
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 2

Metric-centered and technology-independent architectural views for software comprehension
The maintenance of applications is a crucial activity in the software industry. The high cost of this process is due to the effort invested on software comprehension since, in most of cases, there is no up-to-...
- View Full Text
Back to the future: origins and directions of the “Agile Manifesto” – views of the originators
In 2001, seventeen professionals set up the manifesto for agile software development. They wanted to define values and basic principles for better software development. On top of being brought into focus, the ...
Investigating the effectiveness of peer code review in distributed software development based on objective and subjective data
Code review is a potential means of improving software quality. To be effective, it depends on different factors, and many have been investigated in the literature to identify the scenarios in which it adds qu...
On the benefits and challenges of using kanban in software engineering: a structured synthesis study
Kanban is increasingly being used in diverse software organizations. There is extensive research regarding its benefits and challenges in Software Engineering, reported in both primary and secondary studies. H...
Challenges on applying genetic improvement in JavaScript using a high-performance computer
Genetic Improvement is an area of Search Based Software Engineering that aims to apply evolutionary computing operators to the software source code to improve it according to one or more quality metrics. This ...
Actor’s social complexity: a proposal for managing the iStar model
Complex systems are inherent to modern society, in which individuals, organizations, and computational elements relate with each other to achieve a predefined purpose, which transcends individual goals. In thi...
Investigating measures for applying statistical process control in software organizations
The growing interest in improving software processes has led organizations to aim for high maturity, where statistical process control (SPC) is required. SPC makes it possible to analyze process behavior, pred...
An approach for applying Test-Driven Development (TDD) in the development of randomized algorithms
TDD is a technique traditionally applied in applications with deterministic algorithms, in which the input and the expected result are known. However, the application of TDD with randomized algorithms have bee...
Supporting governance of mobile application developers from mining and analyzing technical questions in stack overflow
There is a need to improve the direct communication between large organizations that maintain mobile platforms (e.g. Apple, Google, and Microsoft) and third-party developers to solve technical questions that e...
Working software over comprehensive documentation – Rationales of agile teams for artefacts usage
Agile software development (ASD) promotes working software over comprehensive documentation. Still, recent research has shown agile teams to use quite a number of artefacts. Whereas some artefacts may be adopt...
Development as a journey: factors supporting the adoption and use of software frameworks
From the point of view of the software framework owner, attracting new and supporting existing application developers is crucial for the long-term success of the framework. This mixed-methods study explores th...
Applying user-centered techniques to analyze and design a mobile application
Techniques that help in understanding and designing user needs are increasingly being used in Software Engineering to improve the acceptance of applications. Among these techniques we can cite personas, scenar...
A measurement model to analyze the effect of agile enterprise architecture on geographically distributed agile development
Efficient and effective communication (active communication) among stakeholders is thought to be central to agile development. However, in geographically distributed agile development (GDAD) environments, it c...
A survey of search-based refactoring for software maintenance
This survey reviews published materials related to the specific area of Search-Based Software Engineering that concerns software maintenance and, in particular, refactoring. The survey aims to give a comprehen...
Guest editorial foreword for the special issue on automated software testing: trends and evidence
Similarity testing for role-based access control systems.
Access control systems demand rigorous verification and validation approaches, otherwise, they can end up with security breaches. Finite state machines based testing has been successfully applied to RBAC syste...
An algorithm for combinatorial interaction testing: definitions and rigorous evaluations
Combinatorial Interaction Testing (CIT) approaches have drawn attention of the software testing community to generate sets of smaller, efficient, and effective test cases where they have been successful in det...
How diverse is your team? Investigating gender and nationality diversity in GitHub teams
Building an effective team of developers is a complex task faced by both software companies and open source communities. The problem of forming a “dream”
Investigating factors that affect the human perception on god class detection: an analysis based on a family of four controlled experiments
Evaluation of design problems in object oriented systems, which we call code smells, is mostly a human-based task. Several studies have investigated the impact of code smells in practice. Studies focusing on h...
On the evaluation of code smells and detection tools
Code smells refer to any symptom in the source code of a program that possibly indicates a deeper problem, hindering software maintenance and evolution. Detection of code smells is challenging for developers a...
On the influence of program constructs on bug localization effectiveness
Software projects often reach hundreds or thousands of files. Therefore, manually searching for code elements that should be changed to fix a failure is a difficult task. Static bug localization techniques pro...
DyeVC: an approach for monitoring and visualizing distributed repositories
Software development using distributed version control systems has become more frequent recently. Such systems bring more flexibility, but also greater complexity to manage and monitor multiple existing reposi...
A genetic algorithm based framework for software effort prediction
Several prediction models have been proposed in the literature using different techniques obtaining different results in different contexts. The need for accurate effort predictions for projects is one of the ...
Elaboration of software requirements documents by means of patterns instantiation
Studies show that problems associated with the requirements specifications are widely recognized for affecting software quality and impacting effectiveness of its development process. The reuse of knowledge ob...
ArchReco: a software tool to assist software design based on context aware recommendations of design patterns
This work describes the design, development and evaluation of a software Prototype, named ArchReco, an educational tool that employs two types of Context-aware Recommendations of Design Patterns, to support us...
On multi-language software development, cross-language links and accompanying tools: a survey of professional software developers
Non-trivial software systems are written using multiple (programming) languages, which are connected by cross-language links. The existence of such links may lead to various problems during software developmen...
SoftCoDeR approach: promoting Software Engineering Academia-Industry partnership using CMD, DSR and ESE
The Academia-Industry partnership has been increasingly encouraged in the software development field. The main focus of the initiatives is driven by the collaborative work where the scientific research work me...
Issues on developing interoperable cloud applications: definitions, concepts, approaches, requirements, characteristics and evaluation models
Among research opportunities in software engineering for cloud computing model, interoperability stands out. We found that the dynamic nature of cloud technologies and the battle for market domination make clo...
Game development software engineering process life cycle: a systematic review
Software game is a kind of application that is used not only for entertainment, but also for serious purposes that can be applicable to different domains such as education, business, and health care. Multidisc...
Correlating automatic static analysis and mutation testing: towards incremental strategies
Traditionally, mutation testing is used as test set generation and/or test evaluation criteria once it is considered a good fault model. This paper uses mutation testing for evaluating an automated static anal...
A multi-objective test data generation approach for mutation testing of feature models
Mutation approaches have been recently applied for feature testing of Software Product Lines (SPLs). The idea is to select products, associated to mutation operators that describe possible faults in the Featur...
An extended global software engineering taxonomy
In Global Software Engineering (GSE), the need for a common terminology and knowledge classification has been identified to facilitate the sharing and combination of knowledge by GSE researchers and practition...
A systematic process for obtaining the behavior of context-sensitive systems
Context-sensitive systems use contextual information in order to adapt to the user’s current needs or requirements failure. Therefore, they need to dynamically adapt their behavior. It is of paramount importan...
Distinguishing extended finite state machine configurations using predicate abstraction
Extended Finite State Machines (EFSMs) provide a powerful model for the derivation of functional tests for software systems and protocols. Many EFSM based testing problems, such as mutation testing, fault diag...
Extending statecharts to model system interactions
Statecharts are diagrams comprised of visual elements that can improve the modeling of reactive system behaviors. They extend conventional state diagrams with the notions of hierarchy, concurrency and communic...
On the relationship of code-anomaly agglomerations and architectural problems
Several projects have been discontinued in the history of the software industry due to the presence of software architecture problems. The identification of such problems in source code is often required in re...
An approach based on feature models and quality criteria for adapting component-based systems
Feature modeling has been widely used in domain engineering for the development and configuration of software product lines. A feature model represents the set of possible products or configurations to apply i...
Patch rejection in Firefox: negative reviews, backouts, and issue reopening
Writing patches to fix bugs or implement new features is an important software development task, as it contributes to raise the quality of a software system. Not all patches are accepted in the first attempt, ...
Investigating probabilistic sampling approaches for large-scale surveys in software engineering
Establishing representative samples for Software Engineering surveys is still considered a challenge. Specialized literature often presents limitations on interpreting surveys’ results, mainly due to the use o...
Characterising the state of the practice in software testing through a TMMi-based process
The software testing phase, despite its importance, is usually compromised by the lack of planning and resources in industry. This can risk the quality of the derived products. The identification of mandatory ...
Self-adaptation by coordination-targeted reconfigurations
A software system is self-adaptive when it is able to dynamically and autonomously respond to changes detected either in its internal components or in its deployment environment. This response is expected to ensu...
Templates for textual use cases of software product lines: results from a systematic mapping study and a controlled experiment
Use case templates can be used to describe functional requirements of a Software Product Line. However, to the best of our knowledge, no efforts have been made to collect and summarize these existing templates...
F3T: a tool to support the F3 approach on the development and reuse of frameworks
Frameworks are used to enhance the quality of applications and the productivity of the development process, since applications may be designed and implemented by reusing framework classes. However, frameworks ...
NextBug: a Bugzilla extension for recommending similar bugs
Due to the characteristics of the maintenance process followed in open source systems, developers are usually overwhelmed with a great amount of bugs. For instance, in 2012, approximately 7,600 bugs/month were...
Assessing the benefits of search-based approaches when designing self-adaptive systems: a controlled experiment
The well-orchestrated use of distilled experience, domain-specific knowledge, and well-informed trade-off decisions is imperative if we are to design effective architectures for complex software-intensive syst...
Revealing influence of model structure and test case profile on the prioritization of test cases in the context of model-based testing
Test case prioritization techniques aim at defining an order of test cases that favor the achievement of a goal during test execution, such as revealing failures as earlier as possible. A number of techniques ...
A metrics suite for JUnit test code: a multiple case study on open source software
The code of JUnit test cases is commonly used to characterize software testing effort. Different metrics have been proposed in literature to measure various perspectives of the size of JUnit test cases. Unfort...
Designing fault-tolerant SOA based on design diversity
Over recent years, software developers have been evaluating the benefits of both Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and software fault tolerance techniques based on design diversity. This is achieved by creat...
Method-level code clone detection through LWH (Light Weight Hybrid) approach
Many researchers have investigated different techniques to automatically detect duplicate code in programs exceeding thousand lines of code. These techniques have limitations in finding either the structural o...
The problem of conceptualization in god class detection: agreement, strategies and decision drivers
The concept of code smells is widespread in Software Engineering. Despite the empirical studies addressing the topic, the set of context-dependent issues that impacts the human perception of what is a code sme...
- Editorial Board
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
software engineering Recently Published Documents
Total documents.
- Latest Documents
- Most Cited Documents
- Contributed Authors
- Related Sources
- Related Keywords
Identifying Non-Technical Skill Gaps in Software Engineering Education: What Experts Expect But Students Don’t Learn
As the importance of non-technical skills in the software engineering industry increases, the skill sets of graduates match less and less with industry expectations. A growing body of research exists that attempts to identify this skill gap. However, only few so far explicitly compare opinions of the industry with what is currently being taught in academia. By aggregating data from three previous works, we identify the three biggest non-technical skill gaps between industry and academia for the field of software engineering: devoting oneself to continuous learning , being creative by approaching a problem from different angles , and thinking in a solution-oriented way by favoring outcome over ego . Eight follow-up interviews were conducted to further explore how the industry perceives these skill gaps, yielding 26 sub-themes grouped into six bigger themes: stimulating continuous learning , stimulating creativity , creative techniques , addressing the gap in education , skill requirements in industry , and the industry selection process . With this work, we hope to inspire educators to give the necessary attention to the uncovered skills, further mitigating the gap between the industry and the academic world.
Opportunities and Challenges in Code Search Tools
Code search is a core software engineering task. Effective code search tools can help developers substantially improve their software development efficiency and effectiveness. In recent years, many code search studies have leveraged different techniques, such as deep learning and information retrieval approaches, to retrieve expected code from a large-scale codebase. However, there is a lack of a comprehensive comparative summary of existing code search approaches. To understand the research trends in existing code search studies, we systematically reviewed 81 relevant studies. We investigated the publication trends of code search studies, analyzed key components, such as codebase, query, and modeling technique used to build code search tools, and classified existing tools into focusing on supporting seven different search tasks. Based on our findings, we identified a set of outstanding challenges in existing studies and a research roadmap for future code search research.

Psychometrics in Behavioral Software Engineering: A Methodological Introduction with Guidelines
A meaningful and deep understanding of the human aspects of software engineering (SE) requires psychological constructs to be considered. Psychology theory can facilitate the systematic and sound development as well as the adoption of instruments (e.g., psychological tests, questionnaires) to assess these constructs. In particular, to ensure high quality, the psychometric properties of instruments need evaluation. In this article, we provide an introduction to psychometric theory for the evaluation of measurement instruments for SE researchers. We present guidelines that enable using existing instruments and developing new ones adequately. We conducted a comprehensive review of the psychology literature framed by the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing. We detail activities used when operationalizing new psychological constructs, such as item pooling, item review, pilot testing, item analysis, factor analysis, statistical property of items, reliability, validity, and fairness in testing and test bias. We provide an openly available example of a psychometric evaluation based on our guideline. We hope to encourage a culture change in SE research towards the adoption of established methods from psychology. To improve the quality of behavioral research in SE, studies focusing on introducing, validating, and then using psychometric instruments need to be more common.
Towards an Anatomy of Software Craftsmanship
Context: The concept of software craftsmanship has early roots in computing, and in 2009, the Manifesto for Software Craftsmanship was formulated as a reaction to how the Agile methods were practiced and taught. But software craftsmanship has seldom been studied from a software engineering perspective. Objective: The objective of this article is to systematize an anatomy of software craftsmanship through literature studies and a longitudinal case study. Method: We performed a snowballing literature review based on an initial set of nine papers, resulting in 18 papers and 11 books. We also performed a case study following seven years of software development of a product for the financial market, eliciting qualitative, and quantitative results. We used thematic coding to synthesize the results into categories. Results: The resulting anatomy is centered around four themes, containing 17 principles and 47 hierarchical practices connected to the principles. We present the identified practices based on the experiences gathered from the case study, triangulating with the literature results. Conclusion: We provide our systematically derived anatomy of software craftsmanship with the goal of inspiring more research into the principles and practices of software craftsmanship and how these relate to other principles within software engineering in general.
On the Reproducibility and Replicability of Deep Learning in Software Engineering
Context: Deep learning (DL) techniques have gained significant popularity among software engineering (SE) researchers in recent years. This is because they can often solve many SE challenges without enormous manual feature engineering effort and complex domain knowledge. Objective: Although many DL studies have reported substantial advantages over other state-of-the-art models on effectiveness, they often ignore two factors: (1) reproducibility —whether the reported experimental results can be obtained by other researchers using authors’ artifacts (i.e., source code and datasets) with the same experimental setup; and (2) replicability —whether the reported experimental result can be obtained by other researchers using their re-implemented artifacts with a different experimental setup. We observed that DL studies commonly overlook these two factors and declare them as minor threats or leave them for future work. This is mainly due to high model complexity with many manually set parameters and the time-consuming optimization process, unlike classical supervised machine learning (ML) methods (e.g., random forest). This study aims to investigate the urgency and importance of reproducibility and replicability for DL studies on SE tasks. Method: In this study, we conducted a literature review on 147 DL studies recently published in 20 SE venues and 20 AI (Artificial Intelligence) venues to investigate these issues. We also re-ran four representative DL models in SE to investigate important factors that may strongly affect the reproducibility and replicability of a study. Results: Our statistics show the urgency of investigating these two factors in SE, where only 10.2% of the studies investigate any research question to show that their models can address at least one issue of replicability and/or reproducibility. More than 62.6% of the studies do not even share high-quality source code or complete data to support the reproducibility of their complex models. Meanwhile, our experimental results show the importance of reproducibility and replicability, where the reported performance of a DL model could not be reproduced for an unstable optimization process. Replicability could be substantially compromised if the model training is not convergent, or if performance is sensitive to the size of vocabulary and testing data. Conclusion: It is urgent for the SE community to provide a long-lasting link to a high-quality reproduction package, enhance DL-based solution stability and convergence, and avoid performance sensitivity on different sampled data.
Predictive Software Engineering: Transform Custom Software Development into Effective Business Solutions
The paper examines the principles of the Predictive Software Engineering (PSE) framework. The authors examine how PSE enables custom software development companies to offer transparent services and products while staying within the intended budget and a guaranteed budget. The paper will cover all 7 principles of PSE: (1) Meaningful Customer Care, (2) Transparent End-to-End Control, (3) Proven Productivity, (4) Efficient Distributed Teams, (5) Disciplined Agile Delivery Process, (6) Measurable Quality Management and Technical Debt Reduction, and (7) Sound Human Development.
Software—A New Open Access Journal on Software Engineering
Software (ISSN: 2674-113X) [...]
Improving bioinformatics software quality through incorporation of software engineering practices
Background Bioinformatics software is developed for collecting, analyzing, integrating, and interpreting life science datasets that are often enormous. Bioinformatics engineers often lack the software engineering skills necessary for developing robust, maintainable, reusable software. This study presents review and discussion of the findings and efforts made to improve the quality of bioinformatics software. Methodology A systematic review was conducted of related literature that identifies core software engineering concepts for improving bioinformatics software development: requirements gathering, documentation, testing, and integration. The findings are presented with the aim of illuminating trends within the research that could lead to viable solutions to the struggles faced by bioinformatics engineers when developing scientific software. Results The findings suggest that bioinformatics engineers could significantly benefit from the incorporation of software engineering principles into their development efforts. This leads to suggestion of both cultural changes within bioinformatics research communities as well as adoption of software engineering disciplines into the formal education of bioinformatics engineers. Open management of scientific bioinformatics development projects can result in improved software quality through collaboration amongst both bioinformatics engineers and software engineers. Conclusions While strides have been made both in identification and solution of issues of particular import to bioinformatics software development, there is still room for improvement in terms of shifts in both the formal education of bioinformatics engineers as well as the culture and approaches of managing scientific bioinformatics research and development efforts.
Inter-team communication in large-scale co-located software engineering: a case study
AbstractLarge-scale software engineering is a collaborative effort where teams need to communicate to develop software products. Managers face the challenge of how to organise work to facilitate necessary communication between teams and individuals. This includes a range of decisions from distributing work over teams located in multiple buildings and sites, through work processes and tools for coordinating work, to softer issues including ensuring well-functioning teams. In this case study, we focus on inter-team communication by considering geographical, cognitive and psychological distances between teams, and factors and strategies that can affect this communication. Data was collected for ten test teams within a large development organisation, in two main phases: (1) measuring cognitive and psychological distance between teams using interactive posters, and (2) five focus group sessions where the obtained distance measurements were discussed. We present ten factors and five strategies, and how these relate to inter-team communication. We see three types of arenas that facilitate inter-team communication, namely physical, virtual and organisational arenas. Our findings can support managers in assessing and improving communication within large development organisations. In addition, the findings can provide insights into factors that may explain the challenges of scaling development organisations, in particular agile organisations that place a large emphasis on direct communication over written documentation.
Aligning Software Engineering and Artificial Intelligence With Transdisciplinary
Study examined AI and SE transdisciplinarity to find ways of aligning them to enable development of AI-SE transdisciplinary theory. Literature review and analysis method was used. The findings are AI and SE transdisciplinarity is tacit with islands within and between them that can be linked to accelerate their transdisciplinary orientation by codification, internally developing and externally borrowing and adapting transdisciplinary theories. Lack of theory has been identified as the major barrier toward towards maturing the two disciplines as engineering disciplines. Creating AI and SE transdisciplinary theory would contribute to maturing AI and SE engineering disciplines. Implications of study are transdisciplinary theory can support mode 2 and 3 AI and SE innovations; provide an alternative for maturing two disciplines as engineering disciplines. Study’s originality it’s first in SE, AI or their intersections.
Export Citation Format
Share document.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Software Engineering
Title: the general index of software engineering papers.
Abstract: We introduce the General Index of Software Engineering Papers, a dataset of fulltext-indexed papers from the most prominent scientific venues in the field of Software Engineering. The dataset includes both complete bibliographic information and indexed ngrams (sequence of contiguous words after removal of stopwords and non-words, for a total of 577 276 382 unique n-grams in this release) with length 1 to 5 for 44 581 papers retrieved from 34 venues over the 1971-2020 period.The dataset serves use cases in the field of meta-research, allowing to introspect the output of software engineering research even when access to papers or scholarly search engines is not possible (e.g., due to contractual reasons). The dataset also contributes to making such analyses reproducible and independently verifiable, as opposed to what happens when they are conducted using 3rd-party and non-open scholarly indexing services.The dataset is available as a portable Postgres database dump and released as open data.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Software Design and Architecture The once and future focus of software engineering
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Can GPT-4 Replicate Empirical Software Engineering Research?
- Jenny Liang ,
- Carmen Badea ,
- Christian Bird ,
- Robert DeLine ,
- Denae Ford ,
- Nicole Forsgren ,
- Tom Zimmermann
| October 2023
Empirical software engineering research on production systems has brought forth a better understanding of the software engineering process for practitioners and researchers alike. However, only a small subset of production systems is studied, limiting the impact of this research. While software engineering practitioners benefit from replicating research on their own data, this poses its own set of challenges, since performing replications requires a deep understanding of research methodologies and subtle nuances in software engineering data. Given that large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, show promise in tackling both software engineering and science-related tasks, these models could help democratize empirical software engineering research. In this paper, we examine LLMs’ abilities to perform replications of empirical software engineering research on new data. We specifically study their ability to surface assumptions made in empirical software engineering research methodologies, as well as their ability to plan and generate code for analysis pipelines on seven empirical software engineering papers. We perform auserstudywith14participants with software engineering research expertise, who evaluate GPT-4-generated assumptions and analysis plans (i.e., a list of module specifications) from the papers. We find that GPT-4 is able to surface correct assumptions, but struggle to generate ones that reflect common knowledge about software engineering data. In a manual analysis of the generated code, we find that the GPT-4-generated code contains the correct high-level logic, given a subset of the methodology. However, the code contains many small implementation-level errors, reflecting a lack of software engineering knowledge. Our findings have implications for leveraging LLMs for software engineering research as well as practitioner data scientists in software teams.
- Follow on Twitter
- Like on Facebook
- Follow on LinkedIn
- Subscribe on Youtube
- Follow on Instagram
- Subscribe to our RSS feed
Share this page:
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit
Understanding peer review of software engineering papers
- Published: 17 July 2021
- Volume 26 , article number 103 , ( 2021 )
Cite this article
- Neil A. Ernst ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5992-2366 1 ,
- Jeffrey C. Carver ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7824-9151 2 ,
- Daniel Mendez ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0619-6027 3 , 4 &
- Marco Torchiano ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5328-368X 5
649 Accesses
6 Citations
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Peer review is a key activity intended to preserve the quality and integrity of scientific publications. However, in practice it is far from perfect.
We aim at understanding how reviewers, including those who have won awards for reviewing, perform their reviews of software engineering papers to identify both what makes a good reviewing approach and what makes a good paper.
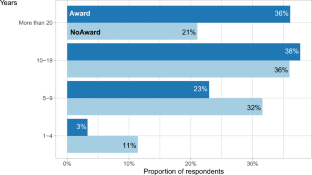
We first conducted a series of interviews with recognised reviewers in the software engineering field. Then, we used the results of those interviews to develop a questionnaire used in an online survey and sent out to reviewers from well-respected venues covering a number of software engineering disciplines, some of whom had won awards for their reviewing efforts.
We analyzed the responses from the interviews and from 175 reviewers who completed the online survey (including both reviewers who had won awards and those who had not). We report on several descriptive results, including: Nearly half of award-winners (45%) are reviewing 20+ conference papers a year, while 28% of non-award winners conduct that many. The majority of reviewers (88%) are taking more than two hours on journal reviews. We also report on qualitative results. Our findings suggest that the most important criteria of a good review is that it should be factual and helpful, which ranked above others such as being detailed or kind. The most important features of papers that result in positive reviews are a clear and supported validation, an interesting problem, and novelty. Conversely, negative reviews tend to result from papers that have a mismatch between the method and the claims and from papers with overly grandiose claims. Further insights include, if not limited to, that reviewers view data availability and its consistency as being important or that authors need to make their contribution of the work very clear in their paper.
Conclusions
Based on the insights we gained through our study, we conclude our work by compiling a proto-guideline for reviewing. One hope we associate with our work is to contribute to the ongoing debate and contemporary effort to further improve our peer review models in the future.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Developers perception of peer code review in research software development
Nasir U. Eisty & Jeffrey C. Carver

Rapid Reviews in Software Engineering

An Empirical Analysis of Newcomers’ Contributions to Software-Engineering Conferences
http://tiny.cc/rosefest
A good tutorial on data disclosure when using a double-blind review process is provided by Daniel Graziotin: https://tinyurl.com/DBDisclose .
See, e.g., artifact evaluation track of ICSE 2021 https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.gshare.14123639 or the open science initiative of the EMSE journal https://github.com/emsejournal/openscience
https://github.com/acmsigsoft/EmpiricalStandards
https://github.com/researchart/patterns/blob/master/standards/artifact.md
http://www.icse-conferences.org/reports.html
https://neuripsconf.medium.com/what-we-learned-from-neurips-2020-reviewing-process-e24549eea38f
https://cs.gmu.edu/~offutt/stvr/17-3-sept2007.html
https://peerj.com/articles/cs-111/reviews/
https://openreview.net/forum?id=rklXaoAcFX¬eId=HyeF-4_9hm
https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.gshare.5086357.v1
https://www.slideshare.net/aserebrenik/peer-reviews-119010210
https://reviewqualitycollector.org
http://www.inf.fu-berlin.de/w/SE/ReviewQualityCollectorHome
http://cscw.acm.org/2019/CSCW-2020-changes.html
https://conf.researchr.org/track/icse-2021/icse-2021-papers#Call-for-Papers
Drubin DG (2011) Any jackass can trash a manuscript, but it takes good scholarship to create one (how MBoC promotes civil and constructive peer review). Mol Biol Cell 22(5):525–527. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e11-01-0002
Article Google Scholar
Fernandes JM (2014) Authorship trends in software engineering. Scientometrics 101(1):257–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1331-6
Horbach SPJM, Halffman W (2018) The ability of different peer review procedures to ag problematic publications. Scientometrics 118(1):339–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-018-2969-2
Kitchenham B, Peeger SL (2002) Principles of survey research: part 1-6. ACM SIGSOFT Softw Eng Notes 27(5):17–20
MacAuley D (2012) The role of the manuscript assessor. In: How to write a paper, chap. 16. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118488713.ch16 . Wiley, pp 102–114
Mathew G, Agrawal A, Menzies T (2019) Finding trends in software research. IEEE Trans Softw Eng :1–1. https://doi.org/10.1109/tse.2018.2870388
Mendez D, Graziotin D, Wagner S, Seibold H (2020) Open science in software engineering. In: Felderer M, Travassos G-H (eds) Contemporary empirical methods in software engineering. arXiv: 1908.05899 . Springer
Nierstrasz O (1998) Identify the champion. Pattern Languages of Programming (PLoP). WUCS-98-25
Ozkaya I (2021) Protecting the health and longevity of the peer-review process in the software engineering community. IEEE Softw 38(1):3–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ms.2020.3028681
Peterson DAM (2020) Dear reviewer 2: Go F’ Yourself. Soc Sci Q. https://doi.org/10.1111/ssqu.12824
Petre M, et al. (2020) Reviewing computing education papers. In: Proceedings of the 2020 ACM conference on innovation and technology in computer science education. https://doi.org/10.1145/3341525.3394994 . ACM
Prechelt L, Graziotin D, Mendez D (2018) A community’s perspective on the status and future of peer review in software engineering. Inf Softw Technol 95:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2017.10.019
Price E (2014) The NIPS Experiment. http://blog.mrtz.org/2014/12/15/thenipsexperiment.html . Online; accessed August 2020
Ragone A, Mirylenka K, Casati F, Marchese M (2013) On peer review in computer science: analysis of its effectiveness and suggestions for improvement. Scientometrics 97(2):317– 356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-013-1002-z
Ralph P, Robbes R (2020) The ACM SIGSOFT paper and peer review quality initiative. ACM SIGSOFT Softw Eng Notes 45(2):17–18. https://doi.org/10.1145/3385678.3385681
Schimel J (2011) Writing science: how to write papers that get cited and proposals that get funded. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Google Scholar
Seeber M, Bacchelli A (2017) Does single blind peer review hinder newcomers?. Scientometrics 113(1):567–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2264-7
Shaw M (2003) Writing good software engineering research papers: minitutorial. In: Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE international conference on software engineering, pp 726–736
Shepperd M, Ajienka N, Counsell S (2018) The role and value of replication in empirical software engineering results. Inf Softw Technol 99:120–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infsof.2018.01.006
Smith AJ (1990) The task of the referee. Computer 23(4):65– 71
Smith E, Loftin R, Murphy-Hill E, Bird C, Zimmermann T (2013) Improving developer participation rates in surveys. In: CHASE workshop at ICSE
Soldani J, Kuhrmann M, Pfahl D (2020) Pains and gains of peer-reviewing in software engineering. ACM SIGSOFT Softw Eng Notes 45(1):12–13. https://doi.org/10.1145/3375572.3375575
Spier R (2002) The history of the peer-review process. Trends Biotechnol 20 (8):357–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-7799(02)01985-6
Squazzoni F, Brezis E, Marušić A (2017) Scientometrics of peer review. Scientometrics 113(1):501–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-017-2518-4.
Storey M-A, Ernst NA, Williams C, Kalliamvakou E (2019) The who, what, how of software engineering research: a socio-technical framework. arXiv: 1905.1284
Tennant JP, et al. (2017) A multi-disciplinary perspective on emergent and future innovations in peer review. In: F1000Research. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.12037.3 , vol 6, p 1151
Terrell J, Kofink A, Middleton J, Rainear C, Murphy-Hill E, Parnin C, Stallings J (2017) Gender differences and bias in open source: pull request acceptance of women versus men. Peer J Comput Sci 3:e111. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.111
Theisen C, Dunaiski M, Williams L, Visser W (2017) Writing good software engineering research papers: revisited. In: Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE international conference on software engineering. https://doi.org/10.1109/icse-c.2017.51
Tomkins A, Zhang M, Heavlin WD (2017) Reviewer bias in single- versus double-blind peer review. Proc Natl Acad Sci 114(48):12708–12713. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1707323114
Tung AKH (2006) Impact of double blind reviewing on SIGMOD publication. ACM SIGMOD Record 35 (3):6–7. https://doi.org/10.1145/1168092.1168093
Winslett M, Braganholo V (2016) H V Jagadish speaks out on PVLDB, CoRR and data-driven research. In: SIGMOD Record 42.2
Wolfram D, Wang P, Hembree A, Park H (2020) Open peer review: promoting transparency in open science. Scientometrics 125(2):1033–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03488-4
Zerbe WJ, Paulhus DL (1987) Socially desirable responding in organizational behavior: a reconception. Acad Manag Rev 12(2):250. https://doi.org/10.2307/258533
Zong Q, Xie Y, Liang J (2020) Does open peer review improve citation count? Evidence from a propensity score matching analysis of PeerJ. Scientometrics 125 (1):607–623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03545-y.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Victoria, Victoria, Canada
Neil A. Ernst
University of Alabama, Tuscaloosa, AL, USA
Jeffrey C. Carver
Blekinge Institute of Technology, Karlskrona, Sweden
Daniel Mendez
fortiss GmbH, Munich, Germany
Politecnico di Torino, Turin, Italy
Marco Torchiano
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Neil A. Ernst .
Additional information
Communicated by: Romain Robbes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ernst, N.A., Carver, J.C., Mendez, D. et al. Understanding peer review of software engineering papers. Empir Software Eng 26 , 103 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-021-10005-5
Download citation
Accepted : 16 June 2021
Published : 17 July 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10664-021-10005-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Peer review
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Publications
- News and Events
- Education and Outreach
Software Engineering Institute
Cite this post.
AMS Citation
Schmidt, D., 2024: The Latest Work from the SEI: an OpenAI Collaboration, Generative AI, and Zero Trust. Carnegie Mellon University, Software Engineering Institute's Insights (blog), Accessed April 9, 2024, https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/blog/the-latest-work-from-the-sei-an-openai-collaboration-generative-ai-and-zero-trust/.
APA Citation
Schmidt, D. (2024, April 9). The Latest Work from the SEI: an OpenAI Collaboration, Generative AI, and Zero Trust. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/blog/the-latest-work-from-the-sei-an-openai-collaboration-generative-ai-and-zero-trust/.
Chicago Citation
Schmidt, Douglas. "The Latest Work from the SEI: an OpenAI Collaboration, Generative AI, and Zero Trust." Carnegie Mellon University, Software Engineering Institute's Insights (blog) . Carnegie Mellon's Software Engineering Institute, April 9, 2024. https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/blog/the-latest-work-from-the-sei-an-openai-collaboration-generative-ai-and-zero-trust/.
IEEE Citation
D. Schmidt, "The Latest Work from the SEI: an OpenAI Collaboration, Generative AI, and Zero Trust," Carnegie Mellon University, Software Engineering Institute's Insights (blog) . Carnegie Mellon's Software Engineering Institute, 9-Apr-2024 [Online]. Available: https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/blog/the-latest-work-from-the-sei-an-openai-collaboration-generative-ai-and-zero-trust/. [Accessed: 9-Apr-2024].
BibTeX Code
@misc{schmidt_2024, author={Schmidt, Douglas}, title={The Latest Work from the SEI: an OpenAI Collaboration, Generative AI, and Zero Trust}, month={Apr}, year={2024}, howpublished={Carnegie Mellon University, Software Engineering Institute's Insights (blog)}, url={https://insights.sei.cmu.edu/blog/the-latest-work-from-the-sei-an-openai-collaboration-generative-ai-and-zero-trust/}, note={Accessed: 2024-Apr-9} }
The Latest Work from the SEI: an OpenAI Collaboration, Generative AI, and Zero Trust

Douglas Schmidt (Vanderbilt University)
April 9, 2024, published in.
Software Engineering Research and Development
As part of an ongoing effort to keep you informed about our latest work, this blog post summarizes some recent publications from the SEI in the areas of large language models for cybersecurity , software engineering and acquisition with generative AI , zero trust , large language models in national security , capability-based planning , supply chain risk management , generative AI in software engineering and acquisition , and quantum computing .
These publications highlight the latest work of SEI technologists in these areas. This post includes a listing of each publication, author(s), and links where they can be accessed on the SEI website.
Considerations for Evaluating Large Language Models for Cybersecurity Tasks by Jeff Gennari, Shing-hon Lau, Samuel J. Perl, Joel Parish (OpenAI), and Girish Sastry (OpenAI)
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) and large language models (LLMs) have taken the world by storm. The ability of LLMs to perform tasks seemingly on par with humans has led to rapid adoption in a variety of different domains, including cybersecurity. However, caution is needed when using LLMs in a cybersecurity context due to the impactful consequences and detailed particularities. Current approaches to LLM evaluation tend to focus on factual knowledge as opposed to applied, practical tasks. But cybersecurity tasks often require more than just factual recall to complete. Human performance on cybersecurity tasks is often assessed in part on their ability to apply concepts to realistic situations and adapt to changing circumstances. This paper contends the same approach is necessary to accurately evaluate the capabilities and risks of using LLMs for cybersecurity tasks. To enable the creation of better evaluations, we identify key criteria to consider when designing LLM cybersecurity assessments. These criteria are further refined into a set of recommendations for how to assess LLM performance on cybersecurity tasks. The recommendations include properly scoping tasks, designing tasks based on real-world cybersecurity phenomena, minimizing spurious results, and ensuring results are not misinterpreted. Read the white paper .
The Future of Software Engineering and Acquisition with Generative AI by Douglas Schmidt (Vanderbilt University), Anita Carleton, James Ivers, Ipek Ozkaya, John E. Robert, and Shen Zhang
We stand at a pivotal moment in software engineering, with artificial intelligence (AI) playing a crucial role in driving approaches poised to enhance software acquisition, analysis, verification, and automation. While generative AI tools initially sparked excitement for their potential to reduce errors, scale changes effortlessly, and drive innovation, concerns have emerged. These concerns encompass security risks, unforeseen failures, and issues of trust. Empirical research on generative AI development assistants reveals that productivity and quality gains depend not only on the sophistication of tools but also on task flow redesign and expert judgment.
In this webcast, SEI researchers explore the future of software engineering and acquisition using generative AI technologies. They examine current applications, envision future possibilities, identify research gaps, and discuss the critical skill sets that software engineers and stakeholders need to effectively and responsibly harness generative AI’s potential. Fostering a deeper understanding of AI’s role in software engineering and acquisition accentuates its potential and mitigates its risks.
The webcast covers
- how to identify suitable use cases when starting out with generative AI technology
- the practical applications of generative AI in software engineering and acquisition
- how developers and decision makers can harness generative AI technology
View the webcast .
Zero Trust Industry Days 2024 Scenario: Secluded Semiconductors, Inc. by Rhonda Brown
Each accepted presenter at the SEI Zero Trust Industry Days 2024 event develops and proposes a solution for this scenario: A company is operating a chip manufacturing facility on an island where there may be loss of connectivity and cloud services for short or extended periods of time. There are many considerations when addressing the challenges of a zero trust implementation, including varying perspectives and philosophies. This event offers a deep examination of how solution providers and other organizations interpret and address the challenges of implementing zero trust. Using a scenario places boundaries on the zero trust space to yield richer discussions.
This year’s event focuses on the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), legacy systems, smart cities, and cloud-hosted services in a manufacturing environment. Read the white paper .
Using Large Language Models in the National Security Realm By Shannon Gallagher
At the request of the White House, the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI) began exploring use cases for large language models (LLMs) within the Intelligence Community (IC). As part of this effort, ODNI sponsored the Mayflower Project at Carnegie Mellon University’s Software Engineering Institute from May 2023 through September 2023. The Mayflower Project attempted to answer the following questions:
- How might the IC set up a baseline, stand-alone LLM?
- How might the IC customize LLMs for specific intelligence use cases?
- How might the IC evaluate the trustworthiness of LLMs across use cases?
In this SEI Podcast, Shannon Gallagher, AI engineering team lead, and Rachel Dzombak, former special advisor to the director of the SEI’s AI Division, discuss the findings and recommendations from the Mayflower Project and provide additional background information about LLMs and how they can be engineered for national security use cases. Listen/View the SEI Podcast .
Navigating Capability-Based Planning: The Benefits, Challenges, and Implementation Essentials By Anandi Hira and William Nichols
Capability-based planning (CBP) defines a framework that has an all-encompassing view of existing abilities and future needs for strategically deciding what is needed and how to effectively achieve it. Both business and government acquisition domains use CBP for financial success or to design a well-balanced defense system. The definitions understandably vary across these domains. This paper endeavors to consolidate these definitions to provide a comprehensive view of CBP, its potential, and practical implementation of its principles. Read the white paper .
Ask Us Anything: Supply Chain Risk Management By Brett Tucker and Matthew J. Butkovic
According to the Verizon Data Breach Report , Log4j-related exploits have occurred less frequently over the past year. However, this Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) flaw was originally documented in 2021. The threat still exists despite increased awareness. Over the past few years, the Software Engineering Institute has developed guidance and practices to help organizations reduce threats to U.S. supply chains. In this webcast, Brett Tucker and Matthew Butkovic, answer enterprise risk management questions to help organizations achieve operational resilience in the cyber supply chain. The webcast covers
- enterprise risk governance and how to assess organization’s risk appetite and policy as it relates to and integrates cyber risks into a global risk portfolio
- regulatory directives on third-party risk
- the agenda and topics to be covered in the upcoming CERT Cyber Supply Chain Risk Management Symposium in February
The Measurement Challenges in Software Assurance and Supply Chain Risk Management by Nancy R. Mead, Carol Woody, and Scott Hissam
In this paper, the authors discuss the metrics needed to predict cybersecurity in open source software and how standards are needed to make it easier to apply these metrics in the supply chain. The authors provide examples of potentially useful metrics and underscore the need for data collection and analysis to validate the metrics. They assert that defining metrics, collecting and analyzing data to illustrate their utility, and using standard methods requires unbiased collaborative work to achieve the desired results. Read the white paper .
The Cybersecurity of Quantum Computing: 6 Areas of Research
By Tom Scanlon
Research and development of quantum computers continues to grow at a rapid pace. The U.S. government alone spent more than $800 million on quantum information science research in 2022. Thomas Scanlon, who leads the data science group in the SEI CERT Division, was recently invited to be a participant in the Workshop on Cybersecurity of Quantum Computing, co-sponsored by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy, to examine the emerging field of cybersecurity for quantum computing. In this SEI podcast, Scanlon discusses how to create the discipline of cyber protection of quantum computing and outlines six areas of future research in quantum cybersecurity.
Listen to/view the podcast .
Additional Resources
View the latest SEI research in the SEI Digital Library . View the latest podcasts in the SEI Podcast Series . View the latest installments in the SEI Webcast Series .

Author Page
Digital library publications, send a message, more by the author, applying large language models to dod software acquisition: an initial experiment, april 1, 2024 • by douglas schmidt (vanderbilt university) , john e. robert, 10 benefits and 10 challenges of applying large language models to dod software acquisition, january 22, 2024 • by john e. robert , douglas schmidt (vanderbilt university), the latest work from the sei, january 15, 2024 • by douglas schmidt (vanderbilt university), the top 10 blog posts of 2023, january 8, 2024 • by douglas schmidt (vanderbilt university), applying generative ai to software engineering: navigating ethical and educational landscapes, december 11, 2023 • by john e. robert , douglas schmidt (vanderbilt university), more in software engineering research and development, applying the sei sbom framework, february 5, 2024 • by carol woody, get updates on our latest work..
Sign up to have the latest post sent to your inbox weekly.
Each week, our researchers write about the latest in software engineering, cybersecurity and artificial intelligence. Sign up to get the latest post sent to your inbox the day it's published.
VideoPoet: A large language model for zero-shot video generation
December 19, 2023
Posted by Dan Kondratyuk and David Ross, Software Engineers, Google Research
A recent wave of video generation models has burst onto the scene, in many cases showcasing stunning picturesque quality. One of the current bottlenecks in video generation is in the ability to produce coherent large motions. In many cases, even the current leading models either generate small motion or, when producing larger motions, exhibit noticeable artifacts.
To explore the application of language models in video generation, we introduce VideoPoet ( website , research paper ), a large language model (LLM) that is capable of a wide variety of video generation tasks, including text-to-video, image-to-video, video stylization, video inpainting and outpainting , and video-to-audio. One notable observation is that the leading video generation models are almost exclusively diffusion-based (for one example, see Imagen Video ). On the other hand, LLMs are widely recognized as the de facto standard due to their exceptional learning capabilities across various modalities, including language, code, and audio (e.g., AudioPaLM ). In contrast to alternative models in this space, our approach seamlessly integrates many video generation capabilities within a single LLM, rather than relying on separately trained components that specialize on each task.
The diagram below illustrates VideoPoet’s capabilities. Input images can be animated to produce motion, and (optionally cropped or masked) video can be edited for inpainting or outpainting. For stylization, the model takes in a video representing the depth and optical flow, which represent the motion, and paints contents on top to produce the text-guided style.
Language models as video generators
One key advantage of using LLMs for training is that one can reuse many of the scalable efficiency improvements that have been introduced in existing LLM training infrastructure. However, LLMs operate on discrete tokens, which can make video generation challenging. Fortunately, there exist video and audio tokenizers, which serve to encode video and audio clips as sequences of discrete tokens (i.e., integer indices), and which can also be converted back into the original representation.
VideoPoet trains an autoregressive language model to learn across video, image, audio, and text modalities through the use of multiple tokenizers ( MAGVIT V2 for video and image and SoundStream for audio). Once the model generates tokens conditioned on some context, these can be converted back into a viewable representation with the tokenizer decoders.
Examples generated by VideoPoet
Some examples generated by our model are shown below.
For text-to-video, video outputs are variable length and can apply a range of motions and styles depending on the text content. To ensure responsible practices, we reference artworks and styles in the public domain e.g., Van Gogh’s “Starry Night”.
For image-to-video, VideoPoet can take the input image and animate it with a prompt.
For video stylization, we predict the optical flow and depth information before feeding into VideoPoet with some additional input text.
VideoPoet is also capable of generating audio. Here we first generate 2-second clips from the model and then try to predict the audio without any text guidance. This enables generation of video and audio from a single model.
By default, the VideoPoet model generates videos in portrait orientation to tailor its output towards short-form content. To showcase its capabilities, we have produced a brief movie composed of many short clips generated by VideoPoet. For the script, we asked Bard to write a short story about a traveling raccoon with a scene-by-scene breakdown and a list of accompanying prompts. We then generated video clips for each prompt, and stitched together all resulting clips to produce the final video below.
When we developed VideoPoet, we noticed some nice properties of the model’s capabilities, which we highlight below.
We are able to generate longer videos simply by conditioning on the last 1 second of video and predicting the next 1 second. By chaining this repeatedly, we show that the model can not only extend the video well but also faithfully preserve the appearance of all objects even over several iterations.
Here are two examples of VideoPoet generating long video from text input:
It is also possible to interactively edit existing video clips generated by VideoPoet. If we supply an input video, we can change the motion of objects to perform different actions. The object manipulation can be centered at the first frame or the middle frames, which allow for a high degree of editing control.
For example, we can randomly generate some clips from the input video and select the desired next clip.
Image to video control
Similarly, we can apply motion to an input image to edit its contents towards the desired state, conditioned on a text prompt.
Camera motion
We can also accurately control camera movements by appending the type of desired camera motion to the text prompt. As an example, we generated an image by our model with the prompt, “Adventure game concept art of a sunrise over a snowy mountain by a crystal clear river” . The examples below append the given text suffix to apply the desired motion.
Evaluation results
We evaluate VideoPoet on text-to-video generation with a variety of benchmarks to compare the results to other approaches. To ensure a neutral evaluation, we ran all models on a wide variation of prompts without cherry-picking examples and asked people to rate their preferences. The figure below highlights the percentage of the time VideoPoet was chosen as the preferred option in green for the following questions.
Text fidelity
Motion interestingness.
Based on the above, on average people selected 24–35% of examples from VideoPoet as following prompts better than a competing model vs. 8–11% for competing models. Raters also preferred 41–54% of examples from VideoPoet for more interesting motion than 11–21% for other models.
Through VideoPoet, we have demonstrated LLMs’ highly-competitive video generation quality across a wide variety of tasks, especially in producing interesting and high quality motions within videos. Our results suggest the promising potential of LLMs in the field of video generation. For future directions, our framework should be able to support “any-to-any” generation, e.g., extending to text-to-audio, audio-to-video, and video captioning should be possible, among many others.
To view more examples in original quality, see the website demo .
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported by a large body of contributors, including Dan Kondratyuk, Lijun Yu, Xiuye Gu, José Lezama, Jonathan Huang, Rachel Hornung, Hartwig Adam, Hassan Akbari, Yair Alon, Vighnesh Birodkar, Yong Cheng, Ming-Chang Chiu, Josh Dillon, Irfan Essa, Agrim Gupta, Meera Hahn, Anja Hauth, David Hendon, Alonso Martinez, David Minnen, David Ross, Grant Schindler, Mikhail Sirotenko, Kihyuk Sohn, Krishna Somandepalli, Huisheng Wang, Jimmy Yan, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Xuan Yang, Bryan Seybold, and Lu Jiang.
We give special thanks to Alex Siegman,Victor Gomes, and Brendan Jou for managing computing resources. We also give thanks to Aren Jansen, Marco Tagliasacchi, Neil Zeghidour, John Hershey for audio tokenization and processing, Angad Singh for storyboarding in “Rookie the Raccoon”, Cordelia Schmid for research discussions, David Salesin, Tomas Izo, and Rahul Sukthankar for their support, and Jay Yagnik as architect of the initial concept.
** (a) The Storm on the Sea of Galilee , by Rembrandt 1633, public domain. (b) Pillars of Creation , by NASA 2014, public domain. (c) Wanderer above the Sea of Fog , by Caspar David Friedrich, 1818, public domain (d) Mona Lisa , by Leonardo Da Vinci, 1503, public domain.
- Generative AI
- Machine Intelligence
- Machine Perception
Other posts of interest

March 29, 2024
- Climate & Sustainability ·

March 28, 2024
- Algorithms & Theory ·
- Machine Intelligence ·
- Open Source Models & Datasets

March 20, 2024
- Health & Bioscience ·
- Human-Computer Interaction and Visualization ·
Explore our brand new website! We hope you like the improvements we've made. We'd love to hear your feedback and please let us know if you find something that requires our attention – Website feedback .
Software Engineering Industry Project
B Trimester
COMPX202 or COMPX242.
Students work in small groups to engineer a prototype for a medium-sized software project. Following established software engineering design principles, they elicit requirements and document specifications, design the system architecture and user interface, carry out documentation preparation, implementation, and plan for maintenance. To this end, the paper introduces design methodologies in Software Engineering Management, such as project initiation, planning and closure, and Software Engineering Methods, such as agile, formal, heuristic and prototyping. Additionally, this paper includes a component on professional interaction skills within the workplace and CV preparation.
Teaching Periods and Locations
If your paper outline is not linked below, try the previous year's version of this paper .
Timetabled lectures and tutorials
Indicative fees.
You will be sent an enrolment agreement which will confirm your fees. Tuition fees shown are indicative only and may change. There are additional fees and charges related to enrolment - please see the Table of Fees and Charges for more information.
Available subjects
Software engineering, computer science, additional information.
Subject regulations
- Paper details current as of 27 Jan 2024 23:44pm
- Indicative fees current as of 8 Apr 2024 01:30am
You’re viewing this website as a domestic student
You’re currently viewing the website as a domestic student, you might want to change to international.
You're a domestic student if you are:
- A citizen of New Zealand or Australia
- A New Zealand permanent resident
You're an International student if you are:
- Intending to study on a student visa
- Not a citizen of New Zealand or Australia

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
They wanted to define values and basic principles for better software development. On top of being brought into focus, the ... Philipp Hohl, Jil Klünder, Arie van Bennekum, Ryan Lockard, James Gifford, Jürgen Münch, Michael Stupperich and Kurt Schneider. Journal of Software Engineering Research and Development 2018 6 :15.
Because the paper is predominantly about evaluating software engineering research, we chose EO. Its research method is LR, 'literature review/analysis.'. As to reference discipline, this paper is most readily categorized into the 'None' or 'Not applicable' category, as were so many of the SE research papers.
Design science is recognized as a pragmatic research paradigm, addressing this and other characteristics of applied and prescriptive research. Applying the design science lens to software ...
For this theme issue on the 50th anniversary of software engineering (SE), Redirections offers an overview of the twists, turns, and numerous redirections seen over the years in the SE research literature. Nearly a dozen topics have dominated the past few decades of SE research—and these have been redirected many times. Some are gaining popularity, whereas others are becoming increasingly ...
End To End . Predictive Software. The paper examines the principles of the Predictive Software Engineering (PSE) framework. The authors examine how PSE enables custom software development companies to offer transparent services and products while staying within the intended budget and a guaranteed budget.
Software Engineering. At Google, we pride ourselves on our ability to develop and launch new products and features at a very fast pace. This is made possible in part by our world-class engineers, but our approach to software development enables us to balance speed and quality, and is integral to our success. Our obsession for speed and scale is ...
Profession and Education. Technical Interests. Need Help? US & Canada:+1 800 678 4333. Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060. Contact & Support. About IEEE Xplore. Contact Us. Help.
The Journal of Systems and Software publishes papers covering all aspects of software engineering. All articles should provide evidence to support their claims, e.g. through empirical studies, simulation, formal proofs or other types of validation. Topics of interest include, but are not limited to:
Journal of Software: Evolution and Process is a computer science and software engineering journal that enables the software community to communicate new ideas for developing, managing and improving software, systems and services. We publish original research, empirical studies, surveys and more covering topics including software testing, continuous improvement of software processes and ...
Skip 1INTRODUCTION Section 1 INTRODUCTION. Software engineering (SE) research investigates questions pertaining to the design, development, maintenance, testing, and evolution of software systems. As software continues to pervade a wide range of industries, both open- and closed-source code repositories have grown to become unprecedentedly large and complex.
To investigate the state of sampling in software engineering, we conduct a critical review. For the purposes of this paper, a critical review is similar to a systematic review, except for two key differences: . 1. A systematic review typically aggregates evidence regarding causal relationships to generate evidence-based recommendations, whereas a critical review critically evaluates issues.
Software engineering is a socio-technical endeavor, and while many of our contributions focus on technical aspects, human stakeholders such as software developers are directly affected by and can benefit from our research and tool innovations. In this paper, we question how much of our research addresses human and social issues, and explore how much we study human and social aspects in our ...
An analysis of the most cited papers in software engineering journals-2002 • The top cited paper is "Preliminary guidelines for empirical research in software engineering" with 64 citations. [25] 2008: An analysis of research topics in software engineering-2006 • The paper examines all the 691 papers published in a selected list of ...
Software engineering (SE) research should be relevant to industrial practice. There have been regular discussions in the SE community on this issue since the 1980's, led by pioneers such as Robert Glass. As we recently passed the milestone of "50 years of software engineering", some recent positive efforts have been made in this direction, e.g., establishing "industrial" tracks in ...
This paper provides guidelines and advice on how to design mixed and multi method research, and to encourage the intentional, rigourous, and innovative use of mixed methods in software engineering. It also presents key characteristics of core mixed method research designs. Through a number of fictitious but recognizable software engineering ...
We introduce the General Index of Software Engineering Papers, a dataset of fulltext-indexed papers from the most prominent scientific venues in the field of Software Engineering. The dataset includes both complete bibliographic information and indexed ngrams (sequence of contiguous words after removal of stopwords and non-words, for a total of 577 276 382 unique n-grams in this release) with ...
In software engineering, research papers are customary vehicles for reporting results to the research community. In a research paper, the author explains to an interested reader what he or she accomplished, and how the author accomplished it, and why the reader should care. A good research paper should answer a number of questions:
ABSTRACT. Software engineering is dynamic disciplines that have continuous growth in research in identifying. new methods, tools and methodologies that have cause vast improvement in software ...
In this new column Trending Topics in Software Engineering, we aim at providing insights, reports, and outlooks on how researchers and practitioners around the world are working (or planning to work) on those trends. We intend to collect the challenges they are facing or foresee, and explore them in future issues.
The design of software has been a focus of software engineering research since the field's beginning. This paper explores key aspects of this research focus and shows why design will remain a principal focus. The intrinsic elements of software design, both process and product, are discussed: concept formation, use of experience, and means for representation, reasoning, and directing the design ...
While the report is published in 2023, the paper reflects the work at the time of writing. Publication Project. ColDeco: An End User Spreadsheet Inspection Tool for AI-Generated Code ... Appendix to The Health of Software Engineering Research David Lo, Tom Zimmermann, Nachi Nagappan MSR-TR-2014-119 | September 2014 ...
5) Software Testing. 6) Software Measurement. 7) Software Product Lines. 8) Software Architecture. 9) software verification. 10) software business. 11) Software Refactoring. 12) software design ...
Empirical software engineering research on production systems has brought forth a better understanding of the software engineering process for practitioners and researchers alike. However, only a small subset of production systems is studied, limiting the impact of this research. While software engineering practitioners benefit from replicating research on their own data, this poses its own […]
This paper summarizes the challenges that the Software Engineering for Services and Applications (SE4SA) cluster is considering as relevant. © 2016 The Authors. ... coding patterns, requirements, user behaviours, user profiles, etc. Research challenges for software engineering in this direction include novel tools employing techniques of ...
A majority of software engineering research papers are computational data studies (e.g., a study validating new test approaches) (Storey et al. 2019). For these papers, as well as for papers conducting survey research and sampling (such as this one!), the authors are often recommended to provide replication packages (Mendez et al. 2020 ) to ...
COMPX341. Software Engineering is the systematic design, construction, testing and maintenance of software systems. The various processes (and engineering specialisations) comprising the methods of Software Engineering will be presented with a specific focus on assuring a high quality of software in requirements, design, construction, testing ...
As part of an ongoing effort to keep you informed about our latest work, this blog post summarizes some recent publications from the SEI in the areas of large language models for cybersecurity, software engineering and acquisition with generative AI, zero trust, large language models in national security, capability-based planning, supply chain risk management, generative AI in software ...
Additional information. This paper continues object-oriented software development in Java introducing design methodologies in software architecture, detailed design, design patterns, software configuration management, and software testing. Project work starts with GUI development and works through to the development of mobile applications.
Posted by Dan Kondratyuk and David Ross, Software Engineers, Google Research. A recent wave of video generation models has burst onto the scene, in many cases showcasing stunning picturesque quality. ... (website, research paper), a large language model (LLM) that is capable of a wide variety of video generation tasks, including text-to-video ...
Research Rangahau. Discover impactful research at New Zealand's top-ranked research university. ... To this end, the paper introduces design methodologies in Software Engineering Management, such as project initiation, planning and closure, and Software Engineering Methods, such as agile, formal, heuristic and prototyping. Additionally, this ...