
Blog about all things SAP
ERProof » SAP CO » SAP CO Training » SAP Cost Allocation

SAP Cost Allocation
Let us look at a simple example on how cost allocation comes into effect and why it becomes the most integral part of controlling.
CSN Ltd operates as an IT equipment service center for reputed brands across the UK. This company deals with after-sales services including repair and refurbishment services for products like laptops, PC, LCD monitors, etc. CSN Ltd has a division in the UK comprising of departments like Management, Logistics, Warehouse, Service and Quality Control.
Each of the departments has its own mode of operation running daily which incurs significant amount of cost which can be attributed as Direct and also Indirect. CSN management has come out with a strategy on how these costs can be charged to each impacted cost center to come out with the most efficient costing report. This is where cost allocation planning comes to the picture where the company will consider impacted cost centers where costs will be allocated in related proportion. In the allocation planning, amount and quantities will be periodically determined and allocated from sender cost objects (like cost center) to receiver cost objects. In this case, we will be using CSN departments as primary cost centers which will act as both sender and receiver cost objects.
In this tutorial, we will try to understand different cost allocation methods in SAP which a successful organization can adapt in order to get clear insight about its cost accounting report.
- Cost Allocation Cycle
- Cost Allocation – Distribution
- Cost Allocation – Assessment
Basics of SAP Cost Allocation
For a dynamic organization with complex operations where multiple projects / activities are running on daily basis adding up to the company’s profitability, accurate costing flow between related cost objects becomes one of the vital factor to look at when it comes to project based costing. SAP provides the most systematic foundation on how cost allocation process can contribute to the effecting reporting related to cost management.
Let’s take the scenario of CSN Ltd. The following image will give us a good idea on organizational structure of CSN.
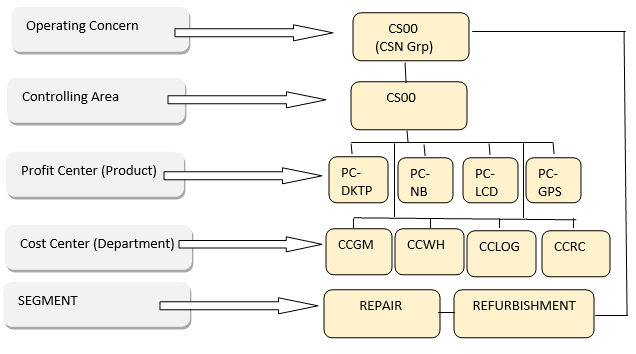
In course of daily operation, various department as given above incur costs which are captured under related cost centers: CCGAM, CCWH, CCLOG, CCRC , CCSERV.
Cost Element Structure
In SAP Cost Allocation process, cost element plays the key role since costs flow from FI direct postings to related cost objects in Controlling . As we know, in Controlling there are two kinds of cost elements .
Primary Cost Element
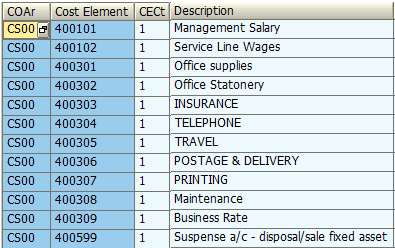
Being directly associated with G/L, it is linking FI and CO via FI direct posting to related cost objects (cost center, internal order, CO-PA object). In SAP, all primary cost elements are categorized as ‘1’ under CS00 controlling area.
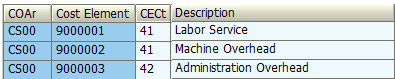
Secondary Cost Elements
These cost elements are maintained based on specific category, so that they can be used for reposting, cost assessment and revenues inside the CO .
CSN has also listed specific cost elements in a form of overheads which need to be used and allocated only within controlling area ‘CS00’ to related cost objects.
In order to cater to the requirement of cost flow across the related cost objects ( FI to CO or within CO ), SAP has come out with unique methods of SAP cost allocation.
What is Cost Allocation in SAP?
Within cost center accounting and overhead cost controlling, allocations plays a vital role enabling the business users to periodically allocate amounts and quantities from sender cost objects to receiver cost objects based on cost center allocation planning and structure. Both actual and planning data can be allocated from sender cost object to receiver cost object in SAP cost allocation process using allocation cycle.
SAP Cost Allocation Methods
Taking the above scenario where primary cost elements and secondary cost elements are listed within a company and there is a requirement of correct cost evaluation from operation perspective, SAP recommends the following two types of Cost Allocation process:
- Distribution – for Primary Cost Element
- Assessment – for Secondary Cost Element
SAP Cost Allocation Method – Distribution
Distribution process is mainly used for allocating the amount and quantities (both plan and actual) of one or more sender cost objects to multiple receiver cost objects. Generally, in this type of SAP cost allocation, debit and credit of amount and quantities between sender cost objects (e.g., cost center) and receiver cost objects takes place under the original primary cost element, which means amount in the primary (original) cost element remains the same as before. Let’s consider the following scenario.
CSN has occupied building which is shared by its department as listed above in the structure. Monthly CSN’s building management incurs rental charges for the building which is stated as primary cost element and it needs to be allocated to various department (maintained as cost centers).
To address this requirement, SAP propose to define distribution process within the system since it is related to allocation of costs incurred within primary cost elements.
In SAP, there is customizing related to calculation of both actual and planning overhead rates. On the following screenshot, rates of overhead are related to planning. On the basis of these rates, overhead is allocated.
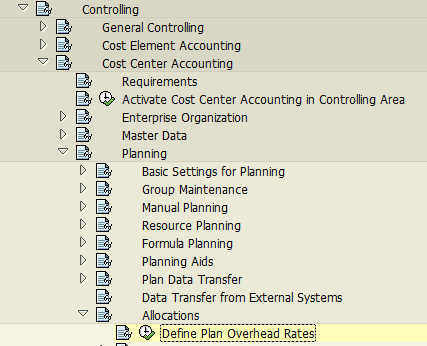
In the following windows, there are multiple options to plan overhead rate.
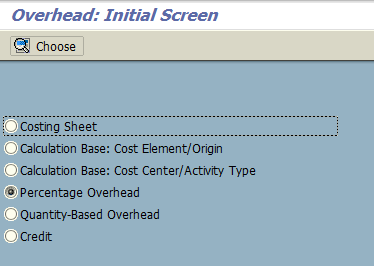
For overhead cost allocation, there are three things we need to maintain as we are in the phase of planning:
- Calculation Base: Cost Elements / Origin
- Calculation Base: Cost Center / Activity Type
- Percentage Overhead
The reason we choose the above options is because for all sorts of allocations methods, a calculation base is required both for cost elements and cost centers. We need percentage rate to be planned for related overheads on the basis of which cost allocation will be carried on.
Now, let’s go back to the scenario where we have to allocate building rental costs of CSN group. We need to first put the related cost element / cost center as the calculation base for CSN rental cost.
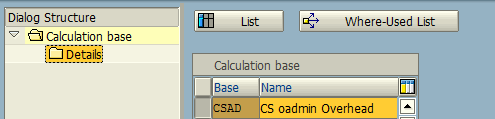
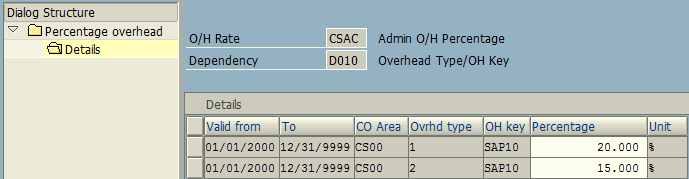
Choose the option “Calculation Base: Cost Elements / Origin” and click “New Entries” button. Then, create a new calculation base for CSAD: CS Admin Overhead.
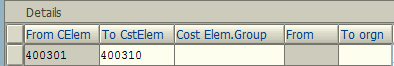
Under the CSN’s controlling area CS00, update the following cost element (Admin O/H) rate as calculation base.
Now, go back to the initial screen and choose the option “Calculation Base: Cost Center / Activity Type”. Create new entries and update the related cost center in this allocation planning.
Finally, choose the option “Percentage Overhead”. In this option, we need to plan the percentage rate at which the CSN Admin Overhead will be allocated.
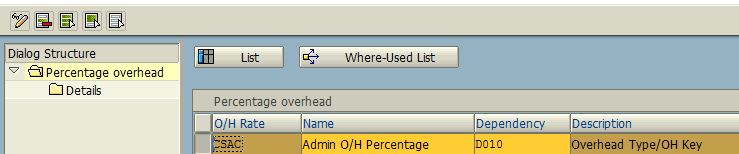
Click Details tab and update Validity Period, Rate of Percentage, Controlling Area, etc.
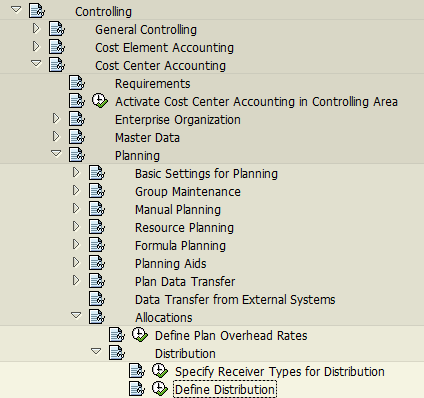
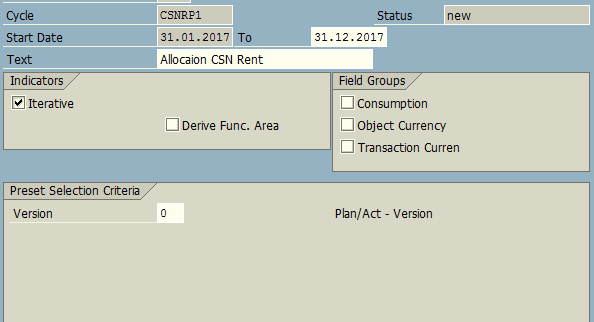
Define Distribution Cycle
We need to define a Distribution Cycle (with a specific naming convention containing up to 6 digits), e.g. CSNRP1.
IMG -> Controlling -> Cost Center Accounting -> Planning -> Allocations -> Distribution -> Define Distribution
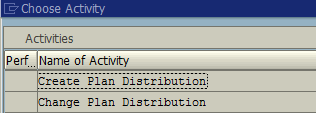
In the next screen, we will choose the option “Create Plan Distribution”.
Choose controlling area CS00.
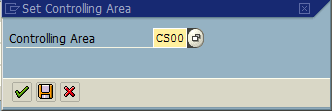
Next, create a Distribution Cycle (transaction KSV1 ).
Within the distribution cycle we need to attach a segment consisting of the details of sender and receiver cost centers and cost allocation percentage.
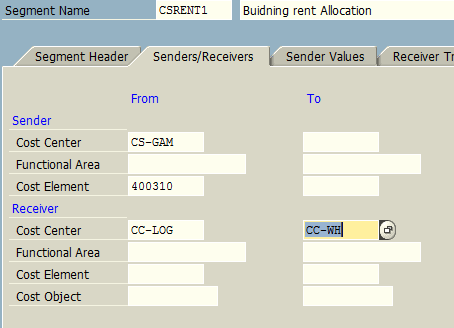
We maintain the following under Senders/Receivers tab:
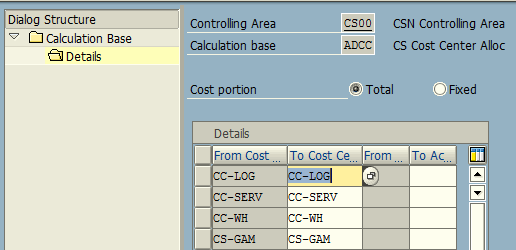
- Sender cost center: CS-GAM
- Receiver cost centers: CC-LOG (Logistics), CC-WH (Warehouse), CC-SERV (Service Center)
Under Receiver Tracing Factor tab, we specify cost element 400310 – Building Rent which needs to be allocated to the receiving cost centers. Finally, under Receiver Weighing Factor tab, we maintain the receiver cost center and the allotted percentage at which rent cost will be allocated as primary cost element.
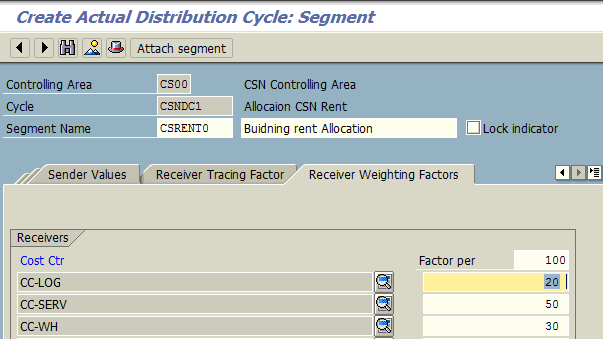
After saving the segment, we can save the distribution cycle.
Execute Distribution Cycle (Transaction KSV5)
This activity is carried out during the period end closing. All distribution cycles are generally executed in order to fulfill the accomplishment of primary cost allocations like the above scenario where CSN rent cost is allocated to receiver cost centers CC-LOG, CC-WH, and CC-SERV based on the percentage allotted in the distribution cycle.
Enter the following data in KSV5 transaction:
- Period: 02 to 12 (Cost allocation will be performed according to the period stated in the distribution cycle)
- Select distribution cycle within the validitiy period
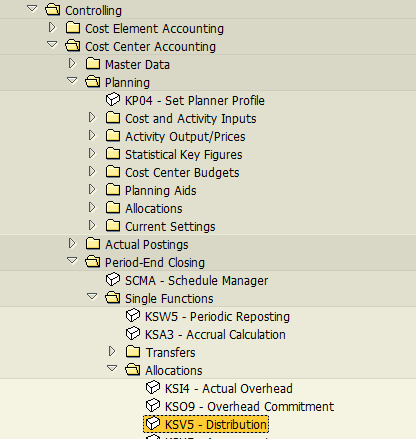
Once executed the system will display the following screen (see below). The screen displays the cycle structure: sender cost center of CSN building rental.
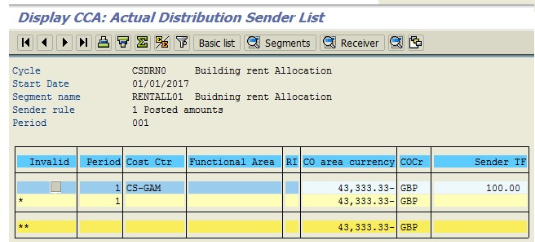
The following screenshot tells how CSN building rental cost is allocated to receiver cost centers CC-LOG, CC-SERV, and CC-WH.
SAP Cost Allocation Method – Assessment
In this method, internal SAP cost allocation is performed based on both primary and secondary cost elements. For example, during product costing we use assessment method to allocate the internal cost from a production cost center to a related production order.
This method is about grouping multiple cost elements and reclassifying them under a secondary cost element.
Process Prerequisites
Create assessment cost element (secondary) and specify receiver types for assessment where we can specify which table fields are active and whether a single value, an interval, or a group can be entered for these fields. You make these settings per controlling area and separately for plan and actual data respectively.
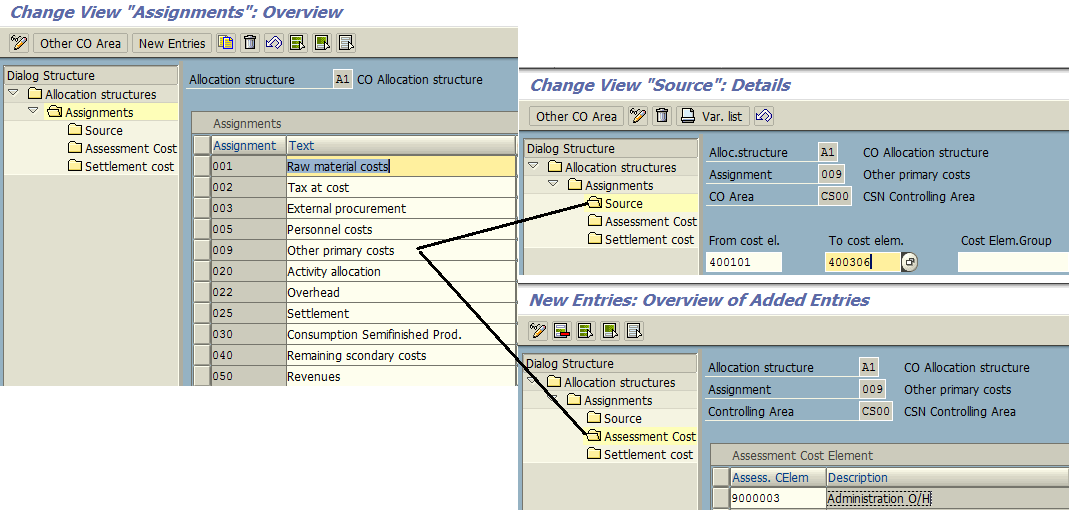
Allocation Structure
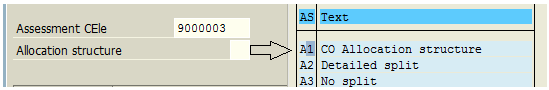
Process related to cost allocation via assessment usually requires predefined settings comprising of segment containing a source cost element being assigned to desired assessment cost elements. The whole setup gives the formation of the allocation structure which can be used during assessment cycle definition instead of an assessment cost element in the segment. Usage of allocation structure during assessment cycle setup is always optional and depends on the business scenario.
In SAP system, allocation structure is defined under the following path:
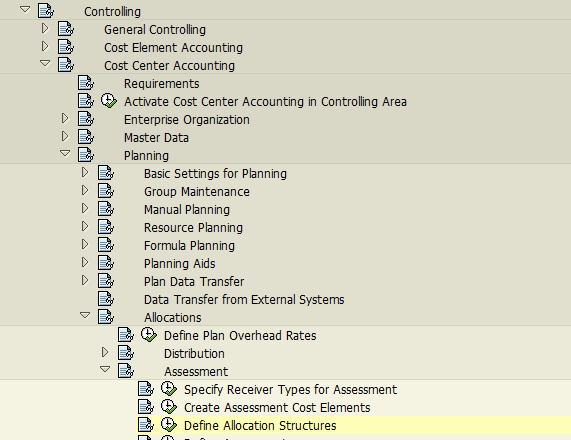
New allocation structures can be created as demonstrated below where we will assign a source cost element and assessment cost element and save the settings.
Now, coming back to SAP cost allocation process with assessment method, where cost is allocated using the assessment cost element which generally wipes out the traceability of original cost element at the time when cost is getting allocated from a sender cost center to a receiver cost center. Finally, when the process completes, assessment of cost elements gets updated in both sender and receiver cost centers.
Allocation process continues with creation of plan assessment (transaction KSU7 ) under controlling area CS00.
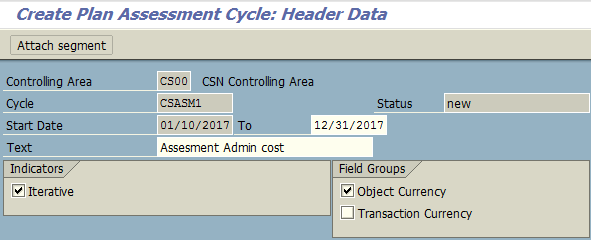
Next, you should assign the secondary cost element, specify sender rules and receiver tracing factor. In many cases, cost assessment can use the allocation structure instead which already consists of allocation rules of sender and receiver. In SAP, that is optional.
In Sender/Receiver tab, we also assign the sender and receiver values (preferably, cost centers and cost element).
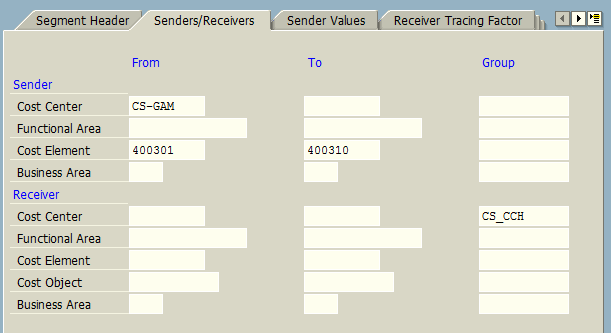
In the Receiver Tracing Factor tab, we provide the list of cost elements. In this example, we selected all cost elements related to administration expenses.
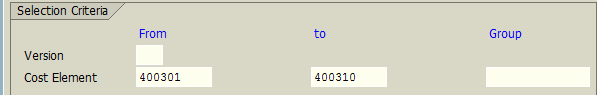
Finally, in the Receiver Weighting Factors tab, we will input the percentage of cost allocation for the related cost receivers. Percentages are generally based on a client’s discretion considering how much indirect cost can be allocated between cost receivers (to each department).
After all the necessary settings, an assessment cycle is saved. Once the assessment cycle is in place, we can use the transaction code KSUB for execution of Plan/Actual assessment as per requirements. The process of execution is the same as for the transaction code KSV5 – Execute Distribution Cycle.
The above screen shows how administration costs are allocated to related cost centers using assessment method of SAP cost allocation based on charging cost through secondary cost element as defined above.
Did you like this tutorial? Have any questions or comments? We would love to hear your feedback in the comments section below. It’d be a big help for us, and hopefully it’s something we can address for you in improvement of our free SAP CO tutorials.
Navigation Links
Go to next lesson: SAP Indirect Activity Allocation
Go to previous lesson: SAP Periodic Reposting
Go to overview of the course: Free SAP CO Training
7 thoughts on “SAP Cost Allocation”
Hello, One question, I don’t arrive to do the link between cost center receiver and cost element assessment for the method assessment cost allocation. I explain, for me in the last step, the screenshoot should show costs under cost assessment element define in the assessment plan? I am wrong ? Or I have miss one step for my understanding?
What is a purpose of cost center CS_CCH? because it appears nowhere, same for cost element assessment 9000003 Administration O/H
Best Regards
Dear Diomande, During assessment he uses cost center group CS_CCH in receiver, it is nothing but the group created for cost centers CC-LOG, CC-SERV, CC-WH, i.e. you have both options either enter cost center range or enter cost center group. Cost Center group is a better option in my opinion because here you can create a group for selected cost centers only.
In assessment the cost will be captured on secondary cost element 9000003, see how: first the cost from multiple cost elements (400301 to 400310) that are defined as sender will be collected on the secondary cost element 9000003 (that is defined as receiver), Now cost for allocation among different cost centers (from sender CS-GAM to receiver CS_CCH) is collected under 9000003, and this will be allocated. When it is allocated, the information of original cost element is lost, because the cost is already collected on 9000003 and this secondary cost element will be used for allocation i.e. same will appear in Debit/credit entries.
I hope, the above explanation is worth reading for you. 🙂 BR MJ
On the 2nd half of your explanation, when you say the information of the original cost is lost, what i understand is that if i use Tcode S_ALR_87013611 to open cost center admin overhead, the debit part will show the value of cost elements 400301 to 400310 while the Credit part will show cost element 9000003 with the value collected from the multiple cost elements (400301 to 400310) instead of showing each cost element 400301 to 400310 is being credited. Is that correct ?
Could you clarify more on the difference between Assessment and Distribution Allocation? like can distribution do the same function as assessment and vice versa? and when we would want to use one but not the other ?
You understood correctly (part 2).
Without going into complexities, the primary difference between Assessment & Distribution are as follows: 1) Assessment is used when we do not required the original sender information i.e. fewer records e.g. all cost collected on 90000003 (can be from multiple cost centers) and then allocated to CS_CCH.
writing few record = better performance 🙂 (in general)
2) if you need sender information in doc. as well , you can use distribution
Another difference is distribution can allocate primary cost while the assessment can allocate both primary & secondary.
In the ERProof “SAP Cost Allocation” tutorial, in the “SAP Cost Allocation Method – Assessment” section it indicates that you want to move a cost from a production cost center to a related production order, but it appears later that it is actually moving the cost to a different cost center. Is it possible to allocate a cost from a cost center to a production order?
Hi all; I have an Assessment cycle where the segments were setup as: Sender Rule Poste Amounts / Plan value origin and the Receiver rule is fix percentages. When I ran the cycle; even I saw $$ in actuals and also in plan; the cycle posted cero values, instead the amount recorded in planned module. I already tried to find the root cause without luck. Any comment will be appreciatte.
HI all, May i ask also a simple question for you GURU? How should i do if I when to run a cycle at year end closing, with the total value of the cost centers and proportion given ones per year? Thank you Loo
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Do you have a question and want it to be answered ASAP? Post it on our FORUM here --> SAP FORUM !
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Knowledge Base
SAP Cost Allocation
- Created 2021-09-19
- Author SAP Online Tutorials
- Category SAP CO
Welcome to the SAP cost allocation tutorial. In every organization, there are costs involved in various departments. In this tutorial, we will discuss how these costs can be allocated across different SAP cost objects like cost center or internal order and help to create a cost analysis report.
Let us look at a simple example on how cost allocation comes into effect and why it becomes the most integral part of controlling.
CSN Ltd operates as an IT equipment service center for reputed brands across the UK. This company deals with after-sales services including repair and refurbishment services for products like laptops, PC, LCD monitors, etc. CSN Ltd has a division in the UK comprising of departments like Management, Logistics, Warehouse, Service and Quality Control.
Each of the departments has its own mode of operation running daily which incurs significant amount of cost which can be attributed as Direct and also Indirect. CSN management has come out with a strategy on how these costs can be charged to each impacted cost center to come out with the most efficient costing report. This is where cost allocation planning comes to the picture where the company will consider impacted cost centers where costs will be allocated in related proportion. In the allocation planning, amount and quantities will be periodically determined and allocated from sender cost objects (like cost center) to receiver cost objects. In this case, we will be using CSN departments as primary cost centers which will act as both sender and receiver cost objects.
In this tutorial, we will try to understand different cost allocation methods in SAP which a successful organization can adapt in order to get clear insight about its cost accounting report.
- Cost Allocation Cycle
- Cost Allocation – Distribution
- Cost Allocation – Assessment
Basics of SAP Cost Allocation
For a dynamic organization with complex operations where multiple projects / activities are running on daily basis adding up to the company’s profitability, accurate costing flow between related cost objects becomes one of the vital factor to look at when it comes to project based costing. SAP provides the most systematic foundation on how cost allocation process can contribute to the effecting reporting related to cost management.
Let’s take the scenario of CSN Ltd. The following image will give us a good idea on organizational structure of CSN.
In course of daily operation, various department as given above incur costs which are captured under related cost centers: CCGAM, CCWH, CCLOG, CCRC , CCSERV.
Cost Element Structure
In SAP Cost Allocation process, cost element plays the key role since costs flow from FI direct postings to related cost objects in Controlling. As we know, in Controlling there are two kinds of cost elements.
PRIMARY COST ELEMENT
Being directly associated with G/L, it is linking FI and CO via FI direct posting to related cost objects (cost center, internal order, CO-PA object). In SAP, all primary cost elements are categorized as ‘1’ under CS00 controlling area.
SECONDARY COST ELEMENTS
These cost elements are maintained based on specific category, so that they can be used for reposting, cost assessment and revenues inside the CO.
CSN has also listed specific cost elements in a form of overheads which need to be used and allocated only within controlling area ‘CS00’ to related cost objects.
In order to cater to the requirement of cost flow across the related cost objects ( FI to CO or within CO ), SAP has come out with unique methods of SAP cost allocation.
What is Cost Allocation in SAP?
Within cost center accounting and overhead cost controlling, allocations plays a vital role enabling the business users to periodically allocate amounts and quantities from sender cost objects to receiver cost objects based on cost center allocation planning and structure. Both actual and planning data can be allocated from sender cost object to receiver cost object in SAP cost allocation process using allocation cycle.
SAP Cost Allocation Methods
Taking the above scenario where primary cost elements and secondary cost elements are listed within a company and there is a requirement of correct cost evaluation from operation perspective, SAP recommends the following two types of Cost Allocation process:
- Distribution – for Primary Cost Element
- Assessment – for Secondary Cost Element
SAP Cost Allocation Method – Distribution
Distribution process is mainly used for allocating the amount and quantities (both plan and actual) of one or more sender cost objects to multiple receiver cost objects. Generally, in this type of SAP cost allocation, debit and credit of amount and quantities between sender cost objects (e.g., cost center) and receiver cost objects takes place under the original primary cost element, which means amount in the primary (original) cost element remains the same as before. Let’s consider the following scenario.
CSN has occupied building which is shared by its department as listed above in the structure. Monthly CSN’s building management incurs rental charges for the building which is stated as primary cost element and it needs to be allocated to various department (maintained as cost centers).
To address this requirement, SAP propose to define distribution process within the system since it is related to allocation of costs incurred within primary cost elements.
In SAP, there is customizing related to calculation of both actual and planning overhead rates. On the following screenshot, rates of overhead are related to planning. On the basis of these rates, overhead is allocated.
In the following windows, there are multiple options to plan overhead rate.
For overhead cost allocation, there are three things we need to maintain as we are in the phase of planning:
- Calculation Base: Cost Elements / Origin
- Calculation Base: Cost Center / Activity Type
- Percentage Overhead
The reason we choose the above options is because for all sorts of allocations methods, a calculation base is required both for cost elements and cost centers. We need percentage rate to be planned for related overheads on the basis of which cost allocation will be carried on.
Now, let’s go back to the scenario where we have to allocate building rental costs of CSN group. We need to first put the related cost element / cost center as the calculation base for CSN rental cost.
Choose the option “Calculation Base: Cost Elements / Origin” and click “New Entries” button. Then, create a new calculation base for CSAD: CS Admin Overhead.
Under the CSN’s controlling area CS00, update the following cost element (Admin O/H) rate as calculation base.
Now, go back to the initial screen and choose the option “Calculation Base: Cost Center / Activity Type”. Create new entries and update the related cost center in this allocation planning.
Finally, choose the option “Percentage Overhead”. In this option, we need to plan the percentage rate at which the CSN Admin Overhead will be allocated.
Click Details tab and update Validity Period, Rate of Percentage, Controlling Area, etc.
DEFINE DISTRIBUTION CYCLE
We need to define a Distribution Cycle (with a specific naming convention containing up to 6 digits), e.g. CSNRP1.
IMG -> Controlling -> Cost Center Accounting -> Planning -> Allocations -> Distribution -> Define Distribution
In the next screen, we will choose the option “Create Plan Distribution”.
Choose controlling area CS00.
Next, create a Distribution Cycle (transaction KSV1 ).
Within the distribution cycle we need to attach a segment consisting of the details of sender and receiver cost centers and cost allocation percentage.
We maintain the following under Senders/Receivers tab:
- Sender cost center: CS-GAM
- Receiver cost centers: CC-LOG (Logistics), CC-WH (Warehouse), CC-SERV (Service Center)
Under Receiver Tracing Factor tab, we specify cost element 400310 – Building Rent which needs to be allocated to the receiving cost centers. Finally, under Receiver Weighing Factor tab, we maintain the receiver cost center and the allotted percentage at which rent cost will be allocated as primary cost element.
After saving the segment, we can save the distribution cycle.
EXECUTE DISTRIBUTION CYCLE (TRANSACTION KSV5)
This activity is carried out during the period end closing. All distribution cycles are generally executed in order to fulfill the accomplishment of primary cost allocations like the above scenario where CSN rent cost is allocated to receiver cost centers CC-LOG, CC-WH, and CC-SERV based on the percentage allotted in the distribution cycle.
Enter the following data in KSV5 transaction:
- Period: 02 to 12 (Cost allocation will be performed according to the period stated in the distribution cycle)
- Select distribution cycle within the validitiy period
Once executed the system will display the following screen (see below). The screen displays the cycle structure: sender cost center of CSN building rental.
The following screenshot tells how CSN building rental cost is allocated to receiver cost centers CC-LOG, CC-SERV, and CC-WH.
SAP Cost Allocation Method – Assessment
In this method, internal SAP cost allocation is performed based on both primary and secondary cost elements. For example, during product costing we use assessment method to allocate the internal cost from a production cost center to a related production order.
This method is about grouping multiple cost elements and reclassifying them under a secondary cost element.
Process Prerequisites
Create assessment cost element (secondary) and specify receiver types for assessment where we can specify which table fields are active and whether a single value, an interval, or a group can be entered for these fields. You make these settings per controlling area and separately for plan and actual data respectively.
Allocation Structure
Process related to cost allocation via assessment usually requires predefined settings comprising of segment containing a source cost element being assigned to desired assessment cost elements. The whole setup gives the formation of the allocation structure which can be used during assessment cycle definition instead of an assessment cost element in the segment. Usage of allocation structure during assessment cycle setup is always optional and depends on the business scenario.
In SAP system, allocation structure is defined under the following path:
New allocation structures can be created as demonstrated below where we will assign a source cost element and assessment cost element and save the settings.
Now, coming back to SAP cost allocation process with assessment method, where cost is allocated using the assessment cost element which generally wipes out the traceability of original cost element at the time when cost is getting allocated from a sender cost center to a receiver cost center. Finally, when the process completes, assessment of cost elements gets updated in both sender and receiver cost centers.
Allocation process continues with creation of plan assessment (transaction KSU7 ) under controlling area CS00.
Next, you should assign the secondary cost element, specify sender rules and receiver tracing factor. In many cases, cost assessment can use the allocation structure instead which already consists of allocation rules of sender and receiver. In SAP, that is optional.
In Sender/Receiver tab, we also assign the sender and receiver values (preferably, cost centers and cost element).
In the Receiver Tracing Factor tab, we provide the list of cost elements. In this example, we selected all cost elements related to administration expenses.
Finally, in the Receiver Weighting Factors tab, we will input the percentage of cost allocation for the related cost receivers. Percentages are generally based on a client’s discretion considering how much indirect cost can be allocated between cost receivers (to each department).
After all the necessary settings, an assessment cycle is saved. Once the assessment cycle is in place, we can use the transaction code KSUB for execution of Plan/Actual assessment as per requirements. The process of execution is the same as for the transaction code KSV5 – Execute Distribution Cycle.
The above screen shows how administration costs are allocated to related cost centers using assessment method of SAP cost allocation based on charging cost through secondary cost element as defined above.
Was this article helpful?
Related articles, leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- SAP Training Blog ›
Introduction to Universal Cost Allocation in S/4HANA
.png)
by Daniel Mateo

With this functionality, just a few Fiori Apps are used to perform the allocations of cost centers, profit centers, and margin analysis considering both actual and plan records. Indeed, financial and Controlling allocations are built in one architecture using the core tables for Universal Journal actual line items (ACDOCA) and plan items (ACDOCP).
Challenges Associated With Traditional Cost Allocations
With the traditional cost allocation processes, organizations face some challenges. Mainly they are related to difficulties to understand their allocation cycles and the resultant cost flows, struggling to explain them to the relevant stakeholders. Also, there is a lack of traceability to analyze the cost allocated compared to the actual cost invoiced; without having granular visibility at the reporting level.
In addition, the organizations are managing uncertainty in current times having dynamic and complex processes. That may lead to difficulties to define the desired scenarios in allocation cycles and without having tools to simulate possible financial effects of changed allocation rules on their financial data. Also, the execution of the allocation processes and reporting may take long runtime.
Please refer to the image below for further challenges:
Main Benefits
The new Universal Cost Allocation functionality in SAP S/4HANA reduces the number of transactions to run the cost allocations compared to previous versions. It is needed to run just a few Fiori Apps , that are user friendly and having guided procedures and validations to make the user more confident with the tool.
In addition, it provides a simplified data model by removing a handful of core tables which in return reduces the database size significantly. Besides, significant benefits are listed in the image below:
Features
Universal Cost Allocation offers several features and capabilities to make easier the cost allocation processes, and the related reporting and analysis performed to make business decisions. Customers can quickly identify the possible financial effects of changed allocation rules on their financial data.
The solution can perform allocations for actual data and plan data, providing simulation capabilities with the definition of predictive ledgers. It also offers user-friendly reporting built-in Fiori with the capability to analyze the records in multiple currencies.
Refer to the image below for further features:
However, the new solution does not cover the following allocation processes that require to keep using the original transactions in SAP GUI system:
- Direct activity allocations
- Template allocations
- Settlements of internal orders or WBS Elements
Key Processes and Fiori Apps
Universal Cost Allocation allows you the creation and execution of the following type of allocation cycles using the same Fiori Apps for all of them.
- Distribution : Reallocate primary costs from one or more cost centers to other cost centers or WBS elements, or profit centers to other profit centers. The allocation credits and debits the objects using the original G/L accounts, so it makes more sense for fewer senders
- Overhead Allocations : Similar to distributions, for primary and secondary costs. Instead of debiting and crediting the original G/L account, a secondary cost account with category 42 is used. It can be useful when the original account is not so important or multiple senders.
- Top-Down Distribution : New term for account-based profitability analysis. Used for costs such as freight/insurance at a generic level, such as company code, customer group, or product group, and then want to do a top-down distribution to a more specific profit segment level. It is available on SAP S/4HANA 1909 FPS01 release or newer.
The Fiori Apps to perform the allocation processes are listed in the picture below:
- Manage Allocation App : Enable you to maintain the allocation cycles and their corresponding segments to allocate and distribute primary and secondary costs from one object to one or many others. You can search for specific allocation cycles or filter the allocation cycles by various criteria, ensuring that the assigned rules are accurate.
- Run Allocations App: Perform a test run or actual run of any existing allocation cycle and then display the details of the completed runs. You can also reverse a completed run.
- Allocation Results App: View the results of allocation runs, for both test runs and live runs. You can analyze any errors or warnings that occurred. It is available on SAP S/4HANA 1909 FPS01 release or newer.
- Allocation Flow App: Display a visual flow of senders and receivers for an allocation and the respective debit and credit amounts. It is an ongoing improvement for SAP S/4HANA 2020 .
- Organize Allocations App: Identify and maintain the allocation cycles collectively according to specific filter criteria. It is an application that will be available in future releases.
- Allocation Tags App: Create and assign allocation tags. Assign the tags to allocation cycles in order to simplify the management of your allocation cycles. It is an application that will be available in future releases.
- Import Statistical Key Figure Plan Data App: Upload statistical key figure plan data from a comma-separated values file (CSV file). A statistical key figure is a number providing information about non-monetary data assigned to cost centers. For instance: number of employees, number of computers, building surface... Statistical key figures can be used as a reference for universal cost allocation.
- Manage Statistical Key Figures App : Modify and display the statistical key figures available in the system according to specific filter criteria. It is also possible to create and copy statistical key figures as master data elements.
The next post in this 2 part blog series will be an overview of Cost Allocations . It will dive into a deeper look at one of the key functions and processes within Universal Cost Allocation in S/4HANA.
More Blogs by Daniel Mateo

Statistical Key Figures and Reporting in Universal...
This is the third and final blog in a series of three about Universal ...
by Daniel Mateo
May 05, 2021
Posted in SAP

A Look At Cost Allocations in SAP S/4HANA
This is the second blog in a series of three about ...
April 27, 2021
Group Reporting Process Flow in S/4HANA
This is the final part of a three-series blog discussing Group Reporti...
April 12, 2021
Related Blogs
A Look at Main Configuration and Master Data Elements...
This is the second blog in a series of three about SAP Group Reporting...

This is the third and final blog in a series of three about Universal Cost...

We offer thousands of SAP courses and real-world SAP sandboxes for individuals and corporate teams.
Support: [email protected]
Sales: [email protected]
+1 (415) 360-6249
- Success Stories
- Become an Affiliate
- Become an Instructor
- Scholarships
- Search Entire Website
- SAP Transaction Codes
- SAP Error Messages
- Authenticate Certificate

Have Questions?
Get In Touch.
Training License Required
Analyzing Overhead Allocation Cycles
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
- Describe the allocation cycle logic in SAP S/4HANA
Allocation Cycles
There are cost postings that are relevant for management accounting, but identifying the correct controlling account assignment at the time of posting is difficult. Postings such as telephone costs, postage costs, insurance, and so on, are entered as they arise in financial accounting. The accountant initially posts to an auxiliary cost center created specifically for collecting specific costs. This way, instead of splitting the initial posting into as many cost line items as there are relevant cost centers, the accountant makes a single cost entry.
In management accounting, special allocation cycles are configured for distribution or allocation of auxiliary cost postings. The cycles contain segments, each of which details a sender/receiver relationship. First, the sender rules are defined: Which cost centers and accounts send which values with which cost account. Then, you define the receiver rules: to which cost centers and which values to each cost center.
When you run the allocation cycles periodically, the auxiliary cost center is credited as a sender and the receiver cost centers are debited according to their defined cost share.
In the figure below, you can see these points illustrated, together with more details about the allocation rule definitions:
In overhead cost allocations, the original primary and secondary G/L accounts are not used to credit the sender and debit the receiver. Instead, the costs on both sides are transferred through a secondary cost G/L account with cost element category 42 (assessment).
Statistical Key Figures and Receiver Weighting Factors
In the animation below, you will see how you can further manipulate the values allocated to receivers through the application of weighting factors on statistical key figures:
Executing the Cycle Run
After setting up all your allocation cycles, you run them at the end of each fiscal period after all financial postings are completed.
Depending on the number and complexity of the allocation cycles, there are various ways to process them:
Log in to track your progress & complete quizzes
Mastering Cost Center Allocation in SAP: Best Practices and Strategies
Introduction.
Cost center allocation is a crucial component of financial management in SAP, which is used by many businesses worldwide. Proper cost center allocation helps organizations accurately allocate costs to various departments and business units, enabling them to make informed financial decisions. In this article, we will explore the best practices, strategies, and challenges of cost center allocation in SAP , along with solutions to overcome these challenges.

Understanding Cost Center Allocation in SAP
Cost center allocation in SAP refers to the process of allocating costs incurred by a department or business unit to a specific cost center. This is done by assigning a percentage or amount of the costs to the cost center. Cost center allocation is necessary to ensure that costs are accurately and equitably distributed among departments and business units. Some key terms and concepts related to cost center allocation in SAP include:
- Cost center: A cost center is a unit within an organization that incurs costs, such as a department or a specific project.
- Allocation cycle: The allocation cycle refers to the period during which costs are allocated to cost centers, such as a month, quarter, or year.
- Allocation basis: The allocation basis is the method used to determine the amount of costs to be allocated to a cost center. This could be based on headcount, square footage, or other relevant factors.
- Activity type: An activity type is a classification of a specific activity or process within a cost center.
There are several types of cost center allocations in SAP, including direct allocations, indirect allocations, and statistical key figures.
Best Practices for Cost Center Allocation in SAP
To ensure accurate cost center allocation in SAP, businesses should follow best practices, such as:
- Accurate and Timely Data Entry: Accurate data entry is critical for proper cost center allocation. It is essential to ensure that all data entered into SAP is accurate, complete, and timely.
- Consistency in Allocation Methodology: To ensure consistency in cost center allocation, organizations should develop standard allocation methodologies that are consistently applied across all departments and business units.
- Monitoring and Tracking Cost Center Allocations: Regular monitoring and tracking of cost center allocations are essential to identify discrepancies or inaccuracies and take corrective action.
- Use of Automated Processes: Automation can help improve the efficiency and accuracy of cost center allocation in SAP. Using automated tools and processes can reduce errors, save time, and improve overall accuracy.
Strategies for Effective Cost Center Allocation in SAP
Some strategies for effective cost center allocation in SAP include:
- Aligning Cost Center Allocation with Organizational Goals: The allocation of costs should align with the organization’s overall goals and objectives. This helps ensure that cost center allocation supports the organization’s strategic initiatives.
- Use of Cost Center Hierarchies: SAP enables the use of cost center hierarchies to better organize and manage cost center allocations. The use of hierarchies can provide a more granular view of costs and facilitate more accurate cost center allocation.
- Incorporating Forecasting and Budgeting: Incorporating forecasting and budgeting into the cost center allocation process can help organizations better plan and allocate costs for the future. It can also help identify potential cost savings opportunities.
- Collaborating with Other Departments: Collaboration between departments can help ensure that shared costs are properly allocated. It is essential to establish clear communication channels to facilitate collaboration and ensure that all departments are aware of cost center allocation processes.
Challenges in Cost Center Allocation in SAP
Despite the benefits of cost center allocation in SAP, there are several challenges that organizations may face, including:
- Inaccurate Data Entry and Lack of Consistency: Inaccurate data entry and lack of consistency in allocation methodologies can lead to inaccurate cost center allocation.
- Manual Allocation Processes Leading to Errors and Inefficiencies: Manual allocation processes can be time-consuming and prone to errors, leading to inefficiencies in the cost center allocation process.
- Difficulty in Identifying Relevant Allocation Bases: Identifying the appropriate allocation basis for each cost center can be challenging, especially when costs are shared across multiple departments.
- Difficulty in Managing Complex Allocation Scenarios: Complex allocation scenarios, such as those involving shared services or joint ventures, can be challenging to manage and allocate accurately.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges in Cost Center Allocation in SAP
To overcome these challenges, organizations can implement several solutions, including:
- Data Validation: Regular data validation can help identify inaccuracies in data entry, ensuring that only accurate data is used for cost center allocation.
- Automation of Allocation Processes: Automation can reduce errors and increase efficiency in the allocation process, freeing up resources for other tasks.
- Use of Advanced Allocation Methodologies: Advanced allocation methodologies, such as activity-based costing, can help identify more accurate allocation bases and improve the accuracy of cost center allocation.
- Collaborative Approach: Collaboration between departments can help identify and resolve complex allocation scenarios, ensuring that costs are allocated accurately and equitably.
Cost center allocation is a critical component of financial management in SAP. Proper cost center allocation ensures that costs are accurately and equitably distributed among departments and business units, enabling organizations to make informed financial decisions. By following best practices, implementing effective strategies, and overcoming common challenges, organizations can improve the accuracy and efficiency of cost center allocation in SAP, leading to better financial outcomes.
About Enteros
Enteros UpBeat is a patented database performance management SaaS platform that helps businesses identify and address database scalability and performance issues across a wide range of database platforms. It enables companies to lower the cost of database cloud resources and licenses, boost employee productivity, improve the efficiency of database, application, and DevOps engineers, and speed up business-critical transactional and analytical flows. Enteros UpBeat uses advanced statistical learning algorithms to scan thousands of performance metrics and measurements across different database platforms, identifying abnormal spikes and seasonal deviations from historical performance. The technology is protected by multiple patents, and the platform has been shown to be effective across various database types, including RDBMS, NoSQL, and machine-learning databases.
The views expressed on this blog are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the opinions of Enteros Inc. This blog may contain links to the content of third-party sites. By providing such links, Enteros Inc. does not adopt, guarantee, approve, or endorse the information, views, or products available on such sites.
Are you interested in writing for Enteros’ Blog? Please send us a pitch!
RELATED POSTS
Revolutionizing database management: enteros upbeat’s impact on organizational efficiency and performance.
- Software Engineering
In today’s data-driven world, the effective management of databases is paramount for organizational success. Enteros UpBeat stands at the forefront of…
Continue Reading
Elevating Database Performance: The Power of Enteros UpBeat in Driving Efficiency and Innovation
- Database Performance Management
Introduction: In the ever-evolving landscape of database management, organizations require robust solutions to optimize performance and foster innovat…
Empowering Data-Driven Excellence: Enteros UpBeat Revolutionizes Database Management
- 26 April 2024
Enteros UpBeat is a patented database performance management SaaS platform that helps businesses identify and address database scalability and perform…
Revolutionizing Database Management: Enteros UpBeat Leads the Way to Efficiency and Innovation
- Programming
- Admin & EIM
- BI & BW
- FICO & BPC
- CRM & Sales
- Introductions
- SAP PRESS Subscription
From EasyABC to SAP PaPM: a Journey of Corporate Cost Allocation

In a world where controllable cost is used for performance management, the allocation of corporate overhead in determining full cost is still necessary for product costing and segment reporting for footnote disclosures to the financial statements.
This is a question with an answer that often eludes finance and accounting professionals: how to handle corporate cost allocation? SAP Profitability and Performance Management (PaPM) is a viable option to facilitate management and financial reporting because of its traceability.
My History of Activity-Based Costing
Before coming to discover and utilize SAP solutions, I (Alvin) started working with activity-based costing (ABC) in 1999 to resolve a fundamental issue that a client had in regard to preventing cost distortion when allocating corporate overhead. We conducted extensive interviews of all departments under the corporate umbrella to understand the underlying headquarter functions. The insight gained from the interviews would help determine an appropriate cost driver and overall methodology to allocate corporate cost.
Using a desktop application called EasyABC by Oros, I developed my first model by setting up a simple organizational and general ledger hierarchy, and applied allocation percentages to drive resource costs to activities and then to cost objects. After delivering our findings, the client ultimately realized that the largest headquarters’ cost, executive compensation, drove the outcome of the results. It was then determined that the most reasonable resource driver was one that could correlate the time the executive spent with the subsidiary or affiliate—in this case, aviation flight logs.
Fast forward 20 years and after working in both the oil & gas and manufacturing industries, I have come full circle and back to utilizing the same basic management accounting concept to provide performance management and financial accounting reports to facilitate proper and informed decision making. The main difference today, compared to back then, is the level of granularity and traceability available using PaPM.
Discovering SAP PCM
I have been working with the SAP Profitability and Cost Management (PCM) solution since 2015, and the tool has come a long way to provide clarity on how costs are being allocated. SAP PCM has the capability of expressing values in the form of tabular reports or grids by selecting the required dimensions and referencing underlying system tables.
The shortcoming with SAP PCM was the need to aggregate responsibility centers and simplify line items, because the combination of all the required dimensions put a lot of calculation load on the CPU processing architecture and RAM memory. This is because the SAP PCM application was written to utilize only 64 logical CPUs, which was plenty at the time (SAP Note 1918921), but allows the use of a limited-number dimension combination. I was restricted by SAP PCM system limitations in the development of detailed and comprehensive models. Therefore, I had to limit my analysis, for example, to the top 200 organization entities and top 30 general ledger cost categories for the models to function, let alone for the calculations to complete.
Getting Started with SAP PaPM
SAP recognized that more functionality was desired by customers and rolled out PaPM. In 2019, we ran our pilot PaPM project; there were no longer any limits on dimensions (column fields) and table size (row records). With PaPM, we could deliver the most granular level of detail while also providing aggregated results, all without taking a performance hit. These calculations utilize the SAP S/4HANA in-memory computing capability, giving us traceability for every available value.
This traceability starts with the function configuration and then graphically through the visual modeler. The results can then be expressed visually using tables or through graphs. The calculation can be validated and available to be audited at each step of the process; this was a challenge using SAP PCM because you had to know which internal table or grid could show the desired results, and it required considerable system resources for traceback for example.
SAP PaPM facilitates a natural progression in the development of analytical and visualization tools which was not possible before the advent of in memory computing. In a way, SAP PaPM complements my experience with SAP PCM because I am able to draw on a library of SAP PCM allocation functions. SAP PaPM has additional promising capabilities to allow an analyst to run what-if scenarios without having to extract data from the original data source into a spreadsheet, but be able to leverage the tool’s capabilities to do this. Even though the double entry accounting and activity-based costing has not changed, the application of these concepts with the level of detail now available with SAP PaPM provides a powerful combination in delivering sound insight to management.
Learn more about project planning for SAP PaPM here .
My journey with SAP PaPM is just beginning, but I am looking forward to utilizing more of its integrated capabilities like what-if simulations for decision support and approval workflows to drive process accountability. Perhaps these will lead to additional blog posts on these topics in the future. Be sure to subscribe to SAP PRESS’ weekly blog recap so that you can be notified when any new posts become available. I welcome your comments below, especially from anyone who was in my original ABC training class at Vero Beach, Florida from the Culinary Institute of America.
Recommendation

Get your SAP S/4HANA Finance configuration right the first time! Whether you’re running a new implementation or transitioning from SAP ERP, this comprehensive guide walks you through each project task. Start by setting up an organizational structure and defining global master data. Next, follow step-by-step instructions organized by functional area: general ledger, AP, AR, controlling, margin analysis, predictive accounting, and more. Your new system awaits!
Alvin Tolentino graduated from the Univ. of St. Thomas in Houston with an MBA in Finance and MSc in Accounting. He started his professional career in 1997 with the Ernst & Young (EY) Houston office, then worked as a Dell badged employee from 2004 in Austin before being called home and worked to modernize the accounting function at Mitsubishi Caterpillar Forklift America (MCFA) from 2008 to 2012. He is currently working for a national oil company delivering innovative planning and reporting solutions. Michael Mkpadi is a certified SAP consultant who has worked on over 40 SAP Enterprise Performance Management (SAP EPM) and data analytics projects, including SAP PaPM spanning multiple industries. He has more than 12 years of experience designing and building SAP Business Planning and Consolidation and SAP Profitability and Cost Management solutions at the enterprise level.
Latest Blog Posts

Drilldown Reporting with the SAP S/4HANA Material Ledger
Lessons Learned from an SAP PaPM Implementation
The official sap press blog.
As the world’s leading SAP publisher, SAP PRESS’ goal is to create resources that will help you accelerate your SAP journey. The SAP PRESS Blog is designed to provide helpful, actionable information on a variety of SAP topics, from SAP ERP to SAP S/4HANA. Explore ABAP, FICO, SAP HANA, and more!
SAP Blog Topics
- Administration
- Business Intelligence
Blog curated by
- Legal Notes
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- Guest Posting
US House Democrats Voted To Give 'Illegal Immigrants' New Representation in Elections?
Various posts repeated stephen miller's claim that this was "invasion by design.", anna rascouët-paz, published may 10, 2024.
On May 8, 2024, Stephen Miller, former adviser to 2024 U.S. Republican presidential candidate (and former president) Donald Trump, claimed on X that U.S. House Democrats had voted to give Electoral College representation to undocumented immigrants ( archived ):
His post, viewed nearly 61 million times and liked 32,000 times as of this writing, was reshared by X owner Elon Musk, who added an emoji indicating agreement ( archived ):
This post had received 58 million views as of this writing.
The Gateway Pundit ( archived ), a far-right online publication known for its amplification of conspiracy theories, added more to the claim (emphasis theirs):
House Democrats on Wednesday night voted unanimously to give illegal aliens – including Joe Biden's 11 million illegal border crossers – representation in Congress and the Electoral College. Democrats continue to put Americans and American workers in line behind alien invaders.
Many readers appeared to take Miller's post to mean that with the passage of H.R. 7109, Democrats gave "new rights" to undocumented immigrants, and worried about the legality of the move:

( archived )
Others, contrasting Miller's words with the table he posted, worried that in fact Republicans were responsible for passing H.R. 7109 ( archived ):
But that phrasing of the claim obfuscated the fact that Democrats unanimously voted against the bill, the wording of which actually removes representation of undocumented immigrants and legal non-citizen residents in the U.S. Census. In other words, they voted to keep existing U.S. Census rules in place, under which those non-citizens were already represented, based on a principle the U.S. Supreme Court affirmed in 2019.
Bill H.R. 7109
On May 8, the U.S. House of Representatives voted on bill H.R. 7109 , sponsored by Rep. Chuck Edwards, a Republican from North Carolina. The bill aimed to add a question to the U.S. Census, which occurs every 10 years, asking respondents whether they are U.S. citizens. Edwards said in a news release on his website that the goal of the bill was "to protect America's democracy and electoral integrity by making sure that only American citizens are counted when apportioning congressional seats and, consequently, Electoral College votes."
As Miller correctly pointed out, the bill passed the House with a vote split along political party lines. Republicans voted unanimously in favor of it, while Democrats voted unanimously against it. The bill was unlikely to pass the U.S. Senate, where Democrats hold a slim majority. The White House also said it "strongly" opposed the bill :
H.R. 7109 would increase the cost of conducting the census and make it more difficult to obtain accurate data. It would also violate the Fourteenth Amendment of the Constitution, which requires that the number of seats in the House of Representatives "be apportioned among the several States according to their respective numbers, counting the whole number of persons in each State ..."
'Protect Electoral Integrity'?
Every 10 years, the U.S. Census has a constitutional mandate to count residents — as opposed to citizens — in every U.S. state. Article 1, section 2 of the U.S. Constitution reads (emphasis ours):
Representatives and direct Taxes shall be apportioned among the several States which may be included within this Union, according to their respective Numbers, which shall be determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service for a Term of Years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three fifths of all other Persons.
The total number of residents in any given state is what determines the number of representatives in the U.S. House, as well as in the Electoral College. This means that states with the most residents get the most U.S. representatives and the most electors in the Electoral College . For example, the two states with the most electors in 2024 were California, with 54 electors, and Texas, with 40 electors.
The Republicans' bill would change this, ensuring that the number of representatives and electors is proportional not to the overall population of a state, but to the population of citizens . Democrats voted to maintain the system as it was mandated by the U.S. Constitution. Critics have argued that such a change would cause respondents to feel intimidated, resulting in population undercounting and unreliable data.
Critics also suspect that such a change would tip the electoral balance towards Republicans, allowing them to draw electoral maps in favor of their candidates and hurting the representation of more diverse communities.
It is important to note that, by law, only U.S. citizens are allowed to vote in federal elections.
This is not the first time Republicans attempted to add a citizenship question to the decennial census. In 2019, the U.S. Supreme Court blocked the Trump administration's attempt to change then 2020 census in a 5-4 decision, saying the reasoning behind it was "contrived" (read full decision ).
Breaking: House Democrats Vote UNANIMOUSLY to Give Illegal Aliens Representation in Congress and the Electoral College | The Gateway Pundit | by Jim Hoft . 9 May 2024, https://web.archive.org/web/20240509121941/https://www.thegatewaypundit.com/2024/05/breaking-house-democrats-vote-unanimously-give-illegal-aliens/.
'Distribution of Electoral Votes'. National Archives , 19 Sept. 2019, https://www.archives.gov/electoral-college/allocation.
Edwards, Chuck. Equal Representation Act . H.R. 7109, https://www.congress.gov/bill/118th-congress/house-bill/7109.
House of Representatives Passes Edwards' Bill to Only Include U.S. Citizens in Congressional Representation | Congressman Chuck Edwards . 8 May 2024, http://edwards.house.gov/media/press-releases/house-representatives-passes-edwards-bill-only-include-us-citizens.
'READ: Supreme Court Ruling on 2020 Census Citizenship Question | CNN Politics'. CNN , 27 June 2019, https://www.cnn.com/2019/06/27/politics/read-supreme-court-ruling-2020-census-citizenship-case/index.html.
Rep. Fleischmann Votes to Add Citizenship Question to Census and End Counting of Illegal Aliens for Congressional Representation and Electoral College Votes | Congressman Chuck Fleischmann . 8 May 2024, http://fleischmann.house.gov/media/press-releases/rep-fleischmann-votes-to-add-citizenship-question-to-census-and-end-counting-of-illegal-aliens-for-congressional-representation-and-electoral-college-votes.
STATEMENT OF ADMINISTRATION POLICY . Executive Office of the President, 6 May 2024, https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/SAP-HR7109.pdf.
Sullivan, Ariane de Vogue, Kate. 'Supreme Court Blocks 2020 Census Citizenship Question | CNN Politics'. CNN , 27 June 2019, https://www.cnn.com/2019/06/27/politics/census-supreme-court/index.html.
U.S. Constitution, Article 1 . https://constitution.congress.gov/constitution/article-1/.
Washington, U. S. Capitol Room H154, and DC 20515-6601 p:225-7000. 'Roll Call 193 Roll Call 193, Bill Number: H. R. 7109, 118th Congress, 2nd Session'. Office of the Clerk, U.S. House of Representatives , 8 May 2024, https://clerk.house.gov/Votes/2024193.
By Anna Rascouët-Paz
Anna Rascouët-Paz is based in Brooklyn, fluent in numerous languages and specializes in science and economic topics.
Article Tags
Asking the better questions that unlock new answers to the working world's most complex issues.
Trending topics
AI insights
EY Center for Board Matters
EY podcasts
EY webcasts
Operations leaders
Technology leaders
EY helps clients create long-term value for all stakeholders. Enabled by data and technology, our services and solutions provide trust through assurance and help clients transform, grow and operate.
EY.ai - A unifying platform
Strategy, transaction and transformation consulting
Technology transformation
Tax function operations
Climate change and sustainability services
EY Ecosystems
EY Nexus: business transformation platform
Discover how EY insights and services are helping to reframe the future of your industry.
Case studies
How Mojo Fertility is helping more men conceive
26-Sep-2023 Lisa Lindström
Strategy and Transactions
How a cosmetics giant’s transformation strategy is unlocking value
13-Sep-2023 Nobuko Kobayashi
How a global biopharma became a leader in ethical AI
15-Aug-2023 Catriona Campbell
We bring together extraordinary people, like you, to build a better working world.
Experienced professionals
EY-Parthenon careers
Student and entry level programs
Talent community
At EY, our purpose is building a better working world. The insights and services we provide help to create long-term value for clients, people and society, and to build trust in the capital markets.
Press release
Extreme E and EY publish Season 3 report, recording 8.2% carbon footprint reduction as female-male performance gap continues to narrow
09-Apr-2024 Michael Curtis
EY announces acceleration of client AI Business Model adoption with NVIDIA AI
20-Mar-2024 Barbara Dimajo
EY announces launch of artificial intelligence platform EY.ai following US$1.4b investment
13-Sep-2023 Rachel Lloyd
No results have been found
Recent Searches

How do you steady the course of your IPO journey in a changing landscape?
EY Global IPO Trends Q1 2024 provides insights, facts and figures on the IPO market and implications for companies planning to go public. Learn more.
How can the moments that threaten your transformation define its success?
Leaders that put humans at the center to navigate turning points are 12 times more likely to significantly improve transformation performance. Learn More.

Artificial Intelligence
EY.ai - a unifying platform
Select your location
close expand_more
EY announces alliance with SAP Fioneer to help deliver broad and large-scale financial transformations
Press contact

Assistant Director, Media Relations and Social Media Ecosystems, Ernst & Young LLP
- Send e-mail to Barbara Dimajo
- Open LinkedIn profile of Barbara Dimajo
Related topics
- Develops insurance and banking industry cloud solutions
- Offers detailed financial transformations that include managed services
- Shares information on future projects, services and implementation and transformation strategies
The EY organization today announces an alliance between SAP Fioneer, a world-class software solution provider for financial services, and EY ifb SE to help facilitate software selection, business transformation, training and change management in the financial services industry.
With new tech-enabled market entrants to the financial services industry, the need to roll out large-scale financial transformations in the next decade is expected to increase. In addition, the modernization of finance functions continues to impact customers and clients. The EY–SAP Fioneer Alliance will help develop flexible commercial business models and industry-specific cloud solutions like the EY organization’s global insurance industry cloud initiative.
The EY–SAP Fioneer Alliance focuses on banking and insurance solutions and offerings for the CFO in areas such as financial products subledger, financial control, insurance collections and disbursements and sustainability solutions.
Daniel Ruschmeier, EY–SAP Fioneer Alliance Leader at EY ifb SE, says:
“Through the EY–SAP Fioneer Alliance, EY teams are positioned to continue help strengthen the financial landscape through market finance transformations and industry cloud solutions. Furthermore, the established working relationships between SAP Fioneer’s global team and EY teams serve as a catalyst in the Alliance’s focus on joint solutions, implementations and engagements.”
Christian Jaeger, SAP Fioneer Global Partner Management, says:
“Collaborations are a key component of SAP Fioneer’s DNA, and the EY-SAP Fioneer Alliance builds on years of successful work together on joint customer projects. We are committed to working closely with EY teams to bring about sustainable and impactful change in the financial services industry.”
For more information, visit ey.com/alliances.
EY exists to build a better working world, helping to create long-term value for clients, people and society and build trust in the capital markets.
Enabled by data and technology, diverse EY teams in over 150 countries provide trust through assurance and help clients grow, transform and operate.
Working across assurance, consulting, law, strategy, tax and transactions, EY teams ask better questions to find new answers for the complex issues facing our world today.
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients. Information about how EY collects and uses personal data and a description of the rights individuals have under data protection legislation are available via ey.com/privacy. EY member firms do not practice law where prohibited by local laws. For more information about our organization, please visit ey.com.
This news release has been issued by EYGM Limited, a member of the global EY organization that also does not provide any services to clients.
About SAP Fioneer
SAP Fioneer was launched in 2021 as a joint venture between global technology leader SAP and entrepreneurial investor Dediq to become the world’s leading provider of financial services software solutions and platforms. With a broad ecosystem of partners, over 800 financial services customers and more than 1,000 employees, SAP Fioneer is a global business present in 17 countries across Europe, North and Latin America, Middle East and Asia-Pacific.
By combining the speed and agility of a start-up with the proven capabilities of a best-in-class software company, SAP Fioneer enables banks, insurance companies and challengers to run, transform and grow while meeting their need for speed, scalability, and cost-efficiency through digital business innovation, cloud technology, and solutions that cover banking and insurance processes end-to-end.
Related news

EY launches OpsChain Contract Manager solution to support secure private business agreements on public Ethereum
LONDON, April 17, 2024 – The EY organization today announces the launch of EY OpsChain Contract Manager (OCM), a transformative blockchain-enabled solution for contract management. EY OCM helps enterprises to execute complex business agreements, supporting confidentiality, helping improve time efficiency, and achieving cost reduction, with automatic adherence to the agreed terms.
EY and Saïd Business School study reveals that leaders prioritizing a human-centered approach to transformation turning points are up to 12x more successful
LONDON,16 April 2024. The EY organization’s latest research with Saïd Business School, at the University of Oxford, reveals new insights into what happens when a transformation program’s leadership believes a transformation has or will go off-course and intervenes with the intent of improving its performance (turning points).

LONDON, 9 APRIL 2024. Extreme E has published its third Sustainability Report, compiled, and produced in collaboration with EY. Continuing to race the series’ ODYSSEY 21 off-road electric vehicles and leveraging solar and green hydrogen energy, the report reveals that the racing series maintained its carbon-neutral status and reduced its overall carbon footprint by 8.2%.

Major shift in global IPO market share from the past five years
London, 28 March 2024. The year kicked off on a cautiously optimistic note, marked by a selective thaw following a quieter period. The Americas and EMEIA IPO markets had a bright start in 2024, increasing global proceeds. However, the Asia-Pacific region started on a weak note, weighing down the overall global volume.

EY announces 18 women entrepreneurs selected for the EY Entrepreneurial Winning Women™ Asia-Pacific class of 2024
HONG KONG, 27 MARCH 2024 — The EY organization today announces the details of 18 female entrepreneurs selected for the EY Entrepreneurial Winning Women™ Asia-Pacific class of 2024 — a bespoke executive program that identifies and champions a select group of high-potential entrepreneurs who have built profitable companies and provides them with connections and resources needed to unlock their potential and sustainably scale their companies.

LONDON, 20 March 2024. The EY organization today announces Ernst & Young LLP (EY US) will help clients implement and accelerate their artificial intelligence (AI) journeys using NVIDIA’s industry-leading technology and solutions.

- Connect with us
- Our locations
- Legal and privacy
- Open Facebook profile
- Open X profile
- Open LinkedIn profile
- Open Youtube profile
EY refers to the global organization, and may refer to one or more, of the member firms of Ernst & Young Global Limited, each of which is a separate legal entity. Ernst & Young Global Limited, a UK company limited by guarantee, does not provide services to clients.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Welcome to the SAP cost allocation tutorial. In every organization, there are costs involved in various departments. In this tutorial, we will discuss how these costs can be allocated across different SAP cost objects like cost center or internal order and help to create a cost analysis report.. Let us look at a simple example on how cost allocation comes into effect and why it becomes the ...
Activities can be entered in the cost center or business process. For some business processes or activity types, you can determine for each cost center the amount of activities carried out. You can then use indirect activity allocation to distribute these posted activity quantities from the cost centers or business processes to the receivers.
These costs should have been allocated to the "General Administration" cost center. In this case you can use manual allocation to make the necessary adjustments. You should proceed as follows: 1. Manually allocate the heating costs of 1,000 USD again, this time, however, negative, from the "Energy" cost center to the trade fair order. 2.
Manual Cost Allocation; Cost Center Accounting (CO-OM-CCA) 6.0 EHP3 Latest. Available Versions: 6.0 EHP8 Latest ; 6.0 EHP7 Latest ; 6.0 EHP6 on HANA Latest * 6.0 EHP6 Latest ; 6.0 EHP5 Latest ; ... If you do not have an SAP ID, you can create one for free from the login page. Log on
Select the allocation type, and choose Go. Select your cycle. In the Create a new run window, check the selection of the cycle. Choose Test Run or Run depending on whether you want to affect the actual data or not. In the Run Allocation window, if needed, complete the Run name and the timeframe. Choose OK.
To cost activities, enter the cost center to which the activity types have been assigned. The cost center must be defined in the controlling area. The controlling area is specified via the plant. Note. Keep in mind that the cost center to which you want to assign a resource must already exist in the system. If you want to assign the resource to ...
Generally, in this type of SAP cost allocation, debit and credit of amount and quantities between sender cost objects (e.g., cost center) and receiver cost objects takes place under the original primary cost element, which means amount in the primary (original) cost element remains the same as before. Let's consider the following scenario.
The necessity to allocate data regularly arises during closure. SAP S/4HANA offers a solution, universal allocation, which is a comprehensive term covering all forms of allocations.The tool encompasses multiple capacities for both financial and managerial allocations, including cost center allocation, profit center allocation, top-down distribution, intercompany allocation, and also allocation ...
To configure an allocation structure that can be used in allocation cycles (overhead allocation or intercompany allocation), you perform the following steps: Using the Manage your solution app, in the Application area Finance, Sub Application area Overhead Cost Management, configuration step 2-Maintain Allocation Structures:
This is the second blog in a series of three about Universal Cost Allocation in SAP S/4HANA. This blog details the Cost Allocations process as part of the Universal Cost Allocation functionality. The screenshots are based on the SAP S/4HANA 1909 release. Cost Allocations. Cost Allocations create allocation cycles with their respective segments ...
Universal Cost Allocation is the new simplified functionality in SAP S/4HANA to allocate and distribute cost periodically from one controlling object to one or more others. For example, the costs incurred at a cost center that provided services for other cost centers can be transferred to these cost centers with defined rules.
This video will guide you how to allocate cost in sap fico, what is cost allocation in sap. How to assign & assess cost center in sap.Subscribe our channel f...
In the figure below, you can see these points illustrated, together with more details about the allocation rule definitions: In overhead cost allocations, the original primary and secondary G/L accounts are not used to credit the sender and debit the receiver. Instead, the costs on both sides are transferred through a secondary cost G/L account ...
Sample Content for Simple Cost Allocation Management PUBLIC 9 3 Simple Cost Allocation Management in Detail Simple Cost Allocation Management is an important task for every enterprise in the industry. It enables them to optimize profitability and minimize costs by providing deep insights into granular
Some key terms and concepts related to cost center allocation in SAP include: Cost center: A cost center is a unit within an organization that incurs costs, such as a department or a specific project. Allocation cycle: The allocation cycle refers to the period during which costs are allocated to cost centers, such as a month, quarter, or year. ...
Universal allocation helps you manage and perform various overhead allocation and distribution tasks for different allocation contexts, like cost centers for...
Material Cost Estimate Release View. Update Inventory Costs View. Production Lots - Overhead Absorption View. WIP Clearing View. GR/IR Clearing View. Material Cost Accumulation View. FIFO Cost Determination View. Actual Cost Rollup View. Actual Cost Allocation View.
I have been working with the SAP Profitability and Cost Management (PCM) solution since 2015, and the tool has come a long way to provide clarity on how costs are being allocated. SAP PCM has the capability of expressing values in the form of tabular reports or grids by selecting the required dimensions and referencing underlying system tables.
On May 8, 2024, Stephen Miller, former adviser to 2024 U.S. Republican presidential candidate (and former president) Donald Trump, claimed on X that U.S. House Democrats had voted to give ...
LONDON, 30 April 2024. The EY organization today announces an alliance between SAP Fioneer, a world-class software solution provider for financial services, and EY ifb SE to help facilitate software selection, business transformation, training and change management in the financial services industry.