Business Environment – Definition, Components, & Features

Several internal and external factors directly or indirectly influence business operations. While some of these are within the business’s control, most of these are not; and the business has to adapt itself to avoid being affected by changes in such factors. Both of them combined forms the business environment.
Today’s fast-paced business world witnesses a trend of a rather dynamic business environment – that is, it’s never stable. Hence, keeping track of these changing trends, demands, strategies, and policies is crucial in the business world.
But first, what is a business environment and what are the factors that influence it?

What Is Business Environment?
A business environment is a combination of internal and external factors and forces that significantly influence the operations of a business.
The business environment comprises an internal and external environment that directly or indirectly affects business operations.
- Internal Environment: It includes all the factors that are well within the control of a company. These factors are relatively predictable and can be worked on by the company to eliminate forces that negatively impact its operations.
- External Environment: It includes factors that exist outside the company’s control. They tend to be unpredictable as a company cannot possibly control or predict a change in them. Their unpredictable nature has the potential to abruptly hinder or even boost a company’s functioning.
Components Of Business Environment
The business environment can be categorised into two types based on the factors within the control or outside the control of a business.
Internal Environment
The internal business environment constitutes several internal forces or elements within the control of a business that influences its operations. These include:
- Value System: It is the ethical belief that guides the business towards achieving its mission and objective. The value system includes all components that form a business’s regulatory framework – organisational culture , climate, work processes, management practices and organisational norms.
- Vision, Mission, and Objectives: The vision, mission, and objective of a business relate to what it wants to achieve or accomplish in future. It is the reason why the business exists.
- Organisational Structure: It outlines how the activities are directed within the organisation to achieve its goals. It includes the rules, roles, and responsibilities, along with how tasks are delegated and how the information flows among the organisation’s levels.
- Corporate Culture: It is a powerful system of shared norms and attitudes that works as a homogenising factor for an organisation’s employees and gets appropriated by them.
- Human Resources: Human resources form all the employees and other personnel associated with the business. It forms the most valuable asset of the organisation as success or failure depends on it.
- Physical Resources and Technological Capabilities: It includes tangible assets and the technical know-how that play an essential role in ascertaining the business’s competitive capability and future growth prospects.
External Environment
External components are those factors that a business cannot control. These exist beyond a business’ jurisdiction and supervision limit. External components influencing a business environment are further classified into two categories:
Micro Environment
- Macro Environment
Micro environment is the business’s immediate external environment that influences its performance as it has a direct bearing on the firm’s regular business operations.
It includes factors outside of the business’s control but can be analysed and worked upon by managing the business to prevent any business losses.
Micro factors include:
- Customers comprise the target group of the business.
- Competitors are other market players who target a similar target group and provide similar offerings.
- Media is the channel the business use to market its offering to the customer.
- Suppliers include all the parties that provide the business with the resources it needs to perform its operations.
- Intermediaries comprise the parties involved in delivering the offering to the final customers.
- Partners are all external entities like advertising agencies, market research organisations, consultants, etc., who conduct business with the organisation and satisfy customer needs.
- Public includes any group with actual or potential interest in the business’s operations or a group that affects its ability to serve its customers.
Macro Environment: PESTLE
The macro environment includes remote environmental factors that influence an organisation. The extent of influence a macro element can have on a business is significant as they usually affect the industry as a whole.
These factors are classified under PESTLE: P – Political, E – Environmental, S – Social, T – Technological, L – Legal, E – Economical.

- Political Factors comprise government policies, political stability, corruption in the system, tax policies, labour laws, and trade restrictions that affect the business or the industry.
- Economical Factors relate to the economy of the country. They include economic growth, exchange rate, interest and inflation rates, etc.
- Social Factors comprise the demographics of the country. They include population growth rate, age distribution, career attitudes, health consciousness, etc.
- Technological Factors pertain to innovation in technology that affects the operations of the business. This refers to automation, research and development activities, technological awareness, etc.
- Legal Factors are laws that affect business operations. They include business-specific, industry-specific, and even state-specific laws.
- Environmental Factors comprise of all those that influence or are determined by the environment a business operates in. It includes the weather, climate, environmental policies, and even pressure from NGOs to care for the environment.
Importance of Business Environment
The market is essentially flooded with competing businesses. It is, thus, integral for a business to keep a lookout for the forces that affect it.
Emphasis is laid on maintaining continuous interaction with a company’s business environment. Understanding this environment allows companies to –
- Plan For Long Term: A sound knowledge of the business environment helps the company know its advantages and limitations, making it easier to choose the better positioning and plan to stay in the market for the long term.
- Identify Opportunities and Trends – Timely analysis allows a company to identify and consequently explore new opportunities and better performance ideas. A business opportunity is a factor that, upon identifying, allows the initiation of a business venture or aids the development of an existing business. An example of this is Nokia , a company that has previously held a whopping 49.9% of the global market share for mobile phones. However, the company did not adapt to the market’s changing demands as it failed to analyse new trends. Keeping a constant lookout for the new trends that rival firms are setting allows the company to adapt accordingly.
- Identify threats – Identifying potential threats to the business is another reason why a company needs to keep a watch on its environment. Threats are factors that have the potential to hurt a business. Steering clear of any possible threats ahead of time is integral for the survival of a company. Staying updated and adapting to the turbulent state of the overall business environment grants the company better flexibility when it comes to coping when a sudden, unexpected threat approaches the company. Understanding these conditions and forces thoroughly allows analysts to determine what direction the company should steer towards to stay relevant in the market.
- Gain First- Mover Advantage – A company gains the first-mover’s advantage if it succeeds to identify market demands at the right time. This allows the company to create its brand and gain brand recognition which benefits the business in the long run. As time passes, competitors try to enter the market after having examined the product’s expansive market demand. By that time, the first mover has plenty of time to establish strong customer loyalty and hence a significant market share which will be hard to compete with. A closer look at the history of Amazon shows how Jeff Bezos had recognised the power of the internet after having come across a statistic that claimed that the internet would change the way businesses operate. Identifying the internet’s potential ahead of time has made Amazon the world’s largest e-commerce company today.
Features Of Business Environment
A business environment is:
- Dynamic : The constant changing of the environment – be it socially, politically, economically and technologically – results in the dynamic nature of the business environment. A heavy interrelatedness of factors that consequently lead to this ever-changing environment is witnessed.
- Unpredictable : Due to its dynamic nature, an air of uncertainty always persists. Precognition is impossible, and hence, there is no way to foresee a future event that might impact the business environment.
- Complex : The interrelatedness of factors and circumstances form a rather tangled environment which is often difficult to analyse. It is an arduous task to keep track of the sources and their impacts on conditions and forces that make up the business environment. Hence, it is a complex task to measure the relative impact a certain force may have on a business.
- Susceptible : It is difficult to foresee the impact a slight change in the environment can have on a business. An insignificant change may influence a company’s operations largely. It has the potential to impact a business’ entire existence, its revenue and development.
- Relative : The business environment is not the same at all places. It varies from place to place. The political crisis in one nation affects the business environment only in that nation, not elsewhere. Hence, the business environment is a relative concept.
- Multiple-angled : A social, political or economic occurrence may have different impacts on different businesses. A political move that seems beneficial for one business might seem threatening to another. Hence, there exist multiple perceptions in a business environment.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think of our article on the business environment in the comments section.
A startup enthusiast who enjoys reading about successful entrepreneurs and writing about topics that involve the study of different markets.
Related Posts:

Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- Career Advice
- Business Environment:...
Business Environment: Definition, Factors, Importance, and Types
8 min read · Updated on December 13, 2023

What is a business environment and what factors affect it?
What constitutes a business environment extends beyond a company's four walls. It encapsulates the dynamic interplay of internal and external factors influencing its operations.
The complex ecosystem of a business environment presents opportunities for growth and potential challenges, making understanding these factors paramount for business success.
In this article, we define a business environment and explain its importance and the factors that affect it, so you can create effective business strategies in response to the ever-changing dynamics of your operational landscape.
What is a business environment?
A business environment refers to the internal and external factors affecting a business's operations. These factors are dynamic and constantly evolving. As a result, a business environment often results from a business sinking or swimming.
The factors that influence a business environment are split into the following primary categories:
General factors: Economic and social issues impacting businesses universally, including law, technology, and social-political norms.
Specific factors: Unique elements directly related to a particular business, such as competitors, target markets, suppliers, and customers.
Uncertainty factors: Future-shaping factors that are hard to predict and often external, requiring businesses to adapt, e.g. new technology or changes in foreign trade restrictions.
The interrelation of factors: Factors can influence each other, creating a ripple effect - for instance, a general factor like a pandemic can affect business environments, leading to specific and uncertain factors.
Changing factors: Constant evolution of the business landscape will impact sectors differently. Rapid changes, especially in dynamic sectors like technology, require close attention to ensure the business adapts in time
A chain reaction of factors: Causal relationships between factors can be complex. A small change in one factor may lead to a chain reaction, affecting various areas of the business and resulting in significant changes.
Distribution of factors: Factors are not evenly distributed. Businesses must adapt to external factors, as they may benefit some while being detrimental to others, creating variations in their impact.
Why is a business environment important?
Business leaders and managers need to understand the business environment of their organisation so that they can respond to the conditions appropriately. Here are four key reasons why understanding a business environment is essential:
Supports and improves performance: Understanding the business environment enables development of proactive strategies, allowing companies to adapt and optimise performance
Improves strategic planning and organisation: Maintaining awareness of the business environment facilitates strategic planning, enhancing organisational preparedness for future changes and expansion
Identifies business opportunities: Continuous analysis of the dynamic business environment uncovers growth opportunities, enabling the creation of new products or services to capitalise on market gaps
Highlights business threats: Recognising and analysing potential threats, such as new competitors or profit losses, allows businesses to address challenges and remain competitive in the market proactively
External business environment factors
Professionals tend to break down business environment factors into internal and external. Here is a list of the top external factors that shape a business environment from the outside. It's often referred to as PESTLE:
Political factors
Businesses are subject to the influence of political decisions and changes, such as those affecting international relations and regulatory frameworks. Political choices can affect businesses both positively and negatively. For example, the political climate in one country may help a business to flourish, while in another it may impose restrictions on business activities.
Companies affected by political decisions must amend their processes to comply with new legislation, or review them to ensure minimal risk to the business's future.
Economic factors
Economic factors can also have a significant impact on a business. The state of the economy plays a vital role in every way, from staff well-being to the company's ability to operate. For example, economic downturns often bring rising unemployment, which means businesses may have to work harder to sustain revenue streams.
Economic features which affect a business environment include the rate of inflation, supply and demand, and economic policies, such as import-export, tax structure, and public expenditure.
Social factors
Every society has its unique culture and social norms. A company must be cognisant of these factors to understand their business environment. Social factors are important because they affect how a business presents its brand and engages with its regional or global customer base.
Examples of how social factors affect a business environment include catering to specific preferences and expectations of underrepresented groups and businesses entering markets that are becoming more Westernised.
Social factors that affect a business environment can be grouped into culture and traditions, social trends, and values.
Technological factors
Technological developments affect every sector. You only need to look at the advent of ChatGPT and AI to see the impact of tech advancements. Businesses employing these technologies for customer service, data analysis, or content creation gain a competitive edge, while those resistant to adaptation may face hurdles.
Similar to the impact of GPS integration on personal car devices, companies need to strategise to address challenges posed by technological advancements. The ability to embrace and integrate such technological developments is crucial in determining a company's position in the evolving business environment.
Legal factors
Businesses globally must conduct themselves under the law. Legal factors shape businesses differently - it depends on their legal jurisdiction.
One sub-section of legal factors is compliance and regulations, such as product safety standards and employment law. Another is intellectual property law, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights. Then, there are contractual obligations, such as relationships with suppliers and customers. Taxation, environmental, data protection, privacy, and antitrust and competition laws also impact business environments.
Environmental factors
The natural environment significantly influences business environments. For example, severe weather events like floods can reshape a business landscape and require a change in operations.
In today's context of heightened environmental concerns, businesses are increasingly adapting to be more environmentally friendly. For instance, the government's net-zero carbon targets by 2050 mandate businesses to participate actively in sustainable practices, fostering a shift toward eco-friendly operations and influencing the overall business environment.
Internal business environment factors
In addition to external factors, internal factors affect a business environment. The most common factors include:
Organisation structure
The business's organisational structure influences all aspects of a business environment because it dictates how decisions are made. A business with a flat organisational structure tends to have a more laissez-faire approach to work, whereas a company with a functional organisational structure is more hierarchically rigid.
Value framework
A company's values profoundly impact its environment by shaping its culture, guiding decision-making, and influencing interactions with employees and stakeholders. Values are the foundation of a company's identity and set the standard for behaviour, corporate culture, products, and services. When aligned with the broader business environment, values help businesses to thrive.
Overarching vision and goals
A long-term, overarching vision and achievable goals shape a business environment because they inform every critical decision in the company. Guiding principles provide a clear direction, influencing strategic decisions, resource allocation, and organisational priorities. A well-defined vision fosters alignment among employees, creating a shared sense of purpose and motivation.
Technology and technological advancements shape business environments internally, too. Harnessing new tech in the right way can unlock a whole host of benefits. For example, technology facilitates data-driven decision-making, enabling companies to respond swiftly to market changes.
Technology empowers businesses to stay competitive by embracing automation, artificial intelligence, and digital solutions, influencing how tasks are executed, products are developed, and services are delivered. It becomes a driving force that modernises internal operations and positions the business for sustained growth and resilience in a dynamic landscape.
Resource management
Effective resource management directly influences operational efficiency, productivity, and overall competitiveness. Resources could include human capital, financial assets, or physical assets. If business leaders and managers efficiently allocate resources, the business's capabilities can be fully realised, directly impacting the broader business environment.
Operational processes
Operational processes significantly shape a business environment. Well-optimised internal workflows contribute to cost-effectiveness, timely product or service delivery, and enhanced customer satisfaction. In contrast, inefficient or outdated operational processes can lead to delays, errors, and increased costs, negatively impacting the overall business environment.
The continuous improvement and innovation of operational processes are essential for businesses to stay competitive.
Knowledge of business environments is precious in the workplace, especially if you're in a leadership position. Check that you're effectively emphasising your understanding of business environments and your experience in reacting to changing factors on your CV by submitting your CV for a free review .
Recommended reading:
How to develop a winning business strategy (with examples)
What is the first mover advantage? Definition, examples, advantages, and disadvantages
How to perform a situational analysis (and the benefits)
Related Articles:
Professional email salutations that work (with examples)
What is an employee evaluation and how do I conduct one?
Management styles: a guide for every leader
See how your CV stacks up.
Career Advice Newsletter
Our experts gather the best career & CV tips weekly. Delivered weekly, always free.
Thanks! Career advice is on its way.
Share this article:
Let's stay in touch.
Subscribe today to get job tips and career advice that will come in handy.
Your information is secure. Please read our privacy policy for more information.

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Business Environment Analysis? A Detailed Comparison
Explore this blog and learn the process of Business Environment Analysis and identify the key factors influencing the success of a business. This strategic analysis helps pinpoint external and internal factors that impact a company's performance, including market trends, competition, economic conditions, and regulatory factors.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- BCS Foundation Certificate in Organisational Behaviour
- BCS Foundation Certificate in Architecture Concepts and Domains
- BCS Business Analysis Diploma Oral Preparation Workshop
- Certified Agile Business Analyst Professional (CABAP)
- BCS Practitioner Certificate in Digital Product Management Training Course

Business Environment Analysis is a systematic process for determining how a business can run effectively and achieve its targets. It involves identifying the different pillars affecting business performance, such as the economy, which helps shape society and politics, technological development, law, and the environment.
This results in pointing out the strengths and weaknesses of market situations and assisting in developing strategic and decision-making plans. Learning how to read the dynamics of the market is critical for businesses. Read this blog further to learn how Business Environment Analysis can help your business succeed by understanding the organisation's strengths and weaknesses.
Table of Contents
1) What is Business Environmental Analysis?
2) Importance of Business Environment Analysis
3) Purpose of Business Environmental Analysis
4) Types of Business Environment Analysis
5) Steps involved in Business Environmental Analysis
6) PESTLE Model of Business Environment Analysis
7) Advantages of conducting Business Environmental Analysis
8) Conclusion
What is Business Environmental Analysis?
Business Environmental Analysis is a strategic tool which helps companies know how external and internal environment factors influence their operations and performances. It, as a function, is used to examine things like economic trends, technological advancements, regulatory landscapes, competitive dynamics and social changes that can influence the business's ability to meet its objectives.
This analysis spotlights a company’s distinctive features, areas for improvement, market weak spots, and threats to the organisation. Such discoveries can help derive strategies that exploit strengths while eliminating weaknesses. It’s a preventive method that would guarantee the flexibility, competitiveness, and relevance of a business in a dynamic economy.

Importance of Business Environment Analysis
Business Environment Analysis is crucial to do business because it reflects the overall environment of an organisation clearly showing the company what it entails. It serves as a preventive and an innovative measure because it assists firms to foresee changes, recognise new tendencies, adjust to the emerging market trend and avoid possible risks.
By means of this analysis, companies can wind up how external factors affect their strategic objectives and operational planning. This allows them to perform well in the way they deploy resources.
It makes a business active, flexible, sustainable, and a powerful means of preparation for the unexpected and targeted dealing with fierce rivalry. Since the Analysis of the Business Environment forms the base for strategic planning, sustainable growth, and risk management of the business, it cannot be overlooked.
Purpose of Business Environmental Analysis
Let us now discuss the purpose of Business Environmental Analysis:
1) Recognising opportunities
Recognising business opportunities that may take longer to become noticeable is the primary goal of the Environmental Analysis of a Business. Through an in-depth analysis of market data such as trends, customer tastes, technology, and law, businesses can learn about opportunities for growth and innovation. This upfront movement makes companies leverage early opportunities to create a significant advantage and opens the chance for them to expand to new markets/segments for growth.
2) Managing threats
Identifying and managing potential risks is also an essential purpose of Business Environmental Analysis. External factors such as competitive responses, economic fluctuations, and changes in legislation create serious risks for the operations.
Through identifying these risks beforehand, enterprises may develop alternative plans, complement their product lines or modify their strategies to maintain continuity of their operations and profitability in the long run.
3) Crafting strategies
The insights delivered by Business Environmental Analysis are valuable for developing an intelligent and successful business strategy. Internal and external business environments understanding enables connecting company's strengths and weaknesses with the available opportunities and threats. This alignment is important for the setting of clear objectives, sound strategic decision making, and the allocation of resources wisely that can deliver intended results.
4) Strengthening competitive edge
Business Environmental Analysis is a major tool that helps a company increase its competitive advantage. Through an active and ongoing assessment of the wider business environment, companies will be able to stay ahead of emerging trends and needs of customers, innovate in response to changing factors and differentiate themselves from their competitors. Such successive series of adaptation to the changes is key to remaining relevant in the market and having a long-term competitive advantage.
Elevate your career with the BCS Advanced International Diploma in Business Analysis Course — register now to become a certified Business Analysis expert!
Types of Business Environment Analysis
These are the four different types of Business Environment Analysis; let’s have a close look at each one of them:
1) Internal environment
The Internal Environment Analysis encompasses considerations that could weaken the organisation to fulfil the customers' needs and its business objectives. This would entail an appraisal of the organisation's culture, sub-culture, physical resources, human resources, and technology.
The focus is to pinpoint factors within the organisation that could hinder its operational efficiency and progressive strategic orientation. Major elements usually scrutinised include the type of leadership, morale of employees, operating processes, and IT capabilities that will help them harness their strengths and rectify their weaknesses.
2) External environment
External Environment Analysis involves examining factors outside the company that could affect its performance and strategic options. This analysis is typically split into two further categories:
a) Microenvironment: A microenvironment is made up of those elements that influence business and are within the small circle of interests of the business, which can be the competitors, suppliers, distributors, and industry trends. Such an analysis allows companies to be aware of the existing competition, clients, and the market by studying the client's needs and preferences, as well as the supply chain dynamics.
b) Macro environment: Macro environment determines everything in society and is not limited to the organisation. This includes PESTEL factors: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal framework. Understanding the factors, the organisation attains the ability to identify major trends and changes in the international business environment and thus, long-term strategy ability is provided.
Steps involved in Business Environmental Analysis
If you want to conduct a Business Environmental Analysis, then these are the steps that are involved:
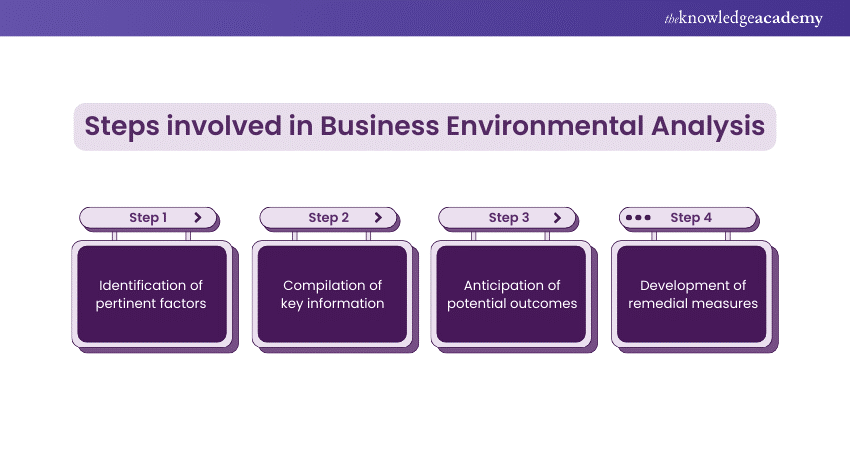
Step 1: Identification of pertinent factors
The first step in this process is the identification of aspects that are directly responsible for shaping the organisation's growth process. Here, the team differentiates between the inner and the outside environment, addressing the micro and macro factors.
It requires a deep knowledge of that business, industry, and the whole economic and social context in which it operates. Identifying those determinants correctly is consequential for the next business process analysis and selecting the most powerful factors that impact the business.
Step 2: Compilation of key information
After the critical factors have been isolated, the next stage involves the collection of information pertinent to these factors. The focus in this case is on the collection of data on market tendencies, competition strategies, regulatory changes, technology innovations and socio-economic conditions, to mention but a few.
The exercise aims to compile exhaustive and fresh information to serve as a base for further analysis. This step typically involves information from multiple sources, such as market studies, industry reports, financial documents, and legal papers.
Step 3: Anticipation of potential outcomes
Of utmost importance is decision-making with the help of the existing and anticipated current and forecasted environment. This includes examining the collected data to forecast how the identified factors will be modified and what kind of consequences the changes could be.
Scenarios planning can be useful in the frame, helping entrepreneurs to investigate possible scenarios and then make a connection among different elements in complex ways. The aim is to envisage possibilities and hazards that could be derived from the ever-changing business environment.
Step 4: Development of remedial measures
The final level is to develop the remedial measures, or the decision-making strategies based on the expected results. It refers to the construction of strategies which benefit from the insights obtained through the analysis, minimise the risks identified and support the overall objectives.
a) Diversifying product lines
b) Entering new markets
c) Adjusting marketing strategies
d) Investing in new technologies
e) Altering operational processes
The key is to formulate flexible and resilient strategies that enable the organisation to effectively adapt to changes in the business environment.
Unlock the power of agility in business- join now for our BCS Foundation Certificate in Agile Course !
PESTLE model of Business Environment Analysis
The PESTLE model is a comprehensive business framework used to analyse the external macro-environment that impacts an organisation's operations. It examines the following six key dimensions:
Political
The Political side looks into the part where government policies can affect business operations. Instability of government, for example, in a country or its tax policies and labour laws can be detrimental to a business. Trade restrictions can also affect a business's operation.
This dimension is very significant for establishing the ways in which political decision-making and changes in legislative structure deteriorate the business environment, operational ability and strategic decisions of businesses.
Economic
On an economic dimension, an organisation looks into the economic factors that might be influencing its profitability. Such types of fluctuations can be noted in interest rates, exchange rates, inflation rates, economic growth dynamics, unemployment indices, and fiscal policy mechanisms.
Reading the indicators which are present within the economic environment helps business foresee the possible developments, plan their budgeting and strategic evolution to avoid being misled into making wrong decisions on expansion, putting a price on their product and controlling the costs.
Social
Social situations are related to demographic shifts, cultural practices, lifestyle characteristics and persons attitudes towards a particular product or services. This component gives firms a good perception of the social background in which they operate to ensure that they can fine-tune goods and services, as well as market strategies, in line with changing needs and preferences of their targeted market.
Technological
The tech components include the speed of technology change, technology implementation, the advancement of technologies, R&D activities, and automation. Examining this element shows us the constant search for new technological opportunities, careful consideration of how the technologies affect operations, and finally, responding to the developing technologies by increasing efficiency and offering new products to the customers.
Legal
The legal dimension is typically looking at how laws and regulatory impact the conduct of the business. This is more in employment laws, health and safety act, consumer protection law, and environment regulation. Having the legal environment in mind is essential as businesses first establish compliance, minimise legal risks, and investigate the business-specific legal system in the host country.
Environmental
Environmental factors cover the effect of the physical environment and climate change on business operations. Such regulations include ecological requirements, sustainable operation, and the people’s recognition towards environmental issues like no waste issues.
Companies, on the other hand, assess this dimension to create an environmentally sustainable culture in their business settings, adapt to environmental challenges, comply with regulations, and integrate sustainability into their operational and corporate social responsibility strategies.
Advance your skills in delivering value and ensuring success – register now for our BCS Practitioner Certificate in Benefits Management and Business Acceptance Course !
Advantages of conducting Business Environmental Analysis
Conducting a Business environmental analysis offers significant advantages to businesses by providing a clearer understanding of the market dynamics, helping to mitigate risks, and facilitating strategic planning:
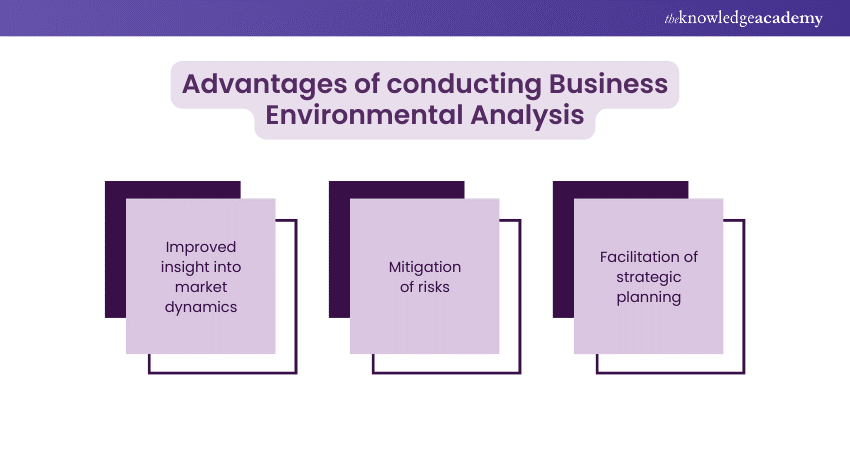
Improved insight into market dynamics
Business Environmental analysis enhances understanding of market dynamics, enabling businesses to detect trends, consumer needs, and competitive actions. This knowledge supports product development, market positioning, and competitive anticipation, which are vital for relevance and success in evolving markets.
Mitigation of risks
Business may find out, and manage operational, financial and growth risks by analysing the external environment it is working in. Firms can implement resistive methods such as aforementioned understanding of the risks from regulations, competition, and socio-economic shifts, and facilitating the acceptance of volatility in their organisation.
Facilitation of strategic planning
The core of strategic planning lies in environmental analysis, that is, data-driven facts for better-informed decisions. It guides businesses to link strengths to opportunities and resolve weaknesses, such that strategic goals are pertinent, resources are optimally allocated, and the company is dynamic to changes in markets.
Conclusion
We hope this blog has helped you understand the importance of Business Environment Analysis and why every organisation must conduct this process. Through this process, organisations can figure out their strengths and weaknesses, which can help them progress towards success.
Drive transformative change effectively—register for the BCS Foundation Certificate in Business Change Course today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Factors affecting the Business Environment include economic conditions, political and legal frameworks, technological advancements, social and cultural trends, and environmental concerns.
Analysing the business environment is crucial for identifying opportunities and threats, understanding market dynamics, and making informed strategic decisions. It enables businesses to adapt to changes, capitalise on emerging trends, and maintain competitiveness in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Analysis Courses , including BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice Course, BCS Practitioner Certificate in Requirements Engineering Course, and BCS Practitioner Certificate in Modelling Business Processes Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Business Analysis .
Our Business Analysis blog covers a range of topics related to Business Analysis, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Analysis skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Thu 16th May 2024
Sat 18th May 2024
Thu 13th Jun 2024
Thu 11th Jul 2024
Thu 8th Aug 2024
Sat 10th Aug 2024
Thu 12th Sep 2024
Thu 24th Oct 2024
Sat 16th Nov 2024
Thu 21st Nov 2024
Thu 12th Dec 2024
Thu 9th Jan 2025
Thu 6th Feb 2025
Thu 6th Mar 2025
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 15th May 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 10th Jul 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Business Environment: Definition, Features, Types, Importance, and Strategies
Table of Contents
What is Business Environment?
The business environment encompasses all the factors, both internal and external, that directly or indirectly impact a company’s operations. In other words, the business environment is where the business organizations operate.
It constitutes employees , customer needs, supply and demand, management , clients, suppliers, government activities, technological innovations, social and market trends, and economic changes. These elements directly or indirectly influence how a company functions and the overall situation it faces.
The business environment creates an ecosystem where resources, people, and strategies unite to manage operations and deliver solutions to clients. By understanding this environment, businesses can identify new revenue opportunities, enhance planning , and improve performance and profitability.
However, it is crucial for companies to adapt to the dynamic business environment to thrive in the long term.
Characteristics of Business Environment
The business environment consists of a set of conditions and factors that affect (directly or indirectly) the operations of companies. Broadly speaking the following includes its major features:
Dynamic Nature
The business environment is constantly evolving, with factors like social trends, economic conditions, and technological advancements driving changes. This ever-shifting landscape requires companies to adapt swiftly and embrace innovation to stay competitive.
Unpredictability
Due to its dynamic nature, the business environment is inherently uncertain. It’s challenging to foresee future events or their impact on business operations. Companies must remain agile and responsive to navigate unforeseen challenges.
Also Read: Principles of Effective Directing
The business environment consists of interconnected factors, making it complex and difficult to analyze. Understanding the interplay between economic, social, and political forces is essential for making informed decisions.
Susceptibility to Change
Even minor alterations in the environment can ripple across a company’s operations, affecting its performance and future prospects. Companies must anticipate potential disruptions and plan proactively.
Relative Nature
The business environment varies across regions, industries, and company sizes. Factors influencing one business may have different effects on another. Recognizing this relativity helps companies tailor their strategies accordingly.
Multi-Faceted Impact
Events or trends in the business environment can yield diverse consequences for different companies. A social change that presents an opportunity for one company might pose a threat to another. A fine understanding of the multi-faceted impact is vital.
Types of Business Environment
The business environment consists of two types – internal environment and external environment.
Internal Environment
The internal environment of a company comprises its own controllable factors, shaping the organization’s inner workings and overall culture. Let’s delve into the components that form this vital aspect:
- Organizational Structure: This defines how the company’s activities are directed, clarifying roles and responsibilities. It outlines the hierarchy, how tasks are assigned, and how information flows across different levels.
- Corporate Culture: The powerful fabric of shared values and norms among employees that sets the tone for the company. It shapes behaviors, attitudes, and the overall work atmosphere, fostering a sense of unity.
- Human Resources: The heart of the organization, consisting of employees and personnel. Their skills, dedication, and effectiveness drive the company’s success and determine its competitive edge.
- Vision, Mission, and Objectives: The guiding compass that defines the company’s purpose, aspirations, and future goals. It helps align efforts toward a common direction.
- Physical Resources and Technology: Tangible assets like facilities and equipment, coupled with technical capabilities, influence the company’s competitive capacity and its ability to adapt to changing demands.
Also Read: Management Hierarchy
External Environment
External environment refers to the environment outside of the organization. And, the factors of the external environment are uncontrollable to the management . The external environment also consists of two – macro and microenvironment.
Micro Environment:
The microenvironment of a company encompasses the immediate external factors that directly impact its day-to-day operations and performance. These factors are closely related to the company and can be influenced to some extent. Let’s explore its components:
- Customers: The lifeblood of any business, customers are at the heart of the microenvironment. Understanding their needs, preferences, and expectations is crucial for crafting products and services that resonate with their desires.
- Competitors: Rival players in the market who target a similar customer base and offer similar products or services. Analyzing competitor strategies and strengths helps companies fine-tune their own approach and gain a competitive edge.
- Suppliers: Vital partners providing the necessary resources for the company’s operations. Building strong supplier relationships ensures a steady supply of goods and services, impacting the company’s efficiency and reliability.
- Intermediaries: Entities facilitating the distribution and delivery of the company’s offerings to the end customers. Collaborating with effective intermediaries streamlines the distribution process and enhances market reach.
- Partners: External entities like advertising agencies, market research organizations, and consultants who engage in business transactions and cater to customer needs. Partnering with the right entities can add value to the company’s offerings and expand its capabilities.
- Public: Groups with a vested interest in the company’s operations or those who can influence its ability to serve customers. Public perception and sentiment can impact the company’s reputation and brand image.
Macro Environment:
The macro environment of a company encompasses the broader external factors that influence its overall business landscape. The macro environment is also called PESTLE analysis. Let’s explore its components:
- Political Factors: The impact of government policies, stability, and regulations on the business. Political decisions can influence market conditions, trade relations, and business operations.
- Economic Factors: The overall economic conditions of the country or region in which the company operates. This includes factors like economic growth, inflation rates, exchange rates, and consumer spending patterns.
- Social Factors: The demographic and societal aspects that shape consumer behavior and preferences. These factors include population trends, cultural attitudes, lifestyle choices, and social values.
- Technological Factors: The advancements and innovations in technology that affect the industry and the company’s operations. Keeping up with technological changes is crucial for staying competitive.
- Legal Factors: The legal framework governing business operations, including industry-specific regulations, labor laws, and intellectual property rights.
- Environmental Factors: The impact of the natural environment and societal concerns about sustainability and eco-friendliness. This includes climate change, environmental regulations, and consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Importance of Understanding Business Environment
The business environment plays a crucial role in shaping a company’s success and influencing its performance. Let’s explore eight key reasons why understanding and adapting to the business environment is vital for organizations:
Strategic Planning
By understanding the business environment, companies can develop informed strategic plans . Understanding market trends, customer preferences, and competitive landscapes enables organizations to make well-informed decisions to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks.
Identifying Opportunities
The business environment helps identify new revenue streams and growth prospects. Recognizing emerging trends and consumer demands allows organizations to innovate and offer products or services that meet evolving customer needs.
Risk Management
Assessing the business environment aids in identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities. Companies can proactively address risks, such as economic fluctuations or changes in regulations, to safeguard their operations and assets.
Read Also: Modern Management Theory
Enhancing Performance
A favorable business environment fosters employee engagement and productivity. When employees understand the market dynamics and perceive growth opportunities, they become more motivated and committed to achieving organizational goals.
Competitive Advantage
Understanding competitors and market conditions gives companies a competitive edge. Organizations can differentiate themselves by offering unique value propositions that resonate with customers in the current business landscape.
Long-Term Sustainability
A sound understanding of the business environment enables companies to plan for the long term. By aligning their strategies with market trends and customer expectations, organizations can ensure sustainable growth and longevity.
Customer Satisfaction
The business environment helps organizations anticipate customer needs and preferences. Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and advocate for the brand, contributing to increased sales and profitability.
Adaptability and Resilience
The business environment is ever-changing, and organizations must adapt to survive. Embracing flexibility and resilience allows companies to weather challenges and remain relevant in the face of disruptions.
How To Adapt To Changing Business Environment?
Adapting to a changing business environment is crucial for companies to thrive in the ever-evolving market. Here are six strategies to effectively adapt to it.
Read Also: How To Manage Diversity in the Workplace ?
Continuous Learning
Encouraging a culture of continuous learning is key to adapting effectively. Employees should be open to acquiring new skills, staying updated on industry trends, and embracing innovative approaches. Investing in training programs and workshops empowers teams to tackle new challenges with confidence.
Flexibility and Agility
Being flexible and agile allows companies to respond instantly to changes in the business marketplace. This means staying receptive to feedback, adjusting strategies as needed, and being open to exploring new opportunities. An agile organization can pivot quickly to seize emerging prospects.
Customer-Centric Approach
Prioritizing customer needs and preferences ensures that companies remain relevant in the evolving market. Gathering feedback, conducting market research, and actively listening to customers help companies understand shifting demands and tailor offerings accordingly.
Digital Transformation
Embracing digital technologies is vital for thriving in today’s fast-paced world. Companies must integrate digital solutions into their operations, such as e-commerce platforms, digital marketing, and data analytics, to enhance efficiency and customer engagement.
Collaboration and Networking
Building strategic partnerships and networking with industry peers enables companies to access valuable resources and knowledge. Collaborating with like-minded organizations fosters mutual growth and provides insights into best practices.
Resilience and Risk Management
Preparing for potential disruptions and uncertainties is essential for staying resilient. Companies should conduct risk assessments, develop contingency plans, and diversify supply chains to mitigate the impact of unforeseen events.
Read Next: Importance of Management To Business
By profession, Sujan Chaudhary is a BBA (Bachelor in Business Administration) graduate, and by passion a blogger. He loves to share his business knowledge with the rest of the world. While not writing, he will be found reading and exploring the world.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar

Business Jargons
A Business Encyclopedia
Business Environment
Definition : Business Environment means a collection of all individuals, entities and other factors, which may or may not be under the control of the organisation, but can affect its performance, profitability, growth and even survival.
Every business organisation operates in a distinctive environment, as it cannot exist in isolation. Such an environment influence business and also gets affected by its activities.
Salient Features of Business Environment

- Dynamic : The environment in which the business operates changes continuously because there is a wide variety of factors that exist in the environment, causing it to change its shape and character.
- Complex : There are many forces, events and conditions that constitute business environment, arising from various sources. So, it is a bit difficult to understand the relative influence of a particular factor, on the operation of the organisation.
- Uncertain : Uncertainty is an inherent characteristic of the business environment because no one can predict what is going to happen in future.
- Multi-faceted : A single change in the business environment, can be viewed differently by different observers because their perceptions vary.
- Far-reaching Impact : The survival, growth and profitability, of a business enterprise, depends largely on the environment in which it exists. A small change in the environment has a far-reaching impact on the organisation in different ways.
- Relative : The notion of a business environment is relative since it varies from one location to another.
Components of Business Environment

- Value System
- Vision and Mission
- Corporate Culture
- Human Resources
- Labor Union
- Micro Environment : The immediate periphery of the business that has a continuous and direct impact on it is called Micro Environment. It includes suppliers, customers, competitors, market, intermediaries, etc. which are specific to the business.
- Macro Environment : Macro Environment, is one such environment that influences the functioning and performance of every business organisation, in general. It comprises of the demographic, socio-cultural, legal, political, technological, and global environment.
All business enterprises, functions within an environment, called as the business environment. An individual business firm survives and grows within the periphery of its environment.
A firm is only a part of a big environment, and so there are only a few factors which are under the control of the firm.
So, the firm has no other option, but to respond and adapt accordingly. If business persons possess a good understanding of the business environment, they can easily recognise, analyse and react to the forces that affect the firm.
Related terms:
- Marketing Environment
- Macro Environment
- Micro Environment
- Business Ethics
- Internal Environment
Reader Interactions
Suman Pandit says
January 31, 2020 at 7:12 pm
Nice Article.
ishika says
September 25, 2020 at 7:32 pm
helped a lot
Julien Nachinsambwe says
September 6, 2023 at 10:43 pm
Nice information
March 27, 2021 at 10:08 pm
Thanks alot for your help
Richard . U . Noliwafu says
April 5, 2021 at 5:42 pm
Thanks, very nice, straight forward and understandable.
Slindile says
May 31, 2021 at 6:32 pm
It is understandable ,and it helped me a lot.
June 26, 2021 at 11:53 am
Very Useful and understandable
abdul qadir says
October 6, 2021 at 4:00 pm
Very nice article
October 18, 2021 at 4:43 pm
Usefull and understanding
S.Divya Pillay says
December 26, 2021 at 11:29 am
Thank you! it helped me a lot.
Yubraj Gautam says
November 4, 2022 at 12:24 am
Got a Clear Information of Business Environment Introduction
January 26, 2023 at 10:53 pm
Its an better way to understand the concept . Thank you..!
sony rajan says
July 21, 2023 at 12:49 pm
SO THANKFUL FOR THIS NOTE!
August 15, 2023 at 8:40 pm
Sonia Edwin says
September 27, 2023 at 12:30 pm
This is a very helpful article. It helped me alot. Thank you
vinod kumar Nalavadi says
December 26, 2023 at 10:16 am
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?

15 Ways to Advertise Your Business in 2024
What Is a Proxy Server?
How To Get A Business License In North Dakota (2024)
How To Write An Effective Business Proposal
Best New Hampshire Registered Agent Services Of 2024
Employer Staffing Solutions Group Review 2024: Features, Pricing & More
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
Kelly Main is a Marketing Editor and Writer specializing in digital marketing, online advertising and web design and development. Before joining the team, she was a Content Producer at Fit Small Business where she served as an editor and strategist covering small business marketing content. She is a former Google Tech Entrepreneur and she holds an MSc in International Marketing from Edinburgh Napier University. Additionally, she is a Columnist at Inc. Magazine.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary

Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

A Comprehensive Guide to Business Environmental Analysis: What is It, and Why is It Important?
- Ossian Muscad
- August 28, 2022
- No Comments

Last Updated on January 3, 2024 by Ossian Muscad
Every business exists in an environment, and it’s important to understand that environment to be successful. Unfortunately, businesses sometimes tend to ignore this importance, leading to strategic planning failures. By getting to know the business environment and conducting regular environmental analysis, businesses can make the right decisions to stay ahead of the competition.
But what exactly is environmental analysis, and how do you conduct one? This article will discuss environmental analysis, its importance, and how to use it to improve your business’ strategic planning.
What is Business Environmental Analysis?
Business environmental analysis is studying the external factors that affect a business. This includes things like the political landscape, the economic conditions, the technological environment, and more. By understanding these factors, a company can develop strategies to optimize its performance within this context.
This environmental analysis examines industry and organizational factors that positively or negatively affect the business. By determining short-term and long-term impacts, organizations can readily respond to them when they appear.
Purpose of Environmental Analysis
An environmental analysis helps organizations define factors that can influence their business operations. Business leaders can make better decisions about moving forward by assessing and weighing these factors.
Additionally, environmental analysis can help business leaders anticipate changes in the market and adjust their strategies accordingly. Apart from that, here are other reasons why environmental analysis is essential for businesses:
- Identifying Opportunities: Environmental analysis can help businesses spot emerging trends and changes in the market. This allows them to seize new opportunities before their competitors do.
- Mitigating Threats: By understanding potential threats in the environment, businesses can design strategies to mitigate these risks, avoiding potential pitfalls.
- Formulating Strategies: Environmental analysis provides critical insights that can shape a company’s strategic planning process, ensuring alignment with the external environment.
- Enhancing Competitive Advantage: By understanding the external environment better than competitors, businesses can leverage this knowledge for a competitive advantage.
- Anticipating Change: Environmental analysis helps businesses anticipate and prepare for changes in the market, regulatory landscape, or technology trends.
Elements of Environmental Analysis
Two main elements of a business environmental analysis are internal and external factors.
Internal Factors
Internal factors are elements within a business that can influence its operation and success. These factors are primarily under the control of the business and can be altered or manipulated according to business needs. Here are some key internal factors:
- Resources: This includes all tangible and intangible assets a company has at its disposal to use in producing goods or services. Tangible resources include physical assets such as infrastructure, raw materials, and human resources. Intangible resources encompass elements like brand reputation, intellectual property, and corporate culture.
- Capabilities: A company’s capabilities are its skills or competencies in deploying resources to achieve business goals. It involves marketing effectiveness, production efficiency, technological innovation, customer service, etc.
- Management and Organization Structure: The organizational structure and quality of its management team can significantly impact a company’s operation. Effective leadership and a well-defined structure can facilitate smooth decision-making, coordination, and control, contributing to business success.
- Business Processes and Operations: These involve the methods and procedures for coordinating and conducting business activities. Efficient processes can enhance productivity and customer satisfaction, leading to higher profitability.
Identifying and evaluating these internal factors through an environmental business analysis can help businesses leverage their strengths, address weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and ward off potential threats.
External Factors
External factors are elements outside the control of a business that can significantly influence its performance. Recognizing and understanding these external factors can help a business to react and adapt to changing circumstances. Here are the key external factors:
- Political Factors: These include government policies, regulations, and legal issues that define formal and informal rules under which the firm must operate. Political stability, tax guidelines, trade regulations, and employment laws all influence the business environment.
- Economic Factors: Economic factors are determinants of a country’s economic performance that directly impact a company and have resonating long-term effects. These include inflation rates, interest rates, foreign exchange rates, economic growth patterns, and unemployment rates.
- Sociocultural Factors: These factors encompass the societal and cultural forces that shape consumer behavior. They include population growth rates, age distribution, attitudes towards health, and cultural trends.
- Technological Factors: Technological changes can create new industries and market opportunities. A company’s ability to manage its IT infrastructure might also affect its ability to compete and its efficiency.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental factors include weather, climate, and climate change. These factors can especially affect industries such as tourism, farming, and insurance.
- Legal Factors: These are related to the legal environment in which firms operate. They include consumer law, employment law, antitrust law, discriminatory law, and copyright law.
By evaluating these external factors during an environmental business analysis, businesses can develop effective strategies that align with their operating environment, thereby improving their chances of success.
Business Environmental Analysis Process
A business environmental analysis systematically uncovers factors affecting your business and its operations. When there aren’t any fixed and definitive rules on doing an environmental assessment, the following steps can guide you into making the most out of this process:
Step 1: Identify the Environmental Factors
Every environmental analysis will need a list of the factors that will undergo evaluation. These factors will depend on the business and its specific goals for conducting the analysis. This list should include micro- and macro-environmental factors that have short- and long-term effects on business.
For example, a company selling organic products might consider environmental factors such as changing consumer preferences, government regulations on organic labeling, and the availability of raw materials.
Step 2: Collect Further Information About These Factors
After outlining which factors will be included in the analysis, the next step is to conduct research and gather more information about each of these factors. This can be done through desk research, surveys, interviews, and focus groups . Again, you can utilize various sources to ensure accurate, relevant, and up-to-date information.
For instance, organic product companies may gather data on consumer buying patterns through surveys and consumer behavior reports. They may also research government regulations and consult with suppliers to understand the availability of raw materials.
Step 3: Check the Competitors
When conducting an environmental analysis, your research isn’t limited to your organization’s business standing. It also involves understanding your competitors and how they’re faring in the business landscape. This will give you a better idea of where you stand and what you must do to stay ahead of the competition.
For example, the organic products company may analyze its competitors’ marketing strategies, product offerings, and financial performance to identify potential threats or opportunities.
Step 4: Determine the Impacts on the Organization
Once you’ve collected all the relevant information, it’s time to determine how these environmental factors will affect your business. This is where you need to weigh the risks and opportunities of each business situation. Doing so will help you develop strategies to take advantage of the opportunities and minimize the risks.
For instance, the organic products company may diversify its product offerings and invest in sustainable raw materials to capitalize on changing consumer preferences and government regulations. They may also implement cost-cutting measures to mitigate potential risks of rising production costs due to the limited availability of raw materials.
Step 5: Formulate an Effective Strategic Plan
The final step is creating a strategic plan to guide your business decisions and actions. This plan should be based on your insights from the environmental analysis. It should also be aligned with your business goals and objectives. Having a well-informed and strategic plan allows your organization to stay adaptable and competitive in the ever-changing business environment.
For example, based on their environmental analysis, the organic products company may decide to expand their market reach and invest in innovative technologies for sustainable packaging. They may also set goals for increasing sales and reducing costs.
Types of Environmental Analysis Techniques
There are two environmental analysis Techniques: PESTLE analysis and SWOT analysis. These methods help organizations assess their strategic positions based on the business environment and a wide range of internal and external factors.
PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE analysis is a framework that helps organizations assess the factors that can influence their business on a larger scale outside the organization. It provides essential insights into the market status based on relevant trends concerning the market, technology, customers, and more. PESTLE has six key elements:
Political factors refer to government policies, regulations, and laws that regulate business operations. It is important to conduct business in any country. Other political factors include:
- Local, federal, and state policies.
- Tax regulations
- Trade rules
- Safety regulations
- Governmental stability
Economic factors are determinants of a country’s economic performance that directly impact the organization. By assessing the economic factors, organizations can anticipate potential opportunities and challenges. These include:
- Unemployment rates
- Inflation rates
- Economic growth rates
- Interest rates
- Foreign exchange rates
Social factors reflect the society in which an organization operates. It helps organizations to understand the evolving customer needs, preferences, and behaviors. These include:
- Attitudes and opinions towards health and work-life balance
- Key demographic trends
- Consumer buying patterns
- Cultural values
- Lifestyle trends
Technological
Technology is a significant driver of change in the business environment. It has revolutionized how businesses operate, compete, and interact with customers. Key technological factors include:
- Research and development areas
- Technological incentives
- Up-and-coming technologies
- Disruptive technologies
- Technology transfer speeds
Legal factors are the laws and regulations that govern businesses. Organizations must comply with these laws to operate legally and avoid penalties. Legal factors include:
- Employment laws
- Product regulations
- Health and safety regulations
- Antitrust laws
- Environmental regulations
Environmental
Environmental factors encompass the natural environment in which an organization operates. These factors can impact industries such as tourism, agriculture, and energy. Environmental factors include:
- Energy consumption regulations
- Environmental policies
- Climate and weather conditions
- Sustainability efforts
- Natural disasters
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool organizations use to identify their Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats – hence the acronym SWOT. The technique provides a framework to evaluate an organization’s competitive position and understand how the business can leverage its capabilities to succeed.
Strengths refer to the positive internal attributes of an organization, including resources, capabilities, and advantages that give it a competitive edge over others. This can range from strong brand recognition and skilled personnel to a robust financial position.
Weaknesses are the internal factors that prevent an organization from realizing its full potential and might hinder its performance. Examples could include poor infrastructure, lack of skilled labor, operational inefficiencies, or outdated technology.
Opportunities
Opportunities include the external factors that an organization could exploit to its advantage. These include market trends, shifts in customer behavior, technological advances, or changes in government policies.
Threats involve external factors that pose challenges or risks to an organization. These could include competitive rivalry, regulatory changes, unfavorable economic conditions, or technological disruptions.
Through a SWOT analysis, an organization can gain a comprehensive understanding of its internal and external environments. Consequently, it can develop strategies that leverage strengths, mitigate weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and defend against threats. This can ultimately lead to increased competitiveness and success.
Benefits of Environmental Analysis
Environmental analysis provides a strategic advantage to organizations by offering insights into the factors that might impact their business. By understanding the internal and external environments, a business can make informed decisions and develop robust strategies to respond to potential opportunities and threats. Here are three crucial benefits of conducting an environmental analysis:
Enhanced Market Understanding
Through an environmental analysis, businesses can comprehensively understand their market, including customer needs, competitor strategies, and current trends. This information can be instrumental in identifying viable market opportunities and potential threats, allowing businesses to make proactive decisions. Moreover, it helps define the market segment, understand the competitive landscape, and set realistic targets.
Risk Management
Environmental analysis also plays a vital role in risk management. By identifying potential threats in the business environment, organizations can develop contingency plans and mitigate the impact of adverse events. This includes changes in regulatory laws, economic downturns, technological disruptions, or social and political instability.
Strategic Planning
Conducting an environmental analysis can significantly inform the strategic planning process. The insights gained can help set realistic goals, strategize market entry or expansion, optimize resource allocation, and make informed investment decisions. It also facilitates the development of strategies that leverage organizational strengths and mitigate weaknesses, thereby enhancing business competitiveness and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: what is the importance of a business environmental analysis.
A business environmental analysis is crucial as it helps organizations understand both their internal and external environments. This understanding allows them to identify opportunities and threats and develop strategies to leverage them and mitigate them. It facilitates informed decision-making and proactive planning.
Q2: In what ways does technology impact business environmental analysis?
Technology significantly impacts business environmental analysis by revolutionizing how businesses operate, compete, and interact with customers. Upcoming technologies, research and development, and technology transfer speeds are all crucial factors that need to be considered in an environmental analysis.
Q3: How do legal factors affect a business’s environmental analysis?
Legal factors, including employment laws, product regulations, health and safety regulations, and environmental regulations, affect a business’s environmental analysis by determining the legal constraints an organization must operate within. Non-compliance can lead to penalties and can negatively impact a company’s reputation.
Q4: How does the SWOT analysis process fit into business environmental analysis?
SWOT analysis is a part of the business environmental analysis that focuses on the organization’s internal factors (Strengths and Weaknesses) and external factors (Opportunities and Threats). It helps organizations understand their competitive position and leverage their capabilities for success.
Q5: Why is understanding social factors important in a business environmental analysis?
Social factors are essential in a business environmental analysis because they help organizations understand evolving customer needs, preferences, and behaviors. This can include attitudes towards work-life balance, buying patterns, cultural values, and lifestyle trends.
Q6: Does the size of a business influence the need for a business environmental analysis?
Regardless of the size, every business can benefit from conducting a business environmental analysis. It provides insights into the market, aids in risk management, and informs strategic planning. However, the scale and depth of the analysis may vary based on the size and nature of the organization.
Streamline Business Environmental Analysis with DATAMYTE
DATAMYTE is a quality management platform with low-code capabilities. Our Digital Clipboard , in particular, is a low-code workflow automation software that features a workflow, checklist, and smart form builder. This tool lets you streamline the process of conducting a business environmental analysis by automating data collection, analysis, and reporting.
DATAMYTE also lets you conduct layered process audits, a high-frequency evaluation of critical process steps, focusing on areas with the highest failure risk or non-compliance. Conducting LPA with DATAMYTE lets you effectively identify and correct potential defects before they become major quality issues.
With DATAMYTE , you have an all-in-one solution for quality management and environmental analysis, allowing you to make data-driven decisions for business success. Get in touch with us today to learn more about how DATAMYTE can help your organization thrive in a dynamic business environment!
While it may seem like a lot of work, business environmental analysis is crucial for any organization. With it, you can better understand your business’s strengths and weaknesses and the opportunities and threats of operating in a certain business environment.
So, if you haven’t tried implementing this process in your business yet, now is the time. Use the information and insights gained from a business environmental analysis to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and drive business growth. As the global marketplace continues to evolve, regularly conducting an environmental analysis will be essential for staying competitive and successful.
Related Articles:
- Floor Inspection Checklist: How To Create This Tool To Simplify Reporting
- Management of Change Procedure Template

- Implementation
- Case-Studies
- White Papers
- Knowledge Base
Experts in the Connected Factory

- 1-800-455-4359
- (763) 553-0455 ext. 1
- [email protected]
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Business Environment: Meaning, Definition, Components, Dimension, Importance, and Impacts

Meaning of Business Environment
The term “Business environment” represents the sum of all the individuals, institutions, competing organisations, government, courts, media, investors, and other factors outside the power of the business organisations but affects the business performance. Hence, changes in government economic policies, rapid changes in technology, changes in consumer tastes and preferences, increasing market competition, etc. are outside the business organisations' power but affect the business performance immensely.
For example, an increase in taxes by the government makes everything expensive in the market; technology changes may make the existing product obsolete, political uncertainty creates fear in the mind of investors, increase in competition in the market due to competitors may affect business profit, and changing in demand and preferences may increase the need for a new product and decrease the demand for old product.
Business Environment Definition
The term “Business environment " is the sum of all conditions, events, and influences that surround and affect business activities and growth.
Components of Business Environment
Internal - It combines the factors that exist within the company. These are –
Human resources
Value system
Vision and mission
Labour union
Corporate culture
External - An external Environment includes those outside factors that exercise an influence on a business’s operations. It is further classified into two segments.
Macro - Socio-cultural, political, legal, and global factors fall into this category.
Micro - This environment has a direct and immediate impact on a business. It consists of customers, investors, suppliers, etc.
Features of Business Environment
The business environment is the sum of all external factors that affect its growth.
The business environment includes both general and specific forces. Specific forces include investors, customers, competitors, and suppliers. These factors affect individual enterprises directly and immediately in their day-to-day working. General forces include social, political, legal, and technological conditions. The general forces affect the business environment individually.
The business environment is dynamic.
The business environment is highly uncertain.
The business environment is a relative concept as it differs from country to country and even region to region.
Dimensions of Business Environment
The dimension of the business environment refers to the sum of all factors, enterprises, and forces that constitute direct or indirect influence over business activities. Such five key elements are listed below.
Social Environment
It implies the tradition, culture, customs, and values of a society in which the business exists.
Tradition: In India, festivals like Diwali, Christmas, and Holi provide a financial opportunity for several market segments like sweet manufacturers, gifting products suppliers, etc.
Value: A company that follows long-held values like social justice, freedom, equal opportunities, gender equality, etc. excels in that given society.
Recurrent Trends: It refers to development or general changes in a society like consumption habits, fitness awareness, literacy rate, etc. which influence a business. For example, the demand for organic vegetables and gluten-free food is increasing; therefore, companies that manufacture food items keep this in mind to attract more crowds.
2. Legal Environment
It includes the laws, rules, regulations, and acts passed by the government. A company has to operate by abiding by the rules and regulations of laws like the Consumer Protection Act 1986, Companies Act 1956, etc. A proper understanding of these laws assists in the smooth operations of a company.
Example: A cigarette-selling company compulsorily has to put the slogan “smoking is injurious to health” on every packaging.
Economic Environment
It involves market conditions, consumer needs, interest rate, inflation rate, economic policies, etc.
Interest Rate - For example, interest rates of fixed-income instruments prevalent in an economic environment impact the interest rate it will offer on its debentures.
Inflation Rate - A rise in the inflation rate leads to a price hike; hence, it limits businesses.
Customer’s Income - If the income of customers increases, the demand for goods and services will rise too.
Economic Policies - Policies like corporate tax rate, export duty, and import duty influence a business.
Political Environment
It consists of forces like the government's attitudes towards businesses, ease-of-doing-business policies, the stability of the governing body, and peace within the country. All of these factors are extremely crucial for a company to sustain itself. If the central and local government sanctions, policies, or acts are in favour of businesses, the nation's overall economy strengthens due to increasing employment, productivity, and import and export of various products.
Example - A pro-business government will make foreign investments more attractive in that country.
Technological Environment
It comprises the knowledge of the latest technological advancements and scientific innovations to improve the quality and relevance of goods and services.
A company that regularly keeps track of these news can mould its business strategies accordingly.
Example: A Watch Company that sells smartwatches and traditional watches will prosper as smartwatches are trendy recently.
Practice Questions on Business Environment Dimensions with Answers
____________ consists of economic conditions, economic policies, industrial policies, and economic systems.
Business Environment
Economic Environment
Natural Environment
None of the above
Ans. b)
The External Environment of business is
Demographic
All of these
Importance of Business Environment
The business environment and its importance are necessary for the following reasons:
Enabling the identification of opportunities and taking immediate steps to explore the benefits.
Helping identify threats and early warning signals
To cope with the immediate changes.
Support in planning and policy.
Improving the business performance.
Impact of Government Policies on Business and Industry
The different policies of the government, including liberalisation, privatisation, and globalisation, immensely impacts the working of enterprises in business and industry in terms of:
Increasing competition
More demanding customers
Rapidly changing technological environment
Necessity for change
Need for developing human resource
Market orientation
Loss of budgetary support to the public sector.

FAQs on Business Environment: Meaning, Definition, Components, Dimension, Importance, and Impacts
1. Why is the business environment important?
The business environment provides several opportunities, and it is essential to identify them to improve a business's growth and performance. Early identification of opportunity helps an enterprise be the first to explore benefits instead of losing them to competitors.
2. What does Micro Environment mean?
Micro Environment relates to the immediate factors that influence the direct and daily operations of a business. It is also called the task Environment. It includes suppliers, customers, etc.
3. Who are the major players in the Business Environment?
The major players in the business environment include competitors, suppliers, investors, customers, media, government, economic conditions, and several other external working factors.
4. What are the five main elements of the business environment?
The five main elements of the business environment include the following:

What are the Business Environments?

Written by Scott Wilson

What is business environment? The business environment is a term that is used to refer to the overall collection of internal and external factors that impact business staffing, operations, and sales. Keeping a clear understanding of the overall state of the business environment is an important responsibility for organizational leaders.
The business environment is the total range of different, dynamic internal and external factors that an organization operates within. The business environment creates the opportunities that allow a successful business to operate in the first place, but it also offers constraints on business actions.
The business environment is a powerful thing that every organizational leader has to address. The environmental conditions within the organization are those that the leader is expected to set and maintain. But many conditions that impact organizations will be outside your immediate control.
In both cases, understanding the business environment is key to creating a strong, resilient organization to accomplish your goals.
What Goes Into the Business Environment Definition Your Organization Operates Within?

A better question is “what are the business environments?” Because no matter what kind of organization you work with, you will find that you are operating in a number of different kinds of business environment:
The External Business Environment
Many leaders focus, understandably, on the environment and culture within their own organizations. That’s the kind of environment they have the most control over, and what they engage with most often from day-to-day.
Smart organizational leaders understand that outside factors play a big role in internal dynamics.
The external business environment is all of the surrounding factors that impact the business and its operations. These are typically separated into the macro and micro factors:
- Macro-environment - The larger economic, environment, social, legal, and technical trends that impact business operations. This can be everything from interest rates to global warming. They are all factors that the business itself has no direct control over, but still affect the business process and the overall market for its products or services.
- Micro-environment - These are external issues with a more direct, immediate impact on business. An organization may have more control or influence with micro-environment issues, such as marketing perceptions, financial relationships, or distributor impacts.
At the end of the day, all of the other business environment factors listed here are just parts of the external business environment.
The Legal Environment of Business

So having a general understanding of the law and the legal system is important for leaders. This can be made of up local, state, and national laws, as well as international treaty and regulatory agreements. It also consists of both statute code, written directly by legislators, and administrative regulations, laid down by various regulatory agencies.
The legal and regulatory environment of business is also shaped by case law, which is the way that judges over the years have interpreted various other laws and regulations. And on top of the actual laws and regulations that govern business, leaders have to understand the enforcement mechanisms and the process of rule development.
Different businesses may have different aspects of the legal environment that concern them. For starters, it will be shaped by their location since different states and localities can have different laws and regulations. But the nature of the business also applies. In some cases, consumer safety laws will shape the business environment in important ways, as with agribusiness or product manufacturers. For finance businesses, security laws will be more important. And all businesses with employees have to deal with employment and health and safety obligations.
The Global Business Environment

The global business environment represents all the different international aspects that can impact your business no matter where it is located. These can include:
- Geopolitical stability
- Resource constraints
- International shipping concerns
- Global brand reputation and cultural perception
Different businesses have different levels of exposure to the global business environment, but all of them operate within it.
The Social Environment of Business
Businesses also operate within the cultural, moral, and psychological environment created by their society. The social environment of a small-town five-and-dime in a deeply conservative rural setting is going to be considerably different than a hip clothing retailer running in a liberal urban center. And a major multinational corporation has yet another set of social factors to consider.
The social environment has a great impact on the external environment of business such as marketing, product development, and pricing. But it also influences internal factors, such as employee opinions and work habits, general education in the workforce, and other cultural considerations.
The social environment of business today can involve both local, internal, and global contexts delivered through social media.
The Technological Environment of Business
The importance of technology to businesses today has made it critical to understand and adapt to the technological environment they operate in. With new technologies offering competitive and strategic advantages, leaders have to be in tune with the latest and greatest tech… everything from 3D printing to cloud storage services could be a critical differentiator, depending on your industry.
But the technology environment also presents risks. New technologies represent new points of failure, sometimes not yet well understood. The impact of tech can be negative as well as positive.
The business world is littered with examples of corporations that made poor investments in new technologies and ended up at the back of the pack.
A good organizational leader has to keep all of these and more in mind at all times. But organizational leadership degrees teach you all about looking in-depth at your environment and the individuals in it. One of the distinguishing characteristics of the organizational leadership model is observation and assessment. Effective leaders absorb information about their organization and industry to develop broad, strategic thinking. They account for every element that can impact their staff or organization.
How Organizational Leadership Training Prepares You To Deal with The Business Environment

Empathy and understanding are important parts of organizational leadership theory. They are also critical in developing a clear understanding of the social and cultural environments operating within and outside of your business.
OL education also places a heavy premium on strategic planning that looks at the big picture. The big picture, of course, is the business environment. In order to develop the kind of planning and vision that leadership requires, keeping tabs on that larger environment is critical.
Although organizational leadership degree studies may not come out and say it directly, much of their curriculum will effectively be about helping you to understand your business environment better.
Some concentrations within organizational leadership studies may offer more explicit training in business environment assessment, or even in particular aspects of the business environment. An MBA in Organizational Leadership , for example, will almost certainly include coursework on the technological and the legal environment of business, not to mention studies in global business and other external environmental factors.
Understanding what the business environment is and how to respond and position your organization is not the only element of organizational leadership. But it is a key part of the puzzle, and one you’ll master through a degree in the field.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
PESTLE Analysis
Insights and resources on business analysis tools
PEST Analysis: Examples and Meaning in Business
Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 by Jim Makos Filed Under: PEST Analysis
What is a PEST analysis, and what are its four parts? What is the difference between PESTLE analysis and PEST, and why is it important for every business? As a business student, analyst, manager or owner, you are called to conduct a PEST analysis sooner or later. In the next 10 minutes, I’ll go through everything you need to know about PEST analysis and how you can do a PEST analysis of an organization starting from scratch. I promise you’ll know more about PEST analysis than 99% of people out there, as I’m explaining everything as concisely as possible. Let’s start with the PEST analysis definition.
What is a PEST Analysis?
PEST analysis is a strategic tool for organizations to identify and assess how Political, Economic, Social, and Technological external factors impact operations so that they can gain a competitive edge. A PEST analysis helps you determine how these factors will affect a business’s performance and strategy in the long term. It is often used in collaboration with other analytical business tools. For example:
- A combination of PEST and SWOT analysis usually gives a clearer understanding of a situation with related internal and external factors
- PESTLE analysis is an extension of PEST analysis that covers legal and environmental factors
I’m going to explain the PEST analysis as simply as possible with examples and a template for better understanding. I will also show how to do a PEST analysis starting from scratch, even for people without any business education like me!
Why Do a PEST Analysis
It’s simple: to succeed. For a business to be successful, they need a few things:
- A solid product
- Marketing plan
- Identifiable brand
- Happy customers
- Thorough budget
- An investor or two
- Unique selling position
- And a whole lot of research
Throughout the endless market research, customer acquisition costs, and project risk assessments, business managers could forget about outside influences ( we call these external factors in this type of analysis). Aside from the company’s internal resources and industry factors, PEST’s macroeconomic factors can impact a company’s performance in a big way.
By being aware of external factors, managers can aid their business. But if they don’t know them, they can cripple their business before it begins. That’s how advantageous PEST analysis is .
What are the four parts of PEST analysis?
Now, let me explain each of the four parts of a PEST analysis more thoroughly. You’ll better understand what each of these external factors in this analysis is all about.
- Political – Here, government regulations and legal factors are assessed in terms of their ability to affect the business environment and trade markets. The main issues addressed in this section include political stability, tax guidelines, trade regulations, safety regulations, and employment laws.
- Economic – Next, businesses examine the economic issues that have an impact on the company. This would include factors like inflation, interest rates, economic growth, the unemployment rate and policies, and the business cycle followed in the country.
- Social – At this stage, businesses focus on the society and people. Elements like customer demographics, cultural limitations, lifestyle attitudes, and education come into play here. This part allows a business to understand how consumer needs are shaped.
- Technological – This may come as a surprise, but technology may not always be an ally for businesses. Depending on the product, technology may affect the organization positively but also negatively. In PEST’s last section we find technological advancements, the role of the Internet, and how an industry’s innovation creates winners and losers.
Every business is different. Some factors may not affect a firm or industry as they would with others. But it’s beneficial to have a well-rounded view of the many factors that could affect them. Along with the ones that will affect them.
This is why we do PEST analysis for a business — to be aware of risks, opportunities, influences, and limitations. Let’s go deeper into these external factors that impact the success of a business. I’ll also briefly mention a specific example for each of them.
Political Factors
Political factors in PEST analysis refer to the extent to which the government and political actions in a country influence the business climate. Here are some examples that will occasionally make it into the (P) of my PEST analysis:
- Tax policies
- Tax incentives
- Political tensions
- Employment laws
- Import restrictions
- Health and safety laws
- Consumer protection laws
- Tariff and Trade restrictions
- Regulation and deregulation
For instance, a country’s foreign policy often plays an important role in determining trade regulations. This can either result in trade restrictions or trade incentives and can affect an organization’s operations. Read my dedicated page on political factors with more examples here .
Economic Factors
In the (E) part of PEST Analysis, we run into how the economy affects the organization. I consider the following economic factors when doing a PEST analysis:
- Interest rate
- Inflation rates
- Exchange rates
- Unemployment rate
For instance, exchange rates affect a global organization by influencing the cost of imported and exported goods. Furthermore, interest rates influence the cost of capital available to the organization. Thus they are significant in the expansion and growth of a business. Find more economic factors and examples of how they affect businesses here .
Social Factors
Social factors include different cultural and demographic aspects of society. These can affect the macro-environment in which the organization operates.
In the ‘S’ part of the PEST analysis I usually examine:
- Age distribution
- Cultural diversity
- Demographics shifts
- Population growth rate
- Health consciousness and trends
- Changing consumer lifestyles and preferences
A study of these factors can help organizations understand the dynamics of existing and emerging potential markets along with future customer needs.
Social factors are more unpredictable than economic and political factors, simply because people are unpredictable. But every business needs customers. And what and how they buy has an immediate effect on an organization’s profitability.
Based on these social factors, marketers create buyer personas. These avatars are necessary for businesses to target the ideal customer.
For example, if you’re selling whey powder, you go after fitness enthusiasts and bodybuilders. You are looking for people that follow an active lifestyle. Hence, a declining trend in health consciousness doesn’t seem encouraging.
That’s the tip of the iceberg. Learn more about social factors here .
Technological Factors
Technological factors aren’t important only for tech-related businesses. The (T) part in PEST analysis may affect even the most old-school organization that’s been operating for a century.
Technology is evolving at a rapid pace and consumers are becoming extremely tech-savvy. With the advent of new technology, older technology gets outdated and obsolete. If an organization does not look out for technological changes, it can lag behind its competitors.
I often include the following technological factors when conducting a PEST analysis:
- Cybersecurity Threats
- Emerging Technologies
- Big data and computing
- AI and Machine Learning
- Supply Chain Automation
Let’s consider the advancements in computing; more specifically, networking.
If a business offers the latest and fastest Wi-Fi in their store, it’s an added luxury. It’s annoying if it still operates on 3G speeds, but won’t ruin sales. However, if they handle all receipts in an online database and that goes offline because they didn’t keep their network infrastucture up-to-date then they have a major problem. Especially in big holidays like Black Friday.
Again, this is about impact on the business operation. How will ‘X’ technology affect the business in the long and short term? That’s what we’re trying to figure out with PEST analysis.
A ton more technological factors can be found here .
PEST Analysis Examples
Here is a hypothetical PEST analysis example that can give you a clear understanding of how this works:
Here at PESTLEanalysis.com I rarely limit myself to PEST analysis. I almost always go the extra mile and include the Legal and Environmental factors when I initiate a PEST analysis. This leads to a more detailed analysis called PESTLE.
PESTLE Analysis: An extension of PEST Analysis
PESTLE analysis is an extension of PEST that is used to assess two additional macroeconomic factors. These factors are the Legal and Environmental conditions that can have an impact on a organization. Examples of PESTLE analysis are similar to those of a PEST analysis, but they will include factors such as these:
- Discrimination laws
- Copyright and patent laws
Environment:
- Waste management
- Changes in weather and climate
- Laws regarding pollution and recycling
- Use of green or eco-friendly products and practices
So, if you want to assess a business situation comprehensively, a PESTLE analysis is a definite must. You can find more about that analysis here .
Why PEST Analysis Is Important For Every Business
So, now that we did a PEST analysis, how’s that going to help the business?
What does a five-year business plan look like? Or a ten-year plan? It likely involves growth.
Whether it’s the expansion of a product line or opening stores in new locations, business changes need proper preparation. And that’s where the PEST analysis comes in.
PEST analysis is the foolproof plan for business expansion !
Both new business owners and veterans should include PEST analysis in their business plan. By breaking down the critical influences in the P.E.S.T. categories, businesses get a better understanding of whether their next business move is strategic or doesn’t make sense.
For example, politics isn’t just about political tensions, unrest and elections. Politics are also about trade policies, regulations and taxation. Companies doing business worldwide have to consider laws in the countries they operate, as well. Even if they aren’t doing international trade yet, it could be a possibility in the future, and going in blind is a good way to toss success out the window.
PEST analysis helps people become aware.
Aware of how political parties and regulations can impact a business. And how the economy (past, present, and future) affects an industry. It allows people to understand consumers — who they are, what they buy, and why they don’t buy. And finally, it identifies what technology is necessary for the development and success of a product, business, or industry.
It’s almost like an outline. It shows people what influences impact the quality, success, or devastation of businesses and industries. You can’t stop the four influences, but if you’re aware of them and their impact, you can plan around, against, or with them.
PEST analysis is often used by business analysts, marketers, students, and business owners, since it’s super important for every business!
All you need to do a proper PEST analysis is time. And the payoff is worth every second.
How PEST analysis works
PEST analysis requires research and data, sometimes ten years old, sometimes only a couple. The more information I have to go through, the more accurate my final results will be. By looking into the past and the present, I can make predictions for the future.
By studying these recent developments through a PEST analysis lens, organizations are deciding whether to jump into this for the long haul or for the time being.
You want to look at your industry in a similar light. Ten years ago, did it exist? Has it slowed down within the last two years or are more companies diving in? More competition can be a strong sign an industry is booming, but it could also be the first sign of oversaturation.
Break down your assessment into the four categories of PEST analysis. Start with politics and work your way through the remaining factors. Or start from the bottom. Whatever gets the job done and makes the analysis enjoyable.
How to Do a PEST Analysis From Scratch
I’ve written dozens of PEST analyses over the last couple of years. Below I document my process on how to do a PEST analysis , even when you’ve never written one before.
You should have a topic in mind. Most PEST analyses are about a specific business, industry, or product. However, they can also be applied to countries, too. You can’t start without a topic, though, so have it ready.
Where to find information for your PEST analysis
It’ll be easier to find and segment information if you break your analysis down into four sections, like the acronym implies:
- Technological
Each section will require its own information. However, some of this information will overlap.
For instance, the economy is often closely tied to political (in)stability. And the state of the economy always affects consumers (social). You don’t need to look for these patterns specifically— it’ll become apparent as you discover new information.
Start with the history
You should be familiar with your topic. If you’re not, read about its history. Learn how it was established, how long it has been around, and who founded it. Read about any major achievements on the organization in question over the last few years. Jot down notes whenever something that seems relevant or important pops up.
After this informational primer, it’s time to start on the four sections. I do my PEST analysis in order of the acronym because the information often bleeds into the next section.
Finding Political Information
Political information is easier to find than in other sections of the analysis (social and technological, specifically). Here, you’ll want to investigate the current political climate.
For instance, if the organization originates from America, you’ll research the current political parties. Who is in charge? Has this affected business operations in any way?
If your topic (business, product, industry) was established years ago, what was the political climate like then? Are different parties in power now? If this is the case, then you’ll want to compare how things have changed for your topic from then to now.
This is also the section where you’ll look into laws and regulations affecting business. Remember the list we went through in the beginning.
I find this information with a simple Google search. Such as “tariff laws USA” (plug in the country you’re searching for if it’s not the United States).
It’s best to get this information from a government site. These sites end in .gov. You may also find information from organizations (websites ending in .org) but not all of these sites are legitimate organizations. Be wary while you research.
Honestly, most of the information you’ll find is dense. But it’s easier if you have a goal. Look for signs of:
- Government (in)stability
- Possible political corruption
- New bills/regulations that may impact your topic
- Any issues your topic has had with current/former regulations or political parties
If your topic is a company, finding the right information may be easier. Search for “company name + political issues” or “company name + policies” and see what comes up. Avoid any information from untrustworthy sites and sites with no legitimate source.
Finding Economic Information
While you’re researching political information, you may come across connections to the current economy. For instance, political instability often leads to economic instability. This causes unemployment rates to rise and employee strikes. This affects how much disposable income people have.
You may have already found information in your political section that confirms economic problems. But if you haven’t, search government sites for current tax rates, interest rates (if your topic involves international business), and the current state of the economy. Is it good? Thriving? Or bad and declining?
Again, use government websites. Search for economic statistics over the last few years. If your topic is an industry, see how many companies (startups) have started within the last few years.
If your topic is a business that has international stores, look into the relationship between the country of origin and each country the company does business. If the relationship is good, it’s often a good outlook for the company. But if it’s bad, it may lead to problems. What problems? Do a bit of digging online.
Also, if your PEST analysis is for a company, you may look into stocks . Have they been declining? On the rise? Because if it’s the former, then the business may not be looking good. And you’ll want to find out why .
If my topic is a business, I sometimes check out the competition. I’ll look into how that other company has been fairing economically, specifically how its sales have risen or fallen over the last couple of years. If it’s dropped products, shifted marketing efforts, etc., I want to know why . A competitor analysis isn’t always necessary , but it can shed light on possible problems your topic may face.
Finding Social Information
This section is a bit trickier. Political and economic sectors rely heavily on data and evidence. You can find this information on government websites. News sites too, even. And although you can find databases about demographics and population growth for this section — all applicable in a PEST analysis — I wouldn’t stop there.
In the social section, I often examine how consumers are impacted by political and economic factors. You can draw conclusions based on the information you’ve already gathered from your political and economic segments.
For instance, if there is political instability and the economy is on the fritz, then consumers may feel uneasy. They may have fewer job options. And that means they’re less likely to spend frivolously. If your topic is a luxury product, it may mean the company that makes it may have lower sales this year.
But you also want to learn about how consumers feel about your topic. If it’s a company, do consumers generally like it? Or is public opinion souring? There should be a reason for why.
Consider Facebook. The company’s CEO, Mark Zuckerberg, has consistently been in hot water over the years. If not for data breaches affecting millions of users, but for their shady involvement with fake news and political tampering.
This has led many consumers to shy away from using Facebook. And this affects businesses that use Facebook to reach new customers.
In this section of the PEST analysis, I’m more likely to search for my topic on news sites and publications. The more popular the topic, the easier it’ll be to find articles written about it. But if the topic has ever been in the news, you’ll likely find it online.
Websites to search include :
- Consumer Reports
- Local news websites
- Other reputable sources
If you know your topic has been in the news for something bad, you can search the topic + the problem.
Although the information may overlap, take keynotes here. See how the problem is affecting consumer opinion. You may even want to take a look at the comments (if there are any) and see what people are saying. It’s coming straight from the lion’s mouth (consumers).
I think many PEST analyses favor numbers too much. We live in a world where anyone with an opinion can be heard, thanks to the internet. And enough of those voices can cause a business to change its policies and products. It can even cause the company to collapse.
So it’s important to search for how consumers feel about your topic too.
Finding Technological Information
This section of the PEST analysis is a bit abstract as well. You’re looking into how new technological advancements has affected your topic positively or negatively. You should also look into what technology your topic uses (currently). And what technology they may want to incorporate.
You may want to look at competitors if your topic is a product or business. See what others are using. And think about why they are.
Press releases
It may be beneficial to search for press releases involving your topic, if possible. If your company is using new technology, they may have announced it through a press release. You can search “company name + press release” or search through these press release websites:
- PR NewsWire
- NPR: National Public Radio
You may also find other information here for the other sections of the PEST analysis. Which is just an overall bonus. If all else fails, check if your topic has a website (unless it’s an industry or country). Discuss how they use social media (if they don’t, then… discuss that too!). In this section, you’re assessing what your topic uses, what it doesn’t, and why.
Putting it all together in a final PEST analysis
You’ll likely have heaps of information at hand. For some it’ll feel like too much — but that’s never the case for a PEST analysis. As you begin to read through each section’s notes, incorporate the most interesting, pressing, or surprising information. If anything overlaps with other sections, include that too.
I write each section of a PEST analysis at a time. I take my notes and create coherent sentences. Sometimes I make a list of the most important points and include them that way. If the section is long, I’ll use subheadings to break up the information.
Work on each section separately. And then if there are overlapping themes, incorporate those in. You may want to use those at the end of each section to connect to the next.
Once you’ve done this, you’ve completed your PEST analysis! Most of the work is in finding the information and making it coherent. The last 10-20 percent is putting it all together. So, once the research phase is done, you’re basically done too!
Understanding PEST Analysis: Taking Action
In conclusion, developing an understanding of what is PEST analysis becomes even more important when a company is about to launch a new business or a new product. In general, when they are about to change something drastically. That’s when all these factors play an important role in determining the feasibility and profitability of the new venture.
Therefore, developing an understanding of PEST analysis is useful for organizations for analyzing and understanding the ground realities of the environment they have to operate in.
Realizing what is PEST and knowing how to take this analysis into consideration, the organization can be in a better position to analyze the challenges, environment, factors, opportunities, restrictions and incentives it faces. In case an organization fails to take into account any one of these factors, it may fail to plan and operate properly.
But don’t PEST analysis stop you. Here are some variations that may come in handy when assessing how the external environment affects an organization:
- STEEP Analysis
- STEEPLED Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
Richest NJ ZIP Code Fights Plan for Low-Cost Homes on Toxic Dump
By Nacha Cattan

Josh Bauers has long had his sights set on the town dump in Millburn.
Bauers wants to put 75 affordable apartments on the site where piles of Styrofoam and food scraps lie in heaps.
But that’s a bridge too far for many residents of New Jersey’s richest ZIP code , Short Hills, where multimillion dollar Tudor and colonial-style mansions are perched atop grassy hillocks less than an hour’s commute from Manhattan.

Many in the community, favored by finance types and lawyers, are up in arms over the development’s potential effect on the environment and its highly-rated schools. But the ...
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Oil Companies Expand Offshore Drilling, Pointing to Energy Needs
Shell and others say they plan to drill for oil and gas in the Gulf of Mexico in part because doing so releases fewer greenhouse gases than drilling on land.

By Ivan Penn
Reporting from Shell’s Appomattox offshore platform, New Orleans, Houston and Los Angeles
About 80 miles southeast of Louisiana’s coast, 100,000 metric tons of steel floats in the Gulf of Mexico, an emblem of the hopes of oil and gas companies.
This hulk of metal, a deepwater platform called Appomattox and owned by Shell, collects the oil and gas that rigs tap from reservoirs thousands of feet below the seafloor. Equipment on the platform pipes that fuel to shore.
Political and corporate leaders have pledged to reduce planet-warming emissions to net-zero by 2050. But oil companies like Shell are betting that the world will need oil and gas for decades to come. To serve that demand, they are expanding offshore oil and gas drilling into deeper and deeper waters, especially here in the Gulf of Mexico.
Offshore production, oil executives argue, is not only crucial to power cars, trucks and power plants but also better for the planet than drilling on land. That’s because such operations emit far less of the greenhouse gases that are warming the planet than producing the same amount of oil and gas on land, according to industry estimates.
“The world will continue to need oil, by the way, even in 2050,” Wael Sawan, chief executive of Shell, said in a recent interview. “It will have to be lower and lower emissions.”
The greenhouse gas emissions associated with extracting a barrel of oil from the Gulf of Mexico are as much as a third lower than emissions from producing a barrel of oil from fields on U.S. soil, according to a report published last year by the National Ocean Industries Association , an industry group for offshore oil, gas and wind businesses. (Those numbers do not include the emissions created when fossil fuels are burned in engines or power plants, which are much greater than emissions from producing and refining oil and gas.)
Oil production in the Gulf of Mexico fell for several years after the 2010 Deepwater Horizon explosion caused the worst offshore oil spill in U.S. history. But the gulf’s oil output has been rising over the last decade. The renewed interest in offshore production is part of a larger trend: The United States has recently set records for oil production, extracting more crude than any other country.
Booming oil and gas production in the United States has alarmed climate activists and scientists who want the energy industry to pivot more quickly to cleaner fuels and technologies like wind and solar power and electric vehicles.
“We’re not talking about stopping oil production today,” said Brettny Hardy, a senior lawyer in the Oceans Program at Earthjustice, a nonprofit environmental law organization. “But no matter how you look at it, there’s a really dire need to accelerate this shift to clean energy. The things the industry is doing now is not going to help that transition.”
To many environmentalists, offshore fossil fuel production’s potential for disaster is significant. The spill caused by the Deepwater Horizon rig , which was operated by BP, resulted in significant damage to marine life, the fishing industry and the Gulf of Mexico’s beaches.
The spill helped bring attention to Rice’s whale , which lives only in the Gulf of Mexico and is classified by the federal government as an endangered species. Fewer than 100 of these whales are left because of incidents like the Deepwater Horizon spill and collisions with vessels.
“The concern and worry is there for the right reasons because we have been burned once because of Deepwater Horizon,” said Najmedin Meshkati, a professor of engineering at the University of Southern California who served on a National Academies committee that studied that spill.
The Biden administration had planned to scale back lease sales for oil drilling in the gulf, which environmentalists said would help protect Rice’s whales. In August, the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management reduced the area available for leases from 73 million acres to 67 million acres.
But in November, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit rejected the administration’s plans. A month later, oil companies offered $382 million for the right to drill for more oil and gas.
Oil executives say offshore oil operations are far less dangerous now thanks to advances in technology and improvements in standards and regulations. “Offshore oil and natural gas exploration and production is the safest it’s ever been,” said Holly Hopkins, vice president of upstream policy at the American Petroleum Institute, a trade group.
Energy companies favor drilling in the gulf because there is a lot of oil and gas there, especially under very deep waters. The number of deep water platforms have grown dramatically over the last three decades, while those in shallow waters have declined, according to the American Petroleum Institute.
Federal government analysts estimate that oil production in the Gulf of Mexico will grow through 2027. Natural gas production in the gulf is expected to largely remain flat through the early 2030s.
Shell is the biggest oil and gas producer in the region’s waters. Its outsize presence in the gulf is on display at Appomattox, which has a displacement bigger than the world’s largest aircraft carrier, according to the company.
The platform was brought online in 2019 and can house up to 180 people. It stays in place as ships drill wells near it and connect those wells by pipe to the platform, where equipment separates oil, natural gas and water.
Shell recently launched a smaller floating platform, the Whale, which can house up to 60 people. Another unit, Sparta, is under development. In all, Shell, a London-based global energy giant, operates nine active platforms — including four with built-in drill rigs — in the Gulf of Mexico.
On a reporter’s recent visit to Appomattox, about 130 people were working on board, including oil and gas engineers, cooks, janitors, a medic and laundry facility operators who keep washers and dryers spinning 24 hours a day.
Crews live on the platform for 14 consecutive days, working 12-hour shifts. They return to homes across the world for two weeks, before coming back for another 14-day stint.
There is a sense of pride among those aboard, though they recognize that many people think their industry is destroying the planet.
“There is another side that people don’t talk about,” said Matt Flanakin, a ballast control operator on Appomattox for Shell. “We know there’s a need to reduce carbon emissions. But we still need fossil fuels.”
The platform floats on the deep blue waters with little else in sight. On occasion, a drill rig ship appears in the distance. These vessels are scouring the seafloor for sources of oil.
The platforms create artificial reefs that attract fish and dolphin pods to Appomattox, said Rich Howe, executive vice president of Shell’s global deepwater business.
Shell is not alone in expanding its operations offshore. BP, Chevron and other energy giants are also expanding or planning to expand operations in the Gulf of Mexico.
“This is the cradle of global deepwater,” Mr. Howe said. “It’s where a lot of the technologies were invented.”
The gulf has an extensive network of pipelines and equipment that helps deliver the oil and gas directly to onshore facilities with little processing through pipelines. That makes extracting oil and gas from underground reservoirs in the gulf more efficient, ultimately helping to produce less emissions.
Technology has also reduced the need for as many offshore workers, who are flown by helicopter to platforms and drill rigs. Some control room operators work remotely onshore. And the companies say they are minimizing the amount of natural gas they burn off during a process called “flaring.”
“We want it to be as secure, affordable and as low-carbon as it can be,” said Andy Krieger, a senior vice president for the Gulf of Mexico and Canada at BP, which has five platforms in the Gulf of Mexico.
But plans by oil giants, especially those based in Europe, to invest in offshore production strike some climate experts as a retreat from the companies’ renewable-energy investments in recent years.
Mr. Sawan, the Shell chief executive, is clear that the company should focus on the businesses it knows best, a category that includes oil, natural gas and hydrogen. He said it should let other companies, including businesses with which Shell has financial and commercial relationships, develop renewable sources like solar power.
That doesn’t mean Shell is uninterested in newer parts of the energy sector, he added. He singled out electric vehicle charging as an area where his company plans to expand. To that end, Shell recently announced that it would close 1,000 gasoline stations, or about 2 percent of its retail presence, in 2024 and 2025 and expand its electric vehicle charging network to 200,000 public charging points globally by 2030, from about 55,000 now.
“At the end of the day,” Mr. Sawan said at a recent energy conference in Houston, “the real intent here is to be able to bring that multidimensional nature of the energy transition and move this dialogue that seems to fixate on ‘Is it oil and gas, or is it solar and wind?’ It’s all, and we need them in abundance.”
Ivan Penn is a reporter based in Los Angeles and covers the energy industry. His work has included reporting on clean energy, failures in the electric grid and the economics of utility services. More about Ivan Penn
Explore Our Business Coverage
Dive deeper into the people, issues and trends shaping the world of business..
Turbulence in TV News: As an especially divisive presidential race looms, ABC, NBC, CBS and CNN all face questions about their future .
Start-Up Stocks: Tensions in Silicon Valley over the shadowy and often enigmatic market of private company stocks have reached a boiling point.
Finding a Powerful Voice: Women in Shanghai are gathering in bars, salons and bookstores to reclaim their feminist identities as China’s leader calls for the country to adopt a “childbearing culture.”
Tesla’s Pullback: The automaker led by Elon Musk is no longer planning to take the lead in expanding the number of places to fuel electric vehicles. It’s not clear how quickly other companies will fill the gap .
A ‘Not Charlotte’ Recipe: North Carolina’s Triad region was built on tobacco, textiles and furniture. Now it’s trying to forge a new economy from more highly skilled manufacturing .
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Japan proposes expanding commercial whaling to fin whales, a larger species than the 3 allowed now
People walk nearby a life size model of a whale displayed at the National Science Museum, Thursday, May 9, 2024, in Tokyo. Japan’s Fisheries Agency on Thursday said it has proposed a plan to allow catching fin whales in addition to three smaller whale species currently permitted under the country’s commercial whaling around its coasts. (AP Photo/Eugene Hoshiko)
- Copy Link copied
TOKYO (AP) — Japan’s Fisheries Agency has proposed expanding commercial whaling along the country’s coast to fin whales, a larger species than the three currently permitted.
The proposal comes five years after Japan resumed commercial whaling within its exclusive economic zone after withdrawing from the International Whaling Commission in 2019. It ended 30 years of what Japan called “research whaling” that had been criticized by conservationists as a cover for commercial hunts banned by the commission in 1988.
Chief Cabinet Secretary Yoshimasa Hayashi, whose electoral district is traditionally known for whaling, said Thursday the government supports sustainable use of whales as part of Japan’s traditional food culture and plans to promote the industry.
“Whales are an important food resource and we believe they should be sustainably utilized just like any other marine resources, based on scientific evidence,” Hayashi told reporters. “It is also important to carry on Japan’s traditional food culture.”
The Fisheries Agency said it is seeking public comments until June 5 on the proposed plan and will seek its approval at the next review meeting in mid-June.
The agency decided to propose adding fin whales to the allowable catch list after stock surveys confirmed a sufficient recovery of the fin whale population in the North Pacific.
The plan is not meant to increase whale meat supply and whalers who catch fin whales do not necessarily have to meet a quota, an agency official said, speaking on condition of anonymity to discuss the issue. For this year, the agency has set a combined catch quota of 379 for the three other whale species.
Last year, Japanese whalers caught 294 minke, Bryde’s and sei whales — less than 80% of the quota and fewer than the number once hunted in the Antarctic and the northwestern Pacific under the research program.
Japan’s whaling has long been a source of controversy and attacks from conservationists, but anti-whaling protests have largely subsided after Japan terminated its much-criticized Antarctic research hunts in 2019 and returned to commercial whaling limited to Japanese waters.
Whale meat consumption in Japan was an affordable source of protein during the malnourished years after World War II, with annual consumption peaking at 233,000 tons in 1962. However, whale was quickly replaced by other meats and supply has since fallen to around 2,000 tons in recent years, according to Fisheries Agency statistics.
Japanese officials want to increase that to about 5,000 tons, to keep the industry afloat.
On a visit to the former Tsukiji fish market area in downtown Tokyo, Yuuka Fujikawa from Hokkaido, said she has hardly seen whale meat sold at supermarkets. “I’ve actually never tried it myself,” she said.
“I want more people to appreciate the taste of whale,” said Hideyuki Saito, from neighboring Saitama prefecture. “I want it to be more popularized.”
Carlos Sempere Santos, a 28-year-old tourist from Spain, said he couldn’t imagine eating whale as whales are special and smart animals.
Shirley Bosworth from Australia said she opposes whaling because whales “should be protected.” Whales often get beached in Australia, where people unite to try and “push them back in the sea.”
A whaling operator Kyodo Senpaku Co. last year launched whale meat vending machines. The company also completed construction of its new 7.5 billion yen ($48 million) Kangei Maru — a 9,300-ton mother ship — and pledges to use it for sustainable commercial whaling.
AP journalist Ayaka McGill contributed to this report.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business environment is all the components that affect a business. These include both internal factors, like employees and resources, and external factors, like customers and markets. Each of these contributes to a company's working environment and can influence how the business functions. ... Related: Marketing Environments: Definition ...
The internal business environment constitutes several internal forces or elements within the control of a business that influences its operations. These include: Value System: It is the ethical belief that guides the business towards achieving its mission and objective. The value system includes all components that form a business's ...
The factors that influence a business environment are split into the following primary categories: General factors: Economic and social issues impacting businesses universally, including law, technology, and social-political norms. Specific factors: Unique elements directly related to a particular business, such as competitors, target markets ...
Business Environmental Analysis is a strategic tool which helps companies know how external and internal environment factors influence their operations and performances. It, as a function, is used to examine things like economic trends, technological advancements, regulatory landscapes, competitive dynamics and social changes that can influence ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
The business environment encompasses all the factors, both internal and external, that directly or indirectly impact a company's operations. In other words, the business environment is where the business organizations operate. It constitutes employees, customer needs, supply and demand, management, clients, suppliers, government activities ...
Business Environment. Definition: Business Environment means a collection of all individuals, entities and other factors, which may or may not be under the control of the organisation, but can affect its performance, profitability, growth and even survival. Every business organisation operates in a distinctive environment, as it cannot exist in ...
This external business environment is composed of numerous outside organizations and forces that we can group into seven key subenvironments, as Exhibit 1.4 illustrates: economic, political and legal, demographic, social, competitive, global, and technological. Each of these sectors creates a unique set of challenges and opportunities for ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
1. Complex. Complexity is a significant characteristic of the business environment. Since the business environment comprises many factors, a sudden change in a business enterprise sometimes cannot be traced to one aspect. A business's overall performance summarizes all the environmental factors' inputs and effects. 2.
The business environment is a complex and multifaceted concept that encompasses various internal and external factors influencing a company's decision-making process and overall operations. Understanding the business environment is of paramount importance for organisations as it enables them to adapt to changing circumstances, identify ...
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are ...
Business plans are written documents that define your business goals and the strategies you'll use to achieve those goals. In addition to exploring the competitive environment in which the business will operate, a business plan also analyses a market and different customer segments, describes the products and services, lists business ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
A business environmental analysis is crucial as it helps organizations understand both their internal and external environments. This understanding allows them to identify opportunities and threats and develop strategies to leverage them and mitigate them. It facilitates informed decision-making and proactive planning.
A business environment analysis report usually targets issues, patterns, and factors that reside or exist outside the influence of the manager of the business. These external factors include the ...
Components of Business Environment. Internal - It combines the factors that exist within the company. These are -. Human resources. Value system. Vision and mission. Labour union. Corporate culture. External - An external Environment includes those outside factors that exercise an influence on a business's operations.
The business environment is the total range of different, dynamic internal and external factors that an organization operates within. The business environment creates the opportunities that allow a successful business to operate in the first place, but it also offers constraints on business actions. The business environment is a powerful thing ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
A business plan can be an organizational roadmap, that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and ...
business plan: A business plan is a document demonstrating the feasibility of a prospective new business and providing a roadmap for its first several years of operation.
PEST analysis is the foolproof plan for business expansion! Both new business owners and veterans should include PEST analysis in their business plan. By breaking down the critical influences in the P.E.S.T. categories, businesses get a better understanding of whether their next business move is strategic or doesn't make sense.
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is the No. 1 type of AI solution deployed in organizations, according to a new survey by Gartner, Inc.. According to the survey conducted in the fourth quarter of 2023, 29% of the 644 respondents from organizations in the U.S., Germany and the U.K. said that they have deployed and are using GenAI, making GenAI the most frequently deployed AI solution.
AT&T Services Inc.'s bid to have the US Supreme Court review ERISA's prohibited transaction rules has drawn support from a handful of industry groups, which said the dispute implicates the efficient operation of every retirement plan in the country.. The justices' prompt intervention is needed to prevent plaintiffs' attorneys from expanding the ongoing flood of litigation over retirement ...
It included 'Target 3' to protect 30% of the world's surface by 2030, the so-called 30 x 30 deal, which requires a huge expansion of designated conservation areas. The agreement also committed states to protect the rights of Indigenous Peoples to their lands, cultural heritage, and to obtaining consent for any projects on their lands.
But that's a bridge too far for many residents of New Jersey's richest ZIP code, Short Hills, where multimillion dollar Tudor and colonial-style mansions are perched atop grassy hillocks less than an hour's commute from Manhattan. Millburn's town dump, where 75 units of affordable housing may be built. Many in the community, favored by ...
In August, the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management reduced the area available for leases from 73 million acres to 67 million acres. But in November, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fifth Circuit ...
TOKYO (AP) — Japan's Fisheries Agency has proposed a plan to allow catching fin whales in addition to three smaller whale species currently permitted under the country's commercial whaling around its coast, officials said Thursday. The proposal comes five years after Japan resumed commercial whaling within its exclusive economic zone ...