- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers

How to Cite a Research Paper in APA
Last Updated: October 19, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff . Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 158,870 times. Learn more...
If you’re citing a research article or paper in APA style, you’ll need to use a specific citation format that varies depending on the source. Assess whether your source is an article or report published in an academic journal or book, or whether it is an unpublished research paper, such as a print-only thesis or dissertation. Either way, your in-text citations will need to include information about the author (if available) and the date when your source was published or written.
Sample Citations

Writing an In-Text Citation

- For example, you may write, “Gardener (2008) notes, ‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (p. 199).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (Meek & Hill, 2015, p.13-14).”
- For articles with 3-5 authors, write out the names of all the authors the first time you cite the source. For example: (Hammett, Wooster, Smith, & Charles, 1928). In subsequent citations, write only the first author’s name, followed by et al.: (Hammett et al., 1928).
- If there are 6 or more authors for the paper, include the last name of the first author listed and then write "et al." to indicate that there are more than 5 authors.
- For example, you may write, "'This is a quote' (Minaj et al., 1997, p. 45)."

- For example, you may write, “‘The risk of cervical cancer in women is rising’ (American Cancer Society, 2012, p. 2).”

- For example, you may write, “‘Shakespeare may have been a woman’ (“Radical English Literature,” 2004, p. 45).” Or, “The paper notes, ‘There is a boom in Virgin Mary imagery’ (“Art History in Italy,” 2011, p. 32).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (“Iconography in Italian Frescos,” 2015, p.13-14).”

- For example, you may write, “‘There are several factors to consider about lobsters’ (Gardner, 2008, p. 199).” Or, “The paper claims, ‘The fallen angel trope is common in religious and non-religious texts’ (“Iconography in Italian Frescos,” 2015, p.145-146).”

- For example, you may write, “‘The effects of food deprivation are long-term’ (Mett, 2005, para. 18).”
Creating a Reference List Citation for a Published Source
- Material on websites is also considered “published,” even if it’s not peer-reviewed or associated with a formal publishing company.
- While academic dissertations or theses that are print-only are considered unpublished, these types of documents are considered published if they’re included in an online database (such as ProQuest) or incorporated into an institutional repository.

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M.” Or, “Meek, P. Q., Kendrick, L. H., & Hill, R. W.”
- If there is no author, you can list the name of the organization that published the research paper. For example, you may write, “American Cancer Society” or “The Reading Room.”
- Formally published documents that don’t list an author or that have a corporate author are typically reports or white papers .

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008).” Or, “American Cancer Society. (2015).”

- For example, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008). Crustaceans: Research and data.” Or, “American Cancer Society. (2015). Cervical cancer rates in women ages 20-45.”

- For example, for a journal article, you may write, “Gardner, L. M. (2008). Crustaceans: Research and data. Modern Journal of Malacostracan Research, 25, 150-305.”
- For a book chapter, you could write: “Wooster, B. W. (1937). A comparative study of modern Dutch cow creamers. In T. E. Travers (Ed.), A Detailed History of Tea Serviceware (pp. 127-155). London: Wimble Press."

- For example, you may write, “Kotb, M. A., Kamal, A. M., Aldossary, N. M., & Bedewi, M. A. (2019). Effect of vitamin D replacement on depression in multiple sclerosis patients. Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders, 29, 111-117. Retrieved from PubMed, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30708308.
- If you’re citing a paper or article that was published online but did not come from an academic journal or database, provide information about the author (if known), the date of publication (if available), and the website where you found the article. For example: “Hill, M. (n.d.). Egypt in the Ptolemaic Period. Retrieved from https://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/ptol/hd_ptol.htm”
Citing Unpublished Sources in Your Reference List

- Print-only dissertations or theses.
- Articles or book chapters that are in press or have been recently prepared or submitted for publication.
- Papers that have been rejected for publication or were never intended for publication (such as student research papers or unpublished conference papers).

- If the paper is currently being prepared for publication, include the author’s name, the year when the current draft was completed, and the title of the article in italics, followed by “Manuscript in preparation.” For example: Wooster, B. W. (1932). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Manuscript in preparation.
- If the paper has been submitted for publication, format the citation the same way as if it were in preparation, but instead follow the title with “Manuscript submitted for publication.” For example: Wooster, B. W. (1932). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Manuscript submitted for publication.
- If the paper has been accepted for publication but is not yet published, replace the date with “in press.” Do not italicize the paper title, but do include the title of the periodical or book in which it will be published and italicize that. For example: Wooster, B. W. (in press). What the well-dressed man is wearing. Milady’s Boudoir.

- If the paper was written for a conference but never published, your citation should look like this: Riker, W. T. (2019, March). Traditional methods for the preparation of spiny lobe-fish. Paper presented at the 325th Annual Intergalactic Culinary Conference, San Francisco, CA.
- For an unpublished paper written by a student for a class, include details about the institution where the paper was written. For example: Crusher, B. H. (2019). A typology of Cardassian skin diseases. Unpublished manuscript, Department of External Medicine, Starfleet Academy, San Francisco, CA.

- For example, you may write, “Pendlebottom, R. H. (2011). Iconography in Italian Frescos (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). New York University, New York, United States.”
Community Q&A
- If you want certain information to stand out in the research paper, then you can consider using a block quote. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libraryguides.vu.edu.au/apa-referencing/7JournalArticles
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_author_authors.html
- ↑ https://bowvalleycollege.libguides.com/c.php?g=714519&p=5093747
- ↑ https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide/intext
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://libguides.southernct.edu/c.php?g=7125&p=34582#1951239
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_electronic_sources.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_articles_in_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_books.html
- ↑ https://morlingcollege.libguides.com/apareferencing/unpublished-or-informally-published-work
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/general_apa_faqs.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/reference_list_other_print_sources.html
About This Article

To cite a research paper in-text in APA, name the author in the text to introduce the quote and put the publication date for the text in parentheses. At the end of your quote, put the page number in parentheses. If you don’t mention the author in your prose, include them in the citation. Start the citation, which should come at the end of the quote, by listing the author’s last name, the year of publication, and the page number. Make sure to put all of this information in parentheses. If there’s no author, use the name of the organization that published the paper or the first few words from the title. To learn how to cite published and unpublished sources in your reference list, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

- MJC Library & Learning Center
- Research Guides
Format Your Paper & Cite Your Sources
- APA Style, 7th Edition
- Citing Sources
- Avoid Plagiarism
- MLA Style (8th/9th ed.)
APA Tutorial
Formatting your paper, headings organize your paper (2.27), video tutorials, reference list format (9.43).
- Elements of a Reference
Reference Examples (Chapter 10)
Dois and urls (9.34-9.36), in-text citations.
- In-Text Citations Format
- In-Text Citations for Specific Source Types
NoodleTools
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Style
- Other Styles
- Annotated Bibliographies
- How to Create an Attribution
What is APA Style?
APA style was created by social and behavioral scientists to standardize scientific writing. APA style is most often used in:
- psychology,
- social sciences (sociology, business), and
If you're taking courses in any of these areas, be prepared to use APA style.
For in-depth guidance on using this citation style, refer to Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th ed. We have several copies available at the MJC Library at the call number BF 76.7 .P83 2020 .
APA Style, 7th ed.
In October 2019, the American Psychological Association made radical changes its style, especially with regard to the format and citation rules for students writing academic papers. Use this guide to learn how to format and cite your papers using APA Style, 7th edition.
You can start by viewing the video tutorial .
For help on all aspects of formatting your paper in APA Style, see The Essentials page on the APA Style website.
- sans serif fonts such as 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, or 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode, or
- serif fonts such as 12-point Times New Roman, 11-point Georgia, or normal (10-point) Computer Modern (the default font for LaTeX)
- There are exceptions for the title page , tables , figures , footnotes , and displayed equations .
- Margins : Use 1-in. margins on every side of the page.
- Align the text of an APA Style paper to the left margin . Leave the right margin uneven, or “ragged.”
- Do not use full justification for student papers.
- Do not insert hyphens (manual breaks) in words at the end of line. However, it is acceptable if your word-processing program automatically inserts breaks in long hyperlinks (such as in a DOI or URL in a reference list entry).
- Indent the first line of each paragraph of text 0.5 in . from the left margin. Use the tab key or the automatic paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program to achieve the indentation (the default setting is likely already 0.5 in.). Do not use the space bar to create indentation.
- There are exceptions for the title page , section labels , abstract , block quotations , headings , tables and figures , reference list , and appendices .
Paper Elements
Student papers generally include, at a minimum:
- Title Page (2.3)
- Text (2.11)
- References (2.12)
Student papers may include additional elements such as tables and figures depending on the assignment. So, please check with your teacher!
Student papers generally DO NOT include the following unless your teacher specifically requests it:
- Running head
- Author note
For complete information on the order of pages , see the APA Style website.
Number your pages consecutively starting with page 1. Each section begins on a new page. Put the pages in the following order:
- Page 1: Title page
- Page 2: Abstract (if your teacher requires an abstract)
- Page 3: Text
- References begin on a new page after the last page of text
- Footnotes begin on a new page after the references (if your teacher requires footnotes)
- Tables begin each on a new page after the footnotes (if your teacher requires tables)
- Figures begin on a new page after the tables (if your teacher requires figures)
- Appendices begin on a new page after the tables and/or figures (if your teacher requires appendices)
Sample Papers With Built-In Instructions
To see what your paper should look like, check out these sample papers with built-in instructions.
APA Style uses five (5) levels of headings to help you organize your paper and allow your audience to identify its key points easily. Levels of headings establish the hierarchy of your sections just like you did in your paper outline.
APA tells us to use "only the number of headings necessary to differentiate distinct section in your paper." Therefore, the number of heading levels you create depends on the length and complexity of your paper.
See the chart below for instructions on formatting your headings:

Use Word to Format Your Paper:
Use Google Docs to Format Your Paper:
Placement: The reference list appears at the end of the paper, on its own page(s). If your research paper ends on page 8, your References begin on page 9.
Heading: Place the section label References in bold at the top of the page, centered.
Arrangement: Alphabetize entries by author's last name. If source has no named author, alphabetize by the title, ignoring A, An, or The. (9.44-9.48)
Spacing: Like the rest of the APA paper, the reference list is double-spaced throughout. Be sure NOT to add extra spaces between citations.
Indentation: To make citations easier to scan, add a hanging indent of 0.5 in. to any citation that runs more than one line. Use the paragraph-formatting function of your word processing program to create your hanging indent.
See Sample References Page (from APA Sample Student Paper):

Elements of Reference List Entries: (Chapter 9)

References generally have four elements, each of which has a corresponding question for you to answer:
- Author: Who is responsible for this work? (9.7-9.12)
- Date: When was this work published? (9.13-9.17)
- Title: What is this work called? (9.18-9.22)
- Source: Where can I retrieve this work? (9.23-9.37)
By using these four elements and answering these four questions, you should be able to create a citation for any type of source.
For complete information on all of these elements, checkout the APA Style website.
This infographic shows the first page of a journal article. The locations of the reference elements are highlighted with different colors and callouts, and the same colors are used in the reference list entry to show how the entry corresponds to the source.
To create your references, you'll simple look for these elements in your source and put them together in your reference list entry.
American Psychological Association. Example of where to find reference information for a journal article [Infographic]. APA Style Center. https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/references/basic-principles
Below you'll find two printable handouts showing APA citation examples. The first is an abbreviated list created by MJC Librarians. The second, which is more comprehensive, is from the APA Style website. Feel free to print these for your convenience or use the links to reference examples below:
- APA Citation Examples Created by MJC Librarians for you.
- Common References Examples (APA Handout) Printable handout from the American Psychological Association.
- APA Style Quick Reference Guide See how to format three typical types of references.
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Edited Book Chapter
- Webpage on a Website
Classroom or Intranet Sources
- Classroom Course Pack Materials
- How to Cite ChatGPT
- Dictionary Entry
- Government Report
- Legal References (Laws & Cases)
- TED Talk References
- Religious Works
- Open Educational Resources (OER)
- Archival Documents and Collections
You can view the entire Reference Examples website below and view a helpful guide to finding useful APA style topics easily:
- APA Style: Reference Examples
- Navigating the not-so-hidden treasures of the APA Style website
- Missing Reference Information
Sometimes you won't be able to find all the elements required for your reference. In that case, see the instructions in Table 9.1 of the APA style manual in section 9.4 or the APA Style website below:
- Direct Quotation of Material Without Page Numbers
The DOI or URL is the final component of a reference list entry. Because so much scholarship is available and/or retrieved online, most reference list entries end with either a DOI or a URL.
- A DOI is a unique alphanumeric string that identifies content and provides a persistent link to its location on the internet. DOIs can be found in database records and the reference lists of published works.
- A URL specifies the location of digital information on the internet and can be found in the address bar of your internet browser. URLs in references should link directly to the cited work when possible.
When to Include DOIs and URLs:
- Include a DOI for all works that have a DOI, regardless of whether you used the online version or the print version.
- If an online work has both a DOI and a URL, include only the DOI.
- For works without DOIs from websites (not including academic research databases), provide a URL in the reference (as long as the URL will work for readers).
- For works without DOIs from most academic research databases, do not include a URL or database information in the reference because these works are widely available. The reference should be the same as the reference for a print version of the work.
- For works from databases that publish original, proprietary material available only in that database (such as the UpToDate database) or for works of limited circulation in databases (such as monographs in the ERIC database), include the name of the database or archive and the URL of the work. If the URL requires a login or is session-specific (meaning it will not resolve for readers), provide the URL of the database or archive home page or login page instead of the URL for the work. (See APA Section 9.30 for more information).
- If the URL is no longer working or no longer provides readers access to the content you intend to cite, try to find an archived version using the Internet Archive , then use the archived URL. If there is no archived URL, do not use that resource.
Format of DOIs and URLs:
Your DOI should look like this:
https://doi.org/10.1037/a0040251
Follow these guidelines from the APA Style website.
APA Style uses the author–date citation system , in which a brief in-text citation points your reader to the full reference list entry at the end of your paper. The in-text citation appears within the body of the paper and briefly identifies the cited work by its author and date of publication. This method enables your reader to locate the corresponding entry in the alphabetical reference list at the end of your paper.
Each work you cite must appear in the reference list, and each work in the reference list must be cited in the text (or in a table, figure, footnote, or appendix) except for the following (See APA, 8.4):
- Personal communications (8.9)
- General mentions of entire websites, whole periodicals (8.22), and common software and apps (10.10) in the text do not require a citation or reference list entry.
- The source of an epigraph does not usually appear in the reference list (8.35)
- Quotations from your research participants do not need citations or reference list entries (8.36)
- References included in a statistical meta-analysis, which are marked with an asterisk in the reference list, may be cited in the text (or not) at the author’s discretion. This exception is relevant only to authors who are conducting a meta-analysis (9.52).
Formatting Your In-Text Citations
Parenthetical and Narrative Citations: ( See APA Section 8.11)
In APA style you use the author-date citation system for citing references within your paper. You incorporate these references using either a parenthetical or a narrative style.
Parenthetical Citations
- In parenthetical citations, the author name and publication date appear in parentheses, separated by a comma. (Jones, 2018)
- A parenthetical citation can appear within or at the end of a sentence.
- When the parenthetical citation is at the end of the sentence, put the period or other end punctuation after the closing parenthesis.
- If there is no author, use the first few words of the reference list entry, usually the "Title" of the source: ("Autism," 2008) See APA 8.14
- When quoting, always provide the author, year, and specific page citation or paragraph number for nonpaginated materials in the text (Santa Barbara, 2010, p. 243). See APA 8.13
- For most citations, the parenthetical reference is placed BEFORE the punctuation: Magnesium can be effective in treating PMS (Haggerty, 2012).
Narrative Citations
In narrative citations, the author name or title of your source appears within your text and the publication date appears in parentheses immediately after the author name.
- Santa Barbara (2010) noted a decline in the approval of disciplinary spanking of 26 percentage points from 1968 to 1994.
In-Text Citation Checklist
- In-Text Citation Checklist Use this useful checklist from the American Psychological Association to ensure that you've created your in-text citations correctly.
In-Text Citations for Specific Types of Sources
Quotations from Research Participants
Personal Communications
Secondary Sources
Use NoodleTools to Cite Your Sources
NoodleTools can help you create your references and your in-text citations.
- NoodleTools Express No sign in required . When you need one or two quick citations in MLA, APA, or Chicago style, simply generate them in NoodleTools Express then copy and paste what you need into your document. Note: Citations are not saved and cannot be exported to a word processor using NoodleTools Express.
- NoodleTools (Login Full Database) This link opens in a new window Create and organize your research notes, share and collaborate on research projects, compose and error check citations, and complete your list of works cited in MLA, APA, or Chicago style using the full version of NoodleTools. You'll need to Create a Personal ID and password the first time you use NoodleTools.
See How to Use NoodleTools Express to Create a Citation in APA Format
Additional NoodleTools Help
- NoodleTools Help Desk Look up questions and answers on the NoodleTools Web site
- << Previous: MLA Style (8th/9th ed.)
- Next: Chicago Style >>
- Last Updated: Mar 20, 2024 11:36 AM
- URL: https://libguides.mjc.edu/citeyoursources
Except where otherwise noted, this work is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0 and CC BY-NC 4.0 Licenses .
- The Complete Guide to APA Format in 2020
- Headings and Subheadings
- Discussion Section
- Websites and Online Sources
- Journals and Periodicals
- Other Print Sources
- Other Non-Print Sources
- In-text Citations
- Footnotes and Endnotes
- Using MyBib Responsibly
- Miscellaneous Questions

APA Format is the official writing style of the American Psychological Association, and is primarily used in subjects such as psychology, education, and the social sciences.
It specifies how to format academic papers and citations for publication in journals, periodicals, and bulletins.
This guide will show you how to prepare and format a document to be fully compliant with APA Format in 2020.
Before You Start Writing...
There are several steps you must take to prepare a new document for APA style before you start writing your paper:
- Make sure the paper size is 8.5" x 11" (known as 'Letter' in most word processors).
- Set the margin size to 1" on all sides (2.54cm).
- Change the line spacing to double-spaced .
- Add page numbers to the top-right corner of every page.
- Add a running head to the top-left corner of every page.
We have a pre-made APA style template document you can download to be sure you are ready to start writing. You can download it below:
When your document is ready, proceed to writing the title page .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References
APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References
Published on 18 January 2021 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on 17 January 2024.

This citation guide outlines the most important citation guidelines from the 7th edition APA Publication Manual (2020). Scribbr also offers free guides for the older APA 6th edition , MLA Style , and Chicago Style .
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Apa in-text citations, apa references, formatting the apa reference page, free lecture slides.
In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else’s ideas or words.
An APA in-text citation consists of the author’s last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system). If you’re citing a specific part of a source, you should also include a locator such as a page number or timestamp. For example: (Smith, 2020, p. 170) .
Parenthetical vs. narrative citation
The in-text citation can take two forms: parenthetical and narrative. Both types are generated automatically when citing a source with Scribbr’s APA Citation Generator.
- Parenthetical citation: According to new research … (Smith, 2020) .
- Narrative citation: Smith (2020) notes that …
Multiple authors and corporate authors
The in-text citation changes slightly when a source has multiple authors or an organization as an author. Pay attention to punctuation and the use of the ampersand (&) symbol.
Missing information
When the author, publication date or locator is unknown, take the steps outlined below.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
APA references generally include information about the author , publication date , title , and source . Depending on the type of source, you may have to include extra information that helps your reader locate the source.
Reference examples
Citing a source starts with choosing the correct reference format. Use Scribbr’s Citation Example Generator to learn more about the format for the most common source types. Pay close attention to punctuation, capitalization, and italicization.
Generate APA citations for free
It is not uncommon for certain information to be unknown or missing, especially with sources found online. In these cases, the reference is slightly adjusted.
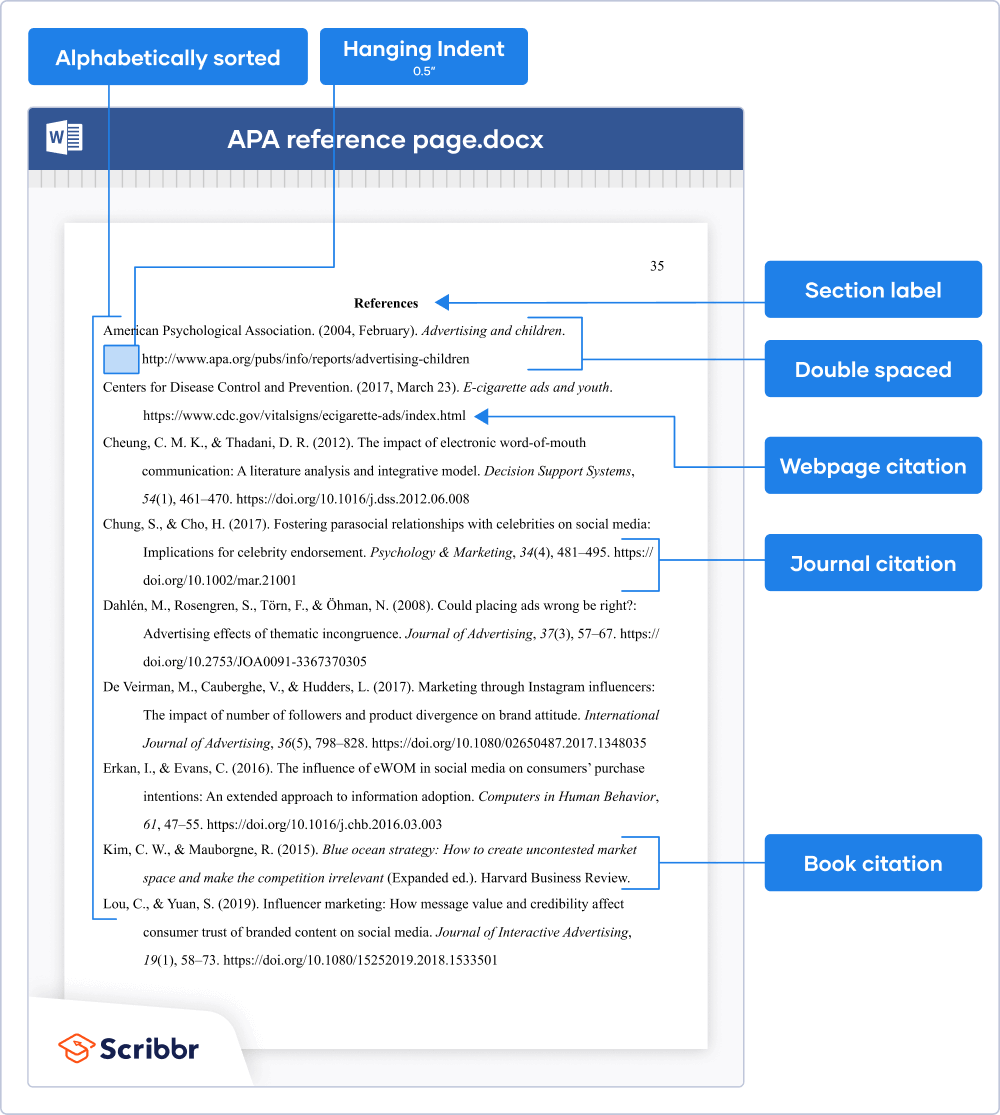
On the first line of the page, write the section label “References” (in bold and centred). On the second line, start listing your references in alphabetical order .
Apply these formatting guidelines to the APA reference page:
- Double spacing (within and between references)
- Hanging indent of ½ inch
- Legible font (e.g. Times New Roman 12 or Arial 11)
- Page number in the top-right header
Which sources to include
On the reference page, you only include sources that you have cited in the text (with an in-text citation ). You should not include references to personal communications that your reader can’t access (e.g. emails, phone conversations or private online material).
Are you a teacher or professor looking to introduce your students to APA Style? Download our free introductory lecture slides, available for Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2024, January 17). APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/apa-style/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, mhra referencing | a quick guide & citation examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

APA Style 7th Edition: Citing Your Sources
Apa 7th edition, what is the purpose, quick links.
- In Text Quick View
- Block Quotes
- Books & eBooks
- Thesis/Dissertation
- Audiovisual
- Conference Presentations
- Social Media
- Legal References
- Reports and Gray Literature
- Academic Integrity and Plagiarism
- Additional Resources
- Reference Page
APA Publications in the Library

This guide pertains to the 7th edition of the APA Manual.
This guide is designed to support the citation and reference needs of USC students, staff, and faculty. The 7th edition of the manual does make distinctions between formatting certain components for academic use over publication. This guide will distinguish student/academic formatting where applicable.
This guide is designed as a "quick" reference to common APA citation, reference and formatting criteria. When in doubt, we encourage users to consult with the APA publication manual or APA website for further clarification as the authority on formatting.
Attribution for guide: Adapted from American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
What is the purpose of citations?
Citations help readers locate your sources. They help to continue the scholarly conversation. To learn more about how citations can help you avoid plagiarism, view this interactive tutorial:
USC Library Lessons: Avoiding Plagiarism through Citations
When considering citations and references for your papers, you can ask yourself, "could someone find this information in the future?"
A client's personal file would not need a citation because your reader cannot go find that information again. Census statistics would require a citation because your reader could go locate that information again.
APA requires FOUR ELEMENTS of every citation:
- Who- Author of content
- When- Date content was published
- What- Title of content
- Where- Publication information. This can be the website you got it from or the journal or book's publication information.
If any of the elements listed above are unavailable, check out "Missing Reference Information" from APA for more information.
- APA Style Website As part of our Style and Grammar Guidelines, we explain the basics of paper format, grammar, punctuation, in-text citations, references, bias-free language, and more. Much of what you used to find on the sixth edition blog, you can now find on the APA Style website.
- Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper by Robert V. Labaree Last Updated Apr 9, 2024 453329 views this year
- Owl Purdue 7th Edition Style Guide and Formatting Writing guide from Owl Purdue covering the 7th edition of the APA Manual
- Quick Reference Guide Quick guide on how to identify components to configure a reference for Journal article, book, and chapter from an edited book.
- Annotated Sample Student Paper Sample student paper with formatting annotations.
- Sample student paper
- Annotated Sample Professional Paper Sample professional paper with formatting annotations
- Sample professional paper
- USC Libraries APA Style Quick Guide
- Next: In Text Citations >>
- Last Updated: Nov 1, 2023 3:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/APA7th
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- How to cite a journal article in APA Style
How to Cite a Journal Article in APA Style | Format & Example
Published on November 5, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 17, 2024.
An APA Style citation for a journal article includes the author name(s), publication year, article title, journal name, volume and issue number, page range of the article, and a DOI (if available). Use the buttons below to explore the format, or try the free APA Citation Generator to quickly and easily create citations.
Cite a journal article in APA Style now:
Table of contents, basic format for an apa journal citation, citing an article with an elocator or article number, citing unpublished journal articles, special issue of a journal, frequently asked questions about apa style citations.
The article title appears in plain text and sentence case, while the journal name is italicized and in title case (all major words capitalized).
When viewing a journal article online, the required information can usually be found on the access page.
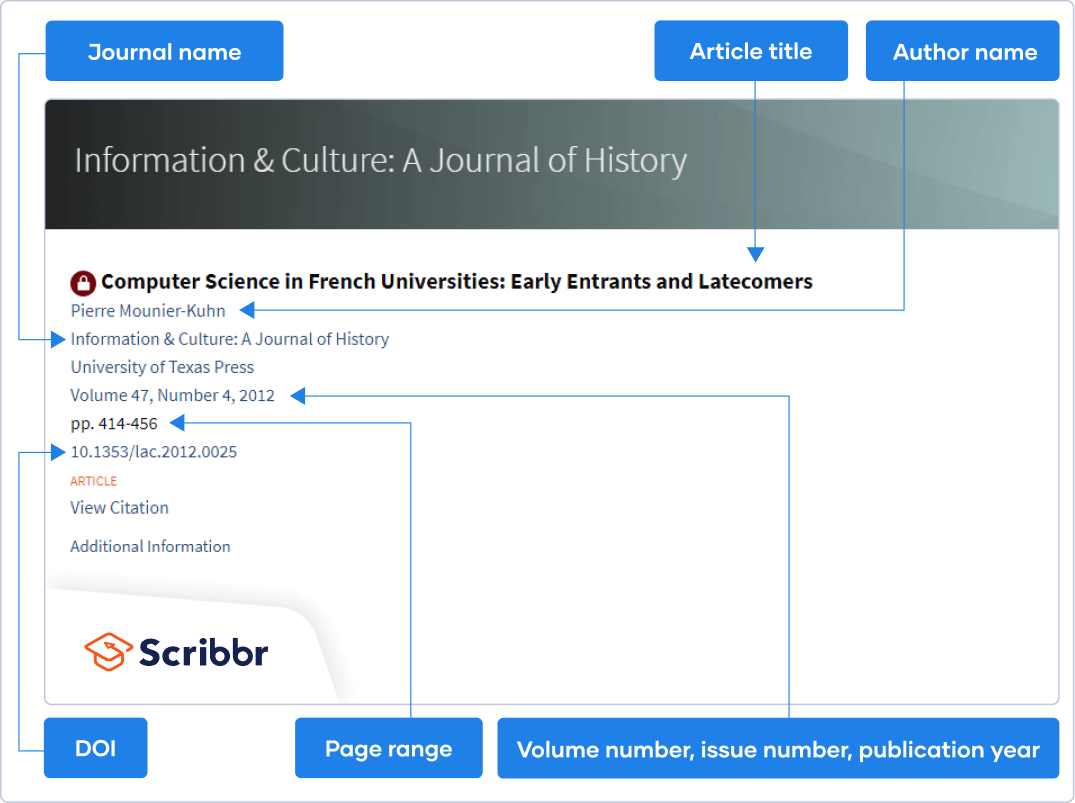
Linking to online journal articles
A DOI should always be used where available. Some databases do not list one, but you may still find one by looking for the same article on another database. You don’t need to include the name of the database in your citation.
If no DOI is available and the article was accessed through a database, do not include a URL.
If the article is not from a database, but from another website (e.g. the journal’s own website), you should ideally use a stable URL: this is often provided under a “share” button. Otherwise, copy the URL from your browser’s address bar.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Articles published only in PDF form may provide an article number or “eLocator” instead of a page range; in this case, include the number in your citation, preceded by the word “Article.”
When citing from an article that has not yet been formally published, the format varies depending on whether or not it has already been submitted to a journal. Note that different formats are used for unpublished dissertations and raw data .
Unpublished article
The text of an article which has not yet appeared online or in publication (i.e. which is only available directly from the author) should be cited as an “Unpublished manuscript.” The title is italicized and information about the author’s university is included if available:
Article submitted for publication
An article that has been submitted to a journal but not yet accepted is cited as a “Manuscript submitted for publication.” The title is italicized, and the name of the journal to which it was submitted is not included:
Article in press
An article that has been submitted and accepted for publication in a journal is cited as “in press.” Here, the name of the journal is included, university information is omitted, and “in press” is written in place of the year (both in the reference list and the in-text citation):
If you want to cite a special issue of a journal rather than a regular article, the name(s) of the editor(s) and the title of the issue appear in place of the author’s name and article title:
Note that if you want to cite an individual article from the special issue, it can just be cited in the basic format for journal articles.
In an APA journal citation , if a DOI (digital object identifier) is available for an article, always include it.
If an article has no DOI, and you accessed it through a database or in print, just omit the DOI.
If an article has no DOI, and you accessed it through a website other than a database (for example, the journal’s own website), include a URL linking to the article.
Include the DOI at the very end of the APA reference entry . If you’re using the 6th edition APA guidelines, the DOI is preceded by the label “doi:”. In the 7th edition , the DOI is preceded by ‘https://doi.org/’.
- 6th edition: doi: 10.1177/0894439316660340
- 7th edition: https://doi.org/ 10.1177/0894439316660340
APA citation example (7th edition)
Hawi, N. S., & Samaha, M. (2016). The relations among social media addiction, self-esteem, and life satisfaction in university students. Social Science Computer Review , 35 (5), 576–586. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894439316660340
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (meaning “and others”) is used to shorten APA in-text citations with three or more authors . Here’s how it works:
Only include the first author’s last name, followed by “et al.”, a comma and the year of publication, for example (Taylor et al., 2018).
You may include up to 20 authors in a reference list entry .
When an article has more than 20 authors, replace the names prior to the final listed author with an ellipsis, but do not omit the final author:
Davis, Y., Smith, J., Caulfield, F., Pullman, H., Carlisle, J., Donahue, S. D., James, F., O’Donnell, K., Singh, J., Johnson, L., Streefkerk, R., McCombes, S., Corrieri, L., Valck, X., Baldwin, F. M., Lorde, J., Wardell, K., Lao, W., Yang, P., . . . O’Brien, T. (2012).
In an APA reference list , journal article citations include only the year of publication, not the exact date, month, or season.
The inclusion of volume and issue numbers makes a more specific date unnecessary.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, January 17). How to Cite a Journal Article in APA Style | Format & Example. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-examples/journal-article/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, beginner's guide to apa in-text citation, setting up the apa reference page | formatting & references (examples), how to cite a book in apa style, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!
× All floors of the JFK Library are open for summer quarter. For details see Library Access
Research Guides
Eastern Washington University Libraries
APA Style 7th Edition Tutorials for Students in Psychology and Social Work
What is apa style.
- The Importance of Citing
Why is APA Style needed?
How do i get started with apa style, let us practice what we have learned, attribution and acknowledgement.
- Basics of APA Style Tutorial
- Reference Entry Elements
- Reference Examples
- Reference List
- In-Text Citations
- Student Paper Format
- Managing References - Zotero
Origination of APA Style
- Where did APA Style come from?
Commonly Used APA Related Terms
Abstract : Abstract is a brief synopses of article. It provides a brief but comprehensive summary of the article.
Citing : In the context of academic writing, citing is the act of acknowledging the sources of information you have used when writing your work.
Citation: A citation gives credit to a source, and contains publication information such as author(s), title and date.
DOI (digital object identifier): It is a unique alphanumeric string assigned to a digital object, mainly a scholarly article, to provide a persistent link to its location on the internet.
In-Text Citation : It is a brief note that appears within the body of the paper and briefly identifies the cited work by its author and date of publication. An in-text citation should always match the corresponding entry in the reference list at the end of paper.
Paraphrasing : A paraphrase restates another’s idea (or your own previously published idea) in your own words.
Plagiarism : It is the act of presenting the words, ideas, or images of another as your own; it denies creators of content the credit they are due.
Quoting : It is the act of reproducing the exact wording used by the original author. Direct quotations appear within quotation marks and end with a citation.
Reference : It contains details about one cited work, generally including four elements: author, date, title, and source.
Reference List : It identifies all the sources you cited in the text of your paper. It generally is at the end of the paper and definitely on a new page after the text of your paper.
APA Style is the most common writing style used in college and career. Its purpose is to promote excellence in communication by helping writers create clear, precise, and inclusive sentences with a straightforward scholarly tone. It addresses areas of writing such as how to
- format a paper so it looks professional;
- credit other people’s words and ideas via citations and references to avoid plagiarism; and
- describe other people with dignity and respect using inclusive, bias-free language.
APA Style is primarily used in the behavioral sciences, which are subjects related to people, such as psychology, education, and nursing. It is also used by students in business, engineering, communications, and other classes. Students use it to write academic essays and research papers in college, and professionals use it to conduct, report, and publish scientific research.
In addition, APA Style provides you with a powerful tool that will hep you avoid deliberate or unintentional plagiarism. Please review the Avoiding Plagiarism Guide created by the APA experts to understand what two common types of plagiarism are and how to avoid them.
Why is learning citations important? Citations help readers understand where the information used in your paper comes from, enabling them to trace the path of that information. When readers wish to explore a specific point or reference cited in the text, citations make it easier by providing information about your sources in a standardized format.
Besides showing readers where you obtained information, using citations also has a strong ethical purpose. In academic writing, it is important to credit ideas that are not your own. Citations allow you to integrate the ideas of others with your own thoughts in a fair and honest way.
The reference formats for APA Style manuals are as follows:
APA Style provides a foundation for effective scholarly communication because it helps authors present their ideas in a clear and concise, and organized manner. Uniformity and consistency enable readers to (a) focus on the ideas being presented rather than formatting and (b) scan works quickly for key points, findings, and sources. When style works best, ideas flow logically, sources are credited appropriately, and papers are organized predictably and consistently.
Students are encouraged to first learn about APA Style by reading works written in APA Style. A couple of guides created by APA experts from the American Psychological Association can help you with that:
Anatomy of a Journal Article https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/anatomy-journal-article.pdf
Scholarly journal articles share a common anatomy or structure. Each part of an article serves a specific purpose. The handout of Anatomy of a Journal Article explains how journal articles are structured and how to become more efficient at reading and understanding them. Understanding the structure of a scholarly article and the purpose of each part helps you grasp a strategy called targeted reading. Targeted reading means to read specific sections of research articles first to determine if the article seems useful for your research topic. This way you will save time, find useful article faster, and choose which articles to read in full.
Reading and Understanding Abstracts https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/reading-abstracts.pdf
Abstracts are short summaries of scientific research articles. The handout of Reading & Understanding Abstracts explains the definition and purpose of abstracts and the benefits of reading them, including analysis of a sample abstract. The skill of reading and understanding abstracts of scholarly articles not only saves time but also helps you conduct better research and write more effectively.
APA Style Writing Principles https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/writing-principles.pdf
The poster created by APA experts shows the three main principles of APA Style: clarity, precision, and inclusion and lists steps on how to achieve them. As a student writer, you always should write your academic paper with clarity, precision, and inclusion.
Research Article Activity https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/apa-style-research-activity.pdf
Reading research articles is not an easy task for you as a student. The Research Article Activity designed by APA Style experts aims to make it easy to read and understand a scholarly article. This activity worksheet helps you find, cite, analyze, and summarize a research article. Completing this activity breaks down a lengthy research article into easily understandable chunks. This way helps you better understand the study in the article before you write about it.
The information in this Guide is courtesy of the official APA Style website by the American Psychological Association.
Source Credit: Information on this LibGuide comes from APA Style website https://apastyle.apa.org/ This website has a wealth of free and authoritative resources designed to help anyone new to APA Style.
- Next: Basics of APA Style Tutorial >>
- Last Updated: Apr 6, 2024 12:06 PM
- URL: https://research.ewu.edu/APAStyleTutorial

- Research Guides
- Schlesinger Library on the History of Women in America
- Archival Materials
- Additional Resources
- Research Tips
- Ask a Schlesinger Librarian
Fundamentals of APA
American Psychological Association (APA) style includes parenthetical in-text citations and a reference list .
APA uses parenthetical citations as its form of in-text citation. Provide a parenthetical citation before the period directly following the information you are citing. These citations should correspond to a more detailed citation in the reference list but only need to specify a page number if directly quoting or borrowing from the source material. The essential elements for this in-text citation are the author's last name and the date for the specific publications. The last name may be omitted if the sentence states or makes clear the source material.
APA uses a reference list , an alphabetized list of sources following the end of the book or paper, for its complete list of sources referenced. This list should be titled "References" in bold and alphabetized by the first item in the citation, which, in most cases, is the author's last name. Each reference from this list must be cited in your paper and vice versa.
Basic Format
Author Last Name, Author First Initial. (Year of publication). Title . Publisher Name.
Print Articles
Author Last Name, Author First Initial, & Author Last Name, Author First Initial. (Year). Article Title. Periodical Title , volume number(issue number), pages.
Electronic Articles
Author Last Name, Author First Initial. (Year). Article Title. Periodical Title , volume number(issue number), pages. doi or static url.
Physical Images/Artwork
Artist Last Name, Artist First Initial. (Year). Artwork Title [medium]. Host Institution Name, City, State, Country. URL of institution.
Electronic Images/Artwork
Artist Last Name, Artist First Initial. (Year). Image Title [medium]. Source Title. URL of image.
In-text Citation Examples
Standard case :
"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet , consectetur adipiscing elit" (Last name, 2000, p.10).
If the author is not available , the title of the source may be used:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet , consectetur adipiscing elit ("Source title", 2000, pp.10-11).
If multiple authors cited have the same last name , use the author's first initial along with their last name:
"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet , consectetur adipiscing elit" (E. Bronte, 1847, p.10).
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet , consectetur adipiscing elit (C. Bronte, 1847, p.10).
Full Citation Examples for the Reference List
Archival material :
Child, J. (1974). Journal, 1974 . [Unpublished journal]. Papers of Julia Child, 1925-1993(MC 644, item 4). Schlesinger Library on the History of Women in America, Radcliffe Institute, https://id.lib.harvard.edu/ead/c/ sch00222c00006 /catalog .
Child, P. (1967). Julia Child at the White House [Photograph]. Schlesinger Library on the History of Women in America, Radcliffe Institute, https://id.lib.harvard.edu/images/olvwork539731/urn-3:RAD.SCHL:4510469/catalog.
Beck, S., Bertholle, L., & Child, J. (1961). Mastering the art of French cooking. Knopf.
Child, J. & Child, P. (1968). The French chef cookbook . Alfred A. Knopf .
Journal article :
Muneal, M. (2011). Studies in Popular Culture , 34(1), 152–154. www.jstor.org/stable/23416357.
Nussbaum, D. (2005). "In Julia Child's Kitchen, October 5 1998". Gastronomica , 5(3), 29-38. doi: 10.1525/gfc.2005.5.3.29.
- APA Style website The online version of the APA Style Manual, this website offers to help with the technical elements of formatting in APA as well as writing and citing your work.
- Purdue OWL APA Guide The Purdue Online Writing Lab (OWL) is one of the most complete citation guides available online. The APA Guide explains how to format a paper in APA and breaks down citations by type with numerous examples.
- << Previous: MLA
- Next: Chicago >>
- Harvard Library
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2024 9:31 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/schlesinger/citation_guide
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
How to Write an APA Research Paper
Psychology/neuroscience 201, v iew in pdf format.
An APA-style paper includes the following sections: title page, abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references. Your paper may also include one or more tables and/or figures. Different types of information about your study are addressed in each of the sections, as described below.
General formatting rules are as follows:
Do not put page breaks in between the introduction, method, results, and discussion sections.
The title page, abstract, references, table(s), and figure(s) should be on their own pages. The entire paper should be written in the past tense, in a 12-point font, double-spaced, and with one-inch margins all around.
(see sample on p. 41 of APA manual)
- Title should be between 10-12 words and should reflect content of paper (e.g., IV and DV).
- Title, your name, and Hamilton College are all double-spaced (no extra spaces)
- Create a page header using the “View header” function in MS Word. On the title page, the header should include the following: Flush left: Running head: THE RUNNING HEAD SHOULD BE IN ALL CAPITAL LETTERS. The running head is a short title that appears at the top of pages of published articles. It should not exceed 50 characters, including punctuation and spacing. (Note: on the title page, you actually write the words “Running head,” but these words do not appear on subsequent pages; just the actual running head does. If you make a section break between the title page and the rest of the paper you can make the header different for those two parts of the manuscript). Flush right, on same line: page number. Use the toolbox to insert a page number, so it will automatically number each page.
Abstract (labeled, centered, not bold)
No more than 120 words, one paragraph, block format (i.e., don’t indent), double-spaced.
- State topic, preferably in one sentence. Provide overview of method, results, and discussion.
Introduction
(Do not label as “Introduction.” Title of paper goes at the top of the page—not bold)
The introduction of an APA-style paper is the most difficult to write. A good introduction will summarize, integrate, and critically evaluate the empirical knowledge in the relevant area(s) in a way that sets the stage for your study and why you conducted it. The introduction starts out broad (but not too broad!) and gets more focused toward the end. Here are some guidelines for constructing a good introduction:
- Don’t put your readers to sleep by beginning your paper with the time-worn sentence, “Past research has shown (blah blah blah)” They’ll be snoring within a paragraph! Try to draw your reader in by saying something interesting or thought-provoking right off the bat. Take a look at articles you’ve read. Which ones captured your attention right away? How did the authors accomplish this task? Which ones didn’t? Why not? See if you can use articles you liked as a model. One way to begin (but not the only way) is to provide an example or anecdote illustrative of your topic area.
- Although you won’t go into the details of your study and hypotheses until the end of the intro, you should foreshadow your study a bit at the end of the first paragraph by stating your purpose briefly, to give your reader a schema for all the information you will present next.
- Your intro should be a logical flow of ideas that leads up to your hypothesis. Try to organize it in terms of the ideas rather than who did what when. In other words, your intro shouldn’t read like a story of “Schmirdley did such-and-such in 1991. Then Gurglehoff did something-or-other in 1993. Then....(etc.)” First, brainstorm all of the ideas you think are necessary to include in your paper. Next, decide which ideas make sense to present first, second, third, and so forth, and think about how you want to transition between ideas. When an idea is complex, don’t be afraid to use a real-life example to clarify it for your reader. The introduction will end with a brief overview of your study and, finally, your specific hypotheses. The hypotheses should flow logically out of everything that’s been presented, so that the reader has the sense of, “Of course. This hypothesis makes complete sense, given all the other research that was presented.”
- When incorporating references into your intro, you do not necessarily need to describe every single study in complete detail, particularly if different studies use similar methodologies. Certainly you want to summarize briefly key articles, though, and point out differences in methods or findings of relevant studies when necessary. Don’t make one mistake typical of a novice APA-paper writer by stating overtly why you’re including a particular article (e.g., “This article is relevant to my study because…”). It should be obvious to the reader why you’re including a reference without your explicitly saying so. DO NOT quote from the articles, instead paraphrase by putting the information in your own words.
- Be careful about citing your sources (see APA manual). Make sure there is a one-to-one correspondence between the articles you’ve cited in your intro and the articles listed in your reference section.
- Remember that your audience is the broader scientific community, not the other students in your class or your professor. Therefore, you should assume they have a basic understanding of psychology, but you need to provide them with the complete information necessary for them to understand the research you are presenting.
Method (labeled, centered, bold)
The Method section of an APA-style paper is the most straightforward to write, but requires precision. Your goal is to describe the details of your study in such a way that another researcher could duplicate your methods exactly.
The Method section typically includes Participants, Materials and/or Apparatus, and Procedure sections. If the design is particularly complicated (multiple IVs in a factorial experiment, for example), you might also include a separate Design subsection or have a “Design and Procedure” section.
Note that in some studies (e.g., questionnaire studies in which there are many measures to describe but the procedure is brief), it may be more useful to present the Procedure section prior to the Materials section rather than after it.
Participants (labeled, flush left, bold)
Total number of participants (# women, # men), age range, mean and SD for age, racial/ethnic composition (if applicable), population type (e.g., college students). Remember to write numbers out when they begin a sentence.
- How were the participants recruited? (Don’t say “randomly” if it wasn’t random!) Were they compensated for their time in any way? (e.g., money, extra credit points)
- Write for a broad audience. Thus, do not write, “Students in Psych. 280...” Rather, write (for instance), “Students in a psychological statistics and research methods course at a small liberal arts college….”
- Try to avoid short, choppy sentences. Combine information into a longer sentence when possible.
Materials (labeled, flush left, bold)
Carefully describe any stimuli, questionnaires, and so forth. It is unnecessary to mention things such as the paper and pencil used to record the responses, the data recording sheet, the computer that ran the data analysis, the color of the computer, and so forth.
- If you included a questionnaire, you should describe it in detail. For instance, note how many items were on the questionnaire, what the response format was (e.g., a 5-point Likert-type scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree)), how many items were reverse-scored, whether the measure had subscales, and so forth. Provide a sample item or two for your reader.
- If you have created a new instrument, you should attach it as an Appendix.
- If you presented participants with various word lists to remember or stimuli to judge, you should describe those in detail here. Use subheadings to separate different types of stimuli if needed. If you are only describing questionnaires, you may call this section “Measures.”
Apparatus (labeled, flush left, bold)
Include an apparatus section if you used specialized equipment for your study (e.g., the eye tracking machine) and need to describe it in detail.
Procedure (labeled, flush left, bold)
What did participants do, and in what order? When you list a control variable (e.g., “Participants all sat two feet from the experimenter.”), explain WHY you did what you did. In other words, what nuisance variable were you controlling for? Your procedure should be as brief and concise as possible. Read through it. Did you repeat yourself anywhere? If so, how can you rearrange things to avoid redundancy? You may either write the instructions to the participants verbatim or paraphrase, whichever you deem more appropriate. Don’t forget to include brief statements about informed consent and debriefing.
Results (labeled, centered, bold)
In this section, describe how you analyzed the data and what you found. If your data analyses were complex, feel free to break this section down into labeled subsections, perhaps one section for each hypothesis.
- Include a section for descriptive statistics
- List what type of analysis or test you conducted to test each hypothesis.
- Refer to your Statistics textbook for the proper way to report results in APA style. A t-test, for example, is reported in the following format: t (18) = 3.57, p < .001, where 18 is the number of degrees of freedom (N – 2 for an independent-groups t test). For a correlation: r (32) = -.52, p < .001, where 32 is the number of degrees of freedom (N – 2 for a correlation). For a one-way ANOVA: F (2, 18) = 7.00, p < .001, where 2 represents the between and 18 represents df within Remember that if a finding has a p value greater than .05, it is “nonsignificant,” not “insignificant.” For nonsignificant findings, still provide the exact p values. For correlations, be sure to report the r 2 value as an assessment of the strength of the finding, to show what proportion of variability is shared by the two variables you’re correlating. For t- tests and ANOVAs, report eta 2 .
- Report exact p values to two or three decimal places (e.g., p = .042; see p. 114 of APA manual). However, for p-values less than .001, simply put p < .001.
- Following the presentation of all the statistics and numbers, be sure to state the nature of your finding(s) in words and whether or not they support your hypothesis (e.g., “As predicted …”). This information can typically be presented in a sentence or two following the numbers (within the same paragraph). Also, be sure to include the relevant means and SDs.
- It may be useful to include a table or figure to represent your results visually. Be sure to refer to these in your paper (e.g., “As illustrated in Figure 1…”). Remember that you may present a set of findings either as a table or as a figure, but not as both. Make sure that your text is not redundant with your tables/figures. For instance, if you present a table of means and standard deviations, you do not need to also report these in the text. However, if you use a figure to represent your results, you may wish to report means and standard deviations in the text, as these may not always be precisely ascertained by examining the figure. Do describe the trends shown in the figure.
- Do not spend any time interpreting or explaining the results; save that for the Discussion section.
Discussion (labeled, centered, bold)
The goal of the discussion section is to interpret your findings and place them in the broader context of the literature in the area. A discussion section is like the reverse of the introduction, in that you begin with the specifics and work toward the more general (funnel out). Some points to consider:
- Begin with a brief restatement of your main findings (using words, not numbers). Did they support the hypothesis or not? If not, why not, do you think? Were there any surprising or interesting findings? How do your findings tie into the existing literature on the topic, or extend previous research? What do the results say about the broader behavior under investigation? Bring back some of the literature you discussed in the Introduction, and show how your results fit in (or don’t fit in, as the case may be). If you have surprising findings, you might discuss other theories that can help to explain the findings. Begin with the assumption that your results are valid, and explain why they might differ from others in the literature.
- What are the limitations of the study? If your findings differ from those of other researchers, or if you did not get statistically significant results, don’t spend pages and pages detailing what might have gone wrong with your study, but do provide one or two suggestions. Perhaps these could be incorporated into the future research section, below.
- What additional questions were generated from this study? What further research should be conducted on the topic? What gaps are there in the current body of research? Whenever you present an idea for a future research study, be sure to explain why you think that particular study should be conducted. What new knowledge would be gained from it? Don’t just say, “I think it would be interesting to re-run the study on a different college campus” or “It would be better to run the study again with more participants.” Really put some thought into what extensions of the research might be interesting/informative, and why.
- What are the theoretical and/or practical implications of your findings? How do these results relate to larger issues of human thoughts, feelings, and behavior? Give your readers “the big picture.” Try to answer the question, “So what?
Final paragraph: Be sure to sum up your paper with a final concluding statement. Don’t just trail off with an idea for a future study. End on a positive note by reminding your reader why your study was important and what it added to the literature.
References (labeled, centered, not bold)
Provide an alphabetical listing of the references (alphabetize by last name of first author). Double-space all, with no extra spaces between references. The second line of each reference should be indented (this is called a hanging indent and is easily accomplished using the ruler in Microsoft Word). See the APA manual for how to format references correctly.
Examples of references to journal articles start on p. 198 of the manual, and examples of references to books and book chapters start on pp. 202. Digital object identifiers (DOIs) are now included for electronic sources (see pp. 187-192 of APA manual to learn more).
Journal article example: [Note that only the first letter of the first word of the article title is capitalized; the journal name and volume are italicized. If the journal name had multiple words, each of the major words would be capitalized.]
Ebner-Priemer, U. W., & Trull, T. J. (2009). Ecological momentary assessment of mood disorders and mood dysregulation. Psychological Assessment, 21, 463-475. doi:10.1037/a0017075
Book chapter example: [Note that only the first letter of the first word of both the chapter title and book title are capitalized.]
Stephan, W. G. (1985). Intergroup relations. In G. Lindzey & E. Aronson (Eds.), The handbook of social psychology (3 rd ed., Vol. 2, pp. 599-658). New York: Random House.
Book example: Gray, P. (2010). Psychology (6 th ed.). New York: Worth
Table There are various formats for tables, depending upon the information you wish to include. See the APA manual. Be sure to provide a table number and table title (the latter is italicized). Tables can be single or double-spaced.
Figure If you have more than one figure, each one gets its own page. Use a sans serif font, such as Helvetica, for any text within your figure. Be sure to label your x- and y-axes clearly, and make sure you’ve noted the units of measurement of the DV. Underneath the figure provide a label and brief caption (e.g., “Figure 1. Mean evaluation of job applicant qualifications as a function of applicant attractiveness level”). The figure caption typically includes the IVs/predictor variables and the DV. Include error bars in your bar graphs, and note what the bars represent in the figure caption: Error bars represent one standard error above and below the mean.
In-Text Citations: (see pp. 174-179 of APA manual) When citing sources in your paper, you need to include the authors’ names and publication date.
You should use the following formats:
- When including the citation as part of the sentence, use AND: “According to Jones and Smith (2003), the…”
- When the citation appears in parentheses, use “&”: “Studies have shown that priming can affect actual motor behavior (Jones & Smith, 2003; Klein, Bailey, & Hammer, 1999).” The studies appearing in parentheses should be ordered alphabetically by the first author’s last name, and should be separated by semicolons.
- If you are quoting directly (which you should avoid), you also need to include the page number.
- For sources with three or more authors, once you have listed all the authors’ names, you may write “et al.” on subsequent mentions. For example: “Klein et al. (1999) found that….” For sources with two authors, both authors must be included every time the source is cited. When a source has six or more authors, the first author’s last name and “et al.” are used every time the source is cited (including the first time).
Secondary Sources
“Secondary source” is the term used to describe material that is cited in another source. If in his article entitled “Behavioral Study of Obedience” (1963), Stanley Milgram makes reference to the ideas of Snow (presented above), Snow (1961) is the primary source, and Milgram (1963) is the secondary source.
Try to avoid using secondary sources in your papers; in other words, try to find the primary source and read it before citing it in your own work. If you must use a secondary source, however, you should cite it in the following way:
Snow (as cited in Milgram, 1963) argued that, historically, the cause of most criminal acts... The reference for the Milgram article (but not the Snow reference) should then appear in the reference list at the end of your paper.
Tutor Appointments
Peer tutor and consultant appointments are managed through TracCloud (login required). Find resources and more information about the ALEX centers using the following links.
Office / Department Name
Nesbitt-Johnston Writing Center
Contact Name
Jennifer Ambrose
Writing Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tables and Figures

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resources for the older APA 6 style can be found at this page as well as at this page (our old resources covered the material on this page on two separate pages).
The purpose of tables and figures in documents is to enhance your readers' understanding of the information in the document; usually, large amounts of information can be communicated more efficiently in tables or figures. Tables are any graphic that uses a row and column structure to organize information, whereas figures include any illustration or image other than a table.
General guidelines
Visual material such as tables and figures can be used quickly and efficiently to present a large amount of information to an audience, but visuals must be used to assist communication, not to use up space, or disguise marginally significant results behind a screen of complicated statistics. Ask yourself this question first: Is the table or figure necessary? For example, it is better to present simple descriptive statistics in the text, not in a table.
Relation of Tables or Figures and Text
Because tables and figures supplement the text, refer in the text to all tables and figures used and explain what the reader should look for when using the table or figure. Focus only on the important point the reader should draw from them, and leave the details for the reader to examine on their own.
Documentation
If you are using figures, tables and/or data from other sources, be sure to gather all the information you will need to properly document your sources.
Integrity and Independence
Each table and figure must be intelligible without reference to the text, so be sure to include an explanation of every abbreviation (except the standard statistical symbols and abbreviations).
Organization, Consistency, and Coherence
Number all tables sequentially as you refer to them in the text (Table 1, Table 2, etc.), likewise for figures (Figure 1, Figure 2, etc.). Abbreviations, terminology, and probability level values must be consistent across tables and figures in the same article. Likewise, formats, titles, and headings must be consistent. Do not repeat the same data in different tables.
Data in a table that would require only two or fewer columns and rows should be presented in the text. More complex data is better presented in tabular format. In order for quantitative data to be presented clearly and efficiently, it must be arranged logically, e.g. data to be compared must be presented next to one another (before/after, young/old, male/female, etc.), and statistical information (means, standard deviations, N values) must be presented in separate parts of the table. If possible, use canonical forms (such as ANOVA, regression, or correlation) to communicate your data effectively.

A generic example of a table with multiple notes formatted in APA 7 style.
Elements of Tables
Number all tables with Arabic numerals sequentially. Do not use suffix letters (e.g. Table 3a, 3b, 3c); instead, combine the related tables. If the manuscript includes an appendix with tables, identify them with capital letters and Arabic numerals (e.g. Table A1, Table B2).
Like the title of the paper itself, each table must have a clear and concise title. Titles should be written in italicized title case below the table number, with a blank line between the number and the title. When appropriate, you may use the title to explain an abbreviation parenthetically.
Comparison of Median Income of Adopted Children (AC) v. Foster Children (FC)
Keep headings clear and brief. The heading should not be much wider than the widest entry in the column. Use of standard abbreviations can aid in achieving that goal. There are several types of headings:
- Stub headings describe the lefthand column, or stub column , which usually lists major independent variables.
- Column headings describe entries below them, applying to just one column.
- Column spanners are headings that describe entries below them, applying to two or more columns which each have their own column heading. Column spanners are often stacked on top of column headings and together are called decked heads .
- Table Spanners cover the entire width of the table, allowing for more divisions or combining tables with identical column headings. They are the only type of heading that may be plural.
All columns must have headings, written in sentence case and using singular language (Item rather than Items) unless referring to a group (Men, Women). Each column’s items should be parallel (i.e., every item in a column labeled “%” should be a percentage and does not require the % symbol, since it’s already indicated in the heading). Subsections within the stub column can be shown by indenting headings rather than creating new columns:
Chemical Bonds
Ionic
Covalent
Metallic
The body is the main part of the table, which includes all the reported information organized in cells (intersections of rows and columns). Entries should be center aligned unless left aligning them would make them easier to read (longer entries, usually). Word entries in the body should use sentence case. Leave cells blank if the element is not applicable or if data were not obtained; use a dash in cells and a general note if it is necessary to explain why cells are blank. In reporting the data, consistency is key: Numerals should be expressed to a consistent number of decimal places that is determined by the precision of measurement. Never change the unit of measurement or the number of decimal places in the same column.
There are three types of notes for tables: general, specific, and probability notes. All of them must be placed below the table in that order.
General notes explain, qualify or provide information about the table as a whole. Put explanations of abbreviations, symbols, etc. here.
Example: Note . The racial categories used by the US Census (African-American, Asian American, Latinos/-as, Native-American, and Pacific Islander) have been collapsed into the category “non-White.” E = excludes respondents who self-identified as “White” and at least one other “non-White” race.
Specific notes explain, qualify or provide information about a particular column, row, or individual entry. To indicate specific notes, use superscript lowercase letters (e.g. a , b , c ), and order the superscripts from left to right, top to bottom. Each table’s first footnote must be the superscript a .
a n = 823. b One participant in this group was diagnosed with schizophrenia during the survey.
Probability notes provide the reader with the results of the tests for statistical significance. Asterisks indicate the values for which the null hypothesis is rejected, with the probability ( p value) specified in the probability note. Such notes are required only when relevant to the data in the table. Consistently use the same number of asterisks for a given alpha level throughout your paper.
* p < .05. ** p < .01. *** p < .001
If you need to distinguish between two-tailed and one-tailed tests in the same table, use asterisks for two-tailed p values and an alternate symbol (such as daggers) for one-tailed p values.
* p < .05, two-tailed. ** p < .01, two-tailed. † p <.05, one-tailed. †† p < .01, one-tailed.
Borders
Tables should only include borders and lines that are needed for clarity (i.e., between elements of a decked head, above column spanners, separating total rows, etc.). Do not use vertical borders, and do not use borders around each cell. Spacing and strict alignment is typically enough to clarify relationships between elements.

Example of a table in the text of an APA 7 paper. Note the lack of vertical borders.
Tables from Other Sources
If using tables from an external source, copy the structure of the original exactly, and cite the source in accordance with APA style .
Table Checklist
(Taken from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th ed., Section 7.20)
- Is the table necessary?
- Does it belong in the print and electronic versions of the article, or can it go in an online supplemental file?
- Are all comparable tables presented consistently?
- Are all tables numbered with Arabic numerals in the order they are mentioned in the text? Is the table number bold and left-aligned?
- Are all tables referred to in the text?
- Is the title brief but explanatory? Is it presented in italicized title case and left-aligned?
- Does every column have a column heading? Are column headings centered?
- Are all abbreviations; special use of italics, parentheses, and dashes; and special symbols explained?
- Are the notes organized according to the convention of general, specific, probability?
- Are table borders correctly used (top and bottom of table, beneath column headings, above table spanners)?
- Does the table use correct line spacing (double for the table number, title, and notes; single, one and a half, or double for the body)?
- Are entries in the left column left-aligned beneath the centered stub heading? Are all other column headings and cell entries centered?
- Are confidence intervals reported for all major point estimates?
- Are all probability level values correctly identified, and are asterisks attached to the appropriate table entries? Is a probability level assigned the same number of asterisks in all the tables in the same document?
- If the table or its data are from another source, is the source properly cited? Is permission necessary to reproduce the table?
Figures include all graphical displays of information that are not tables. Common types include graphs, charts, drawings, maps, plots, and photos. Just like tables, figures should supplement the text and should be both understandable on their own and referenced fully in the text. This section details elements of formatting writers must use when including a figure in an APA document, gives an example of a figure formatted in APA style, and includes a checklist for formatting figures.
Preparing Figures
In preparing figures, communication and readability must be the ultimate criteria. Avoid the temptation to use the special effects available in most advanced software packages. While three-dimensional effects, shading, and layered text may look interesting to the author, overuse, inconsistent use, and misuse may distort the data, and distract or even annoy readers. Design properly done is inconspicuous, almost invisible, because it supports communication. Design improperly, or amateurishly, done draws the reader’s attention from the data, and makes him or her question the author’s credibility. Line drawings are usually a good option for readability and simplicity; for photographs, high contrast between background and focal point is important, as well as cropping out extraneous detail to help the reader focus on the important aspects of the photo.
Parts of a Figure
All figures that are part of the main text require a number using Arabic numerals (Figure 1, Figure 2, etc.). Numbers are assigned based on the order in which figures appear in the text and are bolded and left aligned.
Under the number, write the title of the figure in italicized title case. The title should be brief, clear, and explanatory, and both the title and number should be double spaced.
The image of the figure is the body, and it is positioned underneath the number and title. The image should be legible in both size and resolution; fonts should be sans serif, consistently sized, and between 8-14 pt. Title case should be used for axis labels and other headings; descriptions within figures should be in sentence case. Shading and color should be limited for clarity; use patterns along with color and check contrast between colors with free online checkers to ensure all users (people with color vision deficiencies or readers printing in grayscale, for instance) can access the content. Gridlines and 3-D effects should be avoided unless they are necessary for clarity or essential content information.
Legends, or keys, explain symbols, styles, patterns, shading, or colors in the image. Words in the legend should be in title case; legends should go within or underneath the image rather than to the side. Not all figures will require a legend.
Notes clarify the content of the figure; like tables, notes can be general, specific, or probability. General notes explain units of measurement, symbols, and abbreviations, or provide citation information. Specific notes identify specific elements using superscripts; probability notes explain statistical significance of certain values.

A generic example of a figure formatted in APA 7 style.
Figure Checklist
(Taken from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7 th ed., Section 7.35)
- Is the figure necessary?
- Does the figure belong in the print and electronic versions of the article, or is it supplemental?
- Is the figure simple, clean, and free of extraneous detail?
- Is the figure title descriptive of the content of the figure? Is it written in italic title case and left aligned?
- Are all elements of the figure clearly labeled?
- Are the magnitude, scale, and direction of grid elements clearly labeled?
- Are parallel figures or equally important figures prepared according to the same scale?
- Are the figures numbered consecutively with Arabic numerals? Is the figure number bold and left aligned?
- Has the figure been formatted properly? Is the font sans serif in the image portion of the figure and between sizes 8 and 14?
- Are all abbreviations and special symbols explained?
- If the figure has a legend, does it appear within or below the image? Are the legend’s words written in title case?
- Are the figure notes in general, specific, and probability order? Are they double-spaced, left aligned, and in the same font as the paper?
- Are all figures mentioned in the text?
- Has written permission for print and electronic reuse been obtained? Is proper credit given in the figure caption?
- Have all substantive modifications to photographic images been disclosed?
- Are the figures being submitted in a file format acceptable to the publisher?
- Have the files been produced at a sufficiently high resolution to allow for accurate reproduction?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
APA in-text citations The basics. In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else's ideas or words to avoid plagiarism.. An APA in-text citation consists of the author's last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system).
1. Name the author and the publication date in-text before a quote. To simplify the in-text citation, place the last name of the author in the text to introduce the quote and then the publication date for the text in parentheses. You can then leave the author's name and the publication date out of the quote itself. [1]
Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats. Basic Rules Basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper Author/Authors Rules for handling works by a single author or multiple authors that apply to all APA-style references in your reference list, regardless of the ...
Reference List: Basic Rules. This resourse, revised according to the 7 th edition APA Publication Manual, offers basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper. Most sources follow fairly straightforward rules. However, because sources obtained from academic journals carry special weight in research writing, these sources are subject to special ...
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here. Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
References provide the information necessary for readers to identify and retrieve each work cited in the text. Check each reference carefully against the original publication to ensure information is accurate and complete. Accurately prepared references help establish your credibility as a careful researcher and writer. Consistency in reference ...
Placement: The reference list appears at the end of the paper, on its own page(s). If your research paper ends on page 8, your References begin on page 9. Heading: Place the section label References in bold at the top of the page, centered. Arrangement: Alphabetize entries by author's last name. If source has no named author, alphabetize by the ...
There are several steps you must take to prepare a new document for APA style before you start writing your paper: Make sure the paper size is 8.5" x 11" (known as 'Letter' in most word processors). Set the margin size to 1" on all sides (2.54cm). Change the line spacing to double-spaced.
APA in-text citations The basics. In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else's ideas or words.. An APA in-text citation consists of the author's last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system).
Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association by American Psychological Association The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition is the official source for APA Style. With millions of copies sold worldwide in multiple languages, it is the style manual of choice for writers, researchers, editors, students, and educators in the social and ...
If you want to cite a special issue of a journal rather than a regular article, the name (s) of the editor (s) and the title of the issue appear in place of the author's name and article title: APA format. Last name, Initials. (Ed. or Eds.). ( Year ). Title of issue [Special issue]. Journal Name, Volume ( Issue ).
This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and ...
Abstract: Abstract is a brief synopses of article.It provides a brief but comprehensive summary of the article. Citing: In the context of academic writing, citing is the act of acknowledging the sources of information you have used when writing your work.. Citation: A citation gives credit to a source, and contains publication information such as author(s), title and date.
APA uses a reference list , an alphabetized list of sources following the end of the book or paper, for its complete list of sources referenced. This list should be titled "References" in bold and alphabetized by the first item in the citation, which, in most cases, is the author's last name. Each reference from this list must be cited in your ...
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
In-text Citation. The in-text component of APA citation includes two main elements: the author's last name and the year of the publication (Ross, 1997), and a third: the page number, whenever quoting directly or paraphrasing a specific section of the text (Ross, 1997, p. 2).
General formatting rules are as follows: Do not put page breaks in between the introduction, method, results, and discussion sections. The title page, abstract, references, table (s), and figure (s) should be on their own pages. The entire paper should be written in the past tense, in a 12-point font, double-spaced, and with one-inch margins ...
APA Citation Basics. When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
Paper Format. Consistency in the order, structure, and format of a paper allows readers to focus on a paper's content rather than its presentation. To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments.
In MLA, the Works Cited page lists full details of the sources cited in the paper, arranged alphabetically by the author's last name (or title if no author is available). The general format for common sources is as follows: Books: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Year.
Please see our Sample APA Paper resource to see an example of an APA paper. You may also visit our Additional Resources page for more examples of APA papers.. How to Cite the Purdue OWL in APA Individual Resources. The page template for the new OWL site does not include contributors' names or the page's last edited date.
This paper offers a brief overview of the historically predominant form of psychotherapy research both for individual and group psychotherapies, the randomized control trial (RCT), and its surrounding controversies and critiques as the backdrop from which new directions in both clinical theory building and research are being pursued, including efforts at building integrative models of ...
The ongoing re-animation of objects from the earlier research materialised our desire to disrupt conventional pathways and temporalities of research from the field to output to dissemination as distinct linear stages. They 'blur distinctions between research, engagement, pedagogy, and activism' (Renold et al Citation 2024 forthcoming).
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resources for the older APA 6 style can be found at this page as well as at this page (our old resources covered the material on this page on two separate pages). The purpose of tables and figures in documents is to enhance your readers' understanding of the ...