

The 5 Key Elements of Strategic Planning

All great strategies have goals, actions, and metrics. No matter the strategy’s scope and complexity or even the company’s size, great strategies include these elements. So, successful strategic planning accounts for all three.
\When a strategic planning process incorporates these elements, strategies become simple and guide decisions. If you want to kick start your strategy development, use this strategic planning template that thousands of organizations apply at the start of their strategy formulation.
Effective strategic planning elements overview:
- Defining your Vision
- Crafting your Values
- Determining desired Outcomes
- Declaring explicit Accountability
- Establishing leading KPIs

4 critical components of a strategic plan:
- Where do I want to take my business? The destination
- Where are we right now? The starting point
- How will we get there? The journey
- How will I know if I'm succeeding? The checkpoints
Everyone reading the strategic plan should be able to answer these questions. This includes employees, business partners, investors, or other stakeholders.

5 Key Elements of Strategic Planning
1. defining your vision.
Start by defining your organization’s vision (its destination). In the words of Thibault Mesqui, Managing Director at Heineken in the state of strategy report , "make your strategy based on a vision".
This is an expression of the unique Point Of View you bring to the market. Make it simple, different, inspiring, and positive.
People who read your vision should be able to understand exactly what you stand for. Take a look at our guide on how to write a good vision statement to help you in the process.
Your vision will help you to:
- Bring alignment to your organization. People will unify their efforts towards a common goal, driving increased efficiency.
- Create strategies that are cohesive and focused.
- Inspire employees, investors, and other stakeholders to invest emotionally and commercially in your business.
Knowing your vision isn’t enough. Create a vision statement to articulate it and explicitly define it.
Mission statement vs Vision statement
You may also want to create a mission statement. A mission statement differs from a vision statement . A vision statement defines where you want to be in the future. A mission statement defines broadly how you will get there (part of your journey).
Many organizations are moving away from separate vision and mission statements due to the confusion surrounding their differences. Instead, you might want to try converting your mission statement into a series of focus areas.
For example, Patagonia's vision statement is:
"To share our love for the outdoors and create a diverse range of products for all facets of outdoor life."
And their focus areas are:
- "Best product"
- "Reduce environmental harm"
- "Encourage discussion on the environmental crisis”
Their focus areas essentially describe how they will achieve their vision and act as the bedrock for most of their strategic goals and KPIs.
2. Crafting your core Values
Values really don't get the credit they deserve. People often see them as a throw-away and vacuous - more aimed at marketing the organization than guiding its true internal behaviors. But a well-crafted set of values can be the difference between success and failure in the execution of your strategic plan.
Follow this guide to craft your company’s values , so they help you to:
- Assess your current state (the starting point) as an honest reflection of what you do well and are proud of doing.
- Make better decisions by ruling out courses of action that are not appropriate for your company
- Recruit better people who share your beliefs and passions
The values that go into your strategic plan shape your culture and are not aimed at customers.
Instead, they are a frank self-assessment of how your organization’s people behave as they deliver against your vision and Focus Areas.
They should reflect the values of your very best people and the values that have helped you to succeed the most in your journey to date.
If your strategy clashes with your company’s culture or values, it will fail. Identifying your core values is a critical component towards defining your starting point and your journey.
3. Defining desired Outcomes
A strategic plan leads nowhere without a set of clearly defined outcomes. Visions, missions, and focus areas are a great starting point - but no one will take your plan seriously unless you can clearly articulate what steps you are going to take to get there - and what success looks like for each of those steps.
Not all of your outcomes will be immediately quantifiable - and that's ok (your KPIs below will help you in those cases). But when you define your outcomes, make sure they look like this:
Action + Detail + Metric + Unit + Deadline
For example:
Expand our international operations into 3 new markets by 21st December 2022
Starting with a verb forces you to be specific about what you’re trying to do. If you can include a metric and a unit – do so.
It will keep you focused and honest when tracking your progress. Having a deadline works in much the same way.
Our guide on how to create strategic objectives walks you through the process of creating achievable and executable outcomes.
4. Declaring explicit Accountability
This is such a small detail, but it is also one of the key elements of a strategic plan that so many organizations fail to implement.
A lack of accountability will absolutely destroy your strategy execution . Lacking or confusing accountability results in:
- Outcomes not being delivered because no one knew who was in charge
- Conflicting interpretations of what the business should be working on
- Increased “finger pointing” and hearsay when things don't go to plan
- No one taking any satisfaction or pride in the outcomes delivered by their team
Define accountability in the initial strategic plan as part of defining your journey. Ideally, the people responsible for a particular segment of your plan should also have been critical contributors to the plan itself.
Contribution drives engagement. Engagement enforces self-accountability. Accountability enables execution.
For each of your outcomes, simply state ONE single person who will have primary accountability for that outcome. Avoid defining yourself accountable for every single outcome.
It's fine for the owner to invite other people to work on the outcome (either by cascading the goal or inviting collaborators), but it needs to be clear that the PRIMARY accountability sits with the one individual initially assigned to the outcome and no one else.
5. Establishing leading KPIs
Creating KPIs is probably the hardest of all the key elements of a strategic plan. But without KPIs, you won't know until it's too late whether or not you're succeeding towards your vision.
Note that KPIs are not the metrics you set to create your outcomes from step 3. Rather, KPIs should relate to how well you're delivering against the components of your mission or focus areas.
Let's take a look at some examples:
Patagonia's first Focus Area was “Best product.” A KPI for this focus area could be their Net Promoter Score - i.e., how many customers would recommend Patagonia's products and services to others.
Patagonia's second Focus Area was “Reduce Environmental Harm.” They could have a KPI for maintaining their carbon footprint at 0 (i.e., being carbon neutral).
Patagonia's third Focus Area was “Encourage discussion on the environmental crisis.” Probably the hardest to set an effective KPI. They could measure the number of mentions of the company on social media that also reference the environmental crisis.
Don't let establishing leading KPIs become harder than it needs to be. Follow this easy 4 step formula on how to write KPIs to be effective. Make sure that your KPIs accurately reflect what success looks like for each Focus Area and that you can accurately measure the KPI regularly.
Selecting the right KPIs is, therefore, one of the key elements of a strategic plan.
Crucial elements for a strategy's success
Companies that incorporate all five elements in their strategic planning process build easier-to-execute strategies.
People understand them and make consistent decisions throughout the organization. Pair them with regular reviewing organizational habits and you have highly adaptive companies that go beyond reacting to market changes. They anticipate and lead them.
Check out the features of the world's #1 strategic planning software!
Popular articles

Viva Goals Vs. Cascade: Goal Management Vs. Strategy Execution

What Is A Maturity Model? Overview, Examples + Free Assessment
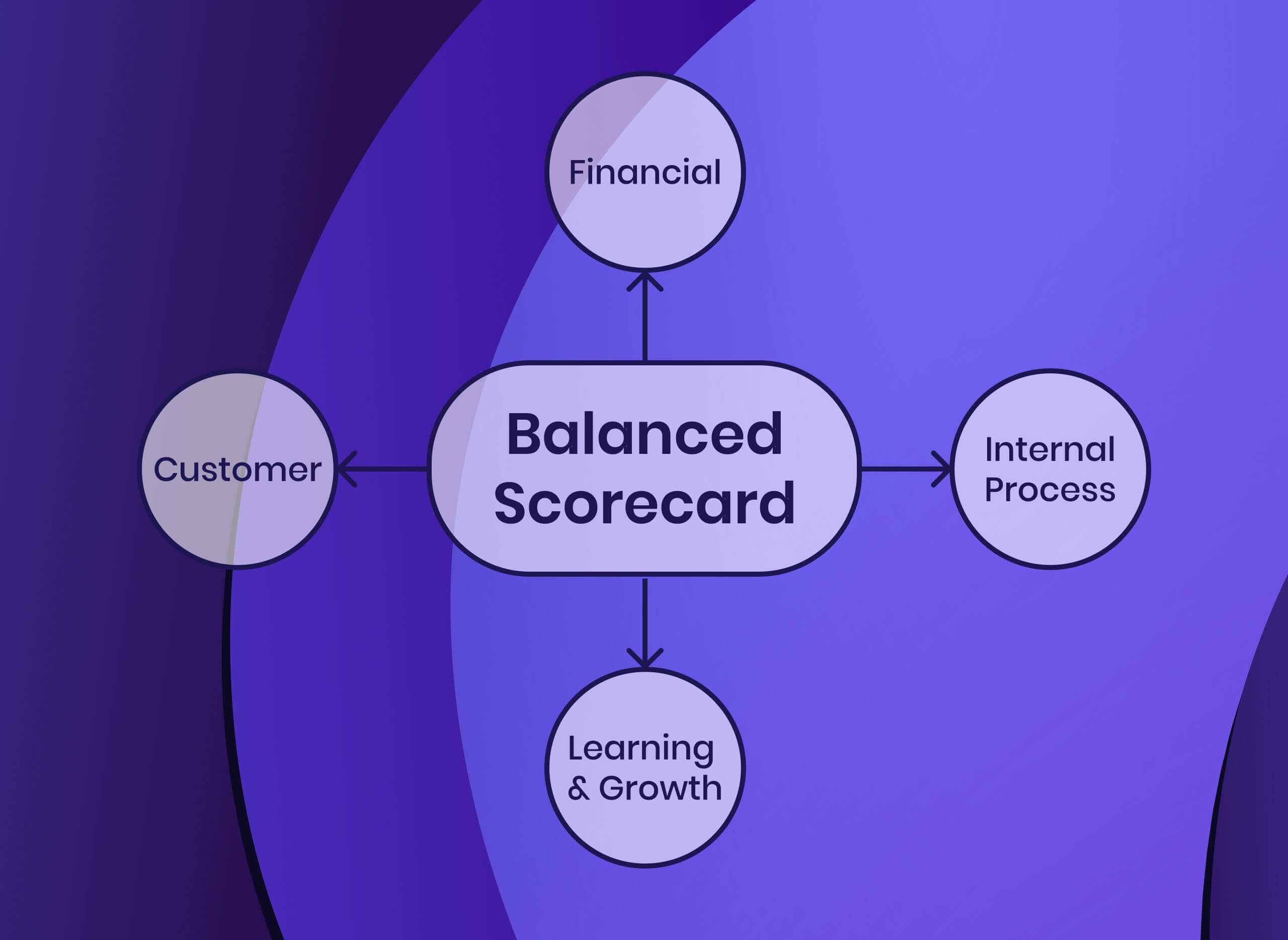
How To Implement The Balanced Scorecard Framework (With Examples)

The Best Management Reporting Software For Strategy Officers (2024 Guide)
Your toolkit for strategy success.

The Complete Guide to Writing a Strategic Plan
By Joe Weller | April 12, 2019 (updated March 26, 2024)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Writing a strategic plan can be daunting, as the process includes many steps. In this article, you’ll learn the basics of writing a strategic plan, what to include, common challenges, and more.
Included on this page, you'll find details on what to include in a strategic plan , the importance of an executive summary , how to write a mission statement , how to write a vision statement , and more.
The Basics of Writing a Strategic Plan
The strategic planning process takes time, but the payoff is huge. If done correctly, your strategic plan will engage and align stakeholders around your company’s priorities.
Strategic planning, also called strategy development or analysis and assessment , requires attention to detail and should be performed by someone who can follow through on next steps and regular updates. Strategic plans are not static documents — they change as new circumstances arise, both internally and externally.
Before beginning the strategic planning process, it’s important to make sure you have buy-in from management, a board of directors, or other leaders. Without it, the process cannot succeed.
Next, gather your planning team. The group should include people from various departments at different levels, and the planning process should be an open, free discussion within the group. It’s important for leaders to get input from the group as a whole, but they don’t necessarily need approval from everyone — that will slow down the process.
The plan author is responsible for writing and putting the final plan together and should work with a smaller group of writers to establish and standardize the tone and style of the final document or presentation.
Sometimes, it’s a good idea to hire an external party to help facilitate the strategic planning process.

“It often can be helpful to have a really good facilitator to organize and pursue strategic conversations,” says Professor John M. Bryson, McKnight Presidential Professor of Planning and Public Affairs at the Hubert H. Humphrey School of Public Affairs, University of Minnesota and author of Strategic Planning for Public and Nonprofit Organizations: A Guide to Strengthening and Sustaining Organizational Achievement .
Byson says the facilitator can be in-house or external, but they need experience. “You need to make sure someone is good, so there needs to be a vetting process,” he says.
One way to gauge a facilitator’s experience is by asking how they conduct conversations. “It’s important for facilitators to lead by asking questions,” Bryson says.
Bryson says that strong facilitators often ask the following questions:
What is the situation we find ourselves in?
What do we do?
How do we do it?
How do we link our purposes to our capabilities?
The facilitators also need to be able to handle conflict and diffuse situations by separating idea generation from judgement. “Conflict is part of strategic planning,” Bryson admits. “[Facilitators] need to hold the conversations open long enough to get enough ideas out there to be able to make wise choices.”
These outside helpers are sometimes more effective than internal facilitators since they are not emotionally invested in the outcome of the process. Thus, they can concentrate on the process and ask difficult questions.
A strategic plan is a dynamic document or presentation that details your company’s present situation, outlines your future plans, and shows you how the company can get there. You can take many approaches to the process and consider differing ideas about what needs to go into it, but some general concepts stand.
“Strategic planning is a prompt or a facilitator for fostering strategic thinking, acting, and learning,” says Bryson. He explains that he often begins planning projects with three questions:
What do you want to do?
How are we going to do it?
What would happen if you did what you want to do?
The answers to these questions make up the meat of the planning document.
A strategic plan is only effective when the writing and thinking is clear, since the intent is to help an organization keep to its mission through programs and capacity, while also building stakeholder engagement.
Question 1: Where Are We Now?
The answer (or answers) to the first question — where are we now? — addresses the foundation of your organization, and it can serve as an outline for the following sections of your strategic plan:
Mission statement
Core values and guiding principles
Identification of competing organizations
Industry analysis (this can include a SWOT or PEST analysis)
Question 2: Where Are We Going?
The answers to this question help you identify your goals for the future of the business and assess whether your current trajectory is the future you want. These aspects of the plan outline a strategy for achieving success and can include the following:
Vision statement about what the company will look like in the future
What is happening (both internally and externally) and what needs to change
The factors necessary for success
Question 3: How Do We Get There?
The answers to this question help you outline the many routes you can take to achieve your vision and match your strengths with opportunities in the market. A Gantt chart can help you map out and keep track of these initiatives.
You should include the following sections:
Specific and measurable goals
An execution plan that identifies who manages and monitors the plan
An evaluation plan that shows how you plan to measure the successes and setbacks that come with implementation
What to Include in a Strategic Plan
Strategic planning terminology is not standardized throughout the industry, and this can lead to confusion. Instead, strategic planning experts use many names for the different sections of a strategic plan.

“The terms are all over the map. It’s really the concept of what the intention of the terms are [that is important],” says Denise McNerney, President and CEO of iBossWell, Inc. , and incoming president of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). She recommends coming up with a kind of glossary that defines the terms for your team. “One of the most important elements when you’re starting the strategic planning process is to get some clarity on the nomenclature. It’s just what works for your organization. Every organization is slightly different.”
No matter what terms you use, the general idea of a strategic plan is the same. “It’s like drawing a map for your company. One of the first steps is committing to a process, then determining how you’re going to do it,” McNerney explains.
She uses a basic diagram that she calls the strategic plan architecture . The areas above the red dotted line are the strategic parts of the plan. Below the red dotted line are the implementation pieces.

While the specific terminology varies, basic sections of a strategic plan include the following in roughly this order:
Executive summary
Elevator pitch or company description
Vision statement
Industry analysis
Marketing plan
Operations plan
Financial projections
Evaluation methods
Signature page
Some plans will contain all the above sections, but others will not — what you include depends on your organization’s structure and culture.
“I want to keep it simple, so organizations can be successful in achieving [the strategic plan],” McNerney explains. “Your plan has to be aligned with your culture and your culture needs to be aligned with your plan if you’re going to be successful in implementing it.”
The following checklist will help you keep track of what you have done and what you still need to do.
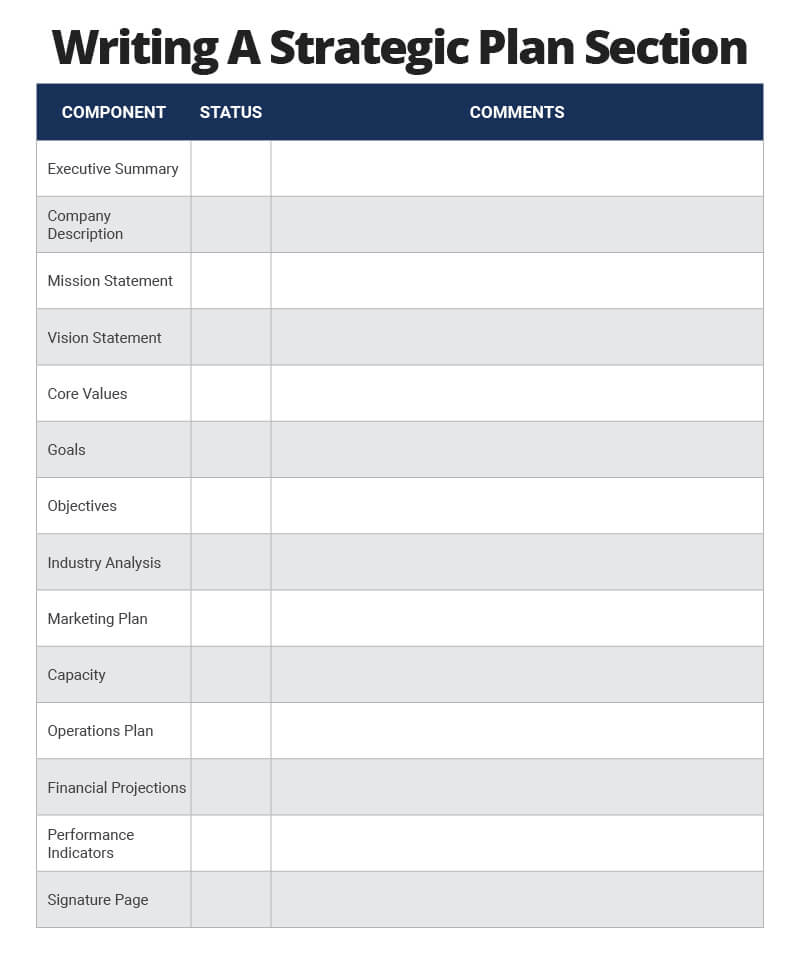
Download Strategic Plan Sections Checklist
How to Write a Strategic Plan
Once you’ve assembled your team and defined your terms, it’s time to formalize your ideas by writing the strategic plan. The plan may be in the form of a document, a presentation, or another format.
You can use many models and formats to create your strategic plan (read more about them in this article ). However, you will likely need to include some basic sections, regardless of the particular method you choose (even if the order and way you present them vary). In many cases, the sections of a strategic plan build on each other, so you may have to write them in order.
One tip: Try to avoid jargon and generic terms; for example, words like maximize and succeed lose their punch. Additionally, remember that there are many terms for the same object in strategic planning.
The following sections walk you through how to write common sections of a strategic plan.
How to Write an Executive Summary
The key to writing a strong executive summary is being clear and concise. Don’t feel pressured to put anything and everything into this section — executive summaries should only be about one to two pages long and include the main points of the strategic plan.
The idea is to pique the reader’s interest and get them to read the rest of the plan. Because it functions as a review of the entire document, write the executive summary after you complete the rest of your strategic plan.

“If you have a plan that’s really lengthy, you should have a summary,” says Jim Stockmal, President of the Association for Strategic Planning (ASP). He always writes summaries last, after he has all the data and information he needs for the plan. He says it is easier to cut than to create something.
For more information about writing an effective executive summary, a checklist, and free templates, read this article .
If you want a one-page executive summary, this template can help you decide what information to include.
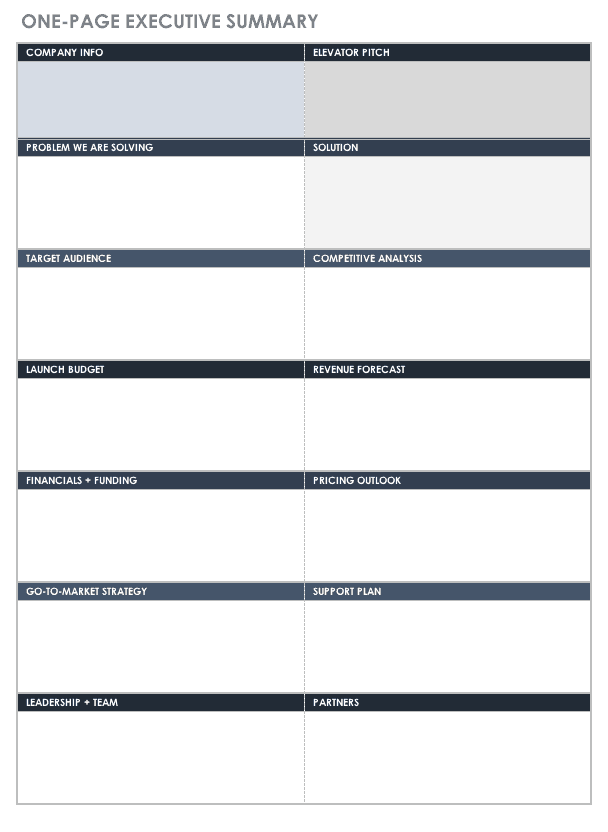
Download One-Page Executive Summary Template
Excel | Word | PDF
How to Write a Company Description
Also called an elevator pitch , the company description is a brief outline of your organization and what it does. It should be short enough that it can be read or heard during the average elevator ride.
The company description should include the history of your company, the major products and services you provide, and any highlights and accomplishments, and it should accomplish the following:
Define what you are as a company.
Describe what the company does.
Identify your ideal client and customer.
Highlight what makes your company unique.
While this may seem basic, the company description changes as your company grows and changes. For example, your ideal customer five years ago might not be the same as the current standard or the one you want in five years.
Share the company description with everyone in your organization. If employees cannot accurately articulate what you do to others, you might miss out on opportunities.
How to Write a Mission Statement
The mission statement explains what your business is trying to achieve. In addition to guiding your entire company, it also helps your employees make decisions that move them toward the company’s overall mission and goals.
“Ideally, [the mission statement is] something that describes what you’re about at the highest level,” McNerney says. “It’s the reason you exist or what you do.”
Strong mission statements can help differentiate your company from your competitors and keep you on track toward your goals. It can also function as a type of tagline for your organization.
Mission statements should do the following:
Define your company’s purpose. Say what you do, who you do it for, and why it is valuable.
Use specific and easy-to-understand language.
Be inspirational while remaining realistic.
Be short and succinct.
This is your chance to define the way your company will make decisions based on goals, culture, and ethics. Mission statements should not be vague or generic, and they should set your business apart from others. If your mission statement could define many companies in your line of work, it is not a good mission statement.
Mission statements don’t have to be only outward-facing for customers or partners. In fact, it is also possible to include what your company does for its employees in your mission statement.
Unlike other parts of your strategic plan that are designed to be reviewed and edited periodically, your company’s mission statement should live as is for a while.
That said, make the effort to edit and refine your mission statement. Take out jargon like world class, best possible, state of the art, maximize, succeed , and so on, and cut vague or unspecific phrasing. Then let your strategic planning committee review it.
How to Write a Vision Statement
Every action your company does contributes to its vision. The vision statement explains what your company wants to achieve in the long term and can help inspire and align your team.
“The vision is the highest-ordered statement of the desired future or state of what you want your business to achieve,” McNerney explains.
A clear vision statement can help all stakeholders understand the meaning and purpose of your company. It should encourage and inspire employees while setting your company’s direction. It also helps you rule out elements that might not align with your vision.
Vision statements should be short (a few sentences). They should also be memorable, specific, and ambitious. But there is a fine line between being ambitious and creating a fantasy. The vision should be clearly attainable if you follow the goals and objectives you outline later in your strategic planning plan.
Because you need to know your company’s goals and objectives to create an accurate vision statement, you might need to wait until you have more information about the company’s direction to write your vision statement.
Below are questions to ask your team as you craft your vision statement:
What impact do we want to have on our community and industry?
How will we interact with others as a company?
What is the culture of the business?
Avoid broad statements that could apply to any company or industry. For example, phrases like “delivering a wonderful experience” could apply to many industries. Write in the present tense, avoid jargon, and be clear and concise.
Vision statements should accomplish the following:
Be inspiring.
Focus on success.
Look at and project about five to 10 years ahead.
Stay in line with the goals and values of your organization.
Once you write your vision statement, communicate it to everyone in your company. Your team should be able to easily understand and repeat the company’s vision statement. Remember, the statements can change as the environment in and around your company changes.
The Difference Between Mission and Vision Statements
Mission and vision statements are both important, but they serve very different purposes.
Mission statements show why a business exists, while vision statements are meant to inspire and provide direction. Mission statements are about the present, and vision statements are about the future. The mission provides items to act upon, and the vision offers goals to aspire to.
For example, if a vision statement is “No child goes to bed hungry,” the accompanying mission would be to provide food banks within the city limits.
While many organizations have both mission and vision statements, it’s not imperative. “Not everyone has a vision statement,” McNerney says. “Some organizations just have one.”
If you choose to have only one statement, McNerney offers some advice: “Any statement you have, if you have just one, needs to include what [you do], how [you do it], why [you do it], and who you do it for.”
During the planning process, these key statements might change. “Early on in the process, you need to talk about what you are doing and why and how you are doing it. Sometimes you think you know where you want to go, but you’re not really sure,” McNerney says. “You need to have flexibility both on the plan content and in the process.”
How to Write Your Company’s Core Values
Company core values , sometimes called organizational values , help you understand what drives the company to do what it does. In this section, you’ll learn a lot about your company and the people who work with you. It should be relatively easy to write.
“The values are the core of how you operate [and] how you treat your people, both internally and externally. Values describe the behaviors you really want to advance,” McNerney says.
There are both internal and external values looking at your employees and coworkers, as well as customers and outside stakeholders. Pinpointing values will help you figure out the traits of the people you want to hire and promote, as well as the qualities you’re looking for in your customers.
Your values should align with your vision statement and highlight your strengths while mitigating weaknesses. McNerney says many organizations do not really consider or are not honest about their company’s values when working on strategic plans, which can lead to failure.
“Your strategies have to align with your values and vice versa,” she explains.
Many companies’ values sound like meaningless jargon, so take the time to figure out what matters to your company and push beyond generic language.
How to Write about Your Industry
When planning ahead for your business, it’s important to look around. How are matters inside your company? What are your competitors doing? Who are your target customers?
“[If you don’t do a thorough industry analysis], you’re doing your planning with your head in the sand. If you’re not looking at the world around you, you’re missing a whole dimension about what should inform your decision making,” McNerney advises.
Writing about your industry helps you identify new opportunities for growth and shows you how you need to change in order to take advantage of those opportunities. Identify your key competitors, and define what you see as their strengths and weaknesses. Performing this analysis will help you figure out what you do best and how you compare to your competition. Once you know what you do well, you can exploit your strengths to your advantage.
In this section, also include your SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis. You can choose from many templates to help you write this section.
Next, identify your target customers. Think about what they want and need, as well as how you can provide it. Do your competitors attract your target customers, or do you have a niche that sets you apart?
The industry analysis carries a price, but also provides many benefits. “It takes some time and money to do [a thorough industry analysis], but the lack of that understanding says a lot about the future of your organization. If you don’t know what is going on around you, how can you stay competitive?” explains McNerney.
How to Write Strategic Plan Goals and Objectives
This section is the bulk of your strategic plan. Many people confuse goals and objectives, thinking the terms are interchangeable, but many argue that the two are distinct. You can think of them this way:
Goals : Goals are broad statements about what you want to achieve as a company, and they’re usually qualitative. They function as a description of where you want to go, and they can address both the short and long term.
Objectives : Objectives support goals, and they’re usually quantitative and measurable. They describe how you will measure the progress needed to arrive at the destination you outlined in the goal. More than one objective can support one goal.
For example, if your goal is to achieve success as a strategic planner, your objective would be to write all sections of the strategic plan in one month.
iBossWell, Inc.’s McNerney reiterates that there are not hard and fast definitions for the terms goals and objectives , as well as many other strategic planning concepts. “I wouldn’t attempt to put a definition to the terms. You hear the terms goals and objectives a lot, but they mean different things to different people. What some people call a goal , others call an objective . What some people call an objective , others would call a KPI. ” They key, she explains, is to decide what the terms mean in your organization, explain the definitions to key stakeholders, and stick to those definitions.
How to Write Goals
Goals form the basis of your strategic plan. They set out your priorities and initiatives, and therefore are critical elements and define what your plan will accomplish. Some planning specialists use the term strategic objectives or strategic priorities when referring to goals, but for clarity, this article will use the term goals.
“[Goals] are the higher level that contain several statements about what your priorities are,” McNerney explains. They are often near the top of your plan’s hierarchy.
Each goal should reflect something you uncovered during the analysis phase of your strategic planning process. Goals should be precise and concise statements, not long narratives. For example, your goals might be the following:
Eliminate case backlog.
Lower production costs.
Increase total revenue.
Each goal should have a stated outcome and a deadline. Think of goal writing as a formula: Action + detail of the action + a measurable metric + a deadline = goal. For example, your goal might be: Increase total revenue by 5 percent in three product areas by the third quarter of 2020.
Another way to look at it: Verb (action) + adjective (description) = noun (result). An example goal: Increase website fundraising.
Your goals should strike a balance between being aspirational and tangible. You want to stretch your limits, but not make them too difficult to reach. Your entire organization and stakeholders should be able to remember and understand your goals.
Think about goals with varying lengths. Some should go out five to 10 years, others will be shorter — some significantly so. Some goals might even be quarterly, monthly, or weekly. But be careful to not create too many goals. Focus on the ones that allow you to zero in on what is critical for your company’s success. Remember, several objectives and action steps will likely come from each goal.
How to Write Objectives
Objectives are the turn-by-turn directions of how to achieve your goals. They are set in statement and purpose with no ambiguity about whether you achieve them or not.
Your goals are where you want to go. Next, you have to determine how to get there, via a few different objectives that support each goal. Note that objectives can cover several areas.
“You need implementation elements of the plan to be successful,” McNerney says, adding that some people refer to objectives as tactics , actions , and many other terms.
Objectives often begin with the words increase or decrease because they are quantifiable and measurable. You will know when you achieve an objective. They are action items, often with start and end dates.
Use the goal example from earlier: Increase total revenue by 5 percent in three product areas by the third quarter of 2020. In this example, your objectives could be:
Approach three new possible clients each month.
Promote the three key product areas on the website and in email newsletters.
Think of the acronym SMART when writing objectives: Make them specific, measurable, achievable, realistic/relevant, and time-bound.
Breaking down the process further, some strategic planners use the terms strategies and tactics to label ways to achieve objectives. Using these terms, strategies describe an approach or method you will use to achieve an objective. A tactic is a specific activity or project that achieves the strategy, which, in turn, helps achieve the objective.
How to Write about Capacity, Operations Plans, Marketing Plans, and Financial Plans
After you come up with your goals and objectives, you need to figure out who will do what, how you will market what they do, and how you will pay for what you need to do.
“If you choose to shortchange the process [and not talk about capacity and finances], you need to know what the consequences will be,” explains McNerney. “If you do not consider the additional costs or revenues your plan is going to drive, you may be creating a plan you cannot implement.”
To achieve all the goals outlined in your strategic plan, you need the right people in place. Include a section in your strategic plan where you talk about the capacity of your organization. Do you have the team members to accomplish the objectives you have outlined in order to reach your goals? If not, you may need to hire personnel.
The operations plan maps out your initiatives and shows you who is going to do what, when, and how. This helps transform your goals and objectives into a reality. A summary of it should go into your strategic plan. If you need assistance writing a comprehensive implementation plan for your organization, this article can guide you through the process.
A marketing plan describes how you attract prospects and convert them into customers. You don’t need to include the entire marketing plan in your strategic plan, but you might want to include a summary. For more information about writing marketing plans, this article can help.
Then there are finances. We would all like to accomplish every goal, but sometimes we do not have enough money to do so. A financial plan can help you set your priorities. Check out these templates to help you get started with a financial plan.
How to Write Performance Indicators
In order to know if you are reaching the goals you outline in your strategic plan, you need performance indicators. These indicators will show you what success looks like and ensure accountability. Sadly, strategic plans have a tendency to fail when nobody periodically assesses progress.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) can show you how your business is progressing. KPIs can be both financial and nonfinancial measures that help you chart your progress and take corrective measures if actions are not unfolding as they should. Other terms similar to KPIs include performance measures and performance indicators .
Performance indicators are not always financial, but they must be quantifiable. For example, tracking visitors to a website, customers completing a contact form, or the number of proposals that close with deals are all performance indicators that keep you on track toward achieving your goals.
When writing your performance indicators, pay attention to the following:
Define how often you need to report results.
Every KPI must have some sort of measure.
List a measure and a time period.
Note the data source where you will get your information to measure and track.
ASP’s Stockmal has some questions for you to ask yourself about picking performance indicators.
Are you in control of the performance measure?
Does the performance measure support the strategic outcomes?
Is it feasible?
Is data available?
Who is collecting that data, and how will they do it?
Is the data timely?
Is it cost-effective to collect that data?
ls the goal quantifiable, and can you measure it over time?
Are your targets realistic and time-bound?
Stockmal also says performance indicators cannot focus on only one thing at the detriment of another. “Don’t lose what makes you good,” he says. He adds that focusing on one KPI can hurt other areas of a company’s performance, so reaching a goal can be short-sided.
Some performance indicators can go into your strategic plan, but you might want to set other goals for your organization. A KPI dashboard can help you set up and track your performance and for more information about setting up a KPI dashboard, this article can help.
Communicating Your Strategic Plan
While writing your strategic plan, you should think about how to share it. A plan is no good if it sits on a shelf and nobody reads it.

“After the meetings are over, you have to turn your strategy into action,” says Stefan Hofmeyer, an experienced strategist and co-founder of Global PMI Partners . “Get in front of employees and present the plan [to get everyone involved].” Hofmeyer explains his research has shown that people stay with companies not always because of money, but often because they buy into the organization’s vision and want to play a part in helping it get where it wants to go. “These are the people you want to keep because they are invested,” he says.
Decide who should get a physical copy of the entire plan. This could include management, the board of directors, owners, and more. Do your best to keep it from your competitors. If you distribute it outside of your company, you might want to attach a confidentiality waiver.
You can communicate your plan to stakeholders in the following ways:
Hold a meeting to present the plan in person.
Highlight the plan in a company newsletter.
Include the plan in new employee onboarding.
Post the plan on the employee intranet, along with key highlights and a way to track progress.
If you hold a meeting, make sure you and other key planners are prepared to handle the feedback and discussion that will arise. You should be able to defend your plan and reinforce its key areas. The goal of the plan’s distribution is to make sure everyone understands their role in making the plan successful.
Remind people of your company’s mission, vision, and values to reinforce their importance. You can use posters or other visual methods to post around the office. The more that people feel they play an important part in the organization’s success, they more successful you will be in reaching your goals of your strategic plan.
Challenges in Writing a Strategic Plan
As mentioned, strategic planning is a process and involves a team. As with any team activity, there will be challenges.
Sometimes the consensus can take priority over what is clear. Peer pressure can be a strong force, especially if a boss or other manager is the one making suggestions and people feel pressured to conform. Some people might feel reluctant to give any input because they do not think it matters to the person who ultimately decides what goes into the plan.
Team troubles can also occur when one or more members does not think the plan is important or does not buy into the process. Team leaders need to take care of these troubles before they get out of hand.
Pay attention to your company culture and the readiness you have as a group, and adapt the planning process to fit accordingly. You need to find the balance between the process and the final product.
The planning process takes time. Many organizations do not give themselves enough time to plan properly, and once you finish planning, writing the document or presentation also takes time, as does implementation. Don’t plan so much that you ignore how you are going to put the plan into action. One symptom of this is not aligning the plan to fit the capacity or finances of the company.
Stockmal explains that many organizations often focus too much on the future and reaching their goals that they forget what made them a strong company in the first place. Business architecture is important, which Stockmal says is “building the capabilities the organization needs to fulfill its strategy.” He adds that nothing happens if there is no budget workers to do the work necessary to drive change.
Be careful with the information you gather. Do not take shortcuts in the research phase — that will lead to bad information coming out further in the process. Also, do not ignore negative information you may learn. Overcoming adversity is one way for companies to grow.
Be wary of cutting and pasting either from plans from past years or from other similar organizations. Every company is unique.
And while this may sound obvious, do not ignore what your planning process tells you. Your research might show you should not go in a direction you might want to.
Writing Different Types of Strategic Plans
The strategic planning process will differ based on your organization, but the basic concepts will stay the same. Whether you are a nonprofit, a school, or a for-profit entity, strategic plans will look at where you are and how you will get to where you want to go.
How to Write a Strategic Plan for a Nonprofit
For a nonprofit, the strategic plan’s purpose is mainly how to best advance the mission. It’s imperative to make sure the mission statement accurately fits the organization.
In addition to a SWOT analysis and other sections that go into any strategic plan, a nonprofit needs to keep an eye on changing factors, such as funding. Some funding sources have finite beginnings and endings. Strategic planning is often continuous for nonprofits.
A nonprofit has to make the community care about its cause. In a for-profit organization, the marketing department works to promote the company’s product or services to bring in new revenue. For a nonprofit, however, conveying that message needs to be part of the strategic plan.
Coming up with an evaluation method and KPIs can sometimes be difficult for a nonprofit, since they are often focused on goals other than financial gain. For example, a substance abuse prevention coalition is trying to keep teens from starting to drink or use drugs, and proving the coalition’s methods work is often difficult to quantify.
This template can help you visually outline your strategic plan for your nonprofit.
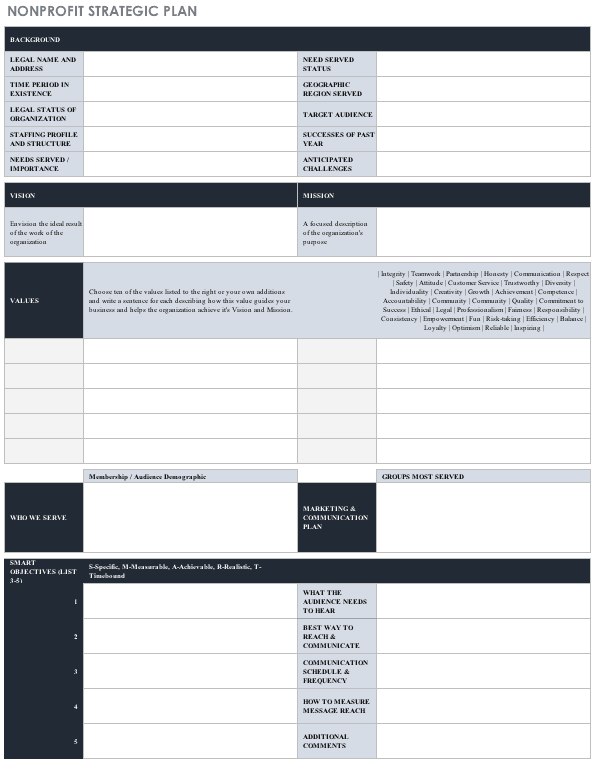
Download Nonprofit Strategic Plan Template
Excel | Smartsheet
How to Write a Strategic Plan for a School
Writing a strategic plan for a school can be difficult because of the variety of stakeholders involved, including students, teachers, other staff, and parents.
Strategic planning in a school is different from others because there are no markets to explore, products to produce, clients to woo, or adjustable timelines. Schools often have set boundaries, missions, and budgets.
Even with the differences, the same planning process and structure should be in place for schools as it is for other types of organizations.
This template can help your university or school outline your strategic plan.
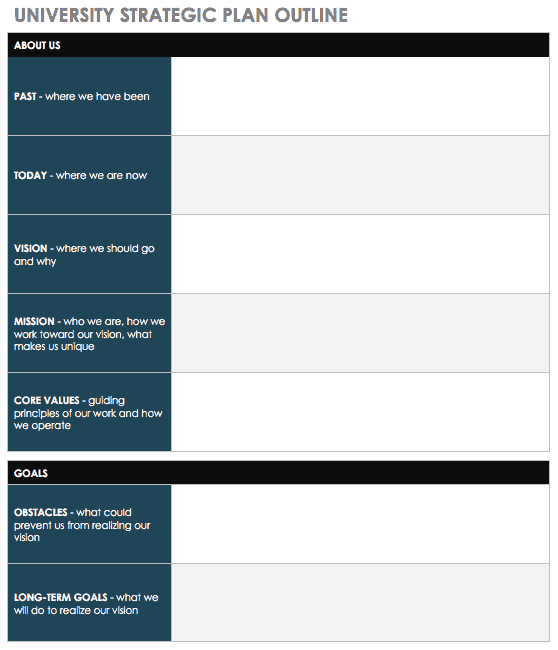
Download University Strategic Plan Outline – Word
How to Write a 5-Year Strategic Plan
There is no set time period for a strategic plan, but five years can be a sweet spot. In some cases, yearly planning might keep you continually stuck in the planning process, while 10 years might be too far out.
In addition to the basic sections that go into any strategic plan, when forecasting five years into the future, put one- and three-year checkpoints into the plan so you can track progress intermittently.
How to Write a 3-Year Strategic Plan
While five years is often the strategic planning sweet spot, some organizations choose to create three-year plans. Looking too far ahead can be daunting, especially for a new or changing company.
In a three-year plan, the goals and objectives have a shorter timeframe and you need to monitor them more frequently. Build those checkpoints into the plan.
“Most organizations do a three- to five-year plan now because they recognize the technology and the changes in business that are pretty dynamic now,” Stockmal says.
How to Write a Departmental Strategic Plan
The first step in writing a strategic plan for your department is to pay attention to your company’s overall strategic plan. You want to make sure the plans align.
The steps in creating a plan for a department are the same as for an overall strategic plan, but the mission statement, vision, SWOT analysis, goals, objectives, and so on are specific to only the people in your department. Look at each person separately and consider their core competencies, strengths, capabilities, and weaknesses. Assign people who will be responsible for certain tasks and tactics necessary to achieve your goals.
If you have access to a plan from a previous year, see how your department did in meeting its goals. Adjust the new plan accordingly.
When you finish your departmental plan, make sure to submit it to whomever is responsible for your company’s overall plan. Expect to make changes.
How to Write a Strategic Plan for a Project
A strategic plan is for the big picture, not for a particular project for an organization. Instead of a strategic plan, this area would fall under project management.
If you have a failing project and need to turn it around, this article might help.
How to Write a Personal Strategic Plan
Creating a strategic plan isn’t only for businesses. You can also create a strategic plan to help guide both your professional and personal life. The key is to include what is important to you. This process takes time and reflection.
Be prepared for what you discover about yourself. Because you will be looking at your strengths and weaknesses, you might see things you do not like. It is important to be honest with yourself. A SWOT analysis on yourself will give you some honest feedback if you let it.
Begin with looking at your life as it is now. Are you satisfied? What do you want to do more or less? What do you value most in your life? Go deeper than saying family, happiness, and health. This exercise will help you clarify your values.
Once you know what is important to you, come up with a personal mission statement that reflects the values you cherish. As it does within a business, this statement will help guide you in making future decisions. If something does not fit within your personal mission, you shouldn’t do it.
Using the information you discovered during your SWOT and mission statement process, come up with goals that align with your values. The goals can be broad, but don’t forget to include action items and timeframes to help you reach your goals.
As for the evaluation portion, identify how you will keep yourself accountable and on track. You might involve a person to remind you about your plan, calendar reminders, small rewards when you achieve a goal, or another method that works for you.
Below is additional advice for personal strategic plans:
There are things you can control and things you cannot. Keep your focus on what you can act on.
Look at the positive instead of what you will give up. For example, instead of focusing on losing weight, concentrate on being healthier.
Do not overcommit, and do not ignore the little details that help you reach your goals.
No matter what, do not dwell on setbacks and remember to celebrate successes.
Improve Strategic Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![5 key elements of a strategic plan [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning

How Asana uses work management for organizational planning

Solve your tech overload with an intelligent transformation
The Skyline G Blog: New ideas and perspectives focused on results
What is Strategic Planning? The Key Components, Process & Role Leaders Play in Ensuring a Strategy's Success
by Thuy Sindell, PhD. and Milo Sindell, MS.
Strategic planning is a process that is essential for companies to ensure successful and sustainable growth.
An intelligent and actionable strategic plan is a vital part of competing within the marketplace. It directs businesses to take meaningful action to help them reach their organization’s goals by mapping out a clear direction, creating measurable goals, and allocating resources to pursue these specific objectives.
What is Strategic Planning?
A strategic plan is an essential process and strategy execution document for any company looking to make the most of its resources and reach long-term organizational goals.
This vital and continually evolving document outlines a clear direction, sets objectives that must be achieved, and provides an actionable roadmap for success; it also helps organizations stand out from competitors by allowing them to differentiate themselves in the marketplace with their unique approach.
A well-crafted strategic plan will help companies stay focused on their mission while making decisions based on core values guiding them toward achieving desired results by ensuring everyone is moving in the same direction.

What are the Key Components of a Strategic Plan?
Several key components make up a well-developed strategic plan. These key components include:
A Mission Statement
An organization’s mission statement states the company’s purpose and the reasons why it exists. Although you might be already clear on the mission, reiterating your mission statement and connection to the plan acts as a foundation for the strategic plan and your strategy.
A Vision Statement
The company vision is the bigger objective that the company aspires to achieve. This may be as broad as making the world a better place through your product or service or ridding bathrooms of mildew. Whatever your vision, it should be connected to your strategic plan
Aligning the company mission and vision statements is the first crucial step to strategic planning.
SWOT Analysis
An overall evaluation of the company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Knowing these points will help you leverage your resources, shore up gaps, and realistically plan your path and the potential risks. Your SWOT analysis will help ensure that your strategic plan is based upon reality and play an important part in your strategic management process.
Goals & Objectives
Goals and objectives need specific, measurable, achievable, and time-bound targets the company wants to achieve. Ensure your goals are achievable, measurable, and can be clearly communicated as part of your strategic planning. High-level company objectives should cascade and align with the objectives of various divisions and teams. The Strategic plans of each division and team should map directly to broader company goals and methods.
The specific courses of action that the company will take to achieve its measurable goals and specific strategic issues.
Action Plans
Detailed project plans outlining the specific steps that will be taken to implement the strategies.
Resource Allocation
The allocation of financial, human, and other resources to implement the action plans.
Evaluation and Control
Evaluation and control are based on measures and systems to monitor the company’s progress toward achieving its organization’s goals, objectives, and financial plan and to make adjustments as necessary.

Who is Responsible for Creating a Strategic Plan?
In general, creating a strategic plan is the responsibility of the company’s top management team - the CEO, CFO, other executives, etc.
However, though the top management will do the strategic thinking, it’s essential for key members throughout the entire organization to be involved in the strategic planning process as different departments, employees, and human resources will have valuable insights and perspectives to contribute to the strategy formation. Also, when various constituents are a part of and the planning process a sense of ownership and commitment to the strategic plan’s success is reinforced.
It’s also common for companies to seek input from external stakeholders, customers, suppliers, and industry experts as part of the strategic planning process. As part of your planning process make sure to identify any critical stakeholders outside of your company.
What Makes the Strategic Planning Process Effective?
Below are some key factors that contribute to the overall effectiveness of a successful strategic plan and the strategic planning process. Understanding these points will help make your strategic planning process more effective:
The plan needs to be clear & concise, with specific strategic goals & objectives that are easy for everyone to understand. Senior leadership plays a critical role in ensuring that each objective is clear and how objectives will be achieved is understood.
The strategic plan needs to take the company’s resources & capabilities into account, and the goals need to be realistic & achievable based on the market data.
The plan needs to be flexible enough to allow for adjustments to be made in response to changes in the external environment after deployment.
The plan must be aligned with the company’s mission, vision & values and should support the organization’s overall direction in terms of business plan and annual budgets.
Easily Communicated
The plan needs to be communicated effectively to all stakeholders & investors, including employees & customers.
The plan needs clear & actionable steps and a timeline for implementation. It must be followed consistently to ensure progress toward business goals like increasing sales and maximizing profit.
The plan needs to measure & evaluate progress, collect feedback, and be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure continuous progress toward company goals and that the plan remains relevant and practical and targets logical key performance indicators.
An effective strategic plan identifies potential factors that might derail the plan and, at a minimum, provides high-level alternatives should the plan become derailed.

When Do Strategic Plans Fail?
Listed below are a few potential reasons why strategic planning might fail. Understanding why strategic plans fail will help create more effective strategic planning outcomes:
Lacks Clarity
Plans need to be clear and specific. If not, it may be difficult to understand and challenging to implement. When a strategic plan is ambitious it is tough for people to feel connected and motivated to take action.
Lack of Realistic Options and Objectives
Plans need to be realistic. If the plan cannot really be achieved, it’ll be difficult to implement and lead to frustration, disappointment, and potential failure.
Lack of Flexibility
The plan needs to be flexible; if it’s not is not flexible and doesn’t allow for adjustments in response to changes in the environment (internal and external) or from evaluation or measurement, it may become irrelevant or ineffective.
Lack of Alignment
The plan needs to be aligned with the company’s mission, vision, and values; if not consistent with the organization’s overall direction, it can quickly become out of sync with its underlying purpose and be ineffective in helping to reach desired goals.
Lack of Understanding
The plan needs to be communicated effectively to all key stakeholders and take feedback from all stakeholders; otherwise, it may be misunderstood or, worse - ignored or seen as not valuable.
Lack Actionable Steps
The strategic plan needs to be implemented swiftly and consistently; if the action steps are not clear or too hard to implement, they may not be implemented effectively.
Lack of Measurable Outcomes
The strategic plan needs to be reviewed and updated regularly, and its performance evaluated after implementation; otherwise, it may become ineffective or outdated, therefore ineffective at achieving desired outcomes.
External Factors
Changes in the external environment can have a huge effect. Changes like shifts in the economy or customer preferences, if not accounted for, can seriously impact the effectiveness of a once brilliant strategic plan.
However, as in life and business, things change, and every business must be able to adapt quickly to changing circumstances. This is why an effective plan includes contingencies.

What is a Company Leader’s Role in Ensuring the Strategic Plan is Implemented Successfully?
Strategic management.
Company leaders are responsible for ensuring that the strategic plan is implemented successfully.
Some specific ways business leaders can ensure the plan is implemented properly are:

Clearly Communicate the Plan
Business leaders need to communicate the strategic plan effectively to all key stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors. Any questions need to be answered and clarified, so everyone is aligned. The strategic plan should be shared in a way that you (the leader) demonstrate ownership and enthusiasm and can share with your team how each role is vital to achieving the plan’s objectives.
Providing Resources
Leaders need to ensure that resources, such as funding, personnel, and technology, are available to everyone needed in order to implement the plan successfully.
Setting Expectations
Leaders need to set clear expectations for implementing the plan and hold the designated employees accountable for meeting those expectations. Clear and achievable timelines need to be established and committed to by each stakeholder.
Leading by Example
Leaders need to model the behaviors and values outlined in the plan and encourage others to do the same.
Providing Support
Leaders need to provide support and guidance to employees as they work through problems toward achieving the strategic goals and objectives of the plan.
Monitoring Progress
Leaders need to monitor the progress towards achieving the goals and objectives outlined in the plan and make adjustments in the operational plans as they see fit, as needed.
Celebrating Successes
Leaders need to recognize and celebrate wins along the way to help keep morale high and encourage continued progress toward the ultimate goals.

What’s the Role of Each Individual Employee in Implementing & Supporting the Strategic Plans Success?
Employees are the driving force and critical in implementing and supporting the strategic plan’s success. Your employees will be the eyes and ears of how the strategic plan works. This is why it is vital for leaders to create a business environment where there is open communication and all types of information can be shared and reviewed in relation to its impact on the long- term strategy. Leaders must foster an open environment where questions can be asked and bad and good news shared. Leaders can help employees play their part by ensuring employees are supported and are clear on their ability to do the following:
Understand the Plan
Employees need to understand the strategic plan, how it aligns with the company’s mission, the steps to take, and most importantly, the goals.
Aligning Work and Job Goals with the Plan
Leaders, managers, and employees need to align their work with the strategic plan and prioritize tasks that support achieving the plan’s goals & strategic objectives.
Manage Implementation
Employees must consistently follow through on their assigned tasks and responsibilities to implement the plans, steps, and processes.
Provide Feedback
During the initial review of the organization’s current status, employees must provide feedback and suggestions to improve the plan. During its implementation, employees need to provide feedback based on performance and potentially adjust the plan if needed for better performance and goals.
Communicate Laterally and Up
Employees need to communicate with coworkers to ensure everyone is working towards the same goals & objectives and, most importantly, employees need to communicate to their manager on how their contribution is proceeding.
Seek Support and Guidance
Employees need to seek support and guidance from leaders if they need help implementing any steps of the plan or achieving goals.

Do Some Companies Believe that Strategic Planning is a Waste of Time?
Sure. It’s possible some companies may view strategic planning as a waste of time. This could be due to a variety of reasons: resources required upfront, lack of understanding of the benefits of strategic planning, a lack of buy-in from senior management, or a lack of resources to dedicate to the process.
However, for massively successful companies, strategic planning is recognized as an invaluable tool to help organizations achieve their long-term goals and be outstanding in a competitive marketplace.
Strategic planning can also help companies be more agile and adapt to changes in the external environment. For these reasons, it’s generally recommended that companies engage in strategic planning and review results on a regular basis.
What Makes a Great Strategy?
What makes a great competitive strategy? Several characteristics are often considered to be key elements of great strategy execution:
A great strategy is clear & easy to understand, with specific goals & strategic objectives that are well-defined.
A great strategy is a focused strategy. A great strategy is focused on a specific area of the business and doesn’t try to do too many things at once.
A great strategy is aligned with the company’s overall mission, vision for the future, and values, supporting the organization’s overall direction.
Flexibility
A great strategy is flexible and allows for adjustments to be made in response to results and changes in the external environment.
A great strategy is realistic & achievable, taking into account the company’s resources & capabilities and what can actually get done.
Differentiation
The great strategy sets the company apart from its competitors in the marketplace and helps it to differentiate itself from competitors to customers.
A great strategy can be executed effectively, with clear action steps, a timeline for implementation, and who is responsible for each action step.
Evaluation & Feedback
The great strategy includes measures for evaluating progress and collecting feedback, and it needs to be reviewed regularly & potentially updated to ensure it remains relevant & effective.
When is a Great Strategy Not Enough to Ensure Company Success?
While a great strategy can certainly be a key factor in a company’s success, it’s not the only factor needed to be successful. There are a number of other internal and external factors that can impact a company’s success, including:
Even the best strategy will not be a successful strategy if executed poorly.
A company needs resources, period. Resources like funding, personnel, and technology, are essential to implement strategy effectively.
Changes in external factors are equally important as the internal environment. For example, economic shifts or customer preferences can impact a company’s success.
Competition
A company’s success can also be impacted by its competitors’ actions and even competitors’ reactions to strategy implementation.
Market Demand
A company’s success will depend partly on the market demand for its products or services. Demand should absolutely be a part of the strategy formulation.
A company’s success will highly depend on the quality of its products or services and its ability for its products to meet customer needs.
The senior leadership of a company can play a key role in its success, or failure, as they set the vision & direction of the organization.
How Does Company Leadership Play a Critical Part in a Company’s Strategic Success?
Without involved leadership, a strategic plan will more than likely fail. A company’s leadership plays a critical role in strategic success in several ways:
Setting the Direction
A company’s leadership is responsible for setting the organization’s vision and direction and creating a strategic management plan that aligns with that direction.
A company’s Leadership is responsible for ensuring that the necessary resources, such as funding, personnel, and technology, are available to implement the strategic plan.
Communicating the Plan
A company’s leadership communicates the strategic management plan effectively and consistently to all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and investors.
A company’s leadership needs to model the behaviors and values aligned with the plan and encourage others to do the same.
A company’s leadership needs to provide support & guidance to employees as they work towards achieving the goals and objectives of the strategic plan. This will help in employee retention and strategic success.
A company’s leadership needs to monitor progress toward achieving the goals & objectives of the plan and make necessary adjustments as needed.
A company’s leadership needs to recognize and celebrate successes along the way to help keep team morale high and encourage continued progress to achieve goals.
How Can Companies Prepare & Support their Leaders to Implement & Ensure Strategic Planning Success?
There are many ways in which companies can prepare and support their leaders to implement and ensure the success of their strategic planning initiative.
Provide Proper Training
Companies need to provide training & strategy development opportunities to help their leaders acquire the knowledge and skills they need to implement & support the strategic vision effectively.
Encourage Open Communication
Companies need to foster an environment of open, clear communication and encourage leaders to seek input & feedback from their teams within the strategic framework - even when the strategy map is not positive.
Align Leadership with Company Values
Companies must ensure that their leadership’s values align with the company’s values and culture and that their leaders are committed to the mission and vision of the organization.
Encourage Collaboration
Companies need to encourage collaboration & cross-functional teamwork as a part of project management to ensure that all departments work towards the same goals & objectives.
Provide Resources
As part of the strategic planning process, companies need to ensure their leadership has the necessary resources, such as funding, personnel, & technology, to implement the strategic plan effectively for the entire duration.
Establish Clear Expectations
Companies must set clear expectations for how strategic planning should be activated and implemented and hold leadership accountable for meeting expectations as per the strategic plan document.
Monitor Progress
Company leaders need to monitor the progress toward achieving the goals and objectives of the strategic plan and provide their support and guidance as needed. Strategic planning is essential for business success, and the key to achieving successful results lies in the hands of leadership. For leaders to ensure a strategy’s success, they must become strategic planners and the details of the business’s strategic plan must be organized and understood by each person responsible.
Leaders and managers need to communicate the strategic plan through consistent discussions that foster collaborative decision-making. Responsibilities for the planning process and success also extend beyond the leader and onto each individual employee to help realize the steps of an effective strategic plan. Companies must set clear strategic objectives that align with their mission and strategic goals while preparing business leaders to carry out those plans. When done correctly, with careful attention paid to all levels of the organization, successful strategic planning can lead a company in the right direction toward long-term sustainability and future opportunities.
Having a clear strategic plan is one of those obvious items that every company should have in place yet many companies don’t.
Although the effort of investing the time and resources into creating a strategic planning template can be demanding, the value and impact of your investment can return a healthy multiple.
Once your mission and vision statements and strategic plan are in place they become a touchstone to focus your business, align teams, and what makes your way of navigating your market and competition unique.
We hope that this resource provides a road map and helps facilitate the development of your strategic plan if you don’t have one yet. For those that do have strategic plans, we hope this resource helps act as a checklist to fortify the strategy development you’ve already created.
What is Leadership? A Guide To The Core Elements of Great Leadership & Behaviors That Make an Effective Leader
Business Goal Setting: How to Improve Team Performance & Morale
- What is executive coaching? The definition, benefits, process & why even good leaders need coaching
- Emotional intelligence in leadership: what it is & why it's Important
- Imposter syndrome: definition, types, symptoms, causes & strategies
- Self awareness in leadership: the x factor in team performance
- Effective decision-making: skills, process & strategies to improve as a leader
- 360 feedback assessment: what it is, who its for & how to implement at your organization
- Leadership transition: plan, process, challenges & best practices
- Toxic Leadership & Toxic Employees: How to Fix a Toxic Workplace
- Effective Communication in the Workplace: Strategies & Tips
- Leadership vs Management: Traits, Differences & Responsibilities
Let's explore how we can help you achieve your goals
More Like this
Key elements on how to write a strategic plan.
Some organizations get stumped during the beginning steps of how to write a strategic plan. Strategic planning can definitely seem daunting with all the guides, recommendations, books, and consultants out there telling you to do it one way or another. Sometimes the best thing to do is step back and take a look at the key elements of a strategic plan. Not to oversimplify the planning process, but by dividing a strategic plan into four areas, you can clearly see how to pieces fit together.
The four pieces of the puzzle are found in these questions:
- Where are we now?
- Where are we going?
- How will we get there?
- How will we measure our progress?
Each area has certain elements to show you how and where things fit. Below is a bird’s-eye view of the elements of a strategic plan.
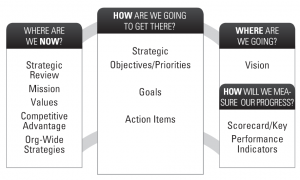
What matters most is having a strategy and, therefore, an effective strategic plan. An effective plan and execution process require the following attributes:
- Purpose-driven: A plan based on a mission and a real, true competitive advantage is key. Without it, what’s the point of the plan or the organization?
- Integrated: Each element supports the next. No objectives are disconnected from goals, and no strategies sit all alone.
- Systematic: Don’t think of the plan as one big document. Instead, give it life by break it into executable parts.
- Dynamic: The plan isn’t a static document but a living one.
- Holistic: All areas of the organization are included. Don’t plan based on departments first because you risk limiting your thinking. Plan by thinking about the organization as a whole entity and then implement on a department-by-department basis.
- Understandable: Everyone gets it. If anyone, from the top of the organization to the bottom, doesn’t understand the plan or how he or she fits in, it won’t work.
- Realistic: You can implement the plan. Don’t over plan. Make sure you have the resources to support the goals you decide to focus on.
One Comment
Basics of Action plan
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
Mastering the building blocks of strategy
Left unchecked, market forces continually conspire to deplete profits. Powerful business strategies can counteract those tendencies, but good strategy is difficult to formulate. 1 1. A 2011 McKinsey survey asked executives to evaluate their strategies against ten objective tests of business strategy. It found that 65 percent of companies passed just three or fewer tests. For more, see Chris Bradley, Martin Hirt, and Sven Smit, “ Have you tested your strategy lately? ,” McKinsey Quarterly , January 2011. Indeed, the latest McKinsey research (see “ The strategic yardstick you can’t afford to ignore .”) finds that a very small number of companies create most economic profit. 2 2. What’s left over after subtracting the cost of capital from net operating profit. The research also shows that a significant number of good companies outperform even in so-called bad industries, where the average economic profit is less than the market average.
How do they do it? In other words, where do powerful strategies come from? Sometimes it’s luck, or good timing, or a stroke of inspiration. In our experience, it’s also possible to load the dice in favor of developing good strategies by focusing on the core building blocks that often get overlooked. One is the need to gain agreement—before creating strategy—on the essential decisions and the criteria for making them. Another is to ensure that the company is prepared and willing to act on a strategy once it is adopted. Too much of what passes for strategy development, we find, consists of hurried efforts that skip one or more of the essentials. The resulting strategies are often flawed from the start.
It’s also easy, though, to go too far in the other direction and make the creation of strategy a rigid, box-checking exercise. Appealing as a formula-driven approach might be, it ignores the truth that strategy creation is a journey—and an inherently messy one at that. Proprietary insights are hard to come by. Shaping keen insights into good strategies requires deep interpersonal engagement and debate from senior executives, as well as the ability to deal with ambiguity in charged and often stressful circumstances. When would-be strategists overlook these dynamics, they cover the essentials in name only. Consequently, they miss opportunities and threats, or create great paper strategies that remain unfinished in practice.
In this article, we’ll outline a middle path—an end-to-end way of thinking that views the creation of strategy as a journey, not a project. This method, developed through our work with some 900 global companies over the past five years, can help senior executives approach strategy in a rigorous and complete way. We’ll also describe some principles that strategists should keep in mind as they use the method to ensure that their strategic-planning processes embody the spirit of debate and engagement, which, in turn, yields inspiration. By better understanding both the method and how to get the most out of it, companies can boost the odds that the strategies they create will beat the market.
Do justice to strategy’s building blocks
Most companies we’re familiar with demonstrate a variety of good habits when they create strategies, and they get many things right. But what they miss can be critical. Consider these examples:
- a technology company that prided itself on analytical rigor but never accurately diagnosed how difficult it would be for a targeted customer group to provide reasonable returns
- a beer company that rightly focused on industry structure in its core business but made a losing bet on a related business—wine—after failing to forecast declining returns stemming from structural shifts there
- a telecommunications company’s strategy team, which recognized the importance of involving senior managers but ended up alienating them by holding a series of time-consuming workshops that focused on alignment around strategic choices, though the full set of choices hadn’t yet been identified
These problems don’t have to happen. We find that companies do better when they ground all their strategy-development efforts and processes in an understanding of the building blocks of strategy. These straightforward modes of activity (exhibit) track the progression of a strategy from its roots as an idea through its emergence as an operational reality.
The building blocks of strategy help companies make strategic choices and carry them through to operational reality.
One central building block is deep insight into the starting position of the company: where and why it creates—or destroys—value (diagnose). Executives also need a point of view on how the future may unfold (forecast). By combining insights into a company’s starting position with a perspective on the future, the company can develop and explore alternative ways to win (search) and ultimately decide which alternative to pursue (choose). With the strategy selected, the company needs to create an action plan and reallocate resources to deliver it (commit).
These five core building blocks are book-ended by two others. One is an initial block (frame) to ensure that the team properly identifies and agrees to both the questions asked and the decisions made as the strategy is developed. The final block (evolve) is dedicated to the constant monitoring and refreshing of the strategy as conditions change and new information becomes available.
To some extent, the building blocks simply represent a thorough list of activities that all good strategists perform. And while all are important and should be included in the creation of strategy, slavishly following this or any other framework won’t bring success. Depending on the situation, some blocks will be more critical than others and therefore require more attention (see sidebar, “Re-create, recommit, and refresh”).
Re-create, recommit, and refresh
For a number of years, we, our colleagues, and many others who are engaged in the practice of strategy have been pointing out how ill-suited traditional strategic-planning processes are to the dynamism and pace of 21st-century business life. Less clear is what should happen to many organizations’ well-oiled approaches. Shut them down? Morph them into budgeting and operational-planning processes? Use them to synthesize the valuable insights emerging from more frequent strategic dialogues involving larger numbers of executives?
The building blocks of strategy shed fresh light on what strategic planning should and shouldn’t try to do. For starters, we’d emphasize that periodically—perhaps as often as every three to five years, if new competitors arrive or markets unexpectedly shift—companies must re-create their strategies. This cannot be accomplished through typical planning processes, as it requires broader skills, wider engagement, and more flexibility to make big strategic choices than they allow. So forget about strategic planning when you need to revamp your strategy; instead, take a more immersive strategy-development approach using all of the seven building blocks described in this article.
At the other end of the spectrum is what we would describe as the need to recommit organizations to established strategies. Traditional strategic planning is tailor-made for this purpose, and thinking about the task in these terms helps elevate it above the glorified budgeting exercise into which some processes lapse. Two of the building blocks we have described in this article—commit and evolve—are useful reminders of what any such strategic- planning process should accomplish: the constant monitoring of strategy, the reallocation of resources, the alignment of management on strategic priorities, and the creation of targets, budgets, and operational plans.
Between these two extremes lies the strategic refresh, which is particularly relevant for organizations where a lot of valuable, ongoing strategy dialogue takes place among members of the top team. Such engagement can highlight nagging issues that might one day necessitate a strategic redo but certainly merit attention now. For example, if signs suggesting that one or more key assumptions have become less valid emerge from strategic dialogues at the business-unit level, it might be time to update the company’s perspective on long-term trends. This exercise could be elevated in importance by making it a core theme of the upcoming strategic-planning process. In such situations, it’s a good idea to check all seven building blocks quickly, with an emphasis on understanding the strategic implications of underlying changes. If they are big enough, that could be a red flag signaling the need to re-create the strategy and thus to elevate the discussion beyond strategic-planning parameters.
For a closer look at how to improve strategic planning, see “ Managing the strategy journey ” and “ Dynamic management: Better decisions in uncertain times .”
That’s why taking some time to frame issues at the outset is so important. When strategists do so, they are better able to identify the real choices and constraints facing their organizations and to see which building blocks are likely to matter most given the situation at hand. Unfortunately, many executives feel that taking the time to frame strategy choices thoughtfully and to decide where to focus strategy-development efforts is a luxury they don’t have.
We’ve seen evidence of this pressure firsthand and in the responses to an executive survey we’ve been conducting as part of an ongoing research project. Fully two-thirds of the 200 executives we’ve surveyed so far report that they feel rushed to provide outputs in their strategic-planning processes. This pressure is understandable in today’s always-on, fast-changing environment, but it can be hazardous to a company’s strategic health. That’s especially true in the all-too-common situations when it’s not immediately obvious what factors will determine the success or failure of a change to strategy.
A financial-services institution in the Asia–Pacific region, for example, was investigating a growth opportunity involving the creation of an online business. Changing the company’s focus in this way would be a big undertaking, but the upside potential was large. Moreover, the members of the strategy team could already see that demonstrating the channel’s significant potential to the top team would be straightforward. Before doing that, however, they stepped back to spend some time thinking through the idea’s broader strategic context—framing, in other words.
When they did, they saw a serious risk of cannibalization for one of the company’s existing businesses. The new venture would also require substantial funding over the next three to five years before it contributed financially. This had important implications, and the team’s members needed to convince themselves that the risk was worth taking. Moreover, if the company made the move, would it stick with the effort when the time came to provide funding for people and technology?
Instead of steaming ahead with analytical work to prove the potential, the team recognized that it would be critical to invest a disproportionate amount of time and effort to the commit building block. The strategy team did this, in part, by developing a powerful multimedia concept prototype to capture the imaginations of the top team and the executives representing key support functions. The team’s focus on gaining commitment was prescient; the prototype and the communication around it helped convince the leaders that the concept was so compelling for consumers that if the company didn’t cannibalize its existing business, a competitor would probably come up with the idea. The effort also helped motivate the leaders of the finance and IT functions to support the new offer. The company launched it in record time, to promising early results in both customer acquisition and levels of customer engagement.
In retrospect, the team credits the conversations and debates held during this framing period as necessary to identify and resolve the potential stumbling blocks related to the organization’s strategic direction. Although messy at times, this activity helped build an organizational commitment to the strategy and its importance to the company.
Myth-bust your story
A focus on strategic building blocks also can help companies develop penetrating insights. While “insight” conjures up visions of research, data crunching, and “aha” moments, real strategic insight also rests on a seemingly mundane and easy-to-overlook factor: a thorough understanding of how and why a company, its competitors, and others in the industry value chain make money. Absent dumb luck, a strategy that doesn’t tap directly into such an understanding will underperform.
The difficulty, as professor Phil Rosenzweig of the International Institute for Management Development has explained so well, 3 3. See Phil Rosenzweig, “ The halo effect, and other managerial delusions ,” McKinsey Quarterly , February 2007. is that a company’s performance—good or bad—creates strong impressions that powerfully shape the way people perceive strategies, leaders, cultures, and organizational effectiveness. A commodity company, for instance, might falsely attribute its strong performance to the efficiency of its operations. Yet despite its efficiency, the economics of those operations could be swamped by market-structure changes that have significant pricing implications or by unexpectedly volatile demand.
One way senior executives can address the challenge, we find, is explicitly questioning received corporate wisdom—much as the popular US television show MythBusters does when it takes apparent axioms, urban legends, and popular assumptions and (in entertaining fashion) tries to prove or disprove them. In the creation of strategy, this approach means dispassionately identifying the elements that contribute to performance, while discounting any factor contaminated by perceptions of the company’s supposed greatness. It also requires a curiosity that’s woefully lacking in some strategic-planning processes. Nearly eight in ten executives we surveyed, for example, say that the processes of their companies are more geared to confirming existing hypotheses than to testing new ones.
To see how these dynamics play out in practice, consider the experience of a global retailer that was revisiting its strategy after the previous one had delivered five years of strong earnings. The positive results, most in the company believed, reflected good execution and the success of a recent initiative to refresh the store format. Still, the leader of the business felt there could be more to the story and worried that continuing along the same path might not produce the same results in the future. To determine what was actually driving performance, the leader met with the company’s strategy team, as well as other executives.
This was time well spent. The resulting discussions sparked important insights—revealing, for example, that while overall performance was good, there were problems under the surface. On the positive side, the company was steadily improving its margins and winning customers from a higher-cost competitor. Nonetheless, the solid network growth at the top-line level appeared to be masking a worrisome decline in the productivity of older stores. The big drag on performance, the team discovered, was the loss of mainstream customers to a cheaper competitor, which careful analysis showed to have an unassailable advantage on cost. Increasing promotional activity had so far seemed to stem the march of this aggressive rival, but the retailer was running out of steam and hitting practical limits. Significant changes would be necessary.
Let them grapple
This realization was the product of more than just number crunching. The thoughtful argument and debate surrounding the analysis from day one played a vital part in generating the insights. In our experience, many companies forget this truth when they create strategy. Instead, they put too much emphasis on preparing documents and completing analyses and not enough on stimulating the productive debates that lead to better decisions.
Getting executives to grapple with the issues can be a messy process, and the debates may be quite personal. After all, formulating good strategies typically involves revisiting fundamental and deeply held beliefs about a company’s past and future, and people tend not to shift their views without a fight. 4 4. We also know that executives exhibit a number of biases that lead them to be overconfident about their beliefs and adept at finding facts to confirm them and reject challenges. To learn more about addressing this problem, see Dan Lovallo and Olivier Sibony, “ The case for behavioral strategy ,” McKinsey Quarterly , March 2010. But without the necessary fights, and without the use of carefully designed decision-making techniques, companies may end up with rubber-stamped strategies whose flaws are exposed during implementation—or afterward, by competitors.
When companies find ways to get executives grappling—throughout the strategy-development process—with the choices that matter, they make better, less biased decisions. They also improve the likelihood that the relevant stakeholders will be on board when the time comes to make and act on choices. 5 5. The importance of gaining social support for a strategy is often overlooked. Fully 62 percent of executives in our survey say that their strategy processes focus on the strategy itself, not on building a support base of influencers who will drive implementation.
To exemplify our point, let’s look again at the retailer’s strategy team as it engaged with the company’s broader leadership group to share its observations. Most strategy teams interact with decision makers by presenting management with a summary report and recommendations. But this team understood that senior managers needed time to debate the issues themselves and reach their own conclusions—and that such collective discussions would improve the resulting strategy.
Because the senior managers had a very hands-on attitude, the strategy team designed a series of weekly meetings called think tanks to let them work through a profit-deconstruction exercise illuminating the company’s past. In each session, the analysis was tabled after a certain point, and the management team’s members took turns drawing out conclusions or identifying further questions that needed answering. The strategy team was prohibited from bringing any conclusions of the analysis to these meetings, much to its discomfort. This ensured that company leaders were invested in the decision-making process and could challenge the strategy team with new ideas.
Through a series of small-group meetings, the leadership team (with analytical help from the strategy team) debated the reasons for the company’s past success and how to continue it. By unpacking these complex dynamics together, the leadership team arrived at an accurate, sharp diagnosis: the company needed to restore mainstream shoppers’ trust in its prices. The result was a simple, focused strategy for delivering “value” products and reinforcing that market position with customers. Furthermore, because the management team was deeply involved in the diagnosis, its members had a strong incentive to drive implementation.
Don’t leave the strategy unfinished
In conversations with senior executives, we occasionally hear some version of this saying: “I’d rather have a good strategy and great execution than vice versa.” We believe that this attitude reflects confusion about what great strategy is. Such a strategy creates a path for action and is inherently incomplete without it. Yet many companies fail to get the conditions for successful implementation right, and fully two-thirds of the executives in our survey admit that their companies struggle with the issue.
It’s a crucial struggle. No strategy, however brilliant, can be implemented successfully unless the people who have the most important jobs know what they need to do differently, understand how and why they should do it, and have the necessary resources. An added challenge, of course, is that strategic choices often involve big changes over long, three- to five-year time frames.
Finishing a strategy, therefore, requires creating tangible, proximate goals that connect to the longer-term strategy. It’s easy to create a high-level list of next steps and things to do differently on Monday morning. It’s much harder to roll back the future and connect it to the present so that people understand what they need to do differently and actually do it.
When companies fail to set proximate goals, the results can be disappointing. An Asian telecommunications company, for example, had landed on an intriguing and counterintuitive strategy involving two big shifts: it wanted to move its target customer base from big business to the midmarket and to standardize its products rather than provide customized service to large clients. Making the changes work, however, would require salespeople to start saying no to new business from large and complex clients so that the company could redirect its efforts to midmarket customers. The short-term pain (lower revenues and higher costs) would ultimately lead the company to a market-beating position.
The management team understood and encouraged the shift and was ready to act. But the strategy team did not do enough to prepare the organization for the moves, instead spending its time on detailed initiative-planning exercises. Absent any effort to translate the company’s strategic desires into proximate goals for its employees, those employees balked at the changes.
Sales managers, for example, not only viewed saying no to larger customers as a short-term loss for the business but also were simply not as excited about pursuing midmarket customers with simpler needs. They understood the strategy intellectually and believed the analysis, but their skills, incentives, and ways of working and even thinking had not changed. Without such changes, they couldn’t connect the necessary steps to a longer-term goal and naturally reverted to their old ways, creating a backlash that inevitably undermined the strategy. Only afterward did the team recognize the kinds of activities that might have helped—for example, changing the salespeople’s goals, resetting the overall budget to acknowledge the transition from one customer segment to another, and using the reallocated funding to generate a new product-development road map.
Creating strategy in today’s environment of complexity, ever-changing priorities, and conflicting agendas is a daunting task. Yet when senior executives invest the time and effort to develop a more thorough, thoughtful approach to strategy, they not only increase the odds of building a winning business but also often enjoy a positive spin-off: the gifts of simplicity and focus, as well as the conviction to get things done.
Chris Bradley is a principal in McKinsey’s Sydney office, where Angus Dawson is a director and Antoine Montard is a senior expert.
The authors wish to thank Matthew Chapman, Pia Mortensen, and Victoria Newman for their contributions to the development of this article.
Explore a career with us
- AI Transformation
- Application Development
- Audience Engagement
- Channel Management
- Content Development
- Data Analytics
- Growth Initiatives
- Program Operations
- Strategic Planning
- Marketing Management
- Sales Management
- Operations Management
- Product Management
- Resource Center
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Community & Culture
- Contact Sales
- Contact Hiring
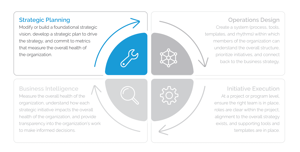
6 Elements of Effective Strategic Planning
While the business operations framework is a continuous cycle in which each stage informs the next, developing a strategic plan is the best place to start.
During the strategic planning process, an organization performs three steps:
- Builds or modifies the foundational strategic vision and mission
- Commits to goals that drive overall health
- Develops a long-term plan to achieve the goals
A strong strategic plan positions the organization for success and clearly defines it at every level.
A common mistake we see businesses make is starting tactical initiative execution without first communicating and aligning on the goal. Skipping these important steps can leave your organization without direction.
Read ahead to learn more about the six vital elements of strategic planning: vision , mission , objectives , strategy , approach , and tactics .
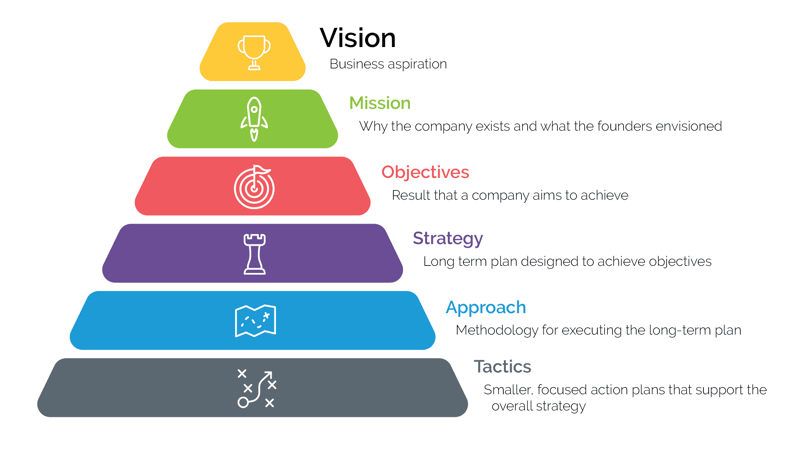
1. Define your vision
An organization’s vision statement is an aspirational description of what it wants to achieve in the future..
A vision statement serves as a clear guide for choosing current and future courses of action — a definition of where you want your organization to be in the long term. It sets the tone and provides a North Star on the horizon.
One example of a company with a strong vision statement is Warby Parker, the online prescription glasses retailer founded in 2010 that is now worth an estimated $3 billion.
Warby Parker’s vision statement has two parts: “We believe that buying glasses should be easy and fun. It should leave you happy and good-looking, with money in your pocket. We also believe that everyone has a right to see.”
With just three sentences, the vision statement tells you exactly what the company aims to achieve. Namely, to make the process for buying prescription glasses and sunglasses fun and straightforward (unlike the traditional method). The vision also aims for customers to have fashionable frames, but at a lower cost than existing options.
The last sentence of the vision statement adds in a purpose statement (aka why the company exists): “We also believe that everyone has a right to see.” Since the beginning, Warby Parker has touted its “Buy a Pair, Give a Pair” program that donates glasses to people who can’t otherwise afford them. According to the CEO, this purpose is what motivates employees to join and stay with the company. Not all leaders include a social impact focus in their company’s vision and purpose statement, but it’s becoming increasingly popular with the growing buying power of Millennial and Gen Z consumers.
A powerful vision statement helps company employees focus their work in the right direction — and a strong vision statement will do the same for your organization.
2. Create your mission
While your vision is an organization-wide goal, your mission how you plan to achieve the vision..
Without a mission, your organization lacks the why and how. If everyone in your organization has their own interpretation of the vision, it can lead to conflicting strategies and initiatives.
For Warby Parker, there are many possible routes to achieve the company vision that states “buying glasses should be easy and fun. It should leave you happy and good-looking, with money in your pocket.”
The company’s mission statement is: “By circumventing traditional channels, designing glasses in-house, and engaging with customers directly, we’re able to provide higher-quality, better-looking prescription eyewear at a fraction of the going price.”
After the founding team realized early on that one large company dominated the eyewear industry with inflated prices, they decided to find a way to lower prices and increase quality, while also turning a profit. The resulting actions included bringing many traditionally outsourced services in-house, such as design and consumer marketing/sales.
3. Set your objectives
Objectives are specific results that a person or system aims to achieve within a time frame..
Defining success early lets you know if you are on the path to achieve your mission and vision. Clearly articulating your objectives creates goal posts by which your organization can measure its overall health and the impact of strategic initiatives.
In general, good objectives should be clear, measurable and be supported by multiple strategic initiatives across the organization.
While Warby Parker isn’t a public company and is not legally required to release annual financial statements, the organization does voluntary release an annual impact report. The report provides a window into the company’s strategic objectives with the inclusion of priority issues relevant to both stakeholders and the company. For the most recent 2019 report , the top issues cited are the Buy a Pair, Give a Pair program, customer experience, innovation, product safety, and responsible sourcing.
For the Buy a Pair, Give a Pair program, Warby Parker’s relevant objective might be aimed at growing the program, while the innovation priority may be tied to the objective of innovating to meet the strategic vision and mission. The issue of responsible sourcing could lead to an objective of using all recycled packaging or becoming carbon neutral. While the listed issues are presented through an impact lens, they also have a financial purpose.
4. Develop your strategy
Your strategy is a long-term plan that enables you to achieve your organization’s objectives..
An effective strategy brings together vision and execution. Strategies are much more specific than an organization’s vision, mission, and objectives. They are typically only shared within an organization and ideally built around an organization’s needs and market context. Strategies should map long-term plans to objectives and actionable steps, foster innovative thinking, as well as anticipate and mitigate potential pitfalls.
Strategic plans often look out 3-5 years, and there may be a separate plan for each individual objective within the organization. In the Warby Parker annual impact report, we have insight into the strategy for each of the objectives identified above. We’ll highlight potential strategies for two areas: the Buy a Pair, Give a Pair program and innovation.
By the end of 2019 Warby Parker had distributed seven million pairs of glasses to 23 countries through the Buy a Pair, Give a Pair Program and will be likely focus on expanding those numbers in 2021 and beyond. According to the impact report, 2.5 billion people around the world lack access to affordable glasses to learn and work. In order to make a positive impact, Warby Parker needed to develop strategies to continue chipping away at that need, as well as meet company objectives, mission and vision. An example strategy for this program could be expanding the US-based Pupils Project, which gives school children access to free vision services and glasses. In the 2019-2020 school year, Warby Parker expanded the program from New York City and Baltimore to Philadelphia, providing vision services to an estimated 25,000 students in the School District of Philadelphia.

In addition, Warby Parker has traditionally been focused on eyewear and reimagining the customer experience for glasses wearers, so naturally the company’s leadership identified an innovation opportunity to add daily contact lenses in November 2019, which was likely the result of a multi-year strategic plan. Like Warby Parker’s eyeglasses process, the company allows a trial period for contact wearers, who can request 6 days of contacts in their prescription before committing to a full 90-day supply.
5. Outline your approach
An approach provides a methodology for executing your strategy..
The approach is a framework for answering key questions that will later determine tactics. Plus, it guides an organization on how to execute the strategic plan.
Within our Warby Parker example, each strategic plan included an approach that guided the leadership team in their analysis and plan execution. While we won’t cover each decision the company made in 2019, we’d like to focus on two big ones: the Pupils Project expansion and the launch of the contact lens brand Scout.
When it came to expanding the Pupils Project, the Warby Parker leadership team needed an approach for addressing each key decision for the program. There were likely more decisions than we can cover in one whitepaper, but will focus on two: whether to partner with existing non-profits or create its own program and how to make the greatest impact with the funds available.
Leading up to the decision points, like whether to expand the Pupils Program to Philadelphia, the leadership’s approach probably included a consideration of whether to develop the program infrastructure and manage it internally or partner with existing non-profits. The approach also likely included a cost-benefit analysis of that question, evaluating the financial ROI and social impact of each option. The company ultimately choose to work with two local Philadelphia nonprofits.
Another key decision requiring a strong approach within the Pupils Program was how to have the greatest impact with the funds available. The company needed an approach that would help them answer and inform key decisions. Those decisions could have included an analysis of whether to contribute the glasses directly or make a cash equivalent donation to the nonprofits, how to identify schools for the project (for example considering the greatest overall need or the number of glasses Warby Parker can provide), as well as who should manage the logistics of the screenings and eyeglasses deliveries.
On the innovation side, Warby Parker needed a quality approach to ensure the contact lens brand launch (called Scout) was aligned with the existing mission, vision, objectives and strategies. In order to create a contact lens that was high quality, affordable, and with lower waste packaging, the company needed a multi-pronged approach. Two crucial areas of planning for the Scout contact lenses were undoubtedly the design of the product and choosing the right manufacturer.
Because contact lenses were completely new to the company, Warby Parker needed to either design them in house or hire an outside design team that would meet the high standards the leadership outlined in the 2019 impact report , “On top of creating a great shopping experience for our customers, we have high expectations for what a daily contact lens should be—high quality, moist, breathable, comfortable, innovative, and affordable. It’s a lot to ask of one product, but we were relentless in our search for a contact lens that checked all of those boxes.”
While the company does not say in the report which route it chose for design, the leadership likely did a cost benefit analysis of designing it in-house vs. working with an outside design company or freelance designers. The key considerations were likely the cost to design, the strategic importance of certain attributes (like breathability, moisture content, shape), the cost to manufacture, and the sustainability considerations.
In terms of the approach to find the right manufacturer, Warby Parker needed to find a partner that met the company’s quality, cost, and environmental standards. The sustainability standards included finding packaging with significant less waste and incorporating recycled materials from the manufacturing process. The company’s approach to finding a manufacturer probably included research and a ranking of multiple companies with the above criteria in mind, then doing a comparison across the top choices and additional due diligence before choosing a partner.
Through these examples, you can see how an approach ladders up to strategies, outcomes and eventually the company’s mission.
6. Get down to tactics
Tactics are focused initiatives, projects, or programs that allow organizations to execute a strategic plan..
Tactics are the key to execution. They are the actions you take to make it all happen.
Within each decision Warby Parker made, the company used different tactics to move it from an idea to actual product or program. While each decision could have dozens of tactics, we’ve highlighted one or two examples for each.
For the Pupils Project at Warby Parker, the decision for how to have the largest impact possible required several tactics or initiatives to make that happen. The company choose to have the nonprofit partners run the screenings while Warby Parker provided the glasses and had the students choose their styles from 40 options in a truck show. One necessary tactic was bringing together the design and logistics teams to narrow down the style options that would be appealing to kids, cost effective, and easy to produce in large numbers.
Another important tactic was likely determining how to produce and deliver the glasses to the students, whether the glasses should deliver to their homes or the schools, and how to ensure the glasses fit correctly after they arrived. The Pupils Project’s overall goal is for children to have glasses to enable their ability to learn, and in order to do that, they need to actually use the glasses for the long-term, so it’s important to have styles that appeal to children, as well as well-fitting frames.

In terms of tactics for the Scout contact lens launch, once the company made the decision on a design team, the project leaders determined tactics to make the contacts idea a reality. The designers had specific research guidelines to find material and construction that fit the criteria of “high quality, moist, breathable, comfortable, innovative, and affordable.” The final product is made with a material that resists drying and constructed using new technology to increase eye comfort during wear.
The company design team also created flat pack packaging that is more hygienic, uses less raw materials, and takes up less space compared to traditional contact lens packaging. Even the placement of the contact (upside down) was intentional to reduce the chance of contamination from dirt or bacteria when the wearer puts them in their eye. Each of these items were likely framed as tactics and initiatives used to create the Scout lenses. Each was directly related to Warby Parker’s approach to the decision, the overall strategy, and aligned with the larger mission and vision.
On the surface, each tactic might not seem connected, but as you dig deeper, you’ll find that effective tactics should always tie back to the strategy, objectives, mission, and vision of the company.
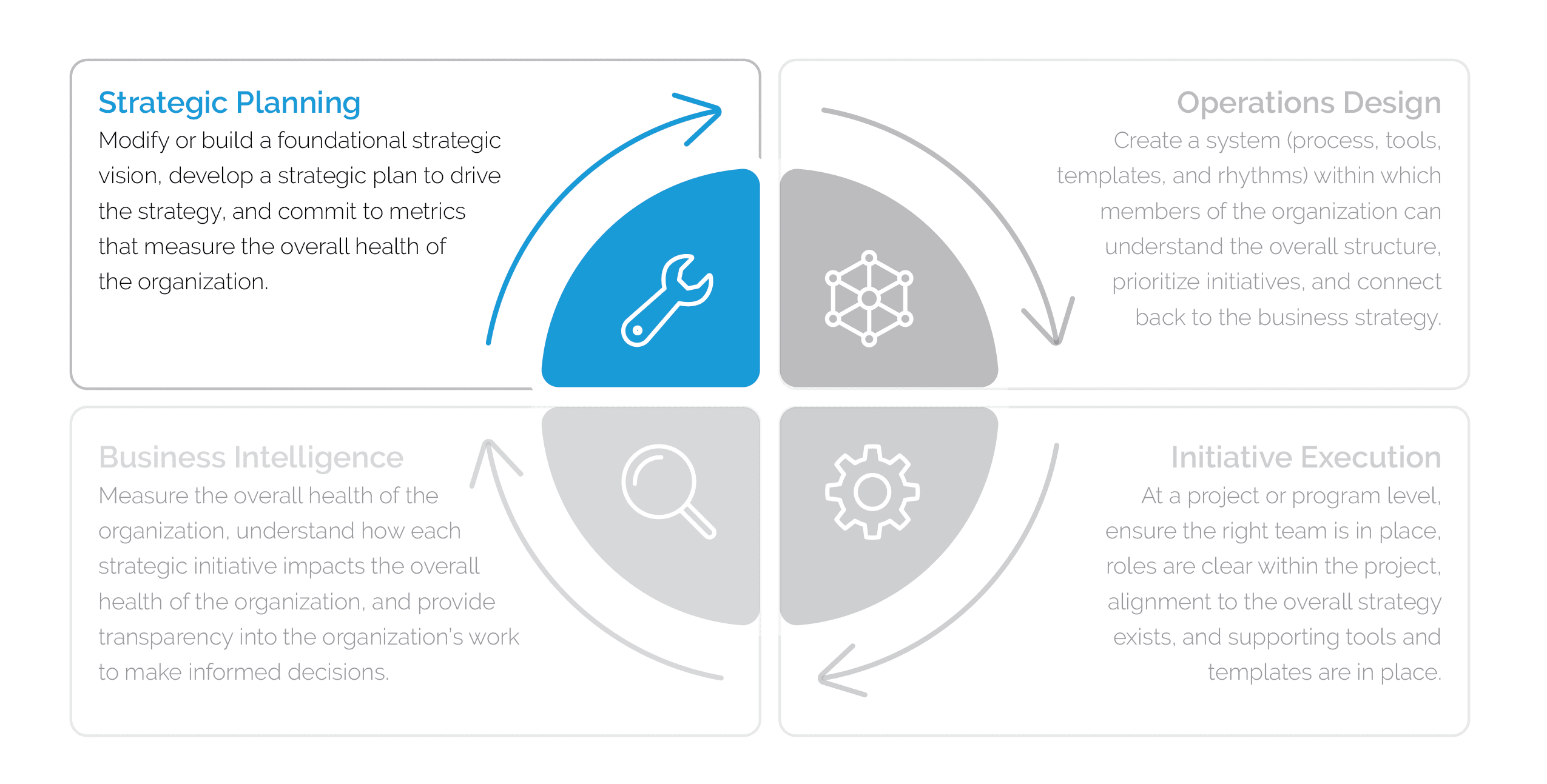
This is the second in a 5-part blog series defining Spur Reply’s unique perspective on the often overlooked, but incredibly valuable world of business operations.
Part 1: Overall business operations
Part 2: this blog focuses on strategic planning, part 3: operations design, part 4: initiative execution, part 5: business intelligence.

Dan Overgaag
Related articles.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
6 Steps to Make Your Strategic Plan Really Strategic
- Graham Kenny

You don’t need dozens of strategic goals.
Many strategic plans aren’t strategic, or even plans. To fix that, try a six step process: first, identify key stakeholders. Second, identify a specific, very important key stakeholder: your target customer. Third, figure out what these stakeholders want from you. Fourth, figure out what you want from them. Fifth, design your strategy around these requirements. Sixth, focus on continuously improving this plan.
Why is it that when a group of managers gets together for a strategic planning session they often emerge with a document that’s devoid of “strategy”, and often not even a plan ?
- Graham Kenny is the CEO of Strategic Factors and author of Strategy Discovery . He is a recognized expert in strategy and performance measurement who helps managers, executives, and boards create successful organizations in the private, public, and not-for-profit sectors. He has been a professor of management in universities in the U.S. and Canada.
Partner Center
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
5 Keys to Successful Strategy Execution

- 17 Nov 2020
You’ve set organizational goals and formulated a strategic plan . Now, how do you ensure it gets done?
Strategy execution is the implementation of a strategic plan in an effort to reach business goals and objectives . It comprises the daily structures, systems, and operational goals that set your team up for success.
Access your free e-book today.
Why Is Strategy Execution Difficult?
There are several factors that make successful execution of your business strategy challenging.
According to the Harvard Business School Online course Strategy Execution , some of the most common factors include:
- Poor communication of strategic objectives
- Lack of employee buy-in
- Ineffective risk management
All of these can cause the best strategic plans to fall flat in their execution. In fact, poor execution is more common than you may realize. According to research from Bridges Business Consultancy , 48 percent of organizations fail to reach at least half of their strategic targets, and just seven percent of business leaders believe their organizations are excellent at strategy implementation.
“If you’ve looked at the news lately, you’ve probably seen stories of businesses with great strategies that have failed ,” says Harvard Business School Professor Robert Simons, who teaches the online course Strategy Execution . “In each case, we find a business strategy that was well formulated but poorly executed.”
How can you equip yourself and your team to implement the plans you’ve crafted? Here are five keys to successful strategy execution you can use at your organization.
Keys to Successful Strategy Execution
1. commit to a strategic plan.
Before diving into execution, it’s important to ensure all decision-makers and stakeholders agree on the strategic plan.
Research in the Harvard Business Review shows that 71 percent of employees in companies with weak execution believe strategic decisions are second-guessed, as opposed to 45 percent of employees from companies with strong execution.
Committing to a strategic plan before beginning implementation ensures all decision-makers and their teams are aligned on the same goals. This creates a shared understanding of the larger strategic plan throughout the organization.
Strategies aren’t stagnant—they should evolve with new challenges and opportunities. Communication is critical to ensuring you and your colleagues start on the same page in the planning process and stay aligned as time goes on.
2. Align Jobs to Strategy
One barrier many companies face in effective strategy execution is that employees’ roles aren’t designed with strategy in mind.
This can occur when employees are hired before a strategy is formulated, or when roles are established to align with a former company strategy.
In Strategy Execution , Simons posits that jobs are optimized for high performance when they line up with an organizational strategy. He created the Job Design Optimization Tool (JDOT) that individuals can use to assess whether their organization's jobs are designed for successful strategy execution.
The JDOT assesses a job’s design based on four factors, or “spans”: control, accountability, influence, and support.
“Each span can be adjusted so that it’s narrow or wide or somewhere in between,” Simons writes in the Harvard Business Review . “I think of the adjustments as being made on sliders, like those found on music amplifiers. If you get the settings right, you can design a job in which a talented individual can successfully execute your company’s strategy. But if you get the settings wrong, it will be difficult for any employee to be effective.”
3. Communicate Clearly to Empower Employees
When it comes to strategy execution, the power of clear communication can’t be overlooked. Given that a staggering 95 percent of employees don’t understand or are unaware of their company’s strategy, communication is a skill worth improving.
Strategy execution depends on each member of your organization's daily tasks and decisions, so it’s vital to ensure everyone understands not only the company's broader strategic goals, but how their individual responsibilities make achieving them possible.
Data outlined in the Harvard Business Review shows that 61 percent of staff at strong-execution companies believe field and line employees are given the information necessary to understand the bottom-line impact of their work and decisions. In weak-execution organizations, just 28 percent believe this to be true.
To boost your organization’s performance and empower your employees, train managers to communicate the impact of their team's daily work, address the organization in an all-staff meeting, and foster a culture that celebrates milestones on the way to reaching large strategic goals.

4. Measure and Monitor Performance
Strategy execution relies on continually assessing progress toward goals. To effectively measure your organization’s performance metrics, determine numeric key performance indicators (KPIs) during the strategic planning stage . A numeric goal serves as a clear measure of success for you and your team to regularly track and monitor performance and assess if any changes need to be made based on that progress.
For instance, your company’s strategic goal could be to increase its customer retention rate by 30 percent by 2026. By keeping a record of the change in customer retention rate on a weekly or monthly basis, you can observe data trends over time.
If records show that your customer retention rate is decreasing month over month, it could signal that your strategic plan requires pivoting because it’s not driving the change you desire. If, however, your data shows steady month-over-month growth, you can use that trend to reasonably predict whether you’ll reach your goal of a 30 percent increase by 2026.
5. Balance Innovation and Control
While innovation is an essential driving force for company growth, don’t let it derail the execution of your strategy.
To leverage innovation and maintain control over your current strategy implementation, develop a process to evaluate challenges, barriers, and opportunities that arise. Who makes decisions that may pivot your strategy’s focus? What pieces of the strategy are non-negotiable? Answering questions like these upfront can allow for clarity during execution.
Also, remember that a stagnant organization has no room for growth. Encourage employees to brainstorm, experiment, and take calculated risks with strategic initiatives in mind.
Related: 23 Resources for Mobilizing Innovation in Your Organization
Building the Skills to Successfully Execute Strategy
Setting strategic goals, formulating a plan, and executing a strategy each require a different set of skills and come with their own challenges. Keeping in mind that even the best formulated strategy can be poorly executed, consider bolstering your execution skills before setting strategic goals and putting a plan in place. Developing these skills can have a lasting impact on your organization's future performance.
Are you interested in designing systems and structures to meet your organization’s strategic goals? Explore our eight-week Strategy Execution course and other online strategy courses to hone your strategic planning and execution skills. To find the right HBS Online Strategy course for you, download the free flowchart .
This post was updated on November 9, 2023. It was originally published on November 17, 2020.

About the Author
7 Important Elements of a Strategic Plan
If You Take These Recommended Steps, You Could Change the World
Compassionate Eye Foundation/Hiep Vu/Getty Images
- Management & Leadership
- Human Resources
- Employee Benefits
Vision Statement
Mission statement, core values.
- SWOT Analysis
Long-Term Goals
Yearly objectives, action plans.
Dan McCarthy is a management and leadership expert who's spoken, written, and taught on management topics for more than 20 years.
A strategic plan is a document that establishes the direction of an organization. It can be a single page or fill up a binder, depending on the size and complexity of the business and work.
Most managers can benefit from having a strategic plan. The process of developing a plan helps the manager (and the team) step back and examine where they are, where they want to go, and how they are most likely to get there. In the absence of a plan, work still gets done on a day-to-day basis but often lacks a sense of purpose and priority.
There are seven basic elements of a strategic plan. While much more is often included in the plan, these seven elements will help you get started.
A vision statement describes the way you envision your business. As such, it should communicate that dream to your employees and customers in an inspirational manner.
A vision statement should be reviewed continuously to ensure it is still aligned with the way you see your company.
Harley-Davidson's vision statement focuses on keeping its brand internationally known and valued, using the combined power of its stakeholders and employees to drive value and innovation:
Harley-Davidson, Inc. is an action-oriented, international company, a leader in its commitment to continuously improve our mutually beneficial relationships with stakeholders (customers, suppliers, employees, shareholders, government, and society). Harley-Davidson believes the key to success is to balance stakeholders’ interests through the empowerment of all employees to focus on value-added activities.
While a vision describes how you view your business to your customers and stakeholders, a mission statement describes what you do currently. It often describes what you do, for who, and how. Focusing on your mission each day should enable you to reach your vision. A mission statement could broaden your choices, and/or narrow them.
RedHat has been a provider of Linux operating systems for over 25 years. It has a simple mission statement:
To be the catalyst in communities of customers, contributors, and partners creating better technology the open source way.
A vision and mission can also be combined in the same statement. The Walt Disney Company does this:
The mission of The Walt Disney Company is to entertain, inform and inspire people around the globe through the power of unparalleled storytelling, reflecting the iconic brands, creative minds and innovative technologies that make ours the world’s premier entertainment company.
Note that the statement is both aspirational (“is to…”) and descriptive of what they do and how they do it ("through the...").
Core values describe your beliefs and behaviors. They are the beliefs you have that will enable you to achieve your vision and mission.
The Coca-Cola Company lists it's core values as:
Leadership: The courage to shape a better future
Collaboration: Leverage collective genius
Integrity: Be real
Accountability: If it is to be, it's up to me
Passion: Committed in heart and mind
Diversity: As inclusive as our brands
Quality: What we do, we do well
SWOT Analysis
SWOT is an acronym for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. A SWOT analysis provides businesses a situational investigation into their position in the market. It allows you to spot and name the important aspects, happenings, and adversaries of your business.
A business's strength could be its ability to attract local customers, while its weakness might be an inability to break into a non-local consumer base. A local competitor with ties to non-local customers could be facing a financial situation, giving this business an opportunity.
However, the other business remains a threat if it pulls out of the crises. If another competitor is trying to expand its customer base, it is a threat as well.
Long-term goals are statements that drill down a level below the vision and describe how you plan to achieve it. This set of goals usually starts three years out and extends to around five years into the future, directly aligning with the mission and vision statements.
Long-term goals are the milestones a company sets to guide operations toward their far-reaching objectives. Some examples of long-term goals could be for a business to strengthen its hold on the local market, increasing profits, or expanding its operations and sales.
Each long-term goal should have a few one-year objectives that advance your goals. Each objective should be as SMART as possible: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-based.
After you make your yearly objectives, you might break each one down further into short-term goals, which define the actions and objectives for the next three months to get you to your yearly goals. The plans for achieving your short-term goals are your action plans.
Each objective should have a plan that details how it will be achieved. The amount of detail depends on the amount of flexibility you want your managers and team to have. The more detail provided the less flexibility exists for those that follow the plan.
It’s been said that “A vision without a plan is just a dream. A plan without a vision is just drudgery. But a vision with a plan can change the world.” Creating a plan to achieve your business objectives may not change the world—but it is possible. Some of the most successful corporations started in garages, and through planning became industry giants.

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
The Essential Elements of Strategic Thinking
Explore the critical components of The Essential Elements of Strategic Thinking. Delve into the concept of strategic thinking, its definition, and how it shapes decision-making. Uncover the five key elements that define strategic thinking, including intent focus, a system perspective, thinking in time, intelligent opportunism, and hypothesis-driven planning.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Effective Communication Skills
- Assertiveness Skills Training
- Business Communication Course
- Dealing with Difficult People
- Sentiment Analysis Training

Table of Contents
1) What is Strategic Thinking?
2) What are the 5 key elements of Strategic Thinking?
a) Intent focus
b) A system perspective
c) Thinking in time
d) Intelligent opportunism
e) Hypothesis-driven
3) Benefits of Strategic Thinking Elements
4) Conclusion
What is Strategic Thinking?
Strategic Thinking can be defined as a cognitive process that involves analysing complex situations, thinking critically, and making informed decisions to achieve long-term goals. It goes beyond day-to-day problem-solving and focuses on the bigger picture, considering the broader context and envisioning the desired future state.
Strategic Thinking involves analysing complex situations, making informed decisions, and envisioning long-term goals. It requires a proactive, systems-oriented, and analytical approach coupled with adaptability and collaboration.
At its core, Strategic Thinking involves taking a proactive approach, anticipating challenges, and positioning oneself for success. Analytical thinking and collaboration are crucial aspects of Strategic Thinking. Moreover, Strategic Thinking requires adaptability and the ability to respond to changes in the business landscape.
Strategic thinkers embrace innovation, remain open to new ideas, and adjust strategies as necessary. They proactively seek feedback, learn from failures, and iterate their approaches, enabling them to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving environment. Developing Strategic Thinking skills takes time and practice, but the rewards are substantial—a sharper strategic focus, improved decision-making, and a competitive advantage in the modern world.
Take charge of your personal and professional growth with our Strategic Planning and Thinking Course. Unlock your Strategic Thinking potential today!
What are the 5 key elements of Strategic Thinking?
Intent focus
Intent focus in Strategic Thinking Elements is about having a clear and unwavering direction in Strategic Thinking. It involves setting specific and measurable goals that align with the overarching vision. Strategic thinkers clearly define their intent and communicate it effectively to their team or stakeholders.
By maintaining a clear focus on the desired outcomes, they can prioritise their efforts, make informed decisions, and allocate resources strategically. Intent focus provides a guiding compass that keeps everyone aligned and motivated, driving progress towards long-term success.
A system perspective
A system perspective in Strategic Thinking Elements involves understanding the interconnected nature of various components within a system. Strategic thinkers recognise that actions or changes in one part of the system can have ripple effects on other Strategic Thinking Elements. They consider the broader ecosystem, including internal and external factors, stakeholders, market dynamics, and industry trends.
By analysing the complex web of relationships and dependencies, strategic thinkers can identify leverage points, anticipate potential bottlenecks, and develop holistic strategies that address multiple aspects of the system. A system perspective allows for comprehensive decision-making and minimises unintended consequences.
Thinking in time
Thinking in time refers to the ability to integrate historical perspectives and future projections into Strategic Thinking. Strategic Thinkers delve into the past to understand patterns, trends, and lessons learned from previous successes and failures. They gain valuable insights that inform their decision-making process by studying historical data and analysing past strategies.
Additionally, thinking in time involves considering future scenarios and potential developments. Strategic Thinkers engage in foresight activities, scenario planning, and trend analysis to anticipate future challenges and opportunities. By thinking in time, they make informed decisions that draw from both the past and future, increasing the likelihood of achieving long-term success.
Intelligent opportunism
Intelligent opportunism involves being receptive to unexpected opportunities that arise during the strategic journey. Strategic Thinkers remain agile and adaptable, continuously scanning the environment for emerging trends, market shifts, and unforeseen circumstances. They embrace ambiguity and uncertainty, recognising that hidden opportunities often lie within challenging situations.
When an opportunity aligns with their strategic objectives, they seize it strategically, leveraging their resources and capabilities. Intelligent opportunism allows for flexibility in adjusting strategies, capitalising on unanticipated events, and staying ahead of the competition.
Hypothesis-driven
A hypothesis-driven approach is characterised by formulating assumptions or hypotheses and actively testing them through data analysis and experimentation. Strategic Thinkers develop hypotheses based on available information and prior knowledge. They gather relevant data, conduct research, and engage in rigorous analysis to validate or invalidate their assumptions.

Benefits of Strategic Thinking Elements
Strategic Thinking offers numerous benefits for individuals and organisations. By cultivating and applying Strategic Thinking Elements, individuals can enhance their decision-making, problem-solving, and planning capabilities, leading to greater success and effectiveness in various aspects of their lives. Here are some key benefits of Strategic Thinking:
Clear direction
Strategic Thinking Elements provide individuals with a clear direction and purpose. By aligning goals and actions with a larger vision, individuals gain a sense of focus and clarity. They can identify what is truly important and make decisions that support long-term objectives. This clarity enables individuals to prioritise their efforts, allocate resources effectively, and avoid getting overwhelmed by day-to-day distractions.
Proactive approach
Strategic Thinking Elements empower individuals to adopt a proactive rather than reactive approach. Instead of merely responding to immediate challenges, they anticipate future trends, risks, and opportunities. By thinking ahead and considering different scenarios, they can prepare for potential obstacles, mitigate risks, and capitalise on emerging opportunities. This proactive mindset allows individuals to stay ahead of the curve and take advantage of changing circumstances.
Improved decision-making
Strategic Thinking Elements enhance decision-making by providing a structured framework for evaluating options and assessing potential outcomes. It involves gathering and analysing relevant data, considering multiple perspectives, and weighing the pros and cons of different courses of action. Strategic thinkers make informed decisions based on evidence and long-term considerations. This leads to more effective and successful outcomes, as decisions are grounded in careful analysis and strategic alignment.
Effective problem-solving
Strategic Thinking Elements equip individuals with a systematic approach to problem-solving. Rather than merely addressing symptoms, strategic thinkers identify underlying causes and develop comprehensive solutions. They consider the broader context, stakeholders' perspectives, and potential consequences. By applying critical thinking and creativity, strategic thinkers can tackle complex problems and generate innovative solutions that address the root causes.
Enhanced adaptability
Strategic Thinking Elements enable individuals to adapt and respond effectively to new challenges and opportunities. It encourages flexibility and open-mindedness, allowing individuals to adjust their strategies as needed. Strategic thinkers embrace change, leverage their strengths, and explore new approaches. This adaptability helps them thrive in dynamic environments, seize emerging trends, and navigate uncertainties with agility.
Competitive advantage
Strategic Thinking Elements provide individuals and organisations with a competitive edge. Strategic thinkers can position themselves ahead of competitors by analysing the market landscape, identifying gaps, and anticipating future trends. They can identify untapped opportunities, design innovative products or services, and separate themselves from the competition. Strategic Thinking enables individuals and organisations to anticipate market shifts, stay relevant, and maintain a competitive advantage.
Long-term success
Strategic Thinking Elements are essential for long-term success. Strategic thinkers can ensure sustainability and avoid short-term thinking by considering the broader implications of actions and decisions. They take a holistic view of success, considering financial, social, and environmental factors. Strategic thinkers focus on creating value and achieving sustainable growth, leading to long-term success and resilience.
Conclusion
All in all, Strategic Thinking is a multifaceted skill that combines visionary perspective, systems thinking, analytical mindset, adaptive agility, and collaborative engagement. By cultivating these five Strategic Thinking Elements, individuals and organisations can enhance their ability to navigate complex challenges, make informed decisions, and achieve long-term success. Developing Strategic Thinking skills takes time and practice, but the rewards are substantial—a sharper strategic focus, improved decision-making, and competitive advantage.
Transform your potential into success with our comprehensive Personal Development Training Courses. Join now and unlock your true capabilities!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 3rd May 2024
Fri 19th Jul 2024
Fri 20th Sep 2024
Fri 1st Nov 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
More From Forbes
Five components of a successful strategic communications plan.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Director of Marketing at haseebtariq.com. I help fix large revenue retention & growth issues.
Communication is a critical part of any organization's success. Once, I was working closely with the senior leadership to create an email that addressed late deliveries. I remember that when we first started, there were so many ideas swirling in our heads about how to approach this project and what tone of voice would be best for our company. I wished I had someone with a communications strategy plan who could tell me the "best" way to approach this project in order to be successful.
I started reading and researching, looking for what I felt was a good strategy to communicate with our target audience. Luckily, after some research and conversations with others who had more experience than myself on the topic at hand, what finally developed was a communications strategy plan that we used over and over again for all of our marketing and communication efforts.
What Is A Communications Strategy Plan?
A communications strategy is a plan for communicating with your target audience. It includes who you are talking to, why you are talking to them, how and when you will talk to them, what form of communication the content should take and what channels you should use to share it.
1. What Is The Purpose Of Your Communications Plan?
A clear purpose helps keep everyone on board. Make sure the right people hear your message when they are ready and in a way that you want them to hear it. Your communication objectives should be to answer these questions: Who do I need to reach? Why do I need to reach them? What will my communications say? How will I deliver this message at the time that will have the best impact on my audience (and for me)? And what channels am I using or can I use for delivery?
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
2. Who Are You Communicating With (Or Who Is Your Target Audience) And What Message Do They Need To Hear?
Target audiences can vary from one time to another and may include your customers, employees or the media. Define who needs to hear what is happening in your organization. Every communications plan is different, but they should never be one-size-fits-all. It's a good idea to create an audience map that identifies key audiences and the messages they need to hear about your organization or cause in order for them to take action.
3. How Will This Message Be Communicated?
Your communications strategy provides the framework for the company's outreach activities, including what needs to get out there through communication channels like social media, email marketing, blog posts, video content on YouTube or Vimeo and so on. In my experience, the more specific you are with your messaging (and visuals) — even if it seems repetitive — the better your chances of getting people engaged and taking action are.
4. When Should This Communication Happen — Right Now Or Later On?
Organizations have to use their communications wisely and strategically in order to be successful with them. But the importance of timing is also important for communicating effectively. Your communications strategy should specify when the message should be communicated, including whether that's right now or later on. Your communications team should take these considerations into account as they develop your messaging and timing plan. In addition, I recommend developing two equally effective strategies: one for "now" and another that can be deployed in anticipation of events that might happen later down the road. A crisis communication plan helps cushion against unexpected turns of events, no matter what happens.
5. Who Will Be Responsible For The Communication?
Communications professionals should be the ones responsible for communicating with external audiences, and they should do so often during a crisis. However, human resources departments may also need to communicate internally about any changes that may affect employees. Define key messages, and then decide who will deliver them. Define the audience and focus on what they need to know about this change. Be sure to provide information in a timely way, but also keep the message concise so that employees can digest it easily.
Bottom Line
A strategic communications plan can help you communicate your message to the right people at the most opportune time. By considering these five components, you can put together a solid strategy that could drive more success for your business and bring about your desired results in less time.
Forbes Communications Council is an invitation-only community for executives in successful public relations, media strategy, creative and advertising agencies. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5 Key Elements of Strategic Planning. 1. Defining your Vision. Start by defining your organization's vision (its destination). In the words of Thibault Mesqui, Managing Director at Heineken in the state of strategy report, "make your strategy based on a vision". This is an expression of the unique Point Of View you bring to the market.
Overcoming Challenges and Pitfalls. Challenge of consensus over clarity. Challenge of who provides input versus who decides. Preparing a long, ambitious, 5 year plan that sits on a shelf. Finding a balance between process and a final product. Communicating and executing the plan. Lack of alignment between mission, action, and finances.
Goals and objectives. Every strategic plan should include a goals and objectives section. You can include both short- and long-term goals as they relate to your overall business vision. Example: Short-term goals: Hire five new employees within the next four months. Increase sales quotas by 10% within the next six months.
Highlight the plan in a company newsletter. Include the plan in new employee onboarding. Post the plan on the employee intranet, along with key highlights and a way to track progress. If you hold a meeting, make sure you and other key planners are prepared to handle the feedback and discussion that will arise.
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee.
4. Develop focus areas. Focus areas are the high-priority elements the company plans to focus its efforts on in working toward its vision. For each value in the strategic plan, state a focus area to accompany that value. These focus areas may be more specific than the vision statement and include a quantifiable metric to achieve.
A well-crafted strategic plan will help companies stay focused on their mission while making decisions based on core values guiding them toward achieving desired results by ensuring everyone is moving in the same direction. What are the Key Components of a Strategic Plan? Several key components make up a well-developed strategic plan.
Vision = A clear, specific, compelling picture of what the organization will look like at a specific time in the future (one, two, or five years), including those few key metrics that define success. Values = The boundaries within which the organization will operate in pursuit of its vision. Strategy = A clear plan, time- and market-based, that ...
For example: "Improve the quality of the customer experience." Also, keep the length of your strategic plan in mind and create goals accordingly. If you have a five-year strategic plan, a goal to "Double revenue in five years" is better than "Grow revenue by 20% this year." Note: Some companies choose to combine elements #1 and ...
Integrated: Each element supports the next. No objectives are disconnected from goals, and no strategies sit all alone. Systematic: Don't think of the plan as one big document. Instead, give it life by break it into executable parts. Dynamic: The plan isn't a static document but a living one.
1. Assess your industry, competitors and market trends. The initial step in creating an effective strategic plan is to assess the external forces shaping your industry, understanding the ...
The building blocks of strategy help companies make strategic choices and carry them through to operational reality. One central building block is deep insight into the starting position of the company: where and why it creates—or destroys—value (diagnose). Executives also need a point of view on how the future may unfold (forecast).
During the strategic planning process, an organization performs three steps: Builds or modifies the foundational strategic vision and mission. Commits to goals that drive overall health. Develops a long-term plan to achieve the goals. A strong strategic plan positions the organization for success and clearly defines it at every level.
Share. Save. Summary. Many strategic plans aren't strategic, or even plans. To fix that, try a six step process: first, identify key stakeholders. Second, identify a specific, very important key ...
The major parts of a standard strategic plan include the following: 1. Mission, vision, and aspirations. A mission statement is your overall, lasting formulation of why your company exists and ...
4. Measure and Monitor Performance. Strategy execution relies on continually assessing progress toward goals. To effectively measure your organization's performance metrics, determine numeric key performance indicators (KPIs) during the strategic planning stage.A numeric goal serves as a clear measure of success for you and your team to regularly track and monitor performance and assess if ...
The core components of a strategic plan are: • Vision statement: The highest-level purpose of your organisation; a description of what the world would look like if you are 100% successful. • Mission statement: A summary of your organisation's purpose, the means you will use to achieve it and the core values that guide your work.
Creating a plan to achieve your business objectives may not change the world—but it is possible. Some of the most successful corporations started in garages, and through planning became industry giants. Here are the seven basic elements of a strategic plan: vision, mission, SWOT analysis, core values, goals, objectives, and action plans.
The key elements of a strategic plan include your vision and mission statements, detailed goals and objectives, and action plans and scorecards to help you track your progress. Make sure you include each of these key parts of a strategic plan in order to create a plan that will serve your small business. Including these detailed sections will ...
Avoid setting Goals that are simply deadline driven. Set Goals that measure the anticipated impact of the team's efforts and use the SMART goal concept when possible. There should be strong ...
Uncover the five key elements that define strategic thinking, including intent focus, a system perspective, thinking in time, intelligent opportunism, and hypothesis-driven planning. Home Resources Business Skills The Essential Elements of Strategic Thinking. Strategic Planning and Thinking Course Top Rated Course. Exclusive 40% OFF.
Let's take a look at the 5 key elements of a strategic plan that will help us to answer those questions: 1. A Vision. No surprises here - we need to start off by defining our vision for the ...
Define key messages, and then decide who will deliver them. Define the audience and focus on what they need to know about this change. Be sure to provide information in a timely way, but also keep ...
The 5 key elements of workforce planning. There are five key elements your organization should consider throughout the workforce planning process. 1. Case Studies ... Strategic workforce planning process. You begin the process by assessing and forecasting your current situation and future needs. Then, you create a workforce that can fill the gaps.
Strategy without execution is just wishful thinking. We'll show you how to create a strategic plan that delivers results, empowering your organization to accelerate on-strategy delivery while ...