RS-232 DB9 Pinout and Usage

RS-232 DB9 Overview
The RS232C DE-9, often mistakenly referred to as a DB-9 port used to be the industry standard for serial data transmission. A RS-232 serial port was a standard feature of personal computers as it was the preferred way to connect modems, keyboards, mice, external storage and many other peripheral devices.

The background of the 9 pin serial port
First introduced in the 60s, RS-232 is a protocol that defines how the data is transferred, bit by bit from a Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) such as a computer terminal, to Data Communication Equipment (DCE) such as a modem.
RS-232 is the common standard used in serial ports. It defines the electrical properties and the timing of signals, as well as the interpretation of signals, and the physical size and pinout configuration of a connector.
Modern day computers seldom have RS-232 ports. Universal Serial Bus (USB) has replaced the traditional RS-232 interface. RS-232 has many shortcomings when compared to later technologies such as RS-422 , RS-485 and even Ethernet . These shortcomings include low transmission speed, limited cable length, substantial voltage fluctuations, and limited multidrop capabilities.
It is however possible to use an external USB-to-RS-232 converter or an internal expansion card with one or more serial ports to connect a RS-233 serial peripheral device to your computer. Many motherboards also feature a COM port header which makes it possible to install a bracket with a DE-9 port.

Despite the shortcomings and the technology advancements, RS-232 interfaces are still very much in use with large industrial machines, networking equipment and scientific instruments where point to point, low speed wired data connections is sufficient.
A PC serial port interface is single ended. This means that you can only connect two devices using a RS232 serial cable. The data that is transferred between these two devices is transferred at a rate less than 20 kbps.
RS232 allows for full-duplex communication – this means that both devices can interface with each other simultaneously. A common ground between the computer and the connected serial device is mandatory. This is represented by voltage levels defined by the RS232 protocol.
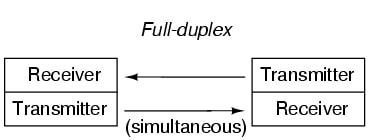
With RS232, hot-plugging or hot-swapping is not supported, though it is sometimes possible to plug in a serial device and it will work while the computer is running. With current technology, only a 9-pin connector is in use with most personal computers.

Related Articles
Standard RS232 data packet
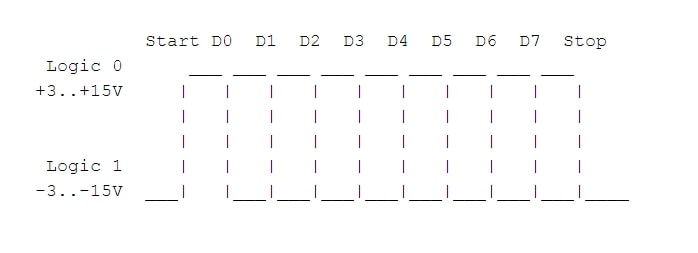
A RS232 transmission begins with a start bit. A start bit notifies the receiving computer of the incoming transmission. The data packets consist of 7 or 8 bit words. The start bit is generally a low voltage bit, between +3v and +15v. The data bits then follow the start bit on a LSB basis ( least significant bit ) - this is the bit with the lowest numerical value. A parity bit would generally follow the data, and then the transmission is ended with a stop bit.
An example of how RS232 serial port works with the help of the serial mouse

A serial mouse comprises sensors, mouse controller, communication link, data interface, driver and software. Movement of the mouse as well as button clicks is detected by the sensors. The mouse controller takes note of the current mouse position as well as the state of the various sensors.
When this information changes, a data packet is transmitted by the mouse controller to the computer’s serial data interface controller. It is the mouse driver that is installed on the computer that receives the data packet and decodes it, then executing the appropriate action based on the instructions received.
PC RS232 serial mouse voltage levels:
A standard mouse expects a RS-232C output signal with an approximate 12V level as its input signal. The RS-232C port will have a number of output lines from which the mouse can take current (about 10mA). The mouse then sends data to the computer’s receiver chip. The data being sent must be at a level that can be understood by the receiver chip. Average mouse outputs range between +5V, -.5V and +12V. On average, a mouse will use about +5 volts to perform.
Serial device hardware implementation
A serial mouse makes use of DTR (Data Terminal Ready) and RTS (Request to send) lines to generate approximately 5V of power for its microcontroller circuit. An optomechanical mouse (one that makes use of optical sensors) that has LEDs will require power to light those LEDs.
Diodes are often used to take current from the DTR and RTS lines – intercepting the diodes and resistor. Negative supply for the transmitter is taken from the TD pin. The TD pin is the pin that carries the data from the DTE to the DCE.
A standard serial mouse takes 10 mA total current operating at a voltage range between 6 and 15 volts. The data is sent using standard asynchronous RS-232C serial format:
An explanation of serial RS-232 mouse pinout
When DTR link is toggled, the mouse should identify itself by sending one data byte containing the letter M ( ASCII 77 ). For the mouse to work correctly, both RTS and DTR lines must be positive.
Ensure the DTR-DSR and RTS-CTS lines are not shorted. To implement the RTS toggle, set the RTS line to negative and then positive again. The negative pulse width is at least 100ms.
This is a cold boot, after which the RTS line will be set to negative. Setting the RTS line to a positive level is considered a RTS toggle. Here is the layout and function of the 9 pins:
RS232 serial data parameters and packet formats
Serial data parameters are 1200bps, 7 databits, 1 stop-bit.
A data packet consists of 3 bytes. Every time the mouse state changes, the mouse sends that packet to the computer.

Note: X denotes a 0 when the mouse received 7 databits and 2 stop bits format. 8 databits and 1 stop bit is also possible . When that happens, X is then 1. The safest options is to use a 7 databits and 1 stopbit format when the mouse is receiving information. For sending information use the 7 databits and 2 stop bits format.
The bite marked with 1 is sent first, (lowest numerical value) then the others follow. Should the data transmission go out of sync, the bit D6 is the first byte for synchronizing the software to mouse packets.
LB represents the left mouse button where 1 denotes that it is pressed down.
RB is the right button.
X7 - X0 describes movement in a X direction since the last data packet transmission (signed byte)
Y7 - Y0 is movement in a Y direction since last data packet transmission (signed byte)
- serial port communication

Serial communication interface. RS232 pinout.
- What is the RS232 Protocol?
What does RS232 stand for?
- ❒ COM Port Pinout and Configuration
- RS232 cables
What is RS232 Protocol?
The RS232 protocol is a popular serial interface that is used to connect computers to peripheral devices such as modems. We will take a look at the serial port pinouts used to implement RS232 as well as some additional reference information concerning the protocol.
The RS232 protocol transmits data of wires employing signal levels that differ from the standard 5V in order to minimize signal interference. It performs asynchronous transmission at a constant rate that is synchronized with the start pulse signal’s level. Distances of up to 20 meters are the limit for reliable data transfer using the RS232 interface.
Data transfer standards are developed by the Electronic Industry Association (EIA). The prefix RS denotes a Recommended Standard, and all of the EIA standards begin with those characters. The formal specification of RS232 is that it is an interface which uses serial binary data exchange to communicate between DTE and DCE devices. DTE is the acronym for Data Terminal Equipment and DCE represents Data Communication Equipment. The basic example of these two types of equipment defines a computer as a DTE device with a modem filling the role of DCE.
Serial communication is implemented by the transmission of serial data between the DTE and DCE. For instance, a computer (DTE) might send the binary data “11011101” serially to the modem (DCE) which then replies by sending “11010101” back to the DTE device.
The RS232 protocol specifies the operation mode, electrical standards, number of bits, and voltage levels to be used when transferring data between a DTE and DCE.
Serial connectors
Serial communication devices make use of 9 or 25 pin D-type connectors for their cabled connections. They are commonly designated as DB-9 or DB-25 with the number used to differentiate between the pin counts. Various manufacturers’ names may replace the DB in the specifications. The plugs contain sockets and pins, with each pin numbered and labeled. A serial pinout diagram is presented below.
The RS232 protocol uses a 9 pin serial port that can have either male or female connectors. The most recent version of the protocol is known as RS232C.
RS232C retains the features of RS232 but uses 25 pins rather than a 9 pin serial pinout. Whether a DB9 serial pinout or a 25 pin connection is used, only three of the pins are required to connect terminal devices.
COM Port Pinout and Configuration
RS232 manages communication flowing between the DTE and DCE using serial pinouts of either the DB9 or DB25 variety. These D-sub connectors can terminate with an RS232 female pinout or DB25 or DB9 male connector pins. Each pin in a 9 or 25 serial connector pinout has its own distinct function. You can also learn RS485 pinout.
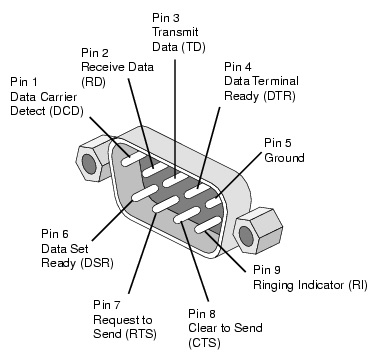
Functional Description:
In addition to defining electrical characteristics, RS232 specifies the signals used in serial cable pinouts and serial ports. Familiar items such as timing signals and ground are included in these specifications.
Following is a list of the signals used in an RS232 COM port pinout:
Protective Ground -This signal is connected to the chassis ground of the metallic connector.
Common Ground - Zero reference voltage level for all the control signals.
TxD (Transmit Pin) - To transmit data from DTE to DCE.
RxD (Receive Pin) - Sends data from DCE to DTE.
DTR (Data Terminal Ready) - DTE is ready to accept the request.
DCD (Data carrier Detect) - DCE accepts a carrier from a DTE located at a remote location.
DSR (Data Set Ready) - DCE is prepared to send and receive the information.
RI (Ring Indicator) - Detects the incoming ring tone on the telephone line.
RTS (Request to Send) - DTE call for DCE to send the data.
RTR (Ready to Receive) - DTE is geared up to receive data coming from DCE.
CTS (Clear To Send) - DCE is in a ready state to accept data coming from DTE.
These signals are the primary RS232 signals, but the protocol allows for secondary signals as well. They include secondary DTE, RTS, DCD, TxD, and RxD. The secondary signals are used to optionally connect DTE and DCE equipment.
RS-232 cables
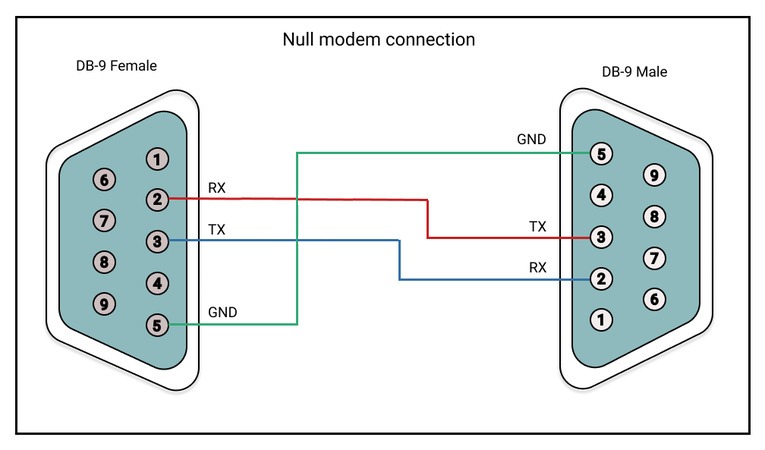
Null modem connection.
Null modems enable serial communication between DTE and DCE devices. An RS232 null modem pinout links the Tx pin of a male connector with the Rx pin on an RS232 female and the Rx male’s pin to the female’s Tx pin.
Using the RS232 protocol you can connect two computers that do not have modems by using a null modem cable. This highlights one of the original uses of the RS232 protocol, which was developed in order to let teletype machines communicate with each other through their modems.
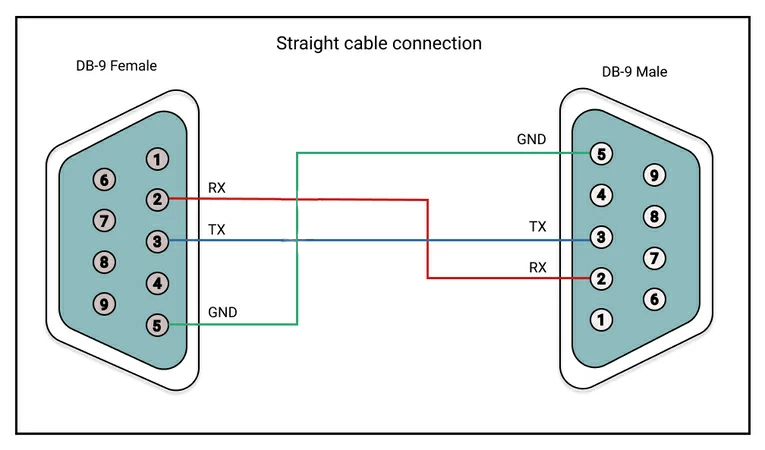
Straight-through cable
The other type of RS-232 Cable is the Straight-through cable. It is a one to one connector, It transmits a pin of one device that is connected to the transmit pin of another device and the receiver pin of one device is connected to the receiver pin of another device.
Conclusion:
Modern hardware designs use innovative serial communication protocols like USB, Ethernet, and Wi-Fi.
But still, RS232 has proven to be used. The reason is, RS232 signals spread over longer distances. Moreover, it has better noise immunity. It is proven to be compatible across different manufacturers for interfacing computer and modems.
- Serial Port Software
- What is Serial Port
- RS232 Pinout

Access denied under U.S. Export Administration Regulations.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
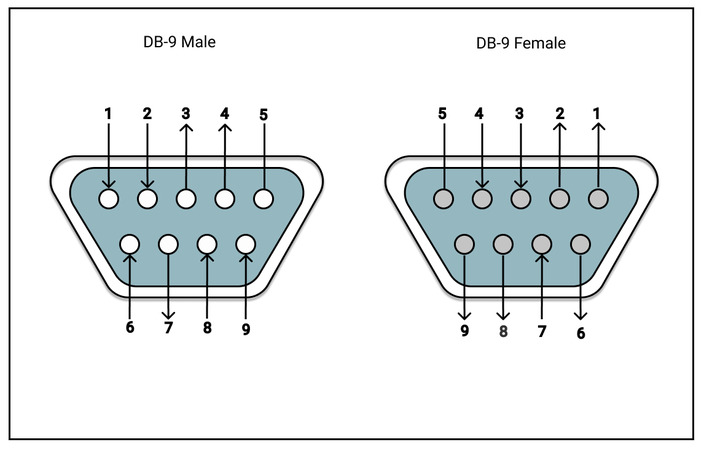
Below is the pinout of a typical standard male 9-pin RS232 connector, this connector type is also referred to as a DB9 connector. A computer's serial COM port (DTE) is usually a male port as shown below, and any peripheral devices you connect to this port usually has a female connector (DCE).
9 pin RS-232 pinout. So here is a simplified version of the serial connection pinout used on personal computers: the RS-232 9 pin pinout. Pin 1: DCD ← Data Carrier Detect. Pin 2: RxD ← Receive Data. Pin 3: TxD → Transmit Data. Pin 4: DTR → Data Terminal Ready. Pin 5: 0V/COM − 0V or System Ground. Pin 6: DSR ← Data Set Ready
What is RS232 DB9 serial port | RS232 pinout. RS-232 DB9 Pinout and Usage. Olga Weis Jun 22, 2020. Table of Contents: RS-232 DB9 Overview. Standard RS232 data packet. Example of how RS232 serial port works. RS232 serial data parameters and packet formats. RS-232 DB9 Overview.
Understanding the purpose of each pin on the DB9 connector is essential for proper wiring and connection. 1. Pin 1 (CD): This pin, also known as Carrier Detect, is used to detect the presence of a carrier signal in RS232 communications.
There are several DB9 connector Pinout schemes to address different standards and technologies. Here we take a look at two of the predominantly used configurations. DB9 connectors used for RS232 communications. DB9 connectors have long been used in serial communications to attach peripherals to PCs.
Whether a DB9 serial pinout or a 25 pin connection is used, only three of the pins are required to connect terminal devices. COM Port Pinout and Configuration. RS232 manages communication flowing between the DTE and DCE using serial pinouts of either the DB9 or DB25 variety.
In order to link these devices, an RS232 D9 pinout is essential, as this pinout will allow you to connect two devices successfully. An RS232 pinout 9 pin cable features nine pins: 1. Data Carrier Detect – After a data terminal is detected, a signal is sent to the data set that is going to be transmitted to the terminal. 2.
Signal Pinout DB25 DB9 Name ABBR. DTE ⇔DCE 1 Frame Ground FG 2 3 Transmit Data TD ⇒ 3 2 Receive Data RD ⇐ 4 7 Request to Send RTS ⇒ 5 8 Clear to Send CTS ⇐ 6 6 Data Set Ready DSR ⇐ 7 5 Signal Ground SG 8 1 Data Carrier Detect DCD ⇐ 9 (Reserved) 10 (Reserved) 11 Unassigned 12 Sec. Carrier Detect (S) CD ⇐ 13 Sec. Clear to Send (S ...