- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
- How to Use Your Business Plan Most Effectively
- The Basics of Writing a Business Plan
- 12 Reasons You Need a Business Plan
- The Main Objectives of a Business Plan
- What to Include and Not Include in a Successful Business Plan
- The Top 4 Types of Business Plans
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Presenting Your Business Plan in 10 Slides
- 6 Tips for Making a Winning Business Presentation
- 12 Ways to Set Realistic Business Goals and Objectives
- 3 Key Things You Need to Know About Financing Your Business
- How to Perfectly Pitch Your Business Plan in 10 Minutes
- How to Fund Your Business Through Friends and Family Loans and Crowdsourcing
- How to Fund Your Business Using Banks and Credit Unions
- How to Fund Your Business With an SBA Loan
- How to Fund Your Business With Bonds and Indirect Funding Sources
- How to Fund Your Business With Venture Capital
- How to Fund Your Business With Angel Investors
- How to Use Your Business Plan to Track Performance
- How to Make Your Business Plan Attractive to Prospective Partners
- Is This Idea Going to Work? How to Assess the Potential of Your Business.
- When to Update Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Management Team Section to Your Business Plan
- How to Create a Strategic Hiring Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary That Sells Your Idea
- How to Build a Team of Outside Experts for Your Business
- Use This Worksheet to Write a Product Description That Sells
- What Is Your Unique Selling Proposition? Use This Worksheet to Find Your Greatest Strength.
- How to Raise Money With Your Business Plan
- Customers and Investors Don't Want Products. They Want Solutions.
- 5 Essential Elements of Your Industry Trends Plan
- How to Identify and Research Your Competition
- Who Is Your Ideal Customer? 4 Questions to Ask Yourself.
- How to Identify Market Trends in Your Business Plan
- How to Define Your Product and Set Your Prices
- How to Determine the Barriers to Entry for Your Business
- How to Get Customers in Your Store and Drive Traffic to Your Website
- How to Effectively Promote Your Business to Customers and Investors
- What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan
- How to Make a Balance Sheet
- How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
- How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
- How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Manufacturers
- What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan
- How to List Personnel and Materials in Your Business Plan
- The Role of Franchising
- The Best Ways to Follow Up on a Buisiness Plan
- The Best Books, Sites, Trade Associations and Resources to Get Your Business Funded and Running
- How to Hire the Right Business Plan Consultant
- Business Plan Lingo and Resources All Entrepreneurs Should Know
- How to Write a Letter of Introduction
- What To Put on the Cover Page of a Business Plan
- How to Format Your Business Plan
- 6 Steps to Getting Your Business Plan In Front of Investors

How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan Your income statement shows investors if you are making money. Here's everything you'll need to create one.
By Eric Butow • Oct 27, 2023
Key Takeaways
- An income statement is your business's bottom line: your total revenue from sales minus all of your costs.
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
This is part 2 / 11 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 5: Organizing Operations and Finances series.
Financial data is always at the back of the business plan, but that doesn't mean it's any less important than up-front material such as the description of the business concept and the management team. Astute investors look carefully at the charts, tables, formulas, and spreadsheets in the financial section because they know that this information is like the pulse, respiration rate, and blood pressure in a human being. It shows the condition of the patient. In fact, you'll find many potential investors taking a quick peek at the numbers before reading the plan.
Related: How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
Financial statements come in threes: income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Taken together they provide an accurate picture of a company's current value, plus its ability to pay its bills today and earn a profit going forward. This information is very important to business plan readers.
Why You Need an Income Statement
In his article, How to Do a Monthly Income Statement Analysis That Fuels Growth , Noah Parsons writes: "In short, you use your income statement to fuel a greater analysis of the financial standing of your business. It helps you identify any top-level issues or opportunities that you can then dive into with forecast scenarios and by looking at elements of your other financial documentation.
Related: How to Make a Balance Sheet
You want to leverage your income statement to understand if you're performing better, worse or as expected. This is done by comparing it to your sales and expense forecasts through a review process known as plan vs actuals comparison. You then update projections to match actual performance to better showcase how your business will net out moving forward."
What Is In an Income Statement
An income statement shows whether you are making any money. It adds up all your revenue from sales and other sources, subtracts all your costs, and comes up with the net income figure, also known as the bottom line.
Related: How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
Income statements are called various names—profit and loss statement (P&L) and earnings statement are two common alternatives. They can get pretty complicated in their attempt to capture sources of income, such as interest, and expenses, such as depreciation. But the basic idea is pretty simple: If you subtract costs from income, what you have left is profit.
To figure out your income statement, you need to gather a bunch of numbers, most of which are easily obtainable. They include your gross revenue, which is made up of sales and any income from interest or sales of assets; your sales, general, and administrative (SG&A) expenses; what you paid out in interest and dividends, if anything; and your corporate tax rate. If you have those, you're ready to go.
Related: Tips and Strategies for Using the Balance Sheet as Your Franchise Scorecard
Sales and Revenue
Revenue is all the income you receive from selling your products or services as well as from other sources such as interest income and sales of assets.
Gross Sales
Your sales figure is the income you receive from selling your product or service. Gross sales equals total sales minus returns. It doesn't include interest or income from sales of assets.
Interest and Dividends
Most businesses have a little reserve fund they keep in an interest-bearing bank or money market account. Income from this fund, as well as from any other interest-paying or dividend-paying securities they own, shows up on the income statement just below the sales figure.
Related: How to Measure Franchise Success With Your Income Statement
Other Income
If you finally decide that the branch office out on County Line Road isn't ever going to turn a decent profit, and you sell the land, building, and fixtures, the income from that sale will show up on your income statement as "other income." Other income may include sales of unused or obsolete equipment or any income-generating activity that's not part of your main line of business.
Costs come in all varieties—that's no secret. You'll record variable costs, such as the cost of goods sold, as well as fixed costs—rent, insurance, maintenance, and so forth. You'll also record costs that are a little trickier, the prime example being depreciation.
Related: How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold, or COGS, includes expenses associated directly with generating the product or service you're selling. If you buy smartphone components and assemble them, your COGS will include the price of the chips, screen, and other parts, as well as the wages of those doing the assembly. You'll also include supervisor salaries and utilities for your factory. If you're a solo professional service provider, on the other hand, your COGS may amount to little more than whatever salary you pay yourself and whatever technology you may use for your business.
Related: My Company Hears Hundreds of Pitches Every Year — Here's What Investors Are Actually Looking For.
Sales, General, and Administrative Costs
You have some expenses that aren't closely tied to sales volume, including salaries for office personnel, salespeople compensation, rent, insurance, and the like. These are split out from the sales-sensitive COGS figure and included on a separate line.
Depreciation
Depreciation is one of the most baffling pieces of accounting wizardwork. It's a paper loss, a way of subtracting over time the cost of a piece of equipment or a building that lasts many years even though it may get paid for immediately.
Related: 10 Mistakes to Avoid When Pitching Investors (Infographic)
Depreciation isn't an expense that involves cash coming out of your pocket. Yet it's a real expense in an accounting sense, and most income statements will have an entry for depreciation coming off the top of pretax earnings. It refers to an ongoing decrease in asset value.
If you have capital items that you are depreciating, such as an office in your home or a large piece of machinery, your accountant will be able to set up a schedule for depreciation. Each year, you'll take a portion of the purchase price of that item off your earnings statement. Although it hurts profits, depreciation can reduce future taxes.
Paying the interest on loans is another expense that gets a line all to itself and comes out of earnings just before taxes are subtracted. This line doesn't include payments against the principal. Because these payments result in a reduction of liabilities—which we'll talk about in a few pages in connection with your balance sheet—they're not regarded as expenses on the income statement.
Related: How to Craft a Business Plan That Will Turn Investors' Heads
The best thing about taxes is that they're figured last, on the profits that are left after every other thing has been taken out. Tax rates vary widely according to where your company is located, how and whether state and local taxes are figured, and your special tax situation. Use previous years as a guidepost for future returns. If you are just opening your business, work carefully with your accountant to set up a system whereby you can pay the necessary taxes at regular intervals.
Buzzword: EBIT
EBIT stands for earnings before interest and taxes. It is an indicator of a company's profitability, calculated as revenue minus expenses, excluding tax and interest.
Related: Don't Make This Huge Mistake on Your Financial Model
Important Plan Note
Don't confuse sales with receipts. Your sales figure represents sales booked during the period, not necessarily money received. If your customers buy now and pay later, there may be a significant difference between sales and cash receipts.
More in Write Your Business Plan
Section 1: the foundation of a business plan, section 2: putting your business plan to work, section 3: selling your product and team, section 4: marketing your business plan, section 5: organizing operations and finances, section 6: getting your business plan to investors.
Successfully copied link
Income Statement Template
Your business plan should include a three-year forecast of your income statement..
Refer to the sample income statement in the tab below while reviewing this section as a guideline or income statement template for your own business. The income statement shows revenue and expenses, usually by month. At the bottom, total expenses are subtracted from total revenue to arrive at Net Ordinary Income—which is essentially profit, though in an actual business there will be some accounting and tax adjustments made to arrive at true profit. That’s why profit is often referred to as “the bottom line.” Your business plan should include a three-year forecast of your income statement. Here’s a closer look at some specifics of the income statement, and guidance on how to prepare your own income statement.
Sample Income Statement
Finish your business plan in one day., getting started.
It’s much easier to think ahead for one year than it is for three. So, start with a one-year view. After putting together a reasonably thorough view of year one, it will be relatively easy to create years two and three by thinking of the changes that are expected to occur in the following years.
Notice how the income statement template is organized. Each column is labeled and represents a time period (usually a month) with totals for the year in the far right column.
Review from top to bottom the leftmost column of the sample income statement, to see all the categories of revenue and expenses, plus some subtotals for organization.
Again, looking at the sample income statement, notice that a separate line is used for each major revenue category. The sample company includes lines for Programming Services, Software Sales and Network Maintenance. Think of the significant distinctions in your areas of revenue and create your own categories. Remember at this point to keep it simple. As you put together your income forecast, think carefully about the timing (when sales will begin) and growth rates you project. You will be asked if the business is ready to support the sales you are forecasting and whether you will have done in advance the necessary things to drive the level of sales you’re predicting in the time periods shown.
Cost of Goods Sold
Moving down the left column, look at the Cost of Goods Sold section, which is right below our Income categories. For companies selling products, the cost of the products being sold goes into this section. In our sample company, notice that in February they forecasted software income of $250, and there is a corresponding cost of goods sold of $150. This represents a product they purchase for $150 and resell for $250.
Some service businesses have costs associated with the services they sell. These would be treated in the same way, but would be called ‘costs of sales’ instead of costs of goods sold. Even sales commissions are sometimes included in the cost of sales category, both for product businesses and service businesses.
Whether it’s a cost of goods sold or cost of sales, this section should include outside expenses that are incurred whenever a sale takes place.
Gross Profit
Gross profit is completely different from the more common term “profit.” Gross profit is the total revenue, minus the cost of goods sold or the cost of sales. If your business sells furniture and you buy a desk for $300 and sell it for $500, your gross profit is $200. If you are a consultant and you invoice a customer for $500 and you have no cost of goods sold, your gross profit is the same as your sales ($500 sales minus $0 cost of sales = $500 gross profit).
The sample company sells mostly services, with some software sales. So their gross profit is quite high. Look, for example, at July and notice that they have $24,500 in total sales and cost of goods sold of $1,200. Why so low? Because the cost of goods sold is for software they purchase and resell. In July they had software sales of only $2,000. If we were to break it down further (this is not shown on the sample statement) they had software gross margin of $800 ($2,000 sales minus $1,200 cost of goods = $800 gross profit.)
Businesses that sell mostly products need to watch their gross profit carefully. What matters in this type of business is not how much you sell, but how much you keep—that’s gross profit.
The expenses for the sample company are broken down into 14 categories. The major categories are self-explanatory (payroll expense, rent, etc.). When creating the list of expense categories for your business, keep it simple, using as few as 5 and no more than 20. It’s not critical whether you include the cost for small expenses in their own category, such as “office supplies,” or in a more general category such as “Office Expenses” (which would also include telephone, Internet and similar expenses).. The important thing is that all of your expenses are accounted for in one category or another.
Pay special attention to payroll costs, marketing costs and rent. These are likely to be your largest expenses. In your business plan you have probably addressed adding staff and marketing activities. Be sure that the income statement reflects the expense for these things in the time period when you said you were going to initiate the activity (or in advance, to allow for preparation time). Also make sure that your rent keeps pace with your payroll or headcount. You would expect to need more office space for 10 employees than for 3. There will be other corresponding expenses that grow with head count.
Look carefully at your revenue, payroll expense and overall expenses to be sure they are all moving in a logical pattern. If you study this carefully , you will get in tune with what it’s going to take to grow your business. You’ll soon find that you’re “living your business” on paper and able to make changes and decisions that will have a significant impact on your business. That’s what it’s about!
Net Ordinary Income. Net ordinary income is what is left when you subtract all of the expenses from all of the income:
Total Income – Cost of Goods Sold – Total Expenses = Net Ordinary Income
Since gross profit already subtracts the cost of goods sold from income, another way to calculate net ordinary income is:
Gross Profit – Total Expenses = Net Ordinary Income
So for year one in our sample company, the Total Income was $236,000, gross profit was $226,100, total expenses $204,597 and Net Ordinary Income was $21,503.
Wait a minute—isn’t that profit? Almost. If these become your actual numbers, your accountant will add a few more lines to take into account taxes, depreciation and a few of those other details we said were not critical for small-business-plan financial statements. For your business plan, rather than forecast profit, stop here at Net Ordinary Income.
Take your time to study our income statement template and get comfortable with it. For additional perspective, you might want to review the Wikipedia article on income statements which is linked here .
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Prepare an Income Statement

- 09 Dec 2021
When it comes to financial statements , each communicates specific information and is needed in different contexts to understand a company’s financial health.
The income statement is one of the most important financial statements because it details a company’s income and expenses over a specific period. This document communicates a wealth of information to those reading it—from key executives and stakeholders to investors and employees. Being able to read an income statement is important, but knowing how to generate one is just as critical.
Here’s an overview of the information found in an income statement, along with a step-by-step look at the process of preparing one for your organization.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is an Income Statement?
An income statement is a financial report detailing a company’s income and expenses over a reporting period. It can also be referred to as a profit and loss (P&L) statement and is typically prepared quarterly or annually.
Income statements depict a company’s financial performance over a reporting period. Because the income statement details revenues and expenses, it provides a glimpse into which business activities brought in revenue and which cost the organization money—information investors can use to understand its health and executives can use to find areas for improvement.
Related: How to Read & Understand an Income Statement
An income statement typically includes the following information:
- Revenue: How much money a business took in during a reporting period
- Expenses: How much money a business spent during a reporting period
- Costs of goods sold (COGS): The total costs associated with component parts of whatever product or service a company makes and sells
- Gross profit: Revenue minus costs of goods sold
- Operating income: Gross profit minus operating expenses
- Income before taxes: Operating income minus non-operating expenses
- Net income: Income before taxes
- Earnings per share (EPS): Net income divided by the total number of outstanding shares
- Depreciation: Value lost by assets, such as inventory, equipment, and property, over time
- EBITDA: Earnings before interest, depreciation, taxes, and amortization
Related: 13 Financial Performance Measures Managers Should Monitor
Steps to Prepare an Income Statement
1. choose your reporting period.
Your reporting period is the specific timeframe the income statement covers. Choosing the correct one is critical.
Monthly, quarterly, and annual reporting periods are all common. Which reporting period is right for you depends on your goals. A monthly report, for example, details a shorter period, making it easier to apply tactical adjustments that affect the next month’s business activities. A quarterly or annual report, on the other hand, provides analysis from a higher level, which can help identify trends over the long term.
2. Calculate Total Revenue
Once you know the reporting period, calculate the total revenue your business generated during it.
If you prepare the income statement for your entire organization, this should include revenue from all lines of business. If you prepare the income statement for a particular business line or segment, you should limit revenue to products or services that fall under that umbrella.
3. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Next, calculate the total cost of goods sold for any product or service that generated revenue for your business during the reporting period. This encompasses direct and indirect costs of producing and selling products or services, including:
- Direct labor expenses
- Material expenses
- Parts or component expenses
- Distribution costs
- Any expense directly tied to the production of your product or service
4. Calculate Gross Profit
The next step is to determine gross profit for the reporting period. To calculate this, simply subtract the cost of goods sold from revenue.

5. Calculate Operating Expenses
Once you know gross profit, calculate operating expenses (OPEX).
Operating expenses are indirect costs associated with doing business. These differ from cost of goods sold because they’re not directly associated with the process of producing or distributing products or services. Examples of expenses that fall under the OPEX category include:
- Office supplies
6. Calculate Income
To calculate total income, subtract operating expenses from gross profit. This number is essentially the pre-tax income your business generated during the reporting period. This can also be referred to as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
7. Calculate Interest and Taxes
After calculating income for the reporting period, determine interest and tax charges.
Interest refers to any charges your company must pay on the debt it owes. To calculate interest charges, you must first understand how much money you owe and the interest rate being charged. Accounting software often automatically calculates interest charges for the reporting period.
Next, calculate your total tax burden for the reporting period. This includes local, state, and federal taxes, as well as any payroll taxes.
8. Calculate Net Income
The final step is to calculate net income for the reporting period. To do this, subtract interest and then taxes from your EBIT. The number remaining reflects your business’s available funds, which can be used for various purposes, such as being added to a reserve, distributed to shareholders, utilized for research and development, or to fuel business expansion.
Income Statement Example
Below is an example income statement for a fictional company. As you can see at the top, the reporting period is for the year that ended on Sept. 28, 2019.
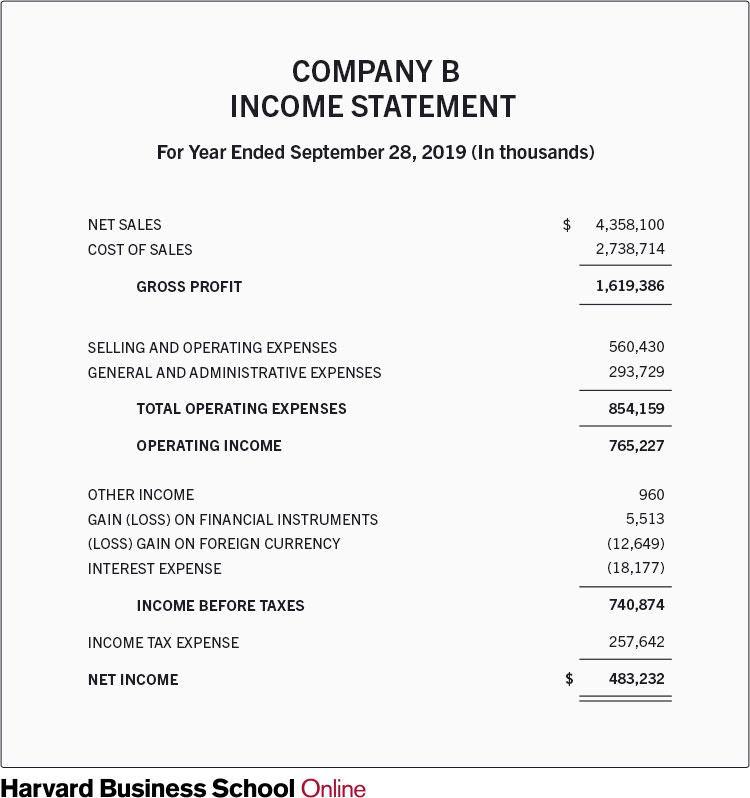
Go to the alternative version .
During the reporting period, the company made approximately $4.4 billion in total sales. It cost the business approximately $2.7 billion to achieve those sales. As a result, gross profit was about $1.6 billion.
Next, $560.4 million in selling and operating expenses and $293.7 million in general administrative expenses were subtracted. This left the company with an operating income of $765.2 million. To this, additional gains were added and losses subtracted, including $257.6 million in income tax.
At the bottom of the income statement, it’s clear the business realized a net income of $483.2 million during the reporting period.

A Critical Skill for Business Leaders
Although the income statement is typically generated by a member of the accounting department at large organizations, knowing how to compile one is beneficial to a range of professionals.
Whether you’re an individual contributor, a member of the leadership team in a non-accounting role, or an entrepreneur who wears many hats, learning how to create an income statement can provide a deeper understanding of the financial metrics that matter to your business. It can also help improve your financial analysis capabilities .
Do you want to take your career to the next level? Consider enrolling in Financial Accounting —one of three courses comprising our Credential of Readiness (CORe) program —which can teach you the key financial topics you need to understand business performance and potential. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .
Data Tables
Company b income statement.
For Year Ended September 28, 2019 (In thousands)
Go back to the article .

About the Author
How to Make an Income Statement

What is an Income Statement?
An income statement, also called a profit and loss statement (or P&L), is a helpful tool you can use to track the financial health of your business. It allows you to determine, at a glance, whether your business is making or losing money.
Put simply, there are three main parts of an income statement: revenues, expenses, and profit. But how these are calculated depends on a number of factors.
As a business owner, you need to be familiar with your company’s income statement and financial performance. It’s a document you should create and recreate frequently, ideally on a monthly or quarterly basis.
Why is an Income Statement Important for Small Businesses?
Not only do income statements allow you to keep a finger on the financial pulse of your company’s profitability, they may also be important when your business applies for financing. Lenders frequently ask for income statements (along with other financial statements , like a statement of cash flows) whenever you fill out a loan application. Depending on the lender’s requirements, the statement will likely need to cover a specific period of time, like a month, a quarter, or a year.
Income statements are a great way to track your business’s progress toward long-term goals. When you create multiple income statements, you can view your company’s financial growth or decline over time. For example, you can compare this quarter’s income statement with the statement from the same period of time last year to learn if your company is earning more or less money.
Positive income statements may be useful when you try to attract investors or apply for new commercial financing like business loans or lines of credit . If you have several income statements in a row that show financial growth, it may demonstrate that your company is potentially a good investment or a lower credit risk for lending purposes.

Let’s Find the Right Loan for Your Business
Nav serves nearly every kind of business, and our experts will match you to the right fit for your business needs.
Options for Creating an Income Statement
Although the thought of preparing financial statements can be intimidating to many small business owners, it’s actually not that difficult to prepare an income statement for your business once you know what you’re doing. There are a few methods for creating an income statement.
First, you should choose whether you want to use the single or multi-step method. A single step income statement is simpler, as you only have to add up revenue and then subtract expenses, which you can do in a spreadsheet. The multi-step income statement is more complex and separates everything into operating expenses and non-operating expenses so you have a better idea of where your costs are coming from. This is done by calculating gross profit (the money left after subtracting the cost of your goods sold from your revenue), operating revenue, operating expenses, operating income, pre-tax income, and non-operating revenues and expenses.
You can easily create a spreadsheet of your own to produce your income statements. You can also use accounting software to set up and manage the income statement for you.
Benefits of Accounting Software for Small Business
As a small business owner, you may want to save money wherever you can, but accounting software can help simplify your bookkeeping and accounting overall. Plus, accounting software makes it easier to produce financial reports, like your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Cloud-based software helps you stay up-to-date, and the automated prompts can help you reduce errors, or more easily find and fix them when you need to.
Other benefits of using accounting software to create your income statement is that you can easily customize it, save it, print it, or send it via email to appropriate people. Choosing an accounting software for your small business doesn’t have to be difficult. Most accounting software, like Quickbooks, Freshbooks , and Bench, offer tiered service levels, so you only pay for what you need.
How to Make an Income Statement Using Accounting Software
If you use accounting software like QuickBooks or FreshBooks , you’ll find it easy to create, print, or send an income statement. If you’ve been doing proper bookkeeping, the numbers will automatically populate based on your entries.
However, there are many ways to customize the financial statement, so you’ll want to know how to do a little setup work before you run the report. Here are a few basic steps for creating an income statement, or profit and loss statement, depending on which software you’re using.
1. Find the income statement function
As noted, some accounting software may refer to the income statement as a profit and loss (or P&L) statement, so don’t get confused. You can usually find it in the “reports” or “insights” tab or search for the function in the search bar.
2. Choose the report format you wish to use
There will be several different report formats available for you to choose from, depending on the reason you’re generating the income statement. For instance, if you’re sending your income statement to the IRS for tax purposes, the standard income statement would be ideal. But if you’re applying for a business loan, you’ll need a different format, which your loan officer will determine for you. Internally, your management team may find the income statement that shows profit and loss by customer or as a percent of total income more useful.
3. Customize the statement
Once you’ve chosen your format, you can customize the income statement further by choosing a time period or date range, choosing between cash and accrual basis, and deleting or adding columns. You can also choose certain filters that compare date ranges or further customize columns with headers and footers.
4. Run report
This is easy – just click “run report” and the report will be generated for you. For some more advanced versions of accounting software, the report will update automatically as you create it, so you don’t even need to hit a button. Make sure you refresh to make sure any customizations you’ve selected have updated.
5. Print, save, or send
You’ll be given the option to save the report within the software or export it to your desktop or other folder. Make sure you have a good naming convention so you can easily find your report. You can also save your customized report so you can run it again the next time you need it. Most accounting software has an easily recognizable “print” button at the top of the statement, but you can also print the exported or saved report from your desktop.
How to Make an Income Statement in a Spreadsheet
If you’re going to be making an income statement via spreadsheet, you’ll probably select the single step method. It can be slightly less accurate, but it’s less complicated. To make your own spreadsheet, we recommend that you start with an income statement template , so you know what you’re looking at and what you can expect. Here are some simple steps to starting your income statement in a spreadsheet.
1. Open Up a Spreadsheet
Open a basic spreadsheet on your computer. Excel and Google Sheets are the most popular options in this space.
2. Choose a Time Frame
Before you can prepare an income statement, you’ll first need to choose a specific period of time that the statement will cover. Most statements are based on one of the following three time frames:
If you choose to create a monthly income statement, it will help you calculate your business’s earnings or losses during that particular month. Quarterly and annual income statements look for the same information (profit or loss), but over a different time frame.
3. Create Two Sections: Income and Expenses
An income statement answers the following question: What is your business’s net income? The basic formula used to calculate net income is as follows:
Income – Expenses = Net Income
Before you can figure out your company’s net income, you need to separate your business’s finances into two sections on your spreadsheet. These sections are income and expenses (aka profit and loss).
On your spreadsheet itself, create two different columns to record business income and expenses. Once you’ve reviewed your bank statement(s) and separated the credits from the debits, you’ll need a place to enter this information.
4. List Out Your Sources of Income
Next, you’ll need to list out of your business’s income sources as separate line items. This will include all of your company’s revenues earned during the reporting period (e.g. one month, one quarter, one year, etc.).
Possible income sources might include:
- Sales Revenue
- Revenue from Services Provided
- Interest Income Earned
- Affiliate Commission Revenue
- Rent Received
Once you have a list of all of the individual deposits into your business bank account for a given period of time, you should separate them into groups or subcategories. For example, you can tally all of the revenue collected from sales onto a single line. Underneath that line, you could list the total income from another source (like affiliate commissions earned). Repeat the process until every category (and every penny) of money earned has been included on your spreadsheet.
If you want to calculate your company’s operating income by itself, only include money generated from the business’s primary operations and exclude all other sources of income. This, however, won’t give you a true view of your overall net income, just the portion earned (or lost) from your primary business operations.
5. List Out Your Expenses
Now that you’ve listed out all of your company’s income sources, it’s time to switch your focus. The next line items you’ll need to add to your spreadsheet are company expenses. You should comb through your bank statement(s) or general ledger and record every instance that money left your business bank account for any reason.
Possible expenses might include:
- Cost of Goods Sold – COGS (Direct Labor, Materials, Equipment Depreciation and Amortization, etc.)
- Operating and Administrative Expenses (Salaries and Wages, Utilities, Rent, Advertising, etc.)
- Spending from Employee Expense Accounts (Travel, Meals, etc.)
- Tax Costs (Income Tax Expense, etc.)
- Interest Expense (Interest Paid on Financing)
Like income sources, you can combine expenses into broader groups or categories instead of listing them line by line. You can add up the cost of all wages/salaries paid and enter the combined amount as a single entry on your spreadsheet. Next, you might add individual lines for the total cost of sales, rent paid, utilities paid, etc. Or, you might opt to combine all of those expenses and list the business’s total operating expenses for the period of time in question.
However you list your company’s expenses on your spreadsheet, be sure that every penny spent has been included and is deducted from income earned. In order for your business’ income statement to be accurate, the data you put into your spreadsheet must be 100% correct.
6. Calculate Your Net Income at the Bottom
The final step in creating an income statement is calculating your net income (also called net profit or net earnings) at the bottom of the spreadsheet. If you’ve ever heard someone refer to a company’s “bottom line,” the term refers to this final entry on an income statement.
First, you’ll need to add up all of the income listed on your spreadsheet to find your total revenue. Next, you should subtract all of the expenses listed from the amount of money earned. Be sure to double check your math for good measure.
The final number you’re left with will be your company’s net income for the period of time you included in your spreadsheet. This number tells you how much money your business earned or lost during the accounting period selected.

Access better funding options with a solution you can’t get anywhere else
Reduce the pain in financing with streamlined applications, instant offers and approval rates that are 3.5X higher than industry averages.
This article was originally written on November 11, 2019 and updated on April 4, 2022.
Rate This Article
This article currently has 5 ratings with an average of 4 stars.

Kat Cox works to provide answers to the questions small business owners have about how to set up, run, or fund their businesses. When she’s not writing blogs, articles, short fiction, or (kind of bad) French poetry, Kat can be found lacing up her tennis shoes for a run or walk with her pup or scouting for the best karaoke spot in Austin, Texas.
Have at it! We'd love to hear from you and encourage a lively discussion among our users. Please help us keep our site clean and protect yourself. Refrain from posting overtly promotional content, and avoid disclosing personal information such as bank account or phone numbers. Reviews Disclosure: The responses below are not provided or commissioned by the credit card, financing and service companies that appear on this site. Responses have not been reviewed, approved or otherwise endorsed by the credit card, financing and service companies and it is not their responsibility to ensure all posts and/or questions are answered.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Business Plan Income Statement: Everything You Need to Know
Business plan income statement is an important financial document, which shows a company's profitability in a given period of time. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
Business plan income statement is an important financial document, which shows a company's profitability in a given period of time.
Understanding an Income Statement
An income statement or a profit and loss statement helps to understand a company's sources of revenue and various items of expenses. In other words, it tells you where the money is coming from and where it's going. A glance at the income statement can tell anyone whether the business is profitable. Basically, an income statement lists out various items and amounts of revenue and expenses, with the net profit figure at the bottom.
You might have heard people talking about a company's bottom line. It's the last line in an income statement, which shows you the amount of net profit of a company in a given period of time after meeting all expenses.
This is the “profit” referred to in a profit and loss statement or the letter “P” of “P & L” account. The “loss” or “L” is the figure that appears if the total amount of expenses exceeds the total amount of revenue.
An income statement is probably the most common and standard financial statement. Another similar statement called the projected profit and loss statement is a standard financial projection tool used in business planning.
Breakdown of a Business Plan Income Statement
It's essential to include a projected income statement in your business plan. Whether you are planning for the internal purpose of the company or preparing a financial document to present before your investors, it's important to know whether you expect the business to be profitable over a specific period of time.
You should start a business plan with an executive summary, followed by other standard components. It must include a financial plan section, complete with a projected balance sheet, cash flow, and income statement. In business planning, the word “projected” is often replaced with the word “pro-forma,” but it means the same thing.
An income statement typically includes the following components:
- Direct cost of sales.
- Production expenses.
- Gross margin.
- Operating expenses.
- Marketing expenses.
- Depreciation .
- Utility expenses.
- Insurance premiums.
- Payroll taxes .
- Profit before interest and taxes.
- Interest expenses.
- Net profit.
Sales or Revenue
The top line in your income statement represents revenue from sales. It's the net sales amount remaining after deducting goods returns and sales discounts. All the direct expenses associated with sales will be deducted from this figure.
Direct Costs of Sales
The cost of goods sold includes all the direct costs incurred in making and delivering the products or services that contributed to sales. It does not include office rent, salaries, and other expenses that are not directly connected with sales.
Gross Margin or Gross Profit
Subtracting the direct cost of goods sold from the number of net sales gives you gross margin. This is the profit before considering operating expenses and taxes.
Operating Expenses
Except for the cost of goods sold, all other expenses necessary to run the business are covered under this head. Rent, utilities, payroll, and marketing costs are examples of operating expenses.
Operating expenses include marketing and administrative expenses like:
- Sales salaries.
- Collateral and promotions.
- Advertising.
- Travel, meetings, client meals, etc.
- Office salaries.
Operating Income
Operating income or earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) is the most reliable indicator of a company's profitability.
If the company is making any interest payments on a loan, it should be included under this head.
Total Expenses
This is the sum total of all expenses, excluding taxes and interest.
Depreciation and Amortization
These are the expenses incurred on tangible and intangible assets. Since the assets do not lose their utility in a single accounting period, the total cost of assets is spread over their total lifetime. The cost applicable for a single accounting period is deducted from revenue as depreciation.
Net Income Before Taxes
This figure represents total earnings of the business before paying income taxes.
This item represents the amount of income tax paid or owed to the federal, state, and local governments. Some companies allocate an estimated amount of taxes they expect to pay in the future.
Net Income or Net Profit
This is the net profit of the business remaining after paying income taxes. This is the bottom line figure that tells at a glance whether a company is making profits or incurring losses.
If you need help with business plan income statement, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- S Corp Business Expenses
- Business Income Tax
- Cost of Doing Business Definition
- What Is Liability Business - Everything You Need to Know
- Schedule C 1040
- Partnership Start Up Costs
- Do Corporations Pay State Taxes
- LLC Schedule C
- Are Incorporation Fees Tax Deductible?
- Statement of Information
Be Stress Free and Tax Ready 🙌 70% Off for 4 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
70% Off for 4 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Free Invoice Generator
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Estimate Templates
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Mark Up Calculator
Call Toll Free: 1.866.303.6061
1-888-674-3175
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Bookkeeping
Resources for Your Growing Business
How to prepare an income statement.

To prepare an income statement, small businesses must analyze and report their revenues, operating expenses, and the resulting gross profit or losses for a specific reporting period. The income statement, also called a profit and loss statement, is one of the major financial statements issued by businesses, along with the balance sheet and cash flow statement.
If you have found yourself struggling to find the time to create your own profit and loss report, or P&L, from scratch, a free invoice statement template is the perfect solution.
FreshBooks provides free template income statements that are pre-formatted for your needs. All you need to do is fill in the empty fields with the numbers you’ve calculated. No stress, just results.
Key Takeaways
- Profit and loss documents are one of the key financial statements a company uses
- You can choose to report annually, quarterly, or on a monthly basis
- Publicly traded companies must prepare financial statements quarterly and annually
- Your revenue includes all the money earned for your services during the period
- Include all of your business operating expenses to get an accurate financial landscape
- Profit and loss statements provide a future understanding for the coming fiscal period
These topics will show you how to prepare an income statement:
What Is An Income Statement?
Steps to prepare an income statement, importance and uses of an income statement, income statement example.
- What’s the Difference Between a Balance Sheet and Income Statement?
Frequently Asked Questions
NOTE: FreshBooks Support team members are not certified income tax or accounting professionals and cannot provide advice in these areas outside of supporting questions about FreshBooks. If you need income tax advice, please contact an accountant in your area.

Income statements or profit and loss accounts are financial statements used to calculate the financial health of the company.
It shows the company’s revenues and expenses during a particular period, which can be selected according to the company’s needs. A P&L, which stands for profit and loss, indicates how the revenues are transformed into net profit.
A quarterly income statement shows the gross profit or loss generated by your business over a three-month period. It can also be referred to as a profit or loss account and is a crucial financial statement that shows the business’s operating income and expenditures, detailing your net income or net profits.
Below is a 10-step guide on how to write a professional income statement. Using this process, along with the FreshBooks income statement template , allows you to simply fill in the details rather than spending time creating an entire document from scratch.
1. Pick a Reporting Period
The first step in preparing an income statement is to choose the reporting period your report will cover. Businesses typically choose to report their P&L on an annual, quarterly, or monthly basis. Publicly traded companies are required to prepare financial statements on a quarterly and yearly basis, but small businesses aren’t as heavily regulated in their reporting.
Creating monthly income statements can help you identify trends in your gross profit and expenditures over time. That information can help you make business decisions to make your company more efficient and profitable.
2. Generate a Trial Balance Report
To create an income statement for your business, you’ll need to print out a standard trial balance report. You can quickly generate the trial balance through your cloud-based accounting software . Trial balance reports are internal documents that list the end balance of each account in the general ledger for a specific reporting period.

Creating balance sheets is a crucial part of creating a profit and loss, as it’s how a company gathers data for its account balances. It will give you all the end balance figures you need to create an income statement.
3. Calculate Your Revenue
Next, you’ll need to calculate your business’s total sales revenue for the reporting period. Your revenue includes all the money earned for your services during the reporting period, even if you haven’t yet received all the payments. Add up all the revenue line items from your trial balance report and enter the total amount in the revenue line item of your P&L.
FreshBooks accounting software provides an easy-to-follow accounting formula to make sure that you’re calculating the right amounts and creating an accurate income statement.

4. Determine the Cost of Goods Sold
Your cost of goods sold includes the direct labor, materials, and overhead operating expenses you’ve incurred to provide your goods or services. Add up all the cost of goods sold line items on your trial balance report and list the total cost of goods sold on the statement directly below the revenue line item.
5. Calculate the Gross Margin
Subtract the cost of goods sold total from the revenue total on your income statement. This calculation will give you the gross margin , or the gross amount earned from the sale of your goods and services.
6. Include Operating Expenses
Add up all the operating expenses listed on your trial balance report. Each expense line should be double-checked to make sure you have the correct figures. Enter the total amount into the statement as the selling and administrative operating expenses line item. It’s located directly below the gross margin line.
7. Calculate Your Income
Subtract the selling and administrative expenses total from the gross margin. Doing this will give you the amount of pre-tax operating income. Enter the amount at the bottom of the income statement.
8. Include Income Taxes
To calculate income tax, multiply your applicable state tax rate by your pre-tax income figure. Add this to the statement below the pre-tax income figure.
9. Calculate Net Income
To determine your business’s net income, subtract the income tax from the pre-tax income figure. Enter the figure net income into the final line item of your income statement. This will give you a general understanding of your business performance, letting you see how profitable you have been.
10. Finalize the Income Statement
To finalize your statement, add a header to the report identifying it as an income statement. Add your business details and the reporting period covered by the profit and loss. With all of the data you’ve compiled, you’ve now created an accurate statement.
This statement will give you a future understanding of your company’s fiscal health that will be of great benefit to you and your business practice.
Don’t let income statements monopolize your time. FreshBooks offers a wide variety of accounting services that save you time and money when creating financial statements. Learn more about FreshBooks accounting software and give them a try for free.
Income statements help business owners discover if they can generate profit by increasing revenues, decreasing costs, or a combination of both. They also show the outcome of strategies a business sets at the beginning of a fiscal period, allowing them to make impactful adjustments to maximize profit.
By using income statements, management can make informed decisions. A detailed income statement can lead to expansion, pushing sales, increasing production capacity, streamlining the sale of assets, or shutting down a specific department, project, or product line. Companies can also use competitors’ income statements to gain insights into the success of a company and how they focus their time and resources in various focus areas.
This is an example of an income statement created by FreshBooks. It can give you a better understanding of what’s reported on a statement, the format, and how the data should be laid out:
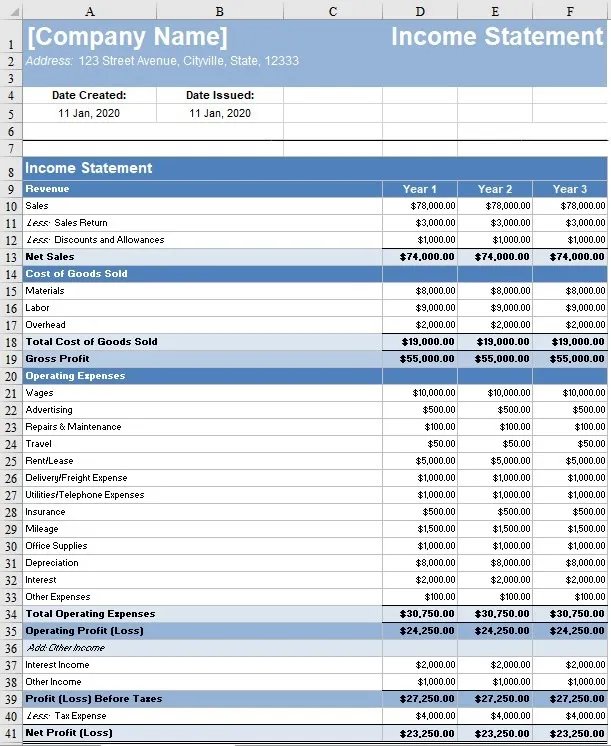
What’s the Difference Between a Balance Sheet and Income Statement?
There are a few key differences between the balance sheet and the statement, including:
- Timing: While the profit and loss document reports financial activity for a specific reporting period, usually a month, a quarter, or a year, the balance sheet reports financial activity at a specific point in time for a snapshot view of a business’s finances.
- Information reported: The statement reports on a business’s revenues and expenses and, ultimately, the amount of gross profit or loss generated, whereas a balance sheet reports on a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
Keep track of your business finances easily and efficiently. FreshBooks offers bookkeeping services that take the guesswork out of your accounting. Learn more about how FreshBooks bookkeeping services can support your accounting needs.

Whether you’re an individual contributor, a leadership team member, or an entrepreneur wearing many hats, knowing how to write an income statement provides a deeper understanding of the financial state of your business. It can also help improve financial analysis, allowing you to plan for the future and scale your business successfully. Informed use of income statements leads to new projects, streamlined practices, and a healthy financial landscape to continue accelerating long-term.
What are the most important figures in an income statement?
The most important figures in your statement include your gross margin, operating earnings, and pretax earnings. These figures are critical for the equity and credit analysis processes that will benefit the future growth of your business.
What is not included in an income statement?
Income statements don’t differentiate cash and non-cash receipts or cash vs. non-cash payments and disbursements. EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization ) can be included but are not present on all P&Ls.
Is profit and loss the same as an income statement?
Yes. There is no difference between an income statement and a profit and loss report. The terms can be used interchangeably.
How do I know if my income statement is correct?
Avoiding common accounting errors is the best way to ensure the accuracy of your income statement. Keeping an audit trail, double-checking your work, having a consistent process, conducting routine reconciliations, and allowing a fresh set of eyes to review your work are the best ways to keep information on your income statement correct.
Should the balance sheet and income statement match?
No. You will not get your balance sheet and income statement to match. These two reports feature different line items, meaning the end number and the data being gathered are not identical.
Do you put negative in the income statement?
Yes. A negative income figure appears on a company’s income statement. A negative net income means a company has a loss over that given account period, not a profit. While your business may have positive sales, you’ll end up with a negative net income if expenses and other costs exceed that amount.

Jason Ding, CPA
About the author
Jason Ding is a seasoned accountant with over 15 years of progressive experience in senior finance and accounting across multiple industries. Jason holds a BBA from Simon Fraser University and is a designated CPA. Jason’s firm, Notion CPA, is an accounting firm with a business-first focus. The firm specializes in preparing personal and corporate taxation while providing fractional CFO work and leading the accounting and finance function for several small-to-medium-sized businesses. In his free time, you’ll find Jason on the basketball court, travelling, and spending quality time with family.
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » startup, business plan financials: 3 statements to include.
The finance section of your business plan is essential to securing investors and determining whether your idea is even viable. Here's what to include.

If your business plan is the blueprint of how to run your company, the financials section is the key to making it happen. The finance section of your business plan is essential to determining whether your idea is even viable in the long term. It’s also necessary to convince investors of this viability and subsequently secure the type and amount of funding you need. Here’s what to include in your business plan financials.
[Read: How to Write a One-Page Business Plan ]
What are business plan financials?
Business plan financials is the section of your business plan that outlines your past, current and projected financial state. This section includes all the numbers and hard data you’ll need to plan for your business’s future, and to make your case to potential investors. You will need to include supporting financial documents and any funding requests in this part of your business plan.
Business plan financials are vital because they allow you to budget for existing or future expenses, as well as forecast your business’s future finances. A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Sections to include in your business plan financials
Here are the three statements to include in the finance section of your business plan:
Profit and loss statement
A profit and loss statement , also known as an income statement, identifies your business’s revenue (profit) and expenses (loss). This document describes your company’s overall financial health in a given time period. While profit and loss statements are typically prepared quarterly, you will need to do so at least annually before filing your business tax return with the IRS.
Common items to include on a profit and loss statement :
- Revenue: total sales and refunds, including any money gained from selling property or equipment.
- Expenditures: total expenses.
- Cost of goods sold (COGS): the cost of making products, including materials and time.
- Gross margin: revenue minus COGS.
- Operational expenditures (OPEX): the cost of running your business, including paying employees, rent, equipment and travel expenses.
- Depreciation: any loss of value over time, such as with equipment.
- Earnings before tax (EBT): revenue minus COGS, OPEX, interest, loan payments and depreciation.
- Profit: revenue minus all of your expenses.
Businesses that have not yet started should provide projected income statements in their financials section. Currently operational businesses should include past and present income statements, in addition to any future projections.
[Read: Top Small Business Planning Strategies ]
A strongly written finance section also helps you obtain necessary funding from investors, allowing you to grow your business.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your company’s finances, allowing you to keep track of earnings and expenses. It includes what your business owns (assets) versus what it owes (liabilities), as well as how much your business is currently worth (equity).
On the assets side of your balance sheet, you will have three subsections: current assets, fixed assets and other assets. Current assets include cash or its equivalent value, while fixed assets refer to long-term investments like equipment or buildings. Any assets that do not fall within these categories, such as patents and copyrights, can be classified as other assets.
On the liabilities side of your balance sheet, include a total of what your business owes. These can be broken down into two parts: current liabilities (amounts to be paid within a year) and long-term liabilities (amounts due for longer than a year, including mortgages and employee benefits).
Once you’ve calculated your assets and liabilities, you can determine your business’s net worth, also known as equity. This can be calculated by subtracting what you owe from what you own, or assets minus liabilities.
Cash flow statement
A cash flow statement shows the exact amount of money coming into your business (inflow) and going out of it (outflow). Each cost incurred or amount earned should be documented on its own line, and categorized into one of the following three categories: operating activities, investment activities and financing activities. These three categories can all have inflow and outflow activities.
Operating activities involve any ongoing expenses necessary for day-to-day operations; these are likely to make up the majority of your cash flow statement. Investment activities, on the other hand, cover any long-term payments that are needed to start and run your business. Finally, financing activities include the money you’ve used to fund your business venture, including transactions with creditors or funders.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Join us for our Small Business Day event!
Join us at our next event on Wednesday, May 1, at 12:00 p.m., where we’ll be kicking off Small Business Month alongside business experts and entrepreneurs. Register to attend in person at our Washington, D.C., headquarters, or join us virtually!
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
More tips for your startup
Micro-business vs. startup: what’s the difference, micro businesses: what are they and how do you start one, how to use ai tools to write a business plan.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated March 18, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan

Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information you need to cover in a business plan sometimes isn’t quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
If you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template to get you started, download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

5 Min. Read
How To Create a Compelling Message With Your Business Plan to Help Sell Your Idea

7 Min. Read
8 Reasons Business Plans Fail That No One Wants to Talk About

8 Min. Read
How to Write an Auto Repair Shop Business Plan + Free PDF

9 Min. Read
How to Create a Sales Plan for Your Business
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- Sample Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Upmetrics AI Assistant: Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights. Learn How
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai pitch deck generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
Small Business Tools
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Strategic Planning
How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)

Free Financial Statements Template
Ajay Jagtap
- December 7, 2023
13 Min Read

If someone were to ask you about your business financials, could you give them a detailed answer?
Let’s say they ask—how do you allocate your operating expenses? What is your cash flow situation like? What is your exit strategy? And a series of similar other questions.
Instead of mumbling what to answer or shooting in the dark, as a founder, you must prepare yourself to answer this line of questioning—and creating a financial plan for your startup is the best way to do it.
A business plan’s financial plan section is no easy task—we get that.
But, you know what—this in-depth guide and financial plan example can make forecasting as simple as counting on your fingertips.
Ready to get started? Let’s begin by discussing startup financial planning.
What is Startup Financial Planning?
Startup financial planning, in simple terms, is a process of planning the financial aspects of a new business. It’s an integral part of a business plan and comprises its three major components: balance sheet, income statement, and cash-flow statement.
Apart from these statements, your financial section may also include revenue and sales forecasts, assets & liabilities, break-even analysis , and more. Your first financial plan may not be very detailed, but you can tweak and update it as your company grows.
Key Takeaways
- Realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of the market are the key to reliable financial projections.
- Cash flow projection, balance sheet, and income statement are three major components of a financial plan.
- Preparing a financial plan is easier and faster when you use a financial planning tool.
- Exploring “what-if” scenarios is an ideal method to understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in the business operations.
Why is Financial Planning Important to Your Startup?
Poor financial planning is one of the biggest reasons why most startups fail. In fact, a recent CNBC study reported that running out of cash was the reason behind 44% of startup failures in 2022.
A well-prepared financial plan provides a clear financial direction for your business, helps you set realistic financial objectives, create accurate forecasts, and shows your business is committed to its financial objectives.
It’s a key element of your business plan for winning potential investors. In fact, YC considered recent financial statements and projections to be critical elements of their Series A due diligence checklist .
Your financial plan demonstrates how your business manages expenses and generates revenue and helps them understand where your business stands today and in 5 years.
Makes sense why financial planning is important to your startup, doesn’t it? Let’s cut to the chase and discuss the key components of a startup’s financial plan.
Say goodbye to old-school excel sheets & templates
Make accurate financial plan faster with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Key Components of a Startup Financial Plan
Whether creating a financial plan from scratch for a business venture or just modifying it for an existing one, here are the key components to consider including in your startup’s financial planning process.
Income Statement
An Income statement , also known as a profit-and-loss statement(P&L), shows your company’s income and expenditures. It also demonstrates how your business experienced any profit or loss over a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of your business that shows the feasibility of your business idea. An income statement can be generated considering three scenarios: worst, expected, and best.
Your income or P&L statement must list the following:
- Cost of goods or cost of sale
- Gross margin
- Operating expenses
- Revenue streams
- EBITDA (Earnings before interest, tax, depreciation , & amortization )
Established businesses can prepare annual income statements, whereas new businesses and startups should consider preparing monthly statements.
Cash flow Statement
A cash flow statement is one of the most critical financial statements for startups that summarize your business’s cash in-and-out flows over a given time.
This section provides details on the cash position of your business and its ability to meet monetary commitments on a timely basis.
Your cash flow projection consists of the following three components:
✅ Cash revenue projection: Here, you must enter each month’s estimated or expected sales figures.
✅ Cash disbursements: List expenditures that you expect to pay in cash for each month over one year.
✅ Cash flow reconciliation: Cash flow reconciliation is a process used to ensure the accuracy of cash flow projections. The adjusted amount is the cash flow balance carried over to the next month.
Furthermore, a company’s cash flow projections can be crucial while assessing liquidity, its ability to generate positive cash flows and pay off debts, and invest in growth initiatives.
Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a financial statement that reports your company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity at a given time.
Consider it as a snapshot of what your business owns and owes, as well as the amount invested by the shareholders.
This statement consists of three parts: assets , liabilities, and the balance calculated by the difference between the first two. The final numbers on this sheet reflect the business owner’s equity or value.
Balance sheets follow the following accounting equation with assets on one side and liabilities plus Owner’s equity on the other:
Here is what’s the core purpose of having a balance-sheet:
- Indicates the capital need of the business
- It helps to identify the allocation of resources
- It calculates the requirement of seed money you put up, and
- How much finance is required?
Since it helps investors understand the condition of your business on a given date, it’s a financial statement you can’t miss out on.
Break-even Analysis
Break-even analysis is a startup or small business accounting practice used to determine when a company, product, or service will become profitable.
For instance, a break-even analysis could help you understand how many candles you need to sell to cover your warehousing and manufacturing costs and start making profits.
Remember, anything you sell beyond the break-even point will result in profit.
You must be aware of your fixed and variable costs to accurately determine your startup’s break-even point.
- Fixed costs: fixed expenses that stay the same no matter what.
- Variable costs: expenses that fluctuate over time depending on production or sales.
A break-even point helps you smartly price your goods or services, cover fixed costs, catch missing expenses, and set sales targets while helping investors gain confidence in your business. No brainer—why it’s a key component of your startup’s financial plan.
Having covered all the key elements of a financial plan, let’s discuss how you can create a financial plan for your startup.
How to Create a Financial Section of a Startup Business Plan?
1. determine your financial needs.
You can’t start financial planning without understanding your financial requirements, can you? Get your notepad or simply open a notion doc; it’s time for some critical thinking.
Start by assessing your current situation by—calculating your income, expenses , assets, and liabilities, what the startup costs are, how much you have against them, and how much financing you need.
Assessing your current financial situation and health will help determine how much capital you need for your startup and help plan fundraising activities and outreach.
Furthermore, determining financial needs helps prioritize operational activities and expenses, effectively allocate resources, and increase the viability and sustainability of a business in the long run.
Having learned to determine financial needs, let’s head straight to setting financial goals.
2. Define Your Financial Goals
Setting realistic financial goals is fundamental in preparing an effective financial plan. So, it would help to outline your long-term strategies and goals at the beginning of your financial planning process.
Let’s understand it this way—if you are a SaaS startup pursuing VC financing rounds, you may ask investors about what matters to them the most and prepare your financial plan accordingly.
However, a coffee shop owner seeking a business loan may need to create a plan that appeals to banks, not investors. At the same time, an internal financial plan designed to offer financial direction and resource allocation may not be the same as previous examples, seeing its different use case.
Feeling overwhelmed? Just define your financial goals—you’ll be fine.
You can start by identifying your business KPIs (key performance indicators); it would be an ideal starting point.
3. Choose the Right Financial Planning Tool
Let’s face it—preparing a financial plan using Excel is no joke. One would only use this method if they had all the time in the world.
Having the right financial planning software will simplify and speed up the process and guide you through creating accurate financial forecasts.
Many financial planning software and tools claim to be the ideal solution, but it’s you who will identify and choose a tool that is best for your financial planning needs.

Create a Financial Plan with Upmetrics in no time
Enter your Financial Assumptions, and we’ll calculate your monthly/quarterly and yearly financial projections.
Start Forecasting
4. Make Assumptions Before Projecting Financials
Once you have a financial planning tool, you can move forward to the next step— making financial assumptions for your plan based on your company’s current performance and past financial records.
You’re just making predictions about your company’s financial future, so there’s no need to overthink or complicate the process.
You can gather your business’ historical financial data, market trends, and other relevant documents to help create a base for accurate financial projections.
After you have developed rough assumptions and a good understanding of your business finances, you can move forward to the next step—projecting financials.
5. Prepare Realistic Financial Projections
It’s a no-brainer—financial forecasting is the most critical yet challenging aspect of financial planning. However, it’s effortless if you’re using a financial planning software.
Upmetrics’ forecasting feature can help you project financials for up to 7 years. However, new startups usually consider planning for the next five years. Although it can be contradictory considering your financial goals and investor specifications.
Following are the two key aspects of your financial projections:
Revenue Projections
In simple terms, revenue projections help investors determine how much revenue your business plans to generate in years to come.
It generally involves conducting market research, determining pricing strategy , and cash flow analysis—which we’ve already discussed in the previous steps.
The following are the key components of an accurate revenue projection report:
- Market analysis
- Sales forecast
- Pricing strategy
- Growth assumptions
- Seasonal variations
This is a critical section for pre-revenue startups, so ensure your projections accurately align with your startup’s financial model and revenue goals.
Expense Projections
Both revenue and expense projections are correlated to each other. As revenue forecasts projected revenue assumptions, expense projections will estimate expenses associated with operating your business.
Accurately estimating your expenses will help in effective cash flow analysis and proper resource allocation.
These are the most common costs to consider while projecting expenses:
- Fixed costs
- Variable costs
- Employee costs or payroll expenses
- Operational expenses
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Emergency fund
Remember, realistic assumptions, thorough research, and a clear understanding of your market are the key to reliable financial projections.
6. Consider “What if” Scenarios
After you project your financials, it’s time to test your assumptions with what-if analysis, also known as sensitivity analysis.
Using what-if analysis with different scenarios while projecting your financials will increase transparency and help investors better understand your startup’s future with its best, expected, and worst-case scenarios.
Exploring “what-if” scenarios is the best way to better understand the potential risks and opportunities involved in business operations. This proactive exercise will help you make strategic decisions and necessary adjustments to your financial plan.
7. Build a Visual Report
If you’ve closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using “what-if” scenarios.
Now, we’ll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
Don’t worry—it’s no extra effort. You’ve already made a visual report while creating your financial plan and forecasting financials.
Check the dashboard to see the visual presentation of your projections and reports, and use the necessary financial data, diagrams, and graphs in the final draft of your financial plan.
Here’s what Upmetrics’ dashboard looks like:
8. Monitor and Adjust Your Financial Plan
Even though it’s not a primary step in creating a good financial plan, it’s quite essential to regularly monitor and adjust your financial plan to ensure the assumptions you made are still relevant, and you are heading in the right direction.
There are multiple ways to monitor your financial plan.
For instance, you can compare your assumptions with actual results to ensure accurate projections based on metrics like new customers acquired and acquisition costs, net profit, and gross margin.
Consider making necessary adjustments if your assumptions are not resonating with actual numbers.
Also, keep an eye on whether the changes you’ve identified are having the desired effect by monitoring their implementation.
And that was the last step in our financial planning guide. However, it’s not the end. Have a look at this financial plan example.
Startup Financial Plan Example
Having learned about financial planning, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop startup financial plan example prepared using Upmetrics.
Important Assumptions
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some months revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wanes in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp- up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
Projected Balance Sheet
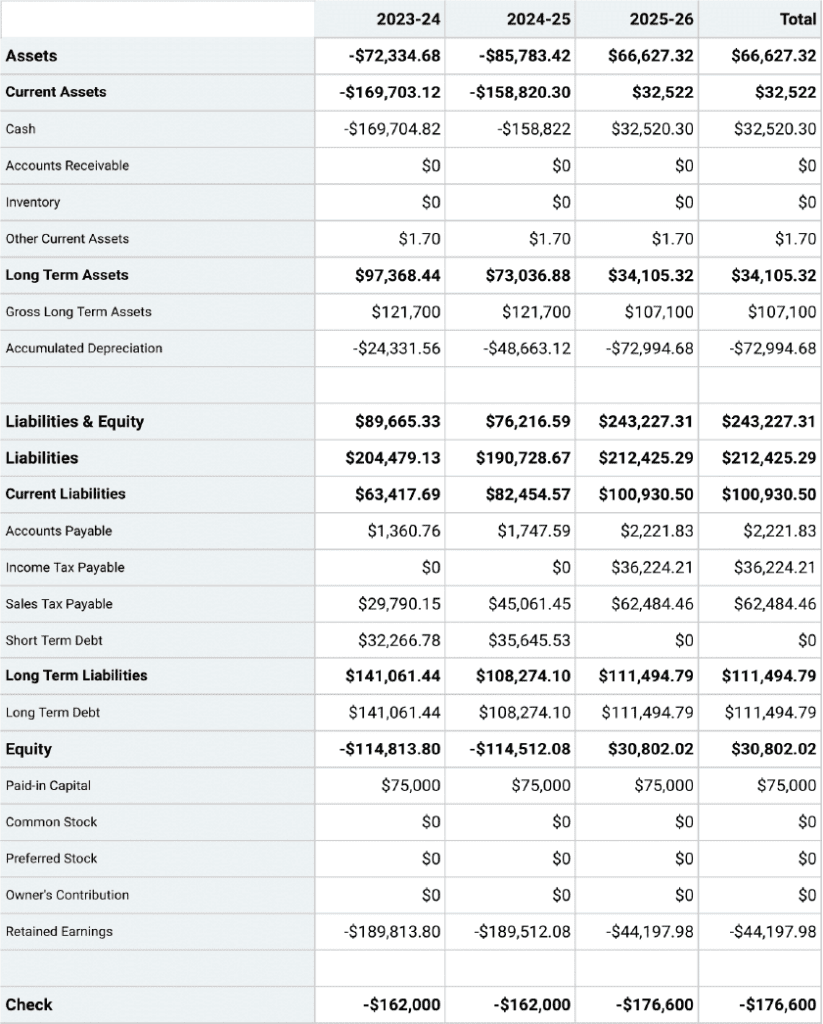
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
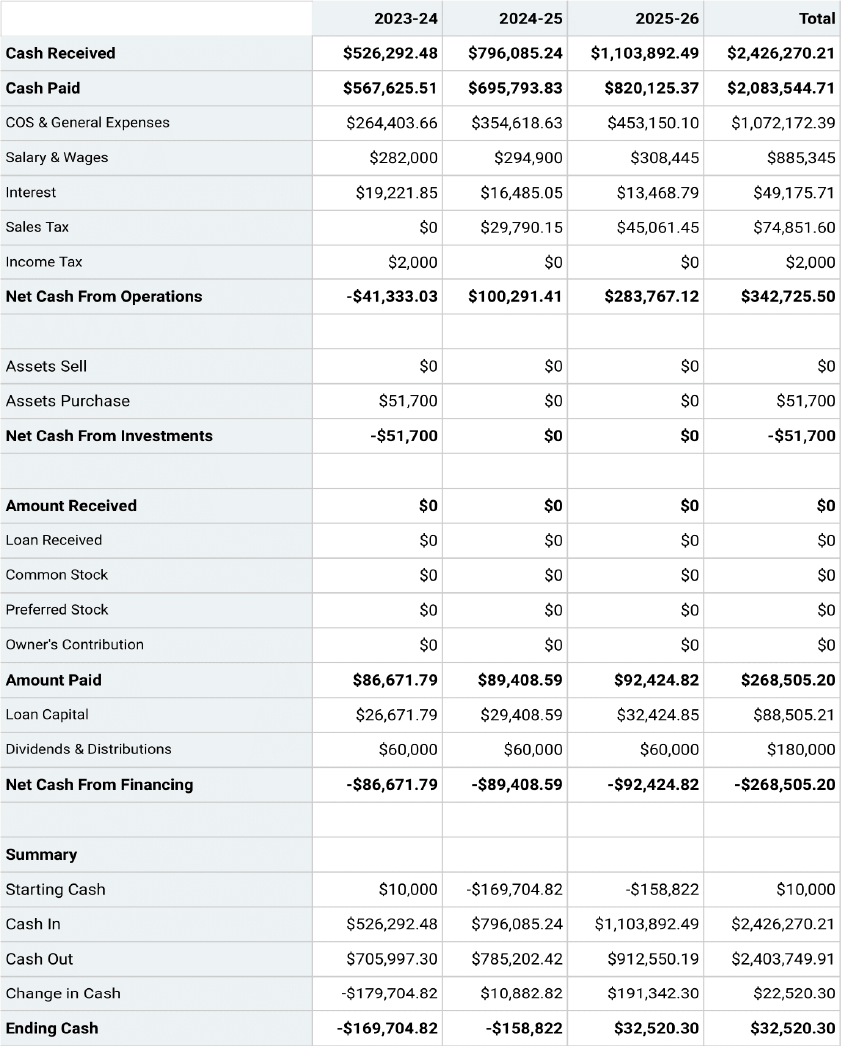
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
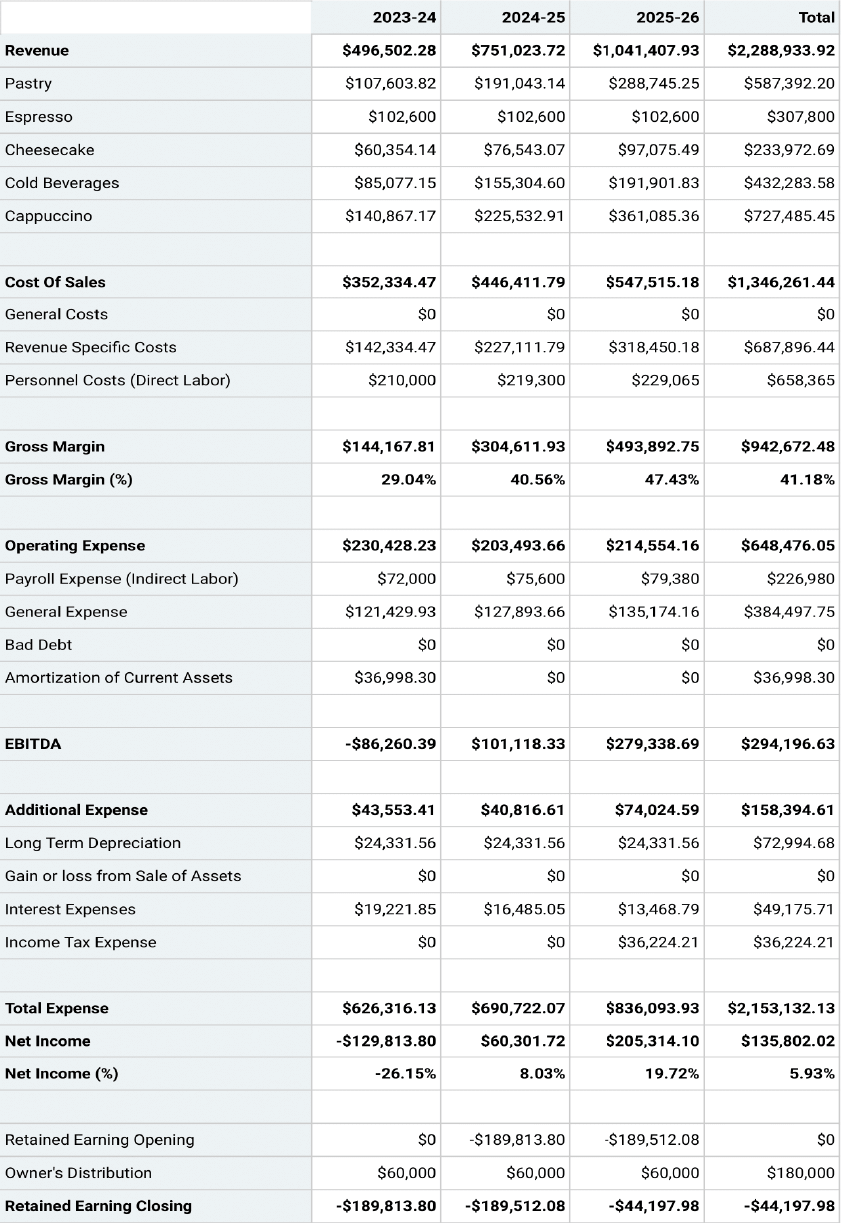
Break Even Analysis
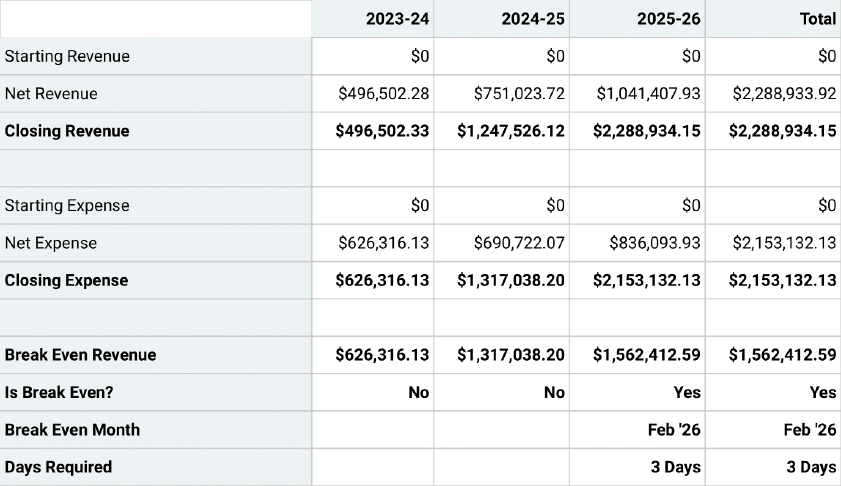
Start Preparing Your Financial Plan
We covered everything about financial planning in this guide, didn’t we? Although it doesn’t fulfill our objective to the fullest—we want you to finish your financial plan.
Sounds like a tough job? We have an easy way out for you—Upmetrics’ financial forecasting feature. Simply enter your financial assumptions, and let it do the rest.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your financial plan in a snap.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

Frequently Asked Questions
How often should i update my financial projections.
Well, there is no particular rule about it. However, reviewing and updating your financial plan once a year is considered an ideal practice as it ensures that the financial aspirations you started and the projections you made are still relevant.
How do I estimate startup costs accurately?
You can estimate your startup costs by identifying and factoring various one-time, recurring, and hidden expenses. However, using a financial forecasting tool like Upmetrics will ensure accurate costs while speeding up the process.
What financial ratios should startups pay attention to?
Here’s a list of financial ratios every startup owner should keep an eye on:
- Net profit margin
- Current ratio
- Quick ratio
- Working capital
- Return on equity
- Debt-to-equity ratio
- Return on assets
- Debt-to-asset ratio
What are the 3 different scenarios in scenario analysis?
As discussed earlier, Scenario analysis is the process of ascertaining and analyzing possible events that can occur in the future. Startups or businesses often consider analyzing these three scenarios:
- base-case (expected) scenario
- Worst-case scenario
- best case scenario.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates


- Getting Started
- Growing a Business
- Success Stories
How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan
Financial data is always at the back of the business plan, but that doesn’t mean it’s any less important than up-front material such as the description of the business concept and the management team. Astute investors look carefully at the charts, tables, formulas, and spreadsheets in the financial section because they know that this information is like the pulse, respiration rate, and blood pressure in a human being. It shows the condition of the patient. In fact, you’ll find many potential investors taking a quick peek at the numbers before reading the plan.
Financial statements come in threes: income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Taken together they provide an accurate picture of a company’s current value, plus its ability to pay its bills today and earn a profit going forward. This information is very important to business plan readers.
Why You Need an Income Statement
In his article, How to Do a Monthly Income Statement Analysis That Fuels Growth, Noah Parsons writes: “In short, you use your income statement to fuel a greater analysis of the financial standing of your business. It helps you identify any top-level issues or opportunities that you can then dive into with forecast scenarios and by looking at elements of your other financial documentation.
You want to leverage your income statement to understand if you’re performing better, worse or as expected. This is done by comparing it to your sales and expense forecasts through a review process known as plan vs actuals comparison. You then update projections to match actual performance to better showcase how your business will net out moving forward.”
What Is In an Income Statement
An income statement shows whether you are making any money. It adds up all your revenue from sales and other sources, subtracts all your costs, and comes up with the net income figure, also known as the bottom line.
Income statements are called various names—profit and loss statement (P&L) and earnings statement are two common alternatives. They can get pretty complicated in their attempt to capture sources of income, such as interest, and expenses, such as depreciation. But the basic idea is pretty simple: If you subtract costs from income, what you have left is profit.
To figure out your income statement, you need to gather a bunch of numbers, most of which are easily obtainable. They include your gross revenue, which is made up of sales and any income from interest or sales of assets; your sales, general, and administrative (SG&A) expenses; what you paid out in interest and dividends, if anything; and your corporate tax rate. If you have those, you’re ready to go.
Sales and Revenue
Revenue is all the income you receive from selling your products or services as well as from other sources such as interest income and sales of assets.
Gross Sales
Your sales figure is the income you receive from selling your product or service. Gross sales equals total sales minus returns. It doesn’t include interest or income from sales of assets.
Interest and Dividends
Most businesses have a little reserve fund they keep in an interest-bearing bank or money market account. Income from this fund, as well as from any other interest-paying or dividend-paying securities they own, shows up on the income statement just below the sales figure.
Other Income
If you finally decide that the branch office out on County Line Road isn’t ever going to turn a decent profit, and you sell the land, building, and fixtures, the income from that sale will show up on your income statement as “other income.” Other income may include sales of unused or obsolete equipment or any income-generating activity that’s not part of your main line of business.
Costs come in all varieties—that’s no secret. You’ll record variable costs, such as the cost of goods sold, as well as fixed costs—rent, insurance, maintenance, and so forth. You’ll also record costs that are a little trickier, the prime example being depreciation.
Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold, or COGS, includes expenses associated directly with generating the product or service you’re selling. If you buy smartphone components and assemble them, your COGS will include the price of the chips, screen, and other parts, as well as the wages of those doing the assembly. You’ll also include supervisor salaries and utilities for your factory. If you’re a solo professional service provider, on the other hand, your COGS may amount to little more than whatever salary you pay yourself and whatever technology you may use for your business.
Sales, General, and Administrative Costs
You have some expenses that aren’t closely tied to sales volume, including salaries for office personnel, salespeople compensation, rent, insurance, and the like. These are split out from the sales-sensitive COGS figure and included on a separate line.
Depreciation
Depreciation is one of the most baffling pieces of accounting wizardwork. It’s a paper loss, a way of subtracting over time the cost of a piece of equipment or a building that lasts many years even though it may get paid for immediately.
Depreciation isn’t an expense that involves cash coming out of your pocket. Yet it’s a real expense in an accounting sense, and most income statements will have an entry for depreciation coming off the top of pretax earnings. It refers to an ongoing decrease in asset value.
If you have capital items that you are depreciating, such as an office in your home or a large piece of machinery, your accountant will be able to set up a schedule for depreciation. Each year, you’ll take a portion of the purchase price of that item off your earnings statement. Although it hurts profits, depreciation can reduce future taxes.
Paying the interest on loans is another expense that gets a line all to itself and comes out of earnings just before taxes are subtracted. This line doesn’t include payments against the principal. Because these payments result in a reduction of liabilities—which we’ll talk about in a few pages in connection with your balance sheet—they’re not regarded as expenses on the income statement.
The best thing about taxes is that they’re figured last, on the profits that are left after every other thing has been taken out. Tax rates vary widely according to where your company is located, how and whether state and local taxes are figured, and your special tax situation. Use previous years as a guidepost for future returns. If you are just opening your business, work carefully with your accountant to set up a system whereby you can pay the necessary taxes at regular intervals.
Buzzword: EBIT
EBIT stands for earnings before interest and taxes. It is an indicator of a company’s profitability, calculated as revenue minus expenses, excluding tax and interest.
Important Plan Note
Don’t confuse sales with receipts. Your sales figure represents sales booked during the period, not necessarily money received. If your customers buy now and pay later, there may be a significant difference between sales and cash receipts.
Read the full article here
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign up to receive our weekly email
Our selection of the week's biggest startup news and features sent directly to your inbox. Enter your email address, confirm you're happy to receive our emails.
Latest News
Elon musk admits he ‘may have done more to financially impair’ x than to help it, things keep getting worse for tesla, creators explain how to start making money with the tiktok creative challenge program, including what type of content is most popular with brands, microsoft is about to pump billions more into ai data centers, ibm’s marketing chief explains how the company is harnessing ai to boost productivity, follow us on socials.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
- Business Planning
Business Plan Financial Projections
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Financial projections are an important part of your business plan. The projections give investors and lenders an idea of how well your business is likely to do in the future. Financial projections include both income statements and balance sheets.
Financial projections are important for a number of reasons. First, they give investors and lenders an idea of how well your business is likely to do in the future. This can help you secure the funding you need to get your business off the ground. Financial projections also help you track your progress over time. You can use them to make sure your business is on track to meet its goals. Finally, financial projections can help you spot potential problems early on, so you can take corrective action.
What Are Business Plan Financial Projections?
Financial projections are an estimate of your company’s future financial performance through financial forecasting. They are typically used by businesses to secure funding, but can also be useful for internal decision-making and planning purposes. There are three main financial statements that you will need to include in your business plan financial projections:
1. Income Statement Projection
The income statement projection is a forecast of your company’s future revenues and expenses. It should include line items for each type of income and expense, as well as a total at the end.
There are a few key items you will need to include in your projection:
- Revenue: Your revenue projection should break down your expected sales by product or service, as well as by month. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
- Expenses: Your expense projection should include a breakdown of your expected costs by category, such as marketing, salaries, and rent. Again, it is important to be realistic in your estimates.
- Net Income: The net income projection is the difference between your revenue and expenses. This number tells you how much profit your company is expected to make.
Sample Income Statement
2. cash flow statement & projection.
The cash flow statement and projection are a forecast of your company’s future cash inflows and outflows. It is important to include a cash flow projection in your business plan, as it will give investors and lenders an idea of your company’s ability to generate cash.
There are a few key items you will need to include in your cash flow projection:
- The cash flow statement shows a breakdown of your expected cash inflows and outflows by month. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
- Cash inflows should include items such as sales revenue, interest income, and capital gains. Cash outflows should include items such as salaries, rent, and marketing expenses.
- It is important to track your company’s cash flow over time to ensure that it is healthy. A healthy cash flow is necessary for a successful business.
Sample Cash Flow Statements
3. balance sheet projection.
The balance sheet projection is a forecast of your company’s future financial position. It should include line items for each type of asset and liability, as well as a total at the end.
A projection should include a breakdown of your company’s assets and liabilities by category. It is important to be realistic in your projections, so make sure to account for any seasonal variations in your business.
It is important to track your company’s financial position over time to ensure that it is healthy. A healthy balance is necessary for a successful business.
Sample Balance Sheet
How to create financial projections.
Creating financial projections for your business plan can be a daunting task, but it’s important to put together accurate and realistic financial projections in order to give your business the best chance for success.
Cost Assumptions
When you create financial projections, it is important to be realistic about the costs your business will incur, using historical financial data can help with this. You will need to make assumptions about the cost of goods sold, operational costs, and capital expenditures.
It is important to track your company’s expenses over time to ensure that it is staying within its budget. A healthy bottom line is necessary for a successful business.
Capital Expenditures, Funding, Tax, and Balance Sheet Items
You will also need to make assumptions about capital expenditures, funding, tax, and balance sheet items. These assumptions will help you to create a realistic financial picture of your business.
Capital Expenditures
When projecting your company’s capital expenditures, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the type of equipment or property your business will purchase. You will also need to estimate the cost of the purchase.
When projecting your company’s funding needs, you will need to make a number of assumptions about where the money will come from. This might include assumptions about bank loans, venture capital, or angel investors.
When projecting your company’s tax liability, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the tax rates that will apply to your business. You will also need to estimate the amount of taxes your company will owe.
Balance Sheet Items
When projecting your company’s balance, you will need to make a number of assumptions about the type and amount of debt your business will have. You will also need to estimate the value of your company’s assets and liabilities.
Financial Projection Scenarios
Write two financial scenarios when creating your financial projections, a best-case scenario, and a worst-case scenario. Use your list of assumptions to come up with realistic numbers for each scenario.
Presuming that you have already generated a list of assumptions, the creation of best and worst-case scenarios should be relatively simple. For each assumption, generate a high and low estimate. For example, if you are assuming that your company will have $100,000 in revenue, your high estimate might be $120,000 and your low estimate might be $80,000.
Once you have generated high and low estimates for all of your assumptions, you can create two scenarios: a best case scenario and a worst-case scenario. Simply plug the high estimates into your financial projections for the best-case scenario and the low estimates into your financial projections for the worst-case scenario.
Conduct a Ratio Analysis
A ratio analysis is a useful tool that can be used to evaluate a company’s financial health. Ratios can be used to compare a company’s performance to its industry average or to its own historical performance.
There are a number of different ratios that can be used in ratio analysis. Some of the more popular ones include the following:
- Gross margin ratio
- Operating margin ratio
- Return on assets (ROA)
- Return on equity (ROE)
To conduct a ratio analysis, you will need financial statements for your company and for its competitors. You will also need industry average ratios. These can be found in industry reports or on financial websites.
Once you have the necessary information, you can calculate the ratios for your company and compare them to the industry averages or to your own historical performance. If your company’s ratios are significantly different from the industry averages, it might be indicative of a problem.
Be Realistic
When creating your financial projections, it is important to be realistic. Your projections should be based on your list of assumptions and should reflect your best estimate of what your company’s future financial performance will be. This includes projected operating income, a projected income statement, and a profit and loss statement.
Your goal should be to create a realistic set of financial projections that can be used to guide your company’s future decision-making.
Sales Forecast
One of the most important aspects of your financial projections is your sales forecast. Your sales forecast should be based on your list of assumptions and should reflect your best estimate of what your company’s future sales will be.
Your sales forecast should be realistic and achievable. Do not try to “game” the system by creating an overly optimistic or pessimistic forecast. Your goal should be to create a realistic sales forecast that can be used to guide your company’s future decision-making.
Creating a sales forecast is not an exact science, but there are a number of methods that can be used to generate realistic estimates. Some common methods include market analysis, competitor analysis, and customer surveys.
Create Multi-Year Financial Projections
When creating financial projections, it is important to generate projections for multiple years. This will give you a better sense of how your company’s financial performance is likely to change over time.
It is also important to remember that your financial projections are just that: projections. They are based on a number of assumptions and are not guaranteed to be accurate. As such, you should review and update your projections on a regular basis to ensure that they remain relevant.
Creating financial projections is an important part of any business plan. However, it’s important to remember that these projections are just estimates. They are not guarantees of future success.
Business Plan Financial Projections FAQs
What is a business plan financial projection.
A business plan financial projection is a forecast of your company's future financial performance. It should include line items for each type of asset and liability, as well as a total at the end.
What are annual income statements?
The Annual income statement is a financial document and a financial model that summarize a company's revenues and expenses over the course of a fiscal year. They provide a snapshot of a company's financial health and performance and can be used to track trends and make comparisons with other businesses.
What are the necessary financial statements?
The necessary financial statements for a business plan are an income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
How do I create financial projections?
You can create financial projections by making a list of assumptions, creating two scenarios (best case and worst case), conducting a ratio analysis, and being realistic.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business
How to Write a Business Plan Outline [Examples + Templates]
By Letícia Fonseca , Aug 11, 2023

When venturing into crafting a business plan, the initial hurdle often lies in taking that first step.
So, how can you evade those prolonged hours of staring at a blank page? Initiate your journey with the aid of a business plan outline.
As with any endeavor, an outline serves as the beacon of clarity, illuminating the path to confront even the most formidable tasks. This holds particularly true when composing pivotal documents vital to your triumph, much like a business plan.
Nonetheless, I understand the enormity of a business plan’s scope, which might make the task of outlining it seem daunting. This is precisely why I’ve compiled all the requisite information to facilitate the creation of a business plan outline. No need to break a sweat!
And if you’re seeking further assistance, a business plan maker and readily available business plan templates can offer valuable support in shaping your comprehensive plan.
Read on for answers to all your business plan outline questions or jump ahead for some handy templates.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a business plan outline (and why do you need one), what format should you choose for your business plan outline, what are the key components of a business plan outline.
- Business plan template examples
- Writing tips to ace your outline
A business plan outline is the backbone of your business plan. It contains all the most important information you’ll want to expand on in your full-length plan.
Think of it this way: your outline is a frame for your plan. It provides a high-level idea of what the final plan should look like, what it will include and how all the information will be organized.
Why would you do this extra step? Beyond saving you from blank page syndrome, an outline ensures you don’t leave any essential information out of your plan — you can see all the most important points at a glance and quickly identify any content gaps.
It also serves as a writing guide. Once you know all the sections you want in your plan, you just need to expand on them. Suddenly, you’re “filling in the blanks” as opposed to writing a plan from scratch!
Incidentally, using a business plan template like this one gives you a running head start, too:

Perhaps most importantly, a business plan outline keeps you focused on the essential parts of your document. (Not to mention what matters most to stakeholders and investors.) With an outline, you’ll spend less time worrying about structure or organization and more time perfecting the actual content of your document.
If you’re looking for more general advice, you can read about how to create a business plan here . But if you’re working on outlining your plan, stick with me.
Return to Table of Contents
Most business plans fit into one of two formats.
The format you choose largely depends on three factors: (1) the stage of your business, (2) if you’re presenting the plan to investors and (3) what you want to achieve with your business plan.
Let’s have a closer look at these two formats and why you might choose one over the other.
Traditional format
Traditional business plans are typically long, detailed documents. In many cases, they take up to 50-60 pages, but it’s not uncommon to see plans spanning 100+ pages.
Traditional plans are long because they cover every aspect of your business. They leave nothing out. You’ll find a traditional business plan template with sections like executive summary, company description, target market, market analysis, marketing plan, financial plan, and more. Basically: the more information the merrier.
This business plan template isn’t of a traditional format, but you could expand it into one by duplicating pages:

Due to their high level of detail, traditional formats are the best way to sell your business. They show you’re reliable and have a clear vision for your business’s future.
If you’re planning on presenting your plan to investors and stakeholders, you’ll want to go with a traditional plan format. The more information you include, the fewer doubts and questions you’ll get when you present your plan, so don’t hold back.
Traditional business plans require more detailed outlines before drafting since there’s a lot of information to cover. You’ll want to list all the sections and include bullet points describing what each section should cover.
It’s also a good idea to include all external resources and visuals in your outline, so you don’t have to gather them later.
Lean format
Lean business plan formats are high level and quick to write. They’re often only one or two pages. Similar to a business plan infographic , they’re scannable and quick to digest, like this template:

This format is often referred to as a “startup” format due to (you guessed it!) many startups using it.
Lean business plans require less detailed outlines. You can include high-level sections and a few lines in each section covering the basics. Since the final plan will only be a page or two, you don’t need to over prepare. Nor will you need a ton of external resources.
Lean plans don’t answer all the questions investors and stakeholders may ask, so if you go this route, make sure it’s the right choice for your business . Companies not yet ready to present to investors will typically use a lean/startup business plan format to get their rough plan on paper and share it internally with their management team.
Here’s another example of a lean business plan format in the form of a financial plan:

Your business plan outline should include all the following sections. The level of detail you choose to go into will depend on your intentions for your plan (sharing with stakeholders vs. internal use), but you’ll want every section to be clear and to the point.
1. Executive summary
The executive summary gives a high-level description of your company, product or service. This section should include a mission statement, your company description, your business’s primary goal, and the problem it aims to solve. You’ll want to state how your business can solve the problem and briefly explain what makes you stand out (your competitive advantage).
Having an executive summary is essential to selling your business to stakeholders , so it should be as clear and concise as possible. Summarize your business in a few sentences in a way that will hook the reader (or audience) and get them invested in what you have to say next. In other words, this is your elevator pitch.

2. Product and services description
This is where you should go into more detail about your product or service. Your product is the heart of your business, so it’s essential this section is easy to grasp. After all, if people don’t know what you’re selling, you’ll have a hard time keeping them engaged!
Expand on your description in the executive summary, going into detail about the problem your customers face and how your product/service will solve it. If you have various products or services, go through all of them in equal detail.

3. Target market and/or Market analysis
A market analysis is crucial for placing your business in a larger context and showing investors you know your industry. This section should include market research on your prospective customer demographic including location, age range, goals and motivations.
You can even include detailed customer personas as a visual aid — these are especially useful if you have several target demographics. You want to showcase your knowledge of your customer, who exactly you’re selling to and how you can fulfill their needs.
Be sure to include information on the overall target market for your product, including direct and indirect competitors and how your industry is performing. If your competitors have strengths you want to mimic or weaknesses you want to exploit, this is the place to record that information.

4. Organization and management
You can think of this as a “meet the team” section — this is where you should go into depth on your business’s structure from management to legal and HR. If there are people bringing unique skills or experience to the table (I’m sure there are!), you should highlight them in this section.
The goal here is to showcase why your team is the best to run your business. Investors want to know you’re unified, organized and reliable. This is also a potential opportunity to bring more humanity to your business plan and showcase the faces behind the ideas and product.

5. Marketing and sales
Now that you’ve introduced your product and team, you need to explain how you’re going to sell it. Give a detailed explanation of your sales and marketing strategy, including pricing, timelines for launching your product and advertising.
This is a major section of your plan and can even live as a separate document for your marketing and sales teams. Here are some marketing plan templates to help you get started .
Make sure you have research or analysis to back up your decisions — if you want to do paid ads on LinkedIn to advertise your product, include a brief explanation as to why that is the best channel for your business.

6. Financial projections and funding request
The end of your plan is where you’ll look to the future and how you think your business will perform financially. Your financial plan should include results from your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow projections.
State your funding requirements and what you need to realize the business. Be extremely clear about how you plan to use the funding and when you expect investors will see returns.
If you aren’t presenting to potential investors, you can skip this part, but it’s something to keep in mind should you seek funding in the future. Covering financial projections and the previous five components is essential at the stage of business formation to ensure everything goes smoothly moving forward.

7. Appendix
Any extra visual aids, receipts, paperwork or charts will live here. Anything that may be relevant to your plan should be included as reference e.g. your cash flow statement (or other financial statements). You can format your appendix in whatever way you think is best — as long as it’s easy for readers to find what they’re looking for, you’ve done your job!
Typically, the best way to start your outline is to list all these high-level sections. Then, you can add bullet points outlining what will go in each section and the resources you’ll need to write them. This should give you a solid starting point for your full-length plan.
Business plan outline templates
Looking for a shortcut? Our business plan templates are basically outlines in a box!
While your outline likely won’t go into as much detail, these templates are great examples of how to organize your sections.
Traditional format templates
A strong template can turn your long, dense business plan into an engaging, easy-to-read document. There are lots to choose from, but here are just a few ideas to inspire you…
You can duplicate pages and use these styles for a traditional outline, or start with a lean outline as you build your business plan out over time:

Lean format templates
For lean format outlines, a simpler ‘ mind map ’ style is a good bet. With this style, you can get ideas down fast and quickly turn them into one or two-page plans. Plus, because they’re shorter, they’re easy to share with your team.

Writing tips to ace your business plan outline
Business plans are complex documents, so if you’re still not sure how to write your outline, don’t worry! Here are some helpful tips to keep in mind when drafting your business plan outline:
- Ask yourself why you’re writing an outline. Having a clear goal for your outline can help keep you on track as you write. Everything you include in your plan should contribute to your goal. If it doesn’t, it probably doesn’t need to be in there.
- Keep it clear and concise. Whether you’re writing a traditional or lean format business plan, your outline should be easy to understand. Choose your words wisely and avoid unnecessary preambles or padding language. The faster you get to the point, the easier your plan will be to read.
- Add visual aids. No one likes reading huge walls of text! Make room in your outline for visuals, data and charts. This keeps your audience engaged and helps those who are more visual learners. Psst, infographics are great for this.
- Make it collaborative. Have someone (or several someones) look it over before finalizing your outline. If you have an established marketing / sales / finance team, have them look it over too. Getting feedback at the outline stage can help you avoid rewrites and wasted time down the line.
If this is your first time writing a business plan outline, don’t be too hard on yourself. You might not get it 100% right on the first try, but with these tips and the key components listed above, you’ll have a strong foundation. Remember, done is better than perfect.
Create a winning business plan by starting with a detailed, actionable outline
The best way to learn is by doing. So go ahead, get started on your business plan outline. As you develop your plan, you’ll no doubt learn more about your business and what’s important for success along the way.
A clean, compelling template is a great way to get a head start on your outline. After all, the sections are already separated and defined for you!
Explore Venngage’s business plan templates for one that suits your needs. Many are free to use and there are premium templates available for a small monthly fee. Happy outlining!
.png)
Pro Forma Financial Statements (with Templates and Examples)
Bryce Warnes
Reviewed by
Janet Berry-Johnson, CPA
April 21, 2022
This article is Tax Professional approved
Pro forma definition
According to Merriam-Webster , “pro forma” means:
- Made or carried out in a perfunctory manner or as a formality
- Based on financial assumptions or projections
I am the text that will be copied.
Pro forma is actually a Latin term meaning “for form” (or today we might say “for the sake of form, as a matter of form”).
When it comes to accounting, pro forma statements are financial reports for your business based on hypothetical scenarios. They’re a way for you to test out situations you think may happen in the future to help you make business decisions.
There are three major pro forma statements:
- Pro forma income statements
- Pro forma balance sheets
- Pro forma cash flow statements
Pro forma statements look like regular statements, except they’re based on what ifs, not real financial results. As in, “What if my business got a $50,000 loan next year?” Your pro forma statements for that scenario would show what your income, account balances, and cash flow would look like with a $50,000 loan.
Since pro forma statements deal with potential outcomes, they’re not considered GAAP compliant . This is because GAAP compliant reports must be based on historical information.
Pro forma statements don’t need to meet the strictest accounting standards , but must be clearly marked as “pro forma” and can’t be used for things like filing taxes. Using pro forma statements that aren’t marked as such to misrepresent your business to investors, the IRS, or financial institutions can be penalized by the Securities and Exchange Commission).
However, pro forma statements are still extremely useful. They can help you make a business plan, create a financial forecast, and even get funding from potential investors or lenders.
Different but related: you can send clients pro forma invoices to let them know how much their order would be if they placed it today.
Why create pro forma statements?
Creating pro forma statements for future scenarios can help you:
- Get financed, by showing lenders or investors how you would use their money to sustainably grow your business.
- Plan for the future, by considering best, worst, and most likely case scenarios in detail.
- Anticipate changes that may affect your business as it grows, such as entering a new tax bracket.
For these purposes, pro forma statements are typically created as a part of a financial forecast in financial accounting. Big corporations who have in-house accountants use pro forma statements for financial modeling and forecasting different scenarios.
Pro forma statements vs. budgets
It may be tempting to think of a pro forma statement as the same as a business budget . After all, you create both in anticipation of the future. And both help you plan how you’ll use your money. But budgets and pro forma statements are two distinct financial tools.
Think of it this way: A pro forma statement is a prediction, and a budget is a plan. Your budget may be based on the financial information of your pro forma statements—after all, it makes sense to make plans based on your predictions.
For example: Your income this year is $37,000. According to your pro forma annual income statement, your financial projections show it will be $44,000 next year. So, when you create next year’s budget, you can include that extra $7,000—maybe spending $4,000 over the course of the year to pay down the principal on a loan , while adding $3,000 to savings.
Types of pro forma statement
There are four main types of pro forma statements. While they all fall into the same categories—income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement—they differ based on the purpose of the financial forecast.
1. Full-year pro forma projection
This type of pro forma projection takes into account all of your financials for the fiscal year up until the present time, then adds projected outcomes for the remainder of the year. That can help you show investors or partners what business finances could look like by the end of the fiscal year.
2. Financing or investment pro forma projection
You may be courting investors or trying to convince your business partners of the value of a capital investment or additional financing. In that case, you can use a financing pro forma projection to make your case. It takes into account an injection of cash from an outside source—plus any interest payments you may need to make—and shows how it will affect your business’s financial position.
3. Historical with acquisition pro forma projection
This type of pro forma projection looks at the past financial statements of your business, plus the past financial statements of a business you want to buy . Then it merges them to show what your financials would have looked like if you made a business combination (or merger) earlier. You can use this scenario as a model of what may happen in the future if you buy the other business and restructure now.
4. Risk analysis pro forma projection
Looking at both best case and worst case scenarios helps you make financial decisions based on challenges you may face in the future. For instance, what happens if your main vendor raises their prices like they did last year? Or how will that proposed transaction of buying new equipment impact you long term? Risk analysis lets you take the future for a test ride, and try out different outcomes.
Pro forma templates
To create a pro forma statement, you can use the same template you’d use for a normal financial statement. You may want to use Bench’s free templates:
- Income statement
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
How to create pro forma statements
The sample pro forma statements below may look different from the statements you create, depending on what your template looks like. But generally, these are the steps you need to take to create them—and the info your pro forma statements should include.
Creating a pro forma income statement
There are five steps to creating a pro forma income statement:
- Set a goal for sales in the period you’re looking at. Let’s say you want to increase your income by $18,000 over the course of one year.
- Set a production schedule that will let you reach your goal, and map it out over the time period you’re covering. In this case, you’ll want to earn an additional $1,500 income every month, for 12 months.
- Plan how you’ll match your production schedule. You could do this by growing your number of sales a fixed amount every month, or gradually increasing the amount of sales you make per month. It’s up to you—trust your experience as a business owner.
- It’s time for the “loss” part of “ Profit and Loss .” Calculate the cost of goods sold for each month in your projection. Then, deduct it from your sales. Deduct any other operating expenses you have, as well.
- Prepare your pro forma income statement using data you’ve compiled in the prior four steps.
One note: your pro forma statements will be much more accurate if your bookkeeping is up to date. That way, when you project future periods, you’re basing it off the reality of your business today.
How Bench can help
To predict the future, you first need to understand the past. With Bench, you get a crystal clear image of your financial history so you can focus on planning your future. We’re America’s largest bookkeeping service helping thousands of business owners better understand the financial health of their operations so they can keep focused on growth and planning. When it comes time to create a pro forma statement, you have reliable numbers and reports to get started. We may not be a crystal ball, but we’re the next best thing. Learn more .
Example pro forma income statement:
Rosalia’s Reliable Recordings
Creating a pro forma cash flow statement
You create a pro forma cash flow statement much the same way you’d create a normal cash flow statement. That means taking info from the income statement, then using the cash flow statement format to plot out where your money is going, and what you’ll have on hand at any one time. This pro forma statement can be part of a larger cash flow forecast used for decision making.
Your projected cash flow can give you a few different insights. If it’s negative, it means you won’t have enough cash on-hand to run your business, according to your current trajectory. You’ll have to make plans to borrow money and pay it off.
On the other hand, if net cash flow is positive, you can plan on having enough extra cash on hand to pay off loans, or save for a big investment.
Example pro forma cash flow statement
Mickie’s Murakami Museum
Creating a pro forma balance sheet
By drawing on info from the income statement and the cash flow statement, you can create pro forma balance sheets. However, you’ll also need previous balance sheets to make this useful—so you can see how your business got from “Balance A” to “Balance B.”
The balance sheet will project changes in your business accounts over time. So you can plan where to move money, when.
Example pro forma balance sheet
Daily Dumpling Deliveries
Once you’ve created your pro forma income statements, and cast your eyes forward to the future of your business, you can start planning how you’ll spend your money. It’s time to create a small business budget .
Related Posts

How to Pay Off Your Business Debt, Fast
Buried in small business debt? Follow this plan to dig yourself out.

Understanding an Income Statement (Definition and Examples)
How profitable is your business? Your income statement will tell you.

The Top Trucking Accounting Software
Find the best trucking accounting software for your business with our comparison guide. Read about features, pricing, and more to make the best decision for your company.
Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
Get a regular dose of educational guides and resources curated from the experts at Bench to help you confidently make the right decisions to grow your business. No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
How To Create Financial Projections for Your Business
Learn how to anticipate your business’s financial performance
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ScreenShot2020-03-26at1.24.14PM-16d178cb2ee74d71946d658ab027e210.png)
- Understanding Financial Projections & Forecasting
Why Forecasting Is Critical for Your Business
Key financial statements for forecasting, how to create your financial projections, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Maskot / Getty Images
Just like a weather forecast lets you know that wearing closed-toe shoes will be important for that afternoon downpour later, a good financial forecast allows you to better anticipate financial highs and lows for your business.
Neglecting to compile financial projections for your business may signal to investors that you’re unprepared for the future, which may cause you to lose out on funding opportunities.
Read on to learn more about financial projections, how to compile and use them in a business plan, and why they can be crucial for every business owner.
Key Takeaways
- Financial forecasting is a projection of your business's future revenues and expenses based on comparative data analysis, industry research, and more.
- Financial projections are a valuable tool for entrepreneurs as they offer insight into a business's ability to generate profit, increase cash flow, and repay debts, which can be attractive to investors.
- Some of the key components to include in a financial projection include a sales projection, break-even analysis, and pro forma balance sheet and income statement.
- A financial projection can not only attract investors, but helps business owners anticipate fixed costs, find a break-even point, and prepare for the unexpected.
Understanding Financial Projections and Forecasting
Financial forecasting is an educated estimate of future revenues and expenses that involves comparative analysis to get a snapshot of what could happen in your business’s future.
This process helps in making predictions about future business performance based on current financial information, industry trends, and economic conditions. Financial forecasting also helps businesses make decisions about investments, financing sources, inventory management, cost control strategies, and even whether to move into another market.
Developing both short- and mid-term projections is usually necessary to help you determine immediate production and personnel needs as well as future resource requirements for raw materials, equipment, and machinery.
Financial projections are a valuable tool for entrepreneurs as they offer insight into a business's ability to generate profit, increase cash flow, and repay debts. They can also be used to make informed decisions about the business’s plans. Creating an accurate, adaptive financial projection for your business offers many benefits, including:
- Attracting investors and convincing them to fund your business
- Anticipating problems before they arise
- Visualizing your small-business objectives and budgets
- Demonstrating how you will repay small-business loans
- Planning for more significant business expenses
- Showing business growth potential
- Helping with proper pricing and production planning
Financial forecasting is essentially predicting the revenue and expenses for a business venture. Whether your business is new or established, forecasting can play a vital role in helping you plan for the future and budget your funds.
Creating financial projections may be a necessary exercise for many businesses, particularly those that do not have sufficient cash flow or need to rely on customer credit to maintain operations. Compiling financial information, knowing your market, and understanding what your potential investors are looking for can enable you to make intelligent decisions about your assets and resources.
The income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flow are three key financial reports needed for forecasting that can also provide analysts with crucial information about a business's financial health. Here is a closer look at each.
Income Statement
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement or P&L, is a financial document that provides an overview of an organization's revenues, expenses, and net income.
Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a snapshot of the business's assets and liabilities at a certain point in time. Sometimes referred to as the “financial portrait” of a business, the balance sheet provides an overview of how much money the business has, what it owes, and its net worth.
The assets side of the balance sheet includes what the business owns as well as future ownership items. The other side of the sheet includes liabilities and equity, which represent what it owes or what others owe to the business.
A balance sheet that shows hypothetical calculations and future financial projections is also referred to as a “pro forma” balance sheet.
Cash Flow Statement
A cash flow statement monitors the business’s inflows and outflows—both cash and non-cash. Cash flow is the business’s projected earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization ( EBITDA ) minus capital investments.
Here's how to compile your financial projections and fit the results into the three above statements.
A financial projections spreadsheet for your business should include these metrics and figures:
- Sales forecast
- Balance sheet
- Operating expenses
- Payroll expenses (if applicable)
- Amortization and depreciation
- Cash flow statement
- Income statement
- Cost of goods sold (COGS)
- Break-even analysis
Here are key steps to account for creating your financial projections.
Projecting Sales
The first step for a financial forecast starts with projecting your business’s sales, which are typically derived from past revenue as well as industry research. These projections allow businesses to understand what their risks are and how much they will need in terms of staffing, resources, and funding.
Sales forecasts also enable businesses to decide on important levels such as product variety, price points, and inventory capacity.
Income Statement Calculations
A projected income statement shows how much you expect in revenue and profit—as well as your estimated expenses and losses—over a specific time in the future. Like a standard income statement, elements on a projection include revenue, COGS, and expenses that you’ll calculate to determine figures such as the business’s gross profit margin and net income.
If you’re developing a hypothetical, or pro forma, income statement, you can use historical data from previous years’ income statements. You can also do a comparative analysis of two different income statement periods to come up with your figures.
Anticipate Fixed Costs
Fixed business costs are expenses that do not change based on the number of products sold. The best way to anticipate fixed business costs is to research your industry and prepare a budget using actual numbers from competitors in the industry. Anticipating fixed costs ensures your business doesn’t overpay for its needs and balances out its variable costs. A few examples of fixed business costs include:
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Operating expenses (also called selling, general and administrative expenses or SG&A)
- Utility bills
- Insurance premiums
Unfortunately, it might not be possible to predict accurately how much your fixed costs will change in a year due to variables such as inflation, property, and interest rates. It’s best to slightly overestimate fixed costs just in case you need to account for these potential fluctuations.
Find Your Break-Even Point
The break-even point (BEP) is the number at which a business has the same expenses as its revenue. In other words, it occurs when your operations generate enough revenue to cover all of your business’s costs and expenses. The BEP will differ depending on the type of business, market conditions, and other factors.
To find this number, you need to determine two things: your fixed costs and variable costs. Once you have these figures, you can find your BEP using this formula:
Break-even point = fixed expenses ➗ 1 – (variable expenses ➗ sales)
The BEP is an essential consideration for any projection because it is the point at which total revenue from a project equals total cost. This makes it the point of either profit or loss.
Plan for the Unexpected
It is necessary to have the proper financial safeguards in place to prepare for any unanticipated costs. A sudden vehicle repair, a leaky roof, or broken equipment can quickly derail your budget if you aren't prepared. Cash management is a financial management plan that ensures a business has enough cash on hand to maintain operations and meet short-term obligations.
To maintain cash reserves, you can apply for overdraft protection or an overdraft line of credit. Overdraft protection can be set up by a bank or credit card business and provides short-term loans if the account balance falls below zero. On the other hand, a line of credit is an agreement with a lending institution in which they provide you with an unsecured loan at any time until your balance reaches zero again.
How do you make financial projections for startups?
Financial projections for startups can be hard to complete. Historical financial data may not be available. Find someone with financial projections experience to give insight on risks and outcomes.
Consider business forecasting, too, which incorporates assumptions about the exponential growth of your business.
Startups can also benefit from using EBITDA to get a better look at potential cash flow.
What are the benefits associated with forecasting business finances?
Forecasting can be beneficial for businesses in many ways, including:
- Providing better understanding of your business cash flow
- Easing the process of planning and budgeting for the future based on income
- Improving decision-making
- Providing valuable insight into what's in their future
- Making decisions on how to best allocate resources for success
How many years should your financial forecast be?
Your financial forecast should either be projected over a specific time period or projected into perpetuity. There are various methods for determining how long a financial forecasting projection should go out, but many businesses use one to five years as a standard timeframe.
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Market Research and Competitive Analysis ."
Score. " Financial Projections Template ."

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An income statement is your business's bottom line: your total revenue from sales minus all of your costs. Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own. This is part 2 / 11 of ...
An income statement summarizes your revenue and costs and shows your net profit in your business plan. Take a look at how a gift shop called Broad Street Emporium uses income statements to manage business finances. The figure shows the company's annual revenues, costs, and profits for the most recent year as well as for the previous year.
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business. . Download Startup Financial Projections Template.
Whether you want to launch a side gig, a solo operation or a small business, you need a simple business plan template to guide you. Forbes Advisor offers you a comprehensive and easy-to-follow ...
The income statement shows revenue and expenses, usually by month. At the bottom, total expenses are subtracted from total revenue to arrive at Net Ordinary Income—which is essentially profit, though in an actual business there will be some accounting and tax adjustments made to arrive at true profit. That's why profit is often referred to ...
Steps to Prepare an Income Statement. 1. Choose Your Reporting Period. Your reporting period is the specific timeframe the income statement covers. Choosing the correct one is critical. Monthly, quarterly, and annual reporting periods are all common. Which reporting period is right for you depends on your goals.
Here are a few basic steps for creating an income statement, or profit and loss statement, depending on which software you're using. 1. Find the income statement function. As noted, some accounting software may refer to the income statement as a profit and loss (or P&L) statement, so don't get confused. You can usually find it in the ...
It must include a financial plan section, complete with a projected balance sheet, cash flow, and income statement. In business planning, the word "projected" is often replaced with the word "pro-forma," but it means the same thing. An income statement typically includes the following components: Sales. Direct cost of sales. Production ...
Subtract the selling and administrative expenses total from the gross margin. Doing this will give you the amount of pre-tax operating income. Enter the amount at the bottom of the income statement. 8. Include Income Taxes. To calculate income tax, multiply your applicable state tax rate by your pre-tax income figure.
Sections to include in your business plan financials. Here are the three statements to include in the finance section of your business plan: Profit and loss statement. A profit and loss statement, also known as an income statement, identifies your business's revenue (profit) and expenses (loss). This document describes your company's ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Write the Executive Summary. This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what's in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company. Add a Company Overview. Document the larger company mission and vision.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Download Now: Free Business Plan Template. Writing a business plan doesn't have to be complicated. In this step-by-step guide, you'll learn how to write a business plan that's detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
7. Build a Visual Report. If you've closely followed the steps leading to this, you know how to research for financial projections, create a financial plan, and test assumptions using "what-if" scenarios. Now, we'll prepare visual reports to present your numbers in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
An income statement shows whether you are making any money. It adds up all your revenue from sales and other sources, subtracts all your costs, and comes up with the net income figure, also known as the bottom line. Income statements are called various names—profit and loss statement (P&L) and earnings statement are two common alternatives ...
There are three main financial statements that you will need to include in your business plan financial projections: 1. Income Statement Projection. The income statement projection is a forecast of your company's future revenues and expenses. It should include line items for each type of income and expense, as well as a total at the end.
The goal here is to showcase why your team is the best to run your business. Investors want to know you're unified, organized and reliable. This is also a potential opportunity to bring more humanity to your business plan and showcase the faces behind the ideas and product. 5. Marketing and sales.
The resulting total represents your projected operating income, which is a critical business metric. Plan to create an income statement monthly until your projected break-even, or the point at which future revenues outpace total expenses, and you reflect operating profit. From there, annual income statements will suffice.
Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis. Forecast expenses. Forecast sales. Build financial projections. The following five steps can help you break down the process of developing financial projections for your company: 1. Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections.
Your budget may be based on the financial information of your pro forma statements—after all, it makes sense to make plans based on your predictions. For example: Your income this year is $37,000. According to your pro forma annual income statement, your financial projections show it will be $44,000 next year.
Financial projections are a valuable tool for entrepreneurs as they offer insight into a business's ability to generate profit, increase cash flow, and repay debts. They can also be used to make informed decisions about the business's plans. Creating an accurate, adaptive financial projection for your business offers many benefits, including: