

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, the homework debate: the case against homework.

This post has been updated as of December 2017.
It’s not uncommon to hear students, parents, and even some teachers always complaining about homework. Why, then, is homework an inescapable part of the student experience? Worksheets, busy work, and reading assignments continue to be a mainstay of students’ evenings.
Whether from habit or comparison with out-of-class work time in other nations, our students are getting homework and, according to some of them, a LOT of it. Educators and policy makers must ask themselves—does assigning homework pay off?
Is there evidence that homework benefits students younger than high school?
The Scholastic article Is Homework Bad? references Alfie Kohn’s book The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing , in which he says, “There is no evidence to demonstrate that homework benefits students below high school age.”
The article goes on to note that those who oppose homework focus on the drawbacks of significant time spent on homework, identifying one major negative as homework’s intrusion into family time. They also point out that opponents believe schools have decided homework is necessary and thus assign it simply to assign some kind of homework, not because doing the work meets specifically-identified student needs.
“Busy work” does not help students learn
Students and parents appear to carry similar critiques of homework, specifically regarding assignments identified as busy work—long sheets of repetitive math problems, word searches, or reading logs seemingly designed to make children dislike books.
When asked how homework can negatively affect children, Nancy Kalish, author of The Case Against Homework: How Homework is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It , says that many homework assignments are “simply busy work” that makes learning “a chore rather than a positive, constructive experience.”
Commenters on the piece, both parents and students, tended to agree. One student shared that on occasion they spent more time on homework than at school, while another commenter pointed out that, “We don’t give slow-working children a longer school day, but we consistently give them a longer homework day.”
Without feedback, homework is ineffective
The efficacy of the homework identified by Kalish has been studied by policy researchers as well. Gerald LeTendre, of Penn State’s Education Policy Studies department points out that the shotgun approach to homework, when students all receive the same photocopied assignment which is then checked as complete rather than discussed individually with the student, is “not very effective.” He goes on to say that, “If there’s no feedback and no monitoring, the homework is probably not effective.”
Researchers from the Curry School of Education at the University of Virginia had similar findings in their study, “ When Is Homework Worth The Time ?” According to UVAToday, these researchers reported no “substantive difference” in the grades of students related to homework completion.
As researcher Adam Maltese noted, “Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be.” The report further suggested that while not all homework is bad, the type and quality of assignments and their differentiation to specific learners appears to be an important point of future research.
If homework is assigned, it should heighten understanding of the subject
The Curry School of Education report did find a positive association between standardized test performance and time spent on homework, but standardized test performance shouldn’t be the end goal of assignments—a heightened understanding and capability with the content material should.
As such, it is important that if/when teachers assign homework assignments, it is done thoughtfully and carefully—and respectful of the maximum times suggested by the National Education Association, about 10 minutes per night starting in the first grade, with an additional 10 minutes per year after.
Continue reading — The Homework Debate: How Homework Benefits Students
Monica Fuglei is a graduate of the University of Nebraska in Omaha and a current adjunct faculty member of Arapahoe Community College in Colorado, where she teaches composition and creative writing.
You may also like to read
- The Homework Debate: How Homework Benefits Students
- Ending the Homework Debate: Expert Advice on What Works
- Advice on Creating Homework Policies
- Elementary Students and Homework: How Much Is Too Much?
- Homework in Middle School: Building a Foundation for Study Skills
- Homework Helps High School Students Most — But it Must Be Purposeful
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Leadership and Administration , Pros and Cons , Teacher-Parent Relationships
- Certificates in Administrative Leadership
- Teacher Resources for Social-Emotional Develo...
- Degrees and Certificates for Teachers & Educa...
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
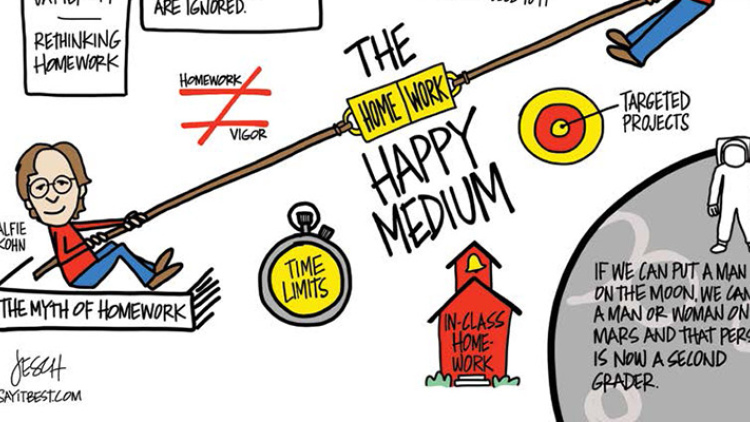
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners

Reshaping Teacher Licensure: Lessons from the Pandemic
Olivia Chi, Ed.M.'17, Ph.D.'20, discusses the ongoing efforts to ensure the quality and stability of the teaching workforce

Special Topic / The Case For and Against Homework

The Case for Homework
The case against homework, the dangers of ignoring the research, grade level, time spent on homework, parent involvement, going beyond the research.

Premium Resource
Special Topic / The Case For and Against Homework - table
Two meta-analyses by Cooper and colleagues (Cooper, 1989a; Cooper, Robinson, & Patall, 2006) are the most comprehensive and rigorous. The 1989 meta-analysis reviewed research dating as far back as the 1930s; the 2006 study reviewed research from 1987 to 2003. Commenting on studies that attempted to examine the causal relationship between homework and student achievement by comparing experimental (homework) and control (no homework) groups, Cooper, Robinson, and Patall (2006) noted, With only rare exceptions, the relationship between the amount of homework students do and their achievement outcomes was found to be positive and statistically significant. Therefore, we think it would not be imprudent, based on the evidence in hand, to conclude that doing homework causes improved academic achievement. (p. 48)
In a third book, The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing (2006a), Kohn took direct aim at the research on homework. In this book and in a recent article in Phi Delta Kappan (2006b), he became quite personal in his condemnation of researchers. For example, referring to Harris Cooper, the lead author of the two leading meta-analyses on homework, Kohn noted, A careful reading of Cooper's own studies . . . reveals further examples of his determination to massage the numbers until they yield something—anything—on which to construct a defense of homework for younger children. (2006a, p. 84)He also attacked a section on homework in our book Classroom Instruction that Works (Marzano, Pickering, & Pollock, 2001).
- Grades 4–6: ES = .15 (Percentile gain = 6)
- Grades 7–9: ES = .31 (Percentile gain = 12)
- Grades 10–12: ES = .64 (Percentile gain = 24)
The pattern clearly indicates that homework has smaller effects at lower grade levels. Even so, Cooper (1989b) still recommended homework for elementary students because homework for young children should help them develop good study habits, foster positive attitudes toward school, and communicate to students the idea that learning takes work at home as well as at school. (p. 90)
- For students in the earliest grades , it should foster positive attitudes, habits, and character traits; permit appropriate parent involvement; and reinforce learning of simple skills introduced in class.
- For students in upper elementary grades , it should play a more direct role in fostering improved school achievement.
- In 6th grade and beyond , it should play an important role in improving standardized test scores and grades.
One of the more contentious issues in the homework debate is the amount of time students should spend on homework. The Cooper synthesis (1989a) reported that for junior high school students, the benefits increased as time increased, up to 1 to 2 hours of homework a night, and then decreased. The Cooper, Robinson, and Patall (2006) study reported similar findings: 7 to 12 hours of homework per week produced the largest effect size for 12th grade students. The researchers suggested that for 12th graders the optimum amount of homework might lie between 1.5 and 2.5 hours per night, but they cautioned that no hard-and-fast rules are warranted. Still, researchers have offered various recommendations. For example, Good and Brophy (2003) cautioned that teachers must take care not to assign too much homework. They suggested that homework must be realistic in length and difficulty given the students' abilities to work independently. Thus, 5 to 10 minutes per subject might be appropriate for 4th graders, whereas 30 to 60 minutes might be appropriate for college-bound high school students. (p. 394)
Cooper, Robinson, and Patall (2006) also issued a strong warning about too much homework: Even for these oldest students, too much homework may diminish its effectiveness or even become counterproductive. (p 53)
- Parents receive clear guidelines spelling out their role.
- Teachers do not expect parents to act as experts regarding content or to attempt to teach the content.
- Parents ask questions that help students clarify and summarize what they have learned.
Good and Brophy (2003) provided the following recommendations regarding parent involvement: Especially useful for parent-child relations purposes are assignments calling for students to show or explain their written work or other products completed at school to their parents and get their reactions (Epstein, 2001; Epstein, Simon, & Salinas, 1997) or to interview their parents to develop information about parental experiences or opinions relating to topics studied in social studies (Alleman & Brophy, 1998). Such assignments cause students and their parents or other family members to become engaged in conversations that relate to the academic curriculum and thus extend the students' learning. Furthermore, because these are likely to be genuine conversations rather than more formally structured teaching/learning tasks, both parents and children are likely to experience them as enjoyable rather than threatening. (p. 395)
Riehl (2006) pointed out the similarity between education research and medical research. She commented, When reported in the popular media, medical research often appears as a blunt instrument, able to obliterate skeptics or opponents by the force of its evidence and arguments. . . . Yet repeated visits to the medical journals themselves can leave a much different impression. The serious medical journals convey the sense that medical research is an ongoing conversation and quest, punctuated occasionally by important findings that can and should alter practice, but more often characterized by continuing investigations. These investigations, taken cumulatively, can inform the work of practitioners who are building their own local knowledge bases on medical care. (pp. 27–28)
Research-Based Homework Guidelines
Assign purposeful homework. Legitimate purposes for homework include introducing new content, practicing a skill or process that students can do independently but not fluently, elaborating on information that has been addressed in class to deepen students' knowledge, and providing opportunities for students to explore topics of their own interest.
Design homework to maximize the chances that students will complete it. For example, ensure that homework is at the appropriate level of difficulty. Students should be able to complete homework assignments independently with relatively high success rates, but they should still find the assignments challenging enough to be interesting.
Involve parents in appropriate ways (for example, as a sounding board to help students summarize what they learned from the homework) without requiring parents to act as teachers or to police students' homework completion.
Carefully monitor the amount of homework assigned so that it is appropriate to students' age levels and does not take too much time away from other home activities.
Balli, S. J. (1998). When mom and dad help: Student reflections on parent involvement with homework. Journal of Research and Development in Education, 31 (3), 142–148.
Bangert-Drowns, R. L., Kulik, C. C., Kulik, J. A., & Morgan, M. (1991). The instructional effects of feedback in test-like events. Review of Educational Research, 61 (2), 213–238.
Bennett, S., & Kalish, N. (2006). The case against homework: How homework is hurting our children and what we can do about it . New York: Crown.
Bloom, B. S. (1984). The search for methods of group instruction as effective as one-to one tutoring. Educational Leadership, 41 (8), 4–18.
Cooper, H. (1989a). Homework . White Plains, NY: Longman.
Cooper, H. (1989b). Synthesis of research on homework. Educational Leadership, 47 (3), 85–91.
Cooper, H. (2007). The battle over homework (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1–62.
Corno, L. (1996). Homework is a complicated thing. Educational Researcher, 25 (8), 27–30.
Epstein, J. (2001). School, family, and community partnerships: Preparing educators and improving schools . Boulder, CO: Westview.
Epstein, J. L., & Becker, H. J. (1982). Teachers' reported practices of parent involvement: Problems and possibilities. Elementary School Journal, 83 , 103–113.
Fraser, B. J., Walberg, H. J., Welch, W. W., & Hattie, J. A. (1987). Synthesis of educational productivity research [Special issue]. International Journal of Educational Research, 11 (2), 145–252.
Gill, B. P., & Schlossman, S. L. (2000). The lost cause of homework reform. American Journal of Education, 109 , 27–62.
Good, T. L., & Brophy, J. E. (2003). Looking in classrooms (9th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Graue, M. E., Weinstein, T., & Walberg, H. J. (1983). School-based home instruction and learning: A quantitative synthesis. Journal of Educational Research, 76 , 351–360.
Hattie, J. A. (1992). Measuring the effects of schooling. Australian Journal of Education, 36 (1), 5–13.
Hoover-Dempsey, K. V., Bassler, O. C., & Burow, R. (1995). Parents' reported involvement in students' homework: Strategies and practices. The Elementary School Journal, 95 (5), 435–450.
Kavale, K. A. (1988). Using meta-analyses to answer the question: What are the important influences on school learning? School Psychology Review, 17 (4), 644–650.
Kohn, A. (2006a). The homework myth: Why our kids get too much of a bad thing . Cambridge, MA: Da Capo Press.
Kohn, A. (2006b). Abusing research: The study of homework and other examples. Phi Delta Kappan. 88 (1), 9–22.
Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2000). The end of homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning . Boston: Beacon.
Marzano, R. J., & Pickering, D. J. (2007). Response to Kohn's allegations . Centennial, CO: Marzano & Associates. Available: http://marzanoandassociates.com/documents/KohnResponse.pdf
Marzano, R. J., & Pickering, D. J. (in press). Errors and allegations about research on homework. Phi Delta Kappan .
Marzano, R. J., Pickering, D. J., & Pollock, J. E. (2001). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement . Alexandria, VA: ASCD.
National Education Commission on Time and Learning (1994). Prisoners of time . Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education.
Paschal, R. A., Weinstein, T., & Walberg, H. J. (1984). The effects of homework on learning: A quantitative synthesis. Journal of Educational Research, 78 , 97–104.
Perkins, P. G., & Milgram, R. B. (1996). Parental involvement in homework: A double-edge sword. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth, 6 (3), 195–203.
Riehl, C. (2006). Feeling better: A comparison of medical research and education research. Educational Researcher, 35 (5), 24–29.
Van Voorhis, F. (2003). Interactive homework in middle school: Effects on family involvement and science achievement. Journal of Educational Research, 96 , 323–338.
Walberg, H. J. (1999). Productive teaching. In H. C. Waxman & H. J. Walberg (Eds.), New directions for teaching practice research (pp. 75–104). Berkeley, CA: McCutchen.
Wallis, C. (2006). Viewpoint: The myth about homework. Time, 168 (10), 57.
• 1 For a more detailed response to Kohn's views on homework, see Marzano & Pickering (2007) and Marzano & Pickering (in press).

Robert Marzano is the CEO of Marzano Research Laboratory in Centennial, CO, which provides research-based, partner-centered support for educators and education agencies—with the goal of helping teachers improve educational practice.
As strategic advisor, Robert brings over 50 years of experience in action-based education research, professional development, and curriculum design to Marzano Research. He has expertise in standards-based assessment, cognition, school leadership, and competency-based education, among a host of areas.
He is the author of 30 books, 150 articles and chapters in books, and 100 sets of curriculum materials for teachers and students in grades K–12.

The late Debra J. Pickering consulted with schools and districts nationally and internationally as vice president of field services for Marzano Research Laboratory. She passed away in 2020.
In addition to her work with schools, Pickering coauthored (with Robert Marzano) educational books and manuals, including Dimensions of Learning , Classroom Instruction That Works , Classroom Management That Works , and Building Academic Vocabulary .
With a combination of theoretical grounding and more than three decades of practical experience, Pickering worked with educators to translate theory into practice. In later years her work continued to focus on the study of learning and the development of resources for curriculum, instruction, and assessment to help all educators meet the needs of all students.
Pickering had a master's degree in school administration and a doctorate in curriculum and instruction, with an emphasis in cognitive psychology.
ASCD is a community dedicated to educators' professional growth and well-being.
Let us help you put your vision into action., from our issue.

To process a transaction with a Purchase Order please send to [email protected]

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.

6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
- Writing services
- Proofreading
- Math/Science
- Copywriting
- Dissertation services
- Admission services
- Our Writers
Too Much Homework Persuasive Essay

Table of contents:
- Introduction
- Body paragraphs
Homework can be such a controversial topic. Teachers apparently love to give it, students hate to receive it, and parents are often confused by it. When you sit down to write a persuasive essay, which you were presumably given as homework, it can be very tempting to say that we should just get rid of all homework completely.
However, make sure you’re considering the nuances of the situation. There are both disadvantages and advantages to homework, and your teacher or professor may not love giving you homework as much as you think they do. After all, they presumably have to grade it, taking up valuable hours of their free time. Try considering the case for less or no homework from the teacher’s perspective. What pros or cons would they see homework having?
Start your essay with an attention-grabbing hook. You should also make clear who your audience is from the start. Then move on to lay out your statement of purpose, or thesis, which explains the aim you are trying to achieve. Any titles you are considering should reflect your thesis, as well.
Introduction examples
Introduction: Teachers! Abolish homework and reclaim your evenings for yourselves. Why struggle under the burden of grading thirty students’ excuses for essays when you could be out having fun?
Introduction: Should students have homework? The latest studies into student health say they should have much less. When teachers give too much homework, it’s very stressful for young minds, who should be free to enjoy themselves and grow up naturally without worries and stress.
The body of your essay, then, consists of your persuasive points backed up with your arguments. These can be emotional or evidence-based. When you’re thinking about your audience, it’s important to consider what sort of appeal will work better on them. Is an audience of teachers going to see right through your heartfelt emotional appeal? Perhaps they would respond better to hard evidence showing the disadvantages of homework.
Body paragraphs examples
Body: Parents’ help with homework is another reason to avoid assigning too much. If children are confused, they will simply go to their parents, who frequently end up doing most of the homework for them. It’s far better to thoroughly learn with supervision from a teacher, with most or all of the work done in class. When teachers assign too much to be done every evening, it just stresses students out and makes the situation where parents do the work inevitable.
Your conclusion is pretty much your last chance to persuade your audience, so save your best zinger for the end. Close with a brief summary of your points, followed by calling your audience to action of some kind, even if it’s just to have a different perspective on the topic.
Conclusion examples
Conclusion: Homework should be reduced, although it should not be banned altogether, and children should do the vast majority of their work during school lessons. That’s better for teachers, better for parents, and better for students. So next time you plan your lessons, be sure to consider what’s best.
- Essay samples
- Infographics
- Essay writing
- Crafting a Powerful Essay on Political Polarization
- Oral Health Overview Essay: Preventing Tooth Decay in Australia
- How to Write a Good Expository Essay About Macbeth
- How to Write An Expository Essay About Love
- How to Write a Great Expository Essay About Life
Price per page
Total price:
Limitless Amendments
Bibliography
Plagiarism Report
Get all these features for A$93.12 FREE
If you don't know exactly what type of paper you need or can't find the necessary one on the website - don't worry! Contact us and we'll help you out!
- Terms of Use
- Money Back Guarantee
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Write My Essay
- Custom Essay
- Essay Writer
- Do My Essay
- Type My Essay
- Pay For Essay
- Cheap Essay
- Write My Paper
- Write My Assignment
- Assignment Writer
- Buy Assignment
- Assignment Help
- Do My Assignment
- Nursing Essay Writing Service
- Management Essay
- Business Essay
- Law Essay Writing Service
- Education Essay Service
- Marketing Essay
- Accounting Essay
- Sociology Essay
Before continuing to use our service please make sure you got acquainted with our Cookie Policy and accepted it by clicking OK
Persuasive Essay Sample: Homework Should Not Be Required
Seven hours is a long time right? Now imagine you spend seven hours in school, then you have to go home and finish all your homework for the next class. Learning is great and sometimes even fun but homework after school can cause stress, anxiety, homework can prevent sleep, homework can be difficult to complete at home and teenagers need a balance between school and home. These reasons lead me to believe that homework does more harm than good and should not be required to get done.
Homework should not be required because it causes stress and anxiety. In the article Heavy Homework Load May Be Detrimental to Health it says “More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep.” (Moniuszko.) This shows that homework has a negative effect on a teenagers mental health. Some teenagers already struggle with mental health issues and adding the workload of homework could just make it worse for them. Is homework really more important than a person's mental health?
One important reason homework should not be required is because it can cut into teenagers' sleep schedule. “Sleep benefits the brain and promotes attention, memory and analytical thought. It makes thinking sharper, recognizing the most important information to consolidate learning. Sleep also facilitates expansive thinking 2 that can spur creativity3. Whether it’s studying for a test, learning an instrument, or acquiring job skills, sleep is essential for teens4..(Suni.) Sleep is crucial for the human mind to function especially for teenagers as their minds are developing. Homework can cut into a teenagers sleep schedule which can cause them to be tired in class not learning to the best of their ability, some could say that homework helps learn and memorize what you did in class that day but how are you supposed to remember what you did in class that day if you were tired. If homework was not required students wouldn't have to stay up late on an assignment and have a lack of sleep in the morning.
Personally, homework can become very overwhelming and I’m sure other students would agree with me on that. Not all homework is bad but it can cause anxiety. Not only can that be a problem for the student but it can also be hard for their parents. “Homework anxiety is a condition in which students stress about and fear homework, often causing them to put homework off until later. It is a self-exacerbating condition because the longer the student puts off the homework, the more anxiety they feel about it, and the more pressure they experience to finish the work with less time. Homework anxiety can cripple some kids who are perfectly capable of doing the work, causing unfinished assignments and grades that slip.”(Tips for Minimizing the Homework Battle.) This can be a problem for the students because they may be very good at a subject but if they don't complete the homework it could reflect poorly on their grades. There might be a missing assignment in their grade book but teenagers not wanting to do the assignment isn't always the case, it can also be because of anxiety not requiring homework would just make life easier.
Homework is a controversial topic should homework be required or should it not? Although homework can be helpful sometimes, there needs to be a balance between school work and home. In the article Pilling Homework on Kids Is a Mistake That Undermines Work/Life balance it says “Even before I realized years ago that my students were not deriving much, if anything, of educational value from homework, I could never grade homework assignments equitably, because each student's homework was being attempted in home environments that could be vastly different.” (Geoff.) For example Teenagers who have activities after school have less time to get their homework done compared to teens who have nothing to do after school. You also have to keep in consideration that Teens also need to sleep, eat and spend time with family and friends. This is why homework shouldnt be required because there should be a healthy balance for it all.
I would also like to add that after school activities are not the only reason homework can be hard to get done for students.The environment where a student is doing homework has a part ot play “Some parents simply did not have space available at home to set up quiet spaces where students could focus on their work uninterrupted by the distractions common to every household.”(Geoff.) It could be hard for parents to help their kids with homework if they're working or taking care of their younger children. It could also be hard for them to help with homework if they don't know how to do it. Also phones and other electronics can be distracting at home because there's not that expectation to be working the whole time which can cause homework not to get done. There are many more reasons a student's environment could prevent them from finishing homework. Everyone's environment is different and there's a difference between a school environment and a homes environment. It can be difficult to have that type of learning environment at home which makes homework hard for students. This is why it shouldn't be required.
After school students should have free time to wind down and give their brains a break “Emer O'Connor says homework for her children will "typically take an hour". "Although teachers say the homework should only take a short amount of time, this is not my experience. The children are tired and distracted.”(Hogan.) The truth of the matter is that homework can take a long time to complete. The homework we have to do may not be too hard but it can be distracting when completing it which could cause the homework to last longer and students could end up putting little effort into. In this case I feel like boundaries should be put in place because homework taking an hour or more is ridiculous when we might not be checking it over in class anyways so we won't get the chance to correct our mistakes.
In conclusion, homework should not be required because homework can affect your mental health badly, everyone has a different home environment and might not be able to complete it at home, homework can take time away from a good night's sleep, and there needs to be a boundary between school and home. These reasons prove that homework does more harm than good and shouldnt be required.
Works Cited
Author(s). "Title of Article." Title of Publication, Day Month Year. Database Title, URL. Accessed day month year.
Sleep for Teenagers | Sleep Foundation
https://www.brainbalancecenters.com/blog/homework-anxiety-explained
https://explore.proquest.com/sirsissuesresearcher/document/2521204097?accountid=9496
https://explore.proquest.com/sirsissuesresearcher/document/2564234859?accountid=9496
https://explore.proquest.com/sirsissuesresearcher/document/2578243016?accountid=9496
Related Samples
- Weights Class is Benefiting Students More Than Some Would Think
- The Importance of Praise in Learning Essay Example
- Research Paper about Peer Pressure
- Essay Sample on How to Write a Critical Analysis
- Persuasive Essay Example on Less Homework
- Non-Profit Organizations Essay Example
- Students With Disabilities Essay Example
- The Golden Life in Co-Educational Schools Essay Example
- Maria Montessori's Theory of Learning Essay Sample
- Reflective Essay about Studying Abroad
Didn't find the perfect sample?

You can order a custom paper by our expert writers
Why Homework Is So Important Essay
Education plays an important role in ensuring children are taught career, survival and intellectual skills that will enable them to live comfortably in the future. Learning institutions have been established to ensure everyone goes to school and gets the required knowledge essential for human survival.
These learning institutions have come up with various programs aimed at ensuring that students make good use of their time while attending schools and also when out of classes. Homework and holiday assignments are the most common tasks that students are given when they are not in school to enhance their learning.
However, the debate continues to rage on regarding the importance of homework to students. The discussion below outlines the significance of homework to the development of the learning process of a student. Every human being has a unique ability to grasp various ideas and information depending on their age, exposure to different environments and levels of interests.
This makes it very impossible for every student to grasp all concepts being taught in class by their teachers. Therefore, when students are given homework, they can take time and study the concepts they did not understand during normal class time, and this makes them be at the same level with other students (Bader 12). Homework plays an important role in ensuring that students can learn at the same pace.
The fact that students have different abilities to memorize what they were taught means that their levels of learning differences and when they are given the same homework slow learners can catch up with fast learners, and this ensures they all stand equal chances of competing effectively.
Also, ninety percent of students are in their active stages of life, and therefore they like playing very much. These plays make students forget what they were taught during the day as their minds are occupied with games and other entertainment activities. When these students are given homework, they have limited time to attend to other activities like games and sports.
It is well known that all children and young adults like playing very much and when left idle they can spend the whole day playing at the expense of their education. Homework plays an important role in ensuring they are kept very busy and indulge in games only after they have finished their work.
Furthermore, homework enables students to make their studies and identify areas they did not understand very well. Sometimes students tend to cheat in their examinations and other class assignments by coping from others, and this earns them false grades.
However, when they are given homework they are not able to copy from their friends and in fact, they make all efforts to ensure they put their brains at work to answer all questions assigned (Bader 134). Therefore, teachers can identify areas that their students did not understand well and go over them again by organizing remedial classes.
Students are also able to identify topics that were not understood and seek the necessary assistance from their teachers. Moreover, homework enables students to be busy during their free time and avoid indulging in bad behavior. The fact that an idle mind gives way to irrational thinking should sound an alarm bell to all parents and students who shy away from homework.
When students are kept busy with homework, they will be in a position to avoid indulgence in bad behavior like drug abuse and premarital sex. When students are given homework, they get prepared for future career obligations that involve assignments and duties out of office.
This offers them an opportunity to develop the flexibility to time schedules and roles assigned in the future when they are employed. Also, they will be in a position to schedule their work programs effectively to meet all the demands of their jobs.
Lastly, homework enables students to read widely regarding other topics to be covered by their teachers. Assignments that are designed to give students an insight into their forthcoming topics makes them mentally prepared for other “hard topics,” and this makes them understand the concepts of such topics with ease (Bader 134).
Some homework is meant to break down complicated topics into subtopics that are easily covered and understood by students within the shortest time possible. Therefore, homework enables teachers and students to take the shortest time possible to handle complicated topics.
However, despite the above benefits associated with homework, there are other factors that make them ineffective in performing their intended roles in students’ developments. The first reason that disqualifies the suitability of homework to access student’s intelligence is the fact that in most cases homework assigned to students is not done by them.
Students ask their elder siblings to do their assignments for them as they sit and chat while watching television. When the teachers mark the assignments, they are pleased to note the outstanding performance by their students. However, the same students register low grades when examinations and assignments are done within the school compound.
Therefore, homework does not help teachers in assessing students’ understanding of various concepts. Also, it does not offer reliable criteria to test the students’ ability to remember and present the ideas learned from teachers. Secondly, students are usually very tired after spending the whole day in class and require time to relax and think of other things that may distract their attention from books for a while.
Over concentration on books and academic materials exposes the students to risks like developing obesity due to their inactiveness. It is known the world over that too much work without play or exercise makes an individual very dull and thus ineffective. Most students are usually between the ages of five years and twenty-seven, and they are still growing and developing (Bader 134).
For them to develop their physical fitness, they need time to indulge in sports and games to ensure their bodies get enough exercise. Moreover, the mind needs some time to reflect on other things and enable the brain and the blood vessels to relax as the student reduces pressure from thinking about school assignments and tests.
It is estimated that homework and other assignments are responsible for a huge percentage of causes of stress and depressions in many youths. This is due to the pressure to finish their homework in time and deliver quality results that drive most students to concentrate on them and ignore meals and stay awake the whole night.
Human beings have varying degrees of learning and memorizing, and thus homework helps students to ensure they do not forget what they were taught. It enables students and teachers to identify the study areas that need more attention. However, it should not compromise the students’ time to indulge in other equally beneficial activities like sleeping and exercising.
Works Cited
Bader, John. Dean’s List: Eleven Habits of Highly Successful College Students. Maryland: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 2011. Print.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, October 31). Why Homework Is So Important. https://ivypanda.com/essays/homework-significance/
"Why Homework Is So Important." IvyPanda , 31 Oct. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/homework-significance/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Why Homework Is So Important'. 31 October.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Why Homework Is So Important." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/homework-significance/.
1. IvyPanda . "Why Homework Is So Important." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/homework-significance/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Why Homework Is So Important." October 31, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/homework-significance/.
- How to Help Children Study Well and Share Time?
- Students’ Performance and Progress Monitoring Table
- First Grade Behavior Management Plan
- Admission of International Students to the U.S. Universities
- Tone Impact in Distance Education
- The Legal Education of the School Official
- Public vs. Parochial Schools: The Principle Points of Conflict
- Self-Directed Learning Competence
Home Essay Examples Education Homework
No Homework Policy: My Arguments Against
- Category Education
- Subcategory Learning
- Topic Homework

“No Homework Policy”
Introduction.
In the present day, Filipinos are beginning to complain on everything. Even the simplest task that we used to do, often receive a negative reaction from us. From the childhood, parents taught their children to be responsible for their actions. But what is the responsibility? What does it mean for everyone?
The responsibility is the understanding of the consequences, which can be caused by the actions of the person. It is setting goals and their reaching. It means to be responsible for all your words, actions and even thoughts. It is one’s responsibility for their own improvement and professional development. Every year, people get a lot of responsibility. For example, parents are always responsible for their children, the head of the organization is always responsible for the workers. The interesting fact is, that even if the person is wise and have a lot of talents, but do not have the responsibility, he will not reach the success. He will lose the support of other people. They will not trust him, because he is unreliable.
The 21st Century generation of students is one of the best example on portraying the responsibility. It has also been said on Dr. Rizal’s quotation, “Youth is the hope of the nation”. The youth, the students are carrying a heavy responsibility realizing the fact that we are the only hope of our country. But what if doing a single task appears as a burden to us?
Homework is a vital part of education. Homework is a waste of time. Homework is a burden. These are the thoughts of some students whenever they feel stressed on doing a task assigned to them at home. I, myself is one of those students who think ill of homework but I know the bright side of doing it. Homework is important. It is necessary and a must. We all know that it is a part of school life. Some people think that homework is an effective way to reinforce the concepts and knowledge that were learned at school. Others feel like the time homework demands would be better spent with a meaningful activity that brings the family together.
In the past month, two members of Philippine Congress presented their own respective measures seeking to ban homework. According to House Bill 388, teachers are prohibited from giving assignments to their students if they will be done during weekends. Homework is also prohibited in House Bill 3611 for the health of the children. The Department of Education (DepEd) has also expressed their support for the “No Homework Policy” bills proposed by our lawmakers at the House of Representatives. It said that the policy would allow students to find ways to balance between their academic development and personal growth by having ample time for enjoyable activities with family.
Some people suggest students must be spared from homework so they can get into any sports or get to have more bonding time with their families and friends. In other countries like America, homework is guided by what is called, ‘the ten-minute rule’ which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level.
As much as I want to be free from extra works at home, I know that doing homework will help students like me, to retain what I have learned in school and to get advanced lessons. Home works also helps us be responsible even at a small task. It encourages the discipline of practice. Answering questions and solving problems over and over can be boring and difficult, but it also reinforces the practice of discipline. It gets parents involved with a child’s life and it seems favorable. There are situational problems we can ask to our parents because they are more experienced than us. It teaches time management skills. Homework goes beyond completing a task. It forces children to develop time management skills.
To be responsible for your future, family and actions, it is the important quality of a successful person. It means that such person will do everything, that he or she promised to him/herself. The possibility to promise something and to fulfill it is one of the fact, that this person is reliable. It is the ground of the leadership and professional growth. If the person does not want to take any responsibility, it means that this person cannot do a lot in the real life. These people will not be able to reach the success in this life or create the family, because the family is a huge responsibility.
But people that are not afraid of the responsibility and can take it are successful and can control the situation and even the life of other people. They increase their opportunities and they are doing their best to reach the success.
I totally disagree to the “No Homework Policy” because it will only makes us, students, lazier on doing tasks and will only let students be less prepared for higher education or the workforce, and ultimately the entire country will suffer the consequences.
We have 98 writers available online to start working on your essay just NOW!
Related Topics
Related essays.
By clicking "Send essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
By clicking "Receive essay" you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
We can edit this one and make it plagiarism-free in no time
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
English Compositions
Short Essay on Importance of Homework [100, 200, 400 Words] With PDF
Our today’s session is targeted to discuss writing essays on the topic of the ‘Importance of Homework.’ Here, you will have a holistic idea after going through three different sets of essays on this topic covering different word limits.
Table of Contents
Short essay on importance of homework in 100 words, short essay on importance of homework in 200 words, short essay on importance of homework in 400 words.

Homework is the work that students get assigned to do at home. It can often include going through the chapters that have already been taught at school, answering questions related to those chapters as well as writing assignments to increase one’s knowledge. Doing homework is very important because it helps students understand chapters better.
It makes them memorise important details and realise if they have any doubts regarding the chapters. It can also improve their reading and writing skills. If students don’t practice at home, they may forget whatever they have been taught in class. However, it is important to not give students too much homework. Excessive homework can burden young kids, making them lose their interest in learning. When given in the right amount, homework helps a student learn and perform better.
Students often get a lot of classwork as well as homework to do. Classwork is the work students do in class while homework is the work that students are asked to do at home. Usually, homework includes going through whatever has been taught in class and answering questions related to the same. It can also include making students read a chapter that is meant to be taught in class next.
This helps students understand the chapter better and see if they are able to understand new concepts by themselves. Practising at home also improves their reading and writing skills. It makes them memorise important details and realise if they have any doubts regarding the chapters.
Sometimes, students complain about getting too much homework. Excessive homework can burden young kids and make them lose interest in learning. Even if they finish all the work, they may do it just for the sake of finishing it instead of trying to learn in the process. It is important to give students the right amount of homework that may help them learn better without burdening them or stressing them out.
Students also must understand that doing homework is important and benefits them. It makes them memorise important details and realise if they have any doubts regarding the chapters. Homework makes students learn and perform better. This in turn helps them secure good grades.
When students go to schools or colleges to study, they are often given a lot of classwork and homework. Classwork is the work students do in class while homework is the work that students are assigned to do at home. Teachers usually explain new chapters to students in class and show them how to solve problems. But a class is at most an hour long and one cannot practice a lot in an hour.
For this reason, students are given assignments to do at home. Homework can include going through the chapters that have already been taught at school, answering questions related to those chapters as well as writing assignments to increase one’s knowledge. Sometimes, teachers also ask students to read a chapter at home before it is taught in class. This helps students understand the chapter better and see if they are able to understand new concepts by themselves.
Practising at home improves the reading and writing skills of students. It also helps them memorise important details and understand if they have any doubts regarding the chapters. At times, students complain about getting a lot of homework and do not want to do it. Too much homework can often burden children and make them lose interest in learning new things.
Even if they finish all the work, they may do it just for the sake of doing it instead of trying to learn something from it. This would then make homework meaningless. Students should have the time to play and engage in other fun activities apart from studying, or else they may feel dull and sad. It is important to give students the right amount of homework so that it doesn’t burden them.
Students must also understand that doing homework is important for them and benefits them. If they want to understand and learn a chapter better, they must do their homework diligently. If they want to perform well in tests and examinations, homework prepares them for that as well. Since there is no teacher to discipline the student when he does the homework given to him, it also develops a sense of personality responsibility and discipline in the student.
He must control his urges to go play outdoors or get busy on his computer and focus on doing the homework. It also helps him develop time management skills as he needs to finish the work assigned to him in a limited amount of time. All of these things help students develop good habits and skills that help them throughout their lives.
In this session, I have tried to write the essays in very simple language that all kinds of students can easily understand. If you still have any doubts post them in the comment section below. Keep browsing our website for more such sessions.
Connect us on Telegram to get all the latest updates on our upcoming sessions. Thank you.
Argumentative Essay on Homework
Every student in the world is stressed about their homework, and some even cry. I know I have, many times. This is homework; reading is, it’s not like we haven’t been in school for eight hours doing any work. The school itself is already under pressure, and doing homework, which is a place of relaxation, is beyond the reach of the individual. Some people argue that it helps students become more familiar with what they are learning at school; others say it dramatically affects children.
Robert Nevilis founded homework in 1905. He was a teacher who thought that students needed more practice at home. From then on, reading was essential to all teachers and schools. Teachers claim that it improves a student’s ability to understand a subject better, but it does more than that. Homework has been linked to stress and depression in studies. Students have to be in school for eight hours; then they have to go home and work on other things from school is very difficult. Everyone likes to relax after a long, stressful day, but some students don’t because they have too much homework.
Homework does not necessarily mean that you will improve or get better grades. Sometimes it can make you worse. It can make a person feel stupid when he does not fully understand a subject. Every student has personal problems, ranging from bullying, difficult separation to family problems. The school board of education needs to realize that we students have a personal life outside of school.
Homework can go either way, it can be a good thing, but it can also be a bad dream for the student. Students who take more than one AP class or honors class know how difficult it is to maintain good marks without pressure. Sometimes a student has a lot of upcoming tests to study or projects, which is a very stressful thing to deal with. That has happened to all students at some point. For example, during the term of this school year, I had an upcoming official geometry test; for AP Spanish, I had to do a World History project and answer two questions about Edmodo Chemistry and all my homework from other classes. All in one week. I would go to bed at 2 am early to finish all my work, and I did not procrastinate, so think how late I would have gone to bed if I had postponed.
The public thinks that children need more sleep. What many do not know is that teenagers need more sleep as children. Studies have shown that when adolescents start puberty, which is usually between the middle and high school, they need to sleep for at least nine hours. Most teens do not even get 6 hours of sleep with all the homework done. Doing homework until 12/1 a.m. and getting up early can make a student feel tired and weak. I do not mean that every student has this problem, but I am sure that more than three-quarters have gone through this at some point.
Late sleep for a student is one of the hardest things to deal with. Getting up early and getting ready for school is not an easy task, especially if you are like me and do not enjoy getting up early. I was exhausted at school, fell asleep in the classroom, and when I woke up, I was utterly lost in what we were learning. Even after school, I was so tired from being in school that I wanted to go home and sleep. But I could not. I had to clean my room, wash the dishes, clean the floor, and help my mother cook dinner. After dinner, I would have to clean my kitchen again, help my mom with anything she needed and do my homework.
Being a student with someone is not easy, at least not for me anyway. As a teenager, you want to have fun, explore this fascinating world, but do your homework and marks. There is always a stop. The community always encourages young people to be diligent, but they do not realize that they do not know because of their homework. They need to understand that we have many things to do outside of school as students. I know that teachers want their students to succeed, but schoolwork that overwhelms students discourages them. Once a student has reached that point, they will be less interested in doing their homework and will be left behind, resulting in worse grades, or worse, leading to dropping out of school.
On the other hand, I understand why homework is so important. It may help you get better at something, giving you more practice. If you do not understand something, taking it home and working on it may help you know. Perhaps after a long day at school, your mind can gradually focus on a single lesson, enhancing your comprehension. Probably if the most important classes were the only ones giving you homework, life would be easier.
As pressure from teens has increased over the past few years, students who do not do their homework are more likely to cheat. So with all the stress around students, having good grades is more important than getting an education. This generation of children is more concerned with passing and getting better rates than understanding a subject and getting an education.
Teachers may say they leave their little homework to their students, but they do not realize that some students have seven more classes and teachers need to worry about them. Sure, they may leave you a small worksheet or just read the words, but that adds another ton of homework you have to your other classes. We, as students, do not get long breaks. We get two days off a week to rest but guess what again, we have homework for our free days.
The suggestion I have for the school board is as follows: if a student thinks they do not need homework, they should not get it. But on the other hand, if a student wants to exercise more at home, he can do homework. Depending on the teacher, it can be counted as additional credit, but if you do not include any task, it will not hurt your grade.
If a student does not understand the homework, we do not have a teacher or teacher to help us. In my opinion, it is very stressful to try to do your homework without help, especially if you do not fully understand it. It is also tough to get help online, and not all students have access to the internet at home because of economic problems. Also, when you get service online, it isn’t easy to concentrate, and you do not get that one at a time with the instructor.
Yes, I believe that homework can be good in some cases, but reading is more stressful than helpful when you look at the features and the results. Once you become a student, you will always be a student rather than a teenager. If you add up all the hours you are in school and the hours you spend doing homework or studying, you spend ¾ your day doing homework. Teachers need to understand that students live outside the school.
Download Pdf of Argumentative Essay on Homework
If you want to Download the Pdf of Argumentative Essay on Homework then click on the given link it is free of cost.
All Argumentative Essay
3 thoughts on “Argumentative Essay on Homework in 1200-1300 words | Free Pdf”
Hii, Thanks for visiting our blog to know the “Argumentative Essay on Homework” and if you have any doubts or suggestions. Please comment below.
I honestly think it’s good, but I hate having to come home and stay up and do homework.
Thank u for your feedback.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Editorial Board
A Way Back From Campus Chaos

By The Editorial Board
The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views are informed by expertise, research, debate and certain longstanding values . It is separate from the newsroom.
Protesting the world’s wrongs has been a rite of passage for generations of American youth, buoyed by our strong laws protecting free speech and free assembly. Yet the students and other demonstrators disrupting college campuses this spring are being taught the wrong lesson — for as admirable as it can be to stand up for your beliefs, there are no guarantees that doing so will be without consequence.
The highest calling of a university is to craft a culture of open inquiry, one where both free speech and academic freedom are held as ideals. Protest is part of that culture, and the issue on which so many of the current demonstrations are centered — U.S. involvement in the Israel-Hamas conflict — ought to be fiercely and regularly debated on college campuses.
The constitutional right to free speech is the protection against government interference restricting speech. Therefore, leaders at public universities, which are funded by government, have a heightened duty to respect those boundaries. Private institutions don’t have the same legal obligations, but that doesn’t relieve them of the responsibility to encourage open dialogue whenever and wherever possible on their campuses. It’s essential to the pursuit of learning.
In the real world, though, this can get messy, and nuance is required when free speech comes into tension with protecting academic freedom. The earliest universities to adopt the principle of academic freedom did so to thwart interference and influence from totalitarian states and religious zealotry. Today, the American Association of University Professors defines it as “the freedom of a teacher or researcher in higher education to investigate and discuss the issues in his or her academic field and to teach or publish findings without interference from political figures, boards of trustees, donors or other entities.”
Student codes of conduct and other guidelines are meant to relieve some of the tension between free speech and academic freedom, as well as to ensure that schools are in compliance with government regulations and laws. Every campus has them. But rules matter only when guardrails are consistently upheld. It’s in that enforcement that the leadership of too many universities has fallen short.
The point of protest is to break such rules, of course, and to disrupt daily routines so profoundly as to grab the world’s attention and sympathies. Campuses should be able to tolerate some degree of disruption, which is inherent to any protest. That makes it even more important that school administrators respond when the permissible limits for speech are violated.
During the current demonstrations, a lack of accountability has helped produce a crisis.
It has left some Jewish students feeling systematically harassed. It has deprived many students of access to parts of campus life. On campuses where in-person classes or commencement exercises were canceled, students have watched their basic expectations for a university experience evaporate. And at times, the protesters themselves have been directly endangered; the disarray and violence of the past weeks have been escalated by the continued involvement of both the police and external agitators.
Amid the protests, there has been much discussion of both antisemitism and Islamophobia and when the line is crossed into hate speech. There are profound risks to imposing overly expansive definitions of inappropriate speech, and universities were rightly chided for doing so in the past. But it should be easy to agree that no student, faculty member, administrator or university staff member on a campus should be threatened or intimidated. School policies should reflect that, and they should be enforced when necessary.
In the longer term, a lack of clarity around acceptable forms of expression and a failure to hold those who break those norms to account, has opened up the pursuit of higher learning to the whims of those motivated by hypocrisy and cynicism.
For years, right-wing Republicans, at the federal and state level, have found opportunities to crusade against academic freedom, with charges of antisemitism on campus serving as the latest vehicle. Speaker Mike Johnson of the House of Representatives used this moment of chaos as cover to begin a legislative effort to crack down on elite universities, and lawmakers in the House recently passed a proposal that would impose egregious government restrictions on free speech. The Senate should reject those efforts unequivocally.
The absence of steady and principled leadership is what opened the campus gates to such cynicism in the first place. For several years, many university leaders have failed to act as their students and faculty have shown ever greater readiness to block an expanding range of views that they deem wrong or beyond the pale. Some scholars report that this has had a chilling effect on their work, making them less willing to participate in the academy or in the wider world of public discourse. The price of pushing boundaries, particularly with more conservative ideas, has become higher and higher.
Schools ought to be teaching their students that there is as much courage in listening as there is in speaking up. It has not gone unnoticed — on campuses but also by members of Congress and by the public writ large — that many of those who are now demanding the right to protest have previously sought to curtail the speech of those whom they declared hateful.
Establishing a culture of openness and free expression is crucial to the mission of educational institutions. That includes clear guardrails on conduct and enforcement of those guardrails, regardless of the speaker or the topic. Doing so would not only help restore order on college campuses today but would also strengthen the cultural bedrock of higher education for generations to come.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views are informed by expertise, research, debate and certain longstanding values. It is separate from the newsroom.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students.
Gerald LeTendre, of Penn State's Education Policy Studies department points out that the shotgun approach to homework, when students all receive the same photocopied assignment which is then checked as complete rather than discussed individually with the student, is "not very effective.". He goes on to say that, "If there's no ...
This essay will explore the arguments for and against homework, examine the impact of homework on students, and propose potential solutions to address the issue of excessive homework. ... Persuasive Essay On The Importance Of Homework Essay. Homework has long been a controversial topic in education, with some arguing that it is essential for ...
From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. []While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word "homework" dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home.
1. **Quality Over Quantity**. One of the primary reasons students should have less homework is to prioritize the quality of assignments over their quantity. When students are inundated with numerous assignments, they often rush through them to meet deadlines, compromising the quality of their work. Instead of encouraging deep learning ...
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.)
Advocates against homework emphasize the importance of allocating time for essential activities beyond academics. Students are not only learners but also individuals with physical, emotional, and social needs. A deluge of homework assignments leaves limited room for leisure, relaxation, and participation in extracurricular activities.
The Case for Homework. Homework is typically defined as any tasks "assigned to students by school teachers that are meant to be carried out during nonschool hours" (Cooper, 1989a, p. 7). A number of synthesis studies have been conducted on homework, spanning a broad range of methodologies and levels of specificity (see fig. 1).
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can't see it in the moment. 6. Homework Reduces Screen Time.
Importance Of Homework Essay. Above all, homework allows the students to gain responsibility, time-management, perseverance, and self-esteem. "The act of completing homework has benefits in terms of developing good habits in students.". This shows that, students are gaining many skills from homework.
Praise "Parents of America, unite! You have nothing to lose but your frustration. The Case Against Homework is an important book that takes on the 500-pound gorilla—homework overload—long ignored by educational policy makers. Every parent of a school-age child should buy it and follow the authors' excellent advice in order to protect their children from an educational system gone ...
When teachers give too much homework, it's very stressful for young minds, who should be free to enjoy themselves and grow up naturally without worries and stress. The body of your essay, then, consists of your persuasive points backed up with your arguments. These can be emotional or evidence-based. When you're thinking about your audience ...
One important reason homework should not be required is because it can cut into teenagers' sleep schedule. "Sleep benefits the brain and promotes attention, memory and analytical thought. It makes thinking sharper, recognizing the most important information to consolidate learning. Sleep also facilitates expansive thinking 2 that can spur ...
Parents don't want homework because they must supervise or the student has activities. Family time is another argument against if the assignments are very long and take up the entire evening. The ...
Homework historically was first practiced in the 19th century. It was like reflection of the era in which the school was in. During the 1940's and 1950's homework had been used like a 'drill and kill', such as rote learning or it served as a negative punishment to the children and students.
To protect the anonymity of contributors, we've removed their names and personal information from the essays. When citing an essay from our library, you can use "Kibin" as the author. Kibin does not guarantee the accuracy, timeliness, or completeness of the essays in the library; essay content should not be construed as advice.
Why Homework Is So Important Essay. Education plays an important role in ensuring children are taught career, survival and intellectual skills that will enable them to live comfortably in the future. Learning institutions have been established to ensure everyone goes to school and gets the required knowledge essential for human survival.
Homework is a waste of time. Homework is a burden. These are the thoughts of some students whenever they feel stressed on doing a task assigned to them at home. I, myself is one of those students who think ill of homework but I know the bright side of doing it. Homework is important. It is necessary and a must.
In this persuasive essay, we will delve into the importance of homework in the academic journey of students. By examining the benefits of homework in enhancing academic performance, fostering discipline, and preparing students for future challenges, we will make a compelling case for why homework should be an integral part of every student's ...
Those who are against homework believe that homework has no benefit to learning and no correlation to test scores. in his essay "The Case Against Homework", Kohn stated "Backpacks stuffed with assignments leave students exhausted, frustrated, less interested in intellectual pursuits and lacking time to do things …show more content… 2).
The Pros of Homework. 1. Reinforcement of Learning: One of the primary purposes of homework is to reinforce what students have learned in class. It provides an opportunity for students to practice and apply the concepts and skills they have been taught, helping to solidify their understanding of the material. 2.
Short Essay on Importance of Homework in 200 Words. Students often get a lot of classwork as well as homework to do. Classwork is the work students do in class while homework is the work that students are asked to do at home. Usually, homework includes going through whatever has been taught in class and answering questions related to the same.
Studies have shown that when adolescents start puberty, which is usually between the middle and high school, they need to sleep for at least nine hours. Most teens do not even get 6 hours of sleep with all the homework done. Doing homework until 12/1 a.m. and getting up early can make a student feel tired and weak.
The editorial board is a group of opinion journalists whose views are informed by expertise, research, debate and certain longstanding values. It is separate from the newsroom. A version of this ...