About Supliful
Supliful is dropshipping platform that lets you launch an online consumer brand with no upfront cost or risks.
You can choose from 100+ white label products and launch your brand as soon as today


Search white-label product supliers
Discover 100s of white label products ready to be customised and sold in your online store
Understanding Amazon's Business Model Canvas
Decode amazon's business model canvas, the foundation of their triumph in the e-commerce landscape. delve into their value creation, revenue model, and customer segments.
In the modern era of digital dominance, Amazon has emerged as a retail behemoth, disrupting the traditional brick-and-mortar model and revolutionizing the way we shop.
To truly grasp the success and intricacies of this e-commerce giant, it is essential to delve into Amazon's business model canvas. By exploring the various components that make up this canvas, we can gain valuable insights into the strategies employed by Amazon and understand what sets them apart from their competitors.
Decoding Amazon's Business Model Canvas: The Foundation of Their Triumph
Before we dive headfirst into the details, let's take a moment to understand the essence of Amazon's business model. At its core, Amazon is an online marketplace that connects buyers and sellers.
However, their model extends far beyond this simple concept. Amazon has built an empire on the principles of customer obsession, technological innovation, and an unmatched range of products and services.
When we talk about customer obsession, we mean that Amazon places the customer at the center of everything they do. They are constantly striving to improve the customer experience, whether it's through fast and reliable shipping, personalized recommendations, or their renowned customer service.
This customer-centric approach has been a key driver of Amazon's success, fostering trust and loyalty among millions of customers worldwide.
Technological innovation is another crucial aspect of Amazon's business model. From the early days of online book selling, Amazon recognized the importance of leveraging technology to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
They have invested heavily in cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics to optimize their supply chain, improve inventory management, and enhance the overall shopping experience for customers.
But what truly sets Amazon apart is the vast range of products and services they offer. From books and electronics to clothing, home goods, and even groceries, Amazon has become a one-stop-shop for almost anything you can imagine.
In addition to their e-commerce platform, they have expanded into various other areas such as streaming services with Amazon Prime Video, cloud computing with Amazon Web Services (AWS), and even physical retail with their acquisition of Whole Foods Market.
The Evolution of Amazon's Business Model
Amazon's journey began in 1994 as an online bookstore, founded by Jeff Bezos. Over the years, it has evolved into a sprawling platform that encompasses everything from consumer electronics to cloud computing services. By constantly adapting and expanding, Amazon has maintained its position at the cutting edge of the digital revolution.
As Amazon grew, they recognized the need to diversify their offerings and cater to a wider audience. They expanded their product categories to include not just books, but also music, movies, and eventually a wide range of consumer goods. This diversification allowed Amazon to tap into new markets and attract a larger customer base.
Furthermore, Amazon's expansion into digital services has been a game-changer. With the introduction of Amazon Prime, they revolutionized the concept of subscription-based services, offering customers fast and free shipping, access to a vast library of streaming content, and exclusive deals and discounts.
This move not only increased customer loyalty but also created a recurring revenue stream for Amazon.
Key Components of Amazon's Business Model
Now, let's explore the key components that form the foundation of Amazon's business model. These elements work together synergistically to create a seamless and customer-centric experience.
- First and foremost, Amazon's marketplace is the heart of their business model. It serves as a platform where millions of sellers can reach a global customer base and sell their products. This marketplace model allows Amazon to offer an extensive selection of products, ensuring that customers can find almost anything they need in one place.
- Next, Amazon's logistics and fulfillment infrastructure play a crucial role in their business model. With a vast network of warehouses, distribution centers, and delivery partners, Amazon is able to offer fast and reliable shipping to customers around the world. Their advanced logistics capabilities enable them to fulfill orders quickly and efficiently, ensuring customer satisfaction.
- Another key component is Amazon's data-driven approach. They collect and analyze vast amounts of customer data to gain insights into their preferences, shopping habits, and behavior. This data-driven approach allows Amazon to personalize the shopping experience, recommend relevant products, and target customers with tailored marketing campaigns.
- Lastly, Amazon's commitment to continuous innovation sets them apart. They are constantly experimenting with new technologies and business models to stay ahead of the competition.
Whether it's through the introduction of voice-controlled devices like Amazon Echo, the expansion of their Prime membership program, or the development of autonomous delivery drones, Amazon is always pushing the boundaries of what's possible.
Amazon's Value Proposition
Amazon's success can be attributed, in large part, to its unwavering commitment to delivering value to its customers. Let's take a closer look at the aspects that contribute to their undeniable appeal.
Customer-Centric Approach
One of the cornerstones of Amazon's business model is an unwavering focus on the customer. They have mastered the art of personalization, tailoring product suggestions and recommendations based on individual browsing and purchasing habits.
Moreover, their customer service is second to none, with efficient returns and hassle-free interactions.
Amazon's commitment to customer satisfaction goes beyond just personalization and customer service. They have also developed an extensive review system that allows customers to share their opinions and experiences with products.
This not only helps other customers make informed decisions but also provides valuable feedback to Amazon and its sellers, enabling continuous improvement.
Furthermore, Amazon has implemented various initiatives to ensure the safety and security of its customers. They have robust fraud detection systems in place to protect against unauthorized transactions, and they prioritize the privacy of customer information by adhering to strict data protection policies.
Wide Range of Products and Services
When it comes to choice, Amazon leaves no stone unturned. From books to electronics, clothing to household essentials, you can find virtually anything your heart desires on their platform. This vast array of products is a testament to Amazon's commitment to being a one-stop-shop for all consumer needs.
In addition to their extensive product selection, Amazon offers a range of services that further enhance the customer experience. For instance, they provide fast and reliable shipping options, including same-day and next-day delivery in many areas.
They also offer subscription services like Amazon Prime, which provides access to exclusive deals, streaming services, and more.
Furthermore, Amazon has expanded its ecosystem to include various digital services. They have their own streaming platform, Amazon Prime Video, which offers a wide selection of movies and TV shows. They also have a digital content store, where customers can purchase and download e-books, music, and apps.
Technological Innovation
Amazon has always pushed the boundaries of technology, using it as a catalyst for growth. From pioneering one-click ordering and predictive shipping algorithms to leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning, they continuously strive to enhance the customer experience and stay ahead of the competition.
One of Amazon's notable technological innovations is their use of robotics in their fulfillment centers. They have automated processes such as picking, packing, and sorting, which not only increases efficiency but also allows for faster order processing and delivery.
Moreover, Amazon has been at the forefront of voice-activated technology with their virtual assistant, Alexa. Customers can interact with Alexa-enabled devices to perform various tasks, such as placing orders, playing music, and controlling smart home devices.
This seamless integration of technology into everyday life has further solidified Amazon's position as a leader in the industry.
Additionally, Amazon has made significant investments in renewable energy and sustainability. They have implemented initiatives to reduce their carbon footprint, such as using solar panels and electric delivery vehicles.
By prioritizing environmental responsibility, they not only contribute to a greener future but also resonate with customers who value sustainability.

Amazon's Revenue Streams
While their customer-centric approach and wide product selection are crucial to Amazon's success, it is their diverse revenue streams that truly set them apart from their counterparts. Let's delve into the key sources of Amazon's revenue.
E-commerce Sales
At its core, Amazon is an e-commerce powerhouse. Their digital marketplace serves as a platform for sellers to showcase and sell their products to a global audience. Through commissions and fees, Amazon generates substantial revenue from every transaction that takes place on their platform.
With millions of products available, Amazon has created a seamless shopping experience for customers. Their advanced search algorithms and personalized recommendations make it easy for users to find exactly what they are looking for.
Additionally, Amazon's customer reviews and ratings provide valuable insights for potential buyers, further enhancing the shopping experience.
Furthermore, Amazon's commitment to fast and reliable shipping has contributed to their e-commerce success. They have established a vast network of fulfillment centers and partnered with various shipping carriers to ensure timely delivery.
This focus on customer satisfaction has not only increased sales but also earned Amazon a reputation for exceptional service.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon's foray into cloud computing services through AWS has proven to be a game-changer. By offering scalable and flexible infrastructure solutions, Amazon has become the go-to choice for businesses worldwide.
The revenue generated from AWS not only bolsters their bottom line but also contributes significantly to their overall growth.
With AWS, companies can easily access computing power, storage, and databases without the need for expensive hardware and maintenance. This has revolutionized the way businesses operate, allowing them to scale their operations quickly and efficiently.
Moreover, AWS offers a wide range of services, including machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data analytics, empowering businesses with advanced technological capabilities.
In addition to serving businesses, AWS also caters to individual developers and startups. Their pay-as-you-go pricing model and comprehensive suite of tools have made it accessible for developers to build and deploy applications. This has fostered innovation and entrepreneurship, contributing to the overall success of AWS.
Subscription Services
In addition to their e-commerce and cloud computing offerings, Amazon has diversified their revenue streams further through subscription services like Amazon Prime.
With its attractive benefits, including free two-day shipping and access to exclusive content, Amazon Prime has become a major revenue driver for the company, fostering loyalty among its subscribers.
Amazon Prime offers a wide range of services beyond fast shipping. Subscribers have access to Prime Video, a streaming platform with a vast library of movies and TV shows.
They also enjoy Prime Music, a streaming service with millions of songs, and Prime Reading, which provides access to a collection of e-books and magazines. Additionally, Amazon Prime members benefit from exclusive deals and discounts during major sales events like Prime Day.
The success of Amazon Prime can be attributed to its ability to create a comprehensive ecosystem that caters to various aspects of customers' lives. By offering a combination of convenience, entertainment, and savings, Amazon Prime has become an indispensable part of many households, driving significant recurring revenue for the company.
Amazon's Key Resources
Behind every successful business model lies a strong foundation built on key resources. Amazon's relentless pursuit of excellence is underpinned by the following assets.
Physical Resources
Warehouses, distribution centers, and fulfillment networks form the backbone of Amazon's physical resources. These strategically located facilities enable them to fulfill orders rapidly and efficiently, contributing to their reputation for speedy delivery.
Amazon's warehouses are not just ordinary storage spaces; they are technological marvels. Equipped with state-of-the-art robotics and automation systems, these facilities optimize the picking, packing, and shipping processes.
The integration of advanced technologies, such as AI-powered sorting algorithms and autonomous delivery vehicles, further enhances their operational efficiency and enables Amazon to handle millions of orders daily.
Moreover, Amazon's commitment to sustainability is evident in their physical resources. They have invested heavily in renewable energy sources to power their facilities, reducing their carbon footprint and contributing to a greener future.
Human Resources
Amazon's success can be attributed, in no small part, to its dedicated workforce. The company boasts a vast pool of talented individuals who are passionate about delivering exceptional customer experiences and driving innovation.
Amazon's human resources strategy goes beyond mere recruitment. They prioritize diversity and inclusion, ensuring that their workforce reflects the global communities they serve.
This diverse talent pool brings together individuals with unique perspectives, fostering creativity and enabling Amazon to cater to a wide range of customer needs.
Furthermore, Amazon nurtures a culture of continuous learning and development. They provide extensive training programs and opportunities for employees to upskill and grow within the organization.
By investing in their people, Amazon cultivates a workforce that is adaptable, knowledgeable, and equipped to tackle the challenges of an ever-changing digital landscape.
Intellectual Resources
Finally, Amazon's intellectual resources, including their patents, trademarks, and proprietary technologies, play a vital role in their business model.
Amazon's relentless pursuit of innovation is evident in their vast patent portfolio. They constantly push the boundaries of technology, developing new solutions to enhance customer experiences and streamline operations.
Their intellectual property not only protects their innovations but also serves as a foundation for future advancements.
Moreover, Amazon's intellectual resources extend beyond their own innovations. They actively collaborate with external partners, fostering a culture of knowledge sharing and co-creation.
By leveraging the collective expertise of industry leaders and researchers, Amazon stays at the forefront of technological advancements and maintains a competitive edge.
As we unravel the intricacies of Amazon's business model canvas, it becomes evident that their success is not a result of any single factor. Instead, it is the seamless integration and constant evolution of various components that have propelled Amazon to the forefront of the retail landscape.
By understanding their business model, we gain valuable insights into their strategies and can draw inspiration for our own ventures in the ever-changing digital landscape. Whether it is optimizing physical resources, nurturing a talented workforce, or leveraging intellectual property, Amazon's approach serves as a testament to the importance of building a strong foundation for sustainable growth and success.
Further Insights into E-commerce Giants
For those eager to delve deeper into the business strategies of leading e-commerce platforms, the following articles are a treasure trove of information:
https://supliful.com/blog/how-does-nike-business-model-look-like
https://supliful.com/blog/what-is-apples-business-model
https://supliful.com/blog/how-long-does-it-take-to-make-money-on-shopify.
These resources will provide a comprehensive view of how different companies have carved their niche in the e-commerce landscape.
Suggested posts

How to Sell Products on Instagram Without a Website
Whether you’re selling physical products, digital products, or services, there are several strategies you can use to successfully sell on Instagram.

What Are The Best Selling Items On Facebook Marketplace
With an ever-growing user base of 2.6 billion people, Facebook Marketplace is quickly becoming one of the most popular places to buy and sell items online. As more and more people discover the platform, they're looking to learn the best tips and tricks to maximize their success. This article will explore some of the top strategies for discovering the best selling items on Facebook Marketplace.

How Much Does It Cost to Create a Personal Brand?
In this article, we will cover the various costs associated with creating a personal brand and how to calculate the return on investment for your efforts.

- How it works
- Help center
- Get label or store design Crash course
- Liability insurance
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy IP policy
- Returns Social Responsibility
- Affiliate program
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to content
- Skip to footer

Denis Oakley & Co
I HELP BOLD LEADERS TRANSFORM THEIR BUSINESSES AND THE INDUSTRIES THEY COMPETE IN
September 13, 2018 By Denis Oakley
What is the Amazon Business Model?
Amazon has an exceptionally powerful business model. In this post, using the business model canvas, I describe the different parts of the Amazon business model and how it all works together to create an e-commerce behemoth.

Amazon can be described as a two-sided marketplace where buyers and sellers come together. I think that for a variety of reasons it isn’t really one and I’ll explain that in detail later in the article.
Amazon targets the mass-market consumer . With a focus on cost and low margins to drive market share Amazon cannot focus on a narrow niche. It is the everyman, as well as the everything store. However whilst a significant part of the US population, and populations in the other markets it operates in, uses Amazon customers can be segmented on a behavioural basis.
Demographically usage of Amazon broadly mirrors technological adoption trends. Where people are wired and connected they tend to use it more, especially in the bugs cities.
Behaviourally Amazon has increasingly focused on people who are not only comfortable shopping online but also prepared to replace many of their traditional shopping habits with one click one hour delivery satisfaction. These are people who are price-sensitive and time-poor. Typically urbanites.
Value Proposition
Amazon offers its customers a strong value proposition based around 4 key ideas
- Convenience
- Fulfillment

- Audible Business Model Canvas
- Souq Business Model Canvas
- The Value Proposition in the Business Model Canvas: What Problem are We Solving?
- Do Business Models Make Your Value Proposition Stronger?
- Blinkist Business Model Canvas
About Denis Oakley
Explorer | Trail Runner | Mountain Lover
'Big' companies are civilisation. I stay in the wilderness guiding entrepreneurs and startups on their journey to becoming 'Big'.
Then I head back to the frontier
Strategy | Marketing | Operations
Ready to start?

I help entrepreneurs transform their industries through wiser choices
Outcome : More Traction, Bigger Rounds, Better Products
Method : Problems, Customers, Business Models, Strategy
Profitable Business Models > Business models of large companies
Check how Amazon’s main focus allowed the company to thrive. Amazon’s Business Model Canvas and how it changed from the very beginning.
- by Joanne Moyo
- May 25, 2021
So what does it take to create the world’s largest online marketplace? It seems impossible to fully comprehend how a small startup online bookseller became one of today’s most profitable companies.
The numbers don’t lie; according to Statista, Amazon’s annual revenue in 2020 was reported at 21.33 billion U.S. dollars, compared to 11.6 billion U.S. dollars in 2019. It keeps growing.
So how did the company grow its business? What decisions (good and bad) were they making? What challenges did they encounter, and how did they overcome them? There are many business lessons to be learned by examining Amazon’s history.

How and why it all began
Back in 1991, a Silicon Valley bookshop called Computer Literacy was the first to offer books online. When Amazon came into the picture, its business strategy was to provide convenience to the customer. It was different from what Computer Literacy was offering. Amazon thrived on delivering online orders to the customer directly at their chosen location anywhere in the world.
According to Jeff Bezos, the founder of Amazon, the motto was always “get big fast.” That’s exactly what Amazon did.
Back in the early to mid-90’s the internet was still very much in its infancy. In 1994, Bezos came across a statistic which predicted that internet users were likely to grow at 2300% annually.
It piqued his interest, and he jumped on the bandwagon, leaving his reasonably successful career as an investment banker. Of the top 20 things that made it to his list of things to sell, books appealed to him the most.
In a video from June 1997, Bezos explains why he chose books over everything else.
Books were great as the first best because books are incredibly unusual in one respect, that is that there are more items in the book category than there are items in any other category by far.
So the idea for Amazon (then called Cadabra.com) was to sell books online because:
- Customers would know precisely what they are buying.
- Amazon could easily cut off dealing with the thousands of publishers by negotiating with the two biggest book distributors in the 90s (Ingram and Baker & Taylor.)
- Of the sheer volume of inventory that Amazon could sell.
But that wasn’t all. Bezos had a plan to sell more than just books on the online marketplace. The vision was to expand and evolve into a tech company that offered online convenience to the customer.

After moving his family from New York to Seattle, Washington, Jeff Bezos opened Amazon.com in his rented home garage on the 5th of July 1994. He officially registered Amazon on the 1st of November 1994. A year later, after the formation of Amazon, the company would get its first order.
On the 3rd of April 1995, Amazon received its first order. John Wainwright ordered a book called “Fluid concepts and creative analogies: Computer models of the fundamental mechanics of thought” by Douglas Hofstadter.
Early Competition
It was during these first years that Amazon experienced a lot of criticism from industry and financial experts. Journalists highly criticized the business model, comparing it to a ticking time bomb with the phrase “Amazon.bomb” often being coined. It seems impossible that promising to deliver goods to customers anywhere in the world or the U.S. would work out in the long run.
Bookstore giants like Barnes and Nobles were expected to drown the startup once they launched their own online book-selling marketplace.
As we all know, that didn’t happen. By the end of 1996, Amazon had 180,000 customers, and towards the end of 1997, Amazon was sitting at 1 million customers with active accounts. The company closed off that year with 148 million U.S. dollars in revenue.
This early success caused concern among the book industry giants. First, no one had matched up to Amazon’s online capacity. The combination of low prices, convenience, and selection was hard to compete against. As any company would, most bookstores felt the heat. Amazon was making ripples in the industry. To top it all off, they began diversifying from just selling books.
But it was not smooth sailing for the rising powerhouse. Apart from book industry giants, eBay and Alibaba were some of Amazon’s earliest competitors. Alibaba launched in December 1998 made it extremely difficult for Amazon to expand into China. And when Amazon tried to compete with eBay by building a rival auction site, it failed dismally. We will see more of some of Amazon’s failures and why they failed later on.
1997-2000 : Amazon becomes public and presents long term strategy
Up until May 1997, Amazon had been a private company. However, it soon became apparent that for the company to expand, it needed more capital. In May 1997, Amazon was listed as a public company. The initial shares that were made available were three million, and each share was worth $18. By the end of the first day, Amazon stock was selling at $30. Bezos raised 54 million U.S. dollars on the NASDAQ exchange market.
In his first letter to shareholders at the end of 1997, Bezos coined the “Day 1” phrase, a core principle that Amazon still adheres to today. In that letter, Bezos presented the key elements that would make Amazon a success:
- Relentless focus on customers
- Creating long-term value over short-term corporate profit
- Bold innovation
“This is Day 1 for the Internet,” Bezos wrote, “and, if we execute well, for Amazon.com.”
The “Day 1” attitude is both culture and a way of operating the business that puts customers at the center of everything. The goal was and still is first to understand the customer and their pain or challenge. Then use that pain to develop innovative and convenient solutions for it. Amazon, always geared towards amplifying its value proposition in the eyes of the customer.
Despite this focus, Amazon was still not making a profit even with the tens of thousands of dollars in revenue it was making a week. It was a standard for startups. With investors becoming worried, Bezos explained that the goal was to defer profitability for at least five years to build infrastructure and technology.
This strategy is in line with the business model of modern-day Amazon. The concentration on infrastructure and technology was brilliant because Bezos understood that these would become part of the key resources that the company would need to thrive.
To this day, we see the same focus. Amazon pours millions of dollars towards developing data centers for its AWS services and the acquisition of robotics for its logistical operations.
Luckily, the lack of profit didn’t throw investors off, and in November 1997, Amazon opened its first fulfillment center in Delaware. It was in preparation for the expansion that was to come in 1998.
At the beginning of 1998, Amazon expanded its business and offered music and videos. The company also expanded to Germany and the United Kingdom by buying books sellers in the countries. It allowed Amazon to access customers outside of the U.S. at a low cost.
By the time 1999 rolled out, Amazon had fulfilled over 20 million orders in all fifty states and to over 150 countries around the world. Time Magazine honored Jeff Bezos as the “Person of The Year” in 1999. They also gave him the title “king of cyber-commerce,” and he was the youngest person to be recognized by Time magazine.

Amazon’s 1-Click patent
1999 also saw Amazon applying for and securing its first patent named 1-Click. It opened the door for split-second choices from the consumer, encouraging them to buy more items with ease. This technology was to be one of Amazon’s most significant advantages over its competitors.
“(…) the 1-Click patent (…) allowed Amazon to create a very strong position in the market (…) Most importantly, it allowed Amazon to show customers that there was a good reason to give them their data and the permission to charge them on an incremental basis.” R. Polk Wagner, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania Law School
The 1-Click technology played right into one of Amazon’s key value propositions: convenience. It did away with the tiresome checkout process that most online shops still use today. In fact, Amazon made a lot of money licensing the technology to other big companies. For example, Apple bought the right to use it for its iTunes platform in 2000.
From 1997 to 2000, we see Amazon laying the foundations of the giant that we know today. Record-breaking sales, enormous revenue generation, mind-boggling, innovative expansions (such as Amazon’s highly profitable Affiliate Program launched in 1996), and extraordinary market dominance, it was unheard of. The transition from a bookstore to an ‘everything store’ had begun.

Despite all these strides, the company was yet to make a profit, and there were many missteps Amazon embarked on within these three years.
Early Failures
Between 1998 and 2000, Bezos went on a shopping spree, acquiring different companies in different industries at an alarming speed. His first venture was branching into toys, which differed utterly from books.
The challenge with toys was that there were no leading distributors. Amazon would have to buy the toys from the manufacturers and store them physically, hoping they would sell. It was the total opposite of Amazon’s business model, but Bezos was adamant, spending 120 million U.S. dollars to buy toys against the advice of his executives.
By the end of that adventure, over 50 million toys were left with no one to sell them to and nowhere to keep them. Amazon ended up having to sell the toys to exporters at ridiculously low prices and donating some of them to various charities. It was a big lesson for the company and Bezos.
As mentioned earlier, Amazon tried to compete with eBay by creating its own option, named Amazon Auctions. The company poured out 175 million U.S. dollars to acquire a company called Accept.com, which handled the transactions between buyers and sellers.
It was an epic fail because eBay had a significant market dominance that Amazon could not compete with. Amazon didn’t have enough buyers, it didn’t have enough sellers, and it did not have enough things to sell. But true to its M.O., the failed Amazon Auctions became one of the building blocks that led to the formation of Amazon Marketplace.
Also, in 1998, Amazon purchased a site called Junglee, meant to compete with Google and Yahoo search sites to cater for comparison shoppers. Amazon spent 170 million buying Junglee, but it was a very unpopular purchase within Amazon because executives felt it sent Amazon customers to third-party websites and encouraged competition. Within months, they abandoned the project.
Other notable purchases by Amazon within this period included imdb.com (a movie site), alexa.com (a data company), and the social networking company called planetall.com. The company also invested in several groceries, pets, and gear shops which all failed because Amazon lacked the capacity to handle all these diverse industries.

By the end of 2000, analysts and critics declared that Amazon was a failed company. An excerpt from an August 2000 newspaper clipping stated:
Unless shareholders get rid of Bezos and the buffoons in the boardroom, those clowns may add a new chapter to the books sold by AMZN called Chapter 11. This company is a joke, and so is its leadership.
It was a fitting analysis because right in the middle of 2000, the dot.com bubble burst happened.
Dot.com bubble burst
The dot.com bubble was a particularly glorious time for online-based companies. The growing interest in technology and startups by investors culminated in a rush to join the gravy train that lasted two years.
Throwing caution to the wind, most investors poured capital into companies that did not have business plans, did not have a track record of success, and did not know how to turn their ideas into profit.
In fact, some companies did not have a complete or working product before they went public. From 1998 to 2000, many startups in the Tech industry gained enormous value overnight. Unfortunately, it all came crashing down when panic selling of stocks began.
Most of the dot.com bubble companies became worthless in a matter of months. Surprisingly, Amazon and a few other online companies like eBay survived the dot.com bubble burst.
It is a notable event in the history of Amazon because it did away with most competitors in the industry. But it also showed that Amazon was doing something right. While most of the startups were crashing, for Amazon, it was business as usual. Seen as the “poster boy for ‘Internet 1.0’ excess of promises over reality.” Amazon proved its critics wrong.
When the crash happened, Amazon had yet to make a profit on its annual statement. It put it in grave danger because investors were also worried about the company failing.
Amazon survived because it had an actual working business model. Its value proposition was solid because it addressed a genuine need in the market. Amazon’s customers were very willing to spend on the convenience that the company brought into their lives.
Although the company survived the initial burst, it eventually felt the ripple effects of the dot.com bubble crash a year later. Amazon had to lay off over 1,000 employees and closed off some of its centers in Seattle. The company also had to downsize some of its operations in order to ride the wave.
2002 – 2010 : The road to success
A lot of significant things happened from 2002 onwards. It seems they had thoroughly scratched the acquisition itch, and now the focus shifted to expanding Amazon but sticking to its original business model.
It proved to be a successful strategy because the 2000s were an excellent decade for Amazon. Many of its biggest successes today were founded in the early and mid-2000s. In 2002 Amazon ventured into selling clothes online by partnering with 400 clothing brands to cater to a wide range of customers.
Amazon was finally in its element, and the brutal lessons learned from the 90s seemed to pay off. At the end of 2003, Amazon finally made a profit of 35.5 million U.S. dollars. It was a first for the company who had recorded a loss the previous year.
In 2004, Amazon also managed to venture into the Chinese market by investing $75 million into Joyo.com. Amazon could finally start selling books, music, and videos through this Chinese retail company.
Amazon Prime
As if things couldn’t get any better, Amazon launched its Prime subscription services in February 2005. Initially aimed at faster delivery only, Prime has morphed into one of the company’s highest revenue streams. With millions of subscribers, Amazon Prime now offers access to shorter delivery times, free unlimited storage, access to millions of songs on Amazon Music, video streaming services, and so much more.
Amazon Kindle
Going back to its online bookstore roots, the company launched its first product, the Kindle, in November 2007. This e-book platform and the device allow users to download and browse through an enormous selection of literature.
Over the years, Amazon has continuously worked toward improving and tweaking its Amazon Kindle product. From producing newer Kindle devices to launching the Amazon Kindle Program, the rate at which the company adapts is astonishing.
Jeff Bezos’ vision for Amazon finally came to light with the launch of the Amazon AWS service. But that was not the initial plan.
They launched AWS as a way to bring in third-party merchants onto the Amazon e-commerce platform. Amazon developers were having a hard time figuring out how to integrate Amazon’s e-commerce engine with that of third-party merchants like Target.
Since its launch, AWS has become one of the world’s most successful cloud infrastructure service companies. As of 2016, AWS had more than a 30% share of the market, more than Microsoft, IBM and Google combined.
In December 2007, Amazon announced it would consolidate its workforce by bringing them into one building. They launched the new headquarters for the company in Seattle.
Again in 2008, Amazon decided that it wanted to dominate and capitalize on the popularity of audiobooks. It bought Audible for $300 million, outbidding Apple. The last year of the decade saw even more expansion from Amazon when it bought Zappos in 2009. It allowed the company to have a foothold in the online shoe retail industry, where it had been struggling to beat Zappos.

2010-2020 : Boosting logistics
During this decade, an essential purchase for Amazon came in 2012 when it bought Kiva, a robotic company. The robots can move packages that weigh as much as 700 lbs. It was a great move in terms of enhancing the logistics and operational side of the business. The fulfillment centers were now fully equipped and more efficient in managing operations. It certainly furthered the competitive advantage that Amazon had.
This decade would see Amazon take steps into gaming (Twitch Interactive, 2014), grocery business (Whole Foods, 2017), and so much more. They also struck a deal with USPS in 2013 to begin delivering orders on Sunday , meaning customers could now get their products 24/7.

Some grand failures plagued Amazon during this area. The most significant being the Fire Phone released in 2014. It wasn’t well-received because there were better mobile phones on the market. It was overpriced and without a lot of the functions and apps that standard phones had. Amazon lost over $200 million on this miss-adventure.
How Amazon achieved worldwide dominance
Throughout the year’s Amazon has focused on building infrastructure, expanding channels, and partnering with key companies. They wanted to:
- ensure that they had enough resources to keep prices low or competitive,
- widen their selection of goods and services,
- enhance their delivery, and
- keep improving on their customers’ convenience.
These four elements are the backbone of Amazon’s value proposition. Everything the company embarked on was (and still is) focused on strengthening these core elements of the business.
The appeal of convenience is still the number one reason why Amazon is successful today. Customers can search and find anything they want in the comfort of their own homes.
It is not about the goods that Amazon sells; it is the customer loyalty they have earned by continuously finding ways to deliver fast and giving the customer what they need and want whenever they want it.
Customer loyalty is strongly tied to the product review tools that the Amazon site offers. When you throw in customer trust and foster good customer relationships, success seems almost inevitable.
The bottom line is this: Amazon’s success results from innovation, a bit of luck, and finding the balance between sticking to what you know works versus taking calculated risks that may or may not pay off.

Conclusion
So what can businesses learn from the successes and failures of Amazon? A lot! But the most crucial lesson we think we can glean from Amazon is to treat each day as if it’s “Day 1”. We can interpret the famous Bezos phrase in many ways. But if we examine what has kept Amazon afloat and thriving all these years, it will most certainly be the “Day 1” attitude.
- Tags: aws , books , business model canvas , dotcom bubble , ebay , ecommerce , google , ipo , jeff bezos , kindle , logistics , yahoo
Most Popular

Netflix’s Business Model Canvas Evolution (2021)

McDonald’s: Business Model Canvas, its evolution and company’s history

18 Must-Read Business Books
- Business books reviews (27)
- Business Ideas (8)
- Business Model Canvas (9)
- Business models of large companies (26)
Business Tools

Download Free Business Model Canvas Template in Word / docx / PDF / SVG format
Inspire yourself with Business Ideas Generator
Get INSPIRING stories and TIPS on making your business model PROFITABLE!
- Recently trending business ideas
- Inspiring business models
- Examples of profitable businesses from all over the world
Related Posts

Twitter: Becoming The World’s Fastest Information Hub
Today, Twitter is one of the most recognizable and influential social media platforms on the planet. As of February 2022, Twitter is valued at $27.48

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Cost Structure
The last (but not least) segment on the Business Model Canvas is the cost structures. In this segment, you must ask yourself, how much will

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Key Partners
No man is an island; the same goes for your business. They are other companies, 3rd parties, and people that you will need to achieve

The Business Model Canvas Explained: Key Resources
On the Business Model Canvas, the Key Resources segment refers to the supplies, assets, and materials required to deliver your value proposition to your customer
Privacy Overview

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
Amazon: Business Model, SWOT Analysis, and Competitors 2023
Inside This Article
In this blog article, we will delve into the business model of Amazon, one of the most influential and successful companies in the world. We will explore how Amazon has revolutionized e-commerce and expanded its operations beyond just online retail. Additionally, we will conduct a comprehensive SWOT analysis to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that Amazon faces in the dynamic market. Lastly, we will examine the key competitors that Amazon will likely encounter in the year 2023 and analyze their strategies to understand how they might impact Amazon's growth and dominance.
What You Will Learn:
- Who owns Amazon and the key individuals behind the company's success
- The mission statement of Amazon and how it drives their business decisions and strategies
- How Amazon makes money through its various revenue streams and business models
- An explanation of the Amazon Business Model Canvas and how it shapes their overall operations
- The main competitors of Amazon and how they compare in terms of market share, customer base, and offerings
- A comprehensive SWOT analysis of Amazon, highlighting its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the global market.
Who owns Amazon?
The shareholders of amazon.
Amazon, one of the world's largest multinational technology companies, has a diverse and extensive ownership structure. As a publicly traded company, Amazon is owned by a wide range of shareholders, including institutional investors, individual investors, and company insiders.
The largest shareholders of Amazon are typically institutional investors, such as mutual funds, pension funds, and other asset management firms. These institutional investors often hold significant ownership stakes in the company, with some having billions of dollars invested in Amazon's stock. For example, as of the latest available data, the Vanguard Group is one of the largest institutional shareholders of Amazon, holding around 6% of the company's outstanding shares.
In addition to institutional investors, individual investors also play a significant role in Amazon's ownership. Many retail investors, including everyday individuals, own Amazon shares directly or indirectly through investment vehicles like exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or index funds. These investors may have different motivations for owning Amazon stock, ranging from long-term investment strategies to short-term trading opportunities.
Furthermore, company insiders, such as executives, directors, and employees, also hold a portion of Amazon's ownership. These insiders often acquire shares as part of their compensation packages or through stock option grants. Their ownership stakes align their interests with the company's performance and demonstrate their confidence in Amazon's future prospects.
It is important to note that the ownership of Amazon's stock can change over time due to various factors, including buying and selling by investors, stock splits, and new issuances of shares. Therefore, the exact ownership distribution can vary from one period to another.
In conclusion, Amazon is owned by a broad and diverse group of shareholders, including institutional investors, individual investors, and company insiders. This ownership structure reflects the widespread interest and confidence in Amazon's business model and its potential for future growth.
What is the mission statement of Amazon?
The mission statement of amazon: to be earth's most customer-centric company.
Amazon's mission statement can be summarized in one powerful phrase: "To be Earth's most customer-centric company." This mission statement encapsulates the core values and principles that drive Amazon's business strategies and decisions.
By emphasizing the customer-centric approach, Amazon places the utmost importance on meeting and exceeding customer expectations. This commitment is reflected in the company's relentless pursuit of innovation, convenience, and customer satisfaction.
Amazon's mission statement implies that they strive to understand and anticipate customer needs better than any other company. They aim to build a seamless and personalized shopping experience that caters to a diverse range of customers' preferences and demands. By doing so, Amazon aims to establish long-term relationships with customers, fostering loyalty and trust.
To fulfill its mission, Amazon places a strong emphasis on technological advancements. They continuously invest in state-of-the-art infrastructure, cutting-edge automation, and advanced analytics to enhance their operations. This enables Amazon to provide a wide array of products and services efficiently and at competitive prices.
Furthermore, Amazon's customer-centricity extends beyond its e-commerce platform. The company aims to provide exceptional customer experiences across all its subsidiaries and services, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Amazon Prime, and Amazon Studios. The mission statement acts as a guiding principle, ensuring that every aspect of Amazon's business revolves around delivering value to customers.
In conclusion, Amazon's mission statement, "To be Earth's most customer-centric company," reflects a strong commitment to putting customers at the center of everything they do. This mission drives their focus on innovation, convenience, and exceptional customer experiences, making Amazon a trusted brand that continues to revolutionize the way people shop and consume various products and services.
How does Amazon make money?
E-commerce sales.
Amazon primarily generates revenue through its e-commerce platform, which allows individuals and businesses to buy and sell products online. As one of the largest online retailers globally, the company offers an extensive range of products across various categories, including electronics, books, household goods, and clothing. Through its user-friendly interface and efficient delivery services, Amazon has built a loyal customer base, resulting in consistent sales growth. The company charges a commission fee from third-party sellers for each item sold on its platform, contributing to its revenue stream.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Another significant source of revenue for Amazon is its cloud computing service, known as Amazon Web Services (AWS). AWS offers a suite of cloud-based products and solutions, including storage, database management, analytics, and artificial intelligence, to individuals, businesses, and government organizations. As a pioneer in the field, AWS has become a leading provider of cloud infrastructure services, catering to a wide range of customers globally. With a pay-as-you-go pricing model, AWS generates revenue by charging users for the storage, computing power, and other resources they utilize.
Subscription Services
Amazon offers several subscription-based services that contribute significantly to its revenue. One of the most notable examples is Amazon Prime, which provides subscribers with various benefits, including free two-day shipping, access to streaming services like Prime Video, exclusive deals, and more. By charging an annual or monthly fee for Prime membership, Amazon not only generates revenue but also fosters customer loyalty and encourages repeat purchases. Additionally, the company offers subscription services like Amazon Music and Amazon Kindle Unlimited, allowing customers to access a vast library of music or e-books for a fixed monthly fee.
Advertising
Amazon has also entered the digital advertising space, leveraging its vast customer base and extensive product information to offer targeted advertising solutions. Through its advertising platform called Amazon Advertising, the company enables businesses to promote their products and brands on its website and other affiliated platforms. Amazon Advertising utilizes customer browsing and purchase data to deliver relevant ads, increasing the chances of conversion. As more businesses adopt Amazon's advertising solutions, this segment has become a significant revenue generator for the company.
Other Ventures
In addition to its core revenue streams, Amazon has diversified its business by venturing into various industries. This includes the production and streaming of original content through Amazon Studios, the manufacturing of consumer electronics such as Kindle e-readers and Fire tablets, and the acquisition of Whole Foods Market to enter the grocery retail sector. While these ventures may not be the primary sources of revenue for Amazon, they contribute to the company's overall growth and brand presence in the market.
Amazon Business Model Canvas Explained
What is the business model canvas.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that helps businesses visualize and understand the various components of their business model. It provides a framework for analyzing and designing business models, enabling organizations to identify key activities, resources, and relationships required to create and deliver value to customers.
Introduction to Amazon's Business Model Canvas
Amazon, founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994, started as an online bookstore but has rapidly expanded into a global e-commerce giant. The company has revolutionized the retail industry and disrupted traditional brick-and-mortar stores by leveraging technology and a customer-centric approach.
Key Components of Amazon's Business Model Canvas
1. customer segments.
Amazon serves a wide range of customer segments, including individual consumers, small businesses, and enterprise customers. The company caters to diverse needs by offering a vast selection of products and services, from books and electronics to cloud computing solutions.
2. Value Propositions
Amazon's value propositions revolve around convenience, selection, competitive pricing, and fast delivery. The company strives to make online shopping effortless and enjoyable for customers, providing them with a seamless buying experience and access to a vast catalog of products.
3. Channels
Amazon operates through multiple channels, including its website, mobile applications, and voice-activated devices like Amazon Echo. These channels enable customers to browse and purchase products, access digital content, and interact with Amazon's services.
4. Customer Relationships
Amazon values its customer relationships and focuses on building long-term loyalty. The company achieves this through personalized recommendations, customer reviews, and excellent customer service. Moreover, Amazon Prime, a subscription-based service, enhances customer relationships by offering benefits like free and fast shipping, exclusive discounts, and access to streaming services.
5. Revenue Streams
Amazon generates revenue through various streams, primarily e-commerce sales. Additionally, the company earns from advertising services, subscription fees (e.g., Amazon Prime), and its cloud computing platform, Amazon Web Services (AWS).
6. Key Activities
Amazon's key activities include sourcing and purchasing products from suppliers, managing inventory, operating warehouses, developing and maintaining technological infrastructure, and delivering products to customers. The company also invests heavily in research and development to innovate and expand its offerings.
7. Key Resources
Key resources for Amazon include a vast network of fulfillment centers, advanced technology for inventory management and logistics, strong relationships with suppliers, and an extensive customer base. Additionally, Amazon's brand reputation, data analytics capabilities, and intellectual property (such as patents) are crucial resources.
8. Key Partnerships
Amazon collaborates with various partners to enhance its offerings and reach. These partnerships include suppliers who provide products, shipping and logistics companies, payment processors, and developers who create applications for Amazon's platform. The company also partners with content creators and publishers to offer digital content to customers.
9. Cost Structure
Amazon's cost structure consists of various elements, including costs associated with fulfillment and logistics, technology infrastructure, marketing, customer service, and investments in new ventures. The company strives for operational efficiency and cost optimization to offer competitive prices to customers while maintaining profitability.
By analyzing Amazon's Business Model Canvas, it becomes evident that the company's success is rooted in its ability to deliver value to customers through convenience, selection, and excellent service. Amazon's continuous innovation, focus on customer relationships, and diverse revenue streams have propelled it to become a dominant force in the global e-commerce landscape.
Which companies are the competitors of Amazon?
Traditional retailers.
One of the main competitors of Amazon is traditional brick-and-mortar retailers. Companies such as Walmart, Target, and Best Buy have been in the retail industry for decades and have established a strong presence both online and offline. These retailers have recognized the importance of e-commerce and have made significant investments to compete with Amazon in the online space. They offer a wide range of products, competitive pricing, and convenient shipping options to attract customers.

Online Marketplaces
Several online marketplaces pose a significant competition to Amazon. eBay, for instance, is a well-known platform that allows individuals and businesses to buy and sell products. While eBay operates differently than Amazon, as it primarily serves as a platform for third-party sellers, it still attracts a large customer base. Additionally, Alibaba, a Chinese e-commerce giant, is a major competitor on a global scale. Alibaba offers a similar range of products and services as Amazon, focusing on both business-to-consumer (B2C) and consumer-to-consumer (C2C) transactions.
Tech Giants
Tech giants like Google and Apple have also entered the e-commerce space and are challenging Amazon. Google, with its Google Shopping platform, allows users to search for products and compare prices from various retailers. Apple, on the other hand, has its own online store where it sells a wide range of electronics and accessories. These companies leverage their existing user base and brand loyalty to attract customers away from Amazon.
Another group of competitors for Amazon includes subscription-based services that offer similar benefits to Amazon Prime. Walmart+, for example, is a membership program launched by Walmart that provides free shipping on eligible items, fuel discounts, and other perks. Costco, a membership-based warehouse club, also competes with Amazon by offering a wide range of products at discounted prices to its members. These subscription services aim to provide convenience and value to customers, just like Amazon Prime does.
Niche E-Commerce Platforms
While Amazon dominates many product categories, there are niche e-commerce platforms that focus on specific industries or types of products. For example, Etsy is a marketplace specifically for handmade or vintage items. Wayfair specializes in furniture and home decor. These platforms attract customers who are looking for unique or specialized products that may not be readily available on Amazon. By catering to specific niches, these platforms provide a different shopping experience and offer a viable alternative to Amazon for certain customer segments.
Amazon SWOT Analysis
- Strong brand recognition: Amazon is one of the most recognized brands globally, known for its wide range of products and services.
- Extensive product offerings: The company offers a diverse range of products and services, ranging from e-commerce to cloud computing, which allows it to cater to a broad customer base.
- Advanced technology infrastructure: Amazon has invested heavily in developing a robust technology infrastructure, enabling it to handle massive volumes of online transactions efficiently.
- Customer-centric approach: The company prioritizes customer satisfaction and has built a reputation for delivering exceptional customer service.
- Efficient supply chain management: Amazon's efficient supply chain management ensures quick order fulfillment and delivery, contributing to its competitive advantage.
Weaknesses:
- Dependence on third-party sellers: A significant portion of Amazon's revenue comes from third-party sellers, which makes the company vulnerable to any changes in their business practices or relationships.
- Counterfeit products: Due to the large number of third-party sellers, Amazon has faced challenges with counterfeit products, which can harm its reputation and erode customer trust.
- High competition: The e-commerce industry is highly competitive, with numerous players trying to capture market share. Amazon faces intense competition from both established companies and emerging startups.
- Overreliance on online sales: While Amazon has expanded into physical retail with the acquisition of Whole Foods, its primary revenue source still heavily relies on online sales. This concentration poses risks if there is a significant shift in consumer behavior or a disruption in online services.
Opportunities:
- Expansion into new markets: Amazon has the opportunity to expand its business into new markets, such as healthcare, grocery, and international regions, to drive future growth.
- Growing demand for cloud services: Amazon Web Services (AWS) has experienced significant growth, and the increasing demand for cloud computing presents an opportunity for the company to further expand its market share.
- Acquisition potential: With its strong financial position, Amazon has the opportunity to acquire other companies to diversify its offerings or gain a competitive advantage in certain sectors.
- Emerging technologies: As technology continues to evolve, Amazon can leverage emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, voice assistants, and virtual reality to enhance customer experience and develop new revenue streams.
- Regulatory challenges: As Amazon expands its operations and influence, it faces increased scrutiny from regulators regarding issues such as antitrust concerns, data privacy, and labor practices.
- Intense competition: Competitors such as Walmart, Alibaba, and Google pose a threat to Amazon's market dominance. These companies have the financial resources and infrastructure to challenge Amazon's position.
- Rapidly changing consumer preferences: Consumer preferences and behaviors are continually evolving, and Amazon needs to adapt quickly to meet these changing demands. Failure to do so could lead to a loss of market share.
- Supply chain disruptions: Any disruptions in Amazon's supply chain, such as natural disasters or labor strikes, could impact its ability to fulfill customer orders, resulting in potential revenue loss and customer dissatisfaction.
Key Takeaways
- Amazon is owned by its founder and CEO, Jeff Bezos, who holds a significant majority stake in the company.
- The mission statement of Amazon is to be the most customer-centric company, offering a wide range of products and services at competitive prices, while providing a seamless and convenient shopping experience.
- Amazon makes money primarily through its e-commerce platform, where it sells products directly to customers and charges fees to third-party sellers for using its marketplace. Additionally, the company generates revenue from its cloud computing services, advertising, and subscription-based services like Amazon Prime.
- The Amazon Business Model Canvas explains how the company creates value by focusing on key activities such as customer relationship management, logistics, and technology infrastructure, while maintaining a strong customer base and efficient supply chain.
- Amazon's main competitors include Walmart, Alibaba, eBay, and other e-commerce giants. However, the company faces competition across various industries, including traditional brick-and-mortar retailers, streaming services, and cloud computing providers.
- In a SWOT analysis, Amazon's strengths include its vast product selection, strong brand recognition, and efficient logistics network. Its weaknesses may include issues related to counterfeit products and worker conditions. Opportunities for Amazon include expanding into new markets and industries, while threats may arise from increasing regulatory scrutiny and competition.
In conclusion, Amazon is owned by its founder, Jeff Bezos, who started the company in 1994 and has since grown it into a global e-commerce giant. The mission statement of Amazon is to be Earth's most customer-centric company, offering a wide range of products and services to meet the needs of its customers.
Amazon primarily makes money through its e-commerce platform, where it sells products directly to consumers and charges fees to third-party sellers. It also generates revenue from its subscription services like Amazon Prime, its cloud computing division Amazon Web Services (AWS), and advertising.
The Amazon Business Model Canvas provides a comprehensive overview of how the company operates. It outlines key activities such as sourcing products, maintaining a robust logistics network, and continuously improving customer experience. The canvas also highlights important partnerships, customer segments, and revenue streams that contribute to Amazon's success.
As for competition, Amazon faces fierce rivalry from companies like Walmart, Alibaba, and eBay, who also operate in the e-commerce space. These companies continuously strive to capture a larger share of the online retail market, leading to intense competition and innovation.
In a SWOT analysis of Amazon, its strengths lie in its vast product selection, strong brand recognition, and efficient logistics network. However, weaknesses such as counterfeit products and third-party seller issues pose challenges. Opportunities for growth include expanding into new markets and industries, while threats include regulatory challenges and potential disruptions in supply chains.
Overall, Amazon's ownership, mission statement, revenue streams, business model, competitors, and SWOT analysis all contribute to its position as a dominant player in the global e-commerce industry.
What are Amazon's strengths and weaknesses?
Amazon's strengths are as follows:
Strong brand recognition: Amazon is one of the most well-known and trusted brands globally, which helps attract customers and gain their loyalty.
Extensive product range: The company offers a wide range of products, including books, electronics, clothing, and more. This extensive selection appeals to a diverse customer base.
Efficient logistics and distribution network: Amazon has built a robust network of warehouses and fulfillment centers, enabling fast and reliable delivery to customers worldwide.
Customer-centric approach: Amazon prioritizes customer satisfaction, offering features like easy returns, personalized recommendations, and excellent customer service.
Technological innovation: The company has continually invested in technology, enabling it to develop advanced systems for inventory management, order fulfillment, and customer analytics.
Amazon also has a few weaknesses:
High competition: Amazon faces intense competition from both large retailers and smaller niche online stores. Competitors like Walmart and Alibaba pose a significant challenge.
Counterfeit products: Due to the extensive number of third-party sellers on Amazon, the platform has faced issues with counterfeit products, resulting in negative customer experiences.
Reliance on third-party sellers: While third-party sellers contribute to Amazon's product range, the company faces challenges in ensuring the quality and authenticity of these products.
Negative public perception: Amazon has been criticized for its labor practices and the impact on local businesses. These criticisms have led to negative public perception and potential reputation damage.
Regulatory challenges: As Amazon expands into various industries, the company faces increasing regulatory scrutiny, which may impact its operations and growth strategies.
What are Amazon's major weaknesses?
Some of Amazon's major weaknesses include:
Reliance on third-party sellers: Amazon's marketplace heavily relies on third-party sellers, who account for a significant portion of its sales. This reliance may lead to issues like counterfeit products, poor quality items, and unreliable sellers, which can negatively impact customer satisfaction.
Counterfeiting concerns: Amazon has faced criticism for its inability to effectively tackle the issue of counterfeit products on its platform. This can harm the trust and reputation of the company, as customers may be uncertain about the authenticity of the products they purchase.
Labor practices and working conditions: Amazon has been criticized for its treatment of warehouse employees, with concerns raised about long working hours, intense productivity demands, and poor working conditions. Such criticisms can damage the company's reputation and lead to negative public perception.
Environmental impact: Amazon's rapid growth has led to concerns about its environmental impact. The company's extensive logistics network, packaging waste, and carbon emissions contribute to environmental degradation. As sustainability becomes increasingly important to customers, this weakness may become a significant disadvantage for Amazon.
Regulatory scrutiny: Amazon operates in various countries, and its dominant position in e-commerce has attracted regulatory scrutiny. The company faces antitrust investigations and allegations of unfair business practices, which can result in fines, legal challenges, and increased regulatory oversight.
Data privacy and security: As a major player in e-commerce and cloud computing, Amazon handles vast amounts of customer data. Any data breaches or security vulnerabilities could harm customer trust and result in legal consequences, especially with the increasing focus on data privacy and protection.
International expansion challenges: While Amazon has expanded globally, it faces challenges in various international markets, including cultural barriers, regulatory differences, and competition from local e-commerce players. These challenges may limit the company's growth potential in certain regions.
What are the threats of Amazon?
Competition: Amazon faces intense competition from other e-commerce giants like Walmart, Alibaba, and eBay, as well as niche players in specific industries. This can result in price wars, loss of market share, and reduced profitability.
Regulation and Antitrust: Amazon's market dominance has attracted regulatory scrutiny and antitrust investigations in various countries. If found guilty of anticompetitive practices, Amazon could face fines, restrictions on business practices, and potential breakup.
Counterfeit and Fraudulent Products: The vast number of third-party sellers on Amazon's platform increases the risk of counterfeit products, fake reviews, and fraudulent activities. This can damage Amazon's reputation and erode customer trust.
Data Breaches and Privacy Concerns: As a large repository of customer data, Amazon is a prime target for hackers and cybercriminals. Any data breach or privacy violation could lead to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal consequences.
Labor and Employment Issues: Amazon has faced criticism for its treatment of warehouse workers, including concerns about working conditions, low wages, and limited labor rights. These issues can lead to negative publicity, employee dissatisfaction, and potential labor disputes.
Logistics and Supply Chain Disruptions: Amazon's extensive logistics and supply chain network is vulnerable to disruptions, such as natural disasters, labor strikes, or transportation disruptions. These can result in delayed deliveries, increased costs, and customer dissatisfaction.
Negative Public Perception: Amazon has been criticized for its environmental impact, tax avoidance strategies, and its effects on local businesses. These criticisms can damage the company's reputation and lead to consumer boycotts or regulatory action.
Technological Disruptions: Rapid advancements in technology, such as the rise of voice assistants or augmented reality, can disrupt Amazon's business model and require significant investment to adapt and stay competitive.
Dependence on Cloud Services: Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a significant revenue generator for Amazon. However, increased competition in the cloud computing market and the risk of service disruptions or security breaches may impact AWS's growth and profitability.
International Expansion Challenges: Expanding into new markets brings regulatory, cultural, and logistical challenges. Amazon faces regulatory complexities, local competition, and the need to adapt its business model to different regions, which can hinder its international growth.
What are Amazon's biggest strengths?
Amazon's biggest strengths include:
Wide product selection: Amazon offers a vast range of products across various categories, including electronics, books, clothing, home goods, and more. This extensive selection gives customers a one-stop destination for their shopping needs.
Customer-centric approach: Amazon prioritizes customer satisfaction and convenience. With initiatives like Amazon Prime, which offers fast and free shipping, as well as excellent customer service, Amazon ensures a positive shopping experience.
Strong distribution network: Amazon has built a robust logistics infrastructure, including fulfillment centers, warehouses, and delivery services. This enables efficient and timely delivery to customers, contributing to their satisfaction.
Technological innovation: Amazon is at the forefront of technological advancements, utilizing technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and data analytics. These technologies are employed to improve customer experience, personalize recommendations, optimize supply chain operations, and enhance overall efficiency.
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS is a major player in cloud computing, providing scalable and cost-effective solutions to businesses. This segment is highly profitable and contributes significantly to Amazon's overall success.
Brand recognition and trust: Amazon has established itself as a reputable and trustworthy brand. Its reliable services, secure payment options, and customer reviews contribute to building trust among consumers.
Remarkable retail ecosystem: Amazon's ecosystem includes various services like Amazon Prime, Amazon Fresh, Amazon Music, and Kindle. This ecosystem creates a seamless experience for customers, encouraging loyalty and repeat purchases.
Data-driven decision-making: Amazon excels in leveraging data to make informed business decisions. By collecting and analyzing vast amounts of customer data, they can optimize their offerings, pricing, and marketing strategies.
Continuous innovation: Amazon consistently introduces new products, services, and features to meet evolving customer demands. This focus on innovation helps them stay ahead of the competition and maintain customer loyalty.
Global presence: Amazon operates in numerous countries, allowing it to cater to a diverse customer base. Its global reach and localized services contribute to its success on a global scale.
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
Case study: Amazon

Amazon is a large international company that operates in a number of sectors. Amazon is best-known for its core business of selling goods online (=Amazon Marketplace). But it also offers a very profitable online platform called Amazon Web Services (AWS) which is aimed at developers and other companies. Additionally it earns significant money through “Amazon Advertising”.
In this analysis we focus on Amazon Marketplace only. Let’ have a look at how the business model canvas could be filled out:
1. Customer segments:
As always, we start with the customer segments. Amazon has a variety of customer segments located in different markets. Key customer segments for Amazon could be following:
Consumers: Those are the classical users, that buy good at the webshop. Amazon has a large customer base of consumers who use the platform to purchase products in many different categories, such as electronics, books, clothing, and household goods.
Small Businesses: Amazon also offers solutions for small businesses that want to sell their products on the platform, like: retailers, manufacturers, and wholesalers.
Enterprise Customers: Amazon has enterprise customers that use the platform to streamline their purchasing processes and reduce costs.
Publishers and media companies: Amazon also has partnerships with publishers and media companies to sell content such as books, magazines and movies through its platform. Wide selection: Amazon offers a huge selection of products and services, including its own brands and third-party products. This means that customers can find everything they need in one place.
2. Value proposition:
Next we jump to Amazons Value proposition. Why are you using Amazon?
Convenience: Ohh it is just so much more convenient to sit in front of your computer, tablet or phone and do the shopping. Without the hassle of driving somewhere. Amazon allows customers to easily shop from home and have products delivered quickly and reliably. Customers can also reach the customer service 24/7 via email, phone, or live chat.
Large selection: Of course Amazon has a large palette of products at competitive prices. The company has a wide range of products available for purchase on its website, including books, electronics, clothing, household goods, and more.
Cost efficiency: Amazon often offers lower prices than traditional retailers due to lower costs for rent and personnel. Customers can also benefit from the Prime membership, which offers free shipping and other perks.
Fast delivery: When you want to buy something, you usually want to have it quick. Amazon is also known for its fast and reliable delivery options. The company offers a range of delivery options, including standard shipping, express shipping, and same-day delivery depending on the customer’s location and the product being purchased. Amazon also has a network of fulfillment centers around the world, which helps the company deliver products quickly and efficiently to customers.
Customer is king: Another aspect of Amazon’s value proposition is its commitment to customer satisfaction. The company has a generous return policy and offers excellent customer service through its website and mobile app, as well as phone and email support. Amazon’s focus on customer satisfaction helps strengthen customer loyalty and encourage customers to return.
3. Channels:
Next, lets have a look at Amazon’s key marketing and distribution channels:
Web-shop: Well, it is not just a web-shop, it is a complete e-commerce platform, that Amazon has. This allows you to buy products and offers various functions and tools to make shopping easier for users, such as personalized recommendations and search filter options.
Mobile Apps: “All about apps” - Amazon also offers mobile apps for iOS and Android that allow users to purchase products through their smartphones and tablets.
Partnerships: Amazon has partnerships with other companies to provide its products and services. These include partnerships with retailers that sell Amazon products in their stores and partnerships with logistics companies that help Amazon ship products to customers.
Advertising: Amazon also uses advertising to promote its products and services. This includes ads in online and offline media as well as social media advertising.
Email marketing: Amazon also uses email marketing to send users personalized offers and recommendations and to inform them about new products and services.
4. Customer relations:
Loyal, long-term clients will increase revenue from repeat purchases. So, how does Amazon develop this customer loyalty?
“A brand for a company is like a reputation for a person. You earn reputation by trying to do hard things well.” Jeff Bezos - CEO Amazon
Customer Service: First, Amazon offers a really good customer service. If you have a question or a problem, you can easily contact customer service. Usually they are very helpful, friendly and your problem is fixed very quickly.
Personalized recommendations: Many big companies do it nowadays, but Amazon is one of the industry pioneers in this regard. Amazon uses lots of your data such as previous purchases, reviews, and browsing behavior to create personalized recommendations for each customer. These recommendations appear on the Amazon website and in emails to the customer, and can help customers discover interesting new products. For sure you have seen Amazon products pop up on a completely different website.
Prime membership: Amazon also offers a Prime membership that gives customers access to various benefits, including free shipping, access to streaming services, and more. This membership can help customers remain loyal Amazon customers.
Customer reviews and feedback: Amazon also encourages customers to leave reviews and feedback on products, which can help other customers decide whether to buy a product. This feedback can also help Amazon improve its products and services.
Partnerships and collaborations: Amazon also maintains partnerships and collaborations with other companies and organizations to offer customers a wider choice of products and services. This can help customers stay with Amazon because they can find everything they need in one place.
5. Revenue streams:
Amazon actually has multiple revenue streams. For this case study, however we just focus on the revenue streams of its market place:
Sale of products: Focusing on the Market Place, Amazon’s main revenue stream comes from the sale of products. Amazon sells both its own products and third-party products.
Advertising: What many people do not realize, Amazon also offers advertising for other companies. This advertising can appear in the form of ads or Sponsored Products.
Services: Amazon also offers services such as selling e-books and music, renting movies and TV shows, and access to streaming services like Prime Video.
Prime membership: Amazon heavily promotes its Prime membership that gives customers access to various benefits, including free shipping, access to streaming services, and more. Membership is paid annually or monthly.
Cloud-Computing: Amazon also operates a cloud computing platform called Amazon Web Services (AWS), which provides businesses with access to server capacity and other resources. Companies pay for the use of these resources based on their usage.
6. Key Resources
What are Amazons most important assets needed to make their business model work? Amazon has a broad range of key resources which its business model depends on:
Online platform: The Amazon website is the central platform for selling products and providing services. The platform is also the main source of customer reviews and feedback.
Customer Data: Amazon collects and analyzes customer data to provide personalized recommendations and advertising, and to improve the site’s offerings and usability.
Delivery and Logistics Infrastructure: Amazon operates a comprehensive delivery and logistics infrastructure to deliver products to customers quickly and reliably. This infrastructure includes its own warehouses and logistics centers as well as partnerships with freight forwarders and courier services.
Manufacturer and Retailer Relationships: Amazon maintains relationships with manufacturers and retailers to offer a wide range of products. These relationships enable Amazon to respond quickly to customer needs and introduce new products.
Technology and IT Infrastructure: Amazon relies on advanced technology and IT infrastructure to improve website functionality and user experience and to optimize its delivery and logistics services.
7. Key activities
Again, when we just focus on Amazons market place, then following key activities need to be considered:
Sale of products: The products on its online platform need to be offered to the customer and in the end sold to them. This includes both the sale of its own products and the sale of third-party products.
Marketing: Although Amazon is already very popular and often “the only market place” that people use, it also has a marketing strategy to strengthen the brand. This includes advertising on the Amazon website and social media, Personalized Recommendations and customer reviews.
Customer Service: Customers are King: Therefore Amazon operates a customer service that is available via email, phone, or live chat. Customers can contact customer service if they have questions or problems, or if they need assistance using Amazon products or services.
Logistics and delivery: Amazon operates an extensive delivery and logistics infrastructure to deliver products to customers quickly and reliably. This infrastructure includes its own warehouses and logistics centers, as well as partnerships with freight forwarders and courier services.
8. Key partners:
Amazon has following key partners:
Manufacturers and Retailers: Manufacturers and retailers allow Amazon to offer a wide range of products
Logistic Partner: Amazon works with various freight forwarders and courier services to deliver products to customers quickly and reliably.
Payment Partner: Amazon works with payment service providers such as PayPal and credit card companies to enable customers to conveniently and securely pay for their purchases.
Content Providers: In order to offer e-books, music, and movies Amazons partners with authors, film studios and music labels.
Cloud Computing Partners: Amazon also operates a cloud computing platform called Amazon Web Services (AWS) that provides businesses with access to server capacity and other resources. AWS works with various partners to provide these resources.
9. Cost structure
Following costs occur with operating Amazons business:
Website / Hosting: This includes all costs that are necessary to operate its platform. For example, the cost of developing websites and apps, providing cloud services and maintaining databases.
Marketing and advertising costs: Marketing costs include the cost for search engine advertising, social media advertising and the placement of ads in print and online media.
Staff costs: These include the cost of salaries and wages, the cost of employee training and development, and the cost of human resources management, etc…
General and administrative costs: These include the cost of office equipment and supplies, the cost of travel and lodging, the cost of insurance and taxes, and the cost of general administrative activities.
Financing costs: This means paying back loans
Direct costs include, for example, the cost of procuring, storing, packing, and shipping goods . They also include the payment of commissions to sellers as well as rent and other real estate costs .
Amazon’s indirect costs include, for example, the costs of developing technologies and platforms, marketing and advertising, personnel management and development, and general and administrative tasks

- Search 77147
- Search 12112

Amazon Business Model | How does Amazon make money
Last updated: Feb 13, 2021
Company : Amazon CEO : Andrew Jassy Year founded : 1994 Headquarter : Seattle, Washington United States
Business world has never been the same since the inception of Amazon . The e-commerce enterprise started as a bookstore in 1994 and found surprising popularity. Its success allowed it to expand and transform into the “everything store” in its literal sense.
Today, Amazon is widely considered as having the best online site available which even other competitor sites such as Walmart have not been able to catch up to since 2015. Amazon successfully
overtook Walmart into becoming the most valuable retailer in the USA. It became the largest Internet Company by revenue as well as the eighth largest employer in the US. It has since bought out Whole Foods in 2017 for $13.4 billion and increased its retailing presence.
Amazon has also launched its physical stores which enabled it in 2017 to garner 5 billion dollars in revenue. In 2020, Amazon is projected to increase its global market share of e-commerce sales to 38% from 37.3% in 2019. [ 1 ]
Amazon’s subscription service called Amazon Prime has also been a critical component in cementing its customer retention and winning over new customers in the process.
Amazon has adopted multiple marketing strategies to continue reaching out to new demographics via solid tech infrastructure and lowering of prices . These provide for a myriad of reasons as to why Amazon has continued to thrive and innovate throughout its operation .
It continues to adapt and undergo evolutionary changes to beat out its competition and remain at the pinnacle of its supremacy.
Table of Contents
Business Model Canvas of Amazon
Known to be the largest online retailer worldwide, Amazon functions at a diverse pace in their product offerings. More and more customers access its sites to purchase the products they are looking for more so at an affordable rate.
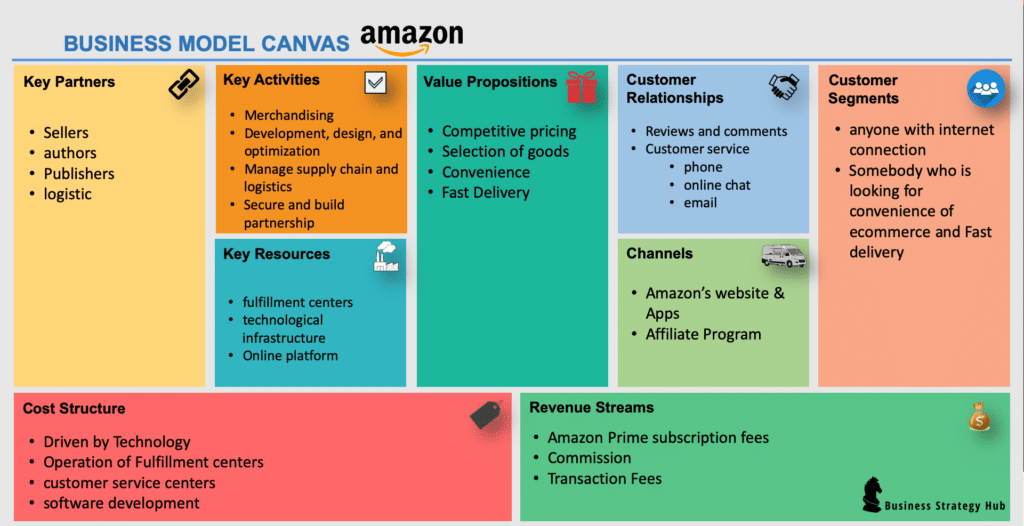
1. Customers of Amazon
Both buyers and sellers can come together in Amazon’s platform considering how it is a mass market. Where its brand is concerned, anyone that inherits internet connection is a potential customer.
Amazon’s customer base is also its most loyal one. Millions of people across the world have a Prime subscription and pay their fee for its services respectively.
2. Value Proposition of Amazon
Competitive pricing , selection of goods , convenience and fast fulfillment all carry weightage to Amazon’s value.
The consumers who buy various goods on Amazon are directly responsible for their current successes. Amazon has cemented its position as providing a safe, reliable and well-stocked platform for shopping which is why they continue to utilize its services repeatedly. To boost sales during the holidays, Amazon holds Prime Day to kick start the holiday shopping season early. This annual shopping event offers products at throwaway prices, promotions, and discounts. [ 2 ]
The Amazon brand in and of itself cannot be replicated. It has remained consistently diverse and consistent throughout the years. The selection of goods it sponsors is authentic and widely sought after. It’s convenient, and fast-tracked services make for a robust strategy as well.
The convenience of Amazon’s deliveries was evident in 2020, with millions of customers turning to the e-commerce giant to avoid leaving the safety of their homes or venturing into crowded malls, supermarkets, and retail stores. [ 3 ]
#Amazon ups its hourly wage today for all US workers. Check out how its competitors stack up https://t.co/VD8tlwrhdn pic.twitter.com/0U9BxtN4Bi — Statista (@StatistaCharts) November 1, 2018
3. Channel of Amazon
Amazon’s website operates as its largest channel. Different versions exist on its site that aids and abets customers worldwide. Nowadays, apps have been created to accelerate sales growth. Many affiliates have also taken their role in acting as a channel for Amazon like the Amazon Affiliate Program .
As of October 2020, Amazon has 14 e-commerce sites worldwide that offer its own products and marketplace products. Sales through Amazon’s sites totaled $340.4 billion in 2019, which is a 22.9% increase from $277.0 billion in 2018. Its global e-commerce sale is projected to reach $416.48 billion in 2020 as recent events push more consumers to e-commerce sites. [ 4 ]
4. Customer Relationships of Amazon
Amazon is a brand that is heavily invested in the retention of its consumers. It has enjoyed a healthy and productive relationship with its customers for a long period of time. Some of their customer interactions take place with the reviews or comments shoppers can leave on their webpage. Amazon also offers customer service through phone, online chat or email.
5. Key Activities of Amazon
Amazon’s key activities are as follows:
- Merchandising of its digital and physical goods.
- Development, design, and optimization of its Platform (website or apps).
- Manage supply chain and logistics
- Secure and build a partnership with its supplier and sellers
- Support the production of movies or show on its prime video platform
- Acquire new ventures to support its ecosystem
6. Key Resources of Amazon
Amazon’s physical resources such as fulfillment centers (warehouses), and supply chain automation help in its physical resources. Its technological infrastructure , in particular, is crucial for its everyday business model . The company recently announced that it is on track to open 33 new fulfillment centers in the US by the end of 2020 and has invested over $30 billion in sellers’ programs and technology to boost capacity and fulfillment services within one and a half years. [ 5 ]
The same is the case with its software engineers who are responsible for the creation of its online platform infrastructure. Much of the popular culture has also served the purposes of Amazon well where it is used to generate attractive product sales.
7. Key Partners of Amazon
Among Amazon’s key partners – Sellers are by far it’s most important who singularly generate the most revenue for Amazon. Other authors , publishers, and logistic partners increase its value and aid in the conversion of many people into customers. Amazon values such partners and has many times credited them for their assistance.
Their assistance was critical as recent events halted global supply chains. The events highlighted the importance of reliable partners. In Britain, online shopping spiked from 7% at the start of the crisis to about 15% in September 2020. The sudden increase prompted Amazon’s UK partner, Morrisons, to add more than 1,000 employees to process Amazon orders. [ 6 ]
8. Cost Structure of Amazon
Amazon’s cost structure is driven by value. It means that Amazon function on a system that only benefits them economically. It’s IT , and fulfillment centre is also a vital component in this regard as it enables Amazon to operate on a global scale. Other essential elements utilized in the cost structure of Amazon include its customer service centers as well as software development centers across the world.
9. Revenue Stream of Amazon
Prime remains Amazon’s primary Revenue Stream as it is accessible to more customers and in turn, generate the most revenue for them.
Other Amazon Revenue Models includes the Commission and Transaction Fees it makes from its products as well as the recent sale of E-books and digital content it has been utilizing in its sales.
How Does Amazon Make Money?
That fundamental question can be answered extensively owing to the different models the company operates on in terms of revenue.
Amazon Marketplace
The Amazon Marketplace, or rather the Amazon.com website is Amazon’s primary revenue generator with millions of people seeking to buy products on its site. Amazon Marketplace (amazon.com) is a world class e-commerce platform where products from Amazon and third parties are sold to the buyers.
Third party sellers whose function is to sell Amazon items are either Fulfilled by Amazon (FBA) or Fulfilled By Merchant (FBM). FBA goods are held in Amazon’s fulfillment centers where Amazon handles the delivery services. Sales revenue from third-party marketplace sellers make up the largest portion of Amazon’s worldwide sales and has grown rapidly from 34% in 2010, 58% in 2018, and over 60% in the year ending in May 2020. [ 7 ]
On the other hand, FBM goods are stored in a third-party seller’s inventory and delivered by a third-party merchant. Amazon also makes a substantial amount by charging its sellers to promote and advertise their products .
Amazon Prime
The subscription model that Amazon proceeded with has been a vital element in its growth strategy. It has led to more customers joining to gain memberships who then purchase the products en masse from online stores. The more products they purchase, the more revenue Amazon receives.
Prime has been a pioneer in providing its customers with faster delivery services via streaming. Its predictable and stable method of operation has established consistent income over time.
Some of the more prominent Amazon Prime Premium subscriptions offer to include:
- Twitch Prime
- Instant access to video streaming
- Free Two-Day Shipping with Amazon Prime
- Free unlimited photo storage
- Over two million songs on Amazon Music. Thousands of playlists and stations.
As of March 2020, Twitch Prime had 56,000 concurrent broadcasters and 1.44 million concurrent viewers on average. The number of unique Twitch broadcasters surpassed 4 million by April 2020. [ 8 ]
Amazon Web Services
AWS or the Amazon Web Services offered their IT infrastructure services in 2006. The Amazon web services stand today as one of the most scalable and reliable platforms in its entire industry. What makes it stand out is its low-cost infrastructure that connects limitless business worldwide. AWS continues to function as Amazon’s cloud business as well as providing computing for everyone be it startups or government institutions.
Amazon Kindle
Thanks to this e-readers series on Amazon, users can now buy, browse and download any newspaper, e-book, and magazine that want. All these are available at the Kindle Store .
The Kindle has been successful in winning over new users and converting them to buy Amazon products and content at an exceeding rate. Through this experience, users are then driven to opt for Prime. It usually comes with a Prime Trial which is free for approximately 30 days.
It’s important to note that Amazon does not generate profit from Kindles, at least not directly. It is more of effective planning that is solely responsible for increasing traffic of a membership plan. The effectiveness of this strategy signifies the innovative magnitude of Amazon.
Amazon Media and Content
The Amazon Company has already advanced to the next stage by entering the video and music marketing industry. This strategy has proven to be successful owing to the sizable revenue from which Amazon has accumulated since.
Amazon acquired IMBD in 1998 (Internet Movie Database) is considered to be the most popular TV, celebrity and movie content source today. IMBD generates its revenue via subscriptions, advertisements, and promotions.
Amazon’s music store called Amazon Music much like its competitors like Spotify, encourages users to subscribe to get their favorite music at an unlimited rate. The music subscription is offered at a fixed monthly cost .
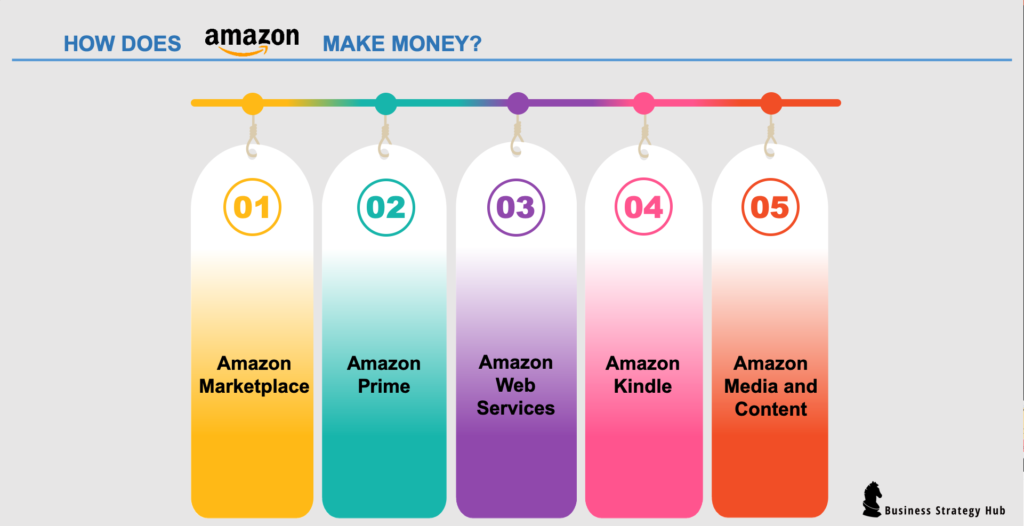
In Conclusion
Amazon is an international enterprise that has become inseparable from the global economy. It has become more and more productive and has adapted throughout its inception with originality and unorthodoxy. It will continue to grow and remain supreme unless its competitors finally catch up to it.
So far, it is running unopposed and unparalleled. As long as it continues to develop new ideas and stay ahead of its competition, it is destined to remain at top.
References & more information
- Levy, A. (2020, Jun 10). Amazon Could Still Gain E-Commerce Market Share in 2020 . Fool
- Data, T. (2020, Sept. 28). Amazon to hold the Prime Day event on October 13-14 . Reuters
- Soper, S. (2020, May 13). Amazon Says Delivery Speed Returning to Normal After Coronavirus Crush . Time
- Droesch, B. (2020, Jul 9). Amazon’s worldwide sales will rise 20.2% this year as reliance on e-commerce grows . Business Insider
- Steiner, I. (2020, July 18). Amazon Adds 33 New US Fulfillment Centers in 2020 . E-commerce Bytes
- Davey, J. (2020, Sept. 30). Britain’s Morrisons creates 1,000 jobs to process Amazon orders . Reuters
- Ali, F. (2020, Jul 22). US Amazon marketplace sellers sold 3.4 billion products in the last 12 months . Commerce 360
- Iqbal, M. (2020, July 23). Twitch Revenue and Usage Statistics (2020) . Business of Apps.
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.
A management consultant and entrepreneur. S.K. Gupta understands how to create and implement business strategies. He is passionate about analyzing and writing about businesses.
Cancel reply
What month and year was this article published?
First published: Nov 11, 2018 Last updated: July 23, 2020
Thanks for insights
You may also like

How Does Craigslist Make Money? (2022)
Last updated: May 23, 2020 Company: Craigslist, Inc. Industry: Classified advertisements forum Founder: Craig Newmark CEO: Jim Buckmaster Year founded: 1995 Headquarter: San Francisco, California, United States Number...
20 Most Unique Business Models
Every company follows a certain business model. The growth and success of a company are based on the business model it follows. Therefore, it is essential for a business model to be diverse and adaptable. However, there...

What is ProctorU, how it works and makes money?
Company: ProctorU Founders: Jarrod Morgan Year founded: 2008 CEO: Scott McFarland Headquarter: Birmingham, Alabama Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 400+ Type: Private Ticker Symbol: NYSE: UBER Annual Revenue (Dec...
How does DealDash work & make money?
Company: DealDash Founders: William Wolfram CEO: Pasi Lohi Year founded: 2009 Headquarter: Minneapolis, MN Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 50 Type: Private Annual Revenue (Dec 2018): Estimated $9.7M Products...

How does Fabletics work and make money?
Company: Fabletics Founders: Kate Hudson, Adam Goldenberg, Don Ressler Year founded: 2013 CEO: Don Ressler and Adam Goldenberg Headquarter: El Segundo, CA Employees (2020): Est. 500 Annual Revenue (2020): Est...
Etsy Business Model | How Does Etsy Make Money?
Technological advancements, increased adoption of mobile devices, globalization, better and cheaper internet connection, and safe payment gateways are driving the growth of online marketplaces like Etsy. But what is...

How Does Tinder Make Money?
Company: Tinder CEO: Sean Rad Year founded: 2012 Headquarter: Dallas, US Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 200 Parent Company: Interactive Corp (IAC) Type: Private Valuation (March 2019): $10 billion Annual Revenue (Dec...

How Does Uber Eats Make Money?
Company: Uber Eats (a subsidiary of Uber Technologies Inc.) CEO: Dara Khosrowshahi Founders: Travis Kalanick and Garret Camp Year founded: 2014 Headquarter: San Francisco, California, USA Revenue (Quarterly...
Walmart Business Model | How does Walmart Make Money ?
Company: Walmart Inc. (NYSE: WMT) Founders: Sam Walton Year founded: 1962 CEO: Doug McMillan Headquarter: Bentonville, Arkansas Number of Employees (2023): 2.1 million Type: Public Market Capitalization (July...
How does Letgo make money?
Company: Letgo CEO: Enrique Linares Plaza Founders: Alec Oxenford, Enrique Linares Plaza, and Jordi Castello Year founded: 2015 Headquarter: New York, New York Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 270+ Type:...
Recent Posts
- Top 20 Canva’s Competitors and Alternatives
- Who owns Porsche?
- Who Owns TracFone
- Who Owns Rolex?
- Who Owns Bellagio?
- Who Owns Skechers?
- Who Owns JetBlue?
- Who Owns Ciroc?
- Who owns Aston Martin?
- Top 10 Bed Bath and Beyond Competitors and Alternatives
Business Strategy Hub
- A – Z Companies
- Privacy Policy
Buy us Coffee
If you like our work and would like to show appreciation to our team, buy us coffee!
Subscribe to receive updates from the hub!
- Red Queen Effect
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Only the paranoid survives
- Co-opetition Strategy
- Mintzberg’s 5 Ps
- Ansoff Matrix
- Target Right Customers
- Product Life Cycle
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Bowman’s Strategic Clock
- Pricing Strategies
- 7S Framework
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Strategy Diamond
- Value Innovation
- PESTLE Analysis
- Gap Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Strategy Canvas
- Business Model
- Mission & Vision
- Competitors
- Buy Us Coffee!
Business Model Canvas: Explained with Examples
Got a new business idea, but don’t know how to put it to work? Want to improve your existing business model? Overwhelmed by writing your business plan? There is a one-page technique that can provide you the solution you are looking for, and that’s the business model canvas.
In this guide, you’ll have the Business Model Canvas explained, along with steps on how to create one. All business model canvas examples in the post can be edited online.
What is a Business Model Canvas
A business model is simply a plan describing how a business intends to make money. It explains who your customer base is and how you deliver value to them and the related details of financing. And the business model canvas lets you define these different components on a single page.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that lets you visualize and assess your business idea or concept. It’s a one-page document containing nine boxes that represent different fundamental elements of a business.
The business model canvas beats the traditional business plan that spans across several pages, by offering a much easier way to understand the different core elements of a business.
The right side of the canvas focuses on the customer or the market (external factors that are not under your control) while the left side of the canvas focuses on the business (internal factors that are mostly under your control). In the middle, you get the value propositions that represent the exchange of value between your business and your customers.
The business model canvas was originally developed by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur and introduced in their book ‘ Business Model Generation ’ as a visual framework for planning, developing and testing the business model(s) of an organization.
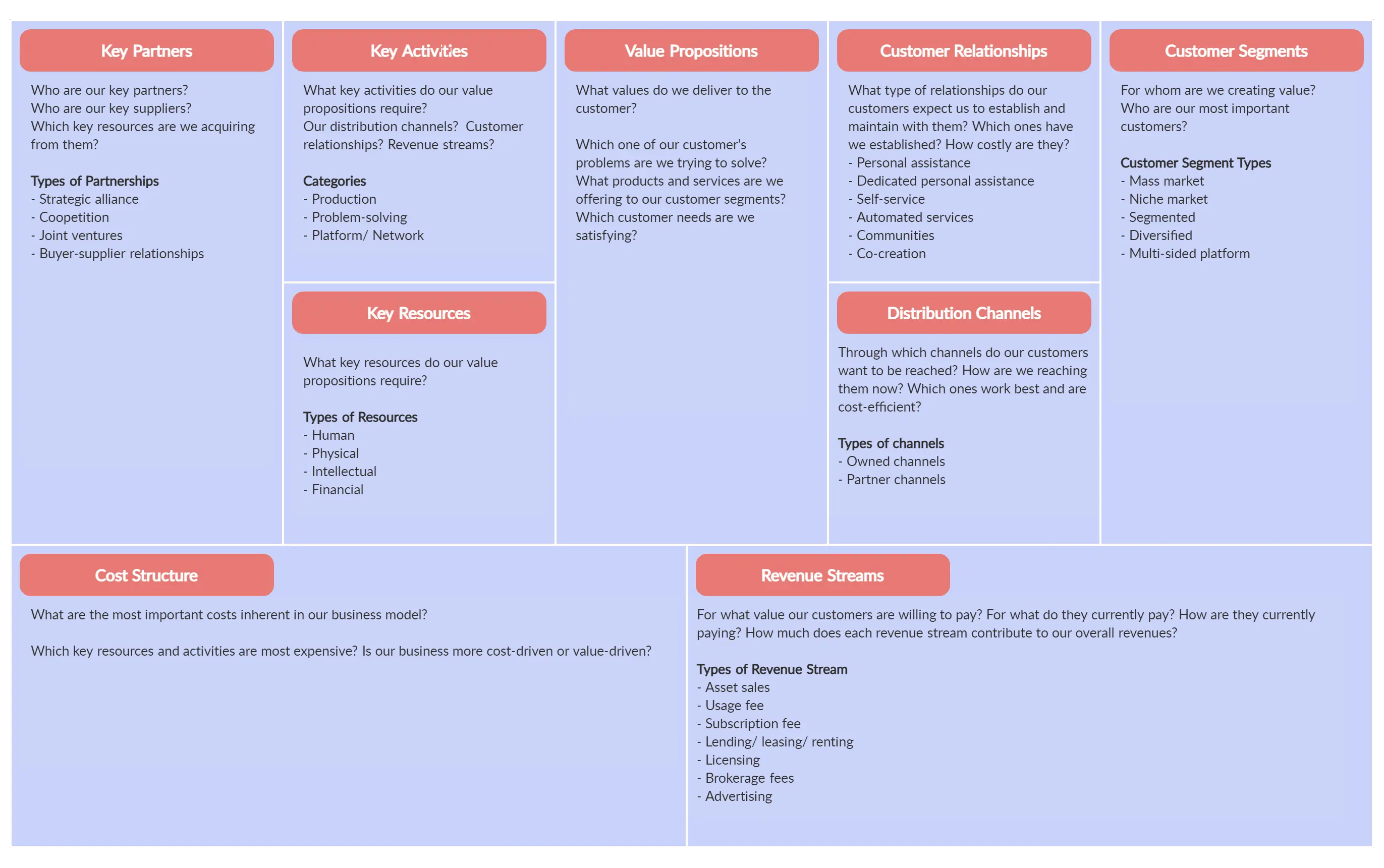
What Are the Benefits of Using a Business Model Canvas
Why do you need a business model canvas? The answer is simple. The business model canvas offers several benefits for businesses and entrepreneurs. It is a valuable tool and provides a visual and structured approach to designing, analyzing, optimizing, and communicating your business model.
- The business model canvas provides a comprehensive overview of a business model’s essential aspects. The BMC provides a quick outline of the business model and is devoid of unnecessary details compared to the traditional business plan.
- The comprehensive overview also ensures that the team considers all required components of their business model and can identify gaps or areas for improvement.
- The BMC allows the team to have a holistic and shared understanding of the business model while enabling them to align and collaborate effectively.
- The visual nature of the business model canvas makes it easier to refer to and understand by anyone. The business model canvas combines all vital business model elements in a single, easy-to-understand canvas.
- The BMC can be considered a strategic analysis tool as it enables you to examine a business model’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges.
- It’s easier to edit and can be easily shared with employees and stakeholders.
- The BMC is a flexible and adaptable tool that can be updated and revised as the business evolves. Keep your business agile and responsive to market changes and customer needs.
- The business model canvas can be used by large corporations and startups with just a few employees.
- The business model canvas effectively facilitates discussions among team members, investors, partners, customers, and other stakeholders. It clarifies how different aspects of the business are related and ensures a shared understanding of the business model.
- You can use a BMC template to facilitate discussions and guide brainstorming brainstorming sessions to generate insights and ideas to refine the business model and make strategic decisions.
- The BMC is action-oriented, encouraging businesses to identify activities and initiatives to improve their business model to drive business growth.
- A business model canvas provides a structured approach for businesses to explore possibilities and experiment with new ideas. This encourages creativity and innovation, which in turn encourages team members to think outside the box.
How to Make a Business Model Canvas
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model.
Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
While you can create a business model canvas with whiteboards, sticky notes, and markers, using an online platform like Creately will ensure that your work can be accessed from anywhere, anytime. Create a workspace in Creately and provide editing/reviewing permission to start.
Step 2: Set the context Clearly define the purpose and the scope of what you want to map out and visualize in the business model canvas. Narrow down the business or idea you want to analyze with the team and its context.
Step 3: Draw the canvas Divide the workspace into nine equal sections to represent the nine building blocks of the business model canvas.
Step 4: Identify the key building blocks Label each section as customer segment, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, and cost structure.
Step 5: Fill in the canvas Work with your team to fill in each section of the canvas with relevant information. You can use data, keywords, diagrams, and more to represent ideas and concepts.
Step 6: Analyze and iterate Once your team has filled in the business model canvas, analyze the relationships to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges. Discuss improvements and make adjustments as necessary.
Step 7: Finalize Finalize and use the model as a visual reference to communicate and align your business model with stakeholders. You can also use the model to make informed and strategic decisions and guide your business.
What are the Key Building Blocks of the Business Model Canvas?
There are nine building blocks in the business model canvas and they are:
Customer Segments
Customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partners, cost structure.
- Value Proposition
When filling out a Business Model Canvas, you will brainstorm and conduct research on each of these elements. The data you collect can be placed in each relevant section of the canvas. So have a business model canvas ready when you start the exercise.
Let’s look into what the 9 components of the BMC are in more detail.
These are the groups of people or companies that you are trying to target and sell your product or service to.
Segmenting your customers based on similarities such as geographical area, gender, age, behaviors, interests, etc. gives you the opportunity to better serve their needs, specifically by customizing the solution you are providing them.
After a thorough analysis of your customer segments, you can determine who you should serve and ignore. Then create customer personas for each of the selected customer segments.
There are different customer segments a business model can target and they are;
- Mass market: A business model that focuses on mass markets doesn’t group its customers into segments. Instead, it focuses on the general population or a large group of people with similar needs. For example, a product like a phone.
- Niche market: Here the focus is centered on a specific group of people with unique needs and traits. Here the value propositions, distribution channels, and customer relationships should be customized to meet their specific requirements. An example would be buyers of sports shoes.
- Segmented: Based on slightly different needs, there could be different groups within the main customer segment. Accordingly, you can create different value propositions, distribution channels, etc. to meet the different needs of these segments.
- Diversified: A diversified market segment includes customers with very different needs.
- Multi-sided markets: this includes interdependent customer segments. For example, a credit card company caters to both their credit card holders as well as merchants who accept those cards.
Use STP Model templates for segmenting your market and developing ideal marketing campaigns
Visualize, assess, and update your business model. Collaborate on brainstorming with your team on your next business model innovation.
In this section, you need to establish the type of relationship you will have with each of your customer segments or how you will interact with them throughout their journey with your company.
There are several types of customer relationships
- Personal assistance: you interact with the customer in person or by email, through phone call or other means.
- Dedicated personal assistance: you assign a dedicated customer representative to an individual customer.
- Self-service: here you maintain no relationship with the customer, but provides what the customer needs to help themselves.
- Automated services: this includes automated processes or machinery that helps customers perform services themselves.
- Communities: these include online communities where customers can help each other solve their own problems with regard to the product or service.
- Co-creation: here the company allows the customer to get involved in the designing or development of the product. For example, YouTube has given its users the opportunity to create content for its audience.
You can understand the kind of relationship your customer has with your company through a customer journey map . It will help you identify the different stages your customers go through when interacting with your company. And it will help you make sense of how to acquire, retain and grow your customers.
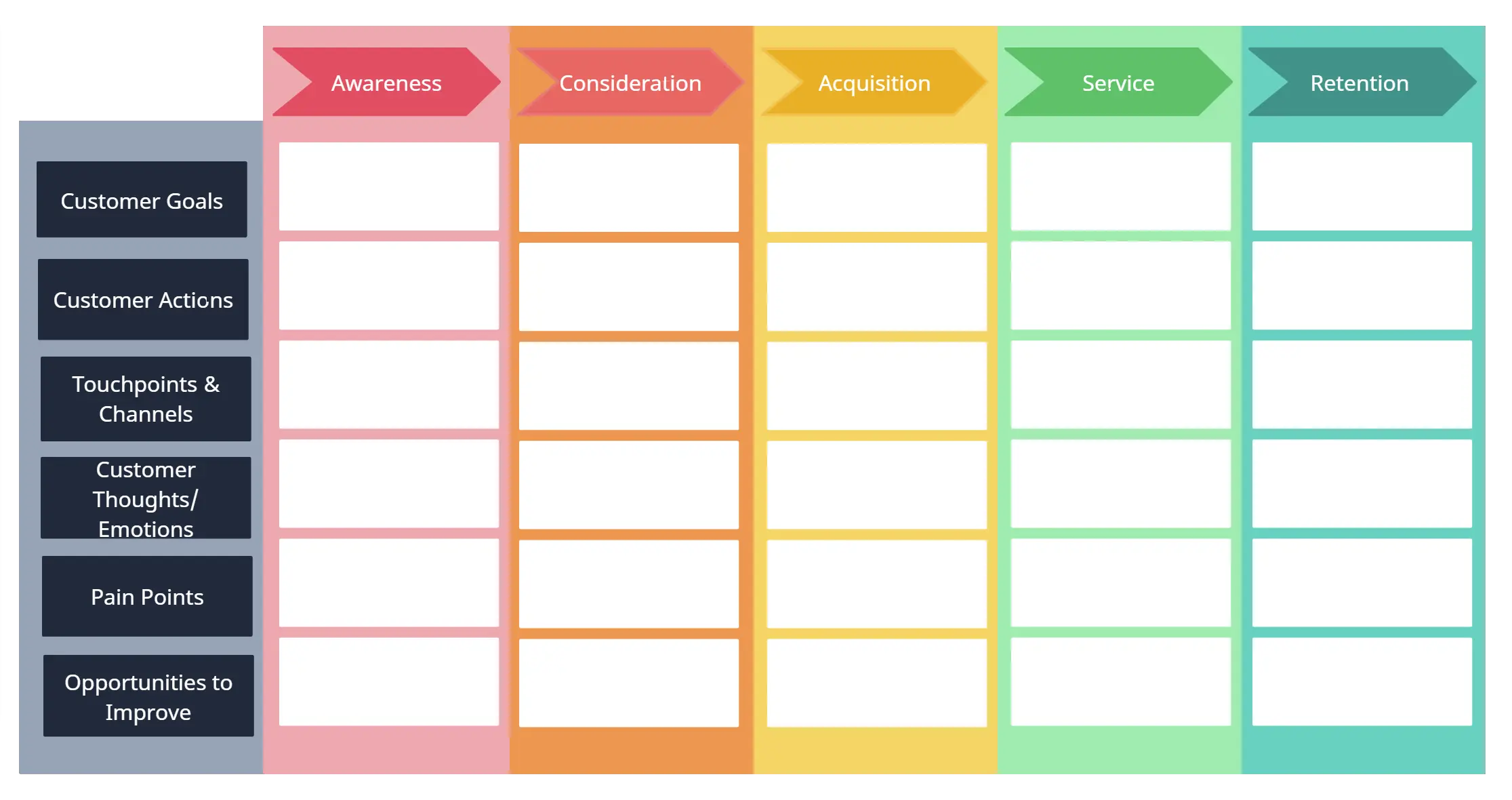
This block is to describe how your company will communicate with and reach out to your customers. Channels are the touchpoints that let your customers connect with your company.
Channels play a role in raising awareness of your product or service among customers and delivering your value propositions to them. Channels can also be used to allow customers the avenue to buy products or services and offer post-purchase support.
There are two types of channels
- Owned channels: company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc.
- Partner channels: partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc.
Revenues streams are the sources from which a company generates money by selling their product or service to the customers. And in this block, you should describe how you will earn revenue from your value propositions.
A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models,
- Transaction-based revenue: made from customers who make a one-time payment
- Recurring revenue: made from ongoing payments for continuing services or post-sale services
There are several ways you can generate revenue from
- Asset sales: by selling the rights of ownership for a product to a buyer
- Usage fee: by charging the customer for the use of its product or service
- Subscription fee: by charging the customer for using its product regularly and consistently
- Lending/ leasing/ renting: the customer pays to get exclusive rights to use an asset for a fixed period of time
- Licensing: customer pays to get permission to use the company’s intellectual property
- Brokerage fees: revenue generated by acting as an intermediary between two or more parties
- Advertising: by charging the customer to advertise a product, service or brand using company platforms
What are the activities/ tasks that need to be completed to fulfill your business purpose? In this section, you should list down all the key activities you need to do to make your business model work.
These key activities should focus on fulfilling its value proposition, reaching customer segments and maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue.
There are 3 categories of key activities;
- Production: designing, manufacturing and delivering a product in significant quantities and/ or of superior quality.
- Problem-solving: finding new solutions to individual problems faced by customers.
- Platform/ network: Creating and maintaining platforms. For example, Microsoft provides a reliable operating system to support third-party software products.
This is where you list down which key resources or the main inputs you need to carry out your key activities in order to create your value proposition.
There are several types of key resources and they are
- Human (employees)
- Financial (cash, lines of credit, etc.)
- Intellectual (brand, patents, IP, copyright)
- Physical (equipment, inventory, buildings)
Key partners are the external companies or suppliers that will help you carry out your key activities. These partnerships are forged in oder to reduce risks and acquire resources.
Types of partnerships are
- Strategic alliance: partnership between non-competitors
- Coopetition: strategic partnership between partners
- Joint ventures: partners developing a new business
- Buyer-supplier relationships: ensure reliable supplies
In this block, you identify all the costs associated with operating your business model.
You’ll need to focus on evaluating the cost of creating and delivering your value propositions, creating revenue streams, and maintaining customer relationships. And this will be easier to do so once you have defined your key resources, activities, and partners.
Businesses can either be cost-driven (focuses on minimizing costs whenever possible) and value-driven (focuses on providing maximum value to the customer).
Value Propositions
This is the building block that is at the heart of the business model canvas. And it represents your unique solution (product or service) for a problem faced by a customer segment, or that creates value for the customer segment.
A value proposition should be unique or should be different from that of your competitors. If you are offering a new product, it should be innovative and disruptive. And if you are offering a product that already exists in the market, it should stand out with new features and attributes.
Value propositions can be either quantitative (price and speed of service) or qualitative (customer experience or design).
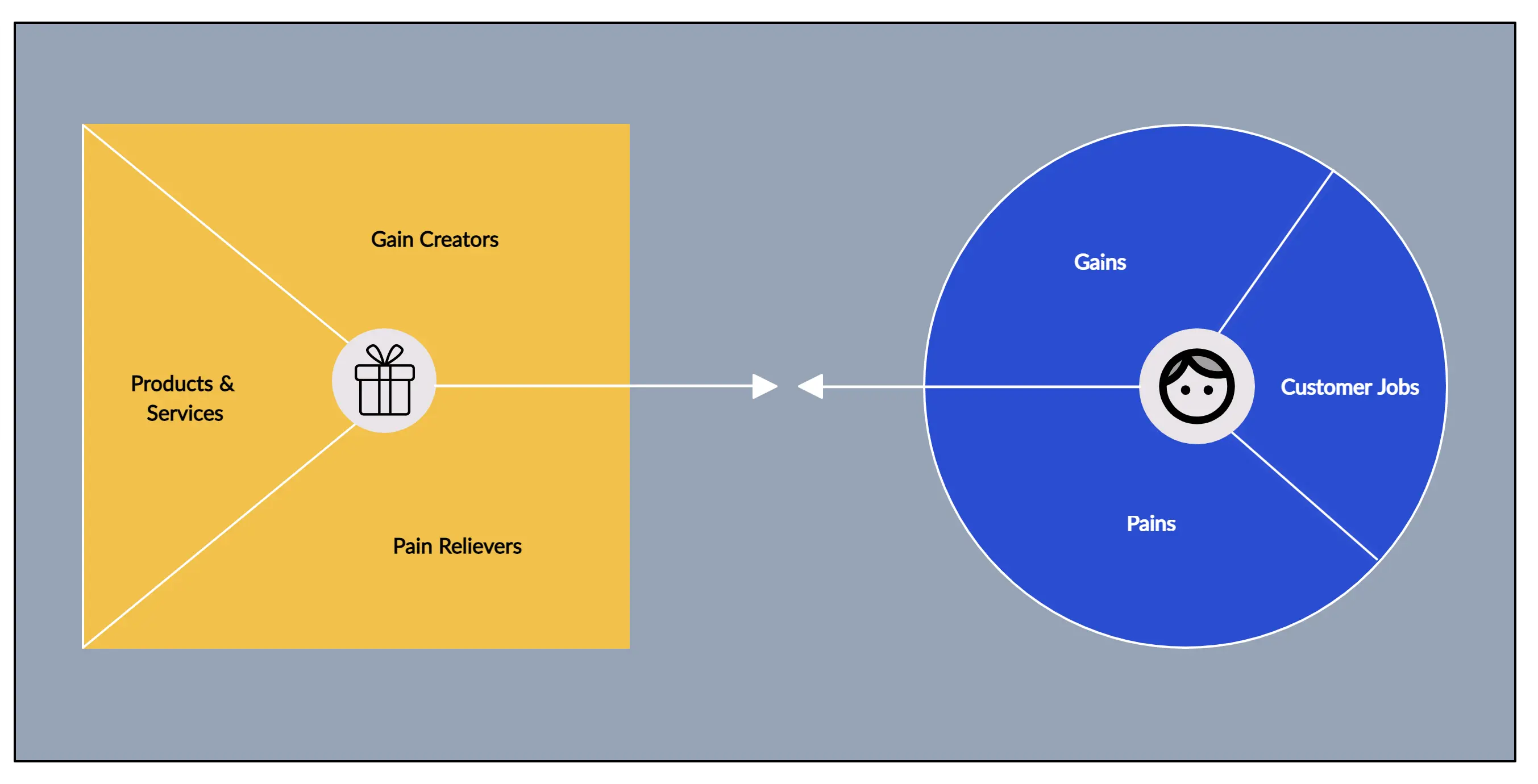
What to Avoid When Creating a Business Model Canvas
One thing to remember when creating a business model canvas is that it is a concise and focused document. It is designed to capture key elements of a business model and, as such, should not include detailed information. Some of the items to avoid include,
- Detailed financial projections such as revenue forecasts, cost breakdowns, and financial ratios. Revenue streams and cost structure should be represented at a high level, providing an overview rather than detailed projections.
- Detailed operational processes such as standard operating procedures of a business. The BMC focuses on the strategic and conceptual aspects.
- Comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. The business model canvas does not provide space for comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. These should be included in marketing or sales plans, which allow you to expand into more details.
- Legal or regulatory details such as intellectual property, licensing agreements, or compliance requirements. As these require more detailed and specialized attention, they are better suited to be addressed in separate legal or regulatory documents.
- Long-term strategic goals or vision statements. While the canvas helps to align the business model with the overall strategy, it should focus on the immediate and tangible aspects.
- Irrelevant or unnecessary information that does not directly relate to the business model. Including extra or unnecessary information can clutter the BMC and make it less effective in communicating the core elements.
What Are Your Thoughts on the Business Model Canvas?
Once you have completed your business model canvas, you can share it with your organization and stakeholders and get their feedback as well. The business model canvas is a living document, therefore after completing it you need to revisit and ensure that it is relevant, updated and accurate.
What best practices do you follow when creating a business model canvas? Do share your tips with us in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs About the Business Model Canvas
- Use clear and concise language
- Use visual-aids
- Customize for your audience
- Highlight key insights
- Be open to feedback and discussion
More Related Articles

Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
This web app uses cookies to compile statistic information of our users visits. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. If you wish you may change your preference or read about cookies
Or explore sectors:
Why amazon prime's business model is so successful.

Amazon Prime business model canvas
Amazon Prime’s Company Overview
Amazon prime is an added value service that allow to amazon's customers to get the goods they purchase online with free delivery.
Country: Washington
Foundations date: 2014
Type: Private
Sector: Consumer Goods
Categories: eCommerce
Amazon Prime’s Customer Needs
Social impact:
Life changing: affiliation/belonging
Emotional: rewards me, badge value, provides access
Functional: reduces effort, avoid hassles, saves time, simplifies, organizes, integrates, variety, quality, sensory appeal
Amazon Prime’s Related Competitors
Amazon prime’s business operations.
An additional item offered to a customer of a primary product or service is referred to as an add-on sale. Depending on the industry, add-on sales may generate substantial income and profits for a firm. For example, when a customer has decided to purchase the core product or service, the salesman at an automotive dealership will usually offer an add-on sale. The pattern is used in the price of new software programs based on access to new features, number of users, and so forth.
Affiliation:
Commissions are used in the affiliate revenue model example. Essentially, you resell goods from other merchants or businesses on your website or in your physical store. You are then compensated for referring new consumers to the company offering the goods or services. Affiliates often use a pay-per-sale or pay-per-display model. As a result, the business can access a more diversified prospective client base without extra active sales or marketing efforts. Affiliate marketing is a popular internet business strategy with significant potential for growth. When a client purchases via a referral link, the affiliate gets a portion of the transaction's cost.
Archetypes of business model design:
The business model archetypes include many business personalities and more than one business model linked to various goods or services. There is a common foundation behind the scenes of each unit, but from a management standpoint, each group may operate independently.
Best in class services:
When a firm brings a product to market, it must first create a compelling product and then field a workforce capable of manufacturing it at a competitive price. Neither task is simple to perform effectively; much managerial effort and scholarly study have been dedicated to these issues. Nevertheless, providing a service involves another aspect: managing clients, who are consumers of the service and may also contribute to its creation.
Multiple products or services have been bundled together to enhance the value. Bundling is a marketing technique in which goods or services are bundled to be sold as a single entity. Bundling enables the purchasing of several goods and services from a single vendor. While the goods and services are often linked, they may also consist of different items that appeal to a particular market segment.
Cashier-as-a-service:
Cashier-as-a-Service (CaaS) describes the practice of paying using a third-party service. When consumers purchase goods online, they often pay the seller indirectly via a third party - the cashier. Both the consumer and the merchant place their confidence in the cashier, who is supposed to facilitate the trustworthy and safe transfer of money. By paying a business through a cashier, consumers may purchase goods without providing merchants with their financial data.
Combining data within and across industries:
How can data from other sources be integrated to generate additional value? The science of big data, combined with emerging IT standards that enable improved data integration, enables new information coordination across businesses or sectors. As a result, intelligent executives across industries will see big data for what it is: a revolution in management. However, as with any other significant organizational transformation, the difficulties associated with becoming a big data-enabled company may be tremendous and require hands-on?or, in some instances, hands-off?leadership.
Corporate innovation:
Innovation is the outcome of collaborative creativity in turning an idea into a feasible concept, accompanied by a collaborative effort to bring that concept to life as a product, service, or process improvement. The digital era has created an environment conducive to business model innovation since technology has transformed how businesses operate and provide services to consumers.
Cross-selling:
Cross-selling is a business strategy in which additional services or goods are offered to the primary offering to attract new consumers and retain existing ones. Numerous businesses are increasingly diversifying their product lines with items that have little resemblance to their primary offerings. Walmart is one such example; they used to offer everything but food. They want their stores to function as one-stop shops. Thus, companies mitigate their reliance on particular items and increase overall sustainability by providing other goods and services.
Culture is brand:
It requires workers to live brand values to solve issues, make internal choices, and provide a branded consumer. Developing a distinctive and enduring cultural brand is the advertising industry's holy grail. Utilizing the hazy combination of time, attitude, and emotion to identify and replicate an ideology is near to marketing magic.
Customer data:
It primarily offers free services to users, stores their personal information, and acts as a platform for users to interact with one another. Additional value is generated by gathering and processing consumer data in advantageous ways for internal use or transfer to interested third parties. Revenue is produced by either directly selling the data to outsiders or by leveraging it for internal reasons, such as increasing the efficacy of advertising. Thus, innovative, sustainable Big Data business models are as prevalent and desired as they are elusive (i.e., data is the new oil).
Customer loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a very successful business strategy. It entails giving consumers value that extends beyond the product or service itself. It is often provided through incentive-based programs such as member discounts, coupons, birthday discounts, and points. Today, most businesses have some kind of incentive-based programs, such as American Airlines, which rewards customers with points for each trip they take with them.
Customer relationship:
Due to the high cost of client acquisition, acquiring a sizable wallet share, economies of scale are crucial. Customer relationship management (CRM) is a technique for dealing with a business's interactions with current and prospective customers that aims to analyze data about customers' interactions with a company to improve business relationships with customers, with a particular emphasis on retention, and ultimately to drive sales growth.
Channel aggregation:
Consolidating numerous distribution routes into one to achieve greater economic efficiency. A business model for internet commerce in which a company (that does not manufacture or warehouse any item) gathers (aggregates) information about products and services from many competing sources and displays it on its website. The firm's strength is in its power to create an 'environment' that attracts users to its website and develop a system that facilitates pricing and specification matching.
A digital strategy is a strategic management and a business reaction or solution to a digital issue, which is often best handled as part of a broader company plan. A digital strategy is frequently defined by the application of new technologies to existing business activities and a focus on enabling new digital skills for their company (such as those formed by the Information Age and frequently as a result of advances in digital technologies such as computers, data, telecommunication services, and the World wide web, to name a few).
Discount club:
The discount club concept is built on perpetual high-discount deals utilized as a continual marketing plan or a brief period (usually one day). This might be seen as a reduction in the face value of an invoice prepared in advance of its payments in the medium or long term.
Disruptive trends:
A disruptive technology supplants an existing technology and fundamentally alters an industry or a game-changing innovation that establishes an altogether new industry. Disruptive innovation is defined as an invention that shows a new market and value network and ultimately disrupts an established market and value network, replacing incumbent market-leading companies, products, and alliances.
Electronic commerce, or e-commerce (alternatively spelled eCommerce), is a business model, or a subset of a larger business model, that allows a company or person to do business via an electronic network, usually the internet. As a result, customers gain from increased accessibility and convenience, while the business benefits from integrating sales and distribution with other internal operations. Electronic commerce is prevalent throughout all four main market segments: business to business, business to consumer, consumer to consumer, and consumer to business. Ecommerce may be used to sell almost any goods or service, from books and music to financial services and airline tickets.
A business ecosystem is a collection of related entities ? suppliers, distributors, customers, rivals, and government agencies ? collaborating and providing a particular product or service. The concept is that each entity in the ecosystem influences and is impacted by the others, resulting in an ever-changing connection. Therefore, each entity must be adaptive and flexible to live, much like a biological ecosystem. These connections are often backed by a shared technical platform and are based on the flow of information, resources, and artifacts in the software ecosystem.
Integrator:
A systems integrator is an individual or business specializing in integrating component subsystems into a unified whole and ensuring that those subsystems work correctly together. A process is known as system integration. Gains in efficiency, economies of scope, and less reliance on suppliers result in cost reductions and may improve the stability of value generation.
Layer player:
Companies that add value across many markets and sectors are referred to be layer players. Occasionally, specialist companies achieve dominance in a specific niche market. The effectiveness of their operations, along with their economies of size and footprint, establish the business as a market leader.
The long tail is a strategy that allows businesses to realize significant profit out of selling low volumes of hard-to-find items to many customers instead of only selling large volumes of a reduced number of popular items. The term was coined in 2004 by Chris Anderson, who argued that products in low demand or with low sales volume can collectively make up market share that rivals or exceeds the relatively few current bestsellers and blockbusters but only if the store or distribution channel is large enough.
Membership club:
Belonging to a group, either individually or collectively. Certain memberships may charge a fee to join or participate, while others are free. Others have particular skill criteria that must be met before membership is granted. Members are entitled to specific benefits or advantages, but not all members may enjoy the same rights and privileges. Another method is taken by a members-only luxury lifestyle management business that offers concierge services such as vacation reservations, restaurant suggestions, and event access.
Mobile first behavior:
It is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices. The term is “mobile first,” and it is intended to mean that as a company thinks about its website or its other digital means of communications, it should be thinking critically about the mobile experience and how customers and employees will interact with it from their many devices.
On-demand economy:
The on-demand economy is described as economic activity generated by digital marketplaces that meet customer demand for products and services via quick access and accessible supply. The supply chain is managed via a highly efficient, intuitive digital mesh built on top of current infrastructure networks. The on-demand economy is transforming commercial behavior in cities worldwide. The number of businesses, the categories covered, and the industry's growth rate are all increasing. Businesses in this new economy are the culmination of years of technological progress and customer behavior change.
Online marketplace:
An online marketplace (or online e-commerce marketplace) is a kind of e-commerce website in which product or service information is supplied by various third parties or, in some instances, the brand itself, while the marketplace operator handles transactions. Additionally, this pattern encompasses peer-to-peer (P2P) e-commerce between businesses or people. By and large, since marketplaces aggregate goods from a diverse range of suppliers, the variety and availability are typically greater than in vendor-specific online retail shops. Additionally, pricing might be more competitive.
Orchestrator:
Orchestrators are businesses that outsource a substantial portion of their operations and processes to third-party service providers or third-party vendors. The fundamental objective of this business strategy is to concentrate internal resources on core and essential functions while contracting out the remainder of the work to other businesses, thus reducing costs.
Regular replacement:
It includes items that must be replaced on a regular basis; the user cannot reuse them. Consumables are products utilized by people and companies and must be returned regularly due to wear and tear or depletion. Additionally, they may be described as components of a final product consumed or irreversibly changed throughout the production process, including semiconductor wafers and basic chemicals.
Self-service:
A retail business model in which consumers self-serve the goods they want to buy. Self-service business concepts include self-service food buffets, self-service petrol stations, and self-service markets. Self-service is available through phone, online, and email to automate customer support interactions. Self-service Software and self-service applications (for example, online banking apps, shopping portals, and self-service check-in at airports) are becoming more prevalent.
Subscription:
Subscription business models are built on the concept of providing a product or service in exchange for recurring subscription income on a monthly or annual basis. As a result, they place a higher premium on client retention than on customer acquisition. Subscription business models, in essence, concentrate on revenue generation in such a manner that a single client makes repeated payments for extended access to a product or service. Cable television, internet providers, software suppliers, websites (e.g., blogs), business solutions providers, and financial services companies utilize this approach, as do conventional newspapers, periodicals, and academic publications.
Supermarket:
A supermarket is a self-service store arranged into aisles and has many foods and home goods. It is bigger and has a greater variety than traditional grocery shops but is smaller and offers a more limited selection than a hypermarket or big-box market. Supermarkets are usually chain shops supplied by their parent firms' distribution centers, allowing for more significant economies of scale. In addition, supermarkets often provide items at competitive rates by using their purchasing power to negotiate lower pricing from producers than smaller shops can.
Embed code:
Recommended companies based on your search:
Wish Business Model
Wanelo business model, livingsocial business model.
Vizologi is a platform powered by artificial intelligence that searches, analyzes and visualizes the world’s collective business model intelligence to help answer strategic questions, it combines the simplicity of business model canvas with the innovation power of mash-up method .
See how Vizologi works View all features
You rock! Thank you for your interest. Before starting the canvas download, we would like to ask you to pay with a tweet.
Download paying with a tweet
Before downloading the canvas, we would like to invite you to our newsletter, from time-to-time we will send you curated content about business strategy
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
These operations have successfully helped the company achieve year-on-year profitability, which has fueled its growth. They are: Amazon Marketplace: The company's first revenue stream, Amazon.com, accounts for more than 42% ($220 billion of $513.98 billion revenue in 2022 from its online stores) of the income.
Decode Amazon's business model canvas, the foundation of their triumph in the e-commerce landscape. Delve into their value creation, revenue model, and customer segments. In the modern era of digital dominance, Amazon has emerged as a retail behemoth, disrupting the traditional brick-and-mortar model and revolutionizing the way we shop.
How Amazon makes money - revenue by segment in 2022: Based on their annual report 2022, Amazon makes 43% of their revenue through their linear/direct eCommerce business model, 23% through their Marketplace (being a platform biz model), 15% through Amazon Web Services, 7% through advertising service, 7% through subscription services (Prime being the biggest one).
The Amazon Business Model Canvas Customers. Amazon can be described as a two-sided marketplace where buyers and sellers come together. I think that for a variety of reasons it isn't really one and I'll explain that in detail later in the article. Amazon targets the mass-market consumer. With a focus on cost and low margins to drive market ...
Amazon's Business Model Canvas: clothes, shoes, AWS, ebooks and audiobooks 2010-2020: Boosting logistics. During this decade, an essential purchase for Amazon came in 2012 when it bought Kiva, a robotic company. The robots can move packages that weigh as much as 700 lbs. It was a great move in terms of enhancing the logistics and operational ...
Introduction to Amazon's Business Model Canvas. Amazon, founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994, started as an online bookstore but has rapidly expanded into a global e-commerce giant. The company has revolutionized the retail industry and disrupted traditional brick-and-mortar stores by leveraging technology and a customer-centric approach.
Additionally it earns significant money through "Amazon Advertising". In this analysis we focus on Amazon Marketplace only. Let' have a look at how the business model canvas could be filled out: 1. Customer segments: As always, we start with the customer segments. Amazon has a variety of customer segments located in different markets.
#2 Amazon Example. The second of these business model canvas examples is for an e-commerce company. This business model canvas example will be a simple look at Amazon, one of the largest e-commerce companies in the world. CFI's Advanced Financial Modeling & Valuation Course takes a deep look at Amazon's strategy, business model, and ...
Business Model Canvas of Amazon. 1. Customers of Amazon. Both buyers and sellers can come together in Amazon's platform considering how it is a mass market. Where its brand is concerned, anyone that inherits internet connection is a potential customer. Amazon's customer base is also its most loyal one.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model. Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
Vizologi is a platform powered by artificial intelligence that searches, analyzes and visualizes the world's collective business model intelligence to help answer strategic questions, it combines the simplicity of business model canvas with the innovation power of mash-up method. See how Vizologi works View all features. Amazoncom often ...
Vizologi is a platform powered by artificial intelligence that searches, analyzes and visualizes the world's collective business model intelligence to help answer strategic questions, it combines the simplicity of business model canvas with the innovation power of mash-up method. See how Vizologi works View all features.
Step 1 (of 10): Customer Segments. This sounds obvious, but when you get into the detail many people overly simply the customer and don't create a clear picture of who they are. As a result, the tendency is to make generalizations. Sections of the Business Model Canvas. 1.
FREE delivery Fri, Sep 29 on $25 of items shipped by Amazon. Kindle. $699. Print List Price: $11.99. Available instantly. Business Model Canvas, 100 templates to fill out: Ideal to fill the canvas business model. | Notebook to build your business model from the Next ... Model. To develop a development strategy.
170+ Business Mode Canvas Examples (Amazon, Netflix, Tesla, Amazon...) PDF File Format; Instant Download
In 50 minutes you will be able to: •Identify the nine factors affected by the Business Model Canvas and why they are important •Analyse concrete applications of the Business Model Canvas with real-life case studies •Learn more about the limits and criticism of the tool, so that you can apply the BMC effectively and use it alongside other ...
Set up an Amazon seller account. Find a high-demand product to resell. Source the product (in this case, from the brand, manufacturer, or distributor) List the product for sale on the brand's existing Amazon listing (or create a new product detail page) Manage and grow your business (including inventory, sales, etc.)
Amazon.com: business canvas. ... Ideal to fill the canvas business model. | Notebook to build your business model from the Next ... Model. To develop a development strategy. by Kaya Longi. 3.5 out of 5 stars 3. Paperback. $8.99 $ 8. 99. FREE delivery Tue, Nov 21 on $35 of items shipped by Amazon.
Kindle. $2299. Print List Price: $37.00. Available instantly. Business Model Canvas, 100 templates to fill out: Ideal to fill the canvas business model. | Notebook to build your business model from the Next ... Model. To develop a development strategy. by Kaya Longi | Dec 27, 2020.
Google Cloud's app developer platform, called Vertex AI, is adding new features underpinned by Gemini 1.5 Pro, which Google has said has the "longest context window" of any large-scale AI ...
The company is seeking to raise a significant sum from investors — $500 million or more at a $5 billion valuation, Bloomberg reported last month. The startup generated $22 million in annualized ...
The Business Model Canvas: Let your business thrive with this simple model (Management & Marketing) Kindle Edition by 50minutes, (Author) Format: Kindle Edition 3.6 3.6 out of 5 stars 121 ratings
business model canvas: new generation (SIMPLE AND PRECISE, READ AND TO UNDERSTAND QUICKLY and BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS OF LARGE COMPANIES TECHNIQUES) by Kalkadai Salomon , Alexender Ostervalder , et al. | Apr 5, 2023