How-To Geek
Where's the 'task manager' on a mac.
New to Mac and looking for the Task Manager? Apple's equivalent is Activity Monitor---we'll show you where it is and and how to use it.

Quick Links
Terminating stubborn programs with "force quit", troubleshooting with more detail: activity monitor.
If you're a veteran of Windows, you're probably familiar with using Task Manager to deal with applications that freeze or checking memory usage. On a Mac, those tasks fall to a Force Quit dialog or a utility called Activity Monitor , which has shipped with every version of Mac OS X and macOS since 2000. Here's how to use them.
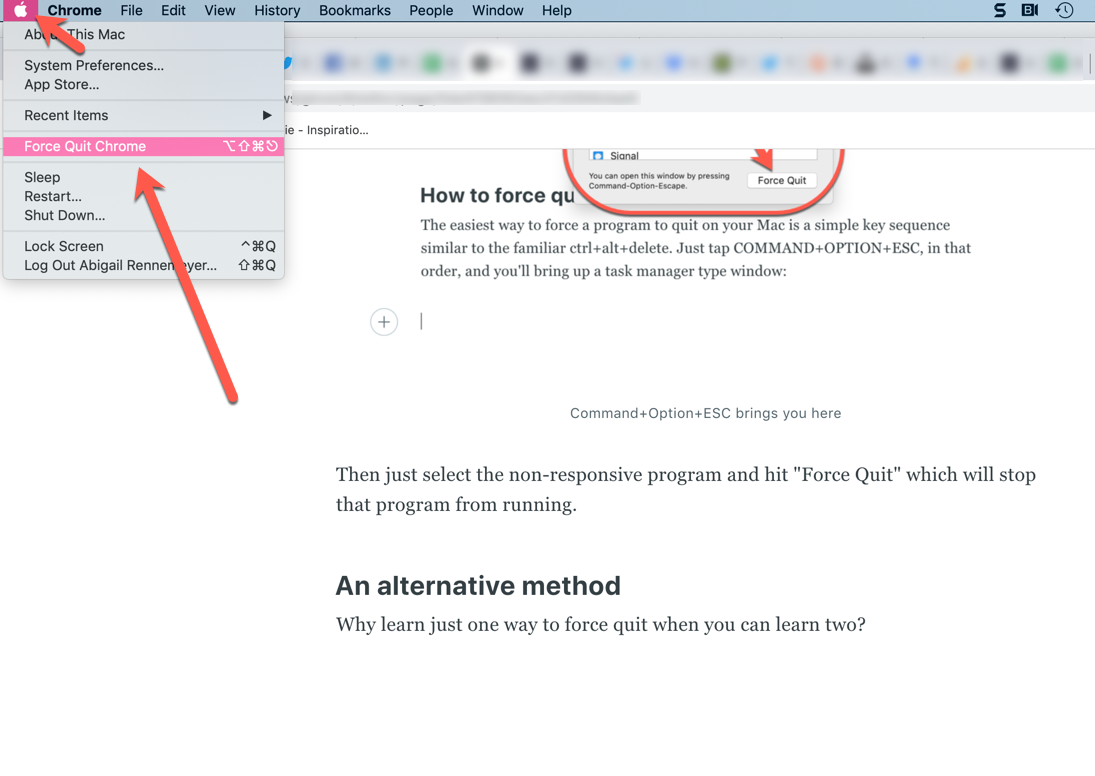
If you're familiar with pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete on a Windows PC to kill a stubborn program, you'll be glad to know that a similar three-finger combo exists on the Mac. When a program becomes unresponsive, simply press Command+Option+Esc to open the "Force Quit Applications" dialog .
A window will pop up that lists currently running apps. To close a stubborn one that refuses to quit normally, select it from the list, and click the "Force Quit" button.
After asking for confirmation, macOS will close the application you selected. Very handy.
Related: How to Control+Alt+Delete on a Mac
If you have a deeper system resource issue to look into on a Mac, such as memory consumption or detailed information on a particular app or process, you'll want to use Activity Monitor. By default, Activity Monitor lives in a folder called "Utilities" within your Applications folder on your Mac.
One of the fastest ways to open Activity Monitor is by using Spotlight. To open "Spotlight," click the small "magnifying glass" icon in your menu bar (or press Command+Space).
When the "Spotlight Search" bar appears, type "activity monitor," and hit "Return." Or you can click the "Activity Monitor.app" icon in the Spotlight results.
Once the "Activity Monitor" window opens, you will see a list of all the processes running on your Mac, similar to this:
Using the five tabs across the top of the window, you can visit displays that show information on running processes sorted by CPU usage ("CPU"), memory usage ("Memory"), energy usage ("Energy"), disk usage ("Disk"), and network usage ("Network"). Click the tab corresponding to the section you'd like to visit.
At any time while listing processes, you can select a process from the list, and click the "Stop" button (which looks like an octagon with an "x" inside it) to force it to quit, or click the "Inspect" button (an "i" in a circle) to see more information about the process.
And if you're overwhelmed by the number of processes listed, you can narrow them down using the "View" menu up in the menu bar. For example, you could select "My Processes," to see only a list of processes associated with your user account.
You can also search for a process using the search bar in the upper-right corner of the window. Just type in the name of the app or process you're looking for, and it will appear in the list (if it is currently running).
Activity Monitor is very handy, so take some time to explore it, and you'll become that much more adept at using it to troubleshoot your Mac . Have fun!
Related: How to Troubleshoot Your Mac With Activity Monitor
- Privacy Policy
- Advertising Disclosure
How To Open And Use Task Manager On A Mac
If you’re looking for the equivalent of Windows Task Manager on Mac, here we show you how to open and use the Task Manager on a Mac including on both Intel and Apple Silicon Macs.
On Windows, pressing Ctrl-Alt-Delete brings up the Task Manager so that you can Force Quit applications and programs that have either crashed or are running slowly.
There are various ways to Force Quit on a Mac the easiest being using the mini equivalent of Task Manager by pressing the Command + Option + Esc keys.
However, the version of Task Manager accessible by the Command + Option + Esc keyboard shortcut doesn’t always shut-down the program that’s locked-up and it doesn’t give you any further information on what’s causing the problem.
The good news is that macOS Activity Monitor gives you far more information on running processes and is the full equivalent of Task Manager on Windows.
Like Windows Task Manager, Activity Monitor also allows you to close files and applications that may be behaving unexpectedly or not functioning properly but also provides far more detailed information on memory usage, CPU usage and other processes running on your Mac.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll show you how to open and use the equivalent of the Windows Task Manager on your Mac or MacBook including on Apple Silicon Macs and the latest version of macOS Sonoma.
You May Also Like:
- Ctrl-Alt-Delete On Mac: How To Force Quit Apps
Quick Navigation
Where Is The Task Manager On a Mac?
How to use the activity monitor task manager, viewing memory usage in the activity monitor, viewing energy usage in activity monitor, checking disk activity in activity monitor, viewing network activity in activity monitor, accessing the task manager through terminal, can’t access the task manager.
The equivalent of Ctrl-Alt-Delete on a Mac is pressing the Command + Option + Esc keys together.

- This instantly brings-up a mini version of the macOS Task Manager showing you a list of applications currently running on your Mac. This “Force Quit Applications” Task Manager window can be used to force programs to close that may be frozen or making your Mac run slow .
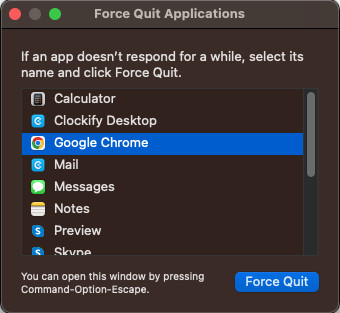
- When the Force Quit Applications window pops up, select the program that needs to be shut down, and click on the Force Quit button.
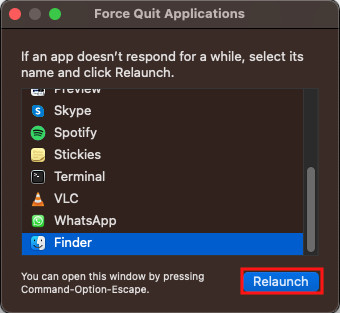
- If Finder doesn’t respond, choose it from the list and click on Relaunch.
The full equivalent of Windows Task Manager on a Mac is Activity Monitor .
Activity Monitor gives detailed information on all running programs and processes in macOS and can be used if the Command + Option + Esc shortcut doesn’t work to force quit a program or application.
You can open the Activity Monitor by doing the following:
- Open Finder , go to Applications , scroll down to Utilities and open it. Click on the Activity Monitor icon. Alternatively, you can press Command + Spacebar and search in Spotlight for “Activity Monitor”.
- You’ll then see detailed information about all the processes and applications running on your Mac. You can see how much of the processor an application is taking-up on your Mac by clicking on CPU to bring up the CPU activity percentages. You will see something like the following:
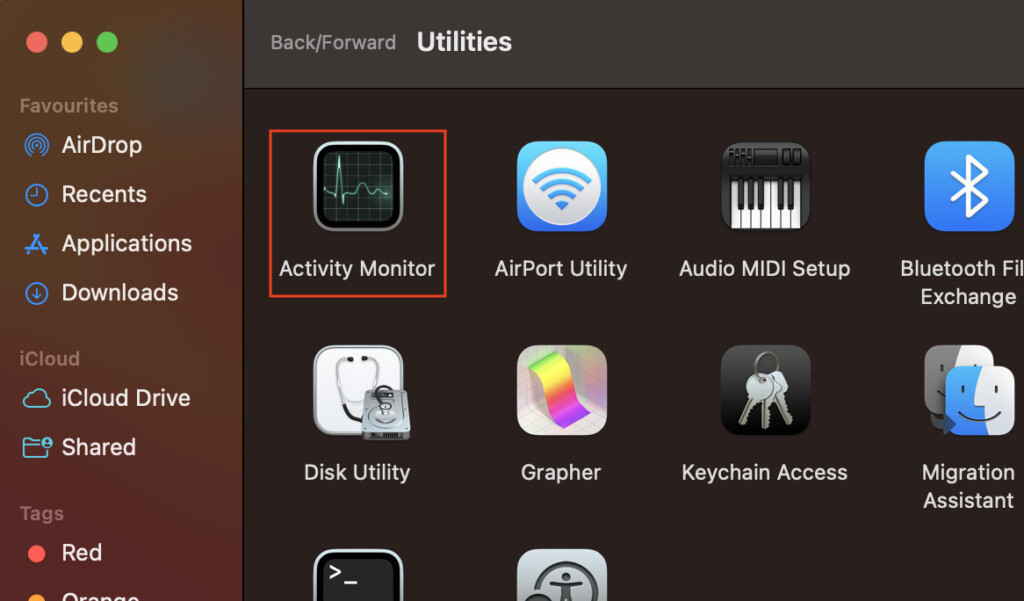
- The System percentage denotes how much of the CPU is being used by macOS processes.
- The User percentage shows how much of the CPU is being used by applications you opened.
- The Idle percentage is the CPU power that isn’t being utilized.
- Click on Window > CPU Usage to view present processor activity.
- Click on Window > CPU History to view recent processor activity.
Activity Monitor also shows how much system memory each application takes-up. You can find out the memory usage of an application, game or program by doing the following:
- Press Command + Space to open Spotlight, type “ Activity Monitor” and press Enter .
- Click on Memory to access the following information:
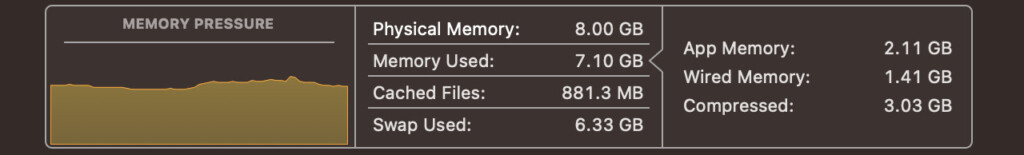
- Memory Pressure: Shows a graphical representation of your Mac’s processing needs being fulfilled by the memory.
- Physical Memory: How much RAM is installed in your Mac.
- Memory Used: The amount of RAM your Mac is utilizing currently. It is divided into App Memory, Wired Memory, and Compressed.
- Cached Files: Shows different cached files and their sizes.
- Swap Used: Shows how much space is allocated on your startup drive to transfer unused files between the RAM and memory.
- Click on View > Columns to display more information about your Mac’s memory usage.
The Activity Monitor also displays energy usage on your Mac, and you can view it in the following way:
- Click on Energy to access the following information:
- Energy Impact: Shows the energy consumption of each app on your Mac.
- 12hr Power: The average energy consumption of each app in the last 12 hours.
- App Nap: Shows whether a particular app has the App Nap feature.
- Graphics Card: Shows whether an app needs a graphics card to run smoothly. This appears if your Mac has multiple graphics cards.
- Preventing Sleep: Shows whether a particular app prevents your Mac from going to Sleep Mode.
- User: Shows which user is running the process.
Here’s how you can check the Disk Activity on your Mac using Activity Monitor:
- Click on Disk to see how much data is read from or written to your disk by each application.
- Click on View > Dock Icon > Show Disk Activity and the Dock icon of the activity monitor will display disk activity in real time.
The Task Manager also displays the network activity of your Mac. You can check it by doing the following:
- Click on Network to see how much data is sent from or received by each application.
- Click on the menu above the graph that shows the network activity, and click on Packets or Data , depending on how you want to view the information.
- If you’d like to view network activity at a glance, you can setup the Dock icon of the activity monitor to present a graph in real time. To set this up, click on View > Dock Icon > Show Network Usage .
An alternate way to monitor or force quit your programs with the Activity Monitor Task Manager on a Mac is through the Terminal by doing the following:
- Click on the Finder icon on your Mac.

- Click on Applications in the left pane.

- Scroll down to Utilities and open it, and then click on the Terminal icon.

- When the Terminal opens, simply type “ top ” and press Enter . The Terminal shows you a list of all running processes and applications.
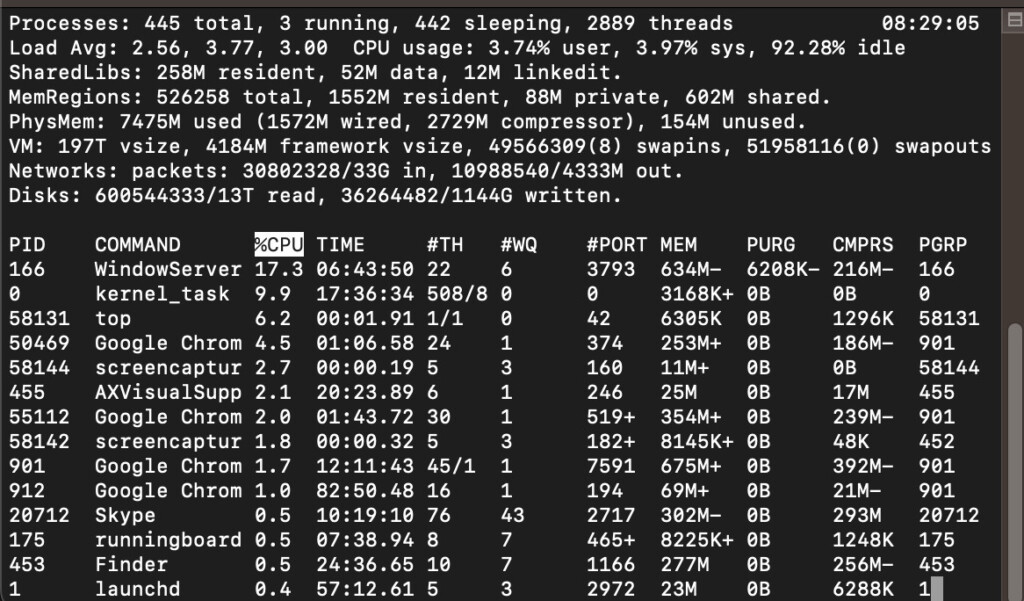
- Check the Process ID (PID) for the application or process you want to terminate in the first column, and then press Q to quit this utility and return to the Terminal.
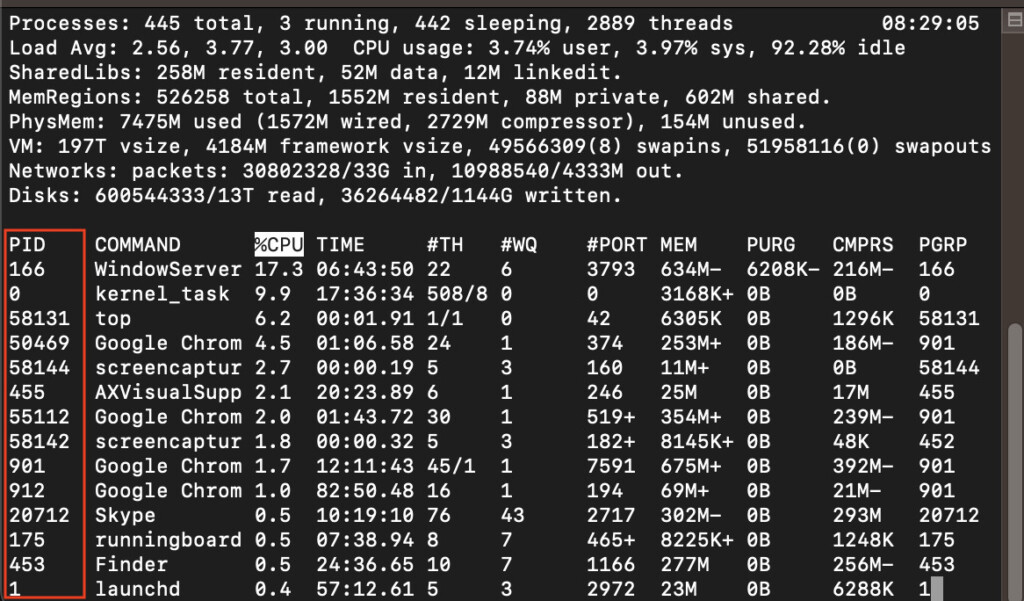
- Type “kill -9 (enter the PID number in these brackets),” entering the actual PID for the application, and press Enter . This will close the application immediately.
One of the main reasons you might not be able to find the Task Manager on a Mac is because you need to search for “Activity Monitor” which is the equivalent of Task Manager on a Mac.
The Task Manager is only a small function of the Activity Monitor that allows you to force quit programs. To access it, simply press the Command + Option + Esc buttons at the same time.
Discover more from MacHow2
Subscribe to get the latest posts to your email.
Type your email…
One more way to Force Quit an app is to hold the Option key and right click a mouse or two-finger tap a trackpad on the Dock icon of the frozen app. There you will see Force Quit at the bottom of the menu.
Also, if you are clicking the Finder icon, you can Relaunch the Finder.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
- Accessories
- Meet the team
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy

For seasoned Windows users, it’s common to launch Task Manager and close apps and background activities to speed up the system. But if you have recently switched from Windows to Mac, you might wonder where the task manager on Mac is. Don’t worry; macOS has its own task manager equivalent, and in this guide, I’ll show you all the possible ways to open it.
Where is task manager on Mac?
The task manager on Mac is called Activity Monitor . Part of the reason why many new Mac users fail to find it is because of this macOS terminology.
Activity Monitor is a built-in Mac tool that functions like Windows Task Manager. It displays resource usage to offer insights into your system’s performance.
By opening Activity Monitor on a Mac, you can monitor real-time CPU, memory, disk space, energy consumption, and network usage. If your Mac is lagging , you can even close some unresponsive apps and diagnose the issue behind it.
6 Ways to open task manager on Mac
Depending on your preference or workflow, you can use various methods to launch task manager (Activity Monitor) on a Mac.
1. Using Spotlight Search
This method is often considered a shortcut to open Activity Monitor on Mac.
- Press the Command + Spacebar keys to access Spotlight Search.
Compared to Windows’s poor search algorithm, which sometimes takes hours to deliver a search result that is often wrong, the Spotlight on Mac is quick and accurate.
2. Using Finder
The Finder on Mac works in the same way as “This PC” on Windows, where you can find anything and everything present on your Mac, including the Activity Monitor.
- Open the Finder app on your Mac.
- Click on Applications under the Favourite section in the left Window pane.

3. Using Launchpad
The Launchpad on your Mac is just like the home screen or App Library on your iPhone or iPad. Unlike Windows, each program or utility is available as a separate app on Mac, and the same is the case with Activity Monitor.
- Launch Spotlight (cmd + space bar), type Launchpad , and hit return .
Alternatively, you can a gesture to open Launchpad. On the trackpad, just pinch in using your Thumb and Three Fingers.
4. Using Dock shortcut
Now that you know how to access the Activity Monitor from the Launchpad, you can easily add the Activity Monitor app to your Dock if you need to access it frequently.
- Drag the Activity Monitor app icon from the Launchpad and place it in the Dock .
5. Using Terminal
You can also use a command line to launch the Activity Monitor app on your Mac.
- Open the Terminal window via Spotlight Search or Launchpad.
- Hit the return key.
6. Using Siri voice command
While Siri may not be the best voice assistant available, it is undoubtedly the best to quickly complete a task with a simple voice command.
If you often use Siri on your Mac , you will find this as the easiest way to open the task manager, aka Activity Monitor, on your Mac.
- Invoke Siri on your Mac.
- Ask, “Siri, Open Activity Monitor.”
On a Mac, you can press the Command + Option + Escape key to open the Force Quit box, from where you can force-quit troublesome programs.
The Alt key on Mac is the Option key, and it is found on both sides of the spacebar.
This was all about how to open the task manager on Mac. If you want to become a pro-Mac user, check out our Mac guides or comment with your queries below; I will happily respond.
Vikhyat has a bachelor's degree in Electronic and Communication Engineering and over five years of writing experience. His passion for technology and Apple products led him to the tech writing space, where he specializes in writing App features, How-to guides, and troubleshooting guides for fellow Apple users. When not typing away on his MacBook Pro, he loves exploring the real world.
View all posts
🗣️ Our site is supported by our readers like you. When you purchase through our links, we earn a small commission. Read Disclaimer .
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles
Why is my iphone touch screen not working and how to fix it, how to pin a post on x (twitter) on iphone, ipad, or desktop, how to check if iphone is original or not: a detailed guide, how to turn off flashlight on iphone (2024 guide).
- a. Send us an email
- b. Anonymous form
- Buyer's Guide
- Upcoming Products
- Tips / Contact Us
- Podcast Instagram Facebook Twitter Mastodon YouTube Notifications RSS Newsletter
'Task Manager' on Mac: How to Find and Use the Activity Monitor
Users on Mac can sometimes face similar issues, and in such cases will usually click the Apple () symbol in the menu bar and select Force Quit... to kill an app from there.
Alternately, they'll fire up the Activity Monitor. Amongst other things, Activity Monitor lets you locate both frozen apps and background processes and force them to quit. Keep reading to learn how it's done.
- Launch the Activity Monitor on your Mac. You can find it in the /Applications/Utilities folder.
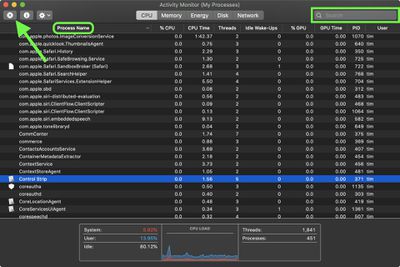
Note that if the app or process has files open, force quitting it may cause you to lose data. Also, bear in mind that if the process you force quit is used by other apps or processes, those apps or processes may experience issues.
For more on how to use Activity Monitor, check out our complete guide .
Get weekly top MacRumors stories in your inbox.
Popular Stories

Troubling iOS 17.5 Bug Reportedly Resurfacing Old Deleted Photos

iMessage Down for Some Users [Update: Service Restored]
Apple Previews Three New CarPlay Features Coming With iOS 18

Hands-On With the New M4 OLED iPad Pro
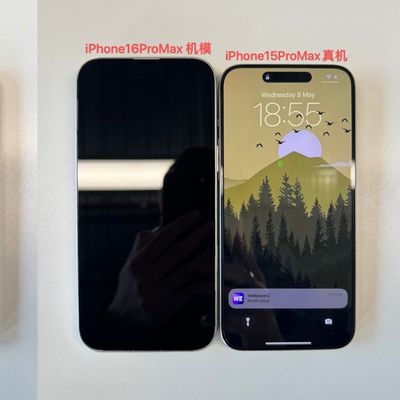

iPhone 16 Pro Max Looks This Much Bigger Beside iPhone 15 Pro Max
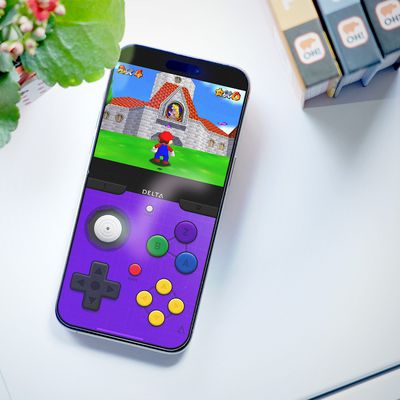

iPhone Emulators on the App Store: Game Boy, N64, PS1, PSP, and More
Next article.
Our comprehensive guide highlighting every major new addition in iOS 17, plus how-tos that walk you through using the new features.

Apple News+ improvements, cross-platform tracker alerts, website app downloads for the EU, and more.

Get the most out your iPhone 15 with our complete guide to all the new features.
A deep dive into new features in macOS Sonoma, big and small.

Apple's annual Worldwide Developers Conference will kick off with a keynote on June 10.

Expected to see new AI-focused features and more. Preview coming at WWDC in June with public release in September.

AI-focused improvements, new features for Calculator and Notes, and more.

Action button expands to all models, new Capture button, camera improvements, and more.
Other Stories

2 days ago by Tim Hardwick

3 days ago by Tim Hardwick

4 days ago by Juli Clover

5 days ago by Tim Hardwick
How to Open the Task Manager on a Mac
Switched to a Mac from Windows and can't find the Task Manager? Let us introduce you to Activity Monitor.
Quick Links
How to open activity monitor, your mac's task manager, how to force quit apps using the mac task manager, what does your mac's task manager do, key takeaways.
- You can open the macOS equivalent to Task Manager, called Activity Monitor, using Spotlight search, Launchpad, or the Applications folder in Finder.
- Keep Activity Monitor in the Dock for easy access by Control -clicking the app icon and selecting "Keep in Dock" from the context menu.
- Activity Monitor can force quit an unresponsive app or process: select it and click the "X" button at the top.
Since macOS is generally more stable than Windows, most people don't feel the need to find a tool like the Task Manager. Nevertheless, there are times when you need it—especially if an app refuses to respond. We'll teach you how to open the Mac equivalent of Task Manager.
Using Spotlight search on your Mac is the easiest way to open almost anything on your system. It can find apps, files, and settings in just a few keystrokes. It's much faster than browsing around manually to find what you need.
To open Spotlight, just press Command + Space on your Mac. Then, start typing Activity Monitor (the first few letters should bring it up) and press Return . In a moment, you'll see the Activity Monitor window.
Don't want to use Spotlight for some reason? You can also open the Mac equivalent of Task Manager by using Launchpad on your Mac . You'll typically find the Launchpad icon on your Mac's Dock, indicated by the grid of multi-colored icons.
Upon opening Launchpad, click the Other folder (you may have to scroll left or right to another page to see it) to find Activity Monitor located alongside other macOS utility apps.
Lastly, you can also find Activity Monitor in the Applications folder on your Mac. Open a new Finder window, select Applications from the sidebar, and click the Utilities folder to find and open it.
Keep Activity Monitor in the Dock for Easy Access
Once you open the Activity Monitor app using any of the above methods, it will appear in the Dock at the bottom of your screen. However, this shortcut disappears once you quit the app.
If you use Activity Monitor often, you may want to keep it on the Dock. To do this, Control -click the Activity Monitor icon on the Dock and choose Options > Keep in Dock from the context menu. From now on, you can access Activity Monitor right from your desktop.
One of the most common reasons for opening the Windows Task Manager is to close apps when they stop responding. While this doesn't happen as often on macOS, you may occasionally need to force quit an app when it's unresponsive or exhibits abnormal behavior.
The easiest way to do this is to use the Force Quit Applications window on your Mac. To open it quickly, simultaneously press Command + Option + Escape . From there, select the unresponsive app and hit Force Quit . When prompted for confirmation, click Force Quit again. Alternatively, you can access this window by clicking Apple menu > Force Quit from the menu bar.
Besides the Force Quit Applications window, you can also close apps using Activity Monitor (like you would with the Task Manager). This is handy if you want to force quit a process rather than an app, since processes don't appear in the Force Quit Applications window.
Open Activity Monitor on your Mac, select the unresponsive app under the CPU tab, and click the Stop (X) button at the top. Click Force Quit when prompted to confirm, and the app will shut off.
This process is similar to closing apps using Task Manager, so it shouldn't be difficult to force close apps on macOS if you recently switched from Windows.
Unlike the Windows Task Manager, which shows your PC's performance graphs in one window, the Activity Monitor has separate tabs for resources an app consumes, such as CPU , Memory , Energy , Disk , and Network usage.
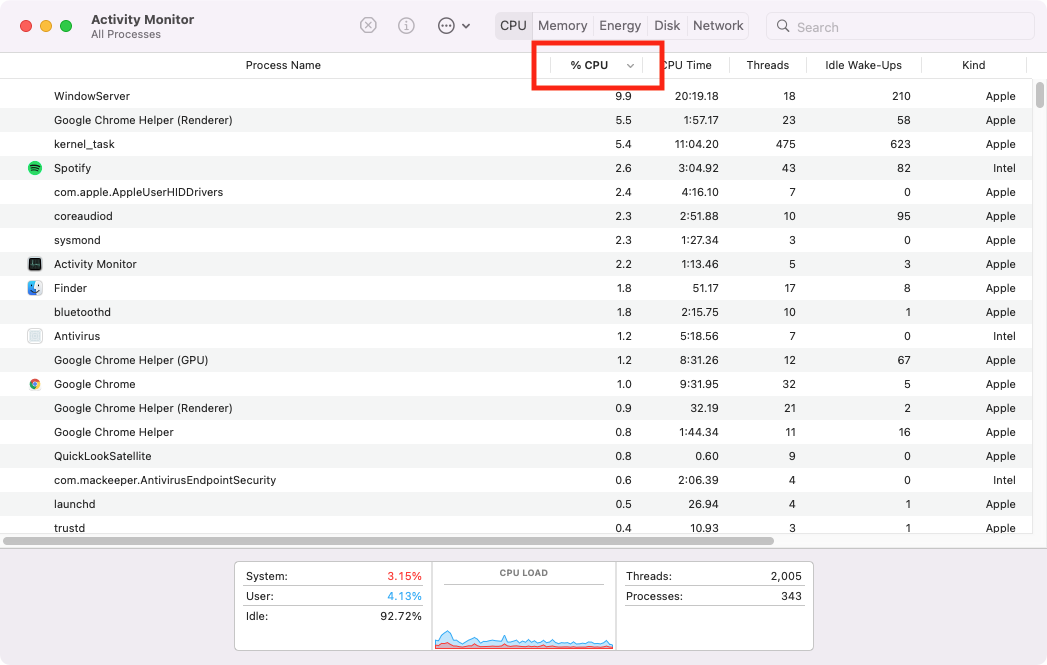
Clicking a heading allows you to sort by that option, making it easy to see what processes are using the most resources. For example, sorting by % CPU shows any processes that are doing a lot of intensive tasks.
If you consistently see an app here that isn't actually doing hard work, it may be misbehaving. For one popular example, we've explained how to fix the "kernel_task" high CPU usage bug if you encounter it.
Energy comes in handy if you're using a MacBook and want to get as much battery life as possible. Sorting by Energy Impact lets you see which apps draw the most power. You can close them to make your MacBook last longer before needing a charge.
To get more information about a process, select it and click the Info (i) button at the top of the Activity Monitor window for more details. As mentioned earlier, you can also click the Stop (X) button to kill any process, though you shouldn't close something unless you're sure you don't need it.
Activity Monitor has a few handy options in the menu bar you should know about. The View tab lets you choose which processes to show. Instead of All Processes , you may want to see only Active Processes to filter out noise, for example. You can also use the Columns option to hide or show more info for each process.
And under the Window menu bar item, you'll find a few options—like CPU Usage and GPU History —that open small windows. These let you monitor resource usage without keeping the full Activity Monitor window open. If you like these, try using View > Dock Icon to change the app's icon from the default to a live graph of CPU, network, or other activity.
These views are great if you like to monitor the performance of your Mac, especially while gaming. For more on what the Mac equivalent of Task Manager can do, see our comprehensive guide to Activity Monitor on Mac .
It's easy to open Activity Monitor and keep an eye on what's happening on your Mac. We've shown you several ways to access it, so managing active processes on your Mac when needed shouldn't be an issue. The more you know about your Mac, the more efficiently you can get work done on your computer.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Technology Simplified.
How to Open Task Manager or Activity Monitor on Mac
By: Salman Patwegar | Filed Under: Mac
The Activity Monitor is the equivalent of a Windows Task Manager on a MacBook and you can find below the steps to open the Task Manager or the Activity Monitor on Mac.

Open Task Manager on Mac
The Task Manager utility on a Windows Computer can be used to start, restart and quit applications, if they get stuck, start misbehaving or start using excessive resources on the computer.
In the case of a MacBook, the Activity Monitor is the equivalent of Windows Task Manager and it is this utility in macOS that provides the option to monitor application running on the computer.
1. Open Task Manager or Activity Monitor On MacBook
If the Activity Monitor Icon is not available on the Dock , you can open the Activity Monitor by launching the Finder on your MacBook.
1. Click on the Finder icon (Happy Face) located at the left corner of the Dock on your Mac.

2. On the next screen, select Applications in the left-pane and open the Utilities Folder by double clicking on it.
3. Once you are in Utilities Folder, click on Activity Monitor (which is usually the first item in the list)
4. On the Activity Monitor screen, you will be able to see the information about Apps and Services located on the MacBook.
2. How to Pin Activity Monitor to Dock on Mac
You can avoid the long way of Opening Activity Monitor by pinning the Activity Monitor Icon to the Dock on your MacBook.
1. Use the Finder to open the Activity Monitor and this will bring the Activity Monitor Icon to the Dock on your Mac.
2. Once the Activity Monitor Icon appears on the Dock, right-click on the Activity Monitor icon > hoover mouse over Options and click on Keep in Dock option.
From now on, you will find the Activity Monitor Icon always pinned to the Dock and you will be able to launch or open Activity Monitor by clicking on its Icon on the Dock.
3. View Resource Usage on Mac Using Activity Monitor
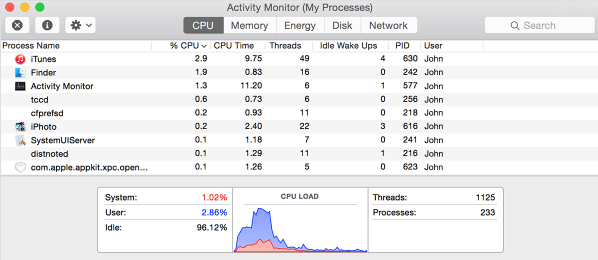
All that is required to view the amount of CPU, Memory and Disk Usage on a MacBook is to open the Activity Monitor and switch to CPU, Memory and Disk tabs.
As you can see in the image below, clicking on the CPU tab provides information about the amount of CPU being used by various apps and services running on the MacBook.
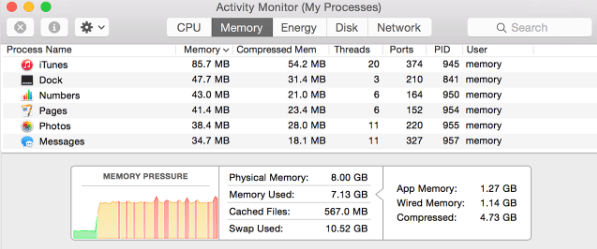
Switching to the Memory tab allows you to see the amount of Memory being used by various Apps and Programs running on the MacBook.
4. Force Quit Apps on Mac Using Activity Monitor
Similar to the Task Manager on a Windows computer, the Activity Monitor on a MacBook can be used to Force Quit Apps, if they happen to get stuck or cause problems.
1. Open Activity Monitor > select the Application that you want to Force Quit and click on the x button (top-left).
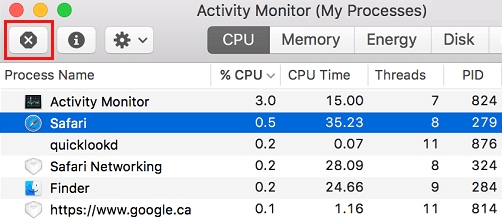
2. On the confirmation pop-up, click on the Force Quit option to Force Quit the selected Application.
- How to Recover Apps Missing From Launchpad on Mac
- How to Format USB Drive on Mac

Press ESC to close
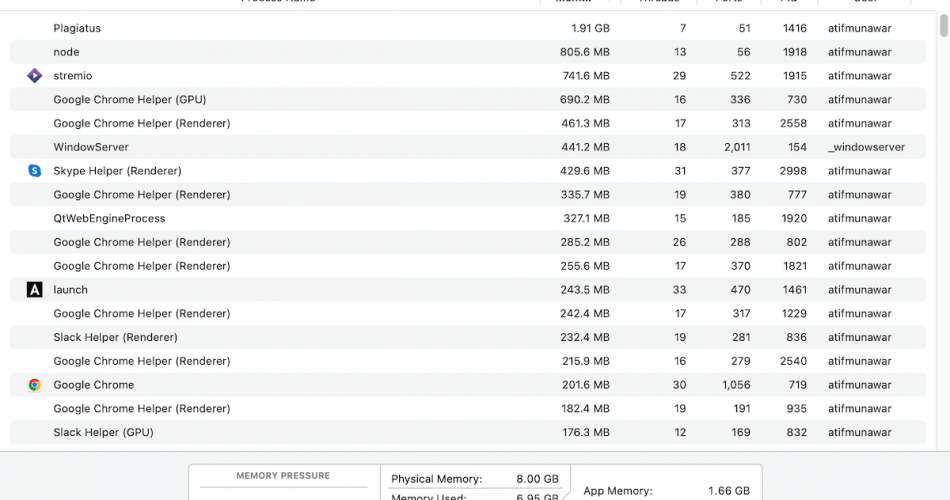
How to Open Task Manager on Mac- An In-depth Guide
Is your Mac lagging, or an active app is affecting its speed? Don’t we all hate a spinning wheel (also called the ‘spinning beach ball of death) hindering our computer’s performance? The MacBook task manager will help you identify and solve these issues.
Many believe a task manager in Mac is not as important as a Windows computer. Thanks to the powerful chipsets and a flawless operating system, Apple integrates into their MacBooks. But, once in a while, having a task manager becomes essential for some inevitable disruptions.
This article is an in-depth guide on Mac OS task manager- The Activity monitor. Activity monitor helps Mac users close tasks that slow down, hinder or freeze the Mac and cause it to lag and underperform.
Task manager also benefits the Mac. For example, it can close apps and change system preferences. Keep reading to find out how to correctly use the task manager on your MacBook to manage apps.
Table of Contents
Activity Monitor – The task manager on Mac
Almost all Windows users know how a task manager works on Windows computers. It helps determine the tasks running on the computer and their effects on the computer’s performance and speed.
A task manager on Mac performs similarly to a windows task manager. Mac equivalent of a task manager is called an Activity monitor. It is a preinstalled app on Mac. Activity monitor helps regulate apps by showing how many apps are active at a time and how much energy they are consuming.
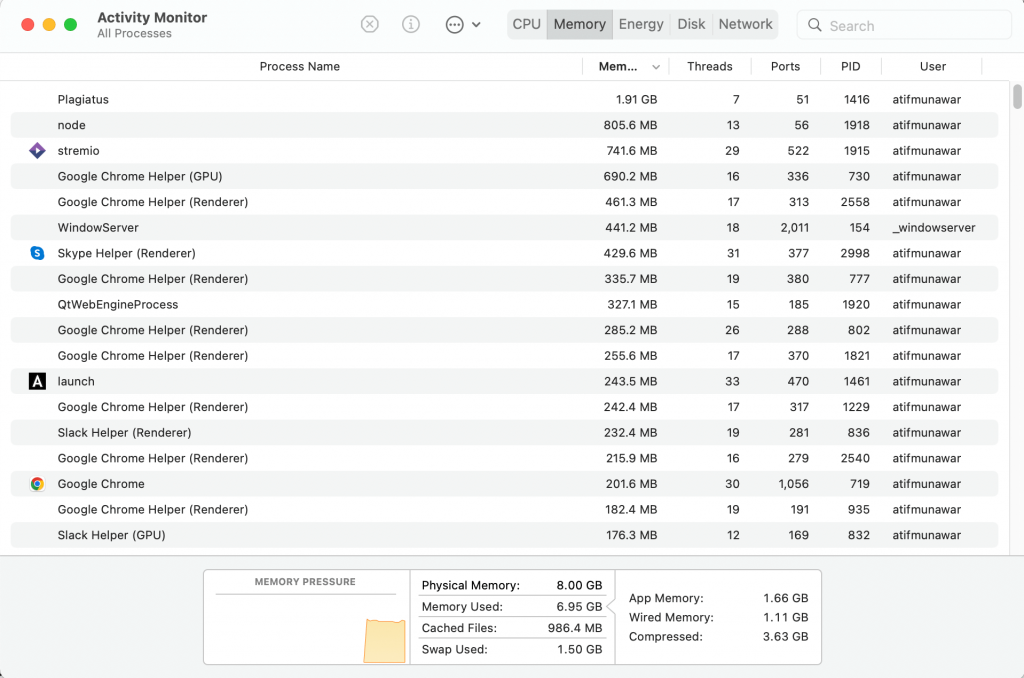
How to launch Mac task manager
There are four easy ways to open a task manager on a Mac. You can use any of these methods below to launch the Activity monitor.
- Use Spotlight search
You can open the activity monitor using Spotlight. For that, follow the steps given below:
- Press Command plus Space keys to launch the Spotlight
- Type ‘Activity monitor,’ and the app will appear highlighted; then click on it or press enter
- The activity monitor window will open
To access task manager on Mac using Finder, follow these steps:
- Click on the Finder icon from the dock
- Click on the ‘Applications’ tab appearing in the sidebar
- Then tap on ‘Utilities folder’ in the applications window
- Launch the Activity Monitor by double-clicking on the ‘Activity monitor icon’ in the utilities folder
- Add in Dock
The easiest way to launch the task manager is to add its dock icon to the main dock. To do that, follow these steps:
- Launch Activity monitor by using any of the processes mentioned above
- Right-click on the icon of ‘Activity monitor’ appearing in the dock
- Then select ‘Option’ and choose ‘Keep in dock.’
- Or, you can drag and drop the Activity monitor icon in the dock
- The above steps will add the app to the dock, and it will remain there even after quitting the application
- Use shortcut
Some versions of macOS provide a Mac task manager shortcut to launch the Activity monitor. To use this, press Command, Option, Shift and Escape keys simultaneously. Keep pressing these four keys for a few seconds until you see the Activity Monitor on screen.
Uses of task manager
Once you open the task manager, it will show you five tabs. These tabs will reveal the running applications and how they affect your Mac. You can then manage or quit all the processes obstructing the macOS from working efficiently.
You can open the task manager using all the options given below to view the apps statues:
- Check CPU usage
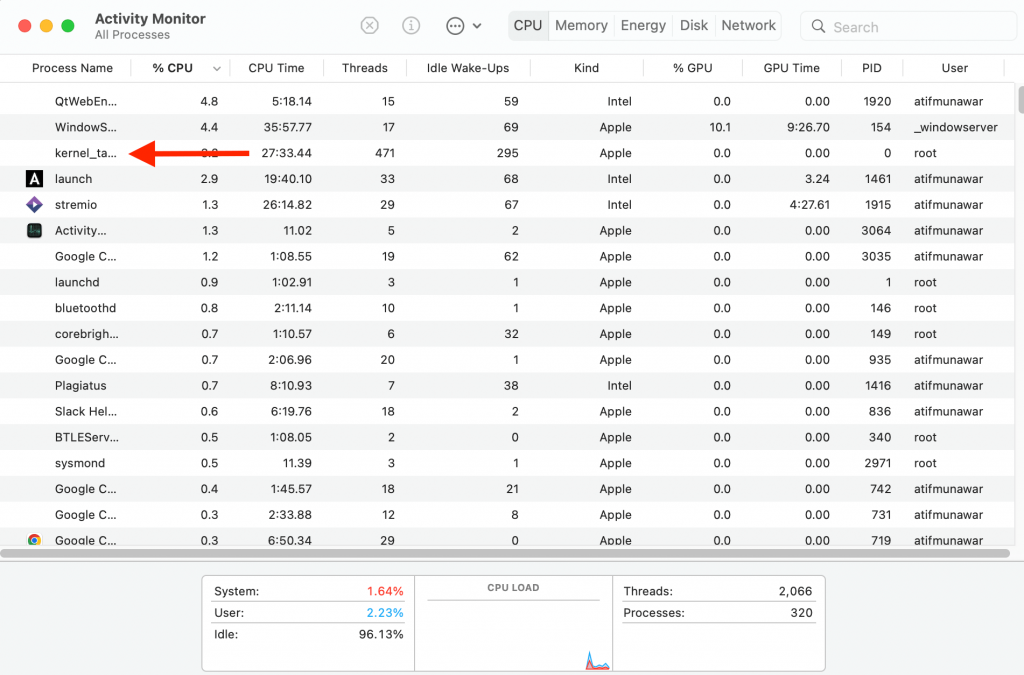
Showing CPU usage is the essential use of the Activity monitor. You can view all the running processes and their effect on the CPU usage and performance in the CPU tab. The CPU pane also displays the exact percentages of the power the apps are consuming and for how long they have been running.
To get information about how much CPU power an app is using, select it and then press the ‘i’ icon on the top of the screen. It will show all the information about the app. Next, press’ x’ to get rid of any app that is not in use.
A continuous process running on your Mac is called ‘kernel_task,’ which might seem like it is using many resources. However, please do not end this process; it monitors all the heavy processing applications on your Mac and tones them down to increase performance.
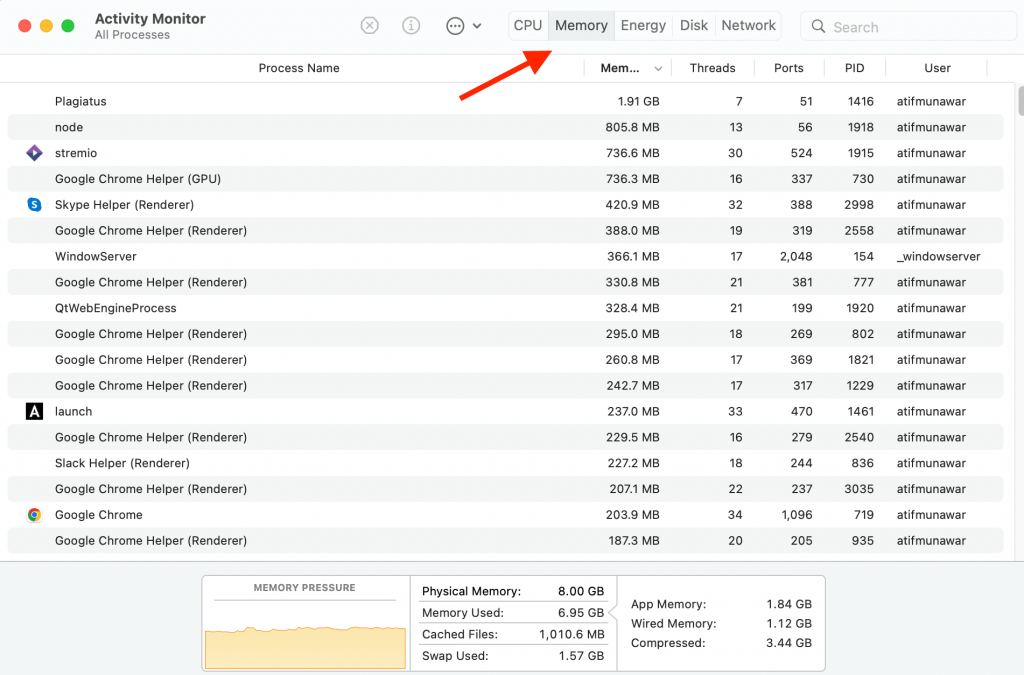
Sufficient RAM is the top reason for Mac’s performance. Lesser RAM means a slower Mac, but your computer will run faster if its memory is sufficient. The memory pane helps in this regard. Try stopping heavy applications to speed up your Mac quickly.
Open the ‘Memory tab’ and view the ‘RAM pressure gauge’ at the bottom. It shows the RAM available on your computer. If the bar is green, there is enough storage available, but the user needs to buy extra memory if it’s red.
Users can also decrease CPU and RAM utilization using the App tamer on the menu bar. It shows all the heavy processes running on your device and slows them down.
- Check energy use
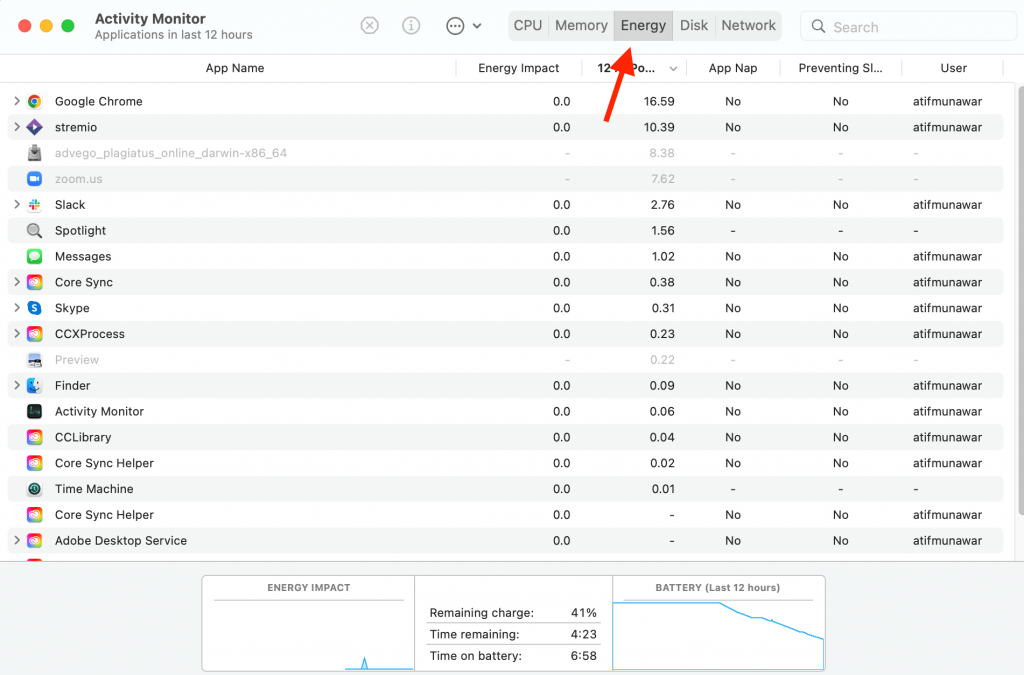
Mac task manager also shows the energy usage of all the active apps. The Energy pane is helpful if you have not plugged your device into a charger and want to extend screen time.
Just click on the Energy pane and see all the running applications. From there, you can quit the processes and apps that use a lot of battery.
You can also check Avg energy impact. It shows how much energy an application uses on average. You can then get rid of applications that degrade battery life faster.
- Check disk activity
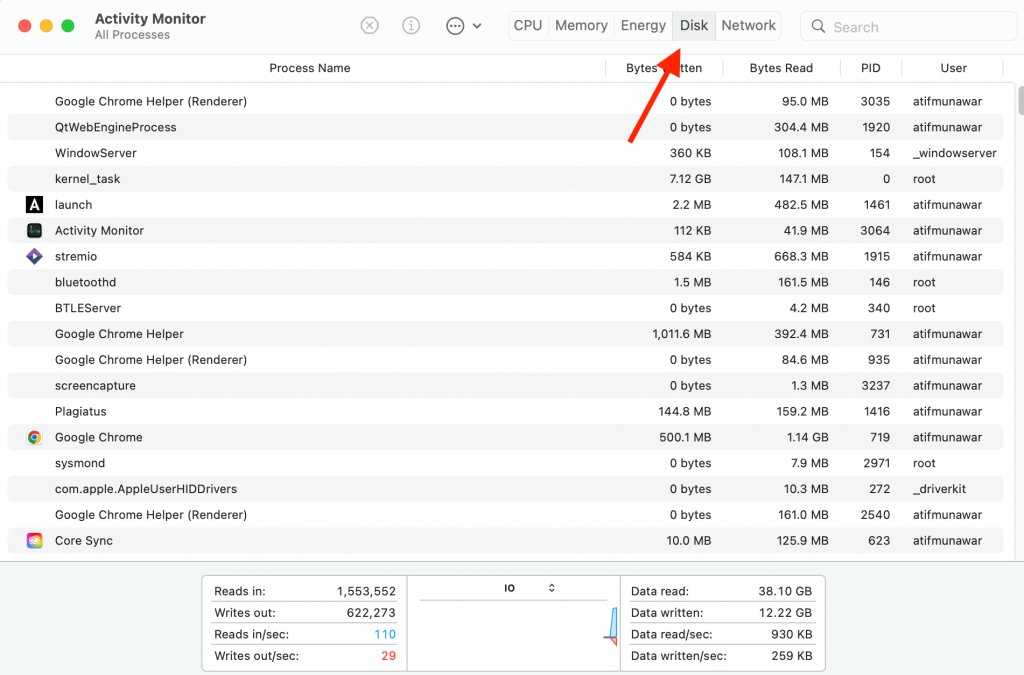
The Disk tab shows how apps affect your Mac’s hard drive by rewriting data. If you have mistakenly downloaded malware or corrupt application, you can view stats on this page and delete the corrupt apps quickly.
- Check network activity
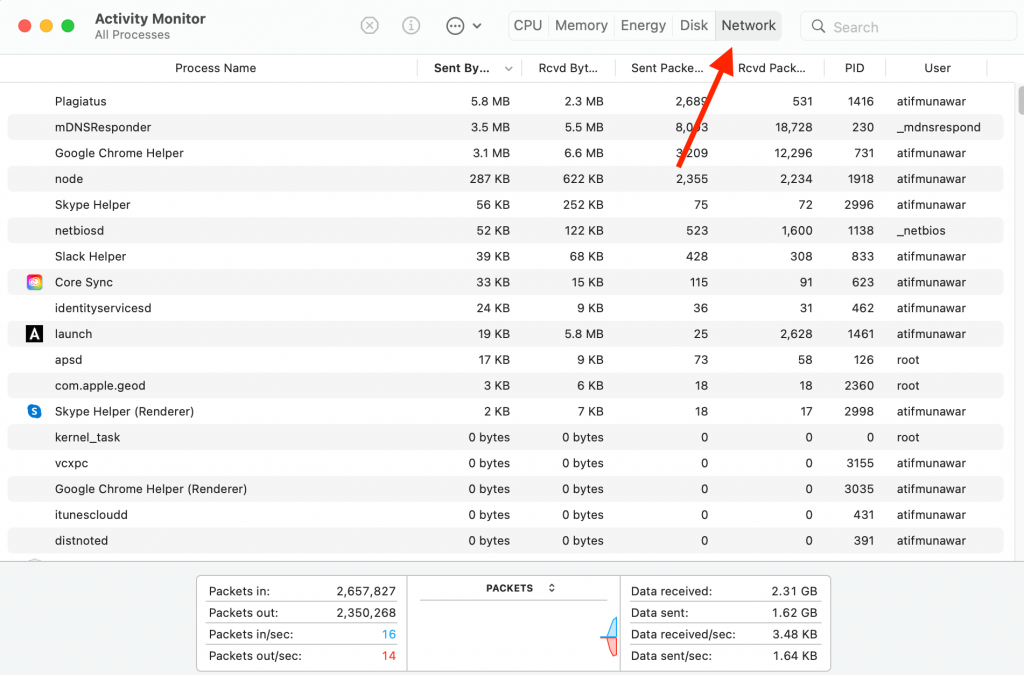
Lastly, the Network pane shows how much data an app sends and receives. The network usage reveals any hidden malware or anomaly running on your Mac.
You can view all the incoming and outgoing data in the network tab and then stop the doubtful apps and delete them.
Examine processes running on Mac
You can examine all the active processes using the Mac Activity monitor. It also has a few valuable options in the menu bar. The ‘View tab’ lets you choose which applications you want to view. You can also select ‘Active processes’ to filter out which processes to consider.
Under the Windows pane of the Activity monitor, you can view the CPU and GPU performance.
If you want to know more about a particular process running on the Mac, use the steps given below:
- Open the task manager(Activity monitor) on your Mac
- Highlight the process on the Activity monitor, then click command plus ‘i’
- Or, go to ‘View’ and click ‘Inspect process.’
- An inspection screen will appear where you can view the CPU performance, RAM, and all other details
Force quit applications
Force quitting is the primary job of a task manager on Mac. You can force quit applications using the Activity monitor. It helps eliminate frozen apps or applications that take too long to process or run.
The task manager on Mac not only shows insights for the five tabs mentioned earlier but also helps to force quit applications that are unresponsive or stuck. Mentioned below are the three easy ways you can force quit applications on your Mac:
If an application is not responding and has frozen, you can use the Apple menu to force quit that process in just a few clicks.
Press and hold the ‘Shift’ key and click on the screen’s Apple icon in the top left corner. You will see the ‘Force quit’ option in the drop-down menu with the application’s name. Click on the ‘force quit’ option to remove the application running in the background.
You can also force quit applications using the dock. However, it will only be possible if the cursor is moving and you can see the dock.
Move the cursor on the top of the app that is not working. Next, select the app you want to force quit and right-click it. Finally, select ‘Force quit’ in the pop-up menu to close the app. It will stop the app’s running process immediately.
- Activity Monitor
Lastly, you can force quit an application using the macOS task manager- The Activity monitor. It will help you not only in closing an app but also show details of it. Open Activity monitor using any of the three ways mentioned above. It will list all the running applications on your Mac.
You can select any app you want to close. Then choose ‘force quit’ and confirm your choice in the dialogue box. It will close the desired application. However, do not use the Activity Monitor to force quit apps regularly. It can sometimes corrupt the apps.
If you cannot close any frozen app using the ‘x’ symbol, you can also use the keyboard shortcut. Press Command+Options+Escape to open the dialogue box of ‘Force quit applications manager.’
You can select any app in the dialogue box and press ‘Force quit’ to close it. You can quickly close otherwise unresponsive apps.
Other options
You can download the application listed below if you want to prevent apps from freezing and get a lag-free performance from your Mac.
CleanmyMac X
CleanmyMac X is an application that continuously scans your Mac and deletes apps to improve its performance. It will optimize apps and regularly delete unused data so your Mac is not overburdened. If you use this app, you will hardly need to use the task manager on Mac.
CleanmyMac X is a free software specially designed for macOS computers. It not only scans the system but also deletes and resets apps, removes the cache, and speeds up the Mac with its maintenance options.
The task manager manages the running processes on your Macbooks. It is easy to use and helps a great deal in increasing work performance. In addition, regularly using the task manager to check apps and software guarantees a better-performing computer.
In this regard, The Activity Monitor is the most helpful task manager for macOS devices. The Activity Monitor is the native task manager on Mac. Hence, it is vital to be aware of its usage. The Activity monitor window has five tabs and shows the effects of applications on Mac’s performance.
From revealing how much CPU power an application uses to the network and energy usage, the Mac task manager is easy to learn and use. This article not only discussed the uses of Apple task manager but also informed users how to use it to force quit slow applications.
Share Article:
Marid is a lifelong tech enthusiast and is the lead editor of Macdentro.com. An expert on all things Apple and a lifelong Mac user. Marid has over 10 years of experience using Apple products including the Apple watch, Ipad and etc
How to Scroll on MacBook – A Beginners Guide
Easy way to turn airdrop on mac devices, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
- Operating Systems
How to Open Task Manager on Mac OS X
Last Updated: March 19, 2024
This article was co-authored by Gonzalo Martinez . Gonzalo Martinez is the President of CleverTech, a tech repair business in San Jose, California founded in 2014. CleverTech LLC specializes in repairing Apple products. CleverTech pursues environmental responsibility by recycling aluminum, display assemblies, and the micro components on motherboards to reuse for future repairs. On average, they save 2 lbs - 3 lbs more electronic waste daily than the average computer repair store. This article has been viewed 60,804 times.
Task Manager, which goes by the name of Activity Monitor on Mac OS X, is an application that allows you to view and monitor all active processes running on your computer. If your computer is running slow or inefficiently, you can open Activity Monitor to determine which applications are consuming the highest amount of resources. Activity Monitor is stored in the Utilities folder on Mac OS X.
Quick Steps
- Click on Applications > Utilities .
- Select Activity Monitor .
- Click through the various tabs to view how your computer's resources are being used.
Opening Activity Monitor

Using Activity Monitor

- Select the option to “Force Quit” any processes that are unresponsive or won’t close after selecting “Quit.” Applications that are looping, unresponsive, or taking an excessive amount of time to load may need to be closed using the “Force Quit” option.

- If there is little to no memory next to “Free,” or any values displayed next to “Swap Used,” you may want to consider purchasing more RAM for your computer. These signs indicate that your computer is out of physical memory and is using a portion of the hard drive for temporary storage -- leading to longer wait times.

Expert Q&A
- If you suspect malware has infected your computer, look for and quit any unfamiliar processes running in Activity Monitor. In many cases, malware will run as a background process and significantly slow down your computer. [3] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you notice that one or more applications continue to run automatically in the background, launch those programs, then search for options in their Settings menus that allow you to prevent the applications from launching upon startup. Sometimes, third-party applications will launch automatically by default when you start your computer, and run continuously in the background without your knowledge. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://osxdaily.com/2010/08/15/mac-task-manager/
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT201464
- ↑ http://www.thexlab.com/faqs/activitymonitor.html
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Is this article up to date?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Keep up with the latest tech with wikiHow's free Tech Help Newsletter
Activity Monitor on Mac
In this article you will find the following:
Every copy of macOS comes with Activity Monitor pre-installed. Like the Task Manager on a Windows PC, Activity Monitor lets you see everything that’s running on your Mac, including apps that you can see and interact with, as well as background services that are normally hidden.
Many of these processes are part of macOS itself, but you’ll also find background processes for other apps, including your web browser, antivirus, and things like VPN clients.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to open Activity Monitor on Mac before looking at some of the ways you can use it:
- Inspect processes
- Run diagnostic reports
- Identify malware
- Save battery power
- Limit internet use
Before we start If you’re looking at the task manager in Mac because your desktop is behaving strangely or slowing down, use MacKeeper’s Find & Fix tool to find out what’s wrong . It’ll scan for spyware and viruses, clean junk files, clear memory, and more. Simply run a full scan to check for a variety of problems: Open MacKeeper , and select Find & Fix . Click Start full scan . Let MacKeeper complete the scan. Carry out the recommended fixes. Sounds good? Then give MacKeeper a try. Now, download it and try it for free, so there’s really nothing to lose.
- What is Activity Monitor?
Activity Monitor is the Mac task manager equivalent. It shows you a complete list of all processes running on your machine, as well as how much of your system’s resources each program is using. You can use task manager on Mac for many things:
- Kill frozen apps that refuse to close properly.
- See which apps and processes are slowing down your system.
- Run diagnostic reports.
- Find hidden spyware and monitoring apps on your Mac.
- Identify background processes that shouldn’t be running.
- See which apps are using your network.
- How to open Task Manager on Mac
There are several ways to activate Activity Monitor—the Mac’s version of task manager. We’ve explained the quickest Activity Monitor Mac shortcuts below so that you can pick the one that works best for you.
To open Activity Monitor on your Mac:
- In Finder, navigate to Applications > Utilities . Find and launch Activity Monitor .
- Another Mac task manager shortcut is to first open Spotlight by clicking the magnifying glass in your Mac’s menu bar. It’s located in the top-right corner of the screen. Find Activity Monitor on Mac by typing in its name, then press Enter to open it.
- You can also bring up Spotlight by using the Command + Space keyboard shortcut, then typing Activity Monitor to find and access the task manager on Mac.
- How to use Activity Monitor on Mac
Once you’ve mastered how to bring up the task manager on Mac, it’s time to make the most out of it by learning how to use it. Here are some of the most useful things you might need:
- Quit apps in Activity Monitor
- Inspect processes in Activity Monitor
- Run diagnostic reports in Activity Monitor
- Fight against malware with Activity Monitor
- Save MacBook battery power with Activity Monitor
- Use Activity Monitor to limit internet use
- Other handy ways to use Activity Monitor
1. Quit apps in Activity Monitor
The macOS Activity Monitor lets you quit out of apps and background processes that you don’t normally see. This can be useful if your Mac is running slowly or an app is behaving oddly.
You can quit apps in Activity Monitor in a few easy steps:
- Start Activity Monitor .
- Look through the list of processes and select one you want to quit.
- Now click the X symbol at the top of the program window.
- Select Quit or Force Quit .
- You can also quit an app by double-clicking it, then clicking the Quit button.
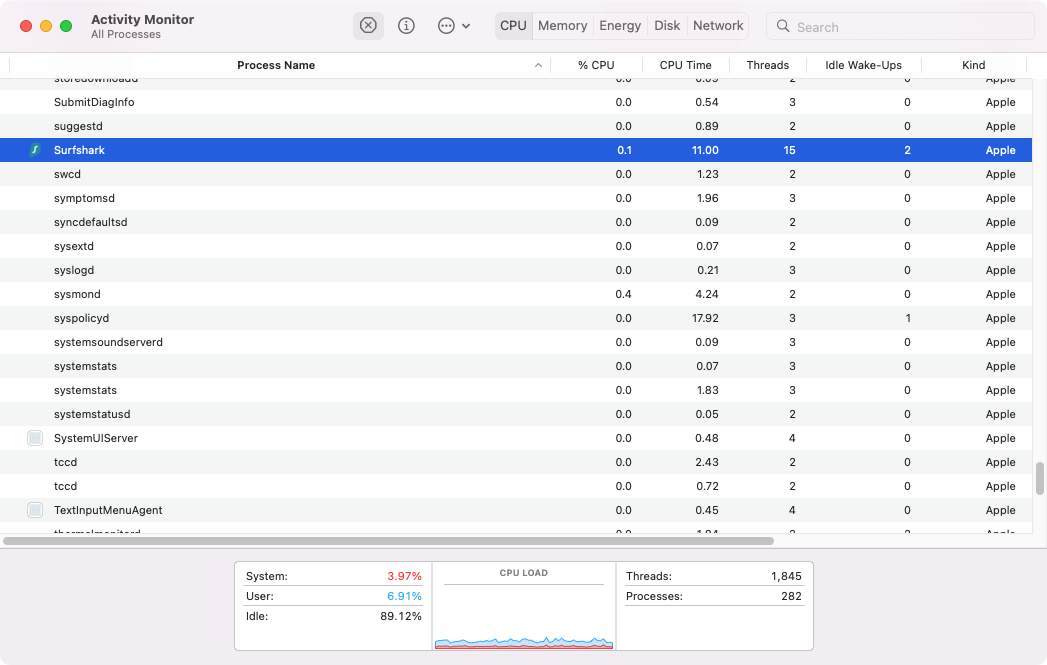
2. Inspect processes in Activity Monitor
If you read the Mac Activity Monitor, you’ll see all kinds of information about what’s running on your Mac. When you’re having issues with your Mac running slowly, this information might help you find the app or background process that’s causing the slowdown.
Here’s how to inspect a process on Mac:
- In Activity Monitor , find a process in the list and double-click it.
- This will open a new window. In the Memory tab, you’ll see how much RAM the process is using.
- Click Statistics to see a view of technical information, including the number of threads a process is using.
- The Open Files and Ports tab shows exactly what the name says. You can see which files an app is using at any given time.
- If you click the Parent Process , it’ll open up another window with details about that process.
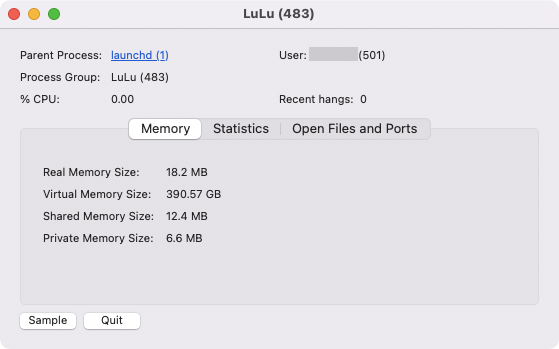
3. Run diagnostic reports in Activity Monitor
You can create various diagnostic reports in Activity Monitor, including a Spindump , which looks at unresponsive apps that were forced to quit, and a Spotlight Diagnostic report based on all the processes running on your Mac. It may be helpful to provide these to Apple Support if you have a problem.
Here’s how to run these reports in Activity Monitor:
- Pull up the task manager on Mac, then click the icon with three dots .
- Select either Sample Process, Spindump, System Diagnostics, or Spotlight Diagnostics , depending on which one you want to run.
- You may need to enter your Mac password . If so, enter it, and let the report build.
- At the end, you’ll have a file you can send to Apple Support .
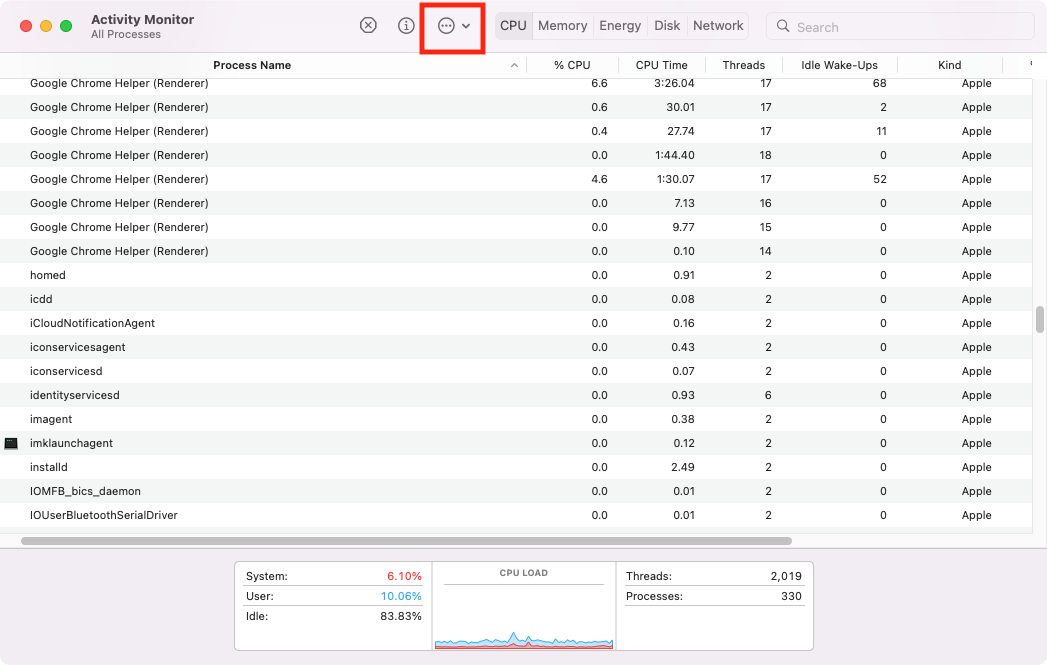
4. Fight against malware with Activity Monitor
Finding and removing malware is an important part of maintaining a healthy Mac—especially if you want the best performance. You can often use Activity Monitor to stop malicious processes running on your machine, but before you quit anything, search for the process online to ensure it’s not something that macOS needs to run properly.
This is how you can use Activity Monitor to find and shut down malware:
- Open Activity Monitor . In the CPU tab, click the % CPU column to sort processes by the percentage of CPU power they’re using. You can also do the same for GPU .
- With the most demanding processes at the top, look for anything you don’t recognize.
- Select anything suspicious, and click the X icon at the top of Activity Monitor to get rid of it.
- Click Quit or Force Quit .
Relevant reading: How to Check for Malware on Mac
5. Save MacBook battery power with Activity Monitor
When apps and other processes use a lot of power, they slow down your Mac and use more energy. If you’re using a MacBook on battery, that could limit how long you’re able to work away from an electricity outlet. Thankfully, you can use Activity Monitor to save some energy on your Mac .
Use these steps to check for energy use in Activity Monitor:
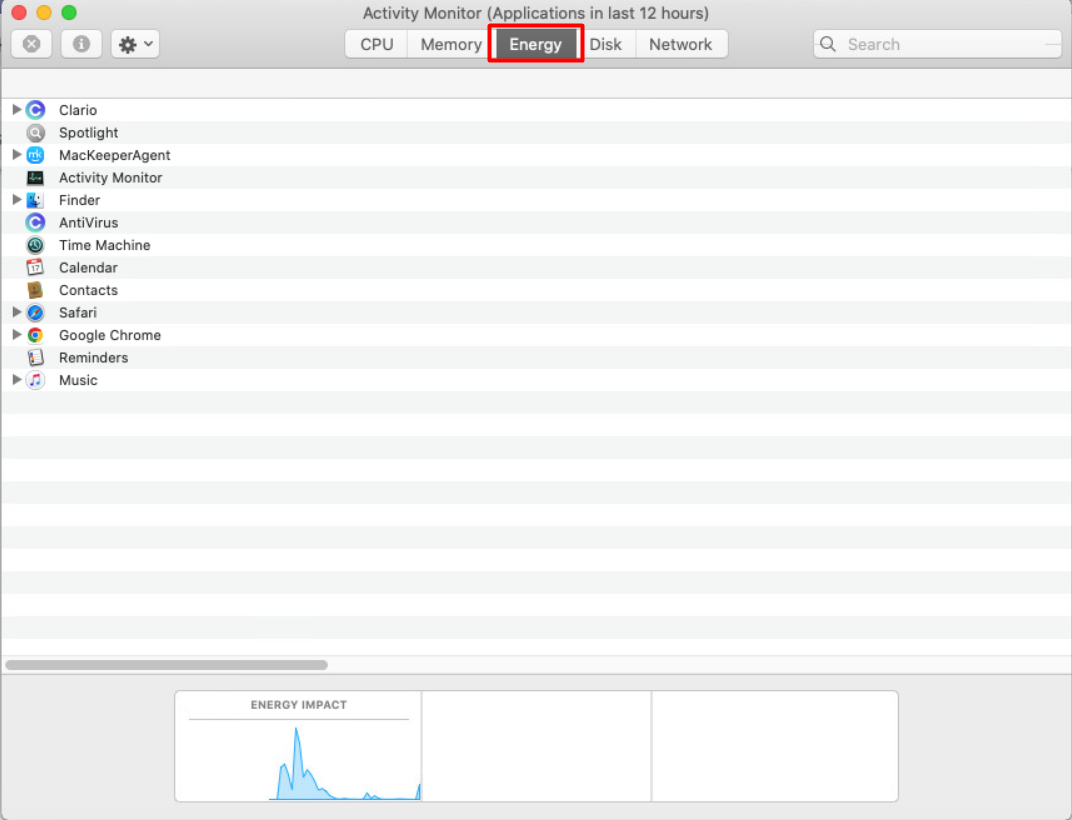
- Open Activity Monitor and go into the Energy tab.
- Look at the Energy Impact tab to see how much power each app is using.
- Use the 12 hr Power tab to see how much energy was spent in the past 12 hours.
- Quit apps that are using a lot of energy.
6. Use Activity Monitor to limit internet use
Most internet providers don’t limit how much you can download in a month anymore, but there are still good reasons to limit network activity on your Mac. Activity Monitor is a great way to keep tabs on which processes are sending and receiving data over the network.
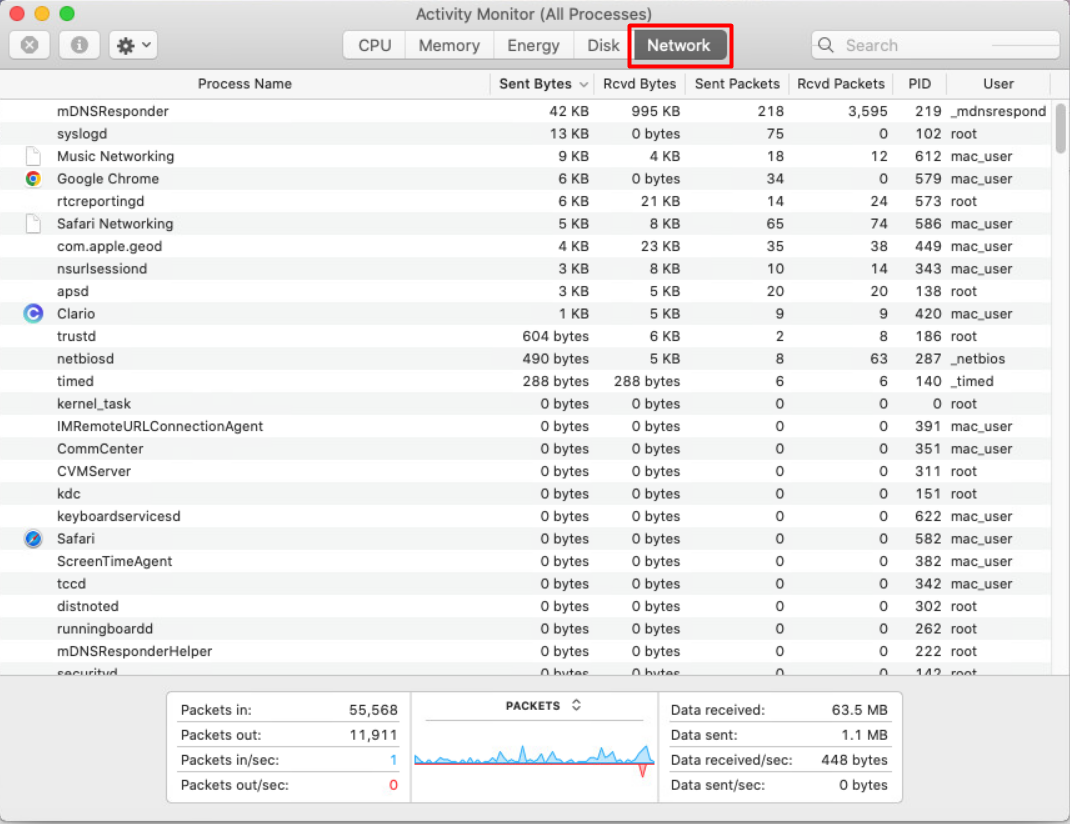
To check what’s being downloaded and uploaded by your Mac:
- After opening Activity Monitor, select the Network tab.
- Click the top of the Sent Bytes column to sort highest to lowest. Note any large and unexpected figures.
- Do the same with the Rcvd Bytes column.
- Kill any apps using a lot of bandwidth.
- If you don’t recognize something, search for its name on the web to find out if it’s malware, then run an antivirus scan if necessary.
7. Other handy ways to use Activity Monitor
These are the key ways to use Activity Monitor on your Mac, but there are other useful things you can do, such as:
- See real-time CPU, network, and disk usage in your Dock .
- Track memory usage with the help of the memory pressure chart to see if you need more RAM. Note that you can’t change the RAM in all computers.
If your goal is to speed up your iMac or laptop, regularly reduce system storage and remove cache files to ensure you have plenty of free space, which will keep things running smoothly.
- Remember, Activity Monitor tells you what’s happening on your Mac
Activity Monitor is a useful utility that gives you insight on what’s going on with your Mac. It’s particularly helpful when you want to find out what’s slowing down your machine, force quit frozen apps, and when you’re worried you have a malware infection. You can also identify and fix common issues by using MacKeeper’s Find & Fix tool , which scans your computer for potential problems and helps you eliminate them quickly and safely.
You’ll love exploring your Mac with us.
Oops, something went wrong.
Try again or reload a page.

- Delete unnecessary system files and caches
- Free up GBs of storage space
- Easily find and delete duplicate files
Exploring Mac functionality? Our tech support can help you master it.
MacKeeper - your all-in-one solution for more space and maximum security.

We respect your privacy and use cookies for the best site experience.
Privacy Preferences Center
We use cookies along with other tools to give you the best possible experience while using the MacKeeper website. Cookies are small text files that help the website load faster. The cookies we use don’t contain any type of personal data meaning they never store information such as your location, email address, or IP address.
Help us improve how you interact with our website by accepting the use of cookies. You can change your privacy settings whenever you like.
Manage consent
All cookies
These cookies are strictly necessary for enabling basic website functionality (including page navigation, form submission, language detection, post commenting), downloading and purchasing software. The website might malfunction without these cookies.
Download MacKeeper when you're back at your Mac
Please enter your email so we can send you a download link
Check your email on your Mac
Install MacKeeper on your Mac computer to rediscover its true power.
Run Application
Click Continue
Click Install
Your macOS version is lower than OS 10.11. We’d like to offer you MacKeeper 4 to solve the cleaning, privacy, and security issues of your macOS.
Control Alt Delete on a Mac - How to Open Task Manager on your Macbook

It happens to the best of us: we're working away on some important project, and our trusty computer freezes. Or rather, a program we're in just stops responding. So what do you do?
If you have a Windows machine, you can just use the familiar CTRL+ALT+DEL sequence to force quit whatever program is misbehaving. But that doesn't work on a Mac.
Don't worry, though - there is one super simple way to force quit on a Mac (and a couple other methods you can keep in your back pocket as well). Let's learn what that is.

How to force quit on a Mac
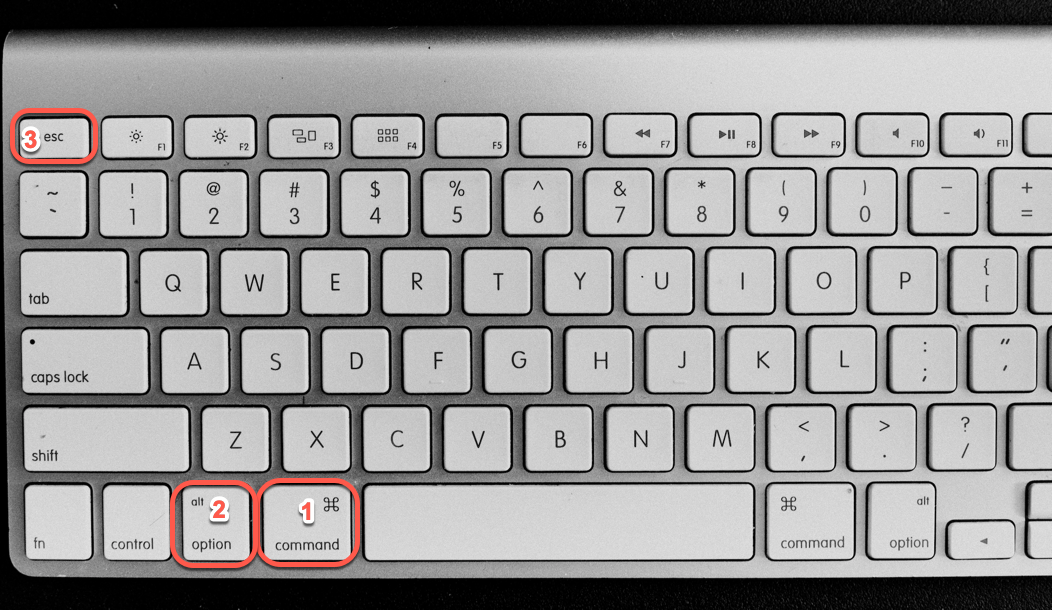
The easiest way to force a program to quit on your Mac is a simple key sequence similar to ctrl+alt+delete. Just tap COMMAND+OPTION+ESC, in that order. Here's where those keys are located on a typical Mac keyboard:

This will bring up a task manager type window that looks like this:
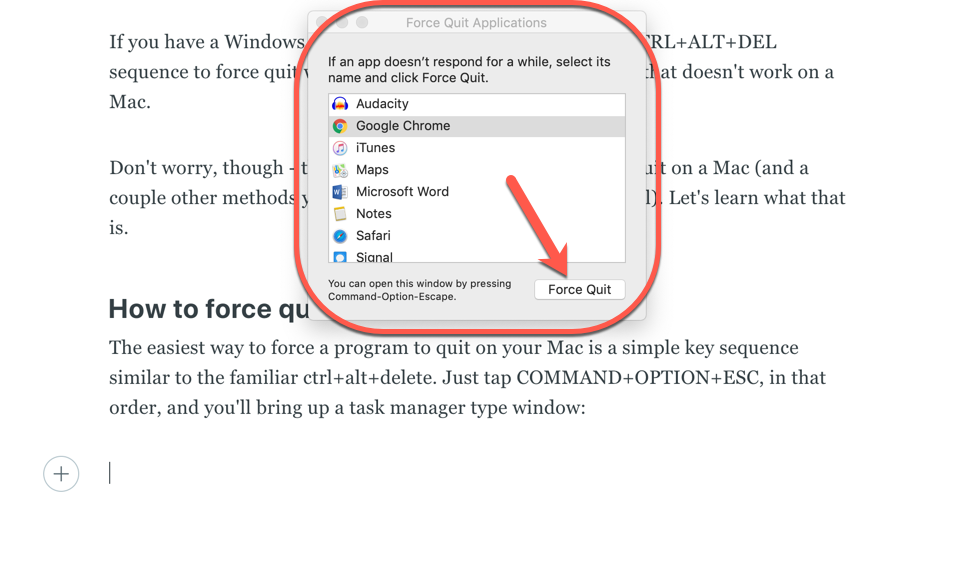
Then just select the non-responsive program and hit "Force Quit" which will stop that program from running.
Note : since you'll be forcing that program to quit in the middle of whatever you were doing, any unsaved data might be lost. Make sure you enable auto-saving, back up your projects often, and keep your computer clean and up to date.
An alternative method
Why learn just one way to force quit when you can learn two? Click the Apple logo at the top left of your screen in the menu bar. Scroll down to "Force Quit" and it'll bring up the same task manager.
Simple as that!
Now that you've dealt with your crashing application, you can get back to work. :)
Former archaeologist, current editor and podcaster, life-long world traveler and learner.
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
- Editorial Process
- Why Trust Us?
- Affiliate Linking Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
Weekly Must-Reads View All
7 things to do if you spilled water on your macbook.
Quick steps to save your MacBook from water damage
How to Boot Your Mac Into Verbose Mode: 4 Best Ways
Boot your Mac into Verbose Mode with this step-by-step guide
How to Fix Your Mac Shutting Down Randomly: 16 Fixes to Try
Troubleshoot random shutdowns on Mac with effective solutions
How Much Space Does macOS Take On Your Mac?
Understand macOS size and analyze your Mac's storage usage
Popular Topics
- What to Do With Your Old MacBook? 13 Useful Ways to Reuse an Old Mac
- What Is the MacBook Flexgate Issue and How to Fix It
- What Is the MacBook Flexgate Issue
- Uninstall Java
- Safely Transfer Files from Mac to Mac
- Safari Bookmarks Disappeared on Mac: 10 Best Ways to Restore Them
- Repairing disk permissions
- Old MacBook
Trending Now View All

- Mac Maintenance
Mac Task Manager Equivalent And How To Use It [Quick Guide]
Hashir Ibrahim
Reviewed by
Last updated: September 6, 2023
Expert verified
Transitioning from Windows to Mac can be challenging, especially when familiar tools like Task Manager have different names and locations. While you can use the Windows Task Manager’s Mac equivalent, the Activity Monitor, to end unresponsive processes, you cannot access it from the familiar Ctrl + Alt + Delete sequence of Windows.
So how to get Task Manager on Mac? If you’re a long-time Windows user who’s recently transitioned to Mac, or even a seasoned Mac user who’s yet to explore this tool, this guide is for you to learn everything you need to know about the Mac Task Manager equivalent and how to use it effectively.
Before We Begin
Although Activity Monitor can help manage system processes and quit unnecessary apps, there’s an even quicker, one-click solution you can use: MacKeeper. This system maintenance utility can close unwanted apps and help free up RAM on your Mac, so your system functions smoothly.
Optimize Your Mac With MacKeeper in One-Click
Say goodbye to sluggish performance and hello to MacKeeper, your ultimate one-click solution for optimizing your Mac. With its advanced features and user-friendly interface, MacKeeper empowers you to speed up a slow Mac , declutter your Mac , and protect your privacy with just a single click.
If you open applications on your Mac that start causing performance issues, you can use MacKeeper to close problematic apps, uninstall corrupt apps, and free up your Mac’s RAM to improve its performance.
Here are the steps to use a MacKeeper’s Memory Cleaner to free up RAM on your Mac :
- Download and install MacKeeper on your Mac.
- Open MacKeeper and click Memory Cleaner under the Performance tab.

3. Click Open .

- Click Clean Memory .

- It will clean your Mac and free up available memory. You can see how much memory it freed under Last Cleanup .

- You can also close a single problematic app on Mac using MacKeeper. To do it, click the Memory Usage tab in the left pane.

- Click Quit to confirm your decision and it will close the selected app.

If you think app cache is causing performance issues on your computer, you can use the Safe Cleanup feature to delete junk files on Mac . Here’s how to use the Safe Cleanup feature to remove cache and junk files on Mac:
- Launch the app and open Safe Cleanup from MacKeeper’s Cleaning section.

- Click Start Scan .

- Select the files you want to remove or click Check All .

- Click Clean Junk Files .

- This will remove the selected junk files from your Mac. You can click Rescan to repeat the process.

Lastly, you can use MacKeeper to uninstall corrupt and problematic apps on your Mac. Here’s how:
- Download and install MacKeeper on your Mac.
- Open MacKeeper and click Smart Uninstaller in the left sidebar under Cleaning .

- When the scan completes, Applications in the left sidebar, select the unused apps and click Remove Selected .

- Tap Remove on the pop-up window.

- This will delete the selected apps from your Mac, and you’ll get a Removal Completed notification. Click Rescan to start the scan again.

What Else Can MacKeeper Do?
Besides freeing up RAM, uninstalling unwanted apps, and clearing the cache on your Mac , you can use MacKeeper to scan your system for virus , delete duplicates on your Mac , and track app updates on your Mac. If you want to learn more, read my detailed MacKeeper review .
What Is the Mac Task Manager Equivalent?
The Mac Task Manager equivalent is called Activity Monitor. It’s a built-in application exclusive to macOS. Despite its different name and location, the Activity Monitor serves the same purpose as the Task Manager, allowing you to oversee your system resources, including CPU, memory, energy, disk, network, and cache usage.

Activity Monitor serves as an alternative to the Windows Task Manager on Mac, functioning as a tool that reveals the amount of memory consumed by processes on your Mac and displays the currently active applications, even if they are not visibly open.
You can also use the Activity Monitor to force quit unresponsive apps when the regular methods fail. If you’re unfamiliar with this Mac Task Manager, it may initially appear overwhelming.
To help you out, I’ve covered how to use open and use the Activity Monitor on Mac in detail below.
What Is the Control-Alt-Delete Shortcut for Mac?
On a Mac, the equivalent to the Windows Control-Alt-Delete shortcut is Command ⌘ + Option ⌥ + Escape . However, this keyboard shortcut doesn’t open the Task Manager Mac equivalent, Activity Monitor. Instead it opens the Force Quit Applications window, which is like a mini version of Activity Monitor.

In the Force Quit Applications window, you can select an unresponsive application and force it to quit which is something Windows Task Manager does.
Here’s how to force quit an app using Force Quit Applications on Mac:
- Press the Command ⌘ + Option ⌥ + Escape shortcut or click the Apple icon and select Force Quit .
- The Force Quit Applications window will appear, displaying a list of currently running applications.

- Find the app you want to force quit from the list. If the application is unresponsive or frozen, its name may be highlighted in red.
- Select the application by clicking it once. Click the Force Quit button in the bottom-right corner of the window.

- A confirmation dialog will appear, asking if you want to force quit the selected application. Click Force Quit to proceed.

- The application will be forcefully terminated, closing all its associated processes.
Please note that force quitting an application may result in any unsaved data being lost, so it’s recommended to save your work before proceeding with force quitting.
How to Open the Task Manager on Mac
To open the Task Manager on Mac, you have to open its equivalent: Activity Monitor. There are different ways to open the Task Manager Mac equivalent. To open the Task Manager on your Mac, you can use Spotlight, Finder, Launchpad, or the Dock.
Below, we’ve shared all the methods you can use to open Activity Monitor on your Mac.
From Spotlight
Spotlight search is a built-in feature on macOS that allows you to quickly search for files, applications, documents, emails, and perform various tasks on your Mac. It provides instant results and suggestions as you type, making it easy to find and access information and perform actions quickly on your Mac.
To open the Activity Monitor from Spotlight, follow these steps:
- Press the Command ⌘ + Space keys or click the magnifying icon in the menu bar to open Spotlight Search .

- In the search bar that appears on your screen, type Activity Monitor .

- As you type, Spotlight will start displaying search results. Look for the Activity Monitor application in the results list.
- Once you see the Activity Monitor app, click to open the utility.

The Activity Monitor will launch, providing you with detailed information about the processes and resource usage on your Mac.
From Launchpad
Launchpad on macOS provides a visually appealing and easy-to-navigate way to access and launch applications installed on your Mac. It displays a grid of icons representing your applications, similar to how apps are organized on iOS devices. Launchpad is especially useful for users who prefer a more app-centric approach to accessing and launching applications on their Mac.
To open the Activity Monitor from Launchpad, you can follow these steps:
- Click the Launchpad icon in the Dock.
- The Launchpad will open, displaying a grid of application icons and a search bar on the top.

- Type Activity Monitor in the search bar and it will display the Activity Monitor app icon.
- Click the Activity Monitor icon to launch the utility.
This will launch the Activity Monitor app on your Mac.
From Finder
To open the Activity Monitor from Finder, you can follow these steps:
- Open a new Finder window by clicking the Finder icon in the Dock.

- Click Applications in the left sidebar.

- Scroll down and find the Utilities folder.

- Navigate through the Utilities folder to find the Activity Monitor application.

- Once you find the Activity Monitor application, double-click to open the utility.
If you frequently use Activity Monitor, you can keep it in your Dock for easy access. But before you can do that, you need to open Activity Monitor using one of the previous methods. Then, once it is active and showing in the Dock, follow these steps to keep it in the Dock for future access:
- Right-click the Activity Monitor icon in the Dock.
- Hover your mouse over Options .
- Select Keep in Dock .

When you select Keep in Dock , a checkmark will appear next to it, indicating the application will remain in the Dock even after quitting. It means, from now on, you can conveniently access the Activity Monitor with a single click from your Dock.

How to Use Activity Monitor on Mac
Using the Activity Monitor is easy but you have to familiarize yourself with the interface and how to use its indicators. When you launch the Activity Monitor, you’ll see the following six tabs in the top toolbar:

You can use these tabs to monitor various aspects of your Mac’s performance. Understanding how to interpret the data in Activity Monitor can help you troubleshoot issues and keep your Mac running smoothly. Here’s a breakdown:
Check CPU Usage on Mac
The CPU pane in Activity Monitor provides information about the central processing unit (CPU) usage on your Mac. It displays real-time data on the percentage of CPU resources being utilized by each process or application.
You can sort by CPU usage to see which processes are using the most CPU. Navigate to the CPU tab in Activity Monitor to view the percentage of CPU capability being used by macOS (System), by your apps (User), and what’s not being used (Idle).
To check CPU usage on Mac using Activity Monitor, follow these steps:
- Open Activity Monitor. You can find it in the Applications folder, under Utilities , or use Spotlight Search (press Command ⌘ + Space and type Activity Monitor ).
- Once Activity Monitor is open, click the CPU tab at the top of the window. This will show you the CPU-related information.
- In the CPU pane, you’ll see a list of processes and applications, with their corresponding CPU usage percentages. The higher the percentage, the more CPU resources that process or application is consuming.

- To sort the processes by CPU usage, click on the % CPU column header. This will arrange the list in descending order, making it easier to identify which processes are using the most CPU.

By monitoring the CPU pane in Activity Monitor, you can keep track of CPU usage and identify any processes causing high CPU usage or impacting system performance.
Check RAM Usage on Mac
The Memory pane in Activity Monitor provides information about the Random Access Memory (RAM) usage on your Mac. It displays real-time data on the amount of memory each process or application uses.
Go to the Memory tab to see how much RAM is being used, including by apps (App Memory), by the system (Wired Memory), and how much is being compressed to make more RAM available (Compressed).

To check RAM usage on Mac using Activity Monitor, follow these steps:
- Open Activity Monitor by going to Finder > Applications > Utilities .
- Once the Activity Monitor is open, click the Memory tab at the top of the window. This will show you the RAM-related information.

- You’ll find a list of processes and applications, along with their corresponding memory usage. The Memory column displays the amount of RAM being used by each process.

- At the bottom of the RAM pane, you’ll see a summary of your Mac’s total physical memory, memory used, cached files, and swap used.

- To sort the processes by memory usage, click the Memory column header. This will arrange the list in descending order, making it easier to identify which processes are using the most memory.

By monitoring the RAM pane in Activity Monitor, you can keep track of RAM usage and identify any processes consuming excessive memory. This information can help you troubleshoot performance issues and manage memory resources effectively on your Mac.
Check Energy Use on Mac
The Energy pane in Activity Monitor provides information about the energy usage of applications and processes on your Mac. It shows how much energy each application consumes and provides insights into the impact on battery life for laptops or power consumption for desktops. The lower the score, the less battery your app is using.
The Energy metrics include energy impact, remaining charge, time remaining, time on battery, and battery in the last 12 hours.

To check energy use on Mac using Activity Monitor, follow these steps:
- Once the Activity Monitor is open, click the Energy tab at the top of the window. This will display the energy-related information.

- In the Energy pane, you’ll see a list of processes and applications, along with their corresponding energy impact. The higher the energy impact value, the more power the application is consuming.

- To sort the processes by energy impact, click the Energy Impact column header. This will arrange the list in descending order, making it easier to identify which processes are using the most energy.

Additionally, you can observe other metrics such as App Nap , 12 hr Power , and Preventing Sleep in the Energy pane to gain further insights into the energy usage of specific applications.

- App Nap : App Nap conserves energy by reducing the power consumption of applications that are not currently visible or actively performing tasks. The App Nap column in the Energy pane shows whether an application is using this feature, indicating its energy-saving behavior.
- 12 hr Power : The 12 hr Power column in the Energy pane shows an estimate of the average energy impact of an application over a 12-hour period. It provides a longer-term perspective on energy consumption.
- Preventing Sleep : The Preventing Sleep column indicates whether an application is preventing the Mac from going into sleep mode or idle sleep, potentially contributing to higher energy usage.
By monitoring the Energy pane in Activity Monitor, you can assess the energy consumption of applications and processes, identify energy-hungry applications, and make informed decisions to optimize energy usage on your Mac. This can be particularly useful for managing battery life on laptops or reducing power consumption on desktop systems.
Check Disk Activity on Mac
The Disk pane in Activity Monitor provides information about the disk activity on your Mac. It displays real-time data on read and write operations performed by applications and processes. The Disk tab shows the amount of data that each process has read from and written to your disk, helping you identify processes accessing the disk frequently.

To check disk activity on Mac using Activity Monitor, follow these steps:
- Open Activity Monitor by typing Activity Monitor in the Spotlight Search. You can open Spotlight by pressing Command ⌘ + Space .
- Once the Activity Monitor is open, click the Disk tab at the top of the window. This will display the disk-related information.

- In the Disk pane, you’ll see a list of processes and applications, with their corresponding read and write data rates. The Bytes Written and Bytes Read columns show the amount of data being read from and written to the disk by each process.

- To sort the processes by disk activity, click the Bytes Written and Bytes Read column header. This will arrange the list in descending order, making it easier to identify which processes are performing the most disk activity.

- You can also check the average disk usage at the bottom of the Disk pane in Data read/sec and Data written/sec options.

By monitoring the Disk pane in Activity Monitor, you can keep track of disk activity, identify processes heavily utilizing the disk, and gain insights into how applications are interacting with your storage system.
This information can help troubleshoot performance issues, manage storage resources efficiently, and identify potential bottlenecks related to disk activity.
Check Network Activity on Mac
The Network pane in Activity Monitor provides information about network activity on your Mac. It displays real-time data on network usage, showing how much data your Mac is sending and receiving over your network.

To check network activity on Mac using Activity Monitor, follow these steps:
- Open Activity Monitor using Spotlight Search. Press Command ⌘ + Space and type Activity Monitor .
- Once the Activity Monitor is open, click the Network tab at the top of the window. This will display the network-related information.

- In the Network pane, you’ll see a list of processes and applications, along with their corresponding network usage. The Sent Bytes and Rcvd Bytes columns show the amount of data being sent and received by each process.

- To sort the processes by network activity, click the Sent Bytes and Rcvd Bytes column header. This will arrange the list in descending order, making it easier to identify which processes are generating the most network traffic.

You can also use the Network pane to monitor other network-related information such as the Sent Packets and Rcvd Packets column, which displays the number of packets being sent and received by each process.

By monitoring the Network pane in Activity Monitor, you can keep track of network activity, identify processes utilizing network resources, and diagnose network-related issues. This information helps troubleshoot network performance, identify bandwidth-intensive applications, and manage network resources effectively on your Mac.
Check Cache on Mac
The Cache pane in Activity Monitor on macOS Ventura allows you to view content cache activity. Here are the steps to access it:
- Open the Activity Monitor app on your Mac, and click the Cache tab.

- If you don’t see the Cache tab in the Activity Monitor window, you need to enable it. To do it, choose Apple menu > System Settings .
- Click General in the sidebar and select Sharing .
- Scroll down and turn on Content Caching .
- After that, quit and reopen Activity Monitor to view Cache information.
- To see data served for a particular period of time, click the pop-up menu at the bottom of the window, then choose a time period.

The Cache pane displays the following content caching statistics:

- Data Served : Total amount of data the content cache has served. When these values are nonzero, the content cache is working.
- Data Served From Cache : Amount of data the content cache has served from its cache. The closer these values are to the Data Served values, the more the content cache is helping.
- Data Dropped : Amount of data the content cache downloaded but couldn’t add to its cache.
- Data Served From Origin : Amount of data the content cache downloaded over the internet.
- Data Served From Parents : Amount of data the content cache downloaded from any of its parent content caches.
- Data Served From Peers : Amount of data the content cache downloaded from any of its peer content caches.
- Data Served To Children : Amount of data the content cache served to any of its child content caches.
- Data Served To Clients : Amount of data the content cache served to client Mac computers, iOS devices, iPadOS devices, and Apple TV devices.
- Data Served To Peers : Amount of data the content cache served to any of its peer content caches.
- Data Uploaded : Amount of data uploaded from clients through the content cache.
- Maximum Cache Pressure : How urgently the content cache needs more disk space. Lower cache pressure is better. If these values are higher than 50%, you should assign the cache more space, move the cache to a larger volume, or add content caches.
How to See Your System Status in the Dock With the Activity Monitor
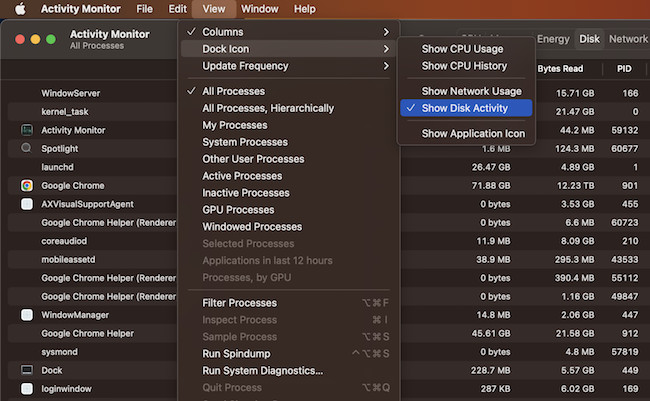
You can monitor your system status right from the Dock by right-clicking the Activity Monitor app icon in the Dock, going to Dock Icon, and choosing the type of data you want to display.
There’s another way to view a quick summary of system status right in your Dock using the Activity Monitor. Here’s how to set it up:
- Open Activity Monitor (You can find it by searching for it in Spotlight, which you can access by pressing Command ⌘ + Space , or access it via the Utilities folder within Applications ).
- With the Activity Monitor open, click View in the menu bar and hover your mouse over Dock Icon .
- From the side menu that appears, select Show CPU Usage , Show CPU History , Show Network Usage , or Show Disk Activity , depending on what you want to monitor.
- The selected option will replace the Activity Monitor icon in the Dock with a live graph showing that system statistic.

Remember, Activity Monitor needs to be open for this to work. If you close the Activity Monitor, the Dock icon will revert back to the standard Activity Monitor icon.
Use Mac Task Manager Equivalent Like a Pro
The Activity Monitor is a powerful tool for managing and understanding your Mac’s performance. From monitoring CPU and memory usage to tracking energy consumption, Activity Monitor provides a comprehensive view of your Mac’s performance.
If you need more help, here are some more tips for you:
- Learn how to use Activity Monitor on your Mac to monitor your system usage and other processes.
- You can monitor Mac CPU, GPU, and RAM usage using the Activity Monitor.
- Activity Monitor can help you free up RAM on your Mac and optimize your system performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i get to task manager on mac.
To access Task Manager on a Mac, open Activity Monitor . Press Command ⌘ + Space to open Spotlight search, type Activity Monitor and hit Enter . It provides detailed information about CPU, memory, energy, disk, network, and cache usage.
Why can’t I open Task Manager on Mac?
If you can’t open Activity Monitor (Task Manager on Mac), it may be due to restricted permissions or system issues. Try restarting your Mac, checking your user permissions, or running Disk Utility to check for disk errors. If problems persist, contact Apple Support.
How to clear RAM Mac using Activity Monitor?
To clear RAM on a Mac using Activity Monitor, open the application, click the Memory tab, select a process that’s consuming a lot of memory, and click the x button to quit the process. This can help free up RAM.
I'm Hashir, a tech journalist with a decade of experience. My work has been featured in some of the top tech publications like MakeUseOf and MakeTechEasier. I have a bachelor's degree in IT, a master's in cybersecurity, and extensive knowledge of Apple hardware, specifically MacBooks. As the senior writer at MacBook Journal, I write in depth guides that help you solve any issues you have with your mac and unbiased reviews that help you make the right buying decisions.
Hi there! I'm Ojash, a tech journalist with over a decade of experience in the industry. I've had the privilege of contributing to some of the world's largest tech publications, making my mark as a respected Mac expert. My passion lies in exploring, using, and writing about MacBooks, and I enjoy sharing my expertise to help others make informed decisions and get the most out of their MacBook experience. Join me as we delve into the fascinating world of MacBooks together!
You May Also Like

How to Check Storage Space on Your Mac: 8 Best Ways
Written by Hashir Ibrahim Reviewed by Ojash Last updated: August 28, 2023 Expert

How to Clear Temp Files on Mac: 4 Tried and Tested Methods
Clear temp files on Mac efficiently to free up space

How to Organize Files on Your Mac: Top 10 Best Ways
Streamline file management with these Mac organization methods

How to Catch and Remove Hidden LaunchDaemons on Mac: 2 Top Ways
Written by Hashir Ibrahim Reviewed by Ojash Last updated: September 6, 2023
- 24/7 Live Chat
+1 877 315 1713
Find anything you need
You have %itemCount% in your cart. Total being %total%
How to Use Task Manager macOS and Activity Monitor
Before I started using a Macbook, I was always a Windows user. Making the change wasn’t easy, as many things are different on the macOS X system than any Windows I’ve seen before. Don't be afraid if you’re in the same shoes as I was. Everything you know and love from Windows can be found on a Mac under a different name.

One frequent thing new Mac users seem to look for is the Task Manager . It’s a useful tool on Windows that allows you to see a plethora of information at once. With the Task Manager, you can force quit apps (known as the “End Task” option on Windows) and see various consumption details.
Coming from Windows , I know that the Task Manager is an essential tool to identify issues or force quit apps. It’s almost a knee-jerk reaction to open it as soon as you suspect something is wrong. However, the classic “ Ctrl-Alt-Del ” shortcut doesn’t work on a Mac. Trust me, I tried.
On macOS X, this tool is called the Activity Monitor . It delivers on the same premise but operates in a slightly different way. If you’re lost and want to know where to find this tool and how to use it on Mac, this article is here to help.
Summary: Task Manager MacOS
The Mac Task Manager is a mini-version of the Activity Monitor. To open it, simultaneously press down the [CMD] + [ALT] + [ESC] keys on your keyboard . This will open a window containing a list of all currently opened programs and applications that are running in the background.
What is Activity Monitor in Mac?
Activity Monitor in Mac is basically the equivalent of Windows Task Manager. This utility shows how much memory your Mac processes are using and which apps are currently active (even if they aren't open), letting you force quit stalled ones if you can't close them the usual way. If you've never used the task manager in Mac before, it can be quite a lot to take in.
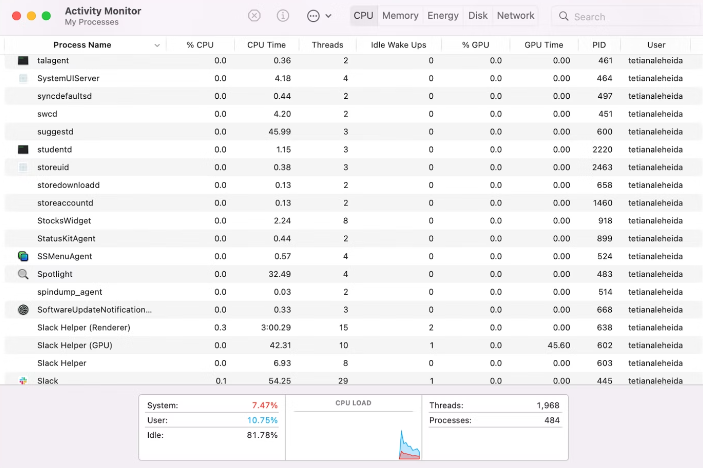
How to open the Task Manager on Mac - Task Manager macOS
Most Windows users know you can quickly fire up the Task Manager by right-clicking on the taskbar. This feature is missing from Mac, as right-clicking on the Dock only brings up some settings.
So, how exactly do you open the Activity Monitor — the Mac equivalent of the Task Manager — if there’s no shortcut or Dock option?
Launching Activity Monitor (Task Manager Mac) is still quite simple. Pick one of the three ways to do it:
Open Activity Monitor from Spotlight:
- Press Command + Space to open Spotlight
- Start typing Activity Monitor
- Once Activity Monitor comes up highlighted, hit Enter or click on it.
Open Activity Monitor from Finder:
- Go to your Launchpad (the rocket icon in your Dock) or Click on Finder in your Dock.
- Double-click on the Activity Monitor icon.
Open Activity Monitor from Dock:
If you're having recurring troubles, setting up Activity Monitor in your Dock is something worth doing. It's essentially a handy one-click Mac Task Manager shortcut. But before you can open Activity Monitor from your Dock, you must first use one of the previous two methods. Then, once Activity Monitor is active:
- Right-click on the Activity Monitor icon in your Dock.
- Select Options.

- You can launch Task Manager mac like any other program.
What is the Control-Alt-Delete shortcut for Mac?
Sadly, there’s no direct shortcut to open the Task Manager on a Mac. However, you can use a shortcut to force quit applications, which is one of the things the Task Manager in Windows is capable of.
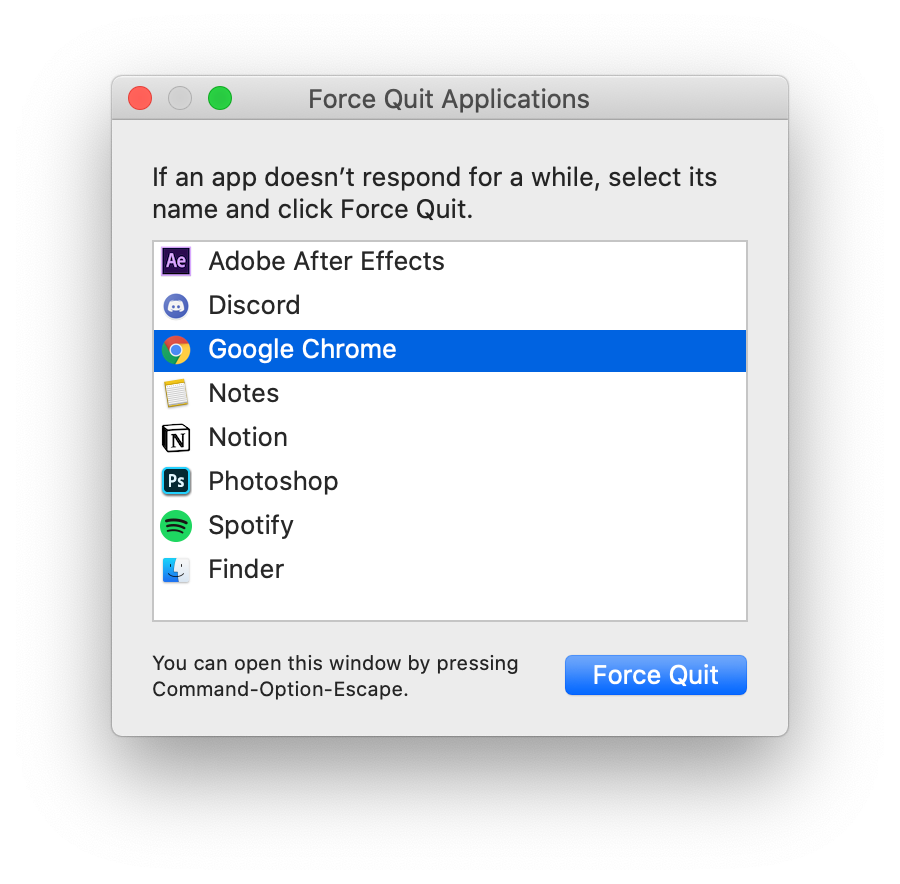
Press the ⌘-Option-Esc shortcut on your Mac to bring up the Force Quit utility. Here, simply select the app you want to close and click on the blue button in the corner. If an application is frozen and not responding, its name will be highlighted in red.
How to use Activity Monitor on a Mac - How to use Mac Task Manager
If you decide to use Activity Monitor as your task manager on Mac, you should learn how to work with its monitor indicators.
When you open the Activity Monitor, you’ll be able to see all of the applications currently running on your Mac. The apps and processes appear even if running in the background, making it easy to spot unusual activity.
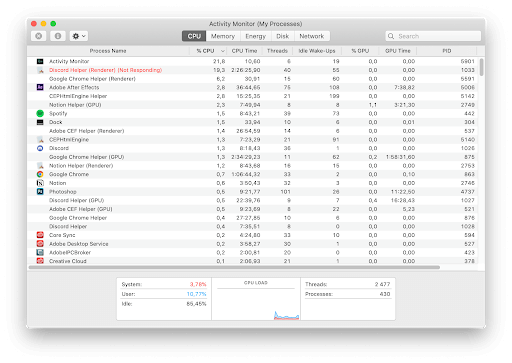
Task Manager mac - CPU usage
By default, the Activity Monitor opens on the CPU tab. This means you can see what’s consuming the most of your Mac's CPU power. It also shows you the exact percentages of power they are consuming and how long each app has been running.
You can sort all processes in Activity Monitor by CPU usage, from highest to lowest, by choosing View > All Processes and clicking on the %CPU column.
You might notice a process in the CPU tab called "kernel_task" that could take a large share of resources. Don't panic, and don't shut it down! The process simply ensures your CPU isn't working too hard by forcing other memory-intensive Mac processes out. As a result, it might seem like one of the heaviest processes on the list. Similarly, "mds" and "mdworker" help index files for the Spotlight search, which sometimes spikes their appetite.
Task Manager mac - Check RAM usage
Switching to the Memory tab (the second tab) in the Activity Monitor, you can see the amount of RAM each process consumes. RAM is directly responsible for the speed of your Mac, so getting rid of heavy users is the fastest way to speed things up. Like Windows, you need to pay attention to having enough RAM for your computer to function properly. If too much of your memory is taken up, you’ll notice that your system is slow and a pain to operate. Make sure to close out apps with high RAM consumption to avoid this.
Another interesting feature you can see in the Memory tab is the RAM Pressure Gauge at the bottom. If the bar is green, then your Mac's RAM isn't being taxed too much. But if it turns red — consider buying additional memory for your machine.
Tip: You can decrease CPU and RAM consumption by apps through the App Tamer, a menu bar utility that spots heavy consumers on your Mac and slows them down automatically.
Check for energy use in macOS task manager
The Energy tab helps you reduce battery usage by monitoring what applications are consuming your battery. Use this tab when your MacBook is unplugged to extend your battery life until you can plug back in.

Tip: check Avg Energy Impact — this will tell you which apps consume the most energy on average. If you don’t use those apps often, consider getting rid of them.
Disk activity on a Mac Task Manager
While the Disk tab is not as useful daily as the others, it’s still a crucial part of the Activity Monitor. Here’s where you can find all processes interacting with your hard drive and rewriting data. If you get a malware infection, you’ll be able to spot and quit the harmful processes here.
Network activity on a Mac Task Manager
The last tab in the Activity Monitor is the Network tab. It displays all the data sent and received by the apps you’re currently using. I personally use this tab to spot any outliers sending large amounts of data when I’m using my Mac to browse or work online.

Inspect processes in Mac Activity Monitor
If you want to go deeper into a specific process running on your Mac, highlight the process in Activity Monitor and press Command + I. Alternatively, to see the process go to View > Inspect Process. On the inspection screen, you’ll find information about how much CPU and memory this process uses, how long it runs, and more.
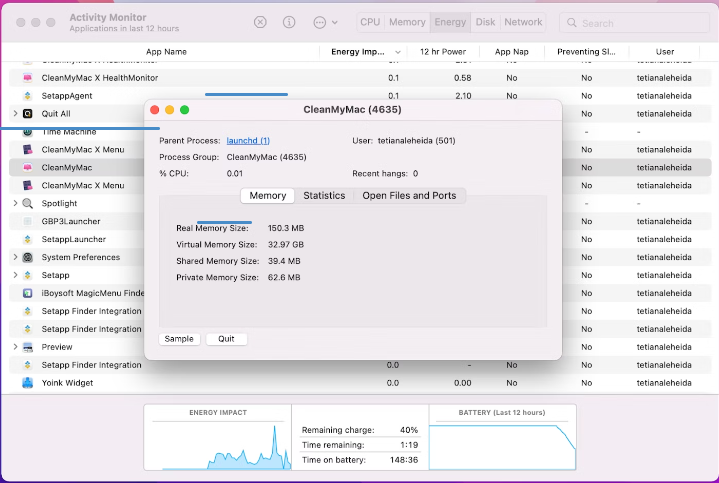
How to see your system status in the Dock with the Activity Monitor
You might think that it’s a hassle to constantly have to keep searching for the Activity Monitor to see the status of your Mac. I thought the same too, which is how I found out that there’s a much easier way.
Keep an eye on your system status right from your Dock by utilizing the live update feature of the Activity Monitor. Simply open the Activity Monitor and expand the View tab in the top-bar of your Mac. Here, hover over the Dock icon and select the desired update you want to see.
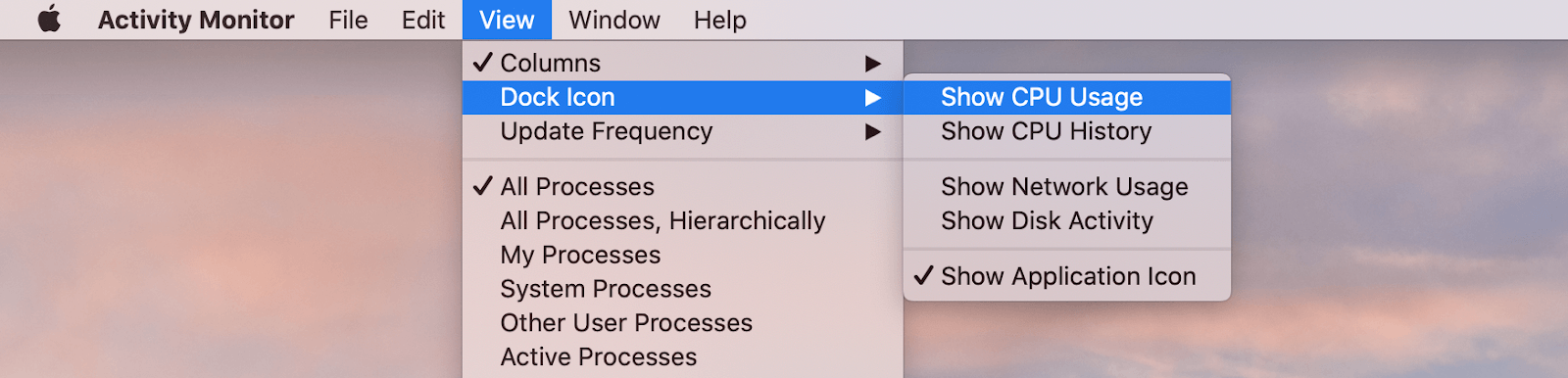
After choosing the option you wish to display, you’ll immediately see the Activity Monitor change to a live update.
Exclusive: New MacBook Pros and Mac minis THIS MONTH!
Final Thoughts
Hopefully, this article has given you the answers to your questions regarding the Task Manager in Mac. If you have anything else you want to know about the macOS system, make sure to visit our Help Center section to find further articles and guides.
Are you looking for more tips? Check out our other guides in the Softwarekeep Blog and our Help Center ! You'll find a wealth of information on how to troubleshoot various issues and find solutions to your tech problems.
Sign up for our newsletter and access our blog posts, promotions, and discount codes early. Plus, you'll be the first to know about our latest guides, deals, and other exciting updates!
> How To Change Folder Color on Mac > Fixed: MacBook Pro Booting Black screen > How To Install Windows on Mac Using Parallels > Power Bi for Mac > How to Hide MacOS Catalina from Mac Software Update
1591 McKenzie Way, Point Roberts, WA 98281, United Sates
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy & Cookies
© SoftwareKeep 2023 | All right reserved
- American Express
- Diners Club
How to open Task Manager on Mac
If you have recently switched from Windows to Mac, you may find that most Windows keyboard shortcuts don’t work on a Mac. While navigating the Mac operating system does have its own method, most users find it intuitive and quick to learn.
The most frequently asked questions from new Mac users include:
- What is Control Alt Delete on a Mac?
- How to get Task Manager on a Mac?
- How to force quit on a Mac, and so on.
In this blog post, we will explain the Mac equivalent of the Windows Task Manager and how to view running processes in macOS.
1. What is the Control Alt Delete for Mac. 2. How to open Mac Task Manager. 3. How to see what programs are running on a Mac. 4. How to use Activity Monitor on a Mac. 5. How to force quit on a Mac. 6. How to monitor memory usage with Memory Cleaner. 7. Frequently asked questions about memory usage on a Mac.
1. What is the Control Alt Delete shortcode for Mac
Control-Alt-Delete is a shortcut to call the Force Quit command for programs on Windows. For the macOS system, you should use the Command-Option-Escape shortcut to call the Force Quit Applications window.
Also, you can get this window by clicking the Apple icon in the Menu bar and selecting Force Quit .
2. How to open Task Manager on a Mac
When an application freezes on Windows, the Ctrl-Shift-Esc command is used to bring up the Task Manager and quit the process in question. But how about on a Mac? How do you end processes that crash Safari or lock the machine up?
First, we would like to mention that the Mac equivalent of Task Manager is called Activity Monitor. Just remember that Apple Task Manager = Activity Monitor .
Use one of these two ways to open Activity Monitor on a Mac:
3. How to see which programs are running on your Mac
1. Use Activity Monitor
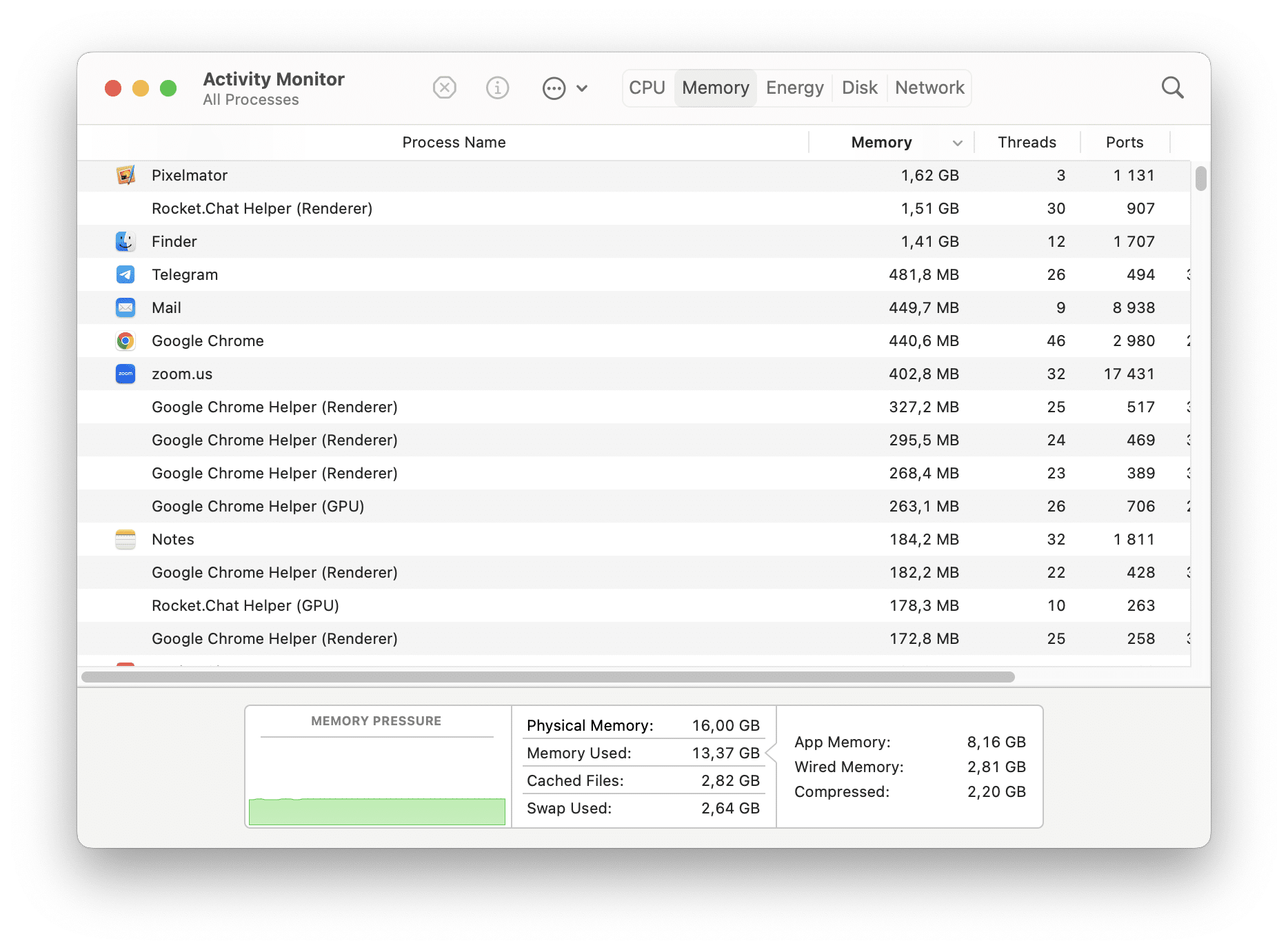
With Activity Monitor, you can monitor many parameters of the system, such as:
- Energy used
- Network monitoring
2. Use Terminal* to view a list of running processes.
For those who prefer working with Terminal, there are simple commands to view the list of running programs. Just open the Terminal and type only one word:
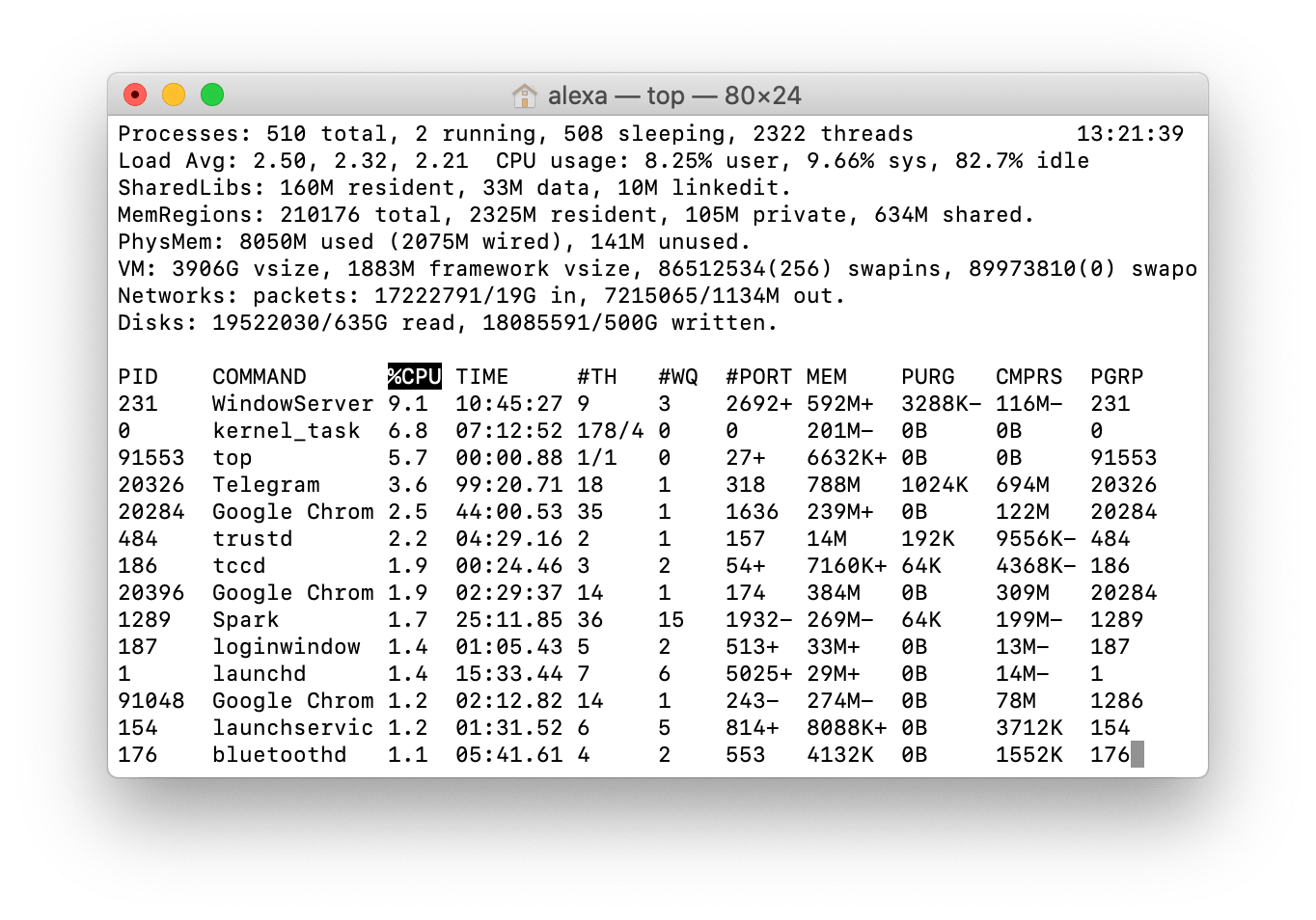
If you need to view a list of the most voracious applications that consume the most bytes, sort them by CPU:
Sort applications by memory usage:
top -p size
*For more tips like this, see our previous article Top 8 most useful Terminal Commands.
4. How to use Activity Monitor on a Mac
Now let’s take a closer look at each parameter of open programs on a Mac. With help from Activity Monitor, we will identify the programs and processes that are consuming too much of your system’s resources.
How to check CPU usage on a Mac
If your Mac starts working too slowly, it overheats , the fans work continuously and make noise, and programs may freeze. Most likely there are some programs that are consuming a large portion of processor load. You can identify such programs with the help of Activity Monitor.
In this case, launch Activity Monitor and go to the CPU tab . Sort the list of programs by CPU column, find out the programs that use most CPU, and close such programs.
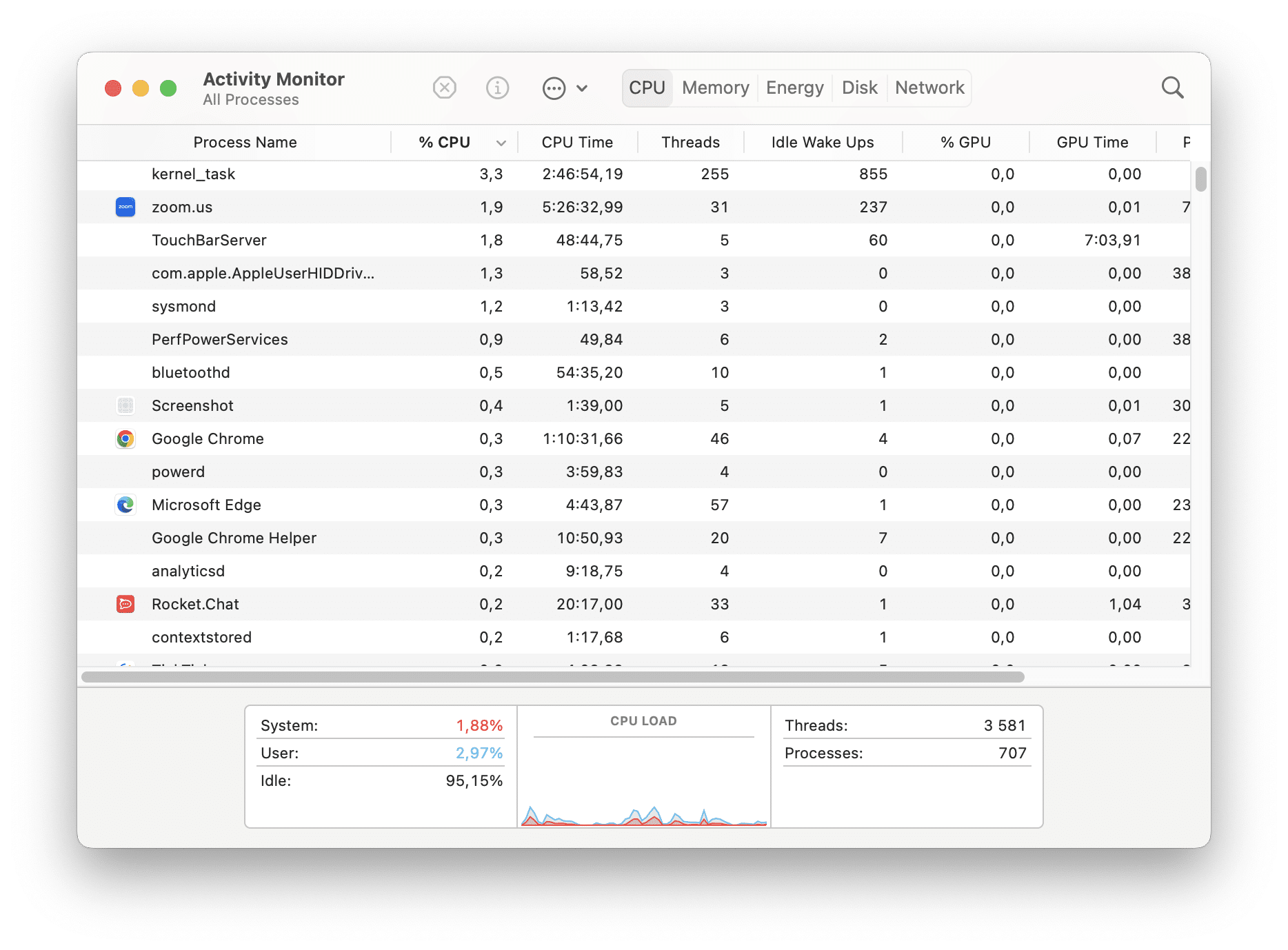
How to check RAM usage on a Mac
If your computer is running slowly, there are several indicators that your Mac’s performance is due to limited RAM. One example is when programs work slowly and documents even open slowly, but without overheating or the fans making noise. In this case, there is most likely not enough free RAM on your Mac for your programs to function properly. To create more free space, find the programs that use the most memory and close unused ones.
In the Activity Monitor app, go to the Memory tab to see memory intensive Mac processes.
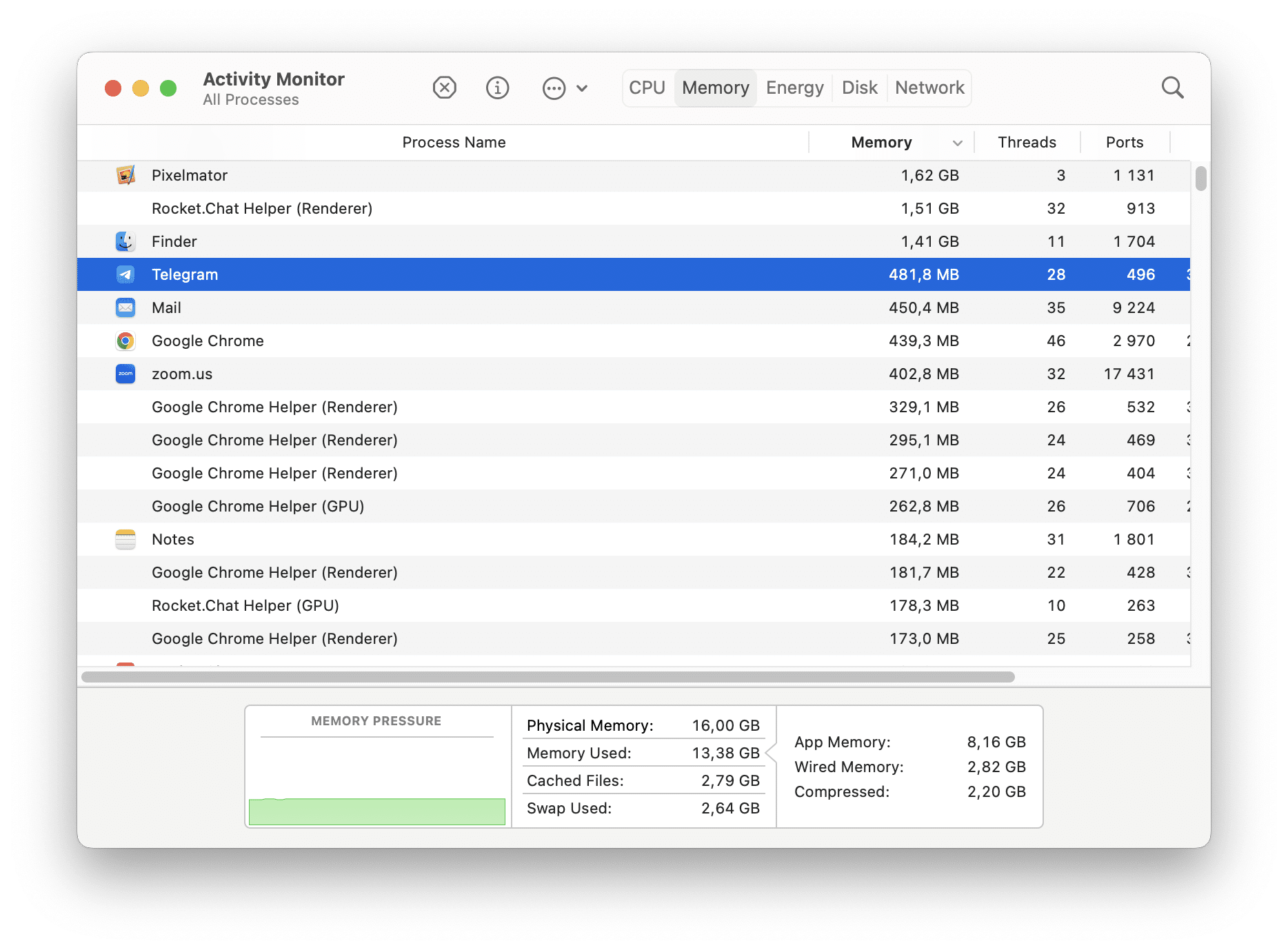
How to find apps that are using and draining the most battery life
If your Macbook’s battery is draining very quickly, we recommend checking the programs which are using the most energy. To get this information, switch to the Energy tab within Activity Monitor . Here you can find the data relating to how apps use your Macbook’s battery. Find the apps that are using the most energy, and if you don’t need them at the moment, close them.
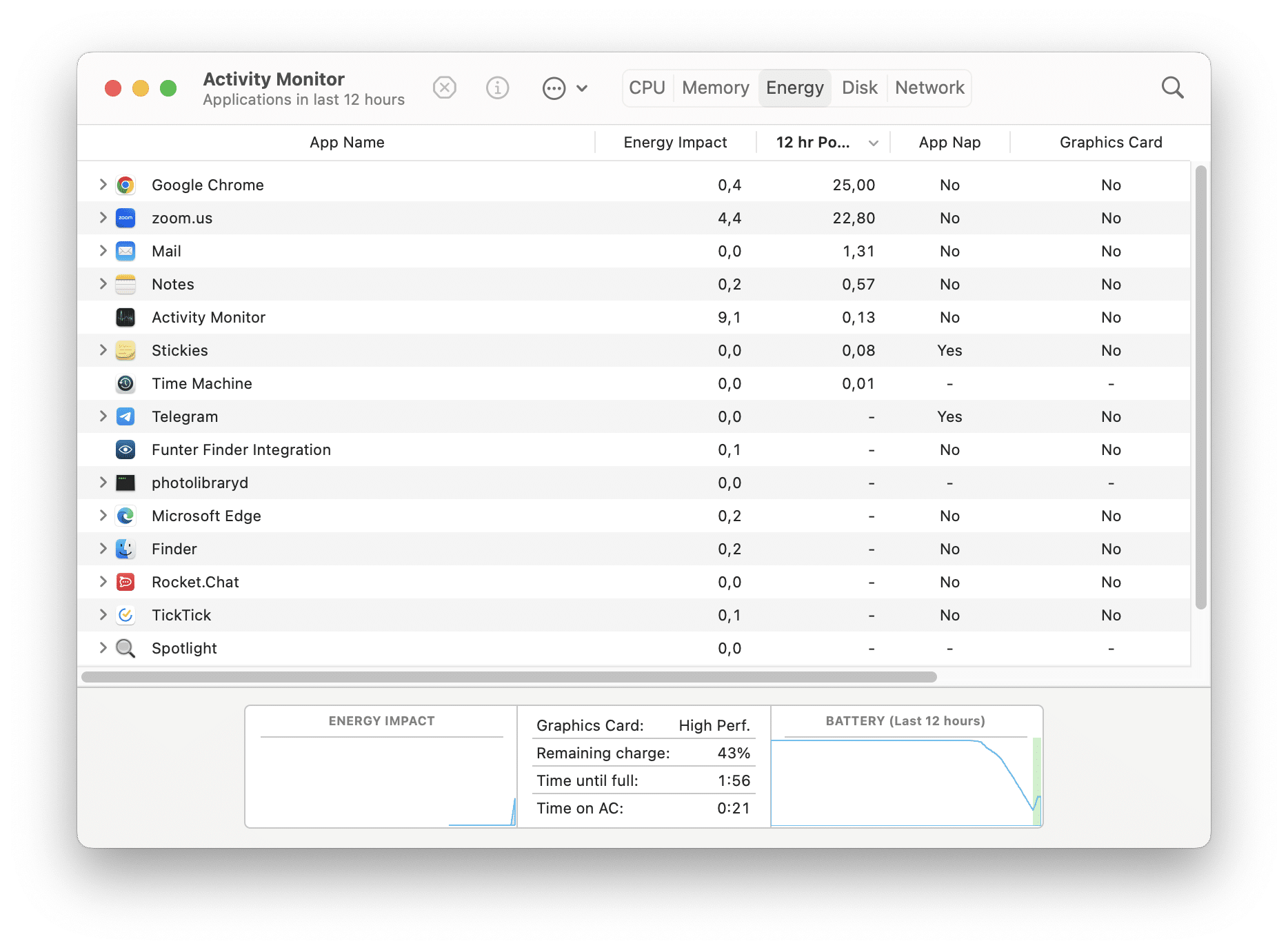
How to check Disk activity on a Mac
Most users don’t need to worry about the Disk tab . This part of Activity Monitor allows users to troubleshoot or monitor real-time disk activity. Here you can check how much data is being written to and read from your Mac’s drive by different processes, as well as the number of times that your Mac accesses the disk.
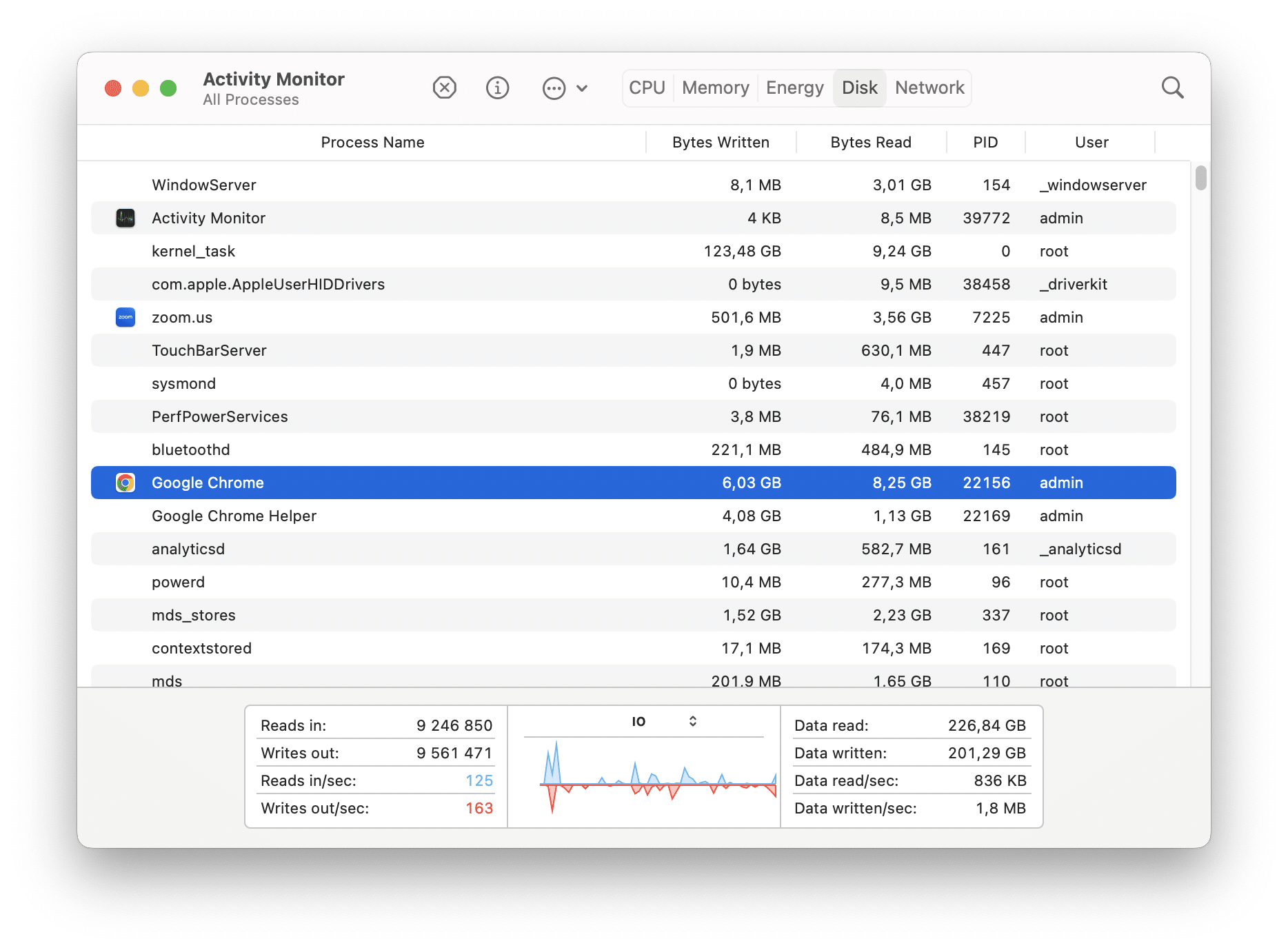
How to check Network activity on a Mac
If you are having internet problems, if some network accounts are unavailable, or if network connections fail often, then you should check Network activity on your Mac. Go to Activity Monitor’s Network tab to see how much bandwidth the processes are using. Then sort the programs by “sent Bytes” or “Read Bytes” to see the most active processes. Finally, close unneeded active programs.
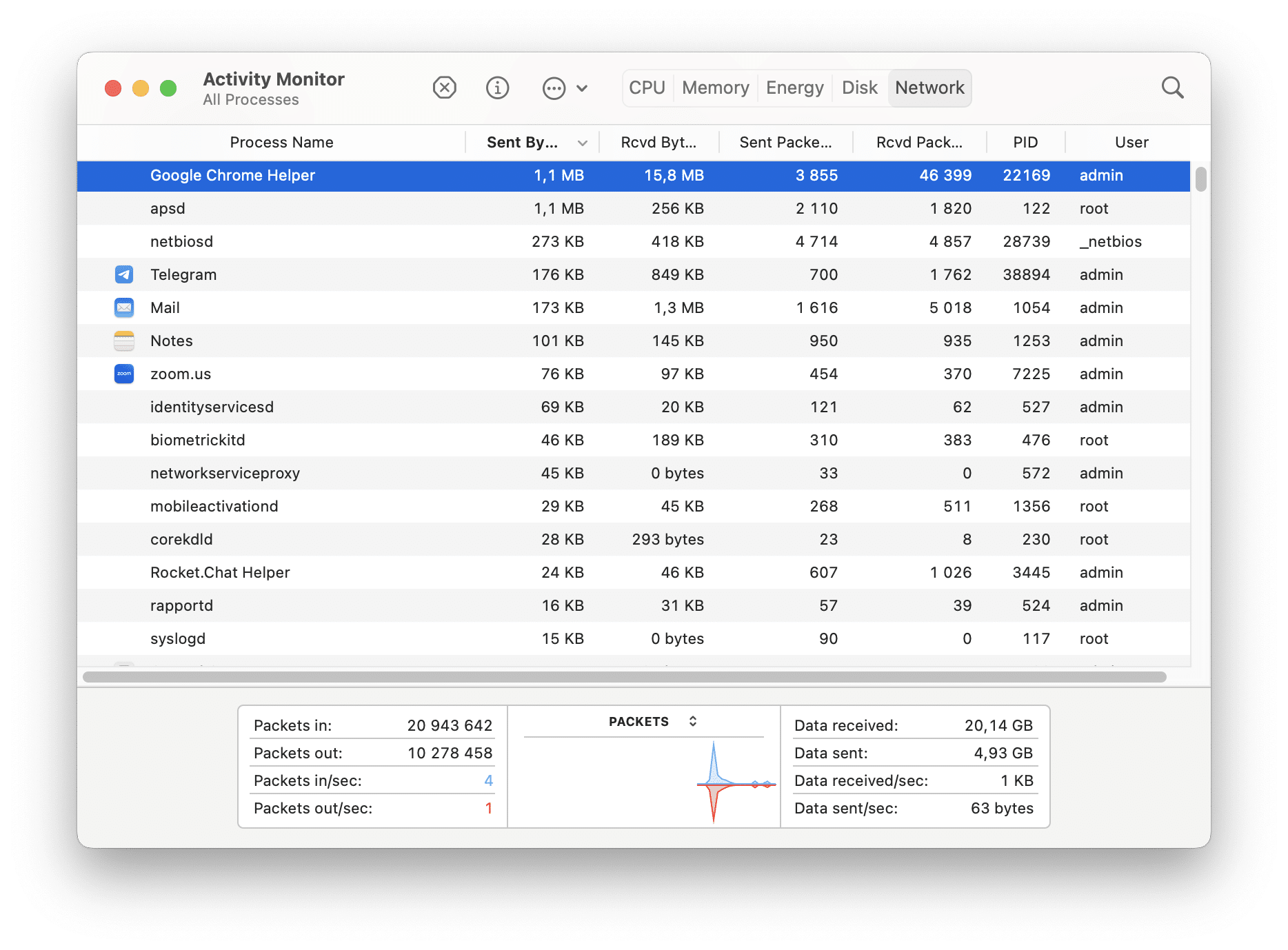
5. How to force quit on a Mac
Whenever any application crashes on your Mac or it doesn’t respond for a while, you may need to force quit it. Here are several ways to do that:
1. Use the Dock panel.
Click the app’s icon in a Dock panel, hold the Option key and select Force Quit command.

2. Use the “Force Quit” dialogue.
What to do when the Dock won’t pop up? A list of open programs can be also viewed via a “Force Quit” dialogue. There are two ways to open the “Force Quit” dialogue:
- Use the simple keyboard shortcut Command + Option + Escape.
- Or go to the System Menu → select Force Quit command.
Then select the app you want to stop and click on Force Quit.
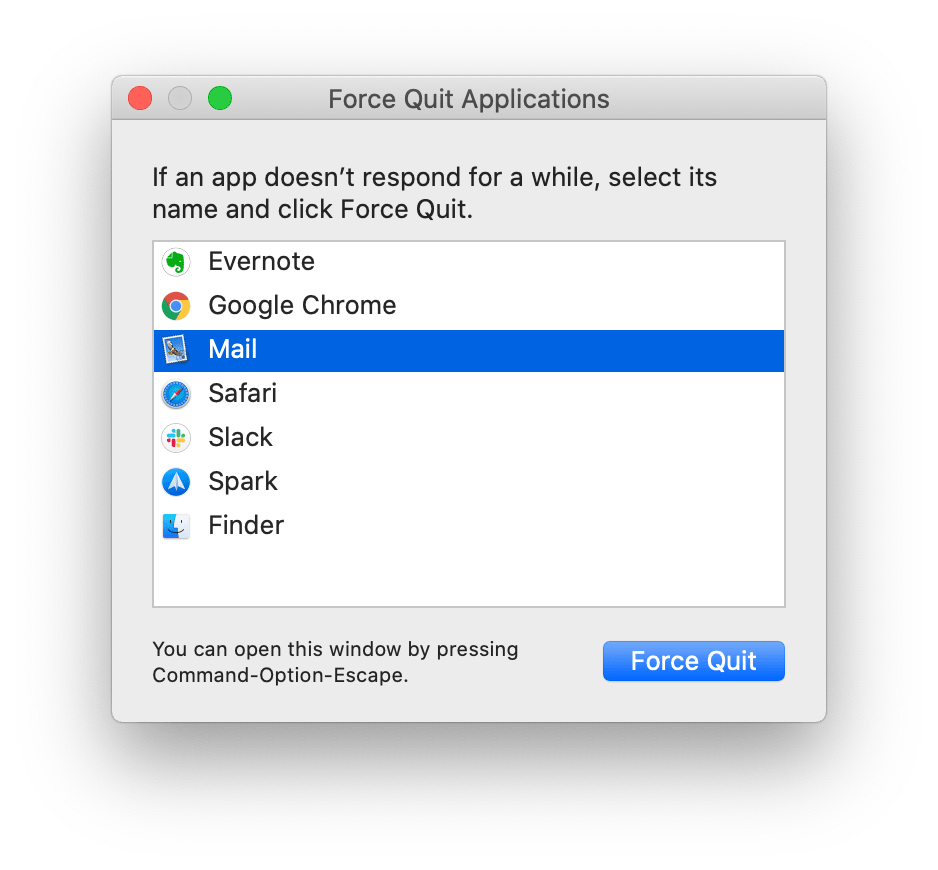
6. How to monitor memory usage with Memory Cleaner
In the previous paragraphs, we showed several ways to force close apps on a Mac in order to find out what apps are running. Now we would like to share an easy way to complete all these tasks and speed up your Mac in just one click. Simply use the free utility, Memory Cleaner .
Memory Cleaner can display the list of apps that use the most memory on your Mac, clear inactive RAM memory with just one click, and stop all running applications. With the app, you can get access to memory usage directly from the menu bar.
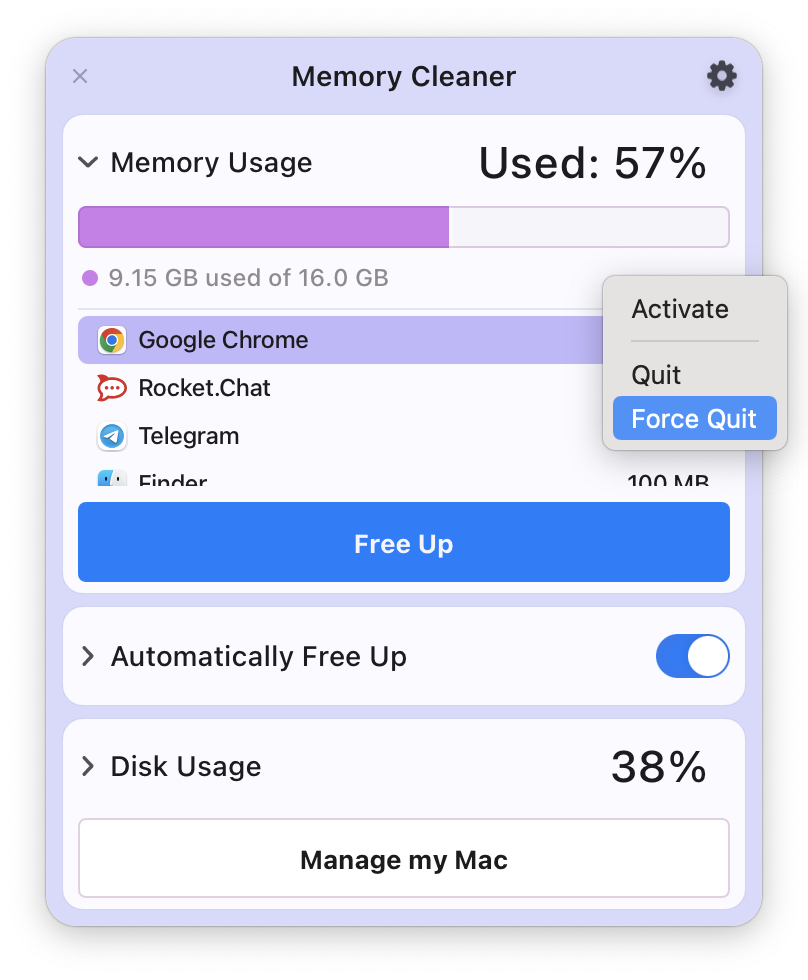
As you can see, there are various equivalents of macOS Task Manager, and Activity Monitor is one of them. It is a built-in utility that is used by most Mac users. However, if you want to monitor RAM memory usage and clear inactive RAM, we would recommend using the free Memory Cleaner app.
Frequently asked questions about memory usage on a Mac
The equivalent of Windows Task Manager on a Mac is the Activity Monitor application. Activity Monitor is the default Apple application, which you can easily find in Launchpad.
Activity Monitor displays open programs on your Mac, as well as detailed information about them, including CPU usage, memory usage, disk usage, network usage, and energy impact. With Activity Monitor you can manage working processes and quit tasks or apps.
Activity Monitor allows you to terminate all the processes and applications running on your system. But since most of the processes are system ones, we do not recommend selecting all the processes and click to force close them all at once. Closing some system processes may prevent your Mac from functioning.
Select an app you want to terminate, and then use the Stop button on the toolbar.
Follow these steps to find malware using Activity Monitor:
- Quit all your network-related apps (web browsers, iTunes, email clients and so on).
- Disable Bluetooth.
- Disable all the options in the System Preferences → Sharing section.
- In Activity Monitor, go to the Network tab.
- Check whether there is unexpected network activity on your Mac.
In the Activity Monitor app, go to the CPU tab. Check which apps are using too much of the CPU’s resources. Select those apps and click the Stop button (X icon on the top).

About the author

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
One of the fastest ways to open Activity Monitor is by using Spotlight. To open "Spotlight," click the small "magnifying glass" icon in your menu bar (or press Command+Space). When the "Spotlight Search" bar appears, type "activity monitor," and hit "Return." Or you can click the "Activity Monitor.app" icon in the Spotlight results.
Click on the Finder icon on your Mac. Click on Applications in the left pane. Scroll down to Utilities and open it, and then click on the Terminal icon. When the Terminal opens, simply type " top " and press Enter. The Terminal shows you a list of all running processes and applications.
Depending on your preference or workflow, you can use various methods to launch task manager (Activity Monitor) on a Mac. 1. Using Spotlight Search. This method is often considered a shortcut to open Activity Monitor on Mac. Press the Command + Spacebar keys to access Spotlight Search. In the Spotlight Search box, type in Activity Monitor → ...
Another solution for force quitting select apps on Mac is to use Activity Monitor: Open Activity Monitor (Press Command + Space to open Spotlight. Start typing Activity Monitor. Once you see the app highlighted, hit Enter). Navigate to either the CPU or the Memory tab and find the slow process. Click to highlight.
Learn how to open the activity monitor on your M1 Macbook air. This represents the task manager found in Windows. Literally how to open task manager on Macbo...
Launch the Activity Monitor on your Mac. You can find it in the /Applications/Utilities folder. Under the Process Name list, select the app or process you want to quit. To make finding the culprit ...
Open Activity Monitor on your Mac, select the unresponsive app under the CPU tab, and click the Stop (X) button at the top. Click Force Quit when prompted to confirm, and the app will shut off. This process is similar to closing apps using Task Manager, so it shouldn't be difficult to force close apps on macOS if you recently switched from Windows.
1. Open Task Manager or Activity Monitor On MacBook. If the Activity Monitor Icon is not available on the Dock, you can open the Activity Monitor by launching the Finder on your MacBook.. 1. Click on the Finder icon (Happy Face) located at the left corner of the Dock on your Mac.. 2. On the next screen, select Applications in the left-pane and open the Utilities Folder by double clicking on it.
To force quit an app from a Mac Task Manager, do the following: Open the Activity Monitor on your Mac and click on the application you want to force quit. Then click on the X button in the top left corner of the Activity Monitor window. You will see a pop-up window asking if you want to quit this process.
Open the task manager (Activity monitor) on your Mac. Highlight the process on the Activity monitor, then click command plus 'i'. Or, go to 'View' and click 'Inspect process.'. An inspection screen will appear where you can view the CPU performance, RAM, and all other details.
The Spotlight button is located in the menu bar at the top right corner of your Mac's screen and looks like a magnifying glass. To access the Spotlight button you can just click on it: 💡 Another way to access Spotlight is by using the Command Spacebar keyboard shortcut. Then, the Spotlight Search will appear.
How to open task manager in MacBook? Learn to use setting on how to open the task manager in the MacBook Pro or Air. A simple tutorial that teaches you the s...
If you're coming Windows, then you're probably used to the task manager and could be wondering where the task manager for mac is. Just like any Windows mach...
5. Click on the "Disk" tab to view total disk activity across all processes, as well as the amount of data each process has read from and written to your disk. 6. Click on the "Network" tab to view the amount of data your Mac is sending and receiving over your network. The Network tab can be useful for identifying the processes sending ...
Activity Monitor is the Mac task manager equivalent. It shows you a complete list of all processes running on your machine, as well as how much of your system's resources each program is using. You can use task manager on Mac for many things: Kill frozen apps that refuse to close properly. See which apps and processes are slowing down your ...
The easiest way to force a program to quit on your Mac is a simple key sequence similar to ctrl+alt+delete. Just tap COMMAND+OPTION+ESC, in that order. Here's where those keys are located on a typical Mac keyboard: This will bring up a task manager type window that looks like this: Command+Option+ESC brings you here.
Here's how to force quit an app using Force Quit Applications on Mac: Press the Command ⌘ + Option ⌥ + Escape shortcut or click the Apple icon and select Force Quit. The Force Quit Applications window will appear, displaying a list of currently running applications. Find the app you want to force quit from the list.
Then, once Activity Monitor is active: Right-click on the Activity Monitor icon in your Dock. Select Options. Choose "Keep in Dock". Note: "Keep in Dock" should now have a checkmark beside it, which means it will stay in the Dock even if you quit the app. You can launch Task Manager mac like any other program.
In that case, you can use Task Manager on your MacBook Air called Activity Monitor, which lives in the "Application > Utilities" folder by default. Or you can find Task Manager on your MacBook Air using Spotlight shortcut: Step 1. Open "Spotlight" on your MacBook Air. Step 2. Select the magnifying glass icon on the Apple menu bar. Step 3.
Whenever any application crashes on your Mac or it doesn't respond for a while, you may need to force quit it. Here are several ways to do that: 1. Use the Dock panel. Click the app's icon in a Dock panel, hold the Option key and select Force Quit command. 2. Use the "Force Quit" dialogue.
How to see task manager on Mac? The activity monitor of macOS is equivalent to the task manager on Windows, where you can track which programs are consuming ...
4. Force Quit From the Terminal. macOS also has its own command line application that allows you to quit open applications with the help of a little code. Head to Launchpad, open the Other folder ...