

Livestock Farming Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Livestock Farming Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their livestock farming companies. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write a livestock farming business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Livestock Farm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your livestock farming business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Livestock Farm
If you’re looking to start a livestock farming business or grow your existing livestock farming company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your livestock farming business to improve your chances of success. Your livestock farming business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Livestock Farming Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a livestock farming business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan (hand it to them in person or email to them as a PDF file) and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for livestock farming companies.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a livestock farming business.
If you want to start a livestock farming business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide and sample below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your livestock farming business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of livestock farming business you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a livestock farming business that you would like to grow, or are you operating several family-owned livestock farming businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overv iew of the livestock farming industry.
- Discuss the type of livestock farming business you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of livestock farming business you are operating.
For example, you m ight specialize in one of the following types of livestock farming businesses:
- Cattle Ranching : In order to effectively raise cattle until market-ready, ranchers must have enough land for cattle to roam and eat grass. The rancher must also provide supplemental food, medicines and a number of procedures to ensure cattle sent to market are healthy and at an optimum weight.
- Sheep Farming: Sheep farming is a process of maintaining order in the herd and corralling sheep when necessary. Farmers must feed and medicate sheep efficiently and they use sheep dogs to assist in many daily efforts. Sheep are prized for their wool and may be sent to slaughter as lambs if they are young. Sheep are often used on vacant fields to graze with an environmentally-friendly outcome.
- Chicken Farming: Chicken farmers need to provide water, food and medications to raise chickens until market-ready. Chickens may be free-range or kept in sheds during growth cycles. While hens produce eggs, roosters provide barnyard protection and enjoyment.
- Hog Farming: Hogs are notoriously expensive to raise, primarily due to food costs and medications; however, they demand high prices at sale and produce generous profits when sent to market. Hogs are grown in pens to control weight gain and are carefully assessed for market-readiness.
In addition to explaining the type of livestock farming business you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of cattle sold each season, the number of sheep successfully shorn each year, reaching X number of ranches owned, etc.
- What is your legal business structure? Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the livestock farming industry. While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the livestock farming industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your livestock farming business plan:
- How big is the livestock farming industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your livestock farming business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your livestock farming business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: corporate buyers, stockyard owners, and individual buyers.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of livestock farming business you operate. Clearly, individuals would respond to different marketing promotions than stockyard owners, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers. Ideally you can speak with a sample of your target customers before writing your plan to better understand their needs.
Finish Your Livestock Farming Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are othe r livestock farming businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes specialty types of beef cattle, such as organic or grass-fed, imported lamb or beef, or eggs that are infused with additional supplements. You need to mention direct competition, as well.
For each direct competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of livestock farming business are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide lower rates for stockyards despite fluctuating higher market prices?
- Will you offer beef cuts that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a livestock farming business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type o f livestock farming company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide uncured, smoked ham and bacon, pasteurized eggs, or free-range chicken?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of yo ur plan, yo u are presenting the livestock you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your livestock farming company. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, does your cattle ranch contain grassy acreage, allowing cattle to eat naturally? Is your chicken ranch situated in a weather-friendly environment? Does your hog farm contain heated and cooled hog pens for the well-being of the hogs?
Promotions : The final part of your livestock farming marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to regional stockyards
- Distribute farmer newsletters to stockyards
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your livestock farming business; including caring for livestock, securing and maintaining food supplies and medications, planning transport to market, invoicing customers and paying bills.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to ship-to-market, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your livestock farming business to a new ranch or farm.
Management Team
To demonstrate your livestock farming business’ potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing livestock farming businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing a livestock farming business or successfully running a livestock stockyard.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance s heet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you ship 500,000 head of cattle this season, or will you expand your farm by several hundred acres? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your livestock farming business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a livestock farming business:
- Cost of breeder chickens, lambs, farrow pigs or calves
- Cost of farming equipment and vehicles
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your ranch deed of ownership or a list of buyers you partner with in buying and selling operations.
Writing a business plan for your livestock farming business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will understand the livestock farming industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful livestock farming business.
Livestock Farming Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my livestock farming business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily write your livestock farming business plan.
How Do You Start a Livestock Farming Business?
Starting a livestock farming business is easy with these 14 steps:
- Choose the Name for Your Livestock Farming Business
- Create Your Livestock Farming Business Plan
- Choose the Legal Structure for Your Livestock Farming Business
- Secure Startup Funding for Your Livestock Farming Business (If Needed)
- Secure a Location for Your Business
- Register Your Livestock Farming Business with the IRS
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
- Get Business Insurance for Your Livestock Farming Business
- Buy or Lease the Right Livestock Farming Business Equipment
- Develop Your Livestock Farming Marketing Materials
- Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your Livestock Farming Business
- Open for Business
Where Can I Download a Free Business Plan Template PDF?
Click here to download the pdf version of our basic business plan template.
Our free business plan template pdf allows you to see the key sections to complete in your plan and the key questions that each must answer. The business plan pdf will definitely get you started in the right direction.
We do offer a premium version of our business plan template. Click here to learn more about it. The premium version includes numerous features allowing you to quickly and easily create a professional business plan. Its most touted feature is its financial projections template which allows you to simply enter your estimated sales and growth rates, and it automatically calculates your complete five-year financial projections including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Here’s the link to our Ultimate Business Plan Template.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Livestock Farming business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to learn about Growthink’s business plan writing services .
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Cattle Farming Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Cattle Farming Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Cattle Farming business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their cattle farms.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Cattle Farm business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm, located in Des Moines, Iowa, is a registered and licensed cattle farming company. The company operates a 500 acre farm that is home to over 300 cows, all of which are raised in an all-natural environment (no antibiotics, hormones, steroids, etc) and all animals are grass-fed. Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is also fully equipped with the latest technology and equipment used in the cattle farming industry.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is founded and run by Matthew Jones. Matthew has been a cattle farm operations manager for the past ten years, so he has in-depth knowledge and experience running a business in this industry. Matthew will run the general operations and administrative functions of the company and hire other employees to manage the sales and day-to-day operations.
Product Offering
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will be involved in the commercial breeding of cows to provide the following products:
- Ground Beef
Customer Focus
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will target all residents living in Des Moines, Iowa and the surrounding areas. We will also target supermarkets, restaurants, and other retailers who are interested in selling our products to the public.
Management Team
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm’s most valuable asset is the expertise and experience of its founder, Matthew Jones. Matthew has been a cattle farm operations manager for the past ten years, so he has in-depth knowledge and experience running a business in this industry. Matthew will run the general operations and administrative functions of the company and hire other employees to manage the sales and day-to-day operations.
Success Factors
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Management: The company’s management team has years of business and marketing experience that allows them to market and serve customers in an improved and sophisticated manner than the competitors.
- Relationships: Having lived in the community for 20 years, Matthew Jones knows all of the local leaders, media, and other influencers. As such, it will be relatively easy for Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm to build brand awareness and an initial customer base.
- Quality products at affordable pricing: The company will provide quality products at affordable pricing, as it has high-quality equipment and uses the latest techniques.
- Good packaging: Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will utilize product-oriented packaging materials that can reduce the damage in the products at the time of supply.
Financial Highlights
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is currently seeking $750,000 to start the company. The funding will be dedicated towards securing the farm land and purchasing the necessary equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff and marketing costs for the farm. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Land and Equipment: $250,000
- Cattle Care Supplies: $100,000
- Overhead Costs: $100,000
- Three Months of Overhead Expenses (Payroll, Rent, Utilities): $150,000
- Marketing Costs: $50,000
- Working Capital: $100,000
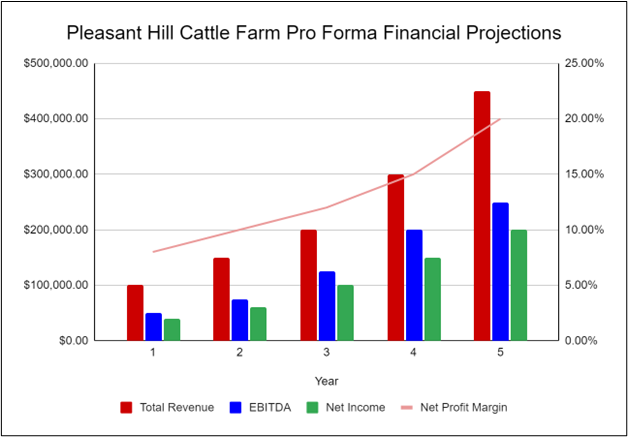
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm.
Company Overview
Who is pleasant hill cattle farm.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is founded and run by Matthew Jones. Matthew has been a cattle farm operations manager for the past ten years, so he has in-depth knowledge and experience running a business in this industry. Matthew will run the general operations and administrative functions of the company and hire other employees to manage the sales and day-to-day operations.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm History
Matthew Jones is an entrepreneur who seeks to contribute to the growing US economy through cattle farming. Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will become a recognized cattle farming company in Des Moines, Iowa, ensuring a continuous supply of cattle, milk, meat, and other dairy products.
Matthew has selected an initial location and is currently undergoing due diligence on it and the local market to assess if it is a suitable location for a commercial cattle farm.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Found a farm location
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Determined supply requirements
- Began recruiting key employees
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm Services
Industry analysis.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm competes against large-scale cattle farmers in the U.S. With the largest fed-cattle industry in the world, the United States is also the world’s largest producer of beef, primarily high-quality, grain-fed beef for domestic and export use. According to the USDA, beef cattle production in the US is one of the largest agricultural industries, making up 17% of the agricultural sector. Though the industry has declined slightly in the past few years, the market size of the Beef Cattle Production industry is expected to increase by 4.5% over the next five years.
Improving the living standards of the people in the country has resulted in a shift in meat preferences, with most choosing beef-based products rather than products derived from pork and chicken. This trend has helped increase revenues and allowed the industry to grow. However, the beef cattle production industry faces many challenges including droughts, the price of feed, and the increasing popularity of plant-based diets.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will primarily serve local residents and retailers of cattle dairy products and meat within a 30-mile radius of the farm. These businesses typically gross from $5 million to $10 million in annual revenues and source their supplies from within a 30-mile radius of their facilities.
The precise demographics for Des Moines, Iowa are:
Customer Segmentation
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Grocery Stores
- Local Residents
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Shayla Farms
Shayla Farms is one of the large-scale cattle farms in the US, owning an 8,000 ha area. It has well-established relationships with local retailers. It has been in business for 32 years. Shayla Farms offers good quality dairy products and meat. It also has automated equipment and machines, which helps in improving its operations. Moreover, it is also known for delivering large orders at the right time without delay.
Crimson Cattle Farm
Crimson Cattle Farm has been operating since 1995 and is a well-known company that provides good quality beef with affordable pricing as it has effective and efficient cattle rearing machines. It majorly targets local companies and retailers and has a large distribution network that can serve customers up to a 500-mile radius. Crimson Cattle Farm also has a very effective distribution and supply chain network. However, Crimson Cattle Farm’s offerings are only limited to beef.
Cattle USA has been in business for the past 50 years and enjoys great success. It is one of the largest beef producers in the 200-mile area. It easily caters to local residents primarily due to its prime location. It provides beef and a variety of dairy products including: cheese, yogurt, meat and milk.
Competitive Advantage
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Efficient and effective delivery network
- Good packaging
- Quality products at affordable pricing
- Providing excellent customer service and customer experiences
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm is as follows:
Social Media Marketing
Social media is one of the most cost-effective and practical marketing methods for improving brand visibility. The company will use social media to develop engaging content, such as sharing pictures of the cows and creating educational content about the cattle farm industry.
Website/SEO
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will develop a professional website that showcases pictures of the farm and the cows. It will also invest in SEO so that the company’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Word of Mouth/Referrals
Matthew Jones has built up an extensive list of contacts over the years by living and working in the midwestern farming industry. Since a number of local cattle farms have ceased operations, they have committed to Matthew that Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will be their cattle supplier. They trust his work ethic and commitment to the local community.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will highlight our location, cows, and products on a major billboard facing the busiest highway in town. The billboard will provide the location of Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm and the website URL.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm’s pricing will be moderate, so customers feel they receive great value when availing of the products. Pricing will be about 50% lower than retail prices to allow wholesalers and retailers to earn their margins.
Operations Plan
Operation Functions: The following will be the operations plan for Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm.
- Matthew Jones will be the Owner and President of the company. He will oversee all staff and manage client relations. Matthew has spent the past year recruiting the following staff:
- Sue Smith – will oversee all administrative aspects of running the cattle farm. This will include bookkeeping, tax payments, and payroll of the staff.
- George Baird– Head Farmhand who will oversee the farming staff and day to day operations.
- Ben Brown– Assistant Farmhand who will assist George.
- Frank White– Distribution Manager who will oversee the packaging and distribution of all products.
Milestones:
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm will have the following milestones complete in the next six months.
- 6/202X – Finalize purchase of farm land
- 7/202X – Purchase farm equipment, supplies and materials
- 8/202X – Finalize contracts for grocery store, chain, and restaurant clients
- 9/202X – Purchase initial set of cows
- 10/202X – Hire and train farm staff
- 11/202X – Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm begins farm operations
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm’s revenues will come from the sales of cattle meat and dairy products to its customers. The major costs for the company will be the cost of land and equipment. The staff will earn competitive salaries allowing Pleasant Hill Cattle Farm to hire experienced workers. In the initial years, the company’s marketing spend will be high, as it establishes itself in the market.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Cows: 300
- Average Revenue per Animal: $500
- Number of Products Sold Per Year: 100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, cattle farming business plan faqs, what is a cattle farming business plan.
A cattle farming business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your cattle farming business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Cattle Farming business plan using our Cattle Farming Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Cattle Farming Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of cattle farming businesses , some examples include: Cow-calf, Backgrounding, Finishing, and Specific Breed.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Cattle Farming Business Plan?
Cattle Farming businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Cattle Farming Business?
Starting a cattle farming business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Cattle Farming Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed cattle farming business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your cattle farming business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your cattle farming business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Cattle Farming Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your cattle farming business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your cattle farming business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Cattle Farming Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your cattle farming business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your cattle farming business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful cattle farming business:
- How to Start a Cattle Farm Business
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
Cattle Farm
Back to All Business Ideas
How to Start a Cattle Farm
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on May 18, 2022 Updated on April 26, 2024

Investment range
$296,550-$959,100
Revenue potential
$208,000 - $520,000 p.a.
Time to build
6 -12 months
Profit potential
$62,000 - $156,000 p.a.
Industry trend
Many people find the idea of farm life alluring – wide open spaces and a slower pace, quality time with animals, and hard work that ultimately produces good food. Cattle farming is a massive and essential US industry; the beef and dairy farm markets are worth about $120 billion and experiencing steady growth.
You could start your own cattle farm and help people get the food that they need while making good money. It will require hard work and a sizable investment, but there are many government programs available to help farmers get started.
You’ll also need to learn some serious business skills. Luckily, this step-by-step guide has you covered, with all the entrepreneurial insight you need to launch a successful cattle farm.
Looking to register your business? A limited liability company (LLC) is the best legal structure for new businesses because it is fast and simple.
Form your business immediately using ZenBusiness LLC formation service or hire one of the Best LLC Services .
Step 1: Decide if the Business Is Right for You
Pros and cons.
Starting a cattle farm has pros and cons to consider before deciding if it’s right for you.
- Rewarding – Provide essential foods
- High Demand – Most Americans consume beef and dairy products
- Pleasant Lifestyle – Slow down with life on the farm
- High Startup Costs – Starting a cattle farm from scratch takes $$$
- Hard Labor – Farm work is not an office job!
Cattle farm industry trends
Industry size and growth.
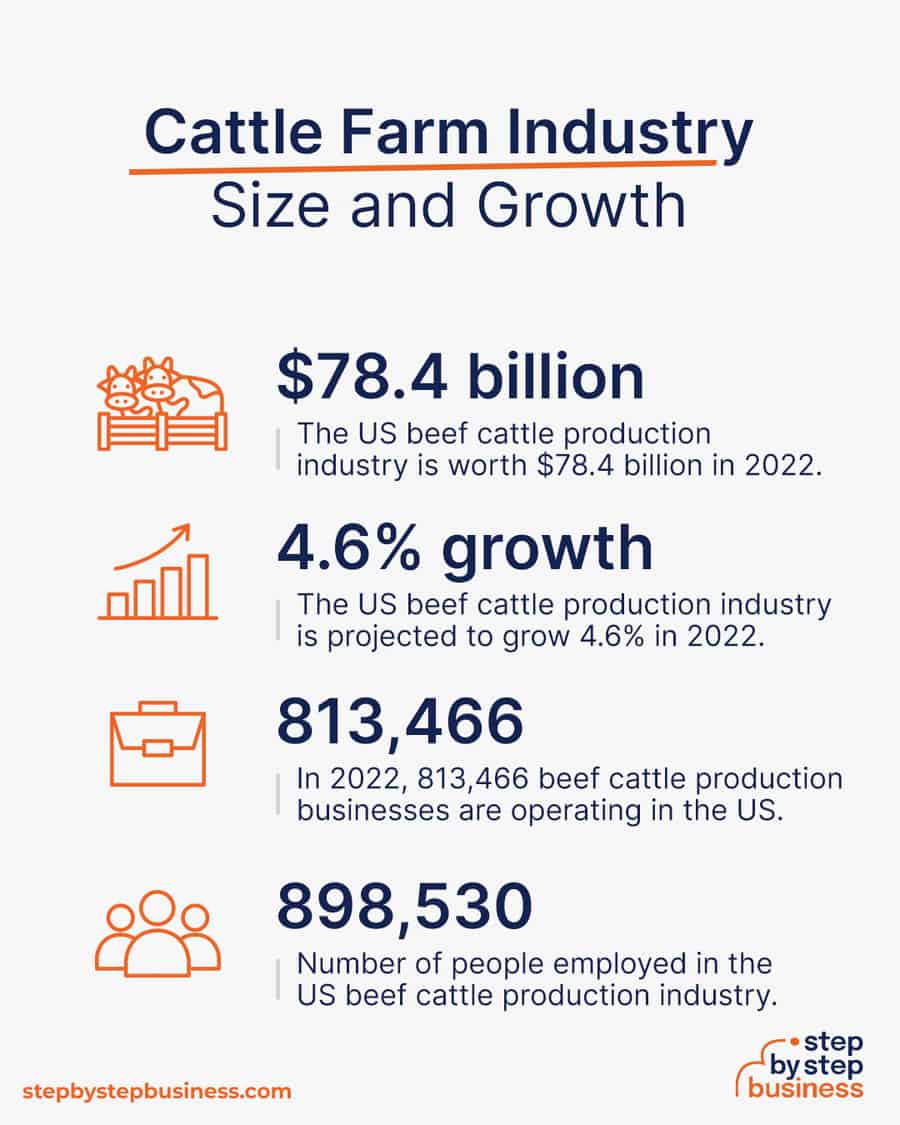
- Industry size and past growth – The US beef cattle production industry is worth $78.4 billion in 2022 after expanding 0.6% annually the last five years.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/market-size/beef-cattle-production-united-states/ ))
- Growth forecast – The US beef cattle production industry is projected to grow 4.6% in 2022.
- Number of businesses – In 2022, 813,466 beef cattle production businesses are operating in the US.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/number-of-businesses/beef-cattle-production-united-states/ ))
- Number of people employed – in 2022, the US beef cattle production industry employs 898,530 people.(( https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/employment/beef-cattle-production-united-states/ ))
Trends and challenges
Trends in the cattle farm industry include:
- Greater understanding of cows’ nutritional needs is producing better feeds, which in turn means better yields.
- Technology is increasingly used in farming, including robotics for feeding and even herder bots. Drones are also being used to track and monitor herds.
Challenges in the cattle farm industry include:
- Cattle prices are extremely volatile and income can be unpredictable.
- Millennials are seeking sustainably-produced foods, which is putting pressure on cattle farms to avoid antibiotic use and growth promoters.

Consumer spending
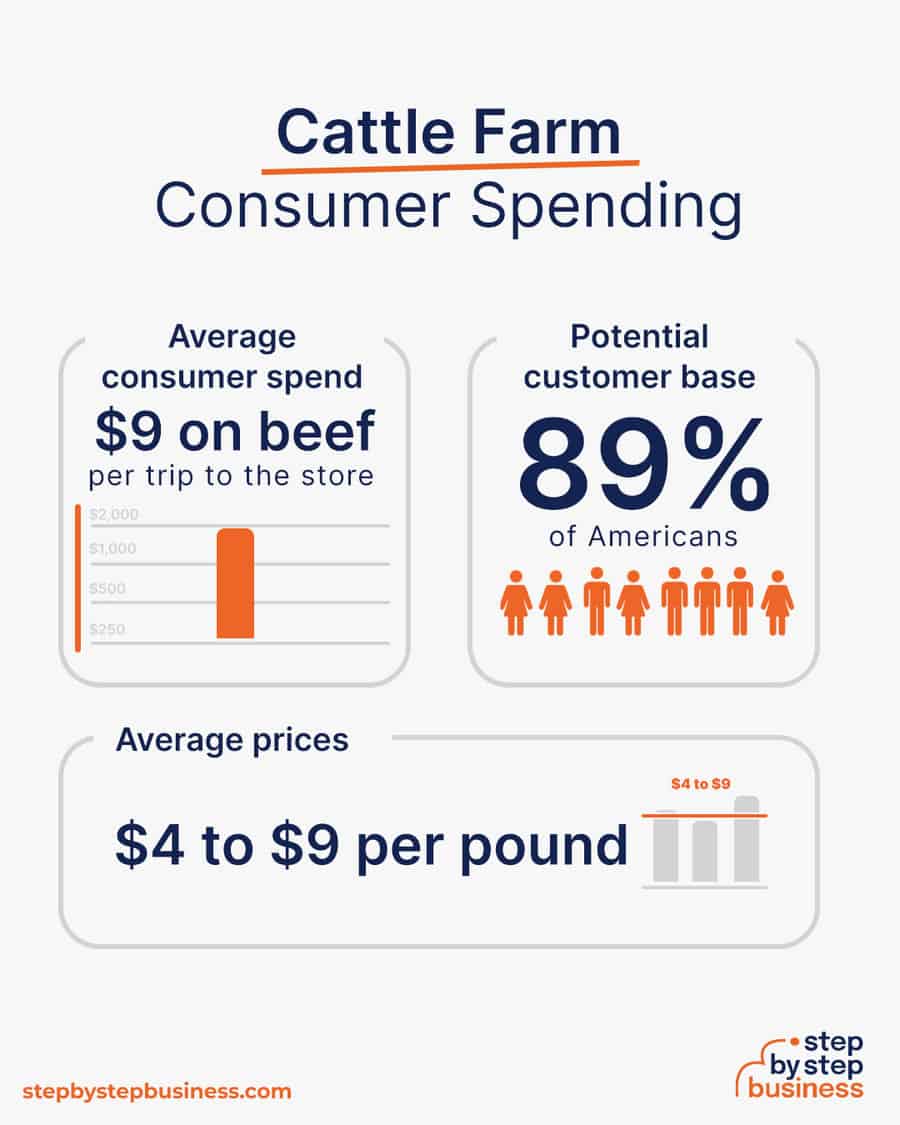
- Average consumer spend – The average consumer in the U.S. spends over $9 on beef per trip to the grocery store.(( https://www.statista.com/statistics/1086365/household-expenditure-on-meat-products-us/ ))
- Potential customer base – 89% of people in the US consume meat.(( https://www.ipsos.com/en-us/news-polls/nearly-nine-ten-americans-consume-meat-part-their-diet ))
- Average prices – Beef prices range from $4 to $9 per pound.(( https://www.bls.gov/regions/mid-atlantic/data/averageretailfoodandenergyprices_usandmidwest_table.htm ))
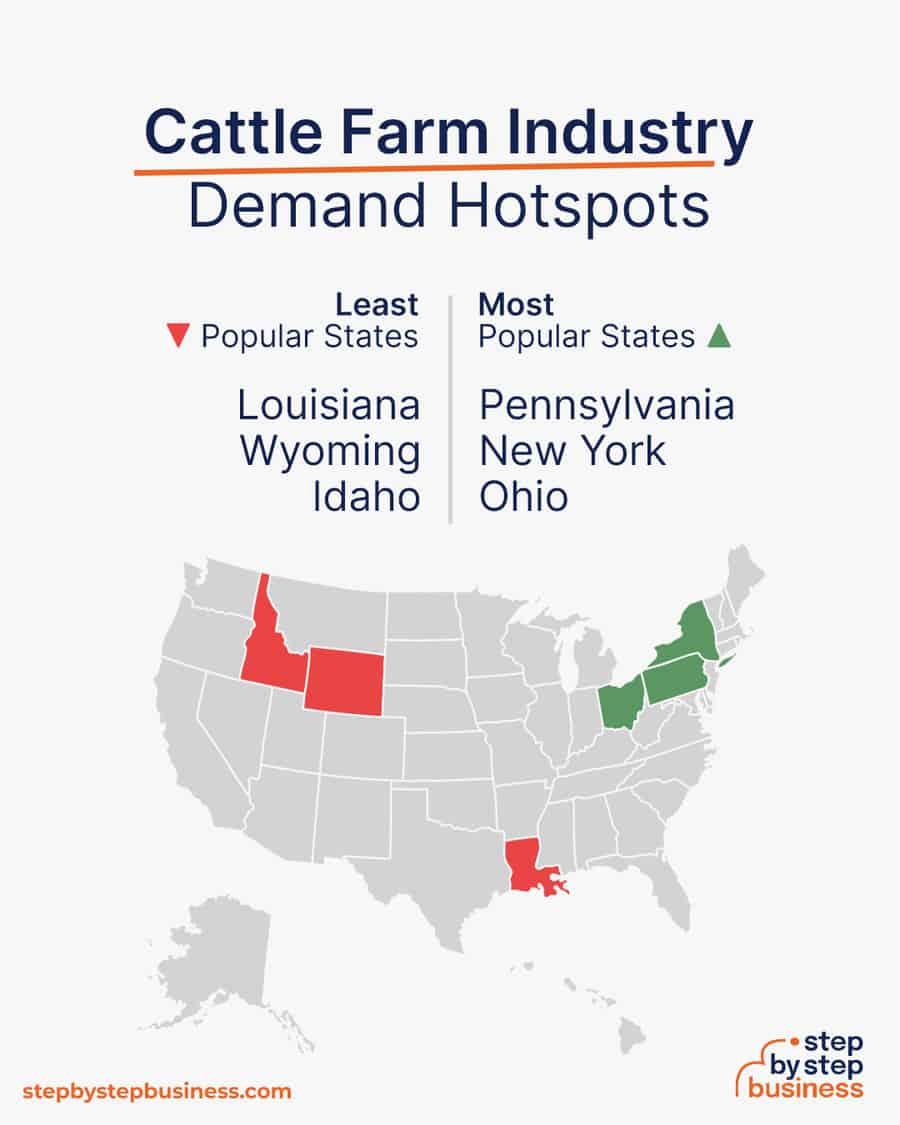
Demand hotspots
- Most popular states – The most popular states for farmers are Pennsylvania, New York, and Ohio. (( https://www.zippia.com/farmer-jobs/best-states/ ))
- Least popular states – The least popular states for farmers are Louisiana, Wyoming, and Idaho.
What kind of people work in cattle farms?
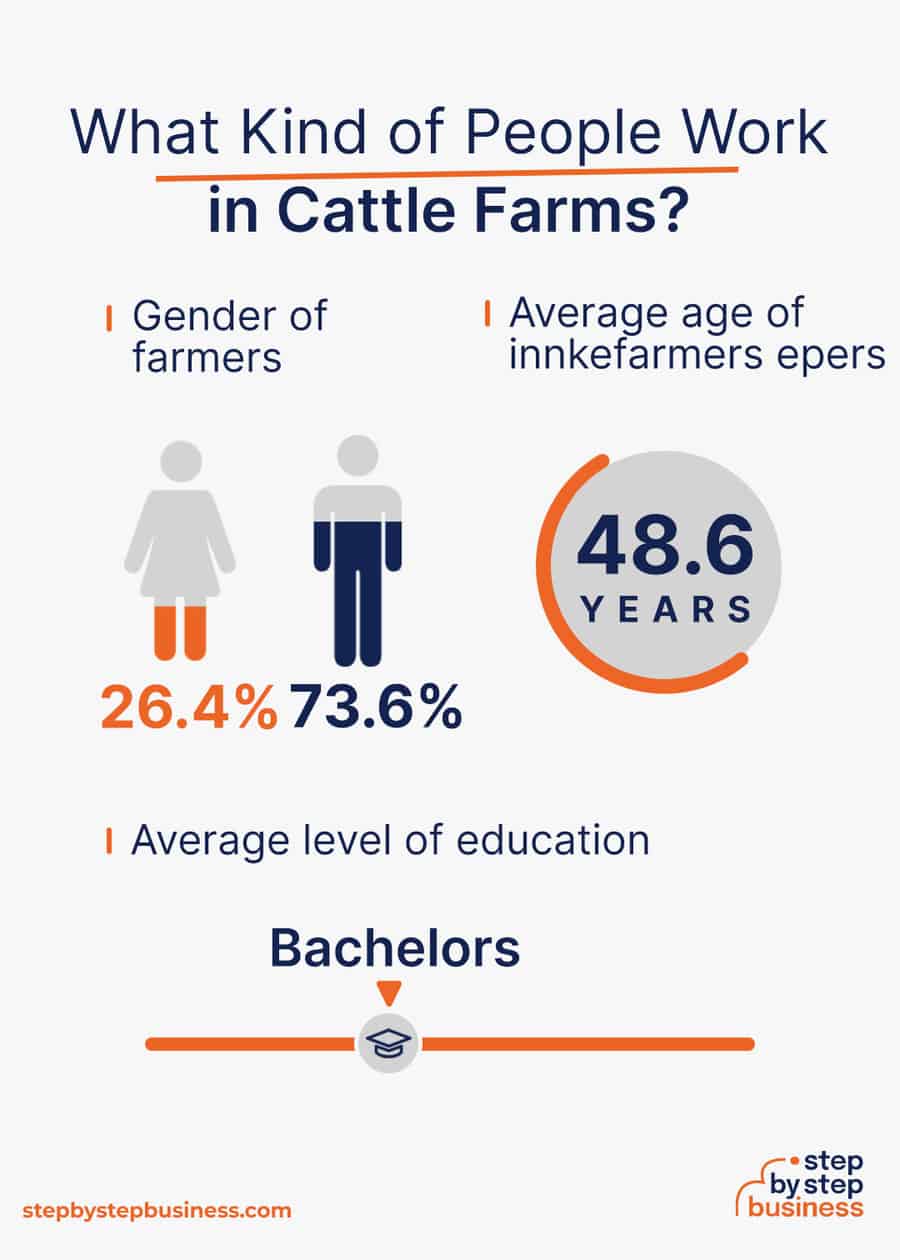
- Gender – 26.4% of farmers are female, while 73.6% are male. (( https://www.zippia.com/farmer-jobs/demographics/ ))
- Average level of education – The average farmer has a bachelor’s degree.
- Average age – The average farmer in the US is 48.6 years old.
How much does it cost to start a cattle farm?
Startup costs for a cattle farm range from $300,000 to $1 million. Costs include the land, land preparation, equipment, starter cattle, and an initial operating budget.
To learn cattle farming, you can get an associate’s or bachelor’s degree in agriculture. You can also get an online agribusiness degree from established institutions like Penn State . Another option is to work as an intern or volunteer for a local cattle farmer to learn the business.
You’ll need a handful of items to successfully launch your cattle farm business, including:
- Watering system
- Cattle health care equipment
- Cattle handling equipment
- Cattle trailers
How much can you earn from a cattle farm business?
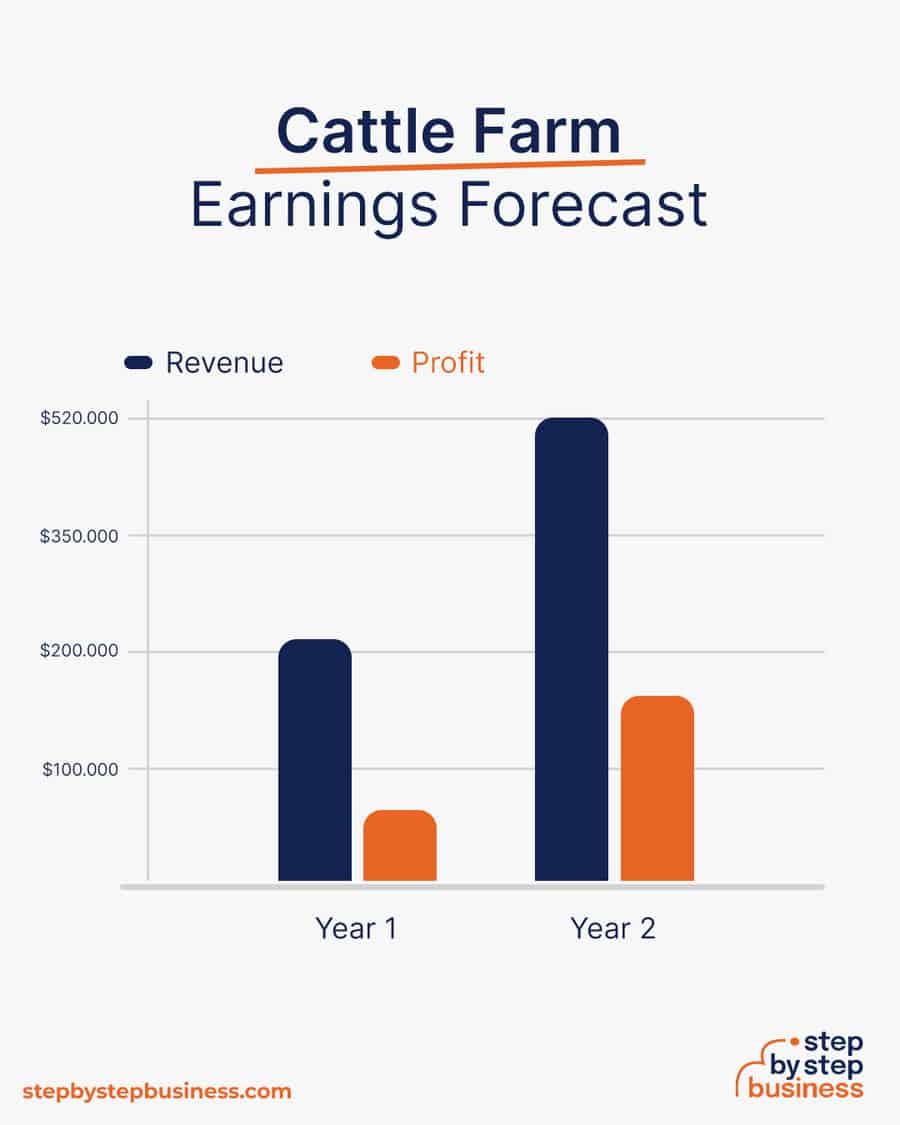
You should be able to bring in $2,000 per cow once they’ve reached full maturity. It will take a year or two to get your calves to that point, so you won’t see a profit for at least 12 months. Your profit margin after all expenses should be about 30%.
In your first year or two after cows reach their ideal weight, you could sell two cows per week, bringing in $208,000 in annual revenue. This would mean $62,000 in profit, assuming that 30% margin. As your herd grows, sales could climb to five cows per week. With annual revenue of $520,000, you’d make a healthy profit of $156,000.
What barriers to entry are there?
There are a few barriers to entry for a cattle farm. Your biggest challenges will be:
- The high startup costs of starting a farm from scratch
- Learning the skills necessary to succeed
Related Business Ideas

How to Start a Farm
How to Start a Fish Farming Business

How to Start a Mushroom Farm
Step 2: hone your idea.
Now that you know what’s involved in starting a cattle farm, it’s a good idea to hone your concept in preparation to enter a competitive market.
Market research will give you the upper hand, even if you’re already positive that you have a perfect product or service. Conducting market research is important, because it can help you understand your customers better, who your competitors are, and your business landscape.
Why? Identify an opportunity
Research cattle farms in your area to examine their products/services, price points, and customer reviews. You’re looking for a market gap to fill. For instance, maybe the local market is missing an organic dairy farm or a sustainable, grass-fed beef farm.
You might consider targeting a niche market by specializing in a certain aspect of your industry, such as black Angus cows or longhorn cows, or fully organic and chemical-free beef and dairy.
This could jumpstart your word-of-mouth marketing and attract clients right away.
What? Define cattle types and methods for raising them
You’ll just need to decide what types of cattle you want to raise. You could raise dairy cows, or you can raise cows for beef. You could raise them with chemicals and growth hormones or go fully organic and sustainable. You could also raise other livestock like chickens and pigs for additional revenue.
How much should you charge for cattle?
Prices for cows are very volatile, so it will depend on the market at any given time. Cows are sold by their total weight. They are currently being sold for about $130 per 100 pounds. You should aim for a profit margin after operating expenses of about 30%.
Once you know your costs, you can use our profit margin calculator to determine your mark-up and final price points. Remember, the prices you use at launch should be subject to change if warranted by the market.
Who? Identify your target market
Your target market will be food production companies, butchers, grocery stores, and restaurants. You can find those business owners and connect with them on LinkedIn, but your best bet is to find them on Google or Yelp and call them directly.
Where? Choose your cattle farm location
Selecting the right location for your cattle farm is essential for its success. Look for a spot with abundant pastureland, access to clean water, and good drainage. Consider accessibility and convenience, ensuring that the location is easily reachable by transportation vehicles and has easy access to veterinary services and other supplies.
Additionally, assess the local regulations and zoning laws to ensure compliance and obtain any necessary permits. By strategically choosing the right location, you can establish a thriving and profitable cattle farm that produces high-quality meat and dairy products.

Step 3: Brainstorm a Cattle Farm Name
Your business name is your business identity, so choose one that encapsulates your objectives, services, and mission in just a few words. You probably want a name that’s short and easy to remember, since much of your business, and your initial business in particular, will come from word-of-mouth referrals.
Here are some ideas for brainstorming your business name:
- Short, unique, and catchy names tend to stand out
- Names that are easy to say and spell tend to do better
- Name should be relevant to your product or service offerings
- Ask around — family, friends, colleagues, social media — for suggestions
- Including keywords, such as “cattle farm” or “Grade-A beef”, boosts SEO
- Name should allow for expansion, for ex: “Legacy Cattle Farms” over “Wagyu Beef Producers”
- Avoid location-based names that might hinder future expansion
Discover over 250 unique cattle farm name ideas here . If you want your business name to include specific keywords, you can also use our cattle farm business name generator. Just type in a few keywords and hit “generate” and you’ll have dozens of suggestions at your fingertips.
Once you’ve got a list of potential names, visit the website of the US Patent and Trademark Office to make sure they are available for registration and check the availability of related domain names using our Domain Name Search tool. Using “.com” or “.org” sharply increases credibility, so it’s best to focus on these.
Find a Domain
Powered by GoDaddy.com
Finally, make your choice among the names that pass this screening and go ahead with domain registration and social media account creation. Your business name is one of the key differentiators that sets your business apart. Once you pick your company name, and start with the branding, it is hard to change the business name. Therefore, it’s important to carefully consider your choice before you start a business entity.
Step 4: Create a Cattle Farm Business Plan
Every business needs a plan. This will function as a guidebook to take your startup through the launch process and maintain focus on your key goals. A business plan also enables potential partners and investors to better understand your company and its vision:
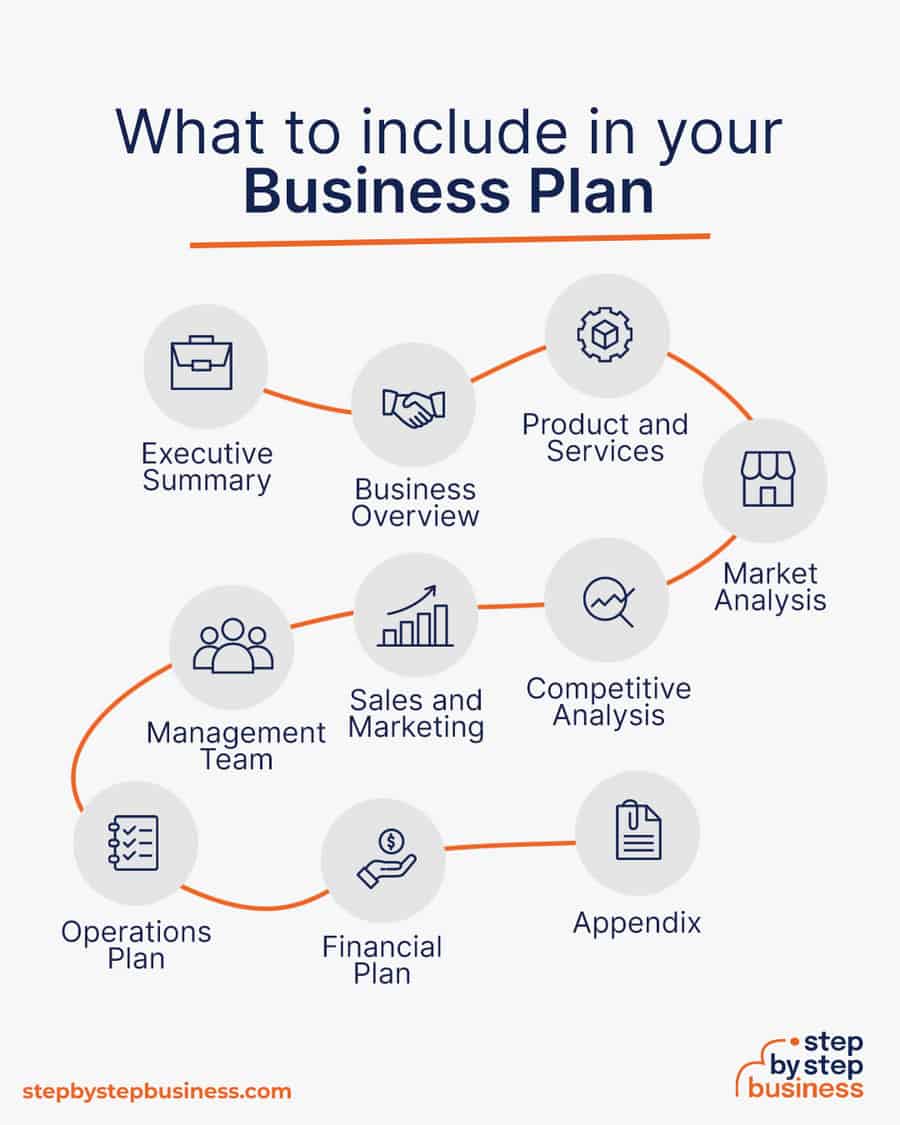
- Executive Summary: Brief summary outlining the core elements of the cattle farm business, including its objectives, target market, and financial projections.
- Business Overview: Comprehensive introduction to the cattle farm, encompassing its mission, vision, and key operational details such as location and scale.
- Product and Services: Details on the specific types of cattle to be raised, breeding practices, and any additional services offered, such as consulting or educational programs.
- Market Analysis: Examination of the demand for beef products, consumer trends, and potential challenges and opportunities within the local and broader market.
- Competitive Analysis: Assessment of other cattle farms in the region, highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and distinctive features to identify the farm’s competitive edge.
- Sales and Marketing: Strategies for promoting the cattle farm, reaching target customers, and maximizing sales, including online presence, advertising, and promotional activities.
- Management Team: Profiles of key individuals responsible for running the cattle farm, outlining their expertise and roles in ensuring effective business operations.
- Operations Plan: Detailed plan outlining day-to-day activities involved in cattle farming, covering feeding, breeding, healthcare, and other essential processes.
- Financial Plan: Comprehensive financial projections, including startup costs, revenue forecasts, and break-even analysis, providing a clear picture of the business’s financial viability.
- Appendix: Supplementary materials, such as permits, licenses, and additional documentation supporting the information presented in the business plan.
If you’ve never created a business plan, it can be an intimidating task. You might consider hiring a business plan specialist to create a top-notch business plan for you.
Step 5: Register Your Business
Registering your business is an absolutely crucial step — it’s the prerequisite to paying taxes, raising capital, opening a bank account, and other guideposts on the road to getting a business up and running.
Plus, registration is exciting because it makes the entire process official. Once it’s complete, you’ll have your own business!
Choose where to register your company
Your business location is important because it can affect taxes, legal requirements, and revenue. Most people will register their business in the state where they live, but if you’re planning to expand, you might consider looking elsewhere, as some states could offer real advantages when it comes to cattle farms.
If you’re willing to move, you could really maximize your business! Keep in mind, it’s relatively easy to transfer your business to another state.
Choose your business structure
Business entities come in several varieties, each with its pros and cons. The legal structure you choose for your cattle farm will shape your taxes, personal liability, and business registration requirements, so choose wisely.
Here are the main options:
- Sole Proprietorship – The most common structure for small businesses makes no legal distinction between company and owner. All income goes to the owner, who’s also liable for any debts, losses, or liabilities incurred by the business. The owner pays taxes on business income on his or her personal tax return.
- General Partnership – Similar to a sole proprietorship, but for two or more people. Again, owners keep the profits and are liable for losses. The partners pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC) – Combines the characteristics of corporations with those of sole proprietorships or partnerships. Again, the owners are not personally liable for debts.
- C Corp – Under this structure, the business is a distinct legal entity and the owner or owners are not personally liable for its debts. Owners take profits through shareholder dividends, rather than directly. The corporation pays taxes, and owners pay taxes on their dividends, which is sometimes referred to as double taxation.
- S Corp – An S-Corporation refers to the tax classification of the business but is not a business entity. An S-Corp can be either a corporation or an LLC , which just need to elect to be an S-Corp for tax status. In an S-Corp, income is passed through directly to shareholders, who pay taxes on their share of business income on their personal tax returns.
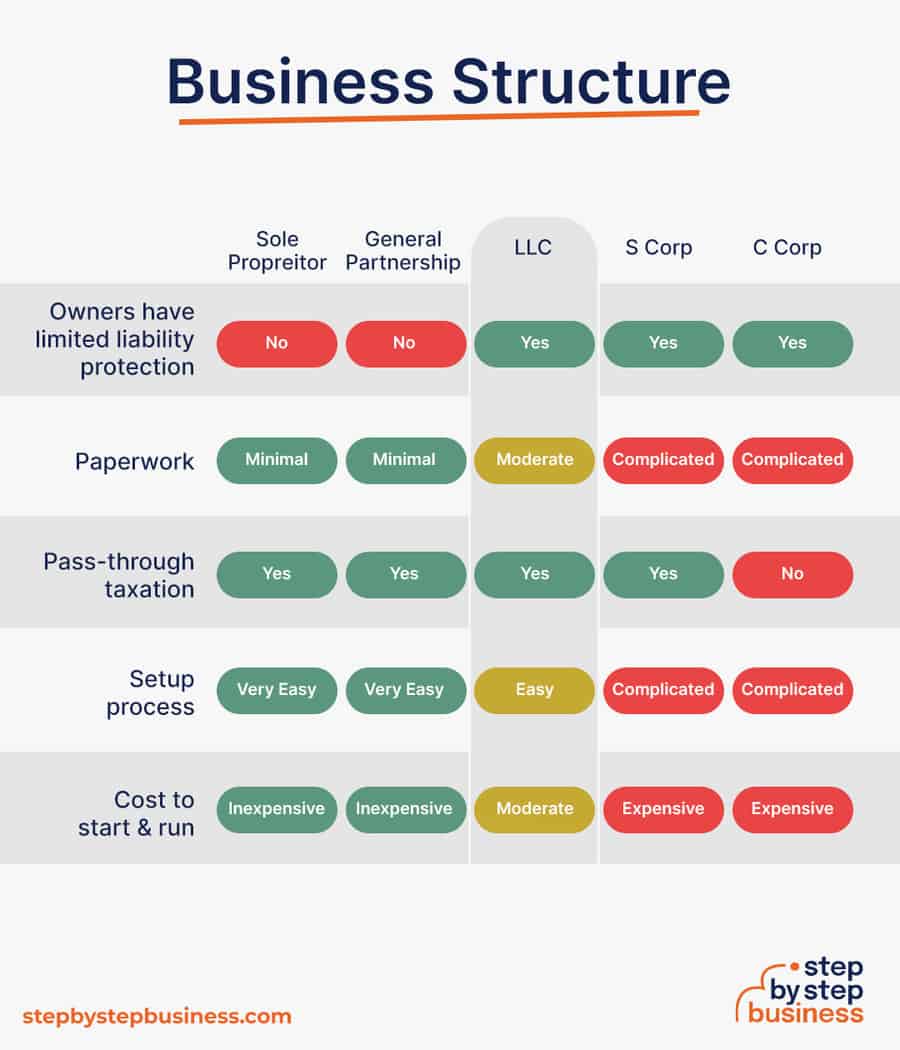
We recommend that new business owners choose LLC as it offers liability protection and pass-through taxation while being simpler to form than a corporation. You can form an LLC in as little as five minutes using an online LLC formation service. They will check that your business name is available before filing, submit your articles of organization , and answer any questions you might have.
Form Your LLC
Choose Your State
We recommend ZenBusiness as the Best LLC Service for 2024

Step 6: Register for Taxes
The final step before you’re able to pay taxes is getting an Employer Identification Number , or EIN. You can file for your EIN online or by mail or fax: visit the IRS website to learn more. Keep in mind, if you’ve chosen to be a sole proprietorship you can simply use your social security number as your EIN.
Once you have your EIN, you’ll need to choose your tax year. Financially speaking, your business will operate in a calendar year (January–December) or a fiscal year, a 12-month period that can start in any month. This will determine your tax cycle, while your business structure will determine which taxes you’ll pay.
The IRS website also offers a tax-payers checklist , and taxes can be filed online.
It is important to consult an accountant or other professional to help you with your taxes to ensure you’re completing them correctly.
Step 7: Fund your Business
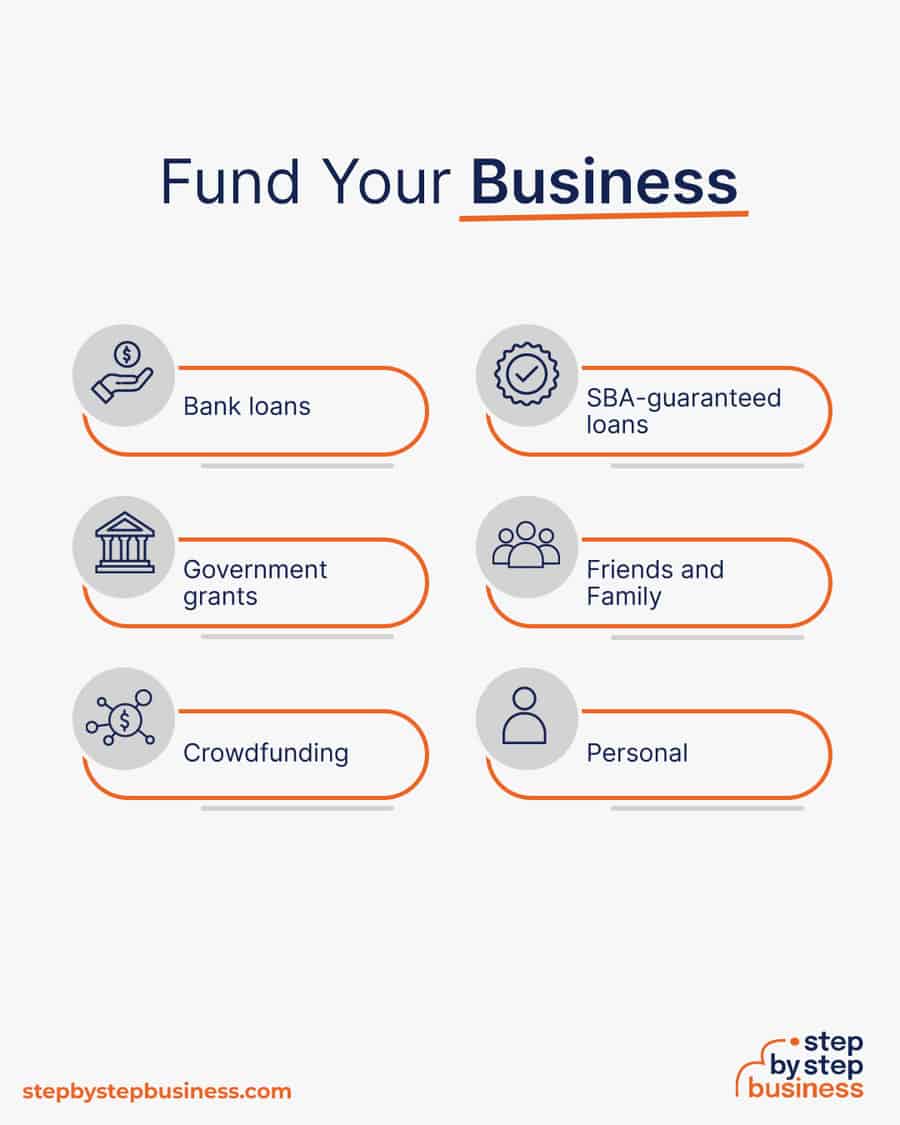
Securing financing is your next step and there are plenty of ways to raise capital:
- Bank loans: This is the most common method but getting approved requires a rock-solid business plan and strong credit history.
- SBA-guaranteed loans: The Small Business Administration can act as guarantor, helping gain that elusive bank approval via an SBA-guaranteed loan .
- Government grants: A handful of financial assistance programs help fund entrepreneurs. Visit Grants.gov to learn which might work for you.
- Friends and Family: Reach out to friends and family to provide a business loan or investment in your concept. It’s a good idea to have legal advice when doing so because SEC regulations apply.
- Crowdfunding: Websites like Kickstarter and Indiegogo offer an increasingly popular low-risk option, in which donors fund your vision. Entrepreneurial crowdfunding sites like Fundable and WeFunder enable multiple investors to fund your business.
- Personal: Self-fund your business via your savings or the sale of property or other assets.
You can visit the USDA website to find various loan and grant programs for startup farms. That’s probably your best bet for financing, although bank loans may also be an option.
Step 8: Apply for Cattle Farm Business Licenses and Permits
Starting a cattle farm business requires obtaining a number of licenses and permits from local, state, and federal governments.
You should contact your state’s department of agriculture to find out if any specific cattle farm licenses or permits are required in your state.
Federal regulations, licenses, and permits associated with starting your business include doing business as (DBA), health licenses and permits from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration ( OSHA ), trademarks, copyrights, patents, and other intellectual properties, as well as industry-specific licenses and permits.
You may also need state-level and local county or city-based licenses and permits. The license requirements and how to obtain them vary, so check the websites of your state, city, and county governments or contact the appropriate person to learn more.
You could also check this SBA guide for your state’s requirements, but we recommend using MyCorporation’s Business License Compliance Package . They will research the exact forms you need for your business and state and provide them to ensure you’re fully compliant.
This is not a step to be taken lightly, as failing to comply with legal requirements can result in hefty penalties.
If you feel overwhelmed by this step or don’t know how to begin, it might be a good idea to hire a professional to help you check all the legal boxes.
Step 9: Open a Business Bank Account
Before you start making money, you’ll need a place to keep it, and that requires opening a bank account .
Keeping your business finances separate from your personal account makes it easy to file taxes and track your company’s income, so it’s worth doing even if you’re running your cattle farm business as a sole proprietorship. Opening a business bank account is quite simple, and similar to opening a personal one. Most major banks offer accounts tailored for businesses — just inquire at your preferred bank to learn about their rates and features.
Banks vary in terms of offerings, so it’s a good idea to examine your options and select the best plan for you. Once you choose your bank, bring in your EIN (or Social Security Number if you decide on a sole proprietorship), articles of incorporation, and other legal documents and open your new account.
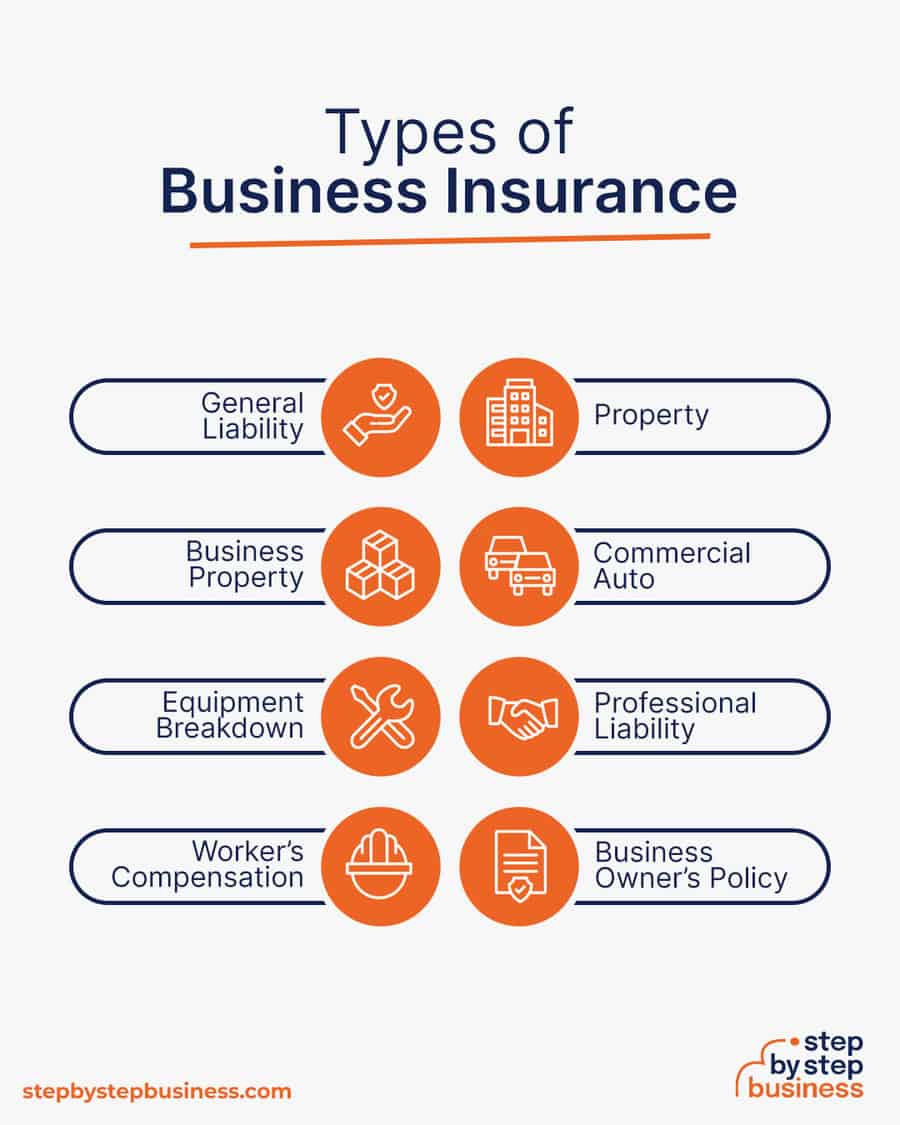
Step 10: Get Business Insurance
Business insurance is an area that often gets overlooked yet it can be vital to your success as an entrepreneur. Insurance protects you from unexpected events that can have a devastating impact on your business.
Here are some types of insurance to consider:
- General liability: The most comprehensive type of insurance, acting as a catch-all for many business elements that require coverage. If you get just one kind of insurance, this is it. It even protects against bodily injury and property damage.
- Business Property: Provides coverage for your equipment and supplies.
- Equipment Breakdown Insurance: Covers the cost of replacing or repairing equipment that has broken due to mechanical issues.
- Worker’s compensation: Provides compensation to employees injured on the job.
- Property: Covers your physical space, whether it is a cart, storefront, or office.
- Commercial auto: Protection for your company-owned vehicle.
- Professional liability: Protects against claims from a client who says they suffered a loss due to an error or omission in your work.
- Business owner’s policy (BOP): This is an insurance plan that acts as an all-in-one insurance policy, a combination of the above insurance types.
Step 11: Prepare to Launch
As opening day nears, prepare for launch by reviewing and improving some key elements of your business.
Essential software and tools
Being an entrepreneur often means wearing many hats, from marketing to sales to accounting, which can be overwhelming. Fortunately, many websites and digital tools are available to help simplify many business tasks.
You may want to use industry-specific software, such as CattleMax , folio3 , or muddyboots , to manage your herds, quality, sales, and reports.
- Popular web-based accounting programs for smaller businesses include Quickbooks , Freshbooks , and Xero .
- If you’re unfamiliar with basic accounting, you may want to hire a professional, especially as you begin. The consequences for filing incorrect tax documents can be harsh, so accuracy is crucial.
Develop your website
Website development is crucial because your site is your online presence and needs to convince prospective clients of your expertise and professionalism.
You can create your own website using website builders . This route is very affordable, but figuring out how to build a website can be time-consuming. If you lack tech-savvy, you can hire a web designer or developer to create a custom website for your business.
They are unlikely to find your website, however, unless you follow Search Engine Optimization ( SEO ) practices. These are steps that help pages rank higher in the results of top search engines like Google.
Here are some powerful marketing strategies for your future business:
- Local SEO — Optimize your website to highlight sustainable cattle farming and ethical practices, boosting visibility in local search results. Regularly update your Google My Business and Yelp profiles to strengthen your local search presence.
- Professional Branding — Ensure all branding reflects your farm’s commitment to quality and ethical standards, from logo to packaging.
- Direct Outreach — Forge relationships with local butchers, restaurants, and farmers’ markets to secure a consistent demand for your products.
- Social Media Engagement — Use platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn to showcase your cattle rearing practices and farm life.
- Farm Life Blog — Publish engaging content about daily operations and sustainable farming techniques.
- Educational Content — Produce videos and infographics to educate on the benefits of grass-fed beef and sustainable practices.
- Farm Tours and Events — Invite the public to tour your farm, enhancing transparency and customer trust.
- Direct Sales Model — Offer beef directly to consumers through sales or subscription services to build loyalty.
- Referral Programs — Encourage word-of-mouth marketing with a referral program rewarding loyal customers.
- Targeted Advertising — Place ads in local and regional publications that align with your target demographics.
- Email Personalization — Segment your email list to provide tailored updates and promotions to different customer groups.
Focus on USPs
Unique selling propositions, or USPs, are the characteristics of a product or service that sets it apart from the competition. Customers today are inundated with buying options, so you’ll have a real advantage if they are able to quickly grasp how your cattle farm meets their needs or wishes. It’s wise to do all you can to ensure your USPs stand out on your website and in your marketing and promotional materials, stimulating buyer desire.
Global pizza chain Domino’s is renowned for its USP: “Hot pizza in 30 minutes or less, guaranteed.” Signature USPs for your cattle farm could be:
- 100% grass-fed, sustainably-raised beef
- The best Angus beef you’ve ever tasted
- Top quality free-range veal, from our home to yours

You may not like to network or use personal connections for business gain. But your personal and professional networks likely offer considerable untapped business potential. Maybe that Facebook friend you met in college is now running a cattle farm business, or a LinkedIn contact of yours is connected to dozens of potential clients. Maybe your cousin or neighbor has been working in cattle farms for years and can offer invaluable insight and industry connections.
The possibilities are endless, so it’s a good idea to review your personal and professional networks and reach out to those with possible links to or interest in cattle farms. You’ll probably generate new customers or find companies with which you could establish a partnership.
Step 12: Build Your Team
If you’re starting out small from a home office, you may not need any employees. But as your business grows, you will likely need workers to fill various roles. Potential positions for a cattle farm business include:
- Farm Hands – assist with farm chores
- Farm Manager – herd management, accounting
- Marketing Lead – SEO strategies, social media
At some point, you may need to hire all of these positions or simply a few, depending on the size and needs of your business. You might also hire multiple workers for a single role or a single worker for multiple roles, again depending on need.
Free-of-charge methods to recruit employees include posting ads on popular platforms such as LinkedIn, Facebook, or Jobs.com. You might also consider a premium recruitment option, such as advertising on Indeed , Glassdoor , or ZipRecruiter . Further, if you have the resources, you could consider hiring a recruitment agency to help you find talent.
Step 13: Run a Cattle Farm – Start Making Money!
If you’ve always dreamed of farm life, your dream can become a reality. You can join an important and thriving industry, make a good living, and provide quality foods to growing families. It will take time, diligence, and a significant investment, but if you have a passion for farming and for producing good food, you can build a lucrative cattle operation.
You’ve got a good understanding of the business now, so it’s time to put on your work boots, roll up your sleeves, and launch your successful cattle farm.
- Cattle Farm Business FAQs
Yes, a cattle farm can be profitable. It will take time to start making money since you have to wait until the cattle get to their ideal weight to sell them, but after a few years, you should be turning a nice profit.
Prices for cows are very volatile, so it will depend on the market at any given time. Cows are sold by their total weight, with the price set per 100 pounds.
Kansas , Oklahoma , and Texas are good states for cattle farming because they have a solid infrastructure to support farmers. Land in those states is also inexpensive.
Montana, Oklahoma, and Wyoming have the cheapest farmland prices. South Dakota and North Dakota are also affordable.
You can’t start a cattle farm with no money. Costs are at least $300,000. However, the USDA can help you access financial resources, and they offer other support services to help beginning farmers.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Decide if the Business Is Right for You
- Hone Your Idea
- Brainstorm a Cattle Farm Name
- Create a Cattle Farm Business Plan
- Register Your Business
- Register for Taxes
- Fund your Business
- Apply for Cattle Farm Business Licenses and Permits
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Get Business Insurance
- Prepare to Launch
- Build Your Team
- Run a Cattle Farm - Start Making Money!
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.

57 Best Service Business Ideas
David Lepeska
Published on December 1, 2022
The services sector is undoubtedly the biggest economic sector in the US as it accounts for nearly 70% of the country’s gross domestic product. It ...

19 Profitable Agriculture Business Ideas
Published on November 4, 2022
Many young people today think it’s not cool to go into agriculture so they shy away from anything related to farms. Well, they’re missing a lot. ...

18 Pet Business Ideas for Animal Lovers
Esther Strauss
Published on July 14, 2022
Americans are spending more on pet care and products as the pet humanization trend, which treats pets as family members, takes root. Annually, anown ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.
How to write a business plan for a cattle farm?

Are you an aspiring cattle farmer looking to start up a business, or an existing one looking to expand and become more profitable? If so, then writing a business plan for your cattle farm is essential.
A well-crafted business plan can help you identify potential opportunities and risks associated with running a cattle farm, as well as guide you on how best to manage the operations of the farm.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll explore why it’s important to write a business plan for your cattle farm, what information is required to create one, what should be included in the document itself, and which tools are available that can make the process easier.
Let’s get started!
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for a cattle farm?
- Information needed to create a business plan for a cattle farm
- What goes into your cattle farm financial forecast?
- The written part of a cattle farm business plan
- What tool should I use to write my cattle farm business plan?
To draw up a roadmap
A business plan for a cattle farm helps you define your objectives and set goals for the next 3-5 years, which can be incredibly useful for achieving success in the long run.
The writing process of a business plan requires careful consideration of all aspects of running your cattle farm, from financial management to sales & marketing strategies and operational procedures.
Having these clear objectives laid out ahead of time will help ensure that your cattle farming venture runs smoothly and achieves its desired outcomes.
To compare financials and track progress
One of the main benefits of writing a business plan for a cattle farm is to be able to regularly compare your actual financial performance against what you planned in your forecast, and make adjustments where needed.
This enables you to maintain visibility on your future cash flows and make informed decisions about investments to grow your farm.
To secure funding
If you want to receive capital from investors or banks, you must have a comprehensive cattle farm business plan.
Financiers will be looking closely at your venture's growth prospects, profitability, and cash flow to estimate the possible returns on their investment.
Now that you know why it’s important to write a business plan for a cattle farm, let's look at the information needed to create one.
Create your cattle farm business plan online!
Think your cattle farm could be profitable? Find out how with a business plan!

What information is needed to create a business plan for a cattle farm?
Carrying out market research for a cattle farm.
Conducting market research is an essential step before creating a business plan for a cattle farm. Market research can help you to estimate revenues and provide insights into potential areas of growth or decline.
When you embark on market research of your cattle business, you seek to answer the following questions:
- Is the cattle industry growing?
- What segments (processed milk products, beef processing and packaging, breeding services, and cowhide sale) of the market are most attractive?
- Who is the competition?
- How long does it take from calving to sales?
- What is the best time for breeding?
- What are sales and profit margins like?
- What are the major trends in the cattle industry? For example, consumers are more interested in organic-bred cattle than those bred using hormones, steroids, and antibiotics.
This information will help you create and communicate in your business plan the strategies that will give your farm the best chance for success.
Developing the marketing plan for a cattle farm
Creating a sales & marketing plan for your cattle farm is the next step.
Having a concrete action plan in place will be necessary to create an accurate budget for sales and marketing expenses in your business plan, and to ensure that you have sufficient resources to deliver your sales forecast.
The staffing and equipment needs of a cattle farm
Before starting a cattle farm business plan, it is also key to take into consideration the investments and recruitment plan.
This will ensure that all necessary costs are accounted for and that sufficient capital is available to launch or grow the venture.
Some of the costs you must be aware of includes:
- Land purchase
- Fencing the land
- Land preparation
- Water source or supplies
- Tools and equipment costs
- Cattle shelter
- Cattle purchases
- Licenses and permits
Once you have gathered all the necessary information to create the business plan for your cattle farm, it is time to start building the financial forecast.
What goes in the financial forecast for a cattle farm?
The financial forecast of a cattle farm’s business plan will include important information like the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, and sources and uses table.
Let’s have a look at each table in a bit more detail.
The projected P&L statement
The projected P&L statement of a cattle farm business plan shows how much revenues it is expected to generate, how sales will evolve and how profitable it can be in the future.
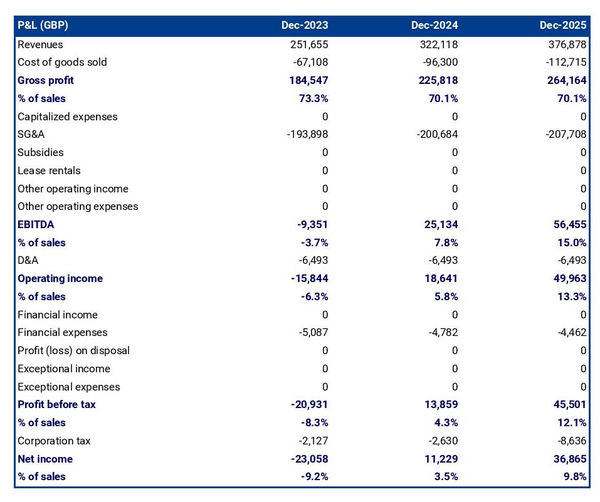
The projected balance sheet of your cattle farm
The balance sheet of a cattle farm is an essential financial statement that provides a snapshot of the farm’s financial position at any given time.
It records the assets, liabilities, and equity of the farm and serves as a valuable tool for owners, investors, and lenders to understand the overall financial health of the venture.
Assets are what a business owns and uses to make money. Examples of assets for a cattle farm include:
- Machinery and equipment
Liabilities on the other hand are what the business owes, they include things like:
- Accounts payable (money owed to suppliers)
- Tax payables
When total liabilities are deducted from total assets, what is left is the owner’s equity which represents the net worth of the business for the owners.
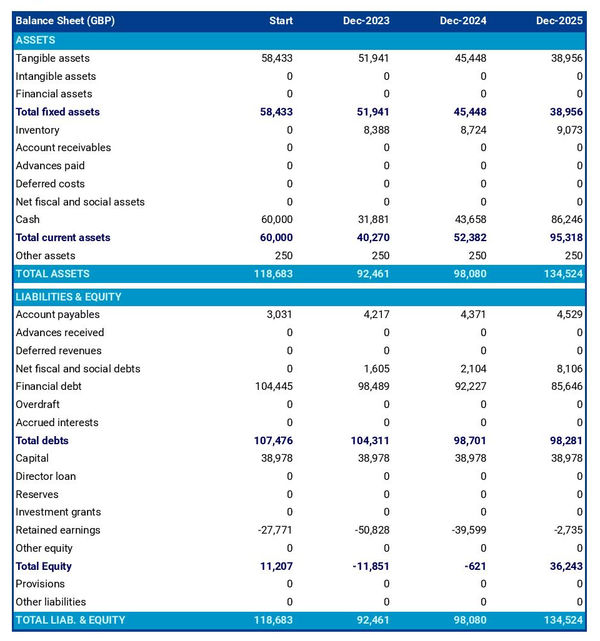
The projected cash flow statement
A projected cash flow statement for a cattle farm is a financial document that shows how much cash the farm will generate and spend in the future.
All transactions that involve the inflow and outflow of cash from a business are recorded in the cash flow statement.
This statement makes it easy for financiers to understand how much money your business produces (or will produce) and how much cash it will need for smooth operations.

The initial financing plan
An initial financing plan is important when writing a cattle farm business plan. It is also called sources and uses table.
This table helps you figure out how much money you will need to start your farm, where it will come from, and what it will be used for.
Having this information all in one place makes it easier to plan your finances and prepare for the future of your business.
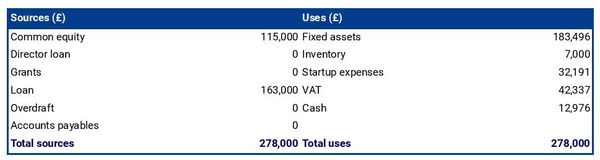
A solid financial forecast is the foundation for any successful cattle farm business plan. But to understand how relevant this financial data is, it's essential to provide context within the written part of the plan.
What goes in the written part of a cattle farm business plan?
The written part of a cattle farm business plan consists of 7 main sections:
The executive summary
The presentation of the company, the products and services section, the market analysis, the strategy section, the operations section, the financial plan.
The executive summary section of your cattle farm’s business plan should be a one-page (two-page maximum) summary presented in such a way that will convince investors and banks to read the rest of the plan.
The executive summary of your cattle farm business plan should begin with an overview of the farm itself, including key points such as the purpose of the business, its legal structure, its management team, and any pertinent information about the geographic area in which it operates.
After this should come a quick market overview highlighting who the farm sells to and who it competes with.
Then you should include key financials such as forecasted sales, growth, and profit, as well as expected cash flow projections and capital requirements.
This section of your business plan should include details about the ownership and legal structure of your cattle farm, your farm’s location, and information about the management team.
When writing about the legal structure, you should include information about the legal entity that owns the farm, such as whether it is a sole proprietorship, limited liability company, partnership, or other type of legal ownership.
You should also list the shareholders (people with a stake in the business) and the percentage of ownership each one holds.
The location section should provide an overview of the geographical area where the farm is located, with information about nearby cities and towns, access to major roads and highways, availability of water sources, climate considerations, and any other factors that could influence the success of the farm.
Then you should continue with the presentation of the management team which provides an in-depth look at who is running the farm’s day-to-day operations, including information about each individual's experience, education, and qualifications for their specific roles on the farm.
When writing the products and services section of your business plan for a cattle farm, it is important to clearly describe what breed of cattle (lisrace lumberjack, bos taurus, Angus cattle, etc.) you will raise and any other related services or products that you may offer.
This should include information about the size and quality of the herd, as well as any specialized breeds or special care practices used in raising them.
It is also important to outline any additional sources of income such as selling hay, feed, or providing agricultural consulting services.
Additionally, outlining plans for expansion into new markets could help convince investors that this is an enterprise with growth potential.

When presenting the conclusion of your market analysis in your cattle farm business plan, you should touch on demographic and segmentation information, your target market and competitors, and details about any barriers to entry and relevant regulations that you must comply with.
The demographic and segmentation section should include information about the different customer segments on the market and their purchasing habits for each of the main categories of products and services.
The target market section then zooms in on the segments you intend to serve and why your products and services match what customers are looking for.
Then you should explain who your main competitors are, and how your products and services compare to theirs.
You should also consider any potential barriers that can impede entry into the market (such as a limited availability of farm land for example) and relevant regulations that must be adhered to for compliance purposes.
In the strategy section of your cattle farm's business plan, you should explain your competitive advantage, price strategy, marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
To demonstrate the financial viability of your farm, you must be able to clearly explain what your competitive advantage is - i.e. how you intend to compete in an already crowded marketplace.
In addition, you should include details of your pricing strategy and show that it is profitable for you and attractive for customers.
Then comes your sales and marketing plan which outlines how you will reach your target markets, followed by any important and realistic milestones which are achievable within specified time frames.
Finally, you must detail any potential risks associated with your farm and possible solutions or mitigations for these risks.
The operations section of your cattle business plan should provide an overview of the functions and activities of your cattle farm.
It should cover information such as the staffing team, roles of staff members, recruitment plan, operating hours, key assets, and intellectual property needed to operate the farm.
A cattle farm may have the following type of staff on its payroll:
- Farm manager
- Slaughterer
- Veterinarian
For example, if you plan on hiring a veterinary technician or farm manager, explain their experience requirements and how they will contribute to the operation of your business.
You should also include your schedule and operating hours to give investors an idea of what a typical business day for your farm looks like, as well as information on the main assets and intellectual property that the business requires to operate.
These assets include any resources such as land, buildings, equipment or technology essential for running the farm. If you plan on leasing or buying any of these assets, provide details about the timelines and costs involved.
Lastly, the operations section should include information about the suppliers that you plan to work with. Be sure to provide details such as the cost of goods, delivery times and any other relevant commercial terms.
This will give investors a better understanding of how you plan on running your farming operation.
The financial plan section of the cattle farm business plan will include the financial forecast (balance sheet, P&L and cash flow statements, and the sources and uses table) that we talked about earlier.
Now that you have a clear understanding of the content of your cattle farm business plan, it's time to look at the tools available for creating one.
What tool should I use to write my cattle farm's business plan?
In this section, we will look at three options for writing a detailed business plan for your cattle farm: writing it yourself with Word and Excel, hiring a consultant to do it, and using online business plan software.
Create your cattle farm's business plan using Word or Excel
Creating a cattle farm business plan with Word or Excel is a possible option but usually not the best one.
On the plus side, both programs are relatively inexpensive. However, there are some significant drawbacks to using these programs to create a business plan.
Excel isn’t an easy tool to use, especially when it comes to creating financial forecasts without making mistakes.
As a result, it will be hard for financiers to trust the accuracy and validity of your numbers, and, therefore, using Excel isn’t recommended unless you are well versed into the art of accounting and finance.
Drafting the written part with Word also suffers from severe flaws. You start from scratch with no instructions to aid you, forcing you to think long and hard before filling up the pages. It is also time-consuming and tedious to format your business plan with Word.
Hire a business plan writer to draft your cattle farm's business plan
Outsourcing the business plan for a cattle farm to a consultant can be a viable solution as they are used to writing such plans. But this solution also comes with certain disadvantages.
Business plan writers may lack the livestock industry expertise needed to anticipate sales and cost accurately, forcing them to rely on your assumptions.
Hiring consultants to write a business plan is also expensive (budget a minimum of $2,000 or £1,500), with additional fees if the business plan needs to be updated after the initial version has been produced.
Finally, hiring a consultant gives you less control over the result than writing it yourself and your vision for the farm's future may not be adequately presented in the business plan.
Use an online business plan software for your cattle farm's business plan
Another alternative is to use online business plan software .
There are several advantages to using specialised software to write a cattle farm’s business plan:
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can be inspired by already written business plan templates
- You can easily make your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you, without error
- You get a professional document, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank
- You can easily update your financial forecast and track it against actual financial performance to see where the farm stands
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try our software for free by signing up here .
We hope that this article has helped you to better understand how to write the business plan for a cattle farm. Do not hesitate to contact us if you still have questions.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to write a business plan for a poultry farm
- How to write a business plan for a fish farm
Know someone in the farming industry? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting a livestock farming business requires careful planning and strategic thinking. To secure financing and attract investors, you need a comprehensive business plan that outlines your goals, strategies, financial projections, and operational details. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers comes in!
This template is specifically designed for livestock farmers and entrepreneurs in the agriculture industry, providing you with a step-by-step guide to creating a detailed and professional business plan. With ClickUp's template, you can:
- Outline your business goals and objectives for long-term success
- Develop strategies to effectively manage and grow your livestock farming business
- Create financial projections to attract investors and secure financing
- Streamline your planning process and save time with a ready-made template
Don't let the complexities of starting a livestock farming business overwhelm you. With ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll have all the tools you need to create a solid foundation for your venture. Start planning for success today!
Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers Benefits
Livestock farmers who use the Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers can enjoy the following benefits:
- Streamlined planning process to effectively outline goals, strategies, and operational details
- Increased chances of securing financing and attracting investors with a comprehensive business plan
- Clear financial projections to guide budgeting and financial decision-making
- Improved organizational and management skills with a structured business plan
- Enhanced ability to adapt to market changes and make informed business decisions
- Increased credibility and professionalism in the eyes of stakeholders and partners.
Main Elements of Livestock Farmers Business Plan Template
Are you a livestock farmer looking to create a comprehensive business plan? Look no further than ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers!
This template includes all the essential elements you need to develop a successful business plan for your livestock farming venture:
- Custom Statuses: Track the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Add specific information to your business plan with custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section, allowing you to keep all relevant details organized and easily accessible.
- Custom Views: Access different views to effectively manage your business plan, such as the Topics view to focus on specific areas, the Status view to track progress, the Timeline view to set deadlines, the Business Plan view to see the complete picture, and the Getting Started Guide view to help you navigate through the template.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers, you can confidently create a professional and comprehensive business plan to take your livestock farming business to new heights.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers
If you're a livestock farmer and want to create a comprehensive business plan, follow these steps using the Business Plan template in ClickUp:
1. Define your vision and mission
Start by clarifying your vision and mission for your livestock farming business. What do you want to achieve? What values and principles guide your operations? Clearly defining your vision and mission will serve as a foundation for your business plan.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to outline and articulate your vision and mission statements.
2. Conduct market research
Next, conduct thorough market research to understand the demand for your livestock products, identify your target audience, and analyze your competitors. Gathering this information will help you make informed decisions about your marketing strategies, pricing, and product development.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your market research data.
3. Develop a detailed financial plan
Creating a comprehensive financial plan is crucial for the success of your livestock farming business. Estimate your startup costs, projected revenue, and expenses. Consider factors such as feed costs, veterinary services, equipment, and labor. This will help you determine your breakeven point and financial viability.
Create custom fields in ClickUp to track your financial projections, budgets, and expenses.
4. Outline your operational plan
Your operational plan should outline how you will manage the day-to-day activities of your livestock farm. Consider aspects such as animal care, breeding and genetics, feed management, waste management, and equipment maintenance. Define standard operating procedures to ensure efficiency and productivity.
Use tasks in ClickUp to break down your operational plan into actionable steps and assign responsibilities to team members.
5. Develop a marketing strategy
To attract customers and promote your livestock products, you need a solid marketing strategy. Identify your unique selling points, determine your pricing strategy, and decide how you will reach your target audience. Consider online marketing, farmers markets, and partnerships with local businesses.
Use the Board view in ClickUp to visualize and track your marketing strategies and initiatives.
6. Monitor progress and adapt
Once your business plan is in motion, it's important to regularly monitor your progress and adapt as needed. Track key performance indicators such as sales volume, customer satisfaction, and profitability. Evaluate your plan's effectiveness and make adjustments to stay on track towards your goals.
Set up Automations in ClickUp to receive progress updates, schedule regular reviews, and ensure accountability.
By following these steps and utilizing the Business Plan template in ClickUp, you'll have a comprehensive roadmap for your livestock farming business. Good luck!
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers
Livestock farmers and entrepreneurs in the agriculture industry can use the Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers in ClickUp to efficiently plan and manage their livestock farming businesses.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to organize your business plan into different sections such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Financial Projections, and Operational Details
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, including statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- Utilize the Timeline View to set deadlines and milestones for each section of your business plan
- The Business Plan View will provide you with a holistic overview of your entire plan, allowing you to easily navigate between sections
- Create a Getting Started Guide View to outline the steps and resources needed to execute your business plan effectively
- Customize the template by adding custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to provide additional context and information
- Update statuses, custom fields, and collaborate with team members to ensure your business plan is comprehensive and accurate
- Business Plan Template for Facebook
- Business Plan Template for Grassroots Organizers
- Business Plan Template for Electricians
- Business Plan Template for Verizon
- Business Plan Template for Grocers
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Occupations
- Farm Animals and Livestock
How to Write a Business Plan for Farming and Raising Livestock
Last Updated: May 4, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Karin Lindquist . Karin Lindquist earned a BSc in Agriculture as an Animal Science major from the University of Alberta, Canada. She has over 20 years of experience working with cattle and crops. She's worked for a mixed-practice veterinarian, as a sales representative in a farm supply store, and as a research assistant doing rangeland, soil, and crop research. She currently works as a forage and beef agriculture extension specialist, advising farmers on a variety of issues relating to their cattle and the forages they grow and harvest. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 17 testimonials and 93% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 382,369 times.
A business plan is essential to have in place before you seek to start up a farm business, no matter what else you've done by way of preparation. In today's world, animal agriculture is more complex and more variable than it was 100 years ago. There are changing markets, high costs, low profit margins, different ways to raise cattle, and niche markets. The type of business plan you make is up to you, but the following step-by-step process of making a proper business plan will help you in the long run.

- You should be mainly brainstorming about your goals and objectives. [1] X Research source It's much more effective to run any business when you have a goal in mind to reach rather than having vague ideas of "wanting to do something with animals". That's simply not enough, and is certainly not going to get you anywhere fast!
- As you consider your goals, remember that strategy is not the same as marketing. The strategy for your business is how you plan to deliver value to your customers (your "value proposition"), how you intend to you convince potential customers to obtain that value from you by communicating your distinctiveness as a producer (or, what makes you different from other farms or ranches), and why you can deliver that value better than other producers (your performance anatomy). Your marketing plan should explain how you intend to communicate your strategy to your existing and potential customers. [2] X Research source

- Such an analysis is very simple and flexible to use, since you can use it to analyze your personal self, your business, or the industry you are wishing to start a career in.
- Internal forces that you have control over such as what breeds you choose, whether you want to run an intensive or extensive operation, how you feed your animals, etc.
- External forces that you have no control over such as the weather, the topography and soil-type of the land you are farming/ranching on, local, national and international industry issues, market prices, product demand and consumer preferences.
- Also analyze your farm, the land your farm sits on and your family. Ask similar questions as mentioned above, only with your family you will need to ask about times you should have to spend with them, what will happen if you put your farming operation before your family, what you can do to encourage and teach your kids to be involved in your operation, etc.
- The more research about what you're getting into that you do at this stage, the more aware you will be of what to expect when surprises do come. When you finally get started on your business plan, you'll be far more aware of the pitfalls, challenges , needs and requirements it takes to be involved and compete in the kind of livestock/farming operation you want to have.

- Where am I at now? Include a SWOT analysis (see earlier step), for these areas: customers, operations, human resources, and finance . If you don't have a business, a SWOT analysis as mentioned in the previous step is totally fine.
- Personal goals include things like working fewer hours, furthering your education in areas like different commodity markets or accounting and production programs, etc.
- Business goals are focused mainly on the farm unit as a business entity; examples include maximum debt load to carry, possibly owning or controlling x number acres, etc.
- How do I get there? This is the most important part of your business plan, because this is the area where you put on paper how you want to get the things you want for a better you, family and business. Brainstorming is great tool to use in this section, as you can always have a Plan B, C, D, etc., in addition to your Plan A.
- How do I know I have arrived? If you visualize your business plan as a journey, it is not difficult to understand that you will need to measure your progress along the way and determine if you are moving towards your goals, spinning your wheels or rolling backwards. This is done by defining, collecting and reviewing metrics, measurements and Key Performance Indicators on a regular basis in order to validate your plan and decisions, direct your future activities, justify any modifications to the plan and intervene when things are not happening according to the plan. All your goals should be measurable. Metrics and measurements will give you the answer to this important question.

- Vision Statement: A statement of what you or your farm will look like in the next 5 to 10 years.
- Mission: This determines or defines the purpose the organization attempts to perform in society. This statement should concisely explain what the company does, for whom and why.
- Values: These are general standards or guidelines that are important to your farm and farm family.
- Situational Analysis: This is the process of identifying and understanding how your business is positioned within the environment you operate, both internal and external. Step 3 is what this part of the strategic plan is all about.
- Goals: What are the major achievements you would like to accomplish in the next 3 to 5 years?
- Objectives: How do you plan on achieving your goals?
- Critical Success Factors: Areas of performance critical to long-term successes of an organization, and its development, growth and achievement. For each CSF you should define one or more Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), which are metrics you will use to determine if you are achieving your CSFs. CSFs are expressed as general statements of goals ("Maintain customer satisfaction.") while KPIs are more specific ("Decrease in number of product packaging complaints.")
- In a nutshell, you don't have to go through the headache of answering all of the questions posted above. Instead, use the three simple questions above in Step 4 as a means to answer all 8 of these standard business-plan questions.
- Production resources are also important to mention: Land base, Equipment base, and Buildings and Structures.
- Marketing Plan: Where and how will you sell your commodities? Remember, selling is just getting rid of what you have. When you market, you have to plan to sell commodities at a good price.
- Financial Plan: This includes budget analysis, revenues and expenses, debt, unpaid labour, opportunity costs, benchmark analysis of yourself from other operations, statements of cash flow , depreciation of machinery, animals, buildings, etc., wages, family living costs, etc.
- Human Resources plan: Most farms rely on one worker (i.e., the owner) to run the operation. But, nonetheless, human resource plans should highlight hiring issues facing the business and how to address them. It should further describe the kind of people that are required to operate the business (general responsibilities, title, skills, availability and any training programs needed.)
- Plan: Establish the objectives for whatever it is you intend to do, the processes necessary achieve those objectives and the metrics and measurements required to control the processes and prove that the objectives are being achieved.
- Do: Execute the plan and collect metrics and measurements along the way as defined in the previous phase.
- Check: Review the results, metrics and measurements and determine if any improvements can and should be made to the plan.
- Act: Implement the improvements so the next time the process is executed the results will be better.
- Succession Planning . This can be the hardest part of a business plan, as one has to plan what should happen if the main operator is injured or worse, dies. Succession planning includes developing a continuity plan for your business and determining the process of transitioning a business to new owners. This transition may be an outside sale (equipment and land auction sale), or an inheritance sale (passing the business down to the next generation). [7] X Research source

- Proprietorship : This is the simplest form of business organization. It primarily involves one person running the whole she-bang. Debts and negligent acts committed by employees are the responsibility of the proprietor. But, all the legal complications and expenses and negotiations for agreements are not required, nor is a business name required.
- General Partnership : This means two or three people running an operation. With more than one person running a farm, this means that the business must have a registered name, and each partner is responsible for all debts, obligations and liabilities of the operation. This partnership automatically dissolves with a death, bankruptcy, or insolvency.
- Limited Partnership : This is basically one person is responsible for everything in the firm, whereas the other is only there to supply capital, nothing more or less. A limited partner has no active part in the goings-on of an operation, but he may inspect the books of the firm and advise management.
- Co-ownership : This is where two or more persons own property jointly.
- Joint Venture : This is commonly used in farming, where there is a joint partnership between parties, and is created in order to conduct a specific or limited commercial venture without creating a partnership. This is commonly a temporary arrangement between two parties.
- Corporations : These are legal entities where shareholders own the corporation through the ownership of shares. It is a separate legal entity, distinct from its shareholders. The individual shareholder's liability is limited to that person's investments in the corporation, unless the shareholder has personally guaranteed the obligations of the corporation. A corporation can provide very flexible framework in terms of succession to the next generation. The owner may also give employees shares in the growth and profit of the operation without giving up management rights of a partner.
- Trust: This is a relationship where legal ownership of the property is separated from beneficial ownership of the property.

Community Q&A
- Ask for help when writing a business plan. Get a professional business analyst or someone similar with lots of experience analyzing and writing up such plans so they can help you if and when you are stuck on a particular section. Thanks Helpful 33 Not Helpful 5
- A business plan is good to have when signing on for a loan at the bank. They will be more interested in the financial portion of your business plan, because they need to see how it will affect them in terms of what they can get out of it in terms of money. Thanks Helpful 30 Not Helpful 9
- Put everything in writing. Nothing's worse than not writing something down and suddenly forgetting it. Also, have a separate file folder for thus business plan so you know where it is and where you can access it in the future. If you have it on the computer, save it on a hard drive or a data stick so if your computer crashes on you and you can't get your work back up, you have it saved on a separate disk. Thanks Helpful 29 Not Helpful 10

- Don't go in over your head and attempt to write out a business plan in one sitting. It may take a week or more before you get it all done, so take your time. Indeed, many established businesses started by spending six months or more preparing business plans; rushing will simply harm your business in the long run. Thanks Helpful 11 Not Helpful 2
- Don't think that you won't have to look at your business plan ever again for the rest of the time you are running your operation. You should always try to analyze what yourself and your business at least once a year to know where you are struggling and where you are doing great. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 2
Things You'll Need
- Computer text program or paper/notepad and pens
- Printer if you want hard copies of computer documents
- Research tools such as the internet, local library, libraries of agricultural bodies, etc.
- Phone numbers of people in the industry that you're interested in so that you can ask any important questions
- Books or websites on making business plans (but don't over-complicate things)
- Books on information about certain livestock interested in raising
- Newspapers and magazines of industry news and events in your area or the area you are interested in pursuing your farming career
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://grasshopper.com/academy/developing-a-business-plan/brainstorming-tips/
- ↑ https://www.forbes.com/sites/michaelskok/2013/06/14/4-steps-to-building-a-compelling-value-proposition/
- ↑ https://www.business.qld.gov.au/starting-business/planning/market-customer-research/swot-analysis/conducting
- ↑ https://www.agriculture.com/farm-management/business-planning/do-a-swot-analysis-on-your-farm
- ↑ https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-strategic-planning-and-operational-planning.html
- ↑ https://fitsmallbusiness.com/business-succession-planning/

About This Article
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Michael Howe
May 11, 2016
Did this article help you?

Nwaokenye Nduka Philip
Oct 8, 2017
Feb 8, 2017
Jamiu Adewole
Aug 30, 2016
Nadia Niyonizeye
Mar 20, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know
- Translations |
- Service Centers |
- Local Dashboard
Farmers.gov is not optimized for this browser. Please use the latest versions of Chrome, Edge, or Safari for the best experience. Dismiss
Find your state/county's agriculture data and USDA resources on your farmers.gov Local Dashboard !
How to Start a Farm: Plan Your Operation
Think about your operation from the ground up and start planning for your business. A good farm business plan is your roadmap to start-up, profitability, and growth, and provides the foundation for your conversation with USDA about how our programs can complement your operation.
Keep reading about planning your business below, get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey , or jump to a different section of the farmer's journey.
On This Page
Why you need a farm business plan.
A comprehensive business plan is an important first step for any size business, no matter how simple or complex. You should create a strong business plan because it:
- Will help you get organized . It will help you to remember all of the details and make sure you are taking all of the necessary steps.
- Will act as your guide . It will help you to think carefully about why you want to farm or ranch and what you want to achieve in the future. Over time, you can look back at your business plan and determine whether you are achieving your goals.
- Is required to get a loan . In order to get an FSA loan, a guarantee on a loan made by a commercial lender, or a land contract, you need to create a detailed business plan . Lenders look closely at business plans to determine if you can afford to repay the loan.
How USDA Can Help
Whether you need a good get-started guide, have a plan that you would like to verify, or have a plan you’re looking to update for your next growth phase, USDA can help connect you to resources to help your decisions.
Your state's beginning farmer and rancher coordinator can connect you to local resources in your community to help you establish a successful business plan. Reach out to your state's coordinator for one-on-one technical assistance and guidance. They can also connect you with organizations that specifically serve beginning farmers and ranchers.
It is important to know that no single solution fits everyone, and you should research, seek guidance, and make the best decision for your operation according to your own individual priorities.
Build a Farm Business Plan
There are many different styles of business plans. Some are written documents; others may be a set of worksheets that you complete. No matter what format you choose, several key aspects of your operation are important to consider.
Use the guidelines below to draft your business plan. Answering these kinds of questions in detail will help you create and develop your final business plan. Once you have a business plan for your operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center. During your visit, we can help you with the necessary steps to register your business and get access to key USDA programs.
Business History
Are you starting a new farm or ranch, or are you already in business? If you are already in business:
- What products do you produce?
- What is the size of your operation?
- What agricultural production and financial management training or experience do you, your family members, or your business partners have?
- How long have you been in business?
Mission, Vision, and Goals
This is your business. Defining your mission, vision and goals is crucial to the success of your business. These questions will help provide a basis for developing other aspects of your business plan.
- What values are important to you and the operation as a whole?
- What short- and long-term goals do you have for your operation?
- How do you plan to start, expand, or change your operation?
- What plans do you have to make your operation efficient or more profitable ?
- What type of farm or ranch model (conventional, sustainable, organic, or alternative agricultural practices) do you plan to use?
Organization and Management
Starting your own business is no small feat. You will need to determine how your business will be structured and organized, and who will manage (or help manage) your business. You will need to be able to convey this to others who are involved as well.
- What is the legal structure of your business? Will it be a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, trust, limited liability company, or other type of entity?
- What help will you need in operating and managing your farm or ranch?
- What other resources, such as a mentor or community-based organization , do you plan to use?
Marketing is a valuable tool for businesses. It can help your businesses increase brand awareness, engagement and sales. It is important to narrow down your target audience and think about what you are providing that others cannot.
- What are you going to produce ?
- Who is your target consumer ?
- Is there demand for what you are planning to produce?
- What is the cost of production?
- How much will you sell it for and when do you expect to see profit ?
- How will you get your product to consumers ? What are the transportation costs and requirements?
- How will you market your products?
- Do you know the relevant federal, state, and local food safety regulations? What licensing do you need for your operation?
Today there are many types of land, tools, and resources to choose from. You will need to think about what you currently have and what you will need to obtain to achieve your goals.
- What resources do you have or will you need for your business?
- Do you already have access to farmland ? If not, do you plan to lease, rent, or purchase land?
- What equipment do you need?
- Is the equipment and real estate that you own or rent adequate to conduct your operation? If not, how do you plan to address those needs?
- Will you be implementing any conservation practices to sustain your operation?
- What types of workers will you need to operate the farm?
- What additional resources do you need?
Now that you have an idea of what you are going to provide and what you will need to run your operation you will need to consider the finances of your operation.
- How will you finance the business?
- What are your current assets (property or investments you own) and liabilities (debts, loans, or payments you owe)?
- Will the income you generate be sufficient to pay your operating expenses, living expenses, and loan payments?
- What other sources of income are available to supplement your business income?
- What business expenses will you incur?
- What family living expenses do you pay?
- What are some potential risks or challenges you foresee for your operation? How will you manage those risks?
- How will you measure the success of your business?
Farm Business Plan Worksheets
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan.
Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans.
- FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet
- FSA-2037 Instructions
Planning for Conservation and Risk Management
Another key tool is a conservation plan, which determines how you want to improve the health of your land. A conservation plan can help you lay out your plan to address resource needs, costs and schedules.
USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) staff are available at your local USDA Service Center to help you develop a conservation plan for your land based on your goals. NRCS staff can also help you explore conservation programs and initiatives, such as the Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP) .
Conservation in Agriculture
Crop insurance, whole farm revenue protection and other resources can help you prepare for unforeseen challenges like natural disasters.
Disaster Recovery

Special Considerations
Special considerations for businesses.
There are different types of farm businesses each with their own unique considerations. Determine what applies to your operation.
- Organic Farming has unique considerations. Learn about organic agriculture , organic certification , and the Organic Certification Cost Share Program to see if an organic business is an option for you. NRCS also has resources for organic producers and offers assistance to develop a conservation plan.
- Urban Farming has special opportunities and restrictions. Learn how USDA can help farmers in urban spaces .
- Value-Added Products . The Agricultural Marketing Resource Center (AgMRC) is a national virtual resource center for value-added agricultural groups.
- Cooperative. If you are interested in starting a cooperative, USDA’s Rural Development Agency (RD) has helpful resources to help you begin . State-based Cooperative Development Centers , partially funded by RD, provide technical assistance and education on starting a cooperative.
Special Considerations for Individuals
Historically Underserved Farmers and Ranchers: We offer help for the unique concerns of producers who meet the USDA definition of "historically underserved," which includes farmers who are:
- socially disadvantaged
- limited resource
- military veterans
Women: Learn about specific incentives, priorities, and set asides for women in agriculture within USDA programs.
Heirs' Property Landowners: If you inherited land without a clear title or documented legal ownership, learn how USDA can help Heirs’ Property Landowners gain access to a variety of programs and services
Business Planning
Creating a good business plan takes time and effort. The following are some key resources for planning your business.
- Farm Answers from the University of Minnesota features a library of how-to resources and guidance, a directory of beginning farmer training programs, and other sources of information in agriculture. The library includes business planning guides such as a Guide to Developing a Business Plan for Farms and Rural Businesses and an Example Business Plan .
- The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers information about starting, managing, and transitioning a business.
SCORE is a nonprofit organization with a network of volunteers who have experience in running and managing businesses. The Score Mentorship Program partners with USDA to provide:
- Free, local support and resources, including business planning help, financial guidance, growth strategies.
- Mentorship through one-on-one business coaching -- in-person, online, and by phone.
- Training from subject matter experts with agribusiness experience.
- Online resources and step-by-step outlines for business strategies.
- Learn more about the program through the Score FAQ .
Training Opportunities
Attend field days, workshops, courses, or formal education programs to build necessary skills to ensure you can successfully produce your selected farm products and/or services. Many local and regional agricultural organizations, including USDA and Cooperative Extension, offer training to beginning farmers.
- Cooperative Extension offices address common issues faced by agricultural producers, and conduct workshops and educational events for the agricultural community.
- extension.org is an online community for the Cooperative Extension program where you can find publications and ask experts for advice.
Now that you have a basic plan for your farm operation, prepare for your visit to a USDA service center.
2. Visit Your USDA Service Center
How to Start a Farm with USDA
Get an overview of the beginning farmer's journey or jump to a specific page below.
Find Your Local Service Center
USDA Service Centers are locations where you can connect with Farm Service Agency, Natural Resources Conservation Service, or Rural Development employees for your business needs. Enter your state and county below to find your local service center and agency offices. If this locator does not work in your browser, please visit offices.usda.gov.
Learn more about our Urban Service Centers . Visit the Risk Management Agency website to find a regional or compliance office or to find an insurance agent near you.

[Pdf Sample] Livestock Farming Business Plan Docx
In the world of agriculture, livestock farming is a prominent and profitable venture. It involves the rearing and management of animals such as cattle, sheep, pigs, and poultry for various purposes.
If you’re an aspiring livestock farmer and the proud owner of Agrolearners.com, this article will guide you through the process of creating a comprehensive livestock farming business plan. By following this plan, you can establish a successful and sustainable livestock farming operation.
Livestock Farming Business Plan Proposal Docx
To write a business plan , here is a breakdown of how it should be structured and what should be in each category. After this instruction, I will provide you with a sample of one I wrote for my farm also subsequently as we go, so, let us go:
Executive Summary
The executive summary provides an overview of your livestock farming business plan. It highlights the key elements of your plan, including your objectives, strategies, and financial projections. The executive summary should be concise yet compelling, capturing the reader’s attention and providing a glimpse into the potential of your venture.
Company Overview
In this section, you will introduce Agrolearners.com and provide a brief background of your livestock farming business . Describe the mission and vision of your company, along with its core values. Explain the goals and objectives you aim to achieve through your livestock farming operations.
Market Analysis
Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand the demand and potential for livestock products in your target market. Identify your target customers and their preferences. Analyze the competition and determine your unique selling points. Explore market trends and opportunities that can give your business a competitive edge.
Livestock Selection
Choose the livestock species and breeds that align with your business goals and market demand. Consider factors such as adaptability to local conditions, market value, and potential for growth and profitability. Outline the specific breeds you plan to raise and justify your choices based on market research.
Infrastructure and Facilities
Feed and nutrition.
Detail the feed and nutrition requirements for your livestock. Outline the types of feed and forage you will provide, including any additional supplements or concentrates. Highlight your approach to feed formulation , sourcing, and quality control. Emphasize the importance of a balanced diet for optimal growth and productivity .
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Palm Oil Farming & Production Business Plan Docx
Breeding and Genetics
Explain your breeding program and genetic selection strategy. Discuss the criteria you will use to select breeding stock and how you plan to improve the genetics of your livestock over time. Address the importance of maintaining genetic diversity and avoiding inbreeding. Describe any partnerships or collaborations you have established with reputable breeders or genetic companies.
Health and Disease Management
Livestock health is crucial for the success of your farming business . Outline your health management practices, including vaccination schedules , deworming protocols, and disease surveillance. Emphasize the importance of biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction and spread of diseases. Establish a working relationship with a veterinarian to ensure regular health check-ups and prompt treatment when needed.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Present your marketing and sales strategy for promoting your livestock products. Identify your target market segments and outline your pricing strategy. Describe your distribution channels, including direct sales to consumers, partnerships with retailers, or participation in farmers’ markets. Highlight any unique selling points or certifications that differentiate your products from competitors.
Financial Projections
Provide a detailed financial analysis and projections for your livestock farming business . Include an income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. Project your revenue streams, expenses, and profitability over a specific period. Consider factors such as initial investment, operational costs, pricing, and market demand. Use realistic assumptions and provide a sensitivity analysis to assess the financial viability of your business.
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Cattle Farming In South Africa Docx
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Here is the Download Link to a sample of the Business Plan For Livestock Farming prepared By Agrolearner.com
How do I write a business plan for Animal Farm?
Discuss your farm’s infrastructure, facilities, feed and nutrition plans, health and disease management protocols, marketing and sales strategies, and financial projections. Finally, evaluate risks, create an implementation plan, and conclude by summarizing key points and expressing confidence in the success of your animal farm .
How do I write a business plan for a cattle farm?
To write a business plan for a cattle farm , follow the general structure mentioned above. Begin with an executive summary highlighting your objectives and financial projections. Provide a company overview, including the legal structure and ownership details.
Conduct a market analysis to identify target market segments, assess competition, and analyze market size and growth trends. Describe your chosen cattle breeds and their market demand. Detail your farm’s infrastructure, housing, equipment, and waste management practices.
Discuss feed and nutrition plans, health and disease management protocols, marketing and sales strategies, and financial projections. Evaluate risks, create an implementation plan, and conclude by summarizing key points.
What is the best livestock business?
Cattle Farming: Cattle can provide a steady income through beef and dairy production. There is consistent demand for beef products, and dairy farming can be lucrative with the right management.
Poultry Farming: The demand for chicken and eggs is consistently high, making poultry farming a profitable venture. It requires relatively less land and can yield quick returns.
Pig Farming: Pig farming can be profitable due to the high demand for pork products. However, it requires careful management and attention to disease prevention.
Ultimately, the best livestock business will depend on your knowledge, resources, market conditions, and personal interests. Thorough market research and analysis of local demand will help you determine the most suitable livestock business for your specific circumstances.
Through diligent execution, collaboration with industry experts, and continuous improvement, Agrolearners.com aims to contribute to the agricultural community while achieving long-term profitability and success.
Share this:
Author: adewebs, you may also like:, [pdf sample] business plan for pig farming docx, starting a poultry farm with limited resources in ghana: a comprehensive guide for new farmers, how to register agribusiness company in kenya (see full guide), starting a poultry farm with limited resources in nigeria: guide for new farmers, one reply to “[pdf sample] livestock farming business plan docx”, leave a reply cancel reply.

How To Create The Perfect Cattle Business Plan For Beginners
Creating a well-thought-out cattle business plan can make all the difference between success for the beginner farmer who makes one, and failure for the one that fails to write it.
This guide will help you create the perfect plan when starting your farm, even with little to no money .
Table of Contents
Reasons To Have A Business Plan
Having a workable business plan is important for the following reasons:
- It helps you raise capital from angel investors, relatives, friends, partners, and financial institutions like banks
- It acts as a living guide for the starting, implementation, operation, and ending of your cattle farm
- It helps keep all the involved persons in organic sync with the farm’s goals and objectives
- It boosts your chances of success with efficient management and acts as the stepping stone for a systematic record-keeping culture
- It helps you to theoretically analyze your business idea to measure its feasibility (practicality) and viability (success potential), and theoretically determine your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats ( SWOT analysis )
- It helps you plan for growth and expansion along the same operational procedures or branching into directly and indirectly related lines of action, such as value addition to your products
How To Write The Perfect Cattle Farm Business Plan
Writing the perfect business plan for a cattle farm doesn’t have to be challenging, whether yours is set to be a small-scale farm or a complex one.
To write an operational business plan, you must include:
- Organizational plan
- Management plan
- Financial plan
- Operations plan
- Marketing plan
- Exit strategy
Let’s take a closer look at each of these aspects.
Organizational Plan
The organizational plan provides a detailed description of the business concerning the reason for its existence, goals, and objectives.
The mission and vision statements usually appear in the executive summary of formal business plans.
If yours is an internal-use-only plan, you could place the two items in the organizational plan or leave them out altogether. However, this second option runs the risk of losing sight of what your vision is for the farm.
The organizational plan basically answers the question, “What business am I in?”. You can answer this question by listing your intended products, services, location, market, and what makes your business unique.
You could raise animals for milk, value-added dairy products, beef production, and high-quality semen. You can also make money selling live animals as calves, lactating cows, pet cows , and bred heifers.
Cattle services aren’t so popular, but you could look into cow tourism/cattle farm agri-tours, cow cuddling/hugging therapy, and educating aspiring and practicing cattle entrepreneurs.
Your organizational plan should also list your short-term and long-term goals and objectives for the farm. These could be guided by your reasons for the establishment of the farm.
Management Plan
The management of most small farms is easy. The farm owner doubles up as the farm manager and field worker, eliminating the need for an elaborate management plan.
Sometimes, family farm owners may receive free or paid assistance from family members or friends, making it necessary to expand the plan.
The management plan must also be detailed if the farm will involve other key players such as investment partners and specialized workers like the driver, farm manager, accountant, sales and marketing officer, and lawyer.
Your plan should provide details such as:
- All stakeholders enlisted by their experience in cattle farming or technical know-how of the business
- Names of staff and partners, together with their respective positions
- General responsibilities of each stakeholder
- The hierarchy of command from the management team down to the lowest employee on the farm
Financial Plan
Your financial plan can make or break your business. It comprises four key aspects:
- Your financial status and funds required: How much money do you have in savings or partner-raised capital? How much start-up capital do you need? And how much is required in operational expenses? Do you have an emergency or risk management fund? If you need outside money, what type of funding are you seeking? This could be credit card debt, grants, and loans from private lenders or commercial banks.
- Use of funds: What will your capital be used for? Typical uses include working capital, licensing, salaries/wages, infrastructure, pasture establishment/development, and daily operational costs. Other uses include cattle purchasing , raw materials for feeds, land, farm machinery and equipment, and unforeseen expenditure.
- Revenue model: How will your farm make money?
- Financial statements: You can’t improve what you haven’t measured. There’s every need to prepare financial reports like balance sheets, profit and loss statements, income statements, tax statements, and break-even analysis . You’ll also need to consider monthly cash flow projections, payback period , and repayment of loans and investor money with interest.
Operations Plan
The operations plan details the technical aspects of your day-to-day cattle-keeping business. It’s a detailed overview of how your business will run and how products will be manufactured.
It includes aspects such as:
- Feeding program: This details what you’ll feed your cattle to achieve the required nutritional levels and desired weights, production levels, and body condition. It shows the types of feeds and how they will be mixed and offered to cows.
- Quality assurance for products or services
- Health program: This details cattle treatment, vaccination procedures, disease prevention mechanisms, breeding protocols, vet and animal nutrition services, post-mortem procedures, and dead cow disposal measures.
- Operational strategy: Will yours be a cow-calf operation, feedlot finishing operation, backgrounding, zero-grazing, or open-range ranching?
Marketing Plan
The marketing plan provides details such as:
- Your target market
- Customer knowledge based on customer analysis of demographics, likes, dislikes, estimated disposable incomes, expectations, consumption behavior for the products you produce, and their location.
- Market analysis to learn cattle industry projections and prevailing market trends
- Pricing strategy for your services or products based on prevailing market prices or private calculations informed by your cost of production
- Competition analysis and how you’ll deal with business competition (both nearby farms and those out of state)
- Marketing strategy, promotion, and distribution of products or services
Exit Strategy
The exit strategy is useful when you want to leave the business permanently or temporarily. It shows when, how, and why you might exit the business. The most common reasons are prohibitive feed costs and ever-increasing operating expenses.
The exit plan details options such as:
- Selling your business to a larger farm (acquisition)
- Selling parts of the business or all of it to other smallholders, for example, through an auction
- Diluting or selling your ownership in a partnership farm
- Succession with a continuity plan for handing over to the next generation if you become incapacitated or your corporeal existence comes to an end.
When To Amend Your Business Plan
You might need to review and amend your cattle farming business plan along the way for the following reasons:
- Desire to change from one product line to another. You could shift from beef cattle like Hereford and Angus to dairy cattle like Friesians and Guernseys .
- Realization of objectives. You might realize the objectives you set out to achieve, making it necessary to change tactics if there’s nothing more to achieve.
- The departure of partners leading to a lower number of partners or a total shift to a sole proprietorship model
- Addition of new partners
- Substantive market changes or disruptions that warrant a change in standardized operation procedures
- The need to retreat to regroup if things haven’t been going according to plan and you wish to overhaul the business
- Changes in cattle, such as a shift from light-feeding cattle breeds to heavy feeders like Holsteins
- Changes in cattle feed crops. You might want to shift from grass-based farming to rearing cows using field forage crops like corn for silage.
Alex grew up in a rural area with chickens, cows, goats, and rabbits. He has always enjoyed waking up at 6 am to tend to his flock and vegetable garden. He bought his first cow at 25 and named her "104". In 2021, he set up an aquarium and now spends his lazy time watching his fish. He is happiest watching small animals and plants grow big, not to mention writing to share his farm-life experiences.
Recent Posts
RBGH: What Is It And Why Is It Given To Cows?
Recombinant bovine growth hormone (rBGH) is a manufactured or synthetic hormone that dairy farmers use to increase milk production in cows. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved rBGH in...
Beef Cuts On A Cow: A Guide For Home Butchering
There are many beef cuts on a cow that can be confusing for a beginner. It's best to start with having a trusted butcher prepare the first one or two animals you slaughter before you take over. Sit...
- Business Plan for Investors
- Bank/SBA Business Plan
- Operational/Strategic Planning Services
- L1 Visa Business Plan
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa Business Plan
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa Business Plan
- EB-1 Business Plan
- EB-2 NIW Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- Innovator Founder Visa Business Plan
- Start-Up Visa Business Plan
- Expansion Worker Visa Business Plan
- Manitoba MPNP Visa Business Plan
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa Business Plan
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa Business Plan
- Self-Employed Visa Business Plan
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream Business Plan
- LMIA Owner Operator Business Plan
- ICT Work Permit Business Plan
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur Business Plan
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA) Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Landlord business plan
- Nonprofit Start-Up Business Plan
- USDA Business Plan
- Cannabis business plan
- Ecommerce business plan
- Online boutique business plan
- Mobile application business plan
- Daycare business plan
- Restaurant business plan
- Food delivery business plan
- Real estate business plan
- Business Continuity Plan
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services
- Financial Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- How it works
- Business Plan Examples
Cattle Farming Business Plan Template
OCT.08, 2013

The demand for livestock products such as milk and beef is at an all-time across the globe. This turn of events has resulted in an increase in the number of cattle farms that are being constructed across the world to meet the demand for these products. If you are thinking of doing the same, it is important that you prepare a cattle farming business plan to help you steer the farm in the right direction.
OGS Capital is a reputable firm that has been offering business plan writing services for the last ten years. We have managed to serve thousands of clients from all parts of the world, and our reputation online and offline is clear proof that we deliver on our clients’ expectations and promises that we make at the start of our engagement.
Reasons Why Cattle Farming is Profitable
Before venturing into any form of business, it is crucial that you understand how the industry works. Get to know the type of services and products that the customers want. Get an estimate of the total amount of money that you would need to start a business. Our team did a research about cattle farming to save you time and money, and here are the top reasons why this form of farming is profitable.
- High demand for high-quality cattle products
- Use of modern equipment has streamlined operations and operating costs
- Full array of Growth Opportunities
To venture into this business through the right channel, you need to understand the importance of a cattle farming business plan . We recently held an open discussion with our staff and clients whom we have in the past written cattle farming business plan for; and here is a summary of that discussion.
Understanding the Market Demographics
The market demographics are important and cannot be ignored no matter the type of business that you intend to start. To write a cattle farming business plan, you will need to understand these demographics and the only way to do that is through a feasibility study. For instance, you need to know the type of feeds that you should purchase and the best cattle breeds in the market.
Hence, the cattle farming business plan will not only require you to do the feasibility study but also give you additional information on how to run the business.
Encouraging Transparency and Avoiding Losses
Transparency will help in ensuring that the cattle farm is not only successful in the short term but also on a long-term basis. Therefore, it is important to come up with concrete ways of promoting transparency in the farm. The accounting department needs to have a system to ensure that it does not make unjustified payments to suppliers and other people who do business with the farm directly.

A cattle farming business plan prepared by one of our experts will provide clear guidelines on how to encourage transparency in the farm. We will also go an extra mile and come up with a decision-making strategy that you can count on to make the right decisions and avert losses.
Makes Hiring Easier and Promotes Efficiency
The cattle farm needs a group of experts to contribute to making the right choices. Our team will help you get experts from the job market that has the required skills and expertise. We will provide ideas on what you should look out for when evaluating the job candidates. Without this information being included in the beef cattle farming business plan, you may not succeed in getting financing for the business plan from investors .
In addition, we will interact with you and give you professional advice on how to promote efficiency in the farm to safeguard its profitability. Note that one of the main reasons most cattle farms fail is due to poor management and lack of efficiency among many other factors.
These are the three most important benefits that you are guaranteed to enjoy by seeking professional cattle farm business plan writing services . Get in touch with our support team for more information on what we can do to ensure that your cattle farm succeeds by filling this quick form.
We will carefully evaluate and consider all information that you provide before embarking on writing the cattle farming business plan, and this will ensure that it is as comprehensive and detailed as possible.
Download Cattle Farming Business Plan Sample in pdf
OGScapital writer specializes business plan themes such as chicken farming business plan , dairy farm business plan , goat farming business plan , pig farm business plan , poultry farming business plan , fish farm business plan and etc.
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rate business plan development, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Add comment
E-mail is already registered on the site. Please use the Login form or enter another .
You entered an incorrect username or password
Comments (0)
mentioned in the press:
Search the site:
OGScapital website is not supported for your current browser. Please use:

JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Business Management
Raising beef cattle for profit requires land, money, and good business management skills. In this section, you will find information and advice on pricing meat cuts, conditioning cattle for market, and understanding beef carcass yields and losses during processing. Tips on applying RFID tags and performing beef quality audits are available as well.
Starting a Small Beef Cattle Farm
To start a beef farm, you will need to select the type of operation and develop a business plan that includes all startup and ongoing expenses. Consider necessary costs such as the purchase of land, animals, feed, and equipment. Other significant expenses include animal care, pasture management, labor, and building handling facilities.
In addition to the cattle farming business plan, you will need a solid management plan. This document should address beef cattle management practices regarding feed, health and nutrition, fencing, housing, and waste.
Note: The costs of beef enterprises are often specific for each operation. In order to better understand the financial aspect of beef production, producers need to consider direct expenses , direct income, and hidden costs.
Learn more about evaluating the potential financial impact of a decision (such as buying new equipment) with Penn State Extension’s Partial Budgeting online course .
Raising Beef Cattle for Profit
Beef farms generate income mainly from calf production . It is therefore recommended that cattle farmers select and maintain productive cows who produce a calf every year. The animals should be able to sustain their body condition and raise calves with a weaning weight that meets the end goals.
The retail beef price depends largely on the cost of production and the cost of getting the animal to slaughter weight. The production expenses vary based on the animals’ breed and production method (i.e. grain-fed or grass-fed cattle ).
The price of beef per pound can further be affected by factors such as fat percentage and type of cut. Obtaining a beef quality grade or an organic beef certification can help increase profits, as well.
Direct Income for Cattle Operations
Apart from the sale of cattle, beef producers can generate direct income from a number of other services. Depending on the enterprise, revenue can be generated from consulting, breeding cattle, hauling, and mowing pastures. Income may also be increased by selling embryos and bull sperm.
Selling hay and feed raised on the farm is another valuable option for cattle farmers. Estimating the expenses of home-raised feed, however, can be challenging.
One way for producers to calculate the actual feed costs is by using Penn State’s CropCents app . Once the data for all on-farm grown crops – including operating expenses – is entered, users can see the yield in tons/acre and the cost/ton.
Beef Cattle Market Trends
With a huge market for beef, raising cattle in the US is one of the most common and profitable farming businesses.
The way cows are raised and fed has a big effect on the retail price. Beef is very nutritious, but different feeds deliver different products and tastes. Currently, there is an increased interest in pasture-raised beef, as well as organic and/or locally grown meat products.
Educational Resources for Cattle Farmers
Raising beef cattle for profit is a huge undertaking. Find comprehensive information on beef cattle management with Penn State Extension’s articles, webinars, online courses, and workshops.
Items 1 - 25 of 33
- Product Name
- Date Posted

Northern Tier Beef Producer Meeting: Should She Stay or Should She Go?

Butcher Apprenticeship Program

Earn While You Learn - Animal Science Apprentice Program

Feeding Beef Cattle

What You Should Know About Buying Livestock

Crop Cents Mobile App

Survey of Pennsylvania Beef Producers

Navigating Pathways to Success: The 2016 National Beef Quality Audit

Grass-fed Beef Production

Advantages of Marketing Your Beef Directly

2017 Calf-fed Holstein Demonstration Results

2016 Calf-fed Holstein Demonstration Results

Calculating the Cost of Beef Production

Replacement Heifers: Management Options Benefit Bottom Line

Benefits of Weighing Beef Cattle

Building an Emergency Response Plan for Livestock Producers

Integrating Grazing into Cropping Systems: Infrastructure

Beef Cow-calf Operation

How Much Should You Charge? Pricing Your Meat Cuts

Beef Production

Understanding Beef Carcass Yields and Losses During Processing

Custom Feeding Cattle

Does the Growing Beef x Dairy Trend Work for the Feeders

The Most Valuable Investment in the Beef Herd - The Bull

Starting a Freezer Beef Business
You may also be interested in..., personalize your experience with penn state extension and stay informed of the latest in agriculture..
Sample Livestock Farming Business Plan
Livestock farming business plan sample.
Do you want a business plan for farming and raising livestock? Here is what you need to know as you kick start your livestock farm.
Business plans are what lies between one’s business resources and business revenues. An excellent plan transforms a business idea into possible results using an actionable roadmap.
In simple words, a business plan acts as a guide to lead your business into the goals you want to achieve. Don’t get absorbed into thinking that a good plan must be officially documented, or contain a complex strategy; you can keep it more straightforward and still get results.
Here are some business plans for starting a livestock farm.
- Cattle farming business plan
- Pig farming business plan
- Dairy farming business plan
- Goat farming business plan
- Rabbit farming business plan
- Horse breeding business plan
- Calf operations business plan
The most common challenge to livestock farmers is earning a high income from their farming business. This challenge is not only confounded to small-scale farmers with relatively low resources but also to large-scale farmers who have the needed funds even to hire professional business managers.
READ: HOW TO BECOME A LIVESTOCK FEED DISTRIBUTOR
In some cases, your business revenue can continuously decrease over some time that you might decide to quit your business as well. These are the times when a good plan can act as your turning point.
HOW TO WRITE A LIVESTOCK FARMING BUSINESS PLAN
Even though you can farm livestock for non-profit purposes, many business experts advocate livestock farming for business. Imagine tapping into lucrative areas like dairy farming, poultry farming, aquafarming, and rabbit farming to supplement your income.
Better still, other areas like snails farming to earn money. To large-scale farmers, it is by default that you are yearning to learn what a good plan comprises. If you are a starter, this article also covers you to ensure you reap profits from your business.
A typical business plan takes any of these forms:
- One-page Plan: This is a plan that is short, simple, and clear to the point. Meant for you alone.
- Internal Plan : Meant for your workforce/employees.
- An External Plan: This is intended for people outside your business, possibly, potential investors or financiers.
How Will a Business Plan for My Livestock Farming Help Me?
If you are still puzzled upon whether to use a business plan for your livestock farming, then below are the various ways you will benefit when using a business plan:
- It is difficult to accomplish goals using a virtual roadmap. You can document and keep your paper for tracing your goals every day
- Helps understand your business better by recording your workforce, services, market demand, and so on.
- Gives you the chance to set achievable milestones, rather than focusing on a general goal
- You have an opportunity to analyze your strategies and use what works
- Comparison between your plan and results to make a result-centered plan.
Components of an Excellent Livestock Farming Business Plan
If you have ever found yourself jotting down points relating to what you want for your business, then you did a business plan. But, a good plan does not only entail writing down your ideas. It involves aspects that are tailored to your business. Thus, it is essential to understand your business and your market before crafting your business plan.
The first component should be a summary of your mission , business resources , and vision statement. This introductory part is known as an executive summary , and it needs to be personalized for your business. For instance, use “we” or “I” but not “you”.
Talk about:
- Location of your business depending on the market.
- What your business entails. Is it dairy farming? Do you want to keep cattle for beef, and which breed?
- How do you want to run the business? Is it through hired experts? Do you have employees, and what is the role of your employee(s) in your company?
Your plan should have a target market and the market advantage you have over your competitors. As an example, state something like, “ Our business will be located in the Lower Desert Region. Because the regions demand fresh daily milk, our workforce will be provided with quality working conditions to discharge their tasks efficiently .”
How will you get revenue? Describe your projection for your business revenue source. For instance, do you intend to generate revenue from actual sales of your livestock, or by selling livestock products?
You should also describe the sales projection of your business from past revenues. You can state the amount earned in the three previous years to understand what can be earned from your business.
Your business plan for livestock farming should also have the marketing and advertising strategies you intend to use. This strategy enables you to budget well.
It is relevant noting that even though an excellent business plan is a roadmap to achieving your goals, the plan should be unique. This is critical when using an external business plan with the sole aim of getting some external funding or lure investors.
The last thing every investor wants is a boring pitch that is repeated over and over. So, use your livestock business plan to detail as much information as possible that best describe your services.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
LIVESTOCK FARMING BUSINESS PLAN + FINANCIALS
Looking for a livestock farming business plan for your new or existing enterprise?
Download this livestock farming business plan, which you can download to present to NIRSAL, TEF BOI, BOA, and other investors.
LIVESTOCK (GOAT, CATTLE, SNAIL, POULTRY) FARMING BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE
1.0. Executive Summary
Joe Farms Ltd is a registered Ilorin-based livestock farming company. Our livestock breeding company will be the standard one that,s involved in the commercial breeding of goats and other livestock. We will be providing the following services boarding services, breeding services, dairy support services, livestock health services, farrier services, and shearing services et al.
We have done our comprehensive market research and probability studies. We were able to secure one hundred hectares of land to set up our livestock breeding business.
Within the first five years of officially operating Joe Farms Ltd, we hope to start our meat processing plant and start exporting our products to other parts of the world.
Aside from the fact that we’ve secured the required farming land for breeding goats at the commercial level, we have also hired some key employees who are currently undergoing training to fit into the ideal picture of the 21st-century livestock breeding workforce that we want to build.
Joe Farms Ltd is a private registered livestock farming company that is owned by Joe Papa. The company will be fully financed and managed by the owner – Joe Papa at least for a while.
Before setting up Joe Farms Ltd, Joe Papa has worked with some of the leading livestock farms in Nigeria. He has worked in the livestock farming industry for ten years before resigning to start his own goat farming business.
2.0. Our Products and Services
Joe Farms Ltd is a licensed livestock farming business that is committed to goat farming, meat processing and packaging for both the Nigerian market and the global market. We will also be in the production of related raw materials for industries in commercial quantities.
These are the areas we will concentrate on in our livestock farming business;
- Boarding service
- Breeding service
- Dairy support service
- Livestock health service
- Farrier service
- Sale and export of cotton wool and other dairy products
- Sale of Cattle and milk (Including goats, sheep, grass – cutters, pigs and rabbits et al)
- Sale of processed meat (beef) / can – beef (Processed Dairy foods, and can beef et al)
- Shearing services
- Livestock farming-related consultancy and advisory services
3.0. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our Vision is to become one of the leading livestock farming brands not just in Ilorin-Kwara, and also in Nigeria.
- Our mission is to sell our product and produce (goats), byproducts, and processed meat in commercial quantities at all market levels (locally, nationally, and internationally).
- Also, We want to establish a livestock farming business that can conveniently compete with other leading livestock farming brands in Nigeria.
4.0. Our Business Structure
Joe Farms Ltd is a livestock farming company that intends to start small in Ilorin-Kwara state but hopefully grow big to compete favorably with leading livestock farms in the business both in Nigeria and on a global stage.
We are aware of the significance of building a solid business structure that can support the idea of the kind of world-class business we want to build. This is why we are dedicated to only hire the best hands in and around Ilorin.
At Joe Farms Ltd, we will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, hardworking, dedicated, customer-centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all the stakeholders (the owners, workforce, and customers).
Given the above, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
Below is the business structure of Joe Farms Ltd;
- Chief Operating Officer
- General Farm Manager
- Administrator / Accountant
- Cattle Ranch Manager / Supervisor
- Sales and Marketing Executive
- Field Employees
- Front Desk Officer
5.0. SWOT ANALYSIS
5.1. Strength
Our strength as a livestock farming business is the fact that we have strong connections with several major agriculture merchants(both suppliers and buyers) in the livestock farming industry within and outside Nigeria.
We own some of the latest livestock farming machines, tools and equipment that will help us breed goats and other livestock in commercial quantities with less stress. Aside from our connection (network) and equipment, we can confidently boast that we are equipped with the most experienced hands in the livestock farming industry.
5.2. Weakness
Our weakness could be that we are new livestock farms in our location. We are aware of this and from our projection will overcome this weakness with time and turn it into a major advantage for the business.
5.3. Opportunities
Some several homeowners and industries will source for goats, goat meat, and milk and also industries that will source for the raw materials from our livestock farms both in Nigeria and other parts of the world which makes the opportunities in this industry limitless.
5.4. Threat
Some of the threats and challenges that we are likely going to face when we start our livestock farm are global economic downturn that can impact negatively on household spending, bad weather cum natural disasters (draughts, epidemics), unfavorable government policies, and the arrival of a competitor (a commercial farm that rear same animals) as our livestock farms within the same location.
6.0. Our Target Market
Our target market is the end consumer of livestock farm produce and those who benefit from the business value chain of the agriculture industry.
Every household consumes livestock farms product be it goat meat, goat milk, and the skin (leather) used for bags, belts and shoe production et al. Also, a large number of manufacturing companies depends on livestock farms for some of their raw materials.
7.0. Our competitive advantage
It is easier to find entrepreneurs crowding towards an industry that is known to generate constant income which is why there are more commercial farmers in Nigeria and of course in most parts of the world.
Entrepreneurs are encouraged by the government to embrace commercial farming/livestock farming. This is so because part of the success of any nation is her ability to cultivate her food and also export foods to other countries of the world.
Joe Farms Ltd is fully aware that there are competitions when it comes to selling livestock and it produces all over the world, which is why we decided to carry out comprehensive market research on how to take advantage of the available market in Nigeria and other parts of the world.
How To Download Livestock Farming Business Plan PDF and Doc (With financial analysis)
Pay the sum of N5000 ( Five thousand naira only) to the account detail below: Bank: GTBank Name: Oyewole Abidemi (I am putting my name and not our company account so you know I am real and you can trust me, and trace me) Ac/No: 0238933625 Type: Saving
P.S: We can also tailor the business plan to your name, business size, capital requirements, and more to fit your direct needs. Call or message +234 701 754 2853 for inquiries.
Thereafter, send us your email address through text message to +234 701 754 2853. The text must contain the title of the business plan you want and also your email address. Immediately after the confirmation of your payment, we will send the livestock farming Business Plan to your email address where you can easily download it.
Dr. Abi Demi is a skilled technical writer and author with specialties in the martech and fintech space. Featured on Tekedia, Coin Review, Business Insider, Fintechna, Cryptocoin.news, Date 360 and several other sterling online publications, Demi is an astute technical writer that specializes in finance, marketing and technology - with over 500 published pieces across the internet ecosystem. Contact Abi Demi - [email protected]
How to Get Loan Without Collateral in Nigeria
Download restaurant business plan with financials, you may also like, feasibility study sample for private school, private school business plan sample, feasibility study template for zobo production, business plan sample for zobo production, ict feasibility study sample, download ict business plan sample, download snailery feasibility study sample, download snailery business plan sample business, 8 farming & agriculture business ideas in nigeria, 5 investment apps for saving, growing your money..., leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Guide On Livestock Farming Business Plan

Setting up a successful livestock farming business requires you to plan and develop a well thought out business plan. Whether you are rearing cattle for meat or dairy, ducks, goats or pigs, livestock farming can be a lucrative business idea. There are many factors that you need to consider when drafting your livestock business plan. These include the market, your finances and risks among other issues. In fact, a livestock business plan has the same components of any other business plan. The only difference is that your business plan is specifically tailored towards rearing animals.
Importance Of Planning
Developing a business plan for your livestock business is critical because it will help you work out how you can achieve your goals, anticipate risks and ways to reduce them as well as determine if there is any extra support that may be required. A business plan can also help you think about how you can make any adjustments or changes to your business model if the need arises.
Types of Livestock Business Plans
There are several kinds of livestock business plans that include:
- Cattle Fattening Business Plan
- Pig Farming Business Plan
- Rabbit Farming Business Plan
- Goat Farming Business Plan
- Dairy Farming Business Plan
- Sheep Farming Business Plan
- Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan
- Mixed Livestock Farming Business Plan
Vision Goals and Objectives
Just like any other business plan, a livestock farming business should have a clear vision, long term goals and short term goals in addition to your objectives. It is important therefore to think about where you want your livestock business to be in the next 5 years or so. Your long term and short term goals will assist you in mapping out what you need to do in order to get where you want to be. In addition, it is important that your goals are time bound, specific, measurable and realistic for you to have an effective business plan.
The next thing after writing out your vision and objectives is writing a summary of your current operations if you have been in the livestock business already. If this will be a start-up you can include information about the farm, where it is located and the amount of space which is available for the project. The information about the specific animals you want to rear should also be included in this section. Such information is necessary especially if you want to present the livestock business plan to investors for funding. You can also add a bit of information about your skills and experience as well the profiles of other business partners if there are any.
Overall Strategic Plan
This section has more detail and requires you to do a lot of research. The strategic plan talks about how you intend on achieving the goals and objectives of your livestock business plan. This section includes your operational plan, sales and marketing plan as well as your financial plan. An industry analysis is critical for you to develop an effective business strategy. You must also study the agricultural market in order to understand the market conditions in which you will operate. You must know who your major competitors are to know what you are up against. Market research is also essential to determine whether or not there are potential buyers for your product. Whether you specialise in rearing one specific animal or diversify your offerings you must know if there is a market for your produce. By studying the industry and agriculture market you can find out if your livestock business will be profitable or not. Also, you can determine earlier on whether you need to change course based on market conditions.
An Internal And External Analysis
After drafting your business strategy the next step would be to conduct an analysis where you can describe what your competitive advantage is and where your weakness lies. Consider doing a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats assessment (SWOT Analysis). That way you can assess what your strengths are and how you can leverage them. You can also determine how you can optimise on any opportunities that may be present in the market. Assessing your weaknesses and threats can also help you see areas which may need improvement. Conducting an internal business analysis will help you determine what you should focus on improving whilst an external business analysis will direct you towards opportunities that you can profit from as well as prepare you for any threats.
Risk Assessment
In Agriculture risks can make or break your business. There are many risks that farmers, including livestock farmers should always prepare for. These risks include production risks, price or market risks, financial risks, as well as personal risks to name a few. A risk analysis will help you prepare for events such as diseases that may negatively affect your livestock production. You should always budget for extra funds in the event that your costs increase due to emergencies, a sudden increase in operational costs or any other activity that can drain your budget. A lot of farmers do not take price risks into consideration when they draft their business plan. To avoid making losses you should plan for all kinds of scenarios when it comes to the selling price of your produce. Always have a contingency plan in the event that your produce sells below your expected average selling price in order to reduce or to avoid making losses. Other risks involved in livestock production that you must also consider include accidents with workers or health related issues that may reduce productivity at your farm.
Tips for Developing A Livestock Business Plan
When developing your livestock business plan or any other business plan in general do not be afraid of aiming high. Make use of the planning phase and consider various options and farming models. Also take time to break down each business plan section and think it through. Ensure that you allocate all the time you need since a lot of research needs to be done. Understand that developing a business plan is not a one time thing but an ongoing process. Make sure that you consider all your available resources and plan for extra support in case you need it. Take time to gather information from other successful livestock farmers for guidance too.
Related Posts

Profitable Crop Farming Business Ideas

Starting Auto Spare Parts Store Business Plan (PDF)

Latest Innovations In Poultry Farming

Starting A Gym Business Plan (PDF)

Join our mailing list to receive the latest posts and updates from our website.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Using partnerships and corporations to transfer farm assets
- Managing a farm
- Transfer and estate planning
- Utilizing partnerships and corporations to transfer farm assets
Quick facts
- Establishing a business entity, such as a partnership or corporation, can help with the process of transferring a farm business to the next generation.
- In Minnesota, there are two major categories of partnerships: partnerships and limited partnerships.
- The two corporation entities available to farm businesses are S corporation and C corporation.
Developing any business entity is a complicated process. Seek assistance from a qualified legal expert and accounting assistance if you plan to explore developing a business entity.
Transferring the farm business to the next generation can be a daunting task. However, there are strategies and methods that can help simplify the process.
When operating as a sole proprietorship, it can be challenging to establish a transition plan. There are many individual assets that need to be accounted for such as machinery, equipment, livestock and land. It is difficult and time consuming to transfer separate, individual assets.
One possible solution is to establish a business entity such as a partnership or a corporation to accomplish the business transition. As members and owners of the entity, the parents are issued ownership shares or shares of stock in the entity. These shares can be sold, gifted or passed through an estate to the entering generation, over time, as a method of transferring the business. This does away with the need to transfer separate, individual assets. This also spreads out the parent’s income and thus tax obligations. It allows the entering generation the ability to acquire assets over time thus minimizing their need for large amounts of capital.
In Minnesota, there are two major categories of partnerships: 1. partnerships and 2. limited partnerships. There are separate entities under each category which function differently.
1. Partnerships
There are two entities: general partnerships and limited liability partnerships.
General partnerships (GP)
Two or more people are required for the GP and are referred to as general partners. All partners are generally liable for all debts and obligations of the GP. There is no liability protection for their personal or partnership assets. Minnesota state law does not require a written partnership agreement. However, such an agreement outlining decision making and job responsibilities might be useful. If the name of the partnership is that of the partners (Henderson Family Partnership), the entity does not have to be registered with the State of Minnesota. The entity is taxed as a partnership, pass-through entity, with income allocated to each partner based on their ownership and included in their personal income tax.
Limited liability partnerships (LLP)
The LLP is similar to the GP with exceptions. All partners are general partners (no limited partners) but their liability exposure is limited to the assets they have placed into the LLP. Their personal assets are protected from liability exposure. The LLP is required to register with the Secretary of State in Minnesota. The LLP is taxed as a partnership, pass-through entity.
2. Limited partnerships
There are three partnership categories: limited partnership (LP), limited liability limited partnership (LLLP), and limited liability company (LLC).
Limited partnership (LP)
Two or more persons are required. There are both general and limited partners. General partners have no liability protection for their business assets but do for their personal assets. The limited partners’ assets in the LP as well as their personal assets have liability protection under the LP. The LP is required to register with the Secretary of State in Minnesota. and the Minnesota Department of Agriculture to comply with the Minnesota Corporate Farm Law. The LP is taxed as a partnership, pass-through entity.
Limited liability limited partnership (LLLP)
Two or more people are required. There are both general and limited partners and they have liability protection of both their LLLP assets and their personal assets. The State of Minnesota requires the LLLP be registered with the Secretary of State and the Minnesota Department of Agriculture to comply with the Minnesota Corporate Farm Law. The LLLP is taxed as a partnership, pass-through entity.
Limited liability company (LLC)
Requires only one person as a member of the entity. From a tax standpoint, the LLC can be taxed as a partnership pass-through entity or as an S Corporation. In addition, the LLC can afford tax savings via discounting assets and potential savings of self-employment taxes. The LLC provides liability protection much like that of a corporation.
The LLC has both members and managers. Members elect or appoint a board of directors. The State of Minnesota requires that the LLC register with the Secretary of State and the Minnesota Corporate Farm Law of Agriculture to comply with the Minnesota Corporate Farm Law.
The LLC can offer one additional level of liability protection by being registered in one of what are referred to as “protective states”. Although the list changes occasionally, some of the protective states include: Alaska, Arizona, Delaware, Nevada, New Jersey, South Dakota, Texas, Virginia and Wyoming. These states have written their LLC statutes to include an additional level of liability protection as long as the LLC members abide by all the statute rules. It is legal to register, for example, your Minnesota farm business in one of these protective states and still operate in Minnesota as you have been. You would need a contact in the state where registered. That contact would establish the entity on your behalf and at year end send you a K-1 form for income and you file your tax return just as you do now. This is a complicated process so seek expert legal help if you decide to develop an LLC in one of the protective states.
Registering with Minnesota Department of Agriculture
For the entities that are required to register with the Minnesota Department of Agriculture for compliance with the Minnesota Corporate Farm Law, this is an annual requirement and there is a $15 fee required to file the documentations. In addition, land held in trust must also register annually with the Minnesota Department of Agriculture for compliance with the Minnesota Corporate Farm Law.
As mentioned, partnerships pay no income taxes. All profit/loss, capital gains and credits are passed through to the partners on a prorated basis, depending upon the percent of ownership. However, the partnership must file a Form 1065 informational tax return, which is due each year by April 15.
Advantages and disadvantages
An advantage over sole proprietorship is that the owners have ownership units or shares. These units or shares can be sold, gifted or passed through an estate as a means of transferring the business over time to the entering generation.
One disadvantage with a partnership, except the LLC, is that the death of a shareholder or willful withdrawal by a partner can seriously disrupt partnership operations. The partnership agreement, if put into place at time of formation of the entity, should clearly describe buy-out provisions or state how the remaining partners are protected, no matter how circumstances change.
Partnership tax laws
Partnership tax laws are similar to individual tax laws. A partnership can generally take over the depreciation schedule of contributed machinery or buildings. A partnership can claim the Section 179 depreciation expense which is passed on pro rata to the partners. Each partner can claim depreciation, which includes his or her portion of the partnership allocation plus any other personal Section 179 depreciation.
Partnership members are self-employed individuals and must pay self-employment tax on their share of earned partnership profits. Partnerships do not receive the favorable tax treatment on fringe benefits (medical, accident and life insurance, housing and meals) as do “C” corporations. However, it generally costs less to form a partnership than a corporation and partnerships can be less formal to operate.
There are two corporation entities available to farm businesses. They are: S corporation and C corporation.
1. S corporation
The S corporation offers a higher level of asset liability protection than a sole proprietorship and some of the partnerships. It must be registered with the Secretary of State in Minnesota. The S corporation is taxed as a pass-through entity with profits allocated to the stock shareholders based upon their ownership percentage. The income then shows up on the shareholders personal income tax. There is no double taxation issue.
Business operating assets can be placed into the S corporation or they can be left out with only the corporate checkbook as part of the corporation operating entity. Placing assets into the corporation is a non-taxable event but getting them out is not. For that reason, it is a general rule of thumb not to place land into the corporation. See your attorney and accountant for advice specific to your situation.
2. C corporation
The C corporation also affords a higher level of asset protection than the sole proprietorship or some of the partnership entities. The C corporation offers longevity to the business because it is technically an entity onto itself with a life of its own. That is, people can enter and leave the C corporation and it continues on without interruption. It also affords many tax advantages regarding deductible expenses.
The C corporation however, can be subject to double taxation. The dividends paid to shareholders are taxed. If the corporation is not growing or acquiring new assets resulting in the corporation retaining earnings, those earnings can be taxed as well. Corporate tax rates are generally higher than other tax rates. Business operating assets can be placed into the C corporation or they can be left out with only the corporate checkbook as part of the corporation operating entity. Placing assets into the corporation is a non-taxable event but getting them out is not. For that reason, it is a general rule of thumb not to place land into the corporation. See your attorney and accountant for advice specific to your situation.
One additional point that applies to both S and C corporations. Shareholders have to maintain an employer-employee relationship with the corporation. If the shareholders maintain personal ownership of what they consider corporate assets, charge corporate business expense against those assets, are audited by the IRS, they may be denied those expense deductions because the assets were owned by the shareholders, not the corporation.
A corporation is established under state law. Each state permits corporations the right to do business. A corporation consists of owners who are called shareholders. The shareholders are the basic decision making group. They elect a board of directors to act for them on most operational decisions. Majority vote governs corporate decisions. Ownership of 51 percent or more of the stock gives you control. Minority shareholders have little if any decision making control unless permitted to do so by the majority shareholders.
Once a corporation is created, it functions much as a self-employed individual might. Corporations must establish their own name and bank accounts. The corporation can become an employer, a lessor or lessee, a buyer or seller, or engage in any other business activity.
Reasons why farms incorporate
- It is easy to transfer shares. Shareholders can gift, sell or pass through an estate, shares to others as they see fit. A majority shareholder can transfer up to 49 percent of the outstanding shares without losing control of the business.
- A corporation may simplify estate settlement in that it may be easier to value shares than individual farming assets.
- Self-employment (SE) tax can sometimes be reduced with a corporate structure. Instead of paying SE tax on all the Schedule F income as a self-employed individual would, the farmer becomes an employee of the corporation and social security taxes are paid only on wages they receive. See your accountant.
- A portion of meals and lodging furnished to employees of a C corporation are generally deductible to the corporation, but not taxable income to the employee. If lodging is provided on the farm and is a condition of employment, the home’s depreciation, heat, electricity and interest become deductible to the corporation. Remember the employer-employee relationship issue.
- Fringe benefits are deductible by C corporations. Health, accident and up to $50,000 of term life insurance is deductible to the corporation, but not taxable to employees.
- The corporation offers perpetual life, some economic efficiencies regarding capital acquisition, and provides income and social security tax flexibility. It can also provide continuation of a farm business through several generations.
Potential concerns related to the corporation
- Getting into a corporation is generally a tax-free event. Getting out is a taxable event. Don’t start a corporation unless you plan to continue it for many years.
- If the C corporation is profitable but is not growing and acquiring new assets, it can be troubled with retained earnings or excess profits. This can result in a tax obligation.
- Corporations have a different set of rules. Corporate meetings, extra record keeping, corporate income tax returns, reporting requirements, and quarterly tax estimates are part of corporate life. Complying with extra legal and regulatory requirements cost time and money each year.
- Minority shareholders have no power in directing the corporate business and can be easily “frozen out.” A majority shareholder (farming heir) can direct that no dividends be paid. Minority (non-farm heirs), may own shares that generate no income, and hence have no practical value.
- Corporate ownership of a house eliminates the use of the exclusion of gain or a sale of personal residence.
- Corporate ownership sometimes reduces independence and individual pride of ownership.
- It can be very difficult for a retired shareholder to receive any retirement income from an operating corporation. This is especially true if the retiree has no rental property, discontinues working for the corporation, and the corporation pays no dividends.
The farm corporation can be a valuable tool in tax planning and in the transfer process. However, it is a major commitment and a complex task to start a farm corporation. Before starting a corporation, make sure it fits your goals, objectives and business personality.
Self-employment tax on land, buildings and facility rent regarding entities
The US Eight Circuit Court of Appeals has ruled that if you are a member of any business entity (such as a partnership or corporation explained above); own land, buildings, or facilities that are outside that entity; and rent those items to the entity; the rental income is exempt for self-employment tax IF the rent is fair and reasonable.
This applies only to those states in the eighth circuit which include Arkansas, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota and South Dakota. With any of these laws, they are subject to change so seek legal advice on this matter.
Discounting business entity assets
An additional strategy that may be useful is the discounting of assets being placed into a business entity, such as any of the partnerships or corporations described earlier.
When you place business assets such as machinery or livestock into the business entity, you can elect to discount those assets. The main reason for discounting assets being placed into the business entity is to reduce the size of an estate in order to get below the federal and perhaps even the state estate applicable exclusion amounts. Doing so will reduce or eliminate any estate tax.
Justification for the discount is based upon lack of marketability of the assets due to a fractional ownership interest.
One disadvantage of discounting is that you have artificially lowered the basis of the assets in the entity. This can be a problem if the entity is discontinued and the assets are sold as a result. This could result in a tax obligation. If the assets are replaced due to use, this is not an issue.
Assets being discounted and placed into an entity should be appraised. If, at a future date, the entity is audited by the IRS, you can document the value of the assets placed into the entity. For machinery and equipment, simply take the depreciation schedule to the local implement or equipment dealer and ask them to put a value on all machinery. Have them put the values in writing on their dealership letterhead along with a signature and date. For livestock you can take a list to a livestock auction facility or someone who deals in livestock and would have a grasp of the values. The values should be put in writing and listed on their letterhead with a signature and date. For land, seek the help of a realtor who deals with ag land. Simply have them do an estimate or appraisal of the land, put it in writing on their letterhead, with a signature and date.
Note: In late 2016, the Internal Revenue Service and the US Treasury Department enacted 2704 rules which drastically changed discounting rules and during which situations they may apply. If assets are transferred and then sold, discounting will definitely not apply. If you are contemplating discounting any assets seek legal and accounting assistance to make sure you are in compliance with 2704 rules.
Business entities and maintaining homestead classification
When using a business entity for ag land ownership, caution must be used in order to maintain eligibility for the Minnesota Qualified Small Business Property Qualified Farm Business Property estate exclusion. In addition, utilizing limited liability companies (LLCs) as a business entity have new rules to comply with due to passage of the Minnesota Revised Uniform Limited Liability Company Act of 2015. The law states the land-owning LLC and its members must be the ones farming the land on behalf of the owner LLC. If the owner LLC rents the land to someone else, even another member of the LLC who then farms it personally, homestead classification is lost and therefore the qualified farm property estate exclusion is also lost. New LLCs must have complied with the new law as of August 1, 2015. Existing LLCs must have complied with the new law by January 1, 2018.
Ag land held in any trust, except a revocable living trust, as well as land in limited partnerships, limited liability limited partnerships, S and C corporations and LLCs must file documentation with the Minnesota Department of Agriculture under the Minnesota Corporate Farm Law in order to be eligible for the qualified farm property exclusion. The application must be done annually and there is a filing fee of $15 per application.
For more details on the Minnesota Homestead Classification requirements see maintaining farm land homestead classification and qualification . This is a complex area and there is a lot at stake regarding the qualified farm property estate exclusion so seek legal advice specific to your situation when establishing any entity that owns ag land.
Farm Service Agency (FSA) payments and business entities
Under the current farm bill, there are some restrictions regarding commodity program payments made to individuals versus entities. Entities that limit member’s liability exposure (all entities except the general partnership) are limited to one maximum payment limit regarding FSA commodity program payments.
This is a complicated issue. If you have any questions or concerns related to your situation, check with your FSA office for details of the program.
Caution: This publication is offered as educational information. It does not offer legal advice. If you have questions on this information, contact an attorney.
Gary Hachfeld, former Extension educator; David Bau, Extension educator and C. Robert Holcomb, Extension educator
Reviewed in 2017
© 2024 Regents of the University of Minnesota. All rights reserved. The University of Minnesota is an equal opportunity educator and employer.
- Report Web Disability-Related Issue |
- Privacy Statement |
- Staff intranet

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a livestock farming business: Cost of breeder chickens, lambs, farrow pigs or calves. Cost of farming equipment and vehicles. Payroll or salaries paid to staff. Business insurance.
Business Overview. Bear Creek Farms is a new livestock farm located just outside of Austin, Texas, near Bear Creek. The company operates a 1000-acre farm that is home to hundreds of pastured cattle, pigs, and sheep. The farm will produce milk, cheese, and meat to sell to grocery stores, restaurants, and individuals located in the Austin area.
Develop A Cattle Farming Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed cattle farming business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
Industry size and growth. Industry size and past growth - The US beef cattle production industry is worth $78.4 billion in 2022 after expanding 0.6% annually the last five years. [1] Growth forecast - The US beef cattle production industry is projected to grow 4.6% in 2022. Number of businesses - In 2022, 813,466 beef cattle production ...
Starting a Livestock Farming Business. When embarking on a livestock farming venture, it is essential to have a well-crafted livestock farming business plan in place. This plan serves as a roadmap for the operation and management of the business, outlining the strategies and actions necessary to achieve your goals.
To get started with a new cattle farm business, you need a proactive business plan in place.Getting some insights into the tricks of the trade can be an excellent way to get a footing on where to start. You can spend some time doing thorough research about the different departments you'd need to take care of for a flourishing Cattle Farm Business.
To draw up a roadmap. A business plan for a cattle farm helps you define your objectives and set goals for the next 3-5 years, which can be incredibly useful for achieving success in the long run. The writing process of a business plan requires careful consideration of all aspects of running your cattle farm, from financial management to sales ...
How To Use Business Plan Template for Livestock Farmers. If you're a livestock farmer and want to create a comprehensive business plan, follow these steps using the Business Plan template in ClickUp: 1. Define your vision and mission. Start by clarifying your vision and mission for your livestock farming business.
Steps. Download Article. 1. Find some paper, a pencil, or a computer with Microsoft Word, One-Note or a similar text program. This will enable you to write or type down everything that comes to your mind, including the goals and aspirations you have for starting up a livestock operation.
The Farm Business Plan Balance Sheet can help gather information for the financial and operational aspects of your plan. Form FSA-2037 is a template that gathers information on your assets and liabilities like farm equipment, vehicles and existing loans. FSA-2037 - Farm Business Plan - Balance Sheet. FSA-2037 Instructions.
The executive summary provides an overview of your livestock farming business plan. It highlights the key elements of your plan, including your objectives, strategies, and financial projections. The executive summary should be concise yet compelling, capturing the reader's attention and providing a glimpse into the potential of your venture.
Realization of objectives. You might realize the objectives you set out to achieve, making it necessary to change tactics if there's nothing more to achieve. Changes in cattle feed crops. You might want to shift from grass-based farming to rearing cows using field forage crops like corn for silage.
We will carefully evaluate and consider all information that you provide before embarking on writing the cattle farming business plan, and this will ensure that it is as comprehensive and detailed as possible. Download Cattle Farming Business Plan Sample in pdf. OGScapital writer specializes business plan themes such as chicken farming business ...
Business Summary. Riverland is currently a small cow/ calf operation with an estimated 50 total calves and cows. The farm sells beef calves to individuals and at the cattle auction. The company is completely operated by the Doe family which entails checking, feeding, giving shots, weaning, tagging, banding, and paperwork.
Beef cattle do not require much maintenance, as just sheltering them is enough. 5. Decide the Purpose of Your Farm. Decide on the type of breed of cattle that you want to farm. The maintenance and budget differ for each breed, so plan accordingly. Most of the time, beginners start it with dairy products or beef.
A Sample Beef Cattle Farming Business Plan Template 1. Industry Overview. The agricultural industry of which livestock farming or better still cattle rearing is a subset of is no doubt among the leading industry in most countries of the world; it is the industry that produce food for the populace and raw materials for industries.
In addition to the cattle farming business plan, you will need a solid management plan. This document should address beef cattle management practices regarding feed, health and nutrition, fencing, housing, and waste. Note: The costs of beef enterprises are often specific for each operation.
This article will outline how to start the cattle production business, and the beef cattle farming business plan - PDF, Word and Excel. Beef cattle farming is a lucrative business project that is providing income for a lot of livestock farmers. There are some important things you need to consider before you setup a beef cattle production ...
Pig farming business plan. Dairy farming business plan. Goat farming business plan. Rabbit farming business plan. Horse breeding business plan. Calf operations business plan. The most common challenge to livestock farmers is earning a high income from their farming business. This challenge is not only confounded to small-scale farmers with ...
How To Download Livestock Farming Business Plan PDF and Doc (With financial analysis) P.S: We can also tailor the business plan to your name, business size, capital requirements, and more to fit your direct needs. Call or message +234 701 754 2853 for inquiries.
The strategic plan talks about how you intend on achieving the goals and objectives of your livestock business plan. This section includes your operational plan, sales and marketing plan as well as your financial plan. An industry analysis is critical for you to develop an effective business strategy. You must also study the agricultural market ...
Transferring the farm business to the next generation can be a daunting task. However, there are strategies and methods that can help simplify the process.When operating as a sole proprietorship, it can be challenging to establish a transition plan. There are many individual assets that need to be accounted for such as machinery, equipment, livestock and land. It is difficult and time ...