
- THE STRATEGY JOURNEY Book
- Videos & Tutorials
- Strategy Journey Analyzer [QUIZ + WORKBOOK]
- COMMUNITY FORUMS
- Transforming Operating Models with Service Design (TOMS) Program
- ABOUT STRATABILITY ACADEMY

Walmart Business Strategy: A Comprehensive Analysis
By Julie Choo
Published: January 5, 2024
Last Update: January 5, 2024
TOPICS: Service Design
In the dynamic landscape of retail, Walmart stands as a behemoth, shaping the industry with its innovative business strategies . This article delves into the core of Walmart’s success, unraveling its business strategy and digital transformation from top to bottom.
Walmart Business Strategy
Walmart’s business strategy is a well-crafted tapestry that combines a variety of elements to secure its position as a retail giant. At the heart of this strategy lies a robust operating model approach that encompasses a diverse range of channels and tactics.
Transition to An OmniChannel Marketplace
The Walmart business strategy includes leveraging its vast physical presence through an extensive network of stores, drawing customers in with the promise of Everyday Low Prices (EDLP). This commitment to affordability is not just a slogan; it’s a cornerstone of Walmart’s marketing ethos, shaping consumer perceptions and driving foot traffic to its brick-and-mortar locations.
Building Strength via its Emerging Digital Operating Model
Walmart’s business business strategy extends beyond traditional advertising methods and its strength is in its operational strategy where it is charging ahead with digital transformation to become a more complete Omnichannel Marketplace to combat competitors such as Amazon. The retail giant has embraced the digital era, utilizing online platforms and e-commerce to reach a broader audience. Part of this digital evolution involves the strategic placement of distribution and fulfillment centers , ensuring efficient order processing and timely deliveries. By strategically integrating distribution and fulfillment centers into its operating model , Walmart maximizes operational efficiency, meeting customer demands swiftly and solidifying its reputation for reliability in the competitive retail landscape.
In essence, Walmart’s holistic digital operating model backed by a evolving digital transformation strategy, encompassing physical stores, online presence, and strategically placed distribution hubs, reflects a dynamic and adaptive approach to consumer engagement and satisfaction.
Walmart’s Existing Business Model Before Digital Transformation
Walmart’s retail business .
Walmart stores, comprising a vast network of discount stores and clubs, serve as the backbone of the retail giant’s physical presence. Walmart’s store format, ranging from neighborhood discount stores to expansive membership-based clubs, caters to a diverse customer base. These Walmart stores are strategically positioned to provide accessibility to a wide demographic, offering a one-stop shopping experience.
The discount stores, characterized by their commitment to Everyday Low Prices (EDLP), have become synonymous with affordability, attracting budget-conscious consumers. Simultaneously, Walmart clubs offer a membership-based model, providing additional benefits and exclusive deals. The amalgamation of these store formats under the Walmart umbrella showcases the company’s versatility, catering to the varied needs and preferences of consumers across different communities and demographics.
Walmart Pricing Strategy
Pricing strategy.
Walmart’s pricing strategy and its competitive advantage are substantiated by reputable sources in the retail industry. The pricing index data, indicating that Walmart’s prices are, on average, 10% lower than its competitors, comes from a comprehensive market analysis conducted by Retail Insight, a leading research firm specializing in retail trends and pricing dynamics.
Everyday Low Prices
Walmart’s success in the retail sector can be attributed to its commitment to Low Price Leadership, a strategic approach that revolves around providing customers with unbeatable prices. Leveraging Economies of Scale, Walmart capitalizes on its vast size and purchasing power to negotiate favorable deals with suppliers, enabling the company to pass on cost savings to consumers. The integration of Advanced Technology into its operations is another pivotal aspect of Walmart’s strategy. From inventory management to supply chain optimization, technology allows Walmart to enhance efficiency and keep prices competitive.
Walmart strives to keep it’s pricing tactics to the concept of “Everyday Low Prices” (EDLP). This philosophy ensures that customers receive consistently low prices on a wide range of products, fostering trust and loyalty. Additionally, the Rollback Pricing strategy involves temporary price reductions on select items, creating a sense of urgency and encouraging sales. Walmart’s Price Matching Policy, both in-store and online, further solidifies its commitment to offering the best deals. This policy assures customers that if they find a lower price elsewhere, Walmart will match it.
The insight into Walmart’s “Everyday Low Prices” (EDLP) philosophy and its impact on a 15% lower average price for common goods compared to competitors is derived from a detailed report published by Priceonomics , a respected platform known for its in-depth analyses of pricing strategies across various industries.
The statistics regarding Walmart’s market share of 22% in the U.S. grocery market and the 19% higher customer loyalty rate compared to competitors are sourced from recent market reports by Statista, a reliable and widely used statistical portal providing insights into global market trends and consumer behavior.
Multiple layers of Discount
Walmart’s embrace of Multiple Discounts adds another layer to its pricing strategy. Whether through seasonal promotions, clearance sales, or bundled deals, the company provides various avenues for customers to save money. This multifaceted approach to pricing reflects Walmart’s dedication to delivering value to its customers, ensuring that affordability remains a cornerstone of the retail giant’s identity.
These sources collectively reinforce the significance of Walmart’s pricing strategy in maintaining its competitive edge and dominating the retail landscape
Walmart’s Servicing Business
Walmart’s strategic expansion into the servicing business marks a transformative shift, positioning the retail giant as a comprehensive one-stop-shop that extends beyond conventional retail offerings. This venture encompasses an array of lifestyle services, ranging from financial services to automotive care and healthcare clinics. Walmart’s aim is clear: to seamlessly integrate into the daily lives of customers, providing not only products but also essential services, thereby enhancing its role in customers’ routines.
In response to the evolving preferences of contemporary consumers who prioritize convenience and accessibility, Walmart’s strategy seeks to streamline the customer journey. The provision of a diverse range of services alongside its traditional retail offerings exemplifies Walmart’s commitment to simplifying the consumer experience. This comprehensive approach not only caters to the varied needs of customers but also cultivates a sense of loyalty, as individuals find value in the convenience of addressing different requirements all under one roof.
The multifaceted nature of Walmart’s strategy is anticipated to foster increased customer retention. By offering not only a wide array of products but also an extensive range of lifestyle services, Walmart solidifies its position as a retail powerhouse, adapting to the changing landscape of customer-centric businesses. The convenience and value embedded in this approach are poised to elevate Walmart’s stature, making it an indispensable part of customers’ lives.
SWOT Analysis of Walmart’s Business strategy
As we navigate Walmart’s digital transformation journey, a SWOT analysis reveals key insights into its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, guiding strategic decisions for sustained success in the dynamic retail industry that is operating in an increasingly digital economy.
SWOT Analysis of Walmart:
- Strong Brand Recognition: Walmart’s strength lies in its widely recognized and trusted brand, fostering consumer confidence and loyalty.
- Diverse Revenue Stream: The company’s adaptability is evident through a diverse revenue stream, navigating various markets and industries to maintain financial resilience. Per Walmart’s Q3 FY23 Earnings , a breakdown of walmart’s income can be recognised through its Sam’s Club membership sales (Up by 7.2%), Walmart U.S Comp Sales (Up 4.9%), Walmart U.S. eCommerce (up by 24%), and Walmart International sales (up by 5.4%).
- Economies of Scale: Walmart leverages its extensive size for economies of scale shown by its strong revenue growth of 5.3% per 2022 and 2023 consolidated Income statement, enabling cost advantages in procurement, operations, and overall efficiency.
- Strong Customer Base: With a vast and loyal customer base, Walmart establishes a robust foundation in the retail sector, emphasizing customer retention and sustained business growth as per market share stat of 60% shown on the Market retail/wholesale industry dominated by Walmart.
Weaknesses:
- Labor Relations: Walmart has faced criticism for labor practices, including low wages and labor disputes.
- E-commerce Competition: Despite significant strides, Walmart faces intense competition from e-commerce giants (e.g, amazon, eBay), impacting its online market share.
- Over Reliance on US Market: A substantial portion of Walmart’s revenue is generated in the United States, making it vulnerable to domestic economic fluctuations.
- Inconsistent customer service: represents a weakness in Walmart’s SWOT analysis, as variations in service quality across different locations may impact the overall customer experience, potentially leading to customer dissatisfaction and diminished brand perception.
Opportunities:
- E-commerce Expansion: Further growth in the online market allows Walmart to capitalize on changing consumer shopping habits.
- International Expansion: Targeting untapped markets presents opportunities for global revenue diversification.
- Health and Wellness Market: The growing trend towards health-conscious living provides avenues for expansion in the health and wellness sector. Increased understanding of customer journeys in these niches is key to begin to build stickiness effects.
- Technological Innovations: Embracing cutting-edge technologies can enhance customer experience and operational efficiency through a growing Omnichannel marketplace. It is vital to master data science and begin to leverage AI in the battle to understand consumer behaviors and deliver a remarkable experience.
- Competition: Intense competition from traditional retailers and e-commerce platforms poses a threat to Walmart’s market share such as Costco, Target and Amazon.
- Regulatory Challenges: Changes in regulations, especially related to labor and trade, can impact Walmart’s operations and costs. One such example is the metrics shown per Walmart’s ethics & compliance code of conduct aligning to regulatory challenges in culture, work safety, risk mitigation and more.
- Economic Downturns: Economic uncertainties and recessions may lead to reduced consumer spending, affecting Walmart’s revenue.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: External factors like natural disasters or geopolitical events can disrupt the global supply chain, impacting product availability and costs. Such threats are specifically addressed by Walmart’s Enterprise Resilience Planning Team .
More on Walmart’s Online Competitors
Walmart faces formidable competition in the online retail arena, with key rivals such as Amazon and Target vying for a share of the digital market. Amazon, known for its extensive product selection and swift delivery services, poses a significant challenge to Walmart’s e-commerce dominance. Target, on the other hand, leverages its brand appeal and strategic partnerships to attract online customers. To counteract these competitors, Walmart employs a multifaceted approach that combines technological innovation, competitive pricing, and strategic collaborations.
Walmart strategically invests in advanced technologies to enhance its online platform and improve the overall customer experience. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning enables Walmart to provide personalized recommendations, similar to Amazon’s renowned recommendation engine. Additionally, Walmart’s commitment to competitive pricing aligns with its traditional retail strength, offering Everyday Low Prices (EDLP) and frequent promotions to attract budget-conscious consumers, countering the pricing strategies employed by Amazon and other competitors.
Conducting a thorough SWOT analysis (such as this example from the Strategy Journey Book – 2nd Edition) allows Walmart to capitalize on its strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate potential threats, contributing to sustained success in the ever-evolving retail landscape.
Walmart’s Digital Transformation Strategy in the new ERA of AI-led Customer Centricity
Walmart’s online business strategy.
Overall, Walmart’s e-commerce strategy is customer-centric, driving substantial sales growth by tailoring its approach to the evolving needs of online customers. Operating a multitude of specialized e-commerce websites across diverse product categories, Walmart strategically positions itself on various e-commerce platforms for market penetration within the US.
Servicing Relevant Customer Journeys & Sustainable Transformation
Walmart’s evolving online strategy is characterized by a dual focus on extensive product offerings and technological sophistication, with concrete examples per its strategic partnership with Adobe in 2021 to integrate walmart’s marketplace, online and instore fulfillment and pickup technologies with Adobe commerce showcasing its commitment to a seamless customer experience. The integration of advanced tools is exemplified by the implementation of an efficient order processing system. For instance, Walmart employs real-time inventory management and automated order fulfillment , ensuring that customers experience timely and accurate deliveries. Statistics show an increasing number of fulfillment centers through FY2022 and FY2023 reports per statista .
Emerging predictive capabilities supported by Data Science and AI
In addition, the technological depth extends to personalized experiences, illustrated by Walmart’s robust recommendation engine. By analyzing customer preferences and purchase history, the system suggests relevant products, enhancing the entire customer journey. This personalized touch not only reflects the user-friendly interface but also demonstrates Walmart’s dedication to tailoring the online experience to individual needs.
Focus on seamless CX and UX to improve customer stickiness
Furthermore, Walmart’s commitment to a seamless online interaction is evident in its streamlined navigation features. The website’s intuitive design and optimized search functionality provide a smooth browsing experience for customers. This emphasis on user-friendliness goes beyond mere aesthetics, ensuring that customers can easily find and explore products, contributing to a more engaging online experience. Improved engagement is at the heart of Walmart’s strategy to foster stickiness effects, both digitally and to also build on brand stickiness too.

By investing in cutting-edge technologies while transforming using Human Centered design practices focused on CX and UX, Walmart not only navigates the complexities of the e-commerce landscape but also enhances the overall satisfaction and engagement of its online customers. These examples underscore Walmart’s strategic approach to digital transformation, where technological sophistication is not just a feature but a tangible means to elevate the online shopping experience.
Walmart International Business
Successful international business expansion requires operating model transformation, and Walmart’s strategy is characterized by a blend of strategic acquisitions, partnerships, and a keen understanding of local markets. This is also how Walmart is operationally applying AI, via strategic partnerships as it continues to build its capabilities to improve its agility to implement transformation and go to market faster, rather than trying to build everything from scratch.
A Sustainable Diversification strategy that adapts to local markets
Walmart’s international business expansion is a testament to its strategic approach in entering diverse markets and adapting to local nuances. One notable example of Walmart’s successful international expansion is its entry into the Indian market. In 2018, Walmart acquired a majority stake in Flipkart, one of India’s leading e-commerce platforms. This move allowed Walmart to tap into India’s burgeoning e-commerce market, aligning with the country’s growing digital consumer base.
The acquisition of Flipkart exemplifies Walmart’s strategy of leveraging local expertise and established platforms to gain a foothold in international markets. Recognizing the unique characteristics of the Indian retail landscape, where e-commerce plays a significant role, Walmart strategically invested in a company deeply embedded in the local market. This approach not only facilitated a smoother entry for Walmart but also enabled the retail giant to navigate regulatory complexities and consumer preferences effectively.
Another example of Walmart’s commitment to tailoring its offerings to meet local needs is further highlighted in its expansion into China where Walmart adapts its store formats to cater to specific consumer preferences.
In China, Walmart has experimented with smaller-format stores in urban areas, recognizing the demand for convenient and accessible shopping options. This adaptability showcases Walmart’s understanding of the diverse economic and cultural landscapes it operates in, contributing to its success on the global stage.
Working with partners to diversify and build a sustainable business model
Collaborations and strategic partnerships play a pivotal role in Walmart’s competitive strategy. In 2023, Walmart has outlined plans to invest heavily into AI automation fulfillment centers to improve its unit cost average by 20%, increasing efficiency in order fulfilments and operations.
The acquisition of Jet.com in 2016 expanded Walmart’s digital footprint and brought innovative talent into the company. Furthermore, Walmart’s partnerships with various brands (such as Adobe, ShipBob) and retailers enable it to diversify its product offerings, providing a competitive edge against the more specialized approaches of some competitors. As part of Walmart’s strategy in marketing, Walmart has announced partnerships with social media giants such as TikTok, Snapchat, Firework and more further boosting its online digital footprint.
The acquisition of Jet.com in 2016 not only expanded Walmart’s digital footprint but it brought innovative talent into the company. It is clear Walmart sees the need for talent as key to its continued efforts to apply human centered design as part of its digital transformation strategy.
By continuously adapting and evolving its strategies, Walmart is clearly implementing digital transformation sustainably, to support its future operating model as Walmart remains a formidable force in the online retail landscape, navigating the challenges presented by its competitors.
In conclusion, Walmart’s business strategy is that of an growing Omnichannel marketplace, a multifaceted approach that combines physical and digital retail, competitive pricing, supply chain excellence, and a commitment to customer satisfaction. Understanding these elements provides insights into the retail giant’s enduring success in a rapid changing and competitive digital economy as it continues to combat emerging new business disruptions.
Q1: How did Walmart become a retail giant?
Walmart’s ascent to retail dominance can be attributed to a combination of strategic pricing, operational efficiency, and a customer-centric approach.
Q2: What sets Walmart’s supply chain apart?
Walmart’s supply chain is marked by innovation and technological integration, allowing the company to streamline operations and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Q3: How does Walmart balance physical and digital retail?
Walmart seamlessly integrates its brick-and-mortar stores with its online presence, offering customers a comprehensive shopping experience.
Q4: What is Walmart’s philosophy on pricing?
Walmart’s commitment to everyday low prices is a fundamental philosophy that underpins its strategy, ensuring affordability for consumers.
Q5: How has Walmart expanded globally?
Walmart’s global expansion involves adapting its strategy to diverse markets, understanding local dynamics, and leveraging its core strengths.
About the author
Julie Choo is lead author of THE STRATEGY JOURNEY book and the founder of STRATABILITY ACADEMY. She speaks regularly at numerous tech, careers and entrepreneur events globally. Julie continues to consult at large Fortune 500 companies, Global Banks and tech start-ups. As a lover of all things strategic, she is a keen Formula One fan who named her dog, Kimi (after Raikkonnen), and follows football - favourite club changes based on where she calls home.
You might also like
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Strategy Journey Fundamentals , Transformation
The Impact of Co Creation in Modern Business
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Transformation
4 steps to create a Winning Game Plan
Service Design
9 Steps to your Winning Customer Journey Strategy

How does Walmart make money: Business Model & Supply Chain Strategy
Walmart helps people worldwide save money and live better – anytime and anywhere – by providing the opportunity to shop in retail stores and through eCommerce and access its other service offerings.
Through innovation, Walmart strives to continuously improve a customer-centric experience that seamlessly integrates its eCommerce and retail stores in an omnichannel offering that saves time for the customers. Each week, Walmart serves approximately 230 million customers who visit more than 10,500 stores and numerous eCommerce websites under 46 banners in 24 countries.
Walmart’s business strategy is to make every day easier for busy families, operate with discipline, sharpen the culture and become more digital, and trust a competitive advantage.
Price leadership has been a cornerstone of Walmart’s business strategy and model. By leading on price, Walmart earns customers’ trust by providing a broad assortment of quality merchandise and services at everyday low prices (“EDLP”).
EDLP is Walmart’s pricing philosophy and business strategy under which it prices items at a low price daily, so customers trust that prices will not change under frequent promotional activity. Everyday low cost (“EDLC”) is Walmart’s commitment to control expenses so the cost savings can be passed to customers.
Let’s closely analyze the business model and supply chain strategy of Walmart.
Business Model Analysis of Walmart
Walmart has global operations of retail, wholesale and other units, as well as eCommerce, located throughout the U.S., Africa, Canada, Central America, Chile, China, India, and Mexico. The business model of Walmart makes money from three segments: Walmart U.S., Walmart International, and Sam’s Club. Walmart made $567.8 billion in fiscal 2022 through these three segments. Each component contributes to the Company’s operating results differently.
Walmart U.S. Segment
Walmart U.S. is the largest segment and operates in the U.S., including in all 50 states, Washington D.C. and Puerto Rico. Walmart U.S. is a mass merchandiser of consumer products, operating under the “Walmart” and “Walmart Neighborhood Market” brands and walmart.com and other eCommerce brands. Walmart U.S. had net sales of $393.2 billion for fiscal 2022, representing 69% of Walmart’s revenue in fiscal 2022.
Omni-channel : Walmart U.S. provides an omnichannel experience to customers, integrating retail stores and eCommerce through services such as pickup and delivery, ship-from-store, and digital pharmacy fulfillment options. As of January 2022, Walmart had approximately 4,600 pickup locations and more than 3,500 same-day delivery locations.
Walmart+ membership offers enhanced omnichannel shopping benefits that include unlimited free shipping on eligible items with no order minimum, unlimited delivery from the store, fuel and pharmacy discounts, and mobile scan & go for a streamlined in-store shopping experience.
Merchandise : Walmart U.S. does business in three strategic merchandise units, listed below:
- Grocery consists of a full line of grocery items, including dry groceries, snacks, dairy, meat, produce, deli & bakery, frozen foods, alcoholic and nonalcoholic beverages, as well as consumables such as health and beauty aids, pet supplies, household chemicals, paper goods, and baby products;
- General merchandise includes Entertainment (e.g., electronics, toys, seasonal merchandise, wireless, video games, movies, music, and books); Hardlines (e.g., automotive, hardware and paint, sporting goods, outdoor living, and stationery); Apparel (e.g., apparel for men, women, girls, boys, and infants, as well as shoes, jewelry, and accessories); and Home (e.g., housewares and small appliances, bed & bath, furniture and home organization, home furnishings, home decor, fabrics, and crafts).
- Health and wellness include pharmacy, over-the-counter drugs, medical products, optical services, and other clinical services.
The Walmart U.S. business also includes an in-house advertising offering via Walmart Connect, supply chain and fulfillment capabilities to online marketplace sellers via Walmart Fulfillment Services, and access to quality, affordable healthcare via Walmart Health.
In Fiscal 2022, Walmart’s U.S. initiatives also included the launch of a B2B last-mile delivery service platform via Walmart GoLocal, and Walmart Luminate, which provides a suite of data products to merchants and suppliers.
Additional service offerings include fuel, financial services, and related products (including through digital channels, stores, and clubs as well as its previously announced fintech joint venture), such as money orders, prepaid access, money transfers, check cashing, bill payment, and certain types of installment lending.
Distribution & supply chain strategy : Walmart U.S. has a total of 157 distribution facilities from which the majority of Walmart U.S.’s purchases of store merchandise are shipped. General and dry grocery merchandise are transported primarily through the segment’s private truck fleet. Walmart ships merchandise purchased through eCommerce platforms by many methods from multiple locations, including its 31 dedicated eCommerce fulfillment centers, or delivers directly from more than 3,500 stores.
Walmart International Segment
Walmart International is the second largest segment, operating in 23 countries outside the U.S. as of January 2022. Walmart International operates through wholly-owned subsidiaries in Canada, Chile, and China and majority-owned subsidiaries in Africa, India, Mexico, and Central America. Walmart International had net sales of $101.0 billion for fiscal 2022, representing 18% of Walmart’s revenue.
Walmart International includes numerous formats divided into two major categories: retail and wholesale. These categories consist of many formats, including supercenters, supermarkets, hypermarkets, warehouse clubs (including Sam’s Clubs), cash & carry, and eCommerce through walmart.com.mx, walmart.ca, flipkart.com, and other sites.
Walmart International’s strategy is to create strong local businesses powered by Walmart, which means being locally relevant and customer-focused in each market it operates.
Omni-channel : Walmart International provides an omnichannel experience to customers, integrating retail stores and eCommerce, such as through pickup and delivery services in most of its markets, its marketplaces such as Flipkart in India, and a digital transaction platform anchored in payments such as PhonePe in India.
Same-day delivery capacity continues to expand in Mexico, including the launch of a membership model which provides unlimited same-day delivery from stores. In China, Walmart’s partnerships with JD.com and JD Daojia provide customers with one-hour delivery by leveraging Walmart stores as fulfillment centers.
A value-based internet and telephone service was recently launched in Mexico, allowing customers to enjoy digital connectivity. Generally, retail units’ selling areas range from 1,400 square feet to 186,000 square feet. Walmart’s wholesale stores’ selling areas range from 24,000 square feet to 158,000 square feet. On January 31, 2022, Walmart International had approximately 2,900 pickup locations and over 1,900 delivery locations.
Merchandise : The merchandising strategy for Walmart International is similar to that of Walmart U.S. in terms of the breadth and scope of merchandise offered for sale. While brand name merchandise accounts for most of its sales, Walmart has leveraged U.S. private brands and developed market-specific private brands to serve customers with high-quality, low-priced items.
In addition, Walmart has developed relationships with regional and local suppliers in each market to ensure reliable sources of quality merchandise equal to national brands at low prices. Walmart International also offers advertising, financial services, and related products in various markets, but they do not contribute significantly to Walmart’s revenue.
TESCO – British Retailer that redefined Grocery Shopping
Distribution & supply chain strategy : Walmart has 179 distribution facilities in Canada, Central America, Chile, China, India, Mexico, and South Africa. Through these facilities, Walmart processes and distributes both imported and domestic products to the operating units of the Walmart International segment.
Across the segment, Walmart connects physical stores and distribution and fulfillment centers which facilitate the movement of goods. Walmart ships merchandise purchased on its eCommerce platforms from its 83 dedicated eCommerce fulfillment centers, more than 3,400 eCommerce sort centers, last-mile delivery facilities in India, and physical retail stores.
Sam’s Club Segment
Sam’s Club operates in 44 U.S. and Puerto Rico states. Sam’s Club is a membership-only warehouse club that also operates samsclub.com. Sam’s Club had net sales of $73.6 billion for fiscal 2022, representing 13% of Walmart’s revenue. As a membership-only warehouse club, membership income is a significant component of the segment’s operating income.
Membership : The following two options are available to members.
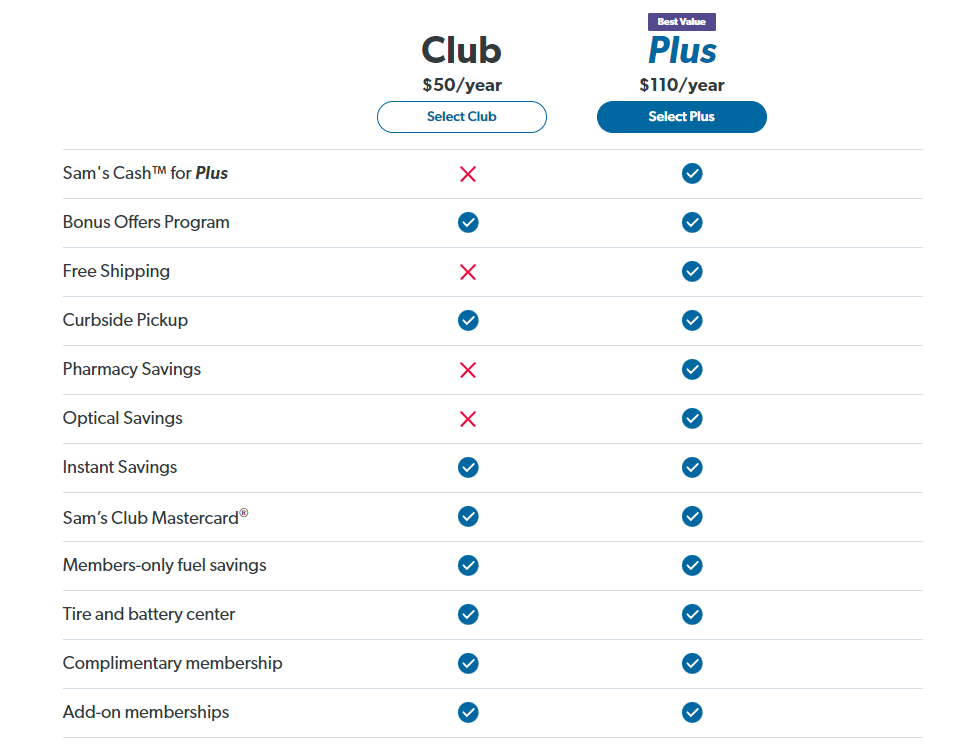
All memberships include a spouse/household card at no additional cost. Plus Members are also eligible for free shipping on most merchandise, with no minimum order size, and receive discounts on prescriptions and glasses. Members may redeem Sam’s Cash on purchases in the Club and online to pay for membership fees or cash in clubs.
Omni-channel : Sam’s Club provides an omnichannel experience to customers, integrating retail stores and eCommerce through such services as Curbside Pickup, mobile Scan & Go, ship-from-club, and delivery-from-club. The warehouse facility sizes generally range between 32,000 and 168,000 square feet, with an average size of approximately 134,000 square feet.
Merchandise : Sam’s Club offers merchandise in the following five merchandise categories:
- Grocery and consumables include dairy, meat, bakery, deli, produce, dry, chilled or frozen packaged foods, alcoholic and nonalcoholic beverages, floral, snack foods, candy, other grocery items, health and beauty aids, paper goods, laundry and home care, baby care, pet supplies, and other consumable items;
- Fuel, tobacco, and other categories;
- Home and apparel includes home improvement, outdoor living, gardening, furniture, apparel, jewelry, tools and power equipment, housewares, toys, seasonal items, mattresses, and tire and battery centers;
- Technology, office and Entertainment include consumer electronics and accessories, software, video games, office supplies, appliances, and third-party gift cards; and
- Health and wellness include pharmacy, optical and hearing services, and over-the-counter drugs.
Distribution & supply chain strategy : Walmart has 28 dedicated distribution facilities located strategically throughout the U.S. Some of the Walmart U.S. segment’s distribution facilities service the Sam’s Club segment for certain items. Most of Sam’s Club’s non-fuel club purchases are shipped from these facilities, while the remainder is shipped directly to Sam’s Club locations by suppliers.
Sam’s Club ships merchandise purchased on samsclub.com and through its mobile commerce applications by several methods, including shipments made directly from clubs, 12 dedicated eCommerce fulfillment centers, and other distribution centers. Sam’s Club uses a combination of Walmart’s private truck fleet and common carriers to transport non-perishable merchandise from distribution facilities to clubs.
Overall Supply Chain strategy of Walmart
As a retailer and warehouse club operator, Walmart utilizes a global supply chain strategy that includes U.S. and international suppliers from whom it purchases merchandise in its stores, clubs, and online.
In many instances, Walmart purchases merchandise from producers near the stores and clubs where such merchandise will be sold, particularly products in the “fresh” category. Walmart offers its suppliers the opportunity to sell significant quantities of their products to Walmart efficiently.
These relationships enable Walmart to obtain pricing that reflects the volume, certainty, and cost-effectiveness these arrangements provide to such suppliers, allowing it to offer low prices to customers.
Walmart’s ability to acquire from its suppliers the assortment and volume of products, to receive those products within the required time through its robust supply chain strategy, and to distribute those products to its stores and clubs, determines the attractiveness of Walmart’s merchandise assortment.
Walmart strongly focuses on building a sustainable supply chain in its business model.
- With respect to people, Walmart’s sustainability efforts focus on sourcing responsibly, helping prevent forced labor, empowering women, creating inclusive economic opportunities, and selling safer, healthier products.
- With respect to the planet, Walmart’s efforts aim to enhance the sustainability of product supply chains by reducing emissions, protecting and restoring nature, and reducing waste.
To help address the effects of climate change, Walmart has set science-based targets for emissions reduction to achieve zero emissions in operations by 2040 —without offsets—and to reduce or avoid one billion metric tons of emissions in its value chain by 2030.
Information Source: Walmart Annual Report Fiscal 2022

A passionate writer and a business enthusiast having 6 years of industry experience in a variety of industries and functions. I just love telling stories and share my learning. Connect with me on LinkedIn. Let's chat...
Related Posts

How does Instacart work and make money: Business Model

What does Zscaler do | How does Zscaler work | Business Model

What does Chegg do | How does Chegg work | Business Model

What does Bill.com do | How does Bill.com work | Business Model

What does Cricut do | How does Cricut work | Business Model

What does DexCom do? How does DexCom business work?

What does CarMax do? How does CarMax business work?

What does Paycom do? How does Paycom work?
What does FedEx do | How does FedEx work | Business Model

How does Rumble work and make money: Business Model

Dollar General Business Model & Supply Chain Explained

What does C3 AI do | Business Model Explained

What does Aflac do| How does Aflac work| Business Model

How does Booking.com work and make money: Business Model

What does Okta do | How does Okta work | Business Model

What does Alteryx do | How does Alteryx work | Business Model
Write a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Advanced Strategies
- Brand Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Luxury Business
- Startup Strategies
- 1 Minute Strategy Stories
- Business Or Revenue Model
- Forward Thinking Strategies
- Infographics
- Publish & Promote Your Article
- Write Article
- Testimonials
- TSS Programs
- Fight Against Covid
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and condition
- Refund/Cancellation Policy
- Master Sessions
- Live Courses
- Playbook & Guides
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Industries Overview
Latest articles, beauty tops us store brand sales growth in 2023, chase pioneers targeted in-app advertising with banking customer data, how big will amazon get, amazon accounted for 40% of ecommerce sales, 4% of retail sales in 2023, tiktok won’t dial back on tiktok shop content, but it may not matter for time spent, ctv, identity consolidation, and more: ad trends that cookie deprecation will—and won’t—change, rebrand lessons from jell-o and its agency partner, google contemplates hubspot deal in what would be its biggest-ever acquisition, pubmatic and instacart join forces to marry retail media data with programmatic advertising, two more banks with baas partnerships hit with fdic consent orders, about emarketer, guide to walmart for marketers, advertisers, and retailers.
How the giant is growing its retail business through click-and-collect grocery, subscriptions, and retail media

Powerful data and analysis on nearly every digital topic
Want more research .
Sign up for the EMARKETER Daily Newsletter
Walmart is one of the biggest and most accessible retailers in the country. It’s the second-largest retailer by US ecommerce sales, behind Amazon, thanks in part to its strengths in grocery and its third-party marketplace.
Though its core retail business is going strong, Walmart is also investing heavily in its other business units, including its retail media network, a B2B membership program, fulfillment services, financial and payment services, and healthcare services.
In this guide, we break down Walmart’s business units; where it could be facing competition; and what this all means for retail marketers, advertisers, and more.
- Want to learn more about Walmart and other retail trends? Sign up for the Retail Daily newsletter.
Walmart’s history, business units, and revenues
Founded in 1962, Walmart has evolved from a brick-and-mortar retail store in Arkansas to a global retail powerhouse with multiple banners. Ninety percent of the US population lives within 10 miles of the nearly 4,616 Walmart stores across the country, per the retailer. These retail stores give Walmart US a vast network of distribution centers and supply chain networks. Outside the US, Walmart International operates more than 5,200 physical locations across 19 countries.
The Walmart Inc. corporation also includes Sam’s Club, a club retailer that was founded by Sam Walton in 1983 to help small businesses save money on merchandise purchased in bulk. Today, there are nearly 600 Sam’s Club stores in the US.
Walmart’s business model includes its physical retail and ecommerce business, its retail media network, a B2B membership program, fulfillment services, financial and payment services, and healthcare services.
Here’s a deeper dive into each business unit:
Walmart Retail
Walmart’s retail business includes its 4,616 Walmart US locations across the country, Walmart.com, and the Walmart mobile app . The grocery category is one of the driving forces of Walmart’s ecommerce and in-person retail success. The retailer also hopes to drive retail sales through its Walmart+ membership program.
Despite the fact that its ecommerce business has more than tripled from 2019 to 2024, Walmart is still a distant second in a market dominated by Amazon. Walmart Inc. will grow its US ecommerce sales by 13.5% in 2024 to reach $94.11 billion, a fraction of Amazon’s 2024 US ecommerce sales, totaling $492.23 billion, per EMARKETER’s forecasts.

Walmart’s US ecommerce business is being driven both by its strength in grocery and its third-party marketplace.
Walmart’s digital grocery business surged in 2020 as consumers leaned on online shopping and delivery during the pandemic. But even now that pandemic-era habits have normalized, Walmart’s grocery business is still booming as inflation on food and beverage prices has increased average transaction values and attracted more higher-income consumers looking to save money.
In 2024, Walmart Inc.’s US grocery ecommerce sales will reach $58.92 billion and make up 26.9% of total grocery ecommerce sales in the US, per EMARKETER’s November 2023 forecast.
Click and collect, online grocery ordering that a customer picks up either in-store or curbside at the store, will be a big contributor to Walmart’s grocery success, according to EMARKETER’s The Power of Walmart report. Click and collect’s share of total grocery ecommerce sales will continue to grow through 2027, when it will represent 40.7% of total US grocery ecommerce sales, per a January 2024 EMARKETER forecast. This shift will directly favor Walmart, giving it an advantage over Amazon and Instacart, its two biggest competitors in digital grocery.
Walmart Marketplace
In 2024, EMARKETER forecasts Walmart’s marketplace ecommerce sales will reach $10.60 billion, a 17.5% increase YoY. A retail marketplace is an ecommerce site selling products from multiple third parties, sometimes in addition to their own products.
By October 2023, Walmart Marketplace had doubled in size within 18 months to reach 100,000 active sellers, according to Marketplace Pulse research. It also offers around 400 million SKUs from marketplace sellers, per EMARKETER’s US Retail Ecommerce Marketplaces Forecast 2023 report.
To keep current sellers loyal and attract new ones to the platform, Walmart announced a slate of new marketplace features at its seller summit, including enhanced fulfillment and logistics services for merchants.
Walmart+, the company’s subscription membership service, launched with a bang in September 2020 but has struggled to sustain its initial growth, per The Power of Walmart . Five months after its launch, Walmart+ had between 7.4 million and 8.2 million members, according to Consumer Intelligence Research Partners as reported by Forbes.
“Walmart hasn’t disclosed the number of Walmart+ subscribers, but estimates from Morgan Stanley, cited by The Wall Street Journal, claimed Walmart+ had 16 million members in May 2022, up from 15 million in November 2021. Consumer Intelligence Research Partners said subscribers reached 11 million in July 2022, which was unchanged from April 2022,” as detailed in The Power of Walmart .
In 2024, the number of Walmart+ users will grow 8.8% to reach 31.8 million, according to EMARKETER’s March 2023 forecast.
Twenty-five percent of respondents ages 18 to 34 had access to a Walmart+ membership, according to a December 2023 EMARKETER survey conducted by Bizrate Insights. That’s a higher figure than for other age groups.

In the hopes of competing better with Amazon Prime, Walmart has added a variety of perks to its Walmart+ membership, including a cash-back rewards program, a members-only sales event, free home pickup for returns, and exclusive access to a limited-edition Oreo flavor, per EMARKETER’s Retail Memberships Forecast 2023 report. However, Prime still offers more comprehensive media features than Walmart+, including video streaming, music, and podcasts.
Private label
In early 2023, Walmart said it would begin marketing its private label products as less expensive alternatives to name-brand goods. In addition, CEO Doug McMillon said the retailer would keep its private label brands—which include Great Value, Equate, George, and Wonder Nation—priced low in an effort to bring inflation down.
Consumer preference for private label has remained strong despite easing grocery inflation, with 90% of consumers saying they are likely to keep purchasing store brands even if inflation and grocery prices fall, per a report by FMI—The Food Industry Association.
Advertising and Walmart’s retail media network
Though ad revenues remain a small fraction of its business, Walmart Connect will be the fastest-growing retail media network we track in 2024, growing 39.5% to reach $4.45 billion in ad revenues, per EMARKETER’s October 2023 forecast.
Once again, Walmart is a distant second to Amazon, which will generate $44.26 billion in US ad revenues in 2024.

Walmart’s advertising capabilities include search, display, connected TV (CTV) , social, and in-store digital media.
- Search represents the majority of the Walmart Connect business today, but other capabilities are growing in importance as retail media moves further up the funnel.
- Walmart DSP, Walmart’s demand-side platform (DSP) built in partnership with The Trade Desk, provides access to digital ad inventory on third-party publishers and CTV, likely encouraging more brand advertising investment.
- Walmart’s partnerships with Roku, TikTok, and Snap offer marketers the ability to advertise across social and CTV.
- As it continues to build out its advertising business, Walmart is bringing retail media in-store , focusing on ad formats like audio and product demos, per the company.
To help advertisers better understand and leverage its retail media network, Walmart introduced an ad certification program that covers the breadth of Walmart’s ad capabilities, including on-site, off-site, in-store, and omnichannel ad formats.
- It also provides more in-depth coverage on sponsored products, sponsored brands, and sponsored video ads.
- Eventually, Walmart Connect plans to add courses on display ads, Walmart’s DSP, in-store advertising, and its new Brand Shops, which the retailer announced at its first seller summit in August 2023.
As the retail media channel evolves, Walmart’s physical footprint, strong ties to consumer packaged goods brands, and partnerships with streaming and social platforms will help it attract and keep advertiser clients looking to reach customers across many different channels.
Walmart’s other business units
Outside of its core retail business, Walmart has several other business units, including a B2B membership, fulfillment services, financial and payment services, and healthcare services.
Walmart Business
Launched in January 2023, Walmart Business is a membership for small and medium-sized businesses that offers free shipping, free pickup and delivery from store, as well as rewards and savings opportunities.
Since then, Walmart has also launched a Walmart Business app , revamped the ordering process to make it easier to order in large quantities, partnered with professional services platform Angi, and added a tool to help businesses track their organizational spending.
With this membership service, Walmart hopes to gain a piece of the $2.091 trillion in B2B ecommerce site sales that EMARKETER forecasts for 2024.
Walmart Fulfillment Services
Walmart Fulfillment Services (WFS), which launched in February 2020, is tightly linked to the expansion of Walmart Marketplace and is crucial to fueling an Amazon-style flywheel , according to The Power of Walmart.
“Third-party sellers are strongly encouraged to take advantage of WFS benefits, which include prioritized search results that highlight two-day shipping, management of customer service, and acceptance of returns via Walmart’s extensive store network, including the recent addition of curbside returns,” the report said.
In October 2023, Walmart announced plans to open its fifth “next-generation” fulfillment center in Stockton, California, in 2026. The 900,000-square-foot facility will increase its fulfillment capacity for West Coast online orders. The retailer said that the next-generation facilities operate far more efficiently than its other centers because they use automation to condense its 12-step fulfillment process down to five steps.
Financial and payment services
Walmart offers low-cost banking and alternative financial services at more than 4,700 Walmart stores, which contribute close to $2 billion to the retailer’s bottom line, per The Power of Walmart. Usually housed within its MoneyCenter store-within-a-store concept, shoppers can find prepaid cards and gift cards as well as a host of payment-related services , including check cashing, tax preparation, and money transfer services. Customers can also pay bills, reload prepaid accounts, and apply for Walmart’s private label and co-branded credit cards. In fact, 700 retail store locations include full-service bank branches operated via lease agreement.
Walmart Pay, the retailer’s proprietary mobile wallet, lets customers make mobile payments at its more than 3,500 US Supercenters (i.e., larger stores that offer full ranges of merchandise beyond grocery). It lets customers select a payment method (including credit, debit, prepaid, and gift cards) before using the app to scan a QR code displayed on the register. It cannot be used at fuel pumps or Sam’s Club stores.
Healthcare services
“ Walmart’s healthcare ambitions are decidedly retail-centric: It aims to give consumers another reason to visit a Walmart Supercenter. That philosophy is built into the 48 Walmart Health clinics now operating in five states. But that modest footprint isn’t going to impact the US healthcare industry in any major way,” per The Power of Walmart.
However, its health and wellness division (including Walmart Health), is a tightly integrated part of its flywheel.
Walmart’s retail ecommerce competitors
Walmart faces competition from both the ecommerce and physical retail sides.

Amazon is the top ecommerce retailer in the US . In fact, it’s larger than the next 15 largest US ecommerce retailers combined. In 2024, Amazon will grow its retail ecommerce sales by 11.5% to reach $492.23 billion, according to EMARKETER’s November 2023 forecast.
To better compete with Amazon and steal market share from its Prime Day events, Walmart has begun hosting its own version of the sales event during the same time period.
As a third-party marketplace platform, Shopify directly competes with Walmart’s marketplace model . Shopify’s retail ecommerce sales will reach $117.34 billion in 2024, an 8.5% increase YoY, per EMARKETER’s April 2023 forecast.
Previously, Shopify also offered logistics services, but in May 2023, the company announced it would offload the offering to cut costs.
Target competes with Walmart in both brick-and-mortar and ecommerce sales, but without Walmart’s strong grocery business, it struggles to keep up . In 2024, Target’s US grocery ecommerce sales will grow 7.5% to reach just $8.10 billion (compared with Walmart Inc.’s estimated $58.92 billion), per EMARKETER’s November 2023 forecast. Target’s total US retail ecommerce sales will grow slower at 4.1%, reaching $21.01 billion in 2024.
The opportunity Walmart offers marketers and advertisers
Walmart’s flywheel—powered by its ecommerce, advertising, and fulfillment businesses—enable marketers to promote, sell, and ship their products to customers across the US. The retailer’s physical reach helps brands connect with hard-to-reach customers, like older generations who prefer to shop in-store or those in rural areas.
Walmart’s innovation within its retail media business also provides value to its advertisers. New ad formats like CTV and in-store media offer creative ways to engage with customers, while its ad certification program ensures marketers are able to maximize the effectiveness of their campaigns.
The retailer’s other business units, including its healthcare and payment networks, help the retailer embed itself into every facet of customers’ lives, giving advertisers a multitude of touchpoints to reach their audience.
Want more retail & ecommerce insights?
Sign up for EMARKETER Retail Daily, our free newsletter.
By clicking “Sign Up”, you agree to receive emails from EMARKETER (e.g. FYIs, partner content, webinars, and other offers) and accept our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy . You can opt-out at any time.
Thank you for signing up for our newsletter!
Editor's Picks

The 10 biggest retail companies in the US, by ecommerce sales

Ecommerce Statistics: Industry benchmarks & growth
Industries →, advertising & marketing.
- Social Media
- Content Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Browse All →
- Value-Based Care
- Digital Therapeutics
- Online Pharmacy
Ecommerce & Retail
- Ecommerce Sales
- Retail Sales
- Social Commerce
- Connected Devices
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Financial Services
- Wealth Management
More Industries
- Real Estate
- Customer Experience
- Small Business (SMB)
Geographies
- Asia-Pacific
- Central & Eastern Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- North America
- Western Europe
- Data Partnerships
Media Services
- Advertising & Sponsorship Opportunities
Free Content
- Newsletters
Contact Us →
Worldwide hq.
One Liberty Plaza 9th Floor New York, NY 10006 1-800-405-0844
Sales Inquiries
1-800-405-0844 [email protected]

- Search 58728
- Search 10182
- Search 53991
Walmart Business Model | How does Walmart Make Money ?
Company: Walmart Inc. (NYSE: WMT) Founders : Sam Walton Year founded: 1962 CEO: Doug McMillan Headquarter: Bentonville, Arkansas Number of Employees (2023): 2.1 million Type: Public Market Capitalization (July 2023): $432.17 billion Annual Revenue (FY 2022) : $572.75 billion Net Income (FY 2022) : $13.67 billion
Products & Services: Grocery, electronics, apparel, toys, and home furnishings (some stores also sell fuel) Means of Sales: Physical Stores and E-commerce. Competitors: Target Corp , Costco , Dollar General, Dollar Tree, Family Dollar, Kroger , Amazon , Best Buy , and BJ’s Wholesale Holdings.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Walmart
Walmart is the largest enterprise in the world in terms of revenue. The retail giant operates 10,500 stores in 24 countries, offering thousands of products to over 230 million customers annually. Besides selling products from its stores, it also sells them via several E-commerce sites like Walmart, Sam’s Club, and Flipkart .
Walmart attracts customers by offering some of the industry’s lowest prices for groceries and merchandise. It does this by buying directly from the manufacturers and is precise with its expenses.
Sam Walton founded Walmart in 1962. He entered the variety retail industry when he opened a Ben Franklin chain variety store, threw away the traditional rules of running a retail shop, and developed his own. Even though he had to shut shop in a little while, the experience was a strategic success and helped him start Walmart.
Today Walmart is a retail behemoth . The company’s revenue grew from $44 million in 1970 to $572 billion in 2022, with share prices rocketing from $0.77 in 1982 to $146.67 in 2022.
Walmart’s Business Model
1. customer segments.
Walmart’s customer base comprises two segments:
- Individual customers
- Business customers
The firm markets to consumers through its two distinct brands . Walmart’s target demographic consists of middle-income and lower-income families who prefer to shop in one location. On the other hand, Sam’s Club caters primarily to the middle and upper-income groups.
Together, the two businesses have a massive customer base that spans the entire country and encompasses virtually every demographic.
2. Value Propositions
Walmart offers customers a range of products at the best possible price and in the most convenient way, living up to its motto of
“ Save Money. Live Better, “
It achieves this by focusing on a strategy that revolves around four key ideas:
- Buy Cheap, Sell Cheap
- Earn profits on volumes
- Focus on customers
- Avoid pointless expenses
The company has also renewed its focus on technology, investing more than $14 billion in automation technology , supply chain, and customer-facing initiatives in FY 2022.
3. Key Partners
Being the largest retailer in the world necessitates establishing a global network of distributors, suppliers, and manufacturers for the company to manage its massive supply chain effectively.
Over 100,000 vendors and 210 warehouses are on-board with the organization. Walmart’s distribution network is among the largest in the world, providing service to shops, warehouse clubs, and home delivery.
In addition, more than 11,000 individuals contribute to Walmart’s transportation system, which includes a fleet of 9,000 tractors, 80,000 trailers, and several other vehicles.
Some of the primary suppliers to Walmart include-
- Plug Power Inc.
- Proctor & Gamble
- Hewlett-Packard
- Green Dot Corp
- Primo Water Corp
4. Key Activities
- Buying Goods : Since Walmart is in the retail sector, it must frequently purchase various products from numerous categories. This method involves extensive negotiations and bulk purchases from suppliers and manufacturers. The company also distributes products under the Great Value
- Transporting and Delivering Goods : The corporation sells around 120,000 distinct types of products. Most of these commodities are purchased in bulk, so the corporation must devote substantial resources to transportation. Additionally, the business must organize conveyance for home deliveries and in-store pickups.
- Inventory Control : To ensure that its shelves are always stocked, it has to confirm an appropriate amount of inventory.
5. Key Resources
- Human Resources : With approximately 2.1 million employees, the corporation is the largest private employer in the world. These individuals are vital to managing its over 10,500 stores, distribution hubs, and virtual infrastructure.
- Mobile app and website: The corporation already reigns supreme among retail outlets. After experiencing intense competition from online retailers like Amazon , the company’s website and shopping app now account for a significant amount of its overall sales.
- Stores: The company operates 10,500 Walmart and Sam’s Club locations. These retail locations generate the majority of Walmart’s revenue.
6. Key Acquisitions
After a certain point, every company augments the traditional organic growth route with strategic acquisitions . Walmart has also followed the same path, with some of its notable acquisitions such as:
- Asda : Walmart Inc. owned this British supermarket until last year when it was sold to the EG group for more than GBP 6.8 billion.
- Seiyu Group : Walmart owns a 15% stake in the Japanese retail company. Seiyu has more than 400 stores in Japan and is worth an estimated $13 billion.
- Flipkart : Walmart acquired a 77% stake in the Indian E-commerce giant in 2018. Currently, Flipkart is India’s second-largest E-commerce company. It also owns other notable online companies like Myntra and PhonePe.
- Massmart : It is the second largest distributor of goods in Africa. The company owns local brands like Makro, Game, and Jumbo, each occupying a different space in the consumer necessity and discretionary market. Walmart bought the company for $2.54 billion in 2011.
7. Key Competitors
The retail industry is ancient, mature, and overcrowded. Even though Walmart is the largest retail chain in the world, it still faces stiff competition from-
- Amazon: Amazon has changed the game in the retail industry. It can offer customers products are extremely low prices since its overhead costs are next to nothing. The online retailer received a significant boost during the pandemic when retail stores were forced to shut down.
- Costco: Costco offers the best hotdog and soda combo in the US and is also one of the favorite places to shop for consumers. Its strategy of a no-frills warehouse-like store that offers everything in bulk is a real challenge to the savings promised by Walmart.
- Target: Just like Walmart, Target also focuses on savings, but it also focuses on online sales, with more than 18% of its revenue coming from online channels. It also has smaller stores with more premium-looking interiors and a youthful feel.
- Dollar General: Dollar General is the largest discount retail chain in the US, with more than 18,000 stores. The company generally targets low-income demography and offers products at significantly low costs. In the current inflationary environment, with forecasts of a recession, Dollar General is expected to increase its footfall.
8. Channels
These are mid-sized stores offering a variety of value-priced items. The discount stores are spread across 107,000 square feet, employ about 225 associates and offer 120,000 items each.
These 24/7 large stores focus on offering customers the convenience of a one-stop shop. These stores have third-party restaurants, hair salons, banks, fuel stations etc.
Supercenters average 187,000 square feet, employ 350 or more associates on average and offer 142,000 different items.
These stores are the smallest of the lot and focus on delivering everyday items like groceries, pharmaceuticals and general merchandise. Neighborhood Markets have an average size of 42,000 square feet, employ 95 associates on average, and offer about 29,000 items.
This members-only warehouse club offers general merchandise and large-volume items at value prices to small business owners and families.
The average size of Sam’s Clubs stores is 132,000 square feet, employ around 160-175 associates, and roughly have 5,500 products.
The company generates a majority of its online revenue in the US from the following two sites:
- samsclub.us
It also has a majority stake in the Indian E-commerce giant Flipkart.
9. Customer Service
Walmart has a long and distinguished history of putting customers first. The company’s founder, Sam Walton, invented the concept of door greeters. The organization also employs a workforce to provide customer service via chat, internet, and telephone, besides in-store customer support representatives.
Today, Walmart’s CRM strategy, customer service strategy , and customer experience initiatives work in tandem to develop customer loyalty that rivals most other retailers. According to InMarket , Walmart has the most loyal customer base of all retailers in the United States.
10. Walmart’s Cost Structure
Walmart is a wholesaler and retailer, acquiring goods from producers and suppliers.
- The cost of buying and transporting these goods (cost of sales) was $429 billion in FY 2022, $9.3 billion more than FY 2021’s cost of sales of $420.3 billion.
- Operating and SG&A costs (short for selling, general, and administrative) amounted to $117.8 billion in FY 2022, up $1.5 billion from $116.29 billion in FY 2021.
11. Walmart’s Revenue Streams
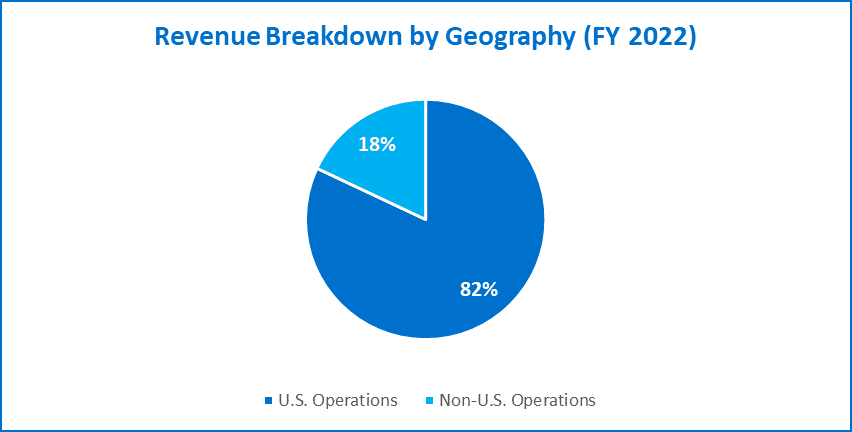
- The company posted revenue of $567.76 billion for FY 2022, an increase of 2% over FY 2021.
- Most of Walmart’s revenue (82%) was from the US, followed by its International business (18%).
- In FY 2022, groceries accounted for 56% of Walmart’s total income in the US, followed by general merchandise (32%), health and wellness (11%), and other categories (1%).
- The company posted a net profit of $13.67 billion in FY 2022, slightly higher than the $13.5 billion profit in FY 2021.
- Walmart also witnessed a surge in inventory from $44.95 billion in FY 2021 to $56.5 billion in FY 2022, indicating a slow movement of products.
Final Thoughts
Walmart is #1 on the list of Fortune 500 companies in the United States for 2022. The annual list of Fortune 500 companies, compiled and published by Fortune magazine, ranks the most significant corporations in the United States in terms of revenue for the fiscal year.
The changes implemented by the company on how consumers shop have influenced the overall culture, leading to its robust growth.
Walmart’s business ethics have also provided investors with astronomical returns on equity. For instance, an investor who bought $1,000 worth of shares in 1972 when the company first listed on the NYSE would have seen its value rise to nearly $3 million at the end of 2022.
References & more information
- Walmart SEC filings: https://stock.walmart.com/financials/sec-filings/default.aspx
- SimilarWeb: https://www.similarweb.com/top-websites/category/e-commerce-and-shopping/
- Linda Shepherd for NCESC: https://www.ncesc.com/companies-owned-by-walmart/
- Liz Flynn (2019, April 19): https://moneyinc.com/companies-you-didnt-know-walmart-owned/
- Marianne Wilson (2021, November 06): https://chainstoreage.com/walmart-has-most-loyal-customers-us-followed-fred-meyer-meijer-and-target
- Sandra Gudat (2022, May 2): https://www.customer.com/blog/retail-marketing/how-walmart-customer-loyalty-rose-to-the-top-and-stayed/
- Elvin Mirzayev (2019, September 03): https://www.investopedia.com/articles/active-trading/070715/target-vs-walmart-whos-winning-big-box-war.asp
- Walmart corporate website: https://corporate.walmart.com/
- Yahoo Finance: https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/WMT?p=WMT&.tsrc=fin-srch
- Richard Best (2022, May 02): https://www.investopedia.com/articles/insights/050116/walmart-stock-analyzing-5-key-suppliers-wmt.asp
- James Moore (2014, January 10): https://www.talkativeman.com/sam-walton-frugality-wal-mart/
- Featured image by Marques Thomas
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.
Kevin Johnson
Add comment, cancel reply, you may also like.

How does Letgo make money?
Company: Letgo CEO: Enrique Linares Plaza Founders: Alec Oxenford, Enrique Linares Plaza, and Jordi Castello Year founded: 2015 Headquarter: New York, New York Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 270+ Type:...
How Does Credit Karma Work and Make Money?
Last updated: May 19, 2020 Company: Credit Karma CEO: Kenneth Lin Founders: Kenneth Lin, Nichole Mustard, Richard Graciano Year founded: 2007 Headquarter: San Francisco, CA Number of...
43 Recession Proof Businesses (2023)
Last updated: Sept 09, 2021 Recession is undoubtedly a time of high crisis, and you’d think that everything will slowly start crumbling. Well, that is not true in most cases. By most cases we mean businesses. We...

ALDI Business Model | How Does ALDI make money?
Grocery stores are a staple of the American economy and raked in over $848.4 billion in sales last year alone. Interestingly, this sector is domineered by international supermarket chains, like ALDI, instead of...

How Does Coffee Meet Bagel Work?
Company: Coffee Meets Bagel Founders: Arum Kang, Dawoon Kang, Soo Kang Year founded: 2012 Headquarter: San Francisco Products & Services: Online Dating, Internet Competitors: Tinder, Bumble, Hinge...
How does Uber Eats work?
Last updated: April 20, 2020 Company: Uber Eats Founders: Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp Year founded: 2014 CEO: Dara Khosrowshahi Headquarter: San Francisco, CA Number of Employees (Dec 2018): Est. 5,000 Type:...
Etsy Business Model | How Does Etsy Make Money?
Technological advancements, increased adoption of mobile devices, globalization, better and cheaper internet connection, and safe payment gateways are driving the growth of online marketplaces like Etsy. But what is...

What is ProctorU, how it works and makes money?
Company: ProctorU Founders: Jarrod Morgan Year founded: 2008 CEO: Scott McFarland Headquarter: Birmingham, Alabama Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 400+ Type: Private Ticker Symbol: NYSE: UBER Annual Revenue (Dec...

How does Sweatcoin work and make money?
Company: Sweatcoin Founders: Oleg Fomenko and Anton Derlyatka Year founded: 2015 CEO: Oleg Fomenko and Anton Derlyatka Headquarter: London, England Type: Private Investor Funding: 6.3M Products &...

Amazon Business Model | How does Amazon make money
Last updated: Feb 13, 2021 Company : Amazon CEO : Andrew Jassy Year founded : 1994 Headquarter : Seattle, Washington United States Business world has never been the same since the inception of...
Recent Posts
- Who Owns TracFone
- Who Owns Rolex?
- Who Owns Bellagio?
- Who Owns Skechers?
- Who Owns JetBlue?
- Who Owns Ciroc?
- Who owns Aston Martin?
- Top 10 Bed Bath and Beyond Competitors and Alternatives
- Who Owns Sheraton?
- Who owns Volkswagen?
Business Strategy Hub
- A – Z Companies
- Privacy Policy
Buy us Coffee
If you like our work and would like to show appreciation to our team, buy us coffee!
Subscribe to receive updates from the hub!
- Red Queen Effect
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Only the paranoid survives
- Co-opetition Strategy
- Mintzberg’s 5 Ps
- Ansoff Matrix
- Target Right Customers
- Product Life Cycle
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Bowman’s Strategic Clock
- Pricing Strategies
- 7S Framework
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Strategy Diamond
- Value Innovation
- PESTLE Analysis
- Gap Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Strategy Canvas
- Business Model
- Mission & Vision
- Competitors
- Buy Us Coffee!
Our Segments Walmart U.S.

The Walmart business model focuses on our unique assets. Assets that work together in a mutually reinforcing way to bring customers into our ecosystem and serve them seamlessly across their everyday journeys. We call it the flywheel.
We start with the customer and design for them. They come to Walmart for the things they want and need, and they also like that we’re a force for good in local communities and for the planet. Our priority is to continue being the first, best place to shop. We’re doing this today with refreshed experiences in stores, services like pickup and delivery, a Walmart+ membership, or delivery directly into the refrigerator. Underpinning this is our aggressive approach with investments in capacity, fulfillment, and automation to ensure Walmart is the primary destination.

We aim to serve families more broadly, deepen our relationship with them, and create a healthy mix of merchandise and services. We’ll continue to add new brands and grow the assortment, especially in general merchandise, through our own assortment and the Walmart marketplace.
Beyond merchandise, we know we can do more to expand the reach of health and wellness. We already play a meaningful role in businesses like pharmacy, optical, hearing, and OTC, and we’re also one of the largest sellers of food in the U.S., which is important as we think about health overall. We recently announced the opening of new healthcare clinics, and we plan to open more. Customers and members want high quality, preventative, accessible, and affordable healthcare – and we can help make it a reality.
Like healthcare, customers are looking for better solutions for their money. Walmart can help them save money, reduce friction, and strengthen their finances through the new fintech startup we’ve announced, which will operate under the "One" brand going forward. We have an opportunity to positively affect the financial well-being of millions of families across the U.S., and we’re working quickly to develop solutions.
We operate at the lowest cost to serve, and we do it in a way that’s sustainable and fits within our goal of becoming a regenerative company. Being more productive and more digital in how we work helps fuel investments in important areas that diversify our profit base. Areas like advertising, data, and last mile delivery.
We are deepening our relationship with customers as we introduce new products and services, which allows them to seamlessly interact with the Walmart brand on their terms and in a way that fits their wants and needs. Connecting these pieces allows us the opportunity to expand our profit pools and pull it together in a way that’s good for shareholders.
We're sorry, but this browser is no longer supported
You will experience limited functionality and unusable pages with your current browser. We recommend upgrading to one of the latest versions of the following browsers:

Walmart Business Model Explained: The Tactics That Led to Its Success
Key takeaways, the beginnings, innovation era, becoming the best, sustainability and longevity.
- Walmart Business Model Explained - How Does It Work?
Leading on Price
Competing on assortment, differentiating on access, providing a great shopping experience, money-back guarantee.
- Walmart's Operations
Procter & Gamble
Green dot corporation, plug power inc., primo water corporation, other partners, customer segments, customer relations, marketing strategy.
- Walmart's Marketing Mix
SWOT Analysis
Opportunities, question: how does walmart afford to have such low prices, question: what is the main business strategy that walmart relies on, question: why does walmart have so many customers.
- Walmart Business Model Explained - Bottom Line
Everyone knows Walmart, the famous US retailer, but few know its unbelievable history and steady growth. Walmart appeared in the ’60, and now operates a wide range of stores, including supermarkets, hypermarkets, neighborhood markets, department stores, grocery stores, and discount shops. Below, you’ll find Walmart’s business model explaine d in detail.
This will give you further insight into how this business developed and became successful nationwide. Walmart would be the world’s largest business if we considered annual revenue. Keep reading for the full Walmart business model explained.
- Walmart was launched in the ’60, and it quickly became one of the largest chain stores in the US;
- By 2022, the company became the most successful business in the world, with annual revenues of approximately $570 billion;
- Walmart is the world’s second-largest employer in the private sector, with around 2.2 million employees. Amazon occupies the first place;
- The company’s business model focuses on four important market segments: within the US, the international market, Sam’s Club, and the brand’s mobile app.
Walmart’s Business History
Let’s see how Walmart went from one store to a vast network of brick-and-mortar and online shops .
The first Walmart store was opened in 1962 in Rogers, Arkansas. Sam Walton, the founder, had a clear marketing strategy: providing the lowest prices on the market, anywhere, anytime. By 1967, Walmart had become a store chain with 24 physical locations. As a result, sales were rising, reaching nearly $13 million.
In 1970, Walmart’s national appeal spread more than ever before. The company had had incredible growth over its first decade of existence. Around this time, the business becomes publicly traded, with one share costing $16.50.
By 1975, Walmart had already been listed on the NYSE (New York Stock Exchange). Before opening its first pharmacy, in 1978, Walmart had over 50 stores and a whopping sales total of almost $80 million. The company established the Walmart Foundation in 1979.
The ’80s represented a decade of many new and exciting things for the business, including the opening of the original Walmart Supercenter. This store mixed general merchandise with supermarket items. The chain had 21,000 employees, 276 stores, and annual sales of $1 billion.
Another fantastic innovation that Walmart revealed was computerized point-of-sale systems. These revolutionized the process of grocery shopping while offering customers quick and accurate checkouts.
The Walton Family Foundation appeared in 1987, the same year in which Walmart linked the corporation’s communication systems and its operations through video, voice, and data, all combined. That’s possible due to the most extensive private satellite system ever seen in the US.
By 1990, Walmart becomes US’s number one retailer. The company’s strategy focuses more on boosting convenience and going international. The first international location was opened in Mexico City in 1991.
Sam Walton, the owner, died in 1992 at the age of 74. His son, Rob Walton, takes on the family’s business and responsibilities. In 1994, the first Canadian stores appeared, followed by an expansion into the Chinese market in 1996. The growth continues because Walmart acquired the UK-based Asda. By 2002, Walmart’s clients could do their shopping online.
After the company’s penetration into the Japanese market, its representatives state their commitment to environmental sustainability. They focused on three main aspects:
- Using renewable energy;
- Creating zero waste;
- Selling sustainable products.
In 2010, Walmart focused more on sustainable agriculture and innovating the retail environment. It did that by supporting local farmers and helping customers save money. The company celebrated 50 years of existence in 2012. By 2015, the retailer served over 200 million customers per week in 27 countries.
This famous store chain changed its legal name to Walmart Inc. in 2018, the same year Judith McKenna became CEO and President of the entire corporation. In 2019, the company launched its InHome Delivery service, and in 2022, it celebrated its 60th anniversary.
Walmart Business Model Explained – How Does It Work?
The company’s mission statement is about helping customers save money , enjoy highly convenient shopping sprees, and lead better lives. So, as you can see, Walmart’s business model is quite simple, very clear, and straightforward: offering the lowest prices on the market.
- Mission – helping people save a lot of money that they would’ve spent on groceries;
- Value proposition – offering a wide range of affordable products in a highly convenient manner;
- Selling channels – physical stores, their online shop, and mobile app.
Walmart’s Strategy Pillars
Walmart relies on five business pillars that support and create the company’s strategy.
Keeping prices as low as they can is the main focus at Walmart. The company’s managers want to ensure the products they sell are affordable and accessible to the whole population. The retailer made efforts to create the world’s largest supply and distribution chain to keep those prices low. That’s possible due to Walmart’s bulk purchases, which tremendously increase its negotiating power.
Sam’s Club, an important part of Walmart, relies on cross-docking to support its affordable prices. This redistribution system operates in an intelligent and organized manner. The products that arrive in the retailer’s warehouses are directly sent to the point of sale or clients. Cross-docking is the opposite of traditional stored goods.
Both these tactics are unique, offering Walmart substantial leverage that helps it differentiate from its main competitors.
Walmart’s business model enables the retailer to provide its customers with a wide range of products and services. Some are sourced from local producers, while others come from international suppliers. Further on, the company sells this wide variety of items across its physical stores and online shops.
This approach has helped Walmart create and develop a massive customer database.
The retailer has made numerous investments in its attempt to differentiate on access. It did that as a response to all the new and competitive strategies other businesses introduced over the years. Although most people still think about supermarkets or hypermarkets when they hear about Walmart, the company diversified its population access.
It did that through small stores where you can find fresh food. Then, there are the online shops and the retailer’s mobile app through which Walmart enhanced its online shopping experience. Clients can purchase their desired items from their mobile phones and then pick them up from the local physical store. Finally, Walmart is the only US-based retailer that owns medical clinics and pharmacy stores.
Both these health services are less accessible than food, so Walmart’s decision to tackle this need was an intelligent business move. Besides wellness products, this company provides preventive health care and regular checkups. If that’s not disruptive and innovative, I don’t know what is?!
Walmart knows that gaining new clients and retaining existing customers can be achieved through a flawless shopping experience. The retailer has recently announced that they will increase their staff’s hourly wage. It’s an attempt that hopefully will lead to a customer satisfaction boost. Moreover, they plan to train or retrain their employees to achieve high ROI* and make their clients happy.
ROI* – return on investment
Any Walmart client who finds the retailer’s services and products unsatisfactory will receive their money back due to the company’s money-back policy. Due to this approach, you can ensure you get the best and freshest veggies, fruits, and other high-quality items.
Walmart’s Operations
There are three market segments that Walmart covers:
- The United States – this is the largest Walmart market segment. It operates in all 50 US states as well as in Puerto Rico. This segment represented around 64% of the company’s net sales in 2018;
- Walmart International – the retailer operates in 27 countries all over the globe. These operations can be found in wholesale, retail, and more. This segment consists of supercenters, hypermarkets, eCommerce, supermarkets, cash & carry, and warehouse clubs;
- Sam’s Club – speaking of clubs, this is a membership-only segment in the form of a warehouse club. Subscribers will have access to consumables, fuel, groceries, electronics, grills, home items, toys, office furniture, pharmacy products, and more.
Then, there’s also the Walmart mobile app . You can download it on both iOS and Android devices. Once installed, you can browse through millions of products sold by Walmart whenever and wherever you are. The app makes your life easier as a Walmart client by saving time and effort.
Furthermore, with this software, you can create customized shopping lists, scan bar codes, check a product’s availability or price, and identify the aisle location of a specific item.
Key Partners
Walmart’s key partners are trustworthy worldwide suppliers. Of course, being a giant global retailer means Walmart has numerous suppliers. But, some of them are more important than others, out of those 100,000 partners worldwide. Walmart’s partners could be grouped into different categories: technology collaborators, solution partners, service suppliers, etc.
This consumer goods business has a long history, being founded in 1837. All Walmart stores sell P&G products. Moreover, the supplier hoped on board when Walmart required tagging based on radio frequency identification.
Through Green Dot and Walmart partnership, the retailer’s clients benefit from the MoneyCard program. In 2019, they launched a checking account called GoBank. Green Dot Corporation serves consumers needing prepaid debit cards.
When Walmart was looking for an innovative fuel like hydrogen cell technology, it found Plug Power Inc. These two companies teamed up in their joint effort to reduce operational costs, power usage, and emissions. The supplier’s primary revenue comes from collaborating with two large market players: Amazon and Walmart.
For instance, Walmart refined its technology approach and machine usage by fueling its warehouse forklifts with energy cells.
Everyone who knows a bit about the tech industry knows what a significant player HP is in this niche. The company was launched in 1939 and had three market segments: corporate investments, personal systems, and printing. Walmart organized the Home Entertainment Design Challenge, and HP won that contest. This supplier has helped the retailer by lowering its computer packaging impact on the surrounding environment.
The retailer gets its self-service water dispensers from this supplier. Primo Water also supplies other major businesses like Lowe and Home Depot. Primo’s headquarters are located in North Carolina, and its 2021 revenue reached $2.07 billion.
- Channel partners – Acenda, BuzzFeed, Channel Sale, Clearoute, Deposco, Fitbit, OpenCart, ShippingChimp, etc.;
- Technology partners – ChannelAdvisor, eHub, Magento, Owler, ShipEngine, WooCommerce, etc.
Financial Performance
Walmart’s two main revenue streams are retail sales and other services . First, the company gains a lot of money through product revenues and retail sales. These products are sold within the US and globally through their stores or local distributors.
Its financial performance is impressive, considering Walmart is one of the top Fortune 500 companies. In 2018, the company’s net sales were almost $500 billion . 64% came from the US market, while Walmart International added 24%. The lowest proportion came from Sam’s Club – only 12%. It’s safe to say that Walmart has a massive economic impact on the food retailing industry .
The company’s gross profit for this year (2023) is estimated at almost $150 billion , representing an increase of nearly 3% compared to the previous year. Walmart’s updated revenue will exceed $611 billion , an essential boost of 6.7% compared to 2022.
See also: Home Depot Business History .
Walmart has two main customer segments:
- Mass market;
- Low-income clients.
The company applies two types of market segmentation:
- Geographical segmentation – based on your location, Walmart will sell specific items. For instance, if you live in a hot area where it doesn’t snow, you won’t find snow shovels in any Walmart store;
- Demographic segmentation – once the location is established, the retailer groups its customers by age to effectively cater to the client’s needs. Teenagers have different needs than young adults or senior customers.
There are three main product categories that Walmart sells:
- Grocery items – foods such as snacks, dairy, beverages, and others;
- Health and wellness – medical and pharmaceutical products;
- General merchandise – home items, apparel, entertainment goods, and hardlines.
Due to its low prices, Walmart’s main clients are individuals who want good-quality yet low-cost items. Some are people with low incomes, while others are simply searching for optimal cost benefits. In short, the company’s target audience would be low to middle-class families who live predominantly in rural areas.
Moreover, these clients want a quick shopping experience, one that’s convenient. They are students, workers, or floor-level employees who seek the best cost advantage out there.
Most of the retailer’s customer services are automated and simplified. For example, clients can contact the company ‘s representatives via phone if they want to clarify something or offer a comment. Besides that, Walmart also offers a few other convenient contact ways through their mail address ( [email protected] ) and return policy.
Walmart’s marketing strategy relies on two pillars:
- A high-sales volume approach;
- Helping customers save money.
The retailer uses multiple advertising channels to promote its services, including outdoor billboards, TV commercials, online ads, and social media. It wants customers to see the brand as highly reputable and trustworthy.
Walmart’s Marketing Mix
- Pricing – everyday low prices by keeping costs as low as possible;
- Product – carefully selected products; high level of diversity; complementary goods; seasonal items;
- Promotion – based on the point of Sale and Point of Purchase. Besides commercials and ads, Walmart also invests in press releases and public relations;
- Placement – Walmart operates through over 150 distribution centers and its e-commerce store.
Future Plans
In the future, Walmart wants to do more than sell products. We expect a more diverse business model based on seamless omnichannel distribution. They plan to provide complementary products to create a one-stop shopping experience. Its delivery service will continue to be greener and greener, more sustainable , and more environmentally friendly .
Regarding the company’s advertising revenue, the staff plans to grow this income stream. They also stated the intention to raise employee wages. We should keep watching Walmart to see what other innovations and disruptions it may do.
Let’s look at what Walmart does best and some of the market challenges it has to overcome.
- Affordable products;
- Convenience;
- Highly trained staff;
- International presence;
- Advanced technology;
- Multiple sales channels, both offline and online;
- A wide range of available products.
- A couple of employee lawsuits;
- Having a business model that’s too simple;
- Poor brand reputation in some cases;
- A few situations of negative publicity;
- High employee turnover;
- Customer service that’s not good enough;
- Relying too much on the US market.
- Expansion possibilities;
- Higher profit margins;
- Automation tools development;
- eCommerce expansion;
- Better shopping experiences due to virtual reality;
- The constant growth estimates regarding the eCommerce market;
- Improving its human resources.
- More regulations regarding wages, food, safety, and work benefits;
- Fierce competition;
- Increasing costs of labor and raw materials;
- The risk of data breaches is rising;
- The risk of new lawsuits could damage Walmart’s brand reputation.
Main Competitors
- It’s the largest retailer worldwide;
- It’s better than Walmart at item inventories, streaming services, and handmade goods;
- Walmart is still better at selling fresh and affordable groceries.
- The international leader in the retail food market;
- Carrefour has lower revenues compared to Walmart;
- Walmart has more affordable items;
- Carrefour has a longer history of 55 years on the market;
- Walmart has stores in only 27 countries, whereas Carrefour is present in 33 countries.
- Walmart is more trusted than eBay because its Marketplace sellers are all verified and approved before they start selling;
- eBay also works as an online auction platform;
- The products featured on eBay are significantly higher than the ones marketed by Walmart.
- Wholesale company with membership discount warehouses;
- For higher prices, Costco provides premium goods and more opportunities;
- Walmart is more approachable, having more stores and a larger footprint.
- Markets only house improvement products, garden furniture, and building materials;
- In the home improvement niche, Home Depot is more profitable than Walmart.
- Very similar to Walmart in terms of products;
- Target is smaller than Walmart and operates only within the US.
Answer : They buy in bulk from their suppliers. Hence, they can negotiate lower prices. This leads to lower costs and further translates into more affordable goods.
Answer : A broad assortment of products sold at low prices every day, without exception. Also, one-stop shopping that’s highly convenient. These are Walmart’s strategy corner stones.
Answer : Clients love this retailer because they find everything they need in one place at affordable prices. So, it’s easy and convenient, without the need to visit multiple stores and waste time.
Walmart Business Model Explained – Bottom Line
Walmart is an excellent example of a massive globally-scaled success. It focused on a simple yet appealing mission right from the start. Moreover, it sticks to that same value proposition to this day. Do you want a wide range of decent-quality products that are affordable? Walmart is the place to go. It helps middle-class people save money without compromising the overall experience and customer satisfaction.
The retailer’s business model relies on building a long-lasting and strong brand, developing a large customer base, and offering low-cost products while boosting the company’s sales.
All images: Walmart.com
Other useful reads:
- Walmart value chain analysis
- Insurance Value Chain Explained
- Transnational Strategy Explained
- Target Competitors Analysis: 5 Major Competitors
- Home Depot Competitors Analysis: 6 of Its Biggest Competitors .
Resources :
- https://fourweekmba.com/walmart-business-model/
- https://businessmodelanalyst.com/walmart-business-model/
- https://thestrategystory.com/2022/12/01/how-does-walmart-make-money-business-model-supply-chain-strategy/
- https://www.marketing91.com/business-model-of-walmart/
- https://www.nbcnews.com/business/business-news/walmart-raise-hourly-wage-how-much-and-where-rcna67213
- https://www.reuters.com/article/us-walmart-services-idUSKCN1PB2K9
- https://www.retaildive.com/news/walmart-connect-ad-network-partnerships/628690/
- https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev-resource-111820-032827
- https://www.nytimes.com/2022/11/15/business/walmart-inflation-sales-profit.html
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/shelleykohan/2022/02/17/walmart-sets-its-sights-on-more-than-just-selling-stuff/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/walterloeb/2021/02/19/walmart-reports-2020-results-and-plans-for-future-growth/
- Latest Posts

- Tesco Business Model Explained – What Makes It Successful? - August 2, 2023
- Tesco SWOT Analysis – The Retailer’s Weaknesses and Threats - August 2, 2023
- Costco vs. Walmart Business Model Comparison – The Retailers’ Marketing Strategy, Customer Segments & More - August 2, 2023

Walmart Business Model and How it Makes Money
Walmart is a household name in the USA and many other parts of the world. Well-known for its retail store chain, Walmart is the world’s leading retail corporation. Its main competitors, such as Tesco, Kroger, Costco, Alibaba don’t even come close to its popularity and business. One of the reasons why Walmart is so successful in its operations is its focus on low-cost products that provide value.
For an even better analysis of why Walmart is successful and generates billions in revenues each year, it is critical to look at its business model. The business model of a company shows the markets it operates in and how it generates revenues. For Walmart, the business model is not as simple as the company has an international presence and business ventures in multiple markets.
Walmart’s Business Model
Walmart’s business model consists of the products it sells. Similarly, it includes its strategies used in generating revenues. As mentioned, Walmart focuses on low-priced goods but generates its revenues by depending on a higher volume of sales. However, its business model is more complicated than just defining its sales strategy.
Walmart’s Products
The primary source of revenue for Walmart comes from the wide range of products that it sells in its stores. While it is impossible to list every product that Walmart sells, some of the popular categories in which it sells products include the following.
- Auto-related suppliers.
- Craft suppliers.
- Electronics.
- Health and beauty.
- Home décor and furniture.
- Pet supplies.
- Sporting and fitness goods.
However, Walmart also offers products in the services industry. While it is well-known for its retail shops in the industry, the services that it provides also generates income for the company. Some of the services rendered by the company include the following.
- Financial services.
- Clinical and health services.
- Movie streaming services.
Apart from its products and services, Walmart’s business model also contains all its segments in various countries.
Walmart’s Segments
There are three primary segments of Walmart based on geographical location.
Walmart USA
Walmart USA is the company’s largest segment and also its oldest. The company has stores in 50 stores across the USA. This segment mainly consists of the stores that the company operates, such as supercenters, discount stores, and other small stores. It also contains other services such as money orders, prepaid cards, wire transfers, and bill payments, which fall under financial services.
Walmart also operates a website that caters to the needs of customers in this segment. Through it, the company gives customers access to merchandise and other services. It also has a feature where customers can interact with physical stores through the website.
Walmart International
Besides the USA, Walmart also operates in 27 other companies where it has stores. In some of these countries, Walmart operates under the same brand while in others, it functions through its various subsidiaries and joint ventures under a different brand. Overall, it has 156 distribution facilities in these countries that provide physical access to its customers.
Named after Walmart’s founder, Sam Walton, Sam’s club is the final segment of Walmart’s business model. This segment consists of membership-only warehouse clubs in 44 states in the USA. It provides a subscription service to both individual customers and business owners. Similar to its other segments, the company also allows digital access to customers.
Walmart’s Revenues
Walmart generated net sales of $519.92 billion in revenues, which was an increase of approximately 2% from the $510.33 billion net sales it generated in 2019. It also earns from other sources, but there hasn’t been a significant change in it. Here’s a breakup of the total revenues generated in both years classified by segment.
From the above breakup, it is apparent that Walmart US is the company’s largest earner making almost 66% and 65% of its net sales in 2020 and 2019 respectively. After Walmart US, Walmart International is the second-highest earner for the company, with 23% and 24% of the overall net sales in both years respectively. Lastly, any remaining net sales come from its Sam’s Club segment.
The net sales of the company consist of all sales revenues, net of sales tax, and estimated sales returns, at the time it sells merchandise or services to its customers. The company calculates its estimated sales returns based on expected returns. It also includes eCommerce sales, including shipping revenue, and recorded when it delivers goods to customers.
Apart from its net sales, the company also generates revenues from membership fees. These fees include revenues from both the US and the international segment. For 2020, the revenue generated from membership fees was $1.5 billion, while for 2019, it was $1.4 billion. Walmart Plus membership is the primary source of income in this category.
The other sources of revenues that Walmart generates comes are gift cards and financial and other services. Gift cards are common in the US and some other countries and do not have an expiration date. Customers can buy these and gift them to others. However, these are not a big part of Walmart’s sales.
Similarly, its financial and other services mainly include revenues from its MoneyCard service. These revenues are not a part of its other income but included in net sales for each segment.
Walmart’s Business Model Strategies
There are a few strategies that power Walmart’s business model. Based on these strategies, the company has become the world’s largest retailer and continues to attract customers in various countries. Some of these strategies are as below.
Lead on Price
The first strategy used by Walmart is ‘Lead on price’. With this strategy, the company maintains low prices so everyone can afford its products. This strategy has worked wonders for the company over the years. It has been one of the prominent factors in its success. While this strategy may sound unfruitful, it helps the company generate high volumes of sales, which make up for the low prices of its products.
Invest to Differentiate on Access
The second strategy used by Walmart is the ‘Invest to differentiate on access’ strategy. Through this strategy, the company increases its retail shops giving customers access to a new location. Similarly, the company is investing in digital marketing and retail. It is to keep up with the technology changes, which can bring in new customers. Likewise, Walmart is also investing in services that are relatively difficult to access through this strategy.
Be Competitive on the assortment
The next strategy that helps the company generate revenues and in its business model is the ‘Be competitive on assortment’ strategy. Walmart promotes the assortment of products and large varieties of items across its physical stores and digital portals. It also customizes its products according to the geographical location in some cases. It helps the company attract the maximum number of customers.
Deliver a Great Experience
Furthermore, the company uses a ‘Deliver a great experience’ strategy that focuses on the customer experience. It is one of the main focuses of Walmart’s business model. The company is the world’s largest employer in the private sector, with 2.2 million employees. To focus on its customer care and relations, the company focuses on its employees to achieve the best results.
Money-Back Guarantee
Lastly, the company also offers customers a “Money-back guarantee”, which is a part of its strategy. Through this strategy, the company achieves maximum customer satisfaction and attracts the most customers in its given locations.
Walmart is the world’s largest retail company that has a significant competitive advantage over others. The company’s success lies in its business model. Walmart’s business model consists of its products, which include both physical products and services. Similarly, it has three segments from which it earns money. Walmart generates revenues from these products and services from its different market segments. Likewise, the company uses strategies that help in its business model.
Related Posts
Business model canvas: a great tools for an innovative business model design, dropshipping business model and how it works, subscription business model and how it works.

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
Walmart: Business Model, SWOT Analysis, and Competitors 2023
Inside This Article
In this blog article, we will delve into the business model of Walmart, one of the largest retail corporations in the world. With a focus on providing affordable products to customers, Walmart has built a reputation for its low prices and wide range of offerings. We will also conduct a SWOT analysis to examine the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Additionally, we will explore the competitive landscape of Walmart, highlighting its key rivals in the retail industry as we look ahead to the year 2023.
What You Will Learn:
- Who owns Walmart and the background of its ownership structure
- Walmart's mission statement and how it guides the company's operations
- The various ways in which Walmart generates revenue and sustains profitability
- An explanation of the Walmart Business Model Canvas and how it applies to the company's success
- Insight into Walmart's competitors and the challenges they pose
- A comprehensive SWOT analysis of Walmart, highlighting its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Who owns Walmart?
The walton family: a legacy of ownership.
When it comes to the question of who owns Walmart, the answer lies in the hands of one of the wealthiest families in the world - the Walton family. Walmart was founded by Sam Walton in 1962, and since then, it has grown into the largest retailer in the world. Sam Walton's vision and entrepreneurial spirit laid the foundation for the success of the company, and his family has continued to play a significant role in its ownership and management.
The Walton family's ownership of Walmart can be traced back to Sam Walton's descendants. After Sam Walton's passing in 1992, his fortune was divided among his immediate family members, primarily his wife, children, and grandchildren. Today, the Walton family collectively owns a majority stake in Walmart, with individual family members holding significant shares in the company.

The Walton Family's Influence on Walmart
The Walton family's influence on Walmart extends beyond their ownership stake. They have been actively involved in the company's management and decision-making processes. The family members have served on Walmart's board of directors and have held key executive positions. Their deep understanding of the company's values and principles has shaped Walmart's culture and business strategies over the years.
Moreover, the Walton family has played a crucial role in shaping Walmart's philanthropic initiatives. They have established the Walton Family Foundation, which focuses on supporting education, environmental conservation, and other charitable causes. Through their foundation, the family has made significant contributions to various communities and organizations around the world.
The Power of Family Ownership
The ownership of Walmart by the Walton family highlights the power of family ownership in shaping the destiny of a company. Their long-term perspective and commitment to the company's growth have been instrumental in Walmart's success. Unlike publicly traded corporations that are subject to the interests of various shareholders, family-owned businesses can often maintain a stronger sense of purpose and continuity.
The Walton family's ownership of Walmart has not been without criticism, with concerns raised about income inequality and the impact on small businesses. However, it is undeniable that their ownership has played a pivotal role in Walmart's rise to dominance in the retail industry.
In conclusion, the question of who owns Walmart is answered by the Walton family, who collectively own a majority stake in the company. Their ownership has been accompanied by a deep involvement in the management and decision-making processes, as well as a commitment to philanthropy. The Walton family's ownership exemplifies the power of family ownership in driving the success and shaping the future of a company.
What is the mission statement of Walmart?
Understanding walmart's mission statement.
Walmart, being one of the largest multinational retail corporations, has a clear and concise mission statement that guides its operations and strategies. The mission statement of Walmart can be summarized as follows: "We save people money so they can live better."
This mission statement emphasizes Walmart's commitment to providing affordable products and services to its customers. By offering low prices, Walmart aims to improve the quality of life for its customers, enabling them to live better within their means. Walmart strives to enhance the financial well-being of its customers by helping them stretch their budgets further.
Core Values supporting the Mission Statement
To achieve its mission, Walmart adheres to a set of core values that align with its overall purpose. These values include:
Customer Focus : Walmart places its customers at the center of everything it does. By understanding their needs and exceeding their expectations, Walmart builds long-term relationships with its customers.
Respect for Individuals : Walmart values diversity and treats every individual with respect and dignity. It encourages an inclusive and supportive work environment for its associates, fostering a sense of belonging and teamwork.
Strive for Excellence : Walmart is committed to continuous improvement and excellence in all aspects of its operations. It aims to be the best retailer by consistently delivering exceptional value, quality, and service to its customers.
Act with Integrity : Walmart conducts its business with the highest level of integrity and ethics. It follows all applicable laws and regulations, ensuring transparency and accountability in its operations.
Embrace Change : Walmart embraces change and innovation to stay ahead in the ever-evolving retail industry. It actively seeks new ideas, technologies, and strategies to enhance the shopping experience and drive business growth.
Impact on Walmart's Business Strategy
Walmart's mission statement serves as a guiding principle for its business strategy. The company focuses on three key strategic priorities to fulfill its mission:
Everyday Low Prices : Walmart's commitment to saving people money is evident through its "Everyday Low Prices" strategy. By leveraging its vast scale and efficient supply chain, Walmart strives to offer the lowest prices on a wide range of products, ensuring affordability for its customers.
Customer Experience : To help people live better, Walmart places significant emphasis on enhancing the overall customer experience. This includes improving store layouts, increasing product variety, and investing in online platforms to provide convenience and accessibility to customers.
Community Engagement : Walmart recognizes the importance of giving back to the communities it serves. Through various charitable initiatives, grants, and volunteer programs, Walmart actively contributes to the well-being and development of local communities, aligning with its mission to help people live better.
In conclusion, Walmart's mission statement reflects its commitment to saving people money and improving their lives. It highlights the core values of customer focus, respect for individuals, excellence, integrity, and embracing change. By aligning its business strategy with this mission, Walmart continues to be a leading global retailer, dedicated to serving its customers and communities.
How does Walmart make money?
Retail sales.
The primary source of revenue for Walmart is through its retail sales. As the largest retailer in the world, Walmart generates a significant portion of its income through the sale of a wide variety of products across multiple categories. From groceries and household goods to electronics and apparel, Walmart offers an extensive range of merchandise to cater to the diverse needs of its customers. By leveraging its massive network of stores and e-commerce platforms, Walmart is able to attract millions of shoppers, both in-store and online, resulting in substantial sales volume and revenue.
Walmart's Store Format
Walmart operates under different store formats, which contribute to its revenue generation. The company operates Walmart Supercenters, which combine a grocery store and general merchandise under one roof. These Supercenters offer convenience to customers by providing a one-stop shopping experience. Additionally, Walmart operates smaller-format stores such as Walmart Neighborhood Market, which focuses primarily on groceries and serves local communities. Each store format has its own revenue stream, further diversifying Walmart's income.
E-commerce and Online Sales
In recent years, Walmart has placed a strong emphasis on expanding its e-commerce presence to adapt to the changing retail landscape. Through its online platform, Walmart.com, the company has witnessed significant growth in online sales. Customers can purchase products from various categories, including electronics, home goods, clothing, and more, without having to visit a physical store. Walmart's e-commerce strategy also includes offering same-day delivery, curbside pickup, and other convenient options, further enhancing the shopping experience for its online customers. E-commerce sales contribute to Walmart's overall revenue and help the company remain competitive in the digital era.
Membership Programs
Walmart offers membership programs such as Walmart+, which provide additional benefits to customers in exchange for a subscription fee. Walmart+ members enjoy perks like unlimited free delivery, fuel discounts, and access to exclusive deals. By offering these membership programs, Walmart not only generates additional revenue but also fosters customer loyalty. The recurring subscription fees contribute to the company's overall financial success.
Advertising and Partnerships
Another way Walmart generates revenue is through advertising and partnerships. Walmart has a vast network of suppliers and brands that pay for advertising space within its stores and on its website. These partnerships allow suppliers to showcase their products and reach a wide customer base. Additionally, Walmart offers sponsored product placements, both online and in-store, enabling brands to increase their visibility and drive sales. Advertising and partnerships provide an additional revenue stream for Walmart while benefiting its suppliers and enhancing the overall shopping experience for customers.
In conclusion, Walmart's revenue primarily comes from its retail sales, encompassing various store formats, including Supercenters and smaller-format stores. The company's e-commerce platform, membership programs, and strategic partnerships also contribute significantly to its financial success. By diversifying its income sources and adapting to changing consumer preferences, Walmart continues to thrive as one of the world's leading retailers.
Walmart Business Model Canvas Explained
Introduction to the walmart business model canvas.
The Walmart Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that provides a comprehensive overview of how Walmart creates, delivers, and captures value. Developed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, the Business Model Canvas helps organizations understand their business model and identify potential areas for improvement and innovation.
Key Elements of the Walmart Business Model Canvas
Customer segments.
Walmart caters to a wide range of customer segments, including individuals and families seeking affordable everyday products, small businesses looking for bulk purchases, and online shoppers seeking convenience and competitive prices. By targeting multiple customer segments, Walmart ensures a diverse customer base and maximizes its market reach.
Value Proposition
Walmart's value proposition lies in its ability to offer "Everyday Low Prices" on a wide range of products. By leveraging its massive scale and strong supplier relationships, Walmart is able to negotiate lower prices and pass on the savings to its customers. In addition to affordability, Walmart also focuses on convenience, providing a one-stop shopping experience with a vast selection of products under one roof.
Walmart operates through a multi-channel approach, combining brick-and-mortar stores, e-commerce platforms, and a strong presence in the grocery sector with its Walmart Supercenter and Neighborhood Market formats. This omni-channel strategy allows Walmart to reach customers through various touchpoints and cater to their diverse shopping preferences.
Customer Relationships
Walmart builds customer relationships by providing a seamless shopping experience. With its focus on low prices and convenience, Walmart aims to establish long-term relationships with its customers, encouraging repeat purchases and building customer loyalty. Additionally, Walmart invests in customer service initiatives to address any issues or concerns promptly.
Revenue Streams
Walmart generates revenue primarily through the sale of products across its various retail formats. In addition, the company also offers financial services, such as money transfers, check cashing, and prepaid cards, generating additional revenue streams. Walmart also earns revenue through advertising and partnerships with suppliers and brands, allowing them to promote their products within Walmart stores.
Key Activities
Walmart's key activities include sourcing and procurement, inventory management, retail operations, and supply chain management. The company focuses on efficient logistics and distribution networks to ensure products are readily available and delivered to stores in a timely manner. Walmart also invests heavily in technology and data analytics to optimize its operations and improve customer experience.
Key Resources
Walmart's key resources include its extensive network of physical stores, strong supplier relationships, advanced IT infrastructure, and a highly efficient supply chain. These resources enable Walmart to maintain a competitive advantage by offering low prices, ensuring product availability, and delivering a seamless shopping experience.
Key Partnerships
Walmart collaborates with a wide range of partners to enhance its business model. This includes suppliers and manufacturers, logistics and transportation providers, technology companies, and financial institutions. By building strategic partnerships, Walmart strengthens its supply chain, improves operational efficiency, and expands its product offerings.
Cost Structure
Walmart's cost structure is focused on achieving operational efficiency and maintaining low prices. The company leverages its scale and bargaining power to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, reducing procurement costs. Walmart also invests in technology and automation to streamline operations and minimize labor costs.
The Walmart Business Model Canvas provides a holistic view of how Walmart operates and creates value for its customers. By understanding the key elements of Walmart's business model, it becomes evident why the company has been able to achieve long-term success and become a dominant player in the retail industry. The Business Model Canvas serves as a valuable tool for analyzing and optimizing business models, enabling organizations to identify areas for improvement and innovation.
Which companies are the competitors of Walmart?
Overview of walmart's competitors.
Walmart, being one of the largest retail corporations in the world, faces competition from various companies across different sectors. These competitors vary in terms of their business models, target markets, and product offerings. Here are some notable companies that compete with Walmart:
Target is one of the most prominent competitors of Walmart, particularly in the United States. Similar to Walmart, Target operates as a general merchandise retailer, offering a wide range of products, including clothing, electronics, home goods, and groceries. Both companies strive to provide customers with affordable prices and convenient shopping experiences. However, Target differentiates itself by focusing on a more upscale and trendy image, catering to a slightly different demographic than Walmart.
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, poses a significant threat to Walmart's dominance. With its vast online marketplace and efficient delivery services, Amazon has transformed the retail industry. The company offers an extensive range of products, including groceries through its acquisition of Whole Foods Market. While Walmart is also expanding its e-commerce operations, Amazon's dominance in the online retail space continues to challenge Walmart's market share.
3. Costco Wholesale
Costco Wholesale is a membership-based warehouse retailer that competes with Walmart's Sam's Club division. Both companies offer bulk purchases at discounted prices, targeting price-conscious consumers and small businesses. While Walmart operates numerous stores across the country, Costco focuses on a smaller number of large-scale warehouse locations. Costco's loyal customer base and reputation for quality products pose a competitive threat to Walmart's membership-based retail business.
Kroger is one of the largest supermarket chains in the United States, specializing in groceries and related products. While Walmart offers groceries in its stores, Kroger focuses solely on this sector and has a strong presence in local communities. Kroger differentiates itself by providing a wide range of fresh produce, organic options, and specialty products. Walmart's expansion into the grocery market has intensified the competition between the two companies, particularly in terms of pricing and product selection.
5. Best Buy
Best Buy, a leading electronics retailer, competes with Walmart in the consumer electronics market. While Walmart offers a wide variety of electronics alongside other products, Best Buy specializes in this sector, providing customers with a more extensive selection and knowledgeable staff. Best Buy's focus on customer service and expertise in the electronics industry gives it a competitive advantage over Walmart in this specific market segment.
While Walmart remains a formidable force in the retail industry, these competitors present ongoing challenges and opportunities for the company. Target, Amazon, Costco Wholesale, Kroger, and Best Buy are just a few examples of the companies that directly compete with Walmart, each offering unique strengths and strategies to attract customers. As the retail landscape continues to evolve, it will be intriguing to see how Walmart adapts and competes with these rivals to maintain its market position.
Walmart SWOT Analysis
Strong brand recognition: Walmart is one of the most well-known retail brands globally. Its logo, store layout, and marketing efforts have created a strong brand image and customer loyalty.
Wide product assortment: Walmart offers a wide range of products, including groceries, electronics, clothing, home goods, and more. Its vast assortment appeals to a broad customer base and allows for one-stop shopping convenience.
Economies of scale: Walmart's massive size and global presence provide it with significant economies of scale. By purchasing large quantities of products, Walmart can negotiate lower prices from suppliers, giving it a competitive advantage in terms of pricing.
Efficient supply chain: Walmart has invested heavily in developing an efficient supply chain system. Through advanced logistics and inventory management, the company ensures that products are delivered to stores in a timely manner, reducing stockouts and improving customer satisfaction.
Negative public perception: Walmart has faced criticism for its labor practices, treatment of employees, and impact on local businesses. These controversies have negatively affected its reputation and may deter some socially conscious consumers from supporting the brand.
Limited international success: While Walmart has a strong presence in the United States, its international operations have not been as successful. The company has struggled to adapt to local preferences and faced challenges in some markets, limiting its growth potential outside of the US.
Reliance on physical stores: Despite its efforts to expand its online presence, Walmart still heavily relies on its brick-and-mortar stores. This dependence on physical locations can be a weakness in an era where e-commerce is rapidly growing.
Opportunities
E-commerce growth: Walmart has made significant investments in its e-commerce capabilities, including the acquisition of online retailers like Jet.com and Flipkart. As more consumers shift towards online shopping, Walmart has an opportunity to capitalize on this trend and expand its online presence.
International expansion: Although Walmart has faced challenges in certain international markets, it still has room for growth in untapped regions. By adapting its strategy to local preferences and investing in local partnerships, Walmart can successfully expand its global footprint.
Sustainability initiatives: With increasing consumer demand for sustainable products and practices, Walmart has the opportunity to enhance its sustainability efforts. By offering more eco-friendly products, reducing its carbon footprint, and supporting responsible sourcing, Walmart can attract environmentally conscious consumers.
Intense competition: Walmart operates in a highly competitive retail industry. It faces competition from traditional retailers, e-commerce giants like Amazon, and discount stores. Intense competition can erode market share and put pressure on pricing and profitability.
Changing consumer preferences: Consumer preferences and shopping behaviors are constantly evolving. If Walmart fails to adapt to these changes, it risks losing customers to competitors that better cater to shifting needs, such as online convenience, personalized experiences, or sustainable options.
Economic fluctuations: Walmart's performance is closely tied to the overall health of the economy. During economic downturns, consumers may reduce discretionary spending, impacting Walmart's sales and profitability. Additionally, inflation, rising labor costs, or fluctuations in exchange rates can also pose challenges for the company.
In conclusion, Walmart has several strengths, including its strong brand recognition, wide product assortment, economies of scale, and efficient supply chain. However, it also faces weaknesses such as negative public perception and limited international success. By capitalizing on opportunities like e-commerce growth, international expansion, and sustainability initiatives, while mitigating threats such as intense competition, changing consumer preferences, and economic fluctuations, Walmart can navigate the dynamic retail landscape and maintain its position as a market leader.
Key Takeaways
- Walmart is owned by its shareholders, with the Walton family being the largest individual shareholders.
- The mission statement of Walmart is to save people money so they can live better.
- Walmart makes money primarily through its retail operations, selling a wide range of products at low prices.
- The Walmart Business Model Canvas highlights key elements such as customer segments, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, and key partnerships.
- Some of the main competitors of Walmart include Amazon, Target, Costco, and Kroger.
- In terms of SWOT analysis, Walmart's strengths include its scale and market dominance, while its weaknesses include labor-related controversies. Opportunities for Walmart include e-commerce growth, while threats include competition and changing consumer preferences.
In conclusion, Walmart is a multinational retail corporation that has gained immense success and recognition over the years. As for who owns Walmart, it is mainly owned by the Walton family, with a significant percentage of shares held by other shareholders.
The mission statement of Walmart is to save people money so they can live better. This mission statement drives the company's focus on providing affordable products and services to its customers.
Walmart makes money through various revenue streams, including the sale of merchandise, groceries, and pharmaceutical products. Additionally, the company generates income through its membership program, advertising, and financial services.
By examining the Walmart Business Model Canvas, we can see how the company utilizes key resources, activities, and partnerships to create value and generate revenue. Through its extensive supply chain, efficient distribution network, and strategic partnerships, Walmart is able to offer its products at competitive prices and maintain its market leadership.
When it comes to competition, Walmart faces numerous competitors in the retail industry. Some of its main rivals include Target, Costco, Amazon, and Kroger. These companies constantly strive to gain market share and compete with Walmart in terms of pricing, product offerings, and customer experience.
Lastly, conducting a SWOT analysis on Walmart reveals the company's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Walmart's strengths lie in its extensive global presence, economies of scale, and strong brand image. However, weaknesses such as labor issues and negative public perception pose challenges. Opportunities for Walmart include expanding into e-commerce and international markets, while threats include intense competition and changing consumer preferences.
Overall, Walmart's success can be attributed to its commitment to its mission statement, innovative business model, and ability to adapt to evolving consumer needs. As the retail industry continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how Walmart continues to position itself and maintain its market dominance.
What is Walmart's SWOT analysis?
- Strong brand image and global presence: Walmart is one of the largest retail companies in the world, with a strong brand reputation and a presence in multiple countries.
- High economies of scale: Walmart's large size allows it to negotiate lower prices with suppliers and gain cost advantages over competitors.
- Extensive product assortment: Walmart offers a wide range of products across various categories, providing customers with a one-stop shopping experience.
- Efficient supply chain management: Walmart has a sophisticated supply chain system that enables it to minimize costs, reduce inventory levels, and deliver products efficiently.
- Strong financial performance: The company consistently generates high revenue and profits, which allows it to invest in growth initiatives and withstand economic downturns.
Weaknesses:
- Negative public perception: Walmart has faced criticism for its labor practices, treatment of employees, and impact on local communities, leading to a negative public image in some cases.
- Employee turnover and labor lawsuits: The company has been involved in various labor-related lawsuits and has high employee turnover rates, which can impact productivity and customer service.
- Limited online presence: Walmart has been relatively slow in adapting to the e-commerce space, which has resulted in a weaker online presence compared to some competitors.
- Dependence on China for sourcing: A significant portion of Walmart's products are sourced from China, which exposes the company to risks related to trade tensions, supply chain disruptions, and rising labor costs.
Opportunities:
- E-commerce growth: Walmart has the opportunity to further develop its online platform and grow its e-commerce business to compete with companies like Amazon.
- Expansion into emerging markets: The company can expand its operations into emerging markets, where there is potential for growth and less competition.
- Sustainability and ethical practices: Walmart can improve its sustainability initiatives and focus on ethical sourcing to meet increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly and socially responsible products.
- Health and wellness trends: Walmart can capitalize on the growing health and wellness industry by expanding its offering of organic, natural, and healthier products.
- Intense competition: Walmart faces intense competition from various retailers, both offline and online, which puts pressure on pricing and market share.
- Changing consumer preferences: Shifts in consumer preferences, such as increased demand for e-commerce and online shopping, can impact Walmart's traditional retail business.
- Economic factors: Economic downturns, inflation, and changes in consumer spending patterns can negatively affect Walmart's sales and profitability.
- Regulatory challenges: Walmart operates in multiple countries and is subject to various regulations, including labor laws, trade policies, and taxation, which can pose challenges and impact its operations.
What are 3 weaknesses of Walmart?
Labor practices: Walmart has faced criticism for its labor practices, including low wages, inadequate benefits, and poor working conditions. This has led to various lawsuits and protests from employees and labor rights organizations.
Negative impact on local economies: Walmart's entry into new markets often results in the closure of smaller, locally-owned businesses. Critics argue that this leads to a loss of jobs, reduced competition, and a decline in the overall economic health of communities.
Environmental concerns: Walmart has been accused of being a major contributor to environmental issues, such as excessive waste, pollution, and unsustainable sourcing practices. Despite some efforts to improve sustainability, the company still faces criticism for not doing enough to mitigate its environmental impact.
What are the threats to Walmart SWOT analysis?
Some of the threats to Walmart in a SWOT analysis include:
Intense competition: Walmart faces competition from various retailers, both brick-and-mortar and online, which can affect its market share and profitability.
Increased online shopping: The rise of e-commerce has made it easier for customers to shop online, which can result in reduced foot traffic in Walmart stores.
Economic factors: Economic downturns and fluctuations in consumer spending can impact Walmart's sales and revenue.
Negative public perception: Walmart has faced criticism in the past for its labor practices and impact on local communities, which can harm its reputation and brand image.
Regulatory challenges: Changes in regulations, such as labor laws or environmental regulations, can increase compliance costs for Walmart and impact its operations.
Supplier relationships: Walmart heavily relies on its suppliers, and any disruptions in the supply chain or conflicts with suppliers can affect its ability to offer products at competitive prices.
Global expansion challenges: Walmart operates in various countries, and political, social, and cultural factors can pose challenges to its international expansion efforts.
Cybersecurity threats: As a large retailer, Walmart is at risk of cyberattacks and data breaches, which can compromise customer information and damage its reputation.
Changing consumer preferences: Shifts in consumer trends and preferences, such as increased demand for sustainable and ethically sourced products, may require Walmart to adapt its offerings and strategies.
COVID-19 pandemic: The ongoing pandemic has affected the retail industry significantly, with lockdowns, supply chain disruptions, and reduced consumer spending impacting Walmart's operations and financial performance.
What are the weaknesses of Walmart business?
Some of the weaknesses of Walmart's business include:
Negative public perception: Walmart has faced criticism for its treatment of employees, including low wages and limited benefits. The company has also been accused of driving small businesses out of business and negatively impacting local communities.
Labor disputes and lawsuits: Walmart has faced numerous labor disputes and lawsuits related to issues such as wage theft, discrimination, and unfair labor practices. These incidents have led to damage to the company's reputation and financial losses.
Dependence on overseas manufacturing: A significant portion of Walmart's products are manufactured overseas, particularly in countries with low labor costs. This dependence exposes the company to risks such as supply chain disruptions, political instability, and changes in trade policies.
Competition from e-commerce giants: With the rise of online shopping, Walmart faces intense competition from e-commerce giants like Amazon. Despite efforts to expand its online presence, Walmart's e-commerce business still lags behind its competitors in terms of market share.
Inability to penetrate certain markets: Walmart has faced challenges in entering and succeeding in certain international markets, such as Germany and South Korea. Cultural differences, regulatory hurdles, and local competition have hindered the company's growth in these markets.
Environmental impact: As one of the largest retailers in the world, Walmart's operations have a significant environmental footprint. The company has been criticized for its carbon emissions, waste generation, and unsustainable sourcing practices. These concerns can impact its reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
Vulnerability to economic downturns: Walmart's business model heavily relies on offering low prices to attract customers. During economic downturns, consumers may reduce their spending and opt for even cheaper alternatives, which can impact Walmart's sales and profitability.
Large size and bureaucracy: Walmart's vast size and bureaucratic structure can make decision-making slow and hinder the company's ability to adapt to changing market conditions. This can result in missed opportunities and an inability to respond quickly to competitive threats.
It's important to note that while Walmart has these weaknesses, it also has numerous strengths that have contributed to its success as one of the largest retailers in the world.
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade

How Walmart Makes Money? – Understanding Walmart Business Model
Walmart is one of the largest retail corporations in the world, with a presence in 27 countries and a revenue of over $500 billion in 2021. Its business model has been successful in bringing value to customers and generating profits for shareholders. In this article, we will explore the Walmart business model and how it makes money.
Walmart Business Segments

Walmart operates through three primary business segments:
- Walmart U.S.: This segment includes the company’s retail operations in the United States, which includes both physical stores and e-commerce. It offers a wide range of products, including groceries, electronics, apparel, and home goods.
- Walmart International: This segment includes the company’s retail operations in markets outside of the United States. Walmart International operates in 27 countries, including Mexico, Canada, the United Kingdom, Japan, and India. The company’s international operations also include e-commerce platforms and financial services.
- Sam’s Club: This segment includes the company’s membership warehouse clubs, which offer bulk goods at low prices to businesses and individual customers. Sam’s Club operates in the United States and Puerto Rico and offers a range of products, including groceries, electronics, and office supplies.
In addition to these primary business segments, Walmart also operates other businesses, including financial services, health and wellness services, and e-commerce platforms. These businesses are part of Walmart’s strategy to diversify its revenue streams and provide customers with a wide range of products and services.
Revenues By Business Segment FY 2020-2022
*Net sales in billion U.S. dollars
Total Revenue in 2022
Walmart reported an annual revenue of $572.754B for 2022, which is a 2.43% increase from the previous year.
For the quarter ending October 31, 2022, the company reported revenue of $152.813B, representing an 8.74% increase year-over-year.
Over the twelve months ending October 31, 2022, Walmart’s revenue increased by 4.92% to reach $600.112B.
This growth is indicative of the company’s continued success in meeting the needs of its customers and providing them with products and services at competitive prices. As Walmart continues to invest in its business segments, expand its e-commerce capabilities, and enhance its in-store experience, it is poised for continued growth and success in the years to come.

Low-Cost Leadership
One of Walmart’s key strategies is its focus on low-cost leadership . The company achieves this by sourcing products directly from manufacturers, reducing supply chain costs, and utilizing advanced inventory management techniques. Walmart also focuses on reducing labor costs by using technology and automation, resulting in lower prices for customers.
Diversified Revenue Streams
Walmart’s revenue streams are diversified, with the company generating income from several sources. In addition to its retail operations, Walmart has a significant presence in the e-commerce industry, with its online marketplace Walmart.com. The company also offers financial services, such as Walmart Pay and Walmart MoneyCard, as well as health and wellness services.
Private Label Brands
Private label brands are another essential part of its business model. The company has a wide range of private-label products that are often sold at a lower price than name-brand equivalents. Walmart’s private label brands include Great Value, Equate, and Sam’s Choice, among others. These products account for a significant portion of Walmart’s revenue and contribute to the company’s low-cost leadership strategy.
Supply Chain Management
It’s supply chain management is another critical element of its business model. The company’s distribution centers and transportation network are optimized to ensure products are delivered quickly and efficiently to stores. Walmart also utilizes cross-docking, a logistics technique that minimizes the time products spend in the distribution center, reducing costs and improving inventory management.
Walmart’s Four Strategic Pillars

In 2017, Walmart introduced four strategic pillars that would guide the company’s growth and success in the coming years. These four pillars are Lead on Price, Invest to differentiate on access, Be competitive on assortment, and Deliver a great experience. Each of these pillars is designed to address different aspects of Walmart’s business and improve the company’s overall performance.
Lead on Price
This strategic pillar is based on Walmart’s long-standing commitment to providing customers with low prices. The company aims to be the lowest-priced retailer in the market by investing in its supply chain and operational efficiency to reduce costs. Walmart also works directly with manufacturers to negotiate lower prices and offers a price matching policy to ensure customers get the best deal.
Invest to differentiate on access
This strategic pillar focuses on expanding Walmart’s reach and providing customers with more convenient shopping options. Walmart has invested heavily in e-commerce and offers a range of options for customers, including home delivery, pickup in-store, and curbside pickup. The company has also introduced new technologies, such as Scan & Go and Walmart Pay, to make the shopping experience more convenient for customers.
Be competitive on assortment
This strategic pillar is focused on offering customers a wide range of products to choose from. Walmart aims to have a product assortment that is competitive with other retailers and offers exclusive products that cannot be found elsewhere. The company also offers a range of private-label products at a lower price than name-brand equivalents.
Deliver a great experience
This strategic pillar is based on providing customers with a positive shopping experience. Walmart aims to create a welcoming and friendly environment in its stores and invests in training for its employees to improve customer service. The company also offers a range of services, such as financial services and health and wellness services, to enhance the overall shopping experience.
By focusing on these four strategic pillars, Walmart aims to maintain its position as a leading retailer in the market and provide customers with a range of products and services at a low price. The company’s commitment to e-commerce and innovation has helped it adapt to changing consumer preferences and compete with other retailers in the market.
How Walmart Generates Revenues?
Walmart generates revenue primarily through the sale of a wide range of consumer goods in its retail stores and online through its e-commerce platforms. The company offers products across various categories, including groceries, apparel, electronics, home and garden, and health and wellness products, among others.
In addition to traditional retail sales, Walmart generates revenue through a range of other services, including financial services such as money transfers, check cashing, and bill payment. The company also offers healthcare services, including pharmacy services and vision centers, as well as photo printing services and tech support services.
Walmart also generates revenue through its membership-based warehouse club, Sam’s Club. Sam’s Club sells products in bulk at a discounted price to its members, who pay an annual membership fee.
The company has also been investing heavily in its e-commerce business to compete with online retail giants like Amazon. The company offers a range of online shopping options, including home delivery, pickup in-store, and curbside pickup, as well as a variety of exclusive products and services on its e-commerce platforms.
Overall, Walmart’s revenue is primarily driven by its retail operations, with additional revenue streams coming from its other services and its e-commerce business.
History of Walmart & Business Development Through the Years

Walmart is a retail giant that has its roots in rural America. The company was founded in 1962 by Sam Walton, who opened the first Walmart store in Rogers, Arkansas. Walton had a vision to offer low prices to customers and provide a better value than competitors. This vision has been the cornerstone of the Walmart business model and has helped the company grow into a global retail giant.
Early Years of Walmart
In the early years, Walmart had a small number of stores and focused on serving rural communities. The company’s first stores were located in small towns, and Walton believed that these areas were underserved by traditional retailers. Walmart’s strategy was to offer a wide range of goods at low prices, which quickly attracted customers.
By the late 1970s, Walmart had expanded to 276 stores and had become a major player in the retail industry. The company continued to focus on low prices, but also introduced new strategies to differentiate itself from competitors. Walmart began offering a range of private-label products, which were often sold at a lower price than name-brand equivalents. The company also invested in technology and supply chain management to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Expansion and Growth
In the 1980s, it continued to expand, opening new stores in larger markets and adding new product categories. The company’s revenue grew rapidly, and by the end of the decade, Walmart was the largest retailer in the United States.
In the 1990s, Walmart expanded globally, opening stores in Mexico, Canada, and the United Kingdom. The company’s international expansion continued in the 2000s, with Walmart entering new markets in Asia, Africa, and South America. By 2021, Walmart had a presence in 27 countries and was one of the largest employers in the world, with over 2.3 million employees.
Walmart Today
Today, Walmart is more than just a retail store. The company has diversified its business and offers a range of services, including financial services, health and wellness services, and e-commerce. Walmart’s online marketplace, Walmart.com, is a significant part of the company’s business, and it has invested heavily in technology to improve its e-commerce capabilities.
In conclusion, Walmart’s business model is built on its low-cost leadership strategy, diversified revenue streams, private label brands, and supply chain management . The company’s focus on providing customers with low prices and value has enabled it to become one of the largest retailers in the world. As Walmart continues to innovate and expand its business, it will likely maintain its position as a leader in the retail industry.
Related Posts:
- The Thrill of Real Money Gaming at Online Casinos in…
- Release and Production Measurement - Understanding…
- Walmart Plans Estimated $173 Million in Florida New…
- Optimizing Supplier Excellence: A Blueprint for…
- 5 Ways to Take Control of Your Business Tech to…
- How to Use Email Marketing in Your Network Marketing…
- Five Forces
- Social Media

Walmart SWOT Analysis 2022 | In-depth SWOT Study of Walmart
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
This article presents SWOT analysis of Walmart by scanning the company’s internal and external business environment. Walmart strengths and weaknesses are analyzed, and threats and opportunities are assessed to the evaluate company’s competitive positioning in the market.
2. What type of business is Walmart?
Walmart is a U.S.A based multinational retailer that operates supermarkets, grocery stores, hypermarkets, neighborhood markets and discount stores.
3. Company Overview
4. walmart swot analysis 2022, 4.1. walmart strengths and weaknesses – internal analysis, 4.1.1. walmart strengths.
Here are some key business strengths of Walmart:
1. Strong competitive positioning
Walmart holds strong competitive positioning against its competitors. Here is comparison of Walmart against top five competitors:
Walmart competitor analysis- 2022
Source: Macro Trends 1 | Macro Trends 2 | Macro Trends 3 | Macro Trends 4
2. Dominance in brick and mortar retailing
Walmart has strong dominance in brick-and-mortar retailing, due to which it remains unbeaten by Amazon, particularly in rural areas.
3. Brand value
Walmart is among world’s most valuable brands. Following graph shows consistent rise in Walmart’s brand value from 2016 to 2022:
Source: Statista
4. Consistent revenue growth
Despite the challenges, company is able to ensure consistent revenue growth from 2009 to 2022:
Walmart revenue growth – 2009-2022
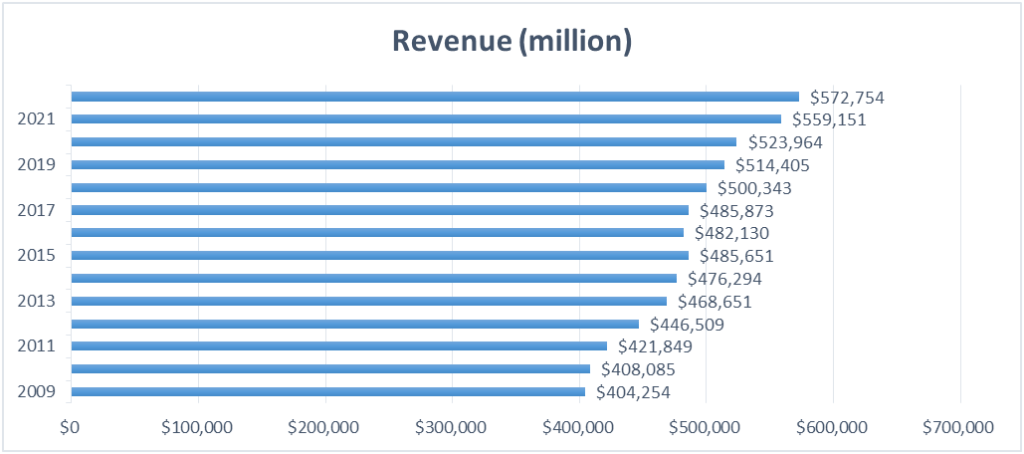
Source: Macro-Trends
5. Strong positioning in the market
Walmart has a huge size with wide market reach, which enables it to exercise strong market power over competitors and suppliers.
6. High market share
Walmart competitive analysis suggests that Walmart holds strong leadership position with high market share relative to competitors:
Source: CSI Market
7. Effective e-commerce platform
After establishing strong foothold in brick and mortar market, Walmart is strengthening its presence in e-commerce sector as well in all key business segments, as depicted in following graph:

8. Investment on technology and innovation
Walmart is heavily investing on technology and innovation to offer customer convenience. Some latest initiatives include-
- Added symbotic robots to 25 distribution centers, deployed robot janitors and shelf checking robots in stores
- Launched Roblox store as a first foray into meta-verse
- Investing on augmented reality features to enhance online shopping experience
9. Strong distribution network
Walmart has a wide network of highly automated distribution centers. Strong logistics system is company’s core competence. Walmart shares strong relationship with manufacturers/suppliers and distributors. The robust supply chain strategy enables company to minimize supply chain disruptions and reduce costs.
10. Walmart economies of scale
Walmart is the cost leader in global retail industry. The company achieves economies of scale by spreading fixed costs over thousands of products, and then translates low costs into low prices.
After analyzing key strengths of Walmart , now lets’ analyze some weaknesses of Walmart:
4.1.2. Walmart Weaknesses
Here are some key Walmart weaknesses:
1. Low customer satisfaction
Compared to competitors, Walmart earns low customer satisfaction score. American customer satisfaction index ranked Walmart ‘70’ in 2021 (-1% compared to 2020), which is lower than many of its competitors in USA.
2. Over dependence on the home market
Walmart excessively relies on home market. Following graph shows that in 2022, Walmart earned $393 billion revenue from USA, and only $175 billion revenue from other world regions.

3. Ineffective inventory management system
Walmart is facing excessive inventory management issues due to poor inventory accounting. According to Forbes , the last-in-first-out inventory accounting method along with demand fluctuations for high and low margin items is causing inventory pileup.
4. Ineffective human resource management
Walmart faces high employee dissatisfaction due to excessive job stress, poor job quality and low wages, which results into whopping 70% employee turnover rate .
5. Sustainability challenges
Despite the commitment to ensure sustainability, Walmart fails to minimize the hazardous impact on environment. Forbes noted that Costco emits 50 percent fewer emissions than Walmart, while Walmart remains unable to achieve its sustainability objectives.
6. Lack of diversity and inclusion
Business Insider reported that at start of pandemic, Walmart fired its black employees twice than its white employee, and in 2021, black employees only accounted for 21% of total workforce.
7. Weak presence in online market
Although, Walmart’s online sales are consistently growing, but Walmart holds weak competitive positioning in ecommerce sector than global e-commerce giants. Following graph shows Walmart holds only 6.3% market share in ecommerce compared to Amazon that holds 37/8% share:
8. Outdated business model
Walmart needs to rebrand itself by making its business model more tech savvy. Current business model is diversified, but can be easily imitated by competitors due to its simplicity. Historically, Walmart was able to keep prices low through low wages and cheap sourcing. But cannot continue cheap prices without business model re-branding.
After analyzing Walmart strengths and weaknesses , now let’s analyze external environment of Walmart.
4.2. Walmart Opportunities and Threats- External Analysis
4.2.1. walmart opportunities, 1. global expansion through e-commerce.
Walmart should expand its operations in the emerging markets, particularly in the e-commerce sector. The analysts predict Asia Pacific region ($3.3 trillion sales in 2022) will be having highest e-commerce growth, followed by North America ($1.15 trillion), and Western Europe ($695 billion).
2. Expand healthcare clinics
Walmart should expand its healthcare services in 2023 to tackle the competition from Amazon who plans to increase revenue from healthcare segment. Currently, Walmart has only 32 clinics in only five states within USA.
3. Automation and robotics
Walmart can invest on robotics and automation to resolve its labor and inventory management issues, which are affecting the company’s profitability.
4. Increase presence in Meta-verse
As per Forbes , Meta-verse in retail will make shopping experience more meaningful and engaging. Walmart seems well-prepared for this opportunity, as it has already partnered with Roblox to venture into Meta-verse .
5. Expand financial services
Walmart has entered in fin-tech market. Analysts expect global fin-tech industry is expected to growth with 25% CAGR from 2022 to 2027 :
Source: iShares.com
Considering the rising inflation and its impact on consumer spending, Walmart can expand its financial services by launching more fin-tech firms that offer ‘buy now, pay latter’ options to the customers.
4.2.2. Walmart threats
1. trade tensions.
Growing US-China trade tensions have now started directly affecting the Walmart’s business operations.
2. Economic downturn
The forecasts suggest U.S economy will slow-down, and real GDP growth will be close to zero in 2023 . Rising inflation is affecting consumer spending, and this economic downturn is affecting profitability of retail giants including Walmart.
3. Intensifying competition in e-commerce
Small and medium companies are likely to give tough competition in the e-commerce sector. Walmart’s weak presence in ecommerce (compared to competitors) increases its vulnerability to this threat.
4. Law suits
Walmart faces around 5,000 lawsuits each year , mostly by its employees that bring discrimination, and wage and hour claims. In 2022, Walmart paid $ 3.1 billion to settle opioid lawsuits . Inability to manage and respond to the lawsuits could intensify this threat and affect company’s reputation and economic performance.
5. Summary – SWOT of Walmart
Wal Mart SWOT analysis
6. Recommendations based on Walmart SWOT Analysis 2022
• Expand business operations to emerging markets to reduce reliance on home market
• Improve human resource management practices by adopting clear anti-discrimination policies
• Respond to lawsuits by strengthening the monitoring and control mechanisms
• Improve image on sustainability grounds by adopting environment friendly practices and reducing emissions
• Strengthen presence in the e-commerce sector by deploying latest technology and capabilities
• Invest more on augmented and virtual reality to offer more engaging online shopping experience
• Improve inventory management system by investing on automation
• Make business model more tech-savvy by accelerating the digitalization process
• Expand healthcare and financial services through collaborations and partnerships
7. Concluding remarks
Walmart’s strong dominance in brick and mortar market shields it from aggressive competition. Highly efficient logistics network and strong bargaining power against suppliers are key strengths that allow Walmart to achieve economies of scale. But labor and supply chain issues are some key weaknesses that need to be addressed. Company needs to further invest on emerging technologies to reduce costs and enhance efficiency besides augmenting the customer experience.
If you want to know more about Walmart marketing strategy, click here (internal linking previous article).
8. References
Walmart Revenue 2010-2022 | WMT . (n.d.-b). MacroTrends.
Costco Revenue 2010-2022 | COST . (n.d.). MacroTrends.
Carrefour SA Revenue 2010-2022 | CRRFY . (n.d.). MacroTrends.
Kroger Revenue 2010-2022 | KR . (n.d.). MacroTrends.
Statista. (2022a, March 25). Walmart: global brand value 2016-2022 .
Walmart Revenue 2010-2022 | WMT . (n.d.-c). MacroTrends.
Walmart Inc Market share relative to its competitors, as of Q3 2022 – CSIMarket . (2022, December 30).
Statista. (2022a, March 25). Walmart: eCommerce sales worldwide FY2019-FY2022, by division .
The American Customer Satisfaction Index. (2022, June 20). Supermarkets .
Statista. (2022d, July 27). Walmart: net sales worldwide FY2008-FY2022, by division .
Banker, S. (2022b, August 17). Walmart’s Supply Chain Woes . Forbes.
Monroe, M. (2022, January 27). How a large employer’s low-road practices harm local labor markets: The impact of Walmart Supercenters . Equitable Growth.
Bansal, T. (2021, December 20). Walmart Appears To Be Greener Than Costco. But Is It Really? Forbes.
Walmart fired Black hourly employees twice as often as their white coworkers at the pandemic’s start, congressional report says . (2022, November 21). Business Insider.
Statista. (2022i, August 26). Biggest online retailers in the U.S. 2022, by market share .
Statista. (2022o, December 21). Retail e-commerce sales value worldwide 2022, by region .
Kestenbaum, R. (2022, March 16). What The Metaverse Means For The Future Of Retail . Forbes.
Maruf, R. (2022, September 26). Walmart enters the metaverse with Roblox experiences . CNN.
Ltd, M. D. F. (n.d.). Market Data Forecast | Research Reports and Business Insights . Market Data Forecast.
Blocked . (n.d.).
Zois, M. A. &. A. L. (2023, January 11). Walmart Store Settlements and Lawsuits .
Access Denied . (2022, November 15).
Recent Analysis

Why You Should Call a Top Personal Injury Lawyer After a Truck Accident: Defending Your Lunch Money Against Big Rigs

Competitive gaming is video games in which players compete against each other or other teams online or offline using skill

Navigating Financial Troubles: How the IRS Fresh Start Program Can Help Entrepreneurs

Dior Marketing Strategy - Success behind the Strategy
- [email protected]
Analysis Category
- SWOT Strategy Analysis
- Marketing Strategy Analysis
- PESTEL Strategy Analysis
- Five Forces Strategy Analysis
Top Companies
Copyright © 2023 StrategyFinders
- SWOT Analysis
- Marketing Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
Copyright © 2023 Strategy Finder
Walmart’s 2022 SWOT Analysis: A Thorough Examination of the Retail Behemoth’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats
As a seasoned bargain hunter and savings-obsessed mom, I closely follow retail giants like Walmart. My wallet depends on it!
Recently, I decided to dive deep into Walmart’s 2022 business profile to understand what makes this company tick. And there’s no better framework than SWOT analysis to evaluate Walmart’s current strategic positioning.
SWOT examines the key Internal strengths and weaknesses of a firm as well as the External opportunities it can capitalize on and threats it faces. This provides a 360-degree perspective.
Let’s get right into an extensive SWOT analysis to decode Walmart’s formidable strengths, lingering weaknesses, promising opportunities and concerning threats.
A Snapshot of Walmart’s Power
- Founded in 1962 in Arkansas, Walmart is the world’s largest company by revenue at $573 billion
- It operates a staggering 11,500 retail stores and clubs in 27 countries
- Walmart employs over 2.3 million associates across the globe
- Over 265 million customers visit Walmart stores and e-commerce sites every week!
These stats make one thing very clear – you don’t get to the size of Walmart without some incredibly powerful strengths.
Walmart’s Key Strengths
Walmart’s strengths arise from its unmatched scale & reach, brand equity, financial firepower and operational excellence.
1. Brand Equity: Walmart’s Trusted Value Brand Connects with Customers
- Walmart is the world’s 9th most valuable brand at $77.5 billion as per Brand Finance
- Shoppers associate Walmart with low prices, good value, convenience, product range and decent store experiences
- This brand equity allows Walmart to drive foot traffic, launch private labels, enter new markets and counter competitors
As a longtime Walmart shopper, I confess a store visit revs up my mood to hunt for deals and score bargains across categories, from groceries to clothes to furnishings. Those “Fall in Love with Low Prices” signs get me every time!
Brand Value of Major Retailers (2022)
Source: Brand Finance
Clearly, Walmart’s brand clout is far ahead of other top retailers.
2. Scale & Purchasing Power: Unrivaled Market Share Helps Extract Supply Side Savings
Thanks to its unmatched scale and industry dominance, Walmart can extract maximum supply-side advantages:
- With over 11,500 stores worldwide, Walmart has unparalleled purchasing power over vendors
- It leverages economies of scale in sourcing, logistics and distribution to keep costs low
- Walmart’s huge volumes (it accounts for nearly 10% of all US retail sales) enable it to demand the lowest prices from suppliers
This amplifies Walmart’s price competitiveness. Its scale economies also create high entry barriers for competitors.
3. Financial Might: Profits Fund Growth and Expansion
Don’t let Walmart’s low-price image fool you. This company prints cash thanks to its industry leadership:
- Walmart‘s revenues in FY 2022 were a staggering $573 billion
- Its net profit totaled $13.5 billion, with a healthy net profit margin of 2.4%
- Free cash flows stood at a robust $12.8 billion in 2022
- As of Jan 2023, Walmart’s market capitalization is over $401 billion
This huge cash pile funds Walmart’s expansion, acquisitions, technology investments and weathering crises. It also unlocks cheap financing for the company.
4. Supply Chain Management: Logistics Wizardry Drives Efficiency
Walmart dominates retail technology, especially in supply chain systems:
- Its supply chain database is considered the world’s second largest after the Pentagon’s!
- Walmart owns one of the biggest private fleets of trucks in the US
- In 2021, automation boosted Walmart’s US distribution center productivity by 20%
- Walmart plans to automate all its regional distribution centers by 2027
This supply chain mastery locks in durable advantages for Walmart.
5. Strategic Expansion Beyond US
Walmart has expanded globally both organically and through acquisitions:
- It operates over 6,300 international stores spanning 27 countries
- Major acquisitions abroad include Asda in UK and Flipkart in India
- International sales account for 24% of Walmart’s total revenue
This geographic diversity insulates Walmart from isolated economic downturns.
Walmart’s Weaknesses: Shortcomings and Deficiencies
However, even the world’s biggest retailer has chinks in its armor as some weaknesses indicate.
1. Disappointing Overseas Performance
Despite strategic international forays, Walmart has struggled to replicate its US success overseas:
- Walmart has exited major markets like South Korea and Germany after years of subpar results
- In Mexico, Canada and UK it plays second fiddle to entrenched domestic retailers
- In growth markets like China and India, Walmart significantly trails local players in market share
- International sales contribute just 24% of total revenue versus 76% from the US market
Clearly, unlocking global growth remains an Achilles heel.
2. Overdependence on US Market
The flipside of Walmart’s muted international success is its overdependence on the American market (76% of revenues):
- While the US remains a steady cash cow, growth is plateauing in this saturated market
- Ramping up overseas expansion is vital to tap into new growth frontiers
- Diversifying globally will also hedge risks if US consumption stagnates amid economic pressures
Walmart must reduce its US concentration.
3. ESG Perception Issues
As the world’s largest company, Walmart attracts huge scrutiny of its ESG (environmental, social and governance) practices:
- Critics routinely accuse Walmart of everything from low wages to supply chain bullying
- Its big-box retail model is blamed for killing small independent businesses
- 16% of shoppers dislike Walmart due to its perceived bad reputation
While many charges may be subjective, poor ESG perception nonetheless damages consumer sentiment and talent retention.
4. Lagging E-Commerce Presence
Though the #3 global e-tailer, Walmart trails category leader Amazon significantly:
- Walmart’s 2021 US e-commerce sales were $73 billion, versus Amazon’s $386 billion
- Amazon accounts for nearly 40% of US e-commerce spending, versus just 7% for Walmart
- In Q3 2022, Walmart’s online sales grew only 8% year-over-year as consumers returned to stores
Closing this gap as overall retail spending normalizes will be challenging for Walmart.
5. Lean Profit Margins
Pursuing an EDLP (every day low price) strategy has resulted in lean margins:
- Costco’s net margin was 2.9%
- Amazon’s net margin was 6.3%
- Lower margins restrict Walmart’s flexibility around prices and compensation
Finding ways to boost productivity and margins is imperative.
External Opportunities: Avenues for Walmart’s Growth
Beyond strengthening internal capabilities, Walmart should leverage emerging external opportunities.
1. Optimizing Supply Chain with Technology
Walmart’s vast supply chain has plenty of room for technology-enabled optimizations:
- Advanced analytics and forecasting can help reduce inventory and out-of-stocks
- Blockchain can significantly enhance traceability across the end-to-end supply chain
- Warehouse automation can drive fulfillment efficiencies
- AI and machine learning can optimize logistics and transportation
McKinsey estimates such supply chain tech can unlock 100 basis point margin gains for retailers like Walmart.
2. Winning in E-commerce & Omnichannel Retail
- While behind Amazon, Walmart’s e-commerce sales grew a brisk 87% in 2021
- Its omnichannel initiatives like buy-online-pickup-in-store (BOPIS) are promising
- Further investments in fulfillment infrastructure and digital capabilities are needed to grab e-commerce share
- Blending physical and digital retail seamlessly will be the next frontier
3. International Market Expansion
Markets like Africa, Latin America and Asia offer fertile ground for Walmart to recharge overseas growth:
- Organic expansion and acquisitions in markets like Mexico, Chile, Africa, India and China are key prospects
- Partnerships with local players can also unlock growth abroad e.g. Walmart’s deal with India’s Reliance Retail
- McKinsey sees emerging markets contributing ~50% of global retail growth through 2023
4. Offering Value-Added Services
To attract foot traffic and boost revenues, Walmart can provide value-added services:
- Health clinics, vision centers, dental care, pharmacies, insurance enrollment, auto care and fuel stations
- Financial services like check cashing, bill payments and money transfers
- These can strengthen brand affinity and community connect
Such initiatives are underway at selected Walmart locations.
5. Boosting Sustainability Credentials
As stakeholders demand eco-friendly practices, sustainability is both an opportunity and imperative:
- Walmart aims to power all operations by 100% renewable energy and achieve zero waste by 2025
- It plans to convert its entire transportation fleet to zero-emissions vehicles
- Such efforts can pay off in customer sentiment and talent retention
ESG is moving up Walmart’s strategic agenda.
Threats: Challenges Walmart Must Counter
Of course, even retail hegemons face external threats that must be strategically mitigated.
1. Cutthroat Competition
The retail space is fiercely contested. Emerging threats for Walmart include:
- Online pure-plays like Amazon with superior e-commerce capabilities
- Omnichannel retailers like Target offering differentiated experiences
- Discount warehouse clubs like Costco vying on value
- Small format local grocers amping up gourmet appeal
- German discounters Aldi and Lidl taking share with rock-bottom prices
This requires Walmart to obsessively refine price, cost, quality and omnichannel effectiveness.
2. Reputational Risks
As recent controversies demonstrate, Walmart’s brand image is vulnerable:
- In 2022, Walmart faced backlash for selling “All Lives Matter” merchandise in Canada
- Past issues range from Mexico bribery charges to supply chain practices
Social media can quickly amplify such events. Walmart must implement proactive risk management.
3. Rising Labor Costs
With unemployment at historic lows, labor costs are rising across the retail sector:
- Walmart recently hiked its average hourly wages to $17.50 but more increases may be needed to address turnover
- However, higher compensation shrinks Walmart’s already thin margins
This balancing act will intensify as the labor market tightens.
4. Geopolitical Events
With its global footprint, Walmart is exposed to geopolitical turmoil:
- The Russia-Ukraine conflict and global trade wars introduce supply uncertainty
- Erratic foreign policies make long-term international capital allocation tricky
- Currency fluctuations create financial volatility
Such external shocks are beyond Walmart’s control.
5. Cybersecurity Threats
As digitalization accelerates across operations, cyber risks amplify:
- Walmart saw a 19% jump in cyber breach incidents in 2022
- Its exposure will expand as e-commerce and supply chain integration increases
- Cyber-attacks bring huge financial losses and reputation damage
Robust cybersecurity strategies are non-negotiable today.
The Verdict: Walmart is Undoubtedly a Retail Juggernaut
Evaluating Walmart using a structured SWOT framework makes its core strengths and opportunities abundantly clear.
Specifically, Walmart wins by leveraging its brand equity, scale, purchasing power, supply chain mastery and financial muscle. When combined, these form potent competitive advantages that few can rival.
However, in an ever-evolving retail landscape, Walmart must also be cognizant of its weak spots and external threats. There are danger signs around the maturity of its US business, lagging e-commerce presence, thin margins and reputational risks.
Going forward, Walmart’s growth blueprint involves:
- Aggressively growing e-commerce and omnichannel capabilities
- Pursuing balanced expansion across high-potential international markets
- Leveraging technology to optimize supply chain and operations
- Building brand affinity through transparency and sustainability
The SWOT analysis provides a 360-degree perspective on Walmart’s existing strategic positioning. It will help the retail behemoth chart its future trajectory amidst the winds of change and competition.
My key takeaway as a bargain hunter? I can expect even sharper prices from Walmart as it leverages SWOT insights to cement its industry leadership!
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
Share this:
You may like to read,.
- Does Walmart Sell Lottery Tickets in 2022? Yes, Here‘s Your Complete Guide to Buying Lottery Tickets at Walmart
- Does Walmart Have Layaway in 2022? Your Complete Guide to Holiday Layaway
- Got Headphones You Need To Return? Here‘s Walmart‘s 2023 Policy
- Why Steelyard Walmart is Considered the Worst Walmart in America for 2024
- Does Walmart Sell Victoria’s Secret Gift Cards In 2023?
- How Does Walmart Track Shoplifting In 2024? (Warning)
- Does Walmart Use TeleCheck and Certegy to Verify Checks in 2024?
- Is Dollar General Owned By Walmart In 2022?


The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

Walmart Mission Statement and Vision Statement
Walmart’s mission can be summarized as “helping people around the world save money and live better – anytime and anywhere – in retail stores and through eCommerce.” Its vision is to “make every day easier for busy families.” Walmart defines “busy families” as the bull’s eye of its business strategy and Walmart’s business model .
Table of Contents
Walmart’s business model evolution
Sam Walton, founder of Walmart , said that “t he secret of successful retailing is to give your customers what they want.”
And he continued, “and really if you think about it from your point of view as a customer, you want everything: a wide assortment of good-quality merchandise; the lowest possible prices; guaranteed satisfaction with what you buy; friendly, knowledgeable service; convenient hours; free parking; a pleasant shopping experience.”
While those are things that people did want in the past, the world has also changed substantially. As technology has evolved, the experience of Walmart customers has also moved from physical to digital.
That has made Walmart adjust its core value proposition , and it also made it adapt its business model . At the core, as we’ll see in this analysis , the three elements (price, assortment, and experience) remain three critical values of Walmart’s mission statement .
Breaking down Walmart’s mission statement
Walmart Inc. helps people around the world save money and live better – anytime and anywhere – in retail stores and through eCommerce.
Therefore, Walmart’s mission informs its business strategy and how also this has changed over the years. For instance, while the core of the Walmart business model has stayed the same, its strategy has adapted to new technologies.
E-commerce was not a core part of the Walmart business strategy. Currently, instead, Walmart has incorporated this part within its mission .
As highlighted in the Walmart Investment Community Meeting of 2017:
90% of Americans live within 10 miles of a Walmart. There’s 1.4 million associates, and Walmart’s the largest grocer in the U.S. So when we think about some of these assets and we think about playing offense, we think about it across 3 dimensions: price, assortment and experience.
Therefore, Walmart’s mission and business strategy revolve around three critical dimensions:
- And Experience
The remaining vital aspects are related to the following:
- Price, by allowing families to “saving money,” therefore low prices
- Assortment, by making Walmart “anytime and anywhere,” which is reinforced by the presence of Walmart stores across the US
- And experience by leveraging experienced and knowledgeable salespeople
Let’s see more in detail about Walmart’s vision statement and why that matters.
Breaking down Walmart’s vision statement
In its Investment Community Meeting of 2017 , Walmart executives highlighted where its direction for the future:
What is the direction? We want to be the destination for customers to save money no matter how they want to shop, whether it be pickup, delivery in 2 days or deliver in 2 hours. The idea is to save customers money at any service level.
And it clarified its vision as:
We want to make every day easier for busy families. That’s our vision
Understanding Walmart’s vision is essential, as well as understanding its business strategy . Which is summarized in the Investment Community Meeting as follows:
In summary, the strategy is very simple. We’re going to be maniacally focused on just nailing the fundamentals. We’re going to look for ways to play offense by leveraging unique assets. And we’re going to be focused on innovating for the future.
Therefore, Walmart’s business strategy leverages three key ingredients:
- Maniacally focusing and nailing the fundamentals
- Play offense by leveraging Walmart unique assets
- Innovating for the future
What does Walmart mean when it says “making every day easier for busy families?”
Understanding its definition and why Walmart picked this market segment will help us capture its direction:
So let’s talk about making every day easier for busy families. Why busy families? Well, it’s a big part of the market, and we’ve learned that what we do to effectively serve them helps us serve everybody else, so they’re the center of the bull’s eye.
Choosing a big enough market is a fundamental problem in the entrepreneurial world.
That is why investors often demand startups clearly understand their TAM or total addressable market .

To clarify, this isn’t a straightforward issue.
When companies are opening up new spaces and markets, none knows how big that market will be.
For instance, when smartphones took over, it became a massive market, and many companies have already moved to a mobile-first world.
Walmart picked the “busy families” because, according to them, it represents a good chunk of the families.
That makes them focus on a particular segment and informs their business strategy .
This focus allows a better and more effective execution. It also creates a flywheel or virtuous cycle .
As Walmart points out, they learned that by serving a specific segment, they end up doing anyone else better.
But who are those busy families? As pointed out in the Investment Community Meeting of 2017:
So we really have 1 member. And I want you to think of them like this. It’s a busy family, typically living in the suburbs of 1 or 2 incomes. They make somewhere between $75,000 and $125,000 a year. They may own a couple of cars. They may be employed or self-employed. They may own a small restaurant or run a small office and purchase a few things for their business.
Walmart has a clear idea of its key market segment.
Once again, this is a simplification. And it allows focus, as specified by Walmart executives:
So we’re moving forward and we’re moving quickly to align the entire business around this more narrow focus. We’re evaluating everything from our membership offering to our merchandise categories to our locations, and we’ve got some important choices to make in the future.
And what’s going on with those busy families, according to Walmart ?
What’s happening with them? Well, you know they’re more connected. They’ve embraced mobile in a big way. In fact, globally, around the world, mobile commerce has grown by about 80% just in 2 years.
Therefore, as technology evolves, Walmart uses it and incorporates it in its mission and vision to serve better its target segment .
And that is why Walmart is becoming more and more of a digital company:
Technology will also help serve up things to customers that they might want to do. So becoming more of a digital company and learning how to work with speed is important to us throughout.
As Walmart’s business model adapts to the future technology landscape, it also adapts its value proposition !
This is critical as a business model is the fruit of a long-term vision and a shorter-term mission .
And as a business strategy changes and adapts, the fundamentals of a business model (its value proposition ) also adapt and change. This is eventually reflected in the financials.
It is important to remark that technology helps an organization to better serve its target. This also implies a change in its monetization strategy .
However, its core values stay the same.
For instance, in 2018, Walmart started to roll out a program called Jetblack to serve “busy families” that, for a fixed membership price, could get a customized sales experience.

Walmart in numbers
Let’s look at some of Walmart’s critical financials for 2021:

Key Highlights
- Walmart’s mission is centered around assisting people globally in achieving savings and improved living standards. This mission is accomplished through a combination of their retail stores and online eCommerce platforms. It emphasizes the company’s commitment to offering cost-effective solutions to its customers. Simultaneously, Walmart’s vision revolves around simplifying the lives of busy families by providing services and products that cater to their convenience and needs.
- Walmart’s mission encapsulates three core values: price, assortment, and experience. The company strives to offer competitive prices that enable customers to save money. Moreover, their commitment to a diverse and extensive assortment of products ensures that customers have access to a wide range of choices. Lastly, Walmart places significant emphasis on providing a positive shopping experience that is both satisfying and enjoyable for their customers.
- Over time, Walmart’s business model has evolved to integrate the growing significance of eCommerce in addition to their traditional retail approach. Recognizing the digital transformation of the retail landscape, Walmart adapted its core value proposition to encompass online shopping experiences alongside physical store visits. This evolution enables customers to access Walmart’s offerings through various channels, aligning with changing consumer preferences.
- Walmart’s business strategy is founded on three key principles. Firstly, they emphasize the importance of mastering the fundamental aspects of their operations to provide consistent quality and value to customers. Secondly, Walmart capitalizes on its unique assets and strengths to proactively engage and satisfy customer needs. Lastly, the company maintains a forward-looking perspective, continuously innovating to adapt to emerging trends and technologies in the retail industry.
- Walmart’s strategic focus centers on catering to the needs of busy families, particularly those residing in suburban areas. These families typically have 1-2 sources of income and earn within the range of $75,000 to $125,000 annually. By understanding and addressing the needs of this specific segment, Walmart is better positioned to create tailored solutions that resonate with their target audience.
- Technology is a pivotal component of Walmart’s strategy to serve its customers effectively. The company recognizes the increasing role of technology in modern life, especially among busy families. This integration involves leveraging digital platforms, mobile applications, and online services to enhance the shopping experience, provide convenience, and offer personalized solutions based on customer preferences.
- The Jetblack program, introduced by Walmart in 2018, exemplifies the company’s commitment to meeting the unique demands of busy families. This initiative offers a subscription-based service that provides personalized shopping experiences to members. Through this program, Walmart aimed to simplify the shopping process for busy families by offering tailored product recommendations, convenient delivery options, and other value-added services
Read: Mission Statement Examples .
Read Also: Walmart Business Model , Walmart Mission Statement Analysis , Walmart SWOT Analysis , Who Owns Walmart .
Related Visual Stories
Who Owns Walmart

Walmart Business Model

Walmart Revenue vs. Profit

Walmart Revenue

Walmart Customers

Walmart Stores

Walmart Employees

Walmart Mission Statement

Walmart Organizational Structure

Walmart SWOT Analysis

Mission Statement Case Studies
Adidas Mission Statement

Uber Mission Statement

Tesla Mission Statement

Amazon Mission Statement

Apple Mission Statement

Netflix Mission Statement

Coca-Cola Mission Statement
Starbucks Mission Statement

Microsoft Mission Statement

Nike Mission Statement

Google Mission Statement

More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Company News
Walmart vs. Target Business Model: What's the Difference?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/photoforinvestopedia_v21-79f8ee2d641648c7b0f25993dc577792.jpg)
Walmart Business Model vs. Target Business Model: An Overview
When it comes to big-box discount stores, Walmart (NYSE: WMT) still dominates the market with its sheer size. But its primary competitor, Target (NYSE: TGT), has been carving out market share with catchy advertising campaigns and hip design partnerships. The differences between the two extend as well to their business models. Walmart prefers the lowest cost, while Target angles more toward profit margin and youthful image.
Key Takeaways
- Walmart and Target are both low-cost retail stores with gigantic revenues. As of 2019, Walmart is about 20 times the size of Target.
- Walmart controls supercenters sometimes over 180,000 square feet, aiming to offer the lowest price possible.
- Target runs large stores as well, but they are more focused on profit margins through the supply chain, which is why they are able to post lower revenues but higher profit margins.
- A short account receivable collection period is typical for the retail sector as proved by these figures. Both companies have lower inventory turnover ratios than the sector.
Walmart Business Model
Walmart Stores Inc ( WMT ) is the world’s largest retail company that operates 11,368 stores worldwide as of the end of June 2019—with around 5,000 of those in the United States (including Sam's Club locations).
Walmart is a retail giant that is at least five times larger than its primary competitor, Target. Walmart also seems more efficient in business operations than Target—this is reflected in its higher inventory and asset turnover, as well as its operational dollar generated per dollar of asset.
Walmart commands nearly 20 times the market share of Target.
It only takes a glance at its balance sheet and market cap to see how huge Walmart is compared to Target. By the financial year ending on June 30, 2018, Walmart’s total assets were $204.5 billion, about five times larger than Target’s comparatively modest $39 billion. In terms of market capitalization , Walmart's $319.67 billion is more than 6.5 times larger than Target’s $44.41 billion, as of early July 2019.
Walmart may be a lot bigger than Target, but size isn’t everything. For one, size does not tell how efficiently a company operates. For that, investors should look towards the inventory turnover , asset turnover , and receivables turnover ratios. By comparing these numbers against competitors’ numbers as well as against the retail sector (Walmart, Target, Costco Wholesale Corp ( COST ), and Dollar General Corporation ( DG ) are large players in the sector), we can figure out how efficient the business is (for FY 2017):
Walmart beat the sector in receivable turnover, but Target lagged behind. Walmart also has a higher receivable turnover ratio and asset turnover than Target.
It takes Walmart about 43 days to turn its inventory , whereas Target needs 62 days. The sector needs 49 days on average. Comparing asset turnover, we can conclude that Walmart is highly efficient compared to both Target and the sector because it has a higher asset turnover than the latter two. High asset turnover implies a high level of sales per dollar of total assets.
Target Business Model
Walmart's main rival, Target Corp ( TGT ) , operates approximately 1,800 stores in the United States. Target has utilized a low pricing strategy similar to Walmart, but is more focused on the e-commerce platform, experiencing over 30% of e-commerce sales growth in 2018. Instead of mega-stores like Walmart, Target's business model focuses on slightly smaller stores, focusing less on direct bottom-line savings than on a younger commercial draw.
In terms of profitability, Target seems to perform better than Walmart and, in some instances, the sector overall. Target beats Walmart in both gross profit margin and net profit margin . This may be in part due to Walmart’s low price guarantee policy under which Walmart promises the lowest possible prices for its products. However, both companies have a below-industry-average net profit margin (for the quarter ending June 30, 2018):
When comparing the two from a financial perspective, Target is slightly more profitable than Walmart. Walmart's lower gross profit margin and net profit margin can be explained by its everyday low price strategy which features a low price guarantee policy.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1310099305-1b5fc9fcdbd34a39959f084e017bf1c8.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The Walmart business model has turned the retail company into the largest supermarket chain in the United States, with more than 11,500 stores (including hypermarkets, supermarkets, and department stores), under 56 banners in 27 countries, and e-commerce websites in 10 countries. They employ approximately 2.2 million associates around the world (1.5 million in the U.S. alone) and serve nearly ...
Walmart's full-year revenue was up 2.4% from the prior year reaching $572.8 billion, The company discussed how a more diversified business model will help drive future growth and provide a ...
Walmart U.S. comp sales $24.2 BILLION in operating cash flow $15.9 BILLION returns to shareholders A focused international business with NET SALES OF $101 BILLION Fiscal 2022 Highlights Invested $13 BILLION in CapEx for growth Revenue grew $14 BILLION YOY INCREASED THE DIVIDEND for the 49th consecutive year in February 2022 eCommerce business
Walmart's Existing Business Model Before Digital Transformation Walmart's Retail Business ... Walmart leverages its extensive size for economies of scale shown by its strong revenue growth of 5.3% per 2022 and 2023 consolidated Income statement, enabling cost advantages in ... Working with partners to diversify and build a sustainable ...
In 1980, Walmart through its business model became the fastest company to reach $1 billion in sales after just 18 years in operation. As the company continued to expand into other U.S. states, so too did Walton's aspirations. ... As of 2022, 2,751,779,629 Shares were outstanding for Walmart. The company's major shareholder is the Walton ...
The business model of Walmart makes money from three segments: Walmart U.S., Walmart International, and Sam's Club. Walmart made $567.8 billion in fiscal 2022 through these three segments. Each component contributes to the Company's operating results differently.
Though ad revenues remain a small fraction of its business, Walmart Connect will be the fastest-growing retail media network we track in 2024, growing 39.5% to reach $4.45 billion in ad revenues, per EMARKETER's October 2023 forecast. Once again, Walmart is a distant second to Amazon, which will generate $44.26 billion in US ad revenues in 2024.
Source: Company reports. In FY 2022, groceries accounted for 56% of Walmart's total income in the US, followed by general merchandise (32%), health and wellness (11%), and other categories (1%). The company posted a net profit of $13.67 billion in FY 2022, slightly higher than the $13.5 billion profit in FY 2021.
2022 Annual Report. The Walmart business model focuses on our unique assets. Assets that work together in a mutually reinforcing way to bring customers into our ecosystem and serve them seamlessly across their everyday journeys. We call it the flywheel. We start with the customer and design for them. They come to Walmart for the things they ...
Published Dec. 12, 2022 Catherine Douglas Moran Reporter. Courtesy of Walmart corporate blog As Walmart's business model evolves, a focus on omnichannel strategy is the thread tying together its e-commerce business, fulfillment services, advertising and more, Walmart President and CEO Doug McMillon said at Morgan Stanley's Global Consumer ...
With US$570 billion in annual revenue, it is the world's largest company by revenue. Walmart's business model relies on leveraging massive economies of scale to be the low-price leader: Physical retail stores - Supercenters, Discount Stores, Neighborhood Markets. EDLP pricing - Everyday low prices enabled by cost control.
The company's gross profit for this year (2023) is estimated at almost $150 billion, representing an increase of nearly 3% compared to the previous year. Walmart's updated revenue will exceed $611 billion, an essential boost of 6.7% compared to 2022. See also: Home Depot Business History.
514.4. From the above breakup, it is apparent that Walmart US is the company's largest earner making almost 66% and 65% of its net sales in 2020 and 2019 respectively. After Walmart US, Walmart International is the second-highest earner for the company, with 23% and 24% of the overall net sales in both years respectively.
The hard work Walmart's WMT -0.9% management invested in their company in 2020 paid off: Revenues jumped $35 billion, or up 6.7%. U.S. e-commerce contributed to the growth by jumping 79% ...
The Walmart Business Model Canvas highlights key elements such as customer segments, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, and key partnerships. Some of the main competitors of Walmart include Amazon, Target, Costco, and Kroger. In terms of SWOT analysis, Walmart's strengths include ...
Walmart's U.S. division posted net sales of $113.7 billion, an 8.5% increase year over year. U.S. same-store sales rose 8.3% as the company continued to gain market share in grocery, especially among higher-income shoppers looking to save money. Specifically, the retailer said that strength in food sales (up by high teens) reflected continued ...
Walmart reported an annual revenue of $572.754B for 2022, which is a 2.43% increase from the previous year. For the quarter ending October 31, 2022, the company reported revenue of $152.813B, representing an 8.74% increase year-over-year. Over the twelve months ending October 31, 2022, Walmart's revenue increased by 4.92% to reach $600.112B.
Following graph shows that in 2022, Walmart earned $393 billion revenue from USA, and only $175 billion revenue from other world regions. Source: Statista. 3. ... Outdated business model. Walmart needs to rebrand itself by making its business model more tech savvy. Current business model is diversified, but can be easily imitated by competitors ...
Recently, I decided to dive deep into Walmart's 2022 business profile to understand what makes this company tick. And there's no better framework than SWOT analysis to evaluate Walmart's current strategic positioning. ... Its big-box retail model is blamed for killing small independent businesses; 16% of shoppers dislike Walmart due to ...
Walmart's business model evolution. ... As of 2022, 2,751,779,629 Shares were outstanding for Walmart. The company's major shareholder is the Walton family, whose mission is to "help people around the world save money and live better - anytime and anywhere - in retail stores and through eCommerce." While its vision is to "make ...
Posted on March 23, 2023 by Daniel Pereira. A comprehensive Walmart SWOT analysis will provide insight into how one of the world's largest retail corporations has faced and overcome several challenges, including competition from online retailers and changing consumer preferences, and has spread its tentacles to multiple countries of the world.
Walmart Business Model Walmart Stores Inc ( WMT ) is the world's largest retail company that operates 11,368 stores worldwide as of the end of June 2019—with around 5,000 of those in the ...
the paper analyses some of the key features of Walmart business model, emphasizing their importance in achieving business success. It also presents the clear interconnection between Walmart strategy and its ... At the end of January 2022, Walmart operated 10,593 retail stores and 364 distribution facilities all over the world (Statista Research ...
Walmart Inc. ranked third for innovation but took last place in employee engagement in a new list of the 250 best-managed U.S. companies in 2023.