Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.

Information Technology Business Plan
Start your own information technology business plan
Information Management Hawaii
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
By focusing on its strengths, its key customers, and the underlying values they need, Information Management Hawai’i, Inc. (IMH) will increase sales steadily in its first three years, while also maintaining the gross margin on sales, with a focus on cash management and working capital.
This business plan leads the way. It renews our vision and strategic focus: adding value to our target market segments, and reinforcing our ties with businesses in our local markets. It also provides the step-by-step plan for improving our sales, gross margin, and profitability.
This plan includes this summary, chapters on the company, products and services, market focus, action plans and forecasts, management team, and the financial plan.

1.1 Objectives
1. Achieve healthy earnings (EBIT) in the first year of operation.
2. Maintain a midrange gross margin throughout the entire operation.
3. Maintain just-in-time (JIT) inventory levels, or 11 turns per year.
4. Increase sales modestly but steadily in the second and third years.
1.2 Mission
To provide the Hawai’i business community with quality brand-name Information Technology business information solutions, reliable and professional Technical Support, and unparalleled Customer Service through the application of the principles of Kina`ole and heartfelt aloha, and to earn a fair profit for our employee-owners and stakeholders by embracing sound, ethical business practices.
1.3 Keys to Success
The keys to our success are:
- Customer Satisfaction Goals vs. Results
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Information Management Hawai’i, Inc., will sell and service digital office information systems for Hawai’i’s businesses, with a focus on the Neighbor Island business community. IMH will be formed as the result of the acquisition of three existing businesses: Maui Office Machines, Inc.; Electronics Hawai’i, Inc.; and, Kauai Office Equipment, Inc.
2.1 Company Ownership
IMH will be privately-held [C corporation] owned in majority by the IMH Employee Stock Ownership Trust. There are currently 15 employees, and all will own equal shares in the ESOT. New employees will be given the opportunity to become vested in the Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) after a suitable probationary period.
2.2 Start-up Summary
Our start-up costs will be $1M, which includes $450,000 for the acquisition of the Maui and Hilo operations of Servco Integrated Office Technology.
The remainder of the funds will be used for:
- Legal, Insurance, Rent & Misc: $125,000
The start-up funding will be financed by loans arranged through the Small Business Development Center, and by the Hawai’i Community Loan Fund, and the Small Business Administration as a guarantor. Start-up assumptions are shown in the following table and chart.

2.3 Company Locations and Facilities
We have two locations, one in Kahului, Maui and the other in Hilo, Hawai’i. The two offices are presently being leased by Servco Pacific, Inc., and we will rent from them on a month-to-month basis until we are able to relocate to more suitable facilities. On Kauai, we have a sub-contractor agreement with Kauai Office Equipment to handle installations and service.
Products and Services
IMH will acquire an existing operation whose primary business has been the sale and service of business appliances (copiers, facsimiles, printers, etc.) and has operated as a part of the office equipment industry. We will build from this base to transform the business into a value-added provider of the emerging services and technologies of the new Information Industry. Following the lead of Canon, USA and other manufacturers which we represent, we will approach the marketplace from a total systems solutions viewpoint.
This new paradigm will begin with an analysis of the client’s existing and planned business processes, and will provide total workflow solutions utilizing multifunctional imaging platforms and information distribution systems. These systems will be backed by professional and reliable technical service and proactive customer service. By forming strategic alliances with local Information Industry Value-Added Resellers, we will be able to offer turnkey Local Area Network (LAN) systems and the ability to retrofit existing LAN and peer-to-peer systems.
3.1 Sales Literature
Copies of our product and sales literature are attached as appendices. Of course, one of our first tasks will be to change the message of our literature to make sure we are selling the company, rather than the product.
3.2 Product and Service Description
IMH will market and sell brand name business information distribution systems and hardware, technical service and support for these products, and the consumable supplies used by these systems. We will be a single-source provider for business information and imaging products and services.
After researching our various manufacturer’s offerings and evaluating our core competencies, we will focus our marketing and sales efforts around the digital products offered by Canon USA and eCopy, Inc. We will supplement this product line with Lexmark and Hewlett Packard printer products. As we continue to transition the company into the digital marketplace, we will form alliances with additional IT manufacturers and suppliers who can round out our product and services line.
Hardware product offerings will include:
- Hewlett Packard Printer products (laser)
Software offerings will include:
- Canon Image Platform (document distribution)
Service Products include:
- Sale of consumable products for all brand names (Canon, Ricoh, Xerox, HP, Lexmark)
Professional Services include:
- Network design and installation (sub-contracted)
3.3 Competitive Comparison
The only way we can hope to differentiate well is to define the vision of the company to be an information technology ally to our clients. We will not be able to compete in any effective way with the large mainland-based office equipment companies by selling boxes or products as appliances. We need to offer a real alliance to our local customers.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Unfortunately, we cannot sell the products at a higher price just because we offer services; the market has shown that it will not support that concept. We have to also sell the service and consumable supplies and charge for them separately. This monthly recurring revenue is the foundation of our financial stability.
3.4 Technology
New technology has changed almost everything about the traditional office equipment (copier) industry, and for all practical purposes it no longer exists. The new Information Industry has emerged because of the technology of convergence. The primary driver of convergence of different forms of information is technological change, specifically the rapid diffusion of digital technology into an ever-wider array of information businesses. Beyond digitization, dramatic changes in computing and telecommunications industries (mainly in faster microprocessors and increasing bandwidth) are also driving convergence.
IMH will make convergence the theme of its vision, planning, and marketing strategies. We will move into the new Information Industry’s technology with the aim of bringing the most efficient workflow solutions to our clients while providing value-added customer support and service, and earning a reasonable profit in the process.
3.5 Service and Support
Our strategy hinges on providing unparalleled service and support, which is critical to setting us apart from the competition. We need to differentiate on service and support in order to become true partners with our clients. Our service offers will include:
- Upgrade analysis : we will periodically assess our client’s business processes and requirements, and offer cost-effective upgrade solutions to meet changing needs.
3.6 Future Products and Services
Beginning at start up, we will explore and research new information technologies for inclusion in our product offerings. The products which we choose will be in line with our vision to transition the company from being an appliance seller, to being a provider of total information management solutions. These convergent information products will include:
- Media transport and reproduction (distribute and print)
3.7 Fulfillment
We have an established relationship with our manufacturers and suppliers, and will be able to take advantage of all discounts and promotions in order to keep our margins at roughly 49% throughout the operation. We will also implement and employ “just-in-time” inventory strategies for hardware, supplies, and service parts orders to further strengthen our margins.
As we continue to grow the business, we will evaluate other IT industry manufacturers and product lines to strengthen our offerings with a view primarily to quality and margin advantages.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
IMH will focus on local markets, including small offices and home offices (1-9 employees), medium to large businesses (10-99 employees), corporate Hawai’i (multiple locations or 100+ employees), and local government offices.
4.1 Market Segmentation
Our market segmentation scheme is fairly straightforward, and focuses on all Neighbor Island businesses. The information contained in our customer analysis table is taken directly from the 2000 US Census and government directories, and clearly shows that our largest market potential is the small office and home office (SOHO) segment. This segment is largely overlooked by most of our competitors because of its “low end” buying habits, and a reluctance to compete with the major retail chain box movers. We will target the SOHO market segment with value-added and affordable business solutions customized to its unique needs, and offer the same quality of service and support as are afforded the larger businesses.
The next largest market segment is medium to large businesses, and is the arena where we now focus most of our sales efforts. We will continue to target this segment, but with a different approach than our predecessors. The strategy used by former management has been to bring in selected products, and then attempt to find a buyer. This resulted in inventory overstock, and obsolescence. We will work with the medium to large businesses to determine their needs, and design customized solutions before ordering the required systems (JIT inventory strategy). This segment will remain an extremely important part of our marketing mix, and contains a large portion of our current clients. A majority of our systems upgrade opportunities and repeat business will come from this market segment initially.
Although the Corporate Hawai’i market segment is the smallest in numbers, it has the potential to provide a significant share of our revenues and growth (the 80/20 rule). We have a scattering of current clients in the Corporate Hawai’i segment, but we need to do a better job of penetrating this lucrative end of the market. We will accomplish this by offering professional services to include workflow and network design, MIS support, and other value-added support benefits such as “uptime guarantees.” We will develop long-term relationships within this segment, and earn their business.
The local government market segment is unique in that we act primarily as a “middle man” for our manufacturers due to GSA price schedules and other national government-only programs. This segment is fiercely competitive, very price-focused, and buying decisions are often influenced by “who you know,” as well as price. We are fortunate in that we have long-established relationships within the County and State government agencies, and have many loyal clients in this segment. We will increase our share of this market segment by offering the same value-added service and support benefits that we bring to our commercial clients.

4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
Developing a market strategy is a departure from the way the company has been managed in the past. We will change the paradigm of being a product- and price-focused sales organization, to that of becoming a customer- and market-focused organization, with all departments sharing responsibility for customer satisfaction. We will accomplish this paradigm shift through the implementation of a balanced scorecard philosophy of management, with special attention to employee learning and growth.
As mentioned previously our market segmentation strategy is straightforward, and addresses all components of the Neighbor Island business community. Planning and implementing specific strategies for each of the four identified segments will be an on-going process, and we will consult with marketing specialists, and our manufacturers, to further refine these efforts as we develop our marketing plan.
4.2.1 Market Trends
That is the primary reason that IMH has chosen Canon USA as its preferred manufacturer. Canon has led the way in the industry with it’s digital technology innovations, and its ability to bring both the product and the concept to the marketplace. We will follow Canon’s lead and bring this efficient, productivity-enhancing technology to Neighbor Island businesses.
4.2.2 Market Growth
As computer prices continue to fall, unit sales increase. The published market research on sales of personal computers is astounding, as the United States market alone is absorbing more than 30 million units per year, and sales are growing at more than 20 percent per year. We could quote Dataquest, Infocorp, IDC, or others; it doesn’t matter, they all agree on high growth of CPU sales.
This rapid growth rate holds true for productivity systems which connect to the computers being sold. The stand-alone analog systems and appliances which abound in the business marketplace today, will be replaced by connected digital convergence systems in the coming months and years. IMH will position itself to be a value-added provider of this rapidly emerging technology for new businesses, while continuing to maintain and upgrade our current analog customer base.
4.2.3 Market Needs
All businesses have in common a need to be continuously productive, and they rely on their service providers and vendors to sustain their productivity. Effectively filling this need requires that the vendor bring to the table sound planning, quality products, reliable service, and a true partnership and support relationship.
Specific business needs include the ability to gather, compile, analyze, and distribute information in various media formats. This is where IMH’s strengths will be most beneficial to our clients, both big and small. Anyone can sell the “box” at an attractive price, but only a true value-added provider can offer the peace-of-mind that comes from a customer-focused approach to the relationship.
Primarily due to geographic isolation and smaller populations, the Neighbor Island business community has an additional common need of being able to rely on other locally-based vendors and suppliers for quick, reliable, customer service and support. Having to call someone on Oahu, or the mainland, to place a service call, or to order supplies, or get an answer to a simple billing question, is both an irritant and a hindrance to most Neighbor Island-based businesses. Our primary goal is to fill this need by bringing true pro-active, and total, customer service to the Neighbor Island business community, and to gain their confidence and loyalty. This will become one of our underlying strengths.
4.3 Service Business Analysis
IMH is a part of the Information Industry, and specializes in providing information management systems and technology for business processes. We envision that a converged information industry operating within the context of an advanced information infrastructure will be a huge boost for U.S. businesses. Several Washington think tanks estimate that it could spur more than $300 billion annually in new sales and increase worker productivity by 20 to 40 percent.
At the present time, an estimated two-thirds of all American jobs are information related, and that number will increase as the shift from manufacturing to service industries continues. The convergence of information industries will continue because the technological and business imperatives are compelling. If one company does not see the possibilities, another will.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
Business decision makers and finance managers understand the concept and value of service and support, and are much more likely to pay for it when the offering is clearly stated.
There is no doubt that we compete more against the box pushers than against other service providers. We need to effectively compete against the idea that businesses should buy information platforms as plug-in appliances that don’t need ongoing service, support, and training.
Our research and experience has indicated that our target market segments think about price, but would buy based on quality service if the offering were properly presented. They think about price because that is what is traditionally presented to them first. We have very good indications that many would rather pay 10-20% more for a relationship with a long-term vendor providing back-up and quality service and support. They end up in the box-pusher channels because they are not aware of the alternatives.
Availability is also very important. The business decision makers tend to want immediate, local solutions to problems.
4.3.2 Distributing a Service
Medium to large business segment buyers are accustomed to buying from vendors who visit their offices. They expect the copy machine vendors, office products vendors, and office furniture vendors, as well as the local graphic artists, freelance writers, or whomever, to visit their office to make their sales.
Unfortunately our SOHO target segment buyers may not expect to buy from us. Many of them turn immediately to the retail superstores (office equipment, office supplies, and electronics), the Web, and mail order to look for the best price, without realizing that there is a better option for them for only a little bit more. We will overcome this hurdle through innovative service offerings, and targeted marketing.
4.3.3 Main Competitors
In our higher-end targeted segments (medium to large businesses, corporate Hawai’i, and government offices), the primary competitors are Xerox and Lanier. The secondary “low end” competitors on the Neighbor Islands are Maui Office Machines and Business Equipment on Maui, and Electronics Hawai’i and Stationers on the Big Island. Our overall competitive strategy in these segments will be Canon’s superior technology, and superior value-added service and support.
In our SOHO target segment, the primary competitors are the superstores: Office Max, Office Depot, Sears, and to some extent Costco, Hopaco, and the Web. While these outlets can offer lower prices, they offer no (or very little) aftermarket service or support. That is our competitive advantage in this segment, and will differentiate us from these “box movers.”
4.3.4 Business Participants
The traditional office equipment (copier) industry has been dominated by only a few major manufacturers: Xerox, Canon, Oce, and Ricoh (and its OEM products – Lanier, Savin, and Gestetner); and then come the low-end players: Sharp, Toshiba, and Minolta. With the exception of Xerox, which maintains its own sales force, the other manufacturers distribute and sell mainly through authorized dealers.
The rapidly emerging Information Industry’s digital convergence products will most likely be dominated by the same participants as described above. While Xerox has been a past leader in the manufacture and sales of analog products, Canon has emerged as both an innovator, and the leader, in the new Information Industry with their ImageRunner digital products and Image Platform information distribution systems. Canon is also (and has been for many years) the front runner in color repro-graphic systems, and holds the most patents of any manufacturer in the industry.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
We must differentiate ourselves from the box pushers. We need to establish our business offering as a clear and viable alternative for our target markets, to the price oriented sales pitch to which they are accustomed.
- 30-day sales window – war with competition mainly on price.
The industry’s cheese has been moved. In order to shift to a more contemporary paradigm, our marketing and sales efforts will need:
- A new marketing concept – customer oriented, profit oriented, integrated efforts.
5.1 Competitive Edge
Our competitive edge is our positioning as a strategic ally with our clients, who are clients more than customers. By building a business based on long-standing relationships with satisfied clients, we simultaneously build defenses against competition. The longer the relationship stands, the more we help our clients understand what we offer them and why they should both stay with IMH, and refer us to other businesses. In close-knit communities like the Neighbor Islands, reputation is extremely important, and word-of-mouth advertising is invaluable.
5.2 Strategy Pyramid
Our main strategy will be placing emphasis on service and support, and our main tactics are networking expertise, systems training, and implementing a customer relationship management system (CRM) from e-automate. Our specific programs for networking include mailers and internal training. Specific programs for end user training include direct mail promotion, and on-site customer programs. Implementing the CRM software and training will be coordinated with the e-automate Corporation.
Our second strategy is emphasizing relationships. The tactics are marketing the company (instead of the products), more regular contacts with the customer, and increasing sales per customer. Programs for marketing the company include new sales literature, and direct mail. Programs for more regular contacts include call-backs after installation, direct mail, and sales management. Programs for increasing sales per customer include upgrade mailings and sales training.
5.3 Value Proposition
IMH offers its clients peace-of-mind by being a vendor who acts as a strategic ally, and delivers quality products backed by premium service and support, at a premium price.
5.4 Sales Strategy
We will sell the company and its ability to act as an ally. We will sell IMH, and the reputation of the industry-leading manufacturers it represents.
We will sell our service and support. The hardware is like the razor, and the support, service, software, and training, are the razor blades. We need to serve our customers with total solutions, and not just product features. The products are a means to arriving at end solutions.
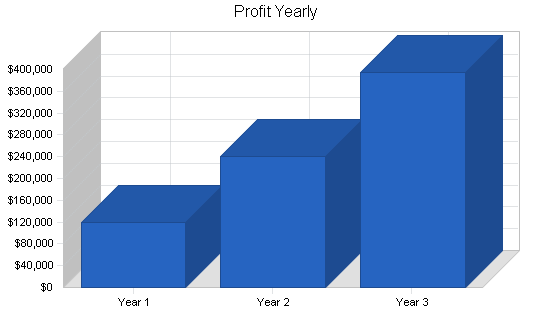
The Yearly Total Sales chart summarizes our conservative sales forecast. We expect sales to increase from $3.1 million in the first year to more than $4 million in the third year of this plan.
5.4.1 Sales Forecast
The important elements of the sales forecast are shown in the following Chart, and Table 5.4.1. Non-hardware sales increase to almost $2 million total in the third year, or 47% of total sales.

5.5 Milestones
The following table lists important program milestones, with dates and managers in charge, and budgets for each. The milestone schedule indicates our emphasis on planning for implementation. The most important programs are the sales and marketing programs listed in detail in the previous topics.
5.6 Marketing Strategy
The marketing strategy is the core of our main strategy:
- Develop specific programs for each target market segment:
- Government Offices – workflow/process surveys, uptime guarantees, GSA rates and incentives
5.6.1 Sales Programs
Specific sales programs will be included in our new Marketing Plan, and will be included in this Business Plan as they are finalized. In general however, our sales programs will be centered around conducting workflow and information distribution analyses, direct mail, and placing an emphasis on the benefits which IMH and its manufacturers will be able to offer its clients through “total care” service and support.
5.6.2 Positioning Statement
For businesses who want to be sure their information distribution systems are always working reliably, IMH is a vendor and trusted strategic ally who makes certain their systems work, their people are trained, and their down time is minimal. Unlike the product/price oriented vendors, it knows the customer and goes to their site when needed, and offers proactive support, service, training, and installation.
5.6.3 Pricing Strategy
We must charge appropriately for the high-end, high-quality service and support we offer. Our revenue structure has to match our cost structure, so the salaries we pay to assure good service and support must be balanced by the revenue we charge.
We cannot build the service and support revenue into the price of products. The market can’t bear the higher prices and the buyer feels ill-used when they see a similar product priced lower with the competition. Despite the logic behind this, the market doesn’t support this concept.
5.6.4 Promotion Strategy
We will employ the following general promotional strategies for the various market segments:
- SOHO: We will depend on periodic local newspaper advertising, to reach new buyers in this segment. We will also utilize direct mail and and the resources of the local Chambers of Commerce and other affinity groups to reach this segment. The message will emphasize service first, and “complete product and service packaging” as a secondary theme.
- Medium to Large Businesses: Direct face-to-face contact (direct sales) will continue to be our primary strategy for this market segment. Direct selling will be supplemented by periodic promotional direct mailings and personalized system upgrade opportunities.
- Corporate Hawai’i: This segment will be handled by direct contact and relationship building only. We will make personal presentations to the decision makers in this group, and stress our service and technical benefits and advantages.
- Government Offices: We will utilize a combination of direct mail and face-to-face promotional strategies with this segment, and the message will be the local service and technical advantages of IMH. We will produce an attractive RFQ/RFP response package to accompany our submissions.
5.6.5 Distribution Strategy
IMH is first and foremost a direct sales organization, meaning that we must present our services and products directly to the majority of our customers and clients. Having said that, for our planned penetration into the SOHO market, we will need to establish a presence as a Value-Added Reseller (VAR) for certain low-end product lines which don’t carry the margins necessary to sustain the costs of direct sales. We will plan our new locations accordingly.
5.6.6 Marketing Programs
As we work to complete this Business Plan, we are simultaneously working on our Marketing Plan. As you can see from the milestones table, we anticipate completion of our detailed Marketing Plan by 9/30/01, or one month from start-up. Because we are acquiring an on-going business, the shift to our vision of customer- and market-focused strategies will not happen overnight. We must plan this shift carefully, and implement it judiciously, so as not to disrupt our immediate operations. We have budgeted for, and will utilize, marketing advisors and consultants (including our manufacturers) in the design of our Marketing Plan.
5.7 Strategic Alliances
Our alliances with our manufacturers, and especially Canon USA, will be the most pivotal to our success. We will remain a Canon Authorized Dealer, and continue to enjoy all of the benefits of this long-standing relationship.
We will form alliances with other locally-based VARs and computer network providers to enable us to provide complete turnkey packages for our clients. These relationships will be included in our Marketing Plan.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Our management philosophy is simple and is an integral part of our values: doing right things right, the first time (Kina’ole).
IMH will be an employee-owned company and we all share the same vision of providing our clients (who in many cases are friends and neighbors) with the very best in customer service – period. We will encourage personal growth, creativity, and enable individual empowerment to achieve this goal. We will manage the business by setting achievable Balanced Scorecard goals, measuring them, and making mid-stream adjustments as necessary.
6.1 Organizational Structure
Our team includes 15 employees initially, and is organizationally flat. The departmental divisions are sales and marketing, service, and administration. Operational managers include:
- Systems Manager (two positions – Big Island and Maui): Oversees all service issues including service agreements, service call prioritization and response, carry-in service, customer support, and systems training and development. Will be assisted by Systems Engineers, and Systems Technicians.
6.2 Personnel Plan
The total head count moving over from Servco at the time of the acquisition will be 13. We are adding two former employees at startup to round out our team, for a total startup head count of 15.
There are an additional six positions shown as “vacant” in the Personnel plan. During each quarterly business plan review, we will assess the need to fund these positions to sustain our growth, and more evenly distribute the workload.
6.3 Management Team
Bill Harding, president and general manager: XX years old, and has lived on Maui for 43 years. Joined SIOT in 1998 as Maui branch manager, and became general manager for Neighbor Island operations six months later. Prior management experience includes: BTA market manager of the Neighbor Islands for VoiceStream Wireless, Neighbor Island area sales manager for Central Security Systems, and radar project manager for Telcom International in Nigeria, West Africa. Bill has attended numerous management and sales training courses and seminars throughout his career.
Laurie Watson, secretary/treasurer and administrative manager: XX years old, and local Maui resident. Has been at the same location through three different owners prior to Servco’s acquisition of The Office Place in 1995, for a total of 15 years of local office equipment industry experience. Laurie has extensive knowledge of service procedures and dispatching, A/R and A/P procedures, inventory control and tracking, as well as an intimate knowledge of our customer base. Her experience and knowledge will be invaluable in recovering our customer base, and in growing the business.
Anne Tioganco, office manager (Hilo): XX years old, and local Hilo resident. Anne has also been with the company through all of the acquisitions, and has XX years experience in the office equipment industry. She will assist Laurie by handling the administrative and customer service tasks for our Hilo branch, and will be instrumental in our Big Island customer recovery efforts.
Earle Oshiro, systems manager (Big Island): XX years old, and local Hilo resident. Like Laurie and Anne above, Earle has been with the company through four different owners, and has XX years of local office equipment service management experience. Earle has also completed Canon’s “train the trainer” course, and will be a great asset in the on-going training and development of our systems engineers and technicians.
Joseph Alfonsi, systems manager (Maui): XX years old, and local Maui resident. Joe joined the Maui branch of SIOT in 1999 as field service manager, after transferring from the SIOT Honolulu branch. He has XX years of local office equipment industry service experience, and is familiar with both Canon and Ricoh products. Joe is an asset to the Maui team, and has outstanding customer service skills.

6.4 Management Team Gaps
We believe we have a good team for covering the main points of the business plan. Key members have the experience and knowledge to manage and grow the business, and are highly motivated by the employee-owner concept.
The obvious management gap is a plan to fill the general manager’s position at some point in the future, before the current GM reaches retirement age. As an employee-owned company, the preferred strategy will be to promote from within, and fill vacancies as they occur. As the company grows, we will seek out additional talent in all operational areas.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
Although we are treating the business as a start-up company, the financial plan is solidly based on past performance. We have taken actual SIOT P&L income and expenses from the past three years, and eliminated corporate overhead expenses such as warehouse and administrative costs, inventory penalties, and corporate nominal interest. We then projected income based on actual past performance, and factored back in the revenue base that was relocated to Honolulu over the past two years (mainly service and supplies).
We approached the financial planning from a conservative standpoint, and based those numbers on achievable gross margins. Also, our actual interest and tax rates will most likely be lower than the assumed rates due to our being structured as an employee-owned corporation (ESOT).
7.1 Important Assumptions
The financial plan depends on important assumptions, most of which are shown in Table 7.1. As mentioned previously, we assumed interest and tax rates based on a “worst case” scenario, and these will be adjusted once we have finalized the initial funding and establish the ESOT. We have also assumed our personnel burden at 30% of payroll in order to allow for above-average benefits for our employees. As we shop around for benefits vendors, this assumption will be subject to revision as well.
Other key business assumptions are:
- We assume access to the start-up funding necessary to re-shape and re-build the company, and to provide adequate initial capitalization.
7.2 Key Financial Indicators
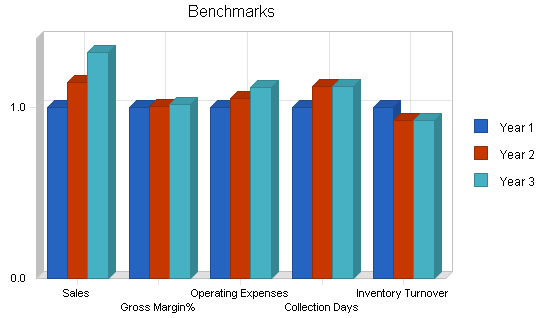
As shown in the Benchmarks chart below, our key financial indicators are:
- Inventory Turnover: We will maintain just-in-time inventory levels, or 11 turns per year. This will require accurate sales forecasting, and working closely with our manufacturers. We have already begun this process under SIOT, and the Neighbor Island inventory levels are well below previous years.
7.3 Break-even Analysis
For our break-even analysis, we assume running costs which include our full payroll, rent, and utilities, and an estimation of other running costs. Payroll alone, at present, is about $65,500 per month (including benefits and taxes).
We will monitor gross margins very closely, and maintain them at a midrange percentage by taking advantage of all promotions and discounts offered by our manufacturers. Canon USA has tentatively agreed to offer us “end column” pricing as a new dealer incentive.
The chart shows what we need to sell per month to break even, according to these assumptions. This is about 78% of our projected sales for our first year, and is well below what we have achieved annually over the past three years under more adverse operating conditions.

7.4 Projected Profit and Loss
Our Pro Forma Profit and Loss statement was constructed from a conservative point-of-view, and is based in large part on past performance. By strengthening our service position, and rebuilding our customer relationships, we will widen our customer base and increase sales.
Month-to-month assumptions for profit and loss are included in the appendix.
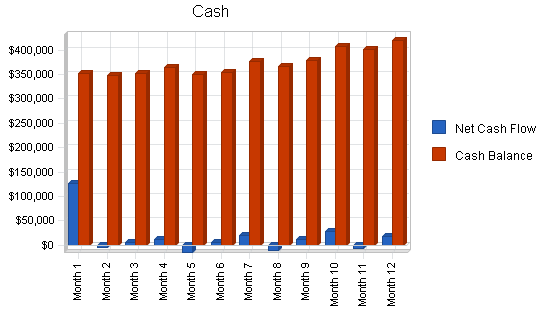
7.5 Projected Cash Flow
Because we are treating the new company as a start-up, the cash flow for FY2002 is somewhat exaggerated by the instant influx of new capital. Subsequent years however show a healthy growth in cash flow, mainly due to the short 60-month repayment of the start-up loan and increased sales.
7.6 Projected Balance Sheet
The Projected Balance Sheet is quite solid. We do not project any trouble meeting our debt obligations as long as we achieve our specific objectives.
7.7 Business Ratios
The following table shows our main business ratios, and is compared to national averages. Our SIC industry class is currently: Office equipment, nec – 5044.99.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Search ITA Search
- Market Overview
- Market Challenges
- Market Opportunities
- Market Entry Strategy
- Agribusiness
- Agriculture Sector
- Automotive Sector
- Aviation/Defense
- Construction Sector
- Education and Training
- Electricity. Power Systems and Renewable Energy
- Franchise Sector
- Media and Entertainment
- Information and Communications Technology
- Logistics Sector
- Oil, Gas, and Mining Sectors
- Safety and Security
- Trade Barriers
- Import Tariffs
- Import Requirements and Documentation
- Labeling/Marking Requirements
- U.S. Export Controls
- Temporary Entry
- Prohibited and Restricted Imports
- Customs Regulations
- Trade Standards
- Trade Agreements
- Licensing Requirements for Professional Services
- Distribution and Sales Channels
- Selling Factors and Techniques
- Trade Financing
- Protecting Intellectual Property
- Selling to the Public Sector
- Business Travel
- Investment Climate Statement
The information and communications technology (ICT) sector in Nigeria continues to play a pivotal role in the nation’s recovery in the wake of an economic lull during the pandemic years. Data from the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) reported that the ICT sector contributed 9.88% to the total nominal GDP in Q4 of 2021, lower than the rate of 10.58 per cent recorded in the same quarter of 2020. The figure reflects a declining shift as foreign exchange disparity widened and most organizations returned to physical business operations.
Nigeria is regarded as Africa’s largest ICT market with about 82% of the continent’s telecoms subscribers and 29% of internet usage. Sub-Saharan Africa is also projected to be the world’s fastest growing region with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.6% and an additional subscriber enrollment of over 167 million in the next five years. Nigeria is expected to account for over 55% of this. The NCC estimates that the country has about 85 million broadband subscriptions (penetration of 44%) and 206 million lines in the voice segment (teledensity of 108%) as of June 2022.
In September 2021, the Nigerian government approved 5G in Nigeria. By December 2021, the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) had completed auctions for the 3.5GHz spectrum, awarding 5G operational licenses to MTN and MAFAB Communications. The NCC licensed Airtel a 5G spectrum on December 5, 2022.
The four major mobile network operators in the country (Airtel, Globacom, MTN, and 9Mobile) continue to strengthen their market share. Collectively, Nigeria has over 206 million mobile subscriptions. As of July 2022, MTN dominates the GSM market with over 79 million subscribers (38.36%). This is closely followed by Airtel with about 58 million subscribers (28.21%), Globacom has over 56 million (27.28%), and 9Mobile with 12.6 million subscribers (6.14%).
The government of Nigeria recognizes ICT as the enabler for developing other critical sectors including education, healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing. In its drive to diversify the economy from oil and gas, the government is encouraging partnerships between local ICT companies and foreign investors. To promote these partnerships and grow an entrepreneurial ecosystem in the technology sector, the Nigerian government has supported government or private sector led incubator hubs, youth innovation programs, and science technology parks.
Much like the federal government, several states have begun to implement policies and ICT projects that may help to attract ICT investments and create an enabling business climate for their regions. The Lagos state government announced the construction of a free tech zone that would allow for growth and financing of innovative ideas and may become one of the major technology clusters in West Africa. Similarly, the Edo state government is promoting a live-work-play project that is expected to support a dynamic environment for innovation, growth, and development in technology.
Prominent among the partnerships with the private sector are collaborations with local accelerators like iDEA and the Co-Creation Hub (CC-Hub) in Lagos. These initiatives have attracted foreign investors like the Silicon Valley’s Y Combinator, who recently participated in pitches by Nigerian startups, and New York ‘s Andela, which established an incubation center in Lagos to recruit and train talented Nigerians to code and subsequently outsource them to foreign firms. In 2022, Microsoft launched its first African Development Center (ADC) in Lagos. The facility is expected to recruit world-class African engineering talent to develop innovative solutions that span the intelligent cloud and edge.
The Federal Ministry of Communications and Digital Economy has overall responsibility for the ICT sector. The ministry also has purview over three different agencies including the NCC as the regulator for the telecoms industry; the National Broadcasting Commission (NBC) regulates the broadcast industry; and the National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA) is responsible for digital policy implementation.
The Nigerian government in November 2019 launched the National Digital Economy Policy and Strategy (2020-2030) aimed at repositioning the Nigerian economy toward opportunities that digital technologies provide and to diversify the economy away from dependence on the oil and gas sector. The program is based on 8-pillars for the acceleration of the Nigerian economy:
- Developmental regulation
- Digital literacy & skills
- Solid infrastructure
- Service infrastructure
- Digital services development & promotion
- Soft infrastructure
- Digital society & emerging technologies
- Indigenous content development & adoption
As part of measures to achieve this objective, the NCC rolled out the National Broadband Plan for 2020-2025.
The Broadband Plan is designed to deliver data download speeds across Nigeria of a minimum 25 Mbps in urban areas, and 10 Mbps in rural areas, with effective coverage available to at least 90% of the population by 2025. As part of the initial broadband expansion plan, Nigerian government is seeking private sector infrastructure partners in expanding last-mile access. To deepen broadband penetration across the country, the NCC granted licenses to telecommunications infrastructure companies (infracos) to provide telecommunication broadband infrastructure across the various geo-political regions of the country, especially the rural populace. The infracos include:
- MainOne Cable Company (Lagos zone)
- IHS Holding Limited (north central and Abuja zone)
- Zinox Technology Ltd (southeast zone) BCN (northwest zone)
- Brinks Integrated Solutions Ltd (northeast zone)
Nigeria aspires to become one of the top economies in the world and the country recognizes ICT development and broadband access as critical requirements to achieve this vision. This ambition, however, remains far from being accomplished as several hurdles have encumbered broadband expansion and investment opportunities for the sector. Some of the major challenges that have affected the sector include long delays in the processing of permits; multiple taxation at federal, state, and local government levels; multiple regulatory bodies; damage to existing fiber infrastructure as a result of cable theft, road works and other operations; and right of way (ROW) charges implemented incongruously by several state governments. This typically leads to the high cost of leasing transmission infrastructure. Following criticisms and outcry by several stakeholders, the federal government has been pushing for the states to review ROW charges as part of promoting ease of doing business and attracting more investment. Currently, many states have started reviewing the charges above the federal-approved rate of $0.37 (145 naira) per linear meter. Some states are providing zero cost for laying broadband or any other telecommunications infrastructures to boost digital infrastructure rollout outside of urban areas.
Following the rapid growth and progress in the country’s ICT landscape, the country’s international connectivity improved from a single international submarine cable system with 340 GB total capacity installed in 2001 to a total of five cable systems with a combined overall capacity of over 40 terabytes. However, much of this remains unutilized because of inadequate distribution infrastructure and channels to areas of need inland. This holds huge potential for Nigeria as increasing data capacity.
The future looks promising for this segment. The Nigerian mobile network operator and owner of the GLO 1 submarine cable already announced ongoing work to launch a second submarine fiber cable – GLO 2. GLO2 is expected to have a capacity of 12 terabit per second and be the first submarine cable in Nigeria to land outside Lagos when completed. It is also intended to scale up for further expansion southwards, including to Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Angola. Meta announced its ‘2Africa’ project, laying subsea internet cables that will stretch 22,990 miles and interconnect Europe to about 16 countries in Africa with 21 landings points, including Nigeria. Facebook notes that the cable, upon completion, will provide nearly three times the total network capacity of all the subsea cables serving Africa today, as well as support growth of 4G, 5G, and broadband access for hundreds of millions of people. In April 2022, Google landed its Equiano subsea cable in Nigeria. Google’s Equiano cable is expected to have nine branching units creating room for more international connectivity. In the Nigerian terminal point, it is expected to yield about 20% reduction in internet retail prices, a sixfold increase in internet speeds, and a 6% increase in internet penetration.
There are several other huge capital projects being championed by U.S. multinationals. U.S. firm Equinix acquired MainOne, which had been one of Nigeria’s major tier-III data centers, with footprints in Ghana and Cote d’Ivoire. Corning recently collaborated with Nigerian cable manufacturer, Coleman Technical Industries Limited, for local manufacturing of fiber optic cables. Cisco Systems got the approval of Nigerian government to develop six internet of things (IoT) labs across the country, with the focus of building the necessary skillset among students. IBM is championing its Digital Nation Africa (IBM DNA) program focused on empowering youths on the continent. The platform is designed to provide digital knowledge with practical understanding and enhance digital careers.
The growth of e-services and cloud computing has fueled the demand for data services, simultaneously creating the need for more reliable and high-quality broadband from service providers. The enterprise application software (EAS) market is currently dominated by products from Asia and Europe, with some imports from the United States, but the market segment for high quality products remains largely available.
Nigeria has been able to maintain footprint in space through its communications satellite (NigComSat-1R), which was launched in 2011. The satellite is expected to be retired around 2025. In March 2021, NigComSat announced its call for expressions of interest (EOI) for additional communications satellites from competent manufacturers, contractors, vendors, and partners in the satellite industry. Firms will be pre-qualified for consideration in the implementation of the design, manufacture, launch, in-orbit test, and commissioning of a high-through satellite (HTS). The statement from the agency notes that it intends to increase its fleet of satellites to address a broad array of the communication needs of the country in the areas of broadcasting, broadband, and internet services by procuring the manufacture and launching of an HTS.
Leading Sub-Sectors
Fiber on air and fiber to the home (FTTH) is receiving interest following the increased bandwidth capacity now available in the country. Local internet service providers (ISPs) in Nigeria are providing improved high-speed wireless to the home (WTTH) services.
Cloud computing is fast becoming a necessary aspect in the operations of large businesses and some government agencies in Nigeria. There are several data centers across the country; Nigeria currently has about four enterprise-grade and multi-tenant data centers categorized as Tier III or Tier IV. These provide any or all major data center offerings:
- Software as a service (SaaS)
- Platform as a service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- Back-up as a service (BaaS)
Commercial activities within this segment of the market are expected to remain buoyant as the government is pursuing a data localization policy. The National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA), the Nigerian government’s body responsible for data protection, is requesting all telecommunications companies host all subscriber and consumer data in Nigeria. Further, they request all ministries, departments, and agencies of the federal government to host their websites locally under a registered.gov.ng domain, along with all sovereign data.
Fintech and digital financial services in Nigeria are gaining widespread use and acceptance as the government continues to campaign for a cashless economy. This is also being fueled by the increasing adoption of mobile phones. NCC, in conjunction with the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), now allows mobile network operators (MNOs) be licensed and perform mobile money payment services. The CBN issued an approval to two of the nation’s MNOs (MTN Nigeria and Airtel Africa) to operate as payment service banks (PSB).
With growing interest in online commerce, Nigerian fintech operators are also gaining traction. In October 2020, U.S. financial tech outfit, Stripe, announced the acquisition of Nigeria’s Paystack to accelerate online commerce across Africa. The acquisition, worth about $200 million, is the culmination of a close partnership between Stripe and Paystack over the last several years. The CBN recently announced that Nigeria’s fintech firms attracted an investment of $500 million between 2015 and 2020 owing to improvement in the ecosystem.
So far, digital financial services in Nigeria mainly provide savings, lending, and payments. The payments acceptance market, especially merchant and bill payment services, is fast becoming dominated by third-party aggregators and other nonbanks including switch operators. Major participants in the space are Cellulant, Flutterwave, Paystack, Systemspec, WebPay, Paga, etranzact, Quickteller, and Payarena.
The viability of Nigeria’s tech industry keeps growing. With five out of seven of the continent’s tech unicorns, Lagos remains the top destination for investments going into what has been dubbed “Africa’s Silicon Valley.” Accounting for over a third of the continent’s tech investment in 2022, Nigerian fintech start-ups raised over $1.3 billion in 2022 out of the $4 billion invested in Africa. The United States remains the leading source of investment, with nearly 60 percent of all fintech investment flowing into Nigeria.
Smart mobility and last-mile logistics is another part of the tech ecosystem that has gained some popularity. Following the launch in Nigeria of Uber’s ride-sharing service in 2014, several other models have been introduced and adopted, including motorbike-hailing services. Smart mobility is a disruptive market force in the global transportation technology sector. There are huge prospects for the vehicle technology industry in Nigeria, especially within the automotive aftermarket space including GPS navigation systems, telematics, mobile electronics, camera systems, security control, and tracking systems.
Opportunities
There are several investment opportunities in Nigeria’s diverse information technology sector for U.S. investors. Nigeria’s cloud service market terrain is still nascent as there are only a few participants currently involved in enterprise-grade deployments. Industry analysts see activity increasing for partnerships, as well as equipment sales and technical services. Also, the digital financial services and financial tech sector is continually evolving with new participants and product launches. This is spurred by both government policy to promote a cashless economy and the high number of digital natives in the ecosystem.
Additionally, there is huge potential in the country’s fiber optic and broadband market given the continued expansion of Nigeria’s international submarine cable system. The landscape currently has a combined overall capacity of over 40 terabytes with other projects proposed to be launched soon. Further opportunities may be explored in the satellite internet and television white space (TVWS) segments as the roll out of terrestrial fiber across the country may not provide the much-needed nationwide coverage, hence the need for alternative technologies. U.S. information technology companies, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and internet service providers (ISPs) may also consider the emerging needs for supply of required devices (antennas, solar kits, cabling, diverse range of wireless communication, and radio products for high-capacity data and voice delivery) in this space.
The Nigeria Startup Act initiated by both the Presidency’s Office of the Chief of Staff and Office of the Minister of Communications and Digital Economy was signed into law October 19, 2022. The Act oversees policy guidelines and regulations in the Nigeria tech space and aims to create a conducive environment for Nigerian startups to launch and scale products, attract foreign capital, and prevent setbacks from events that have occurred in the past like the ban on cryptocurrencies.
In 2020, Lagos State began their Smart City implementation, a that project entails the deployment of metro-fiber infrastructure, intelligent transportation systems, and digital workflow systems for the state government. In a bid to drive further civic digitization and technology outcomes, Lagos state signed an MOU with Microsoft in December 2022 to partner in technology development. This agreement will see Lagos leverage opportunities on Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform to develop technology solutions in the healthcare, education, and energy sectors. Additionally, Lagos and Microsoft propose to explore technical collaborations in data Analytics, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and privacy solutions.
Though Nigeria remains a major ICT powerhouse on the continent, there have been reports of a recent slow-down of the sector caused by rising exchange rates and constrained access to the foreign exchange necessary for the import of inputs. Downstream effects include foreign exchange scarcity, wide disparity between the dollar and the local currency (naira), impacted investment, and increased cost of equipment procurement.
There has been ongoing debate regarding the Nigerian government’s plan to regulate the use of social media. Nigeria currently ranks 120th in the 2021 World Press Freedom Index, down from 115 in 2020.
Significant and frequent policy shifts in Nigerian government’s positions toward ICT are common. Ride hailing services including Uber and Bolt have continued to face threats of stiff regulations in some of the country’s regions. In 2020, Lagos state government, citing safety and security concerns, imposed a ban on the budding two-wheel ride-hailing platforms – Gokada, Max.ng, and ORide. These firms were banned from operating in the city’s central commercial and residential areas. Most of the affected operators now focus on deliveries and other logistics businesses.
In February 2021, the CBN cautioned all banks and financial firms against facilitating the use of cryptocurrency and reminded them that “dealing in crypto currencies or facilitating payments for cryptocurrency exchanges is prohibited.” CBN’s notice also required all recipients to identify persons operating crypto exchanges and ensure their accounts are closed immediately. After sustained chaos in the crypto market, the CBN clarified that the notice did not constitute a total ban, nor was it meant to discourage people from trading cryptocurrency. Instead, the Bank argued, it was merely reiterating a pre-existing ban on banks facilitating crypto transactions that was implemented in 2017, and which was part of the government’s drive for Nigeria to become a cashless society. Nigerians, however, still remain among the most active cryptocurrency traders in the world. In June 2021, the Nigerian government imposed a ban on the use of Twitter in the country, accusing the site of not curtailing content from a successionist movement. Media reports connected the ban to the company’s removal of a post by the President. Twitter’s service was restored in January 2022 with a requirement to appoint a local representative, register with Nigeria’s Corporate Affairs Commission as a legal entity, comply with tax obligations, and abide by regulatory and legal demands. This injunction also applies to other interactive computer service platforms and internet intermediaries.
Local Industry Events
- Digital Africa Conference; Location: Online ( https://www.digitalafrica.com.ng/ )
- NigeriaCom Conference; Location: Online ( https://tmt.knect365.com/nigeria-com/ )
- Social Media Week; Location: TBD ( https://www.smwlagos.com/ )
- Nigerian Communications Commission
For further sector information, e-mail: Ambrose Thomas, Commercial Specialist, U.S. Commercial Service, Lagos, Nigeria at: [email protected]
Licence or Product Purchase Required
You have reached the limit of premium articles you can view for free.
Already have an account? Login here
Get expert, on-the-ground insights into the latest business and economic trends in more than 30 high-growth global markets. Produced by a dedicated team of in-country analysts, our research provides the in-depth business intelligence you need to evaluate, enter and excel in these exciting markets.
View licence options
Suitable for
- Executives and entrepreneurs
- Bankers and hedge fund managers
- Journalists and communications professionals
- Consultants and advisors of all kinds
- Academics and students
- Government and policy-research delegations
- Diplomats and expatriates
This article also features in The Report: Nigeria 2023 . Read more about this report and view purchase options in our online store.

ICT From The Report: Nigeria 2023 View in Online Reader
With a population of close to 220m and an internet penetration rate of 51% at the beginning of 2022, Nigeria’s large ICT consumer market offers room for growth, making it an enticing prospect for local and international investors, particularly with the population forecast to reach 377m by 2050. Inadequate policy implementation has long prevented the sector from reaching its potential, but the government’s willingness to enter into public-private partnerships is a reason for optimism. Moving forwards, the burgeoning, responsive financial technology space and wider start-up ecosystem are bright spots for the domestic economy. Greater public-private cohesion in those areas would give the government an opportunity to collaborate with the country’s most innovative minds to develop effective solutions to macro and socio-economic challenges.
This chapter contains interviews with Kashifu Inuwa, Director-General and CEO, National Information Technology Development Agency; and Olu Akanmu, President and Co-CEO, OPay Nigeria.

Articles from this Chapter
Direct connection: enhanced connectivity and a burgeoning start-up ecosystem are driving improvements in digital services and human capital obg plus.
A strong ICT ecosystem provides the foundation for an efficient modern economy, significantly enhancing business procedures, public services and job creation. With this in mind, Nigeria’s government is following a long-term development blueprint with the aim of harnessing digital technological capabilities to diversify the economy and reduce dependence on hydrocarbons revenue. Sector-specific strategies and roadmaps are designed to boost ICT infrastructure. The telecommunications segment is key…
Streamlined growth: Kashifu Inuwa, Director-General and CEO, National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA), on the necessary steps for digitising the country’s economy OBG plus
Interview:Kashifu Inuwa What steps must be taken to implement Nigeria’s National Digital Economy Policy and Strategy? KASHIFU INUWA: The National Digital Economy Policy and Strategy (NDEPS) outlines eight pillars to facilitate the digitisation of the economy. This comports with former President Muhammadu Buhari’s vision to diversify Nigeria’s economy away from its dependence on oil and gas. To fulfil the NDEPS’ goals, the NITDA developed its Strategic Roadmap and Action Plan 2021-24,…
The way ahead: Olu Akanmu, President and Co-CEO, OP ay Nigeria, on improving financial inclusion and optimising value-added services OBG plus
Interview:Olu Akanmu In your view, how feasible is the central bank’s financial inclusion target for 2024? OLU AKANMU: In 2020 the financial inclusion rate was 64%, which the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) can feasibly grow to 80-90% by leveraging the expanding range of financial technology services. However, roughly 50% of the population holds a formal bank account, whereas informal financial services largely service the 64% figure cited. This represents an enormous opportunity to double…
Innovation destination: The domestic start-up ecosystem continues to attract investment as public-private partnerships seek to improve capacity OBG plus
While the first tech start-ups in Nigeria emerged in the early 2000s, the ecosystem truly began to develop in the years from 2012. Financial technology (fintech), e-commerce and retail technology enterprises dominate the current start-up landscape; however, the ecosystem has expanded to encompass key areas of the national economy including recruitment, mobility and logistics, agri-tech and entertainment. Nigeria, and in particular the largest city Lagos, is the primary hub for African start-up activity.…
Heightened concern: Governments work to counter a global rise in cyberthreats stemming from digitalisation and the shift to remote work OBG plus
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in early 2022 has caused disruptions across the global economy, from food to energy, and prompted an increase in the number and sophistication of cyberattacks – exacerbating similar impacts from the Covid-19 pandemic. According to a poll of 800 chief audit executives conducted by the UK-based Chartered Institute of Internal Auditors, 77% of respondents thought the war had elevated cybersecurity and data-security risks. Senior cybersecurity analysts have said that…

Privacy Overview

| Nigerian Educational Consult - samphina.com.ng
- Business Plan
📑 Download Business Plans in Nigeria

This is samphina.com.ng your #1 plug for any Business Plan (Startups) in Nigeria. We understand the time factor, and we have simplified the process so that you can get your Business Plan ready as soon as possible by making available Business Plan for different businesses in Nigeria.
List of Business Plans in Nigeria
Click on Any Business to Download the Complete Business Plan and Financial Plan
- Agro Commodity Export
- Agrochemical
- Auto Repair
- Bakery / Bread
- Banana Processing
- Banking Agency
- Barbing Salon
- Bike Delivery
- Block Industry
- Bottled and Sachet Water
- Business Hub
- Cashew Nut Processing
- Cassava Farming and Processing
- Catfish (Fish Farming) Production and Processing
- Cattle Rearing / Fattening
- Chicken Slaughter and Processing
- Cinema House
- Cleaning Services
- Cocoa Farming and Processing
- Cocoyam Farming and Processing
- Cooking Gas (LPG) Retailing
- Cosmetology
- Cotton Farming and Processing
- Courier Services
- Crèches and Daycare
- Diary Production
- Diesel Haulage
- Driving School
- E-commerce Platform
- Electric Concrete Pole Manufacturing
- Electrical Equipment Sales
- Event Management
- Fashion Design
- Flavored Plantain Chips
- Frozen Foods
- Ginger Farming
- Goat Farming
- Gold and Jewelry
- Grocery Store
- Groundnut Oil
- Haulage and Logistics
- Healthy Restaurant
- Herbal Medicine Production
- Hide and Skin
- Hydroponics
- Ice Block Production
- Ice Yoghurt Production & Sales
- Information Technology
- Insurance Brokerage
- Integrated AgriBusiness Plan
- Interior Decoration
- Kampala / Adire (Tye & Dye) Textile
- Laundry / Dry Cleaning
- Leather Tanning
- Lighting Installation
- Maize Farming
- Marine Logistics
- Meat Processing
- Media and Entertainment
- Medical Equipment Supplies
- Medical Laboratory
- Microfinance Bank
- Mobile Food Vending
- Mobile Kitchen
- Moringa Farm
- Mushroom Farm
- Musical Equipment Rentals
- Nanny Agency
- Nursery and Primary School
- Nylon Production
- Organic Food Store
- Paint Production
- Palm Kernel Oil Extraction
- Palm Oil Production and Processing
- Paper Recycling
- Petrol Station
- Photography and Videography
- Piggery (Swine) / Pig Farming
- Pineapple Farming
- Plantain Farming and Processing
- Plastic Bottle (PET) Recycling
- Printing and Multimedia
- Real Estate
- Recreation Centre
- Retail Store
- Rice Milling
- Rice Retailing and Distribution
- Shea Butter Production & Processing
- Shoes Making
- Snail Farming
- Soap Making
- Solar Energy Installation
- Sport Equipment
- Tea and Beverages
- Tea Farming and Processing
- Tissue Paper / Serviette Manufacturing
- Tomato Farming and Sales
- Transportation
- Travel Agency
- Unisex Hair and Beauty Salon
- Vegetable Farming
- Vocational Training
- Waste Management
- Welding and Fabrication
- Yam Production
Samphina Academy
Samphina Academy is an Online Educational Resource Center that is aimed at providing students with quality information and materials to aid them in succeeding in their academic pursuit.
- Next story Corrupt Practices And Their Effects On Nigeria Civil Service; An Examination Of Selected Ministries In Ebonyi State Civil Service (2019- 2023)
- Previous story Project / Seminar Research Topics and Materials on Child Welfare Clinic
Catfish (Fish Farming) Production and Processing Business Plan PDF
Bakery / Bread Business Plan PDF
Fashion Design Business Plan PDF
Catering Business Plan PDF
Poultry Business Plan PDF
Healthy Restaurant Business Plan PDF
Bottled and Sachet Water Business Plan PDF
Snail Farming Business Plan PDF

Press ESC to close
Or check our popular categories....

How To Write A Business Plan In Nigeria (Free Samples And Templates)
This post concludes is the last of the series on “How to write a business plan” . The major challenge when it comes to writing a business plan is knowing where to start from. This most business owners and entrepreneurs don’t always get right. Looking through existing business plan templates gives a clear picture of what your business plan should look like.
This post contains a long list of free sample business plan templates that will give you the easy start you really need to write your own business plan.
1. Catering Business Plan
If you love to cook and are thinking about starting a business, combine the two and start a small catering business. But how do you start a small catering business? It’s by having a great business plan detailing every aspect of the business before you get started.
2. Event Planning Business Plan
Starting a catering business in Nigeria is a lucrative business with very good returns, with thousands of events and parties happening every weekend across the country. Event planning business requires a combination of education if necessary, an experience and excellent networking.
Also Read: How to Write a Business Proposal for Clients in Nigeria.
3. Hair & Beauty Salon Business Plan
Salon Business is one of the best and lucrative business in Nigeria right now because it does not cost much and requires little capital to start. Either a barbing salon or beauty salon for women pay a lot because it requires no college degree to start one but skill.
4. Day Care & Child Care Business Plan
Many Nigerian mothers are working at paid jobs or running their own small businesses which consume most of their time. As a result of this trend, there is a growing opportunity for convenience services like child and day care center businesses.
5. Driving School Business Plan
Are you an expert driver? Can you successfully teach others how to drive? If yes, you may be qualified to start a car driving school. There is a great opportunity in this business because most Nigerian are looking forward to owning their own cars. School leavers are also eager to learn how to drive.
6. Agriculture Farm Business Plan
Nigeria is blessed with a favorable soil and climatic condition that can accommodate crops such as onion, carrot, cocoa yam, pear, potatoes, okra, vegetables, beans and so much more. Starting an agriculture farm business is a profitable business opportunity with so much market to serve.
7. Feed and Farm Supply Business Plan
The feed farm production industry has been largely promoted as one of the most profitable agribusinesses to venture into. Africa, especially Nigeria, has a major impact on the worldwide production and distribution of livestock feed.
Also Read: [PART 1] How to write a business plan – Tips when writing your business plan.
8. Fitness Gym Business Plan
Health they say is wealth; the need for health is the need of all both young and old, both for the rich and the poor alike. Would you like to invest in the fitness business, or are you thinking of a business to invest in? You should consider this business option.
9.Pharmacy Business Plan
Pharmacy or drug store business, whether we like or not, has become an integral part of the Nigerian economy today. In a nutshell, drugstores are described as retail establishments that market drugs, be it prescription-based, proprietary, or nonprescription medicine.
10. Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan
The fast-food business in Nigeria is a very profitable business. Food is something we cannot do without even if it’s once a day. The growing population of Nigeria with over 180 million people is also a high contributing factor to the profitability of fast food business in Nigeria. Amidst the current global crisis, one line of business in Nigeria that continues to promise greater returns on investment is the fast food business.
11. Bakery Business Plan
The consumption of bread and other bakery products such as biscuits, chin-chin, gala and meat pie among others, has created a huge market for the wheat flour industry. This sector has provided a lot of opportunities while more opportunities are still open for interested investors that are willing to invest some cash.
12. Internet Cafe Business Plan
The demand for internet cafe services in Nigeria is high especially in business enabled environments like tertiary institutions, offices and in different work areas. This business is one of the profitable medium scale businesses in Nigeria; the business can give a high-profit margin when managed properly.
13. Clothing Boutique Retail Business Plan
Starting your own clothing shop boutique is a good business idea in Nigeria because the fashion industry is one powerful sector that will always be vibrant in any economy because all over the world, people have a basic need for clothing. Beyond this need, fashion is also evolving on daily basis due to the huge and diverse interest in styles.
Also Read: [PART 2] How to write a business plan – Basic template contents & structure.
14. Automotive Car Repair Business Plan
Nigeria is and will always be a big market for cars, both used and new ones. Compared to other African countries, Nigeria alone spends up to $5 billion dollars every year importing vehicles (especially second-hand) from the USA, Canada, Europe, and Asia. Which makes the industry an area worthy of investing.
15. Car Wash Business Plan
The good aspect of this business is that it does not necessarily require a large amount of capital or funding especially when you intend to start. For those who have enough money to invest, this will be a good decision as with more money invested, the business can grow much better and faster leading to better and profitable returns.
Other business plan samples and templates include;
16. Used Cars Sales Business Plan.
17. Online Print Shop Business Plan .
18. E-commerce Retailer Business Plan .
19. Coffeehouse Business Plan.
20. Night Club Business Plan.
Categorized in:
Share Article:
Related Articles
5 ai-powered video marketing tips for small businesses in nigeria, how to start an exportation business in nigeria, 10 most lucrative business in nigeria in 2023, how to use threads by instagram: a step-by-step guide, small business insurance: what you need to know, cac registration: a guide on how to register a company online in nigeria , other stories, bookkeeping for small business why you should hire a bookkeeper., best payment alternative to paypal for nigerians..
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS EDUCATION IN NIGERIA

Technological change and globalization have created a new global economy with Information and Communication Technology (ICT) occupying a complex position in relation to globalization. The emergence of this new global economy has serious implications on the nature and purpose of educational institutions. The paper is basically a theoretical discourse. Data for analysis were obtained from secondary sources. The paper found that significant challenges confront the integration of ICTs in education in the areas of educational policy and planning, infrastructure, language and content, capacity building and financing in Nigeria. The paper concluded that business education needs to be well equipped to anticipate and respond to opportunities created by ICTs in order to participate productively and equitably in an increasingly technology-rich and knowledge-driven world. The paper recommended, among others, that the investments in ICTs should be used to promote the development of basic skills, problem-solving and communication skills and the professional development of teachers.
Related Papers
Muhammad Muhammad Suleiman
Information Technology (IT) increasingly becomes enablers of change in all aspects of human endeavour, particularly education. IT is very relevant to the objectives of increasing Business Education students’ participation in the educational processes and of promoting life-long learning. This paper attempted to discusses the concepts of IT and how IT tools, such as computers, projector, e-learning, video conferencing, multi-media and other audio-visual equipment that can be used for teaching and learning of Business Education in Nigerian Colleges of Education. Among others, this paper recommends that government should release more funds to train and retrain of teachers as well as recruitment of adequate personnel, both teaching and non-teaching staff also government should release funds for purchase all essential IT resources and networking the entire Colleges of Education in the country. Keywords: Information Technology, Business Education, Computer
IOSR Journals
Information and Communication Technology (ICTs) occupies a complex position in relations to teaching and learning of Business Education in Colleges. The emergence of ICTs has serious implications on the nature and purpose of educational institutions. The researcher is basically concerned with academic performances of students if ICTs is used as a tool for teaching. Data for analysis were obtained from a test given to the students in both experimental and the control groups. The data was analyzed using Pearson moment correlation coefficient and t-value was also used for the test of significance. The researcher found that significant value was obtained between the experimental and the control groups. The researchers concluded that business education needs to be well equipped to anticipate and respond to opportunities created by ICTs in order to enhance academic performance of students. The researchers recommended, among others, that the investments in ICTs should be used to promote the development of basic skills, problem-solving, communication skills and the professional development of teachers.
Zaira Hassan SBBU-SBA
Professional Development in Education
Professor William J . Ubulom
Johnny Ogunji
Wokocha Da-kaladokubo
The study examined the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) challenges encountered in teaching business education in Rivers State tertiary institutions. The research adopted a descriptive survey design. Two research questions and two hypotheses were posed to guide the study. The population for the study was 99 Business Education lecturers and the sample size was 70 Business Education lecturers that was randomly selected from three selected tertiary institutions in Rivers State, namely; Rivers State University of Science and Technology Port Harcourt (RSUST), Ignatius Ajuru University of Education (IAUOE) and Federal College of Education (Technical) Omoku (FCET). The Instrument used for data collection was a structured questionnaire titled " ICT Challenges in Teaching Business Education Questionnaire " (ICTBEQ). The reliability of the research instrument was obtained using test-retest method, the Pearson Product Moment Correlation coefficient of .87 was obtained. The instrument was validated by two experts from the department of business education, Rivers State University of Science and Technology. All 70 copies of the questionnaire were retrieved and analyzed using mean for the research questions and analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the hypothesis at .05 level of significance. The results obtained indicated that business education lecturers are yet to fully apply ICT facilities in teaching and this is as a result of the challenges confronting its application. Thus, it is required that both government and relevant stakeholders must come together to put in place the necessary ICT facilities in order to improve its use in teaching business education.
Prof. Amaka U Okeke
The need to ensure quality in business education towards enriching graduates' competitive ability in the global workplace of the current era necessitated this study on assessment of information and communication technologies (ICT) utilization for quality in business education programme in universities in SouthWest Nigeria. Two research questions guided the study and three null hypotheses were tested. Descriptive survey research design was adopted for the study. Population was 550 (52 lecturers and 498 final year students). Purposive sampling technique was used to draw a sample size of 302 (all 52 lecturers and 250 students) for the study. A five-point rating scale questionnaire containing 24 items in two clusters which was validated by three experts was used for data collection. A pilot study was conducted involving 30 (10 lecturers and 20 students) of business education from universities outside the area of the study to establish the reliability of the instrument. Data collected were analyzed using Cronbach alpha and coefficients 0.85 and 0.82 were obtained for the two clusters with an overall reliability coefficient of 0.83. Mean and standard deviation were used to answer the research questions and ascertain the closeness of the respondents' views while z-test was used to test the hypotheses at 0.05 level of significance. Findings revealed a small extent utilization of ICT resources by the subjects, status and institution ownership significantly influenced the respondents' mean ratings but gender did not. Based on the findings, it was concluded that the training of university business education students in southwest Nigeria is not adequate to give them competitive advantage in the global workplace of the current information age which is powered by ICTs. Therefore, it was recommended among others that management of the institutions should ensure adequate provision of ICT resources and sponsor their business education lecturers to retraining programmes to enhance their effective utilization in order to equip the graduates with relevant competencies for the 21 st century global labour market demands.
RELATED PAPERS
Rodrigo Teixeira
Revista "mientras tanto", 91-91, pp. 29-44
Jaime Pastor Verdú
CALL/WA 085704602709|belajar grammar menyenangkan di peace
Kursus Grammar
Annisa Nur Hidayati
Frontiers in psychology
Sara Dellantonio
Syamsu Rosid
International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems
Physical Therapy in Sport
Attention Perception & Psychophysics
James Antes
Ecosystems and Sustainable Development IX
Colby Moeller
The International Journal of Science & Technoledge
Gicheru Onesmus
Christophe Wiart
La Revue de Médecine Interne
jacques Barrier
Pediatric Transplantation
Davide Corbella
The International Journal of Robotics Research
Juan Antonio Corrales Ramon
Cecilia Chan
Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics
Christoph Pflaum
Synthetic Communications
ahmet kocak
Journal of governance : jurnal ilmu pemerintahan Universitas Sultan Ageng Tirtayasa
Muhammad Asep Budiana
Diablotexto Digital. Revista de crítica literaria
Diablotexto Digital
Jose Carlos Vera Jimenez
Discourse: Studies in the Cultural Politics of Education
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Business Plans Nigeria free PDF Docx Download
Business plans nigeria free pdf docx download:.
In this post, samples of free business plans will be provided for users for free download and use. You can download and use the Business plan to give a prototype of business you are thinking about. Or even for the sake of assignment for those that want to submit a school assignment.
Whatever you are planing on doing with the business plans, this post will help out with some random samples that you can check out.
So you can also come up with your own unique type. Business plans may come in different formats. All depending on the individual behind it. But, generally, business plans take the form of a general introduction of the business, location, description of the business, body, implementation, target market, pros, cons, expenses, challenges, tactics, competitions, profits and conclusion.
Therefore, if you are writing a business plan for proposal or just to have a glimpse of what the business might entail. It is important to have one two of the elements listed above or even more.
Most times a comprehensive business plan will give you an overall view of the whole business which generally serves as a guide for starters to have an idea of what to come.
Business plan helps not to deviate from the main business idea. But, to focus on the plan. As the general saying: “When you fail to plan, you plan to fail”.
Without further ado, here are samples of different free business plans for your perusal.
Business Plan List:
- Agro Business Plan
- Shea Butter Production Business Plan
- Restaurant Business Plan
- Cat Fish Business Plan
- Fabric Material Business Plan
- Malaria Business Plan
- Bakery Business Plan
Get Stuffs Like this, to Ur' Inbox:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
www.FASTBusinessPlans.com INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY BUSINESS PLAN (COMPANY NAME) (COMPANY NAME) (STREET ADDRESS) (CITY, STATE ZIP CODE) (CREATION DATE) Here's Your FAST Sample IT Business Plan This IT Business Plan has been written to use a starting point for developing your own business plan. You are free to edit and use this business plan and ...
1. Don't worry about finding an exact match. We have over 550 sample business plan templates. So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details. Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across. So, use this example as a starting point and customize it to your needs.
The Information Technology Business Plan in Nigeria will be of great use: To formulate a strategy for starting and growing the business or existing business by identifying where the business is going and how to get there. To test the viability of the business idea and maximize its opportunities. To Obtain funding and achieve business goals and ...
2.2 Start-up Summary. Our start-up costs will be $1M, which includes $450,000 for the acquisition of the Maui and Hilo operations of Servco Integrated Office Technology. The remainder of the funds will be used for: Initial Inventory: $200,000. Initial Capitalization: $225,000.
FOR THE FULL DETAILS OF THIS BUSINESS PLAN,BUSINESS MODEL, CANVAS,MARKETING PLANS AND FINANCIALS: PLEASE CALL OUR BUSINESS PLAN CONSULTANT: +2348147161686 [email protected]. WE HAVE A TEAM THAT CAN HELP YOU WITH YOUR SPECIFIC BUSINESS PLAN, FEASIBILITY STUDIES, MARKETING RESEARCH, BUSINESS BRAND STORY AND SO ON.
business plan submitted to: central bank of nigeria (creative industry financing initiative for nigerian youths - cifi) through: zenith bank plc by: messrs: t.o computers and multimedia ltd. city mall, hammaruwa way, jalingo, taraba state. (rc510722) may, 2019 table of contents 1 executive summary. 1 business objectives. 1 mission statement
Importance of the ICT Business Plan in Nigeria. The ICT Business Plan in Nigeria is important because. It will assist you in making sound decision in the administration of the commercial enterprise which will make a contribution to the success of the business. It will additionally gives distinctive statistics on all components of the business ...
Overview. The information and communications technology (ICT) sector in Nigeria continues to play a pivotal role in the nation's recovery in the wake of an economic lull during the pandemic years. Data from the Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC) reported that the ICT sector contributed 9.88% to the total nominal GDP in Q4 of 2021, lower ...
We help institutions and organizations write concepts, implement Business plans, and train on business Plan writing in Nigeria. We can help you write a detailed, bankable and comprehensive business plan for your business idea. Call any of our business plan consultants on 08105636015, 08076359735 and 08113205312.
This document, the Nigeria ICT Innovation and Entrepreneurship Vision (NIIEV), comprises of policy recommendations and incentives designed to strengthen the Nigerian technology entrepreneurship ecosystem. It consists of the following sections: Digital Infrastructure; Education Reform, Skills Development and R&D; and, Support the Ecosystem for ...
DEVELOPING YOUR BUSINESS PLAN 8 2.1. What is a business plan? 10 2.2. Use of ICTs in business planning 11 2.3. Generating business ideas 23 2.4. Understanding the business environment and opportunities 33 2.5. Business goals 47 2.6. Identifying business resources 51 2.7. Developing the business financial plan 56 2.8. Schedule of business start ...
A strong ICT ecosystem provides the foundation for an efficient modern economy, significantly enhancing business procedures, public services and job creation. With this in mind, Nigeria's government is following a long-term development blueprint with the aim of harnessing digital technological capabilities to diversify the economy and reduce dependence on hydrocarbons revenue. Sector ...
Sample ICT Business Plan - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Bookmark Services Ltd is expanding into ICT services and renaming to reflect the change. It has provided writing services since 2010. The company aims to deliver ICT services to 15,000 users by 2016/2017 and 25,000 more by 2019. It will offer teleconferencing, audio, and web conferencing ...
ICTFrom The Report: Nigeria 2023View in Online Reader. ICT. With a population of close to 220m and an internet penetration rate of 51% at the beginning of 2022, Nigeria's large ICT consumer market offers room for growth, making it an enticing prospect for local and international investors, particularly with the population forecast to reach ...
ICT IN THE CONTEXT OF NIGERIA's VISION 20:2020 9 4.0 ICT POLICY DEVELOPMENT IN NIGERIA 11 4.1 Industry Indicators 12 5.0 INDUSTRY STRUCTURE AND SUBSECTORALPROFILES 14 5.1 Current Government Institutional Structure 14 5.1.1 Telecommunications 14 5.1.2 Information Technology 17 5.1.3 Postal Services 19 5.1.4 Broadcasting 21 6.0 POLICY OBJECTIVES 24
Information and Communication Technology (ICT) is becoming an essential part of the trade in managing the business flow in Nigeria. It stimulates the global market and overall shift in economic ...
Information is the life wire of today's business organizations, institutions and industries. Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) covers all advanced technologies in manipulating and communicating information. Understanding the ICT three main components: Information; the use of computers to transform data into information,
📑 Download Business Plans in Nigeria This is samphina.com.ng your #1 plug for any Business Plan (Startups) in Nigeria. We understand the time factor, and we have simplified the process so that you can get your Business Plan ready as soon as possible by making available Business Plan for different businesses in Nigeria.
8.0 Breach. Any breach of these Guidelines shall be construed as a breach of the provisions of the NITDA Act of 2007 and other relevant laws or Federal Government directives currently in-force in Nigeria. 9.0 Guidelines for Development of Indigenous ICT Devices.
Looking through existing business plan templates gives a clear picture of what your business plan should look like. This post contains a long list of free sample business plan templates that will give you the easy start you really need to write your own business plan. 1. Catering Business Plan. If you love to cook and are thinking about ...
This fundamental disconnect remains a niggling challenge to ICT use in business education in Nigeria. 5.0 Conclusion and recommendations Though emerging ICT tools offer new opportunities in education through expanding access to formal and informal education, most countries (including Nigeria) face significant challenges in harnessing their ...
Most times a comprehensive business plan will give you an overall view of the whole business which generally serves as a guide for starters to have an idea of what to come. Business plan helps not to deviate from the main business idea. But, to focus on the plan. As the general saying: "When you fail to plan, you plan to fail".
Digital technology is now part of all aspects of the College's activities. It is therefore increasingly important for ICT to become part of the fabric of the College. The intent of this document is to initiate this collaboration and consultation. This document is a starting point to engage with the wider College on shaping ICT's 5-year ...