How to make a business plan
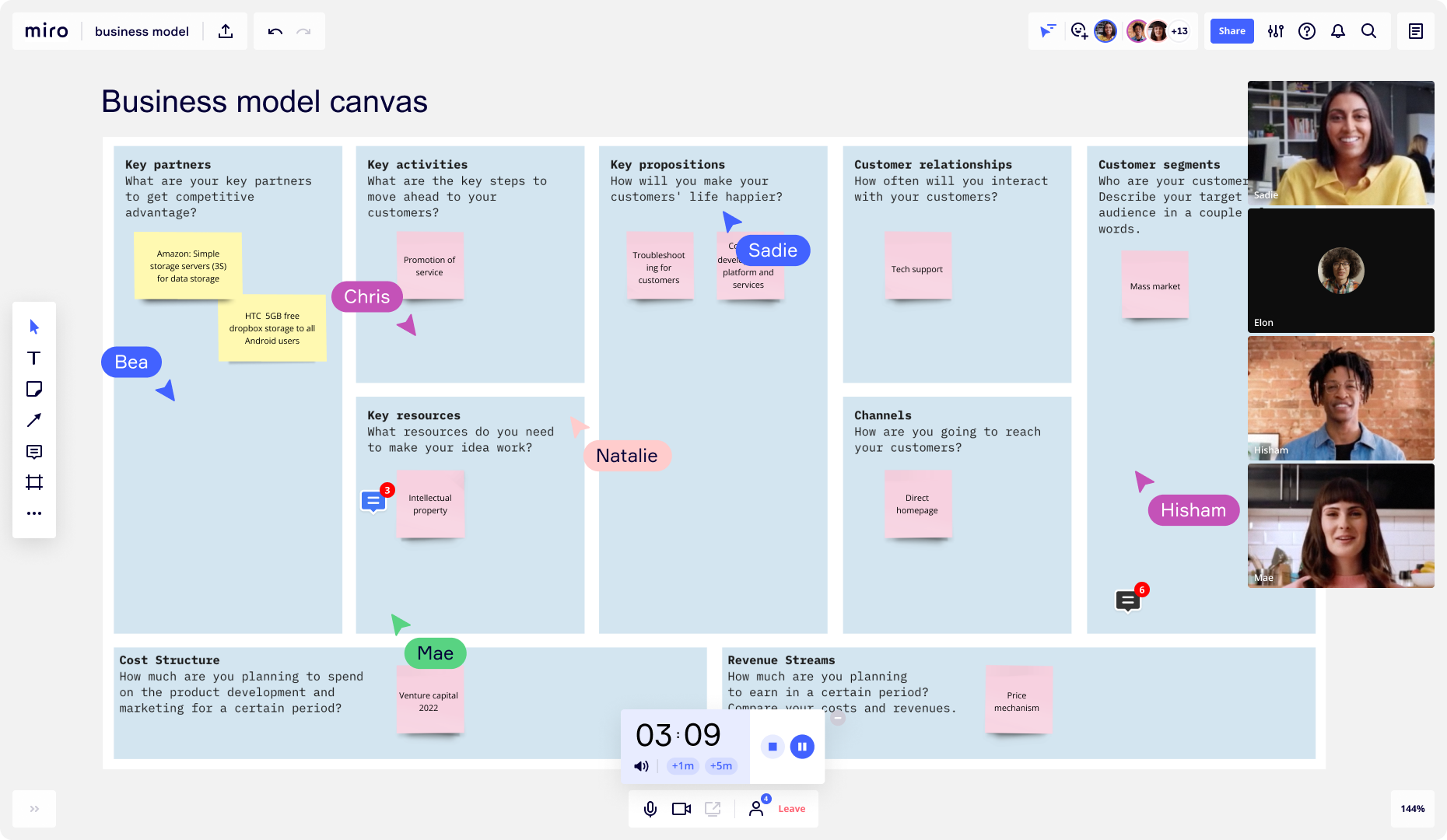

Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business


Build plans, manage results, & achieve more
Learn about the AchieveIt Difference vs other similar tools
We're more than just a software, we're a true partner
Strategic Planning
- Business Transformation
- Enterprise PMO
- Project + Program Management
- Operational Planning + Execution
- Integrated Plan Management
- Federal Government
- State + Local Government
- Banks + Credit Unions
- Manufacturing
Best practices on strategy, planning, & execution
Real-world examples of organizations that have trusted AchieveIt
Ready-to-use templates to take planning to the next level
Research-driven guides to help your strategy excel
Pre-recorded & upcoming webinars on everything strategy & planning
- *NEW!* Podcast 🎙️
The Ultimate Guide to Corporate Strategic Planning
RELATED TAGS:
Corporate strategic planning is essential to businesses and one of the basics of a business plan. It allows you to proceed toward your objectives with direction and focus. However, setting strategic goals is more complex than writing them down during a board meeting. The process requires careful evaluation and analysis to garner the best business results.
Corporate strategy includes all the steps in strategic planning that turn your high-level goals into actionable objectives, maintain and elevate your competitive position and provide quantifiable feedback to keep a flexible and workable strategic framework.
In This Article
What Is Corporate Strategic Planning?
Objective setting, allocating resources, making strategic trade-offs, why is corporate strategic planning important, what is the difference between corporate strategy and business strategy.
- Formulation
- Implementation
- Modification
- Establish the Your Corporate Strategic Objectives
- Develop Strategies for Achieving Goals
- Implement Your Corporate Strategy
- Monitor Your Strategic Plan’s Performance
- Analyze the Plan’s Success
How AchieveIt Helps With Strategic Planning
Sharpen your corporate strategy with achieveit.

Corporate strategic planning is a branch of strategy that focuses on the organization. A corporate strategic plan manages a business’s objectives and overall direction, and the associated processes are critical to the organization’s strategic objectives.
The corporate strategic planning process includes defining companywide strategic goals from the top tiers of an organization and implementing them throughout every level. For many businesses, corporate strategic planning is the first step and strategic planning goals define annual budgeting and allocation of resources.
Corporate strategic plans can be external, focusing on business objectives and the overarching direction for the organization, or internal, such as corporate diversity and inclusion strategic plan.
A corporate strategy — in terms of business planning basics — has four main components, each providing valuable insight through self-evaluation. The four elements of corporate strategic planning include the following:

The Four Elements of Corporate Strategic Planning
Visioning involves creating a high-level direction for your business, including business plan basics like corporate values and vision and mission statements. Setting a vision for your company’s future is a robust tool in corporate leadership. In general, companies plan between three and five years ahead.
Your vision and values will guide your daily operations and procedures, and involving key team members fosters engagement throughout the organization.
Aligning your strategic objectives with the overarching vision for your business is the key to successful objective setting. Strategic objectives are the high-level goals of your business and describe what your team needs to do to fulfill its mission over the next three or five years.
The objective setting takes your qualitative goals into measurable objectives , which is critical to get your ideas into an actionable format. In the context of goal setting in an organization, the most effective strategic goals are specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and time-bound (SMART). Communication is also vital in the objective-setting phase. It ensures that team members are focused on priority tasks and operating in a unified manner, aiming towards furthering the company in the future.
With your objectives outlined, you now have a clear list of priorities to allocate human and capital resources. With a clear and actionable overview of your strategic goals, you can plan, manage and assign resources to facilitate reaching them. Determining how best to allocate resources to teams and business units is integral to your overall planning process.
Also known as prioritization is one of the most challenging core elements of corporate strategy. Taking advantage of every opportunity may not be possible, and almost all business decisions contain an element of risk. Anyone who manages strategic plans and initiatives in an organization must consider all these factors to determine the optimal strategy when setting strategic goals.
Businesses must balance risk and reward and pay close attention to risk management processes to maximize returns and minimize threats to operational procedures.

Strategic plans are more than just abstract ideas conceptualized in a board room. When actualized correctly, they power organizational alignment and allow teams to direct their efforts in the most productive places. Strategic planning communicates your mission and vision throughout your organization to effect strategic change at every level and prioritize your most important objectives in your daily operations.
Strategic planning can highlight your shortcomings and biases and present new opportunities to streamline your operations. Then, you can track your goal process with actionable key performance indicators (KPIs) and align them with your business processes.
Most importantly, a well-conceived strategic plan provides a competitive advantage in your industry, allowing you to anticipate competitors’ next moves and stay one step ahead. With actionable strategies in mind, your business can accomplish goals ahead of the competition and ensure you provide the best possible results for your customers.

There is a marked difference between business-level strategy vs. corporate-level strategy. Corporate strategies operate at a higher level than business strategies and focus on growth and profits. A business strategy, on the other hand, focuses on competing in the marketplace. Organizations should develop their business strategies with their corporate strategy in mind.

Stages of Corporate Strategic Planning
Like any successful strategic plan or initiative, teams must tackle corporate strategic planning in four stages. The four stages of corporate strategic planning include the following:
1. Formulation
For an actionable strategic plan, you must take the time to create a roadmap of your most profitable action to achieve your strategic objectives. In this phase, you and your team will set your strategic plan goals and explore the best means to achieve them. Consider conducting a SWOT analysis — strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats — for your business to reveal growth opportunities and areas within your operations that require attention. Consider looking into successful corporate strategic plan examples as part of your research.
Before you start, ensure you have a purpose for formulating your strategy based on your core vision and mission. You’ll consider current events and trends as part of your SWOT analysis. Ensure you set actionable and measurable goals in the formulation phase of strategic goal setting and communicate them effectively throughout your organization.
Often, organizational leaders formulate a corporate strategy. Every team member adds a different perspective to the process, so drawing on their input could illuminate and provide a more pronounced competitive edge for your business.
2. Implementation
Implementation is the phase where your corporate strategies become corporate actions . Your team has designed and communicated your strategy, so that all members understand their roles and responsibilities. Setting up KPIs aligned with your strategic objectives is critical in the implementation phase, as it provides quantifiable feedback on positive impacts and information on opportunities for change.
During implementation, your team must focus on details and day-to-day processes to implement quick changes. Corporate strategy is a fluid process that requires daily attention to succeed.
3. Evaluation
Evaluating the strategies you executed in the implementation phase provides you with valuable feedback on the efficacy of your corporate strategy. Some businesses perform a gap analysis to identify the need for new products or additions in the gap between their current and desired future positions.
At this stage of the process, your data is vital. An integrated plan management software allows you to track resources, changes, schedules, and the quality of your corporate strategic initiatives. With actionable data on team members and projects, you can make changes and refine your corporate strategy.
4. Modification
In the modification phase, your team can correct and refine underperforming elements of your corporate strategy. You have identified your strongest areas, which your team could leverage to assist in further implementation in areas that need further attention.
How to Create a Successful Corporate Strategic Plan
You and your team may be used to taking a reactive route where you only deal with problems as they arise. However, this can stifle your vision and make it difficult to see the big picture or prepare for obstacles along the way. By following the fundamentals of strategic planning, your company can gain a better understanding of common issues that complicate your short- and long-term goals and make you more proactive in resolving them.
A progressive approach is critical to corporate strategic planning success, so you can pay attention to each step and garner the best results. The five steps in the strategic management process include the following:

1. Establish the Your Corporate Strategic Objectives
Corporate strategic objectives must be clear, achievable and easy to communicate. Consider what business objectives your team needs to achieve and communicate these objectives throughout all levels of your organization. Foster collaboration, allow everyone in your organization to think strategically and offer suggestions for achieving your corporate strategic initiatives.
Employees throughout your organization can provide valuable input to drive your objectives forward. Gather as many insights as possible and set your objectives with as much information as possible. At the end of this step, you should have a broad view of what your business wants to achieve and how the various teams can contribute.
2. Develop Strategies for Achieving Goals
From your broad overview, you can now break your objectives into specific projects and courses of action within those projects. Include metrics and KPIs to quantify the success or failure of each. Establish objectives and key results (OKR) framework so each goal has quantifiable key results to measure the initiative’s success.
Pay attention to your human resources during this critical step. Think outside the box, eliminate silos within your teams, and ensure every team member has roles and responsibilities aligned with their strengths.
3. Implement Your Corporate Strategy
It’s time to take your strategic plan off the boardroom table and implement it into your business workflow . Making your corporate strategy successful requires focus and input from every team member. Ensure everyone in your organization can clearly see and understand their role within your strategy and how their actions move your plan forward.
You can reply heavily on your OKR framework here for each individual to have a solid view of their roles. When team members see their impact on your overall strategy, they will be more engaged and productive in their efforts to achieve your objectives. Team engagement comes from management and managers should focus on managing outcomes, not people, for the best results.
Partnering with an integrated planned management specialist is essential for maximizing employee productivity and engagement. Strategic planning software can give you a competitive edge. User-friendly interfaces, clearly defined goals, and change management will make implementation smoother, faster and easier for team members.

4. Monitor Your Strategic Plan’s Performance
Remember that your strategic plan is fluid and needs regular monitoring for your organization to maintain a competitive position. Again, use your valuable human resources and consult everyone who owns a strategic objective. Foster an environment where you can receive honest input on the strategic plan’s progress so your management doesn’t feel more comfortable concentrating their team’s efforts in weak areas.
Ensure your plan is flexible enough to catch it early if your organization’s efforts go off course. If there’s an opportunity to produce better results, you can stay ahead of the competition and execute it immediately. Measuring your team’s performance with employee performance metrics is an excellent method of assessing where you’re achieving your outcomes and where you may need to rethink the allocation of resources.
Consider organization performance reporting to analyze how your business performance compares with your goals and initiatives. You can assess your successes and make adjustments when necessary.
5. Analyze the Plan’s Success
Analyzing the impact of your corporate strategy is vital to set a benchmark for what elements to continue with and change. It clearly shows areas to improve and strengthens your teams’ engagement and commitment to your strategic initiatives. Include team members from across your organization when you conduct your analysis and foster open and thorough communication so they can share their insights and experiences.
Together, you can define your plan’s strengths and opportunities for improvement . Once you have gathered input from across your teams, your strategic team can apply this insight to your new strategic initiatives and amplify your successes.

Organizations that struggle to get their important initiatives from the boardroom into reality and keep their performance on track may falter with their objectives. With AchieveIt, your business can improve visibility, uniformity and accountability within your strategic planning process.
Our automated platform and strategic planning software enable your teams to connect, execute your goals and evaluate how your essential plans are performing. Integrated plan management solutions from AchieveIt can revitalize how your organization reaches for its goals with dashboards, reporting, updates and more strategic planning tools.
Some of the many ways AchieveIt can help you with your corporate strategy include the following:
- Streamlining your corporate strategic execution: Create alignment and organize your strategic initiatives with our process-focused software to integrate and execute corporate strategies.
- Using automated updates: AchieveIt focuses on the end user, integrating process updates from different sources for a seamless automated update system.
- Consistent expert support and training: AchieveIt conducts regular business reviews, so you can measure your return on investment (ROI) and access quantifiable data about how your corporate strategy aligns with your progress. Your strategic expert is there to provide feedback if needed, and on-site training allows for excellent change management, improved adoption rates and better team engagement.
- Data-driven insights and accessible results: You can filter and create outcome-specific reports aligning with your corporate strategy with a holistic view of your strategic business progress to combine your data with applicable contexts. This actionable information gives you a clear picture of what works and what needs work.

Many businesses use outcomes-based corporate strategies to drive them towards goals, benefit their bottom line and motivate their teams. With AchieveIt, your organization can improve the execution of key plans and initiatives , increase visibility and improve accountability from a centralized, integrated plan management platform.
Whether you have an existing corporate strategy, want an implementation partner, or like some help streamlining your corporate strategy, you can use AchieveIt’s two-pronged approach to strengthen your competitive position . The combination of our management software and an experienced consultant ensures your initiatives are correctly set up for effortless execution.
Schedule a demo today if you would like to learn more about AchieveIt strategic management software. Alternatively, take a self-guided tour and experience the magic of AchieveIt firsthand. Together we can connect, manage and execute key plans and initiatives with innovative corporate strategic plan management.
Related Posts

The Differences Between Long-Term, Mid-Term, and Short-Term Planning

How to Align Company Goals with OKRs: A Step-by-Step Approach

How to Build a Data-Driven Culture
Hear directly from our awesome customers
See first-hand why the world's best leaders use AchieveIt
See AchieveIt in action
Stay in the know. Join our community of subscribers.
Subscribe for plan execution content sent directly to your inbox.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
How to Build a Detailed Business Plan That Stands Out [Free Template]
Updated: March 29, 2022
Published: March 11, 2022
While starting a company may seem easier now than ever before, entrepreneurs have an uphill battle from the moment they start a business. And without a clear, actionable business plan for selling, marketing, finances, and operations, you're almost destined to face significant challenges.

This is why crafting a business plan is an essential step in the entrepreneurial process.
In this post, we'll walk you through the process of filling out your business plan template, like this free, editable version :

Download a free, editable one-page business plan template.
We know that when looking at a blank page on a laptop screen, the idea of writing your business plan can seem impossible. However, it's a mandatory step to take if you want to turn your business dreams into a reality.

That's why we've crafted a business plan template for you to download and use to build your new company. You can download it here for free . It contains prompts for all of the essential parts of a business plan, all of which are elaborated on, below.
This way, you'll be able to show them how organized and well-thought-out your business idea is, and provide them with answers to whatever questions they may have.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Building a Successful Business Plan
In the next section, we'll cover the components of a business plan , such as an executive summary and company description. But before we get to that, let's talk about key elements that should serve as building blocks for your plan.
For some entrepreneurs, the thought of writing a business plan sounds like a chore — a necessary means to an end. But that's a bad take.
A solid business plan is a blueprint for success . It's key to securing financing, presenting your business, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
At the core, your business plan should answer two questions: why your business and why now?
Investors want to know why your business is entering the market, i.e. what problem it's solving and how it's different from what's currently out there. They also want to know why now is the right time for your type of product or service.
At a minimum, your plan should:
- Be more realistic than idealistic: Too often, business plans focus too much on how things could be instead of how they are. While having a vision is important, your plan needs to be rooted in research and data.
- Legitimize your business idea : If an idea fails on paper, it's a signal to go back to the drawing board. In doing so, you avoid losing precious time or money chasing an unrealistic idea.
- Position your business for funding: To get your business off the ground, chances are you'll need financial backing. Even with a solid business idea, investors, lenders, and banks still need convincing. An effective business plan will outline how much money you need, where it's going, what targets you will hit, and how you plan to repay any debts.
- Lay the foundation: Investors focus on risk – if anything looks shaky, it could be a dealbreaker. Ideally, your business plan will lay down the foundation for how you'll operate your business — from operational needs to financial projections and goals.
- Communicate your needs: It's nearly impossible to communicate your needs if you don't know what they are first. Of course, a business’ needs are always changing — but your plan should give you a well-rounded view of how your business will work in the short and long term.
So back to the question of why and why now – consider three things:
- Your industry – How does your product or service fit within your industry? Are you targeting a specific niche? Where do you see the industry going in the next five to 10 years?
- Your target audience – Who are you targeting? What challenges are they facing? How will your product or service help them in their daily lives?
- Your unique selling proposition (USP) – What sets you apart from your competitors? Is it your product/service features? Your company values? Price?
Once you know the answers to these questions, you'll be equipped to answer the question: why your business and why now.
How to Build a Business Plan
- Executive Summary
- Company and Business Description
- Product and Services Line
- Market Analysis
- Marketing Plan
- Legal Notes
- Financial Considerations
Featured Resource: Free Business Plan Template
1. cover page.
Your business plan should be prefaced with an eye-catching cover page. This means including a high-resolution image of your company logo, followed by your company's name, address, and phone number.
Since this business plan will likely change hands and be seen by multiple investors, you should also provide your own name, role in the business, and email address on the cover page.
At the bottom of this page, you can also add a confidentiality statement to protect against the disclosure of your business details.
The statement can read as follows: " This document contains confidential and proprietary information created by [your company name]. When receiving this document, you agree to keep its content confidential and may only reproduce and/or share it with express written permission of [your company name] ."
Remember to keep your cover page simple and concise — and save the important details for other sections.
Why it matters: First impressions are everything, and a clean cover page is the first step in the right direction.
Example of a Cover Page

2. Executive Summary
The executive summary of your business plan provides a one- to two-page overview of your business and highlights the most crucial pieces of your plan, such as your short-term and long-term goals.
The executive summary is essentially a boiled-down version of your entire business plan, so remember to keep this section to the point and filled only with essential information.
Typically, this brief section includes:
- A mission statement.
- The company's history and leadership model.
- An overview of competitive advantage(s).
- Financial projections.
- Company goals.
- An ask from potential investors.
Why it matters: The executive summary is known as the make-or-break section of a business plan. It influences whether investors turn the page or not — so effectively summarizing your business and the problem it hopes to solve is a must.
Think of the Summary as a written elevator pitch (with more detail). While your business plan provides the nitty-gritty details, your Summary describes — in a compelling but matter-of-fact language — the highlights of your plan. If it's too vague, complicated, or fuzzy, you may need to scrap it and start again.
Example of an Executive Summary Introduction
"The future looks bright for North Side Chicago, particularly the Rock Hill Neighborhood. A number of high-end commercial and residential developments are well on their way, along with two new condo developments in nearby neighborhoods.
While the completion of these developments will increase the population within the neighborhood and stimulate the economy, the area lacks an upscale restaurant where residents and visitors can enjoy fine food and drink. Jay Street Lounge and Restaurant will provide such a place."
3. Company & Business Description
In this section, provide a more thorough description of what your company is and why it exists.
The bulk of the writing in this section should be about your company's purpose – covering what the business will be selling, identifying the target market, and laying out a path to success.
In this portion of your business plan, you can also elaborate on your company's:
- Mission statement
- Core values
- Team and organizational structure
Why it matters: Investors look for great structures and teams in addition to great ideas. This section gives an overview of your businesses' ethos. It's the perfect opportunity to set your business apart from the competition — such as your team's expertise, your unique work culture, and your competitive advantage.
Example of a Values/Mission Statement
"Jay Street Lounge and Restaurant will be the go-to place for people to get a drink or bite in an elegant, upscale atmosphere. The mission is to be North Side's leading restaurant, with the best tasting food and the highest quality service."
3. Product & Services Line
Here's where you'll cover the makeup of your business's product and/or services line. You should provide each product or service's name, its purpose, and a description of how it works (if appropriate). If you own any patents, copyrights, or trademarks, it's essential to include this info too.
Next, add some color to your sales strategy by outlining your pricing model and mark-up amounts.
If you're selling tangible products, you should also explain production and costs, and how you expect these factors to change as you scale.
Why it matters: This section contains the real meat of your business plan. It sets the stage for the problem you hope to solve, your solution, and how your said solution fits in the market.
There's no one-size-fits-all formula for this section. For instance, one plan may delve into its ability to market in a more cost-effective way than the competition, whereas another plan focuses on its key products and their unique features and benefits.
Regardless of your angle, it's critical to convey how your offerings will differ from the competition.
Example of a Product/Service Offering
"The menu at Jay Street Lounge and Restaurant will focus on Moroccan cuisine. The stars of the menu (our specialties) are the Moroccan dishes, such as eggplant zaalouk, seafood bastilla, tagine, and chickpea stew. For those who enjoy American dishes, there will also be a variety of options, from burger sliders and flatbread pizza to grilled steak and salads.
The food at Jay Street will have premium pricing to match its upscale atmosphere. During the summer months, the restaurant will have extra seating on the patio where clients can enjoy a special summer menu. We will be open on all days of the week."
4. Market Analysis

It helps to reference your market research documentation in this section, like a Porter's Five Forces Analysis or a SWOT Analysis ( templates for those are available here ). You can also include them in your appendix.
If your company already has buyer personas, you should include them here as well. If not, you can create them right now using the Make My Persona Tool .
Why it matters: Having an awesome product is, well, awesome — but it isn't enough. Just as important, there must be a market for it.
This section allows you to dig deeper into your market, which segments you want to target, and why. The "why" here is important, since targeting the right segment is critical for the success and growth of your business.
It's easy to get lost (or overwhelmed) in a sea of endless data. For your business plan, narrow your focus by answering the following questions:
- What is my market? In other words, who are my customers?
- What segments of the market do I want to target?
- What's the size of my target market?
- Is my market likely to grow?
- How can I increase my market share over time?
Example of a Market Analysis
"Jay Street Lounge and Restaurant will target locals who live and work within the Rock Hill Neighborhood and the greater North Side Chicago area. We will also target the tourists who flock to the many tourist attractions and colleges on the North Side.
We will specifically focus on young to middle-aged adults with an income of $40,000 to $80,000 who are looking for an upscale experience. The general demographics of our target market are women between 20 to 50 years old.
A unique and varied Moroccan-American menu, along with our unique upscale atmosphere, differentiates us from competitors in the area. Jay Street will also set itself apart through its commitment to high-quality food, service, design, and atmosphere."
5. Marketing Plan
Unlike the market analysis section, your marketing plan section should be an explanation of the tactical approach to reaching your aforementioned target audience. List your advertising channels, organic marketing methods, messaging, budget, and any relevant promotional tactics.
If your company has a fully fleshed-out marketing plan, you can attach it in the appendix of your business plan. If not, download this free marketing plan template to outline your strategy.

Free Marketing Plan Template
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
- Pre-Sectioned Template
- Completely Customizable
- Example Prompts
- Professionally Designed
Why it matters: Marketing is what puts your product in front of your customers. It's not just advertising — it's an investment in your business.
Throwing money into random marketing channels is a haphazard approach, which is why it's essential to do the legwork to create a solid marketing plan.
Here's some good news — by this point, you should have a solid understanding of your target market. Now, it's time to determine how you'll reach them.
Example of a Marketing Plan Overview
"Our marketing strategy will focus on three main initiatives:
- Social media marketing. We will grow and expand our Facebook and Instagram following through targeted social media ads.
- Website initiatives. Our website will attract potential visitors by offering updated menus and a calendar of events.
- Promotional events. Jay Street will have one special theme night per week to attract new clients."
6. Sales Plan
It doesn't matter if your sales department is an office full of business development representatives (BDR) or a dozen stores with your products on their shelves.
The point is: All sales plans are different, so you should clearly outline yours here. Common talking points include your:
- Sales team structure, and why this structure was chosen.
- Sales channels.
- Sales tools, software, and resources.
- Prospecting strategy.
- Sales goals and budget.
Like with your marketing plan, it might make sense to attach your completed sales plan to the appendix of your business plan. You can download a template for building your sales plan here .
Why it matters: Among other things, investors are interested in the scalability of your business — which is why growth strategies are a critical part of your business plan.
Your sales plan should describe your plan to attract customers, retain them (if applicable), and, ultimately, grow your business. Be sure to outline what you plan to do given your existing resources and what results you expect from your work.
Example of a Sales Plan Overview
"The most important goal is to ensure financial success for Jay Street Lounge and Restaurant. We believe we can achieve this by offering excellent food, entertainment, and service to our clients.
We are not a low-cost dining option in the area. Instead, the food will have premium pricing to match its upscale feel. The strategy is to give Jay Street a perception of elegance through its food, entertainment, and excellent service."
7. Legal Notes
Your investors may want to know the legal structure of your business, as that could directly impact the risk of their investments. For example, if you're looking for business partners to engage in a non-corporation or LLC partnership, this means they could be on the line for more than their actual investment.
Because this clarification is often needed, explain if you are and/or plan to become a sole proprietor, partnership, corporation, LLC, or other.
You should also outline the steps you have taken (or will need to take) to operate legally. This includes licenses, permits, registrations, and insurance.
The last thing your investor wants to hear after they've sent you a big chunk of change is that you're operating without proper approval from the local, state, or federal government.
Why it matters: The last thing your investor wants to hear after they've sent you a big chunk of change is that you're operating without proper approval from the local, state, or federal government.
Example of Legal Notes
"Jay Street Lounge and Restaurant is up-to-date on all restaurant licenses and health permits. Our business name and logo are registered trademarks, presenting the possibility of expanding locally."
8. Financial Considerations
Ultimately, investors want to know two things:
- When they will earn their money back.
- When they will start seeing returns on their initial investment.
That said, be clear, calculated, and convincing in this section. It should cover:
- Startup costs.
- Sales forecasts for the next several months/quarters.
- Break-even analysis for time and dollars.
- Projected profit and loss (P&L) statement.
Facts and figures are key here, so be as specific as possible with each line item and projection. In addition, explain the "why" behind each of these sections.
However, keep in mind that information overload is a risk, especially when it comes to data. So, if you have pages upon pages of charts and spreadsheets for this section, distill them into a page or two and include the rest of the sheets in the appendix. This section should only focus on key data points.
Why it matters: One of the most important aspects of becoming "investor ready" is knowing your numbers. More importantly, you need to understand how those numbers will enhance your business.
While it's easy to write a number down on paper, it's more important to understand (and communicate) why you need capital, where it's going, and that your evaluation makes sense.
Example of Financial Projections
"Based on our knowledge and experience in the restaurant industry, we have come up with projections for the business.
Starting with an expenditure of $400,000 in year 1, we forecast sales of $1,500,000 and $2,800,000 for years two and three. We expect to achieve a net profit of 15% by year three."
9. Appendix
A detailed and well-developed business plan can range anywhere from 20 to 50 pages, with some even reaching upward of 80.
In many cases, the appendix is the longest section. Why? Because it includes the supportive materials mentioned in previous sections. To avoid disrupting the flow of the business plan with visuals, charts, and spreadsheets, business owners usually add them in the last section, i.e. the appendix.
Aside from what we've already mentioned – marketing plan, sales plan, department budgets, financial documents – you may also want to attach the following in the appendix:
- Marketing materials
- Market research data
- Licensing documentation
- Branding assets
- Floor plans for your location
- Mockups of your product
- Renderings of your office space or location design
Adding these pieces to the appendix enriches the reader's understanding of your business and proves you've put the work into your business plan without distracting from the main points throughout the plan.
Why it matters: An appendix helps the reader do their due diligence. It contains everything they need to support your business plan.
Keep in mind, however, that an appendix is typically necessary only if you're seeking financing or looking to attract business partners.
Use a Business Plan Template to Get Started
Writing a business plan shouldn't be an insurmountable roadblock to starting a business. Unfortunately, for all too many, it is.
That's why we recommend using our free business plan template. Pre-filled with detailed section prompts for all of the topics in this blog post, we're confident this template will get your business plan started in the right direction.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in June 2017 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![what is corporate business plans How to Calculate Your Lead Generation Goals [Free Calculator]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/lead-generation-goal-calculator_5.webp)
How to Calculate Your Lead Generation Goals [Free Calculator]

What Are Direct Costs & How Do They Differ From Indirect Costs?
![what is corporate business plans How to Write a Business Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide [Examples + Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how%20to%20write%20a%20business%20plan.jpg)
How to Write a Business Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide [Examples + Template]

9 Handy Business Calculators That’ll Make Your Life Easier
![what is corporate business plans The Definition of CAC [In Under 100 Words]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hs-fs/hub/53/file-1053926490-jpg/calculate_CAC_%28blog%29.jpg)
The Definition of CAC [In Under 100 Words]
![what is corporate business plans How to Calculate Next Month's Lead Gen Goal [Quick Tip]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hs-fs/hub/53/file-703140114-jpg/Blog_Thinkstock_Images/calculate_monthly_goals.jpg)
How to Calculate Next Month's Lead Gen Goal [Quick Tip]
![what is corporate business plans How to Calculate the Value of Your Social Media Followers [CALCULATOR]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hs-fs/hub/53/file-23155342-png/blog/images/voal-snapshot.png)
How to Calculate the Value of Your Social Media Followers [CALCULATOR]
![what is corporate business plans A Simple Calculator to Determine Your Monthly Traffic & Leads Goals [Template]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hs-fs/hub/53/file-23127769-png/blog/images/leads-goal-calculator1.png)
A Simple Calculator to Determine Your Monthly Traffic & Leads Goals [Template]

How to Calculate & Track a Leads Goal That Sales Supports
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Coaching Skills Training
- Coaching TIPS²™
- Continuous Improvement Coaching
- Courageous Conversations Workshop
- Executive Coaching Program
- Feedback 360
- Safety Coaching
- Sales Coaching Training Program
- Free Consultation
- Applied Strategic Thinking®
- Strategic Leadership Course
- Strategic Teaming
- Strategy Development Processes and Services
- Communication Training for Managers
- Conflict and Collaboration
- Confronting Racism Workshop
- Delegation & Accountability
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Workshop
- Flexible Leadership
- Leading Change
- Leading Groups to Solutions
- Leading Innovation
- Mid-Level Management Training
- Qualities of Leadership
- Bottom Line Leadership
- Customized Leadership Development Programs
- Leadership Development Program Design
- Mini-MBA & Operational Finance
- Problem Solving and Decision Making in the Workplace
- Transition to Leadership
- Virtual Leadership
- High-Performance Teamwork
- Leadership Team Alignment Workshop
- Orienteering
- Corporate Outdoor Training and Team Building
- Retreats for Teams
- Innovation Skills Training
- Personal Impact Workshop
- Supervisor Training Programs
- Customization of CMOE’s Learning Library
- Full Curriculum Development and Design
- Learning & Development Advisory Services
- Bottom Line Leadership Training
- Consulting Services
- Leadership Retreats
- Learning and Development Consulting Services
- Needs Analysis and Organization Assessments
- Transformation & Change Solutions
- Facilitator Training Workshop
- Empathic Leadership
- Supervisor Development Series
- All Courses
- Digital Learning
- Books and Publications
- Assessments and Surveys
- Clients Served
- History and Experience
- Meet the CMOE Team
- Testimonials
- Articles & Tools
- Scenario Templates
- Certified Partners
- Event Resources
- Industry Insights
- Resource Library
- Video Library
- News and Events
- Professional Accreditation and Continuing Education Units
- Surveys & Assessments
- Corporate Strategic Planning
- 360-Degree Leadership Assessment
- Adaptive Communication
- Adaptive Leadership
- Authentic Leadership Style
- Boundary Spanning Leadership
- Business Change Strategies
- Business-Strategy Principles
- Capacity Building
- Cascading Strategy
- Change Management
- Coaching Framework
- Coaching in the Workplace
- Coaching Leadership Style
- Collaborative Coaching
- Competency Assessment
- Conflict Resolution in the Workplace
- Core Competence
- Crisis Leadership
- Critical Success Factors
- DEI in the Workplace
- Directive Leader
- Empathetic Leadership Definition
- Horizontal Leadership
- Inclusive Leadership
- Innovation Strategy
- Leadership Assessment
- Leadership Competency Framework
- Leadership Model
- Management Succession Planning
- Operational Excellence
- Organizational Alignment
- Participative Leadership Style
- Performance Deficiency Coaching
- Persuasive Leadership Style
- Problem Solving in Business
- Servant Leadership Style
- Strategic Agility
- Strategic Alignment
- Strategic Audit
- Strategic Framework
- Strategic Initiatives: Examples and Development
- Strategic Management
- Strategic Mindset Competency
- Strategic Thinking
- Strategy Committee
- Strategy Issues
- Strategy Maps
- Supportive Leadership Style: Definition and Qualities
- Team Building Interventions
- Team Environment
- Team Performance Assessment
- Teamwork Atmosphere
- Total Employee Involvement
- Training Needs Analysis (TNA) Definition
- Transformational Leadership
- Visionary Leadership Style
What is Corporate Strategic Planning?
Corporate Strategic Planning is a companywide approach at the business unit and corporate level for developing strategic plans to achieve a longer-term vision. The process includes defining the corporate strategic goals and intentions at the top and cascading them through each level of the organization. Many organizations confuse the annual budgeting process with corporate planning. Corporate strategic planning should come first and annual budgeting should be driven by the strategy, not by prior year’s budget spend.
Why is Corporate Strategy Important?
A corporate strategy can focus every employee and resource in a company on the same objectives, and it aims to use them all efficiently. It gives every employee a set of guidelines they can use in their everyday work to move toward certain targets, which promote the vision and mission of the company. Corporate level planning can also improve efficiency within the organization and help identify unseen bottlenecks or pain-points.
The corporate strategy gives leaders and employees ideas to use for the improvement of distinctive activities (processes and operations) that create a competitive advantage. The strategy can also help executives to protect the company from entering into costly or irrelevant opportunities. What are the steps involved in strategic corporate planning? Corporate strategic planning begins by clarifying the vision and mission of the organization and the space the business chooses to compete in. Clarifying the organizations position will help you develop and effective strategic planning framework.
1) Competitive Analysis
A competitive analysis needs to be conducted, to understand the trends that could impact the success of your strategy. Common factors that could be analyzed include political, legal, social, environmental, technological. There may be other factors you may want to consider that are relevant to your business and industry.
2) Strategic Goals & Priorities
Once you have completed a competitive analysis, the corporate leadership team will set the overarching strategic goals and priorities for the organization.
Once the strategic goals and priorities are finalized, each business unit needs to define its strategic goals and plans on how it can contribute to the overall direction of the enterprise. That includes not only what is to be accomplished, but how it will be accomplished including high level plans, budgets, human resources, etc.
3) Communication
Once business unit plans and directions have been set, the information needs to be communicated and shared with leadership inside the business unit so that priorities and plans can be aligned and integrated within a single budget.
What is Strategic Business Planning?
At the corporate level, an enterprise develops a portfolio of businesses they choose to compete in. This is a high-level analysis of a business’s competitive and core capabilities, and how each business contributes to the overarching corporate goals. Supported by the corporate strategic business planning process, these businesses are then set up, sponsored, and supported as business units at the operating level.
What Are The Types of Corporate Strategy?
When looking at the types of corporate strategy, it is important to consider a positioning grid that looks at the source of competitive advantage as well as the space where the business competes (markets, geography, size, etc).
Strategy 1: Low Cost Strategy
This type of strategy is one in which your source of advantage is simply competing on cost and being the low-cost provider. With this strategy an organization must exploit all sources of cost advantage. This includes things such as:
- Economies of scale
- Cost of inputs
- Operations excellence to help drive down costs
- This type of strategy requires an organization to compete more broadly (markets, geography, size)
Strategy 2: Differentiated Strategy
In a Differentiated Strategy, the focus is on competing by being unique or distinctively different in your industry. A differentiated strategy provides a product or service in more of a niche market where customers see the importance of offerings and are willing to pay a premium price. While this strategy still has a broad focus on how and where it competes (markets, geography, size), it serves its customers in a differentiated way. Differentiation can include factors such as:
- Technical superiority
- Customization
- Products or services that are difficult to copy
- Customer Service
Strategy 3: Segmented Strategy
A segmented strategy is one in which you have clearly differentiated yourself from the competition. The space in which you compete has a narrow focus. You serve a distinct group of customers with specialized needs. In this space, there are few product or service substitutes that can be offered and while you may not have the volume of customers, profit margins tend to be higher because of the lack of substitutes. and there are few substitutes for your offerings. It is important for every organization to understand where on a strategic position grid it currently sits and where it may want to be — adapted from Michael Porter
What Is the Difference Between Corporate Strategy and Business Strategy?
Corporate strategy, in contrast, involves the plans that a larger enterprise must form when it is composed of multiple smaller businesses or entities. For example a business unit may need to examine factors unique to the industry or competitive landscape that is fundamentally different than its corporate parent.
As a large enterprise, company, or private equity group takes on more acquisitions, it must work with its respective businesses to craft a business strategy and plan that is unique to them and drive competitive advantage through their products, services, and market positioning.
Clients We’ve Worked With
Contact form.
Need More Information? Please fill out the following form and we will be in contact with you with more information.
" * " indicates required fields
As Featured In:
The Better Business Bureau has determined that CMOE meets accreditation standards. These standards verify that CMOE’s product quality and competence enhance customer trust and confidence.
©2024 Center for Management & Organization Effectiveness. All rights reserved.
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![what is corporate business plans [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources
What is management by objectives (MBO)?


Write better AI prompts: A 4-sentence framework

How to find alignment on AI

What is content marketing? A complete guide

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

The Differences Between Business Planning & Corporate Planning
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
What Is the Difference Between a Marketing & Business Plan?
Disaster recovery plan vs. business continuity plan, corporate development & planning.
- What Is a Strategic Business Plan?
- What Happens When an Organization Has No Coherent Strategy?
Business success is dependent upon clear and decisive planning. Sure, strong sales and customer retention drive profit success. However, the increased sales and improved customer retention is a product of the business planning that occurs behind the scenes. Of the many types of planning that businesses use, business planning and corporate planning are the most common.
Business Planning
Business planning defines the strategies the business will use to meet its goals and missions. Business planning provides details on the business’ operations, products and services, and marketing strategies as it relates to the inclusive industry. This process expounds the operation strategies from short- and long-term views while focusing on the overall activity of the company. The business plan does not identify specific employee strategies but rather provides industry strategies.
Corporate Planning
Corporate planning defines the strategies that the employees will take to meet the business’ goals and missions. This type of planning, also known as strategic planning, focuses on staff responsibilities and procedures. As with business planning, strategic planning requires a close look at the company’s missions, strengths and weaknesses. However, corporate planning identifies the step-by-step process of the business, such as the actual steps the staff will take to counteract challenges, train employees and achieve accomplishments. Corporate planning also provides specific, measurable goals with realistic time lines.
Interdependency
Business planning and corporate planning are interdependent. Although business planning can exist without corporate planning, the goals of the business plan are much more attainable with corporate planning. As with business planning, the corporate plan can exist without a business plan. However, without business planning, the overall goals and missions of the business are not clear. Therefore, the corporate planning becomes incomplete.
There are many effects of business and corporate planning. Not only does the planning process help businesses to succeed, it helps businesses to determine when new directions and changes are needed. A close analysis can result in early recognition of potential issues and dangers, as well as help the company to quickly adapt to customer demand and needs.
Considerations
Business and strategic plans should be reviewed periodically. The plans should be reviewed to compare the business’ current standpoints against those that were outlined in the plans. Adjustments should be made, if necessary, to align the business’ actual activities to the defined plans. When analyzing needed changes, consideration should be given to the industry’s environment and trends, as well as the economy’s stability, customer demand and business needs. The balancing of the business and strategic plans should outline the moves or changes that the business will strive to implement and framework the strategies that the employees will use to meet the business’ missions and goals.
- Free Management Library: Basic Description of Strategic Planning
- Plan Ware: Business Planning Papers: Developing a Strategic Plan
- Free Management Library: Business Planning
- MasterCard International: The Plan
- Small Business Administration: Manage Your Business From Start to Finish
Writing professionally since 2004, Charmayne Smith focuses on corporate materials such as training manuals, business plans, grant applications and technical manuals. Smith's articles have appeared in the "Houston Chronicle" and on various websites, drawing on her extensive experience in corporate management and property/casualty insurance.
Related Articles
What is the difference between a marketing plan & a corporate plan, what is the meaning of corporate planning, corporate planning strategies, objectives in workforce planning, what is a business model and how does it differ from a business plan, purpose of corporate planning, business planning as a function of management, swot in marketing analysis, analytical tools for developing a strategic plan, most popular.
- 1 What Is the Difference Between a Marketing Plan & a Corporate Plan?
- 2 What Is the Meaning of Corporate Planning?
- 3 Corporate Planning Strategies
- 4 Objectives in Workforce Planning
Marketing91
Corporate Planning Definition – Strategy, Importance, Objectives and Elements
March 30, 2021 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Management
Corporate planning is a type of strategic planning , responsible for mapping out a course of strategies and their implementations to empower top- management . It optimizes exposure, reach, leads, sales, profits, credibility, loyalty, sustainability , and opportunities of a business .
With the help of corporate strategic planning, a business can efficiently channelize corporate management by leveraging its resources with better acumen than the other market players.
Businesses of any size should incorporate such strategic planning, as it offers-
- Clarity & Direction
- Efficient use of resources
- A way of measuring progress
- Optimized decision-making
- Better coordination in business activities
- Effective allocation of responsibilities
- Motivation and guidance to members
- Analysis Strengths and weaknesses along with opportunities and threats via SWOT analysis , etc.
All in all, corporate planning empowers any kind of business to accomplish its business goals in a more effective and organized manner.
Table of Contents
Corporate Planning Definition
Corporate Planning is defined as forming long-term goals and objectives within the organization’s strengths and weaknesses in the existing and prospective environment.
This is done to ensure the achievement of their plans by combining their short-term and long-term objectives or bringing amendments in the structural working in the organization’s composition.
In the words of David E. Hussey, writer of the book- Corporate Planning: Theory and Practice-
Corporate planning includes the setting of objectives, organizing the work, people and systems to enable those objectives to be achieved, motivating through the planning process and through the plans, measuring performance and so controlling progress of the plans and developing people through better decision-making, clearer objectives, more involvement, and awareness of progress.
What is Corporate Planning Strategy?
Corporate Planning is a strategic process applied by several business organizations to form a roadmap to grow in the market, enhance profits, gain industrial exposure, and strengthen brand identity.
It is a vital tool that successful business organizations use to leverage their existing resources better and more analytically than competitors.
It is the determination of business goals, formulation of diverse strategies for attaining objectives, transforming the goals into tactical plans, implementing and reviewing it to find out the progress of strategies, and finding out loopholes.
Different factors around which corporate planning is channelized via effective SWOT analysis and process of corporate management are-
- Creation of long-range corporate goals and objectives.
- Analysis of Macro and Micro Environments .
- Analysis of Strengths and weaknesses of the business
- Coordination between short term and long term business plans
- Structural changes in the business
- Implementation of the strategic plan as per business goals
- Adept use of scarce financial resources.
- Right evaluation of performance as well as feedback for purposeful corporate planning
Importance of Strategic Corporate Planning

In the current modern era, corporate planning holds a crucial position in a business organization, be it large-sized, medium, or even a new entrant.
The importance of corporate planning can be justified because some companies even hire departmental corporate managers to check the industry’s current scenario and the current status of the organization in the market.
Some of the points that describe the need and importance of corporate planning are mentioned below:
1. Long-term goals
Corporate Planning broadly focuses on long-term goals and sets a blueprint to achieve them in a stipulated period. Long-term goals help an organization keep its core focus on maintaining its efforts, workforce, and efforts on a pre-decided target .
Corporate Planning keeps the employees engaged in their respective tasks with deadlines and ensures effectiveness and efficiency . It also brings harmony, peace, and cooperation among the employees and supervisors in a firm as they all smoothly work towards a common objective.
A strategic business plan helps a business organization provide a focal point not to get deviated or distracted from its end goal. The first and foremost step of corporate planning involves devising a mission statement that tells the world its roles and objectives.
Formulation of a mission statement aids the firm stick to its focus, do all the requisite tasks, assign responsibilities to the employees, and evaluate their work to achieve that final destination.
3. Better Decisions
Developing a strategic plan helps a company make better decisions that are beneficial and helpful in attaining the mission statement. A corporate plan should be structured to spell all the information in the organization’s interest, like the skills required with the employees, machinery or equipment required, etc.
Forming a roadmap to achieve the final goal helps the business people hire the best personnel for their form, arrange funds according to the tasks, and further invest in the most viable propositions.
4. A Measure of Success
Corporate planning also acts as a yardstick to determine an organization’s success in achieving its goals. A firm shall periodically analyze its work to check its progress and make further amendments like replacing personnel, hiring more employees, arranging more funds, upgrading the machinery, etc.
Finding, evaluating, and analyzing the loopholes periodically that block the ways of achieving the mission statement helps in the upgradation of the work and ensure efficiency and effectiveness of the tasks devised. The touchstone function of corporate planning works best in the organizations that devise plans that allow for changes in attaining the tasks.
5. Saves money
The extra benefit associated with corporate planning is that it forms budgets that help save substantial sums. Budgeting allows a firm to allocate its financial resources to the projects that require it the most by cutting out unimportant expenses.
Having a detailed budget tells how much cash is earned, spent, or lent. This wipes out confusion regarding the amount of money allocated to different projects.
Objectives of Corporate planning in Management
Following are the basic objectives of corporate plans:
1. Setting a strategy
The fundamental objective of framing a corporate plan is setting a business strategy . At this stage, companies should look at the opportunities and analyze the threats in the market. For this, they can make a SWOT analysis and select viable propositions for investing their funds.
2. Planning the operations
Once a firm knows its mission statement, it can use these objectives and find ways of attaining them. The sole purpose of corporate planning is to help a firm plan and prepare a list of resources it requires to deliver to achieve its goals.
3. Monitoring and Control
There should be measurable indicators present in a strategic plan to evaluate the progress of the work rate vis-à-vis the initial plans. It mainly includes financial theory related to accounts, the value of output, etc.
Establishing and forming well-devised instruments to devise annual reports is a crux to a successful corporate plan. Since the market environment constantly changes with events happening in the economy, a company regularly needs to review its plans, policies, and even rules and regulations associated with the operations.
Elements of Successful Corporate Plan

There are six elements in a successful corporate plan:
1. Gathering information
Having all the information related to the firm, industry, and competitors are the primary step towards a well-defined corporate plan. Either a business is big or small, it should be aware of the happenings in the market in its sectors, find out opportunities, grab them at the right moment and beware of the threats.
2. Set the objectives of the plan
Having a well-devised mission statement helps a firm stick to its focus of achieving it and keeps all the strategic work smooth in operations. Setting objectives helps form a clear mind about the work done, and the purpose of doing the work makes it fascinating.
3. Devise strategies to meet goals
Having a blueprint helps in effectively achieving the objectives. Forming strategies define the work to be done by the employees. Managers and leaders mainly devise strategies considering the funds available, personnel in the organization, and the deadline to achieve the requisite target. It brings efficiency to the operations of a business.
4. Implementing the plan
The next step is to implement the plans effectively. It involves the execution of the assigned tasks by the personnel within the guidelines and deadlines set. It involves the execution of the assigned tasks by the personnel within the guidelines and deadlines set.
5. Monitor plan performance
An organization should monitor its work by forming progress reports, finding the drawbacks, and work on them immediately.
6. Evaluate the effectiveness of the plan
In the end, a firm should see if the corporate strategy devised by it is competitive or up to the market standards. A plan should be challenging to achieve. A plan that is easy to achieve may not be a viable option in the existing scenario. This may require the organization to reset its plans and considering the market standards.
What to include in a Strategic Corporate Plan?
1. vision statement.
The vision statement of a business talks about business goals that it is supposed to achieve. While planning your corporate strategy , it is important to focus on your vision statement. You should also plan as per your short as well as long term goals. Your goals should be backed for your strategic planning, plus your goals should also be SMART.
2. Mission statement
Next thing upon which you should pay heed while making corporate planning is a mission statement. It tells you how you are going to achieve your vision statement. It will let you know what you are planning to offer, the target market , and the USP of your company. It will offer an elevator pitch to your corporate planning just in a few lines.
3. Resources and scope
Your corporate planning should also pay attention to things that you have in your organization such as your systems, structures, employees, products, accounting, assets, divisions, programs, finance, etc that play a key role in accomplishing your goals. You need to map the current structural existence of your organization to have a proper view of things incorporated and associated with your organization.
4. Objectives
You should also include different business objectives and the ways you are going to measure success in your corporate planning strategy. Here, your objectives need to be measurable, strategic, realistic, achievable, and time-driven. Including vague objectives in your corporate planning statement is of no use here. Different types of objectives might include financial objectives, customer objectives, internal objectives, learning , and growth objectives.
5. Strategies
Finally, you should include strategies that will help you accomplish your business objectives. Such strategic planning can be for launching any new product , or decreasing labour costs by a certain percentage, but your strategies have to directly address the associated objectives. You should also chalk out a proper plan for implementing those strategies.
Here is a video by Marketing91 on Corporate Planning.
Corporate planning vs. Business Planning
Business planning involves strategies that a business uses and applies to attain its goals and objectives. Corporate planning consists of strategies that the employees follow to meet the objectives of an organization. The following points highlight the difference between corporate planning and business planning:
1. Interdependency
A business plan may exist without a corporate plan, but its strategies are linked with corporate plans. Without business planning, the goals and objectives of a firm would be ambiguous. Thus, both business plans and corporate plans are complementary to each other.
A planning process aids a business to succeed in the market and suggests new directions and amendments as per the industry’s short as well as long-range requirements. Thus, there can be several diversified effects on business and corporate plans.
3. Considerations
Corporate planning reviews each step of the working of an organization devised for achieving the mission statement. However, a business plan focuses on the organization’s overall goals, objectives, and progress. To evaluate the tasks, a business should consider several factors such as progress rate, personnel performance, requisite funds for further operations, and many more.
Corporate Planning Jobs in an Organization

Corporate Planning jobs fall under the broader career category of Chief Executives. Corporate planners are responsible for determining and formulating policies and strategies to offer an overall direction for the companies as per the guidelines suggested by the board of directors .
Strategy planning in such jobs revolves around planning, directing, and coordinating different activities at the top-most level of management by taking the services of staff managers and subordinate executives. Corporate planner jobs are also understood as strategic planner jobs.
Common corporate planning jobs are-
- Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates
- Getting Information from all relevant sources
- Communicating with Persons Outside Organization
- Directing, Guiding, and Motivating Subordinates
- Developing and Building Teams
- Establishing and Maintaining Interpersonal Relationships
- Developing Objectives and Strategies
- Monitoring and Controlling Resources
- Analyzing Data or Information
- Judging the Qualities of Things, People, and Services
- Resolving Conflicts and Negotiating with Others
- Evaluating Information to Determine Compliance with Standards
- Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events
- Interacting With Computers
- Organizing, Planning, and Prioritizing Work
- Interpreting the Meaning of Information for Others
- Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge
- Compiling, categorizing, coding, calculating, auditing, tabulating, or verifying information or data
- Coordinating the Work and Activities of Others
- Coaching and Developing Others
- Thinking Creatively
- Staffing Organizational Units
- Selling or Influencing Others
- Monitor Processes, Materials, or Surroundings
- Provide Consultation and Advice to Others
- Estimating the Quantifiable Characteristics of Products, Events, or Information
- Scheduling Work and Activities
- Performing Administrative Activities
- Training and Teaching Others
- Performing for or Working Directly with the Public
- Documenting/Recording Information
Wrapping Up!
The corporate planning process is an activity that involves a series of steps to be followed to achieve the end goal. Specifically, it involves a process that personnel in an organization does to achieve the mission statement.
The process to attain the end goal involves strategies at each level or department with clear and detailed tasks assigned to them within stipulated deadlines. The employees then execute the tasks assigned by their leaders and mentors following some guidelines.
Then managers and leaders analyze the work, make amendments to that, and suggest further improvement guidelines. The organization then check the viability of its plan in terms of its difficulty, market standards, and check whether it is practically achievable or not. Further changes to plans are made after evaluating previous plans to upgrade the formation of plans.
On the concluding note, we hope you would have understood what corporate planning is and how crucial it is for an effective business plan to get favorable outcomes.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Management
Related posts:
- What is Planning? Definition, Importance and Features
- Organisation Development – Definition, Objectives, Features, Importance
- What is Design Thinking? Importance, Advantages & Key Elements
- 7 simple reasons that justify the importance of planning
- Socialization – Definition, Meaning, Elements, Types, Features and Stage
- What is Management System? Definition and Elements
- Features of Planning
- Planning Process
- 6 important factors in planning
- 9 Barriers to Planning -Strategies to Identify and Overcome
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors

What Is Corporate Strategy? The Four Key Components

What Is Corporate Strategy?
Corporate strategy refers to the overall plan or direction of an organization in pursuit of its long-term objectives. It includes defining the company's mission, vision, values, and goals, as well as identifying the markets and products it will focus on, the competitive advantages it aims to build, and the resources and capabilities it needs to achieve its objectives.
Corporate-level strategy involves developing a strategic roadmap for the organization to guide its actions. By doing so, the organization stays focused on its long-term strategic objectives while remaining agile enough to respond to changes in the business environment.

What Are The 4 Components Of Corporate Strategy?
Understanding the components of corporate strategy will help you formulate a well-thought-out strategy that’s easy to follow and execute.
Visioning involves setting the high-level direction of the organization—namely, the vision, mission, and corporate values.
Objective setting
Objective Setting involves defining specific and measurable outcomes you want to achieve over a chosen timeframe.
Resource allocation
This is the practice of allocating human and capital resources to support objectives.
Strategic trade-offs
This is an essential part of corporate strategic planning since companies can’t always take advantage of all feasible opportunities. Leaders must learn how to determine the optimal strategic mix that will balance risks with returns.
👉 Use this free corporate strategy template to quickly start the development of your own company-level strategy.
The Corporate, Business, And Functional Level Strategies
A complete organizational strategy has three levels :

Corporate-level strategy
Corporate-level strategy is the highest level of corporate strategic planning. (We’ll dive deeper into it in this guide).
Business-level strategy
Business-level strategy connects the strategic goals of the company strategy with the needs and capacities of the business unit level.
It turns a corporate-level strategic goal into a practical strategic goal based on business-level knowledge and experience.
Functional-level strategy
Functional-level strategy refers to the specific plans and actions developed by individual departments within an organization to achieve the goals and objectives set out in the corporate-level strategy. These strategies are more detailed than corporate strategies, and they focus on the day-to-day activities of the organization.
Functional-level strategies are developed based on the company's overall goals and objectives. Their aim is to ensure that each functional area of the organization contributes to the company's success in a coordinated and strategic way.
For example, let’s say a company has set a corporate-level goal to reduce costs. One of the functional-level strategies that the operations team can set is to streamline the supply chain to reduce the cost of inventory and raw materials. Another functional strategy would be to optimize the use of technology to reduce costs.
Corporate-Level Strategy vs. Business-Level Strategy
Corporate-level strategy and business-level strategy are two different levels of strategic planning that organizations use to achieve their goals and objectives.
Corporate-level strategy involves making decisions about the overall direction and scope of the organization. This includes deciding which industries and markets to compete in, how to allocate resources across different business units or product lines, and how to diversify the company's portfolio of products or services. This strategy level focuses on long-term goals and objectives and often involves mergers and acquisitions, joint ventures, vertical integration, or other strategic alliances.
Business-level strategy , on the other hand, focuses on how individual business units or product lines will compete in their respective markets. This involves making decisions about product differentiation, pricing, marketing, and resource allocation to achieve specific goals and objectives. This strategy level deals with shorter-term goals and objectives, often involving product development, marketing campaigns, and operational improvements.
Both levels of strategy are crucial for organizational success and should be aligned with each other.
📚 Read more: The 7 Best Business Strategy Examples I've Ever Seen

How The 3 Strategy Levels Relate To Each Other
The three levels of strategy are interdependent and must be aligned to achieve an organization's overall goals and objectives.
For example, a corporate-level strategy of diversifying a company's portfolio by acquiring a new business unit would require a business-level strategy to integrate the new business and align it with the company's existing operations. The functional-level strategy would then focus on optimizing processes, allocating resources, and developing capabilities to support the new business unit's operations and ensure its success.
Understanding how the three strategy levels communicate helps you build a solid strategic plan .
What Are The Benefits Of A Corporate-Level Strategy?
The benefits of a well-defined corporate strategy for an organization increase as the organization scales . It’s possible for small or even medium-sized businesses to get by without investing time in developing their corporate strategy. However, as the needs of an organization grow, it becomes increasingly necessary to develop the strategic planning process in a way that reflects the complexity of that organization.
In the end, corporate strategy benefits any organization, regardless of size .
The three main benefits of having a solid corporate strategy are:
1. Provides strategic direction
By implementing a corporate strategic plan, an organization can establish its desired direction and provide clear guidance to leaders, stakeholders, and employees on how they prioritize decisions, making strategy execution and goal achievement much easier.
2. Helps you stay flexible and adapt when needed
In a dynamic world, organizations need to keep pace with changes as they happen.
By continually defining corporate strategies and strategic goals in relation to opportunities or threats as they appear, your organization will be able to consistently perform optimally.
3. Improves decision making
Without clearly defined strategies at a corporate level, business, and functional level units will perform sub-optimally.
The abstract level of decision-making at the corporate level will translate to better results at other decision-making levels and help employees feel that their organization has a clear direction and purpose.

📚 Recommended read: Strategic Control Simplified: A 6-Step Process And Tools
The Common Problem With Corporate Strategy
One of the most common problems with strategy, especially corporate strategy, is that it gets stuck in the boardroom. Leaders are the experts, they’ve climbed the ropes, and they have the scars to prove it. It is obvious that they are best suited to make strategic decisions and put together a plan that steers the company in the right direction.
That statement seems reasonable, but it contains a lie.
Creating a static PowerPoint document is not a strategy, no matter how long or beautiful it is. As Mike Lardner, former Director of Corporate Strategy at Whirlpool points out in Cascade’s state of strategy report : "The main problem with the strategy is that it's usually not even strategy. It's just the first pass at next year's budget!"
There is an annual cycle of secret meetings that exhaust resources and no one can figure out where, why, or what to do. Often, the strategy is left in a PowerPoint until the next year, and it's so manual to synthesize that it's not even updated or tracked on regular basis.
Types Of Corporate Strategy And Examples
Your corporate strategy must reflect an optimal approach that responds to the needs and the environment of your business. Thus, it’s helpful to divide corporate strategy into four classifications based on external and internal factors.
Growth strategies
These are strategies that focus on a company’s growth and might include entering new markets, increasing or diversifying existing ones, or using forward or backward integration to take advantage of economies of scale.
Growth strategies are typical with most tech companies like Facebook ( Meta ), Google, and Amazon , which consistently take advantage of new opportunities.
When Facebook launched in 2004, it was a small social media network among several competitors. Using a market penetration growth strategy aimed at Harvard college students and eventually a tech acquisition strategy that purchased emerging technology, Facebook grew from that small campus social network into the ubiquitous company it is today.
Stability strategies
These are designed to consolidate an organization's current position, with an eye toward creating a strategic environment that will provide greater flexibility for the future employment of growth or retrenchment strategies.
Stability strategies are more conservative strategies, focused on preserving profit, reducing costs, and investigating future strategic possibilities.
Steel Authority of India adopted a stability strategy focused on increasing efficiency rather than increasing the number of plants. This move helped address the over-capacity in the industry and retain the company’s position as the third-fastest growing steel producer in the world.
Retrenchment strategies
These are a response to unprofitable or damaging elements of a business or organization, such as eliminating unprofitable assets or product lines.
General Motors (GM) , once the world’s largest automaker, started implementing retrenchment strategies as it pulled out its brands from major global markets like Russia, India, and Western Europe. Declining sales and profitability were the main culprits as its competitors consistently took the top sales spots.
📚 Recommended read: Strategy study: The Journey of General Motors
Combination Strategy
Sometimes, organizations combine the above-mentioned strategies even if they appear contradictory.
For example, a company may utilize a stability and retrenchment strategy to keep profits growing while preserving capital. Or they can continue taking risks to pursue growth while keeping certain portions of the enterprise stable.
A combination strategy is useful when organizations are large and operate in complex environments, such as having several enterprises operating in different industries with different needs.
For example, McDonald’s continues to pursue growth by expanding to new markets worldwide while maintaining a profitable core menu and focusing on improving operational efficiency.
Another example is the move by Hewlett-Packard to split the company into two in order to pursue a stability and growth strategy at once. HP Inc., the stagnant arm that sells personal computers and printers, focuses on a stability strategy to maintain profitability. Meanwhile, HPE, the exciting business that sells industrial-grade server computers to enterprises, focuses on a growth strategy as it taps an underserved market segment.
📚 Want to study strategies of leading global companies, including Heineken, Coca-Cola, and Unilever? Click here to check out our Strategy Factory with 100+ strategy studies.
What Should My Corporate Strategy Model Look Like?
There are a number of different models you can apply to the strategic planning process, each with its own merits. We’re going to show you how to build your corporate strategy model based on our tested and proven strategic planning model—the Cascade model, used by +20,000 teams worldwide.

Corporate strategy planning is the highest level of strategic planning within a business or organization and must take into account a huge number of variables.
1. Defining a vision
Reducing complexity is a must . The basis for corporate planning is defining an abstract vision or overarching goal based on the current organization and its environment.
The vision will provide a point of reference for your mission, and the mission will serve as a benchmark for measuring goals and evaluating strategies.
Follow our guide for an in-depth explanation of the process of writing a vision statement .
2. Describe your company’s values
Your company’s vision statement is a destination. Company values describe how you will arrive at this destination.
The values that you outline should be clear, concise, and, above all, real. To get a good sense of how to define your company values, read our guide .
3. Choose focus areas
Think of focus areas as the foundation for your corporate planning. They are strategic priorities that your organization will be focusing on within a given timeframe.
4. Define objectives
Once you’ve defined a clear vision and selected your focus areas, you must outline the strategic objectives .
These objectives will represent a more concrete example of what you want to achieve, with stated deadlines and milestones.
5. Establish KPIs
The corporate planning process ends with the definition of KPIs that will allow corporate strategists to track and adjust the strategic objectives based on results.
📚 Dive deeper into each element with this comprehensive guide on how to write a strategic plan .
Get A Blueprint For Corporate Strategic Planning
Corporate strategic planning gives your company the essential conceptual tools to succeed in competitive markets. Taking the time to plan a well-structured corporate strategy will quickly yield benefits that are quantifiable and provide insights into your operations .
Get your free corporate strategy template to follow a structured approach and create a highly effective corporate strategic plan that keeps everyone aligned with the business objectives.
Popular articles

Viva Goals Vs. Cascade: Goal Management Vs. Strategy Execution

What Is A Maturity Model? Overview, Examples + Free Assessment
How To Implement The Balanced Scorecard Framework (With Examples)

The Best Management Reporting Software For Strategy Officers (2024 Guide)
Your toolkit for strategy success.

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Corporate Governance?
- How It Works
- Board of Directors
- Assessing Corporate Governance
The Bottom Line
- Corporate Finance
Corporate Governance: Definition, Principles, Models, and Examples
Good corporate governance can benefit investors and other stakeholders, while bad governance can lead to scandal and ruin
James Chen, CMT is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/photo__james_chen-5bfc26144cedfd0026c00af8.jpeg)
Amanda Bellucco-Chatham is an editor, writer, and fact-checker with years of experience researching personal finance topics. Specialties include general financial planning, career development, lending, retirement, tax preparation, and credit.
Investopedia / Jessica Olah
Corporate governance is the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. Corporate governance essentially involves balancing the interests of a company's many stakeholders , which can include shareholders, senior management, customers, suppliers, lenders, the government, and the community. As such, corporate governance encompasses practically every sphere of management, from action plans and internal controls to performance measurement and corporate disclosure .
Key Takeaways
- Corporate governance is the structure of rules, practices, and processes used to direct and manage a company.
- A company's board of directors is the primary force influencing corporate governance.
- Bad corporate governance can destroy a company's operations and ultimate profitability.
The basic principles of corporate governance are accountability, transparency, fairness, responsibility, and risk management.
Understanding Corporate Governance
Governance refers to the set of rules, controls, policies, and resolutions put in place to direct corporate behavior. A board of directors is pivotal in governance , while proxy advisors and shareholders are important stakeholders who can affect governance.
Communicating a company's corporate governance is a key component of community and investor relations . For instance, Apple Inc.'s investor relations site profiles its corporate leadership (the executive team and board of directors) and provides information on its committee charters and governance documents, such as bylaws, stock ownership guidelines, and articles of incorporation .
Most successful companies strive to have exemplary corporate governance. For many shareholders, it is not enough for a company to be profitable; it also must demonstrate good corporate citizenship through environmental awareness, ethical behavior, and other sound corporate governance practices.
Benefits of Corporate Governance
- Good corporate governance creates transparent rules and controls, guides leadership, and aligns the interests of shareholders, directors, management, and employees.
- It helps build trust with investors, the community, and public officials.
- Corporate governance can give investors and stakeholders a clear idea of a company's direction and business integrity.
- It promotes long-term financial viability, opportunity, and returns.
- It can facilitate the raising of capital.
- Good corporate governance can translate to rising share prices.
- It can reduce the potential for financial loss, waste, risks, and corruption.
- It is a game plan for resilience and long-term success.
Corporate Governance and the Board of Directors
The board of directors is the primary direct stakeholder influencing corporate governance. Directors are elected by shareholders or appointed by other board members and charged with representing the interests of the company's shareholders.
The board is tasked with making important decisions, such as corporate officer appointments, executive compensation, and dividend policy. In some instances, board obligations stretch beyond financial optimization, as when shareholder resolutions call for certain social or environmental concerns to be prioritized.
Boards are often made up of a mix of insiders and independent members. Insiders are generally major shareholders, founders, and executives. Independent directors do not share the ties that insiders have. They are typically chosen for their experience managing or directing other large companies. Independents are considered helpful for governance because they dilute the concentration of power and help align shareholder interests with those of the insiders.
The board of directors must ensure that the company's corporate governance policies incorporate corporate strategy, risk management, accountability, transparency, and ethical business practices.
A board of directors should consist of a diverse group of individuals, including those with matching business knowledge and skills, and others who can bring a fresh perspective from outside the company and industry.
The Principles of Corporate Governance
While there can be as many principles as a company believes make sense, some of the most common ones are:
- Fairness : The board of directors must treat shareholders, employees, vendors, and communities fairly and with equal consideration.
- Transparency : The board should provide timely, accurate, and clear information about such things as financial performance, conflicts of interest, and risks to shareholders and other stakeholders.
- Risk Management : The board and management must determine risks of all kinds and how best to control them. They must act on those recommendations to manage risks and inform all relevant parties about the existence and status of risks.
- Responsibility : The board is responsible for the oversight of corporate matters and management activities. It must be aware of and support the successful, ongoing performance of the company. Part of its responsibility is to recruit and hire a chief executive officer (CEO) . It must act in the best interests of a company and its investors.
- Accountability : The board must explain the purpose of a company's activities and the results of its conduct. It and company leadership are accountable for the assessment of a company's capacity, potential, and performance. It must communicate issues of importance to shareholders.
Corporate Governance Models
Different corporate governance models may be found throughout the world. Here are a few of them.
The Anglo-American Model
This model can take various forms, such as the Shareholder, Stewardship, and Political Models. The Shareholder Model is the principal model at present.
The Shareholder Model is designed so that the board of directors and shareholders are in control. Stakeholders such as vendors and employees, though acknowledged, lack control.
Management is tasked with running the company in a way that maximizes shareholder interest. Importantly, proper incentives should be made available to align management behavior with the goals of shareholders/owners.
The model accounts for the fact that shareholders provide the company with funds and may withdraw that support if dissatisfied. This is supposed to keep management working effectively.
The board will usually consist of both insiders and independent members. Although traditionally, the board chairperson and the CEO can be the same, this model seeks to have two different people hold those roles.
The success of this corporate governance model depends on ongoing communications among the board, company management, and the shareholders. Important issues are brought to shareholders' attention. Important decisions that need to be made are put to shareholders for a vote.
U.S. regulatory authorities tend to support shareholders over boards and executive management.
The Continental Model
Two groups represent the controlling authority under the Continental Model. They are the supervisory board and the management board.
In this two-tiered system, the management board is composed of company insiders, such as its executives. The supervisory board is made up of outsiders, such as shareholders and union representatives. Banks with stakes in a company also could have representatives on the supervisory board.
The two boards remain entirely separate. The size of the supervisory board is determined by a country's laws and can't be changed by shareholders.
National interests have a strong influence on corporations with this model of corporate governance. Companies can be expected to align with government objectives.
This model also greatly values the engagement of stakeholders, as they can support and strengthen a company's continued operations.
The Japanese Model
The key players in the Japanese Model of corporate governance are banks, affiliated entities, major shareholders called Keiretsu (who may be invested in common companies or have trading relationships), management, and the government. Smaller, independent, individual shareholders have no role or voice. Together, these key players establish and control corporate governance.
The board of directors is usually made up of insiders, including company executives. Keiretsu may remove directors from the board if profits wane.
The government affects the activities of corporate management via its regulations and policies.
In this model, corporate transparency is less likely because of the concentration of power and the focus on the interests of those with that power.
How to Assess Corporate Governance
As an investor, you want to select companies that practice good corporate governance in the hope that you can thereby avoid losses and other negative consequences such as bankruptcy.
You can research certain areas of a company to determine whether or not it's practicing good corporate governance. These areas include:
- Disclosure practices
- Executive compensation structure (whether it's tied only to performance or also to other metrics)
- Risk management (the checks and balances on decision-making)
- Policies and procedures for reconciling conflicts of interest (how the company approaches business decisions that might conflict with its mission statement)
- The members of the board of directors (their stake in profits or conflicting interests)
- Contractual and social obligations (how a company approaches issues such as climate change)
- Relationships with vendors
- Complaints received from shareholders and how they were addressed
- Audits (the frequency of internal and external audits and how any issues that those audits raised have been handled)
Types of bad governance practices include:
- Companies that do not cooperate sufficiently with auditors or do not select auditors with the appropriate scale, resulting in the publication of spurious or noncompliant financial documents
- Executive compensation packages that fail to create an optimal incentive for corporate officers
- Poorly structured boards that make it too difficult for shareholders to oust ineffective incumbents.
Examples of Corporate Governance: Bad and Good
Bad corporate governance can cast doubt on a company's reliability, integrity, or obligation to shareholders. All can have implications for the financial health of the business.
Volkswagen AG
Tolerance or support of illegal activities can create scandals like the one that rocked Volkswagen AG starting in September 2015. The details of "Dieselgate" (as the affair came to be known) revealed that for years, the automaker had deliberately and systematically rigged engine emission equipment in its cars to manipulate pollution test results in the U.S. and Europe.
Volkswagen saw its stock shed nearly half its value in the days following the start of the scandal. Its global sales in the first full month following the news fell 4.5%.
VW's board structure facilitated the emissions rigging and was a reason it wasn't caught earlier. In contrast to a one-tier board system common to most U.S. companies, VW had a two-tier board system consisting of a management board and a supervisory board, in keeping with the Continental Model of corporate governance.
The supervisory board was meant to monitor management and approve corporate decisions. However, it lacked the independence and authority to carry out these roles appropriately.
The supervisory board included a large portion of shareholders. Ninety percent of shareholder voting rights were controlled by members of the board. There was no real independent supervisor. As a result, shareholders were in control and negated the purpose of the supervisory board, which was to oversee management and employees, and how they operated. This allowed the rigged emissions to occur.
Public and government concern about corporate governance tends to wax and wane. Often, however, highly publicized revelations of corporate malfeasance revive interest in the subject.
For example, corporate governance became a pressing issue in the United States at the turn of the 21st century, after fraudulent practices bankrupted high-profile companies such as Enron and WorldCom .
The problem with Enron was that its board of directors waived many rules related to conflicts of interest by allowing the chief financial officer (CFO) , Andrew Fastow, to create independent, private partnerships to do business with Enron.
These private partnerships were used to hide Enron's debts and liabilities. If they'd been accounted for properly, they would have reduced the company's profits significantly.
Enron's lack of corporate governance allowed the creation of the entities that hid the losses. The company also employed dishonest people, from Fastow down to its traders, who made illegal moves in the markets.
The Enron scandal and others in the same period resulted in the 2002 passage of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act . It imposed more stringent recordkeeping requirements on companies and stiff criminal penalties for violating them and other securities laws. The aim was to restore confidence in public companies and how they operate.
It's common to hear examples of bad corporate governance. In fact, it's often why companies end up in the news. You rarely hear about companies with good corporate governance because their corporate guiding policies keep them out of trouble.
One company that seems to have consistently practiced good corporate governance, and adapts or updates it often, is PepsiCo. In drafting its 2020 proxy statement, PepsiCo sought input from investors in six areas:
- Board composition, diversity, and refreshment, plus leadership structure
- Long-term strategy, corporate purpose, and sustainability issues
- Good governance practices and ethical corporate culture
- Human capital management
- Compensation discussion and analysis
- Shareholder and stakeholder engagement
The company included in its proxy statement a graphic of its current leadership structure. It showed a combined chair and CEO along with an independent presiding director and a link between the company's "Winning With Purpose" vision and changes to the executive compensation program.
What Are the 4 Ps of Corporate Governance?
The four P's of corporate governance are people, process, performance, and purpose.
Why Is Corporate Governance Important?
Corporate governance is important because it creates a system of rules and practices that determines how a company operates and how it aligns with the interest of all its stakeholders. Good corporate governance fosters ethical business practices, which lead to financial viability. In turn, that can attract investors.
What Are the Basic Principles of Corporate Governance?
Corporate governance consists of the guiding principles that a company puts in place to direct all of its operations, from compensation, risk management, and employee treatment to reporting unfair practices, dealing with the impact on the climate, and more.
Corporate governance that calls for upstanding, transparent behavior can lead a company to make ethical decisions that will benefit all of its stakeholders, including investors. Bad corporate governance can lead to the breakdown of a company, often resulting in scandal and bankruptcy.
Apple. " Investor Relations. Leadership and Governance ."
BBC. " Scandal Cuts VW Sales by 4.5% This Year ."
Dibra, Rezart. " Corporate Governance Failure: The Case of Enron and Parmalat ." European Scientific Journal , vol.12, no. 16, June 2016, pp. 283-290.
Corporate Secretary. " PepsiCo Finds Governance Success Through Evolution ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-481814784-bea4b49529a74c71b4761999a98c9760.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Business Strategy & Why Is It Important?

- 20 Oct 2022
Every business leader wants their organization to succeed. Turning a profit and satisfying stakeholders are worthy objectives but aren’t feasible without an effective business strategy.
To attain success, leaders must hone their skills and set clear business goals by crafting a strategy that creates value for the firm, customers, suppliers, and employees. Here's an overview of business strategy and why it's essential to your company’s success.
Access your free e-book today.
What’s a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered.
According to Harvard Business School Online's Business Strategy course, an effective strategy is built around three key questions:
- How can my business create value for customers?
- How can my business create value for employees?
- How can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers?
Many promising business initiatives don’t come to fruition because the company failed to build its strategy around value creation. Creativity is important in business , but a company won't last without prioritizing value.
The Importance of Business Strategy
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including:
- Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials
- Suppliers: Whether to source materials sustainably and from which suppliers
- Employee recruitment: How to attract and maintain talent
- Resource allocation: How to allocate resources effectively
Without a clear business strategy, a company can't create value and is unlikely to succeed.
Creating Value
To craft a successful business strategy, it's necessary to obtain a thorough understanding of value creation. In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee explains that, at its core, value represents a difference. For example, the difference between a customer's willingness to pay for a good or service and its price represents the value the business has created for the customer. This difference can be visualized with a tool known as the value stick.
The value stick has four components, representing the value a strategy can bring different stakeholders.

- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The maximum amount a customer is willing to pay for a company's goods or services
- Price : The actual price of the goods or services
- Cost : The cost of the raw materials required to produce the goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to receive for raw materials, or the minimum employees are willing to earn for their work
The difference between each component represents the value created for each stakeholder. A business strategy seeks to widen these gaps, increasing the value created by the firm’s endeavors.
Increasing Customer Delight
The difference between a customer's WTP and the price is known as customer delight . An effective business strategy creates value for customers by raising their WTP or decreasing the price of the company’s goods or services. The larger the difference between the two, the more value is created for customers.
A company might focus on increasing WTP with its marketing strategy. Effective market research can help a company set its pricing strategy by determining target customers' WTP and finding ways to increase it. For example, a business might differentiate itself and increase customer loyalty by incorporating sustainability into its business strategy. By aligning its values with its target audiences', an organization can effectively raise consumers' WTP.
Increasing Firm Margin
The value created for the firm is the difference between the price of an item and its cost to produce. This difference is known as the firm’s margin and represents the strategy's financial success. One metric used to quantify this margin is return on invested capital (ROIC) . This metric compares a business's operating income with the capital necessary to generate it. The formula for ROIC is:
Return on Invested Capital = Net Operating Cost After Tax (NOCAT) / Invested Capital (IC)
ROIC tells investors how successful a company is at turning its investments into profit. By raising WTP, a company can risk increasing prices, thereby increasing firm margin. Business leaders can also increase this metric by decreasing their costs. For example, sustainability initiatives—in addition to raising WTP—can lower production costs by using fewer or more sustainable resources. By focusing on the triple bottom line , a firm can simultaneously increase customer delight and margin.
Increasing Supplier Surplus & Employee Satisfaction
By decreasing suppliers' WTS, or increasing costs, a company can create value for suppliers—or supplier surplus . Since increasing costs isn't sustainable, an effective business strategy seeks to create value for suppliers by decreasing WTS. How a company accomplishes this varies. For example, a brick-and-mortar company might partner with vendors to showcase its products in exchange for a discount. Suppliers may also be willing to offer a discount in exchange for a long-term contract.
In addition to supplier WTS, companies are also responsible for creating value for another key stakeholder: its employees. The difference between employee compensation and the minimum they're willing to receive is employee satisfaction . There are several ways companies can increase this difference, including:
- Increasing compensation: While most companies hesitate to raise salaries, some have found success in doing so. For example, Dan Price, CEO of Gravity Payments, increased his company's minimum wage to $80,000 per year and enjoyed substantial growth and publicity as a result.
- Increasing benefits: Companies can also decrease WTS by making working conditions more desirable to prospective employees. Some offer remote or hybrid working opportunities to give employees more flexibility. Several have also started offering four-day work weeks , often experiencing increased productivity as a result.
There are several ways to increase supplier surplus and employee satisfaction without hurting the company's bottom line. Unfortunately, most managers only devote seven percent of their time to developing employees and engaging stakeholders. Yet, a successful strategy creates value for every stakeholder—both internal and external.

Strategy Implementation
Crafting a business strategy is just the first step in the process. Implementation takes a strategy from formulation to execution . Successful implementation includes the following steps :
- Establish clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Set expectations and ensure employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities
- Delegate work and allocate resources effectively
- Put the plan into action and continuously monitor its progress
- Adjust your plan as necessary
- Ensure your team has what they need to succeed and agrees on the desired outcome
- Evaluate the results of the plan
Throughout the process, it's important to remember to adjust your plan throughout its execution but to avoid second-guessing your decisions. Striking this balance is challenging, but crucial to a business strategy's success.

Learn More About Creating a Successful Business Strategy
Business strategy constantly evolves with changing consumer expectations and market conditions. For this reason, business leaders should continuously educate themselves on creating and executing an effective strategy.
One of the best ways to stay up-to-date on best practices is to take an online course, such as HBS Online's Business Strategy program. The course will provide guidance on creating a value-driven strategy for your business.
Do you want to learn how to craft an effective business strategy and create value for your company's stakeholders? Explore our online course Business Strategy , or other strategy courses , to develop your strategic planning skills. To determine which strategy course is right for you, download our free flowchart .

About the Author
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Environment
- Environment Agency business plans

Environment Agency business plan 2024 to 2025
Published 20 May 2024
Applies to England

© Crown copyright 2024
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: [email protected] .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/environment-agency-business-plans/environment-agency-business-plan-2024-to-2025
1. Introduction
We are the Environment Agency ( EA ), a non-departmental public body established in 1996 and sponsored by the Department for Food and Rural Affairs ( Defra ). In our roles as regulator, operator, adviser, responder, and research centre, we are tasked with:
- protecting and enhancing the environment as a whole
- contributing towards sustainable development
Our remit primarily covers England, though our influence and collaboration with other UK environmental bodies and partners extends beyond England’s borders. England represents approximately:
- 13 million hectares of land
- 22,000 miles (35,000 km) of river
- 3,100 miles (5,000 km) of coastline seawards to the three-mile limit, which includes 2 million hectares of coastal waters
Through our work we contribute towards the UK government’s 25 Year Environment Plan ( 25YEP ) which launched in January 2018. It set out 10 ambitious goals relating to key aspects of our remit including:
- the environment
- biodiversity
- air quality
- waste reduction
- climate change mitigation
The Environment Act 2021 legally enshrined the commitment to refresh the 25YEP every 5 years. In 2023 the first review of the 25YEP resulted in the Environmental Improvement Plan ( EIP ). The plan builds upon the vision of the 25YEP and sets actions to achieve its goals. It reflects the UK’s commitment to environmental stewardship and global biodiversity conservation.
Key areas we contribute to include:
- halting biodiversity decline
- resource management
- climate change adaptation
- enhancing beauty and heritage
EA2025 – our current 5-year corporate action plan – comes to an end in March 2025. It reflects the ambition of the 25YEP .
This business plan sets out our priorities for 2024 to 2025. It will help focus our delivery as we transition to a new corporate action plan in our 30th anniversary year.
2. Foreword from the Chair
As the primary environmental regulator in England, we exist to create better places for people, wildlife, and the environment. We are here to:
- protect and improve the environment
- support sustainable development
This business plan represents a hugely important and exciting step forward for the Environment Agency. It will guide our delivery towards this mission for 2024 to 2025.
As Chair, I regularly meet with our partners, stakeholders, and communities up and down the country. They tell me they want the Environment Agency to:
- keep rivers clean
- hold polluters to account
- protect homes and businesses from the devastating impact of flooding
Their expectations are clear, and we must strive to meet them. Ultimately, we will be judged on our performance and the outcomes we deliver. We must therefore find ways to enhance and improve it in everything we do.
In the year ahead this includes:
- supporting our people to be more integrated and able to work more effectively as one team
- increasing transparency
- improving the way we use data and information to inform our decisions
This is already happening with regards to our role in ensuring people and wildlife have clean and plentiful water. This will continue to be a huge focus for the organisation. It remains one of the biggest challenges we face but also one of the biggest gifts we can give to future generations. This plan highlights work we will do this year to improve water quality. I look forward to meeting many of our new recruits who will drive this work forward in the year ahead.
We will contribute to green growth and a sustainable future for the country through our continued work on:
- the Flood and Coastal Erosion Risk Management Programme
- maintaining our strong performance on regulation
We can look back on 2023 to 2024 and be proud of what we have delivered. Through this business plan we can also look forward with a sense of optimism and determination. We know that if we can deliver it, we can achieve excellence as a leading environmental regulator. And more importantly make many people’s lives, and the places and environments in which they live, much better.
Alan Lovell, Chair
1 April 2024
3. Foreword from the Chief Executive
Our 2024 to 2025 business plan marks the next stage in our journey. We shall focus on:
- meeting the aspirations and standards the public hold for us
- expanding our work on water quality and waste management
- committing to challenging but realistic efficiency and savings targets
We start the year having achieved very good results in 2023 to 2024. This includes:
- protecting more homes from flooding
- delivering an excellent incident response
- cleaner healthier air (year-on-year reduction in pollutants)
- protecting people and the environment through effective regulation (97% compliance at permitted sites)
Our customer service improved too, as we met Freedom of Information deadlines and service standards for permitting.
We have delivered these improved results whilst managing one of the wettest winters on record.
Three years into the second flood asset capital programme , we have protected an additional 88,272 properties (101% of target) on top of more than 314,000 homes protected under the first 6-year programme. Over the last winter period, sadly almost 7,000 properties did flood (with over 240,000 properties protected) which underlines the on-going threat flooding poses to people’s lives and livelihoods.
I pay tribute to all our staff who worked tirelessly, often through weekends and holidays, to deliver an effective response to the weather and flooding we experienced last year.
As we look to 2024 to 2025, we will meet 2 major challenges. Firstly, to deliver a step change in our work on water quality. This follows the government’s approval to invest up to £53m in a new water inspection, enforcement, and data capability. This will ensure we can play a key part in delivering the government’s accelerated Plan for Water , assessing our progress and contribution against our targets and performance framework. We will need to work with all parties to move the dial on water quality and we are determined to succeed as a regulator in this domain.
Our second challenge will be to realise a major step forward on waste management. The coming year has many critical milestones as we deliver the government’s ambitious waste strategy. Core to success will be finding our voice as a confident regulator, which responds to the concerns of communities impacted by poor waste management and waste crime.
Our people are of course at the heart of what we do. In the year ahead we have set targets to improve diversity, building on our success in the last year. We want to introduce new talent schemes, particularly for under-represented groups, expand our work in sponsoring early career professionals, and sign the Armed Forces Covenant.
We know we can rely on our talented, passionate, and skilled staff to deliver for the environment and our communities in the year ahead.
Philip Duffy, Chief Executive and Accounting Officer
4. Final year of our 5-year corporate plan – EA2025
2024 to 2025 will be the final year of our current 5-year corporate action plan – EA2025 .
- reflects and connects with our people’s passion to protect and enhance the environment
- maps our varied and wide-reaching work to the ambition set out in the 25 Year Environment Plan ( 25YEP )
In the period of EA2025 the world came to grips with the Covid 19 global pandemic. For the Environment Agency, EA2025 helped us retain our sense of purpose and come through an enforced transformation on working practice. The pandemic also heightened the public’s awareness and appreciation of the environment and the places people live.
Our delivery of EA2025 has been tracked and published on GOV.UK in regular quarterly updates of our corporate scorecard . Whilst some of the measures have evolved over the period between 2020 to 2024, we can track our progress in delivering for the places and communities we serve. Our results in 2023 to 2024 are the latest in that series.
Looking ahead, we shall replace EA2025 with our new corporate action plan in 2025 when we will celebrate our 30th anniversary. We are focusing increasingly on the things we are uniquely placed and empowered to do to deliver against our long-term goals set out in EA2025. This focus aligns with:
- growing expectations of the public
- contributing to the delivery of the government’s Environmental Improvement Plan ( EIP )
- other significant contributions we make across a range of government policy and environmental legislation, including net zero and levelling-up
This 2024 to 2025 business plan will help us focus on:
- leveraging our roles (regulator, adviser, operator, responder and research centre)
- the powers given to us by government (as part of our statutory duties and legal responsibilities) to deliver on and progress the ambition set out in our long-term goals
In renewing our corporate plan, we shall take the opportunity to ensure we provide clarity to our people, our partners, and stakeholders, those we regulate, and the public on:
- our purpose as an organisation and our vision for the future
- how we shall bring all the resources we have to bear in delivering against that vision
5. Our performance in 2023 to 2024: making a difference
The Environment Agency use a red, amber, green system to see how we are performing:
- green - we are performing at or above the target(s) set
- amber - we are falling slightly short of the target
- red - there are improvements to be made
This table shows the red, amber, green scores for the measures plus the actual and target figures.
5.1 Corporate scorecard 2023 to 2024
6. our priorities and focus for 2024 to 2025.
In 2024 to 2025 we will do all we can to better enable our people to meet the challenges we face in the years ahead.
To do this means embarking on a journey of transformation. This is crucial if we are to secure the developments needed to improve our services to the public and to those we regulate.
A fundamental part of this journey will mean driving efficiencies and delivering better outcomes. In 2024 to 2025 we will focus on:
- developing and recruiting people with new skills
- applying new digital technology tools
- embracing a culture of innovation and agility
- providing clarity on priorities
- streamlining how we do things
- removing duplication
- speeding up decision making and action
Transformation will also underpin our drive to deliver efficiencies against our grant-in-aid and charges income. This will all mean we are better able to align our resources and effort to secure the best possible outcomes for people and the environment.
Our people are central to our future success. We will therefore continue to:
- prioritise their health, safety, and wellbeing
- provide opportunities for personal development and offer flexible working
- provide an inclusive and supportive working environment that reflects the diversity of the communities we serve
7. Focus areas for the year ahead
Our focus on water will mean a significant uplift in resources for our work to improve water quality, and options to address water quantity. We will :
- hire our first new water regulators and begin training them, as we expand our water industry water quality regulation teams from 130 staff to 340 by the end of the year
- deliver 4,000 inspections of wastewater and storm installations, and we will publish our findings
- look at options to use near real time event duration monitoring data, when it becomes available, as a development from the new data capabilities to provide mapped data on storm overflow spills and flow to full treatment data, which are already in use by Area teams
- complete 4,000 agriculture outcomes and farm inspections
- invest an additional £5.8m in 2024 to 2025 in water industry enforcement activity, enabling us to effectively tackle the worst offenders and make full use of voluntary undertaking and variable monetary penalties to tackle serious environmental offending impacting water
- continue to drive water industry investment through Price Review 2024, including securing options to close the 5 billion litre-per-day gap between supply and demand, and ensuring that the water industry deliver on their legal obligations to improve the water environment
- work with all water abstractors to help them understand and secure their water resilience
- deliver government initiatives to identify new water resource options, enable more efficient water use and return more water to the environment
- produce comprehensive classifications for all bathing waters, incorporate new bathing water designations in our operational activities, and ensure action plans are in place to address risk of non-compliance
- deliver the requirements of the River Basin Management Plan cycle and maximise Water Framework Directive delivery to 2027
- increase our Water Environment Improvement Programme delivery to £14.5m through partnership-working, delivering outcomes on Water Framework Directive measures
- deliver the Environment Agency elements of the Plan for Water
7.2 Flood and Coastal Erosion Risk Management Programme
In the year ahead we will:
- continue to deliver the government’s £5.6bn programme for flood protection and resilience including year 4 of our current six-year capital programme; the £200m flood and coastal innovation programme and the £25m natural flood management programme
- deliver the £100m Frequently Flooded Allowance to protect communities that have suffered repeated flooding, and the £75m Internal Drainage Boards fund to protect agricultural land and rural communities
- publish our next National Flood Risk Assessment ( NaFRA2 ) - this will provide an up to date understanding of both current and future flood risk for rivers, the sea and surface water
- develop our long-term investment plans for future flood and coastal resilience in advance of the next spending review
- complete the renewal of our commercial frameworks and establish a new charter for working collaboratively with our suppliers
- develop a strategy for improving the performance and reliability of our flood and navigation assets
- deliver on our Category 1 responder role to deliver a flood warning service under the Civil Contingencies Act (2004)
7.3 Waste and resources regulation
We will work to support the government’s ambitions for waste reduction through:
- focusing on our compliance work on poor performing waste management operators and directing resources to sites presenting a high fire risk or risk of abandonment
- increasing our emphasis on ‘upstream’ interventions, undertaking waste classification, waste acceptance and producer responsibility checks to prevent harm - such as the handling and disposal of non-permitted waste and sulphate waste as landfill and deposit for recovery sites
- directing our response to waste crime on the greatest threat, risk and harm, using best practice in risk assessment - this will mean closing high-risk illegal sites, stopping illegal waste exports and the mis-description of waste
- strengthening our intelligence-led approach and our collaboration with partners to target effort on offending and criminality in the waste sector
- our Waste Regulatory Reforms Programme to develop a new delivery model for new duties and introduce the Extended Producer Responsibility for packaging - this is worth £1.2bn per annum to the UK’s Gross Domestic Product
7.4 Regulation
We will be a confident regulator and maintain our strong performance on regulatory activities, including:
- focusing on high-risk activity, including Control of Major Accidents Hazards ( COMAH ), landfill regulation and abandoned sites, hazardous waste, agriculture compliance, oil refineries, nuclear sites, and radioactive sources to minimise adverse impacts on the environment and communities
- using our regulatory and advisory roles to support the nuclear sector’s contribution to sustainable development by delivering regulation and advice across the civil and defence nuclear lifecycles - delivering the programme to prepare for the regulation of Advanced Nuclear Technologies ( ANT ), including fusion
- ensuring we have a sustainable and class-leading permitting system
- supporting climate resilience and environmental protection and development of decarbonisation – Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage ( CCUS ), hydrogen, decarb ready, advising government, developing regulatory approaches to innovation, implementing relevant legislation
- spatial planning – influencing strategic planning to identify opportunities for improving environmental and climate resilience. This includes working in partnership with others to protect, create and restore wildlife rich habitats and support nature recovery. Identification of environmental limitations that may shape and inform development programmes, particularly around water quality and water scarcity.
- focusing on our service to customers, delivering permit reviews, reservoir permits, Environmental Permitting Regulation ( EPR ) permits, water industry permits, digitalisation and standardisation of low-risk permits. We will adopt the new triage approach to enforcement, ensuring it is timely, intelligence-led and target effort based on threat, risk, and harm.
7.5 Organisational transformation
We will modernise our services and working environment through:
- creating a new unit in the business - the Strategy, Transformation and Assurance Directorate - to deliver ‘do it once’ services, improve our IT-enabled transformation effort, raise standards in our offer to our staff and provide better assurance of compliance across the business
- identifying and targeting key functions such as permitting that can benefit from digitalisation and service revision, through which we will deliver better customer experience and improved operational efficiency
- progressing towards our high ambitions for our staff through keeping them safe, strengthening our culture, offering a new talent scheme, greater interchange, new governance and initiatives to improve representation of staff from minority ethnic backgrounds by 1.5 percentage points
- improving our employee offer through targeted skills development, attraction and recruitment actions, and a continuous focus on how we reward our people, all guided by our People Strategy
- maintaining our performance against the Information Commissioner’s Office ( ICO ) standards for Freedom of Information and advancing plans to proactively publish more information
7.6 Efficiencies and value for money
We will improve management of our finances and value for money by:
- delivering £15m efficiencies to fulfil our Spending Review commitment, whilst maintaining performance
- reprioritising £8m of spending towards front line water quality work, which will be delivered by efficiencies
- reviewing more of our fees and charges, to ensure that the true cost of services is met by those that use them and bring our charges into line with other government bodies
- establishing a robust commercial plan to make best use of our assets to deliver greater taxpayer value and improve maintenance of our assets wherever possible
- continuing our close collaboration with the National Audit Office ( NAO ) to improve our understanding of our asset base, with a view to removing remaining accounting qualifications and holding significantly improved technical data
7.7 Providing advice to government
We will deliver on our role as the government’s adviser on pollution and environmental risks by:
- reinforcing our nuclear programme, with dedicated focus on Sizewell C nuclear power station
- continuing our programme of managing emerging threats, including work with the Health and Safety Executive on the management of per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances ( PFAS or ‘forever chemicals’), the implementation of our Methane Plan, and further advisory work on emerging technologies
- reviewing and revising our monitoring work for further opportunities to leverage digital technology to improve the insights and evidence it provides
- advising on, influencing, and implementing planning reforms and levelling up agenda through informing changes to the town and country planning regime and accelerated Nationally Significant Infrastructure Project delivery
- providing a strategic overview role on all sources of flood risk from rivers and the sea
- driving the government’s waste reform projects in partnership with Defra , to deliver a more circular economy and reduce waste crime
8. How we will know we are succeeding
Our 2024 to 2025 priorities, targets and corporate scorecard measures.
8.1 Incident response
We will prepare for, respond to and support recovery from high-risk flooding and environmental incidents including major incidents.
Target and measure for 2024 to 2025
We will target 90% resilience in our capability to respond to incidents.
8.2 Capital programme
We will deliver the agreed capital programme for both the Environment Agency and Risk Management Authorities to better protect properties from flooding by 2027 and deliver wider environmental benefits.
We will target:
- a cumulative total of 114,000 properties better protected from flooding as part of the second programme of the Flood and Coastal Erosion Risk Management Capital Investment Programme (2021 to 2027)
- 80% on track / complete innovation actions delivered in flood and coastal resilience to adapt to a changing climate
8.3 Planning
We will influence local authority planning decisions and Nationally Significant Infrastructure Projects ( NSIPs ) to deliver good environmental outcomes.
- 97% of local authority planning decisions that we successfully influence
- 97% of Development Consent Orders ( DCOs ) for Nationally Significant Infrastructure Projects ( NSIPs ) that we successfully influence
8.4 Asset operation and maintenance
We will maintain our assets to ensure reliable operation and response.
We have a target of 94.5% of assets at required condition. The winter storms between 2023 and 2024 have had a significant impact on existing assets. While we will endeavour to repair and maintain our assets, the more likely outcome for 2024 to 2025 is 92%.
8.5 Compliance
We will ensure effective compliance with a focus on our statutory duties.
- 97% compliance with environmental permits
- reducing the number of serious environmental incidents from permitted sites, activities, and sources we regulate directly to an annual limit of 150
We will deliver the Environment Agency elements of the Plan for Water.
- conduct 4,000 water company compliance inspections
- target 90% of non-compliant water company sewage treatment works to be brought back into compliance
- target completing 4,000 agriculture outcomes and farm inspections
We will reduce the impact of regulated and illegal waste on the environment.
We will target at least 90 high-risk illegal waste sites ( IWS ). They will be ‘stopped’ which means either:
- there is subsequently no activity for a minimum of 28 days
- that site has been brought into compliance
8.8 Habitat restoration
We will deliver environmental enhancement and restoration where we have a statutory duty.
We will target creating or restoring 1,250 hectares of wildlife-rich habitat, delivering Environmental Net Gains to benefit people and wildlife.
8.9 Sustainability
We will deliver our corporate sustainability commitments to meet government targets.
- reduce our carbon emissions to 250,697 tonnes
- become a net zero organisation by 2045 to 2050
8.10 Transformation
As part of a wider transformation programme, we shall review and revise our end-to-end services and the use of digital technology to support our people to deliver.
We will target the equivalent of £15m savings in grant-in-aid and £8m savings in charges income.
8.11 People
Our people’s safety is our top priority. We also want people to be their best selves when working at the Environment Agency and strive to ensure our people reflect the diversity of the communities we serve.
- a 0.11 Lost Time Incident ( LTI ) frequency rate limit per 100,000 hours
- a rate of 50% of executive managers who are female, and 7.6% of staff from minority ethnic backgrounds
9. Our funding
The Environment Agency’s total budget for 2024 to 2025 is £2,086m. This is an increase of £125m compared to our £1,961m budget in 2023 to 2024 and includes:
- government approval to invest up to £53m to deliver the Plan for Water
- a £9m increase in water resources charges relating to Kielder Water in Northumberland (the largest man-made lake in Northern Europe)
As shown in the table, funding to deliver:
- our flood related outcomes is predominately received from government
- environment protection outcomes is predominately generated through our fees and charges
This budget has been allocated across the business to:
- maximise our ability to deliver as one organisation
- enable the delivery of our priorities set out in this business plan
We are committed to efficiencies as a public body. We will deliver £15m of efficiencies this financial year to fulfil our Spending Review commitment. We have also committed to provide an additional £8m from existing resources to fund the commitments set out in the Plan for Water. We aim to deliver these savings by efficiencies. As such a new corporate scorecard measure has been included to capture this commitment.
Our budget will also change throughout 2024 to 2025 as we are expecting to receive £5.8m to fund water quality enforcement. Our charge income may also increase depending on the outcome of charge reviews in progress.
We are also looking to the future and will develop an over-arching funding strategy to prepare us for future years. This will include proposals such as:
- a commercial plan
- maximising cost-recovery
- work to a prioritised fees and charges programme
- gaining agreement to have greater flexibility in our funding
The aim is to enable us to be more agile and responsive to fast evolving priorities so we can deliver the expectations placed upon us.
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .
Comcast Business Mobile Introduces New, Unlimited Plans
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Philadelphia, PA
Comcast Business today announced that it has made Comcast Business Mobile more affordable than ever with the introduction of a series of new mobile plans designed to drive greater value and performance for small business customers.
The new Comcast Business Mobile plans can save customers money on their wireless bill. Comcast Business Mobile – exclusively available to Comcast Business Internet customers – is designed for business with flexible data options including Unlimited data, and nationwide 5G coverage.
“Today’s complex, fast-paced world calls for solutions that small businesses can rely on, with the flexibility to evolve as quickly as they do,” said, Colleen McKelvey, Sr. Director of Product Management, Comcast Business. “With Comcast Business, today’s small businesses get flexible and reliable advanced connectivity solutions that work together – from the company with 99.9% network reliability alongside offering an internet backup solution, advanced WiFi, and advanced security to help protect against cyberthreats. When combined with Comcast Business Mobile, reliable connectivity goes wherever business takes them.”
Business connectivity requirements are constantly evolving, and no two businesses are alike. For that reason, Comcast Business Mobile offers unlimited data options for the evolving needs of each business. Customers have the flexibility to mix and match data options for each line. Calls, texts, and roaming within the U.S. and to and from Canada and Mexico are also included with unlimited plans at no extra charge.
With an all-in-one connectivity provider, combining Internet and Mobile, small businesses can realize greater simplicity and savings – spending less time managing vendors and more time tending to their business. We’re proud to extend these savings further with our latest Comcast Business Mobile plans.
Comcast Business Mobile customers also have access to the recently announced, WiFi Boost. As consumers increasingly want to enjoy experiences on the go, Xfinity Mobile and Comcast Business Mobile have tapped into the nation’s largest and most powerful WiFi network to deliver customers even more speed on the go.
WiFi Boost is made possible by Comcast’s fiber-based network which has been built to deliver an exceptional Internet experience, ubiquitously, to the more than 60 million homes and businesses and across more than 23 million WiFi hotspots in Comcast’s footprint. It is a culmination of years of research, technological breakthroughs, and massive investments, including more than $20 billion since 2018 alone, in development and infrastructure.
Comcast Business Mobile is available exclusively to Comcast Business Internet customers in all of Comcast Business’s service areas. To sign up for Comcast Business Mobile, visit: https://business.comcast.com/learn/mobile
Related Stories
More from comcast, our company, connectivity & platforms, content & experiences.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Design a Corporate Wellness Plan That Actually Works
- Hector De La Torre
- Ron Goetzel, Ph.D.
No more “biggest loser” contests, for one.
Lately, there’s been some debate about whether workplace health promotion programs, more commonly known as wellness programs, work. To us, it’s similar to asking whether reviews, training programs, employee assistance services, or other company initiatives are effective for both worker performance and the bottom line. The honest answer is that some are successful while others fail. And most of the time this comes down to how they’re designed and executed.
- HT Hector De La Torre is the executive director of the Transamerica Center for Health Studies , a national nonprofit, private foundation and division of the Transamerica Institute. Through broad-based analysis and research findings, the center helps consumers and employers navigate the financial implications of the health care decisions they are facing today.
- RG Ron Goetzel, Ph.D. , is senior scientist and director of the Institute for Health and Productivity Studies (IHPS), a collaborative established between the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and Truven Health Analytics. IHPS conducts empirical research on the relationship between employee health and well-being, health care utilization and costs, and work-related productivity.
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are ...
Israel offers five essential tips for creating a strong corporate plan: 1. A corporate plan is not a strategic or business plan. A business plan explains how a new or existing company or project brings in money and how the business is run on a daily basis, including the budget and needed resources. Meanwhile, a strategic plan is a blueprint for ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Corporate planning is a complex process that requires time and dedication at each stage. The corporate planning process follows three defined stages: Formulation. Forming the corporate plan is the first step. It should build on the business plan and will require input from critical stakeholders.
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement.
Corporate planning is the process through which companies draw a map of their plan of action that enables their growth in quantifiable terms. It is typically carried out through the top-level management of the company. It is a medium-term goal that acts as the basis for macro-level planning, called strategic planning.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Corporate strategic planning is a branch of strategy that focuses on the organization. A corporate strategic plan manages a business's objectives and overall direction, and the associated processes are critical to the organization's strategic objectives. The corporate strategic planning process includes defining companywide strategic goals ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
A business plan is a document that communicates a company's goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered. A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals.
Corporate planning is the process by which businesses create strategies for meeting business goals and achieving objectives. It involves strategy definition, strategy direction, decision-making and resource allocation. Corporate planning ensures that business operations are orderly and that the team works towards the same goals.
This is why crafting a business plan is an essential step in the entrepreneurial process. In this post, we'll walk you through the process of filling out your business plan template, like this free, editable version: Download a free, editable one-page business plan template. We know that when looking at a blank page on a laptop screen, the idea ...
Corporate Strategic Planning is a companywide approach at the business unit and corporate level for developing strategic plans to achieve a longer-term vision. The process includes defining the corporate strategic goals and intentions at the top and cascading them through each level of the organization. Many organizations confuse the annual ...
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse ...
Corporate planning defines the strategies that the employees will take to meet the business' goals and missions. This type of planning, also known as strategic planning, focuses on staff ...
Corporate planning is a type of strategic planning, responsible for mapping out a course of strategies and their implementations to empower top- management. It optimizes exposure, reach, leads, sales, profits, credibility, loyalty, sustainability, and opportunities of a business. With the help of corporate strategic planning, a business can ...
Corporate strategy refers to the overall plan or direction of an organization in pursuit of its long-term objectives. It includes defining the company's mission, vision, values, and goals, as well as identifying the markets and products it will focus on, the competitive advantages it aims to build, and the resources and capabilities it needs to ...
1. Helps formulate better strategies using a logical, systematic approach. This is often the most important benefit. Some studies show that the strategic planning process itself makes a significant contribution to improving a company's overall performance, regardless of the success of a specific strategy. 2.
Corporation: A corporation is a legal entity that is separate and distinct from its owners. Corporations enjoy most of the rights and responsibilities that an individual possesses; that is, a ...
Corporate governance is the system of rules, practices and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. Corporate governance essentially involves balancing the interests of a company's ...
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered. According to Harvard Business School Online's Business ...
This business plan sets out our priorities for 2024 to 2025. It will help focus our delivery as we transition to a new corporate action plan in our 30th anniversary year. 2.
The new Comcast Business Mobile plans can save customers money on their wireless bill. Comcast Business Mobile - exclusively available to Comcast Business Internet customers - is designed for business with flexible data options including Unlimited data, and nationwide 5G coverage. "Today's complex, fast-paced world calls for solutions ...
To us, it's similar to asking whether reviews, training programs, employee assistance services, or other company initiatives are effective for both worker performance and the bottom line. The ...