
What’s Included: Research Paper Template
If you’re preparing to write an academic research paper, our free research paper template is the perfect starting point. In the template, we cover every section step by step, with clear, straightforward explanations and examples .
The template’s structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research papers. The template structure reflects the overall research process, ensuring your paper will have a smooth, logical flow from chapter to chapter.
The research paper template covers the following core sections:
- The title page/cover page
- Abstract (sometimes also called the executive summary)
- Section 1: Introduction
- Section 2: Literature review
- Section 3: Methodology
- Section 4: Findings /results
- Section 5: Discussion
- Section 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language , followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover within each section. We’ve also included links to free resources to help you understand how to write each section.
The cleanly formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
FAQs: Research Paper Template
What format is the template (doc, pdf, ppt, etc.).
The research paper template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What types of research papers can this template be used for?
The template follows the standard best-practice structure for formal academic research papers, so it is suitable for the vast majority of degrees, particularly those within the sciences.
Some universities may have some additional requirements, but these are typically minor, with the core structure remaining the same. Therefore, it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalise your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Masters or PhD-level research paper?
This template can be used for a research paper at any level of study. It may be slight overkill for an undergraduate-level study, but it certainly won’t be missing anything.
How long should my research paper be?
This depends entirely on your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. We include generic word count ranges for each section within the template, but these are purely indicative.
What about the research proposal?
If you’re still working on your research proposal, we’ve got a template for that here .
We’ve also got loads of proposal-related guides and videos over on the Grad Coach blog .
How do I write a literature review?
We have a wealth of free resources on the Grad Coach Blog that unpack how to write a literature review from scratch. You can check out the literature review section of the blog here.
How do I create a research methodology?
We have a wealth of free resources on the Grad Coach Blog that unpack research methodology, both qualitative and quantitative. You can check out the methodology section of the blog here.
Can I share this research paper template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template. If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, all we ask is that you reference this page as your source.
Can Grad Coach help me with my research paper?
Within the template, you’ll find plain-language explanations of each section, which should give you a fair amount of guidance. However, you’re also welcome to consider our private coaching services .


APA Formatting and Style (7th ed.) for Student Papers
- What's New in the 7th ed.?
- Principles of Plagiarism: An Overview
- Basic Paper Formatting
- Basic Paper Elements
- Punctuation, Capitalization, Abbreviations, Apostrophes, Numbers, Plurals
- Tables and Figures
- Powerpoint Presentations
- Reference Page Format
- Periodicals (Journals, Magazines, Newspapers)
- Books and Reference Works
- Webpage on a Website
- Discussion Post
- Company Information & SWOT Analyses
- Dissertations or Theses
- ChatGPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Online Images
- Online Video
- Computer Software and Mobile Apps
- Missing Information
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Group Authors
- Missing Author
- Chat GPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Secondary Sources
- Block Quotations
- Fillable Template and Sample Paper
- Government Documents and Legal Materials
- APA Style 7th ed. Tutorials
- Additional APA 7th Resources
- Grammarly - your writing assistant
- Writing Center - Writing Skills This link opens in a new window
- Brainfuse Online Tutoring
APA 7th ed. Fillable Word Template and Sample Paper
- APA 7th ed. Template Download this Word document, fill out the title page and get writing!
- Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper.
- APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl
- << Previous: Block Quotations
- Next: Government Documents and Legal Materials >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 10:02 AM
- URL: https://national.libguides.com/apa_7th
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms, including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies, or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data, conducting interviews, or doing field research.
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research. Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research. Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

APA Style (7th ed.)
- Cite: Why? When?
- Book, eBook, Dissertation
- Article or Report
- Business Sources
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- In-Text Citation
- Format Your Paper
Format Your Paper
Download and use the editable templates for student papers below: .
- APA 7th ed. Template Document This is an APA format template document in Google Docs. Click on the link -- it will ask for you to make a new copy of the document, which you can save in your own Google Drive with your preferred privacy settings.
- APA 7th ed. Template Document A Microsoft Word document formatted correctly according to APA 7th edition.
- APA 7th ed. Annotated Bibliography template A Microsoft Word document formatted correctly for an annotated bibliography.
Or, view the directions for specific sections below:
Order of sections (section 2.17).
- Title page including Title, Author, University and Department, Class, Instructor, and Date
- Body (including introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion)
- Appendices (including tables & figures)
Margins & Page Numbers (sections 2.22-2.24)
- 1 inch at top, bottom, and both sides
- Left aligned paragraphs and leave the right edge ragged (not "right justified")
- Indent first line of each paragraph 1/2 inch from left margin
- Use page numbers, including on the title page, 1/2 inch from top and flush with right margin
Text Format (section 2.19)
- Times New Roman, 12 point
- Calibri, 11 point
- Arial, 11 point
- Lucinda Sans Unicode, 10 point
- Georgia, 11 point
- Double-space and align text to the left
- Use active voice
- Don't overuse technical jargon
- No periods after a web address or DOI in the References list.
Tables and Figures In-Text (chapter 7)
- Label tables and figures numerically (ex. Table 1)
- Give each table column a heading and use separating lines only when necessary
- Design the table and figure so that it can be understood on its own, i.e. it does not require reference to the surrounding text to understand it
- Notes go below tables and figures
Title Page (section 2.3)
- Include the title, your name, the class name , and the college's name
- Title should be 12 words or less and summarize the paper's main idea
- No periods or abbreviations
- Do not italicize or underline
- No quotation marks, all capital letters, or bold
- Center horizontally in upper half of the page
Body (section 2.11)
- Align the text to the left with a 1/2-inch left indent on the first line
- Double-space
- As long as there is no Abstract, at the top of the first page, type the title of the paper, centered, in bold , and in Sentence Case Capitalization
- Usually, include sections like these: introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion -- but the specific organization will depend on the paper type
- Spell out long organization names and add the abbreviation in parenthesis, then just use the abbreviation
- Spell out numbers one through nine and use a number for 10 or more
- Use a number for units of measurement, in tables, to represent statistical or math functions, and dates or times
Headings (section 2.26-2.27)
- Level 1: Center, bold , Title Case
- Level 2: Align left, bold , Title Case
- Level 3: Alight left, bold italics , Title Case
- Level 4: Indented 1/2", bold , Title Case, end with a period. Follow with text.
- Level 5: Indented 1/2", bold italics , Title Case, end with a period. Follow with text.

Quotations (sections 8.26-8.33)
- Include short quotations (40 words or less) in-text with quotation marks
- For quotes more than 40 words, indent the entire quote a half inch from the left margin and double-space it with no quotation marks
- When quoting two or more paragraphs from an original source, indent the first line of each paragraph a half inch from the left margin
- Use ellipsis (...) when omitting sections from a quote and use four periods (....) if omitting the end section of a quote
References (section 2.12)
Begins on a new page following the text of your paper and includes complete citations for the resources you've used in your writing.
- References should be centered and bolded at the top of a new page
- Double-space and use hanging indents (where the first line is on the left margin and the following lines are indented a half inch from the left)
- List authors' last name first followed by the first and middle initials (ex. Skinner, B. F.)
- Alphabetize the list by the first author's last name of of each citation (see sections 9.44-9.49)
- Capitalize only the first word, the first after a colon or em dash, and proper nouns
- Don't capitalize the second word of a hyphenated compound
- No quotation marks around titles of articles
Appendices with Tables, Figures, & Illustrations (section 2.14, and chapter 7)
- Include appendices only to help the reader understand, evaluate, or replicate the study or argument
- Put each appendix on a separate page and align left
- For text, do not indent the first paragraph, but do indent the rest
- If you have only one appendix, label it "Appendix"
- If you have two or more appendices, label them "Appendix A", "Appendix B" and so forth as they appear in the body of your paper
- Label tables and figures numerically (ex. Table 1, or Table B1 and Table B2 if Appendix B has two tables) and describe them within the text of the appendix
- Notes go below tables and figures (see samples on p. 210-226)
Annotated Bibliography
Double-space the entire bibliography. give each entry a hanging indent. in the following annotation, indent the entire paragraph a half inch from the left margin and give the first line of each paragraph a half inch indent. see the template document at the top of this page..
- Check with your professor for the length of the annotation and which elements you should evaluate.
These elements are optional, if your professor or field requires them, but they are not required for student papers:
Abstract (section 2.9).
- Abstract gets its own page
- Center "Abstract" heading and do not indent the first line of the text
- Summarize the main points and purpose of the paper in 150-250 words maximum
- Define abbreviations and acronyms used in the paper
Running Head (section 2.8 )
- Shorten title to 50 characters or less (counting spaces and punctuation) for the running head
- In the top margin, the running head is aligned left, with the page number aligned on the right
- On every page, put (without the brackets): [SHORTENED TITLE OF YOUR PAPER IN ALL CAPS] [page number]
More questions? Check out the authoritative source: APA style blog
- << Previous: In-Text Citation
- Last Updated: Mar 7, 2024 2:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uww.edu/apa

Formatting a Research Paper in Word: Home
- Resources for Visually Impaired
This page will help you set up a Microsoft Word document to write an MLA or APA research paper. It includes keystroke commands where possible.
Keyboard shortcuts from Microsoft
Header for MLA Style
Insert header.
(ALT + N, H spacebar)
- To create the header, click on the Insert tab on the toolbar.
Page number
(Alt+N, N, U) , T (selects top of page from menu options), Enter , Right align (Ctrl+R), Type Last name and a space
- Click page number in the Header & Footer box. Choose Top of Page in the drop down menu, and select Plain Number 3.
- While your cursor is still on the page number, type your last name and a space.
Format Font to Times New Roman, size 12
Alt+A to select all font, Ctrl+D to open font dialog box, type Times, tab twice to get to size box, type 12, then Enter to close box and header.
- Highlight all text if needed, then on the Home tab, in the Font section, select Times New Roman, size 12.
To Close Header
(Alt+J, H, C)
- Click on Close Header & Footer or double-click on the body of the document
To Edit Header
(Alt+N, H, Alt+E)
- Open header & footer box or double click in header space
Header for APA Style
Running head.
In all caps, enter your running head, which is a short version of your title.
Page Set up
Format font to times new roman, size 12, double space lines.
Alt+K, arrow down to 2.0, enter
- On Home Tab, in the Paragraph section, choose 2.0 or Double for line spacing.
Paragraph Spacing
Alt+P, S, A, type the number zero, enter
- On Home Tab, in the Paragraph section, enter 0 (zero) for space before and after paragraphs.
Set Margins to 1 inch
Alt+P opens Page Layout, Alt+M online Margins, use arrows to select Normal Template. Enter.
- Under Layout Tab, open Margins and select Normal.
To Save this Format as the Default
Your information and title of paper, left align text (this should be the default).
- Under Home tab, in the Paragraph box, click Left Align icon
Your Information:
- Your first and last name <Enter>
- Your Instructor's name <Enter>
- Class name and course number <Enter>
- Date in format day, month, year <Enter>
Title of Paper
Center Align Text using Ctrl+C
Type the title of your paper, capitalizing the first letter of the of the first word and then the first letter of every word except conjunctions, prepositions, and articles. <Enter>
Note: You will need to left align text (Ctrl+L) before beginning body of the paper.
Body of Text
Make sure you have already completed the Page Set up.
If your preceding line was center justified, left align the text with Ctrl+L or using the Left Align icon on the toolbar.
Indent first line of paragraphs
You can tab to indent the first line of the paragraphs OR
Alt+O, P to open paragraph dialogue box, Alt+S to chose Special indentation. From dropdown, select First Line. Enter.
- On Home Tab, in the Paragraph section, under Indentation, in Special, use dropdown to select First Line.
Indenting block quotations
- (Alt+P, I, L) type .5 to indent by 1/2 inch. <enter> Or, with text highlighted, click the Increase indent button in the Paragraph settings section of the Home or Layout tab.
- Type your block quotation.
- To cancel indenting the block quotation, change the indent back to 0 using (Alt+P, I, L), 0. <enter> OR click the decrease indent to return back to the left margin.
Works Cited or References List
Start a new page.
- On the Insert tab, in the Pages section, slick on the Page Break icon
Center the title of the section
Ctrl+E, type "Works Cited" for MLA or "References" for APA, <enter> (return to Left alignment with Ctrl+L)
- On the Home Tab, in the Paragraph section, click the Center Align icon
- Type Works Cited for MLA or References for APA
- Return to Left Alignment using the Left Align icon
Format page for hanging indent
Alt+H, P, G opens paragraph dialog box, Tab to Special Indent, Arrow down to Hanging indent, <enter>
- On Home Tab, in the Paragraph section, under Indentation, in Special, use dropdown to select Hanging Indent <OK>
Alphabetize your Works Cited
This feature enables you to quickly alphabetize your works cited section. However, be aware that it does not ignore citations starting with A, An, or The, as you should according to MLA and APA style. Therefore, if any of your citations start with these words, you will need to manually move them into place.
- Select the text you want to sort.
- On the Home tab, in the Paragraph section, click the Alphabetize icon.
Preformatted Word Documents
- MLA Document Formatted This Word document is formatted in MLA style. Download this document then replace the text with your own text.
- APA Document Formatted Word document in APA format, including a cover page, was adapted from a document from Evergreen Valley College. Download this paper and replace the text with your own.
- Next: Resources for Visually Impaired >>
- Last Updated: Jul 14, 2023 9:56 AM
- URL: https://research.library.gsu.edu/format
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Sample Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Media File: MLA Sample Paper
This resource is enhanced by an Acrobat PDF file. Download the free Acrobat Reader
This resource contains a sample MLA paper that adheres to the 2016 updates. To download the MLA sample paper, click this link .
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Table of Contents

Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings . The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing , and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall presentation and coherence. Adhering to the appropriate research paper format is vital for ensuring that the research is accurately and effectively communicated to the intended audience. In this era of information, it is essential to understand the different research paper formats and their guidelines to communicate research effectively, accurately, and with the required level of detail. This post aims to provide an overview of some of the common research paper formats used in academic writing.
Research Paper Formats
Research Paper Formats are as follows:
- APA (American Psychological Association) format
- MLA (Modern Language Association) format
- Chicago/Turabian style
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) format
- AMA (American Medical Association) style
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- ACS (American Chemical Society) style
- ASA (American Sociological Association) style
- APSA (American Political Science Association) style
APA (American Psychological Association) Format
Here is a general APA format for a research paper:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of your paper, your name, and your institutional affiliation. It should also include a running head, which is a shortened version of the title, and a page number in the upper right-hand corner.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary of your paper, typically 150-250 words. It should include the purpose of your research, the main findings, and any implications or conclusions that can be drawn.
- Introduction: The introduction should provide background information on your topic, state the purpose of your research, and present your research question or hypothesis. It should also include a brief literature review that discusses previous research on your topic.
- Methods: The methods section should describe the procedures you used to collect and analyze your data. It should include information on the participants, the materials and instruments used, and the statistical analyses performed.
- Results: The results section should present the findings of your research in a clear and concise manner. Use tables and figures to help illustrate your results.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret your results and relate them back to your research question or hypothesis. It should also discuss the implications of your findings and any limitations of your study.
- References : The references section should include a list of all sources cited in your paper. Follow APA formatting guidelines for your citations and references.
Some additional tips for formatting your APA research paper:
- Use 12-point Times New Roman font throughout the paper.
- Double-space all text, including the references.
- Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
- Use a hanging indent for the references (the first line should be flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines should be indented).
- Number all pages, including the title page and references page, in the upper right-hand corner.
APA Research Paper Format Template
APA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
Title Page:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Institutional affiliation
- A brief summary of the main points of the paper, including the research question, methods, findings, and conclusions. The abstract should be no more than 250 words.
Introduction:
- Background information on the topic of the research paper
- Research question or hypothesis
- Significance of the study
- Overview of the research methods and design
- Brief summary of the main findings
- Participants: description of the sample population, including the number of participants and their characteristics (age, gender, ethnicity, etc.)
- Materials: description of any materials used in the study (e.g., survey questions, experimental apparatus)
- Procedure: detailed description of the steps taken to conduct the study
- Presentation of the findings of the study, including statistical analyses if applicable
- Tables and figures may be included to illustrate the results
Discussion:
- Interpretation of the results in light of the research question and hypothesis
- Implications of the study for the field
- Limitations of the study
- Suggestions for future research
References:
- A list of all sources cited in the paper, in APA format
Formatting guidelines:
- Double-spaced
- 12-point font (Times New Roman or Arial)
- 1-inch margins on all sides
- Page numbers in the top right corner
- Headings and subheadings should be used to organize the paper
- The first line of each paragraph should be indented
- Quotations of 40 or more words should be set off in a block quote with no quotation marks
- In-text citations should include the author’s last name and year of publication (e.g., Smith, 2019)
APA Research Paper Format Example
APA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health
University of XYZ
This study examines the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Data was collected through a survey of 500 students at the University of XYZ. Results suggest that social media use is significantly related to symptoms of depression and anxiety, and that the negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users.
Social media has become an increasingly important aspect of modern life, especially among young adults. While social media can have many positive effects, such as connecting people across distances and sharing information, there is growing concern about its impact on mental health. This study aims to examine the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students.
Participants: Participants were 500 college students at the University of XYZ, recruited through online advertisements and flyers posted on campus. Participants ranged in age from 18 to 25, with a mean age of 20.5 years. The sample was 60% female, 40% male, and 5% identified as non-binary or gender non-conforming.
Data was collected through an online survey administered through Qualtrics. The survey consisted of several measures, including the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for depression symptoms, the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) for anxiety symptoms, and questions about social media use.
Procedure :
Participants were asked to complete the online survey at their convenience. The survey took approximately 20-30 minutes to complete. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression analysis.
Results indicated that social media use was significantly related to symptoms of depression (r = .32, p < .001) and anxiety (r = .29, p < .001). Regression analysis indicated that frequency of social media use was a significant predictor of both depression symptoms (β = .24, p < .001) and anxiety symptoms (β = .20, p < .001), even when controlling for age, gender, and other relevant factors.
The results of this study suggest that social media use is associated with symptoms of depression and anxiety among college students. The negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users. These findings have important implications for mental health professionals and educators, who should consider addressing the potential negative effects of social media use in their work with young adults.
References :
References should be listed in alphabetical order according to the author’s last name. For example:
- Chou, H. T. G., & Edge, N. (2012). “They are happier and having better lives than I am”: The impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15(2), 117-121.
- Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L., & Martin, G. N. (2018). Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among U.S. adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clinical Psychological Science, 6(1), 3-17.
Note: This is just a sample Example do not use this in your assignment.

MLA (Modern Language Association) Format
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format is as follows:
- Page Layout : Use 8.5 x 11-inch white paper, with 1-inch margins on all sides. The font should be 12-point Times New Roman or a similar serif font.
- Heading and Title : The first page of your research paper should include a heading and a title. The heading should include your name, your instructor’s name, the course title, and the date. The title should be centered and in title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- In-Text Citations : Use parenthetical citations to indicate the source of your information. The citation should include the author’s last name and the page number(s) of the source. For example: (Smith 23).
- Works Cited Page : At the end of your paper, include a Works Cited page that lists all the sources you used in your research. Each entry should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the medium of publication.
- Formatting Quotations : Use double quotation marks for short quotations and block quotations for longer quotations. Indent the entire quotation five spaces from the left margin.
- Formatting the Body : Use a clear and readable font and double-space your text throughout. The first line of each paragraph should be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
MLA Research Paper Template
MLA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
- Use 8.5 x 11 inch white paper.
- Use a 12-point font, such as Times New Roman.
- Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper, including the title page and works cited page.
- Set the margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Use page numbers in the upper right corner, beginning with the first page of text.
- Include a centered title for the research paper, using title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- Include your name, instructor’s name, course name, and date in the upper left corner, double-spaced.
In-Text Citations
- When quoting or paraphrasing information from sources, include an in-text citation within the text of your paper.
- Use the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses at the end of the sentence, before the punctuation mark.
- If the author’s name is mentioned in the sentence, only include the page number in parentheses.
Works Cited Page
- List all sources cited in alphabetical order by the author’s last name.
- Each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and medium of publication.
- Use italics for book and journal titles, and quotation marks for article and chapter titles.
- For online sources, include the date of access and the URL.
Here is an example of how the first page of a research paper in MLA format should look:
Headings and Subheadings
- Use headings and subheadings to organize your paper and make it easier to read.
- Use numerals to number your headings and subheadings (e.g. 1, 2, 3), and capitalize the first letter of each word.
- The main heading should be centered and in boldface type, while subheadings should be left-aligned and in italics.
- Use only one space after each period or punctuation mark.
- Use quotation marks to indicate direct quotes from a source.
- If the quote is more than four lines, format it as a block quote, indented one inch from the left margin and without quotation marks.
- Use ellipses (…) to indicate omitted words from a quote, and brackets ([…]) to indicate added words.
Works Cited Examples
- Book: Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Year.
- Journal Article: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, publication date, page numbers.
- Website: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Webpage.” Title of Website, publication date, URL. Accessed date.
Here is an example of how a works cited entry for a book should look:
Smith, John. The Art of Writing Research Papers. Penguin, 2021.
MLA Research Paper Example
MLA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
Your Professor’s Name
Course Name and Number
Date (in Day Month Year format)
Word Count (not including title page or Works Cited)
Title: The Impact of Video Games on Aggression Levels
Video games have become a popular form of entertainment among people of all ages. However, the impact of video games on aggression levels has been a subject of debate among scholars and researchers. While some argue that video games promote aggression and violent behavior, others argue that there is no clear link between video games and aggression levels. This research paper aims to explore the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults.
Background:
The debate on the impact of video games on aggression levels has been ongoing for several years. According to the American Psychological Association, exposure to violent media, including video games, can increase aggression levels in children and adolescents. However, some researchers argue that there is no clear evidence to support this claim. Several studies have been conducted to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels, but the results have been mixed.
Methodology:
This research paper used a quantitative research approach to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults. A sample of 100 young adults between the ages of 18 and 25 was selected for the study. The participants were asked to complete a questionnaire that measured their aggression levels and their video game habits.
The results of the study showed that there was a significant correlation between video game habits and aggression levels among young adults. The participants who reported playing violent video games for more than 5 hours per week had higher aggression levels than those who played less than 5 hours per week. The study also found that male participants were more likely to play violent video games and had higher aggression levels than female participants.
The findings of this study support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to note that the study only examined the impact of video games on aggression levels and did not take into account other factors that may contribute to aggressive behavior. It is also important to note that not all video games promote violence and aggression, and some games may have a positive impact on cognitive and social skills.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, this research paper provides evidence to support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to conduct further research to examine the impact of video games on other aspects of behavior and to explore the potential benefits of video games. Parents and educators should be aware of the potential impact of video games on aggression levels and should encourage young adults to engage in a variety of activities that promote cognitive and social skills.
Works Cited:
- American Psychological Association. (2017). Violent Video Games: Myths, Facts, and Unanswered Questions. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2017/08/violent-video-games
- Ferguson, C. J. (2015). Do Angry Birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 10(5), 646-666.
- Gentile, D. A., Swing, E. L., Lim, C. G., & Khoo, A. (2012). Video game playing, attention problems, and impulsiveness: Evidence of bidirectional causality. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 1(1), 62-70.
- Greitemeyer, T. (2014). Effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 106(4), 530-548.
Chicago/Turabian Style
Chicago/Turabian Formate is as follows:
- Margins : Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
- Font : Use a readable font such as Times New Roman or Arial, and use a 12-point font size.
- Page numbering : Number all pages in the upper right-hand corner, beginning with the first page of text. Use Arabic numerals.
- Title page: Include a title page with the title of the paper, your name, course title and number, instructor’s name, and the date. The title should be centered on the page and in title case (capitalize the first letter of each word).
- Headings: Use headings to organize your paper. The first level of headings should be centered and in boldface or italics. The second level of headings should be left-aligned and in boldface or italics. Use as many levels of headings as necessary to organize your paper.
- In-text citations : Use footnotes or endnotes to cite sources within the text of your paper. The first citation for each source should be a full citation, and subsequent citations can be shortened. Use superscript numbers to indicate footnotes or endnotes.
- Bibliography : Include a bibliography at the end of your paper, listing all sources cited in your paper. The bibliography should be in alphabetical order by the author’s last name, and each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and date of publication.
- Formatting of quotations: Use block quotations for quotations that are longer than four lines. Indent the entire quotation one inch from the left margin, and do not use quotation marks. Single-space the quotation, and double-space between paragraphs.
- Tables and figures: Use tables and figures to present data and illustrations. Number each table and figure sequentially, and provide a brief title for each. Place tables and figures as close as possible to the text that refers to them.
- Spelling and grammar : Use correct spelling and grammar throughout your paper. Proofread carefully for errors.
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template is as folows:
Title of Paper
Name of Student
Professor’s Name
I. Introduction
A. Background Information
B. Research Question
C. Thesis Statement
II. Literature Review
A. Overview of Existing Literature
B. Analysis of Key Literature
C. Identification of Gaps in Literature
III. Methodology
A. Research Design
B. Data Collection
C. Data Analysis
IV. Results
A. Presentation of Findings
B. Analysis of Findings
C. Discussion of Implications
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
B. Implications for Future Research
C. Conclusion
VI. References
A. Bibliography
B. In-Text Citations
VII. Appendices (if necessary)
A. Data Tables
C. Additional Supporting Materials
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Example
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Political Engagement
Name: John Smith
Class: POLS 101
Professor: Dr. Jane Doe
Date: April 8, 2023
I. Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. People use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to connect with friends and family, share their opinions, and stay informed about current events. With the rise of social media, there has been a growing interest in understanding its impact on various aspects of society, including political engagement. In this paper, I will examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, specifically focusing on how social media influences political participation and political attitudes.
II. Literature Review:
There is a growing body of literature on the impact of social media on political engagement. Some scholars argue that social media has a positive effect on political participation by providing new channels for political communication and mobilization (Delli Carpini & Keeter, 1996; Putnam, 2000). Others, however, suggest that social media can have a negative impact on political engagement by creating filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue (Pariser, 2011; Sunstein, 2001).
III. Methodology:
To examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, I conducted a survey of 500 college students. The survey included questions about social media use, political participation, and political attitudes. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Iv. Results:
The results of the survey indicate that social media use is positively associated with political participation. Specifically, respondents who reported using social media to discuss politics were more likely to have participated in a political campaign, attended a political rally, or contacted a political representative. Additionally, social media use was found to be associated with more positive attitudes towards political engagement, such as increased trust in government and belief in the effectiveness of political action.
V. Conclusion:
The findings of this study suggest that social media has a positive impact on political engagement, by providing new opportunities for political communication and mobilization. However, there is also a need for caution, as social media can also create filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue. Future research should continue to explore the complex relationship between social media and political engagement, and develop strategies to harness the potential benefits of social media while mitigating its potential negative effects.
Vii. References:
- Delli Carpini, M. X., & Keeter, S. (1996). What Americans know about politics and why it matters. Yale University Press.
- Pariser, E. (2011). The filter bubble: What the Internet is hiding from you. Penguin.
- Putnam, R. D. (2000). Bowling alone: The collapse and revival of American community. Simon & Schuster.
- Sunstein, C. R. (2001). Republic.com. Princeton University Press.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Format
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Research Paper Format is as follows:
- Title : A concise and informative title that accurately reflects the content of the paper.
- Abstract : A brief summary of the paper, typically no more than 250 words, that includes the purpose of the study, the methods used, the key findings, and the main conclusions.
- Introduction : An overview of the background, context, and motivation for the research, including a clear statement of the problem being addressed and the objectives of the study.
- Literature review: A critical analysis of the relevant research and scholarship on the topic, including a discussion of any gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Methodology : A detailed description of the methods used to collect and analyze data, including any experiments or simulations, data collection instruments or procedures, and statistical analyses.
- Results : A clear and concise presentation of the findings, including any relevant tables, graphs, or figures.
- Discussion : A detailed interpretation of the results, including a comparison of the findings with previous research, a discussion of the implications of the results, and any recommendations for future research.
- Conclusion : A summary of the key findings and main conclusions of the study.
- References : A list of all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to IEEE guidelines.
In addition to these elements, an IEEE research paper should also follow certain formatting guidelines, including using 12-point font, double-spaced text, and numbered headings and subheadings. Additionally, any tables, figures, or equations should be clearly labeled and referenced in the text.
AMA (American Medical Association) Style
AMA (American Medical Association) Style Research Paper Format:
- Title Page: This page includes the title of the paper, the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and any acknowledgments or disclaimers.
- Abstract: The abstract is a brief summary of the paper that outlines the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of the study. It is typically limited to 250 words or less.
- Introduction: The introduction provides a background of the research problem, defines the research question, and outlines the objectives and hypotheses of the study.
- Methods: The methods section describes the research design, participants, procedures, and instruments used to collect and analyze data.
- Results: The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and charts where appropriate.
- Discussion: The discussion section interprets the results, explains their significance, and relates them to previous research in the field.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the main points of the paper, discusses the implications of the findings, and suggests future research directions.
- References: The reference list includes all sources cited in the paper, listed in alphabetical order by author’s last name.
In addition to these sections, the AMA format requires that authors follow specific guidelines for citing sources in the text and formatting their references. The AMA style uses a superscript number system for in-text citations and provides specific formats for different types of sources, such as books, journal articles, and websites.
Harvard Style
Harvard Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title page: This should include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date of submission.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your paper, usually no more than 250 words. It should outline the main points of your research and highlight your findings.
- Introduction : This section should introduce your research topic, provide background information, and outline your research question or thesis statement.
- Literature review: This section should review the relevant literature on your topic, including previous research studies, academic articles, and other sources.
- Methodology : This section should describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including any data collection methods, research instruments, and sampling techniques.
- Results : This section should present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables, graphs, and other visual aids if necessary.
- Discussion : This section should interpret your findings and relate them to the broader research question or thesis statement. You should also discuss the implications of your research and suggest areas for future study.
- Conclusion : This section should summarize your main findings and provide a final statement on the significance of your research.
- References : This is a list of all the sources you cited in your paper, presented in alphabetical order by author name. Each citation should include the author’s name, the title of the source, the publication date, and other relevant information.
In addition to these sections, a Harvard Style research paper may also include a table of contents, appendices, and other supplementary materials as needed. It is important to follow the specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or academic institution when preparing your research paper in Harvard Style.
Vancouver Style
Vancouver Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The Vancouver citation style is commonly used in the biomedical sciences and is known for its use of numbered references. Here is a basic format for a research paper using the Vancouver citation style:
- Title page: Include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your research paper, usually no more than 250 words.
- Introduction : Provide some background information on your topic and state the purpose of your research.
- Methods : Describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including the study design, data collection, and statistical analysis.
- Results : Present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables and figures as needed.
- Discussion : Interpret your results and explain their significance. Also, discuss any limitations of your study and suggest directions for future research.
- References : List all of the sources you cited in your paper in numerical order. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the article or book, the name of the journal or publisher, the year of publication, and the page numbers.
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The American Chemical Society (ACS) Style is a citation style commonly used in chemistry and related fields. When formatting a research paper in ACS Style, here are some guidelines to follow:
- Paper Size and Margins : Use standard 8.5″ x 11″ paper with 1-inch margins on all sides.
- Font: Use a 12-point serif font (such as Times New Roman) for the main text. The title should be in bold and a larger font size.
- Title Page : The title page should include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the date of submission. The title should be centered on the page and written in bold font. The authors’ names should be centered below the title, followed by their affiliations and the date.
- Abstract : The abstract should be a brief summary of the paper, no more than 250 words. It should be on a separate page and include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the text of the abstract.
- Main Text : The main text should be organized into sections with headings that clearly indicate the content of each section. The introduction should provide background information and state the research question or hypothesis. The methods section should describe the procedures used in the study. The results section should present the findings of the study, and the discussion section should interpret the results and provide conclusions.
- References: Use the ACS Style guide to format the references cited in the paper. In-text citations should be numbered sequentially throughout the text and listed in numerical order at the end of the paper.
- Figures and Tables: Figures and tables should be numbered sequentially and referenced in the text. Each should have a descriptive caption that explains its content. Figures should be submitted in a high-quality electronic format.
- Supporting Information: Additional information such as data, graphs, and videos may be included as supporting information. This should be included in a separate file and referenced in the main text.
- Acknowledgments : Acknowledge any funding sources or individuals who contributed to the research.
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page of an ASA style research paper should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, and the institutional affiliation. The title should be centered and should be in title case (the first letter of each major word should be capitalized).
- Abstract: An abstract is a brief summary of the paper that should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page. The abstract should be no more than 200 words in length and should summarize the main points of the paper.
- Main Body: The main body of the paper should begin on a new page following the abstract page. The paper should be double-spaced, with 1-inch margins on all sides, and should be written in 12-point Times New Roman font. The main body of the paper should include an introduction, a literature review, a methodology section, results, and a discussion.
- References : The reference section should appear on a separate page at the end of the paper. All sources cited in the paper should be listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the date of publication.
- Appendices : Appendices are optional and should only be included if they contain information that is relevant to the study but too lengthy to be included in the main body of the paper. If you include appendices, each one should be labeled with a letter (e.g., Appendix A, Appendix B, etc.) and should be referenced in the main body of the paper.
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, the name of the course or instructor, and the date.
- Abstract : An abstract is typically not required in APSA style papers, but if one is included, it should be brief and summarize the main points of the paper.
- Introduction : The introduction should provide an overview of the research topic, the research question, and the main argument or thesis of the paper.
- Literature Review : The literature review should summarize the existing research on the topic and provide a context for the research question.
- Methods : The methods section should describe the research methods used in the paper, including data collection and analysis.
- Results : The results section should present the findings of the research.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret the results and connect them back to the research question and argument.
- Conclusion : The conclusion should summarize the main findings and implications of the research.
- References : The reference list should include all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to APSA style guidelines.
In-text citations in APSA style use parenthetical citation, which includes the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) if applicable. For example, (Smith 2010, 25).
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

- Master Your Homework
- Do My Homework
Formatting a Research Paper: The Google Docs Way
As educational institutions move towards a more collaborative and technology-based approach to learning, the need for students to become familiar with the use of digital tools for completing assignments is becoming increasingly important. Google Docs is one such tool which can be used in conjunction with other software programs such as Microsoft Word or Adobe Acrobat Pro to create professional quality research papers. This article provides an overview of how formatting a research paper using Google Docs can enhance student productivity while maintaining a high level of accuracy and precision. Topics discussed include setting up document features, organizing sources within the text, applying styles, formatting citations correctly according to accepted guidelines, and sharing documents securely online.
I. Introduction to Formatting a Research Paper in Google Docs
Ii. advantages of using the google suite for writing and formating papers, iii. accessing an existing document or creating a new one within the platform, iv. a step-by-step guide to formatting your research paper utilizing the features of google docs, v. customizing margins, fonts, and spacing for optimal reading comfort, vi. making use of different styles and headings to make your content easier to follow, vii. finishing touches: checking spelling & grammar; inserting citations; and exporting/downloading your finished work.
Formatting Your Research Paper in Google Docs Google Docs is a powerful and user-friendly platform for creating and formatting research papers. This guide will walk you through the steps of setting up your document to make sure that it follows all of the standard academic requirements, such as margins, font size, line spacing, title page information and more. It can also help you ensure consistency throughout your paper by utilizing its helpful features like numbered lists and bolded headings.
To get started with formatting a research paper using Google Docs first create an account if necessary. Next open or create a new document within “My Drive”. Be sure to start with the correct type; from there select either “blank” or choose one of their many templates available specifically tailored towards writing essays or scholarly work including MLA format research paper template google docs or APA style templates which include running headers & footers along with other specifications needed for college level assignments
Real Time Collaboration Google Suite’s cloud-based functionality makes it easier for students to work together on projects, even if they are located in different parts of the world. By syncing documents and allowing multiple users to access them at the same time, Google Drive facilitates collaboration that can help turn an average paper into something more impressive. And by providing a chat window within each document as well as version control capabilities—which track every change made to any part of a paper—students have unprecedented ways to communicate with each other about their written assignments.
Simple Formatting & Styling Tools For those without much experience formatting papers according to style guidelines (e.g., APA or MLA), fear not! The Google Suite offers features like Heading Styles and Line Spacing which make writing research papers simpler than ever before. Students can also use templates in applications like Google Docs , making it easy for them quickly create outlines and adhere to standard format requirements while saving valuable time on tedious tasks such as setting page margins.
- No longer do you need expert knowledge of Microsoft Word.
. Additionally, basic styling tools enable novice writers perfect their professional presentation skills by adding stylistic elements such as italics or bolds with ease . All these features come together seamlessly so that students get the most out of their writing process regardless of how familiar they are with advanced word processing software
Users of the platform can easily create a new document or access an existing one. With the help of Google Docs , users have multiple options for creating and editing their documents:
- Create from scratch, using Google’s powerful online word processor.
- Start with an existing template to get you going in the right direction.
Once they’ve chosen which type of document to work on, users are then able to customize it however they want by adding text, images, videos and other forms of media. For more advanced projects like research papers or presentations, there are plenty of tools available for formatting them according to academic standards – including predefined templates specifically designed for different types of formats such as APA or MLA. Furthermore, features like revision history and sharing capabilities make it easy to collaborate with others on projects while ensuring that everyone is working off the same version.
Creating a Research Paper Format with Google Docs Creating the perfect research paper format can be daunting. But with Google Docs, it’s as easy as 1-2-3! Here is a step-by-step guide to formatting your document using all of its features:
1) Begin by opening up an empty Document in Google Docs. 2) To ensure that you are utilizing proper research paper format, use the built in Heading styles – Heading 1 for your title; and Heading 2 and 3 for subsequent sections throughout your work. This will keep all the titles consistent throughout. 3) With text highlighted, choose whether or not you’d like it to be bolded or italicized – both options are available within Google Docs. Additionally, there are many other font sizes and colors available if desired. 4) Utilize unnumbered lists when outlining items such as points or steps within each section. 5) Insert images into documents directly from either Bing Image search results or saved pictures already uploaded onto Drive (Google’s cloud storage). You also have complete control over placement on page and size adjustments of images.. 6 ) Incorporate tables to show numerical data related to your topic. 7 ) Add hyperlinks so readers can quickly access information related to topics presented in your writing. Once completed, double check links before submitting finished product – this ensures accuracy . 8 ) After these basic formatting tasks are completed , utilize ‘research tools’ feature located at top right corner : just highlight any word in article , click ‘Research Tools’ icon & relevant sources appear immediately below selection ! It ‘ s never been easier reference materials while composing one’ s own thoughts ..
By following these simple instructions found above , users should find no difficulty completing their very own professional looking research papers while utilizing only the powerful capabilities provided through google docs !
For a reader to have optimal reading comfort, customizing the document’s margins, fonts and spacing is essential. When looking at a research paper format on Google Docs for instance, we see that some of these settings are pre-configured.
- Margins: 1 inch all around
- Font: Times New Roman size 12
Spacing: Double spaced throughout; no extra spaces between paragraphs or sections. .
As you write a paper, it is important to think about how your readers will process the information. By using different styles and headings, you can help make your content easier for them to follow.
One of the most effective techniques for structuring content in research papers is through the use of Google Docs’ Research Paper Format. This format provides an outline structure which enables easy navigation between sections as well as adding visual cues that draw attention to key points or areas of interest. For example, each section heading should be bold and have its own number; subheadings within those sections can then be denoted with bullets or other symbols:
- Subheading 1
- Subheading 2
. Additionally, when introducing new topics in a paragraph, begin with an interesting sentence that captures readers’ attention so they are more likely to stay engaged throughout your writing. To further break up text-heavy material into easily digestible chunks while keeping main ideas clearly visible on the page, consider utilizing lists – both numbered and unnumbered -to present sequential steps in processes such as experiments or summarizing arguments/discussions that otherwise could become difficult for readers to understand due their lengthiness . When done correctly these features add depth and clarity allowing any reader unfamiliar with topic at hand engage quickly without becoming overwhelmed by volumes of dense textual content. Ultimately ensuring all elements work together harmoniously yields concise yet comprehensive documents; this serves not only benefit current audiences but also may create lasting impressions among future viewers who come across materials long after original authors may have forgotten how certain things were originally structured!
It’s finally time to take your hard work and turn it into something tangible. Now that you’ve finished your research paper, all that remains is to check for any errors in spelling and grammar, add the correct citations, then download/export the file as a PDF or other accepted format.
As far as checking for mistakes goes, Google Docs , Microsoft Word (or other similar applications) have spell-checkers available which can help identify misspelled words or incorrect punctuation. Once these are corrected be sure double-check with an online grammar tool such as Grammarly so no mistakes slip through the cracks. After this final step has been completed inserting citations should be easy; there are numerous citation generators available depending on what type of research paper you’re writing such as MLA 8th Edition Format Generator or APA 7th Edition Format Generator – even Google Scholar provides access to properly formatted references based on peer review articles from its database! Finally save/download your document using either a .docx (Microsoft Word), .odt (OpenOffice Writer) or .pdf(Adobe Acrobat Reader).
At the end of this article, it is hoped that readers now have a better understanding of how to format a research paper using Google Docs. With its user-friendly platform and extensive range of features, Google Docs provides an excellent platform for researching and crafting academic papers in an organized manner. As academics continue to embrace technology into their writing process, tools like Google Docs are becoming increasingly important for students hoping to take advantage of digital resources while maintaining scholarly standards. By having a comprehensive knowledge on how to use the functionality within these programs they can save time and improve productivity during all stages of the research paper drafting process.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- IEEE Paper Format | Template & Guidelines
IEEE Paper Format | Template & Guidelines
Published on August 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on April 6, 2023.
IEEE provides guidelines for formatting your paper. These guidelines must be followed when you’re submitting a manuscript for publication in an IEEE journal. Some of the key guidelines are:
- Formatting the text as two columns, in Times New Roman, 10 pt.
- Including a byline, an abstract , and a set of keywords at the start of the research paper
- Placing any figures, tables, and equations at the top or bottom of a column, not in the middle
- Following the appropriate heading styles for any headings you use
- Including a full list of IEEE references at the end
- Not including page numbers
To learn more about the specifics of IEEE paper format, check out the free template below. Note that you may not need to follow these rules if you’ve only been told to use IEEE citation format for a student paper. But you do need to follow them to submit to IEEE publications.
Table of contents
Ieee format template, ieee heading styles, frequently asked questions about ieee.
The template below can be used to make sure that your paper follows IEEE format. It’s set up with custom Word styles for all the different parts of the text, with the right fonts and formatting and with further explanation of key points.
Make sure to remove all the explanatory text in the template when you insert your own.
Download IEEE paper format template
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
IEEE recommends specific heading styles to distinguish the title and different levels of heading in your paper from each other. Styles for each of these are built into the template.
The paper title is written in 24 pt. Times New Roman, centered at the top of the first page. Other headings are all written in 10 pt. Times New Roman:
- Level 1 text headings begin with a roman numeral followed by a period. They are written in small caps, in title case, and centered.
- Level 2 text headings begin with a capital letter followed by a period. They are italicized, left-aligned, and written in title case.
- Level 3 text headings begin with a number followed by a closing parenthesis . They are italicized, written in sentence case, and indented like a regular paragraph. The text of the section follows the heading immediately, after a colon .
- Level 4 text headings begin with a lowercase letter followed by a closing parenthesis. They are italicized, written in sentence case, and indented slightly further than a normal paragraph. The text of the section follows the heading immediately, after a colon.
- Component headings are used for the different components of your paper outside of the main text, such as the acknowledgments and references. They are written in small caps, in title case, centered, and without any numbering.
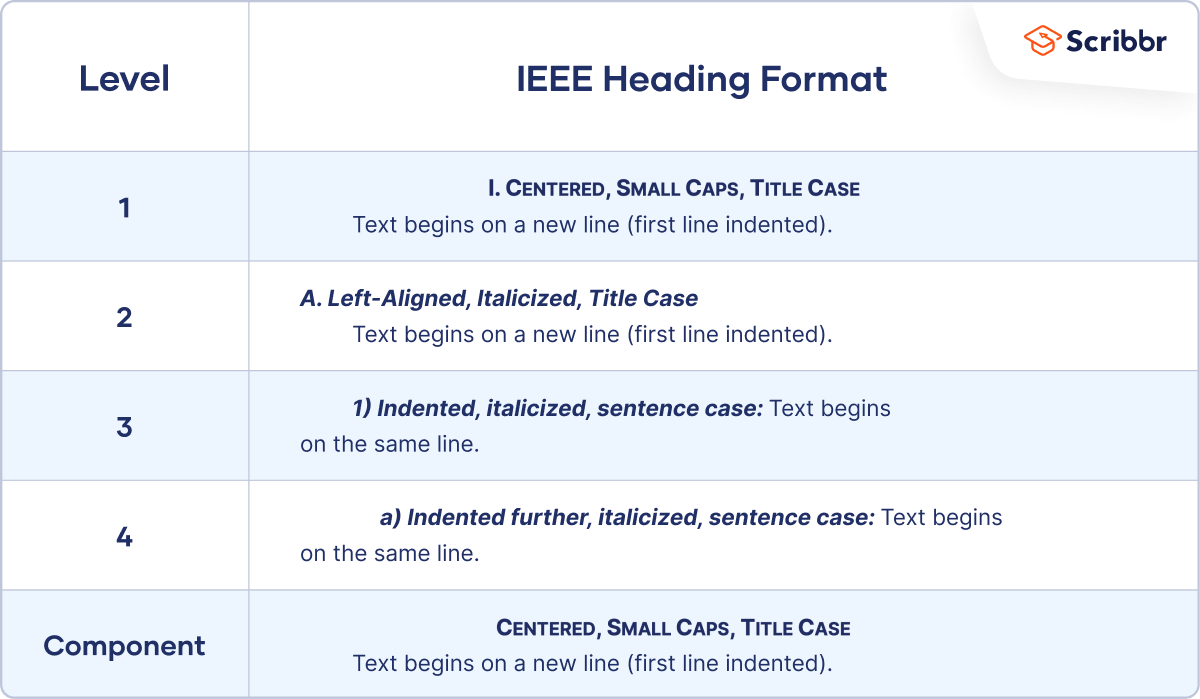
You should use 10 pt. Times New Roman font in your IEEE format paper .
For the paper title, 26 pt. Times New Roman is used. For some other paper elements like table footnotes, the font can be slightly smaller. All the correct stylings are available in our free IEEE format template .
No, page numbers are not included in an IEEE format paper . If you’re submitting to an IEEE publication, page numbers will be added in the final publication but aren’t needed in the manuscript.
IEEE paper format requires you to include an abstract summarizing the content of your paper. It appears at the start of the paper, right after you list your name and affiliation.
The abstract begins with the word “Abstract,” italicized and followed by an em dash. The abstract itself follows immediately on the same line. The entire section is written in bold font. For example: “ Abstract —This paper discusses … ”
You can find the correct format for your IEEE abstract and other parts of the paper in our free IEEE paper format template .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, April 06). IEEE Paper Format | Template & Guidelines. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/ieee/ieee-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, ieee reference page | format & examples, ieee in-text citation | guidelines & examples, ieee journal citation | guide with examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Don't Miss a Post! Subscribe
- Guest Posts

- Educational AI
- Edtech Tools
- Edtech Apps
- Teacher Resources
- Special Education
- Edtech for Kids
- Buying Guides for Teachers

Educators Technology
Innovative EdTech for teachers, educators, parents, and students
10 Great AI Tools for Researchers
By Med Kharbach, PhD | Last Update: April 8, 2024

Today, I want to talk about some really cool AI tools that are changing the way we do research. This is just a small preview of what I’m putting together in an eBook full of AI tools for researchers like us. If you don’t want to miss out on the full thing, be sure to sign up for our email updates.
There’s a lot of talk about AI in universities, and not everyone agrees about using it. But, like it or not, AI is becoming a big part of research, and it’s here to stay. I believe we should use AI the right way. It’s not about just copying and pasting stuff; that’s not real research. You still have to do the hard work of reading and writing yourself. But, AI can be a huge help, kind of like having an extra assistant who’s always there when you need it. I’m all for using AI to make our research better, as long as we keep doing the important parts ourselves.
AI Tools for Researchers
Here are are some good AI Tools I recommend for student researchers and academics:
Litmaps is a tool for research students that makes finding papers and authors on a topic easy and quick. Instead of spending lots of time reading through hundreds of papers, you can use Litmaps to find the important ones in seconds. It helps you find papers you might miss otherwise and keeps you updated on new research without getting overwhelmed. You can see which papers are connected and important for your work through visual maps, making it simple to keep track of your literature review.
Jenni is an AI-powered writing tool that helps you write, edit, and reference your work easily. It’s like having a helpful friend who’s always there to get you past writer’s block, suggest ways to say things differently, and make sure your citations are in order. More specifically, Jenni can:
- Suggest words and sentences as you write to help you keep going.
- Help you cite sources correctly in styles like APA, MLA, and others, using your own PDFs or research.
- Let you change the wording of any text to match the tone you need.
- Turn your research papers into written content by analyzing and summarizing them.
- Chat with your PDFs to quickly understand and summarize them.
- Import a bunch of sources at once if you have them saved.
- Export your work to LaTeX, Word, or HTML without messing up your formatting.
- Create an outline for your paper just from a prompt you provide.
- Work in multiple languages, including English (US and British), Spanish, German, French, and Chinese.
- Keep all your research organized in one place for easy citing in any document.
- Offer suggestions and help expand notes into full paragraphs, so you’re never stuck staring at a blank page.
3. Paperpa l
Paperpal is a handy tool for anyone who writes academic texts like essays, theses, dissertations, or research papers. It checks your writing for grammar mistakes and makes sure you’re using the right language for academic work. With the help of generative AI, Paperpal can also create outlines, abstracts, and titles for your papers. This tool makes it easy to paraphrase your work for clarity .You can also check your work for plagiarism with detailed reports, get help generating various parts of your academic text, and even translate text from over 25 languages to English.
Related: 6 Best Text to Video AI Tools
4. Unriddle
Unriddle is a cool tool that changes how students and researchers work with documents. It gives you an AI helper for any document you’re looking at, making it super quick to find info, sum up tricky topics, and take notes easily. Unriddle is all about making your research easier and faster, so you don’t have to read every single word to find what you need.
Unriddle also helps you write and reference sources the right way. It can point out the most important sources when you highlight text, so your references are spot-on. It works in over 90 languages and has some cool extra features like a Chrome extension to summarize online articles, settings you can change to fit your needs, and the ability to work with many documents at once.

5. Connected Papers
Connected Papers helps you discover recent important works without needing to maintain extensive lists. It is a visual tool for research students and academics who are diving into a new field or ensuring their research is comprehensive. It starts with a paper you’re interested in and creates a graph showing similar papers in that field. This visual approach helps you understand the trends and main contributors quickly. It’s especially useful in fast-moving fields where new studies are constantly published.
With Connected Papers, you can also build a bibliography for your thesis more efficiently. By starting with a few key references, it finds additional relevant papers, helping you to fill in the gaps. It offers views for finding significant prior works or the latest reviews and state-of-the-art papers following your chosen study.
6. Scite Assistant
Scite Assistant is like a research companion powered by large language models (LLMs), designed to make your research process smoother and more insightful. You can ask scite Assistant any research-related question and you will get insights and explanations for its responses, helping you understand the reasoning behind its conclusions.
scite Assistant offers customizable settings to tailor the tool to your specific research needs. You can control whether you want references included, filter your searches by year, topics, or journals, and even specify the sources the Assistant should use, like your own dashboard collection or preferred journals. This level of customization ensures that the responses and sources are relevant to your specific research questions and preferences, making it an invaluable tool for academics and researchers seeking detailed and reliable information.
7. DocAnalyzer
DocAnalyzer.ai makes talking to your documents easy and smart. You can upload one or many documents and start chatting right away, getting answers to your questions in real time. This tool is great because it understands the context of your documents, making it super helpful for finding exactly what you need without any confusion. What makes docAnalyzer.ai special is how simple and smart it is to use. You can ask your PDFs questions and get back clear, detailed answers quickly. You can even share your document chats with others, making teamwork easier.
8. SciSummary
SciSummary is all about making it easier to get the gist of scientific articles fast. You can email or upload a document, and in minutes, you’ll get a summary sent right back to you. This is perfect for scientists, students, and anyone who’s busy but needs to stay on top of the latest research without reading long articles.
SciSummary uses advanced AI, like a super smart robot that can summarize any scientific article. The AI gets better over time, learning from summaries that experts check. This means you can quickly understand new discoveries and research without spending hours reading. SciSummary offers a free option for summarizing articles, and if you need more, there are affordable plans with more features.
9. Explainpaper
Explainpaper is like having a smart friend that helps you understand research papers quickly. You just upload a paper, highlight the parts you find confusing, and get an explanation. This tool is perfect for diving into complex topics and for speeding up your review process. With Explainpaper, you’re not alone when facing intimidating jargon or complex concepts.
10. SciSpace
SciSpace aims to make finding and understanding research papers a breeze. It’s an all-in-one platform where you can read papers, get straightforward explanations from AI, and explore related research. SciSpace is designed to cut down on the time researchers spend looking for information and dealing with the hassle of formatting papers. With access to metadata for over 200 million papers and more than 50 million full-text PDFs, SciSpace provides tools like a citation generator, AI detector, and paraphraser to make your research process smoother and more productive. It’s a dedicated workspace for researchers, publishers, and institutions to collaborate and discover information effortlessly.
Final thoughts
As I mentioned, these tools are just a part of the bigger picture I’m assembling in the upcoming eBook. The AI tools we explored today are stepping stones towards a more efficient, insightful, and innovative research process. But remember, they’re tools to aid us, not to replace the foundational skills of rigorous research. Embracing AI in our work, when used ethically and wisely, opens up new horizons for discovery and understanding. Stay tuned for the full eBook release, and let’s navigate this promising future of research together.

Join our mailing list
Never miss an EdTech beat! Subscribe now for exclusive insights and resources .

Meet Med Kharbach, PhD
Dr. Med Kharbach is an influential voice in the global educational technology landscape, with an extensive background in educational studies and a decade-long experience as a K-12 teacher. Holding a Ph.D. from Mount Saint Vincent University in Halifax, Canada, he brings a unique perspective to the educational world by integrating his profound academic knowledge with his hands-on teaching experience. Dr. Kharbach's academic pursuits encompass curriculum studies, discourse analysis, language learning/teaching, language and identity, emerging literacies, educational technology, and research methodologies. His work has been presented at numerous national and international conferences and published in various esteemed academic journals.

Join our email list for exclusive EdTech content.
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Business and industry
- Science and innovation
- Artificial intelligence
AI Foundation Models: Update paper
Update paper as part of the CMA's AI Foundation Models: initial review, following initial report in September 2023.

Update paper
PDF , 3.15 MB , 24 pages
The CMA launched its AI Foundation Models: initial review in May 2023. We published our initial report in September 2023, in which we proposed principles to guide the development and deployment of FMs to positive outcomes for competition and consumer protection. More information about the review is available on the AI foundation models case page .
Following extensive engagement and our ongoing monitoring of market developments, this paper:
provides an overview and discussion of key changes in the FM sector since the publication of our initial report
confirms final principles for guiding the market to positive outcomes for competition and consumer protection
sets out risks to competition and consumer protection, including three key risks to fair, open and effective competition that we see arising from current and potential developments in the FM sector, assessing how they would be mitigated by the CMA’s principles and identifying the actions we are taking now, and are considering taking in the near future to seek to address these risks
outlines the next steps for the CMA’s AI FM programme of work
Press notice: CMA outlines growing concerns in markets for AI Foundation Models
Sarah Cardell, CEO of the CMA: Opening remarks at the American Bar Association (ABA) Chair’s Showcase on AI Foundation Models
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 11.4.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
This is a member publication of Imperial College London (Jisc)
Regulatory Standards and Guidance for the Use of Health Apps for Self-Management in Sub-Saharan Africa: Scoping Review
Authors of this article:

- Benard Ayaka Bene 1, 2 , MBBS, MPH ;
- Sunny Ibeneme 3 , MD, PhD ;
- Kayode Philip Fadahunsi 1 , MBBS, MPH ;
- Bala Isa Harri 4 , MBBS, MPH, MSc ;
- Nkiruka Ukor 5 , MSc ;
- Nikolaos Mastellos 1 , BSc, PhD ;
- Azeem Majeed 1 , MD ;
- Josip Car 1, 6 , MSc, MD, PhD
1 Department of Primary Care and Public Health, School of Public Health, Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom
2 Department of Public Health, Federal Ministry of Health, Abuja, Nigeria
3 Digital Health Specialist, UNICEF East Asia Pacific Regional Office, Bangkok, Thailand
4 Department of Health Planning, Research and Statistics, Federal Ministry of Health, Abuja, Nigeria
5 Strategic Health Information Cluster, World Health Organization, Abuja, Nigeria
6 School of Life Course & Population Sciences, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom
Corresponding Author:
Benard Ayaka Bene, MBBS, MPH
Department of Primary Care and Public Health
School of Public Health
Imperial College London
The Reynolds Building
St Dunstan’s Road
London, W6 8RP
United Kingdom
Phone: 44 7598439185
Email: [email protected]
Background: Health apps are increasingly recognized as crucial tools for enhancing health care delivery. Many countries, particularly those in sub-Saharan Africa, can substantially benefit from using health apps to support self-management and thus help to achieve universal health coverage and the third sustainable development goal. However, most health apps published in app stores are of unknown or poor quality, which poses a risk to patient safety. Regulatory standards and guidance can help address this risk and promote patient safety.
Objective: This review aims to assess the regulatory standards and guidance for health apps supporting evidence-based best practices in sub-Saharan Africa with a focus on self-management.
Methods: A methodological framework for scoping reviews was applied. A search strategy was built and applied across the following databases, gray literature sources, and institutional websites: PubMed, Scopus, World Health Organization (WHO) African Index Medicus, OpenGrey, WHO Regional Office for Africa Library, ICTworks, WHO Directory of eHealth policies, HIS Strengthening Resource Center, International Telecommunication Union, Ministry of Health websites, and Google. The search covered the period between January 2005 and January 2024. The findings were analyzed using a deductive descriptive content analysis. The policy analysis framework was adapted and used to organize the findings. The Reporting Items for Stakeholder Analysis tool guided the identification and mapping of key stakeholders based on their roles in regulating health apps for self-management.
Results: The study included 49 documents from 31 sub-Saharan African countries. While all the documents were relevant for stakeholder identification and mapping, only 3 regulatory standards and guidance contained relevant information on regulation of health apps. These standards and guidance primarily aimed to build mutual trust; promote integration, inclusion, and equitable access to services; and address implementation issues and poor coordination. They provided guidance on systems quality, software acquisition and maintenance, security measures, data exchange, interoperability and integration, involvement of relevant stakeholders, and equitable access to services. To enhance implementation, the standards highlight that legal authority, coordination of activities, building capacity, and monitoring and evaluation are required. A number of stakeholders, including governments, regulatory bodies, funders, intergovernmental and nongovernmental organizations, academia, and the health care community, were identified to play key roles in regulating health apps.
Conclusions: Health apps have huge potential to support self-management in sub-Saharan Africa, but the lack of regulatory standards and guidance constitutes a major barrier. Hence, for these apps to be safely and effectively integrated into health care, more attention should be given to regulation. Learning from countries with effective regulations can help sub-Saharan Africa build a more robust and responsive regulatory system, ensuring the safe and beneficial use of health apps across the region.
International Registered Report Identifier (IRRID): RR2-10.1136/bmjopen-2018-025714
Introduction
Health apps are the most widely used digital health products globally [ 1 , 2 ]. Harnessing the potential of health apps creates a huge opportunity in providing support for health care delivery, including patient communication, patient education, and decision support for self-management [ 3 - 8 ]. Health apps can be an effective tool to strengthen health systems worldwide, especially in low- and middle-income countries including those in sub-Saharan Africa [ 4 , 5 , 9 ]. As a result, the attainment of universal health coverage (UHC) and sustainable development goal (SDG) 3, good health and well-being, can be accelerated [ 8 , 10 ].
Many health apps fall below the expected quality threshold [ 11 ]. Several studies have found that widely used health apps are often technically unreliable and clinically unsafe [ 12 - 14 ] and do not comply with ethical standards and the principles of confidentiality of information and data privacy [ 15 , 16 ]. In addition, many commercially available health apps were not developed using interoperability standards that are widely accepted in sub-Saharan Africa (eg, Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources [FHIR]) [ 17 - 20 ]. Consequently, it becomes difficult to integrate these apps into a clinical workflow.
Hence, regulation through robust mechanisms is crucial to enhance the development, implementation, and adoption of health apps. Regulatory standards and guidance are essential for the safety of patients as they ensure quality assurance of any new technology in health care and contribute to building mutual trust while promoting the optimal use of the technology [ 21 - 23 ]. Therefore, to ensure that health apps that are used to support the self-management of patients are technically reliable and clinically safe, interoperable across systems, and compliant with the principles of confidentiality of information and data privacy, there is a need for effective regulatory standards. Furthermore, effective regulation can help ensure that health apps for self-management are culturally functional and competent and are accessible to those who need them regardless of gender, ethnicity, geographical location, or financial status [ 24 - 31 ].
Since 2005, there have been ongoing efforts to strengthen digital health governance at both the national and international levels [ 32 , 33 ]. In 2018, the World Health Organization (WHO) member states renewed their commitment to using digital health technologies (DHTs) to advance UHC and SDG 3 [ 33 ]. However, to date, the extent to which the use of health apps for self-management is regulated across countries within the WHO African Region (also known as sub-Saharan Africa) remains unclear. Therefore, this review was conducted to identify available regulatory standards and guidance and assess the extent to which they regulate health apps for self-management in sub-Saharan Africa. The review also mapped out the key stakeholders and their roles in regulating health apps for self-management across sub-Saharan Africa.
Review Questions
The review attempted to answer the following questions: (1) What regulatory standards and guidance are available for regulating health apps for self-management across sub-Saharan Africa? (2) To what extent do regulatory standards and guidance regulate health apps for self-management in terms of what aspects are regulated; why, how, and for whom; and what aspects are not regulated? (3) Who are the key stakeholders and what are their roles in regulating health apps for self-management?
Study Design
The process of this scoping review followed the methodological framework for conducting a scoping study originally described by Arksey and O’Malley [ 34 ] and the updated methodological guidance for conducting a Joanna Briggs Institute scoping review [ 34 - 37 ]. The reporting of the review was guided by the PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) checklist [ 38 ]. A completed PRISMA-ScR checklist is provided in Multimedia Appendix 1 . The protocol of this scoping review was published in BMJ Open [ 30 ].
Identifying Relevant Documents
Two reviewers (BAB and SI) developed the search strategy with the assistance of a librarian and in consultation with other research team members (KPF, BIH, NU, NM, AM, and JC). The following key terms were included: policy, legislation, strategy, regulation, standard, criterion, framework, guidance, guideline, digital health, eHealth, app, WHO African Region, and sub-Saharan Africa, and the names of all sub-Saharan African countries.
Owing to the absence of regulatory standards and guidance in scientific databases, the search focus was narrowed down to gray literature sources and institutional websites, including OpenGrey, WHO Regional Office for Africa (AFRO) Library, repositories for digital health policies (ICTworks, WHO’s Directory of eHealth Policies, and Health Information System Strengthening Resource Center), as well as the websites of WHO, International Telecommunication Union (ITU), and Ministries of Health (MOHs). The only scientific databases searched were PubMed, Scopus, and WHO AIM. PubMed was not included in the protocol. We also conducted a systematic search on Google. We used truncation to increase the yield of the results. The search strategy was then applied across PubMed, Scopus, and WHO AIM databases using Boolean terms (mainly OR and AND ) to combine search results. Gray literature sources and institutional websites were searched using phrases containing ≥2 keywords such as “eHealth regulation,” “digital health regulatory standard,” “eHealth regulatory standard,” “digital health regulation,” “digital health policy,” “eHealth policy,” “digital health strategy,” and “eHealth strategy.” For Google search, we added the names of the country to the phrases (eg, “digital health regulation Nigeria”). The reference lists of the included documents were also searched, and key individuals at the MOHs, WHO Country Offices, and the WHO AFRO were contacted for related documents. When our search was conducted, the WHO Directory of eHealth policies website was unavailable, and the WHO AFRO Library was undergoing reconstruction. The search strategies for PubMed, Scopus, and WHO AIM are provided in Multimedia Appendix 2 . The search was conducted between 2005 and January 2024.
Study Selection
The search results obtained from PubMed, Scopus, and WHO AIM were imported into Mendeley (Elsevier) [ 39 ] to remove duplicates. The search conducted on OpenGrey did not yield any results, whereas relevant records obtained from institutional websites, repositories, and Google were downloaded as PDF copies and uploaded to Mendeley. After removing duplicates, the remaining results were imported into Covidence (Veritas Health Innovation) [ 40 ] for screening. Two reviewers (BAB and SI) applied the predefined eligibility criteria ( Textbox 1 ) to screen the documents in 2 stages (title and abstract or executive summary). All discrepancies were discussed until the reviewers reached agreement.
Inclusion criteria
- Type of document: Regulatory standards, guidance, policies, strategies, and committee or government reports that address regulatory issues related to the use of health apps for self-management
- Location: Documents developed and implemented in countries within sub-Saharan Africa
- Date of publication: Documents developed since 2005; the global efforts toward promoting standards to minimize variability and potential harms that could arise from poorly regulated use of digital health began in 2005 [ 33 ]
- Language: Documents written in English language and other official languages of sub-Saharan African countries (Portuguese and French)
Exclusion criteria
- Type of document: Standards, guidance, policies, strategies, and reports not related to regulation of health apps
- Location: Documents from countries outside sub-Saharan Africa
- Date of publication: Documents developed before 2005
- Language: None
Data Charting (Extraction)
Two reviewers (BAB and SI), in consultation with the other members of the research team, developed the data extraction forms using an iterative process that included piloting data extraction and refinement until a consensus was reached.
We proposed in the study protocol [ 30 ] that data extraction would be conducted by the 2 reviewers independently. However, owing to the approach adopted for data extraction (deductive qualitative content analysis), 1 reviewer, rather than 2, initially extracted data from the included documents, and any concerns were discussed with a second reviewer [ 41 ]. Unresolved issues were then discussed and resolved with a third reviewer in a steering group meeting.
Collating, Summarizing, and Reporting Results
To address the research questions (particularly question 2), we adopted a deductive descriptive qualitative content analysis method to analyze and report the key findings. The policy analysis framework by Walt and Gilson [ 42 ] was adapted and applied to ensure that there was a consistent way of organizing the key findings: (1) Content (which aspects are regulated and which aspects are not?)—these are the components that directly or indirectly address regulatory issues related to the use of health apps for self-management, including areas that have not been addressed. (2) Context (why are those aspects regulated?)—this characterizes the rationale indicated for addressing regulatory issues related to the use of health apps for self-management. (3) Process (how are the regulatory standards developed and implemented?)—this describes the methods or approaches used to develop and implement regulatory standards. (4) Actors (who are the regulatory standards targeted toward?)—these are the key actors targeted by the standards.
Using a deductive descriptive qualitative content analysis approach, we examined each included document to systematically identify texts for concepts, patterns, and other relevant information. We then categorized them under content, context, process, or actors in relation to regulating health apps for self-management. The findings under content and context were further organized based on 4 predefined regulatory categories or themes as documented in the literature, namely (1) technical and clinical safety [ 12 - 14 ], (2) data protection and security [ 15 , 16 ], (3) standards and interoperability [ 28 , 31 ], and (4) inclusion and equitable access [ 24 - 29 ].
To address the third research question, the Reporting Items for Stakeholder Analysis (RISA) tool [ 41 ] was used as a guide to group key stakeholders based on role categorization as recognized globally by the WHO, the ITU, and UNESCO [ 32 , 33 , 43 ].
Ethical Considerations
Primary data were not collected in this study. Therefore, no ethics approval was required.
Search Results
A total of 2900 records were obtained after removing duplicates. Although the literature search was conducted in English, the search also yielded documents written in French and Portuguese from the ICTworks repository [ 44 ]. Following the initial screening of the title and abstract (or executive summaries), 73 documents were retrieved for full-text assessment. After applying the inclusion criteria for the full-text assessment, 49 documents were found eligible for inclusion in the review.
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram [ 45 ] showing the study selection process is presented in Figure 1 .

Types of Documents
On the basis of the inclusion criteria, 3 categories of documents were considered for this review, namely “stand-alone regulatory standards and guidance that potentially regulate health apps for self-management,” “national policies and strategies on digital health,” and “other national documents that relate to the regulation of health apps for self-management.” Table 1 presents the types of documents obtained for each country within sub-Saharan Africa.
Characteristics of the Included Documents
Stand-alone regulatory standards and guidance.
We identified and included 6 stand-alone regulatory standards [ 18 , 19 , 46 - 49 ] from 3 countries (Ethiopia, Kenya, and Nigeria). All 6 documents were written in English. The years of development ranged between 2013 and 2021, as indicated in Multimedia Appendix 3 . The years of implementation were not specifically stated.
Although none of the included regulatory standards were exclusively developed to regulate health apps for self-management, 3 of them (Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ], Kenya Standards and Guidelines for E-Health Systems Interoperability [ 47 ], and Health Sector Information and Communications Technology Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ]) provided concept and information relevant to the regulation of health apps and were included in the qualitative content analysis. The Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] provides standards and guidelines on the design, development, and implementation of mobile health (mHealth) solutions to ensure they are interoperable, scalable, and sustainable. The Kenya Standards and Guidelines for E-Health Systems Interoperability [ 47 ] outlines the principles, requirements, and standards for eHealth systems interoperability in Kenya. The Health Sector Information and Communications Technology Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] provide guidance and a consistent approach across the health sector in Kenya for establishing, acquiring, and maintaining current and future information systems and information and communications technology (ICT) infrastructure that foster interoperability across systems. These 3 documents are a good combination of regulatory standards and guidance that provide content and context relevant to the regulation of health apps in sub-Saharan Africa.
The remaining 3 standards (standard for electronic health record [EHR] system in Ethiopia [ 19 ], standards and guidelines for electronic medical record systems in Kenya [ 46 ], and the health information exchange standard operating procedure and guideline [ 49 ]) were exclusively developed for EHRs or electronic medical records. However, they contain information relevant for mapping stakeholders with potential roles in regulating health apps for supporting self-management.
National Policies and Strategies on Digital Health
This review includes 35 national policies and strategies that are related to digital health (potentially covering health apps) [ 50 - 84 ] from 31 countries written in English, French, and Portuguese (Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Comoros, Côte d’Ivoire [Ivory Coast], Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Kenya, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Africa, Tanzania, Togo, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe). Although the literature search was conducted in English, it also yielded documents written in French and Portuguese from the ICTworks repository. The years of development and implementation range between 2005 and 2030. Policies and strategies written in French and Portuguese were translated into English using Google Translate. Documents labeled as national development plans, strategic plans, and strategic development plans were considered as national strategies.
National policies and strategies do not offer specific standards or guidance, but rather outline the country’s vision, policy directions, and strategies for using digital technologies in health care. They provide useful information for identifying digital health stakeholders who can play a role in regulating health apps for self-management. For example, Nigeria has a separate National Digital Health Policy [ 72 ] and a National Digital Health Strategy [ 71 ]. Both documents were developed by building on the lessons learned from the end-term evaluation of the previous National Health ICT Strategic Framework [ 85 ]. They describe Nigeria’s renewed vision, mission, goals, objectives, and strategies for the development and implementation of digital health with the aim to improve the quality, efficiency, and effectiveness of health service delivery and health outcomes.
It is worth noting that for countries with >1 policy or strategy, we included only the most recent versions. For instance, as mentioned earlier, Nigeria now has both a national digital health policy and a national digital health strategy. These 2 documents supersede and thus replace the old National Health ICT Strategic Framework [ 86 ]. Details of included documents are presented in Multimedia Appendix 3 .
Other Related National Documents
We included 8 other documents [ 20 , 85 , 87 - 92 ] from 6 countries (Ethiopia, Kenya, Liberia, Nigeria, South Africa, and Tanzania) that did not fall under either stand-alone regulatory standards and guidance or national policies and strategies. These were mostly frameworks, road maps, and reports that potentially provide information relevant to the use of health apps. The years of development and implementation range from 2016 to 2025. These documents do not provide standards or guidance, but they contain information that can help map the digital health stakeholders that potentially play a role in regulating health apps for self-management. When multiple versions of a document exist, only the latest version was taken into consideration. Multimedia Appendix 3 provides details of the included documents.
Content: Aspects That Are Regulated and Aspects That Are Not
Technical and clinical safety.
Technical and clinical safety standards are required to prevent or minimize the harm that may arise from the use of the health ICT systems (including mHealth systems) as well as to improve the health outcomes and user satisfaction. As shown in Figure 2 , two subthemes were generated from included standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] as content under technical and clinical safety: v(1) guidance on system quality and (2) guidance on software or app development, acquisition, support, and maintenance.

Notably, 2 of the included standards [ 18 , 47 ] provide guidance on system quality to ensure the quality, security, reliability, performance, and maintenance of eHealth and mHealth systems. The Kenya Standards and Guidelines for E-Health Systems Interoperability [ 47 ] recommend the implementation of a data quality protocol to ensure that the data collection, collation, analysis, interpretation, dissemination, and use are managed in accordance with the quality standards. Similarly, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] recommends the inclusion of the following requirements in the technical manual: (1) minimum hardware requirements that should incorporate the preferred hardware architecture, (2) minimum software requirements that should include the minimum version of the underlying operating system as well as acceptable versions of related software, and (3) a detailed list of software dependencies (external libraries) necessary for the system to function properly.
The included standards [ 18 , 48 ] cover guidance on software or app development, acquisition, support, and maintenance, which aim to ensure the efficiency and effectiveness of eHealth and mHealth systems. The Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] recommends a technical manual to provide a detailed description of the system’s installation and maintenance processes for system administrators and implementers; a developer’s guide for software developers and programmers to provide them with an overview of the system, description of the software design methodologies, description of the system architecture, and technical design diagrams; and a user manual to aid users in understanding how the system works and how each feature operates; in addition, the technical manual contains instructions for operating the software; entering and updating data; and generating, saving, and printing reports.
Although the contents generated here provide guidance that is relevant to health apps, they are not specific to health apps. Moreover, there are no clear measures to enable individuals or organizations that use health apps to manage clinical risk appropriately.
Data Protection and Security
Data protection and security are crucial aspects of managing patient information, thus ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data as well as the rights and interests of the patient. Two subthemes related to data protection and security are (1) security measures for adequate protection of patients’ digital records and (2) guidance on data exchange.
The included standards [ 18 , 48 ] provide security measures for eHealth or mHealth systems to ensure the adequate protection of digitally accessible patient records. These measures include authentication, accountability, identification, authorization, integrity, confidentiality, availability, security, administration, and audit. This will help to achieve confidentiality, integrity, availability, and nonrepudiation of patient data or health records. Additional levels of security such as data encryption are required when there is a need to store sensitive information on removable devices or media or outside the MOH premises.
The Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] provide the following guidance on data exchange to ensure privacy: (1) anonymize client data as much as possible before they can be shared; (2) where possible, use pseudonyms for the client data before they can be shared; (3) aggregate client data before they can be shared to reduce possibilities of tracing the data back to the client; and (4) minimize data so that access is available only to the data set required for that particular use. With regard to privacy rules, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for E-Health Systems Interoperability [ 47 ] propose that a notice of privacy practices should be given to patients describing how their information may be used or shared while also specifying their legal rights.
Standards and Interoperability
Standards and interoperability are essential concepts in the field of IT, especially for systems that need to communicate and exchange data, as seen in the use of health apps for self-management. Two subthemes related to standards and interoperability are (1) interoperability as a basic requirement and (2) minimum standards to enable integration.
All the regulatory standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] highlight the importance of having interoperability as a basic requirement when selecting software products or services for use within the health system. This facilitates interaction across systems. For instance, to facilitate seamless interaction between mHealth systems and primary information systems for data capture, reporting, and decision support in various domains of the health system, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] recommends the incorporation of at least 3 types of interoperability, namely, technical interoperability, semantic interoperability, and process interoperability.
Furthermore, 2 regulatory standards [ 18 , 47 ] proposed minimum interoperability standards to enable the integration of services and data exchange between various systems in health care. For instance, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] suggests standards (for interoperability) for mHealth systems that are consistent with the recommendations in internationally accepted standards. They include the following: (1) clinical messaging—ensuring mHealth systems conform to Health Level 7 (HL7) version 3 standards and corresponding implementation guideline; (2) clinical terminology—ensuring terminologies and classifications for clinical concepts (eg, International Classification of Diseases, tenth revision—for diseases; Systemized Nomenclature of Medicine—for clinical data coding; Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes—for laboratories; and RxNorm—for Pharmacies); (3) the mHealth system must use the latest versions of international standards, such as HL7 Clinical Document Architecture for electronic sharing of clinical documents; (4) concepts—mHealth systems will use the idea of “concepts” so that information can be transmitted between systems without losing meaning or context, and HL7 Reference Implementation Model or other appropriate standards are recommended for implementing concepts; (5) architecture—to develop mHealth systems, developers should define the system architecture that should include data elements and business logic. Furthermore, to define how mHealth systems interact with other systems, developers of mHealth solutions must provide application programming interfaces. FHIR is the preferred application programming interface interoperability standard.
Inclusion and Equitable Access
Inclusion and equitable access are essential principles to ensure that health apps are culturally appropriate and relevant and accessible to everyone, regardless of gender, ethnicity, location, or economic status.
All the included regulatory standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] indicate that they were developed based on a combination of participatory and consultative approaches involving multiple actors or stakeholders, thus promoting inclusion. However, there are no specific measures or guidance to ensure adequate engagement and representation of all the relevant stakeholders and to sustain that engagement.
The Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] proposes the following systems attributes to ensure equitable access to mHealth services at all times and from anywhere: (1) allocation of adequate storage and bandwidth capacity; (2) fast response time; (3) fast recovery capabilities; (4) performance monitoring; (5) business continuity processes, for example, backups; and (6) redundant sites and links. Furthermore, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] prescribes the following metrics for measuring system availability: (1) downtime per year, (2) mean time between failure, (3) mean time to repair, and (4) failure in time.
Although the abovementioned systems attributes and metrics for measuring system availability are important, the included standards do not offer any concrete guidance or model for achieving a sustainable funding mechanism for health apps to ensure that they are readily available and accessible to those who need them.
Context: Reasons Why Those Aspects Are Regulated
The 3 standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] were developed to address unsafe, isolated, and inconsistent implementation. The Health Sector ICT Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] suggest that although there has been a lot of ICT investment in the health sector leading to improvement in service delivery and information exchange, there remains the challenge of inconsistency in ICT implementation and harmonization of the health sector system requirements. Hence, there is a need to adopt global best practices for software development, acquisition, support, and maintenance by the MOH. In addition, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] indicates that standards and guidelines are necessary to ensure a consistent approach to the development of ICT systems. Similarly, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for E-Health Systems Interoperability [ 47 ] recognize the need to ensure that the processes of collecting, collating, analyzing, interpreting, disseminating, and using data are consistent with data quality standards.
To build mutual trust and maximize the benefits of eHealth information exchange, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for E-Health Systems Interoperability [ 47 ] reiterate that as health data are constantly being exchanged across health information systems, robust security standards are required to maintain their integrity and confidentiality. This will build the trust of service users and consequently help to maximize the benefits of eHealth information exchange such as in self-management.
Two of the included regulatory standards [ 47 , 48 ] indicate that the context for standards and interoperability was (1) to address poor coordination, duplication of efforts, and inefficient use of resources and (2) to promote the integration of ICT systems.
The Kenya Standards and Guidelines for E-Health Systems Interoperability [ 47 ] acknowledge that the absence of interoperability standards over the years has led to the duplication of efforts and the inefficient use of ICT resources in health care. Now that ICT has become increasingly relevant in improving efficiency in health service delivery, the Kenya MOH recognizes the need to adopt a standardized approach, hence the development of interoperability standards for eHealth systems. In addition, the Health Sector ICT Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] emphasize the relevance of interoperability as a requirement for addressing the inconsistency in implementing ICT in the health sector.
The Health Sector ICT Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] consider “integration of ICT systems” as one of its key guiding principles, acknowledging the lack of information systems integration as a challenge experienced by ICT services across Kenya.
The contexts for inclusion and equitable access as generated from included standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] were (1) to promote inclusion and (2) to promote equitable access to services.
To promote inclusion, the standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] highlight the importance of involving and engaging multiple actors and stakeholders during the development process. However, no emphasis was placed on the need to sustain stakeholder engagement during the implementation process.
Pertaining to equitable access, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] acknowledges that the public health care system is largely unavailable to most of the population in many developing countries because of geographical location, resource constraints, inefficiencies, and lack of awareness. Hence, it recognizes the importance of ensuring that mHealth services are always accessible by users and from anywhere as well as the need to put in place mechanisms to make this happen.
Process: How the Regulations Are Developed and Implemented
Two themes were generated from the included standards: development and implementation processes [ 18 , 47 , 48 ].
Development Process
All the included standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] indicate that they were developed through a participatory process and in consultation with a range of subject experts and interest groups. In addition, the standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] adopted a multisectoral approach to engage health-related stakeholders from government ministries or agencies and development partners and a range of subject experts and interest groups. It has also been reported that these standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] were developed based on international best practices and with reference to international standards. However, there is no indication that a stakeholder engagement strategy was adopted to sustain the engagement of stakeholders through the entire development and implementation process.
Implementation Process
The 3 regulatory standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] identify the key requirements to ensure effective implementation of IT services in the health sector. These are (1) legal authority, (2) coordination, (3) building capacity, and (4) monitoring and evaluation.
The included standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] were established based on the legal provisions enshrined in the health and other related acts and laws of Kenya as well as the relevant policies and strategies. Hence, it is expected that their implementation will comply with and be backed by those legal provisions. For example, the Health Sector ICT Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] indicate that its implementation will be supported by the authority from the Kenya Communications Act 2009, E-Government Strategy, and National ICT Policy. Similarly, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] asserts that it will be implemented by complying with existing and relevant national policies, legal frameworks, strategies, and standards, including the Health Information Policy, ICT Standards, and System Interoperability Principles.
The included standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] report that the implementation of regulations will require robust coordination mechanisms. For instance, the Health Sector ICT Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] indicate that, as the Ministry’s ICT resource manager, the principal secretary (also the head of ICT), in collaboration with the ICT Governance Committee, is responsible for coordinating the implementation of the standard. The ICT Governance Committee comprises representatives from the heads of departments and ICT development partners in the health sector. The committee’s responsibilities include overseeing, enforcing, and reviewing standards as well as initiating ICT projects.
The Health Sector ICT Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] highlight the need for capacity building or training of the MOH staff and stakeholders who are the primary users of the Ministry’s ICT services. This will enhance their capacity to implement the guidelines provided in the document in line with the ministry’s human resource development policies, regulations, and rules. However, it is acknowledged that building capacity for health ICT is a challenge given that there is low adoption of ICT among health providers, and ICT is not routinely included in the course content of most training programs. The Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] listed the “number of mHealth practitioners trained on the standards and guidelines” as one of the indicators for monitoring and evaluating mHealth interventions.
The Health Sector ICT Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] assert that monitoring and evaluation is an essential role of the MOH to ensure efficiency, accountability, and transparency throughout the implementation period. It further stresses that all those who use the Ministry’s ICT services are required to adhere to the provisions in the standard as the MOH will carry out quarterly monitoring exercises on the use of the standard to ensure compliance based on clear indicators. Furthermore, the ICT Governance Committee will periodically review and amend the standard to keep it relevant and effective. Similarly, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] establishes the following key indicators for effectively monitoring and evaluating the implementation of the standards and guidelines: (1) the number of counties in which the MOH has disseminated the standards and guidelines, (2) the number of counties successfully implementing the standards and guidelines, (3) the number of mHealth practitioners trained on the standards and guidelines, (4) the number of mHealth practitioners accessing the standards and guidelines, (5) the number of mHealth practitioners who correctly understand the standards and guidelines, (6) the number of stakeholders who adhere to the standards and guidelines, (7) the number of mHealth systems that follow the required development steps, and (8) the number of mHealth practitioners who have implemented their systems by using the standards and guidelines. In addition, the Kenya Standards and Guidelines for mHealth Systems [ 18 ] indicates that the outlined standards will be reviewed every 3 years to ensure they are up to date with new changes including the changes in policies and systems upgrades.
Although all the abovementioned indicators are relevant, the implementation process is not explicit on the approach for regulating health apps and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and guidance.
Actors: Those the Regulations Are Targeted at
The included standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] identified 2 main groups of actors for whom the regulations and guidance were targeted. They included (1) those who provide digital health services and (2) those who use the ICT infrastructure of the MOH.
Two of the standards [ 47 , 48 ] indicated that the regulations should be implemented by all individuals and organizations that provide ICT-related health care services to the public. Similarly, the Health Sector ICT Standards and Guidelines [ 48 ] state that all those who access or use the MOH ICT infrastructure are expected to adhere to the guidelines outlined in the document.
Mapping of Stakeholders
To address the third research question, we conducted a stakeholder mapping guided by the RISA tool [ 41 ].
A total of 11 categories of key stakeholders were identified from all 49 included documents (6 stand-alone regulatory standards and guidance, 35 national policies or strategies, and 8 other related documents). These categories are consistent with the digital health stakeholders recognized by the WHO, ITU, and UNESCO [ 32 , 33 , 43 ]. Table 2 presents the mapping of stakeholders according to their role categorization. A more detailed table with a potential role description with regard to regulating health apps for self-management is presented in Multimedia Appendix 4 .
a WHO: World Health Organization.
This paper presents the findings of a scoping review of regulatory standards and guidance for the use of health apps for self-management in sub-Saharan Africa. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that attempted to identify and assess the extent to which regulatory standards and guidance regulate and guide the use of health apps for self-management in sub-Saharan Africa as well as map out the key stakeholders and their potential roles.
Our findings reveal that only 1 country (Kenya) in sub-Saharan Africa currently has national regulatory standards that could potentially regulate the use of health apps for self-management. The included standards failed to adequately address adequate attention to inclusion and equitable access. This is concerning given the growing need to promote the adoption of culturally appropriate and relevant health apps and to ensure that they are available to those who need them regardless of gender, ethnicity, geographical location, or financial status [ 24 - 29 ]. Consequently, this review provides insights into the regulation of health apps for self-management in sub-Saharan Africa, which needs to be given more attention if the potential of these apps is to be harnessed in the region.
Principal Findings
We identified 49 documents from 31 countries in sub-Saharan Africa. Although none of the included standards provided a specific set of regulations on health apps for self-management, we identified 3 standards [ 18 , 47 , 48 ] that provided relevant information regarding the regulation of health apps. The included national policies and strategies, in contrast, only outline the goals and commitments made by national governments to promote the adoption of digital technologies in the health sector and the plans and paths set forth to achieve these goals. However, the information they provided was relevant for identifying and mapping digital health stakeholders who potentially have vital roles in regulating the use of health apps for self-management.
The policy analysis framework (content, context, process, and actors) [ 42 ] was adapted and applied to organize the key findings. The content covered the following areas: guidance on systems quality; guidance on software and app development, acquisition, support, and maintenance; security measures for adequate protection of patients’ digital records; guidance on data exchange; interoperability as a basic requirement; minimum standards to enable integration; involvement and engagement of relevant stakeholders; and system attributes for equitable access to services. Meanwhile, the context was to address unsafe, isolated, and inconsistent implementation; to build mutual trust and maximize the benefits of eHealth information exchange; to address poor coordination, duplication of efforts, and inefficient use of resources; to promote the integration of ICT systems; and to promote inclusion and equitable access to services. The process involved the development process (which covers participatory and consultative processes and multisectoral approach, with reference to international standards and best practices) and the implementation process (which covers legal authority, coordination, capacity building, and monitoring and evaluation). The targeted actors were those who provided digital health services and those who used the ICT infrastructure of the MOH.
Furthermore, key stakeholders with potential roles in regulating health apps for self-management were identified. They include the government, regulatory bodies, funders, intergovernmental and nongovernmental organizations, academia, and the health care community.
Implications of the Study Findings for Practice
Regulatory standards and guidance act as a bridge between technological innovation and its safe and effective use in health care. They ensure that while technology continues to advance, the safety and trust of patients are never compromised. Among the plethora of health apps on the market, the over-the-counter, nonregulated apps such as wellness and fitness apps are the most mainstream [ 93 - 95 ]. On the other side of the spectrum, there are regulated health apps that are classified under medical devices or software as medical device products [ 94 , 95 ]. Some of these are prescription-only apps, such as digital therapeutics (DTx) apps for managing substance dependence [ 95 , 96 ].
Although some high-income countries have made significant strides in ensuring the safety, effectiveness, and accessibility of health apps, the journey has indeed not been without challenges and hurdles. Sub-Saharan Africa, although dealing with its own unique set of challenges, has the opportunity to learn from the experiences of these high-income countries. This could potentially allow the region to bypass some of the hurdles encountered by high-income countries in their journeys.
Technical and clinical safety are essential requirements that health apps must meet before they can be considered for use for self-management to minimize the risk of harm to patients. It is well documented that health apps that function poorly pose a serious threat to the safety of patients. An example illustrating how health apps used for self-management can threaten patient safety is evident in a study [ 12 ]. This study [ 12 ] revealed that widely used health apps designed to calculate and estimate insulin doses could endanger patients by providing incorrect or inappropriate dose recommendations. Similarly, 2 successive studies that assessed the contents and tools of apps for asthma discovered that none of the apps in the first study offered comprehensive information or adequate tools for asthma self-management, whereas the follow-up study, which was conducted 2 years later, showed a 2-fold increase in the number of asthma apps, yet there was no improvement in the content and tools offered by the newer apps. In fact, many apps recommended self-management procedures that were not supported by evidence [ 13 , 14 ]. Accordingly, some health apps that support the self-management of long-term conditions do not adhere to evidence-based guidelines and are unresponsive to the evolving health needs of patients.
Although the context of included regulatory standards with regard to technical and clinical safety was to address unsafe, isolated, and inconsistent implementation, the guidance provided by these regulatory standards is not specific to health apps, and they do not provide appropriate guidance and standards for health organizations and other key stakeholders to establish a framework for managing the clinical risks associated with deploying and implementing self-management health apps. Considering the rapid advancements in digital health (including artificial intelligence [AI] or machine learning and big data), health apps will increasingly play a crucial role in supporting self-management through digitally enabled care pathways that will improve personalized care and health outcomes [ 97 , 98 ]. Therefore, it is imperative to ensure the technical reliability and clinical safety of health apps for self-management through robust regulatory standards and guidance. For instance, a guide on the criteria for health app assessment, developed by the UK government, includes technical stability and clinical safety as criteria for deciding whether health apps should be considered for use in the National Health Service (NHS) [ 99 ]. In addition, medical device apps are required to conform to the NHS clinical risk management standards as part of the clinical safety requirements [ 99 , 100 ]. In the event of any concerns regarding the safety of a medical device app, the Yellow Card reporting system can be used by a responsible clinical safety officer or any other individual to notify the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) [ 101 , 102 ].
To adequately manage patient information when health apps are used for self-management, data protection and security standards and guidance are required. They guarantee that data are kept and handled safely and responsibly within the provisions of the law and that patients’ rights and interests are respected.
There have been ongoing concerns about compliance with ethical standards, the principles of confidentiality of information, and data privacy. For example, an assessment of apps that had previously been endorsed by the former UK NHS Apps Library revealed substantial gaps in compliance with data protection principles regarding the collection, storage, and transmission of personal information. This has raised a fundamental concern about the credibility of developer disclosures and whether these disclosures can be trusted by certification programs [ 15 ]. A study assessed the privacy practices of the 36 most popular apps for depression and smoking cessation for Android and iOS in the United States and Australia [ 16 ]. The findings revealed that although only 69% (25/36) of the apps included a privacy policy, 92% (33/36) of the apps shared data with a third party, and only 92% (23/25 with privacy policy) of the apps disclosed sharing data with a third party in their policy. Although 81% (29/36) of the apps shared data with Google and Facebook for the purposes of advertising, marketing, or analytics, only 43% (12/28) of the apps that shared data with Google and 50% (6/12) of the apps that shared data with Facebook disclosed this in their policy [ 16 ].
In this regard, health app developers and providers in the United Kingdom are required to conduct a data protection risk assessment before they launch or update their apps to ensure compliance with the United Kingdom General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other relevant regulations, including the Data Protection Act 2018 [ 103 ]. By conducting a data protection risk assessment, health app developers and providers can demonstrate that they are accountable; they respect the privacy and dignity of their users; and that they deliver safe, effective, and ethical solutions [ 104 ].
Health apps are expected to play an increasingly important role in supporting self-management. However, this ambition can only be achieved if citizens trust that these apps are collecting and analyzing data safely and in accordance with robust regulatory standards and guidance. It is also crucial that these apps provide reliable information that clinicians can act on [ 98 ]. The context of the standards included in this study regarding data protection and security was to build mutual trust and maximize the benefits of eHealth information exchange. Trust is a key factor in the successful adoption and use of health apps, and transparency in data handling and clinical decision-making is essential to build and maintain that trust. This is also paramount for the widespread acceptance and impact of health apps on health care outcomes in sub-Saharan Africa.
We acknowledge the existence of numerous national laws related to data protection and security outside the health sector. Hence, guidelines that link these legislations together must be provided to ensure compliance with all relevant laws and guidance when using patient data. An example of how to achieve this is the United Kingdome’s guide to good practice for digital and data-driven health technologies that provides guidelines on how to abide by the laws and principles that govern data security and protection in the United Kingdom, including the GDPR, Data Protection Act 2018, and Caldicott Principles [ 105 ].
Standards and interoperability are essential for effectively developing, deploying, and implementing health apps to support self-management in sub-Saharan Africa. Interoperability is the ability of different systems, devices, or applications to communicate and exchange data with each other in a coordinated manner, thus providing timely and seamless portable information across organizational, regional, and national boundaries and optimizing both individual and population health [ 106 ]. In the same vein, standards enable interoperability between systems or devices through a common language and a common set of expectations [ 106 ].
Interoperability is crucial in improving the quality, safety, and efficiency of care delivery as well as empowering patients and providers with access to relevant and timely information [ 99 ]. One of the most widely used and accepted interoperability standards for health care data exchange is FHIR [ 106 , 107 ]. FHIR is a global industry standard developed by HL7 International. FHIR is designed to be quick to learn and implement and to support a variety of use cases, including self-management [ 108 ]. By using apps that are based on an FHIR standard, patients can benefit from data analytics that show how their health data relate to their chronic conditions or wellness goals [ 109 ]. They could also access all their health information from one place, even if they visit different health professionals who use different electronic medical records or EHR, thus promoting integrated care [ 28 , 31 , 33 , 109 - 115 ]. As a result, patient care can easily be coordinated.
The context of the included regulatory standards with regard to standards and interoperability was to address poor coordination, duplication of efforts, and inefficient use of resources and to promote the integration of ICT systems. However, in sub-Saharan Africa, there are many challenges and barriers to the adoption and implementation of interoperability standards, such as the lack of awareness or knowledge of the benefits and requirements of interoperability standards among stakeholders; lack of incentives or regulations to encourage or enforce the adoption of interoperability standards by app developers and vendors; lack of resources or capacity to implement interoperability standards, including technical expertise, infrastructure, funding, or governance; and lack of alignment or coordination among the different actors and initiatives involved in developing, deploying, and implementing the digital health interventions [ 30 , 116 - 119 ]. To address these challenges, some possible solutions may include raising awareness and education on the importance and value of interoperability standards for health apps among all relevant actors; developing and implementing policies and guidelines that promote or mandate the use of interoperability standards by app developers and vendors; providing technical assistance and support for app developers and vendors to adopt and implement interoperability standards, such as tools, frameworks, testing, certification, or accreditation; and establishing and strengthening collaboration and coordination among the different stakeholders and initiatives involved in health app development, deployment, and implementation in sub-Saharan Africa. In addition, the Digital Health Platform Handbook, a toolkit developed by the collaborative efforts of the WHO and ITU [ 120 ], can help countries in sub-Saharan Africa to develop and implement digital health platforms as the underlying infrastructure for interoperable and integrated national digital health systems. The digital health platform is a system-wide approach to developing digital health solutions with the aim to overcome the problems of siloed, vertical, and isolated applications and systems that hamper data management, innovation, efficiency, and impact in the health sector.
Inclusion and equitable access are crucial to ensuring that health apps and related services are culturally appropriate and relevant as well as accessible to all who need them, regardless of gender, ethnicity, geographical location, ability, or financial status [ 24 - 29 ]. This is the key to promoting a “sense of belonging” and “ownership” and thus underscoring the importance of stakeholder mapping and involvement or engagement through the development and implementation process [ 22 ].
In this study, the included regulatory standards demonstrate the importance of inclusion by adopting both a participatory and consultative approach involving multiple stakeholders from different sectors. However, the standards do not provide clear guidance to ensure the adequate participation and sustained engagement of all relevant stakeholders. The lack of concise guidance to ensure the adequate participation and engagement of all relevant stakeholders, especially the susceptible and disadvantaged groups, can increase the risk of tokenistic tendencies, which can undermine the cultural appropriateness of health apps [ 25 , 121 ]. Some susceptible groups, such as women and people with low socioeconomic status, may face additional barriers to accessing and using health apps, such as lack of digital literacy, privacy concerns, cultural norms, or stigma [ 25 ]. Similarly, the cost of developing, maintaining, and updating health apps may not be covered by public or private health insurance schemes, which could limit their affordability and availability for low-income or uninsured populations [ 95 ]. However, there is no specific guidance or model for an effective funding mechanism for health apps in the included regulatory standards.
To address these challenges and ensure equitable access to health apps for self-management in sub-Saharan Africa, possible measures may include developing policies and regulations that support integrating health app interventions into existing health systems and financing mechanisms and engaging with stakeholders from different sectors and backgrounds (including health professionals, patients, communities, governments, civil society, academia, and industry) to co-develop and co-implement frameworks or models that promote the use of health apps for self-management in ways that are responsive to the local context and needs. Moreover, establishing regulations that provide appropriate financing or reimbursement options will reduce the risk of developers of good quality health apps turning to data mining for revenue, thus increasing privacy concerns [ 95 ]. For instance, in Germany, the reimbursement of health apps classified as medical devices (Digitale Gesundheitsanwendungen) was introduced in 2021 under the statutory health insurance [ 122 , 123 ]. When a medical device is prescribed by a physician or a physiotherapist, the manufacturer must submit an application to the German Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (Bundesinstitut für Arzneimittel und Medizinprodukte) for approval [ 123 ]. The Federal Association of the Statutory Health Insurance Funds (Spitzenverband Bund der Krankenkassen) determines and negotiates the reimbursement thresholds following approval. However, the manufacturer must demonstrate that the app is safe, functional, and of good quality; complies with data protection requirements; and benefits patient care [ 123 ].
The process of regulating health apps essentially involves the development and implementation of regulatory standards and guidance. According to our study, the development process comprises a participatory and consultative process, a multisectoral approach, and a reference to international standards and best practices. In contrast, the implementation process is ongoing and requires appropriate legal authority, coordination, capacity building, and monitoring and evaluation.
We recognize that health apps can be accessed and used by patients from different parts of the world, and this means that countries need to carefully consider whether health apps that are accessed and used by their citizens meet the national or regional legal and ethical requirements, including their cultural and linguistic needs [ 23 ]. For countries in sub-Saharan Africa, a cross-border or regional collaboration between national legal authorities through the coordination of agencies such as the African Medicines Regulatory Harmonization (AMRH) may help to ensure that health apps built for the region are safe, effective, and user-friendly for everyone, considering the contextual differences of the countries [ 23 ]. For instance, all medical device companies that want to sell their products in the European market must obtain a Conformité Européenne (CE) mark for their devices, which indicates that they meet the legal requirements and can be freely circulated within the European Union [ 124 ]. Although the European Union member states regulate medical devices, the European Medicines Agency is involved in the regulatory process.
The regulation of health apps is extremely complex and involves a wide range of stakeholders. Therefore, a robust coordination mechanism is essential to reduce the risk of fragmentation and duplication of efforts and to promote the efficient use of resources. Most countries in sub-Saharan Africa have units in health ministries that coordinate and oversee the regulation of medical products. These units should be autonomous, full-fledged departments with legal authority (boards or commissions) to ensure independent, transparent, and accountable decision-making, but this is often not the case [ 125 ]. These units are recognized by the national authorities as regulators (eg, the National Medicines Regulatory Authority [NMRA]) [ 126 ]. Such organizational structures hinder the effectiveness of the national regulatory authorities in fulfilling their mandate and prevent the establishment of quality management systems to ensure transparent and accountable decision-making [ 125 ].
Furthermore, Essén et al [ 23 ] analyzed health app policy or regulation in 9 high-income countries (Sweden, Norway, Denmark, Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, England, the United States, and Singapore) and found that most of these countries adopted centralized approaches to app evaluation. Although centralized approaches might have advantages over self-evaluation, they may create bottlenecks and limit the availability of high-quality health apps for users. As suggested by Essén et al [ 23 ], a decentralized approach, such as the accreditation of evaluation agencies, maybe a worthwhile solution. However, this will require adequate coordination to ensure the consistency and reliability of the evaluation criteria and methods across different agencies as well as the transparency and accountability of the accreditation process. A possible way to achieve this is to adopt a common framework that can guide the evaluation and accreditation of health apps.
Similarly, the postmarket surveillance (PMS) system, which is a new regulation for medical devices in Europe, is a process of collecting and analyzing data on medical devices after they have been launched into the market to ensure their safety and performance and to identify any problems or need for improvements [ 127 , 128 ]. The PMS system is important because premarket data, which are obtained from testing a medical device before it is launched, have limitations in capturing the long-term performance and risks of the device [ 128 ]. Currently, the PMS system does not cover fitness and wellness apps, which are commonly used in self-management. Hence, Yu [ 93 ] proposed that the PMS system should also be applied to DHTs, such as fitness and wellness apps. They argue that the postmarket data would help regulators periodically review and adjust the regulatory standards for these groups of health apps based on their risks and benefits.
Drawing on the experience of the United Kingdom, it can be clearly demonstrated that the regulation of health apps is a complex, a multifaceted, and an evolving process that involves different regulators and criteria depending on the nature and function of the app. For instance, a centralized NHS Apps Library was launched as a beta site in April 2017 to provide patients with a collection of trusted and easy-to-use digital health tools [ 129 ]. The library provided access to a range of health apps that were reviewed and approved by the NHS, including apps that could help patients manage conditions such as diabetes, mental health, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [ 130 ]. However, the library was closed in December 2021 [ 131 ]. Although no reason for the closure was provided on the website, it is likely because of persistent concerns regarding the safety of patients and data privacy involving multiple apps including those listed in the library [ 12 , 14 - 16 , 131 , 132 ]. The NHS App was introduced in January 2019 before the closure of the NHS Apps Library to serve as the gateway for accessing NHS services including ordering repeat prescriptions and booking or managing appointments [ 133 ].
Furthermore, the United Kingdom Health Security Agency, formerly known as Public Health England, issued a guidance on criteria for health app assessment in October 2017 [ 99 ]. The purpose of this guidance was to ensure that all health apps built for the UK population work well and provide clear information about their functions, benefits, and intended outcomes for patients and health care professionals. On the basis of this guidance, those intending to build an app are required to conform to certain regulations before being considered for the app assessment process. The 2 main regulations are the medical device regulation and the Care Quality Commission (CQC) registration. Apps that are considered as medical devices must register with the MHRA and have a CE mark. Apps providing health or social care that fit into 1 of 14 regulated activities are required to register with the CQC before they can be assessed [ 134 ]. CQC is an independent regulator of health and social care services in England.
Similarly, the Organisation for the Review of Care and Health Apps (ORCHA) is a UK-based organization that independently evaluates and distributes health apps. It provides services such as app review, accreditation, curation, and recommendation within the United Kingdom and across the world [ 135 ]. ORCHA also enables organizations (including the NHS) to build a decentralized web-based digital health library of consumer-friendly over-the-counter apps [ 135 - 137 ]. These apps are continuously assessed by ORCHA against the standards and regulations in clinical and professional assurance, data quality and privacy, and usability and accessibility [ 137 ].
In addition, the Digital Technology Assessment Criteria (DTAC) were introduced in beta in October 2020, and its first official version was subsequently launched in February 2021 [ 138 ]. The DTAC plays a crucial role in ensuring that digital health tools meet the necessary standards in areas such as clinical safety, data protection, technical security, interoperability, usability, and accessibility. By serving as the national baseline criteria for DHTs in the NHS and social care, it provides a valuable framework for health care organizations during procurement. It also offers guidance for developers on the expectations for their digital technologies within the NHS and social care. This is an example of how a harmonized framework can help ensure the quality and safety of DHTs, including health apps.
In addition, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Evidence Standards Framework is a set of evidence standards for a wide range of DHTs designed to help evaluators and decision makers in the health care system to consistently identify DHTs that are likely to offer benefits to the users and the health care system [ 139 ]. The Evidence Standards Framework was first published in March 2019 and is ideally used before DHTs (including health apps) are considered for commissioning or procurement by the NHS [ 140 ]. It is a crucial tool for ensuring that DHTs are clinically effective and offer value to the health and care system in the United Kingdom. In August 2022, the framework was updated to include AI and data-driven technologies with adaptive algorithms [ 140 ].
Furthermore, DTx apps, which are a type of medical device, are not allowed into the UK market unless they comply with the UK GDPR and meet the requirements of DTAC. In addition, they must bear the CE or UK Conformity Assessed marks [ 141 ]. This means that DTx apps must demonstrate their safety and efficacy through clinical trials and comply with the relevant regulations for data protection and quality standards as regulated by the MHRA. DTx products are also recognized as DHTs under the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Evidence Standards Framework [ 142 ]. DTx incorporates software to treat, prevent, or manage specific diseases or conditions [ 143 , 144 ]. The fact that DTx products typically focus on a narrow clinical indication and generate evidence of clinical efficacy underscores their potential to make a substantial contribution to self-management and health care delivery in general. The increasing recognition of the role of DTx in patient care by regulators is also noteworthy, and the creation of regulatory and reimbursement pathways for approved apps further enables DTx products to continue to play an important role in impacting health care delivery [ 1 , 143 ]. This is a testament to the potential of regulated health apps to revolutionize health care and improve patient outcomes.
Among the many lessons to learn from the experience of the United Kingdom is that the regulation of health apps must evolve to keep pace with advances in DHTs and adapt to the changing needs and demands of digital health. Moreover, efforts are being made to streamline the multifaceted approaches to simplify app regulation and access in the United Kingdom [ 23 ]. Therefore, a robust and dynamic coordination mechanism, along with political will, skilled personnel, reliable funding, and a robust framework for monitoring and evaluating progress and aligning key performance indicators, is essential for countries in sub-Saharan Africa to keep pace with the advancement in the regulation of health apps. There is also a need to strengthen collaboration and ensure regulatory harmonization among national regulatory authorities and continental bodies such as the regional economic communities, AMRH, and the WHO AFRO [ 126 ].
Capacity building and monitoring and evaluation are important factors for ensuring effective regulation of health apps given the complex nature of the process. The regulation of medical products (including health apps) in sub-Saharan Africa generally includes licensing and accreditation, evaluation, inspection, quality control, information dissemination and promotion, and monitoring of adverse events [ 125 ]. Therefore, high-level skills as well as effective monitoring and evaluation will be required to ensure the success of the process. For most countries in sub-Saharan Africa, the NMRA is responsible for coordinating and overseeing the regulatory system of medical products [ 125 , 126 ]. However, in most cases, NMRAs are unable to perform the core regulatory functions expected of them [ 145 ]. More than 90% of African countries have limited or no capacity to regulate medical products, with only 7% having moderately developed capabilities [ 145 ]. The lack of effective NMRAs in Africa exposes the citizens to potential harm by allowing unsafe, low-quality, and fake medical products to circulate and be used [ 145 ].
Although it is the responsibility of governments to establish functional regulatory systems and ensure effective monitoring and evaluation of the regulatory process, the involvement of international and continental organizations to support sub-Saharan African countries improve the regulatory capacity of their national regulatory agencies would be extremely beneficial. For instance, the African Medicines Agency (AMA) was established in November 2019 as a treaty adopted by the African Union Member States to help address the concerns arising from weak regulatory systems on the continent. At present, 37 countries have signed the AMA treaty, including 26 countries that have ratified it [ 146 ]. The main objective of the AMA is to enhance the capacity of States Parties and regional economic communities to regulate medical products to improve the quality, safety, and efficacy of medical products on the continent [ 147 ]. The AMA, in collaboration with other existing capacity building initiatives or organizations, such as the WHO Global Initiative on Digital Health, ITU, AMRH, WHO AFRO, and United Nations Children’s Fund, can assist sub-Saharan African countries in aligning their regulatory requirements with available resources and support them to acquire the necessary tools and skills to build effective and sustainable regulatory systems for health apps. This can be achieved by adopting a decentralized approach to engage a network of technical experts across the African Union similar to the model of the European Medicines Agency [ 148 ].
Actors or Stakeholders
The regulation of health apps often requires working with a wide range of actors or stakeholders. However, in this review, we identified only 2 main actor groups (those who provide digital health services and those who use the ICT infrastructure of the health ministry). These are the groups that are targeted by the included regulatory standards.
From a broader perspective, 12 categories of stakeholders according to their potential role in regulating health apps for the self-management were mapped in this study. The potential contribution of these stakeholders to the regulation of health apps for self-management in sub-Saharan Africa not only depends on their roles and responsibilities but also on their interests, needs, expectations, and influence [ 41 , 149 - 151 ]. Thus, a robust stakeholder analysis is paramount as it can help define the scope of the regulatory process, prioritize the requirements, manage the expectations, and ensure the engagement and participation of stakeholders throughout the regulatory process [ 41 , 152 - 156 ]. Our stakeholder mapping, as presented in Table 2 (refer to Multimedia Appendix 4 for more details), lays the foundation for national governments to conduct a robust stakeholder analysis and to adopt an all-inclusive stakeholder engagement strategy to manage and sustain the engagement and participation of all relevant stakeholders [ 157 , 158 ].
Recommendations
Our review found that the regulation of health apps in sub-Saharan Africa is especially poor and almost nonexistent, as only Kenya has national standards that could address some of the regulatory issues related to health apps. Therefore, we recommend the following actions to help sub-Saharan African countries improve the regulation of health apps to support self-management:
- Establish a clear and consistent definition of what constitutes a health app (considering AI or machine learning) and what level of regulation is required for different types of apps.
- Develop and implement criteria and guidelines that ensure the quality, safety, and usability of health apps.
- Engage with independent app evaluators, such as ORCHA, to adopt a common framework that can guide the evaluation and accreditation of health apps and use the framework to create and maintain decentralized and transparent platforms that showcase and evaluate health apps for users and health care professionals.
- Develop and implement policies and regulations that enable sustainable funding for health apps such as integrating the use of health apps for self-management into existing health systems and financing pathways or mechanisms.
- Support and facilitate innovation and collaboration across the sub-Saharan Africa region, especially in areas including but not limited to data security and privacy, interoperability standards, usability, accessibility, funding, capacity building, and monitoring and evaluation of the regulatory process.
- Manage and sustain the engagement, involvement, and participation of all relevant stakeholders in the regulatory process by conducting a robust stakeholder analysis and adopting an all-inclusive stakeholder engagement strategy.
Strengths and Limitations of the Study
This study has several strengths, which include an extensive search of gray literature and repositories, contact with key individuals, and the use of a systematic approach. Given that regulatory standards and guidance are unavailable in scientific databases, a wide range of gray literature and repositories were searched. In addition, contact was made with key staff members to obtain relevant documents, including those at the MOHs, the WHO country offices, and the WHO AFRO. Second, to enhance the strength of the study, a policy analysis framework was adapted and used to systematically organize the key study findings, whereas a deductive descriptive qualitative content analysis approach was used to identify and analyze texts that contained relevant concepts and other related information based on the 4 predefined themes. Third, the RISA tool was used to guide the mapping of key stakeholders. This has further increased the robustness of the study findings.
The limitations of this study include the fact that our literature search was conducted in English. Although the literature search was conducted in English, it yielded documents written in French and Portuguese from the ICTworks repository. Second, regulatory standards and guidance are not readily available on scientific databases; hence, it is possible that some relevant documents might have been missed. However, efforts were made to obtain these documents by contacting key stakeholders including key contact persons at the WHO AFRO, WHO country offices, and MOHs. In addition, contacting key individuals only for the purposes of requesting documents rather than conducting direct interviews was one of the limitations of this study. Interviewing key contact persons and stakeholders to obtain additional information could have strengthened the review; however, we did not interview any key individuals or stakeholders because it was beyond the scope of this review. Nonetheless, we recommend that future studies consider incorporating interviews to explore the perspectives of key stakeholders.
Conclusions
Health apps are increasingly being used by patients to manage their health, and sub-Saharan African countries can leverage these apps to advance their progress toward achieving SDG 3 (good health and well-being) and UHC, especially given the rapid advancement of AI and big data. However, our study has established that the regulation of health apps in sub-Saharan Africa is inadequate to ensure that health apps are technically reliable and clinically safe; interoperable across systems; compliant with the principles of confidentiality of information and data privacy; culturally appropriate and relevant; and accessible to everyone regardless of gender, ethnicity, location, or income. Therefore, the region can learn from the experiences of some high-income countries such as the United Kingdom and Germany to develop and implement a robust and responsive regulatory system that supports the widespread adoption of safe, effective, and beneficial health apps for its population.
Following the publication of this review, a summary of the findings will be disseminated to the relevant organizations. In addition, the key findings will be summarized and presented at national, regional, and international conferences.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Rebecca Jones, the Library Manager and Liaison Librarian at Charing Cross Library, who advised and assisted with the search strategy for this study. This work is part of the PhD research of BAB, which is sponsored by the government of Nigeria. AM and JC were supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Applied Research Collaboration Northwest London (NIHR200180). The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the government of Nigeria or the NIHR or the Department of Health and Social Care. In the Results and Discussion sections, Microsoft Copilot in Bing [ 159 ] was used to help summarize and modify a few texts as well as suggest some citations.
Data Availability
The search strategy for PubMed, Scopus, and the World Health Organization AIM is presented in Multimedia Appendix 1 . All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files). The documents analyzed are available directly from the relevant institutional websites, ICTworks repository [ 44 ] or upon request from the relevant government departments in each country. Additionally, documents in the list of references that are not accessible on the web can be solicited from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' Contributions
BAB and JC conceived the study. BAB designed the study with contributions from JC and NM. BAB drafted the manuscript, and JC, NM, AM, SI, KPF, BIH, and NU read and contributed to it. AM was the clinical lead, and JC acted as a guarantor for this study. The final manuscript was read and approved by all the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
PRISMA-ScR (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews) checklist.
Database search strategy.
Details of included documents.
Mapping of the stakeholders according to their potential role in regulating health apps for self-management.
- Aitken M, Nass D. Digital health trends 2021: innovation, evidence, regulation, and adoption. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. 2021. URL: https://www.iqvia.com/-/media/iqvia/pdfs/institute-reports/digital-health-trends-2021/iqvia-institute-digital-health-trends-2021.pdf?&_=1669449368070 [accessed 2022-11-26]
- Mobile app threat landscape report. RiskIQ. 2020. URL: https://www.riskiq.com/2020-mobile-threat-landscape-report-thank-you/ [accessed 2021-07-19]
- El-Sappagh S, Ali F, Hendawi A, Jang JH, Kwak KS. A mobile health monitoring-and-treatment system based on integration of the SSN sensor ontology and the HL7 FHIR standard. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. May 10, 2019;19(1):97. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Labrique AB, Vasudevan L, Kochi E, Fabricant R, Mehl G. mHealth innovations as health system strengthening tools: 12 common applications and a visual framework. Glob Health Sci Pract. Aug 06, 2013;1(2):160-171. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Adepoju IOO, Albersen BJA, De Brouwere V, van Roosmalen J, Zweekhorst M. mHealth for clinical decision-making in sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. Mar 23, 2017;5(3):e38. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Vegesna A, Tran M, Angelaccio M, Arcona S. Remote patient monitoring via non-invasive digital technologies: a systematic review. Telemed J E Health. Jan 2017;23(1):3-17. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Use of appropriate digital technologies for public health: Report by the Director-General. World Health Organization. 2016. URL: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/274134 [accessed 2023-05-06]
- El-Osta A, Rowe C, Majeed A. Developing a shared definition of self-driven healthcare to enhance the current healthcare delivery paradigm. J R Soc Med. Nov 2022;115(11):424-428. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hussein R. A review of realizing the universal health coverage (UHC) goals by 2030: part 2- what is the role of eHealth and technology? J Med Syst. Jul 2015;39(7):72. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sustainable development goal 3: Ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages. United Nations. URL: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal3 [accessed 2023-05-07]
- Coronavirus: apps to help the elderly. Organisation for the Review of Care and Health Apps. 2020. URL: https://orchahealth.com/coronavirus-apps-to-help-the-elderly/ [accessed 2021-07-19]
- Huckvale K, Adomaviciute S, Prieto JT, Leow MKS, Car J. Smartphone apps for calculating insulin dose: a systematic assessment. BMC Med. May 06, 2015;13:106. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Huckvale K, Car M, Morrison C, Car J. Apps for asthma self-management: a systematic assessment of content and tools. BMC Med. Nov 22, 2012;10:144. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Huckvale K, Morrison C, Ouyang J, Ghaghda A, Car J. The evolution of mobile apps for asthma: an updated systematic assessment of content and tools. BMC Med. Mar 23, 2015;13:58. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Huckvale K, Prieto JT, Tilney M, Benghozi PJ, Car J. Unaddressed privacy risks in accredited health and wellness apps: a cross-sectional systematic assessment. BMC Med. Sep 07, 2015;13:214. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Huckvale K, Torous J, Larsen ME. Assessment of the data sharing and privacy practices of smartphone apps for depression and smoking cessation. JAMA Netw Open. Apr 05, 2019;2(4):e192542. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ndlovu K, Mars M, Scott RE. Interoperability frameworks linking mHealth applications to electronic record systems. BMC Health Serv Res. May 13, 2021;21(1):459. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kenya standards and guidelines for mHealth systems. Kenya Ministry of Health. 2017. URL: https://www.health.go.ke/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Revised-Guidelines-For-Mhealth-Systems-May-Version.pdf [accessed 2023-03-21]
- Standard for electronic health record system (EHRs) in Ethiopia. Ethiopia Minister of Health. 2021. URL: https://registry.betterehealth.eu/ehealth-policies/standard-electronic-health-record-system-ehrs-ethiopia [accessed 2023-04-21]
- National health normative standards framework for digital health interoperability in South Africa. South Africa Department of Health. 2021. URL: https://www.health.gov.za/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/HNSF_Gazette_21_October_2022.pdf [accessed 2023-05-15]
- Ferretti A, Ronchi E, Vayena E. From principles to practice: benchmarking government guidance on health apps. Lancet Digit Health. Jun 2019;1(2):e55-e57. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Diao JA, Venkatesh KP, Raza MM, Kvedar JC. Multinational landscape of health app policy: toward regulatory consensus on digital health. NPJ Digit Med. May 11, 2022;5(1):61. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Essén A, Stern AD, Haase CB, Car J, Greaves F, Paparova D, et al. Health app policy: international comparison of nine countries' approaches. NPJ Digit Med. Mar 18, 2022;5(1):31. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Brown SA, Garcia AA, Kouzekanani K, Hanis CL. Culturally competent diabetes self-management education for Mexican Americans: the Starr County border health initiative. Diabetes Care. Feb 2002;25(2):259-268. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chaney SC, Mechael P. Self-Care Trailblazer Group. 2020. URL: https://media.psi.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/31000510/Digital-Self-Care-Final.pdf [accessed 2021-05-20]
- Kanzaveli T. Healthcare: shiftingfrom “one size fits all” to “one size fits one”. Medium. 2017. URL: https://tkanzaveli.medium.com/healthcare-shifting-from-one-size-fits-all-to-one-size-fits-one-d56136ded705 [accessed 2022-03-04]
- Myth 1 – one app will fit all!. Organisation for the Review of Care and Health Apps. URL: https://orchahealth.com/myth-1-one-app-will-fit-all/ [accessed 2022-03-04]
- Aitken M, Lyle J. Patient adoption of mHealth: use, evidence and remaining barriers to mainstream acceptance. IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science. Sep 2015. URL: https://www.iqvia.com/-/media/iqvia/pdfs/institute-reports/patient-adoption-of-mhealth.pdf [accessed 2021-05-21]
- Mechael P, Batavia H, Kaonga N. Barriers and gaps affecting mhealth in low and middle income countries: policy white paper. Center for Global Health and Economic Development Earth Institute, Columbia University. 2010. URL: http://www.globalproblems-globalsolutions-files.org/pdfs/mHealth_Barriers_White_Paper.pdf [accessed 2021-03-24]
- Bene BA, Ibeneme S, Fadahunsi KP, Harri BI, Ukor N, Mastellos N, et al. Regulatory standards and guidance for the use of health applications for self-management in Africa: scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. Feb 11, 2022;12(2):e058067. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Aitken M, Gauntlett C. Patient apps for improved healthcare: from novelty to mainstream. IMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics. 2013. URL: https://ignacioriesgo.es/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/iihi_patient_apps_report_editora_39_2_1.pdf [accessed 2024-03-10]
- National eHealth Strategy Toolkit. World Health Organization, International Telecommunication Union. 2012. URL: https://www.itu.int/pub/D-STR-E_HEALTH.05-2012 [accessed 2021-06-28]
- Global strategy on digital health 2020-2025. World Health Organization. 2021. URL: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/documents/gs4dhdaa2a9f352b0445bafbc79ca799dce4d.pdf [accessed 2021-06-23]
- Arksey H, O'Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. Feb 2005;8(1):19-32. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Anderson S, Allen P, Peckham S, Goodwin N. Asking the right questions: scoping studies in the commissioning of research on the organisation and delivery of health services. Health Res Policy Syst. Jul 09, 2008;6:7. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Levac D, Colquhoun H, O'Brien KK. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implement Sci. Sep 20, 2010;5:69. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, et al. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. Oct 2020;18(10):2119-2126. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O'Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. Oct 02, 2018;169(7):467-473. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Leitner C, Potenziani D. Mendeley reference manager. Mendeley. 2022. URL: https://www.mendeley.com/reference-management/reference-manager [accessed 2022-08-03]
- Better systematic review management. Covidence. URL: https://www.covidence.org/ [accessed 2023-02-13]
- Franco-Trigo L, Fernandez-Llimos F, Martínez-Martínez F, Benrimoj SI, Sabater-Hernández D. Stakeholder analysis in health innovation planning processes: A systematic scoping review. Health Policy. Oct 2020;124(10):1083-1099. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Walt G, Gilson L. Reforming the health sector in developing countries: the central role of policy analysis. Health Policy Plan. Dec 1994;9(4):353-370. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Digital health: a call for government leadership and cooperation between ICT and health. Broadband Commission. 2017. URL: https://broadbandcommission.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/WGHealth_Report2017-.pdf [accessed 2021-06-28]
- Vota W. Every African country’s national eHealth strategy or digital health policy. ICT works. 2019. URL: https://www.ictworks.org/african-national-ehealth-strategy-policy/ [accessed 2023-12-10]
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. Jul 21, 2009;6(7):e1000097. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Standards and guidelines for electronic medical record systems in Kenya. Kenya Ministry of Medical Services, Kenya Ministry of Public Health and Sanitation. 2010. URL: http://guidelines.health.go.ke:8000/media/Standards_and_Guidelines_for_EMR_Systems.pdf [accessed 2023-04-21]
- Kenya standards and guidelines for E-health systems interoperability. Kenya Ministry of Health, AfyaInfo Project. 2014. URL: https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PA00TB2K.pdf [accessed 2023-03-21]
- Health sector ICT standards and guidelines. Kenya Ministry of Health. 2013. URL: https://www.medbox.org/pdf/5e148832db60a2044c2d2895 [accessed 2023-03-21]
- Health information exchange standard operating procedure (SOP) and guideline. Nigeria Federal Ministry of Health. Jul 2020.
- National eHealth strategy 2018-2022. Benin Ministry of Health. 2017.
- The eHealth strategy of botswana 2020-2024. Botswana Ministry of Health. URL: https://ehealth.ub.bw/bhdc/Docs/MOH%20ehealth%20Strategy%20Book%20A4.pdf [accessed 2023-04-22]
- Health sector digital strategy 2016-2020. Burkina Faso Ministry of Health.
- National health informatics development plan of Burundi. Burundi Ministry of Public Health. 2015.
- The 2020-2024 national digital health strategic plan. Cameroon Ministry of Public Health. 2020.
- National eHealth strategy 2017-2021. Comoros Ministry of Health. 2016.
- eHealth strategic plan. Cote d’Ivoire Minister of Health and Public Hygiene. 2011.
- National development plan for health informatics. Democratic Republic of Congo Ministry of Public Health. 2014.
- Kingdom of Swaziland eHealth strategy 2016 - 2020. Kingdom of Swaziland Ministry Of Health. 2016.
- Information revolution strategic plan (2018-2025). Ethiopia Ministry of Health. 2018.
- Strategic master plan of the health information system of the Gabon. Gabon Ministry of Public Health and Population. 2017.
- National e-Health strategy. Ghana Ministry of Health. 2010.
- Kenya national e-Health strategy. Kenya Ministry of Medical Services, Kenya Ministry of Public Health & Sanitation. 2011.
- Kenya national eHealth policy 2016-2030. Kenya Ministry of Health. 2016.
- National strategy - Liberia - 2016-2021. Liberia Ministry of Health. 2016.
- Strategic plan for strengthening the health information system of Madagascar 2018–2022. Madagascar Ministry of Public Health. 2017.
- National digital health strategy 2020-2025. Malawi Ministry of Health. 2020.
- National eHealth policy in Mali. Mali Ministry of Health and Public Hygiene. 2013.
- Health 2015: seamless continuity of care. Mauritius Ministry of Health and Quality of Life. 2015.
- Strategic plan of information system for health 2009-2014. Mozambique Ministry of Health. 2009.
- National eHealth strategy 2019-2023. Niger Ministry of Public Health. 2018.
- National digital health strategy 2021-2025. Nigeria Federal Ministry of Health. 2021.
- National digital health policy. Nigeria Federal Ministry of Health. 2021.
- National digital health strategic plan 2018-2023. Rwanda Ministry of Health. 2018. URL: https://elearning.helinanet.org/mod/resource/view.php?id=890 [accessed 2023-05-09]
- Strategic plan for digital health 2018-2023. Senegal Ministry of Health and Social Action. 2018.
- National digital health strategy 2018-2023. Sierra Leone Ministry of Health and Sanitation, Sierra Leone Ministry of Information and Communication. 2018.
- The national digital health strategy 2019 – 2024. Tanzania Ministry of Health, Community Development, Gender, Elderly and Children. 2019.
- National digital health strategy for South Africa 2019 - 2024. South Africa Department of Health. 2019.
- Strategic plan for the development of eHealth in Togo 2013-2015. Togo Ministry of Health. 2012.
- Uganda national eHealth policy. Uganda Ministry of Health. 2016.
- Uganda national eHealth strategy 2017 - 2021. Uganda Ministry of Health. URL: https://health.go.ug/sites/default/files/National%20e_Health%20Strategy_0.pdf [accessed 2023-05-16]
- National eHealth strategy 2017-2021. Zambia Ministry of Health. 2017.
- Zimbabwe’s E-Health strategy 2012-2017. Ministry of Health and Child Welfare. 2012.
- National eHealth strategy 2021-2025. Namibia Ministry of Health & Social Services. 2021. URL: https://www.scribd.com/document/639371316/eHealth-Strategy-Namibia-2021# [accessed 2023-05-13]
- Health sector ICT policy and strategy. Ghana Ministry of Health. 2005. URL: https://www.moh.gov.gh/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Health-Sector-ICT-Policy-and-Strategy.pdf [accessed 2023-05-08]
- Adebola OJ. Beyond national digital health strategy: final report of end term evaluation for the National Health ICT Strategic Framework 2015-2020. Nigeria Federal Ministry of Health. May 2021.
- National Health ICT Strategic Framework 2015 - 2020. Nigeria Federal Ministry of Health. 2016. URL: https://www.health.gov.ng/doc/HealthICTStrategicFramework.pdf [accessed 2023-05-16]
- Digital health blueprint. Ethiopia Ministry of Health. 2021. URL: http://repository.iifphc.org/bitstream/handle/123456789/1658/Ethiopian-Digital-Health-Blueprint.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y [accessed 2023-05-16]
- Kenya health information systems interoperability framework. Kenya Ministry of Health. 2020. URL: https://www.data4sdgs.org/sites/default/files/services_files/Kenya%20Health%20Information%20Systems%20Interoperability%20Framework.pdf [accessed 2023-05-16]
- National community health digitization strategy 2020-2025. Kenya Ministry of Health, Division of Community Health Services. 2021. URL: https://www.eahealth.org/sites/www.eahealth.org/files/content/attachments/2021-08-02/eCHIS-Strategy-2020-2025.pdf [accessed 2023-05-16]
- Leitner C, Potenziani D. Health information systems interoperability in Liberia. IntraHealth International. 2016. URL: https://elearning.helinanet.org/mod/resource/view.php?id=938 [accessed 2023-05-16]
- Narrative for 2022 national digital health annual operational plan (AOP). Nigeria Federal Ministry of Health. 2022.
- Tanzania digital health investment road map 2017-2023. Tanzania Ministry of Health, Community Development, Gender, Elderly and Children, President’s Office Regional Administration and Local Government. 2017.
- Yu H. Regulation of digital health technologies in the European Union: intended versus actual use. In: Cohen GI, Minssen T, Price II NW, Robertson C, Shachar C, editors. The Future of Medical Device Regulation: Innovation and Protection. Cambridge. Cambridge University Press; Mar 31, 2022;103-114.
- Policy for device software functions and mobile medical applications: guidance for industry and Food and Drug Administration staff. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2022. URL: https://www.fda.gov/media/80958/download [accessed 2023-10-10]
- Gordon WJ, Landman A, Zhang H, Bates DW. Beyond validation: getting health apps into clinical practice. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:14. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- FDA clears mobile medical app to help those with opioid use disorder stay in recovery programs. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2018. URL: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-clears-mobile-medical-app-help-those-opioid-use-disorder-stay-recovery-programs [accessed 2021-01-27]
- Digital maturity model: achieving digital maturity to drive growth. Deloitte. 2018. URL: https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/global/Documents/Technology-Media-Telecommunications/deloitte-digital-maturity-model.pdf [accessed 2021-10-20]
- May E. How digital health apps are empowering patients. Deloitte. 2021. URL: https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/blog/health-care-blog/2021/how-digital-health-apps-are-empowering-patients.html [accessed 2023-10-06]
- Guidance: criteria for health app assessment. Public Health England. 2017. URL: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/health-app-assessment-criteria/criteria-for-health-app-assessment [accessed 2023-10-16]
- Clinical risk management standards. National Health Service Digital. 2020. URL: https://digital.nhs.uk/services/clinical-safety/clinical-risk-management-standards [accessed 2023-10-28]
- Report a problem with a medicine or medical device. Gov.uk. URL: https://www.gov.uk/report-problem-medicine-medical-device [accessed 2023-11-07]
- Digital technology assessment criteria for health and social care (DTAC) - Version 1.0. National Health Service X. 2021. URL: https://view.officeapps.live.com/op/view.aspx?src=https%3A%2F%2Ftransform.england.nhs.uk%2Fmedia%2Fdocuments%2FDTAC_version_1.0_FINAL_updated_16.04.odt&wdOrigin=BROWSELINK [accessed 2023-11-07]
- Data protection impact assessment: NHS login - formerly Citizen Identity. National Health Service Digital. 2022. URL: https://digital.nhs.uk/services/nhs-login/data-protection-impact-assessment [accessed 2023-11-07]
- Risks and data protection impact assessments (DPIAs). Information Commissioner’s Office. URL: https://ico.org.uk/for-organisations/uk-gdpr-guidance-and-resources/accountability-and-governance/accountability-framework/risks-and-data-protection-impact-assessments-dpias/ [accessed 2023-11-07]
- A guide to good practice for digital and data-driven health technologies. Department of Health and Social Care. 2021. URL: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/code-of-conduct-for-data-driven-health-and-care-technology/initial-code-of-conduct-for-data-driven-health-and-care-technology [accessed 2023-10-30]
- Interoperability in healthcare. Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS). 2023. URL: https://www.himss.org/resources/interoperability-healthcare [accessed 2023-10-17]
- DAPB4020: UK core Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) release 4 (R4) governance. National Health Service Digital. 2022. URL: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/information-standards/information-standards-and-data-collections-including-extractions/publications-and-notifications/standards-and-collections/dapb4020-uk-core-fhir-r4-governance [accessed 2023-10-17]
- Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR). National Health Service Digital. 2022. URL: https://digital.nhs.uk/services/fhir-apis [accessed 2023-10-17]
- FHIR Interoperability Basics: 4 things to know. Health IT Analytics. 2022. URL: https://healthitanalytics.com/news/4-basics-to-know-about-the-role-of-fhir-in-interoperability [accessed 2023-11-07]
- Giordanengo A, Bradway M, Pedersen R, Grøttland A, Hartvigsen G, Årsand E. Integrating data from apps, wearables and personal electronic health record (pEHR) systems with clinicians’ electronic health records (EHR) systems. Int J Integr Care. Nov 09, 2016;16(5):16. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- A plan for digital health and social care. Department of Health & Social Care. 2022. URL: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/a-plan-for-digital-health-and-social-care/a-plan-for-digital-health-and-social-care [accessed 2022-12-01]
- Ryu B, Kim N, Heo E, Yoo S, Lee K, Hwang H, et al. Impact of an electronic health record-integrated personal health record on patient participation in health care: development and randomized controlled trial of MyHealthKeeper. J Med Internet Res. Dec 07, 2017;19(12):e401. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Winter A, Takabayashi K, Jahn F, Kimura E, Engelbrecht R, Haux R, et al. Quality requirements for electronic health record systems*. A Japanese-German information management perspective. Methods Inf Med. Aug 07, 2017;56(7):e92-e104. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wachter RM. Making IT work: harnessing the power of health information technology to improve care in England. National Advisory Group on Health Information Technology. 2016. URL: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/550866/Wachter_Review_Accessible.pdf [accessed 2021-07-22]
- Framework on integrated people-centred health services (IPCHS). World Health Organisation. 2023. URL: https://www.who.int/teams/integrated-health-services/clinical-services-and-systems/service-organizations-and-integration [accessed 2023-06-05]
- Ibeneme S, Karamagi H, Muneene D, Goswami K, Chisaka N, Okeibunor J. Strengthening health systems using innovative digital health technologies in Africa. Front Digit Health. 2022;4:854339. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ibeneme S, Ukor N, Ongom M, Dasa T, Muneene D, Okeibunor J. Strengthening capacities among digital health leaders for the development and implementation of national digital health programs in Nigeria. BMC Proc. 2020;14(Suppl 10):9. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Delivering safe digital health. Organisation for the Review of Care and Health Apps. URL: https://orchahealth.com/ [accessed 2023-10-22]
- Mamuye AL, Yilma TM, Abdulwahab A, Broomhead S, Zondo P, Kyeng M, et al. Health information exchange policy and standards for digital health systems in Africa: a systematic review. PLOS Digit Health. Oct 2022;1(10):e0000118. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Digital health platform handbook: Building a digital information infrastructure (infostructure) for health. World Health Organization, International Telecommunication Union. 2022. URL: https://www.itu.int/dms_pub/itu-d/opb/str/D-STR-E_HEALTH.10-2020-PDF-E.pdf [accessed 2021-05-22]
- Framework for involving patients in patient safety 2021. National Health Service England. 2021. URL: https://www.england.nhs.uk/patient-safety/framework-for-involving-patients-in-patient-safety/ [accessed 2023-03-23]
- Olesch A. Towards harmonised EU landscape for digital health: summary of the roundtable discussions in selected EIT Health InnoStars countries. EIT Health InnoStars. Jan 2023. URL: https://eithealth.eu/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/EIT_Health_DiGA_report_Jan2023.pdf [accessed 2023-10-10]
- Grieb J, Tschammler D, Färber C, Woitz S. Digital health laws and regulations germany. Global Legal Group. 2023. URL: https://iclg.com/practice-areas/digital-health-laws-and-regulations/germany [accessed 2023-11-03]
- Human regulatory: medical devices. European Medicines Agency. URL: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/overview/medical-devices [accessed 2023-10-12]
- Strengthening the capacity for regulation of medical products in the African region. World Health Organization Regional Office for Africa. 2013. URL: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/94308/AFR_RC63_7.pdf?sequence=1 [accessed 2023-10-17]
- Ncube BM, Dube A, Ward K. Establishment of the African Medicines Agency: progress, challenges and regulatory readiness. J Pharm Policy Pract. Mar 08, 2021;14(1):29. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Post market surveillance system. European Union Medical Device Regulation. 2023. URL: https://eumdr.com/post-market-surveillance-system/ [accessed 2023-10-31]
- Dayal R. Effective post-market surveillance for medical devices: An essential part of medical devices regulation (MDR). Capgemini. 2020. URL: https://www.capgemini.com/insights/expert-perspectives/effective-post-market-surveillance-for-medical-devices-an-essential-part-of-mdr/ [accessed 2023-10-31]
- NHS app library reaches 70 apps in honour of the NHS birthday. Northampton General Hospital NHS Trust. 2018. URL: https://www.northamptongeneral.nhs.uk/News/News-Archive/2018/NHS-App-Library-reaches-70-apps-in-honour-of-the-NHS-birthday.aspx [accessed 2023-09-21]
- Developers invited to add to NHS apps library. National Health Service Digital. 2018. URL: https://digital.nhs.uk/news/2018/developers-invited-to-add-to-nhs-apps-library [accessed 2023-09-22]
- The NHS apps library has closed. National Health Service Digital. 2021. URL: https://digital.nhs.uk/services/nhs-apps-library#:~:text=The%20NHS%20Apps%20Library%20was%20decommissioned%20in%20December%202021.&text=Further%20information%20can%20be%20found%20on%20the%20NHS.UK%20website [accessed 2023-09-22]
- Larsen ME, Huckvale K, Nicholas J, Torous J, Birrell L, Li E, et al. Using science to sell apps: evaluation of mental health app store quality claims. NPJ Digit Med. 2019;2:18. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- About the NHS app. National Health Service. Dec 4, 2023. URL: https://www.nhs.uk/nhs-app/about-the-nhs-app/ [accessed 2023-09-22]
- Scope of registration: regulated activities. Care Quality Commission. 2022. URL: https://www.cqc.org.uk/guidance-providers/scope-registration-regulated-activities [accessed 2023-11-05]
- Distributing great apps into health and care services across the world. Organisation for the Review of Care and Health Apps. 2020. URL: https://orchahealth.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/Health-and-Care-1.pdf [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Our founder, our story and our values: we exist to make digital health healthy. Organisation for the Review of Care and Health Apps. URL: https://orchahealth.com/about-us/ [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Health app library: empower your community with safe access to health apps and digital health products. Organisation for the Review of Care and Health Apps. URL: https://orchahealth.com/our-products/health-app-library/#:~:text=A%20Health%20App%20Library%20is,on%20the%20Health%20App%20Library [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Digital technology assessment criteria (DTAC). National Health Service X. URL: https://www.nhsx.nhs.uk/key-tools-and-info/digital-technology-assessment-criteria-dtac/ [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Evidence standards framework (ESF) for digital health technologies. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. 2023. URL: https://www.nice.org.uk/about/what-we-do/our-programmes/evidence-standards-framework-for-digital-health-technologies [accessed 2023-10-08]
- Tsang L, Kerr-Peterson H. UK NICE updates its evidence standards framework for data-driven digital health technologies. Ropes & Gray. 2022. URL: https://www.ropesgray.com/en/insights/alerts/2022/10/uk-nice-updates-its-evidence-standards-framework-for-data-driven-digital-health-technologies [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Guidance: medical device stand-alone software including apps (including IVDMDs). Medicines and healthcare products regulatory agency. 2023. URL: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1168485/Medical_device_stand-alone_software_including_apps__including_IVDMDs_.pdf [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Digital therapeutics in the United Kingdom. Digital Therapeutics Alliance. 2021. URL: https://dtxalliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/DTA_DTx-Overview_UK.pdf [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Transforming global healthcare by advancing digital therapeutics. Digital Therapeutics Alliance. 2023. URL: https://dtxalliance.org/ [accessed 2023-10-10]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO) digital therapeutic definition. Digital Therapeutic Alliance. Jun 2023. URL: https://dtxalliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/DTA_FS_ISO-Definition.pdf [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Ndomondo-Sigonda M, Miot J, Naidoo S, Dodoo A, Kaale E. Medicines regulation in Africa: current state and opportunities. Pharmaceut Med. 2017;31(6):383-397. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chinele J. East Africa shows solid support for African Medicines Agency treaty. Health Policy Watch. Aug 16, 2023. URL: https://healthpolicy-watch.news/east-africa-shows-solid-support-for-african-medicines-agency-treaty/ [accessed 2023-10-09]
- Treaty for the establishment of the African Medicines Agency 2019. African Union. 2019. URL: https://au.int/sites/default/files/treaties/36892-treaty-0069_-_ama_treaty_e.pdf [accessed 2023-10-17]
- European Medicines Agency: about us. European Medicines Agency. Mar 1, 2023. URL: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/other/about-us-european-medicines-agency-ema_en.pdf [accessed 2023-10-18]
- Bryson JM. What to do when stakeholders matter. Public Adm Rev. Mar 2004;6(1):21-53. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Iyawa G, Herselman M, Botha A. Potential stakeholders and perceived benefits of a digital health innovation ecosystem for the Namibian context. Procedia Computer Science. 2017;121:431-438. [ CrossRef ]
- Ferretti V. From stakeholders analysis to cognitive mapping and multi-attribute value theory: an integrated approach for policy support. European Journal of Operational Research. Sep 2016;253(2):524-541. [ CrossRef ]
- Brugha R, Varvasovszky Z. Stakeholder analysis: a review. Health Policy Plan. Sep 2000;15(3):239-246. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Schmeer K. Guidelines for conducting a stakeholder analysis 1999. Partnerships for Health Reform, Abt Associates. 1999. URL: https://www.ktecop.ca/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/guidelines-stakeholder-analysis-PHR-1999.pdf [accessed 2023-10-17]
- Gilmour J, Beilin R. Stakeholder mapping for effective risk assessment and communication. Australian Centre of Excellence for Risk Analysis, University of Melbourne. Apr 2007. URL: https://cebra.unimelb.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0006/2220990/gilmour0609.pdf [accessed 2023-10-17]
- Quality, service improvement and redesign tools: stakeholder analysis. National Health Service England, National Health Service Improvement. 2022. URL: https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/qsir-stakeholder-analysis.pdf [accessed 2023-10-20]
- Craven MP, Lang AR, Martin JL. Developing mHealth apps with researchers: multi-stakeholder design considerations. Springer; 2014. Presented at: Third International Conference, DUXU 2014, held as a part of HCI International; June 22-27, 2014;15-24; Heraklion, Greece. URL: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07635-5_2 [ CrossRef ]
- How to encourage stakeholder participation. SustaiNet Software International. URL: https://sustainet.com/how-to-encourage-stakeholder-participation/ [accessed 2023-10-20]
- Stakeholder engagement. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. URL: https://www.oecd.org/governance/better-international-rulemaking/compendium/keyprinciples/stakeholderengagement.htm [accessed 2023-10-20]
- Microsoft Copilot in Bing. Microsoft. URL: https://www.bing.com/chat?form=NTPCHB [accessed 2023-03-15]
Abbreviations
Edited by A Mavragani; submitted 19.05.23; peer-reviewed by N O'Brien, A Essén; comments to author 07.09.23; revised version received 08.12.23; accepted 23.02.24; published 11.04.24.
©Benard Ayaka Bene, Sunny Ibeneme, Kayode Philip Fadahunsi, Bala Isa Harri, Nkiruka Ukor, Nikolaos Mastellos, Azeem Majeed, Josip Car. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 11.04.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The cleanly formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX. Download The Research Paper Template. Download Grad Coach's comprehensive research paper template for free. Fully editable - includes detailed instructions and examples.
Fillable Template and Sample Paper; Government Documents and Legal Materials; APA Style 7th ed. Tutorials; Additional APA 7th Resources; Grammarly - your writing assistant ... Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper. APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl << Previous: Block Quotations; Next ...
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Formatting an APA paper. The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial. Set 1 inch page margins. Apply double line spacing. If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines. ... they are different documents. A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic ...
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
The following two sample papers were published in annotated form in the Publication Manual and are reproduced here as PDFs for your ease of use. The annotations draw attention to content and formatting and provide the relevant sections of the Publication Manual (7th ed.) to consult for more information.. Student sample paper with annotations (PDF, 4.95MB)
Body (section 2.11) Align the text to the left with a 1/2-inch left indent on the first line; Double-space; As long as there is no Abstract, at the top of the first page, type the title of the paper, centered, in bold, and in Sentence Case Capitalization; Usually, include sections like these: introduction, literature review or background, discussion, and conclusion -- but the specific ...
Format Font to Times New Roman, Size 12. Alt+A to select all font, Ctrl+D to open font dialog box, type Times, tab twice to get to size box, type 12, then Enter to close box and header. Highlight all text if needed, then on the Home tab, in the Font section, select Times New Roman, size 12.
Do not use a period after your title or after any heading in the paper (e.g., Works Cited). Begin your text on a new, double-spaced line after the title, indenting the first line of the paragraph half an inch from the left margin. Fig. 1. The top of the first page of a research paper.
MLA Sample Paper. This resource contains a sample MLA paper that adheres to the 2016 updates. To download the MLA sample paper, click this link.
Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings.The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing, and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall ...
The title page (or cover page) of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper should contain all the key information about your document. It usually includes: Dissertation or thesis title. Your name. The type of document (e.g., dissertation, research paper) The department and institution. The degree program (e.g., Master of Arts)
To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments. The guidelines for paper format apply to both student assignments and manuscripts being submitted for publication to a journal. If you are using APA Style to create ...
Education. 30 Editable Research Paper Templates (MLA Formats) February 23, 2021 6 Mins Read. A research paper template is a document that contains research questions, variable interpolation, thesis, methodology, and results evaluation. To create an effective research paper, make sure that everything you present comes from reliable sources.
Creating the perfect research paper format can be daunting. But with Google Docs, it's as easy as 1-2-3! Here is a step-by-step guide to formatting your document using all of its features: 1) Begin by opening up an empty Document in Google Docs. 2) To ensure that you are utilizing proper research paper format, use the built in Heading styles ...
Click the "Center" button, and then the "Bold" button. Next, type the paper's title (see Figure 1). Figure 1. Press the enter key, and click the "left align" button. 3. Before setting the first-line indent for the rest of the paper, click the "View" drop-down menu, and make sure "Show ruler" is checked (see Figure 2).
A research paper outline template is a precontrived guideline that helps you create an outline for your paper. It is divided into the necessary sections and paragraphs with enough space for you to fill in the contents of your outline. Simply put, it is a document containing the prerequisite outline format that prevents you from writing your ...
Research Paper Outline Template. Introduction; Attention Grabber: directly relate the hook to your topic, make the hook catch the reader's attention (Can be a surprising statistic, a rhetorical question, an anecdote or a summary of a fact) Background Information: give a brief history of your topic and explain its importance
Search Millions of Research Papers. This fulltext search index includes over 35 million research articles and other scholarly documents preserved in the Internet Archive. The collection spans from digitized copies of eighteenth century journals through the latest Open Access conference proceedings and preprints crawled from the World Wide Web.
Theorem 1.2.1. A homogenous system of linear equations with more unknowns than equations always has infinitely many solutions. The definition of matrix multiplication requires that the number of columns of the first factor A be the same as the number of rows of the second factor B in order to form the product AB.
IEEE provides guidelines for formatting your paper. These guidelines must be followed when you're submitting a manuscript for publication in an IEEE journal. Some of the key guidelines are: Formatting the text as two columns, in Times New Roman, 10 pt. Including a byline, an abstract, and a set of keywords at the start of the research paper.
Unriddle is a cool tool that changes how students and researchers work with documents. It gives you an AI helper for any document you're looking at, making it super quick to find info, sum up tricky topics, and take notes easily. ... SciSpace aims to make finding and understanding research papers a breeze. It's an all-in-one platform where ...
Update paper as part of the CMA's AI Foundation Models: ... Research and statistics. Reports, analysis and official statistics ... Documents Update paper. PDF, 3.15 MB, ...
Background: Health apps are increasingly recognized as crucial tools for enhancing health care delivery. Many countries, particularly those in sub-Saharan Africa, can substantially benefit from using health apps to support self-management and thus help to achieve universal health coverage and the third sustainable development goal. However, most health apps published in app stores are of ...
On Ap ril 11, 2024, the USDA Research, Education, and Economics ( REE) will hold a consultation specific to Tribal data within the federally funded research context. The ir Framing Paper provides additional background and can be found here: Framing Paper: Public Access to USDA -Supported . Research Results and Indigenous Data Sovereignty.