13.5 Research Process: Making Notes, Synthesizing Information, and Keeping a Research Log
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Employ the methods and technologies commonly used for research and communication within various fields.
- Practice and apply strategies such as interpretation, synthesis, response, and critique to compose texts that integrate the writer’s ideas with those from appropriate sources.
- Analyze and make informed decisions about intellectual property based on the concepts that motivate them.
- Apply citation conventions systematically.
As you conduct research, you will work with a range of “texts” in various forms, including sources and documents from online databases as well as images, audio, and video files from the Internet. You may also work with archival materials and with transcribed and analyzed primary data. Additionally, you will be taking notes and recording quotations from secondary sources as you find materials that shape your understanding of your topic and, at the same time, provide you with facts and perspectives. You also may download articles as PDFs that you then annotate. Like many other students, you may find it challenging to keep so much material organized, accessible, and easy to work with while you write a major research paper. As it does for many of those students, a research log for your ideas and sources will help you keep track of the scope, purpose, and possibilities of any research project.
A research log is essentially a journal in which you collect information, ask questions, and monitor the results. Even if you are completing the annotated bibliography for Writing Process: Informing and Analyzing , keeping a research log is an effective organizational tool. Like Lily Tran’s research log entry, most entries have three parts: a part for notes on secondary sources, a part for connections to the thesis or main points, and a part for your own notes or questions. Record source notes by date, and allow room to add cross-references to other entries.

Summary of Assignment: Research Log
Your assignment is to create a research log similar to the student model. You will use it for the argumentative research project assigned in Writing Process: Integrating Research to record all secondary source information: your notes, complete publication data, relation to thesis, and other information as indicated in the right-hand column of the sample entry.
Another Lens. A somewhat different approach to maintaining a research log is to customize it to your needs or preferences. You can apply shading or color coding to headers, rows, and/or columns in the three-column format (for colors and shading). Or you can add columns to accommodate more information, analysis, synthesis, or commentary, formatting them as you wish. Consider adding a column for questions only or one for connections to other sources. Finally, consider a different visual format , such as one without columns. Another possibility is to record some of your comments and questions so that you have an aural rather than a written record of these.
Writing Center
At this point, or at any other point during the research and writing process, you may find that your school’s writing center can provide extensive assistance. If you are unfamiliar with the writing center, now is a good time to pay your first visit. Writing centers provide free peer tutoring for all types and phases of writing. Discussing your research with a trained writing center tutor can help you clarify, analyze, and connect ideas as well as provide feedback on works in progress.
Quick Launch: Beginning Questions
You may begin your research log with some open pages in which you freewrite, exploring answers to the following questions. Although you generally would do this at the beginning, it is a process to which you likely will return as you find more information about your topic and as your focus changes, as it may during the course of your research.
- What information have I found so far?
- What do I still need to find?
- Where am I most likely to find it?
These are beginning questions. Like Lily Tran, however, you will come across general questions or issues that a quick note or freewrite may help you resolve. The key to this section is to revisit it regularly. Written answers to these and other self-generated questions in your log clarify your tasks as you go along, helping you articulate ideas and examine supporting evidence critically. As you move further into the process, consider answering the following questions in your freewrite:
- What evidence looks as though it best supports my thesis?
- What evidence challenges my working thesis?
- How is my thesis changing from where it started?
Creating the Research Log
As you gather source material for your argumentative research paper, keep in mind that the research is intended to support original thinking. That is, you are not writing an informational report in which you simply supply facts to readers. Instead, you are writing to support a thesis that shows original thinking, and you are collecting and incorporating research into your paper to support that thinking. Therefore, a research log, whether digital or handwritten, is a great way to keep track of your thinking as well as your notes and bibliographic information.
In the model below, Lily Tran records the correct MLA bibliographic citation for the source. Then, she records a note and includes the in-text citation here to avoid having to retrieve this information later. Perhaps most important, Tran records why she noted this information—how it supports her thesis: The human race must turn to sustainable food systems that provide healthy diets with minimal environmental impact, starting now . Finally, she makes a note to herself about an additional visual to include in the final paper to reinforce the point regarding the current pressure on food systems. And she connects the information to other information she finds, thus cross-referencing and establishing a possible synthesis. Use a format similar to that in Table 13.4 to begin your own research log.
Types of Research Notes
Taking good notes will make the research process easier by enabling you to locate and remember sources and use them effectively. While some research projects requiring only a few sources may seem easily tracked, research projects requiring more than a few sources are more effectively managed when you take good bibliographic and informational notes. As you gather evidence for your argumentative research paper, follow the descriptions and the electronic model to record your notes. You can combine these with your research log, or you can use the research log for secondary sources and your own note-taking system for primary sources if a division of this kind is helpful. Either way, be sure to include all necessary information.
Bibliographic Notes
These identify the source you are using. When you locate a useful source, record the information necessary to find that source again. It is important to do this as you find each source, even before taking notes from it. If you create bibliographic notes as you go along, then you can easily arrange them in alphabetical order later to prepare the reference list required at the end of formal academic papers. If your instructor requires you to use MLA formatting for your essay, be sure to record the following information:
- Title of source
- Title of container (larger work in which source is included)
- Other contributors
- Publication date
When using MLA style with online sources, also record the following information:
- Date of original publication
- Date of access
- DOI (A DOI, or digital object identifier, is a series of digits and letters that leads to the location of an online source. Articles in journals are often assigned DOIs to ensure that the source can be located, even if the URL changes. If your source is listed with a DOI, use that instead of a URL.)
It is important to understand which documentation style your instructor will require you to use. Check the Handbook for MLA Documentation and Format and APA Documentation and Format styles . In addition, you can check the style guide information provided by the Purdue Online Writing Lab .
Informational Notes
These notes record the relevant information found in your sources. When writing your essay, you will work from these notes, so be sure they contain all the information you need from every source you intend to use. Also try to focus your notes on your research question so that their relevance is clear when you read them later. To avoid confusion, work with separate entries for each piece of information recorded. At the top of each entry, identify the source through brief bibliographic identification (author and title), and note the page numbers on which the information appears. Also helpful is to add personal notes, including ideas for possible use of the information or cross-references to other information. As noted in Writing Process: Integrating Research , you will be using a variety of formats when borrowing from sources. Below is a quick review of these formats in terms of note-taking processes. By clarifying whether you are quoting directly, paraphrasing, or summarizing during these stages, you can record information accurately and thus take steps to avoid plagiarism.
Direct Quotations, Paraphrases, and Summaries
A direct quotation is an exact duplication of the author’s words as they appear in the original source. In your notes, put quotation marks around direct quotations so that you remember these words are the author’s, not yours. One advantage of copying exact quotations is that it allows you to decide later whether to include a quotation, paraphrase, or summary. ln general, though, use direct quotations only when the author’s words are particularly lively or persuasive.
A paraphrase is a restatement of the author’s words in your own words. Paraphrase to simplify or clarify the original author’s point. In your notes, use paraphrases when you need to record details but not exact words.
A summary is a brief condensation or distillation of the main point and most important details of the original source. Write a summary in your own words, with facts and ideas accurately represented. A summary is useful when specific details in the source are unimportant or irrelevant to your research question. You may find you can summarize several paragraphs or even an entire article or chapter in just a few sentences without losing useful information. It is a good idea to note when your entry contains a summary to remind you later that it omits detailed information. See Writing Process Integrating Research for more detailed information and examples of quotations, paraphrases, and summaries and when to use them.
Other Systems for Organizing Research Logs and Digital Note-Taking
Students often become frustrated and at times overwhelmed by the quantity of materials to be managed in the research process. If this is your first time working with both primary and secondary sources, finding ways to keep all of the information in one place and well organized is essential.
Because gathering primary evidence may be a relatively new practice, this section is designed to help you navigate the process. As mentioned earlier, information gathered in fieldwork is not cataloged, organized, indexed, or shelved for your convenience. Obtaining it requires diligence, energy, and planning. Online resources can assist you with keeping a research log. Your college library may have subscriptions to tools such as Todoist or EndNote. Consult with a librarian to find out whether you have access to any of these. If not, use something like the template shown in Figure 13.8 , or another like it, as a template for creating your own research notes and organizational tool. You will need to have a record of all field research data as well as the research log for all secondary sources.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/13-5-research-process-making-notes-synthesizing-information-and-keeping-a-research-log
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Writing a Research Paper: 5. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- Getting Started
- 1. Topic Ideas
- 2. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 3. Appropriate Sources
- 4. Search Techniques
- 5. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 6. Evaluating Sources
- 7. Citations & Plagiarism
- 8. Writing Your Research Paper
Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
How to take notes and document sources.
Note taking is a very important part of the research process. It will help you:
- keep your ideas and sources organized
- effectively use the information you find
- avoid plagiarism
When you find good information to be used in your paper:
- Read the text critically, think how it is related to your argument, and decide how you are going to use it in your paper.
- Select the material that is relevant to your argument.
- Copy the original text for direct quotations or briefly summarize the content in your own words, and make note of how you will use it.
- Copy the citation or publication information of the source.
- << Previous: 4. Search Techniques
- Next: 6. Evaluating Sources >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 5:26 PM
- URL: https://kenrick.libguides.com/writing-a-research-paper

Research Paper: A step-by-step guide: 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Topic Ideas
- 3. Thesis Statement & Outline
- 4. Appropriate Sources
- 5. Search Techniques
- 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
- 7. Evaluating Sources
- 8. Citations & Plagiarism
- 9. Writing Your Research Paper

Taking Notes & Documenting Sources
How to take notes and document sources.
Note taking is a very important part of the research process. It will help you:
- keep your ideas and sources organized
- effectively use the information you find
- avoid plagiarism
When you find good information to be used in your paper:
- Read the text critically, think how it is related to your argument, and decide how you are going to use it in your paper.
- Select the material that is relevant to your argument.
- Copy the original text for direct quotations or briefly summarize the content in your own words, and make note of how you will use it.
- Copy the citation or publication information of the source.
There are different ways to take notes and organize your research. Check out this video, and try different strategies to find what works best for you.
- << Previous: 5. Search Techniques
- Next: 7. Evaluating Sources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2023 12:12 PM
- URL: https://butte.libguides.com/ResearchPaper
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
Refers to notes created by the researcher during the act of conducting a field study to remember and record the behaviors, activities, events, and other features of an observation. Field notes are intended to be read by the researcher as evidence to produce meaning and an understanding of the culture, social situation, or phenomenon being studied. The notes may constitute the whole data collected for a research study [e.g., an observational project] or contribute to it, such as when field notes supplement conventional interview data or other techniques of data gathering.
Schwandt, Thomas A. The SAGE Dictionary of Qualitative Inquiry . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2015.
How to Approach Writing Field Notes
The ways in which you take notes during an observational study is very much a personal decision developed over time as you become more experienced in fieldwork. However, all field notes generally consist of two parts:
- Descriptive information , in which you attempt to accurately document factual data [e.g., date and time] along with the settings, actions, behaviors, and conversations that you observe; and,
- Reflective information , in which you record your thoughts, ideas, questions, and concerns during the observation.
Note that field notes should be fleshed out as soon as possible after an observation is completed. Your initial notes may be recorded in cryptic form and, unless additional detail is added as soon as possible after the observation, important facts and opportunities for fully interpreting the data may be lost.
Characteristics of Field Notes
- Be accurate . You only get one chance to observe a particular moment in time so, before you conduct your observations, practice taking notes in a setting that is similar to your observation site in regards to number of people, the environment, and social dynamics. This will help you develop your own style of transcribing observations quickly and accurately.
- Be organized . Taking accurate notes while you are actively observing can be difficult. Therefore, it is important that you plan ahead how you will document your observation study [e.g., strictly chronologically or according to specific prompts]. Notes that are disorganized will make it more difficult for you to interpret the data.
- Be descriptive . Use descriptive words to document what you observe. For example, instead of noting that a classroom appears "comfortable," state that the classroom includes soft lighting and cushioned chairs that can be moved around by the students. Being descriptive means supplying yourself with enough factual evidence that you don't end up making assumptions about what you meant when you write the final report.
- Focus on the research problem . Since it's impossible to document everything you observe, focus on collecting the greatest detail that relates to the research problem and the theoretical constructs underpinning your research; avoid cluttering your notes with irrelevant information. For example, if the purpose of your study is to observe the discursive interactions between nursing home staff and the family members of residents, then it would only be necessary to document the setting in detail if it in some way directly influenced those interactions [e.g., there is a private room available for discussions between staff and family members].
- Record insights and thoughts . As you take notes, be thinking about the underlying meaning of what you observe and record your thoughts and ideas accordingly. If needed, this will help you to ask questions or seek clarification from participants after the observation. To avoid any confusion, subsequent comments from participants should be included in a separate, reflective part of your field notes and not merged with the descriptive notes.
General Guidelines for the Descriptive Content
The descriptive content of your notes can vary in detail depending upon what needs to be emphasized in order to address the research problem. However, in most observations, your notes should include at least some of the following elements:
- Describe the physical setting.
- Describe the social environment and the way in which participants interacted within the setting. This may include patterns of interactions, frequency of interactions, direction of communication patterns [including non-verbal communication], and patterns of specific behavioral events, such as, conflicts, decision-making, or collaboration.
- Describe the participants and their roles in the setting.
- Describe, as best you can, the meaning of what was observed from the perspectives of the participants.
- Record exact quotes or close approximations of comments that relate directly to the purpose of the study.
- Describe any impact you might have had on the situation you observed [important!].
General Guidelines for the Reflective Content
You are the instrument of data gathering and interpretation. Therefore, reflective content can include any of the following elements intended to contextualize what you have observed based on your perspective and your own personal, cultural, and situational experiences .
- Note ideas, impressions, thoughts, and/or any criticisms you have about what you observed.
- Include any unanswered questions or concerns that have arisen from analyzing the observation data.
- Clarify points and/or correct mistakes and misunderstandings in other parts of field notes.
- Include insights about what you have observed and speculate as to why you believe specific phenomenon occurred.
- Record any thoughts that you may have regarding any future observations.
NOTE: Analysis of your field notes should occur as they are being written and while you are conducting your observations. This is important for at least two reasons. First, preliminary analysis fosters self-reflection and self-reflection is crucial for facilitating deep understanding and meaning-making in any research study. Second, preliminary analysis reveals emergent themes. Identifying emergent themes while observing allows you to shift your attention in ways that can foster a more developed investigation.
Emerson, Robert M. et al. Writing Ethnographic Fieldnotes . 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2011; Ethnography, Observational Research, and Narrative Inquiry. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gambold, Liesl L. “Field Notes.” In Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Edited by Albert J. Mills, Gabrielle Durepos, and Elden Wiebe. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2010; Pace, Tonio. Writing Field Reports. Scribd Online Library; Pyrczak, Fred and Randall R. Bruce. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences . 5th ed. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2005; Report Writing. UniLearning. University of Wollongong, Australia; Ravitch, Sharon M. “Field Notes.” In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Educational Research, Measurement, and Evaluation . Edited by Bruce B. Frey. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2018; Tenzek, Kelly E. “Field Notes.” In The SAGE Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods . Edited by Mike Allen. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2017; Wolfinger, Nicholas H. "On Writing Fieldnotes: Collection Strategies and Background Expectancies.” Qualitative Research 2 (April 2002): 85-95; Writing Reports. Anonymous. The Higher Education Academy.
- << Previous: About Informed Consent
- Next: Writing a Policy Memo >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1924 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,556 quotes across 1924 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!


Research Process :: Step by Step
- Introduction
- Select Topic
- Identify Keywords
- Background Information
- Develop Research Questions
- Refine Topic
- Search Strategy
- Popular Databases
- Evaluate Sources
- Types of Periodicals
- Reading Scholarly Articles
- Primary & Secondary Sources
- Organize / Take Notes
- Writing & Grammar Resources
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Citation Styles
- Paraphrasing
- Privacy / Confidentiality
- Research Process
- Selecting Your Topic
- Identifying Keywords
- Gathering Background Info
- Evaluating Sources
- Zotero Guide by Morgan Rowe-Morris Last Updated Dec 8, 2023 3371 views this year
- EndNote Guide by Engineering Librarian Last Updated May 10, 2024 1438 views this year

Focus on the information in the article that is relevant to your research question (you may be able to skim over other parts). Think critically about what you read and build your argument based on it.
Organize your Notes
- After you take notes, re-read them.
- Then re-organize them by putting similar information together. Working with your notes involves re-grouping them by topic instead of by source. Re-group your notes by re-shuffling your index cards or by color-coding or using symbols to code notes in a notebook.
- Review the topics of your newly-grouped notes. If the topics do not answer your research question or support your working thesis directly, you may need to do additional research or re-think your original research.
- During this process you may find that you have taken notes that do not answer your research question or support your working thesis directly. Don't be afraid to throw them away.
It may have struck you that you just read a lot of "re" words: re-read, re-organize, re-group, re-shuffle, re-think. That's right; working with your notes essentially means going back and reviewing how this "new" information fits with your own thoughts about the topic or issue of the research.
Grouping your notes will enable you to outline the major sections and then the paragraphs of your research paper.
https://www.esc.edu/online-writing-center/resources/research/research-paper-steps/taking-notes/
- << Previous: Step 4: Write
- Next: Writing & Grammar Resources >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 11:24 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uta.edu/researchprocess
University of Texas Arlington Libraries 702 Planetarium Place · Arlington, TX 76019 · 817-272-3000
- Internet Privacy
- Accessibility
- Problems with a guide? Contact Us.
Finally see how to stop getting stuck in a project management tool
20 min. personalized consultation with a project management expert
Smart Note-Taking for Research Paper Writing
How to organize research notes using the Zettelkasten Method when writing academic papers

With plenty of note-taking tips and apps available, online and in paper form, it’s become extremely easy to take note of information, ideas, or thoughts. As simple as it is to write down an idea or jot down a quote, the skill of academic research and writing for a thesis paper is on another level entirely. And keeping a record or an archive of all of the information you need can quickly require a very organized system.

The use of index cards seems old-fashioned considering that note-taking apps (psst! Hypernotes ) offer better functionality and are arguably more user-friendly. However, software is only there to help aid our individual workflow and thinking process. That’s why understanding and learning how to properly research, take notes and write academic papers is still a highly valuable skill.
Let’s Start Writing! But Where to Start…
Writing academic papers is a vital skill most students need to learn and practice. Academic papers are usually time-intensive pieces of written content that are a requirement throughout school or at University. Whether a topic is assigned or you have to choose your own, there’s little room for variation in how to begin.
Popular and purposeful in analyzing and evaluating the knowledge of the author as well as assessing if the learning objectives were met, research papers serve as information-packed content. Most of us may not end up working jobs in academic professions or be researchers at institutions, where writing research papers is also part of the job, but we often read such papers.
Despite the fact that most research papers or dissertations aren’t often read in full, journalists, academics, and other professionals regularly use academic papers as a basis for further literary publications or blog articles. The standard of academic papers ensures the validity of the information and gives the content authority.
There’s no-nonsense in research papers. To make sure to write convincing and correct content, the research stage is extremely important. And, naturally, when doing any kind of research, we take notes.
Why Take Notes?
There are particular standards defined for writing academic papers . In order to meet these standards, a specific amount of background information and researched literature is required. Taking notes helps keep track of read/consumed literary material as well as keeps a file of any information that may be of importance to the topic.
The aim of writing isn’t merely to advertise fully formed opinions, but also serves the purpose of developing opinions worth sharing in the first place.
What is Note-Taking?

Note-taking (sometimes written as notetaking or note-taking ) is the practice of recording information from different sources and platforms. For academic writing, note-taking is the process of obtaining and compiling information that answers and supports the research paper’s questions and topic. Notes can be in one of three forms: summary, paraphrase, or direct quotation.
Note-taking is an excellent process useful for anyone to turn individual thoughts and information into organized ideas ready to be communicated through writing. Notes are, however, only as valuable as the context. Since notes are also a byproduct of the information we consume daily, it’s important to categorize information, develop connections, and establish relationships between pieces of information.
What Type of Notes Can I Take?
- Explanation of complex theories
- Background information on events or persons of interest
- Definitions of terms
- Quotations of significant value
- Illustrations or graphics
Note-Taking 101

Taking notes or doing research for academic papers shouldn’t be that difficult, considering we take notes all the time. Wrong. Note-taking for research papers isn’t the same as quickly noting down an interesting slogan or cool quote from a video, putting it on a sticky note, and slapping it onto your bedroom or office wall.
Note-taking for research papers requires focus and careful deliberation of which information is important to note down, keep on file, or use and reference in your own writing. Depending on the topic and requirements of your research paper from your University or institution, your notes might include explanations of complex theories, definitions, quotations, and graphics.
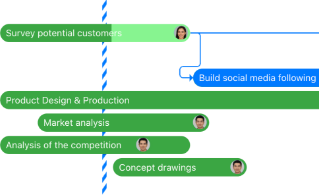
Stages of Research Paper Writing
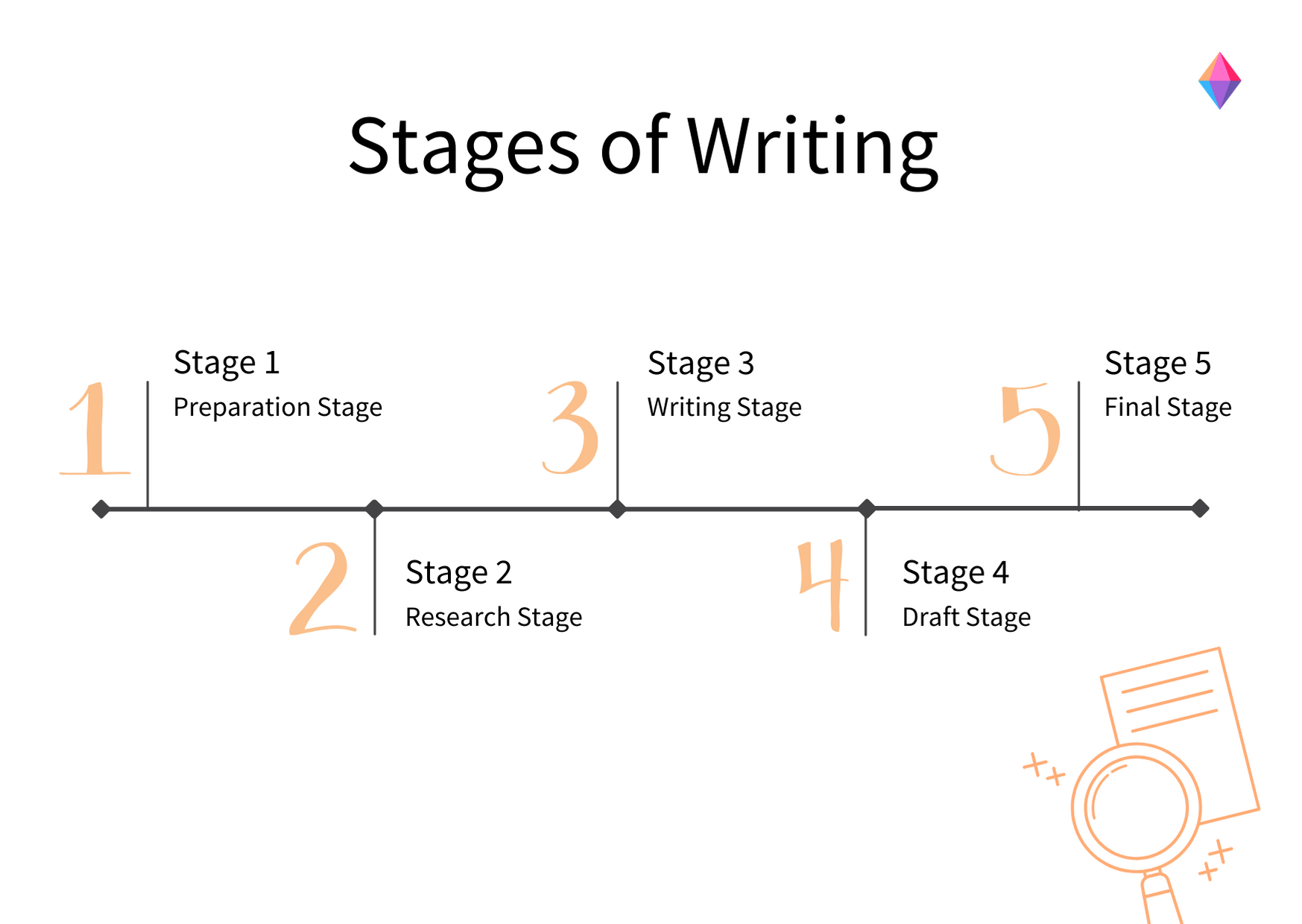
1. Preparation Stage
Before you start, it’s recommended to draft a plan or an outline of how you wish to begin preparing to write your research paper. Make note of the topic you will be writing on, as well as the stylistic and literary requirements for your paper.
2. Research Stage
In the research stage, finding good and useful literary material for background knowledge is vital. To find particular publications on a topic, you can use Google Scholar or access literary databases and institutions made available to you through your school, university, or institution.
Make sure to write down the source location of the literary material you find. Always include the reference title, author, page number, and source destination. This saves you time when formatting your paper in the later stages and helps keep the information you collect organized and referenceable.

In the worst-case scenario, you’ll have to do a backward search to find the source of a quote you wrote down without reference to the original literary material.
3. Writing Stage
When writing, an outline or paper structure is helpful to visually break up the piece into sections. Once you have defined the sections, you can begin writing and referencing the information you have collected in the research stage.
Clearly mark which text pieces and information where you relied on background knowledge, which texts are directly sourced, and which information you summarized or have written in your own words. This is where your paper starts to take shape.
4. Draft Stage
After organizing all of your collected notes and starting to write your paper, you are already in the draft stage. In the draft stage, the background information collected and the text written in your own words come together. Every piece of information is structured by the subtopics and sections you defined in the previous stages.
5. Final Stage
Success! Well… almost! In the final stage, you look over your whole paper and check for consistency and any irrelevancies. Read through the entire paper for clarity, grammatical errors , and peace of mind that you have included everything important.
Make sure you use the correct formatting and referencing method requested by your University or institution for research papers. Don’t forget to save it and then send the paper on its way.
Best Practice Note-Taking Tips
- Find relevant and authoritative literary material through the search bar of literary databases and institutions.
- Practice citation repeatedly! Always keep a record of the reference book title, author, page number, and source location. At best, format the citation in the necessary format from the beginning.
- Organize your notes according to topic or reference to easily find the information again when in the writing stage. Work invested in the early stages eases the writing and editing process of the later stages.
- Summarize research notes and write in your own words as much as possible. Cite direct quotes and clearly mark copied text in your notes to avoid plagiarism.
Take Smart Notes

Taking smart notes isn’t as difficult as it seems. It’s simply a matter of principle, defined structure, and consistency. Whether you opt for a paper-based system or use a digital tool to write and organize your notes depends solely on your individual personality, needs, and workflow.
With various productivity apps promoting diverse techniques, a good note-taking system to take smart notes is the Zettelkasten Method . Invented by Niklas Luhmann, a german sociologist and researcher, the Zettelkasten Method is known as the smart note-taking method that popularized personalized knowledge management.
As a strategic process for thinking and writing, the Zettelkasten Method helps you organize your knowledge while working, studying, or researching. Directly translated as a ‘note box’, Zettelkasten is simply a framework to help organize your ideas, thoughts, and information by relating pieces of knowledge and connecting pieces of information to each other.
Hypernotes is a note-taking app that can be used as a software-based Zettelkasten, with integrated features to make smart note-taking so much easier, such as auto-connecting related notes, and syncing to multiple devices. In each notebook, you can create an archive of your thoughts, ideas, and information.
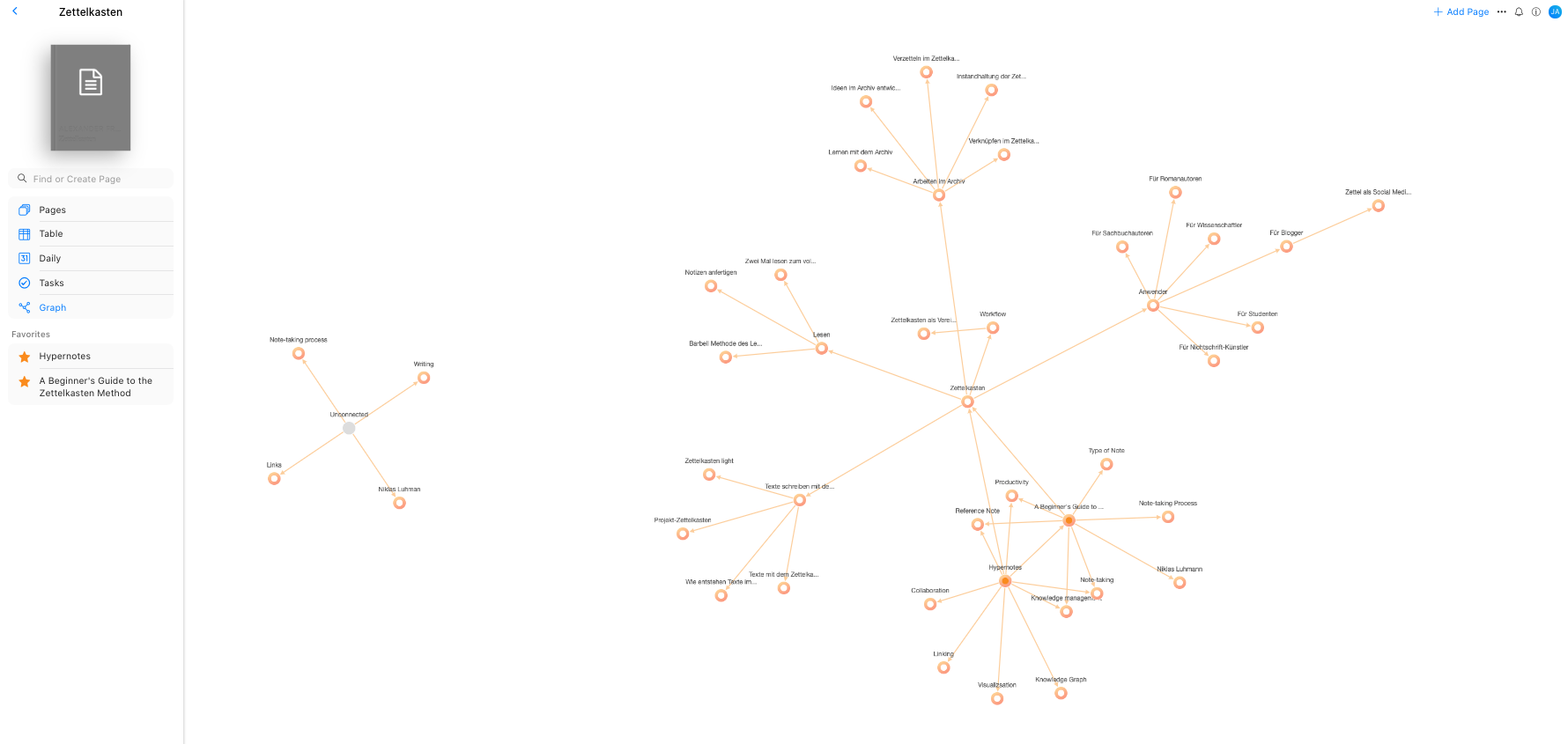
Using the tag system to connect like-minded ideas and information to one another and letting Hypernotes do its thing with bi-directional linking, you’ll soon create a web of knowledge about anything you’ve ever taken note of. This feature is extremely helpful to navigate through the enormous amounts of information you’ve written down. Another benefit is that it assists you in categorizing and making connections between your ideas, thoughts, and saved information in a single notebook. Navigate through your notes, ideas, and knowledge easily.
Ready, Set, Go!
Writing academic papers is no simple task. Depending on the requirements, resources available, and your personal research and writing style, techniques, apps, or practice help keep you organized and increase your productivity.
Whether you use a particular note-taking app like Hypernotes for your research paper writing or opt for a paper-based system, make sure you follow a particular structure. Repeat the steps that help you find the information you need quicker and allow you to reproduce or create knowledge naturally.
Images from NeONBRAND , hana_k and Surface via Unsplash
A well-written piece is made up of authoritative sources and uses the art of connecting ideas, thoughts, and information together. Good luck to all students and professionals working on research paper writing! We hope these tips help you in organizing the information and aid your workflow in your writing process.
Cheers, Jessica and the Zenkit Team

FREE 20 MIN. CONSULTATION WITH A PROJECT MANAGEMENT EXPERT
Wanna see how to simplify your workflow with Zenkit in less than a day?
- digital note app
- how to smart notes
- how to take notes
- hypernotes note app
- hypernotes take notes
- note archive software
- note taking app for students
- note taking tips
- note-taking
- note-taking app
- organize research paper
- reading notes
- research note taking
- research notes
- research paper writing
- smart notes
- taking notes zettelkasten method
- thesis writing
- writing a research paper
- writing a thesis paper
- zettelkasten method
More from Karen Bradford
10 Ways to Remember What You Study
More from Kelly Moser
How Hot Desking Elevates the Office Environment in 2024
More from Chris Harley
8 Productivity Tools for Successful Content Marketing
2 thoughts on “ Smart Note-Taking for Research Paper Writing ”
Thanks for sending really an exquisite text.
Great article thank you for sharing!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Zenkit Comment Policy
At Zenkit, we strive to post helpful, informative, and timely content. We want you to feel welcome to comment with your own thoughts, feedback, and critiques, however we do not welcome inappropriate or rude comments. We reserve the right to delete comments or ban users from commenting as needed to keep our comments section relevant and respectful.
What we encourage:
- Smart, informed, and helpful comments that contribute to the topic. Funny commentary is also thoroughly encouraged.
- Constructive criticism, either of the article itself or the ideas contained in it.
- Found technical issues with the site? Send an email to [email protected] and specify the issue and what kind of device, operating system, and OS version you are using.
- Noticed spam or inappropriate behaviour that we haven’t yet sorted out? Flag the comment or report the offending post to [email protected] .
What we’d rather you avoid:
Rude or inappropriate comments.
We welcome heated discourse, and we’re aware that some topics cover things people feel passionately about. We encourage you to voice your opinions, however in order for discussions to remain constructive, we ask that you remember to criticize ideas, not people.
Please avoid:
- name-calling
- ad hominem attacks
- responding to a post’s tone instead of its actual content
- knee-jerk contradiction
Comments that we find to be hateful, inflammatory, threatening, or harassing may be removed. This includes racist, gendered, ableist, ageist, homophobic, and transphobic slurs and language of any sort. If you don’t have something nice to say about another user, don't say it. Treat others the way you’d like to be treated.
Trolling or generally unkind behaviour
If you’re just here to wreak havoc and have some fun, and you’re not contributing meaningfully to the discussions, we will take actions to remove you from the conversation. Please also avoid flagging or downvoting other users’ comments just because you disagree with them.
Every interpretation of spamming is prohibited. This means no unauthorized promotion of your own brand, product, or blog, unauthorized advertisements, links to any kind of online gambling, malicious sites, or otherwise inappropriate material.
Comments that are irrelevant or that show you haven’t read the article
We know that some comments can veer into different topics at times, but remain related to the original topic. Be polite, and please avoid promoting off-topic commentary. Ditto avoid complaining we failed to mention certain topics when they were clearly covered in the piece. Make sure you read through the whole piece before saying your piece!
Breaches of privacy
This should really go without saying, but please do not post personal information that may be used by others for malicious purposes. Please also do not impersonate authors of this blog, or other commenters (that’s just weird).
How to Do Research: A Step-By-Step Guide: 4a. Take Notes
- Get Started
- 1a. Select a Topic
- 1b. Develop Research Questions
- 1c. Identify Keywords
- 1d. Find Background Information
- 1e. Refine a Topic
- 2a. Search Strategies
- 2d. Articles
- 2e. Videos & Images
- 2f. Databases
- 2g. Websites
- 2h. Grey Literature
- 2i. Open Access Materials
- 3a. Evaluate Sources
- 3b. Primary vs. Secondary
- 3c. Types of Periodicals
- 4a. Take Notes
- 4b. Outline the Paper
- 4c. Incorporate Source Material
- 5a. Avoid Plagiarism
- 5b. Zotero & MyBib
- 5c. MLA Formatting
- 5d. MLA Citation Examples
- 5e. APA Formatting
- 5f. APA Citation Examples
- 5g. Annotated Bibliographies
Note Taking in Bibliographic Management Tools
We encourage students to use bibliographic citation management tools (such as Zotero, EasyBib and RefWorks) to keep track of their research citations. Each service includes a note-taking function. Find more information about citation management tools here . Whether or not you're using one of these, the tips below will help you.
Tips for Taking Notes Electronically
- Try using a bibliographic citation management tool to keep track of your sources and to take notes.
- As you add sources, put them in the format you're using (MLA, APA, Chicago, etc.).
- Group sources by publication type (i.e., book, article, website).
- Number each source within the publication type group.
- For websites, include the URL information and the date you accessed each site.
- Next to each idea, include the source number from the Works Cited file and the page number from the source. See the examples below. Note that #A5 and #B2 refer to article source 5 and book source 2 from the Works Cited file.
#A5 p.35: 76.69% of the hyperlinks selected from homepage are for articles and the catalog #B2 p.76: online library guides evolved from the paper pathfinders of the 1960s
- When done taking notes, assign keywords or sub-topic headings to each idea, quote or summary.
- Use the copy and paste feature to group keywords or sub-topic ideas together.
- Back up your master list and note files frequently!
Tips for Taking Notes by Hand
- Use index cards to keep notes and track sources used in your paper.
- Include the citation (i.e., author, title, publisher, date, page numbers, etc.) in the format you're using. It will be easier to organize the sources alphabetically when creating the Works Cited page.
- Number the source cards.
- Use only one side to record a single idea, fact or quote from one source. It will be easier to rearrange them later when it comes time to organize your paper.
- Include a heading or key words at the top of the card.
- Include the Work Cited source card number.
- Include the page number where you found the information.
- Use abbreviations, acronyms, or incomplete sentences to record information to speed up the notetaking process.
- Write down only the information that answers your research questions.
- Use symbols, diagrams, charts or drawings to simplify and visualize ideas.
Forms of Notetaking
Use one of these notetaking forms to capture information:
- Summarize : Capture the main ideas of the source succinctly by restating them in your own words.
- Paraphrase : Restate the author's ideas in your own words.
- Quote : Copy the quotation exactly as it appears in the original source. Put quotation marks around the text and note the name of the person you are quoting.
Example of a Work Cited Card
Example notecard.
- << Previous: Step 4: Write
- Next: 4b. Outline the Paper >>
- Last Updated: Feb 21, 2024 11:01 AM
- URL: https://libguides.elmira.edu/research
- Writing Home
- Writing Advice Home
Taking Notes from Research Reading
- Printable PDF Version
- Fair-Use Policy
If you take notes efficiently, you can read with more understanding and also save time and frustration when you come to write your paper. These are three main principles
1. Know what kind of ideas you need to record
Focus your approach to the topic before you start detailed research. Then you will read with a purpose in mind, and you will be able to sort out relevant ideas.
- First, review the commonly known facts about your topic, and also become aware of the range of thinking and opinions on it. Review your class notes and textbook and browse in an encyclopaedia or other reference work.
- Try making a preliminary list of the subtopics you would expect to find in your reading. These will guide your attention and may come in handy as labels for notes.
- Choose a component or angle that interests you, perhaps one on which there is already some controversy. Now formulate your research question. It should allow for reasoning as well as gathering of information—not just what the proto-Iroquoians ate, for instance, but how valid the evidence is for early introduction of corn. You may even want to jot down a tentative thesis statement as a preliminary answer to your question. (See Using Thesis Statements .)
- Then you will know what to look for in your research reading: facts and theories that help answer your question, and other people’s opinions about whether specific answers are good ones.
2. Don’t write down too much
Your essay must be an expression of your own thinking, not a patchwork of borrowed ideas. Plan therefore to invest your research time in understanding your sources and integrating them into your own thinking. Your note cards or note sheets will record only ideas that are relevant to your focus on the topic; and they will mostly summarize rather than quote.
- Copy out exact words only when the ideas are memorably phrased or surprisingly expressed—when you might use them as actual quotations in your essay.
- Otherwise, compress ideas in your own words . Paraphrasing word by word is a waste of time. Choose the most important ideas and write them down as labels or headings. Then fill in with a few subpoints that explain or exemplify.
- Don’t depend on underlining and highlighting. Find your own words for notes in the margin (or on “sticky” notes).
3. Label your notes intelligently
Whether you use cards or pages for note-taking, take notes in a way that allows for later use.
- Save bother later by developing the habit of recording bibliographic information in a master list when you begin looking at each source (don’t forget to note book and journal information on photocopies). Then you can quickly identify each note by the author’s name and page number; when you refer to sources in the essay you can fill in details of publication easily from your master list. Keep a format guide handy (see Documentation Formats ).
- Try as far as possible to put notes on separate cards or sheets. This will let you label the topic of each note. Not only will that keep your notetaking focussed, but it will also allow for grouping and synthesizing of ideas later. It is especially satisfying to shuffle notes and see how the conjunctions create new ideas—yours.
- Leave lots of space in your notes for comments of your own—questions and reactions as you read, second thoughts and cross-references when you look back at what you’ve written. These comments can become a virtual first draft of your paper.
Office of Undergraduate Research
- Office of Undergraduate Research FAQ's
- URSA Engage
- Resources for Students
- Resources for Faculty
- Engaging in Research
- Spring Poster Symposium (SPS)
- Ecampus SPS Videos
- Earn Money by Participating in Research Studies
- Transcript Notation
- Student Publications
How to take Research Notes
How to take research notes.
Your research notebook is an important piece of information useful for future projects and presentations. Maintaining organized and legible notes allows your research notebook to be a valuable resource to you and your research group. It allows others and yourself to replicate experiments, and it also serves as a useful troubleshooting tool. Besides it being an important part of the research process, taking detailed notes of your research will help you stay organized and allow you to easily review your work.
Here are some common reasons to maintain organized notes:
- Keeps a record of your goals and thoughts during your research experiments.
- Keeps a record of what worked and what didn't in your research experiments.
- Enables others to use your notes as a guide for similar procedures and techniques.
- A helpful tool to reference when writing a paper, submitting a proposal, or giving a presentation.
- Assists you in answering experimental questions.
- Useful to efficiently share experimental approaches, data, and results with others.
Before taking notes:
- Ask your research professor what note-taking method they recommend or prefer.
- Consider what type of media you'll be using to take notes.
- Once you have decided on how you'll be taking notes, be sure to keep all of your notes in one place to remain organized.
- Plan on taking notes regularly (meetings, important dates, procedures, journal/manuscript revisions, etc.).
- This is useful when applying to programs or internships that ask about your research experience.
Note Taking Tips:
Taking notes by hand:.
- Research notebooks don’t belong to you so make sure your notes are legible for others.
- Use post-it notes or tabs to flag important sections.
- Start sorting your notes early so that you don't become backed up and disorganized.
- Only write with a pen as pencils aren’t permanent & sharpies can bleed through.
- Make it a habit to write in your notebook and not directly on sticky notes or paper towels. Rewriting notes can waste time and sometimes lead to inaccurate data or results.
Taking Notes Electronically
- Make sure your device is charged and backed up to store data.
- Invest in note-taking apps or E-Ink tablets
- Create shortcuts to your folders so you have easier access
- Create outlines.
- Keep your notes short and legible.
Note Taking Tips Continued:
Things to avoid.
- Avoid using pencils or markers that may bleed through.
- Avoid erasing entries. Instead, draw a straight line through any mistakes and write the date next to the crossed-out information.
- Avoid writing in cursive.
- Avoid delaying your entries so you don’t fall behind and forget information.
Formatting Tips
- Use bullet points to condense your notes to make them simpler to access or color-code them.
- Tracking your failures and mistakes can improve your work in the future.
- If possible, take notes as you’re experimenting or make time at the end of each workday to get it done.
- Record the date at the start of every day, including all dates spent on research.
Types of media to use when taking notes:
Traditional paper notebook.
- Pros: Able to take quick notes, convenient access to notes, cheaper option
- Cons: Requires a table of contents or tabs as it is not easily searchable, can get damaged easily, needs to be scanned if making a digital copy
Electronic notebook
- Apple Notes
- Pros: Easily searchable, note-taking apps available, easy to edit & customize
- Cons: Can be difficult to find notes if they are unorganized, not as easy to take quick notes, can be a more expensive option
Combination of both
Contact info.
618 Kerr Administration Building Corvallis, OR 97331
541-737-5105

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Organizing Research: Taking and Keeping Effective Notes
Once you’ve located the right primary and secondary sources, it’s time to glean all the information you can from them. In this chapter, you’ll first get some tips on taking and organizing notes. The second part addresses how to approach the sort of intermediary assignments (such as book reviews) that are often part of a history course.
Honing your own strategy for organizing your primary and secondary research is a pathway to less stress and better paper success. Moreover, if you can find the method that helps you best organize your notes, these methods can be applied to research you do for any of your classes.
Before the personal computing revolution, most historians labored through archives and primary documents and wrote down their notes on index cards, and then found innovative ways to organize them for their purposes. When doing secondary research, historians often utilized (and many still do) pen and paper for taking notes on secondary sources. With the advent of digital photography and useful note-taking tools like OneNote, some of these older methods have been phased out – though some persist. And, most importantly, once you start using some of the newer techniques below, you may find that you are a little “old school,” and might opt to integrate some of the older techniques with newer technology.
Whether you choose to use a low-tech method of taking and organizing your notes or an app that will help you organize your research, here are a few pointers for good note-taking.
Principles of note-taking
- If you are going low-tech, choose a method that prevents a loss of any notes. Perhaps use one spiral notebook, or an accordion folder, that will keep everything for your project in one space. If you end up taking notes away from your notebook or folder, replace them—or tape them onto blank pages if you are using a notebook—as soon as possible.
- If you are going high-tech, pick one application and stick with it. Using a cloud-based app, including one that you can download to your smart phone, will allow you to keep adding to your notes even if you find yourself with time to take notes unexpectedly.
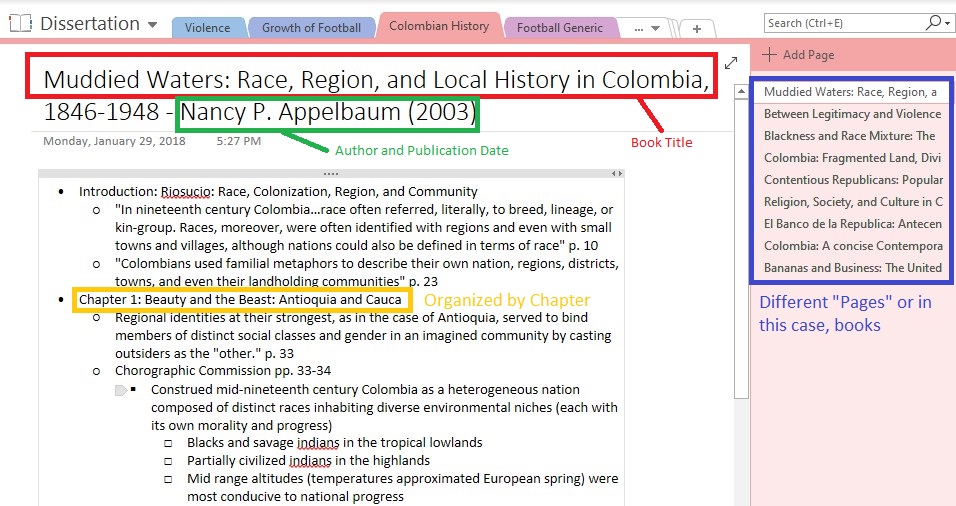
- When taking notes, whether you’re using 3X5 note cards or using an app described below, write down the author and a shortened title for the publication, along with the page number on EVERY card. We can’t emphasize this point enough; writing down the bibliographic information the first time and repeatedly will save you loads of time later when you are writing your paper and must cite all key information.
- Include keywords or “tags” that capture why you thought to take down this information in a consistent place on each note card (and when using the apps described below). If you are writing a paper about why Martin Luther King, Jr., became a successful Civil Rights movement leader, for example, you may have a few theories as you read his speeches or how those around him described his leadership. Those theories—religious beliefs, choice of lieutenants, understanding of Gandhi—might become the tags you put on each note card.
- Note-taking applications can help organize tags for you, but if you are going low tech, a good idea is to put tags on the left side of a note card, and bibliographic info on the right side.
Organizing research- applications that can help
Using images in research.
- If you are in an archive: make your first picture one that includes the formal collection name, the box number, the folder name and call numbe r and anything else that would help you relocate this information if you or someone else needed to. Do this BEFORE you start taking photos of what is in the folder.
- If you are photographing a book or something you may need to return to the library: take a picture of all the front matter (the title page, the page behind the title with all the publication information, maybe even the table of contents).
Once you have recorded where you find it, resist the urge to rename these photographs. By renaming them, they may be re-ordered and you might forget where you found them. Instead, use tags for your own purposes, and carefully name and date the folder into which the photographs were automatically sorted. There is one free, open-source program, Tropy , which is designed to help organize photos taken in archives, as well as tag, annotate, and organize them. It was developed and is supported by the Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media at George Mason University. It is free to download, and you can find it here: https://tropy.org/ ; it is not, however, cloud-based, so you should back up your photos. In other cases, if an archive doesn’t allow photography (this is highly unlikely if you’ve made the trip to the archive), you might have a laptop on hand so that you can transcribe crucial documents.
Using note or project-organizing apps
When you have the time to sit down and begin taking notes on your primary sources, you can annotate your photos in Tropy. Alternatively, OneNote, which is cloud-based, can serve as a way to organize your research. OneNote allows you to create separate “Notebooks” for various projects, but this doesn’t preclude you from searching for terms or tags across projects if the need ever arises. Within each project you can start new tabs, say, for each different collection that you have documents from, or you can start new tabs for different themes that you are investigating. Just as in Tropy, as you go through taking notes on your documents you can create your own “tags” and place them wherever you want in the notes.
Another powerful, free tool to help organize research, especially secondary research though not exclusively, is Zotero found @ https://www.zotero.org/ . Once downloaded, you can begin to save sources (and their URL) that you find on the internet to Zotero. You can create main folders for each major project that you have and then subfolders for various themes if you would like. Just like the other software mentioned, you can create notes and tags about each source, and Zotero can also be used to create bibliographies in the precise format that you will be using. Obviously, this function is super useful when doing a long-term, expansive project like a thesis or dissertation.
How History is Made: A Student’s Guide to Reading, Writing, and Thinking in the Discipline Copyright © 2022 by Stephanie Cole; Kimberly Breuer; Scott W. Palmer; and Brandon Blakeslee is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.

About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Research Guides
Gould library, reading well and taking research notes.
- How to read for college
- How to take research notes
- How to use sources in your writing
- Tools for note taking and annotations
- Mobile apps for notes and annotations
- Assistive technology
- How to cite your sources
Be Prepared: Keep track of which notes are direct quotes, which are summary, and which are your own thoughts. For example, enclose direct quotes in quotation marks, and enclose your own thoughts in brackets. That way you'll never be confused when you're writing.
Be Clear: Make sure you have noted the source and page number!
Be Organized: Keep your notes organized but in a single place so that you can refer back to notes about other readings at the same time.
Be Consistent: You'll want to find specific notes later, and one way to do that is to be consistent in the way you describe things. If you use consistent terms or tags or keywords, you'll be able to find your way back more easily.
Recording what you find

Take full notes
Whether you take notes on cards, in a notebook, or on the computer, it's vital to record information accurately and completely. Otherwise, you won't be able to trust your own notes. Most importantly, distinguish between (1) direct quotation; (2) paraphrases and summaries of the text; and (3) your own thoughts. On a computer, you have many options for making these distinctions, such as parentheses, brackets, italic or bold text, etc.
Know when to quote, paraphrase, and summarize
- Summarize when you only need to remember the main point of the passage, chapter, etc.
- Paraphrase when you are able to able to clearly state a source's point or meaning in your own words.
- Quote exactly when you need the author's exact words or authority as evidience to back up your claim. You may also want to be sure and use the author's exact wording, either because they stated their point so well, or because you want to refute that point and need to demonstrate you aren't misrepresenting the author's words.
Get the context right
Don't just record the author's words or ideas; be sure and capture the context and meaning that surrounds those ideas as well. It can be easy to take a short quote from an author that completely misrepresents his or her actual intentions if you fail to take the context into account. You should also be sure to note when the author is paraphrasing or summarizing another author's point of view--don't accidentally represent those ideas as the ideas of the author.
Example of reading notes
Here is an example of reading notes taken in Evernote, with citation and page numbers noted as well as quotation marks for direct quotes and brackets around the reader's own thoughts.

- << Previous: How to read for college
- Next: How to use sources in your writing >>
- Last Updated: Feb 7, 2024 12:22 PM
- URL: https://gouldguides.carleton.edu/activereading
Questions? Contact [email protected]

Powered by Springshare.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Research Note
- Open access
- Published: 12 May 2024
An inversion-based clustering approach for complex clusters
- Mohammad Mahdi Barati Jozan 1 ,
- Aynaz Lotfata 2 ,
- Howard J. Hamilton 3 &
- Hamed Tabesh 1
BMC Research Notes volume 17 , Article number: 133 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
The choice of an appropriate similarity measure plays a pivotal role in the effectiveness of clustering algorithms. However, many conventional measures rely solely on feature values to evaluate the similarity between objects to be clustered. Furthermore, the assumption of feature independence, while valid in certain scenarios, does not hold true for all real-world problems. Hence, considering alternative similarity measures that account for inter-dependencies among features can enhance the effectiveness of clustering in various applications.
In this paper, we present the Inv measure, a novel similarity measure founded on the concept of inversion. The Inv measure considers the significance of features, the values of all object features, and the feature values of other objects, leading to a comprehensive and precise evaluation of similarity. To assess the performance of our proposed clustering approach that incorporates the Inv measure, we evaluate it on simulated data using the adjusted Rand index.
The simulation results strongly indicate that inversion-based clustering outperforms other methods in scenarios where clusters are complex, i.e., apparently highly overlapped. This showcases the practicality and effectiveness of the proposed approach, making it a valuable choice for applications that involve complex clusters across various domains.
Conclusions
The inversion-based clustering approach may hold significant value in the healthcare industry, offering possible benefits in tasks like hospital ranking, treatment improvement, and high-risk patient identification. In social media analysis, it may prove valuable for trend detection, sentiment analysis, and user profiling. E-commerce may be able to utilize the approach for product recommendation and customer segmentation. The manufacturing sector may benefit from improved quality control, process optimization, and predictive maintenance. Additionally, the approach may be applied to traffic management and fleet optimization in the transportation domain. Its versatility and effectiveness make it a promising solution for diverse fields, providing valuable insights and optimization opportunities for complex and dynamic data analysis tasks.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Clustering is a fundamental technique in data mining and machine learning, aiming to group objects into distinct clusters [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. Objects within a cluster show high similarity to each other and low similarity to objects in other clusters, determined by a similarity measure [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
Selecting an appropriate similarity measure is crucial for clustering algorithms. Studies indicate its significance in algorithm performance [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Various research assesses similarity measures across disciplines like web clustering [ 13 ], trajectory clustering [ 14 ], and chemical databases [ 15 ]. Some research endeavors have further examined performance variations based on the type of data being analyzed, differentiating between categorical data [ 16 ] and continuous data [ 8 ]. Consequently, some scholars [ 17 ] have advocated for the utilization of two fundamental clustering techniques: "similarity measures" for qualitative data and "distance measures" for quantitative data [ 17 ]. In this study, we'll refer to both types of measures as "similarity measures."
Table 1 lists similarity functions for qualitative data, and Table 2 shows distance functions for quantitative data.
A key limitation of similarity measures (e.g., Euclidean distance [ 17 ] and Hamming similarity [ 18 ]) is their exclusive reliance on feature values. Consequently, when two objects or entities exhibit similar feature values, they are considered more similar, regardless of any other pertinent factors. This oversimplification may overlook crucial aspects of the data.
Secondly, similarity measures often assume feature independence, neglecting their interdependence and potential influence on each other's values. This oversight may result in incomplete representations of data relationships. Moreover, most measures overlook feature prioritization, disregarding the varying importance of features in determining similarity. These assumptions do not fully align with real-world complexities, potentially limiting applicability and accuracy. To address these challenges, researchers explore inversion as a promising approach, investigating its theoretical and practical aspects [ 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ].
In one study [ 19 ], a new constructive bijection connects permutations with a specific number of inversions to those with a particular major index, facilitating exploration of mathematical connections. Another work [ 20 ] introduces a probability distribution on the group of permutations of the set of integers, providing insights into inversion's probabilistic aspects for permutation-based data analysis. Furthermore, [ 21 ] presents six bijections linking a specific type of polyominoes called deco polyominoes with permutations, establishing connections between classical statistics and permutation-related analyses. Moreover, [ 22 ] proposes an efficient solution for counting interior edge crossings in bipartite graphs, relevant for layered graph drawing and data visualization enhancement.
This study introduces " Inv ," an inversion-based similarity measure addressing previous challenges. It forms the basis of a new clustering approach grouping objects by inversion-based similarity. The primary goal is to optimize clustering by maximizing intra-cluster similarity and minimizing inter-cluster similarities. By incorporating this measure, we anticipate achieving more meaningful clustering results that better reflect underlying data patterns and relationships.
Data and method
The flowchart of the activities undertaken to assess the new inversion-based clustering approach is presented in the Fig. 1 .
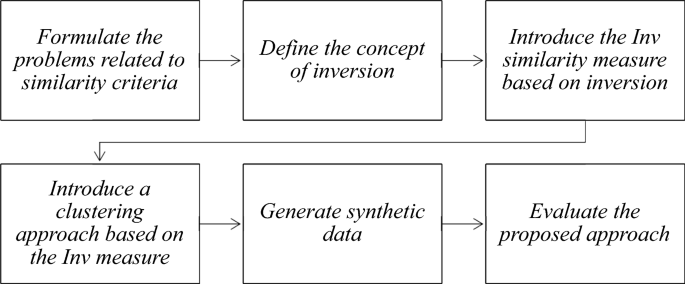
Flowchart of implementation and evaluation of the inversion-based clustering approach
Formulation of challenges related to similarity criteria
Several key terms used in simulation examples are defined below.
Object: Any entity that we intend to cluster is an object . Each object \({obj}_{i}\) has n features and can be represented by a vector: \({obj}_{i}= \langle {f}_{i1}, {f}_{i2}, \dots , {f}_{in}\rangle\) .
Feature space: Each feature has a valid range of values known as its feature space , represented by \({S}_{f}\) for feature \(f\) .
Universe: The set of all objects we want to cluster is known as the universe , represented by \(U= \left\{{obj}_{1}, {obj}_{2},\dots ,{obj}_{k}\right\}.\)
Similarity Measure: A similarity measure is a measure that takes two objects as input and outputs a numeric value representing their similarity.
Clustering problem: A problem of partitioning k objects into m groups \(\langle {C}_{1}, {C}_{2}, \dots , {C}_{m}\rangle\) according to a specified similarity measure, so that the objects in each group are as similar as possible to each other and as different as possible from objects in other groups. These clusters adhere to two constraints [1–7]:
In the following paragraphs, the challenges stated in the introduction section are formulated using the defined terms.
Symmetry challenge
A drawback of distance-based measures is called the Symmetry challenge , where adding or subtracting a value to a feature has the same distance effect. Given that Euclidean distance is widely used in clustering algorithms [ 23 ], it is used as a representative of distance-based measures in the following practices. Practice 1 demonstrates the weakness of similarity criteria when adding or subtracting a specific value to a feature.
Practice 1: Consider the following three objects:
The first feature of \({obj}_{2}\) is v units less that the first feature of \({obj}_{1}\) , and the first feature of \({obj}_{3}\) is v units more than the first feature of \({obj}_{1}\) . All other features are equal in the three objects. The Euclidean distance \(E\) between them, the similarity for adding \(v\) to the first feature is calculated as follows:
and the similarity for subtracting \(v\) from the first feature is calculated as follows:
This challenge can arise for any feature. In general, this challenge can be expressed as follows:
The equality of the distances is mathematically correct, but in the real world, the significance of adding a specific value to a feature may be different from that of subtracting the same amount. An example based on student scores can be found as Supplementary Example 1 (see Additional file 1 ).
Place symmetry challenge
The Place Symmetry challenge is a generalized form of the previous challenge. In this challenge, increasing or decreasing a value can occur for each feature. In Practice 2, the weakness of the similarity criteria when adding or subtracting a certain value to possibly different features of objects is shown.
Practice 2: Consider the following three objects:
if \({V}_{i}\) represents age and \({V}_{j}\) represents weight, both normalized to their respective feature spaces, adding \(v\) units to \({V}_{i}\) and subtracting \(v\) units from \({V}_{j}\) yields the same Euclidean distance between two pairs of objects. However, the implications of increasing or decreasing \(v\) units in weight differ from those in age due to varying value distributions. Hence, altering their values by \(v\) holds distinct meanings for each feature.
Feature independence challenge
The Feature Independence challenge refers to the treatment of features as if they are independent of each other when calculating distance-based measures, whereas in practice they are often interdependent.
Definition of the concept of inversion
To address the challenges defined in section " Formulation of challenges related to similarity criteria ", a similarity measure named Inv , which is based on the concept of inversion, is proposed. The mathematical definition of inversion is as follows:
Inversion: In a sequence \(S= \langle {a}_{1}, {a}_{2}, \dots , {a}_{n}\rangle\) of pairwise comparable elements \({a}_{i} (i=\mathrm{1,2},\dots ,n)\) , a pair \(({a}_{i},{a}_{j})\) is called an inversion if \(i<j\) and \({a}_{i}>{a}_{j}\) [ 22 ].
The concept of inversion is illustrated by Practice 3.
Practice 3: Suppose we have five movies and we ask two people to rate them on a scale of 1 to 10 according to their preferences. In this example, an object is a person and it is represented by a vector with 5 features [ 24 ].
Scores are given in Table 3 .
The definition of inversion for only one person is presented in Supplementary Example 1 (see Additional file 1 ). Let's now explore a more indirect application of the definition to determine the inversions between the scores of the two people. We arrange the movies for each person in a rank sequence based on preferences, with the highest-scoring movie first. Ties are resolved by ranking the movie with the lower movie number first. Person 1's sequence is \(\langle {Movie}_{1}, {Movie}_{5},{Movie}_{2},{Movie}_{3},{Movie}_{4}\rangle\) , while Person 2's is \(\langle {Movie}_{1}, {Movie}_{3},{Movie}_{4},{Movie}_{2},{Movie}_{5}\rangle\) . Renaming the movies based on Person 1's rank sequence, we get 〈1,2,3,4,5〉 for Person 1 and 〈1,4,5,3,2〉 for Person 2. Applying the inversion definition to the second sequence, we find 4 is inverted compared to 3 and 2 (two inversions), 5 is inverted compared to 3 and 2 (two inversions), and 3 is inverted compared to 2 (one inversion), totaling five inversions.
A visual method for counting inversions involves organizing movies for each person by their scores, highest to lowest, and connecting corresponding movies. The intersections of these lines indicate the number of inversions between the two sequences.
In Fig. 2 , the five inversions are indicated by the five points where the lines intersect. The more different the sequences, the greater the number of the inversions. The minimum and maximum number of inversions of two vectors with n features are 0 and \(\frac{n\left(n+1\right)}{2}\) , respectively [ 25 ]. Supplementary Code 1 contains the inversion calculation algorithm (see Additional file 1 ).
Each point of intersection between lines representing an inversion (practice 3)
Notice from Practice3 that the way ties are broken affects the number of inversions. The proposed way of resolving ties is to consider a default sequence for features, and when the values of two or more features are the same, their order will be based on the default order. For instance, in the movies database, priority is given to movies with smaller numbers. Thus, as Person 2 rated Movie 1 and Movie 3 equally at 9, Movie 1 takes precedence in the rank order.
Practice3 illustrates the importance of feature prioritization in cases where values are equal. Depending on specific requirements, certain features may need to be prioritized over others, which can have a considerable impact on the resulting number of inversions.
Introduction of the Inv similarity measure based on the notion of inversion
In this subsection, the Inv inversion-based similarity measure is introduced. The Inv measure of the similarity of two objects is defined as the number of inversions that exist between two objects according to the Count_Inversions function. Formally, the measure is defined as follows:
According to the Inv measure, as inversion count between two sequences rises, their similarity decreases, and vice versa. Although we refer to inversion as a similarity measure, it actually yields a measure of dissimilarity because the greater the similarity between two objects, the lower the number of inversions.
Three advantages of the inversion-based similarity measure are as follows [ 22 ]: the number of inversions is affected by the rank positions of the features in the vector (Feature Independence challenge); the number of inversions when v is added to feature \({f}_{i}\) can be different from the number of inversions when it is subtracted from \({f}_{i}\) (Symmetry challenge); and the number of inversions when v is added to \({f}_{i}\) may not be the same as the number of inversions when v is added to \({f}_{j}\) (Place Symmetry challenge).
The Symmetry challenge in distance-based measures results from the equal impact of adding or subtracting a value from a feature on the distance. In calculating inversions, not only is the value of a particular feature considered, but also the values of other features become integral. The feature's rank position within the object's vector significantly affects the inversion count. Altering a feature's rank position by adding a value may yield different outcomes compared to subtracting the same value, influenced by other features. Consequently, the inversion count varies depending on specific features, emphasizing the nuanced nature of inversion calculations.
The Place Symmetry challenge expands upon the Symmetry challenge by allowing the increase or decrease of a value for each feature individually. As previously noted, the count of inversions is influenced by both the value of a specific feature and other features, so it addresses this challenge as well as the previous challenge.
To challenge the independence of features, since determining the number of inversions requires determining the values and order of all features, hence the features cannot be independent of each other. The explanation of how the proposed measure addresses the outlined challenges are illustrated in Supplementary practice 1 (see Additional file 1 ).
The proposed similarity measure offers an additional advantage by allowing adjustments to consider feature importance in distance calculation. This enables the consideration of feature relevance or priority, enhancing the measure's utility. To accommodate priorities, the inversion measure can be modified to incorporate both feature value and assigned priority. By default, all variables are assumed to have equal priority. Practice 4 demonstrates a method for factoring feature priority into similarity calculation.
Practice 4 : Consider two objects, each with three features, depicted by colored circles in Fig. 3 . Let the orange feature have priority 1 (lowest), the red feature priority 2, and the blue feature priority 3 (highest). An adjusted inversion function is employed, where each inversion detected is weighted by the product of the relevant features' priorities.
Prioritizing features: A All features have the same priority, which is one, B The priority of each feature is displayed within the corresponding circle (Practice 4)
According to Fig. 3 A, there are 2 inversions because there are 2 points where the lines intersect (OB and RB). Since the priority of every feature is one, the adjusted inversion function is as calculated as:
To calculate the adjusted inversion for Fig. 3 B, the products of the priorities of each inversion (represented by a line) are also considered.
Introduction of the clustering approach based on the Inv measure
In this section, we formulate an algorithmic framework for an inversion-based clustering approach as a type of partitioning clustering method and then we instantiate the framework with different measures to specify two inversion-based clustering algorithms. The main steps of a partitioning clustering method are as follows. First, the number of desired clusters is chosen and initial centroids in the range of the feature values are randomly selected. Next, every input object is assigned to the nearest centroid based on its distance from it using the similarity measure. Every centroid is then moved to the mean location of its assigned cluster, and this process is iteratively repeated until convergence is reached, as indicated by no further changes in assignments [ 25 ]. The pseudo-code of proposed algorithmic framework can be found as Supplementary Code 2 (see Additional file 1 ).
Algorithmic framework for inversion-based clustering
The steps of the algorithmic framework are described below.
Input: \(U=\{{obj}_{1}, {obj}_{2}, \dots , {obj}_{k}\}\) , number of clusters ( \(m\) )
Output : \(m clusters \left({C}_{1}, {C}_{2}, \dots , {C}_{m}\right)\)
Step 1) Normalize each feature based on the Min–Max Feature scaling method. The normalized feature value \({F}_{ia}\) for feature \({f}_{a}\) in object \({obj}_{i}\) is calculated as the following equation:
where \({f}_{ia}\) is the original feature value for \({obj}_{i}\) , \({\text{min}}({f}_{a})\) is the minimum value and \({\text{max}}\left({f}_{a}\right)\) is the maximum value of the feature across all objects in universe U , and \({F}_{ia}\) is the normalized value. The feature space for every normalized feature is equal to [0, 1].
Step 2) Initialize the centroids \({c}_{1}, {c}_{2}, \dots , {c}_{m}\) of clusters \({C}_{1}, {C}_{2}, \dots , {C}_{m}\) randomly.
Step 3) Calculate the number of inversions between every combination of an object \({obj}_{i}\) and a centroid \({c}_{j}\) and assign every object to the cluster for the centroid with the fewest inversions.
Step 4) For each cluster \({C}_{j}\) , calculate the new centroid \({c}_{j}\) as the mean of the objects assigned to the cluster:
\({N}_{j}\) is the number of objects assigned to cluster \({C}_{j}\) , and the sum is taken over all objects in this cluster.
Step 5) Repeat Steps 3 and 4 until the clusters do not change, or the number of iterations reaches a predetermined value.
For the third step of the algorithmic framework, which is to assign an object to a cluster using a measure, two measures are proposed, which lead to the Inversion-Based Clustering Algorithm (ICA) and the Regulator Inversion Euclidean distance based Clustering Algorithm (RIECA).
Approach 1) Inversion-Based Clustering Algorithm (ICA)
In the first round of ICA, the centroids are randomly initialized, then inversions between every combination of an object and a centroid are calculated, and finally every object is assigned to the centroid with the fewest inversions. In subsequent rounds, inversions between every combination of an object and an updated centroid are calculated. In other words, the measure function is defined as follows:
where \({obj}_{i}\) is the \({i}^{th}\) object, \({C}_{c}\) is \({c}^{th}\) cluster (which has centroid \({c}_{c}\) ), and \(Inv\left({obj}_{i},{c}_{c}\right)\) is the number of inversions between \({obj}_{i}\) and \({c}_{c}\) .
Approach 2) Regulator Inversion Euclidean distance based Clustering Algorithm (RIECA)
With RIECA, inversion is used as a regulator for Euclidean distance [ 17 ], i.e. the Euclidean distance is multiplied by the number of inversions. If the number of inversions is high, the value of the measure grows more than if the number of inversions is low. In this approach, the Measure function is defined as follows:
where \({Obj}_{i}\) is the \({i}^{th}\) object, \({c}_{c}\) is the \({c}^{th}\) cluster, \(Inv\left({Obj}_{i},{c}_{c}\right)\) is the number of inversions between \({Obj}_{i}\) and \({c}_{c}\) , and \(E\left({Obj}_{i},{c}_{c}\right)\) is the Euclidean distance between \({Obj}_{i}\) and \({c}_{c}\) .
This section describes the generation of synthetic data and the evaluation of the proposed approach, which correspond to the final two steps of the flowchart given in section " Data and method ".
Generation of synthetic data
Synthetic datasets were generated using the MixSim package [ 26 ]. The average pairwise overlap parameter (denoted as ῶ) in package allows for the creation of clusters with varying degrees of complexity, ranging from well-separated (ῶ = 0.001) to highly overlapped ones (ῶ = 0.4) [ 27 ]. The summary of the package documentation can be found as Supplementary Documentation 1 (see Additional file 1 ).
To evaluate the performance of the ICA and REICA algorithms, we generated two types of random data samples for each value of ῶ (0.4, 0.3, 0.2, 0.05, and 0.001). The first type of data sample (referred to as Simulated Dataset1) comprised 200 random data values with 6 features, forming 5 clusters. The second type of data sample (referred to as Simulated Dataset2) included 500 random data values with 7 features, forming 10 clusters. These datasets facilitated comprehensive evaluation of algorithm performance across diverse clustering complexities.
Evaluation of the proposed approach
The proposed ICA and REICA algorithms are compared with EM clustering [ 28 ] from the mclust package [ 29 ], k-means [ 3 ] and hierarchal clustering [ 30 ] from the stats package, and k-medoids [ 31 ] clustering from the cluster package [ 32 ]. For the comparison, 1000 data samples of Simulated Dataset 1 and 1000 of Simulated Dataset 2 were prepared and then each algorithm was run on each sample separately. The ICA and REICA algorithms are implemented in R version 3.4.2 [ 33 ]. This study employs the adjusted Rand index implemented in the MixSim package to evaluated algorithms [ 26 , 34 , 35 , 36 ]. The values obtained for the adjusted Rand index for the algorithms when applied to Simulated Dataset 1 are shown in Table 4 .
Table 4 shows that for complex cluster structures (ῶ = 0.4, 0.3, and 0.2), REICA algorithm outperforms other algorithms in cluster formation. However, for moderately or highly separated clusters (ῶ = 0.05, 0.001), both ICA and REICA algorithms perform poorly compared to other algorithms. This was anticipated, as distance between objects outweighs the influence of inversions in such scenarios.
To evaluate the statistical significance of the adjusted Rand index differences among algorithms, we conducted a one-way ANOVA test. Further details are available in Supplementary statistical test result 1 (see Additional file 1 ).
Tables 5 and 6 reveal the optimal algorithm for each ῶ value, offering insights into algorithm performance across diverse clustering scenarios. These results elucidate the efficacy of ICA and REICA algorithms amidst varying clustering complexities and separations.
In highly or moderately separated clusters, distance becomes more influential, diminishing the role of the number of inversions. Consequently, the proposed algorithms are less effective in handling such scenarios compared to other types of clustering. REICA excelled in complex structures, while no algorithm consistently outperformed others in highly or moderately separated clusters. When ῶ = 0.05, k-means was most effective in both simulations. Conversely, with ῶ = 0.001 and a small number of clusters and samples (Simulated Dataset 1), k-means, EM, K-medoids, and Hierarchical algorithms were highly effective. However, with a large number of clusters and samples (Simulated Dataset 2), EM algorithm proved most effective. These findings highlight algorithm strengths in diverse clustering conditions, revealing performance across varying complexities and separations. The selection of the optimal algorithm depends on specific data characteristics and nature.
Clustering techniques encompass partitioning, hierarchical, density-based, grid-based, and model-based methods [ 25 ]. The proposed algorithms fall under partitioning clustering. ICA is similar to k-means but utilizes an inversion-based similarity measure instead of a distance measure, whereas REICA utilizes inversion as a form of regulation for the Euclidean distance. In REICA, Euclidean distance is multiplied by the number of inversions. As a result, when there are more inversions, the measure value increases more prominently compared to scenarios with fewer inversions. This innovative method enriches the algorithm's ability for intricate cluster handling and enhances data analysis insights.
One strength of this study is that it identified three major challenges for Euclidean distance measures: the Symmetry challenge, the Place Symmetry challenge, and the Feature Independence Challenge. To address these challenges, we introduce the inversion-based measure " Inv. " Our findings show the significance of both Euclidean distance and inversions for similarity measures. Particularly, REICA, which multiplies inversions by Euclidean distance, outperforms ICA, which relies solely on inversions. The effectiveness of REICA, which employs a hybrid measure that considers inversions and Euclidean distance, suggests potential for developing other hybrid measures considering both factors. Such measures could prioritize inversion for complex clusters and emphasize Euclidean distance for well-separated clusters, aligning with k-means and other clustering methods.
Another strength of this study is that it benefits from applying statistical testing techniques like one-way ANOVA to rigorously assess the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms in comparison to existing algorithms. Additionally, simulating diverse data samples covering various clustering complexities enhances the findings' robustness and generalizability.
One strength of the proposed inversion-based algorithm is its ability to prioritize features differently. This prioritization operates at two levels. Firstly, during inversion calculation, equal feature values are sorted based on predetermined priority, influencing the number of inversions. Secondly, priority can be introduced as a coefficient in inversion calculations, where each intersection reflects the multiplication of feature priority values. As a result, the distance between two objects will increase with higher priority values, allowing more flexible and nuanced clustering.
For evaluation, the proposed algorithms' performance was compared with classical clustering methods: k-means [ 3 ], EM clustering [ 28 ], hierarchical clustering [ 30 ], and k-medoids [ 31 ]. Results indicate RIECA outperforms other algorithms with complex cluster structures [ 37 , 38 ]. However, in scenarios of moderate or high cluster separation, the proposed algorithms are less effective, consistent with Berikov [ 39 ] and Cupertino [ 40 ].
A limitation of the inversion-based clustering approach is its effectiveness sensitivity to initial centroid selection, a common challenge in partition-based algorithms [ 25 ]. Mitigation strategies, such as repetition and employing the K-means++ initialization method [ 41 ], can be adapted to address this issue. In this study, we adopt the solution of running the algorithm several times with random initial centroids [ 25 ].
Another limitation is the lack of evaluation on real datasets. Assessing an algorithm's performance on actual data is challenging due to unknown cluster complexity. To address this, one could compare synthetic datasets with known complexity to real databases to gain an understanding of the complexity, then evaluate the algorithms under conditions similar to practical tasks. This approach offers insights into real-world performance, establishing their relevance and reliability for diverse data analysis scenarios.
This paper emphasizes the significant impact of similarity measures on clustering algorithm performance. Existing measures, often reliant on feature values and assuming feature independence, may not yield optimal results in practice. To address this, we introduced the innovative inversion-based Inv measure, which considers other object and feature values through inversion. We proposed two algorithms (ICA and RIECA) based on Inv measure, and evaluated their performance using simulated data. Results showed inversion-based clustering outperformed traditional techniques for complex cluster structures.
Future studies can explore practical applications of the Inv measure in real-world problems to improve clustering performance across domains. Further research could investigate other hybrid measures combining inversions and distance-based measure.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the first author on reasonable request.
Jain AK, Narasimha Murty M, Flynn PJ. Data clustering: a review. ACM Comput Surv. 1999;31(3):264–323.
Article Google Scholar
Lingras P, Huang X. Statistical, evolutionary, and neurocomputing clustering techniques: cluster-based vs object-based approaches. Artif Intell Rev. 2005;23:3–29.
MacQueen J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability. 1967;1(14).
Xu R, Wunsch D. Survey of clustering algorithms. IEEE Trans Neural Netw. 2005;16(3):645–78.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Rodriguez SIR, de Carvalho FAT. Fuzzy clustering algorithms with distance metric learning and entropy regularization. Appl Soft Comput. 2021;113: 107922.
Jothi R, Mohanty SK, Ojha A. Gene expression clustering using local neighborhood-based similarity measures. Comput Electr Eng. 2021;91: 107032.
Nozad SAN, Haeri MA, Folino G. SDCOR: Scalable density-based clustering for local outlier detection in massive-scale datasets. Knowl Based Syst. 2021;228: 107256.
Shirkhorshidi AS, Saeed A, Wah TY. A comparison study on similarity and dissimilarity measures in clustering continuous data. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(12): e0144059.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Boriah S, Chandola V, Kumar V. Similarity measures for categorical data: a comparative evaluation. Proceedings of the 2008 SIAM international conference on data mining. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2008.
Yan Q, et al. A discriminated similarity matrix construction based on sparse subspace clustering algorithm for hyperspectral imagery. Cogn Syst Res. 2019;53:98–110.
Renjith S, Sreekumar A, Jathavedan M. Performance evaluation of clustering algorithms for varying cardinality and dimensionality of data sets. Mater Today Proc. 2020;27:627–33.
Shrifan NHMM, Akbar MF, Isa NAM. An adaptive outlier removal aided k-means clustering algorithm. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci. 2022;34(8):6365–76.
Google Scholar
Strehl A, Ghosh J, Mooney R. Impact of similarity measures on web-page clustering. Workshop on artificial intelligence for web search (AAAI 2000). 2000;58.
Zhang Z, Huang K, Tan T. Comparison of similarity measures for trajectory clustering in outdoor surveillance scenes. 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR'06). IEEE, 2006;3.
Khalifa, Aysha Al, Maciej Haranczyk, and John Holliday. "Comparison of nonbinary similarity coefficients for similarity searching, clustering and compound selection." Journal of chemical information and modeling 49.5 (2009): 1193–1201.
Lourenço, Fernando, Victor Lobo, and Fernando Bacao. "Binary-based similarity measures for categorical data and their application in Self-Organizing Maps." (2004): 1–18.
Xu D, Tian Y. A comprehensive survey of clustering algorithms. Ann Data Sci. 2015;2:165–93.
Taheri R, et al. Similarity-based Android malware detection using Hamming distance of static binary features. Future Gener Comput Syst. 2020;105:230–47.
Vajnovszki V. A new Euler-Mahonian constructive bijection. Discret Appl Math. 2011;159(14):1453–9.
Gnedin A, Olshanski G. The two-sided infinite extension of the Mallows model for random permutations. Adv Appl Math. 2012;48(5):615–39.
Deutsch E, Pergola E, Pinzani R. Six bijections between deco polyominoes and permutations. 2008, arXiv preprint, arXiv:0810.2876 .
Barth W, Jünger M, Mutzel P. Simple and efficient bilayer cross counting. Graph Drawing: 10th International Symposium, GD 2002 Irvine, CA, USA, August 26–28, 2002 Revised Papers 10. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2002
Grabusts P. The choice of metrics for clustering algorithms. Environ Technol Resourc Proc Int Sci Pract Confer. 2011;2:20.
Jozan MM, Taghiyareh F, Faili H. An inversion-based genetic algorithm for grouping of students. Proc. 7th Int. Conf. Virtual Learn. Vol. 1. No. 1. 2012.
Han J, Pei J, Tong H. Data mining: concepts and techniques. Burlington: Morgan kaufmann; 2022.
Melnykov V, Chen W-C, Maitra R. MixSim: an R package for simulating data to study performance of clustering algorithms. J Stat Softw. 2012;51:1–25.
Maitra R, Melnykov V. Simulating data to study performance of finite mixture modeling and clustering algorithms. J Comput Graph Stat. 2010;19(2):354–76.
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J Roy Stat Soc: Ser B (Methodol). 1977;39(1):1–22.
Fraley C, Raftery AE. MCLUST version 3 for R: Normal mixture modeling and model-based clustering. Vol. 504. Technical report, 2006.
Chris D, He X. Cluster merging and splitting in hierarchical clustering algorithms. 2002 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, 2002. Proceedings.. IEEE, 2002.
Kaufman L, Rousseeuw PJ. Partitioning around medoids (Program PAM). Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics, Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1990, pp. 68–125, https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470316801.ch2
Maechler M, Rousseeuw P, Struyf A, Hubert M, Hornik K. Cluster: cluster analysis basics and extensions. R package version 1.14. 3." 2012.
R Core Team, R. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. 2013: 275–286.
Halkidi M, Batistakis Y, Vazirgiannis M. On clustering validation techniques. J Intell Inf Syst. 2001;17:107–45.
Agustı LE, et al. A new grouping genetic algorithm for clustering problems. Expert Syst Appl. 2012;39(10):9695–703.
Rand WM. Objective criteria for the evaluation of clustering methods. J Am Stat Assoc. 1971;66(336):846–50.
Thong PH. Picture fuzzy clustering for complex data. Eng Appl Artif Intell. 2016;56:121–30.
Khan L, Luo F. Hierarchical clustering for complex data. Int J Artif Intell Tools. 2005;14(05):791–809.
Berikov V. Weighted ensemble of algorithms for complex data clustering. Pattern Recogn Lett. 2014;38:99–106.
Cupertino TH, Huertas J, Zhao L. Data clustering using controlled consensus in complex networks. Neurocomputing. 2013;118:132–40.
Hämäläinen J, Kärkkäinen T, Rossi T. Improving scalable K-means++. Algorithms. 2020;14(1):6.
Download references
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Medical Informatics, Faculty of Medicine, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran
Mohammad Mahdi Barati Jozan & Hamed Tabesh
Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology, School Of Veterinary Medicine, University of California, Davis, USA
Aynaz Lotfata
Department of Computer Science, University of Regina, Regina, SK, Canada
Howard J. Hamilton
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.M.B.J.: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—original draft, draft preparation. A.L.: Methodology, validation, formal analysis, review, supervision. H.J.H.: Methodology, validation, formal analysis, review, supervision. H.T.: Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, review, supervision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hamed Tabesh .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors submitting this manuscript have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
13104_2024_6791_moesm1_esm.docx.
Additional file 1. Supplementary Figures, Tables and Codes. This file contains supplementary figures, tables and codes that provide further insights into the experimental setup and results discussed in the article.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Barati Jozan, M.M., Lotfata, A., Hamilton, H.J. et al. An inversion-based clustering approach for complex clusters. BMC Res Notes 17 , 133 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-024-06791-y
Download citation
Received : 08 August 2023
Accepted : 30 April 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-024-06791-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Clustering algorithm
- Inversion-based similarity measure
- Overlapping clusters
- Adjusted Rand index
BMC Research Notes
ISSN: 1756-0500
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
share this!
May 13, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Study reveals insights into protein evolution
by Marcy de Luna, Rice University

Rice University's Peter Wolynes and his research team have unveiled a breakthrough in understanding how specific genetic sequences, known as pseudogenes, evolve. Their paper was published May 13 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences .
Led by Wolynes, the D.R. Bullard-Welch Foundation Professor of Science, professor of chemistry, biosciences and physics and astronomy and co-director of the Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP), the team focused on deciphering the complex energy landscapes of de-evolved, putative protein sequences corresponding to pseudogenes.
Pseudogenes are segments of DNA that once encoded proteins but have since lost their ability to do so due to sequence degradation—a phenomenon referred to as devolution. Here, devolution represents an unconstrained evolutionary process that occurs without the usual evolutionary pressures that regulate functional protein-coding sequences.
Despite their inactive state, pseudogenes offer a window into the evolutionary journey of proteins.
"Our paper explains that proteins can de-evolve," Wolynes said. "A DNA sequence can, by mutations or other means, lose the signal that tells it to code for a protein. The DNA continues to mutate but does not have to lead to a sequence that can fold."
The researchers studied junk DNA in a genome that has de-evolved. Their research revealed that a mutation accumulation in pseudogene sequences typically disrupts the native network of stabilizing interactions, making it challenging for these sequences, if they were to be translated, to fold into functional proteins.
However, the researchers observed instances where certain mutations unexpectedly stabilized the folding of pseudogenes at the cost of altering their previous biological functions.

They identified specific pseudogenes, such as cyclophilin A, profilin-1 and small ubiquitin-like modifier 2 protein, where stabilizing mutations occurred in regions crucial for binding to other molecules and other functions, suggesting a complex balance between protein stability and biological activity .
Moreover, the study highlights the dynamic nature of protein evolution as some previously pseudogenized genes may regain their protein-coding function over time despite undergoing multiple mutations.
Using sophisticated computational models, the researchers interpreted the interplay between physical folding landscapes and the evolutionary landscapes of pseudogenes. Their findings provide evidence that the funnel-like character of folding landscapes comes from evolution.
"Proteins can de-evolve and have their ability to fold compromised over time due to mutations or other means," Wolynes said. "Our study offers the first direct evidence that evolution is shaping the folding of proteins."
Along with Wolynes, the research team includes lead author and applied physics graduate student Hana Jaafari; CTBP postdoctoral associate Carlos Bueno; University of Texas at Dallas graduate student Jonathan Martin; Faruck Morcos, associate professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at UT-Dallas; and CTBP biophysics researcher Nicholas P. Schafer.
The implications of this research extend beyond theoretical biology with potential applications in protein engineering, Jaafari said.
"It would be interesting to see if someone at a lab could confirm our results to see what happens to the pseudogenes that were more physically stable," Jaafari said. "We have an idea based on our analysis, but it'd be compelling to get some experimental validation."
Journal information: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Provided by Rice University
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Exploring the ultrasmall and ultrafast through advances in attosecond science
2 hours ago
Machine learning and AI aid in predicting molecular selectivity of chemical reactions

Persistent strain of cholera defends itself against forces of change, scientists find
Scientists help unravel life's cosmic beginnings
3 hours ago

Physicists create five-lane superhighway for electrons

Fruit fly testes offer potential tool against harmful insects

Researchers find new approach for antibiotic development
Exceptionally large transverse thermoelectric effect produced by combining thermoelectric and magnetic materials
4 hours ago

Chemical analysis of natural CO₂ rise over the last 50,000 years shows that today's rate is 10 times faster

In a reservoir in Southeast Brazil, introduction of a fish native to the Amazon has reduced native species diversity
Relevant physicsforums posts, is it usual for vaccine injection site to hurt again during infection, a brief biography of dr virgina apgar, creator of the baby apgar test.
May 12, 2024
Who chooses official designations for individual dolphins, such as FB15, F153, F286?
May 9, 2024
The Cass Report (UK)
May 1, 2024
Is 5 milliamps at 240 volts dangerous?
Apr 29, 2024
Major Evolution in Action
Apr 22, 2024
More from Biology and Medical
Related Stories

Biologists' mapping method illustrates paths to new proteins
Jul 10, 2023

Researchers reveal evolutionary path of important proteins
Mar 29, 2024
A new model offers an explanation for the huge variety of sizes of DNA in nature
Feb 22, 2023

New method expertly evaluates protein folding stability on a large scale
Jul 19, 2023
Atomic resolution protein models reveal new details about protein binding
Nov 23, 2020

Researchers identify novel pathways responsible for liver cancer
Jan 18, 2022
Recommended for you

Genetic analyses reveal new viruses on the horizon
5 hours ago

Centromere research yields new insights into the mechanisms of chromosome segregation errors

Long-term study finds organic farming leads to adaptations in the genetic material in plants
8 hours ago

Island birds more adaptable than previously thought
7 hours ago
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Better Siri is coming: what Apple’s research says about its AI plans
Apple hasn’t talked too much about ai so far — but it’s been working on stuff. a lot of stuff..
By David Pierce , editor-at-large and Vergecast co-host with over a decade of experience covering consumer tech. Previously, at Protocol, The Wall Street Journal, and Wired.
Share this story
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25430195/247097_Apple__AI__CVirginia_B2B.jpg)
It would be easy to think that Apple is late to the game on AI. Since late 2022, when ChatGPT took the world by storm, most of Apple’s competitors have fallen over themselves to catch up. While Apple has certainly talked about AI and even released some products with AI in mind, it seemed to be dipping a toe in rather than diving in headfirst.
But over the last few months, rumors and reports have suggested that Apple has, in fact, just been biding its time, waiting to make its move. There have been reports in recent weeks that Apple is talking to both OpenAI and Google about powering some of its AI features, and the company has also been working on its own model, called Ajax .
If you look through Apple’s published AI research, a picture starts to develop of how Apple’s approach to AI might come to life. Now, obviously, making product assumptions based on research papers is a deeply inexact science — the line from research to store shelves is windy and full of potholes. But you can at least get a sense of what the company is thinking about — and how its AI features might work when Apple starts to talk about them at its annual developer conference, WWDC, in June.
Smaller, more efficient models
I suspect you and I are hoping for the same thing here: Better Siri. And it looks very much like Better Siri is coming! There’s an assumption in a lot of Apple’s research (and in a lot of the tech industry, the world, and everywhere) that large language models will immediately make virtual assistants better and smarter. For Apple, getting to Better Siri means making those models as fast as possible — and making sure they’re everywhere.
In iOS 18, Apple plans to have all its AI features running on an on-device, fully offline model, Bloomberg recently reported . It’s tough to build a good multipurpose model even when you have a network of data centers and thousands of state-of-the-art GPUs — it’s drastically harder to do it with only the guts inside your smartphone. So Apple’s having to get creative.
In a paper called “ LLM in a flash: Efficient Large Language Model Inference with Limited Memory ” (all these papers have really boring titles but are really interesting, I promise!), researchers devised a system for storing a model’s data, which is usually stored on your device’s RAM, on the SSD instead. “We have demonstrated the ability to run LLMs up to twice the size of available DRAM [on the SSD],” the researchers wrote, “achieving an acceleration in inference speed by 4-5x compared to traditional loading methods in CPU, and 20-25x in GPU.” By taking advantage of the most inexpensive and available storage on your device, they found, the models can run faster and more efficiently.
Apple’s researchers also created a system called EELBERT that can essentially compress an LLM into a much smaller size without making it meaningfully worse. Their compressed take on Google’s Bert model was 15 times smaller — only 1.2 megabytes — and saw only a 4 percent reduction in quality. It did come with some latency tradeoffs, though.
In general, Apple is pushing to solve a core tension in the model world: the bigger a model gets, the better and more useful it can be, but also the more unwieldy, power-hungry, and slow it can become. Like so many others, the company is trying to find the right balance between all those things while also looking for a way to have it all.
Siri, but good
A lot of what we talk about when we talk about AI products is virtual assistants — assistants that know things, that can remind us of things, that can answer questions, and get stuff done on our behalf. So it’s not exactly shocking that a lot of Apple’s AI research boils down to a single question: what if Siri was really, really, really good?
A group of Apple researchers has been working on a way to use Siri without needing to use a wake word at all; instead of listening for “Hey Siri” or “Siri,” the device might be able to simply intuit whether you’re talking to it. “This problem is significantly more challenging than voice trigger detection,” the researchers did acknowledge, “since there might not be a leading trigger phrase that marks the beginning of a voice command.” That might be why another group of researchers developed a system to more accurately detect wake words . Another paper trained a model to better understand rare words, which are often not well understood by assistants.
In both cases, the appeal of an LLM is that it can, in theory, process much more information much more quickly. In the wake-word paper, for instance, the researchers found that by not trying to discard all unnecessary sound but, instead, feeding it all to the model and letting it process what does and doesn’t matter, the wake word worked far more reliably.
Once Siri hears you, Apple’s doing a bunch of work to make sure it understands and communicates better. In one paper, it developed a system called STEER (which stands for Semantic Turn Extension-Expansion Recognition, so we’ll go with STEER) that aims to improve your back-and-forth communication with an assistant by trying to figure out when you’re asking a follow-up question and when you’re asking a new one. In another, it uses LLMs to better understand “ambiguous queries” to figure out what you mean no matter how you say it. “In uncertain circumstances,” they wrote, “intelligent conversational agents may need to take the initiative to reduce their uncertainty by asking good questions proactively, thereby solving problems more effectively.” Another paper aims to help with that, too: researchers used LLMs to make assistants less verbose and more understandable when they’re generating answers.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25431587/CleanShot_2024_05_03_at_09.50.52.png)
AI in health, image editors, in your Memojis
Whenever Apple does talk publicly about AI, it tends to focus less on raw technological might and more on the day-to-day stuff AI can actually do for you. So, while there’s a lot of focus on Siri — especially as Apple looks to compete with devices like the Humane AI Pin, the Rabbit R1, and Google’s ongoing smashing of Gemini into all of Android — there are plenty of other ways Apple seems to see AI being useful.
One obvious place for Apple to focus is on health: LLMs could, in theory, help wade through the oceans of biometric data collected by your various devices and help you make sense of it all. So, Apple has been researching how to collect and collate all of your motion data, how to use gait recognition and your headphones to identify you, and how to track and understand your heart rate data. Apple also created and released “the largest multi-device multi-location sensor-based human activity dataset” available after collecting data from 50 participants with multiple on-body sensors.
Apple also seems to imagine AI as a creative tool. For one paper, researchers interviewed a bunch of animators, designers, and engineers and built a system called Keyframer that “enable[s] users to iteratively construct and refine generated designs.” Instead of typing in a prompt and getting an image, then typing another prompt to get another image, you start with a prompt but then get a toolkit to tweak and refine parts of the image to your liking. You could imagine this kind of back-and-forth artistic process showing up anywhere from the Memoji creator to some of Apple’s more professional artistic tools.
In another paper , Apple describes a tool called MGIE that lets you edit an image just by describing the edits you want to make. (“Make the sky more blue,” “make my face less weird,” “add some rocks,” that sort of thing.) “Instead of brief but ambiguous guidance, MGIE derives explicit visual-aware intention and leads to reasonable image editing,” the researchers wrote. Its initial experiments weren’t perfect, but they were impressive.
We might even get some AI in Apple Music: for a paper called “ Resource-constrained Stereo Singing Voice Cancellation ,” researchers explored ways to separate voices from instruments in songs — which could come in handy if Apple wants to give people tools to, say, remix songs the way you can on TikTok or Instagram.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25431565/CleanShot_2024_05_03_at_09.36.28.png)
Over time, I’d bet this is the kind of stuff you’ll see Apple lean into, especially on iOS. Some of it Apple will build into its own apps; some it will offer to third-party developers as APIs. (The recent Journaling Suggestions feature is probably a good guide to how that might work.) Apple has always trumpeted its hardware capabilities, particularly compared to your average Android device; pairing all that horsepower with on-device, privacy-focused AI could be a big differentiator.
But if you want to see the biggest, most ambitious AI thing going at Apple, you need to know about Ferret . Ferret is a multi-modal large language model that can take instructions, focus on something specific you’ve circled or otherwise selected, and understand the world around it. It’s designed for the now-normal AI use case of asking a device about the world around you, but it might also be able to understand what’s on your screen. In the Ferret paper, researchers show that it could help you navigate apps, answer questions about App Store ratings, describe what you’re looking at, and more. This has really exciting implications for accessibility but could also completely change the way you use your phone — and your Vision Pro and / or smart glasses someday.
We’re getting way ahead of ourselves here, but you can imagine how this would work with some of the other stuff Apple is working on. A Siri that can understand what you want, paired with a device that can see and understand everything that’s happening on your display, is a phone that can literally use itself. Apple wouldn’t need deep integrations with everything; it could simply run the apps and tap the right buttons automatically.
Again, all this is just research, and for all of it to work well starting this spring would be a legitimately unheard-of technical achievement. (I mean, you’ve tried chatbots — you know they’re not great.) But I’d bet you anything we’re going to get some big AI announcements at WWDC. Apple CEO Tim Cook even teased as much in February, and basically promised it on this week’s earnings call. And two things are very clear: Apple is very much in the AI race, and it might amount to a total overhaul of the iPhone. Heck, you might even start willingly using Siri! And that would be quite the accomplishment.
OpenAI releases GPT-4o, a faster model that’s free for all ChatGPT users
Verizon, at&t, and t-mobile’s ‘unlimited’ plans just got a $10m slap on the wrist, the dji pocket 3 is almost everything i wanted my iphone camera to be, the new ipad pro looks like a winner, chatgpt is getting a mac app.
More from Apple
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25432052/installer.png)
The best new browser for Windows
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24205851/HT015_S_Haddad_ios_iphone_14_slideshow.jpg)
How to make the most of Apple Notes
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24401980/STK071_ACastro_apple_0003.jpg)
More details emerge about Apple’s plans for AI in iOS 18
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25431511/VST_0503_Site.jpg)
On The Vergecast: AI gadgets, iPads, and antitrust

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As you gather evidence for your argumentative research paper, follow the descriptions and the electronic model to record your notes. You can combine these with your research log, or you can use the research log for secondary sources and your own note-taking system for primary sources if a division of this kind is helpful.
Grit = passion and perseverance (8) Learning to organize notes in a useful manner will make forming your research paper easier. A useful form of organizing notes is creating index cards. In this method, you write pieces of information from a source on an index card. After recording all your sources, you can organize your notes by topic, which ...
Read the text critically, think how it is related to your argument, and decide how you are going to use it in your paper. Select the material that is relevant to your argument. Copy the original text for direct quotations or briefly summarize the content in your own words, and make note of how you will use it.
Things to keep in mind when considering using either endnotes or footnotes in your research paper:. 1. Footnotes are numbered consecutively throughout a research paper, except for those notes accompanying special material (e.g., figures, tables, charts, etc.). Numbering of footnotes are "superscript"--Arabic numbers typed slightly above the line of text.
Learn how to write a research paper with this step-by-step guide from Scribbr, a leading academic writing service. Find out how to choose a topic, conduct research, develop a thesis, outline, draft, revise, and cite your sources.
Research Paper: A step-by-step guide: 6. Taking Notes & Documenting Sources. 1. Getting Started; 2. Topic Ideas; 3. Thesis Statement & Outline ... Writing Your Research Paper; Taking Notes & Documenting Sources. How to Take Notes and Document Sources. Note taking is a very important part of the research process. It will help you: keep your ...
Note that field notes should be fleshed out as soon as possible after an observation is completed. Your initial notes may be recorded in cryptic form and, unless additional detail is added as soon as possible after the observation, important facts and opportunities for fully interpreting the data may be lost. Characteristics of Field Notes
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment. "Research Paper Planner" (UCLA) UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
Re-group your notes by re-shuffling your index cards or by color-coding or using symbols to code notes in a notebook. Review the topics of your newly-grouped notes. If the topics do not answer your research question or support your working thesis directly, you may need to do additional research or re-think your original research.
Learn how to write a research paper outline with three different formats and tips on language and structure. See an example of an outline on the measles and immunization debate.
Learn how to organize research notes using the Zettelkasten Method when writing academic papers. Find out the types of notes, stages of research paper writing, and best practices for note-taking.
On each note card: Use only one side to record a single idea, fact or quote from one source. It will be easier to rearrange them later when it comes time to organize your paper. Include a heading or key words at the top of the card. Include the Work Cited source card number. Include the page number where you found the information. Taking notes:
Taking Notes from Research Reading. If you take notes efficiently, you can read with more understanding and also save time and frustration when you come to write your paper. These are three main principles. 1. Know what kind of ideas you need to record. Focus your approach to the topic before you start detailed research.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
{the act of annotating, making notes, commenting upon} • There are a few major ways to take notes (mapping, outlining, 2-column, word-for-word), but this is a personal style choice. Try different ways, but use the one that fits you best, and engages you in the topic. • Pay attention to what each section is about. The Abstract,
Learn how to organize and record your research experiments in a notebook or electronically. Find tips on note-taking methods, media, formatting, and avoiding common mistakes.
Historically, "scratch notes" or field notes have been a central component of qualitative research since the early 1900s, originating in the field of ethnographic anthropology (Emerson, Fretz, & Shaw, 2011).Notable anthropologists, including Cushing, Boas, Malinowski, and Mead, developed a style for what are now considered field notes (Ottenberg, 1990).
When doing secondary research, historians often utilized (and many still do) pen and paper for taking notes on secondary sources. With the advent of digital photography and useful note-taking tools like OneNote, some of these older methods have been phased out - though some persist. And, most importantly, once you start using some of the ...
Research Paper Example. Note: The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. ...
The Craft of Research, Third Edition addresses notetaking in a section called "Recording What You Find" (pp. 95-100). Below is a summary of the system outlined in the book. Take full notes. Whether you take notes on cards, in a notebook, or on the computer, it's vital to record information accurately and completely.
This literature overview is designed as a resource for both students and instructors. to gain insight into what education research reveals about note-taking. Specifically, this. review discusses the cognitive mechanisms behind note-taking, how to assess the quality. of notes, and optimal practices.
Guide To Writing A Research Paper in Psychology Introduction A. General Purpose - tell why did the study, tell what the research question is, why its important, how its unique/fits in with previous research - Theoretically this section could be complete with only 4 paragraphs. They would include: the
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
Revised on June 7, 2022. Endnotes are notes that appear at the end of your text in a piece of academic writing. They're indicated in the text with numbers (or occasionally other symbols). Endnotes are used: For citations in certain styles. To add extra information that doesn't fit smoothly into the main text.
Research by Choi et al. (2020) found a significant relationship between sleep duration, sun exposure, and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status. Their study revealed. Perception Research Paper 5 that individuals with greater sun exposure tended to have better sleep quality and higher levels of vitamin D in their bloodstream.
Clustering is a fundamental technique in data mining and machine learning, aiming to group objects into distinct clusters [1,2,3,4,5,6,7].Objects within a cluster show high similarity to each other and low similarity to objects in other clusters, determined by a similarity measure [8,9,10,11].Selecting an appropriate similarity measure is crucial for clustering algorithms.
Rice University's Peter Wolynes and his research team have unveiled a breakthrough in understanding how specific genetic sequences, known as pseudogenes, evolve. Their paper was published May 13 ...
Better Siri is coming: what Apple's research says about its AI plans. Apple hasn't talked too much about AI so far — but it's been working on stuff. A lot of stuff. By David Pierce, editor ...