ideas on what to write about in their blog and share on their podcast, effectively providing value to their end-user before even attempting to make the sale. This name recognition and “expert” status makes the use-case for the product feel more in-line with what the user group is actually interested in.
3rd Party Resources
Companies that actively spend time building up great customer reviews on sites like G2.com or work to be analyzed for trusted reports like Forrester , can use that credibility as an outside proof-point for why their product is valuable when selling into new customers.
Social Media and Influencer Marketing
This strategy is all about going where your end-user is. Build a brand and a voice via social media sites that are popular with your customer. Showcasing your companies voice and personality as well as commenting and sharing insight into trending topics can be an easy way to grow your awareness in an industry. Influencers, or well-known folks in a specific space, can be valuable on social media as well. If a top marketing influencer endorses your marketing SaaS software, folks may come inbound based on that person’s recommendation. Connecting with and offering trials to influencers can be a great way to get this started. Additionally, identifying an exec at your company with a strong following can be a great way to build your company brand via that individual. Folks on LinkedIn, for example, are much more likely to engage with what a person has to say then what a branded company page does.
Tools to Help You Optimize Your SaaS Business Model
We recommend a few tools to start when jumping into a SaaS business model. Free or premium versions are great, but it’s important to invest in tools that allow you to measure the key metrics listed above and track overall business health.
CRM – A customer relationship management tool is key to maintaining an accurate and complete data-base of all of the accounts your team is actively selling to, are active customers, or who have churned. A complete picture of the relationships your company works with will allow you to measure growth and track CAC, MRR and churn. Salesforce, Hubspot, and Oracle all offer quality options but starting out you can build a basic CRM via spreadsheet tools – it will just be a lot more manual.
Analytics Tool – Invest in a tool that will allow you to accurately measure all the metrics for your company. We recommend google analytics or manually tracking your metrics via a spreadsheet tool if you don’t have the budget to invest right away. Looker and Tableau are great options once you have budget to spend.
Visible – We of course have to share how we can help with growing our SaaS business model, too. Once you take on funding, we are the most complete tool for sharing updates with your entire team and managing existing and potential relationships with investors. You can learn more and check out a free trial of us here .
What is SaaS Business Model: A Comprehensive Guide
It is well-known that software as a service (SaaS) is a cornerstone of modern business operations. This innovative business model revolutionizes the traditional approach to software delivery, offering exceptional flexibility, scalability, and accessibility.
At its heart, SaaS revolutionizes software delivery by providing applications via the Internet, eliminating the need for complex installations and constant updates. Users can seamlessly access these applications through a web browser, paying for the services on a subscription basis. This shift from ownership to access democratizes software usage, enabling businesses of all sizes to use cutting-edge technology without prohibitive upfront costs.
As businesses increasingly prioritize agility and efficiency, understanding the complexities of the SaaS business model becomes crucial for staying competitive in the digital era. So, we have prepared a unique guide to help you understand a SaaS business model, its types, advantages, vivid examples, and more.
Let’s start our research together!
Unlocking the basics: what is a SaaS business model?
In a nutshell, the software as a service business model is a prominent player. SaaS fundamentally represents a method of delivering software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis.
Unlike traditional software models where users purchase and install software on their devices, SaaS provides access to applications hosted in the cloud. This approach offers convenience and revolutionizes how businesses utilize and pay for software solutions.

The unique characteristics of the SaaS business model
One of the primary differentiators of the SaaS model is its subscription-based pricing structure. Instead of weighty upfront costs associated with purchasing software licenses, SaaS allows users to pay a recurring fee, typically monthly or annual. This pricing model democratizes access to software, making it more affordable and scalable for businesses of all sizes.
Another distinguishing feature is the cloud-based delivery of services. SaaS applications are hosted on remote servers maintained by the service provider, eliminating the need for users to install, maintain, or update software on their hardware. This reduces IT infrastructure costs and ensures seamless access to the latest features and updates without any manual intervention.
Furthermore, the SaaS model fosters a culture of flexibility and customization. Most SaaS applications offer configurable settings and integrations, allowing users to tailor the software to their needs and workflows. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for businesses operating in dynamic environments where agility and responsiveness are paramount.
Moreover, SaaS providers prioritize customer satisfaction and retention. Since subscribers can easily switch between providers, SaaS companies are stimulated to deliver exceptional customer support, regular updates, and continuous product improvements. This customer-centric approach is designed to make you feel valued and essential, fostering long-term relationships and promoting loyalty within the user base.
Common SaaS business model types
Developing the right pricing strategy is a crucial determinant of success for SaaS businesses. From attracting new users to retaining loyal customers, the pricing model is essential in shaping a SaaS company’s growth course. Understanding the nuances of different pricing approaches empowers businesses to tailor their strategies to meet the diverse needs of their target audience.
Now, let’s delve into the different SaaS business model types:
This model is a popular choice among SaaS businesses. It offers a basic version of the product for free while charging for premium features or functionality. This approach allows users to experience the product before committing to a paid plan, fostering trust and potentially leading to upsells as users discover the value in additional features.
A prime example of this model is Dropbox, which provides free storage space with the option to upgrade for enhanced features and extra storage.

Flat pricing
With flat pricing, SaaS companies offer a single pricing tier with a fixed price, regardless of the features used or the volume of usage. This simplicity appeals to users who prefer straightforward pricing structures and want to avoid dealing with the complexity of usage-based or tiered models. Flat pricing often targets small businesses or individuals looking for affordability and ease of use.
Buffer, a social media management platform, offers a single pricing tier with a fixed monthly fee, regardless of the number of posts or social media accounts managed.

Usage-based pricing
These models charge customers based on their usage of the SaaS product, such as the number of API (application programming interface) calls, storage space used, or active users. This model scales with usage, making it attractive to businesses with fluctuating needs or those seeking a more cost-effective solution that aligns with their usage patterns.
Amazon Web Services (AWS), a leading cloud computing platform, adopts this model by billing customers according to the compute power, storage, and data transfer they utilize. This provides flexibility and cost-effectiveness based on actual usage.

Per-user pricing
This SaaS business financial model charges customers based on the number of users accessing the platform. Each user typically pays a fixed monthly or annual fee, regardless of their activity level within the platform. This model is advantageous for businesses that require user-specific accounts and allows for easy scalability as the organization grows.
Slack, a famous team collaboration tool, follows this model, where companies pay a fixed fee for each team member using the platform. This ensures scalability and aligns costs with organizational growth.

Tiered pricing
This pricing model offers multiple subscription tiers with varying features and functionality at different price points. Customers can choose the tier that best suits their needs and budget, with the option to upgrade or downgrade as their requirements change. Tiered pricing provides flexibility and satisfies a broader range of diverse customer needs.
OpenWeather, a weather data provider, implements this model by offering different tiers of access to weather data APIs based on the volume of requests and features required by users.

Hybrid pricing
This SaaS business model pricing combines elements of different pricing models to offer a customized approach that fits the unique needs of the target market. This could involve a combination of flat pricing for basic features, usage-based charges for additional resources, and per-user fees for access to premium functionality. Hybrid pricing maximizes flexibility and can appeal to a wide range of customers with varying usage patterns and budgets.
Adobe Creative Cloud, a suite of creative software tools, employs this model by offering subscription plans with a combination of flat fees for primary access and usage-based charges for additional services or premium features.

Thus, each of these SaaS business model types has its advantages and considerations, and the choice often depends on factors such as the target market, the nature of the product or service offered, and the competitive landscape. By selecting the most suitable model and continually iterating based on customer feedback and market dynamics, SaaS companies can optimize their pricing strategy for sustainable growth and profitability.
Essential benefits of SaaS business model
The SaaS business model has transformed the technology consumption landscape, offering many advantages for both users and companies. From enhanced flexibility to cost-effectiveness, SaaS has become the preferred choice for software delivery and utilization.

Let’s check the fundamental benefits of SaaS business model.
- Accessibility and convenience. One of the most significant advantages of SaaS for users is its accessibility. Users can access SaaS applications from any Internet-enabled device, eliminating the need for specific hardware or software installations. This accessibility enhances convenience, allowing users to work seamlessly anywhere and anytime.
- Scalability. SaaS applications offer scalable solutions that can adapt to users’ changing needs. These platforms can quickly scale up or down based on demand, whether an individual user or a large enterprise. Users can effortlessly add or remove features, adjust subscription levels, or increase user licenses as their requirements evolve.
- Cost-effectiveness. Traditional software often involves significant upfront costs for licenses, installations, and maintenance. However, SaaS follows a subscription-based model, allowing users to pay only for the services they use regularly. This pay-as-you-go approach eliminates bulky upfront expenses, making SaaS solutions more cost-effective for users of all scales.
- Automatic updates and maintenance. SaaS providers handle all software updates and maintenance tasks, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches without any effort. This relieves users from managing updates manually, allowing them to focus on their core tasks while enjoying a seamlessly updated software environment.
- Enhanced collaboration. Many SaaS applications are designed to facilitate seamless communication and cooperation among users regardless of their geographical location. Features such as real-time editing, shared document access, and integrated communication tools foster collaboration, boosting productivity and efficiency for team users.
For businesses:
- Lower total cost of ownership (TCO). Adopting SaaS solutions can significantly reduce businesses’ total cost of ownership. By eliminating the need for expensive infrastructure, hardware upgrades, and dedicated IT staff for software maintenance, businesses can allocate their resources more efficiently, investing in areas that directly contribute to their growth and innovation.
- Rapid deployment. SaaS applications can be deployed much faster than traditional software solutions. With no need for complex installations or configurations, businesses can start using SaaS applications immediately after subscribing. This agility enables companies to respond swiftly to changing market demands and capitalize on new opportunities without being hindered by lengthy implementation processes.
- Improved security and compliance. SaaS providers prioritize security and compliance measures to safeguard user data and ensure regulatory adherence. By using progressive encryption technologies, access controls, and regular security audits, SaaS solutions offer businesses more data protection than on-premises software deployments. This enhanced security posture protects sensitive information and helps companies to build trust with their customers and partners.
- Predictable budgeting. SaaS subscription models provide businesses with predictable and transparent pricing, making it easier to budget and forecast expenses accurately. Unlike traditional software licenses, which may involve unpredictable upgrade costs or unexpected maintenance fees, SaaS subscriptions offer fixed monthly or annual rates, enabling businesses to plan their expenditures more effectively.
- Focus on core competencies. Outsourcing software management to SaaS providers allows businesses to focus their internal resources on core competencies rather than IT infrastructure management. By offloading routine tasks such as software updates, maintenance, and support to SaaS vendors, businesses can redirect their efforts towards innovation, product development, and customer satisfaction, driving competitive advantage and business growth.
In conclusion, the SaaS business model offers myriad benefits for both users and businesses alike. These solutions empower users to work more efficiently while enabling companies to streamline operations, reduce costs, and accelerate growth. As technology develops, SaaS is poised to remain a cornerstone of modern software delivery, driving innovation and transforming how we work and do business.
Crucial stages of SaaS business model
In general, businesses experience distinct phases characterized by unique challenges and opportunities. Understanding and effectively guiding these stages is vital for sustained success. Here, we explore the crucial stages of the SaaS business model: growth, expansion, and stability.

1. Growth stage
The growth phase marks the initial wave of momentum, where startups strive to gain traction and establish a foothold in the market. During this stage, rapid customer acquisition and revenue growth are paramount. Key elements include:
Customer acquisition
At the heart of the growth stage lies the relentless pursuit of acquiring customers. Startups employ targeted marketing campaigns and referral programs and use social media platforms to expand their user base. By the way, we will discuss this in more detail in the next section.
Product development
Continuous enhancement of the SaaS product is essential to meet evolving customer needs and stay ahead of competitors. Feedback loops from early adopters play a crucial role in refining features and functionalities.
Scalability
Building scalable infrastructure is critical to accommodate increasing demand without compromising performance. Cloud-based solutions offer flexibility and scalability, enabling startups to scale their operations seamlessly.
Financial management
Efficient resource allocation is imperative during the growth stage. Startups must balance aggressive growth and fiscal responsibility to avoid burning through capital prematurely.
2. Expansion stage
As SaaS companies gain traction and solidify their position in the market, they enter the expansion phase. This stage is characterized by scaling operations, penetrating new markets, and diversifying product offerings. Key considerations include:
Market expansion
With a solid customer base established, SaaS companies focus on penetrating new markets. This may involve geographical expansion into international territories or targeting niche industry verticals.
Diversification
To mitigate risk and capitalize on emerging opportunities, diversification of product offerings is essential. SaaS companies may explore adjacent markets or introduce complementary services to address the evolving needs of their customer base.
Partnerships and alliances
Strategic partnerships with complementary businesses can accelerate growth and enhance market reach. Collaborating with industry leaders or integrating with popular platforms can provide access to new customers and drive revenue growth.
Operational efficiency
Streamlining operations becomes increasingly crucial during the expansion stage. Implementing scalable processes and investing in automation technologies can improve efficiency and reduce operational costs.
3. Stability stage
The stability phase represents a maturation stage where SaaS companies focus on sustaining growth, optimizing profitability, and fortifying their position in the market. Key components include:
Customer retention
Maintaining high customer satisfaction levels is vital for long-term success. SaaS companies invest in customer success initiatives, proactive support services, and product enhancements to foster loyalty and reduce churn.
Profitability
While growth remains a priority, achieving profitability becomes a primary objective during the stability stage. Optimizing pricing strategies, reducing customer acquisition costs, and maximizing customer lifetime value are crucial for sustainable profitability.
Continuous innovation
In fact, innovation remains central to staying competitive in the rapidly evolving SaaS landscape. SaaS companies must foster continuous innovation, encourage experimentation, and stay attuned to market trends and customer feedback.
Risk management
Reducing risks becomes increasingly crucial as SaaS companies mature. This includes addressing cybersecurity threats, regulatory compliance, and diversifying revenue streams to reduce dependency on any single source.
Thus, guiding the crucial stages of the SaaS business model requires a strategic approach, agility, and a relentless focus on customer value. SaaS companies can chart a path to sustainable growth and long-term success in the dynamic digital landscape by understanding the unique challenges and opportunities presented at each stage.
SaaS business model metrics
It is essential to understand that these SaaS business model metrics are navigational tools. They guide businesses through the complexities of customer acquisition, revenue generation, and retention.
Let’s delve into the significance of each metric and how they interplay within the SaaS business model.
Lifetime value (LTV)
This metric represents the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their entire relationship with a company. It is a crucial metric that quantifies the long-term value of acquiring a customer.
Calculating LTV involves forecasting customer revenue over time, factoring in churn rates, and upsell opportunities. A higher LTV indicates stronger customer loyalty and profitability, highlighting the importance of delivering ongoing value to customers to maximize their lifetime value.

Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
This metric measures the cost associated with acquiring a new customer. This includes marketing expenses, sales commissions, and other costs directly attributed to customer acquisition efforts.
Keeping CAC in check is essential for sustainable growth, as this excessively high metric can deteriorate profitability and hinder scalability. Efficiently managing CAC involves optimizing marketing channels, refining targeting strategies, and enhancing the sales process to acquire customers cost-effectively.

Monthly recurring revenue (MRR) and annual recurring revenue (ARR)
MRR and ARR are foundational metrics in the SaaS business model, representing the predictable revenue stream of subscription fees. MRR tracks the monthly revenue generated from subscription contracts, while ARR extrapolates this figure annually.
These metrics provide valuable insights into revenue stability and growth, enabling businesses to forecast cash flow, assess performance, and evaluate the impact of pricing changes or customer churn.

The churn rate measures the percentage of customers who discontinue their subscription within a given period. High churn can severely impact revenue and profitability, making it imperative for SaaS companies to address churn drivers and enhance customer retention efforts proactively.
Analyzing churn patterns, identifying pain points, and implementing targeted retention strategies can help decrease churn and foster long-term customer relationships.

Customer retention rate (CRR)
This metric complements the churn rate by measuring the percentage of customers retained over a specific period. A high CRR indicates strong customer loyalty and satisfaction, reflecting positively on the product’s value proposition and customer experience.
Improving CRR involves fostering customer relationships, providing exceptional support, and continuously delivering value to customers to incentivize subscription renewals.

In summary, SaaS business model metrics drive strategic decision-making and foster sustainable growth. By closely monitoring these metrics, SaaS companies can gain actionable insights into their performance, optimize resource allocation, and develop lasting customer relationships.
Top SaaS business model examples
Among the many SaaS businesses, some companies reshaped industries, redefined customer relationships, and set benchmarks for success. Let’s discover their unique business models, exploring how each has used innovation to carve its niche and thrive in the competitive SaaS landscape.
In fact, HubSpot’s prominence is synonymous with its pioneering role in inbound marketing. Built to empower businesses to attract, engage, and delight customers, HubSpot offers an integrated platform encompassing CRM (customer relationship management), marketing, sales, and customer service functionalities. Central to HubSpot’s business model is the “freemium” approach, enticing users with free access to essential tools while offering premium features and services for scalable growth.

Key pillars of HubSpot’s success include:
- Inbound methodology : HubSpot’s business model revolves around the inbound methodology, emphasizing content creation, SEO (search engine optimization), and personalized marketing strategies to attract and retain customers organically.
- All-in-one platform : By consolidating essential marketing, sales, and service tools into a single platform, HubSpot streamlines workflows, enhances collaboration, and provides users with a comprehensive solution for their business needs.
- Customer-centric approach : This SaaS business model template prioritizes customer success through extensive educational resources, community engagement, and responsive support, fostering long-term relationships and advocacy.
- Scalable pricing tiers : HubSpot offers tiered pricing plans tailored to businesses’ needs and growth stages, enabling seamless scalability and customization without overwhelming users with unnecessary features.
This platform is a testament to the transformative power of CRM solutions. Renowned for its cloud-based CRM platform, Salesforce has revolutionized how businesses manage and promote customer relationships, driving efficiency, agility, and growth. At the core of this SaaS business model example lies a determined focus on innovation, accessibility, and ecosystem expansion.

Critical elements of Salesforce’s business model include:
- Cloud-based infrastructure : Salesforce discovered the shift to cloud-based CRM solutions, delivering scalability, accessibility, and real-time insights to businesses of all sizes across diverse industries.
- Platform as a service (PaaS) : Salesforce’s platform-as-a-service model enables developers to build and deploy custom applications and integrations on top of its CRM platform, fostering innovation, customization, and extensibility.
- Trailblazing ecosystem : Salesforce’s expansive ecosystem encompasses various partners, developers, and third-party applications, enriching its core offering and enhancing customer value through seamless integrations and extensions.
- Subscription-based pricing : Salesforce adopts a subscription-based pricing model, offering flexible pricing tiers and add-on features to accommodate varying business needs and budgets while ensuring predictable revenue streams and scalability.
With our robust SaaS development services, our Intobi team developed Viddyoze , a SaaS web-based video editing software. This platform disrupts the conventional notions of video animation, democratizing access to professional-quality animations and motion graphics for businesses and content creators worldwide. Using cloud-based technology and intuitive design tools, this SaaS business model example empowers users to create stunning visual content that captivates audiences and elevates brand storytelling.

Essential aspects of Viddyoze’s business model include:
- Cloud-based platform : Viddyoze’s cloud-based platform eliminates complex software installations and hardware requirements, enabling seamless access and collaboration from any device with an internet connection.
- Template marketplace : This platform offers a vast library of customizable animation templates, ranging from logos and intros to transitions and outros, providing users with diverse creative assets to enhance their videos.
- Subscription-based model : Viddyoze operates on a subscription-based model, offering tiered pricing plans with varying features and usage limits to accommodate individual creators, small businesses, and enterprise clients.
- Community engagement : This platform fosters a vibrant community of users through forums, tutorials, and social media channels, facilitating knowledge sharing, feedback exchange, and collaboration among aspiring and seasoned animators.
Below, you can see the subscription-based model of the Viddyoze video editing platform.

Advanced tools for SaaS business model success
Success in SaaS development hinges on innovative ideas and the adept use of advanced tools tailored for seamless operations and sustained growth. Among the various essential tools, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, analytics solutions, and billing software support the structure of a thriving SaaS business.
Let’s analyze each of these tools and explore how they contribute to the success of the SaaS business model.

CRM systems
They are like nerve centers for SaaS businesses, facilitating and managing customer interactions, sales pipelines, and marketing campaigns. These systems empower SaaS companies to promote strong relationships with customers, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth.
CRM systems centralize customer data and interactions, providing invaluable insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and pain points. Using this data, SaaS businesses can personalize marketing strategies, tailor product offerings, and deliver exceptional customer experiences. CRM platforms also streamline sales processes, enabling sales teams to manage leads, track opportunities, and close deals effectively.
Moreover, CRM systems are crucial in customer retention and churn reduction. SaaS companies can strengthen customer loyalty and minimize attrition through proactive engagement, targeted communication, and timely support. Using advanced features such as predictive analytics and AI-driven recommendations, CRM systems empower SaaS businesses to anticipate customer needs and preemptively address issues, fostering long-term relationships and recurring revenue streams.
Analytics solutions
They are the analytical powerhouse driving informed decision-making and strategic planning within SaaS organizations. These solutions enable SaaS businesses to gain deep insights into user behavior, product performance, market trends, and competitive dynamics.
With robust analytics tools, SaaS companies can track key performance indicators (KPIs), monitor user engagement metrics, and measure the effectiveness of marketing campaigns with precision. By analyzing user data across various touchpoints, SaaS businesses can identify patterns, detect emerging trends, and seize opportunities for optimization and innovation.
Furthermore, advanced analytics solutions empower SaaS companies to conduct cohort analysis, segmentation, and predictive modeling, enabling them to understand user segmentation, forecast future performance, and refine product strategies accordingly. With data visualization techniques like dashboards and reports, analytics solutions facilitate clear communication and actionable insights, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions and drive business growth.
Billing software
This software is key in streamlining revenue operations, optimizing subscription management, and ensuring financial sustainability for SaaS businesses. These platforms automate billing processes, invoice generation, and payment collection, reducing manual overhead and improving operational efficiency.
Billing software enables SaaS companies to satisfy diverse customer needs and maximize revenue potential by offering flexible pricing models, tiered subscription plans, and usage-based billing options. Additionally, these platforms facilitate subscription lifecycle management, from onboarding and upgrades to renewals and churn mitigation, ensuring seamless customer experiences throughout the journey.
Moreover, advanced billing software integrates seamlessly with CRM systems and analytics solutions, enabling comprehensive visibility into customer lifecycles, revenue attribution, and retention metrics. By employing real-time insights and automated workflows, SaaS businesses can optimize pricing strategies, identify upsell opportunities, and reduce revenue leakage, driving sustainable growth and profitability.
In general, CRM systems, analytics solutions, and billing software are essential tools for SaaS business model success. By using the full potential of these advanced tools, SaaS businesses can guide competitive landscapes, adapt to evolving market demands, and achieve long-term success in the digital economy.
The SaaS business model represents a fundamental shift in how software is accessed, utilized, and monetized. Its subscription-based approach empowers companies to streamline operations and drive innovation without the burden of significant investments. By eliminating the need for complex installations and constant updates, SaaS democratizes access to advanced technology, balancing the playing field for businesses of all sizes.
As the digital economy continues evolving, SaaS stands at the forefront of software delivery, shaping how businesses operate and interact with technology. Using the SaaS business model isn’t just about adopting new software; it’s about assuming a philosophy of continuous improvement, innovation, and collaboration. By understanding and employing the potential of the SaaS business model, companies can unlock new opportunities for growth, efficiency, and success in the dynamic digital age.
Search for a reliable development team to transform your business with tailored SaaS solutions. Contact us today at Intobi to discuss how our expertise can drive your business success in the digital era!
- What is SaaS business model?
The SaaS (software as a service) business model involves delivering software applications over the Internet on a subscription basis. Instead of purchasing and installing software locally, users access applications online, typically paying a recurring fee for usage.
- Why SaaS is the best business model?
SaaS is an ideal business model due to its scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. It allows businesses to access software without needing significant investments while allowing for easy updates and maintenance. The subscription-based revenue model provides predictable income streams.
- What is a SaaS business model and how does it work?
A SaaS business model revolves around providing software apps to users via the Internet. The provider hosts and maintains the software, ensuring updates, security, and technical support. Users can access the software from any device online, making it highly convenient and accessible.
- How to build a SaaS business model?
First, identify a niche market and understand its pain points. Based on competitor analysis, determine pricing strategies. Focus on providing excellent customer support and continuously iterate based on user feedback. Implement scalable marketing and sales strategies to attract and retain customers.
Share this:
Let’s chat.
Feel free to reach out, we’d love to hear from you.
Andrew Tsopych. CEO at Intobi
[email protected] +38 093 461 69 19
Type your email…
Discover more from Intobi
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- Cooperation Models
- Dedicated Team
- Fixed price projects
- Time & Material
- Web Application Development
- Software Development
- Mobile Application Development
- Software Development Outsourcing
- High-Converting Landing Page
- UI/UX Design
- QA Consulting
- C#/.NET Development
- JavaScript Development
- Progressive Web App Development
- React Native App Development
- Native App Development
filetypes:pdf|jpeg|png|doc|exe
Choose file (pdf,jpeg,png,doc,xls, max 5Mb)
Home » Blog » SaaS Business Model Explained: Plain Guide to SaaS
SaaS Business Model Explained: Plain Guide to SaaS
Danyl Koltak
Online business is promising, profitable, and modern. To launch a successful online business, you can choose a SaaS business model. The benefits of the SaaS business model are impressive, but you also need to be aware of the disadvantages. So you can understand if such a model is suitable for your business.
What is the SaaS business model, and what pros and cons does it have? In our article, we’ll dive into that topic in detail. Also, we’ll discuss how to build a SaaS business model right.
SaaS business model explained
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS for short) is taking over the market. According to Statista research, about 25,000 companies chose the SaaS business model in 2021. SaaS business involves selling custom software to customers, not a one-time product. The user buys a license and then can use the software by renewing the subscription.
A SaaS company creates a product, supports and develops it, and provides paid access to customers. Most often, the product is billed monthly, but there is also an annual or weekly subscription.
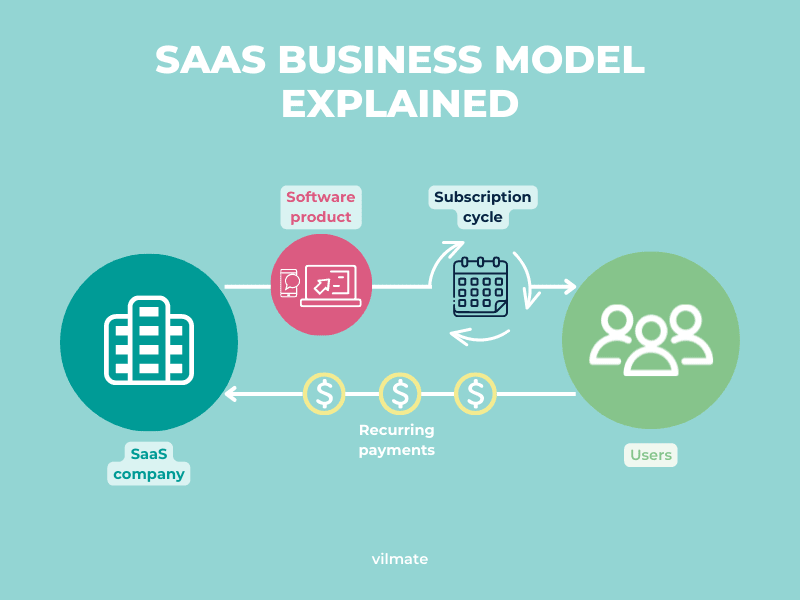
Customers who have purchased a subscription get access to the full software or a separate paid part of it. Users can do this through a mobile SaaS application or web browser, so they don’t need to download and install additional software on a smartphone or computer.
This model is beneficial for clients. Firstly, they don’t have to pay the entire amount at once for an expensive application. And secondly, they don’t have to provide space on their computers. Moreover, they can access complex functions from a device that isn’t the most advanced. It becomes possible thanks to a thorough consideration of cloud storage and database setup.
Consider the most popular types of software for a SaaS business model.
- CRM (customer resource management) systems
They allow the company to coordinate the actions of employees, track sales, and create successful leads.
- Accounting software
It helps to structure the company’s budget and issue invoices.
- Web-hosting
Remote services help companies host their sites on the Internet and provide easy access.
- Data management
SaaS products that help analyze and protect data.
SaaS solutions can be targeted at enterprises or directly at customers. A focus on other businesses (B2B) will help companies grow. Focus on customer service (B2C) will allow you to provide users with interesting products.
We hope the SaaS business model explained above has sparked your interest in starting your startup. And now, we’re ready to discuss the stages of SaaS product development.
Stages of SaaS product development
For your SaaS company to succeed, you need to distribute resources efficiently. Roughly, you’ll have to go through the following main stages:
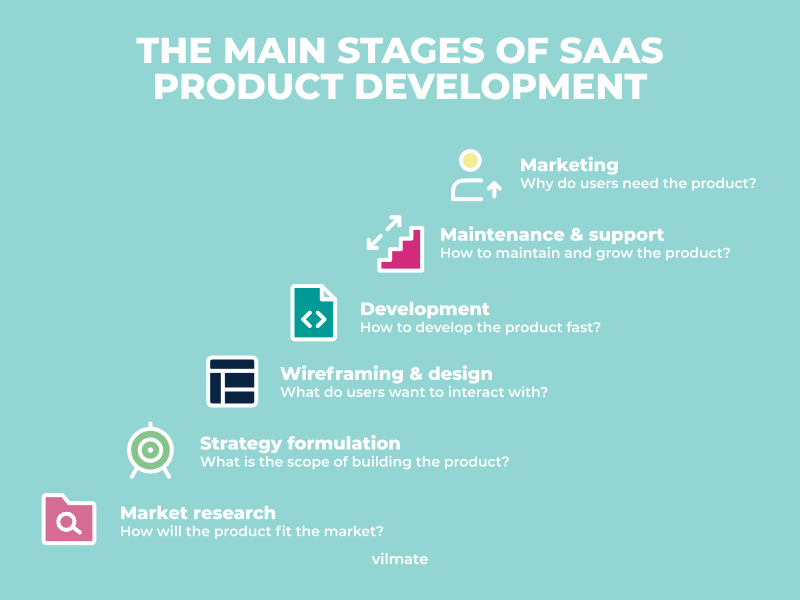
- Market research
SaaS companies must provide a quality product to be successful. You use your own experience and market research to create the perfect platform. Before starting to develop a SaaS business model, you need to understand what features customers will need, what they are willing to pay for, and their “pain and gain”.
- Strategy formulation
A product strategy is a sophisticated plan that outlines the goals of your product and how you intend to do so. A SaaS product strategy gives the team a framework for understanding their tasks and aligns them to make decisions in light of the wider picture.
To create a SaaS product strategy, you may ask yourself the following questions:
- What is the product’s use case?
- What advantages do users get in those use cases?
- What objectives do you hope to accomplish for the product across its entire life cycle?
Your product strategy doesn’t need to be a 1000-page tome. It just needs to clearly identify the target market, the client, and the goals to conquer them.
A product strategy typically does not include a product roadmap geared toward your company's business or software growth. But if you’re interested in developing one, visit our thorough article on how to build a product roadmap .
- Wireframing & design
Building a successful SaaS solution requires a well-designed user interface. Users won’t give your application a chance if they don’t like what they see at first glance.
Users’ perceptions of the overall quality of your SaaS solution are also influenced by UI/UX design . Users will presume it has been extensively tested and is reliable if it has a pleasing appearance. On the other hand, if your SaaS website seems antiquated or poorly designed, users will be less likely to trust it. You should also pay great attention to mobile UX design.
In summary, the success of your product depends on the quality of the SaaS user experience design. A successful design will offer an excellent user experience that promotes ongoing interaction and makes your product stand out from the competition in your sector. With a well-thought design, you get the following benefits:
- Lower costs for acquiring customers
- Differentiate yourself from your rivals
- Improve customer lifetime value
- Boosted scalability and growth
That’s why the design process should be given top priority early in the development of your product.
- Development
After making all the necessary preparations, including defining the concept, validating the idea, and analyzing the market and possible clients, it’s time to start all the development work. SaaS product building requires a thoughtful approach to scalability and security.
Your cloud software needs to meet the demands of an expanding user base. Also, today’s consumers demand their data to be safe and protected, and regulations make the use of top-notch security standards mandatory. Learn more in our article about data management in cloud computing .
- Maintenance & support
The perfect product cannot be created without the first customer feedback. The owner of the SaaS business had to be ready for improvements and endless testing of the project. Even if the user interface looks perfect and is convenient for customers, they may want new features. That’s why the development team works on new features, monitors app performance, and maintains the product.
A good product is only one part of success. Software-as-a-Service business owners must constantly attract new users using marketing tools and techniques. These include advertising, content marketing, product trials, search engine optimization (SEO), referral marketing, and so on. Also, mind that SaaS will not pay off immediately.
Be prepared for your SaaS business model to go through 3 phases:
- Startup : preparing a product for launch.
- Hypergrowth : customer acceptance of the product, a large influx of users.
- Stability : leveling the product in the market with a stable inflow and outflow of customers and stable profits.
All these stages require careful preparation and quick response. The SaaS business model seems like an easy way to make money. However, this solution has its advantages and disadvantages, which you need to know about before starting SaaS development.
Benefits of the SaaS business model
The pros and cons of the SaaS model can be viewed from business and customer service. Let’s talk about the benefits of the SaaS model in terms of profitability.
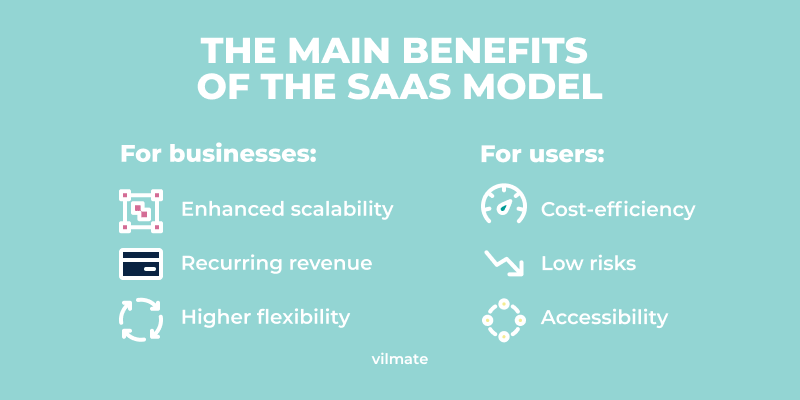
- Scalability
Scaling a SaaS business is considered one of the most important advantages. SaaS resources are stored in the cloud. This approach allows us to provide services to clients from all over the world. Information about customer flows is updated online.
If your platform can give growth to the client’s company, then his profits can positively affect yours. In addition, a repeat customer creates lifetime value.
- Recurring revenue
Recurring revenue is a kind of salary that customers pay to a business. Traditional businesses rely on one-time payments, but the SaaS company requires customers to pay monthly. You can be sure that a certain amount will be credited to your account this month. Revenue will become predictable once the platform is stable.
You just need to keep track of customer acquisition and customer churn. Thus, it will be possible to predict the flow of funds. The SaaS business model eliminates the "good" and "bad" months and allows you to make investment decisions with guaranteed success.
- Flexibility
The SaaS business model allows you to listen to user feedback and respond to their needs instantly. Important updates don’t become a problem for developers. New features can become a source of new revenue. Updating a SaaS product usually happens without downtime, providing continuous customer service. A quick response to user feedback will make the product perfect.
Moreover, the SaaS business model allows you to cover multiple market segments. Some customers will want to purchase a subscription with basic features. Others will need the enhanced version. In this model, you can set different pricing for each customer category, thus attracting a broader range of users. Your client can be a large-scale business, a niche market, or a private entrepreneur. There are no restrictions!
A small business can grow into a big company with the help of your product. Then it will need an extended version, which will bring additional revenue. That’s how customer success in SaaS companies can affect business income.
Of course, the SaaS business model is very good for business. In 2021, the SaaS market capitalization was $272.49 billion, according to BusinessWire . But what benefits can the client get?
- Cost-efficiency
The SaaS is sold by subscription. Own software isn’t cheap. With a SaaS product, the customer doesn’t have to pay a large price right away. It’s much more pleasant to give a small price once a month, which will have little effect on the overall budget.
The user won’t spend big money on a product license. Moreover, they’ll be able to adjust the number of features and pay only for those that they need. And since SaaS products are cloud-based, the customer will have lower infrastructure costs.
If a product that offers a SaaS solution turns out to be useless for a particular customer, they can easily abandon it. The absence of risks will attract more and more users because if they fail, they’ll lose a small amount of money.
In case the SaaS platform is based on a pay-as-you-go model, the client will only pay for the time of use. Such a system is beneficial for users who rarely use the product, so they won’t be afraid to overpay.
- Accessibility
The SaaS apps are accessible at any time and from any location in the world. Additionally, the SaaS service provider maintains the software centrally on a server, allowing users to adjust the usage plan on-the-fly to suit their needs. This kind of configuration is ideal for remote work scenarios when numerous individuals from various locations collaborate on the same project and use the same centralized resource.
Disadvantages of the SaaS business model
Of course, when looking at the pros and cons of the SaaS business model, you can’t just focus on the benefits. Let’s talk about the disadvantages.
- High competition
Many companies have already appreciated the benefits of the SaaS business model and adopted it. Now the SaaS industry is highly competitive, and finding uncovered user needs has become more difficult.
Therefore, you need the original startup or the best metric for SaaS business. Good prices and advanced functionality can take away customers from a competitor, although this isn’t easy – users are often conservative.
- Customer retention
This shortcoming stems from the previous one. Having competitors requires a good churn reduction strategy. It’s necessary to apply marketing techniques, monitor competitors’ prices, and respond sensitively to customer reviews.
- Dependence on the budget
SaaS company revenues are highly dependent on customer sentiment. You need a regular periodic income, which means the product must be very good. Only a good SaaS product can provide the kind of revenue that your business can support a team and be profitable.
Don’t forget that buying an expensive subscription is usually a balanced decision. It isn’t always easy for the client. Therefore, many SaaS companies resort to constant visual demonstrations and free trial subscriptions. They help push the user to buy.
- Strong security requirements
Since the SaaS product uses cloud storage, you need to keep a good eye on security. Leakage of customer data can lead to reputational losses, lawsuits, and significant loss of money.
How to understand if the SaaS model is right for you?
If you’re impressed by the benefits of the SaaS business model and aren’t intimidated by its downsides, it’s time to take the approach to your startup. If you have 4 special qualities, then the SaaS industry is definitely for you.
- Strong development team
A SaaS product is an advanced platform that requires serious technical training. You need talented developers, good marketers, and experienced management.
- The ability to wait
Some entrepreneurs expect quick and big profits. SaaS offers other income options. Choose it only if you are ready for a long sales funnel.
- Financing strategy
SaaS businesses are great at scaling. Of course, it doesn’t come free for business. A strong project needs stable financial support. Therefore, you need to be ready to inject funds at the initial stage.
- Deep analytics
The SaaS business model requires a constant calculation of customer churn, the search for the reasons for the influx of customers, and the development of a customer retention method. Many businesses require serious analytics, but the SaaS industry is literally built on data calculation.
If these 4 points make you enthusiastic rather than annoyed, then the SaaS business model is the perfect solution for a new startup.
SaaS sales approach
SaaS revenue models are shaped by whether you sell a B2C or B2B product. To understand how to set prices, you need to know the key SaaS metrics.
These metrics are important for any business, but in the case of a SaaS venture, some of them are especially important.
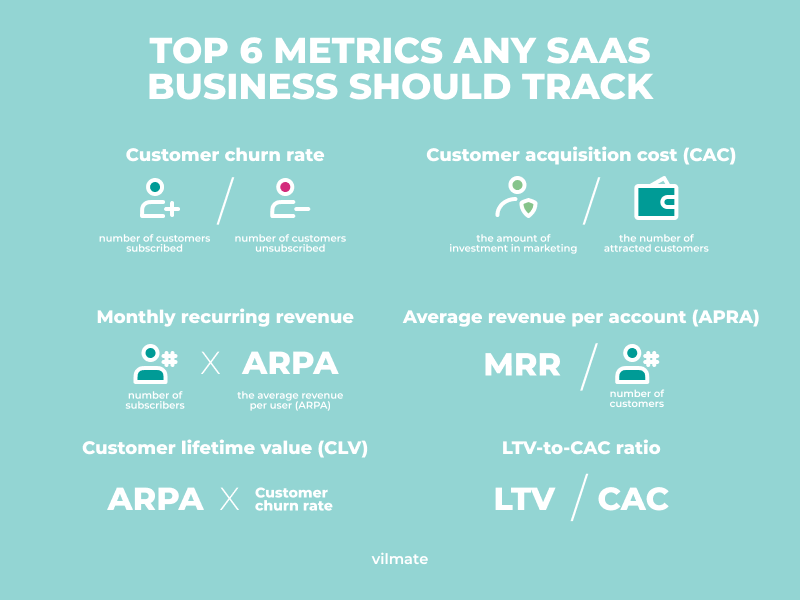
Customer churn is a vital SaaS metric that shows how many customers unsubscribed in a given period. Zero churns are impossible to achieve. But churn rate can show how satisfied users are with a product. An acceptable level for the outflow of SaaS customers is 5-7%.
The churn rate is calculated using a simple formula: the number of customers unsubscribed / number of customers subscribed * 100.
Customer acquisition cost (CAC) . This is a more complex SaaS metric that shows how much money you’re spending to acquire one new user. By the cost of customer acquisition, you can understand how successful the SaaS business model is.
There is also a formula for calculating CAC: the amount of investment in marketing / the number of attracted customers.
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR) & annual recurring revenue (ARR) . Monthly recurring revenue measures the amount of money your product generates overall in a single month. Annual recurring revenue works the same. Thanks to these indicators, you can calculate further investments needed.
To calculate future monthly SaaS revenue, multiply the number of subscribers by the average revenue per user (ARPA).
Average revenue per account (APRA) . If your SaaS product has tiered subscriptions, it’s useful to know how much you’re getting from customers on average. A low figure may indicate that a more expensive subscription isn’t in demand.
To calculate the monthly average income per account, you need to use the following formula: MRR / number of customers.
Customer lifetime value (CLV) . This is the revenue that a business receives from a single customer during the entire subscription period. This indicator depends on how long users are willing to pay for the services of your SaaS product.
To calculate customer lifetime value, you need to use a more complex formula: ARPA x Customer churn rate.
LTV-to-CAC ratio . Your marketing initiatives’ ability to sustain growth can be determined by comparing your acquisition costs (CAC) and lifetime value (LTV). 3:1 is a suitable LTV to CAC ratio. If a customer generates $1,000 in revenue over time, you should only invest a little more than $300 in acquiring them.
As the name suggests, this ratio formula looks the following way: LTV / CAC.
So, now you know the most important SaaS metrics. They will directly depend on the chosen SaaS pricing model and also influence it.
Let’s take a look at the SaaS startup financial models used around the world.

- Fixed pricing
Fixed pricing is the simplest model where a SaaS product is delivered to all customers at the same price. Typically, this model is set with monthly or annual subscriptions. This SaaS pricing model must be used with caution. A small business and a large company aren’t equal in their capabilities. That’s why this approach can alienate a large number of customers. Usually, for a fixed-price model, marketers use free trial subscriptions to attract clients.
- Tier pricing
This SaaS pricing strategy will allow customers to pay for the feature set they need. Typically, SaaS companies use the basic, medium, and Pro tiers. This pricing model allows you to serve all categories of businesses and customers with any budget.
- Custom pricing
In this SaaS financial model, all customers receive the same set of services. But at the same time, the number of users who can use the product is limited. For example, if the company has only 5 employees, then the owner will pay a small price for their access. As the company grows, the payment for the services of your SaaS product will grow along with the number of employees.
Although this is the most popular Software-as-a-Service pricing model, it requires a lot of work from the marketing department. For example, the Slack platform communicates directly with corporate departments to provide the correct price.
Final words
So, we’ve discussed the SaaS business model and explained its peculiarities in our article. The popularity of this solution is both a plus and a minus. Of course, there is a lot of competition waiting for you. But it exists only because many businesses have already appreciated the benefits of the SaaS business model.
The Software-as-a-Service solution allows you to receive a stable income, flexibly adapting to the wishes of customers. There are many variations of SaaS platforms, so it’s easy to choose the right model for your business.
SaaS indicators in the market are only growing, so now is the time to occupy this niche. Of course, building a SaaS platform isn’t easy at the initial stages. You need a strong team of developers and marketers who are ready to work for the perfect result. Experts from the Vilmate team can help you with this.

Choose file (pdf,jpeg,png,doc,xls)
“I’m looking forward to keep on working with Vilmate”
A great technical team and a great partner we’ve been lucky to come across. We have been working together for many years and I’m looking forward to keep on working with Vilmate...
They are “our team” – not “Vilmate's team” and I like that a lot!
- Campus Login
- Join the Team
Understanding the SaaS Business Model: How Does it Work?

The Saas Business Model Explained
Of all the new kinds of enterprise solutions made available by the advent of the internet, one of the most disruptive, most useful and most recent has been the software as a service ( SaaS ) business model. Many a startup has either pivoted to this promising new SaaS business model, or has been founded implicitly to take advantage of the SaaS revenue on offer in today’s active market. With SaaS companies enjoying an aggregated industry-wide market value that’s projected to rise over $25 billion per year going forward, now is an excellent time to move into the SaaS business model in your own organization. However, to succeed in doing so, it’s vital to understand the SaaS business model excellence in action – the tactics, organizational structures, and key metrics by which to gauge your startup company’s prosperity.
What is the SaaS Business Model?
In truth, the SaaS business model is both new and complex enough that understanding its potential, as much as the key metrics and deliverables that will be expected of you when creating one, can prove a somewhat daunting task.
Are you tracking the necessary KPIs? Do you know your CAC ? When do you need to raise more capital? We've helped SaaS founders answer these questions time and time again.
We even have a Business Model Template that will help you set goals and communicate them effectively to investors. Every SaaS startup exists because it has identified – and intends to sell the solution for – a pain point, problem, or area of unnecessary friction in enterprise. Commonly, the SaaS business model targets B2B solutions, such as inventory management and order tracking for ecommerce, or more effective inter-organization communications solutions for companies. Helping business owners and their teams coordinate more effectively within a given company is a strong SaaS business model in today’s market too – as software companies like Zoom and Slack can attest. However, many SaaS business model ideas have also been created with the intention of helping business owners better connect to – and engage with – their customer base. For example, Mailchimp email marketing keeps end users informed and inspired when an organization releases new products – and is especially popular in the rapidly growing ecommerce market . Whatever the intention of the SaaS solutions in question, software companies develop these platforms primarily by utilizing the powers of cloud computing. In fact, a popular startup idea in today’s market is developing a SaaS business model that helps those businesses struggling with their digital transformation to take advantage of cloud computing in a more user-friendly way. As you can imagine, many companies who provide solutions like this do so while relying on revenue streams beyond one-time software purchases. In fact, because SaaS solutions lean on cloud computing so prevalently, their MRR and ARR frameworks charge users a subscription fee.
How Does the SaaS Business Model Actually Work?
With an understanding of the SaaS business model’s success in mind, we can more effectively drill down into what makes for a successful SaaS business model. In order to succeed in marketing any startup offering SaaS solutions, it’s vital to ensure that your team comprises software developers who are able to take complex cloud computing challenges and convert them into user-friendly platforms. SaaS companies are looking to grow their monthly revenue streams and capitalize on a strong and engaged user base for profitable ARR and MRR key metrics. As a result, you will rarely see any SaaS business model using one-time pricing models alone. In fact, even if they do, there’s likely to be some variety of premium subscription offering or “Pro Level” measure of support in most SaaS companies today. This kind of freemium SaaS offering is able to cater to a casual user base effectively, while adding a feeling of prestige and added functionality to its monthly subscription customers. More frequently, however, SaaS business model designs are built to capitalize on recurring monthly revenues. This is true of both enterprise-level startup ideas to solve B2B problems, as it is B2C marketing solutions or consumer-level SaaS solutions to make daily life easier. Because of the monthly subscription model being used throughout the SaaS software market, the customer acquisition cost (CAC) is relatively low – although pricing will be a strong factor in how likely users will be to commit to the monthly subscription. In fact, one of the key metrics to track in any SaaS business model or any software company intends to deploy is the level of customer churn – especially in the early months. Many SaaS solutions use the allure of a free trial period before monthly subscription expenses kick in for end-users. This adds a level of pressure for any SaaS startup to demonstrate excellent value and versatility in their platform before their true subscriptions begin. A big area of customer churn is often found in free trial users who stop using the product before their monthly subscription fees begin – and a key area to overcome in the growth stage of any such startup is removing the friction between that trial period and the more-profitable monthly recurring revenue. To attain strong customer retention, your startup will need to provide an almost flawless level of service, and convenience so compelling that end-users can no longer imagine their personal or professional lives without your SaaS solution. A challenging endeavor – yet one well worth overcoming, thanks to the potential rewards of the SaaS industry (when done right).
Types of SaaS Business Models
All SaaS business model varieties out there require a team of software developers to not only create the SaaS solutions themselves, but also to update and maintain them over time. Not only that, but cybersecurity is a chief concern throughout the SaaS market today. Because of the nature of this kind of startup, it is highly likely that sensitive data on customers, end-users, and other businesses in all kinds of industries will be using your SaaS platform’s cloud computing infrastructure. A data breach or successful hack against your startup could be disastrous. Because of these continuous expenses, on top of the usual costs of developing a startup throughout (and beyond) its growth phase, having a keen understanding of the best SaaS business model – and how to avoid customer churn – becomes one of the key metrics to get right. When creating SaaS software products for use in the everyday consumer market, a freemium SaaS business model often works best. Consumers don’t always have access to the kinds of enterprise-level capital that would enable monthly subscriptions – and they would need to see a tremendous level of value in their personal lives to subscribe to such a SaaS platform. For example, imagine if PayPal used a monthly recurring revenue subscription model for every single one of its users. Paying customers would not see value and would have abandoned the service long before it became as prosperous and ubiquitous as it is today. In fact, PayPal is a great example of a SaaS business model success for transactional revenue models. That’s because PayPal levies a small fee on customers – whether average consumers or enterprise level clients – for certain kinds of transactions. This kind of transactional revenue makes a good SaaS business model for companies such as ecommerce payment gateways. A subscription model would be less successful here by far – it makes sense to simply take a small fee for services rendered per transaction. Cryptocurrency exchanges such as Coinbase are another example of the transactional revenue SaaS business model.
Examples of the SaaS Business Model
The idea of the SaaS business model is older than we might first think – in fact, many of the oldest surviving such software companies are examples of a successful SaaS business model in action, yet came to be before the advent of cloud computing. Many of the free or freemium SaaS solutions active in the market today are ones that have found success by becoming almost indispensable to the way in which companies operate today. Think of examples such as Zoom, Trello, Slack, or Monday. You may well already be aware that these examples include those that use both a freemium and a monthly subscription model – another example of that strategy in action is HootSuite. End-users can scale their monthly subscription level up and down according to the marketing and social media needs of their business – or simply use the SaaS software for free. While it can be tempting to stick with the relative simplicity of a subscription model with competitive pricing, keep an eye on how this affects your customer relationship key metrics and overall customer churn levels. A kind of subscription fatigue is creeping into many areas of entertainment, media and even software companies today – so experimenting with another SaaS business model could work in your favor.
Pros & Cons of the SaaS Business Model
When generating a new startup – after identifying the challenge to overcome or deliverable you intend to offer your end-users – it pays to contemplate what SaaS business model design philosophy truly is going to bring to the table for you. For example, SaaS products often require software developers to remain on board long-term, in order to squash new bugs, keep users’ data safe, add new features, upgrade systems to be compatible with new computer operating systems or smartphone handsets, and so on. Would it be wiser to simply create a startup product that consumers and businesses can purchase from you via an ecommerce website for a one-time fee? That depends on the kind of services you intend to render through your startup innovation. Because the world is so connected today, cloud computing empowers most modern SaaS solutions – meaning SaaS business model strategies need to lean towards the annual recurring revenue (ARR) key metrics required to sustain operating both the business and the SaaS platform. One of the key pros of a successful SaaS business is that its monthly subscription key metrics are very high. This demonstrates a high level of customer loyalty, and this advantage is becoming ever more difficult to secure in the competitive startup landscape of today. On the flip side, it’s vital to remember that one of the biggest disadvantages of the SaaS business model is that it’s capital intensive – both to get your startup going and into its growth phase, and just to operate day to day. This is not a startup idea that will ever generate any entrepreneurs passive income. It will be a lot of work throughout your SaaS product’s lifespan – and that also includes the complexities of ensuring you have good software developers to keep on top of the enormous volume of necessary coding and cloud computing infrastructure.
What are the Key SaaS Business Model Metrics?
Seeing success in your business model means tracking key SaaS metrics, which include:
- Customer churn rate – how many end-users are abandoning or ‘bouncing off’ your product per week, per month, per year?
- Customer acquisition cost – are end-users contributing to your revenue streams or is your product giving away too much for free?
- Monthly subscription numbers – are they growing, stagnant, declining?
- Cash flow – are there areas in the value chain of your SaaS business model where you can strategically employ upsells or value-added solutions?
- Customer Lifetime Value - having your sales team getting new users on board is only part of the work. Whether through monthly fees or upfront payments, how can your business model promote increased LTV?
SaaS Business Model Growth Strategies
The key to successful SaaS solutions in the market comes from identifying and solving a problem – and doing it so well you can charge for the service. As a startup, your goal will be tackling the challenge you want to overcome, and working with software developers on cloud computing solutions that resolve the issue. Once that’s accomplished, you’ll move into your growth phase – marketing to your chosen demographics and, if successful, seeing tremendous numbers coming in for ARR and MRR. However, this is the pivotal moment – sustaining the excellence of your service, and keeping pace with innovation in both your chosen market as well as in the cloud computing ecosystem overall. Over time, you’ll likely identify new challenges, new opportunities and greater potential – and from there, must decide if you want to launch new products within your SaaS business model to address them or create a new startup accordingly.
SaaS Business Model FAQs
What kinds of entrepreneurs suit the saas business model.
This kind of startup is not for everyone and certain entrepreneurs are far more likely to flourish. Investors who are experienced in working with cloud computing and software developers are likely to see promising returns – and likewise, strategically minded or innovative entrepreneurs with solid SaaS solutions will enjoy a very receptive market.
Are all SaaS companies subscription based?
No – this kind of SaaS business model is widespread, but isn’t the only option open to SaaS founders. Understanding your customer base is one of the key metrics to monetizing your SaaS ideas – and you might find greater success through one-time purchasing, freemium models, or transactional revenue fees (remember the PayPal example).
How do I grow my SaaS business?
The growth phase of any startup is exciting – and many of the winning strategies from the startup world will also apply to your SaaS business model. Think organic traffic growth, strong customer retention strategies, wide scale marketing campaigns and effective networking – especially for B2B SaaS platforms.
What is the SaaS Revenue Model?
The most frequent SaaS business model strategies used today are as follows:
- Monthly subscription revenues that charge users a recurring fee to access the cloud computing functional of the SaaS product
- Transactional revenue models , as seen in ecommerce SaaS solutions where fees are cut per monetary transaction, delivery fee, ad placement etc.
- Freemium , often used in a B2C SaaS business model – software is free to use, but has added functionality purchasable within
- Ad-based revenue , in which non-intrusive ads are placed throughout SaaS solutions
Free Founder Community
Join over 5500+ like-minded B2B SaaS founders learning to scale, grow, and exit with Dan Martell and some of the top SaaS Founders in the world.

Join 64K+ SaaS Founders Crushing their Business Goals with Weekly Growth Advice
Related content from saas academy, comments (0), leave a comment, ready to join saas academy.
If you’re a B2B SaaS Founder already over $10K MRR, then we invite you to schedule a Growth Session with our team of Scale Specialists. You’ll walk away from this complimentary call with a Growth Action Plan customized for your SaaS business.

- How We Can Help
- All Programs
- Growth Accelerator Program
- SaaS Academy Program
- Content Library
- Free Resources
- SaaS Founder Community
- Growth Stacking Show
- Case Studies
- Get In Touch
- (615) 632-6055

Copyright 2024 SaaS Growth Coach Inc. | Privacy Policy

SaaS Basics. What Is SaaS, and How Does It Work? An In-Depth Guide.

What is SaaS and what does it stand for?

What are some popular examples of SaaS businesses?

How does the SaaS model work?

Evolution of SaaS

What are the key parts and components of the SaaS business model?
Value proposition, infrastructure, software development and maintenance, revenue model and pricing.

Customer support

7 major advantages of the SaaS business model

9 challenges of the SaaS business model

4 Frequently asked questions about SaaS
1. how can saas companies effectively differentiate themselves in a competitive market, 2. what role does ux and ui design play in the success of a saas business, 3. how do customer acquisition and retention strategies affect the sustainability of a saas business, 4. why is pricing strategy crucial for saas businesses, and what are common mistakes to avoid, what’s next (proven worksheets & templates).

2 min read
SaaS provides an intriguing alternative to standard software installation in the business environment (traditional model), where you must build the server, install the application, and configure it. Instead, the applications reside on a remote cloud network that is accessed through the web or an API, and it works like a rental. You and your organization have the authorization to use it for a period of time and pay for the software that you are using.
The following are five of the top advantages of using SaaS:
1. Reduced time to benefit
Software as a service (SaaS) differs from the traditional model because the software (application) is already installed and configured. You can simply provision the server for an instance in cloud, and in a couple hours, you have the application ready for use. This reduces the time that is spent on installation and configuration and can reduce the issues that get in the way of the software deployment.
2. Lower costs
SaaS can provide beneficial cost savings since it usually resides in a shared or multi-tenant environment , where the hardware and software license costs are low compared with the traditional model.
Another advantage is that you can rapidly scale your customer base since SaaS allows small and medium businesses to use a software that otherwise they would not use due to the high cost of licensing.
Maintenance costs are reduced as well, since the SaaS provider owns the environment and it is split among all customers that use that solution.
3. Scalability and integration
Usually, SaaS solutions reside in cloud environments that are scalable and have integrations with other SaaS offerings. Compared with the traditional model, you don’t must buy another server or software. You only need to enable a new SaaS offering and in terms of server capacity planning, the SaaS provider owns that. Also, you have the flexibility to be able to scale your SaaS use up and down based on specific needs.
4. New releases (upgrades)
With SaaS, the provider upgrades the solution and it becomes available for their customers. The costs and effort that is associated with upgrades and new releases are lower than the traditional model that usually forces you to buy an upgrade package and install it (or pay for specialized services to get the environment upgraded).
5. Easy to use and perform proof-of-concepts
SaaS offerings are easy to use since they already come with baked-in best practices and samples. Users can do proof-of-concepts and test the software functionality or a new release feature in advance. Also, you can have more than one instance with different versions and do a smooth migration. Even for large environments, you can use SaaS offerings to test the software before buying.
IBM Cloud® has embraced the advantages of software as a service (SaaS) and has built a portfolio of over 100 SaaS applications that solve critical business needs for our clients. Explore IBM’®'s SaaS applications for business and IT .
Get the latest tech insights and expert thought leadership in your inbox.
To further explore the differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, see "IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS – IBM Cloud service models."
Get our newsletters and topic updates that deliver the latest thought leadership and insights on emerging trends.
10 Ways a SaaS Model can Improve Your Business
Updated: June 24, 2022
Published: December 27, 2019
As we wrap up 2019, it's clear that companies are no longer limited to brick-and-mortar locations. More people are moving their business to the Cloud, creating a Software as a Service (SaaS) model to market and sell their products. And, these SaaS companies can attest to its benefits, including improved speed and flexibility when distributing and completing tasks.

But, these are only a few advantages that a SaaS model can bring to your business. And while it may seem like a sizeable investment, adding a cloud-based service can significantly improve your customers' experience .
So, if you're considering adopting SaaS, take a look at some practical ways this digital model can elevate your business.
![saas business model advantages → Download Now: The State of Customer Service [Free Report]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/9c545446-aacf-47a3-bfb3-1998f78b79c8.png)
10 Benefits of SaaS
1. saas has a low installation cost..
One big benefit of adopting SaaS is that its cost of implementation will not hurt your capital. There are several free apps you can install such as Google Apps, WeTransfer, and Dropbox, which can help you set up a SaaS structure.
Should you need more features, these programs also offer premium rates that unlock additional tools and reports. And, the cost will still not be as expensive as installing individual software in each of your business devices.
Another option is to sign up for a subscription plan, which will help you save on budget. Many SaaS providers offer a regular subscription plan and some will allow you to adopt one that's personalized to your business's specific needs. While these are more expensive than the generic, free tools, the option to customize your plan helps you save on features that may not be relevant to your business.
Finally, since SaaS saves data on the Cloud, this will cut down costs on supplies like paper, physical storage, maintenance, and printing. These things add up, so be sure to consider these savings when discussing a switch to SaaS.
2. SaaS is easily integrated with business systems.
Unlike traditional software, SaaS apps are relatively easy to integrate into your current systems. Most apps don't need to be installed nor do they require high-end specifications. To work, all that your business needs is a web browser and a stable Internet connection.
Additionally, for most people, SaaS apps are relatively easy to use. But, if you're worried your team may struggle, there are plenty of free online resources that can teach them how to operate your app.
3. SaaS apps are compatible across multiple devices.
Imagine working on a file with your laptop then being able to transfer or access that file on another device. With the demand for mobility on the rise, more B2B SaaS business models are using devices that can be used anywhere.
This is how SaaS can benefit your business because these apps are compatible across multiple devices. This is good for a website's rank and ecommerce search engine optimization (SEO) because of Google's mobile-first and SEO algorithm.
4. SaaS apps remove data silos.
Jumping off from the previous point, employees and/or business owners can use SaaS apps from practically anywhere. This means they can work anytime or any location, so long as they are connected to the Internet.
With SaaS apps, data and files are stored in a central database which can be securely accessed by team members any time they need it. This removes costly data silos that slow functions and creates friction within your business.
5. SaaS fosters team collaboration.
A wonderful thing about SaaS products is that they allow internal teams to collaborate with one another, which is great for companies that are offering ecommerce SEO or other technical services.
Using a SaaS app, team members can leave each other comments, update items, upload files, and assign tasks to help accomplish their goals--all without having to intrude on each other's work.
6. SaaS offers data security.
Which is more secure? On-site software or SaaS applications?
According to GoWhiteOwl , businesses that don't have an I.T. department or don't invest in an anti-virus software leave their systems vulnerable to attack. On the other hand, cloud-computing companies constantly deploy security updates to protect customer data, which makes devices and systems safer to use and store data in.
This means that while your SaaS app is easily integrated into your business, it doesn't provide any additional security risks to your data. Since a third-party company is operating and updating the app, you don't have to run routine maintenance checks to ensure your information is secure.
7. SaaS platforms update automatically.
It's no secret that technology develops rapidly, and this puts pressure on your team to keep up with industry demand. Fortunately, SaaS apps are automatically updated, which keeps them compatible with the latest devices and running smoothly for your employees. You don't have to take downtime to reinstall your software and can continue your normal workflow as the application updates on its own.
8. SaaS apps are onboarded quickly.
When it comes to migrating systems, speed is essential. You wouldn't want your employees lounging around just because your I.T. team is busy installing software on their computers and devices.
SaaS is an out-of-the-box solution. And, since most SaaS apps don't need to be installed, the speed of deployment is impeccably fast. You and your employees can instantly use the system the moment you go online.
9. SaaS apps are scalable.
Worried about the limited features of your free SaaS apps? Don't be. SaaS apps are scalable to suit your business needs.
For a relatively small cost, you can expand your data storage, increase your number of users, and gain access to premium features and tools. This gives you the option to grow your software as you continue to expand your business and customer base .
10. SaaS features are maintained frequently.
SaaS apps undergo frequent updates to maximize security and remove bugs. These updates make these products more user-friendly, provide better features, and protect your organization's data.
Overall, SaaS can have a powerful impact on your business's digital transformation. It's an out-of-the-box solution that offers countless benefits for a fraction of the cost. If you're thinking of migrating to SaaS, this cloud adoption strategy will surely do wonders for your business.
For more information on this business model, read about these SaaS metrics .

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

SaaS Gamification: 14 Examples to Follow

SaaS Customer Support: How & Why You Need to Provide Exceptional Customer Service

ARPU: How to Calculate and Interpret Average Revenue Per User

The Ultimate Guide to Freemium

SaaS: The Ultimate Guide to Software as a Service

Customer Success in SaaS: The Complete Guide

15 Metrics Every SaaS Company Should Care About

30+ SaaS Companies & Products to Watch

IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS: Here's What You Need to Know About Each

5 Head-Turning Examples of SaaS Onboarding That Wowed Their Customers
Lean more about customer service stats and best practices for this year.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
What Is SaaS?
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) is a software delivery method that provides the value of a particular software through the internet instead of installing the software on their device.
SaaS stands for Software-as-a-Service. Customers license SaaS products on a subscription basis and receive them over the internet. The code, servers and database that make up an application are hosted and maintained by software providers like Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud . The customers then access the software through a web browser or a mobile app.
Examples of SaaS Products
A SaaS product is one that’s built by a software vendor and licensed to a company. The company pays for the license on a monthly or yearly basis. Here are a few SaaS companies you may know.
More From Built In’s Tech Dictionary What Is Latency?
How Does SaaS Work?
SaaS works in two parts — a vendor creates the software then a customer licenses the software.
The vendor builds software to solve a problem for a sector of business. They typically gather requirements across the customer base and will likely trade off solving one customer’s problem by solving many customers’ problems at once. Vendors building this way allow for many advantages, such as scalability and lower maintenance to benefit customers. Customers then pay for the software over time (usually as a subscription) with the understanding that their feedback will create improvements down the line. The customer doesn’t own the software, and in exchange, they don’t have to worry about maintaining it.
SaaS Architecture
SaaS applications and services use a multi-tenant approach. In practice, this means there’s a single instance of the application so all customers use the same version and configuration of the product. A multi-tenant approach allows SaaS engineers and cloud providers to manage upgrades and bug fixes much faster than a more bespoke approach, thereby creating a smoother user experience for all customers.
The application is tied to data provided by the customer. That data flows, usually through an API , into the application’s database(s) . So even though there are multiple customers’ data held in a database, that information is secured so it doesn't mix with other customer data. When a customer accesses the application, it uses identifiers (such as a username and password) to understand what data to access. The application then combines the data and app into an “instance” which is what the user sees when they interact with the software.
More From Built In Experts What Is a DDoS Attack?
Advantages of SAAS
SaaS offers an exciting alternative to the typical business model of installing software, which often requires building a server, installing the program and configuring it on-premise. Instead, SaaS products are located on a cloud network that customers can access online or through an API. SaaS differs from the traditional model because the software (application) comes preconfigured.
Several benefits come with using the SaaS model to procure software, such as:
- Lower costs to install : SaaS products are installed in a series of clicks. Even for complex software, the time to end-user benefit is reduced since there is no need to set up servers. All the software needs is the right data, which is generally provided by the user, customer or an API.
- Maintaining and updating software is cheaper for customers : The vendor handles all installation and software updates, then applies those changes globally. This means the software periodically gains new features without any work from the customer.
- Scalability and integration : The software is built on third-party vendors, like AWS, which can scale on demand. This means that even through unexpected increases in utilization, the software is unlikely to break.
Disadvantages of SaaS
Consider factors like support services, data security and hype before signing a contract with a software-as-a-service provider. SaaS has the potential to increase earnings and significantly boost productivity but when things go wrong, it becomes annoying, costly and even unsafe. Knowing the risks and drawbacks of SaaS can help you decide whether a SaaS product is the right option for your company.
- Loss of control and service-level agreements (SLA) : You don’t have software control. Any fix your software needs boils down to the terms of your SLA. Unless you opt to break your SLA, you don’t have much recourse to solve your software’s problems with your in-house engineers.
- Software integration problems : Handing over certain operations to a vendor may make things easier up front but down the road you may find yourself at the mercy of the vendor’s support team. This can, in some instances, harm your reputation with customers. If your software is integrated with a SaaS service and the product downtime negatively impacts your customers, your customers will only see you, not your vendor.
- Potential lack of security : SaaS works by giving your data over to a vendor. Though there are terms to which you agree, you ultimately have no control over how well the vendor secures that data.
Get More From Built In Experts 7 Non-Technical Roles That Need AWS Cloud Skills
SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS: What’s the Difference?
Saas (software-as-a-service).
Think about Netflix as noted above. Customers aren’t responsible for managing IT infrastructure or dealing with any aspect of software management when it comes to SaaS products.
PaaS (Platform-as-a-Service)
These products provide a framework for in-house developers to create customized applications. While developers maintain management of the applications they build, all of the servers and storage can be managed by the enterprise host or a third-party provider. AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Heroku are popular PaaS products.
IaaS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service)
These are products used by companies who seek to outsource their data center or computer resources. IaaS providers host servers, storage and networking hardware. IaaS customers must still manage their data use and operating systems. This is where tools like Microsoft Azure or AWS come into play, thereby allowing companies to access cloud services. While you as an individual customer may have a Netflix subscription, Netflix may have their own contract with an IaaS company.
Recent Expert Contributors Articles

Search the site:
- WordPress Retainers
- Enterprise Development
- Maintenance & Support
What Is a SaaS Business Model and How Does It Work?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is the business model of today. According to a study published by 99 Firms , over 80% of businesses use at least one SaaS application.
SaaS applications run in the cloud, and they are often accessible both through a web interface, as well as through desktop and mobile apps (as needed).
For a recurring monthly fee, people have a powerful online tool at their disposal. SaaS companies benefit from the recurring revenue and can roll out new features as soon as they’re ready.
However, for a novice company that wants to enter the software realm, the SaaS business model can be somewhat difficult to understand than other archetypes. In this article, we hope to clarify what a SaaS business model is and how it works.
How Does a SaaS Company Works?
So, what is SaaS business model? SaaS is software owned, supplied, and managed remotely by one or more of its providers.
SaaS companies maintain servers, databases, and software that enables the product to be used over the internet. Users can also access and use the software from almost any device. Generally, the users pay a recurring subscription fee to have access to the software. The more popular business model for SaaS include:
- Customer Resource Management (CRM) : Allows users to manage client information and track sales.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) : A SaaS application most suitable for big organizations.
- Accounting and Invoicing : Business software focused on billing and invoicing services.
- Project Management : Software that helps teammates communicate projects.
- Web Hosting and eCommerce : Remote servers that handle companies’ online presence.
- Human Resources : SaaS that tracks employee engagement, manages payroll, the hiring process, etc.
- Data Management : SaaS products that facilitate data analysis and protect business data.
Check out if your SaaS is a CRM or similar: How Introducing a CRM Helps Your Sales
Why Do Businesses Adopt the SaaS Model?
Because it works! Software installed on a device can undergo harmful interactions with other software and OS errors. In SaaS business model, users don’t have to install anything to access the product features.*
SaaS is cheaper than software sold via other billing models, which convinces users to adopt the product. Developers love SaaS because it is developed consistently and run on the company’s infrastructure. Investors love SaaS revenue because it is recurring, which leads to predictable cash flow.
The Stages of a SaaS Business
For every SaaS business model , there are three primary stages that they go through:
- Startup : Creating a working product and marketing it to new customers.
- Hypergrowth : Experiencing faster growth as clients adopt the product. This stage implies data expansion, bandwidth, and all sorts of technicalities to support users’ accounts.An inability to successfully handle hypergrowth is where many SaaS companies fail.
- Stability : The stage where your SaaS business model levels out. You are making a healthy profit, acquiring new users quickly, and experiencing churn.
Benefits of the SaaS Business Model
Adopting a SaaS Business model over standard software installations is beneficial to both the product vendor and the customer.
Benefits for the Customer
A business model for SaaS favors your target customers. It minimizes costs and increases product usage flexibility. The key benefits of SaaS for your target customers include:
Lower Costs : SaaS platforms are distributed on a subscription basis. That eliminates licensing fees involved in traditional software installs.
It also allows your clients to increase or decrease their expenses based on usage. Additionally, because SaaS solutions are cloud-based, infrastructure costs for customers are eliminated.
Flexibility & Scalability : The SaaS business model offers your customers greater flexibility. If you base your pricing on a usage metric, then your clients will only pay more if they’re using the product more often.
This provides your customers with the opportunity to grow their business with your software . It also eliminates the risk of paying a hefty fee in advance for a product that might not suit their needs.
Quick Benefits : Because SaaS tools are cloud-based, clients see immediate gains. In most cases, it is as easy as signing up with a name and email address to instantly access product functions.
Higher Adoption : The ability to use SaaS tools anywhere in the world has increased their adoption. If users experience immediate benefits from the software, the chances of sticking with the product are much higher.
Free Upgrades : For many companies, downtime can be costly. In most cases, it happens during product upgrades. SaaS software upgrades are generally done without experiencing user downtime or with shorter maintenance windows.
Benefits of The SaaS Business Model Vendors
The benefits of the SaaS business model for vendors include:
No Sales Friction : Most of the SaaS solutions are priced per user or per month. This price allows the end-users to calculate software costs easily. It eliminates the sales friction that can come as a result of IT budget approval.
Recurring Revenue : One of the greatest benefits of the SaaS business model is that it allows a recurring stream of revenue which helps you control churn.
Pivoting & Improvements : With SaaS, you can continuously update your product. That will help fine-tune your product so that you can increase retention and attract new customers in the process.
Easier Free Trial Support : On-premise software support can be lengthy and tedious. With SaaS, you can provide support to users immediately as well as a free 7, 14 or 30-day trials. Thereupon, the user can continue with the free trial or upgrade to a paid level when they can.
Easier to Update and Support : As a SaaS company owner, you control the system and the environment that the product is being developed in.
Easier to Update and Support: As a SaaS company owner, you have to know how to value a SaaS company, and that includes controlling the system and the environment that the product is being developed.
For example, if you build a product that needs to be installed on multiple devices, it will need to support edge cases and different OSs, etc. With a browser-related SaaS (e.g. Asana ), you control the infrastructure on which it is being used .
SaaS Sales Approaches
There are two major ways to sell SaaS: Low-touch and high-touch sales. The sales approach defines whether you sell to B2C or B2B customers.
Low-Touch SaaS Sales
SaaS is a product that can sell itself. The main sales channels are the SaaS website , email, and in many cases, a free trial optimized for onboarding from the start. In general, low-touch SaaS is sold on a monthly subscription.
Basecamp is an excellent example of a low-touch SaaS business.
High-Touch SaaS Sales
Some prospective users need further persuasion in deciding whether to use a particular product. High-touch SaaS is all about using human staff to convince your potential clients to adopt the software or continue using it.
In SaaS, most of the high-touch sales are B2B focused. The key to the success of this sales model are the sales teams. More specifically, sales development representatives (SDRs), account executives (AEs), and account managers (AMs).
Sales teams are usually strengthened by marketers that keep the lead pipeline full for the sales team to assess and close. Salesforce is a typical example of a high-touch SaaS business.
Key SaaS Metrics
Metrics are the indication for the health of any business model, not only SaaS. However, among the abundance of things that you can measure when growing your software business, some metrics are more important than others, and you need to keep a close eye on:
The churn rate points to the number of customers that left or unsubscribed within a specified period. A SaaS business model without churn does not exist. Products evolve all the time, and users leave one company for another in a flash.
The churn rate can tell you exactly how satisfied the users are. However, if it’s on a constant rise, it’s a sign that things are going downhill in your business. For SaaS, 5-7% of churn rate is the acceptable level.
For calculating churn rate, you can use the following formula:
The # of Churned Customers (for a given period) / Total # of Customers
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Knowing how much time and money you need to invest to acquire a new user is one of the best ways to determine whether your SaaS company is profitable. To calculate it, use the following formula:
Total Investment in Sales & Marketing / # of Acquired Clients
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
MRR is the anticipated revenue that can be expected per month. Measuring MRR can help you understand the month-to-month variations in your income. To calculate it, you can use the following formula:
MRR = # of Customers X Average Revenue
Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA)
The average revenue per account (ARPA) is a metric that shows how much revenue is derived from one client, in most cases, per month, quarterly, or yearly. To calculate it, use the following formula:
Total MRR / Total # of Customers
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Customer lifetime value (CLV) is the average revenue that you can get from users during the period that they’re subscribed to for the software. It can be calculated according to the following formula:
CLV = (ARPA x Gross Margin %) / Churn Rate
Customer Retention Rate (CRR)
Customer retention is a metric that shows you the percentage of customers who have continued to pay for using your software. To calculate the retention rate for a given period, you can use the following formula:
(# of Customers that Continue to use the Software / Total # of Customers at the Start of the Time Period) x 100
WordPress SaaS Considerations
WordPress is no longer a blogging platform . As the most powerful CMS in the marketplace, today, you can practically build anything, including software-as-a-service. It allows SaaS businesses to use a cohesive platform and technology, with a higher product focus and flexibility than any other CMS.
Furthermore, WordPress provides SaaS companies with ready-made plugins that can be used as a foundation for the software. For example, on top of WordPress, we’ve built DX Sales CRM , a high-end CRM plugin:
With WordPress, customization is much smoother, and you can install various plugins and add more functionalities to your layouts. The development process is modular, and you can extend your SaaS according to the requirements.
However, along with the benefits that WordPress provides, there ought to be a few challenges along the way when building SaaS on top of the CMS.
Our CEO, Mario Peshev, throughout the years of developing high-scale WordPress SaaS platforms, learned about and shared some of the biggest infrastructural hurdles that any SaaS business needs to expect on his blog , namely:
- Evolving programming languages that developers need to adapt to can be significant, and predicated on the budget.
- Heavier technology stacks and hosting packages, which imply considerable costs in the long run, but improving the site’s stability, security, and scalability for the SaaS project.
- Developing SaaS on top of a framework such as WordPress is good if you only tailor the environment for your project. A media-based SaaS business model can be built on top of a CMS, whereas an eCommerce SaaS would require a dedicated open-source framework without building something from scratch.
- Finding the right talent to carry out a WordPress SaaS project is pivotal. You need a team with substantial technical experience in the field. On the other hand, popular platforms can bring a significant burden because, in their purpose, they’re usually pretty general. So, a lot of code must be implemented if you want your software to include all the necessary functions and meet your requirements.
Wrapping Up
The SaaS business model provides you with endless business opportunities. It’s widely accepted, and its adoption will continue to rise. Coupled with the market demand and competition, you need to pay attention to the SaaS industry dynamics and work to provide unique solutions and value to your customers.
*This depends on the SaaS product and if there are any apps provided for accessing/using the software on desktop, mobile, and in a web interface.
WordPress SaaS Development
We have built from scratch or developed components for various Software as a Service solutions built on WordPress. Let's work together!
Team DevriX
This article is crafted by DevriX's seasoned marketing team, boasting over four decades of collective expertise in crafting sophisticated marketing funnels, devising comprehensive content frameworks and pillars, implementing engaging email campaigns, and creating impactful social media content designed for scalability.
Our marketing experts specialize in the complete spectrum of inbound marketing strategies. As an accredited HubSpot Agency Partner and a Semrush Partner, we engage in meticulous research, blending our extensive experience with the unique insights of our highly skilled team.
We set benchmarks in content creation by incorporating cutting-edge marketing trends, leveraging in-depth industry research, and utilizing state-of-the-art AI tools for data segmentation and captivating content hooks. Our proficiency extends across a diverse range of sectors, including working with SMEs, Fortune 1000 companies, global B2B brands, major publishing entities, WooCommerce platforms, business directories, and affiliate networks.
More Stories:
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is an industry that is booming! An increasing number of businesses have adopted the SaaS model, with 56% of enterprises that were previously…
SaaS has been all the rage in the last few years and quickly became the go-to tech solution for small businesses and big corporations alike.…
In the past few decades, business marketing has undergone a series of transformations that have changed the game forever. Businesses that once got their message…
Digital technology has totally changed our lives. Over the years, our pace of life continues to increase and a lot of us are living a…
More From Forbes
Four reasons your company should consider the saas business model.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Are you wondering if you should choose the software as a service (SaaS) model for your business? Standard software is quickly becoming a thing of the past, and many companies are making the transition into subscription-based services.
One great example of this is Adobe, a company best known for its photo and graphics editing software Photoshop and Illustrator. Adobe was already a successful licensed software company, but it made the move to go to a completely cloud-based setup in 2012. Instead of paying a one-time fee for the software, customers would now have to pay a monthly fee to access Creative Suite apps available on the cloud.
If you’re wondering why companies like Adobe switched to a SaaS business model and why your business should consider choosing the same model, check out these four advantages of the SaaS business model.
Lower Costs
For startups, one of the biggest advantages of the SaaS business model is the cost-effectiveness. When creating a piece of software that users need to install, you have to worry about supporting multiple operating systems and devices. You also need to provide customer support to your customers for their local device issues. But with the SaaS business model, you only have to worry about supporting different web browsers (much less complicated) and don’t have to deal with local device problems either.
Plus, you don’t need to hire a developer to build a SaaS site for you. In fact, you can use WordPress as a SaaS platform . That’s what our company did when we switched from a WordPress plugin to a stand-alone SaaS. Because of the lower costs for your SaaS business , you can offer more affordable prices to your customers, too.
Recurring Revenue
Another big advantage of the SaaS business model is the recurring revenue and the stability that comes with it. With many other business models, companies are focused on constantly attracting new customers, which can be costly and time-consuming. But with the SaaS model, instead of having customers pay a one-time fee for your software, they pay a monthly fee, which makes it much easier to predict your monthly and annual revenue.
With a solid base of existing customers providing you with recurring revenue, you can work on growing your business without worrying too much about your bottom line.
Easy To Use For Your Customers
As a SaaS business, your offerings are easy to use for your customers. All they have to do is log in, and they’re provided with onboarding, best practices and samples in an instant. Plus, there’s no complicated software to install and figure out, so they can start using the application right away.
In addition, with the SaaS model, it’s easier for your business to offer free trials. Free trials are important because they remove risk for the buyer. With free trials, your leads can try out your offerings before they have to give you their credit card information. After their free trial is over and they know firsthand how great your application is, then they can sign up for a paid plan.
Updates And New Features
Adding new features and upgrades with on-premise software isn’t so easy. Think back to the time when if consumers wanted Microsoft Office, they would have to purchase the CD-ROM and install it. When a new version of Microsoft Office came out with more advanced features, they would have to purchase the new version and install it all over again. But with the SaaS model, you can present cool new features and useful updates to your users in a much easier fashion.
Using the Saas business model, updates and new features can be easily added and offered to your users right away. In fact, SaaS companies can offer upgrades and new features multiple times a day if they want to — that’s how easy it is.
As you can see, there are many reasons to start using the Saas business model. The benefits aren’t just for the company founders, either: Your customers will benefit from the Saas model, too. So whether you want to make the switch from on-premise software to SaaS or you’re interested in starting a Saas business, keep these advantages of the Saas business model in mind when you’re making important decisions for your company and your future customers.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

Top 6 SaaS Business Models That Will Transform Your Company
- May 17, 2024

There are different types of SaaS business models , each with advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will explore the most common examples of SaaS business models that are the most successful businesses.
The software-as-a-service (SaaS) sector has grown exponentially since it burst onto the scene in 2005. SaaS businesses are becoming increasingly popular for a variety of reasons. They are typically more affordable than purchasing traditional software and easy to use. Massive amounts of time and capital are currently going into SaaS companies and businesses, which stand a strong chance of succeeding if they fulfill market demands.
What are the different SaaS Business Models?
Saas business models examples.
- Need Assistance with a SaaS App Development?
SaaS Metrics You Must Track
Conclusion of saas business models, saas business models faqs, what is a saas business.
Software as a service (SaaS) is the practice of offering consumers cloud-based software . It is a way of distributing and licensing software in which the product is accessed online through a monthly/yearly subscription rather than being purchased and installed on specific PCs.
A SaaS business is a type of business model where software is provided to customers on a subscription basis . Customers can access the software remotely, typically through the internet.
SaaS businesses are usually hosted on the cloud, providing scalability and flexibility for the company and the customer. The term “ cloud ” simply refers to the area of the internet where businesses have developed their resource infrastructure and where they allot some of these resources to new customers.
Similarly to other business models, SaaS also has its positive sides and drawbacks. Keep reading to discover the advantages and disadvantages of a SaaS business model.
Advantages of a SaaS Business Model

There are many advantages of operating a SaaS business, including:
- Scalability. The cloud-based infrastructure of a SaaS business makes it easy to scale up or down as needed. This means that SaaS businesses can respond quickly to changes in customer demand.
- Recurring revenue. Because customers pay monthly or yearly, SaaS businesses have a steadier stream of income than companies that rely on one-time sales. This can make it easier to predict and plan for growth.
- Easier pivoting and modification. SaaS businesses can modify their offerings quickly and easily in response to customer feedback or changes in the market. This agility can be a major advantage over traditional software companies .
- More market potential. SaaS is subscription-based and available on the cloud, meaning that SaaS businesses can reach a global market more easily. Customers in any location with an internet connection can subscribe to a SaaS service.
- Loyal customer base. Since customers pay regularly, they are more likely to remain loyal to a SaaS service that they are satisfied with. This can lead to long-term relationships between the company and its customers and long-term income.
Disadvantages of a SaaS Business Model
There are also some disadvantages associated with operating a SaaS business, including:
- More competition . Since the barriers to entry are relatively low, there is a lot of competition in the SaaS market. This can make it difficult for new companies to stand out from the crowd and attract customers.
- Aggressive strategy for customer retention and churn. Since SaaS businesses rely on recurring revenue, they must constantly strive to retain their customers. If a customer ends their subscription, the business loses income. As a result, SaaS businesses often have aggressive strategies for customer retention and churn prevention.
- Capital dependent. SaaS businesses require a substantial amount of initial investment to get off the ground. This can make it challenging for new businesses to get started. Also, SaaS businesses must continuously invest in their product to keep up with the competition and maintain a high level of customer satisfaction. This can be a challenge for small businesses with limited resources.
You can also read our blog on Medium
As you can see, the advantages outweigh the disadvantages leaving no doubt that the SaaS business model is an effective practice used by many companies.
Read our complete guide on SaaS development
Now that you’re familiar with the advantages and disadvantages of a SaaS business model, let’s explore different types of SaaS business models.

1. Freemium
The freemium model provides customers can access a basic version of the software for free. They must pay a monthly or yearly subscription fee if they want to use the advanced features.
This model is often used by companies that want to increase their customer base quickly. Providing the service for free will draw many users in. Once they use the service and see its value, they will likely pay for a more extensive set of features.
2. Flat Pricing
Under the flat pricing model, customers pay a set price for access to the software. This price is not based on usage levels or the number of users. Instead, it is a one-time or monthly/yearly subscription fee that gives the customer unlimited access to the software .
Flat pricing is simple and easy to understand, which can appeal to customers. Because the price is not based on usage, customers don’t have to worry about exceeding their budget. This predictability can make it easier for them to justify the cost of the software.
3. Usage-Based Pricing
Under the usage-based pricing model, customers are charged based on their level of usage.
This model can be appealing to customers because they only pay for what they use . If they don’t use the software often, they won’t have to pay a high price. This pricing model also gives customers the flexibility to increase their usage as their needs change.
Users often think that “pay for what you use” is a fair way to charge, and smaller companies won’t be scared away by high prices.
4. Per-User Pricing
Under the per-user pricing model, customers are charged based on the number of users that have access to the software. The price may be a monthly or yearly subscription fee.
This model is often used by businesses that need to give multiple employees access to the software. For example, a company might need to give five customer service representatives access to a customer relationship management (CRM) system.
Per-user pricing is best for situations where a lot of people need to use your software simultaneously, especially if each person needs access to different features.
5. Tiered Pricing
Under the tiered pricing model, customers are charged based on the features they use. The price may be a monthly or yearly subscription fee.
This model is often used by businesses that offer different levels of service. For example, a company might offer a basic CRM system for small businesses and a more advanced CRM system for larger businesses. The price of the advanced system would be higher because it includes more features.
6. Hybrid Pricing
The hybrid pricing model combines two or more of the other models. For example, a company might offer a basic CRM system for free and charge customers based on usage if they want to use the advanced features.
This model gives businesses the flexibility to tailor their pricing to meet the needs of their customers. It also allows businesses to try different pricing models to see what works best.
Now that you’re familiar with different SaaS business models, let’s check out a few popular SaaS business model examples.
Mailchimp is a SaaS company that provides online marketing tools to small businesses. The company is based on a freemium business model. This means that the customers can test out most features free of charge.
Mailchimp offers three different products to its users: the Marketing Platform, Website & Commerce, and Transactional Email. Most of Mailchimp’s clients are small businesses, but it also works with large companies. Customers can use Mailchimp to create and send email campaigns , design landing pages , and track their marketing progress.
Mailchimp offers a plan that is free of charge for customers who have up to 1,500 subscribers. For customers with more than 1,500 subscribers, Mailchimp offers multiple paid subscription plans that include different features.
Shopify is a SaaS business model example company that provides an e-commerce platform for businesses of all sizes. Customers can use Shopify to create an online store, manage inventory, process payments, and track shipping.
Shopify has a distinct approach to its users- the company wants to do more than just sell its products to customers. It also wants to help its users become more successful by using the platform. Why? When merchants make more money, Shopify makes more money . This is also a major reason why Shopify has grown to where it is now.
The company offers different subscription plans that range from $29 to $299 per month. In other words, Shopify uses the tiered pricing SaaS model. The features included in each plan vary, but all plans include basic features such as a website builder, shopping cart, and product catalog.
Shopify also provides a 14-day trial for customers who want to test the platform before committing.
HostGator is an example of a SaaS business model that provides web hosting and related services to businesses of all sizes. Customers can use HostGator to create a website, host email accounts, and manage their domain name.
The company offers different subscription plans that start at a price as low as $2.75. Similar to Shopify, HostGator uses the tiered pricing model. The features included in each plan vary slightly, but all plans include basic features such as website-building tools and 24/7 customer support.
The market is quickly opened up to people with different budgets thanks to the tiered pricing strategy. Additionally, it enables new users to try out the product at the most basic level before upgrading as necessary.
HostGator also offers a 45-day money-back guarantee for customers who are not satisfied with their service.

In order for SaaS companies to be successful, they need to track the right metrics, so here are the ones that will help them through the path of sustainable growth and profitability.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
It represents the total monthly revenue derived from subscription-based services, serving as a compass for predicting revenue inflow and establishing a foundational benchmark.
MRR offers invaluable insights into the steady revenue stream generated from subscriptions every month, thereby illuminating the company’s revenue trajectory and growth potential.
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
ARR represents the anticipated revenue over a year, furnishing indispensable data for future financial planning and prognostication. It shows a panoramic view of revenue stability and growth across a longer time frame than MRR, offering strategic insights for sustainable business expansion.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
It indicates expenditures on sales, customer service, and marketing efforts, providing indispensable guidance for optimizing customer acquisition strategies.
Understanding CAC is pivotal for ensuring the efficacy of marketing and sales initiatives and maintaining a balanced ratio between acquisition costs and revenue generation.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV/LTV)
It serves as a compass for gauging the total anticipated revenue from a customer throughout their engagement with the company, highlighting the significance of nurturing long-term customer relationships and devising strategies to enhance customer engagement and retention.
CLV/LTV evaluates the long-term profitability of customer acquisition and retention efforts, thereby informing strategic decision-making and resource allocation.
Customer Churn Rate
It is the total amount spent on sales, and marketing to obtain a new clients.The churn rate measures the percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions within a set period. It helps gauge how effective your efforts are in retaining customers.
Discover more SaaS metrics in our blog “SaaS Metrics that Matter: A Guide of What to Track”
Need Assistance with a SaaS App Development? Launch Your App with ClickIT
You can’t run a successful SaaS business even if you don’t have an accompanying app. Launch your SaaS app in time and capture the market share that your idea deserves with a proper SaaS Application Development service.
With the ClickIT team by your side, you’ll be able to cut the layers and unproductive mistakes out of your process. The ability to build SaaS Apps around various ideas for different industries is exactly what sets ClickIT apart from its competitors.
The ClickIT team completed more than 50 projects for startups and enterprises alike. Our services include:
- Multi-tenant and SaaS application architecture
- DevOps for SaaS
- AI ML SaaS app
- FinTech SaaS application
- Enterprise management SaaS solution
- SaaS platform for marketing automation
- Healthcare and patient record SaaS solution
- IoT and wearable tech SaaS applications
SaaS businesses have a lot of flexibility when choosing a business model. The most important thing is to choose a model that aligns with the company’s goals and objectives. If you want your SaaS business models to work, you must make a long-term commitment to customer success, including staying on top of the latest trends and technologies.
Since AI, machine learning, and data automation are becoming more popular, more businesses are looking forward to adding them to their SaaS platform. Ensure optimum customer satisfaction and stay ahead of the competitors by implementing the latest technologies into your services.
Looking to get your SaaS business off the ground? ClickIT is your choice for developing a SaaS application tailored to your specific needs!

A SaaS business is a business model where software is provided to customers on a subscription basis. They are usually hosted on the cloud, providing scalability and flexibility for the company and the customer.
The most commonly used software-as-a-service types businesses purchase are: -Cloud-based -On-premises -Hybrid
A SaaS provider is a business that houses applications and makes them accessible to consumers online. There are many SaaS brands out there, but some of the most popular include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zendesk, and Shopify.
There are numerous SaaS business models available. The most popular are freemium, flat pricing, usage-based pricing, per-user pricing, tiered pricing, and hybrid pricing.
Yes, Netflix is a SaaS company; customers pay a subscription fee for access to this service, making it a classic example of SaaS.
to our newsletter
We make devops easier.

Uber’s System Design: A Technical Overview

How To Build A Successful SaaS MVP | Video
By the end of 2024, 99% of companies will be

Microservices vs SOA Architecture: What’s the Difference?

We provide cost-effective solutions tailored to your needs. Ready to elevate your IT game?
Our Newsletter

Nearshore DevOps Outsourcing
Hire DevOps engineers
Hire Remote DevOps
Nearshore Software Development
Hire Python Developer
Hire React Developer
Hire PHP Developer
Hire Node.js Deve loper
Web development company
Web app development
Custom Software development
SaaS Development Consulting
SaaS Security Services
Fintech app development
Fintech Software Development
Healthcare SaaS
Healthcare Software Development
Healthcare app development
Top Locations
Software Companies in Dallas
Software Companies in San Diego
Software Companies in Los Angeles
Tech Companies in New York
Web Development Company in Houston
Web Development Companies in California
Work with us now!
Innovate your, saas application, with a dedicated team.

The Pros and Cons of SaaS Business Models
- | November 28, 2018
The delivery and management of subscription-based software in the cloud is on the rise and shows no sign of slowing down . The traditional on-premise software model is quickly becoming a relic of the past. So what are the pros and cons of SaaS models compared to a traditional software offerings?
The Pros and Cons of Saas Models
Advantages of the saas business model.
There are a number of good things going for the SaaS model, including licensing flexibility, ease of deployment, the latest software versions, scalability based on users’ needs, and a more predictable revenue stream in the form of less expensive monthly subscriptions.
The ability to manage software versioning
As SaaS is hosted in the cloud, updates only need to be applied from the provider’s end. Customers will always be current on software versions and have the latest features through periodic incremental updates, all of which is built into the subscription price. Contrast the pros and cons of SaaS models with the often expensive on-site software upgrade model, which provides less frequent updates, greater budgetary requirements, and often must enlist the help of a consultant to apply the upgrade.
SaaS is scalable
There are great demands being placed on companies to provide real-time information, which requires large amounts of data to be processed in a timely manner. Fortunately, SaaS applications can be made scalable; they have the ability to handle high data transaction volume and increased swells of activity, such as payroll processing, or month-end closures. Having this ability allows for up-to-date reporting and informed decision making.
Scalability within the SaaS model is not limited to just information processing. SaaS providers often offer several subscription tiers to meet the different needs of their user base, and a customer can usually change between options on the fly. In addition, software in the cloud allows for teams with users based in different locations to collaborate using the same solution.
Cloud deployments
With deployment and installation of software in the cloud, the SaaS company provides membership to the end user simply by granting them access through their online account credentials. All that’s needed is a web browser and connectivity. There’s no need for on-premise software installation or costly infrastructure on the part of the customer to host the software, nor is there a need for an end-user license to activate the software.
Flexible licensing
The SaaS subscription model is much more accommodating to the needs of the customer, and offers adaptability that hosted software cannot provide. SaaS offers flexible monthly and yearly timeframes for subscriptions, and the length of subscriptions are typically on an as- needed basis. In addition, there is no need to purchase a license or install the software, unlike what is required of hosted software.
Predictable revenue
Although we can never perfectly predict revenue, when the software you provide becomes integral to the operation of a business, you’ll build loyal customers and start to see consistent monthly revenue from subscriptions. This is much more predictable than a model based entirely on one-off sales. Customers who pay for your services for longer periods of time are less likely to cancel their subscription services, leading to a more predictable revenue stream.
What disadvantages exist in the SaaS Business Model?
The SaaS model has its share of obstacles as well, compared with traditional software business models. Longer sales cycles, competitors piggybacking off of ideas and pricing structures, security concerns, ease of ability for customers to jump ship due to low costs and competitor offerings, as well as the SaaS marketing challenges and business analytics efforts, should all be considered potential shortcomings.
Longer conversion funnel
In the SaaS business model, the road to turning free users into paying subscribers usually consists of a longer sales cycle — on average several months , which usually includes free trial periods and signups. You’ll spend more time courting your customers and cultivating those leads and prospects.
Easy to copy business models
Where one SaaS company finds success, there are bound to be a slew of imitators to follow. If a company has demonstrated success with a particular SaaS marketing strategy , sales strategy, pricing structure , or email campaign, it is very easy for competitors to emulate these successful strategies by simply navigating the web to copy the approach. In this way, pricing becomes transparent to both customers and competitors alike.
Lower barriers to entry for competition
Easy integration into the SaaS model can also mean easy replacement and lower barriers to entry for the competition. Most purchases in SaaS are subscription based, so once customers are on board, you still need to provide increasing value over competitors, while still up-selling to the next subscription level. Should a customer become dissatisfied with services or support, they can simply move on to a competitor offering a similar pricing structure without having to make a larger upfront investment like one would with other software sales.
Complex analytics
Marketing and business analytics for the SaaS business model is much more complex, as you often have data coming in from all different directions. According to Abhi Jadhav, managing partner at Bay Leaf Digital,
“Even though most SaaS marketing efforts are done online, the use of multiple marketing and automation tools create silos that that make it difficult to get a comprehensive view of marketing efforts. This is particularly exacerbated through the use of marketing automation products, web analytics services, and channel marketing services (e.g. email marketing, PPC management) that are very loosely integrated with each other.”
Just like everything else that resides in the cloud, SaaS offerings are not immune to malicious threats and data loss. Trusting that mission-critical and sensitive data is safe in the hands of third-party providers should be a top concern for both subscribers and providers alike. Understand the limitations for which the software provider is responsible, with regards to keeping your data confidential and ensuring that data integrity is not compromised, can be critical.
Comparing the Pros and Cons of SaaS Models
Compare and analyze the pros and cons of SaaS models to fully understand its scope. Although there are some drawbacks to the SaaS business model, such as the previously mentioned lengthier sales cycles, lack of customer loyalty due to similar competitor service offerings, as well as security concerns, there also exists an even greater amount of benefits that cloud-based SaaS offerings provide. Cost efficiency, flexibility, scalability, up-to-date releases, and predictable revenue streams for providers are all compelling reasons to help explain why all signs point to SaaS continuing to being an integral part of future technology trends.
Does Your SaaS Need a Marketing Boost?
Author profile.

Sandy Smith
Saas resources, about bay leaf digital.
Bay Leaf Digital is a SaaS marketing agency with a proven track record of success for companies since 2013. Our team of SEO, SEM, Paid Social, and content marketing specialists knows the secret to building brand awareness and generating qualified leads for every SaaS from startups establishing product market fit to global enterprises seeking to stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Subscribe to the SaaS Wire Newsletter
Stay ahead in B2B SaaS marketing with our insider insights, trends, and expert tips delivered straight to your inbox monthly.
Alternatively, subscribe to SaaS Wire on LinkedIn:
More To Explore
How to reduce churn in saas during free trials: 5 strategies.
It costs five times more to acquire new customers than to retain them. That’s a lot of time, resources, and money spent on drawing in
How to Choose the Best SaaS Subscription Management Tool
A subscription management tool is a software solution designed to help businesses that offer subscription-based services or products efficiently manage their consumer interactions and billing
Choose a Great SaaS Marketing Agency in Europe
As B2B SaaS companies seek to expand their market presence and refine their marketing strategies, many managers find themselves considering partnership with a SaaS marketing
B2B SaaS Meaning and Everything You Need to Know (Plus Real-Life Examples)
Last updated on May 22nd, 2024 at 12:01 pm
What if I told you that grasping the concept of B2B SaaS could significantly boost your business efficiency and profitability?
Many businesses are already enjoying such benefits.
Today, we will break down B2B SaaS into easy-to-understand terms, providing valuable insights into its purpose and impacts.
Some miss out on these advantages simply because they don’t fully understand the model .
So, let’s ensure your company is not one of them.
Read on to learn how you can apply these insights to optimize your operations and stay competitive in today’s market.
First, let’s dissect the terms.
- B2B SaaS allows businesses to access software applications over the internet without installing them locally.
- It typically uses a subscription-based model, providing cost-effective and scalable solutions that businesses can pay for monthly or yearly.
- Solutions are hosted in the cloud, offering flexibility, easy access, and reduced need for local IT management.
- Applications are designed to meet business needs, from CRM and project management to accounting and HR management.
- When selecting a B2B SaaS tool, consider your specific needs, assess features, check security, and use free trials to ensure it fits your business.
What is B2B SaaS?
B2B SaaS stands for Business-to-Business Software as a Service.
It’s a way for companies to use software applications over the internet instead of having to install and maintain them on their own computers.
Imagine you run a business and need software to manage or supercharge your sales process, marketing campaigns, or customer support.
Instead of buying and installing these programs on your computer, you can subscribe to a B2B SaaS provider.
These SaaS businesses host the software on their servers, and you access it online.
So, B2B SaaS helps businesses get the tools they need without the hassle of managing the software themselves.
B2B SaaS Meaning – What is B2B and SaaS?
At its core, B2B SaaS combines two essential concepts: B2B, which stands for business-to-business interactions, and SaaS, or Software-as-a-Service.
This model is all about providing cloud-based software solutions from one business to another.
The beauty of SaaS lies in its simplicity and convenience—the vendor handles everything from deploying to maintaining the applications.
This means businesses can access vital tools over the cloud using a browser or mobile application, often without worrying about the nitty-gritty of installation or updates.
How is B2B SaaS Different from Traditional Software?
A B2B SaaS brand is basically an enterprise software company that designs software for other enterprise-level businesses to use.
The type of software that SaaS businesses create is different from traditional software in several key ways:
- Access and Installation : With B2B SaaS, you access the software through the internet. There’s no need to install anything on your computer. Traditional software usually requires you to buy, download, and install it on your device.
- Cost : SaaS typically operates on a subscription basis. You pay a recurring fee, which can be monthly or yearly. Traditional software often involves a one-time purchase fee, and you might have to pay extra for updates and support.
- Updates and Maintenance : In B2B SaaS, the provider handles all updates and maintenance. This means your software is always up-to-date without any effort on your part. With traditional software, you’re responsible for installing updates and patches.
- Scalability : SaaS solutions are easy to scale up or down based on your business needs. You can quickly add or remove users. Traditional software can be harder to scale, often requiring additional hardware or complex reinstallation processes.
- Accessibility : Since SaaS is online, you can use it from anywhere with an internet connection. Traditional software is usually tied to the computer where it’s installed, limiting flexibility.
- Support : SaaS providers offer continuous support as part of their service, helping you resolve issues quickly. Traditional software might require separate support contracts or fees.
Cloud-Based Models Aside from SaaS

While SaaS is a significant player in the B2B cloud-hosting game, it’s not the only model out there.
There are several other cloud-based models businesses use.
Here are some of the main ones:
- SaaS (Software as a Service) : Do you need software with minimal setup? This model provides software applications over the Internet. You don’t need to install or maintain anything. The key feature? It’s ready-to-use software. Just log in and start working.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service) : Are you looking to build custom applications without managing the infrastructure? PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. It includes tools and services that make coding easier. The standout feature? It’s a complete development environment.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) : Do you need flexible computing power without the hardware cost? With IaaS, you get virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking. You rent these resources instead of buying hardware. Its key feature? Full control over your infrastructure.
These models provide different levels of control and convenience. Which one fits your needs best?
The Shift to B2B SaaS
The movement towards B2B SaaS is more than just a trend—it’s a significant shift in how businesses think about software.
Predictions suggest that by 2022, a whopping 78 percent of companies will operate solely on B2B SaaS platforms.
This shift isn’t just about the technology itself; it’s about the efficiency, scalability, and accessibility it brings to the table.
With the public SaaS market expected to hit $76 billion by 2020, it’s clear that B2B SaaS is not just the future—it’s the present.
“People want what’s best for them, and they can switch on a dime, because there’s always a new disruptor disrupting the last disruptor. So companies should just strive to keep changing and adapting to their customers’ needs” Ben Chestnut, Co-founder of MailChimp
Key Characteristics of B2B SaaS
The B2B SaaS model has some key features that make it different from other software solutions.
Aside from businesses being their target audience, knowing these important traits is crucial for businesses wanting to use B2B SaaS effectively.
1. Subscription Model
B2B SaaS stands out primarily due to its subscription-based business model.
This model is a departure from the traditional software license approach, offering a more flexible payment structure.
Potential customers can pay a monthly or annual fee for access to the software hosted online.
This shift towards subscription-based payment plans has necessitated operational changes in modern SaaS companies, focusing on customer retention and value provision over time.
The benefits of this model include a predictable revenue stream, easier forecasting of annual and monthly recurring revenue, and the ability to upsell or cross-sell to existing subscribers.
2. Cloud-Based Solutions
Another defining characteristic of B2B SaaS is its cloud-based nature.
SaaS applications are built on cloud infrastructure and are accessible from any device with an internet connection and web browser.
This eliminates the need for local installation and allows for greater flexibility and savings.
The cloud environment is scalable and integrates well with other SaaS offerings, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses.
Upgrades and new releases are managed by the provider, reducing the costs and effort associated with maintaining software.
Cloud-based solutions also offer scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to dynamically adjust resources as demand fluctuates.
3. Business-Focused Applications
B2B SaaS solutions are designed with the specific needs of businesses in mind.
They encompass a wide range of applications, from email and messaging apps like Microsoft Outlook and Slack to CRM solutions and automation tools for marketing campaigns.
These applications are crucial for improving operational efficiency, data management, and interaction with potential customers or other businesses, businesses being more of their main target audience.
The focus on business applications has enabled B2B SaaS to become an integral part of the technology stacks of companies of all sizes, facilitating smooth and efficient business operations.
Integration plays a key role here, as B2B SaaS integration platforms enable seamless connectivity between different applications, enhancing collaboration and operational efficiency across departments and units within organizations.
These key characteristics will help you understand the fundamentals of B2B SaaS solutions better.
But to gauge a SaaS solution’s fit for every business, we should also touch on its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages and Disadvantages of B2B SaaS for Businesses
When entering the B2B SaaS industry or considering B2B SaaS for your own business, it’s important to weigh both the pros and cons.
While there are plenty of benefits that come with using SaaS solutions, there are also some potential downsides to be aware of.
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective : B2B SaaS usually works on a subscription model, which means you pay a regular fee rather than a large upfront cost. This can help manage cash flow better.
- Easy Updates : The software is always up-to-date because the provider handles all the updates. You don’t need to worry about installing patches or upgrades that can sometimes halt business processes.
- Accessibility : Because the software is online, you can access it from anywhere with an internet connection. This is great for remote work or if you have multiple offices.
- Scalability : It’s easy to add or remove users as your business needs change. This flexibility can be very useful for growing companies.
- Less IT Hassle : With SaaS, you don’t need a big IT department to manage the software. The provider takes care of maintenance, security, and support.
- Quick Deployment : Getting started with SaaS is usually fast. There’s no need to wait for long installation processes or extensive setup.
Disadvantages:
- Dependency on the Internet : Since SaaS is cloud-based, you need a reliable internet connection. If your internet goes down, you can’t access the software.
- Subscription Costs Add Up : While the regular payments are manageable, over time, they might add up to more than a one-time purchase of traditional software.
- Limited Customization : SaaS solutions may not offer the level of customization that traditional software can provide. You might need to adjust your processes to fit the software.
- Data Security Concerns : Storing data on the cloud means trusting the provider to keep it secure. While most providers have strong security measures, there’s always some risk.
- Downtime and Reliability : If the service provider has downtime or other issues, it can disrupt your business processes. You are dependent on their uptime.
- Control Over Data : With SaaS, your data is stored on the provider’s servers. If there are issues with the provider, accessing your data could become problematic.
By understanding these pros and cons, you can make a more informed decision about whether B2B SaaS is right for your business.
Now, how do you make that decision?
Let’s talk about the steps that will help you choose the most ideal SaaS application for your business needs.
How to Pick the Ideal B2B SaaS Applications for Your Business

Choosing the right B2B SaaS applications for your business can feel overwhelming.
The market offers so many options that it can be hard to decide on just one.
Here’s a straightforward guide to help you pick the ideal B2B SaaS solution for your business needs:
Step 1: Identify Your Needs
Start by figuring out what problems you need to solve. Do you need help with customer relationship management (CRM), project management, reaching your target audience, or marketing automation? Knowing your needs will narrow down your options.
Step 2: Research Options
Once you know what you need, look for software that offers those solutions. Check online reviews, ask for recommendations, and browse industry-specific forums. Have you found any tools that seem promising?
Step 3: Assess Features
List the features each tool offers. Compare them to your needs. Make sure the software has everything you require. Look out for features like integration with other tools, ease of use, and scalability.
Step 4: Consider Costs
Budget is important. Look at the pricing models of the SaaS options you’re considering. Some charge per user, while others offer flat rates. Which pricing model suits your budget?
Step 5: Check Security
Data security is crucial in the cloud. Ensure the provider has robust security measures. Look for details on encryption, data backup, and compliance with industry standards.
Step 6: Try Before You Buy
Many SaaS providers offer free trials or demos. Use them to get a feel for the software. Does it meet your needs? Is it user-friendly?
Step 7: Evaluate Support
Good customer support can save you a lot of headaches. Check if the provider offers 24/7 support, training resources, and quick response times. What kind of support do they offer?
Step 8: Read Reviews and Testimonials
Other users’ experiences can give you insights into the pros and cons of each tool. Pay attention to feedback on usability, reliability, and customer service.
Step 9: Think About Integration
The software should integrate well with your existing tools. Check if the SaaS can connect with your CRM, email marketing, or accounting software seamlessly.
Step 10: Plan for Growth
Choose a tool that can grow with your business. Ensure it can handle more users, more data, and more features as your business expands.
By following these steps, you’ll be better equipped to choose the right B2B SaaS applications that fit your business needs.
Popular B2B SaaS Applications
Nowadays, B2B SaaS apps are must-have tools for businesses.
They help streamline operations, boost efficiency, and support growth.
These cloud-based solutions handle everything from customer relationships and projects to finances and HR.
Want to know more? Let’s check out some of the top B2B SaaS apps in different categories.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)

- ClickUp : Not just a task manager, ClickUp offers a customer relationship management feature-rich hub for making smart decisions about customer data usage, enhancing work experience, and achieving greater results.
- Zendesk Sell : Designed for productivity, this tool helps manage the sales pipeline and grow revenue, answering the modern SaaS CRM needs.
- Pipedrive : As the first CRM designed by salespeople, it focuses on managing and optimizing sales pipelines and funnels.
- Sales Cloud by Salesforce : A purpose-built CRM for optimizing sales management and storing contact information.
- Dynamics 365 : Microsoft’s suite includes a sales platform for a better view of the customer journey and sales forecasting.
- Oracle Advertising and Customer Experience (CX) : Offers a range of sales, marketing, and service applications for strategic data use.
- NetSuite : Allows building and maintaining client relationships across the entire customer journey.
- SugarCRM : Blends sales, service, and marketing tools for increased efficiency and better customer experiences.
- Freshsales : Freshworks’ powerful sales CRM tool, designed to drive revenue growth and productivity.
- Zoho CRM : Boasts the fastest implementation in the enterprise CRM market.
Project Management Tools

- Wrike : An award-winning project management software used globally for its comprehensive suite of tools.
- Asana : A popular option for businesses of many sizes, combining project roadmaps, dashboards, and file storage.
- Monday.com : Offers templates and tools for optimizing operations and boosting productivity.
- Adobe Workfront : Favored by marketing teams for its wide range of features.
- Smartsheet : Utilizes cloud-based spreadsheets for project and task management.
- Jira : Offers work management assistance for teams of every size.
- ClickUp : Known for its standard management features that are suitable for most team sizes.
- Microsoft Project : Combines project management functionality in one platform .
- Basecamp : An easy-to-use platform for small teams with scheduling and collaborating features.
- Trello : This popular project management software allows for simple project visualization and effective task management.
- Zoho Projects : Ideal for current Zoho users, offering easy data sync between various tools.
Accounting and Financial Software

- Tipalti : Provides AP Automation and Mass Payments and integrates them with various ERP systems.
- Sage Intacct : Offers subscription management, revenue recognition, and SaaS metrics.
- NetSuite : An ERP system with modules including finance, forecasting, and inventory management.
- QuickBooks Online : Cloud-based software that works with third-party app integration for added SaaS functionality.
- Xero : Integrates with third-party apps for AP automation and SaaS revenue recognition.
- ChargeBee : A solution for startups and growing SaaS companies, including subscription management and billing automation.
- Recurly : Scalable subscription billing software for midsize and enterprise companies.
- BillingPlatform : Handles complex recurring subscription billing models and revenue recognition.
- Zuora : Provides automation software for complex hybrid billing models and revenue management.
HR Management Systems

- Deel : A comprehensive platform for onboarding and managing help, especially for small businesses and startups.
- Rippling : An all-in-one software for managing employee aspects from a centralized location.
- Bamboo HR : Popular among small businesses for simplifying employee management.
- Paycor : Offers a range of services, including payroll management and benefits administration.
- Homebase : An all-in-one software with features for scheduling, time tracking, and HR compliance.
- GoCo : Automates onboarding checklists and ensures a memorable first day for new employees.
- Paychex Flex : A cloud-based platform offering a wide range of HR services.
- Remofirst : Helps small businesses comply with tax regulations and labor laws.
- Bambee : Provides access to HR support and guidance from certified HR professionals.
These B2B SaaS applications represent just a fraction of the tools available to modern businesses, each offering unique benefits designed to address specific operational needs.
By leveraging these technologies, companies can optimize their processes, improve productivity, and ultimately drive growth in the digital era.
5 Examples of Really Successful B2B SaaS Companies
We’ve seen how B2B SaaS applications can transform business operations, but what does success look like in this space?
In this section, we’ll look at some standout B2B SaaS companies that have made a significant impact.
Their innovative solutions and dedication to customer success have set them apart as leaders in the industry.
Salesforce, a pioneer in the CRM industry, has significantly shaped the B2B SaaS landscape.
By offering a comprehensive suite that includes sales, marketing, and customer service platforms, Salesforce allows businesses to streamline their operations and enhance relationships with customers and potential customers.
The platform’s success is evident in its widespread adoption, serving as a critical tool for businesses aiming to maintain a competitive edge in customer management.
HubSpot stands out not only for its extensive marketing and sales capabilities but also for its role in helping businesses grow efficiently.
The platform integrates various functions—marketing automation, sales CRM, and customer service—into a single, cohesive system, making it easier for companies to manage their customer interactions and data.
HubSpot’s ability to unify these aspects has made it a favorite among businesses looking to optimize their sales and marketing strategies.
Originally started as a tool for internal team communication, Slack has evolved into a vital part of the enterprise communication stack, particularly in the B2B SaaS sector.
Its intuitive design and extensive integration capabilities make it an essential tool for enhancing team collaboration and productivity.
Slack’s rapid growth and the strong user engagement it fosters are testaments to its effectiveness and popularity in the business world.
Zendesk has revolutionized customer service with its user-friendly interface and powerful functionality.
By focusing on improving customer interactions and support, Zendesk helps businesses build stronger relationships with their clients.
The platform’s success is reflected in its high customer satisfaction rates and its ability to provide a seamless support experience across multiple channels.
Microsoft Office 365
Microsoft Office 365 enhances workplace productivity through its robust suite of office applications combined with cloud-based technology.
Its scalability and the continuous updates it provides ensure that businesses can always access the latest tools and features, which are crucial for maintaining efficiency in today’s fast-paced market environment.
Office 365’s integration capabilities make it a versatile tool that fits various business needs, making it a staple in many B2B SaaS strategies.
5 Common Challenges of Investing in B2B SaaS Solutions
Investing in B2B SaaS solutions can be a game-changer, but it comes with challenges. Let’s break down the five most common ones:
- Data Security Concerns : When you use cloud-based software, your data lives on someone else’s servers. This can make people nervous about data breaches or loss. Are you confident in the provider’s security measures?
- Integration Issues : Not all SaaS tools play well with others. If your new software doesn’t integrate with your existing systems, you could face headaches trying to make everything work together. Have you checked if the SaaS tools you’re considering integrate with your current software?
- Hidden Costs : While SaaS often seems cheaper upfront, costs can add up. Subscription fees, add-ons, and user licenses can become expensive over time. Have you considered the long-term costs?
- Dependence on the Internet : Since SaaS runs online, a stable internet connection is a must. Any downtime can disrupt your operations. Is your internet reliable enough for this?
- User Adoption : New software means a learning curve. Your team might resist change or find it hard to adapt. Training takes time and effort. How will you ensure your team gets up to speed quickly?
These challenges can be tricky, but knowing them helps you prepare and find the right solutions for your business. What challenges are you most concerned about?
B2B SaaS, or Business-to-Business Software as a Service, includes tools designed to alleviate business challenges and enhance operational efficiency.
Common examples include Asana for project management and Confluence for team collaboration.
B2B, or Business-to-Business, refers to transactions or commercial activities conducted between businesses, such as between a wholesaler and a retailer.
Typically, B2B transactions occur within the supply chain, where businesses purchase raw materials from each other for manufacturing purposes.
Marketing for B2B SaaS involves promoting cloud-based software services offered on a subscription basis to other businesses.
This form of marketing focuses on the unique benefits of SaaS products, which are intangible and delivered over various marketing channels on the Internet.
Social media marketing and content marketing is at the top of this goal.
However, aside from social media marketing and content marketing, SEO and paid ads also play a big role in effectively marketing many SaaS businesses for growth .
The main difference lies in their target customers. B2B companies sell directly to other businesses.
In contrast, SaaS companies provide software products or services, often on a subscription basis, to enterprise customers, which may include B2B interactions.
B2B SaaS supports business growth by providing accessible and cost-effective solutions that enhance productivity, streamline processes, and improve operational efficiency.
The scalability of these tools allows businesses to adapt as they grow, without needing to invest in new infrastructure or technologies.
This enables companies to focus on their core competencies while having the necessary technological support for long-term success.
B2B SaaS offers several benefits, including cost-effectiveness, scalability, accessibility, and efficiency.
By streamlining processes and providing flexible solutions for various business needs, B2B SaaS helps companies save time and resources while enhancing productivity and growth potential.
Additionally, its subscription-based payment structure allows for predictable costs and budgeting flexibility.
With these benefits, the next step is a little enterprise resource planning to bring you to the SaaS solution that will best serve your needs.
Key Takeaway
Understanding what B2B SaaS means is key for modern businesses.
Simply put, B2B SaaS lets companies use software over the Internet without having to manage it on their own computers.
It’s easy, saves money, and can grow with your business, making it a great choice for any company.
By using cloud-based solutions, companies can work better and focus on their main tasks. Want to improve your business?
Embrace B2B SaaS! For more tips on digital marketing, business strategies, and growing your business, check out our other blogs.

Meet Brian , the go-to guy in digital marketing with a solid 15 years of breaking new ground. He’s got his hands in everything from AI-driven marketing and SEO to making sure customers have smooth journeys. Businesses big and small—from fresh faces like Globerunner (SEO & marketing agency) to heavy hitters like PowerSchool (SaaS), PFSweb (e-commerce), Southwest Airlines (travel), and Mary Kay (beauty & skincare)—have all felt his impact.
But there’s more to him than just strategy. As an entrepreneurial coach, Brian helps business leaders shake off their doubts and step into their true power. He’s brilliant at turning delay and stress into clarity and action. Under his guidance, entrepreneurs find themselves on paths that lead not only to profits but also purposeful growth. With Brian around, it’s about lighting up the path for visionaries ready to leave their stamp on the world.

COMMENTS
Advantages of the SaaS business model include vendors' predictable revenue streams, with subscription-based pricing contributing to stable income. According to a report by Gartner, by 2025, SaaS is expected to account for 60% of all public cloud services revenue, highlighting its growing significance as a revenue driver for vendors.
This unique business model offers compelling advantages such as scalability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use, making it an attractive choice for businesses and consumers alike. The fundamental equation of the SaaS revenue model is Revenue = ARPU (Average Revenue Per User) x Customer Lifetime.
That, however, is the final and most successful stage of the SaaS business model. Broadly speaking, a SaaS business's life can be broken down into three stages: 1. Early-stage. In the early stage of your SaaS business, you as the business owner or entrepreneur are still operating at the bare-bones level. You're unlikely to have many ...
Numerous advantages and opportunities are provided by the SaaS business model, which can be implemented in a variety of industries and business types: Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs): SaaS solutions offer SMBs affordable access to enterprise-grade software, enabling them to leverage powerful tools and capabilities without significant ...
4 benefits & advantages of choosing SaaS. Moving everything to the cloud, in general, has numerous benefits. For Saas, specifically, the benefits all boil down to cost and ease of use. Let's get right into each direct benefit you'll definitely appreciate once you transition to SaaS.
SaaS is a software distribution model in which a cloud provider hosts applications and makes them available to end-users over the internet. It's an acronym that stands for software as a service and describes any software that isn't run at your premises, never resides on a local machine, and is a full-blown app on its own.
The Software as a Service business model charges users to access and use an application hosted on external cloud servers. The Software as a Service model offers a lot of benefits for users, including reduced costs, scalability, and accessibility. Due to its popularity, software creators who choose the SaaS model have a high chance to succeed ...
Discover the ins and outs of the SaaS business model. Learn how to calculate the vital financial metrics that measure the success of a SaaS company. (844) 493-6249. Log In. ... The user gets a chance to test the product and experience its advantages. Once a free trial is over, the user is likely to be willing to pay for the full functionality. ...
There are five main revenue streams for a SaaS business: Monthly or annual subscriptions. In-app purchases. Custom solutions. Dedicated multi-channel support. Reports and analytics. Here's a guide to the SaaS business model, including its definition, advantages, limitations, and the revenue streams for a SaaS business.
The growth stage in the SaaS business model is focused on scaling extremely quickly by taking on funding via Venture Capital or Angel investors and pushing the limits of your product's success by taking some risks, scaling the team, entering into incubators, taking on more strategic advisors, and selling up-market.
It is well-known that software as a service (SaaS) is a cornerstone of modern business operations. This innovative business model revolutionizes the traditional approach to software delivery, offering exceptional flexibility, scalability, and accessibility. At its heart, SaaS revolutionizes software delivery by providing applications via the Internet, eliminating the need for complex ...
Scaling a SaaS business is considered one of the most important advantages. SaaS resources are stored in the cloud. This approach allows us to provide services to clients from all over the world. ... But it exists only because many businesses have already appreciated the benefits of the SaaS business model. The Software-as-a-Service solution ...
Top 5 Compelling Benefits of the SaaS Business Model. While reading this, you may wonder why SaaS is the best business model. It is because SaaS has some compelling advantages to offer. The most prominent ones are : 1. Speed of Innovation Gives Competitive Edge
The Saas Business Model Explained. Of all the new kinds of enterprise solutions made available by the advent of the internet, one of the most disruptive, most useful and most recent has been the software as a service business model.Many a startup has either pivoted to this promising new SaaS business model, or has been founded implicitly to take advantage of the SaaS revenue on offer in today ...
7 major advantages of the SaaS business model. Below are the 7 key benefits of the SaaS business model that make it a compelling choice for companies in a variety of industries. 1. Accessibility. SaaS applications are typically cloud-based, allowing users to access them from any device with an Internet connection. This accessibility enables ...
The following are five of the top advantages of using SaaS: 1. Reduced time to benefit. Software as a service (SaaS) differs from the traditional model because the software (application) is already installed and configured. You can simply provision the server for an instance in cloud, and in a couple hours, you have the application ready for ...
But, these are only a few advantages that a SaaS model can bring to your business. And while it may seem like a sizeable investment, adding a cloud-based service can significantly improve your customers' experience.. So, if you're considering adopting SaaS, take a look at some practical ways this digital model can elevate your business.
SaaS stands for Software-as-a-Service. Customers license SaaS products on a subscription basis and receive them over the internet. The code, servers and database that make up an application are hosted and maintained by software providers like Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud.The customers then access the software through a web browser or a mobile app.
A business model for SaaS favors your target customers. It minimizes costs and increases product usage flexibility. The key benefits of SaaS for your target customers include: Lower Costs: SaaS platforms are distributed on a subscription basis. That eliminates licensing fees involved in traditional software installs.
Lower Costs. For startups, one of the biggest advantages of the SaaS business model is the cost-effectiveness. When creating a piece of software that users need to install, you have to worry about ...
8 benefits of the SaaS model. The versatile SaaS framework has various benefits for users and software providers, including: 1. Increases cost savings. If a customer wants to purchase a traditional type of on-premise software installation, they may pay high license fees and other costs upfront.
The software-as-a-service (SaaS) sector has grown exponentially since it burst onto the scene in 2005. SaaS businesses are becoming increasingly popular for a variety of reasons. They are typically more affordable than purchasing traditional software and easy to use. ... Advantages of a SaaS Business Model. There are many advantages of ...
Advantages of the SaaS Business Model. There are a number of good things going for the SaaS model, including licensing flexibility, ease of deployment, the latest software versions, scalability based on users' needs, and a more predictable revenue stream in the form of less expensive monthly subscriptions.
Investing in Software as a Service (SaaS) provides exactly that: a revolutionary method for expanding a firm with significant long-term financial advantages. This article explores the many benefits of Software as a Service (SaaS) investments, including consistent revenue streams, unmatched cost-effectiveness, and flexible market options.
1. Subscription Model. B2B SaaS stands out primarily due to its subscription-based business model. This model is a departure from the traditional software license approach, offering a more flexible payment structure. Potential customers can pay a monthly or annual fee for access to the software hosted online.