
Contribute to the Windows forum! Click here to learn more 💡
April 9, 2024

Contribute to the Windows forum!
Click here to learn more 💡
- Search the community and support articles
- Search Community member
Ask a new question
- Article Author
Manually assigning a drive letter using CMD/Diskpart
[Localization from this article: Manuelles Zuweisen eines Laufwerksbuchstaben mit CMD bzw. Diskpart - Microsoft Community ]
Technical Difficulty: Expert
Applies to: Windows 10 & 11
In some cases, Windows will not assign a drive letter automatically to an inserted drive. For example, this can happen when using a Windows installation media.
In that case, you can use diskpart to manually assign a drive letter.
NOTE: If your drive doesn't get assigned a drive letter, even though you are in a normal Windows environment, this can indicate a problem with the drive. Please back up your files in that case.
Open up a command prompt (CMD/PowerShell).
Type "diskpart" to start up diskpart. You will see the prompt change to "DISKPART>".

Type "list vol" to list all available volumes. You can identify the drive by size and file system.
Additionally, the volume doesn't currently have a drive letter.

Select the volume using "sel vol <number>".

Assign the drive letter using "assign letter=<letter>".

You can now exit diskpart by typing "exit" and switch to the drive using "<letter>:".

It should also be available from Windows Explorer now.
56 people found this helpful
- Subscribe to RSS feed
Was this article helpful? Yes No
Sorry this didn't help.
Great! Thanks for your feedback.
How satisfied are you with this article?
Thanks for your feedback, it helps us improve the site.
Thanks for your feedback.
Comments (17)
* Please try a lower page number.
* Please enter only numbers.
Thanks for the tutorial, I don't think I need to use Google for it anymore!
Congrats on Article Author too! :)
Report abuse
6 people found this comment helpful
Was this comment helpful? Yes No
How satisfied are you with this comment?
Thanks for the tutorial, I don't think I need to use Google for it anymore! Congrats on Article Author too! :)
5 people found this comment helpful
Thanks! Happy I could help! :)
1 person found this comment helpful
Very helpful Thanks.
3 people found this comment helpful
Thank for this informative article.
I ran this in PowerShell PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> GWMI -namespace root\cimv2 -class win32_volume | FL -property DriveLetter, DeviceID
The results are below. I need to know more about the DriveLetter, that does not have a letter and I cannot give it a letter, as you can see in DiskPart.
I'm sure someone personally hacking my computer. I'm wondering if this them hiding on it, and that is why I someone is typing over me and has more control at times of my computer then I do. Maybe a hidden AD Hoc.
I have searched for this on Google I'm either getting blocked or there is no information out there on this.
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> GWMI -namespace root\cimv2 -class win32_volume | FL -property DriveLetter, DeviceID
DriveLetter : B:
DeviceID : \\?\Volume{26xxxxxx--xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxxx}\
DriveLetter : C:
DriveLetter :
DeviceID : \\?\Volume{d5xxxxxx--xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxxx}\
DriveLetter : D:
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> DiskPart
Microsoft DiskPart version 10.0.19041.1
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation.
On computer: My Computer
DISKPART> List Volume
Volume ### Ltr Label Fs Type Size Status Info
---------- --- --- -------- ----- ---------- ------- --------- --------
Volume 0 D RAW DVD-ROM 2048 B Healthy
Volume 1 B System Rese NTFS Partition 100 MB Healthy System
Volume 2 C NTFS Partition 698 GB Healthy Boot
2 people found this comment helpful
I followed the instructions to CHANGE the letters assigned for three external hard drives. (The computer had named them E, F, G but gave the names to the wrong external hard drive) I changed the letters to the correct names singly (I disconnected the two not being adjusted) Now, I have 2 E, 2 F, 2 G names in the list (when accessed through File Explorer. When I click on "This PC", it shows just the one of each. If I click on either, or both of the same letter name, the same exact files will open. This is annoying. Anyone have a clue what can be done? This is on a brand new computer running Windows 11.
Sorry about the late reply.
That sounds weird... Usually, windows doesn't allow you to assign a drive letter twice.
If you want to change the letters, you usually have to remove them first and then reassign them.
Can you send me a screenshot of disk management, and of the list of volumes?
the partition that is not shown in diskpart is most likely some sort of recovery or reserved partition.
This is not the typical way of hiding an infection with malware...
Also, do note that your ESP (Volume B) should not be mounted, since modifying it can corrupt your Bootloader.
As for the suspected hacking, what symptoms did you observe? Mouse moving on its own, high resource usage, unexpected firewall prompts? Other things?
If you have a compromised system, its almost impossible to clean it from infections without doing a clean install of windows. I would suggest you do that if you suspect an infection. It will take time though and will delete everything on your PC. (Including files, programs, settings.) Create a backup before you reinstall.
There are no viruses nor malware on this computer. I believe it is a reflection of the original name choice. The information contained on each external hard drive is identical, yet when I go into MY PC, it only shows one set of externals. I am afraid to delete one of the duplicates because it might be just mirrored and it will make everything go away. I have way too many things on these external hard drives to lose any of them.
Thanks for your input. Jan
Forum Article Info
- Devices and drivers
- Norsk Bokmål
- Ελληνικά
- Русский
- עברית
- العربية
- ไทย
- 한국어
- 中文(简体)
- 中文(繁體)
- 日本語
How-To Geek
How to use the diskpart utility to assign and remove drive letters.
The Disk Management tool in Windows gives you an easy-to-use graphical interface to dealing with partitions and drive letters, but what if you want to just quickly change a drive letter on the command prompt? The diskpart utility makes it easy.
The Disk Management tool in Windows gives you an easy-to-use graphical interface to dealing with partitions and drive letters , but what if you want to just quickly change a drive letter on the command prompt? The diskpart utility makes it easy.
You'll need to start by opening an administrator mode command prompt -- type cmd into the search box, and then right-click and choose Run as administrator, or use the CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER keyboard shortcut.
Once there, run the diskpart command, and then type in the following to list out the volumes on your system.
list volume
You'll want to note the volume number next to the drive that you want to change the letter of. In our case, that number is 3.
Now we'll use the select volume command to tell diskpart to make changes to that volume. If your drive number is different, you'll want to replace the 3 with the number in your configuration.
select volume 3
You should see a message that the volume is now selected.
At this point you can easily assign a new drive letter. Just type in this command, substituting R for the drive letter you'd like to use:
assign letter=R
Make sure to hit enter once you're done, of course.
Once you've made that change, your drive should show up again as a new device, and be available for browsing immediately.
If you want to unassign a drive letter in order to hide the drive, you can also use the remove letter command in the same way. We wouldn't necessarily advise doing this, of course.
Don't bother trying to change your C: drive, because that's not going to work.
Sign up for our daily newsletter
- Privacy Policy
- Advertise with Us
How to Remove and Assign Drive Letters in Windows with Diskpart
Diskpart is one of the most powerful Windows command line utilities which first appeared in Windows XP. Diskpart is mainly used by Windows administrators to manage tasks like partition management, formatting, creating, re-sizing and getting a detailed information regarding the hard disk or other removable disks attached to the computer. Even though you have a built-in GUI application called Disk Management utility in Windows, Diskpart is much more flexible and works well in a server environment where you need to set up some advanced features like RAID.
Note: This post isn’t intended for beginners, and doing something wrong while using Diskpart utility may cause drive failures and data losses, so make sure that you have a good backup before continuing. You have been warned.
Assign Drive Letter Using Diskpart
Assigning a new drive letter to a partition or removable device using Diskpart is really easy. First, search for the command prompt in the Start menu, right click on it and select the option “Run as administrator.” If you are using Windows 8, press “Win + X” to open the power user menu and select the option “Command Prompt (Admin).”

The above action will open the command prompt window with administrative rights. Here enter the following command to start the Diskpart utility.

The next step is to list all the volumes in your computer so that you can clearly see all the volume numbers and drive letters of your hard disk partitions and any other removable devices. Use the command below to list all the volumes.

Once the Diskpart utility lists all the volumes, take a note of the volume number of the drive you want to assign a new drive letter. In my case, I’m trying to assign a new drive letter to the drive I:\ , so my volume number is 7 . Now execute the following command to select the volume while replacing the # symbol with an actual volume number.

Once the volume is selected, use the following command to assign a new drive letter. Don’t forget to replace the letter “V” with the drive letter you want to assign.

That’s all there is to do; you have successfully changed or re-assigned a new drive letter to a partition or a removable drive in Windows. In fact, if you open the Windows explorer, you can see that the change is reflected immediately.

Remove Drive Letter using Diskpart
Before moving any further, removing or un-assigning drive letter will effectively hide the drive or partition from plain sight, i.e. you cannot see that drive in the Windows explorer. To remove a drive letter, follow the above steps 1 through 4 and then use the below command to remove the drive letter of a drive or partition. Don’t forget to replace the letter “I” with the actual drive letter.

As soon as you have done that, Diskpart will remove the drive letter for that volume. If you list the volumes again, you will see that the drive you just interacted with will have no drive letter next to it.

Moreover, if you navigate to the Windows explorer, you will see that the drive which got un-assigned isn’t listed anymore. But again, always be careful while you are messing around with Diskpart utility; it may cause irrecoverable data loss if used incorrectly.
Hopefully that helps, and do comment below if you face any problems while following the steps or to simply share your thoughts.
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox
Vamsi is a tech and WordPress geek who enjoys writing how-to guides and messing with his computer and software in general. When not writing for MTE, he writes for he shares tips, tricks, and lifehacks on his own blog Stugon.

Disk Administration, Partition a disk.
DiskPart can be used to automate disk-related tasks, such as creating volumes or converting disks to dynamic disks. Scripting these tasks is useful if you deploy Windows by using unattended Setup or the Sysprep tool, which do not support creating volumes other than the boot volume.
When using the DiskPart command as a part of a script, we recommend that you complete all of the diskpart operations together as part of a single diskpart script. To run consecutive diskpart scripts, allow at least 15 seconds between each script for a complete shutdown of the previous execution before running the DiskPart command again in successive scripts. Otherwise, the successive scripts might fail. Add a pause between consecutive DiskPart scripts by adding a TIMEOUT /t 15 command to the batch file.
When setting up a new drive, create in this order: Create Partition, Format drive, Assign drive letter.
When selecting a volume or partition, you can use either the number or drive letter or the mount point path.
The Windows GUI interface can also be used to assign a mount-point folder path to a drive. In Disk Manager , right-click the partition or volume, and click Change Drive Letter and Paths , then click Add and then type the path to an empty folder on an NTFS volume.
The Windows Recovery Console , includes a simplified DISKPART command. It only provides functionality for adding and deleting partitions, but not for setting an active partition.
Always back up the hard disk before running DiskPart.
The default SAN policy in Windows Server 2008 / R2 is now VDS_SP_OFFLINE_SHARED for all non boot SAN disks. This means that the disks will be offline at server startup (even if the drive contains a paging file).
This Disk Management error message indicates that the drive is offline:
"the disk is offline because of policy set by an administrator".
Query the current SAN policy to see if it is Offline Shared
DISKPART.EXE DISKPART> san SAN Policy : Offline Shared
To manually bring the disks online: Computer Management ➞ Storage ➞ Disk Management , right-click the disk and choose Online .
If these are not part of a cluster, than an alternative is to make a SAN policy change, select the offline disk, clear its readonly flag and bring it online:
“Divide et impera” ~ Latin saying (Divide and conquer)
Related commands
docs.microsoft.com - Configure UEFI/GPT-Based Hard Drive Partitions using Windows PE and DiskPart. docs.microsoft.com - Configure BIOS/MBR-Based Hard Disk Partitions using Windows PE and DiskPart. FORMAT - Format a disk. FSUTIL - File and Volume utilities. DISKSHADOW - Volume Shadow Copy Service. REAGENTC - Configure Windows Recovery Environment (Windows RE) and System Reset. SYSPREP - (Generalize) a Windows installation. PowerShell equivalents: clear-disk , get-disk, set-partition, get-volume Partition Wizard - GUI Disk Partition Manager. Equivalent bash command (Linux): fdisk - Partition table manipulator for Linux.
- Hot Tech Deals at Target Right Now
- The Best Noise-Canceling Headphones to Buy
Diskpart Command
Use the 'diskpart' command to manage hard drive partitions
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/tim-fisher-5820c8345f9b581c0b5a63cf.jpg)
- Emporia State University
In This Article
Jump to a Section
- Availability
Related Commands
The diskpart Command Prompt command is used to create or delete partitions on hard drives .
Diskpart Command Availability
The diskpart command is available from within the Command Prompt in Windows operating systems, including Windows 11, 10, 8, etc.
You can also access this command from the Recovery Console in Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
Managing partitions is also possible without the use of a command from within any version of Windows using the Disk Management tool, or free disk partition software .
Diskpart Command Syntax
diskpart < parameter >
The availability of certain diskpart command switches and other syntax may differ from operating system to operating system. See How to Read Command Syntax if you're not sure how to read the syntax as it's described in this table.
Diskpart Command Examples
Here are some examples showing how the diskpart command can be used:
Create 5 GB Partition
In the above example, the diskpart command creates a 5,000 MB partition on the hard drive located at \Device\HardDisk0 .
Delete Partition by Name
For this one, the diskpart command will remove the Partition1 partition located on the hard drive \Device\HardDisk0 .
Delete Partition by Letter
This command will remove the partition currently assigned the drive letter G .
Select a Disk
Finally, in this multipart command, diskpart is being used to select a particular disk, disk 1 in this example, so we can remove the readonly attribute that's been set on it.
The fixboot , fixmbr , and bootcfg commands are often used with the diskpart command.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- Fixboot Command (Recovery Console)
- Dir Command
- Bootcfg Command
- Format Command
- Rename Command
- AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition v10.3.1 Review
- Fixmbr Command (Recovery Console)
- More Command
- Copy Command
- Expand Command
- Del Command
- How to Remove Write Protection on a Micro SD Card
- Net User Command (Examples, Options, Switches, & More)
- The 34 Best Free Data Destruction Tools of 2024
- 10 Best Free Disk Partition Software Tools
- Help Command
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
- 9 contributors
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008
The diskpart command interpreter helps you manage your computer's drives (disks, partitions, volumes, or virtual hard disks).
Before you can use diskpart commands, you must first list, and then select an object to give it focus. After an object has focus, any diskpart commands that you type will act on that object.
Determine focus
When you select an object, the focus remains on that object until you select a different object. For example, if the focus is set on disk 0 and you select volume 8 on disk 2, the focus shifts from disk 0 to disk 2, volume 8.
Some commands automatically change the focus. For example, when you create a new partition, the focus automatically switches to the new partition.
You can only give focus to a partition on the selected disk. After a partition has focus, the related volume (if any) also has focus. After a volume has focus, the related disk and partition also have focus if the volume maps to a single specific partition. If this isn't the case, focus on the disk and partition are lost.
To start the diskpart command interpreter, at the command prompt type:
You must be in your local Administrators group, or a group with similar permissions, to run diskpart.
You can run the following commands from the Diskpart command interpreter:
Listing available objects
You can view a list of options associated to each command by running the main command followed by what is available to that specific command. Running list by itself will display the four parameters below:
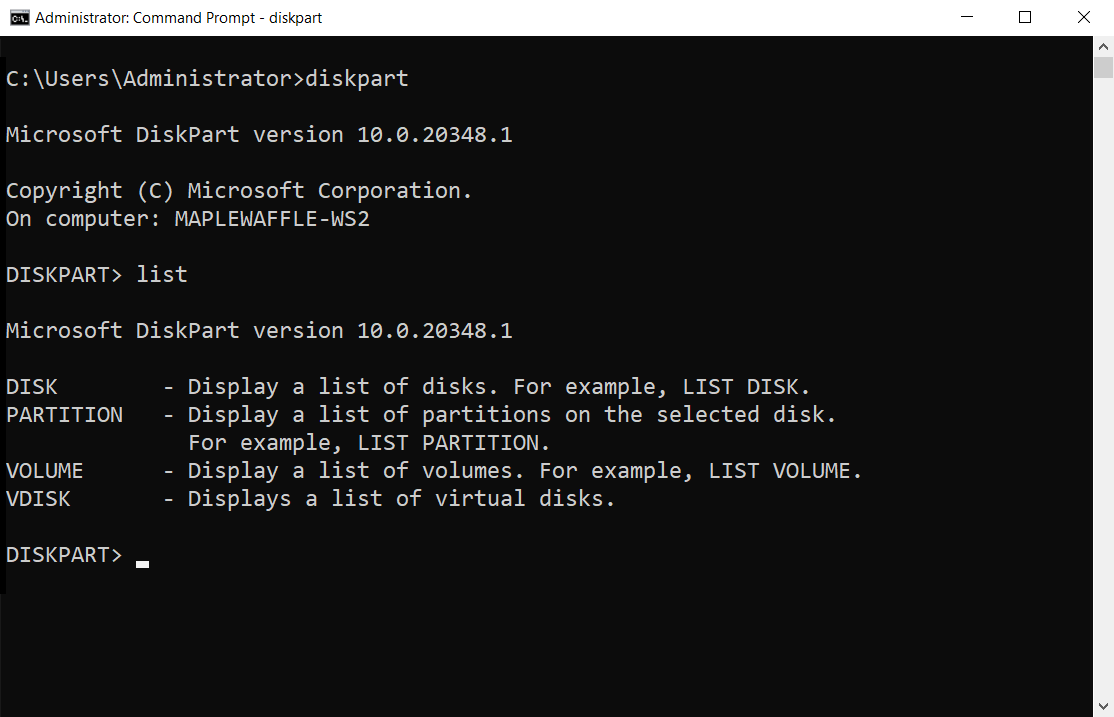
After you run the list command, an asterisk ( * ) appears next to the object of focus.
To see available disk(s), run list disk :
To select a disk, run select disk followed by the disk number. For example:
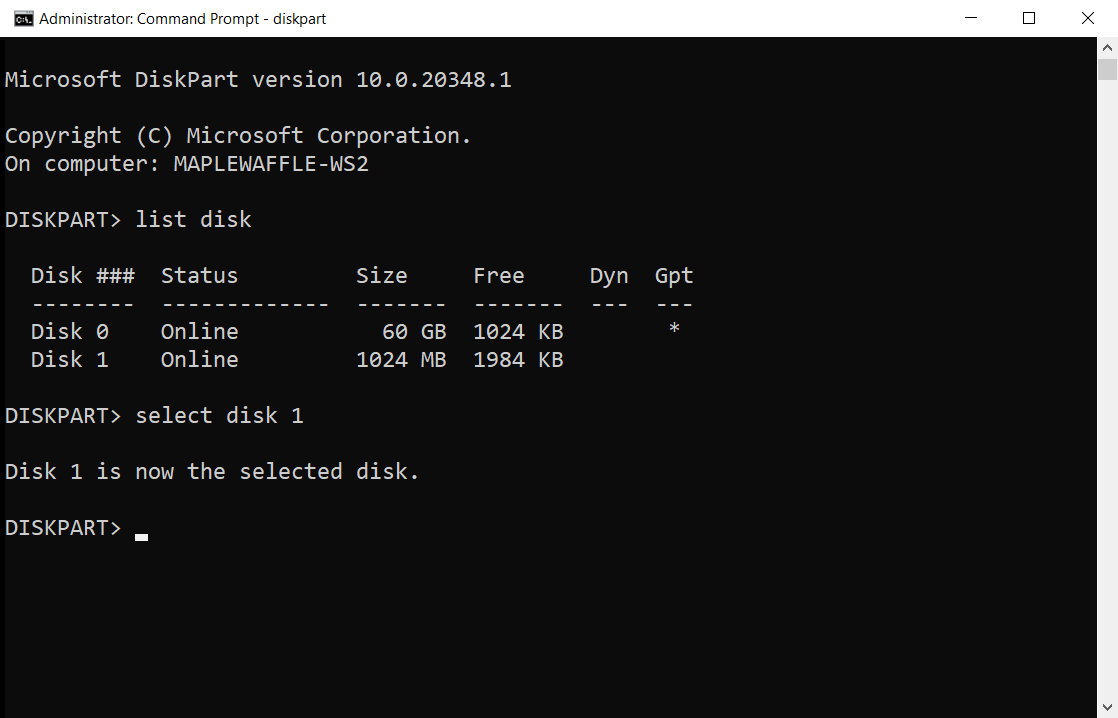
Before disk 1 can be utilized, a partition will need to be created by running create partition primary :
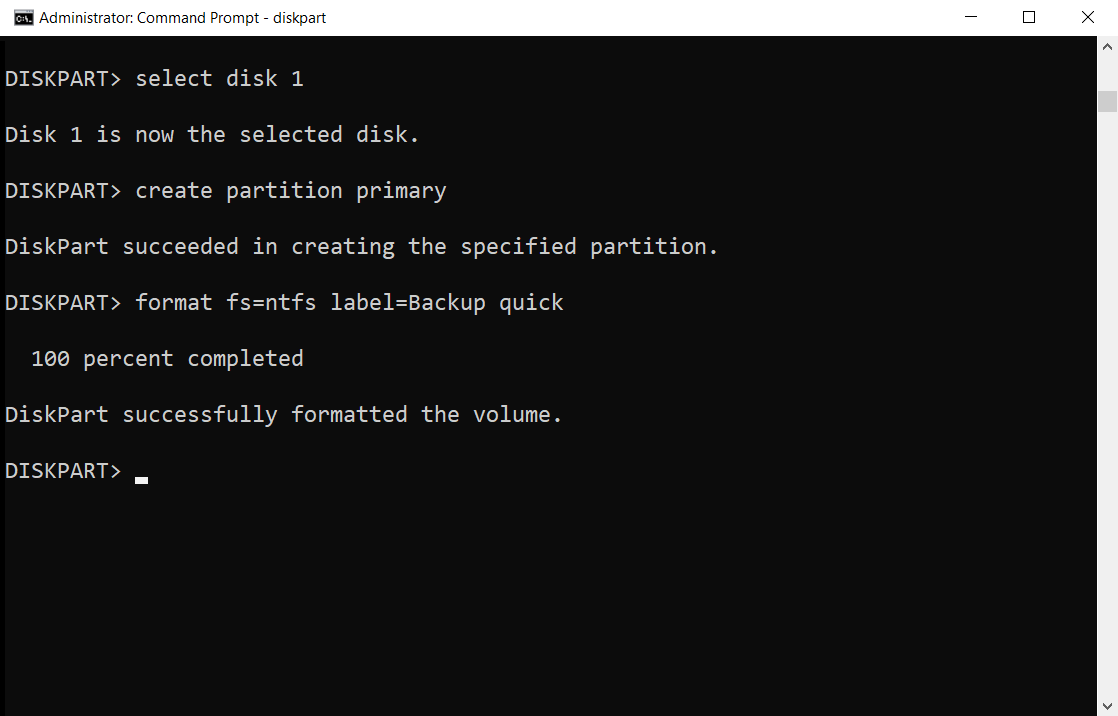
Lastly, we can perform a quick format of disk 1 to NTFS with the label "Backup" by running format fs=ntfs label=Backup quick as seen below:
Related links
Command-Line Syntax Key
Disk management overview
Storage Cmdlets in Windows PowerShell
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback .
Submit and view feedback for
Additional resources
- -More QE for AI Services
- AI-Powered QE
- AI Data Services
- Continuous Automation
- - Explore Other Automation Services
- Cloud Assurance
- - Cloud Hyperscalers
- Data Assurance
- - More Data Services
- Enterprise App Testing
- - ERP Services
- Non-Functional Testing
- - More NFT Services
- IoT/ Phygital Testing
- - More IoT/Phygital Testing Services
- XR Assurance
- Other ERP Packages
- Test Automation
- Performance Testing
- Cyber Security Testing
- ETL Testing
- Multilingual NLP Assurance
- Mobile App and Web Testing
- IV&V and Regulatory Assurance
- PoS Testing
- Accessibility Testing
- Service Virtualization
- Mobile and Web Dev
- DevOps Transformation
- Serverless Cloud Native Development
- Cloud Transformation and Migration Strategy
- API Integration Services
- Business AI
- Modeling Optimization
- Data Governance Services
- Learning Platform Development
- Video Encoding, Streaming and Player Development
- Instructional Design
- Content Remediation Services
- Medical Devices
- Retail & Consumer Goods
- Banking & Financial Services
- Capital Markets
- Media & Entertainment
- Managed Testing Services
- Managed Crowd Testing
- Project-Based Testing
- Strategic Consultancy
- Global Delivery
- Risk-Based Testing
- Test.Predictor
- Test.Consolidator
- Keysight Technologies
- White Papers
- Case Studies
- Podcast: The Testing Show
- Technical Hub
- Categories & Tags
- Leadership Team
- Diversity & Inclusion
How to assign a drive a letter using Diskpart
Industries top insights, delivered to your inbox.
Introduction:
Windows volume drive letters can be altered from the command line using Diskpart.
Requirements:
Access to the Windows command line.
From your taskbar, start a search for
Enter the command:
Example output:
but replace “2” with the desired volume number. Enter the command:
but replace the “q” with any desired letter that is not already being used by another volume.
More Information:
within diskpart for more information.

Other Technical Hub
Introduction: CSV files, or comma-separated-files, are used for storing data. They are a very commonly used text file format. Requirements:…
Introduction: Most SQL tables are non-temporary. Temporary tables can be used as well for convenience, or special purposes. Requirements: An…
Introduction: Relational Databases using SQL (Structured Query Language) may have a need for certain operations to be performed, or triggered,…
Want to talk with a test automation expert?
At the edge of tweaking
Advertisement
Change the drive letter in the command prompt
- Open an elevated command prompt .
- Type diskpart .

You are done.
Change the drive letter in PowerShell
- Open an elevated PowerShell instance .

For example, the command can look as follows:

Winaero greatly relies on your support. You can help the site keep bringing you interesting and useful content and software by using these options:
If you like this article, please share it using the buttons below. It won't take a lot from you, but it will help us grow. Thanks for your support!
Author: Sergey Tkachenko
Sergey Tkachenko is a software developer who started Winaero back in 2011. On this blog, Sergey is writing about everything connected to Microsoft, Windows and popular software. Follow him on Telegram , Twitter , and YouTube . View all posts by Sergey Tkachenko
One thought on “How to Change Drive Letter in Windows 10”
Really thank you this steps very helpful
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Privacy Overview
- Backup & Recovery
- Hard Disk Manager
- HFS+ for Windows
- ExtFS for Windows
- Disk Wiper Professional
- Drive Copy Professional
- Migrate OS to SSD
- Paragon Alignment Tool Professional
- NTFS for Mac
- Hard Disk Manager for Mac
- ExtFS for Mac
Assign, change or remove Drive Letter with Diskpart
Diskpart is very powerful Windows Utility, which allows certain number of operation with hard disk. In this article we will show you how to assign, change or remove drive letter with Diskpart using.
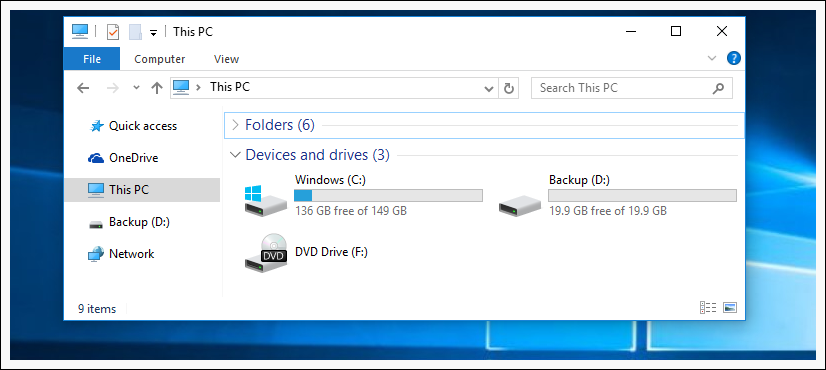
You bought hard drive for Backup, but it has automaticaly gained letter D . You want to change it to E . First we need to open Command Prompt with Administrator Rights.
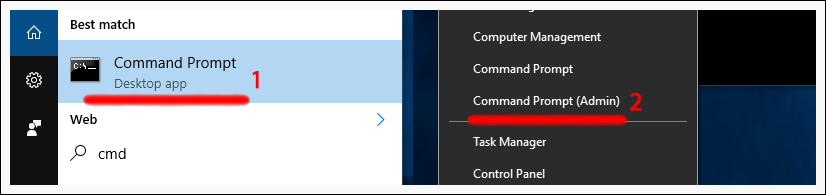
Type cmd into the search box, and then right-click and choose Run as administrator. If you have Windows 10 use the CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER keyboard shortcut on Screen 1 , or click on Start with right click and choose Command Prompt (Admin) on Screen 2 .
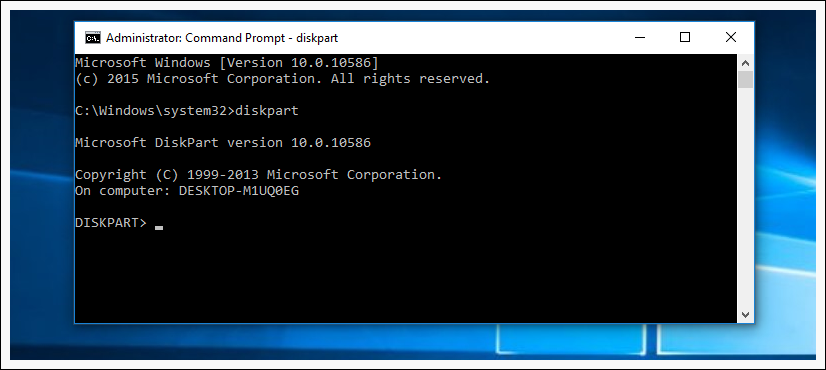
When Command Prompt pops up, run the diskpart command.
Now we type list volume to list our volumes, we need to know the number of our volume.
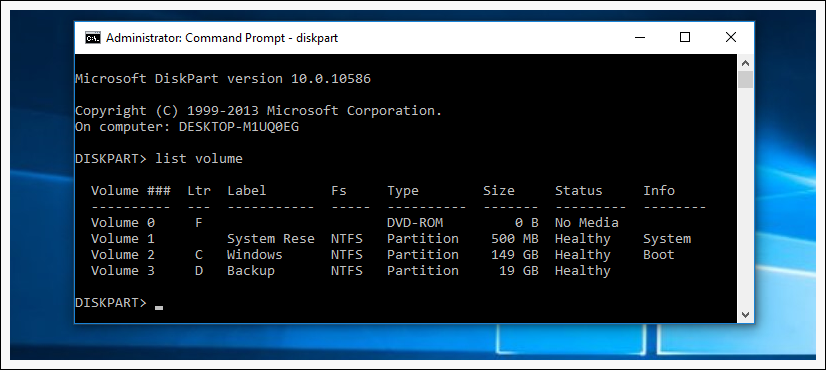
In our case our hard drive is Volume 3 and that number is 3 .
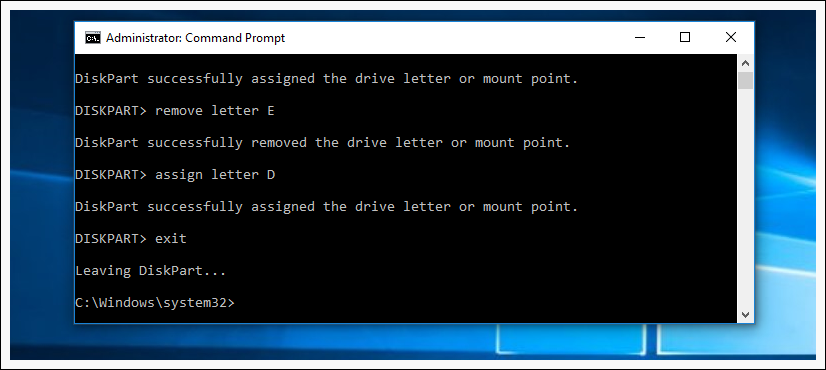
Now we use command select volume 3 to make changes to that volume. If your volume number is different, you need to replace number 3 with the number from your volume. After we have selected our volume we use command assign letter E , to assing letter E to our volume.
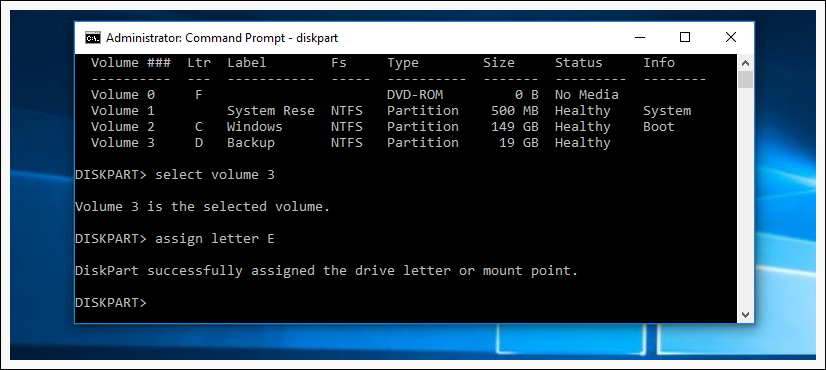
Now you know how to change or assign another letter to your volume, also if you need you can remove volume letter with command remove letter E
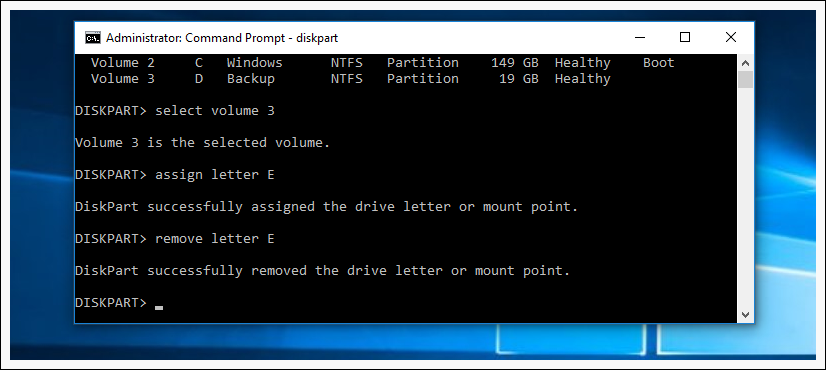
For security reasons you cannot change or remove your current system disk letter (esp C ), it will not work.
To exit diskpart type in exit .
Enter your email and receive updates about special offers and exclusive content!
Connect with us for giveaways, exclusive promotions and last news!

What Is Diskpart? Meaning, Commands, Working, and Importance
Diskpart is a Windows command-line disk partitioning utility used to manage disks, partitions, and volumes. Discover how it works, the importance of Dispkart, and a few top commands.

- Diskpart, a command-line disk partitioning utility by Microsoft, lets you manage disks, partitions, and volumes and assign them various attributes.
- Through its command-line interface, you can interact with your disks directly, offering flexibility and control over disk configurations without needing a graphical user interface.
- This article explains how Diskpart works, the commands you can use, and its role in modern IT infrastructure management.
Table of Contents
What is diskpart, key diskpart commands, how does diskpart work, importance of diskpart.
Diskpart is a command-line disk partitioning utility the Microsoft Windows operating system provides. It allows you to manage disks, partitions, and volumes on your system. With Diskpart, you can create, delete, format, and resize partitions, assign drive letters, and set various attributes to them.
This utility provides advanced functionalities for disk management tasks, catering to both basic and more complex partitioning needs. Through its command-line interface, you can interact with your disks directly, offering flexibility and control over disk configurations without needing a graphical user interface.
Diskpart’s development and evolution
Microsoft Corporation developed Diskpart as part of its Windows operating system platform. It was introduced with Windows 2000, released to manufacturing on December 15, 1999, and made available to the public on February 17, 2000.
The utility has since been included in subsequent versions of Windows, including Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10.
The development of Diskpart was driven by the need for a robust and flexible disk partitioning tool that could be used from the command line interface.
Before Diskpart, disk management tasks in Windows were primarily performed using graphical tools such as the disk management utility (diskmgmt.msc). While these graphical utilities provided basic functionality to manage disks and partitions, they lacked the flexibility and automation capabilities that advanced users and system administrators desired.
So, Microsoft designed Diskpart to address these limitations by offering a comprehensive set of commands for disk partitioning and volume management accessible through a text-based interface.
By providing a command-line utility, the company aimed to cater to the needs of power users, IT professionals, and sysadmins who required more granular control over disk configurations and management tasks. Diskpart also facilitated the automation and scripting of disk management operations, allowing professionals to streamline and automate repetitive tasks in their environments.
Simply put, the development of Diskpart was driven by the increasing complexity of disk storage systems and the growing demand for sophisticated disk management tools in enterprise — and even individual, professional — computing environments.
By offering a powerful and versatile disk partitioning utility, Microsoft sought to enhance the capabilities of its Windows operating system and provide users with the tools they need to manage their disk resources effectively.
Read More: PowerShell Working, Uses and Advantages
Here are some of the top commands you can use with Windows’ Diskpart utility:
1. List disk
This command displays a list of all the disks currently connected to your computer. It provides information such as the disk number, total size, free space, and whether it is online or offline. It helps you identify the disks available for partitioning or other disk management tasks.
2. Select disk [number]
This command selects a specific disk for subsequent operations. You need to specify the disk number as an argument. Once selected, all commands you execute will apply to the chosen disk. It’s useful when you have multiple disks and want to focus on managing a particular one.
The clean command removes all partition or volume formatting from the selected disk, wiping it clean of any existing data or partitions. This is a powerful command and should be used with caution, as it can lead to data loss if executed inadvertently on the wrong disk.
4. Create partition primary [size=xxx]
This command creates a new primary partition on the selected disk. Using the size parameter, you can optionally specify the partition size in megabytes (MB). If no size is specified, Diskpart will create a partition using all available space on the disk.
5. Delete partition [override]
This command deletes the selected partition from the disk. If the partition contains data, you should use the override parameter to force deletion. Deleting a partition removes all data stored within it, so back up any important data before using this command.
6. Format fs=ntfs quick
The format command initializes a disk or partition with a new file system. In this example, fs=ntfs specifies that the partition should be formatted with NTFS or a new technology file system commonly used in Windows. The quick parameter performs a quick format, skipping the process of scanning for bad sectors, which speeds up the formatting process.
7. Assign letter=[letter]
After creating a partition, this command assigns it a drive letter, allowing you to access the partition through Windows Explorer or the command prompt. Replace [letter] with the desired drive letter, such as C, D, E, etc. Once assigned, you can access the partition using the specified drive letter.
8. Extend [size=xxx]
The extend command increases the size of an existing partition to utilize unallocated space on the same disk. You can specify the size of the extension using the size parameter, which indicates the additional space to be added to the partition. This command is useful for expanding the storage capacity of a partition without losing existing data.
9. Shrink [desired=xxx]
This command decreases the size of an existing partition, creating unallocated space that can be used for other partitions or purposes. You can specify the desired size of the shrink operation using the desired parameter, indicating the amount of space you want to free up from the partition. Shrink only works if there is unused space within the partition that can be released safely.
10. List volume
Similar to a list disk, this command displays a list of all volumes (partitions) on the system. It provides information such as the volume number, label, file system, size, status, and drive letter assigned to each volume. Use this command to view the current volume configuration and properties before performing disk management tasks.
11. Resize [size]
This command resizes the selected partition to the specified size. You provide the desired size as an argument. Resizing allows you to adjust the partition boundaries to accommodate changes in disk space requirements. This command is handy when you need to shrink or extend partitions to optimize disk usage.
12. Clean [all]
This command removes all partition or volume formatting from the selected disk. Including the “all” parameter removes all partition and volume information, effectively wiping the disk clean. Use this command with extreme caution, as it permanently erases all data on the disk, making data recovery difficult or impossible.
13. Detail disk
This command provides detailed information about the selected disk, including disk model, firmware version, total size, free space, and disk signature. It gives you a comprehensive overview of the selected disk’s characteristics, aiding in decision-making for disk management tasks.
Read More: .Net Framework Versions, Benefits, and Challenges
Diskpart gives you a direct line to control and manage your computer’s hard drives and partitions through simple commands. When you open Diskpart, you’re essentially opening a tool that lets you communicate directly with your computer’s storage system.
You can tell it to create new partitions, delete old ones, format drives, and even resize partitions to fit your needs. It’s like conversing with your computer: You tell it exactly what you want to do with your disk space, and Diskpart carries out those instructions.
Whether you’re an IT admin looking to fine-tune your storage setup or someone who needs to manage disk space quickly, Diskpart can help you get the job done efficiently.
Now that’s the 30,000-foot view; delving into the backend aspect of it, here is a technical breakdown of how Diskpart works:
1. Initialization
Launching Diskpart initializes and loads necessary system resources, including libraries and drivers required for disk management operations. This initialization process ensures that Diskpart has access to the necessary components to interact with your computer’s storage devices effectively.
2. Identification of disks and volumes
Diskpart scans your system to identify all available disks and volumes. It retrieves information about each disk, such as its size, type, and partition layout, as well as details about existing volumes, including their file systems, sizes, and drive letters. This step is crucial for Diskpart to understand the current state of your storage configuration before performing any disk management tasks.
3. User input
Once Diskpart identifies the disks and volumes on your system, it awaits user input in the form of commands. Users can enter commands through the command-line interface provided by Diskpart. These commands instruct Diskpart on the specific disk management operations to perform, such as creating, deleting, formatting, resizing, or assigning attributes to partitions and volumes.
4. Command execution
Diskpart executes the commands the user enters, carrying out the specified disk management operations. Each command triggers a series of actions within Diskpart, which interact with the operating system’s underlying disk management infrastructure to perform the requested tasks.
For example, if you issue a command to create a new partition, Diskpart will allocate space on the disk, create the partition structure, and update the partition table accordingly.
5. Validation and error handling
Throughout command execution, Diskpart performs validation checks to ensure that the requested operations can be completed safely and without causing data loss or system instability. If Diskpart encounters any errors or inconsistencies during command execution, it provides feedback to the user, indicating the nature of the problem and any potential corrective actions that may be required.
6. Completion and output
Once Diskpart has successfully executed the user’s commands, it provides feedback to the user, confirming the completion of the requested disk management operations. This feedback typically includes details about the actions performed, such as creating new partitions, formatting volumes, or resizing partitions.
Users can review this output to verify that the desired changes have been applied to their storage configuration.
7. Cleanup and termination
After completing the requested disk management tasks, Diskpart performs cleanup activities to release any system resources and temporary buffers used during its operation.
It then terminates its execution, returning control to the command-line interface or shell from which it was launched. This ensures that Diskpart does not consume unnecessary system resources once its tasks are complete, allowing users to continue with other activities on their systems.
Read More: What Is MATLAB (Matrix Laboratory)? Working, Functions, and Applications
Diskpart is important due to its numerous benefits and functionalities, making it an indispensable tool for disk management tasks in Windows environments.
1. More flexibility
With Diskpart, you can access an extensive set of commands and options, giving you the flexibility to perform a wide range of disk management operations. Whether you’re creating and deleting partitions, formatting volumes, assigning drive letters, marking partitions as active, or resizing partitions, Diskpart’s versatility allows you to tailor disk management tasks to your specific needs, whether setting up new disks, reconfiguring existing partitions, or troubleshooting disk-related issues.

2. Greater control
Diskpart’s command-line interface (CLI) empowers you to interact directly with disk resources through text-based commands. Unlike graphical user interfaces (GUIs), which rely on visual elements for interaction, Diskpart’s CLI provides a more efficient and scriptable approach to disk management.
You can automate repetitive tasks, create batch scripts for bulk operations, and integrate Diskpart into your system administration workflows, making it ideal for managing disks in server environments.
3. Advanced disk management
Diskpart supports advanced disk management capabilities that go beyond basic partitioning and formatting. You can resize partitions to adjust their size without data loss, merge multiple partitions into a single partition, split partitions to create smaller partitions, and convert disk types between basic and dynamic disks.
These advanced features enable you to optimize disk layouts, accommodate changes in storage requirements, and reorganize disk configurations as needed without relying on third-party tools or complex procedures.
4. Widespread compatibility
As an integral part of the Windows operating system, Diskpart is compatible with a wide range of Windows-based computers and servers. It is included in all modern versions of Windows, including desktop editions (such as Windows 10) and server editions (such as Windows Server). This broad compatibility ensures that Diskpart can be used across diverse environments, providing a consistent disk management experience regardless of your Windows version or edition.
5. Increased efficiency
Diskpart is designed for efficiency, offering streamlined disk management capabilities that minimize overhead and resource usage. The command-line interface provides a lightweight and responsive interaction model, allowing you to execute commands quickly and efficiently without the overhead of graphical interfaces.
Diskpart’s optimized algorithms ensure swift execution of disk management tasks, reducing the time required to perform operations. This efficiency is particularly valuable in scenarios requiring rapid provisioning, deployment, or maintenance of disk resources, such as in data centers or cloud environments .
6. Sophisticated partitioning
Diskpart offers precise control over disk partitions, allowing you to create, delete, format, and modify partitions according to your requirements. Whether setting up new disks, reorganizing existing partitions, or adjusting your storage configuration, Diskpart enables you to manage your partitions with granularity and flexibility.
You can customize partition attributes such as size, file system type, and allocation unit size. Additionally, Diskpart allows you to assign drive letters, mount points, or volume labels to partitions, making them easily accessible and identifiable within the operating system.
7. Effortless maintenance
Diskpart facilitates various disk maintenance tasks aimed at optimizing disk performance and preserving data integrity. For instance, you can use Diskpart to perform disk cleaning operations, which remove temporary files, cache data, and other unnecessary files to free up disk space and improve system performance.
Additionally, Diskpart allows you to align partitions, ensuring that data is stored efficiently on disk sectors for optimal read and write performance. Furthermore, it supports volume defragmentation, a process reorganizing fragmented data on a disk volume to improve access times and overall disk performance.
8. Reliable data recovery
When disk partitions become corrupted, damaged, or inaccessible, Diskpart can serve as a valuable tool for data recovery and troubleshooting. It can repair partition tables, rebuild corrupted file systems, and recover lost or deleted partitions.
By issuing specific commands within Diskpart, you can scan for and identify damaged partitions, attempt to repair file system structures, and recover data stored within those partitions. This capability is particularly useful when data loss or partition corruption occurs due to software errors, disk failures, or accidental deletion.
9. Optimized storage
Diskpart provides features for optimizing storage configurations to enhance performance, reliability, and security. You can use Diskpart to align partitions to optimize disk access, ensuring that data is stored on disk sectors in a manner that minimizes read and write latency.
It allows you to convert disk types between basic and dynamic disks, enabling advanced storage features such as software RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) and dynamic volumes.
Furthermore, Diskpart supports the management of storage spaces, a feature introduced in newer versions of Windows. This allows you to create resilient storage pools with features like mirroring or parity for fault tolerance and data redundancy.
10. Simplified administration
As a system administrator, Diskpart is an indispensable tool. You can use it to provision storage resources, allocate disk space to servers or applications, and deploy operating systems on new disks or partitions. You can even troubleshoot disk-related issues across multiple systems efficiently.
Diskpart’s comprehensive set of commands makes diagnosing disk failures, repairing corrupted partitions, and recovering lost data easier. Additionally, it supports automation and scripting, which means you can streamline disk management tasks and integrate them into your organization’s IT infrastructure and operations workflows.
Read More: Visual Basic Features and Applications
Diskpart emerges as an essential tool for your enterprise’s disk management needs. With its versatile command-line interface, Diskpart empowers you to take full control of your disk resources, from provisioning storage to optimizing configurations and troubleshooting issues.
Its flexibility, efficiency, and comprehensive feature set make it an invaluable asset for system administrators and IT professionals seeking to streamline disk management operations, automate tasks, and maintain optimal performance and reliability.
By harnessing Diskpart’s power, you can unlock new levels of efficiency, enabling your organization to thrive in today’s dynamic digital landscape and take advantage of the latest technology innovations.
Did this article share everything you wanted to know about Diskpart? Tell us on Facebook Opens a new window , X Opens a new window , and LinkedIn Opens a new window . We’d love to hear from you!
Image source: Shutterstock
MORE ON WINDOWS TOOLS
- Windows Virtual Desktop Architecture, Use Cases, Pricing
- UNIX vs. Linux vs. Windows: How They Compare | Spiceworks
- PowerShell Scripting Features and Best Practices
- WSUS vs. Windows Update for Business: Which Is Better for Enterprises?
- Guide to Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM)
Share This Article:
Technical Writer

Recommended Reads

Microsoft To Charge an Annual Fee for Windows 10 Support

Kubernetes Celebrates 10th Birthday in Paris with Biggest KubeCon Ever

Major Apple and Meta Services Hit by Global Outages

What Is Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)? Meaning, Implementation, and Importance

Microsoft Splits Teams From Office Package Over Antitrust Concerns

How to Address the Cloud Skills Gap in the Digital Era

Diskpart Commands: How to Manage Hard Drive Partitions in Windows 11/10
Pranav Bhardwaj
August 29, 2023

Looking for more How To posts? Check out our How To Page for all the latest tips on Windows, Microsoft Teams, LinkedIn, and more!
In this article
Efficient hard drive management is essential for maintaining an organized and optimized computer system. Windows operating systems offer various tools to help users manage their data, and Diskpart is one such powerful utility. Diskpart allows users to manipulate hard drive partitions directly from the command line, providing granular control over disk space allocation.
Whether you want to create, extend, delete, or format partitions, Diskpart offers a command-line-driven approach that’s particularly useful for system administrators and advanced users. This guide delves into the details of using Diskpart to manage hard drive partitions effectively in Windows 11/10.
What is Diskpart?
Diskpart, short for “Disk Partition,” is a command-line utility included in Windows 11/10 that empowers users to manage disks, partitions, and volumes. Unlike graphical interfaces, Diskpart operates solely through text-based commands, offering a powerful way to interact with storage devices. It’s especially valuable for managing partitions in scenarios where the graphical interface might not be accessible, such as during system recovery or maintenance.
Diskpart provides a comprehensive set of commands that enable users to create new partitions, extend existing ones, format partitions with different file systems, and even remove partitions entirely. Its versatility and direct control over disk structures make it a preferred tool for those who require a more hands-on approach to disk management.
Precautions to take while using Diskpart commands
While Diskpart can be a highly effective tool, it’s essential to take precautions before using its commands to avoid unintended data loss or system disruptions.
Here are some precautions to consider:
- Backup Your Data : Before performing any disk management operations using Diskpart, create backups of your critical data. Diskpart commands can lead to irreversible changes, and having a backup ensures that you can restore your data if something goes wrong.
- Double-Check Disk Selection : Make sure you’re selecting the correct disk and partition when applying Diskpart commands. A wrong selection can result in unintended changes to your system.
- Understand Commands : Familiarize yourself with the specific commands you’re going to use and their implications. Misinterpreting commands can lead to data loss or system instability.
- Use “List” Commands : Utilize commands like list disk, list partition, and list volume to get a clear view of your disk configuration before making any changes. This helps you verify your selections.
- Avoid Direct “Clean” Command : Be cautious with the clean command, as it removes all partitions from a selected disk without confirmation. This command can lead to complete data loss if not used carefully.
List of common Diskpart commands
Diskpart commands are the building blocks of disk management. Here’s a list of common commands along with their purposes:
How to launch Diskpart on Windows 11/10
Launching Diskpart is a straightforward process. Here’s how you can do it:
- Press Windows + R to launch the Run Command box.

- If prompted by User Account Control, click “Yes” to grant administrative privileges to Diskpart. You’ll now be within the Diskpart environment, ready to execute disk management commands.

How to check existing hard drives, volumes, & partitions using DiskPart
Before making any changes, it’s crucial to understand your disk’s current configuration. Diskpart can help you get this information:
- Open the Command Prompt and enter diskpart.

- Type select disk <number> to choose the disk you want to inspect.
- Similarly, use the list partition and list volume commands to see the partitions and volumes on the selected disk.

How to create a partition using Diskpart
Creating a partition using Diskpart provides you with control over its size, file system, and drive letter assignment.
Creating a partition using Diskpart involves a few steps. Let’s go through the process:
- Launch Diskpart as described earlier.
- To access the disk list, use the list disk command, and then choose the desired disk by entering its corresponding number with the select disk # command, where “ # ” is the disk number.

- After selecting the disk, use the clean all command to wipe out the disk. (optional step)
- Once the disk is wiped out, use the create partition primary command to create a partition using the entire space on that drive.
- If you want to create multiple partitions, you can assign how much space a partition could take. For that, use the create partition primary size=X command, where “ X ” is the size that you wish to set to the partition in megabytes.
- After creating the partition, format it with a file system using the format fs=<filesystem> quick command. For instance, use the format fs=ntfs quick for NTFS or format fs=fat32 quick for FAT32.
- Once the formatting process is complete, Diskpart will automatically assign a letter to the partition. In the event that it does not, you can manually set it by using the command assign letter=<letter> . Replace “ <letter> ” with the desired drive letter.

How to extend a partition using Diskpart
Extending a partition allows you to combine unallocated space with an existing partition. It’s an excellent way to make efficient use of available space.
Here’s how you can do it:
- Launch Diskpart using the earlier method.
- Make sure that there is enough free space adjacent to the partition you plan to extend on the same drive without any partitions in between. Verify the contiguous availability of the free space.
- Use the list disk command to list all the attached disks on your system. Choose the disk containing the partition you want to extend using the select disk <number> .
- Next, use the list volume command to get the list of all the volumes under the selected disk.
- Now, choose the volume that you want to extend using the select volume # command. Insert the volume number in place of “ # ”.
- Next, use the extend command to add the entire free space to the selected volume. However, if you don’t want to include the entire unallocated space to the selected volume, use the extend size=# , and replace “ # ” with the amount of space you want to extend in megabytes.

How to shrink a volume using Diskpart
Shrinking a volume allows you to reclaim unused space, which can then be used to create new partitions or extend existing ones. Here’s how you can shrink a volume using Diskpart:
- Launch Diskpart using the previously outlined steps.
- Type list volume to see a list of all volumes on your system. Note the volume number of the one you want to shrink.
- Enter select volume <number> to choose the volume you wish to shrink.
- To initiate the shrinking process, type shrink desired=<size> and press Enter. Replace “ <size> ” with the amount of space you want to shrink the volume by in megabytes.
- Diskpart will calculate the available space that can be shrunk based on the specified size.
- Once the process is complete, you can exit Diskpart by typing exit and pressing Enter.

How to delete a partition using Diskpart
You can easily delete a partition, too, using Diskpart. Removing a partition should be done with caution, as it leads to data loss. Follow these steps:
- Open the Command Prompt and launch Diskpart.
- Select the disk containing the partition you want to delete using select disk <number> . If you don’t know the disk number, use the list disk command.
- Now, use the select partition <number> command to select the partition that you want to delete. Use the list partition command if you don’t know the partition number.
- After selecting the partition, use the delete partition command to delete it.

Similarly, you can use the delete volume command to delete a partition.
How to completely wipe out the hard disk using DiskPart
If you encounter issues when formatting your system’s hard disk, an external hard drive, or a USB pen drive, you can use DiskPart to wipe them clean. However, please note that you cannot clean the disk on which your operating system is installed.
If you need to wipe out an entire hard disk using Diskpart, follow these steps with caution:
- Type list disk and note the disk number you want to wipe.
- Select the disk by typing select disk <number> .
- Now type the clean all command and press Enter. This command will erase all data on the selected disk. Be patient; depending on the size of your hard disk, it could take even hours to complete this command.

Alternatives to Diskpart
While Diskpart is a powerful tool for managing hard drive partitions in Windows 11/10, there are alternative methods and third-party tools available for users who prefer different approaches. Here are a couple of alternatives to consider,
Windows Disk Management

Windows provides a built-in graphical tool called “Disk Management.” To access it, right-click on the “Start” button and select “Disk Management.” This tool offers an intuitive interface where you can perform tasks like creating hard drive partitions , formatting, deleting, and resizing them. While it might not offer the same level of command-driven control as Diskpart, it’s user-friendly and suitable for most basic partition management needs.
Third-Party Partitioning Tools
Several third-party partitioning tools are available that provide advanced features and user-friendly interfaces. Tools like EaseUS Partition Master , MiniTool Partition Wizard , and AOMEI Partition Assistant offer capabilities beyond what Diskpart provides, including visual representations of your disk layout, more flexible partition resizing, and better data protection during operations. These tools can be especially useful for users who prefer not to work with command-line utilities.
Can Diskpart commands be undone?
Unfortunately, Diskpart commands are irreversible and can lead to data loss if executed incorrectly. It’s crucial to double-check your commands and backup your data before making any changes using Diskpart.
Can I use Diskpart on external drives and USB devices?
Yes, Diskpart can be used on internal and external drives, including USB devices. However, exercise caution and make sure you select the correct disk to avoid accidental data loss.
Is it possible to resize volumes using Diskpart?
Yes, resizing the volume is possible using the Diskpart shrink and extend commands.
Manage your system hard drive easily
Effective hard drive management is essential for maintaining a well-organized and optimized computer system. Diskpart provides a versatile and powerful solution for managing hard drive partitions in Windows 11/10. By understanding its commands and following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently create, extend, delete, and manage partitions according to your needs. Remember to exercise caution, back up your data, and double-check your actions before executing Diskpart commands. With this knowledge, you’ll be well-equipped to make the most of your disk space while ensuring the safety of your data.
Looking for more? Check out these OnMSFT.com posts on Diskpart .
Voice Access comes to Windows 11 OOBE in recent Insider builds
Microsoft president demands ‘human oversight’ on ai to avert ‘weaponization’.
OnMSFT.com is built on:
Wordpress GeneratePress Azure
Theme thanks to heather.

Home About Contact Us
Join our team, © copyright 2014 - 2024 onmsft.com llc.

- Disk & Data Manager
- Partition Wizard
- Power Data Recovery
- ShadowMaker
- Media Toolkit
- uTube Downloader
- Video Converter
- Download Partition Wizard Free Edition: Download Pro Edition: Try Demo Server Edition: Try Demo
Diskpart Unassign Drive Letter in Windows 11/10 [Full Guide]
Diskpart is a well-known Windows built-in disk partition utility used to format /create/delete partitions, online/offline disk , wipe disks, etc. However, a lot of users are unclear about how to use this utility. For example, here a user posted a question about how to change drive letter diskpart on the answers.microsoft.com forum:
Is there a way to unassign drive letter diskpart? Windows will not assign a drive letter automatically when I inserted a Windows installation media. https://answers.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/forum/all/manually-assigning-a-drive-letter-using/bbb3baf6-cda4-4d06-b431-eae9e975a5c7
How to Unassign Drive Letter Diskpart in Windows 11/10
A drive letter is a single alphabetic character from A to Z assigned by Windows to a drive or partition connected to the computer. Sometimes, you may need to change drive letter diskpart in some situations. How to let diskpart unassign letter in Windows 11/10? Here are detailed steps:
If you remove the drive letter from a partition, it will no longer show as a drive in File Explorer and the unassigned drive letter can be available to other partitions.
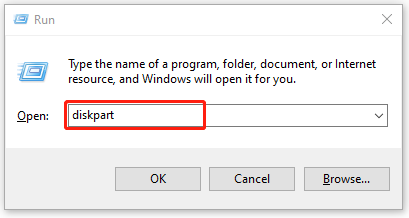
Step 1. Press Win + R keys to open the Run dialog box, and then type diskpart in it and press Enter . Then click on Yes to open the tool in Command Prompt.
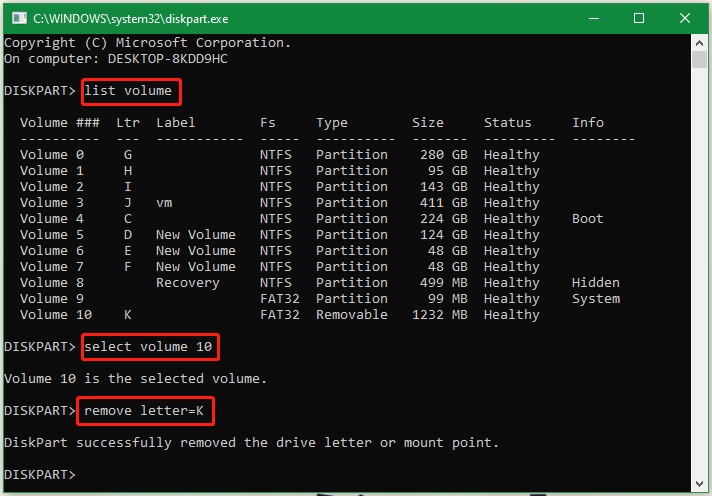
Step 2. To let diskpart unassign drive letter, type the following commands in order and press Enter after each one.
- list volume
- select volume * (replace * with the partition number you want to remove its drive letter from)
- remove letter=K (replace K with the drive letter that you want to remove)
The process of diskpart assign letter is very simple and similar to removing a drive letter. To assign drive letter diskpart, you can open the Command Prompt window again as we explained above, type the following commands in order and press Enter after each one.
- select volume 10
- assign letter=k
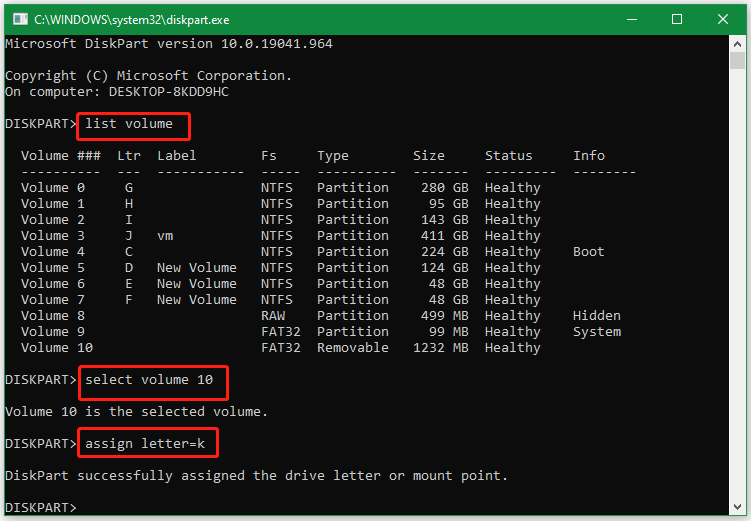
Although Diskpart is a practical partition manager in Windows, sometimes this utility can run into various errors such as “ DiskPart failed to clear disk attributes ”, “ Diskpart virtual disk service error ”, “failed to assign a drive letter”, etc. Is there an alternative to diskpart unassign drive letter? Of course, yes! Let’s keep reading.
Best Alternative to Diskpart Remove Drive Letter
If you can’t change drive letter CMD or Diskpart, MiniTool Partition Wizard is the best alternative. It is a trustworthy and comprehensive partition manager that allows you to change drive letters easily. Besides, this partition software can be used to extend/resize/hide/copy/format partitions, migrate OS , convert FTA to NTFS without data loss , change cluster size, recover lost data , and more.
MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Click to Download 100% Clean & Safe
Step 1. Launch the program to enter its main interface, right-click the partition, and select Change Letter from the pop-up menu.
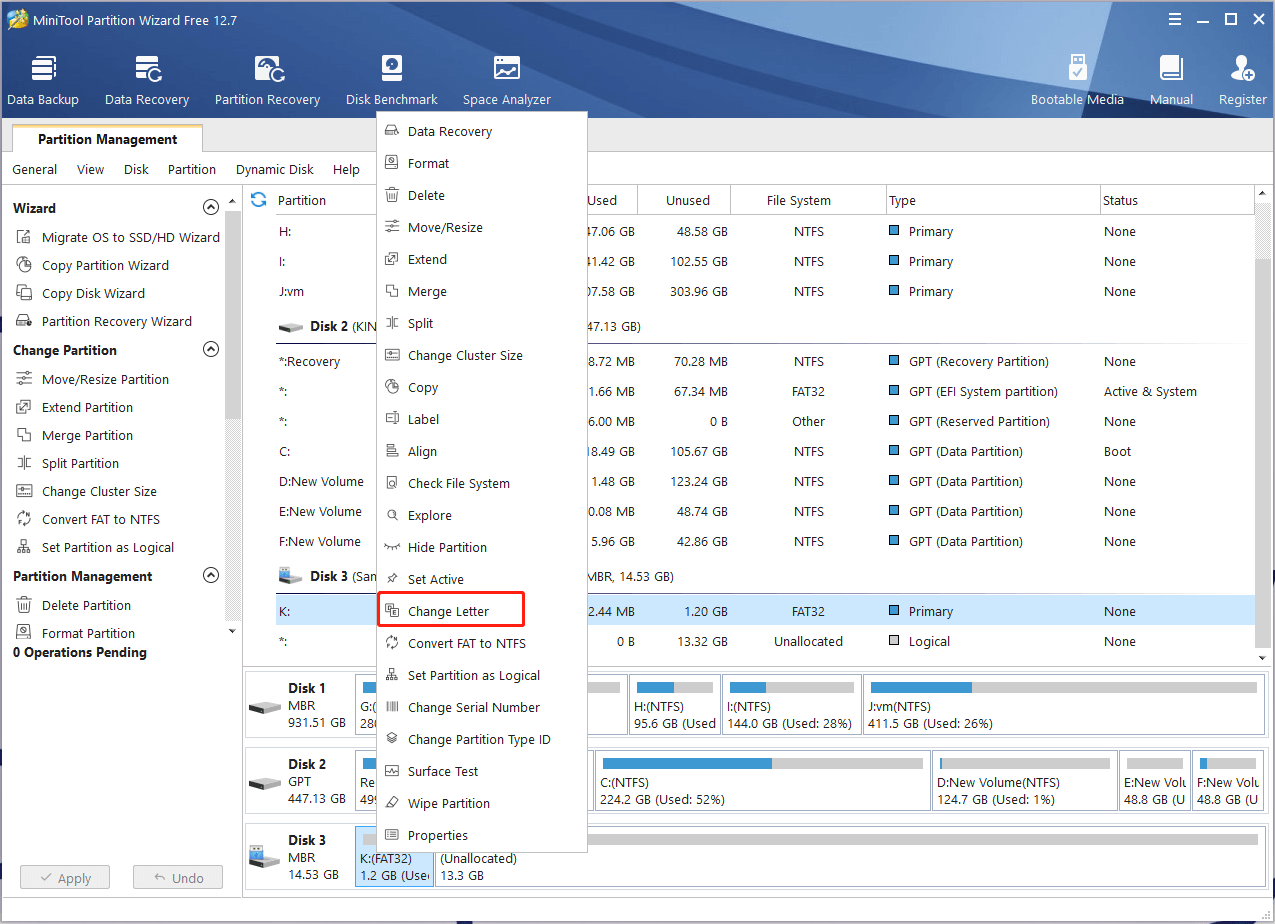
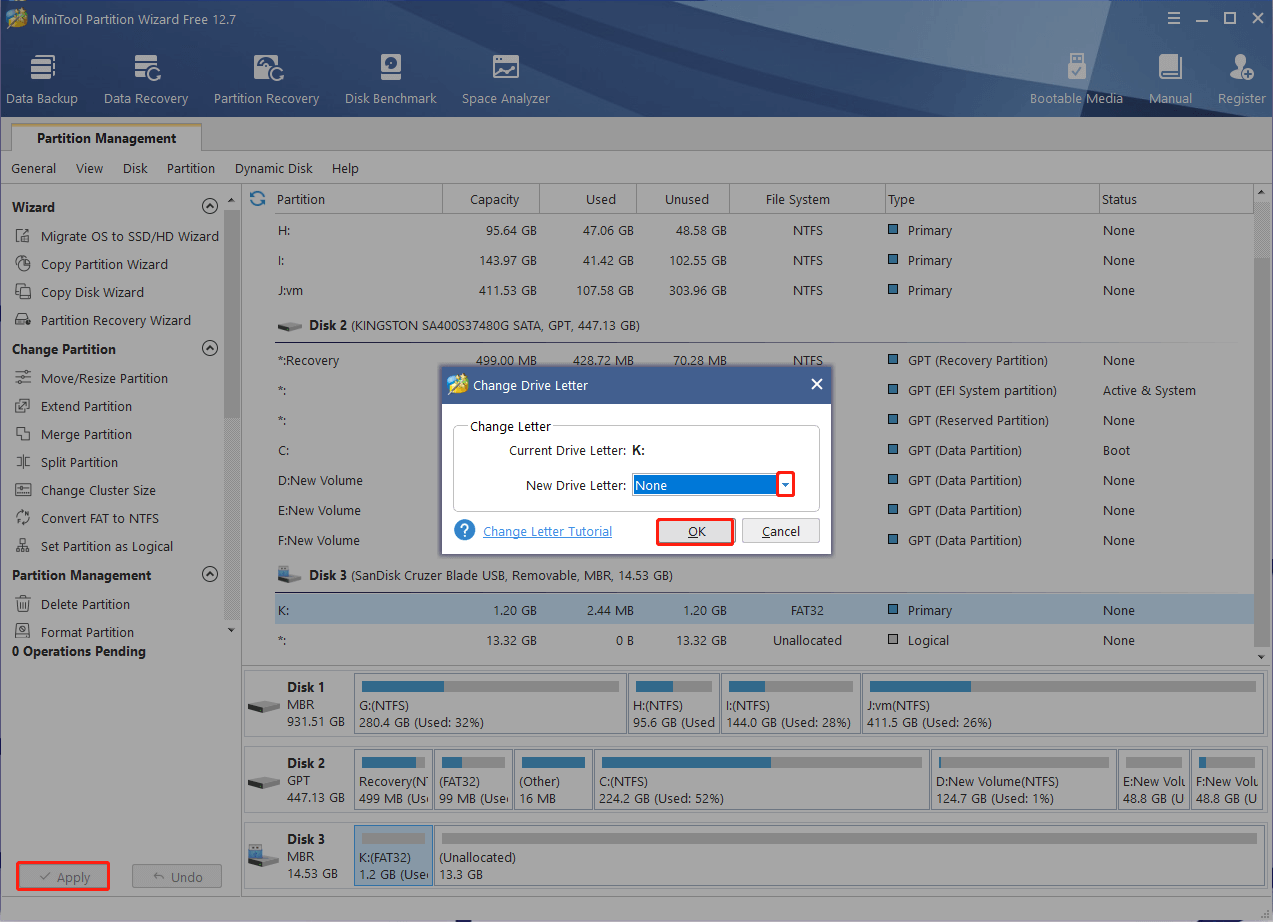
Step 2. If you want to remove the drive letter, select None from the New Drive Letter drop-down menu and click on OK to save the change. Alternatively, you can select a new drive letter from the drop-down menu to assign a drive letter for the partition.
Step 3. Click on Apply to execute the change.
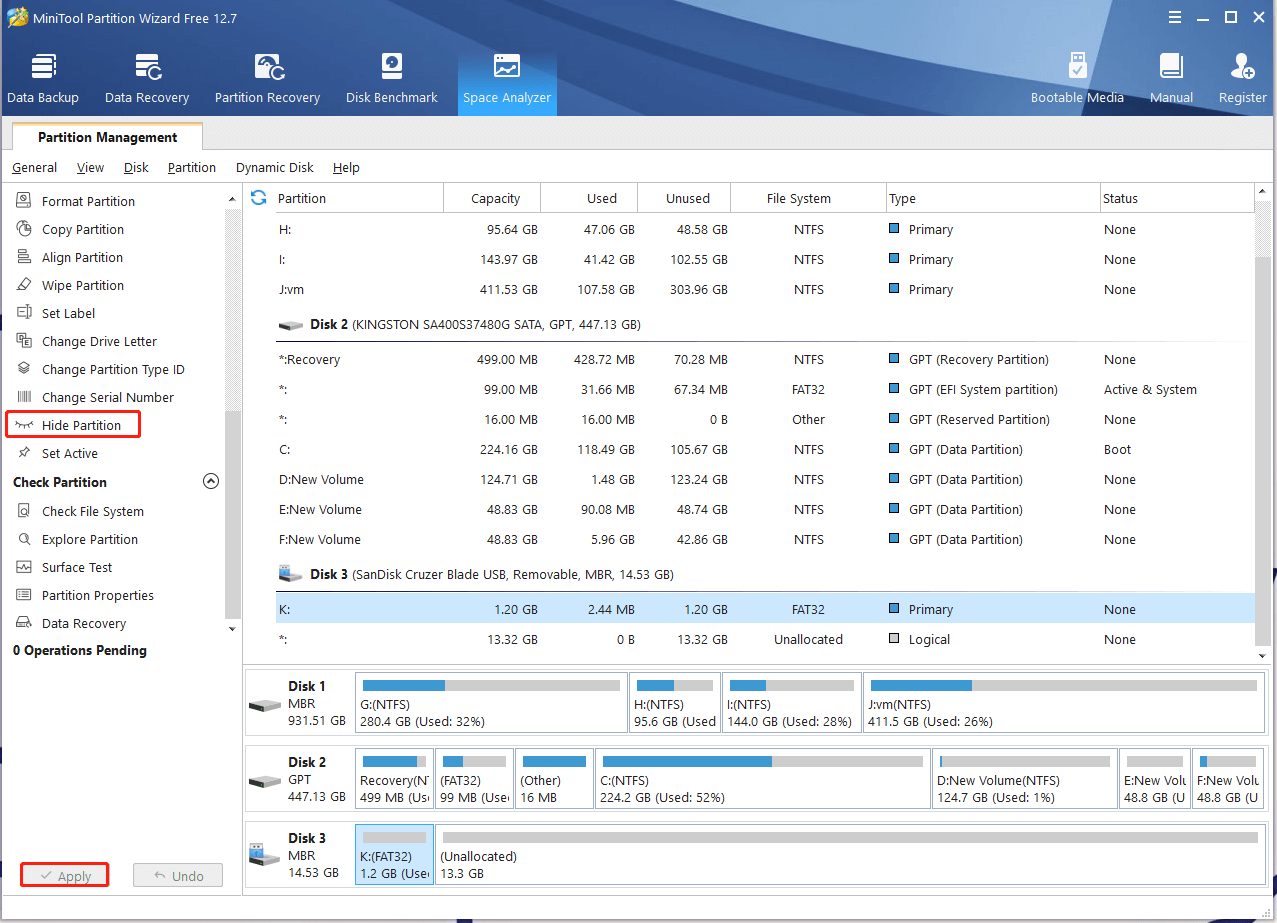
If you just want to hide the partition in File Explorer rather than remove the drive letter, you can select the partition and click Hide Partition > Apply from the left action panel.
How to make diskpart remove drive letter in Windows 11/10? All detailed steps have been illustrated. Now, you can change drive letter using diskpart/CMD. If it doesn’t work, you can use a better alternative – MiniTool Partition Wizard.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
User Comments :
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Diskpart assign letter to partition that is not associated with a volume (windows 10)
I used to have 3 volumes on my disk before something happened to the MBR that messed up my boot.
Now i'm trying to rebuild the boot environment to save all my data but it seems it is all lost. I can see the data through the command promt (from windows 10 DVD)
I am trying to do bcdboot c:\Windows /m {guid} but it is not working
I have also run:
I can find a lot of information on how you assign a drive-letter to a volume, but not how to assign a drive letter to a partition or make a partition associated with a volume.
When selecting the partition through diskpart i 'detail' part tells me: "There is no volume associated with this partition." so i am thinking there must be a way to asscociate it with a volume. but how?
How do i proceed to recover the boot?
- partitioning
- 1 >UDF DVD-ROM 3894 MB healthy <- (this is where my 128MB boot part used to be) ? But this seems to be a DVD-ROM ? – Leo Chapiro Sep 25, 2015 at 13:24
- Yes, but vol 0 used to be the boot part, the dvd was probably vol 3 – fjoesne Sep 25, 2015 at 13:26
- I cannot rebuildbcd or run bcdboot so that windows 10 is functional again. The problem (i think) is that i cannot run bcdboot nor rebuildbcd because the part where the boot is supposed to be installed has no volume. – fjoesne Sep 25, 2015 at 13:29
- By deleting the first (boot) partition and recreating it I was able to create a volume and I was eventually able to make a new BCD manually with bcdedit and bootsect. However, it seems to make no difference what I do to the BCD on the partition because windows boots no matter what now. However the boot is only possible by choosing the UEFI-element as listed in the BIOS, this was not visible before I deleted and recreated the boot-partition. I am still not able to run bootrec /rebuildbcd and get the same error as before. I think the problem now is that the partion and volume type is wrong.(?) – fjoesne Sep 26, 2015 at 23:08
3 Answers 3
I ran into the same issue after using gparted and ntfsclone . diskpart> list partition shows all my partitions, but they don't listed in diskpart> list volume and not associated with an letter.
Find out which partition X you need to associate with an letter:
If your disk has GPT table, set partition type GUID as Microsoft basic data partition (corresponding gdisk partition type is 0700 ):
If your disk in MBR ( 07 = Windows NT NTFS; 17 = Hidden; 27 = OEM Recovery):
Now you can try diskpart> list partition again. bcdboot c:\Windows worked for me just fine.
- 2 This should be the accepted answer. I had the same problem as the original poster and followed these instructions. My EFI partition had also become hidden and this fixed it. I could then follow these instructions to Rebuild the Window BCD bootloader configuration – FlexMcMurphy Oct 31, 2021 at 21:25
- 1 thanks, you saved my hours! – Özgür Apr 5, 2022 at 23:49
- Following this through to set id=EBD0A0A2-B9E5-4433-87C0-68B6B72699C7 worked for me, and immediately mounted the drive in Windows. Can't figure out why this worked or was was needed... – sblair Oct 30, 2022 at 16:26
Goodness sake, be careful!
It sounds like not "all is lost", but it also sounds like you only vaguely know what you're doing, and are proceeding. That is a recipe for "all is lost".
To elaborate, it sounds like you're able to access the vast majority of your data, but you're having troubles booting, which is a much simpler fix overall. But if you're not careful, you could easily lose the vast majority of your data.
First, it will help to make sure you know some basic terminology. The MBR is the first sector on a disk. The "MBR"-style of laying out partitions can handle drives up to 2 TB, and it looks like you're dealing with a drive smaller than that, so you might indeed be using an MBR and not the newer GPT format.
The two main jobs of an MBR are to have some initial boot code (instructions that the computer follows), and having 64 bytes of information to store details for up to 4 partitions (each partition table entry is 16 bytes).
Those 64 bytes of information can be pretty important. If you get some of these details wrong, operating systems may not properly understand some details about your partitions. And since operating systems typically write to disks, such misunderstandings can result in writing incorrect details that damage your ability to access data. So, being careful here is pretty critical.
A "partition" is basically a set of boundaries. You specify the starting sector, and either the ending sector or the size. Either way, you get a starting boundary and an ending boundary.
A "volume", sometimes called a "filesystem", stores your actual data. A volume needs to exist within the boundaries of the partition.
Now what typically happens is that an operating system looks at a partition, and assumes that a volume starts right at the beginning of the partition. Also, the partition specifies a "type", which is meant to be a strong clue about which style of volume is being used.
If the operating system can't find the volume, there are multiple possible reasons. One is that the partition's starting sector is wrong, and so the start of the volume isn't being properly found. Another possibility is that an improper "type" is being used, so the operating system doesn't know how to interact with the volume it is using. Another possibility is that the volume is damaged, and so the operating system is unable to find a volume that matches some details that the operating system checks for.
On my system, which is using GPT and that might cause some slight but significant differences, the "System" drive is the small drive (under a gigabyte), and my important data is stored on the large partition which shows up as a "Primary" type. The "System" type is not assigned a drive letter (although that isn't too hard, or problematic, to change... I would recommend assigning it a high drive letter, like S:, rather than C: or slightly higher. I also recommend avoiding X: since I think the Windows boot disk likes to use that.)
Since your System volume isn't even showing up, to me that suggests that it is damaged. You might need to restore that, providing a fresh copy of the boot files. This might not be something as easy to fix as using BCDEdit, which basically just tries to make slight changes. Your best bet may be to simply re-install the operating system (even to the same drive), which should accomplish a couple of things: placing a fresh (and not-updated) copy of Windows on your hard drive (which may be able to just overwrite, possibly even in-place, your current installation) and adjusting the ability to boot.
There might be an easier/simple way, but I recommend preparing for the possibility that there isn't.
However, I strongly advise you to get a full backup first. If at all possible, I even advise you to not just back up a few files that seem important, but to get a "forensic"/"bit-for-bit" image of the entire drive (onto another drive that is at least as large). That way, you can be comfortable that you're not going to lose your important data while you try to make any changes, and that you can revert in case any attempts go awry.
Having looked over your conversation with GuitarPicker, I am not as worried about your DVD drive showing up as it does. I think that just happens as a result of your boot partition not being detected; if your boot partition were detected, the DVD would automatically be assigned a higher drive letter without a problem. Using SET ID may indeed be helpful (and to find an existing ID, also known as a type, you can SELECT a partition and then say DETAIL PARTITION). But you did say, "I tried again to delete the boot partition with diskpart and recreated it". The problem here is that when you deleted the boot partition, you effectively told the computer to stop keeping track of any data on that partition, such as the critical data used to boot. Then, even if you did create a new partition and volume that are classified as the correct "type" for a boot partition, you still lack that bit of data that is used to boot the operating system. The typical way of getting that data onto a boot drive is called "installing the operating system".
While there might be some way to just transplant such boot data from another computer, some of the data may need to be placed in specific sectors on the volume (a picky detail which is not usually a concern except when dealing with boot files), and so this might or might not be quite as easy as just trying to do a basic copy. In other words, such a transplant has potential for troubles that make this approach not recommended for novices.
Note: I did read your comment about going from Win7 to Win10. You might be okay to just install Win10 over your existing drive, and if you're lucky then maybe your existing licensing might even get preserved, in which case you might not even need to fuss with going through the Windows 7 installation. But, for goodness sake, to make sure you don't introduce yourself to any worlds of new hurt, don't even think of trying that before making your backup. I know that such a task may be an annoyance (especially of money needs to be spent), but I'm re-stressing that issue because sometimes backups are even more worthwhile to make than average, and this is one of those times. So, I strongly advise you to do the wise thing, which is to make that investment in time/energy/supplies before any further mucking.
- 1 Oh, my. And just now, after posting, I see that the answer was from over three years ago, so my information is probably being supplied way too late for the original poster. – TOOGAM Jan 5, 2019 at 11:11
- 1 Which is fine . Remember, answers are for everyone with this same issue, not just the OP. BTW, I think where you said, "operating systems may not properly understand some details about your permissions" you meant permissions . – I say Reinstate Monica Jan 5, 2019 at 12:25
- @TwistyImpersonator : Thanks. But I meant partitions :) [that said, I do appreciate the feedback, and have now fixed the sentence you pointed out.] – TOOGAM Jan 5, 2019 at 12:34
- 1 Arrg, yes, I did the same thing you did and wrote permissions when I meant partitions ! – I say Reinstate Monica Jan 5, 2019 at 12:57
- You may be late to the show, but you already scored more upvotes. Congrats! I like coming back to old answers to see what I used to know. – GuitarPicker Jan 7, 2019 at 13:57
The partition types seem to be out of whack. Before proceeding, get a good backup with a bit-for-bit backup program like the CloneZilla boot disk, and then try editing the MBR. You didn't specify what type of partition your 128 MB was supposed to be, but you can try setting it manually. If you know what the partition type is supposed to be, you can use DISKPART 's SET ID command to set the hexadecimal partition type manually. Wikipedia has a list of partition types . Common ones are 07 for NTFS, 0C for most FAT32, 06 for FAT.
You may be better off starting with TestDisk , which is made for recovering partition tables. It can automatically detect many types of MBR problems. You still may have to follow through with bcdboot and bootrec, but it should get you to a workable starting point.
- Thanks for the tip, I have started a backup to an usb with clonezilla, and i will try to run testdisk either from the win-10 install dvd or my hackintosh install (the install that most likely messed up my window-install in the first-place.) – fjoesne Sep 25, 2015 at 15:01
- TestDisk was to no help for me, I guess its "over my paygrade" so to speak because it requires me to do calculations and estimates on what partitions existed before this happened etc. I tried again to delete the boot partition with diskpart and recreated it, but i still can not make it bootable nor can i rebuild the BCD on it. I guess i can save the data with testdisk, but I cannot save the partition table. Since I got the windows 10 upgrade from a windows 7 install i guess i have to install win7 again and go through that nighmare all over :( Ah well thanks for the help anyways.. :) – fjoesne Sep 25, 2015 at 22:16
- The MBR is only 512 bytes long (1 block), so it doesn't take much to ruin it. If the other partitions are truly intact, TestDisk should find them. There are sites which run you through the whole process . It bothers me that your DVD drive is drive 0 rather than your hard drive. That could be a contributing factor. Were any cables swapped on the board, or did you update motherboard settings or firmware? – GuitarPicker Sep 27, 2015 at 2:25
- 1 Are you confusing drive and vol perhaps? – fjoesne Sep 27, 2015 at 9:44
- Yes, I believe I am. – GuitarPicker Sep 28, 2015 at 1:36
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged hard-drive boot partitioning windows-10 diskpart ..
- The Overflow Blog
- Want to be a great software engineer? Don’t be a jerk.
- Climbing the GenAI decision tree sponsored post
- Featured on Meta
- New Focus Styles & Updated Styling for Button Groups
- Upcoming initiatives on Stack Overflow and across the Stack Exchange network
- Google Cloud will be Sponsoring Super User SE
Hot Network Questions
- Do faster responding low-pass filters exist compared to a traditional RC filter?
- Sight reader or busker?
- Is this formula already known?
- Was Eliphaz in Genesis related to Eliphaz in Job?
- What's the name of the room where you watch a movie inside the movie theater?
- Are wider tires on a road bike a good idea?
- What happens when an automatic transmission completely fails?
- NSF grant proposal not reviewed despite being received
- Am I in my rights to ask a colleague to not take notes on everything I say outside a meeting?
- How to equally split college fund between 2 children going to college 5 years apart?
- Treatment of expl3 variables - registers versus macros
- What caused pink flares during the eclipse
- What is the correct formulation of Newton's Second Law of Motion?
- I have begun to write a science fiction story, is this description of a super soldier a viable, and grounded, creation?
- Should the banker hit?
- Post-apocalyptic movie from the 1980's; mutants live in a wasteland and are assigned color-codes that dictate who they can mate with
- What contemporary hardware was available for the development of Atari 2600 (or other 2nd gen) games?
- Can You Train A Neural Network By Simply Giving It Ratings Each Time It Runs?
- Where is the large cook promotion?
- What is the difference between mind and consciousness?
- "Entrance exam" homework assignment for 3rd-year algorithms?
- python cprofile decorator
- Why does a 1:1 transformer preserve voltage?
- Can "sit" mean "receive no attention"?
How to use DiskPart to clean and format drive not working on Windows 10
If a drive is causing problems on Windows 10, it could be a logical issue that can be fixed with a few commands.
- Fix MBR drive
- Fix GPT drive
On Windows 10 , you can use the DiskPart tool to resolve virtually any logical problem with a storage drive, and in this guide, I'll outline the steps that I typically use to fix most issues (such as data corruption or other logical problems) using DiskPart.
DiskPart is a command-line tool to manage drives, partitions, volumes, and virtual disks through Command Prompt. Usually, it works better than other tools like "Disk Management" and the "Format" feature available on File Explorer.
On Windows 10, you can have different partition styles, including Master Boot Record (MBR) and GUID Partition Table (GPT). The MBR is the legacy partition style for the standard Basic Input/Output System (BIOS). The GPT is a newer partition style, usually found in Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) computers. The difference between the two is that GPT is meant to replace MBR since it supports more than four partitions, and it's required on drives with more than 2TB of space. You typically want to use GPT, but MBR is also a good option for external storage. These instructions will help you use DiskPart on either partition style.
These steps will erase everything on the selected drive, and you cannot undo the changes. If the drive is still accessible, it's recommended to back up the data before proceeding. If multiple drives are connected to your device, disconnect them to avoid selecting the wrong one.
In this how-to guide , I will walk you through the steps to use DiskPart to clean and format a hard drive to fix data corruption and other problems on Windows 10.
How to fix drive (MBR) problems with DiskPart on Windows 10
To fix drive issues on Windows 10 with DiskPart, use these steps:
- Open Start .
- Search for Command Prompt , right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to launch DiskPart and press Enter : diskpart
- Type the following command to list all the active drives and press Enter : list disk
- Type the following command to select the drive to clean and press Enter : select disk DISK-NUMBER
In the command, replace "DISK-NUMBER" with the drive number you want to repair as it appears in the "Disk" column. You could erase the wrong drive if you do not perform this step correctly. Proceed with caution.
Get the Windows Central Newsletter
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Type the following command to wipe out the drive and press Enter : clean
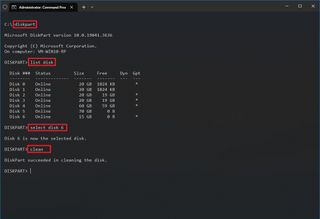
- Type the following command to confirm the drive is still selected, and press Enter : list disk
- Quick note: The output should include an asterisk (*) next to the selected drive. If the correct storage is not specified, perform step 5 again.
- (Optional) Type the following command to convert the drive to an MBR partition style and press Enter : convert mbr
- Quick note: This step is only required if the storage is configured as GPT , and you must use MBR partition style. If the partition is already MBR, you don't have to run the command, but running the command won't affect the process. You should be able to determine the partition type with the "list disk" command. If the drive doesn't have a GPT mark (*), it's an MBR partition.
- Type the following command to create a new partition and press Enter : create partition primary
- Type the following command to select the new primary partition and press Enter : select partition 1
- Type the following command to make the partition active and press Enter : active
- Quick tip: You only have to set a partition as active when using MBR. You can determine if the drive uses an MBR or GPT partition style with the "list disk" command. If the partition has a mark in the GPT column, it's not an MBR partition. If you have to set up a GPT partition style, use the other steps (see below).
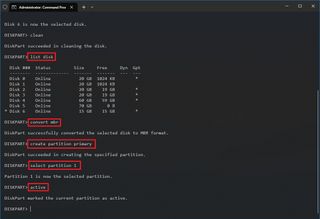
- Type the following command to format the partition using the NTFS file system, set a drive label, and press Enter : format fs=FILE-SYSTEM label=DRIVE-LABEL quick
In the command, replace "FILE-SYSTEM" with the name of the file system to use, such as "NTFS" or "FAT32," and replace "DRIVE-LABEL" with the name of the drive as you want it to appear on File Explorer. The " quick" option isn't required, but it will perform a format faster. However, it's best to skip the option if you are unsure about the drive's condition. The format could take a long time, depending on the hard drive's size. This example formats the drive using the NTFS file system and names the partition "myData": format fs=ntfs label=myData quick
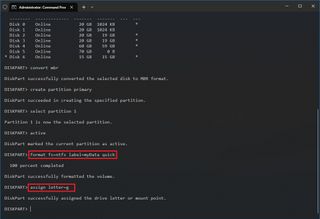
- Type the following command to assign a letter and make the drive available on File Explorer, and press Enter : assign letter=DRIVE-LETTER
In the command, change "DRIVE-LETTER" for the letter to use on the drive, which is not assigned to another device. This example assigns the "G" letter: assign letter=g
- Type the following command to terminate DiskPart and press Enter : exit
- Type the following command to close Command Prompt and press Enter : exit
Once you complete the steps, if the drive does not have physical issues, it should be accessible again through File Explorer.
How to fix drive (GPT) problems with DiskPart on Windows 10
To use DiskPart to fix drive issues with GPT partition style, use these steps:
- Type the following command to run DiskPart and press Enter : diskpart
- Type the following command to select the drive you want to clean and press Enter : select disk DISK-NUMBER
In the command, replace "DISK-NUMBER" with the drive number to repair, as it appears in the "Disk" column.
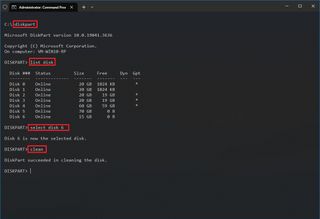
- Type the following command to confirm the drive is still selected and press Enter : list disk
- Quick note: The output should include an asterisk (*) next to the selected drive. If the correct storage is not specified, repeat step 5 one more time.
- Type the following command to convert the partition style to GPT and press Enter : convert gpt
- Type the following command to format the partition with the NTFS file system, set a drive label, and press Enter : format fs=FILE-SYSTEM label=DRIVE-LABEL quick
In the command, replace "FILE-SYSTEM" with the name of the file system you want to use, such as "NTFS" or "FAT32," and replace "DRIVE-LABEL" with the name of the drive as you want it to appear on File Explorer. The quick option is optional to perform a format faster. However, if you are unsure about the drive's condition, it is best to skip the option. The format could take a long time, depending on the hard drive's size. This example formats the drive using the NTFS file system and names the partition "myData": format fs=ntfs label=myData quick
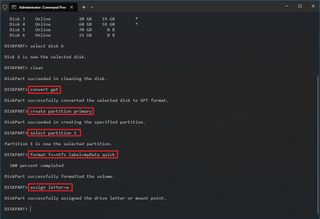
In the command, change "DRIVE-LETTER" for the letter to use on the drive, which is not assigned to another device. This example sets the "W" letter: assign letter=w
After you complete the steps, the drive should be fixed with a GPT partition style and accessible from File Explorer.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know

Mauro Huculak is technical writer for WindowsCentral.com. His primary focus is to write comprehensive how-tos to help users get the most out of Windows 10 and its many related technologies. He has an IT background with professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, and CompTIA, and he's a recognized member of the Microsoft MVP community.
- 2 Microsoft News Roundup: Elon Musk on AI ending humanity, Xbox leadership shake-up, and Windows 10 updates costing a fortune
- 3 EXCLUSIVE: Xbox President Sarah Bond has set up a new team dedicated to game preservation and forward compatibility
- 4 "It's like the gold rush. But it's probably going to come down in a couple of years, and then we'll just be refining the experience." AMD Senior Manager talks AI PCs and NPUs
- 5 One of last year's best PC games just came to Steam, and it's cheaper than a cup of coffee
El Mejor Gestor de Particiones de Disco y Optimizador de PC para Windows
- Utilidad de línea de comandos de DiskPart >
[2022] Cómo usar Diskpart para reparar una partición RAW en Windows
Esta página se centra en cómo surge la unidad RAW y cómo usar Diskpart para reparar la partición RAW. Si desea arreglar la partición RAW sin formatear, pruebe AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional.
Por Catalina / Actualizado el 18/05/2023
1. Reconstruir el MBR de la unidad RAW
2. comprobar los sectores defectuosos en la partición raw, palabras finales, visión general de la partición raw.
Una partición RAW significa una partición sin un sistema de archivos conocido/reconocible. Si el sistema operativo Windows no puede reconocer el sistema de archivos en una partición, los datos en esta partición se volverán inaccesibles. Generalmente, el problema de RAW puede ocurrir en discos duros, unidades flash USB, tarjetas SD, tarjetas de memoria y otros dispositivos de almacenamiento de datos comunes. Si la partición de su unidad (SO) de Windows se convierte en RAW, no podrá acceder al sistema y Windows no podrá arrancar .
¿Cómo surge una partición RAW?
¿Por qué el disco duro se convierte en una partición RAW? Hay muchas causas de este problema. A continuación se describen algunas de ellas:
• infección por virus o malware;
• estructura del sistema de archivos dañada o tabla de particiones MBR;
• el proceso de formateo se interrumpe y falla;
• existen sectores defectuosos en el disco duro;
• corte inesperado de energía;
• apagones accidentales del sistema operativo.
¿Cómo usar Diskpart para reparar una partición RAW (formateando)?
Cuando una partición se convierte en RAW, los usuarios de ordenadores suelen ejecutar CHKDSK para comprobar los sectores defectuosos. Sin embargo, fallará con un mensaje de error " CHKDSK no está disponible para unidades RAW ". En esta situación, la línea de comandos Diskpart es otra opción para arreglar la partición RAW.
El comando Diskpart puede reparar el disco duro RAW formateándolo a un sistema de archivos compatible como FAT32 o NTFS. A continuación se muestra una guía paso a paso para convertir RAW a un sistema de archivos FAT32 utilizando los comandos de Diskpart.
Advertencia: La operación de formateo también destruirá todos los datos guardados en la partición RAW. Así que si desea arreglar la partición RAW sin perder datos, es mejor que recupere los datos de la partición RAW a través de Recoverit Pro de antemano.
1. Abra la ventana del símbolo del sistema: pulse " Win+R " al mismo tiempo e introduzca " cmd " en la ventana de diálogo Ejecutar y pulse Enter .
2. A continuación, introduzca el siguiente comando en secuencia y pulse Enter después de cada comando.
list volume : lista todas las particiones y unidades disponibles. Identifique qué partición es RAW y necesita arreglarla de acuerdo con la información de la partición listada. Aquí, el volumen 6 se muestra como RAW y es la partición objetivo a seleccionar.
select volume 6 : asegúrese de elegir la partición/volumen correcto.
format fs=fat32 : formatea la partición RAW a FAT32. Puede escribir "format fs=ntfs" para convertir RAW a sistema de archivos NTFS usando cmd.
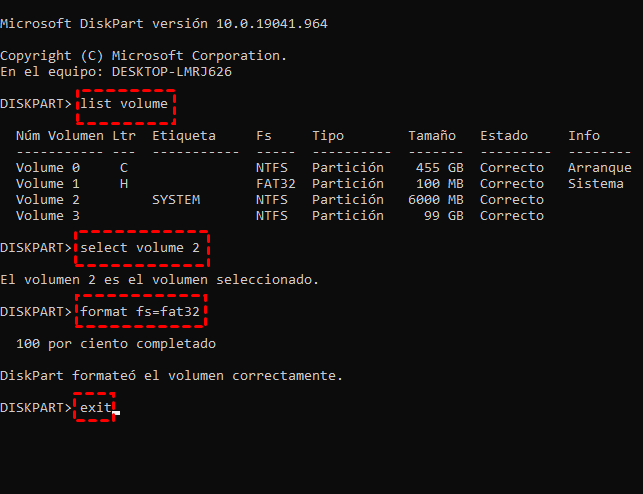
3. Escriba " exit " y pulse " Enter " para cerrar el símbolo del sistema.
O puede ejecutar los siguientes comandos para reparar la unidad RAW con Diskpart.
select disk # (por ejemplo: disk 1): para seleccionar el disco duro externo a formatear y pulsar Enter.
clean : para eliminar toda la información del disco duro externo.
create partition primary : para crear una partición.
format fs=ntfs : para formatear la partición como NTFS.
assign letter=# (por ejemplo: letter=F): para asignar una letra de unidad.
Si estos comandos de Diskpart se procesan con éxito, la partición RAW habrá sido fijada y formateada a FAT32 o NTFS.
Alternativa a Diskpart-arreglar partición RAW sin formatear
Teniendo en cuenta que algunos usuarios no están familiarizados con el uso de Diskpart para reparar la partición RAW, o quieren reparar la unidad RAW sin formatear, aquí nos gustaría presentar una alternativa profesional a Diskpart: AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional (compatible con Windows 11/10/8.1/8/XP/Vista de 64 y 32 bits).
Este programa profesional le permite reconstruir el MBR y comprobar los sectores defectuosos en lugar de formatear la partición RAW utilizando el símbolo del sistema directamente para solucionar el problema. El MBR dañado y los sectores defectuosos también pueden conducir a una partición RAW. Además, si no puede formatear una unidad RAW de más de 32 GB a FAT32 en Diskpart como los pasos anteriores y recibe el mensaje de error " El tamaño del volumen es demasiado grande ", también puede recurrir a AOMEI Partition Assistant, ya que puede formatear un disco duro grande a FAT32 con éxito.
Paso 1. Descargue el software. Instale e inicie AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional para entrar en su interfaz principal. Localice y haga clic con el botón derecho en el disco duro de destino y seleccione " Reconstruir MBR ".
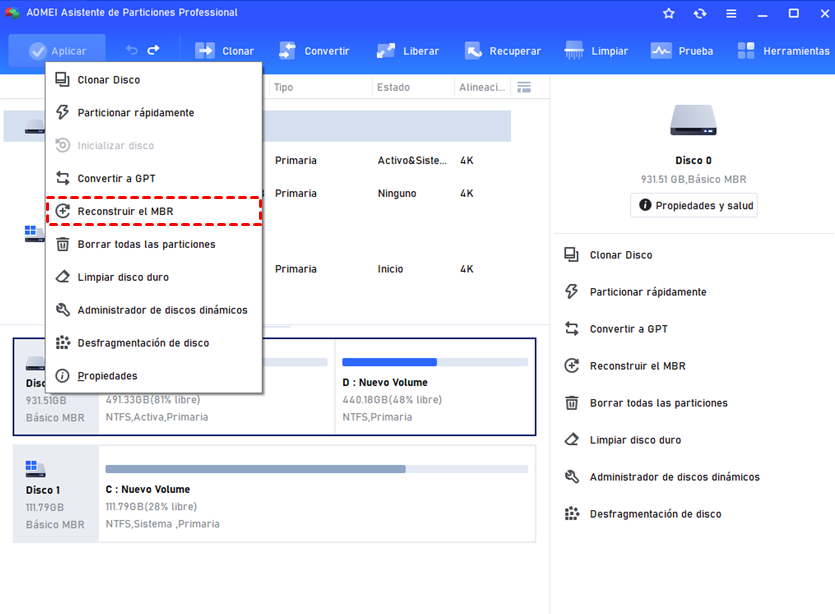
Paso 2. Seleccione un tipo de MBR adecuado para su sistema operativo actual y haga clic en " Aceptar ".
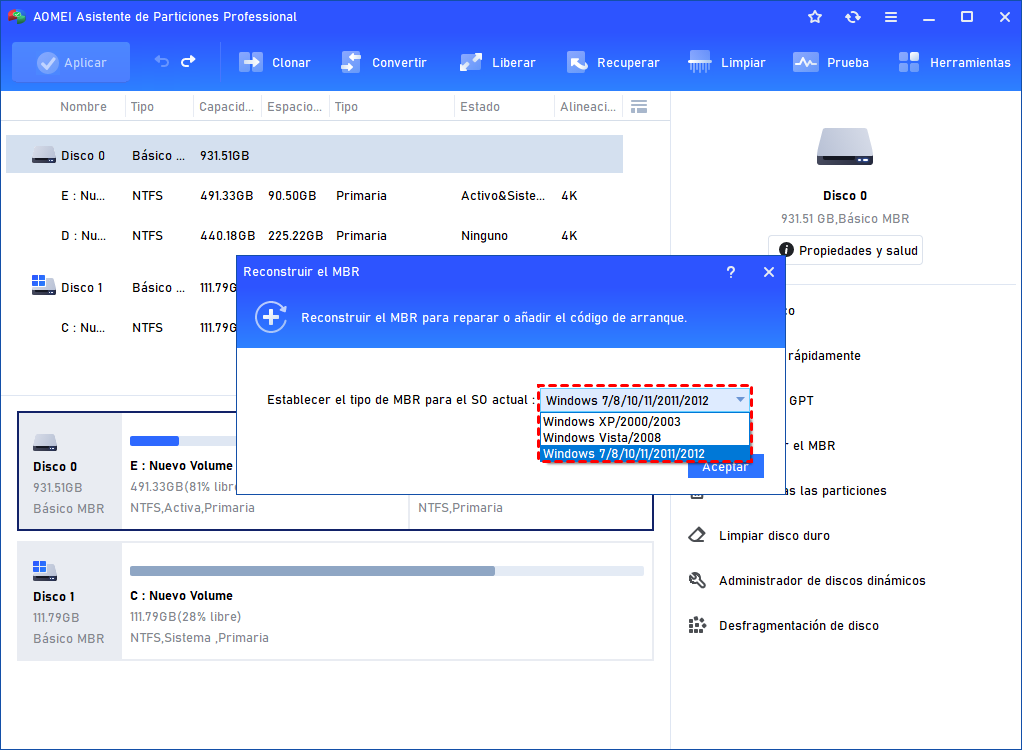
Paso 3. De vuelta a la interfaz principal, haga clic en " Aplicar "> " Proceder " para confirmar la operación pendiente.
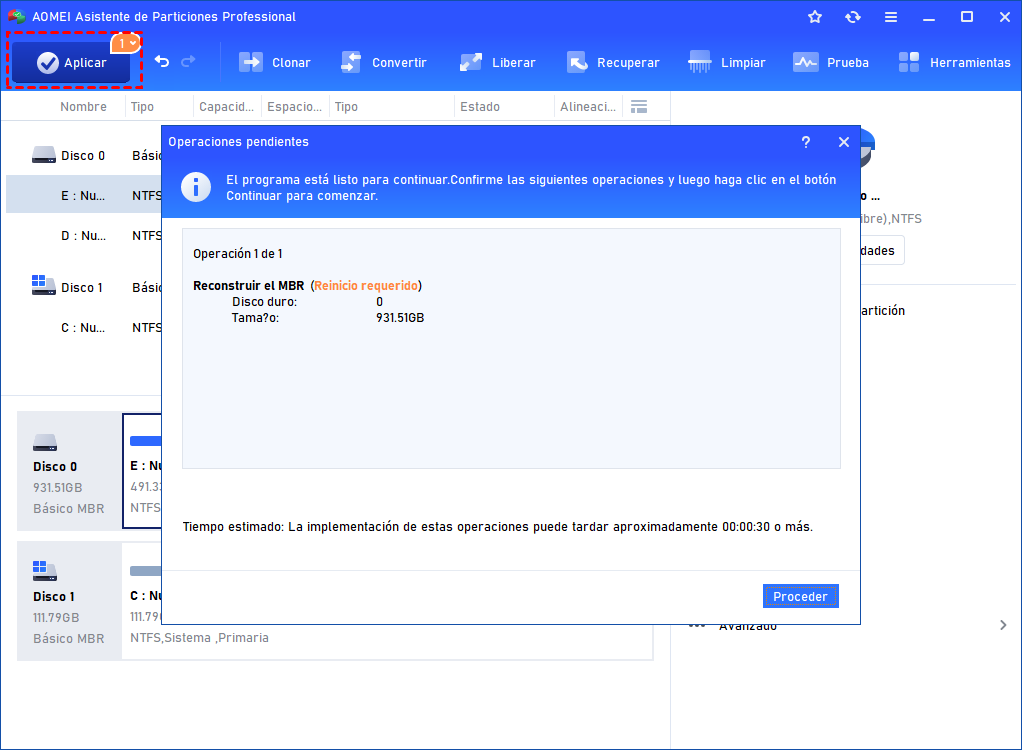
Cuando no pueda ejecutar CHKDSK para comprobar los sectores defectuosos, puede utilizar AOMEI Partition Assistant para realizar dicha tarea.
Paso 1. Abra AOMEI Partition Assistant. Haga clic con el botón derecho en la partición RAW y seleccione " Avanzado "> " Comprobar partición ".
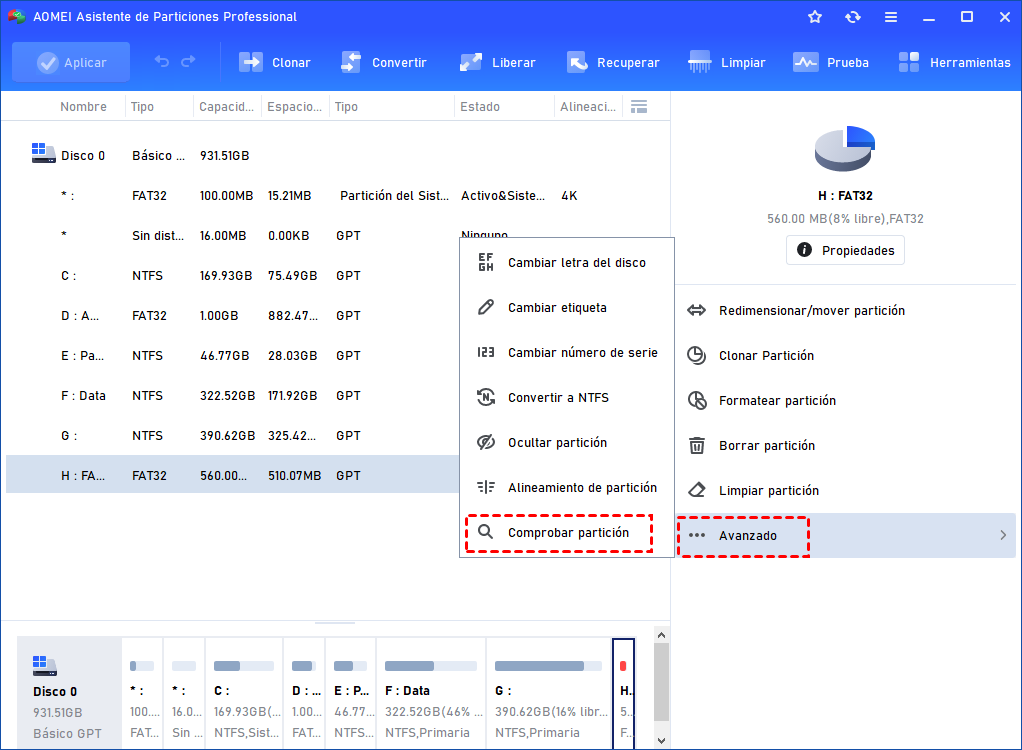
Paso 2. Marque " Comprobar sectores malos en la partición " y haga clic en " Aceptar ".
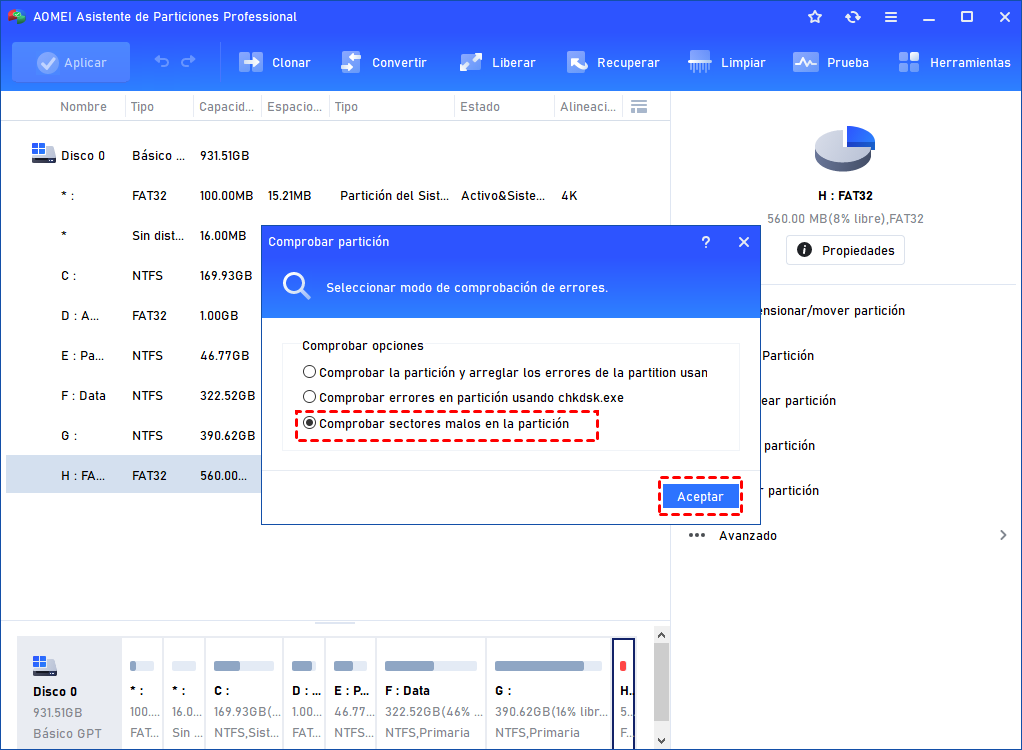
Paso 3. En la ventana de inicio, haga clic en " inicio " y espere a que el proceso se complete.
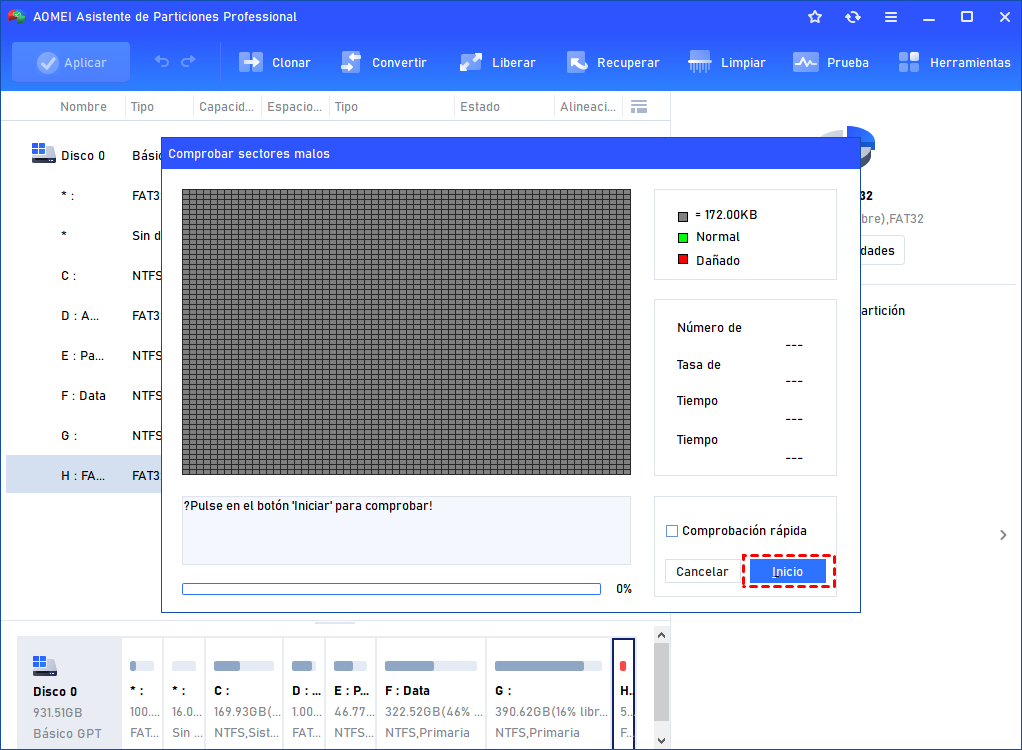
Consejo adicional: cómo arreglar un disco duro interno sin formatear
Si su disco duro interno se convierte en RAW y Windows no puede arrancar como debería, primero puede crear un medio de arranque a través de AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional en un ordenador que funcione. A continuación, inicie su PC con el disco duro interno RAW desde la unidad USB de arranque creada y, finalmente, utilice los métodos anteriores para arreglar el disco duro interno RAW sin formatear.
Ahora está seguro de saber cómo utilizar Diskpart para reparar la partición RAW formateando, así como la forma de utilizar AOMEI Partition Assistant para reparar la unidad RAW sin formatear. AOMEI Partition Assistant Professional también ofrece unas funciones más avanzadas como recuperar particiones perdidas , migrar la unidad del sistema operativo a SSD , crear Windows 11 para ir a USB con el sistema actual. Si la versión de su Windows es Server, pude probar AOMEI Partition Assistant Server .
Descargue gratis AOMEI Partition Assistant y pruébelo ahora

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Open up a command prompt (CMD/PowerShell). Type "diskpart" to start up diskpart. You will see the prompt change to "DISKPART>". Type "list vol" to list all available volumes. You can identify the drive by size and file system. Additionally, the volume doesn't currently have a drive letter. Select the volume using "sel vol <number>".
The diskpart utility makes it easy. You'll need to start by opening an administrator mode command prompt -- type cmd into the search box, and then right-click and choose Run as administrator, or use the CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER keyboard shortcut. Once there, run the diskpart command, and then type in the following to list out the volumes on your ...
Assign Drive Letter Using Diskpart. Assigning a new drive letter to a partition or removable device using Diskpart is really easy. First, search for the command prompt in the Start menu, right click on it and select the option "Run as administrator.". If you are using Windows 8, press "Win + X" to open the power user menu and select the ...
In addition to Diskpart, Disk Management may be another good choice to assign drive letter. Step 1. Press "Win + R" to open the "Run" window and type diskmgmt.msc in the box. Step 2. Right-click the drive you want to assign, and select change Drive Letter and Paths in the pop-up window. Step 3.
Use the select partition command to select a partition and shift the focus to it. ADD disk= n [align= n] [wait] [ noerr ] Mirror the simple volume with focus to the specified disk. ASSIGN [{LETTER= D | mount= path }] [ noerr ] Assign a drive letter or mount point to the volume with focus.
The diskpart command is used to add and delete hard drive partitions. Here's more on this command, including examples of how to use diskpart in Windows. ... assign: Assigns a drive letter or mount point to the volume with focus. attach vdisk: Attaches (sometimes called mounts or surfaces) a virtual hard disk (VHD) so that it appears on the host ...
Next, I will show you how to use Diskpart to change drive letter. Step 1. Press Windows + S at the same time to run the search box. Then type cmd. When the command prompt window appears, right-click it and choose "Run as administrator." Step 2. Type diskpart in the command prompt windows and press Enter. Step 3.
2. How to use diskpart to assign a letter to a partition from the Command Prompt or PowerShell. You can and probably want to also assign a letter to the newly created volume. Assigning a letter to a partition makes it visible in File Explorer so that you can easily access it. To assign a letter to a partition use the assign command.
Displays information about the selected disk, partition, volume, or virtual hard disk (VHD). Exits the diskpart command interpreter. Expands a virtual hard disk (VHD) to the size that you specify. Extends the volume or partition with focus, along with its file system, into free (unallocated) space on a disk.
Search for Create and format hard disk partitions and click the top result to open the Disk Management experience. Right-click the drive and select the Change Drive Letter and Paths option. Click ...
Procedure: From your taskbar, start a search for. Enter the command: Enter the command: Example output: Enter the command: but replace "2" with the desired volume number. Enter the command: but replace the "q" with any desired letter that is not already being used by another volume.
Launch Diskpart. 2. Choose a disk that has some unallocated or unused space. 3. Next, identify a volume by running the list volume command, or execute the detail disk command to view information about the disk and its associated volumes. Volume 2 below is ideal for shrinking, given its NTFS formatting.
Change the drive letter in the command prompt. Open an elevated command prompt. Type diskpart. Type list volume to see all drives and their partitions. Look at the ### column in the output. You need to use its value with the command select volume NUMBER. Substitute the NUMBER portion with the actual partition number for which you want to change ...
Type cmd into the search box, and then right-click and choose Run as administrator. If you have Windows 10 use the CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER keyboard shortcut on Screen 1, or click on Start with right click and choose Command Prompt (Admin) on Screen 2. When Command Prompt pops up, run the diskpart command. Now we type list volume to list our ...
Diskpart is a command-line disk partitioning utility the Microsoft Windows operating system provides. It allows you to manage disks, partitions, and volumes on your system. With Diskpart, you can create, delete, format, and resize partitions, assign drive letters, and set various attributes to them.
Launching Diskpart is a straightforward process. Here's how you can do it: Press Windows + R to launch the Run Command box. Type " cmd " and press Shift+Enter to open the Command Prompt with ...
More on the blog: https://bit.ly/31NoF4GAssign drive letters in the command line with Diskpart.Start a command prompt and type "diskpart". Then you can use "...
Step 1. Press Win + R keys to open the Run dialog box, and then type diskpart in it and press Enter. Then click on Yes to open the tool in Command Prompt. Step 2. To let diskpart unassign drive letter, type the following commands in order and press Enter after each one. list volume.
I ran into the same issue after using gparted and ntfsclone.diskpart> list partition shows all my partitions, but they don't listed in diskpart> list volume and not associated with an letter.. Find out which partition X you need to associate with an letter: diskpart> list partition diskpart> select partition X diskpart> detail partiton # I found that partition was hidden
2. Now type diskpart on the command prompt. If you're running Windows server, you can just run Powershell then launch diskpart on the cli. diskpart. 3. List available disk drives using the command below: list disk. 4. Now select the drive you want to partition using select disk command.
Step 1. In the home interface, right-click the drive that you want to rename and select Advanced > Change Label. Step 2. In the pop-up window, input the new label that you want to assigned to the drive and click OK. Step 3. You'll return to the home interface, click Apply and Proceed to commit the operation.
To fix drive issues on Windows 10 with DiskPart, use these steps: Open Start. Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option. Type the following ...
Abra AOMEI Partition Assistant. Haga clic con el botón derecho en la partición RAW y seleccione " Avanzado "> " Comprobar partición ". Paso 2. Marque " Comprobar sectores malos en la partición " y haga clic en " Aceptar ". Paso 3. En la ventana de inicio, haga clic en " inicio " y espere a que el proceso se complete.