Patent Assignment: Everything You Need to Know
A patent assignment is an irrevocable agreement for a patent owner to sell, give away, or transfer interest to an assignee, who can enforce the patent. 6 min read updated on January 01, 2024
Updated November 5, 2020:

Patent Assignment: What Is It?
A patent assignment is a part of how to patent an idea and is an irrevocable agreement for a patent owner to sell, give away, or transfer his or her interest to an assignee, who can benefit from and enforce the patent. The assignee receives the original owner's interest and gains exclusive rights to intellectual property. He or she can sue others for making or selling the invention or design.
There are four types of patent assignments:
Assignment of Rights - Patent Issued: This is for patents that have already been issued.
Assignment of Rights - Patent Application : This is for patents still in the application process. After filing this form, the assignee can be listed as the patent applicant.
Assignment of Intellectual Property Rights - No Patent Issued or Application Filed: This is for unregistered inventions with no patent.
Exclusive Rights
Advantages of a Patent Assignment
Assignees don't create a unique invention or design. They also don't go through the lengthy patent process . They simply assume exclusive rights to intellectual property.
Profit Potential
Many patents cover intellectual property that can earn the owner money. A patent owner can charge a lump sum sale price for a patent assignment. After the transfer, the assignee can start to earn profits from the patent. Both original owners and assignees can benefit from this business arrangement.
Disadvantages of a Patent Assignment
Too Many or Not Enough Inventors
Patents can have multiple owners who invented the product or design. Sometimes patents list too many or not enough inventors. When this happens, owners can argue about an incorrect filing. This kind of dispute can make a patent assignment impossible.
Limited Recourse
Older patents may already have many infringements. Not all patent assignments include the right to sue for past infringements. This is known as the right to causes of action. This can cost the assignee a lot of potential profit.
Examples of What Happens When You File a Patent Assignment vs. When You File a Patent License
When You File a Patent Assignment
The patent owner changes permanently. You file the paperwork with the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). Information about the new owner is available to the public.
Many owners charge a one-time fee for a patent assignment. The original owner doesn't receive additional payments or profits in the future. The new owner receives future profits.
When You File a Patent License
The patent owner doesn't change permanently. Most licenses have a time limit. At the end of the period, the original owner takes control again. Licensing information isn't always available through an online USPTO search. Contact the recordation office directly to get information about patent licenses.
The licensee can assign rights to another person or company. This adds another layer of ownership over the intellectual property.
Many owners charge royalties for a patent license. The licensee pays royalty fees throughout the license period. If the royalty fees are high and the license period is long, a patent assignment may be a better choice for earning the new owner more money.
Common Mistakes
Not Filing an Assignment Document
A verbal agreement is not official. File a patent assignment to change patent ownership.
Taking Action Before Filing
The assignee shouldn't make or sell the invention before the patent assignment is official. If an error or another problem happens, this could be patent infringement .
Making a Filing Error
Patent assignments are official documents. The assignee's name must be legal and correct. Before filing, check the spelling of the assignee name. If the assignee is a business, confirm the legal name. Many patents have more than one owner. List all names on the assignment.
Misidentifying the Patent
Include as much information about the patent as you can. List the patent number and title. Describe the intellectual property completely.
Not Searching for Security Interests
Patents can be collateral. A bank or another party can file a security interest in a patent, and this can limit how much an assignee can earn from a patent. Check for security interests before filing a patent assignment.
Not Filing a Proprietary Information Agreement
Many businesses file patents, as this is part of a business plan , and it's especially common for startup businesses. Inventorship problems can happen if employees file patents instead of the business.
Often, employees have an obligation to assign inventions to a company. This is true if they developed the invention on the job.
To avoid confusion, require employees to sign a proprietary information agreement. This automatically assigns inventions and designs to the business. Other options include signing an automatic assignment or an explicit assignment. These all clarify patent ownership.
Not Being Notarized
Make sure all official documents concerning your patent are notarized. There is a huge legal advantage to being notarized. It makes it so that your documents will be accepted as correct until it is proven otherwise. If you can't get your documents notarized, gather two witnesses. Have them attest to the signatures.
You have to file a patent assignment within three months of signing the form. If you don't, the assignee could lose ownership rights.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where Do I Record a Patent Assignment?
If you have a U.S. patent, record your patent assignment with the USPTO. If you have a foreign patent, file with the correct national patent offices.
I Can't Get a Signature from the Inventor. What Happens Now?
First, it needs to be officially established that:
- Whoever is pursuing the application has the right to do so.
- The inventor cannot be reached.
In order to establish this, the patent office will need a copy of the following:
- the employee agreement
- the assignment
- other evidence of the rights
After that, the patent office will continue as if the signature has been obtained, even though it hasn't.
If the inventor has died, the patent office will try to contact the person in charge of managing the deceased's estate or the heir. If the invented refuses to sign or is missing, the patent office will ask for a declaration from the person who is trying to contact them. They will also look at the following items that have been sent to the inventor:
- Do I Have to File a Patent Assignment if the Owner's Name Changed?
No, you don't need a patent assignment if only the person's or company's name changed. If the company merged with another, you may need a patent assignment.
What if I Make a Mistake on My Patent Assignment?
You can't correct a patent assignment. You have to assign it back to the original owner. Then you have to reassign with the correct information.
How Much Does a Patent Assignment Cost?
The patent assignment fee is $25. Filing electronically doesn't cost extra. You do have to pay an additional $40 fee if you file on paper.
Should I Hire a Lawyer?
Yes, you should get a lawyer to help with a patent assignment. A lawyer will make sure there are no filing errors. A lawyer knows how to describe the patent correctly. Errors and bad descriptions can limit the power of a patent assignment. This could cost the assignee a lot of money in future profits and legal fees.
Steps to File a Patent Assignment
1. Fill Out a Recordation Form Cover Shee t
The Recordation Form Cover Sheet is an official USPTO document. This includes the names of the assignor(s) and the assignee(s). It also includes the patent title and number.
2. Complete a Patent Assignment Agreement
The patent assignment agreement should list the assignor(s) and the assignee(s). It should state that the assignor has the right to assign the patent. It should also describe the intellectual property clearly and completely. It should also explain any financial or other transactions that have to take place. This includes a description of the lump sum payment.
3. Sign the Patent Assignment Agreement
All patent owners and assignees must sign the patent assignment agreement.
4. Submit the Patent Assignment
Finally, submit the patent assignment with the USPTO. You have to pay the assignment fee at this time.
If you need help with patent assignments, you can post your question or concern on UpCounsel's marketplace . UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Brookfield Patent Lawyers
- Jackson Patent Lawyers
- Katy Patent Lawyers
- Kokomo Patent Lawyers
- Providence Patent Lawyers
- Reno Patent Lawyers
- Southaven Patent Lawyers
- How to Sell a Patent
- Patent Assignment Database
- Patent Companies
- Patent Pending Infringement
- Patent Rights
- Patent Attorney
- What Does a Patent Do
- How to File a Patent
- When Can You Say Patent Pending? Everything You Need to Know
- Atlanta Patent Lawyers
- Austin Patent Lawyers
- Boston Patent Lawyers
- Chicago Patent Lawyers
- Dallas Patent Lawyers
- Houston Patent Lawyers
- Los Angeles Patent Lawyers
- New York Patent Lawyers
- Philadelphia Patent Lawyers
- San Francisco Patent Lawyers
- Seattle Patent Lawyers
- Charlotte Patent Lawyers
- Denver Patent Lawyers
- Jacksonville Patent Lawyers
- Las Vegas Patent Lawyers
- Phoenix Patent Lawyers
- Portland Patent Lawyers
- San Antonio Patent Lawyers
- San Diego Patent Lawyers
- San Jose Patent Lawyers
- View All Patent Lawyers

What is a Patent Assignment?
Whether you’re curious about assigning a patent to someone else or having a patent assigned to you, you might be wondering what a patent assignment is? Patent law allows patent holders to assign patents to other parties. Patent assignments often take place between an employee and his company, however, it’s not uncommon for a person to assign his interest to a patent to a third party. So, what exactly is a patent assignment? We will cover this below.
What is a Patent Assignment ?
A patent assignment is an agreement by the patent holder (assignor) to transfer his interest and ownership of a patent to another party known as the assignee (party receiving patent rights). Once a patent holder executes an assignment agreement assigning his interest in a patent to another party, the assignor loses his rights under the patent. The assignor (transferor) will no longer be able to stop others from using, making, and selling the patent invention. Instead, the assignee gains these rights.
In the United States, patent assignments are very common between an employee and his company because a company or business cannot apply for a patent. An inventor has to apply for a patent and then the inventor then assigns his interest under a patent to the company for which he is working.
An assignment transfers the ownership of the patent from the inventor or employee to the company for which he is working. That said, assignments can also be made by any two parties that agree to transfer ownership of a patent.
So, now we know that a patent holder can transfer his patent rights to a third party, can an inventor assign a pending patent application? Absolutely, yes! An inventor can assign his rights under a pending patent application to another party.
If you’re an inventor and you want to assign your patent to another party, just remember that patent assignments are final. Once an inventor assigns (transfers) his interest in a patent to another party, the assignment (transfer of rights) cannot be undone, it’s final.
What is a Patent Assignor?
A patent assignor is a party that transfers it’s interest and right to the patent to the transferee (assignee) or the party receiving the patent. Once an agreement is executed and recorded with the patent office, the assignee becomes the patent right holder.
What is a Patent Assignee?
A patent assignee is a person to whom the patent rights are transferred to. Said differently, the assignee is the new owner of the patent. An assignee should immediately record an assignment agreement with the patent office to establish his rights as the new patent owner.
Requirements to Execute a Patent Assignment Agreement
For a patent holder to assign (transfer) his interest in a patent to another party, the assignor (person transferring patent rights) must execute a written agreement that includes details, such as the name of the assignor and the assignee, as well as the patent that is to be assigned (transferred) to the assignee.
Once the assignment agreement is executed, it must be filed with the USPTO for the agreement to take effect. Please remember that the agreement needs to be in writing, oral agreements are not sufficient to transfer the rights from the patent holder to the assignee.
The assignment agreement must include the following information:
- The agreement must contain the legal names of both the assignor (person transferring patent rights) and the assignee (person receiving patent rights).
- The agreement must clearly identify the patent by stating the name of the patent, as well as the patent number.
- The terms of the agreement must be included in the assignment agreement.
- Both the assignor(s) and assignee(s) must sign the agreement.
Who Owns the Patent After a Patent Assignment?
Once the assignor and assignee execute an assignment agreement and file the assignment with the USPTO, the assignee owns the patent. As the new patent owner, the assignee will have the right to stops others from using, making, and selling the patented invention for the remaining patent term.
The assignor (person who transferred his rights) loses his rights under the patent and will no longer be able to enforce the patent. Assigning a patent is similar to selling a car and registering the title in someone else’s name. Once the patent is assigned, similar to registering the title of a vehicle in someone else’s name, the new owner is the assignee (person to whom the patent was transferred to). Once the assignment is recorded with the patent office, the records will be updated to show the assignee (new owner) of the patent. This information will then be made available to the public.
Assigning a Patent vs Licensing a Patent
Assigning a patent is much different than licensing a patent. When a patent holder assigns his interest in a patent to another party, he is usually transferring ownership of the patent to the other party. Patent licensing is different in that a license is merely a transfer of the right to use the patent in the manner specified in the licensing agreement. Assignments transfer ownership while a license transfers the right to use the patented invention. That said, if a patent is assigned, the information of the assignor and assignee will become part of the public record. Whereas if an inventor licenses his patent, that information is not typically published to the public.
Does a Patent Assignment Need to be Notarized?
The USPTO does not require patent assignments to be notarized. The patent office only requires that the assignment be executed and signed by both the assignor and the assignee. Once an agreement is executed and signed by the parties, the assignment must be recorded with the patent office.
If the assignee fails to record the assignment, there is nothing to protect the assignee from the assignor assigning the patent to a third party. So, if you’re an assignee, make sure to record your assignment as soon as it’s executed to avoid problems.
Although a patent assignment does not need to be notarized, notarizing it can be beneficial in the event that the previous patent holder claims that he did not make the assignment. It’s an added layer of protection that could prove to be very valuable.
Can Multiple People Own a Patent?
Yes, multiple people can own a patent. For example, if three inventors make a single invention, all three are considered joint inventors and their names should appear on the patent application, as well as the issued patent.
If there are multiple inventors on a patent application, all inventors must execute an assignment agreement to assign each of their interest to the assignee for the assignee to own the entire patent.
For example, if only 1 of 3 inventors assigns his interest, the assignment would be a partial assignment until all 3 inventors each assign (transfer) their interest to the assignee.
Patent Assignment Tips
1) hire an attorney to assist you with your patent assignment.
Any individual who’s either an assignor or assignee should hire an attorney to assist with the assignment of a patent. Attorneys will ensure that the assignment agreement complies with the law and contains all of the information that is required for a successful patent assignment. Although it’s not unheard of for parties to execute an assignment agreement on their own, making a mistake could cause legal troubles down the road.
2) Don’t Forget to Record A Patent Assignment
If you have been assigned a patent, don’t forget to record your assignment with the USPTO. We say this because patent assignments don’t go into effect unless the assignment is recorded with the patent office. Recording a patent assignment tells the patent office that you are the new owner of the patent.
If an assignee does not record the assignment with the patent office, it is as if the assignment never took place. Also, if it’s not recorded, the assignor could possibly assign the patent to a third party. So, make sure to record your assignment as quick as possible.
3) Notarize Your Assignment Agreement
It’s good practice to have an assignment agreement notarized. This helps in a situation where the assignor claims that he did not execute the assignment agreement. In the event that an assignor claims he did not execute the assignment agreement, you will have evidence to show otherwise. The burden may shift to the assignor to prove that he did not execute the assignment agreement. So, notarize your agreement, as well as other documents relating to the assignment of a patent.
4) How Much Does it Cost to Record an Assignment with the USPTO?
It’s currently free to record an assignment with the USPTO if a party submits the assignment electronically. However, if a party chooses to record the assignment agreement by paper, there is a $50 fee for the service. So, record your assignment online if you want to avoid paying anything. That said, you may need to publish your assignment in an official gazette, such publication does cost $25.
Patent Assignment
Let’s do a quick recap. A patent assignment is the transfer of ownership of a patent from one party to another. The party transferring its right is known as the assignor and the party receiving the patent rights is known as the assignee.
To assign a patent, both parties must execute a written assignment agreement to reflect the transfer of ownership. Once the parties execute the agreement, they must record it with the patent office to establish the new ownership. If you have any general questions or comments, please feel free to leave them in the comments section below.
My name is Noah and I love everything about patents and patent law. During my law school years, I studied intellectual property law and took courses in patent law, trademark law, and copyright law. I graduated from Loyola Marymount Law School and obtained my Juris Doctorate in 2014.
Similar Posts

Can You Patent a Supplement Formula?
If you’ve just finished developing an awesome supplement, you might be wondering how you can protect your new supplement formula. The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) offers inventors…

What are Patent Claims?
What Are Patent Claims? Patent claims are arguably the most important part of a patent application. Patent claims set out the aspects of the invention that the patent protects. Patent…

Can You Patent a Song?
If you’ve just finished writing the best song ever, you might be wondering how you can protect your intellectual property (IP). The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) offers…


Who Owns the Patent the Company or the Employee?
Who Owns the Patent the Company or Employee? When an inventor makes something or invents something new, there may be some confusion as to who owns the invention, the company…
What Are Utility Patents?
Whether you’re an inventor who wants to protect his invention or you’re just interested in learning what a utility patent is, you’ve come to the right spot. The USPTO (United…

What is a Patent License Agreement?
If you have an invention that you’ve patented, you might be wondering whether you can license your product or invention for others to use? The short answer is that you…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Who Owns What Assignment and Ownership of Patents and Applications
Why does ownership of a patent/patent application matter.
A patent is a government-granted property right that can be used to exclude others from making, using, selling, offering to sell, and importing an invention for a specified time. Patents provide important commercial benefits (discussed in detail in our companion piece What You Need To Know About Patents ) — but only for patent owners.
So who owns a patent/patent application?
In the US, the inventor is presumed to be the initial owner of a patent or patent application. If there is more than one inventor, there may be more than one owner. Ownership can be transferred or reassigned. If your company values intellectual property and has employees who are encouraged to innovate, here are a few important strategies to ensure that your company can benefit from patents generated through employee inventions.
- Agreements with employees and service providers (Automatic Assignment) : Companies should have all employees sign confidential information and inventions assignment agreements (discussed in detail here ) before employees start generating intellectual property. Having employees sign these agreements at the beginning of their employment, before any work is done, is the best course of action. Likewise, failure to correctly structure IP provisions in agreements with third parties such as service providers and consultants prior to the execution of any work has caused serious issues for many companies. A form of confidential information and inventions assignment agreement for California employees is available here , and a form of consulting agreement for US consultants (which contains IP assignment provisions) is available here .
- Obligation to Assign: In some situations, even if your employees have not signed an agreement, they may still be obligated, either by contract or local law, to assign patent/patent application ownership to your company. For example, this could occur if the invention was developed on the job, the employee was hired specifically to invent for the company, and/or the inventor is an officer of the company.
- Explicit Assignments: Even when employees have signed appropriate agreements, your company should execute new patent-specific assignments whenever patent applications are filed. These assignments name the specific invention, patent, and/or patent application, and can have additional legal weight if the ownership of a patent is disputed.
Joint ownership of patent/patent application rights can be complicated. As with any property right, multiple owners can make for multiple legal scenarios. For example, co-owners would have to join together to bring a patent infringement lawsuit. By contrast, the opposite is true for licensing: a co-owner can license its patent/patent application rights to a third party, independent of the other co-owner(s), unless they have an agreement otherwise. Co-owners can also independently sell, mortgage, transfer, and will their rights to a patent/patent application. To avoid these kinds of issues, most attorneys recommend that a single entity be the patent/patent application owner, whenever possible. If this is not possible, then it is important to correctly structure IP provisions in an agreement, for example, ideally where one party exclusively licenses back all rights in the co-owned patent/patent application.
How do I make sure my company owns these patents/patent applications?
Well-structured ownership assignments are legally binding, but what does “well-structured” mean? Patent/patent application assignments have several formal requirements to be considered valid. Assignments must:
- Be in writing – unlike some other contracts, oral assignments or oral agreements to assign patent/patent application rights are rarely enforceable;
- Clearly identify all parties – recite names, addresses, and relationship of both the assignor(s) and assignee;
- Identify the property clearly – include the patent/patent application number, title, inventors, and filing date;
- Recite exchange of consideration – this is a standard for almost any contract, and here, even nominal consideration (e.g., $1) is sufficient; and
- Execution be notarized or attested to by one, preferably, two non-inventor witnesses – notarization or witnessing serves as evidence that the signatures (and, thus, the assignment) is valid. There is a lot of interest in utilizing an e-signature platform, such as DocuSign, for execution of Assignments. However, this is still a developing area, and the rules differ significantly around the world. If use of e-signatures is an important consideration for your Company, e.g., your employees are geographically diversified, you should consult with your IP counsel so as to understand the local laws and potential ramifications in countries that are important to your business.
Following these rules is a good practice and is an essential starting place to ensure the validity and enforceability of your assignment. However, validity does not end here. As with any contract, the legal language is key to eliminating ambiguity in your agreements.
Finally, make sure that any assignment in a patent/patent application is recorded with the US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) as soon as possible after execution. If an assignment is not recorded with the USPTO within three months from its effective date, the assignee’s claim to ownership could be at risk. For example, if an assignor were to subsequently improperly assign to another purchaser that was not aware of the previous assignment and the previous assignment had not been recorded with the USPTO, the subsequent purchaser may be able to successfully claim ownership.
You’re the new owner!
A patent is only as valuable as it is enforceable, and ownership is a key element of enforceability. Licensing, manufacturing, distributing, or otherwise making exclusive use of your invention can only be ensured if the patent is both valid and enforceable. Having ownership protection in place prior to the development of your intellectual property, as well as the correct legal ownership assignment documents executed afterward, can help ensure that you can make the most of your company’s ingenuity.
Related contacts

Patent Assignment: A Basic Guide
March 12th, 2020 ‧ 5 min read.

When it comes to patents, many people outside of the industry often make the assumption that the person listed as the inventor on a patent is automatically the owner of that patent as well.
While this is certainly true in some cases, there are several instances when another person or even a company may be assigned ownership of the patent. This is called a “patent assignment,” and it is the subject of today’s article.
Table of contents
Patent assignment: a basic definition, an example of a patent assignment, an additional patent assignment in writing, patent assignments and the uspto, patent assignment database, patent assignment search, is a patent assignment a type of licensing, patent assignment: an important element of the patent ecosystem.
Curious about the patent assignment history? Check out the specific data here !
Basically speaking, a patent assignment is a legal way for an inventor to transfer ownership of a patent to a business.
As you may recall, in the United States, only a person (or group of people) can be listed as the inventor of a patent; a business cannot be listed as the inventor. However, a business can be assigned the ownership of the patent by a person (or group of people).
In this type of agreement, the “assignor” transfers their patent rights to the “assignee.”
It might be helpful to look at an example of a patent assignment. Let’s say an employee of a company comes up with a new invention. This individual employee is the inventor of the product and will be listed on the patent application as such. However, since patents can be very valuable, most companies already have a patent assignment agreement with their employees in place.
This type of agreement would typically state that any type of intellectual property created by an employee of a company while employed by that company would become the property of the company.
Since the company in this example made sure that its employee signed a patent assignment form upon being hired, the invention that the employee came up in the company’s R&D facility will be assigned to the company. The inventor will still be listed in the patent application (and on the patent, if granted) as the inventor.
In addition to the patent assignment agreement mentioned above, it is also recommended that a specific written assignment from the inventor to the company be made whenever a patent application is filed.
If this step is taken, then there will be less trouble if an inventor leaves the company before the patent application has been completed or attempts to contest the patent down the road.
In the United States, patent assignments can be recorded at the USPTO. This can be done at the US patent office’s Assignment Recordation Branch .
Although this can be done online (and without any fees if done electronically) using the Electronic Patent Assignment System (EPAS) , it should be noted that all patent assignment paperwork must be submitted within three months of the patent’s assignment date.
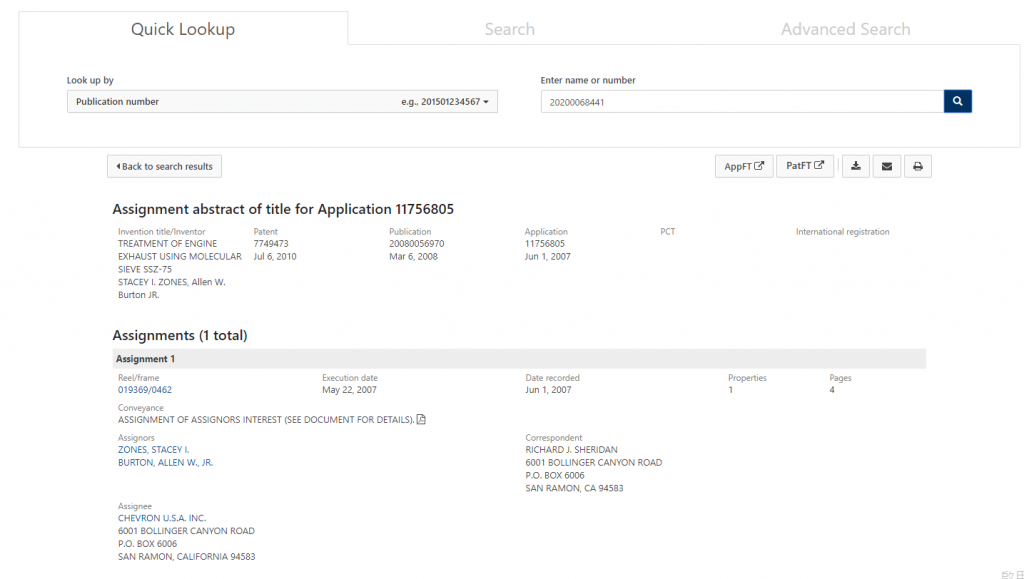
The Patent Assignment Database from USPTO keeps all the patent assignment data records from August 1980 until now. The transfer record will be updated by USPTO, the most recent entry should be the current assignee. However, the system does not check the correctness of the data, specify the current assignee and update timely. It is best to double-check with a third-party database for accuracy.
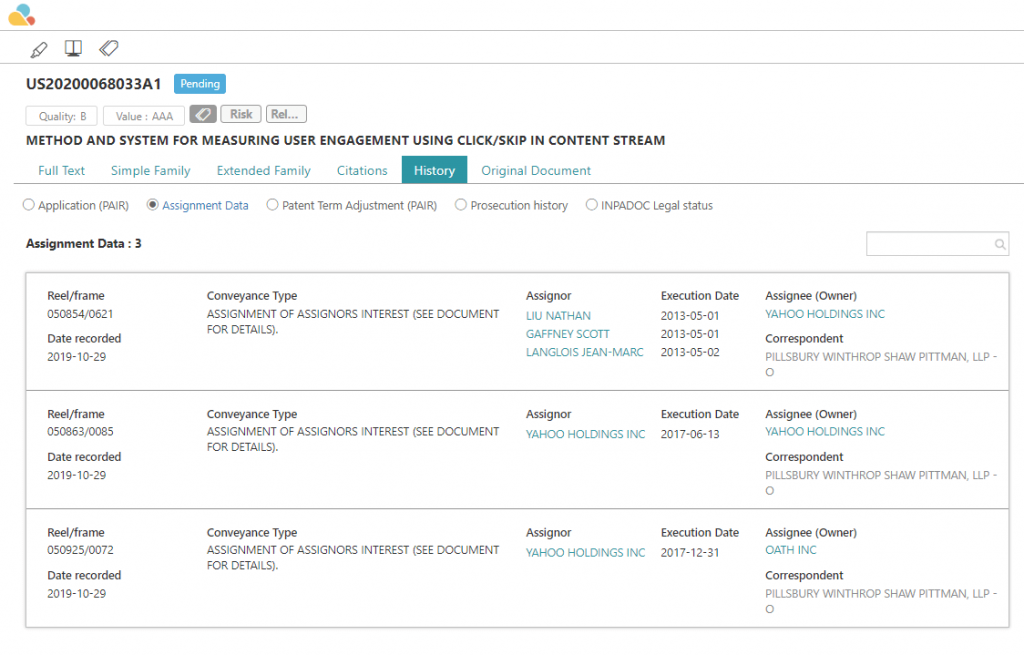
If you need to find out who owns a patent, then you can conduct a patent assignment search. This will tell you who has been assigned a particular patent in the past and who the current assignee is now. The USPTO does offer a free patent assignment search tool on its website, as do other third-party intelligence platforms, such as Patentcloud .
These platforms often feature superior patent assignment databases, with processes that ensure that the assignment data has been cleansed and corrected, meaning more accurate and comprehensive search results.
Start your patent assignment search here with Patentcloud’s Patent Search.
Although similar in some ways, these two patent activities are actually quite different.
A licensing agreement means that the owner of the patent (or “licensor”) gives another person or company (the “licensee”) the right to use the patented technology for an agreed-upon period of time. However, the licensor remains the owner of the patent.
A patent assignment, on the other hand, involves a complete and permanent transfer (or “assignment”) of ownership of a patent from the owner (or “assignor”) to another party (the “assignee”). Put simply, patent assignment involves “ownership” while patent licensing involves “permission to use.”
Assignment data analysis can provide actionable insights for those operating in the transaction market and IP stakeholders alike, enabling them to:
- Anticipate the future strategy of a company: the acquisition of patents covering a specific technology could well be an indicator of the company’s future plans and strategies;
- Anticipate the developments of an industry: multiple companies — especially larger ones — acquiring patents in a certain technology field could also prove to be an indicator of the imminent popularity of a technology field.
The acquisition of Oculus VR by Facebook is a perfect example of this: in 2014, Facebook bought the VR company for around $2 billion. In the deal, Facebook also acquired all of the patents. Facebook’s focus on VR was a significant moment: today, VR technology is one of the most active patent-wise. This activity is not just limited to the gaming sector, the following industries have also experienced increased activity:
- Data visualization;
- The treatment of mental illnesses.
The acquisition by Facebook proved to be a clear signal that:
- Facebook was likely to invest heavily in the development of VR technologies;
- The VR industry was going to be popular in the near future.
There you have it. Though often overlooked and even misunderstood, patent assignments are actually a very important element of the patent ecosystem. With a better understanding of patent assignments, you can gain valuable insights into industry trends and even the business strategies of specific companies. You can also gain a better understanding of a company’s own R&D capabilities.
Share This Information.
Related posts.
Patent Assignment: The Importance of Current Patent Assignee Accuracy
Essential Takeaways from 2020’s Q1 US Patent Assignment Data
Patent Assignment Data: 8 Essential Takeaways from 2019 Q4 US Patent Market
An Inventor’s Guide to Understanding Prior Art
The IP world moves fast
Subscribe to receive the latest insights right in your inbox.
By submitting your contact information, you understand and agree to our GDPR , Terms of Use and Privacy Policy
Get started with Patentcloud today
Discover how Patentcloud’s solutions and tools can work for you.
InQuartik Corporation, as the administrator of this website, uses browser cookies to track your session to provide you with a better experience.
You may opt out of all cookies that are not essential to the administration or maintenance of this website.
You may refer to our Privacy and Cookie Policy for more details. Please note that, by accessing our website, you agree to our Privacy and Cookie Policy.
Privacy Overview
This patent application assignment is between , an individual a(n) (the " Assignor ") and , an individual a(n) (the " Assignee ").
The Assignor has invented certain new and useful inventions (the " Inventions ") and has applied for patents on the Inventions, which are listed on Exhibit A (collectively, the " Applications ").
The Assignor wishes to transfer to the Assignee, and the Assignee wishes to purchase and receive from the Assignor, all of its interest in the Inventions and Applications.
The parties therefore agree as follows:
1. ASSIGNMENT OF APPLICATIONS.
Effective as of the Effective Date, the Assignor assigns to the Assignee, and the Assignee assumes from the Assignor, all of the Assignor's interest in the following in the following in the United States and its territories and throughout the world:
- (a) the Inventions and the Applications listed in Exhibit A ;
- (b) the patent claims, all rights to prepare derivative works, goodwill, and other rights to the Inventions and the Applications;
- (c) all registrations, corresponding domestic and foreign applications, letters patents, or similar legal protections issuing on the Inventions and any divisions, continuations, continuations-in-part, and reissues of the Applications, and all rights and benefits under any applicable treaty or convention;
- (d) all income, royalties, and damages due or payable to the Assignor with respect to the Inventions and Applications, including damages and payments for past or future infringements of any patent that is issued on the Inventions and Applications; and
- (e) all rights to sue for past, present, and future infringements of the Inventions and Applications.
2. CONSIDERATION.
The Assignee shall pay the Assignor a flat fee of as full payment for all rights granted under this agreement. The Assignee shall complete this payment no later than .
3. AUTHORIZATION TO DIRECTOR.
The Assignor hereby authorizes the director of the United States Patent & Trademark Office to issue all patents and registrations that may be granted on the Inventions to the Assignee, as the assignee of the entire interest in those, for the Assignee's sole use to the full end of the term for which those patents may be granted, as fully and entirely as they would have been held by the Assignor had this assignment and sale not been made.
4. NO EARLY ASSIGNMENT.
The Assignee may not assign or otherwise encumber its rights in the Inventions, Applications, or associated registrations until it has paid to the Assignor the full consideration provided for in this assignment. Any assignment or encumbrance contrary to this provision shall be void.
5. ASSIGNOR'S REPRESENTATIONS.
The Assignor hereby represents to the Assignee that it:
- (a) is the sole owner of all interest in the Inventions and the Applications;
- (b) has not assigned, exclusively licensed, or encumbered any Invention or Application or agreed to do so;
- (c) is not aware of any violation or infringement of any third party's rights (or any claim of a violation or infringement) by the Inventions or Applications;
- (d) is not aware of any third-party consents, assignments, or licenses that are necessary to perform under this assignment; and
- (e) was not acting within the scope of employment of any third party when conceiving, creating, or otherwise performing any activity with respect to the Inventions purportedly assigned in section 1.
The Assignor shall immediately notify the Assignee in writing if any facts or circumstances arise that would make any of the representations in this assignment inaccurate.
6. DOCUMENTATION.
The Assignor will, as soon as is reasonably possible following a request from the Assignee, provide the Assignee with a complete copy of all documentation (in any format) relating to the Inventions and Applications for the Assignee's own use, to meet record-keeping requirements of the Assignee, or to allow the Assignee to assert its rights granted pursuant to this assignment. The Assignor will also, on request and without further consideration:
- (a) execute and deliver, or cause to be executed and delivered, to the Assignee any additional papers, including any separate assignments of the Inventions or Applications, reasonably necessary to record the assignment in the United States and throughout the world;
- (b) generally do all other lawful acts reasonable and necessary to record the assignment in the United States and throughout the world; and
- (c) execute all lawful papers that may be required in connection with the filing, prosecution, and maintenance of the Applications or any other patent applications in the United States for the Inventions, including additional documents that may be required to affirm the rights of the Assignee in the Inventions.
7. NO FURTHER USE OF INVENTIONS.
After the Effective Date, the Assignor shall make no further use of the Inventions or any equivalent, except as authorized by the prior written consent of the Assignee, and the Assignor shall not challenge the Assignee's use or ownership, or the validity, of the Inventions.
8. INDEMNIFICATION.
The Assignor shall indemnify the Assignee against: If any of the Applications or Inventions infringe on a United States patent of a third party not affiliated with the Assignee, the Assignor shall indemnify the Assignee against that claim, if all of the following are true:
- (a) any claim by a third party that the Applications, the Inventions, or their creation, use, exploitation, assignment, importation, or sale infringes on any patent or other intellectual property; (a) the Assignee promptly notifies the Assignor of that claim;
- (b) any claim by a third party that this assignment conflicts with, violates, or breaches any contract, assignment, license, sublicense, security interest, encumbrance, or other obligation to which the Assignor is a party or of which it has knowledge; (b) the Assignor controls the defense and settlement of that claim;
- (c) any claim relating to a past, present, or future use, licensing, sublicensing, distribution, marketing, disclosure, or commercialization of the Inventions by the Assignor; and (c) the Assignee fully cooperates with the Assignor in connection with its defense and settlement of that claim; and
- (d) any litigation, arbitration, judgments, awards, attorneys' fees, liabilities, settlements, damages, losses, and expenses relating to (a), (b), or (c) above. (d) the Assignee stops all creation, public use, exploitation, importation, distribution, or sales of or relating to the infringing Applications or Inventions, if requested by the Assignor.
If the Assignee is enjoined from further practice or use of any infringing Applications or Inventions or if the Assignee stops using any of the Inventions because of the Assignor's request (as described in (d) above), the Assignor shall, at its own expense:
- (a) obtain the right for the Assignee to continue to use the infringing Invention;
- (b) modify the infringing Invention to eliminate that infringement;
- (c) provide a substitute noninfringing Invention to the Assignee pursuant to this assignment; or
- (d) refund the amount paid under this assignment for the infringing Inventions gnee.
The Assignor shall have no other obligations or liability if infringement occurs, and shall have no other obligation of indemnification relating to infringement. The Assignor will not be liable for any costs or expenses incurred without its prior written authorization and shall have no obligation of indemnification or any liability if the infringement is based on (i) any modified form of the Applications or Inventions not made by the Assignor or (ii) the laws of any country other than the United States of America or its states.
9. GOVERNING LAW.
- (a) Choice of Law. The laws of the state of govern this agreement (without giving effect to its conflicts of law principles).
- (b) Choice of Forum. Both parties consent to the personal jurisdiction of the state and federal courts in County, .
- (c) Attorneys' Fees. If either party employs attorneys to enforce any rights arising out of or relating to this assignment, the losing party shall reimburse the prevailing party for its reasonable attorneys' fees.
10. AMENDMENTS.
No amendment to this assignment will be effective unless it is in writing and signed by a party or its authorized representative.
11. ASSIGNMENT AND DELEGATION.
- (a) No Assignment. Neither party may assign any of its rights under this assignment, except with the prior written consent of the other party. All voluntary assignments of rights are limited by this subsection.
- (b) No Delegation. Neither party may delegate any performance under this assignment, except with the prior written consent of the other party.
- (c) Enforceability of an Assignment or Delegation. If a purported assignment or purported delegation is made in violation of this section, it is void.
12. COUNTERPARTS; ELECTRONIC SIGNATURES.
- (a) Counterparts. The parties may execute this assignment in any number of counterparts, each of which is an original but all of which constitute one and the same instrument.
- (b) Electronic Signatures. This assignment, agreements ancillary to this assignment, and related documents entered into in connection with this assignment are signed when a party's signature is delivered by facsimile, email, or other electronic medium. These signatures must be treated in all respects as having the same force and effect as original signatures.
13. SEVERABILITY.
If any one or more of the provisions contained in this assignment is, for any reason, held to be invalid, illegal, or unenforceable in any respect, that invalidity, illegality, or unenforceability will not affect any other provisions of this assignment, but this assignment will be construed as if those invalid, illegal, or unenforceable provisions had never been contained in it, unless the deletion of those provisions would result in such a material change so as to cause completion of the transactions contemplated by this assignment to be unreasonable.
14. NOTICES.
- (a) Writing; Permitted Delivery Methods. Each party giving or making any notice, request, demand, or other communication required or permitted by this assignment shall give that notice in writing and use one of the following types of delivery, each of which is a writing for purposes of this assignment: personal delivery, mail (registered or certified mail, postage prepaid, return-receipt requested), nationally recognized overnight courier (fees prepaid), facsimile, or email.
- (b) Addresses. A party shall address notices under this section to a party at the following addresses:
- If to the Assignor:
- If to the Assignee:
- (c) Effectiveness. A notice is effective only if the party giving notice complies with subsections (a) and (b) and if the recipient receives the notice.
15. WAIVER.
No waiver of a breach, failure of any condition, or any right or remedy contained in or granted by the provisions of this assignment will be effective unless it is in writing and signed by the party waiving the breach, failure, right, or remedy. No waiver of any breach, failure, right, or remedy will be deemed a waiver of any other breach, failure, right, or remedy, whether or not similar, and no waiver will constitute a continuing waiver, unless the writing so specifies.
16. ENTIRE AGREEMENT.
This assignment constitutes the final agreement of the parties. It is the complete and exclusive expression of the parties' agreement about the subject matter of this assignment. All prior and contemporaneous communications, negotiations, and agreements between the parties relating to the subject matter of this assignment are expressly merged into and superseded by this assignment. The provisions of this assignment may not be explained, supplemented, or qualified by evidence of trade usage or a prior course of dealings. Neither party was induced to enter this assignment by, and neither party is relying on, any statement, representation, warranty, or agreement of the other party except those set forth expressly in this assignment. Except as set forth expressly in this assignment, there are no conditions precedent to this assignment's effectiveness.
17. HEADINGS.
The descriptive headings of the sections and subsections of this assignment are for convenience only, and do not affect this assignment's construction or interpretation.
18. EFFECTIVENESS.
This assignment will become effective when all parties have signed it. The date this assignment is signed by the last party to sign it (as indicated by the date associated with that party's signature) will be deemed the date of this assignment.
19. NECESSARY ACTS; FURTHER ASSURANCES.
Each party shall use all reasonable efforts to take, or cause to be taken, all actions necessary or desirable to consummate and make effective the transactions this assignment contemplates or to evidence or carry out the intent and purposes of this assignment.
[SIGNATURE PAGE FOLLOWS]
Each party is signing this agreement on the date stated opposite that party's signature.
[PAGE BREAK HERE]
EXHIBIT A LIST OF APPLICATIONS
FORM OF RECORDABLE PATENT APPLICATION ASSIGNMENT
For good and valuable consideration, the receipt of which is hereby acknowledged, between , an individual a(n) (the " Assignor ") and , an individual a(n) (the " Assignee ") all of the Assignor's interest in the Assigned Patent Applications identified in Attachment A to this assignment, and the Assignee accepts this assignment.
Each party is signing this agreement on the date stated opposite that party's signature.
ATTACHMENT A ASSIGNED PATENT APPLICATIONS
Free Patent Application Assignment Template
Transfer the ownership rights or interests in a patent application. a patent application agreement defines the terms of transfer, promotes collaboration, and mitigates risks..
Complete your document with ease
What's a patent application assignment?
Related templates

Assignment of Agreement
Transfer work responsibilities efficiently with an assignment of agreement. Facilitate a smooth transition from one party to another.

Copyright Assignment
Protect your intellectual property with a copyright assignment form. Securely transfer your copyright to another party, clearly defining ownership terms while preserving your rights effectively.

Intellectual Property Assignment Agreement
Safeguard the sale or purchase of assets with an intellectual property assignment agreement. Transfer the ownership of patents, trademarks, software, and other critical assets easily.

Patent Assignment
Simplify the process of transferring patent rights for both buyers and sellers with a patent assignment agreement. Document the ownership transfer clearly and efficiently.

Trademark Assignment
Simplify the buying and selling of trademarks with a trademark assignment agreement. Transfer intellectual property rights and ensure a fair and smooth transaction.

Trademark License Agreement
Ensure fair use of intellectual property with a trademark license agreement. Outline the terms of usage and compensation.

An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know keyboard_arrow_down
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Jump to main content

Greatest in American innovation
From the soil to the skies, learn how National Inventor Hall of Fame inductees have impacted our world
New to Intellectual Property?
The three-year term for new members, who can participate in the Committees remotely, will start on December 1, 2024. Nominations must be electronically submitted on or before July 5, 2024.
The USPTO has issued a notice of proposed rulemaking (NPRM) to add a new requirement for terminal disclaimers filed to obviate (overcome) nonstatutory double patenting.
The Strategy aims to grow the economy, create quality jobs, and address global challenges by increasing participation in STEM, inventorship, and innovation among youth and those from historically underrepresented and underresourced communities.
The Federal Register Notice seeks public feedback on how the proliferation of AI could affect USPTO evaluations on patentability, including what qualifies as prior art and the assessment of the level of ordinary skills in the art.

New map enhancement

IP Identifier

Director's Initiative
Additional information about this page

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
You may email questions about searching patent assignments to [email protected]. For further information, you may contact the Assignment Recordation Branch Customer Service Desk at 571-272-3350 from 8:30 am - 5:00 pm Eastern Time. share. Additional information. During the examination of pending patent application as well as after the ...
A patent assignment is an agreement where one entity (the "assignor") transfers all or part of their right, title and interest in a patent or application to another entity (the "assignee"). In simpler terms, the assignee receives the original owner's interest and gains the exclusive rights to pursue patent protection (through filing ...
To help you with this, three sample patent assignment agreements are provided below. They are intended to be used as follows: ASSIGNMENT OF RIGHTS OF PATENT: An assignment is intended for use for a patent that has been issued by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO). ASSIGNMENT OF RIGHTS TO APPLICATION: This type of assignment is for the ...
A patent assignment is an irrevocable agreement for a patent owner to sell, give away, or transfer interest to an assignee, who can enforce the patent. ... Assignment of Rights - Patent Application: This is for patents still in the application process. After filing this form, the assignee can be listed as the patent applicant. ...
Patent Assignment. This Patent Assignment (hereinafter referred to as the "Assignment") is made and entered into on (the "Effective Date") by and between the following parties: a. , (the "Assignor") AND. , (the "Assignee") WHEREAS, the Assignor is the sole and rightful owner of certain ideas, inventions, patent applications therefor and patents ...
Searching for Patent Assignments. The USPTO maintains a patent assignment database that includes all the assignments recorded since August 1980. Using the database, you can search with the assignor's or assignee's name, the patent number, application number, publication number, or other identifying information. Properly assigning patents ...
A patent assignment is an agreement by the patent holder (assignor) to transfer his interest and ownership in a patent to another party known as the assignee (party receiving patent rights). ... If there are multiple inventors on a patent application, all inventors must execute an assignment agreement to assign each of their interest to the ...
Explicit Assignments: Even when employees have signed appropriate agreements, your company should execute new patent-specific assignments whenever patent applications are filed. These assignments name the specific invention, patent, and/or patent application, and can have additional legal weight if the ownership of a patent is disputed.
Assignment Center is the USPTO's online system for filing and managing patent and trademark assignments. Learn how to use it with our tutorial videos and FAQs.
Published on: January 29, 2024 14:47. Learn how to use start a patent request in Assignment Center. Assignment Center is a publicly available USPTO system for recording assignments and other documents relating to interests in patents and trademarks. Other ways to view this video. Watch it on YouTube.
Patent Assignment: A Basic Definition. Basically speaking, a patent assignment is a legal way for an inventor to transfer ownership of a patent to a business. As you may recall, in the United States, only a person (or group of people) can be listed as the inventor of a patent; a business cannot be listed as the inventor.
This patent application assignment is between , (the " Assignor ") and , (the " Assignee "). The Assignor has invented certain new and useful inventions (the " Inventions ") and has applied for patents on the Inventions, which are listed on Exhibit A (collectively, the " Applications "). The Assignor wishes to transfer to the Assignee, and the ...
Patent Assignment. This Patent Assignment (hereinafter referred to as the "Assignment") is made and entered into on (the "Effective Date") by and between the following parties: a. , (the "Assignor") AND. , (the "Assignee") WHEREAS, the Assignor is the sole and rightful owner of certain ideas, inventions, patent applications therefor and patents ...
Online patent tools. Locate online patent services and information. Patent Center. Single interface replacement for EFS-Web, Private PAIR and Public PAIR. Electronic Business Center; Check application status. Check patent application status with Patent Center. Fees and payment. Pay maintenance fees and learn more about filing fees and other ...