
- C Programming Tutorial
- C - Overview
- C - Features
- C - History
- C - Environment Setup
- C - Program Structure
- C - Hello World
- C - Compilation Process
- C - Comments
- C - Keywords
- C - Identifiers
- C - User Input
- C - Basic Syntax
- C - Data Types
- C - Variables
- C - Integer Promotions
- C - Type Conversion
- C - Booleans
- C - Constants
- C - Literals
- C - Escape sequences
- C - Format Specifiers
- C - Storage Classes
- C - Operators
- C - Arithmetic Operators
- C - Relational Operators
- C - Logical Operators
- C - Bitwise Operators
- C - Assignment Operators
- C - Unary Operators
- C - Increment and Decrement Operators
- C - Ternary Operator
- C - sizeof Operator
- C - Operator Precedence
- C - Misc Operators
- C - Decision Making
- C - if statement
- C - if...else statement
- C - nested if statements
- C - switch statement
- C - nested switch statements
- C - While loop
- C - For loop
- C - Do...while loop
- C - Nested loop
- C - Infinite loop
- C - Break Statement
- C - Continue Statement
- C - goto Statement
- C - Functions
- C - Main Functions
- C - Function call by Value
- C - Function call by reference
- C - Nested Functions
- C - Variadic Functions
- C - User-Defined Functions
- C - Callback Function
- C - Return Statement
- C - Recursion
- C - Scope Rules
- C - Static Variables
- C - Global Variables
- C - Properties of Array
- C - Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- C - Passing Arrays to Function
- C - Return Array from Function
- C - Variable Length Arrays
- C - Pointers
- C - Pointers and Arrays
- C - Applications of Pointers
- C - Pointer Arithmetics
- C - Array of Pointers
- C - Passing Pointers to Functions
- C - Strings
- C - Array of Strings
- C - Structures
- C - Structures and Functions
- C - Arrays of Structures
- C - Pointers to Structures
- C - Self-Referential Structures
- C - Nested Structures
- C - Bit Fields
- C - Typedef
- C - Input & Output
- C - File I/O
- C - Preprocessors
- C - Header Files
- C - Type Casting
- C - Error Handling
- C - Variable Arguments
- C - Memory Management
- C - Command Line Arguments
- C Programming Resources
- C - Questions & Answers
- C - Quick Guide
- C - Useful Resources
- C - Discussion
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary

Assignment Operators in C
In C language, the assignment operator stores a certain value in an already declared variable. A variable in C can be assigned the value in the form of a literal, another variable, or an expression.
The value to be assigned forms the right-hand operand, whereas the variable to be assigned should be the operand to the left of the " = " symbol, which is defined as a simple assignment operator in C.
In addition, C has several augmented assignment operators.
The following table lists the assignment operators supported by the C language −
Simple Assignment Operator (=)
The = operator is one of the most frequently used operators in C. As per the ANSI C standard, all the variables must be declared in the beginning. Variable declaration after the first processing statement is not allowed.
You can declare a variable to be assigned a value later in the code, or you can initialize it at the time of declaration.
You can use a literal, another variable, or an expression in the assignment statement.
Once a variable of a certain type is declared, it cannot be assigned a value of any other type. In such a case the C compiler reports a type mismatch error.
In C, the expressions that refer to a memory location are called "lvalue" expressions. A lvalue may appear as either the left-hand or right-hand side of an assignment.
On the other hand, the term rvalue refers to a data value that is stored at some address in memory. A rvalue is an expression that cannot have a value assigned to it which means an rvalue may appear on the right-hand side but not on the left-hand side of an assignment.
Variables are lvalues and so they may appear on the left-hand side of an assignment. Numeric literals are rvalues and so they may not be assigned and cannot appear on the left-hand side. Take a look at the following valid and invalid statements −
Augmented Assignment Operators
In addition to the = operator, C allows you to combine arithmetic and bitwise operators with the = symbol to form augmented or compound assignment operator. The augmented operators offer a convenient shortcut for combining arithmetic or bitwise operation with assignment.
For example, the expression "a += b" has the same effect of performing "a + b" first and then assigning the result back to the variable "a".
Run the code and check its output −
Similarly, the expression "a <<= b" has the same effect of performing "a << b" first and then assigning the result back to the variable "a".
Here is a C program that demonstrates the use of assignment operators in C −
When you compile and execute the above program, it will produce the following result −
To Continue Learning Please Login
cppreference.com
Assignment operators.
Assignment and compound assignment operators are binary operators that modify the variable to their left using the value to their right.
[ edit ] Simple assignment
The simple assignment operator expressions have the form
Assignment performs implicit conversion from the value of rhs to the type of lhs and then replaces the value in the object designated by lhs with the converted value of rhs .
Assignment also returns the same value as what was stored in lhs (so that expressions such as a = b = c are possible). The value category of the assignment operator is non-lvalue (so that expressions such as ( a = b ) = c are invalid).
rhs and lhs must satisfy one of the following:
- both lhs and rhs have compatible struct or union type, or..
- rhs must be implicitly convertible to lhs , which implies
- both lhs and rhs have arithmetic types , in which case lhs may be volatile -qualified or atomic (since C11)
- both lhs and rhs have pointer to compatible (ignoring qualifiers) types, or one of the pointers is a pointer to void, and the conversion would not add qualifiers to the pointed-to type. lhs may be volatile or restrict (since C99) -qualified or atomic (since C11) .
- lhs is a (possibly qualified or atomic (since C11) ) pointer and rhs is a null pointer constant such as NULL or a nullptr_t value (since C23)
[ edit ] Notes
If rhs and lhs overlap in memory (e.g. they are members of the same union), the behavior is undefined unless the overlap is exact and the types are compatible .
Although arrays are not assignable, an array wrapped in a struct is assignable to another object of the same (or compatible) struct type.
The side effect of updating lhs is sequenced after the value computations, but not the side effects of lhs and rhs themselves and the evaluations of the operands are, as usual, unsequenced relative to each other (so the expressions such as i = ++ i ; are undefined)
Assignment strips extra range and precision from floating-point expressions (see FLT_EVAL_METHOD ).
In C++, assignment operators are lvalue expressions, not so in C.
[ edit ] Compound assignment
The compound assignment operator expressions have the form
The expression lhs @= rhs is exactly the same as lhs = lhs @ ( rhs ) , except that lhs is evaluated only once.
[ edit ] References
- C17 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2018):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 72-73)
- C11 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:2011):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 101-104)
- C99 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:1999):
- 6.5.16 Assignment operators (p: 91-93)
- C89/C90 standard (ISO/IEC 9899:1990):
- 3.3.16 Assignment operators
[ edit ] See Also
Operator precedence
[ edit ] See also
- Recent changes
- Offline version
- What links here
- Related changes
- Upload file
- Special pages
- Printable version
- Permanent link
- Page information
- In other languages
- This page was last modified on 19 August 2022, at 08:36.
- This page has been accessed 54,567 times.
- Privacy policy
- About cppreference.com
- Disclaimers

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.6: Assignment Operator
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 29038

- Patrick McClanahan
- San Joaquin Delta College
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Assignment Operator
The assignment operator allows us to change the value of a modifiable data object (for beginning programmers this typically means a variable). It is associated with the concept of moving a value into the storage location (again usually a variable). Within C++ programming language the symbol used is the equal symbol. But bite your tongue, when you see the = symbol you need to start thinking: assignment. The assignment operator has two operands. The one to the left of the operator is usually an identifier name for a variable. The one to the right of the operator is a value.
The value 21 is moved to the memory location for the variable named: age. Another way to say it: age is assigned the value 21.
The item to the right of the assignment operator is an expression. The expression will be evaluated and the answer is 14. The value 14 would assigned to the variable named: total_cousins.
The expression to the right of the assignment operator contains some identifier names. The program would fetch the values stored in those variables; add them together and get a value of 44; then assign the 44 to the total_students variable.
As we have seen, assignment operators are used to assigning value to a variable. The left side operand of the assignment operator is a variable and right side operand of the assignment operator is a value. The value on the right side must be of the same data-type of the variable on the left side otherwise the compiler will raise an error. Different types of assignment operators are shown below:
- “=” : This is the simplest assignment operator, which was discussed above. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. For example: a = 10; b = 20; ch = 'y';
If initially the value 5 is stored in the variable a, then: (a += 6) is equal to 11. (the same as: a = a + 6)
If initially value 8 is stored in the variable a, then (a -= 6) is equal to 2. (the same as a = a - 6)
If initially value 5 is stored in the variable a,, then (a *= 6) is equal to 30. (the same as a = a * 6)
If initially value 6 is stored in the variable a, then (a /= 2) is equal to 3. (the same as a = a / 2)
Below example illustrates the various Assignment Operators:
Definitions
Adapted from: "Assignment Operator" by Kenneth Leroy Busbee , (Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] ) is licensed under CC BY 4.0
- Skip to main content
- Skip to search
- Skip to select language
- Sign up for free
Assignment (=)
The assignment ( = ) operator is used to assign a value to a variable or property. The assignment expression itself has a value, which is the assigned value. This allows multiple assignments to be chained in order to assign a single value to multiple variables.
A valid assignment target, including an identifier or a property accessor . It can also be a destructuring assignment pattern .
An expression specifying the value to be assigned to x .
Return value
The value of y .
Thrown in strict mode if assigning to an identifier that is not declared in the scope.
Thrown in strict mode if assigning to a property that is not modifiable .
Description
The assignment operator is completely different from the equals ( = ) sign used as syntactic separators in other locations, which include:
- Initializers of var , let , and const declarations
- Default values of destructuring
- Default parameters
- Initializers of class fields
All these places accept an assignment expression on the right-hand side of the = , so if you have multiple equals signs chained together:
This is equivalent to:
Which means y must be a pre-existing variable, and x is a newly declared const variable. y is assigned the value 5 , and x is initialized with the value of the y = 5 expression, which is also 5 . If y is not a pre-existing variable, a global variable y is implicitly created in non-strict mode , or a ReferenceError is thrown in strict mode. To declare two variables within the same declaration, use:
Simple assignment and chaining
Value of assignment expressions.
The assignment expression itself evaluates to the value of the right-hand side, so you can log the value and assign to a variable at the same time.
Unqualified identifier assignment
The global object sits at the top of the scope chain. When attempting to resolve a name to a value, the scope chain is searched. This means that properties on the global object are conveniently visible from every scope, without having to qualify the names with globalThis. or window. or global. .
Because the global object has a String property ( Object.hasOwn(globalThis, "String") ), you can use the following code:
So the global object will ultimately be searched for unqualified identifiers. You don't have to type globalThis.String ; you can just type the unqualified String . To make this feature more conceptually consistent, assignment to unqualified identifiers will assume you want to create a property with that name on the global object (with globalThis. omitted), if there is no variable of the same name declared in the scope chain.
In strict mode , assignment to an unqualified identifier in strict mode will result in a ReferenceError , to avoid the accidental creation of properties on the global object.
Note that the implication of the above is that, contrary to popular misinformation, JavaScript does not have implicit or undeclared variables. It just conflates the global object with the global scope and allows omitting the global object qualifier during property creation.
Assignment with destructuring
The left-hand side of can also be an assignment pattern. This allows assigning to multiple variables at once.
For more information, see Destructuring assignment .
Specifications
Browser compatibility.
BCD tables only load in the browser with JavaScript enabled. Enable JavaScript to view data.
- Assignment operators in the JS guide
- Destructuring assignment
Python Tutorial
File handling, python modules, python numpy, python pandas, python matplotlib, python scipy, machine learning, python mysql, python mongodb, python reference, module reference, python how to, python examples, python assignment operators.
Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables:
Related Pages

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.
Learn Java practically and Get Certified .
Popular Tutorials
Popular examples, reference materials, learn java interactively, java introduction.
- Get Started With Java
- Your First Java Program
- Java Comments
Java Fundamentals
- Java Variables and Literals
- Java Data Types (Primitive)
Java Operators
- Java Basic Input and Output
- Java Expressions, Statements and Blocks
Java Flow Control
- Java if...else Statement
Java Ternary Operator
- Java for Loop
- Java for-each Loop
- Java while and do...while Loop
- Java break Statement
- Java continue Statement
- Java switch Statement
- Java Arrays
- Java Multidimensional Arrays
- Java Copy Arrays
Java OOP(I)
- Java Class and Objects
- Java Methods
- Java Method Overloading
- Java Constructors
- Java Static Keyword
- Java Strings
- Java Access Modifiers
- Java this Keyword
- Java final keyword
- Java Recursion
Java instanceof Operator
Java OOP(II)
- Java Inheritance
- Java Method Overriding
- Java Abstract Class and Abstract Methods
- Java Interface
- Java Polymorphism
- Java Encapsulation
Java OOP(III)
- Java Nested and Inner Class
- Java Nested Static Class
- Java Anonymous Class
- Java Singleton Class
- Java enum Constructor
- Java enum Strings
- Java Reflection
- Java Package
- Java Exception Handling
- Java Exceptions
- Java try...catch
- Java throw and throws
- Java catch Multiple Exceptions
- Java try-with-resources
- Java Annotations
- Java Annotation Types
- Java Logging
- Java Assertions
- Java Collections Framework
- Java Collection Interface
- Java ArrayList
- Java Vector
- Java Stack Class
- Java Queue Interface
- Java PriorityQueue
- Java Deque Interface
- Java LinkedList
- Java ArrayDeque
- Java BlockingQueue
- Java ArrayBlockingQueue
- Java LinkedBlockingQueue
- Java Map Interface
- Java HashMap
- Java LinkedHashMap
- Java WeakHashMap
- Java EnumMap
- Java SortedMap Interface
- Java NavigableMap Interface
- Java TreeMap
- Java ConcurrentMap Interface
- Java ConcurrentHashMap
- Java Set Interface
- Java HashSet Class
- Java EnumSet
- Java LinkedHashSet
- Java SortedSet Interface
- Java NavigableSet Interface
- Java TreeSet
- Java Algorithms
- Java Iterator Interface
- Java ListIterator Interface
Java I/o Streams
- Java I/O Streams
- Java InputStream Class
- Java OutputStream Class
- Java FileInputStream Class
- Java FileOutputStream Class
- Java ByteArrayInputStream Class
- Java ByteArrayOutputStream Class
- Java ObjectInputStream Class
- Java ObjectOutputStream Class
- Java BufferedInputStream Class
- Java BufferedOutputStream Class
- Java PrintStream Class
Java Reader/Writer
- Java File Class
- Java Reader Class
- Java Writer Class
- Java InputStreamReader Class
- Java OutputStreamWriter Class
- Java FileReader Class
- Java FileWriter Class
- Java BufferedReader
- Java BufferedWriter Class
- Java StringReader Class
- Java StringWriter Class
- Java PrintWriter Class
Additional Topics
- Java Keywords and Identifiers
Java Operator Precedence
Java Bitwise and Shift Operators
- Java Scanner Class
- Java Type Casting
- Java Wrapper Class
- Java autoboxing and unboxing
- Java Lambda Expressions
- Java Generics
- Nested Loop in Java
- Java Command-Line Arguments
Java Tutorials
- Java Math IEEEremainder()
Operators are symbols that perform operations on variables and values. For example, + is an operator used for addition, while * is also an operator used for multiplication.
Operators in Java can be classified into 5 types:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Unary Operators
- Bitwise Operators
1. Java Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic operations on variables and data. For example,
Here, the + operator is used to add two variables a and b . Similarly, there are various other arithmetic operators in Java.
Example 1: Arithmetic Operators
In the above example, we have used + , - , and * operators to compute addition, subtraction, and multiplication operations.
/ Division Operator
Note the operation, a / b in our program. The / operator is the division operator.
If we use the division operator with two integers, then the resulting quotient will also be an integer. And, if one of the operands is a floating-point number, we will get the result will also be in floating-point.
% Modulo Operator
The modulo operator % computes the remainder. When a = 7 is divided by b = 4 , the remainder is 3 .
Note : The % operator is mainly used with integers.
2. Java Assignment Operators
Assignment operators are used in Java to assign values to variables. For example,
Here, = is the assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right to the variable on its left. That is, 5 is assigned to the variable age .
Let's see some more assignment operators available in Java.
Example 2: Assignment Operators
3. java relational operators.
Relational operators are used to check the relationship between two operands. For example,
Here, < operator is the relational operator. It checks if a is less than b or not.
It returns either true or false .
Example 3: Relational Operators
Note : Relational operators are used in decision making and loops.
4. Java Logical Operators
Logical operators are used to check whether an expression is true or false . They are used in decision making.

Example 4: Logical Operators
Working of Program
- (5 > 3) && (8 > 5) returns true because both (5 > 3) and (8 > 5) are true .
- (5 > 3) && (8 < 5) returns false because the expression (8 < 5) is false .
- (5 < 3) || (8 > 5) returns true because the expression (8 > 5) is true .
- (5 > 3) || (8 < 5) returns true because the expression (5 > 3) is true .
- (5 < 3) || (8 < 5) returns false because both (5 < 3) and (8 < 5) are false .
- !(5 == 3) returns true because 5 == 3 is false .
- !(5 > 3) returns false because 5 > 3 is true .
5. Java Unary Operators
Unary operators are used with only one operand. For example, ++ is a unary operator that increases the value of a variable by 1 . That is, ++5 will return 6 .
Different types of unary operators are:
- Increment and Decrement Operators
Java also provides increment and decrement operators: ++ and -- respectively. ++ increases the value of the operand by 1 , while -- decrease it by 1 . For example,
Here, the value of num gets increased to 6 from its initial value of 5 .
Example 5: Increment and Decrement Operators
In the above program, we have used the ++ and -- operator as prefixes (++a, --b) . We can also use these operators as postfix (a++, b++) .
There is a slight difference when these operators are used as prefix versus when they are used as a postfix.
To learn more about these operators, visit increment and decrement operators .
6. Java Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operators in Java are used to perform operations on individual bits. For example,
Here, ~ is a bitwise operator. It inverts the value of each bit ( 0 to 1 and 1 to 0 ).
The various bitwise operators present in Java are:
These operators are not generally used in Java. To learn more, visit Java Bitwise and Bit Shift Operators .
Other operators
Besides these operators, there are other additional operators in Java.
The instanceof operator checks whether an object is an instanceof a particular class. For example,
Here, str is an instance of the String class. Hence, the instanceof operator returns true . To learn more, visit Java instanceof .
The ternary operator (conditional operator) is shorthand for the if-then-else statement. For example,
Here's how it works.
- If the Expression is true , expression1 is assigned to the variable .
- If the Expression is false , expression2 is assigned to the variable .
Let's see an example of a ternary operator.
In the above example, we have used the ternary operator to check if the year is a leap year or not. To learn more, visit the Java ternary operator .
Now that you know about Java operators, it's time to know about the order in which operators are evaluated. To learn more, visit Java Operator Precedence .
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Java Arithmetic Operators
- Java Assignment Operators
- Java Relational Operators
- Java Logical Operators
- Java Unary Operators
- Java Bitwise Operators
Sorry about that.
Related Tutorials
Java Tutorial
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Assignment operators (C# reference)
- 11 contributors
The assignment operator = assigns the value of its right-hand operand to a variable, a property , or an indexer element given by its left-hand operand. The result of an assignment expression is the value assigned to the left-hand operand. The type of the right-hand operand must be the same as the type of the left-hand operand or implicitly convertible to it.
The assignment operator = is right-associative, that is, an expression of the form
is evaluated as
The following example demonstrates the usage of the assignment operator with a local variable, a property, and an indexer element as its left-hand operand:
The left-hand operand of an assignment receives the value of the right-hand operand. When the operands are of value types , assignment copies the contents of the right-hand operand. When the operands are of reference types , assignment copies the reference to the object.
This is called value assignment : the value is assigned.
ref assignment
Ref assignment = ref makes its left-hand operand an alias to the right-hand operand, as the following example demonstrates:
In the preceding example, the local reference variable arrayElement is initialized as an alias to the first array element. Then, it's ref reassigned to refer to the last array element. As it's an alias, when you update its value with an ordinary assignment operator = , the corresponding array element is also updated.
The left-hand operand of ref assignment can be a local reference variable , a ref field , and a ref , out , or in method parameter. Both operands must be of the same type.
Compound assignment
For a binary operator op , a compound assignment expression of the form
is equivalent to
except that x is only evaluated once.
Compound assignment is supported by arithmetic , Boolean logical , and bitwise logical and shift operators.
Null-coalescing assignment
You can use the null-coalescing assignment operator ??= to assign the value of its right-hand operand to its left-hand operand only if the left-hand operand evaluates to null . For more information, see the ?? and ??= operators article.
Operator overloadability
A user-defined type can't overload the assignment operator. However, a user-defined type can define an implicit conversion to another type. That way, the value of a user-defined type can be assigned to a variable, a property, or an indexer element of another type. For more information, see User-defined conversion operators .
A user-defined type can't explicitly overload a compound assignment operator. However, if a user-defined type overloads a binary operator op , the op= operator, if it exists, is also implicitly overloaded.
C# language specification
For more information, see the Assignment operators section of the C# language specification .
- C# operators and expressions
- ref keyword
- Use compound assignment (style rules IDE0054 and IDE0074)
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources
- Python Basics
- Interview Questions
- Python Quiz
- Popular Packages
- Python Projects
- Practice Python
- AI With Python
- Learn Python3
- Python Automation
- Python Web Dev
- DSA with Python
- Python OOPs
- Dictionaries
Python Operators
Precedence and associativity of operators in python.
- Python Arithmetic Operators
- Difference between / vs. // operator in Python
- Python - Star or Asterisk operator ( * )
- What does the Double Star operator mean in Python?
- Division Operators in Python
- Modulo operator (%) in Python
- Python Logical Operators
- Python OR Operator
- Difference between 'and' and '&' in Python
- not Operator in Python | Boolean Logic
Ternary Operator in Python
- Python Bitwise Operators
Python Assignment Operators
Assignment operators in python.
- Walrus Operator in Python 3.8
- Increment += and Decrement -= Assignment Operators in Python
- Merging and Updating Dictionary Operators in Python 3.9
- New '=' Operator in Python3.8 f-string
Python Relational Operators
- Comparison Operators in Python
- Python NOT EQUAL operator
- Difference between == and is operator in Python
- Chaining comparison operators in Python
- Python Membership and Identity Operators
- Difference between != and is not operator in Python
In Python programming, Operators in general are used to perform operations on values and variables. These are standard symbols used for logical and arithmetic operations. In this article, we will look into different types of Python operators.
- OPERATORS: These are the special symbols. Eg- + , * , /, etc.
- OPERAND: It is the value on which the operator is applied.
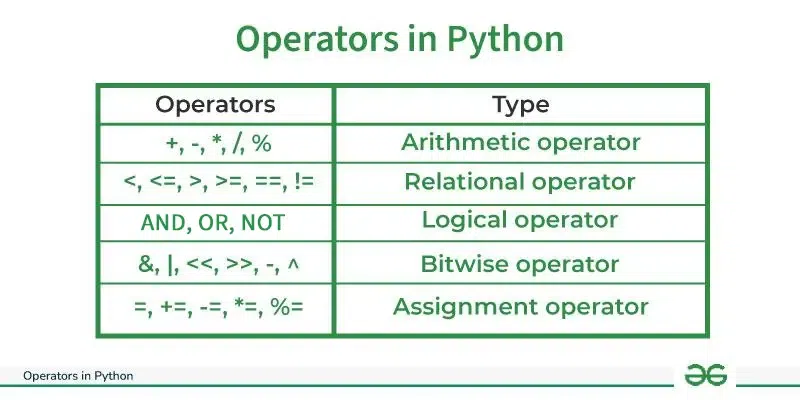
Types of Operators in Python
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Identity Operators and Membership Operators
Arithmetic Operators in Python
Python Arithmetic operators are used to perform basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication , and division .
In Python 3.x the result of division is a floating-point while in Python 2.x division of 2 integers was an integer. To obtain an integer result in Python 3.x floored (// integer) is used.
Example of Arithmetic Operators in Python
Division operators.
In Python programming language Division Operators allow you to divide two numbers and return a quotient, i.e., the first number or number at the left is divided by the second number or number at the right and returns the quotient.
There are two types of division operators:
Float division
- Floor division
The quotient returned by this operator is always a float number, no matter if two numbers are integers. For example:
Example: The code performs division operations and prints the results. It demonstrates that both integer and floating-point divisions return accurate results. For example, ’10/2′ results in ‘5.0’ , and ‘-10/2’ results in ‘-5.0’ .
Integer division( Floor division)
The quotient returned by this operator is dependent on the argument being passed. If any of the numbers is float, it returns output in float. It is also known as Floor division because, if any number is negative, then the output will be floored. For example:
Example: The code demonstrates integer (floor) division operations using the // in Python operators . It provides results as follows: ’10//3′ equals ‘3’ , ‘-5//2’ equals ‘-3’ , ‘ 5.0//2′ equals ‘2.0’ , and ‘-5.0//2’ equals ‘-3.0’ . Integer division returns the largest integer less than or equal to the division result.
Precedence of Arithmetic Operators in Python
The precedence of Arithmetic Operators in Python is as follows:
- P – Parentheses
- E – Exponentiation
- M – Multiplication (Multiplication and division have the same precedence)
- D – Division
- A – Addition (Addition and subtraction have the same precedence)
- S – Subtraction
The modulus of Python operators helps us extract the last digit/s of a number. For example:
- x % 10 -> yields the last digit
- x % 100 -> yield last two digits
Arithmetic Operators With Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Modulo and Power
Here is an example showing how different Arithmetic Operators in Python work:
Example: The code performs basic arithmetic operations with the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ . It adds (‘+’) , subtracts (‘-‘) , multiplies (‘*’) , computes the remainder (‘%’) , and raises a to the power of ‘b (**)’ . The results of these operations are printed.
Note: Refer to Differences between / and // for some interesting facts about these two Python operators.
Comparison of Python Operators
In Python Comparison of Relational operators compares the values. It either returns True or False according to the condition.
= is an assignment operator and == comparison operator.
Precedence of Comparison Operators in Python
In Python, the comparison operators have lower precedence than the arithmetic operators. All the operators within comparison operators have the same precedence order.
Example of Comparison Operators in Python
Let’s see an example of Comparison Operators in Python.
Example: The code compares the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ using various comparison Python operators and prints the results. It checks if ‘a’ is greater than, less than, equal to, not equal to, greater than, or equal to, and less than or equal to ‘b’ .
Logical Operators in Python
Python Logical operators perform Logical AND , Logical OR , and Logical NOT operations. It is used to combine conditional statements.
Precedence of Logical Operators in Python
The precedence of Logical Operators in Python is as follows:
- Logical not
- logical and
Example of Logical Operators in Python
The following code shows how to implement Logical Operators in Python:
Example: The code performs logical operations with Boolean values. It checks if both ‘a’ and ‘b’ are true ( ‘and’ ), if at least one of them is true ( ‘or’ ), and negates the value of ‘a’ using ‘not’ . The results are printed accordingly.
Bitwise Operators in Python
Python Bitwise operators act on bits and perform bit-by-bit operations. These are used to operate on binary numbers.
Precedence of Bitwise Operators in Python
The precedence of Bitwise Operators in Python is as follows:
- Bitwise NOT
- Bitwise Shift
- Bitwise AND
- Bitwise XOR
Here is an example showing how Bitwise Operators in Python work:
Example: The code demonstrates various bitwise operations with the values of ‘a’ and ‘b’ . It performs bitwise AND (&) , OR (|) , NOT (~) , XOR (^) , right shift (>>) , and left shift (<<) operations and prints the results. These operations manipulate the binary representations of the numbers.
Python Assignment operators are used to assign values to the variables.
Let’s see an example of Assignment Operators in Python.
Example: The code starts with ‘a’ and ‘b’ both having the value 10. It then performs a series of operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and a left shift operation on ‘b’ . The results of each operation are printed, showing the impact of these operations on the value of ‘b’ .
Identity Operators in Python
In Python, is and is not are the identity operators both are used to check if two values are located on the same part of the memory. Two variables that are equal do not imply that they are identical.
Example Identity Operators in Python
Let’s see an example of Identity Operators in Python.
Example: The code uses identity operators to compare variables in Python. It checks if ‘a’ is not the same object as ‘b’ (which is true because they have different values) and if ‘a’ is the same object as ‘c’ (which is true because ‘c’ was assigned the value of ‘a’ ).
Membership Operators in Python
In Python, in and not in are the membership operators that are used to test whether a value or variable is in a sequence.
Examples of Membership Operators in Python
The following code shows how to implement Membership Operators in Python:
Example: The code checks for the presence of values ‘x’ and ‘y’ in the list. It prints whether or not each value is present in the list. ‘x’ is not in the list, and ‘y’ is present, as indicated by the printed messages. The code uses the ‘in’ and ‘not in’ Python operators to perform these checks.
in Python, Ternary operators also known as conditional expressions are operators that evaluate something based on a condition being true or false. It was added to Python in version 2.5.
It simply allows testing a condition in a single line replacing the multiline if-else making the code compact.
Syntax : [on_true] if [expression] else [on_false]
Examples of Ternary Operator in Python
The code assigns values to variables ‘a’ and ‘b’ (10 and 20, respectively). It then uses a conditional assignment to determine the smaller of the two values and assigns it to the variable ‘min’ . Finally, it prints the value of ‘min’ , which is 10 in this case.
In Python, Operator precedence and associativity determine the priorities of the operator.
Operator Precedence in Python
This is used in an expression with more than one operator with different precedence to determine which operation to perform first.
Let’s see an example of how Operator Precedence in Python works:
Example: The code first calculates and prints the value of the expression 10 + 20 * 30 , which is 610. Then, it checks a condition based on the values of the ‘name’ and ‘age’ variables. Since the name is “ Alex” and the condition is satisfied using the or operator, it prints “Hello! Welcome.”
Operator Associativity in Python
If an expression contains two or more operators with the same precedence then Operator Associativity is used to determine. It can either be Left to Right or from Right to Left.
The following code shows how Operator Associativity in Python works:
Example: The code showcases various mathematical operations. It calculates and prints the results of division and multiplication, addition and subtraction, subtraction within parentheses, and exponentiation. The code illustrates different mathematical calculations and their outcomes.
To try your knowledge of Python Operators, you can take out the quiz on Operators in Python .
Python Operator Exercise Questions
Below are two Exercise Questions on Python Operators. We have covered arithmetic operators and comparison operators in these exercise questions. For more exercises on Python Operators visit the page mentioned below.
Q1. Code to implement basic arithmetic operations on integers
Q2. Code to implement Comparison operations on integers
Explore more Exercises: Practice Exercise on Operators in Python
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- python-basics
- Python-Operators
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

COMMENTS
Different types of assignment operators are shown below: 1. "=": This is the simplest assignment operator. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. Example: a = 10; b = 20; ch = 'y'; 2. "+=": This operator is combination of '+' and '=' operators. This operator first adds the current ...
Assignment operators are used in programming to assign values to variables. We use an assignment operator to store and update data within a program. They enable programmers to store data in variables and manipulate that data. The most common assignment operator is the equals sign (=), which assigns the value on the right side of the operator to ...
for assignments to class type objects, the right operand could be an initializer list only when the assignment is defined by a user-defined assignment operator. removed user-defined assignment constraint. CWG 1538. C++11. E1 ={E2} was equivalent to E1 = T(E2) ( T is the type of E1 ), this introduced a C-style cast. it is equivalent to E1 = T{E2}
Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables. In the example below, we use the assignment operator (=) to assign the value 10 to a variable called x: Example. int x = 10;
In C++, the addition assignment operator (+=) combines the addition operation with the variable assignment allowing you to increment the value of variable by a specified expression in a concise and efficient way. Syntax. variable += value; This above expression is equivalent to the expression: variable = variable + value; Example.
Assignment Operators in C - In C language, the assignment operator stores a certain value in an already declared variable. A variable in C can be assigned the value in the form of a literal, another variable, or an expression. ... Example = Simple assignment operator. Assigns values from right side operands to left side operand: C = A + B will ...
Assignment performs implicit conversion from the value of rhs to the type of lhs and then replaces the value in the object designated by lhs with the converted value of rhs . Assignment also returns the same value as what was stored in lhs (so that expressions such as a = b = c are possible). The value category of the assignment operator is non ...
Different types of assignment operators are shown below: "=": This is the simplest assignment operator, which was discussed above. This operator is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. For example: a = 10; b = 20; ch = 'y'; +=: This operator is combination of '+' and '=' operators. This operator first ...
The += assignment operator is a combination of + arithmetic operator and = simple assignment operator. For example, x += y; is equivalent to x = x+y;. It adds the right side value to the value of left side operand and assign the result back to the left-hand side operand. #include <stdio.h> int main () { int x = 100, y = 20, z = 50 ...
The built-in assignment operators return the value of the object specified by the left operand after the assignment (and the arithmetic/logical operation in the case of compound assignment operators). The resultant type is the type of the left operand. The result of an assignment expression is always an l-value.
The assignment operators in C can both transform and assign values in a single operation. C provides the following assignment operators: | =. In assignment, the type of the right-hand value is converted to the type of the left-hand value, and the value is stored in the left operand after the assignment has taken place.
The Assignment operators in C are some of the Programming operators that are useful for assigning the values to the declared variables. Equals (=) operator is the most commonly used assignment operator. For example: int i = 10; The below table displays all the assignment operators present in C Programming with an example. C Assignment Operators.
In this example, you chain two assignment operators in a single line. This way, your two variables refer to the same initial value of 0. Note how both variables hold the same memory address, so they point to the same instance of 0. When it comes to integer variables, Python exhibits a curious behavior. It provides a numeric interval where ...
Assignment (=) The assignment ( =) operator is used to assign a value to a variable or property. The assignment expression itself has a value, which is the assigned value. This allows multiple assignments to be chained in order to assign a single value to multiple variables.
Example 2: Assignment Operators # assign 10 to a a = 10 # assign 5 to b b = 5 # assign the sum of a and b to a a += b # a = a + b print(a) # Output: 15. Here, we have used the += operator to assign the sum of a and b to a. Similarly, we can use any other assignment operators as per our needs.
Use the correct assignment operator that will result in x being 15 (same as x = x + y ). Start the Exercise. Well organized and easy to understand Web building tutorials with lots of examples of how to use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, SQL, Python, PHP, Bootstrap, Java, XML and more.
variable operator value; Types of Assignment Operators in Java. The Assignment Operator is generally of two types. They are: 1. Simple Assignment Operator: The Simple Assignment Operator is used with the "=" sign where the left side consists of the operand and the right side consists of a value. The value of the right side must be of the same data type that has been defined on the left side.
C++ Operators. Operators are symbols that perform operations on variables and values. For example, + is an operator used for addition, while - is an operator used for subtraction. Operators in C++ can be classified into 6 types: Arithmetic Operators. Assignment Operators.
Python Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables: Operator. Example. Same As. Try it. =. x = 5. x = 5.
2. Java Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used in Java to assign values to variables. For example, int age; age = 5; Here, = is the assignment operator. It assigns the value on its right to the variable on its left. That is, 5 is assigned to the variable age. Let's see some more assignment operators available in Java.
The Walrus Operator in Python is a new assignment operator which is introduced in Python version 3.8 and higher. This operator is used to assign a value to a variable within an expression. Syntax: a := expression. Example: In this code, we have a Python list of integers. We have used Python Walrus assignment operator within the Python while loop.
The assignment operator = is right-associative, that is, an expression of the form. a = b = c is evaluated as. a = (b = c) The following example demonstrates the usage of the assignment operator with a local variable, a property, and an indexer element as its left-hand operand:
Assignment Operators. Assignment operators are used to assign values to variables in JavaScript. Syntax: data=value. Example: // Lets take some variablesx=10y=20x=y // Here, x is equal to 20y=x // Here, y is equal to 10.
Assignment Operators in Python. Let's see an example of Assignment Operators in Python. Example: The code starts with 'a' and 'b' both having the value 10. It then performs a series of operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and a left shift operation on 'b'.