Stop the War. Support Ukraine. Make a donation to United24 program. Support Ukraine
- Pitch Deck Consulting Services

Business Plan
- Investment Teaser & One pager
- Startup Financial Model
- Investor Targeting and Outreach
- Due Diligence Consulting
- Post-Investment Reporting and Communication
- Pre-seed funding services
- Seed funding for startups
- Series A funding advisory
- Industry Analysis Services
- Executive Summary Consulting
- Company Overview
- Financial Performance Analysis
- Growth Opportunities and Projections
- Management and Organizational Structure
- Business Valuation Services
- Market Research Services
- Market Entry Strategy Analysis
- Pitch Deck Design Services
- Product Demo Presentation
- Event Deck Design Services
- Digital Health
- Pharmaceuticals
- Cannabis Wellness
- Cannabis Biotech
- Cannabis Products
- Psychedelics
- Social Commerce
- Mobile Commerce
- E-commerce Marketplaces
- P2P Marketplaces
- Smart Watches
- Digital Banking
- Financial Exchanges
- Personal Finance
- Flexible Workspace
- Green Building
- Clean Energy
- Solar Energy
- Wind Energy
- Animal Health
- Vertical Farming
- Mobility Tech
- Travel and Tourism
- Renewable Energy Tech
- Energy Efficiency Tech
- ClimateTech
- Car Sharing
- Ride Sharing
- Gig Economy
- P2P Finance
- Smart Government & GovTech
- Smart Building
- Smart Mobility
- Edutainment
- Video Games
- Console Games
- Online Gaming
- Mobile Gaming
- Fantasy Sports
- Online Gambling
- Event Management
- Creator Economy
- Meeting Software
- Social Networks
- Business Intelligence
- Machine Learning
- Predictive Analytics
- Generative AI
- Nanotechnology
- 3D Printing
- Augmented Reality
- Virtual Reality
- Internet of Things
- Cybersecurity
- Remote Work
- Digital Marketing
- Sales Automation
- Crypto Exchange
- Crypto Wallets
- Metaverse Economy
- Success stories
5-minute test to check your chances of raising funding in 2024
Home / Blog / Pitch Deck vs. Business Plan: What is the Difference?
Pitch Deck vs. Business Plan: What is the Difference?
- Core knowledge
- Fundraising
Want to learn more?
More growth and fundraising hacks at your fingertips
Thank you, your sign-up request was successful!
Deciding between a pitch deck and a business plan for your next fundraiser? In reality, both documents play an important part in your fight for the next round.
- Research shows that a clear, concise pitch deck can increase the chances of securing an initial meeting with investors by up to 72% .
- A business plan reduces internal confusion by 25% by clearly outlining the goals, strategies, and financial projections, leading to a 30% increase in team collaboration .
Both documents require heavy research and are designed to convince investors to back your venture. However, they accomplish it in different ways.
Having raised over $505M in 2023 for startups with our pitch decks and business plans , we’ll walk you through a detailed Pitch deck vs. Business plan comparison and their role in the fundraising game.
What is the pitch deck?
A pitch deck is a 10-20-slide presentation showcasing the potential of your business idea and startup to investors. Briefly and compellingly, it introduces your company, product, market, business model and overall strategy.
An effective must showcase your market research, traction to date, and a roadmap to where you want to get. No one-sized pitch deck exists, so you can even pitch someone in the elevator .
Think of it as an introductory sales document designed to pique investor interest and encourage further dialogue.
Components of a pitch deck:
- Introduction: Brief overview of your company and its purpose.
- Problem Statement: Clearly define the problem your product or service solves.
- Solution: Describe your product or service and how it addresses the problem.
- Market Opportunity: Showcase the potential market size and target audience.
- Business Model: Explain how your company plans to generate revenue.
- Traction: Highlight any milestones, achievements, or user statistics.
- Market Strategies: Outline your marketing and sales approaches.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and analyze your competitors.
- Team: Introduce key team members and their roles.
- Financial Projections: Present forecasts for revenue, expenses, and profitability.
- Ask/Investment: Clearly state what you’re seeking from potential investors.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a 30-100-page document showcasing an in-depth analysis of your business idea to potential investors to convince them to invest. It elaborates on things like:
- Your sales, marketing, and operational plans for growth
- Where your company will be in the next 1,3 or 5 years
- A step-by-step plan of how you’ll get there.
The business plan is the first part of the investor’s due diligence process before finalizing the deal. It lays out more detailed research on your industry and competitors, contains many charts, graphs, and pictures, and is very text-heavy.
Think of it as a comprehensive blueprint of your venture designed to persuade interested investors to pull the trigger and invest.
Components of a business plan:
- Executive Summary: A brief business overview, goals, and plans.
- Company Description: Details about your business, mission, vision, and structure.
- Market Analysis: Research your industry, market, and competitors.
- Organization and Management: Information about your team, structure, and key personnel.
- Product or Service Line: Description of your offer and its benefits.
- Marketing and Sales: Your strategies for promoting and selling your product or service.
- Funding Request: If you seek funding, outline your financial needs.
- Financial Projections: Projected financial statements, like income statements and balance sheets.
- Appendix: Additional supporting documents, charts, graphs, etc.
What are the differences between a pitch deck and a business plan?
While the business plan and pitch deck give a view of your venture, they serve different goals, reach different audiences, and build the story differently. These distinctions manifest in the length, format, target audiences, and funding stages.
Length and Format
- Pitch Deck:
Brief and eye-catching 10-20 slides with engaging visuals, like images, charts, and minimal text. Generally highlights critical points, like product or service, target market, business model, and future potential.
- Business Plan:
Detailed 30-100 page text-heavy document armed with visuals like charts and graphs. It typically emphasizes projected revenue, expenses, and profitability through financial statements and forecasts. The document details strategies for sales, marketing, operations, and human resources, along with a description of team members’ expertise, experience, contributions to the company’s success, etc.
Raise money with the free pitch deck template from Waveup

Why startups love our template:
- Investor-proof narrative & design
- Best practices from $3B+ raised
- Powerpoint + Keynote
Success. We just sent the Pitch Deck Template from Waveup to your inbox.
Targeted Audience
- Pitch Deck: Investors (initial stages)
- Business Plan: Investors (due diligence), internal team
Stages and Objectives
- Pitch Deck: 1. Shines in early stages: Pre-seed, seed, Series A. 2. Captivates investors: Concisely delivers the problem, solution, market, and team.
- Business Plan: 1. Dominates later stages: Series B and beyond. 2. Secures substantial funding: Demonstrates viability and potential return on investment (ROI).
Frequency of use
- Pitch Deck: 1. High Frequency: Used frequently and repeatedly throughout the fundraising process. You might prepare several variations tailored to different investors or stages of funding. Examples: Initial investor meetings, pitch competitions, and conferences seeking investment opportunities.
- Business Plan: 1. Lower Frequency: Typically used once during the later fundraising stages, specifically during due diligence. 2. Focus: Providing detailed information for investors to thoroughly assess your business’s viability.

Pros and cons: Pitch Deck vs. Business Plan
Advantages:
- Comprehensive: This thoroughness is crucial for investors, lenders, and internal stakeholders.
- Strategically complete: Aids decision-making, resource allocation, and risk management.
- Supportive fundraising: Studies suggest that companies with a well-crafted business plan are 18% more likely to secure funding than those without one.
Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming: Requires potential expertise in areas like financial modelling and market research.
- Outdated quickly: Market dynamics and business strategies can evolve rapidly, necessitating regular updates to the plan to maintain its accuracy and relevance.
- It may not be read: Lack of time and poorly structured info can push away the potential investor.
- Concise and engaging: Studies reveal that audiences lose focus after 10-20 minutes of presentations. Pitch delivers a clear and quick message.
- Easy to adapt and share: Adapting the pitch deck for various audiences and situations is simpler due to its brevity.
- This can lead to meetings: Engaging presentations foster positive connections with potential partners and lay the groundwork for long-lasting collaborations.
- Sometimes limited information: By definition, it does not provide the in-depth financial analysis, operational details, and market research needed for comprehensive due diligence.
- Less suitable for later stages: As funding requirements and investor expectations increase, a pitch deck alone may not be sufficient for securing more significant investments.
Which is more important, the pitch deck or the business plan?
There is no one-size answer; in most cases, you need both. The importance of each depends on your industry and fundraising stage. The pitch deck is crucial early on , but investors scrutinise the business plan for details as you progress .
The pitch deck is vital for visibility. Without it, you may miss opportunities with investors and hinder connections with mentors and partners essential for your startup’s success.
On the other hand, the business plan is crucial to validate everything you’ve outlined in your pitch deck. Investors can quickly spot unprepared founders or unrealistic propositions. While a compelling pitch may secure a meeting, a thorough plan will convince investors to back your venture.
Important: A well-crafted pitch deck often stems from a strong business plan.
When to use a business plan and not a pitch deck
- If you seek debt financing: Banks rely on business plans, emphasizing their importance for loan applications.
- If you fundraise above $500k: Careful planning is crucial for substantial fundraising. Investors will scrutinize your venture, so be thoroughly prepared.
- If you have cooperative ownership planning: A written plan is essential for co-owners to navigate challenges together, staying true to the initial vision while embracing necessary changes.
When to use a pitch deck and not a business plan
- When attracting equity investment: A concise pitch deck is essential to secure funds from venture capitalists, angel investors, or knowledgeable friends and family.
- When looking for networking with potential investors: Crafting a positive initial impression is paramount.
- For pitching opportunities for founders: Explore pitch competitions in the startup community, seizing opportunities for exposure and honing your pitching abilities with a solid pitch deck.
- When seeking co-founders: If you’re looking for cofounders, there is no better way to convey your concept and the value you can bring to the table than through a pitch deck.
- When applying to accelerator programs: A well-crafted pitch deck is typically required. It is a critical asset in the assessment process for entry into the accelerator’s next cohort.
You need both
Need to grab attention and lock connections? Use a pitch deck. Need to showcase in-depth details and long-term potential? Use a business plan. Both tools are paramount in navigating your fundraising journey effectively.
Want to know how to craft pitch decks that secure investor interest? Check our pitch deck hub to learn all about it straight from the trenches.
CONTENT WRITER
Hey there! I'm Anastasiia, a Content Writer at Waveup. With my marketing expertise and storytelling magic, I turn complex data and industry insights into your startup playbook, making the business world a breeze for you! At Waveup, I work with brilliant folks who make insights a never-ending flow. So, join, read, and enjoy!
Related Posts
Startup funding stages guide: from pre-seed to ipo [2024], top-11 market validation methods, mistakes & slide examples.
- Financial model
6 pro tips for building superior startup KPI dashboard
How to value your startup: pre-seed to series a guidebook, how to calculate the cost of revenue: startup cheat-sheet, how to prove to investors you have product-market fit, a complete rundown of pitch deck mistakes and how to avoid them, startup operating expenses: what should they include, startup math: the key performance indicators you need to track, top 10 venture capital firms in seattle, top 10 venture capital firms in dallas, top 10 vcs investing in e-commerce and consumer products.
Leave your information below and one of our experts will be in touch to schedule a call.
AI Presentation Maker
Pitch deck vs business plan: differences and which to use

Table of Contents
Have you ever spent time deciding between creating a pitch deck vs business plan? For startups and new business owners, where every minute counts, it’s crucial to concentrate on activities that deliver the most significant impact.
This blog article demystifies the pitch deck vs business plan, whether you aim to attract investors, secure a loan, or win over partners and clients. We’ll start with pitch decks, followed by business plans, with the goal of helping you choose wisely – so you can spend less time on paperwork and more time building your business.
1. What is a pitch deck?

A pitch deck is a slideshow that concisely conveys your business idea, market opportunity, and value proposition in a presentation format. Also known as a business or investor deck, they are used to quickly present business ideas, products, or services in 10 to 20 slides.
Purpose of a pitch deck
The purpose of a pitch deck is similar to that of an elevator pitch: tell a compelling story to grab the attention of potential investors, partners, or clients.
The goal isn’t to seal a deal on the spot but to spark sufficient interest to secure follow-up meetings and negotiate potential funding.
How long should a pitch deck be?

Your pitch deck should pack a punch, not bore your investors. Aim for 10-20 impactful slides . For complex ideas or specific industries, slightly more might be okay.
The 10/20/30 rule is your friend: make a 10-slide deck that grabs attention. Investors see hundreds of pitch decks a year. Choose quality over quantity – make each slide count!
💡 Related article: How many slides do you need for a 10-minute presentation?
What should be in a pitch deck
Most successful pitch decks follow a similar flow to keep investors hooked. The tried-and-tested 10-slide pitch deck format is a great starting point but be prepared to adjust or add slides for emphasis.
These are the 10 core slides for a pitch deck based on Guy Kawasaki’s 10/20/30 rule:
- Problem slide
- Solution slide
- Market size and opportunity
- Product/service
- Business model
- Competition
- Financials and key metrics
- Ask (funding needs)
Here are additional slides you may include based on specific business and investor preferences:
- Introduction
- Go-to-market (GTM) slide
- Sales and marketing strategy
- Use of funds
- Exit strategy
💡 Learn more about the 10/20/30 rule: How to create a pitch deck (and the 10 slides you need)
Pitch deck examples
Curious how some tech unicorns have pitched their ideas in the early stages? Here are two examples that have proven successful.
✅ Snapchat pitch deck (2013, Pre-seed)

✅ Tinder pitch deck (2016, Seed)
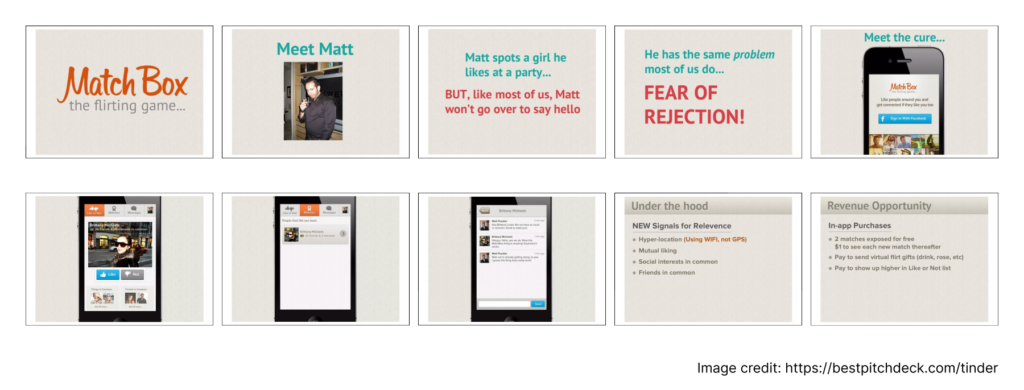
Examples from Best Pitch Decks
2. What is a business plan?

A business plan is a written document with detailed information that acts as a roadmap for your business. A traditional business plan is a formal document that outlines all aspects of your business, including its goals, strategies, market analysis, operational structure, and financial forecasts for the next 3 to 5 years. Most business plans are created in a Word document or report format, ranging from 10 to hundreds of pages long.
There are other types of less formal business plans used by startups or for internal alignment:
- Lean startup plan/Lean canvas: Summarizes the value proposition and business model into a single page, with a focus on the problem-solution fit.
- One-page business plan: Fits the essential information of a business into one page. Great for quickly testing an idea’s viability or getting immediate feedback.
- Internal business plan: Less formal, designed for use within an organization — for example, a feasibility business plan, operations plan, strategic, or expansion plan.
Purpose of a business plan
Business plans aren’t just for paperwork – they drive action and results. Think of your business plan as a multi-purpose tool that serves several vital functions:
- Attract investors
- Fundraising or securing loans
- Map your strategy
- Provide a strategic roadmap
- Track business progress or provide a performance benchmark
- Win over partners, talents, and potential hires
Components of a business plan
Business plans don’t have a right or wrong format; only different situations call for other formats. You can mix different plan types to prioritize components that directly support your objectives.
What to include in a traditional business plan:
- Executive summary: A concise overview of your entire business plan, highlighting the most critical points.
- Company description: What your business does, the problem it solves, your target market, and competitive advantages.
- Market analysis: Research data like market size, trends, competitors, and customer demographics.
- Organization and management: The business structure, roles, and experience of key team members.
- Products or services: Details on your offer, including features, benefits, pricing, and any intellectual property considerations.
- Sales and marketing strategy: How you plan to reach your target customers (market) and tactics to promote and drive sales.
- Financial projections: Forecasts of your income, expenses, cash flow, and profitability for the next 1 to 5 years.
- Funding request: If you are fundraising, state the amount, how it will be used, and the terms you offer investors.
- Appendix: Include any supplemental information and documents.
💡 Pro tip: Customize your plan! Add, remove, or rearrange sections to achieve your goals.
How long should a business plan be?
Think about your reader and your goal. Need a detailed plan for a bank loan? That might be 15-25 pages. Want a quick internal roadmap? A one-page Lean Canvas could work. Consider your industry, who’s reading it, and what you need the plan to do.
💡 Pro tip: Choose quality over quantity. Focus on clarity, regardless of length.
How long does it take to write a business plan?
It can take anything from 20 minutes to 20 weeks. The whole process of creating a business plan can be time-consuming (if opting for a long format), and it can also be quick (for example, the Lean Canvas).
The general advice is: Don’t overthink your first business plan. Start simple, move fast, and build as you grow. Business plans aren’t static, so be prepared to refine and expand your plan as the business evolves.
💡 Pro tip: It’s not uncommon to uncover some challenging sections while writing the plan – the key is to show awareness of these issues and ways to overcome them.
Business plan templates
Not sure where to start? Use these example plans and templates from these reputable sources to get you started:
- SBA.gov: Write your business plan – Has the traditional business plan and lean startup business plan templates
- SCORE.org – Has business plan templates for a startup , an established business , and the Business Model Canvas
- Bplans has over 550 business plan examples across multiple industries, which you can use for inspiration.
3. Pitch deck vs business plan: the differences
Now that you understand pitch decks and business plans, let’s dive into their key differences.
- Pitch decks are short and punchy, designed to grab investors’ attention and get you that crucial meeting.
- Business plans are thorough and detailed documents, perfect for in-depth analysis or large funding requests.
💡 Think of it this way: Pitch decks are the attention-grabbing movie trailers that sell the whole project. Business plans are your complete blueprint.
Both documents can serve you, but understanding their differences helps you select the best tool for attracting investment or charting your company’s path.
4. Do you need a pitch deck or a business plan?
In the past, business plans were the standard document to present a business idea to investors. However, simple business plans and pitch decks are increasingly popular, especially in startups.
Here’s how to choose the right tool for the job:
🎯 Pitches and investor meetings
Pitch decks provide a snapshot of your business or idea’s potential to spark interest and secure future investor meetings.
🎯 Early stages or for idea validation
Use a simple business plan or Lean Canvas, as the format forces you to focus on the core problem you’re solving and the solution.
🎯 Internal roadmap and planning
Formal business plans will aid in longer-term strategic planning, or they can be shorter since they are for internal use.
🎯 Complex business model
Create a thorough business plan with intricate details; short plans and pitch decks wouldn’t cut it for specific industries or complicated business models.
🎯 Fundraising, loans, or traditional financing
Banks, investors, and government-funded grant applications often require a detailed business plan. Whether you seek debt or equity funding, angel investors, VCs, and banks need compelling reasons to support your venture.
💡 Pro tip: You’ll still need a traditional business plan for detailed strategy or significant funding!
5. Conclusion
Pitch decks and business plans aren’t simply documents – they’re essential tools for driving your business forward. Now that you know the difference, consider your current needs. Ready to capture investor attention? Start crafting a compelling pitch deck. Need a detailed roadmap? Begin writing a winning business plan. Use the resources in this guide to get started and put your business on the right track toward success!
When should you write a business plan?
According to research by Harvard Business Review , between six and 12 months after deciding to start a business. For various reasons, crafting a comprehensive business plan either earlier or later doesn’t necessarily impact business success:
- Most startups pivot from their original ideas and plans.
- The time needed to create a thorough plan is better spent on other business activities (at least initially).
- Creating an elaborate plan may distract entrepreneurs from seeing opportunities in real time and responding to real customers’ needs.
Planning is valuable, and entrepreneurs who plan are more likely to start a successful business. However, you don’t need a complex business plan to begin working on your business. It’s okay to create a plan early on but remember; it’s more about being strategic with your time than trying to forecast the future from the start.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a canvas?
They differ in complexity and length. Business plans are longer and more detailed and are typically used to secure funding from investors or financial institutes.
A canvas, Lean Canvas , or business plan canvas, is a 1-page business plan. The Lean Canvas template helps you deconstruct your idea and focus on finding customer problems worth solving without a significant time investment.
It is popular as a direct replacement for traditional business plans within startups. The canvas can be used for quick and efficient brainstorming of multiple business models in a few hours or less.
How do I turn a business plan into a pitch deck?
Once you’ve done the groundwork of creating a business plan, you can reuse some of the insights, data, and information for a pitch deck.
- First, extract the core details from the business plan, such as the problem you solve, the solution, the size of the market, team strengths, and financials.
- Translate that information into your chosen pitch deck template (for example, the 10-slide pitch deck ) or use an AI presentation generator tool such as SlidesAI to structure your slides.
- Add and emphasize visuals. Replace some text with charts, diagrams, and graphs whenever applicable.
- Edit and keep the pitch deck focused and clear. Quality over quantity!
- Get feedback, practice your pitch, and then iterate on the deck until you are ready to show it to investors.
💡 Related article: 5 best free AI pitch deck generators 2024
Is a pitch deck only for investors?
No, while the primary purpose of a pitch deck is to attract funding, it can be adapted for various audiences and goals, such as partnerships, customers (especially enterprise customers), grant applications, startup or pitch competitions, or even for internal alignment within your team.
Save Time and Effortlessly Create Presentations with SlidesAI
Pitch Deck vs Business Plan — Which One Do You Need?
Uncover the differences between a pitch deck and a business plan and discover which is essential for your startup. Learn and create with PitchBob.

In this dynamic world, where ideas can spark revolutions and dreams become realities, two essential companions await your journey: the pitch deck and the business plan. These tools aren’t just documents but the wind beneath your entrepreneurial wings. Let’s set sail into the world of pitch decks and business plans, unraveling their magic and discovering when to wield their power.
Imagine standing at the helm of a ship, gazing at the uncharted waters ahead. Your startup is that ship, and at your disposal, you have instruments that can guide it through the unpredictable currents of the market. These instruments are the pitch deck and the business plan — crafted to impress and chart your course with purpose and strategy.
What is a Pitch Deck?
A pitch deck isn’t just a collection of slides; it’s the vibrant tapestry that weaves your startup’s narrative. Visuals, text, and passion converge to create a captivating story. Think of it as your startup’s cinematic trailer, offering a sneak peek into the adventure you’re embarking upon. It’s not just about presenting facts; it’s about evoking emotions and igniting curiosity.
When you’re at a startup event surrounded by potential investors and decision-makers, it is your chance to condense your startup’s essence into a visually striking, emotionally resonant package. The pitch deck shines brightest in scenarios where time is short, attention spans are fleeting, and impact is paramount.
What is a Business Plan?
Now, let’s steer our ship toward a different horizon. Imagine a comprehensive map that not only outlines your journey but also details every landmark, every challenge, and every resource needed. This map is your business plan — a strategic document that transcends mere ideas and dives deep into strategy, operations, and financial projections. It’s the blueprint that guides your ship through uncharted waters.
Where your startup has gained some traction, you’re no longer just presenting an idea. You’re showcasing a vision backed by research and planning. This is where the business plan takes center stage. The business plan becomes your guiding star when seeking substantial investments, forging partnerships, or outlining your startup’s long-term trajectory. The document demonstrates your commitment, knowledge, and foresight to potential investors and stakeholders.
Main Differences Between Business Plan and Pitch Deck
Let’s pull out our magnifying glass and explore the nuances that set these two powerhouses apart:
1. Purpose and Usage:
- Pitch Deck: The pitch deck is akin to your startup’s captivating movie trailer — a visual and concise introduction that sparks curiosity, leaving the audience eager to learn more about your venture. It’s your chance to pique interest and create a memorable initial impression that lingers.
- Business Plan: In contrast, the business plan is your startup’s comprehensive screenplay. It delves deep into the plot, character development (or market analysis), and intricate details of your venture’s journey. This document captures attention and provides a comprehensive roadmap for potential investors, partners, and your internal team.
- Pitch Deck: Like a thrilling teaser, the pitch deck is succinct, comprising a carefully curated collection of 10-15 impactful slides. Each slide is a trailer frame, revealing essential plot points of your startup’s story.
- Business Plan: In-depth, the business plan reigns supreme. It stretches across 20 to 50 pages, meticulously laying out every scene of your startup narrative. Your comprehensive manuscript covers everything from your startup’s origin story to its grand finale — the financial projections.
3. Audience Focus:
- Pitch Deck: The pitch deck is tailored to a bustling audience, including potential investors and partners. They have limited time, seeking a snapshot of your startup’s possible and unique selling points. The deck’s visuals and succinct content aim to capture their attention swiftly.
- Business Plan: Here’s where you zoom in. The business plan caters to investors, potential partners, and your internal team. It invites them to explore the finer nuances of your startup universe — the market analysis, the competitive landscape, and the intricate strategies that will propel your venture forward.
4. Creation Process:
- Pitch Deck: Crafting a pitch deck is a delicate dance of creativity and strategy. It’s about weaving compelling visuals, impactful messaging, and the right balance of information. Each slide should be visually appealing, grabbing attention and guiding the audience through the story.
- Business Plan: Assembling a business plan is akin to preparing an epic saga. It requires meticulous research, strategic planning, and attention to detail. Your business plan showcases your commitment to realizing your startup’s potential, demanding a systematic approach to ensure each detail is accurate and well-structured.
Pitch Deck vs. Business Plan — At What Stage Will You Need Them?
As you journey through the startup landscape, timing is everything. Knowing when to whip up your pitch deck and business plan is essential for a delectable startup recipe, just as a chef adds ingredients at precisely the right moments. Let’s break it down, shall we?
When Do You Need a Pitch Deck?
Imagine you’re at the starting line of a grand marathon. The gunshot goes off, and you sprint to capture attention, make connections, and spark interest in your startup. This is where the pitch deck becomes your secret weapon. In the early stages of your venture, when your idea is ripe with excitement and potential, your pitch deck steps into the limelight. Think of it as your startup’s dazzling overture — a concise yet impactful introduction that beckons investors, partners, and decision-makers to notice.
You’ll want your pitch deck ready when you’re:
- Introducing your startup idea at networking events, pitch competitions, or investor meet-ups.
- Seeking initial funding to transform your idea into a reality.
- Elevating your startup’s visibility and attracting potential collaborators.
When Do You Need a Business Plan?
Now, picture your startup as a mighty oak tree. It began as a tiny seed, and now it’s growing tall and strong, casting its shadow across the industry. But as it grows, it requires a well-thought-out plan to sustain and nurture its growth. Enter the business plan. When your startup has evolved beyond the ideation phase and is gearing up for significant growth, that’s the cue for your business plan to take center stage. It’s not just about capturing interest; it’s about showcasing your startup’s depth, potential, and strategic prowess.
It’s time to unleash your business plan when you’re:
- Seeking substantial funding from investors who want a comprehensive view of your venture’s future.
- Navigating partnerships and collaborations that require a detailed roadmap.
- Planning the subsequent phases of your startup’s growth and expansion.
How Can PitchBob Help to Create Pitch Deck and Business Plan?
Hold on to your compass because we’re introducing you to a game-changer — PitchBob! Imagine a platform where creating pitch decks and business plans is efficient and creative. PitchBob empowers you with customizable templates, user-friendly tools, and the freedom to infuse your unique voice into your documents. Whether you’re aiming for elegance or innovation, PitchBob has you covered.
In a world where startups rise like constellations, your pitch deck and business plan are the guiding stars that illuminate your path. They’re not just documents^; they’re your dynamic ensemble, your tag team. The pitch deck takes the stage, captivating hearts, and minds, while the business plan works backstage, ensuring your startup’s strategy is solid and future-proof.
As you navigate the waves of uncertainty and opportunity, remember that you’re armed with these potent tools. Whether stepping onto a stage bathed in the spotlight or sitting across the table from investors in a boardroom, your startup’s journey is powered by the fusion of innovation, strategy, and vision. May your pitch be as compelling as your plan is meticulous, and may your startup voyage be filled with discovery, triumphs, and the realization of your dreams.

Disruptive Partners OÜ Harju maakond, Tallinn, Kesklinna linnaosa, Tornimäe tn 3 / 5 / 7, 10145
PitchBob, Inc 2261 Market Street #10281 San Francisco, CA 94114

Case Studies
Resource Hub
Featured post
What is a Pitch Deck: The Definitive Guide for Entrepreneurs

Explore our latest posts
Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities in Green Tech Startups

Navigating the Gig Economy: Strategies for Startups to Leverage Freelance Talent

Leveraging Business Incubators for Startup Success: A Comprehensive Guide

The Entrepreneur's Arsenal: Pitch Deck vs. Business Plan
Learn the differences between a business plan and a pitch deck and when to use each one. Discover the pros and cons of both and how to create a winning pitch deck or compelling business plan.
November 20, 2023
Pitch deck vs. business plan: which one do you need for your business, and when? As a businessman or entrepreneur, do you sometimes wonder why your potential investors aren't responding after you've sent them a long and detailed business plan or a catchy pitch deck? This could be due to the minimal information provided in the pitch deck or the lengthy, boring, and irrelevant details in the business plan that repelled them from reaching back to you. However, you should also know how to send pitch decks to investors. Therefore, it's crucial for an entrepreneur to understand which approach is best for their venture. Before seeking out investors, one should be very well aware of the difference between a pitch deck and a business plan. Luckily, we have all the information you need. Check out our resource on how to send a pitch deck to investors.
Pitch Deck vs Business Plan
What are pitch decks and business plans, and how do you write them? Let’s find out.
A business plan identifies, describes, and analyzes a business opportunity and/or an existing business. It focuses on the technical, financial, and economic viability of the idea, and explains in detail the plans your company has for the next 1, 3, and 5 years. This document is used as a reference point by potential investors when deciding whether or not to invest in your company. Furthermore, it's frequently used in a due diligence step in the funding process. A pitch deck, on the other hand, is a much more summarized version of a business plan that aims to excite investors about a company, to set up a second meeting and the possibility of an investment discussion. It is a pitch presentation used by business owners or entrepreneurs to give potential investors, like venture capitalists or angel investors, a concise but informative overview of their startup or company. Investors can use it to see where your business stands and where it is going, and decide whether they want to support it in getting there. It is purposefully sent to potential investors in order to set up a face-to-face meeting or used as a visual aid during a live presentation to potential investors.
Included Information
A business plan contains the research you have conducted on your industry and competitors as well as your company's operational, marketing, and sales strategies. It also includes financial analysis, growth, success projections, and a road map of where your business will be in the future and how it will get there. These nine sections are combined in a traditional business plan design in one way or another:
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Market research
- Operational plan and management
- Service or line of goods
- Sales and marketing
- Money request
- Financial estimates
If you want a professional business plan, it is highly recommended to use a business plan consultant. On the other hand, a pitch deck usually covers the following sections:
- Introduction
- Target market
- Marketing and sales strategy
- Pitch Deck Competition Slide
- Funding request
- Financial Strength
You can find all the details in our Pitch Deck Outline article. Another element of information that should be included in a pitch deck is how much money the company intends to raise, for what amount of equity, and how the money will be spent. Therefore, it must contain expected financials and a pre-money company valuation. You can also include a timeline of significant events in the company's history, which will help convince investors to approve the funding.

The business plan is a lengthy, in-depth document that typically has 10–100 pages and is created in Word. It is primarily text-based. On the other hand, the pitch deck's length ranges between 10 and 20 pages and is produced using PowerPoint with the intention of using visual aids such as pictures, graphs, tables to convey as much of the critical information as quickly as possible.
Situations Where a Business Plan Is Needed
- Obtaining Debt Financing from Conventional Banks: If you want to obtain any type of loan from a bank, you will need to submit a business plan, as they still review them.
- Company Having Multiple Co-Founders and Co-Owners: A business plan is quite helpful in managing a bigger board of seniors in the company. It ensures that everyone sticks to the company's core values and carries out the intended plans to achieve long-term goals. This should be a dynamic document that is continually updated as circumstances warrant.
- Fundraising over $500K: If you are raising a large amount of cash, you better have a strategy in place for how you are going to use it. Be ready for due diligence from investors.
For an in-depth guide on startup business models , click here.

Situations Where a Pitch Deck is Needed
- Meeting or Starting a Conversation with an Investor: A pitch deck is a conversation starter that encourages investors to get in touch with you. You can email a PDF file or send a printed copy to start building a relationship with investors.
- Pitching in a Competition: The startup community organizes many pitch competitions and events that provide business founders the opportunity to practice pitching their business and gain exposure. In these competitions, a pitch deck is a must-have document that effectively communicates the startup plan.
- Seeking Equity Funding: If you are seeking funding from venture capitalists, angel investors, or knowledgeable friends and family, you need a clear pitch deck.
What to Write First - Business Plan vs Pitch Deck?
At the initial phase of a business, a fundamental document called a business plan is written. This plan is updated as the business develops and as needs and goals change over time. The lengthy document can serve a variety of purposes, including internal use within the company or in banks that still require business plans for loan applications today. Additionally, the business plan document can be very useful in creating a compelling pitch deck. In the eyes of professionals, the pitch deck is considered a child of the business plan. Having a prepared business plan makes it much easier to get depth and length in your plans, which eventually results in more clarity and strong points that you could include in a pitch deck. Research is already completed when writing a business plan, which allows the pitch deck to focus on composing the already-existing information in such a manner that encourages the investor to approve the funding you need.
The Pros and Cons of a Business Plan vs. a Pitch Deck
Both business plans and pitch decks have their advantages and disadvantages. Let's take a closer look at the pros and cons of each.
Business Plan Pros
- Comprehensive: A business plan is a comprehensive document that covers all aspects of your business, from your market research to your financial projections. It may be helpful to seek assistance from a financial modelling agency when creating your financial projections.. It provides potential investors with a detailed understanding of your business and its potential for success.
- Strategic: A business plan helps you to think strategically about your business. By analyzing your industry, your competitors, and your own strengths and weaknesses, you can create a plan that maximizes your chances of success.
- Useful for fundraising: A well-written business plan can be an effective tool for raising funds from investors. It provides potential investors with the information they need to make an informed decision about whether to invest in your business.
Business Plan Cons
- Time-consuming: Writing a comprehensive business plan can be a time-consuming process. It requires a significant amount of research, analysis, and writing.
- Outdated quickly: Business plans can quickly become outdated as your business evolves and circumstances change. This means that you may need to update your business plan regularly to ensure that it remains relevant.
- May not be read: Some investors may not have the time or patience to read a lengthy business plan. This means that your hard work may go to waste if your plan is not read by the right people.

Pitch Deck Pros
- Concise: A pitch deck is a concise document that provides potential investors with a quick overview of your business. It is designed to be easy to read and understand, which makes it more likely that it will be read by potential investors.
- Engaging: A well-designed pitch deck can be an engaging and memorable way to present your business to potential investors. It can help you to stand out from the competition and make a strong impression.
- Can lead to meetings: A pitch deck is often used to secure meetings with potential investors. If your pitch deck is well-received, it can lead to a face-to-face meeting where you can provide more detailed information about your business.
Pitch Deck Cons
- Limited information: A pitch deck provides only a limited amount of information about your business. This means that potential investors may not have a complete understanding of your business and its potential.
- Not suitable for all businesses: A pitch deck is not suitable for all businesses. If your business is complex or requires a significant amount of explanation, a pitch deck may not be sufficient.
- Not as useful for fundraising: While a pitch deck can be used to secure meetings with potential investors, it may not be as effective as a business plan for actually raising funds.

Ultimately, the decision to use a business plan or a pitch deck will depend on the specific needs of your business and the goals you hope to achieve. It's important to understand the pros and cons of each and use them appropriately to effectively communicate your ideas to potential investors.
How to Create a Winning Pitch Deck
Creating a pitch deck that stands out can be a challenging task, but it's essential if you want to attract investors to your business. Here are some tips to help you create a winning pitch deck:
1. Start with a Strong Introduction
Your introduction slide should grab investors' attention and make them want to learn more about your company. Use a catchy tagline, a powerful image, or a compelling statistic to draw them in.
2. Focus on the Problem You're Solving
Your pitch deck should explain the problem you're solving and why it matters. Use real-world examples and statistics to illustrate the problem and show why it's important.
3. Explain Your Solution
After you've described the problem, explain how your product or service solves it. Be clear and concise, and focus on the benefits of your solution.
4. Show Traction
Investors want to see that your company is gaining traction and making progress. Include data on customer acquisition, revenue, and growth to show that your business is on the right track.
5. Describe Your Marketing and Sales Strategy
Your pitch deck should explain how you plan to market and sell your product or service, including specifics on your target market, your marketing channels, your sales process, and any startup market research services you may use to gain insights into your target audience and industry.
6. Highlight Your Competitive Advantage
Investors want to know what sets your business apart from the competition. Explain your competitive advantage and show how it gives you an edge in the market.
7. Be Realistic About Financial Projections
Your pitch deck should include financial projections, but they should be realistic. Don't exaggerate your projections or make unrealistic promises. Instead, focus on achievable goals and realistic timelines.
8. Keep It Simple and Visual
Your pitch deck should be simple and easy to follow. Use visuals, such as graphs, charts, and images, to convey your message and make your presentation more engaging.
9. Practice, Practice, Practice
Finally, practice your pitch deck until you're comfortable delivering it. Practice in front of friends, family, or colleagues, and ask for feedback. Refine your presentation until it's polished and persuasive.
By following these tips, you can create a winning pitch deck that will help you attract investors and grow your business. Remember to start with a strong introduction, focus on the problem you're solving, explain your solution, show traction, describe your marketing and sales strategy, highlight your competitive advantage, be realistic about financial projections, keep it simple and visual, and practice, practice, practice.

Tips for Writing a Compelling Business Plan
Writing a business plan can be a daunting task, but it's an essential step in securing funding for your business. Here are some tips to help you write a compelling business plan:
1. Know Your Audience
Before you start writing your business plan, it's essential to know your audience. Who will be reading your plan? What are their goals and objectives? What information do they need to make a decision? By understanding your audience, you can tailor your plan to their needs and increase your chances of success.
2. Keep It Concise
While a business plan is a detailed document, it's essential to keep it concise. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that your audience may not understand. Instead, use short sentences and simple language to convey your message. Use bullet points and headings to break up the text and make it easier to read.
3. Focus on Your Unique Value Proposition
Your unique value proposition is what sets your business apart from the competition. It's essential to focus on this in your business plan. Explain why your product or service is better than what's already available in the market. Show how you plan to differentiate yourself and capture market share.
4. Be Realistic
When writing your business plan, it's essential to be realistic. Don't exaggerate your projections or make unrealistic promises. Instead, focus on achievable goals and realistic timelines. Provide evidence to back up your claims and show that you've done your research.
5. Include Financial Projections
Financial projections are a crucial part of any business plan. They show how you plan to make money and when you expect to become profitable. Include projected income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Be sure to explain your assumptions and include a sensitivity analysis to show how your projections could change under different scenarios.
6. Get Feedback
Before submitting your business plan, get feedback from others. Ask friends, family, or colleagues to review your plan and provide feedback. Consider working with a business coach or mentor who can provide guidance and support.
By following these tips, you can write a compelling business plan that will help you secure funding and grow your business. Remember to tailor your plan to your audience, keep it concise, focus on your unique value proposition, be realistic, include financial projections, and get feedback.

Key Components of a Business Plan and a Pitch Deck
A business plan and pitch deck have different components that are essential to the success of your company. Here are the key components of each:
Business Plan
- Executive Summary: This section provides an overview of your entire business plan. It should be concise and highlight key points about your company, such as the problem you're solving, your target market, and your competitive advantage.
- Business Description: This section describes your company in more detail, including your mission, vision, and values. It also includes information about your team, your product or service, your target market, and your business model.
- Market Analysis: This section analyzes your industry and your competitors. It includes information about your target market, your competition, your marketing strategy, and your sales strategy.
- Operational Plan and Management: This section explains how your company will operate on a day-to-day basis. It includes information about your organizational structure, your management team, and your operational processes.
- Service or Line of Goods: This section describes your product or service in detail. It includes information about the features and benefits of your product or service, as well as any intellectual property you've developed.
- Sales and Marketing: This section explains how you plan to sell your product or service. It includes information about your sales strategy, your marketing strategy, and your pricing strategy.
- Money Request: This section explains how much money you're raising and how you plan to use it. It includes information about your funding needs, your use of funds, and your financial projections.
- Financial Estimates: This section includes your financial statements, such as your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It also includes any other financial information that investors may need to make a decision.

- Introduction: This slide includes your company name, logo, and tagline. It's the first thing investors will see, so it should be attention-grabbing.
- Problem: This slide explains the problem your company is solving. It should be concise and clearly explain why your product or service is needed in the market.
- Target Market: This slide describes your target market. It should include information about your ideal customer, such as their demographics, psychographics, and buying behavior.
- Solution: This slide explains how your product or service solves the problem you identified earlier. It should be concise and clearly explain the benefits of your product or service.
- Traction: This slide describes any traction your company has gained so far. It should include information about your customer acquisition, revenue, and growth.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy: This slide explains how you plan to market and sell your product or service. It should include information about your marketing channels, your sales process, and your pricing strategy.
- Competition: This slide describes your competition. It should include information about your competitors' strengths and weaknesses, as well as how your product or service is different.
- Funding Request: This slide explains how much money you're raising and how you plan to use it. It should be concise and clearly explain why you need the money.
- Financial Strength: This slide includes your financial projections. It should include your revenue, expenses, and profit margins.
- Team: This slide describes your team. It should include information about your management team, your advisors, and any other key team members.

Keep in mind that these are just the basic components of a business plan and pitch deck. Depending on your industry and your company's unique needs, you may need to include additional information.
Both a pitch deck and a business plan are essential tools for entrepreneurs seeking funding for their ventures. While a business plan provides a comprehensive overview of a company's operations and financial projections, a pitch deck is a more concise and visually appealing document that seeks to excite potential investors about a company's potential. Understanding the differences and appropriate use cases for each document can greatly increase an entrepreneur's chances of securing funding and growing their business. By following the tips outlined in this article, entrepreneurs can create compelling pitch decks and business plans that effectively communicate their vision and attract potential investors.
Key Takeaways
A business plan analyzes a business opportunity and/or an existing business, while a pitch deck aims to excite investors about a company and set up a meeting for an investment discussion.
A business plan is a lengthy, text-based document, while a pitch deck is a concise document that uses visuals to convey critical information as quickly as possible.
A business plan is helpful for obtaining debt financing from conventional banks, managing a bigger board of seniors in the company, and fundraising over $500k, while a pitch deck is useful for starting a conversation with an investor, pitching in a competition, and seeking equity funding.
A business plan is comprehensive and strategic, while a pitch deck is concise and engaging.
Both business plans and pitch decks have their advantages and disadvantages, so it's essential to understand the pros and cons of each and use them appropriately to communicate your ideas effectively.
.webp)
Table Of Content
Explore Our Services

Explore our top-notch pitch deck service
We help discerning startups and growing businesses create powerful pitch decks that attract investors and secure big deals.

Subscribe to our newsletter and keep in touch with us
An error has occurred somewhere and it is not possible to submit the form. Please try again later.
Only available to newsletter subscribers!
Answers, To The Most Asked Questions
What is the difference between a business plan and a pitch deck, when should i use a business plan, when should i use a pitch deck, what are the pros and cons of a business plan, what are the pros and cons of a pitch deck, you may like.

10 Best Cyber Security Startup Ideas
Discover the most promising cybersecurity startup ideas for 2023. Drive innovation, meet market demands, and elevate digital safety. Start your journey now!
Read Article

10 Best Software Startup Ideas
Discover the hottest software startup ideas for 2023. Dive into trends, market potentials, and launch strategies to kickstart your entrepreneurial journey!

10 Pros and Cons of Venture Capital You Should Know
Explore the dynamics of venture capital. Dive into its benefits, potential pitfalls, and learn how it can shape startup trajectories. Make informed decisions with our guide.

10 Unique Clothing Business Ideas
Discover groundbreaking fashion business concepts for 2023! From sustainability to tech trends, master the art of differentiating your brand. Dive in now!
discover the menu
Get Ready For Funding
Pitch Deck Service
Pitch Training
Financial Modeling
Investor Outreach
Fundraising Consultant
We normally respond within 24 hours
View all our blog articles
How do business plans differ from pitch decks?
If you are a new entrepreneur you might get confused with some of the business terminology and have trouble understanding what type of document an investor or other stakeholders may require from you.
Differentiating between business plans and pitch decks in particular is a well known struggle. Whilst they may feel like similar documents that can help you raise capital, a pitch deck varies significantly from a business plan in the way it is created, structured, and used.
Luckily for you, this guide covers what each of the documents are, how they differ, how they are used and what tools businesses can use to create them.
In this guide:
What is a business plan?
What is a pitch deck, business plan vs. pitch deck: what do they have in common, business plan vs. pitch deck: what are the differences, what tools can you use to write a business plan, what tools can you use to create a pitch deck.
A business plan is a document providing detailed information about your business and its objectives for the years to come (usually 3-5 years).
To keep it short and simple, a business plan consists of two parts:
- A financial forecast which provides information about the expected growth and profitability of your business, your potential funding requirements, and cash flow projections.
- A written part which provides the context and details needed to assess the relevance of the forecast: company overview, description of products and services, market analysis, strategy, operations, etc.
Formal business plans are usually written: to secure financing, to get buy-in from stakeholders (board members, investors, business partners) on the plan of action for the coming years, to convince suppliers to do business with the company, or to communicate the company's vision to staff members.
Financial savvy businesses regularly track their actual financial performance against the forecast included in their business plan and re-assess their progress against what was planned, and update their plans as needed.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.

Strictly speaking, a pitch deck is just a generic term to design a document format: a pitch deck consists of slides and can refer to any type of presentation given to stakeholders.
For example, you can use pitch decks to:
- Pitch an investment opportunity to an investor: example pitch deck from Buffer
- Pitch a product to a prospective buyer: example sales pitch deck for Office 365
- Pitch an agency's capabilities: example agency pitch deck from ANL Creative
- Pitch new business ideas internally
Pitch decks are used everywhere, for the rest of this guide however, we will focus specifically on pitch decks designed to help secure new funding from investors.
Business plans and pitch deck share similarities between them, let's have a look at some of them.
Help secure funding for business
Both documents are used when trying to secure funding from investors for a business.
Typically, a pitch deck summarizes key information from the business plan and is used to pitch the highlights to investors before sending them your fully fledged business plan.
Visual elements
While a pitch deck may rely more on visuals, considering it is designed to be a presentation, both items use visual elements.
A business plan, just like a pitch deck, may contain graphs, charts, and pictures to illustrate information, especially in the market analysis section.
Financial information
Since both are intended to provide information to stakeholders regarding the business, both a pitch deck and a business plan will likely contain projected financial information.
Since a pitch deck is more of an introductory pitch, it is likely to not go into as much detail as a business plan does.
Strategy and decision-making
Because both introduce potential investors to the business, a pitch deck and a business plan discuss business strategy.
They typically reflect how a business plans to operate and generate income, showing investors why it makes for a worthwhile investment.
As a result, both are used as decision-making tools regarding investing in the business.
While they boast some similarities, pitch decks and business plans vary significantly in many ways. Some of these differences include:
Means of delivery
The way a pitch deck is presented is very different from a business plan - Being a visual presentation, it contains a series of slides with information about the business.
Pitch decks are not standalone items and are accompanied by a senior manager or partner providing commentary. The contents of the slides also typically do not go into much detail, simply highlighting key messages instead.
While the aim of the pitch deck is to draw investors to the business idea, the business plan provides more in-depth information to help them make a final decision about whether to invest or not.
Business plans carefully detail the business, its strategies, future goals and are written as formal documents that can be read and understood on their own.
Given the different modes of delivery, the format of both documents also differ. As mentioned previously, pitch decks use slides to convey information to the reader, and each slide is likely to hold limited information written in large(r) font.
Pitch decks are also likely to contain far more graphical elements such as charts, images, drawings and graphs. Business plans are often not as visually appealing but richer in substance and more formal.
The length of the two documents can vary but as a general rule, business plans tend to be longer than pitch decks.
A pitch deck will typically consist of about 10 to 15 slides (one slide usually takes 1-2 minutes to be presented), though further appendices may be added to answer specific investor questions.
A business plan usually spans between 20 and 30 pages and contains a lot more information, whilst also including appendices at the end of the document.
Amount of financial information
Both business plans and pitch decks contain financial information but the quantity and type usually differ.
Pitch decks usually have no more than one slide dedicated to financials and prefer to zoom in on key figures.
Business plans, however, include a detailed balance sheet, a profit and loss account, and a cash flow forecast.
Order of creation
In terms of presentation, a pitch deck is offered to investors first as an introduction to the business.
However, it can only be created once the business plan has already been produced, as the pitch deck summarizes the information presented in the plan.
Frequency of use
A pitch deck is typically created for one-off use. Once the financing round is complete and you’ve met with all the potential investors, you’re unlikely to need the same document again.
However, you will need to refer to your business plan down the line to ensure that the business is on track to achieve its forecasted financials and goals (and adjust as needed).
Need inspiration for your business plan?
The Business Plan Shop has dozens of business plan templates that you can use to get a clear idea of what a complete business plan looks like.

In this section, we will review three solutions for writing a professional business plan:
- Using Word and Excel
- Hiring a consultant to write your business plan
- Utilizing an online business plan software
Create your business plan using Word or Excel
Writing a business plan using Word or Excel has both pros and cons. On the one hand, using either of these two programs is cheap and easy to learn.
However, using Word means starting from scratch and formatting the document yourself once written - a process that can be quite tedious. There are also no templates or examples to guide you through each section.
Creating an accurate financial forecast with Excel is also impossible for a business owner without expertise in accounting and financial modeling. As a result, investors and lenders are unlikely to trust the accuracy of a forecast created on Excel.
Ultimately, it's up to you to decide which program is right for you and whether you have the expertise or resources needed to make Excel work.
Hire a consultant to write your business plan
Outsourcing a business plan to a consultant or accountant is another potential solution.
Consultants are used to writing business plans, and accountants are good at creating financial forecasts without errors.
This means that they will be able to create an effective business plan with accurate financial estimates without much effort.
However, accountants often lack the industry expertise to accurately forecast sales. And hiring consultants or accountants will be an expensive endeavour: budget at least £1.5k ($2.0k) for a complete business plan, more if you need to make changes after the initial version (which happens frequently after the initial meetings with investors).
For these reasons, outsourcing your business plan to a consultant or accountant should be considered carefully, weighing both the advantages and disadvantages of hiring outside help.
Ultimately, it may be the right decision for some businesses, while others may find it beneficial to write their own business plan using an online software.

Use an online business plan software for your business plan
Another alternative is to use online business plan software . There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can be inspired by already written business plan templates
- You can easily make your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You get a professional document, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank
- The software will enable you to easily track your actual financial performance against your forecast and update your forecast as time goes by
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try our software for free by signing up here .
A pitch deck is presented as a series of slides and so applications such as Microsoft Powerpoint, Google Slides and Prezi are ideal to create the presentation.
Pitch decks are notoriously time consuming and tedious to produce: designing and correctly alligning elements in order to make the slides "look good" is a real time sink - especially for entrepreneurs who aren't expert at PowerPoint.
Therefore, the polishing of pitch decks is often outsourced to graphic designers or freelancers that specialize in creating presentations in order to save time and get a document that looks professional.
We hope that this guide helped you get a better understanding of the differences between pitch decks vs. business plans. don't hesitate to contact our team if you have any questions left unanswered.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- Business plan steps: everything you need to know
- Business plan vs business case: what's the difference?
Know someone in need of a little guidance in making a business plan? Share this article and help them out!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here

Revenue vs Earnings: Understanding Financial Metrics

CoinLoan vs BlockFi: Crypto Lending Platforms

Nexo vs Voyager: Crypto Interest Account Showdown
Trending tags.
- profile picture
- music production tool
- image editing tool
- image editing platform
- eyewear industry
- Digital avatars

Pitch Deck vs Business Plan: Understanding the Differences for Startup Success
Have you ever wondered what sets successful startups apart from the rest? While many factors contribute to their success, one crucial distinction lies in the way they present their ideas and plans to potential investors. Pitch decks and business plans are two commonly used tools in the startup world, each serving a unique purpose. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of pitch decks and business plans, understanding their differences and exploring how they can lead to startup success.
What is a Pitch Deck?
A pitch deck is a concise and visually appealing presentation that outlines the key aspects of a startup’s business plan. Unlike a traditional business plan, which is typically a detailed document, a pitch deck focuses on capturing the attention and interest of potential investors in a short amount of time. It is designed to be presented in person or virtually, usually accompanied by a verbal pitch. Picture it as a teaser trailer for your startup, where you have just a few slides to captivate your audience and make them eager to learn more.
The Power of Visual Storytelling
One of the key elements that differentiate a pitch deck from a business plan is its emphasis on visual storytelling. While a business plan relies heavily on words and numbers, a pitch deck incorporates compelling visuals to communicate the startup’s vision, market opportunity, product or service, business model, and team. By using eye-catching images, charts, and graphs, a pitch deck can effectively convey complex ideas and data in a visually appealing and easily digestible format.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan, on the other hand, is a comprehensive document that provides an in-depth analysis of a startup’s business model, market research, financial projections, and operational strategies. It serves as a roadmap that outlines the company’s goals, target market, competitive landscape, marketing and sales strategies, and much more. A well-crafted business plan demonstrates a startup’s understanding of its industry and showcases its long-term vision and potential for growth.
The Art of Detailed Planning
Unlike a pitch deck, which focuses on capturing attention through visuals and concise messaging, a business plan delves into the nitty-gritty details. It requires thorough research and analysis, presenting a comprehensive overview of the startup’s market, competition, and financial projections. A business plan provides potential investors with a deeper understanding of the startup’s operations, strategies, and potential risks. It acts as a blueprint that guides the startup’s growth trajectory and helps align the team on a shared vision.
When to Use a Pitch Deck?
Now that we have a basic understanding of what a pitch deck and a business plan entail, let’s explore when it is most appropriate to use a pitch deck. Generally, a pitch deck is the preferred tool for initial investor engagements, such as introductory meetings, networking events, or pitching competitions. Its concise format allows for a quick overview of the startup’s key value proposition, market opportunity, and growth potential. A well-designed pitch deck can leave a lasting impression, leading to further discussions and potential investment opportunities.
The Art of Captivating Investors
When creating a pitch deck, it is essential to strike a balance between providing enough information to pique the interest of potential investors and not overwhelming them with too much detail. The key is to craft a compelling narrative that highlights the startup’s unique selling points, demonstrates market demand, and convinces investors of its growth potential. By focusing on telling a captivating story, a pitch deck can make a strong impact and generate investor excitement.
When to Use a Business Plan?
While a pitch deck is ideal for initial investor engagements, a business plan comes into play as discussions progress and potential investors express deeper interest. A business plan provides a more detailed and comprehensive understanding of the startup’s operations, strategies, and financial projections. It acts as a reference document that potential investors can review at their own pace. Additionally, a business plan is often required when seeking larger investments or securing bank loans.
The Blueprint for Long-Term Success
A business plan serves as a roadmap that guides the startup’s growth and operations. It helps align the team on the company’s goals, strategies, and milestones. A well-crafted business plan demonstrates a startup’s understanding of its industry, target market, and competitive landscape. It provides clarity on the startup’s revenue streams, cost structures, and financial projections. By developing a comprehensive business plan, startups establish a solid foundation for long-term success and growth.
Final Thoughts
In summary, both pitch decks and business plans play crucial roles in startup success. While a pitch deck acts as a visually appealing and concise tool for capturing attention and generating investor interest, a business plan dives deep into the details, outlining the startup’s operations, market strategies, and financial projections. Understanding the differences between these two tools and knowing when to use them can significantly impact a startup’s ability to attract investors and pave the way for long-term success. So, whether you’re preparing for a pitch competition or seeking funding for your startup, make sure you have a compelling pitch deck and a comprehensive business plan ready to showcase your vision and potential to the world.
References:
- Business plan on Wikipedia
- Pitch deck on Wikipedia
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Previous Post

TradeKing vs Scottrade vs E-Trade: A Comparison of Brokerages
Leveraging Chatbots for Customer Service: Enhancing Support and Efficiency
Related posts.


Pitch Deck vs. Business Plan – 3 Differences You Should Know About
by admin | Jul 27, 2017 | Pitch

Pitch deck vs. business plan
Before we start the big pitch deck vs. business plan comparison, we need to understand the basic information.
What is a pitch deck?
A pitch deck is a number of slides which summarizes your company. A pitch deck is not something you present, but rather something you send to potential clients or investors. Because of this, you should make sure that the pitch deck includes all the information required, since you can’t add information during a presentation.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a detailed description of your company. It explains what your company does, how things are going and what your future plans are. A business plan can be as long as anywhere between 10 and 100 pages.
A business plan usually has two functions:
- You send it to investors, to give them information about your company
- You can use it later as a reference guide for yourself, to see if you’re still on track
So now you know a little bit about the differences between a pitch deck and a business plan. Does this mean you should only create one of them?
No. For your company you should always have both of them. I’ll explain why.
Why should you create a pitch deck and a business plan?
It’s not always pitch deck vs. business plan. In fact, you should create them both.
Since a pitch deck and a business plan have a very different set up, you should also treat them differently. A pitch deck is used when a potential investor, partner, or client wants to know the basic information about your company. Since it takes a long time to read a business plan, this one is usually sent over only when an investor is seriously contemplating investing in your company.
Because of this a pitch deck is usually the way to go. The ratio ‘sending a pitch deck’ vs. ‘sending a business plan’ will probably be around 10:1. As a rule of thumb, you only should send a business plan when somebody explicitly asks for it.
What is the difference between a pitch deck and a business plan?
When do you send a pitch deck or a business plan.
Pitch deck: As descried, a pitch deck can be sent early in the process. This can be done through cold ‘acquisition’, but preferably from an introduction via a mutual connection.
business plan: As described, a business plan doesn’t get sent too often. You need to have a business plan for yourself as a reference guide, but also for cases when an investor asks for it.
What is more important: a pitch deck or a business plan?
Since you’ll be sending a pitch deck way more often than a business plan, you might say that a pitch deck is more important. However, a pitch deck is usually created after creating your business plan. The business plan is the foundation for your pitch deck, and therefore is equally important.
We can help you with your pitch deck
If you don’t have experience with creating a pitch deck it can be a tough ride to create one. You want it to have a slick design, but even more important, it should communicate the right things. We can help you with this. Drop your information at https://pitchskills.com/pitch-deck/ and we’ll create one for you!
Pitch Deck vs Business Plan
A relatively common question we get revolves around business plans. A good amount of our customers asks us if we can write a business plan for them, and we always respectfully decline.
I believe a startup should NOT write a business plan. It's a terrible waste of time for the founders in the early stages of the company when they should be focusing on validating their business premises.
We are going to look into why the business plan is an outdated way to approach starting a business, and how new frameworks like The Lean Startup are a much more effective way to build companies.
Definition of a business plan
"A document setting out a business's future objectives and strategies for achieving them."
If you look at most business plan templates available online, you are often looking at a 20-40 page document that touches on The Opportunity, Problem, Market Size, Execution, Sales Plan, Company, Team, Financial Plan...
Well, guess what, a pitch deck touches on every single one of those topics; the difference between a pitch deck and a business plan is that a pitch deck can take a few hours to write (less than an hour if you use that a really awesome tool we've mentioned before). In contrast, a business plan will take you days and days of writing, proofreading...
An angel investor or venture capitalist evaluating a startup for a seed round is not going to sit down and read a 40-page document. They want to know that you are on the right track. They want to confirm that you have a plan to grow the business, but that doesn't need to be a 20-page document.
Any starting business is built on assumptions. On the assumption that this product or service is going to appeal to these users. The assumption that these marketing tactics are going to be effective in converting them. Yet, all of these assumptions might be wrong, and it's the CEO's job to test these assumptions fast, and if the premises incorrect, pivot the company in the right direction as fast as possible.
In the end, it's a race against time. How many iterations of your product, audience, and marketing/sales strategy can you go through before you run out of time? For a startup, time = Funding/Money.
If you had to spend two weeks putting these assumptions on paper, proofreading them, and styling that business plan, you literally wasted two weeks of precious time. You could have run two audience experiments at that time and find out right away, instead of just 'planning.'
That's my problem with business plans, in a nutshell. They take too long to write. You should spend that time validating instead of planning.
This mentality comes from the framework most startups these days abide by, laid out on The Lean Startup by Eric Ries . It's a fantastic book any entrepreneur should read, and we'll be giving away a few- so stay tuned on how to get them.
The methodology that the book proposes is the Build - Measure - Learn cycle.
- First, you BUILD an iteration of your product. That may be an MVP, a website, a version of your app or service.
- Then, you MEASURE . You throw this iteration to the world and measure its success. That may be conversion rate, sales, click-through rate. You need to understand if your premise is correct and if it has a measurable impact on your company performance.
- Finally, you LEARN . You study the results, understand if they were positive or negative, and create a new premise based on them. Once you are done with this analysis, you BUILD again.
Every key aspect of our business was built this way.

We first launched a simple landing page to figure out if people would be interested in this pitch deck, AI design product. We measured conversion rate, compared it to our expectations, and then built our next iteration, which became our first beta.
Every single marketing campaign we do is a Lean Startup product. We come up with a new campaign, "BUILD" it as fast as we can, MEASURE it, LEARN, and then improve on it.
Our last relevant iteration was our pitch deck consulting service. We had a theory that many startups who were using our product to build pitch decks would benefit from a real human assisting them. We didn't know.
Instead of running market studies or business plans, we BUILT a quick landing page, threw some traffic in there, and MEASURED results.
When I say build a landing page, this was a few-hour project. The first few leads were landing directly on my cell phone, and I used to handle both the sales, quoting, writing, and design stuff. This is as lean as you can get.
Only when we LEARNED that this business made sense, that the economics worked, and that we could scale it, we went back to BUILDING a new iteration, with a much more elegant page, sales and nurturing process.
We had the answer to this question in less time than it would have taken us to write a business plan, and that's the moral of the story.
We've also built countless lean startup experiments that have failed, by the way. But that's the point, we MEASURE fast, LEARN that we were wrong, and carry on.
Pitch Deck vs. Business Plan
A pitch deck is The Lean Startup version of a Business Plan.
To write a compelling pitch deck, you also need to have figured out your Total Addressable Market and your Go to Market Strategy. The difference is the pitch deck fulfills the purpose of pitching this to an investor without requiring the extended version.
More importantly, the reality for any company is that they are going to be wrong about their assumptions in the early stages. Their pricing might change, or their 4-page sales plan might not work at all, so they need to be able to change course as fast as possible.
On your pitch deck, you should be passionate about your expansion strategy; you should believe in it, and show your metrics to prove whether it's working or not. Still, everybody in the room knows your success will depend on your ability to come up with new strategies and deploy them faster than your competition.
Another pair of fantastic tools that can help you replace a Business Plan is the Business Model Canvas and the Lean Validation Board. Both of them can help you figure out the answers to these questions.
In summary...
Make sure you can answer these key questions about your business.
- How big can it be? Is it a $1MM, a $10MM or a $100MM company?
- How fast can you get there?
- If you are B2C or business to consumer- Who is your perfect customer? How old are they? Where do they live? What apps do they have on their phone? What do they do for fun?
- If you're a B2B or business to business - Who is your perfect client? How big is the company?
- Who in the company do you need to get in touch with? How makes the call to buy your product? How much money do you make per customer, and therefore, how much can you afford to spend to sign them up?
Most of the companies we work with are missing one of those questions, which makes it really hard to define the type of investor they need to look for.
If YOU can answer them, then summarizing them into a slide is a no-brainer, especially with a platform like Slidebean that takes care of the design for you. Don't forget to subscribe to our channel !
Popular Articles
Financial Modeling Explained: What is Driver-Based Planning?

How Startup Equity Works: Pies vs. Bricks and the Value of Shares

How do Investors Make Money from Startups?

Startup vs Small Business: Main differences


Let’s move your company to the next stage 🚀
Ai pitch deck software, pitch deck services.
Financial Model Consulting for Startups 🚀

Raise money with our pitch deck writing and design service 🚀
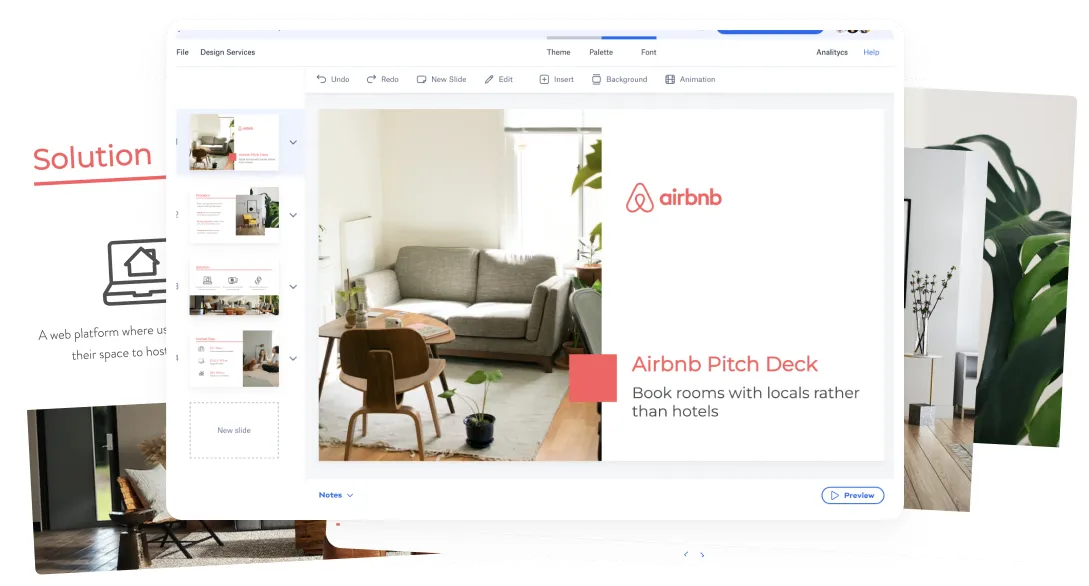
The all-in-one pitch deck software 🚀

A pitch deck is the standard document used by startups to present their case to investors; it’s a brief deck of about 10 to 20 slides. See examples here.

Learn how to create a compelling slide deck for your startup. Explore how to use slide decks as aids for your presentation, and the most common uses for them.

This is a functional model you can use to create your own formulas and project your potential business growth. Instructions on how to use it are on the front page.
Book a call with our sales team
In a hurry? Give us a call at
Weekly Must-Reads View All
Microfinance vs microcredit: financial services.
The Difference Between Microfinance and Microcredit: Unlocking Financial
Revenue vs EBITDA: Financial Performance Metrics
Understanding Revenue vs EBITDA: Which Financial Performance Metric Matters
State Capitalism vs Socialism: Economic Systems Explained
Understanding State Capitalism vs Socialism: Which Economic System Is the Better
LLC Wyoming vs Nevada: Choosing the Right Business Structure
Greetings, entrepreneurs!
Trending Now View All

- Strat Insights
Pitch Deck vs Business Plan: Understanding the Differences for Startup Success
Pitch deck vs business plan: unlocking the secrets to startup success.
Starting a new business can be an exhilarating and challenging endeavor. As an aspiring entrepreneur, you may have heard the terms “pitch deck” and “business plan” being thrown around. But what exactly do these terms mean, and how do they differ? In this article, we will delve into the world of startup essentials and explore the differences between a pitch deck and a business plan. By understanding these distinctions, you can equip yourself with the necessary tools to navigate the competitive landscape and increase your chances of startup success.
What is a Pitch Deck?
Imagine you are an architect designing a grand structure. To showcase your vision, you create a visually captivating presentation filled with stunning images, brief descriptions of each element, and the overall concept that brings it all together. This presentation acts as a window into your architectural masterpiece, capturing the attention of potential investors or clients. Similarly, a pitch deck for startups serves as a visual representation of your business idea, designed to engage and captivate potential investors or stakeholders.
A pitch deck typically consists of a slide deck presentation that varies in length but usually contains around 10-20 slides. These slides may include an introduction to your team, a problem statement, market analysis, unique value proposition, revenue model, marketing strategy, and financial projections. The purpose of a pitch deck is to convey your startup’s story concisely and persuasively, compelling investors to take an interest and potentially fund your venture.
What is a Business Plan?
Now, let’s shift our focus to the traditional aspect of startup planning – the business plan. Think of a business plan as a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the journey of your startup from its inception to its envisioned future. It encompasses every aspect of your business, providing a detailed understanding of your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them.
A business plan is typically a detailed document that covers various sections such as an executive summary, company description, market analysis, organizational structure, product/service offerings, marketing and sales strategies, financial projections, and funding requirements. Instead of relying solely on visual aids, a business plan relies on in-depth descriptions, analysis, and numerical data to convey the potential of your startup to investors, lenders, or partners.
The Differences: Pitch Deck vs Business Plan
Now that we have a basic understanding of what pitch decks and business plans entail, let’s explore the key differences between the two:
The primary purpose of a pitch deck is to deliver a captivating and concise pitch to potential investors or stakeholders. It aims to generate interest and secure funding for your startup. On the other hand, a business plan serves as a comprehensive document that provides a detailed overview of your business, including strategies, market analysis, financial projections, and more. It acts as a roadmap for guiding your startup’s operations, growth, and sustainability.
2. Length and Format
Pitch decks are typically shorter in length, consisting of a slide deck with concise and impactful content. The deck should be visually appealing, utilizing images, graphs, and key points to convey information effectively. In contrast, business plans are longer, detailed documents that can range from 20 to 50 pages or more, depending on the complexity of your business. They follow a standard format and include sections that delve deeper into each aspect of your startup.
3. Visual Appeal
Pitch decks heavily rely on visual elements to engage and captivate the audience. You may use impactful images, infographics, and charts to convey your message effectively. In contrast, business plans focus more on textual content, providing detailed descriptions, analyses, and numerical data without the same emphasis on visual appeal.
4. Delivery and Interactivity
Pitch decks are often presented in person or virtually, allowing for live interaction and engagement with potential investors. This provides an opportunity to showcase your passion, knowledge, and ability to handle questions or objections effectively. Business plans, on the other hand, are typically shared as a document that is reviewed independently by investors or lenders. While there may be subsequent meetings to discuss the plan, the initial delivery does not involve direct interactive engagement.
5. Flexibility and Adaptability
Pitch decks offer flexibility in terms of format, allowing you to tailor your presentation to fit the preferences and expectations of different investors or stakeholders. You can adapt your pitch deck based on the industry, audience, or specific requirements of potential investors. Business plans, however, follow a more standardized format and may require more effort to adapt or customize for different audiences.
Which Should You Choose: Pitch Deck or Business Plan?
Now that we understand the differences between pitch decks and business plans, you may be wondering which one is more suitable for your startup. The truth is, both have their merits and can be valuable tools in different situations. The choice between a pitch deck and a business plan depends on several factors, including your target audience, the stage of your startup, and the purpose of your presentation.
If you are in the early stages of your startup and seeking funding from angel investors, venture capitalists, or participating in pitch competitions, a compelling pitch deck can be your secret weapon. A well-crafted pitch deck has the power to generate excitement, secure meetings, and open doors to potential investors who can provide the financial backing your startup needs.
On the other hand, if you are approaching banks, financial institutions, or more traditional investors, a comprehensive business plan may be more appropriate. These stakeholders often require in-depth analysis, detailed financial projections, and a comprehensive understanding of the market and industry landscape before committing to an investment. A business plan can demonstrate your professionalism, strategic thinking, and ability to mitigate risks effectively.
Ultimately, the key lies in recognizing the purpose and audience of your presentation. Consider the expectations and preferences of your potential investors or stakeholders and choose the format that best aligns with their needs. It is also worth noting that a pitch deck and a business plan are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they can complement each other, with the pitch deck acting as a teaser to generate interest and the business plan serving as the detailed document that follows.
In Conclusion
In the world of startups, the journey to success requires careful planning, effective communication, and adaptability. Understanding the differences between a pitch deck and a business plan can provide you with a strategic advantage. Whether you choose to craft a visually captivating pitch deck or a comprehensive business plan, it is crucial to convey your startup’s potential, uniqueness, and growth opportunities convincingly. Remember, a successful startup requires a solid foundation built upon a compelling story, a well-researched market, and a clear plan for execution. So, equip yourself with the right tools, seek guidance from industry experts, and embark on your entrepreneurial journey with confidence and determination. With the right blend of innovation, preparation, and persistence, you can set your startup on the path to success.
References:
- Pitch deck – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pitch_deck
- Business plan – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business_plan
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Leading with Integrity and Ethics
Leadership integrity is a trait that sets exemplary leaders apart from the rest

Marketing vs. Non-Marketing Activities
Understanding the Difference Between Marketing and Non-Marketing Activities In
You May Also Like

Pvt Ltd vs. LLP: Business Entity Comparison

Business Services: Business Auxiliary vs. Business Support
The Difference between Business Auxiliary Services and Business Support

Consumer-Centric Innovation: Insights for Product Design
In today’s rapidly evolving marketplace, where competition is fierce and

Creating the perfect pitch deck and business plan: Examples and best practices [2022]
- January 7, 2022
I know you’ve probably been told that a good pitch deck and business plan are essential in the world of startups. It’s true — they are — but there is a LOT of conflicting advice out there on how to create them. (Hint: There isn’t just one right way.) I want to share some ideas based on solid research and real-world experience so you can create something that works for you.
What is a pitch deck?
What is its purpose, do you need a pitch deck and a business plan, who should create the pitch deck, how do you create a pitch deck, what is a financial model, what is a financial forecast, how accurate does a startup financial model need to be, what to include in an early-stage pitch deck, what should i avoid putting into my pitch deck, slide #0 – title, slide #1 – executive summary, slide #2 – trends, slide #3 – problem, slide #4 – solution, slide #5 – business model, slide #6 – market, slide #7 – competition, slide #8 – go to market, slide #9 – traction, slide #10 – team, slide #11 – investment proposal (the ask), keep it simple, stick to a consistent layout, make it easy to read, use a pitch deck template, beautiful.ai, key takeaways.
In this article, I’ll discuss what a pitch deck is, explain its purpose and its importance in the outreach process, give you tips and practices to create your perfect pitch deck, and what to include in it. We’ll also look at an example of a pitch deck template, using slides from startups that have raised hundreds of millions from VCs. We’ll also explore why you must build a financial model alongside your pitch deck.
Before we get started, remember that pitching on stage and building your pitch deck are two very different things. Pitching is a form of art. Anyone can present a business plan or startup idea to another person, but only a few pitches are memorable and truly capture the interest of investors.
Practice makes perfect, and the better you get at pitching, the more likely you are to succeed. So sign up to pitch competitions, put yourself out there, and get feedback. The more you pitch, the better you will become at it. It’s better to make mistakes when it doesn’t matter than pitch unprepared to critical investors and risk disaster.
Now let’s dive into what it takes to build a great pitch deck!
Pitch decks are an essential document for every founder to master, but there is a lot of conflicting information out there, and no one-size-fits-all template.
To help you get started, we’ve pulled together pitch deck examples and best practices for new founders and early-stage startups.
Using this information to guide you, you’ll be able to create a pitch that will wow investors and get you the funding that your business needs.
A pitch deck is a condensed business plan that communicates your business idea to investors or partners. It should be clear, concise, and well-organised so that it promotes a conversation, not just information that needs to be digested. The pitch deck is used as an elevator pitch during your outreach process and should highlight the key aspects of your startup in a way that gets investors excited about working with you.
The pitch deck itself isn’t going to fund or run your startup — it’s just one piece of the puzzle — but it’s an important one. As Guy Kawasaki, Chief Evangelist at Canva, former Chief Evangelist at Apple, and author of The Art of the Start puts it .
The purpose of a pitch is to stimulate interest, not to close a deal.
While the pitch deck is an information-packed overview of your startup, it should be more than just numbers and figures. A winning pitch deck also captures the imagination by telling a story and getting the audience emotionally involved. People don’t buy products, they buy stories — pitch decks help people to see your startup as a compelling narrative instead of just an idea on paper.
A pitch deck helps you generate interest from investors so that they will fund or work with your company in some way. It is a way to quickly pitch your business idea and get feedback, without having to go through the entire business plan. The pitch deck should be used as a tool to start a conversation with potential investors so that you can get their feedback and determine if they are interested in what you’re doing.
For an early-stage startup, the pitch deck and financial model are the business plan. There are too many uncertainties to waste time writing a 100-page business plan. Founders should use tools like the Lean Canvas to help them think through the different aspects of their business, but a pitch deck and financial model are essential when trying to raise money and get investment.
The pitch deck should be created by the founder or co-founder of the company. They are the ones who know the most about their business and can best pitch it to investors. Remember, the pitch deck isn’t what wins you the investment, but it will start the conversation and get people interested in what you’re doing.
There is no one-size-fits-all answer for this question, as the pitch deck needs to be tailored to your specific startup and its investors. However, there are some best practices that you can use to make sure your pitch deck is as compelling as possible.
Financial Model
The pitch deck should always include a financial model, typically as a supporting document, that shows financial projections for the next three to five years. This will help investors understand how you will manage the financial risks associated with your startup.
A financial model is a document that shows how your business will make money and what kind of return investors can expect on their investment. It includes projected revenue, expenses, and profits over a specific period of time.
Investors will expect to see a three to five-year financial forecast, broken down by year and month.
The financial model should also include a section on the startup’s burn rate – how much money the company is spending each month and how long it can continue to do so before running out of funds.
A financial forecast is a projection of future income, expenses, and profits. It typically covers a period of three to five years and breaks down revenue, expenses, and net cash flow by month.
The financial model doesn’t need to be complex, but it should show a realistic understanding of the numbers behind your startup.
It is important to remember that venture capitalists and angel investors do not expect your financial forecasts to be 100% accurate – they simply want to see that you have put thought into your business, that your operational plans are accounted for, and that you understand the basics of financial forecasting.
Pitch Deck Structure
As a founder, you’ll quickly learn that you’ll need more than one pitch deck. Different pitch decks are used for different purposes, and you may end up using a pitch deck that is specific to your target investor, the stage of investment, or the format in which you’ll be pitching.
This means that there is no magic formula for your pitch deck structure. However, there are a few essential slides that should be in every business pitch deck.
- Title or cover slide
- Market size and opportunity
These slides will give the pitch deck a good structure and focus on the key elements that you want to talk about. There may be more slides depending on your company, but those are the main ones that should always appear somewhere in every pitch deck.
Early-stage startup pitch decks are used to spark interest in your idea and the founding team. Venture capital firms and angel investors will be comfortable with greater uncertainty and higher risk in this pitch deck, so there is more leeway to experiment with different ideas and concepts. This doesn’t mean that you should just throw in everything without a thought though!
At this early stage, there will be multiple unknowns that you are setting out to solve, including exactly how you’ll build your solution to the problem, how you’ll find your scaleable route to market, and maybe even how you’ll convert users to paying customers.
It’s normal to not have all the answers to these questions, and that’s OK! It doesn’t mean that you should pitch an idea if you don’t know how it will work yet. All of this is just a reality check for potential investors — they need to see that you have a realistic idea of what you need to do and a plan for how you might do it.
It’s a common mistake for first-time founders to try to put too much information into their pitch decks. This can include everything from detailed financial models to a full history of the company’s founding story. While it’s important to have all this information ready, it’s best to save it for when you’re actually speaking with investors.
Your pitch deck should be focused on your idea and the current state of your company. It should be set up in a way that clearly lays out who you are, what problem you’re solving, and how you plan to solve it. You want investors to see the actual value in investing in your startup so avoid including anything that’s not absolutely necessary for them to understand this concept.
– Do not include unnecessary information or graphics
– Keep your pitch deck to a maximum of 20 slides
– Stick to clear and concise language
– Make sure all the data is accurate and up to date
Be cautious about adding in anything that doesn’t support your pitch deck theme or the key points you want to make. If it isn’t relevant, remove it! You don’t have time for extra fluff when pitching investors; be direct and focus on what matters most.
Early-Stage Pitch Deck Example
The following pitch deck template is a good example of how you can tell a story that builds investor confidence in your startup idea. Using this format will set a great first impression and can help you with raising capital.
This is the most important slide in the whole deck, you need to grab the attention of the investor with a title slide that convinces them to keep reading. Your title slide must:
- Showcase your logo and brand name.
- In one phrase, state your value proposition.
- Engage the reader by promising them an interesting pitch.
It’s important to make your startup feel credible and trustworthy. Just as people will judge a book by the cover, investors will judge your pitch deck in less than five seconds, so make sure you have a strong first impression!
A common mistake that founders make with the title slide is not making the most of the opportunity. Taking inspiration from other industries, a prize-winning sticker on a book cover or a wine bottle has a tremendous impact on sales. What can you do to make your pitch deck stand out?

After catching your audience’s attention, you should include a company summary on slide one. Investors are unlikely to know anything about you or your company, so this is where you need to tell them what you do, where you’re going, and why they should care.
In just a few sentences, you should be able to concisely state the following:
- What your company does
- The stage you’re at
- The traction you’ve made so far
- Where you’re heading
If the title slide is about grabbing attention, the executive summary is about keeping it.
You need to get investors hooked and hungry for more information.

With the investor’s attention now captured, it’s time to give them some context. What industry are you in? What trends are happening in that industry?
Trends are the market conditions that you have zero influence over. But, by showing how you understand them and how they impact your startup, you can demonstrate that not only is your startup inevitable, but that the risk of failure is also reduced.
Your goal with the trends slide is to show that your startup idea isn’t some crazy gamble, it’s obvious and inevitable, and that the market is about to change in a big way.
In the context of startup ideas, the important things to consider about trends are whether they are weak or strong, societal and cultural, or technological.
Weak Trends: These are usually easy to spot and include things like the aging population, increasing internet penetration rates, or a growing demand for a new product or service.
Strong Trends: These are hard to argue against. They will be big and happening quickly. They could be something like the rise of mobile payments, a technology reaching critical mass, or a new way of thinking about an old problem.
Technological Trends: These trends focus on the development of new technologies. For instance, the rise of drones, Web3, and artificial intelligence technologies are all technological trends that would be relevant to an investor pitch deck when combined with a startup idea.
Societal and Cultural Trends: These trends are about the way people are living their lives, and integrating new technologies into them. A good example of this is the trend towards health and wellness. This could be anything from the increasing popularity of mindfulness to people taking more interest in their food.
It’s important to consider societal trends alongside advances in technology, just because a technology is possible, doesn’t mean that people will want to use it (remember Google Glass?).
Building into emerging trends can lead to you raising millions without even having a pitch deck , like Hopin, or still whilst the world is in lockdown and your app is still in beta – like Clubhouse.
Now that you’ve got the pitch deck rolling, it’s time to talk about your startup idea. What problem are you solving? What is happening right now? What are people not happy with?
When it comes to the problem slide, be specific. Don’t just say that there is a problem. Tell them what it is and make your audience feel the pain; they should be able to recall having had it themselves or easily empathise with those that do.
As a founder, you need to prove that you have a deep awareness and understanding of the problem you’re solving. You need to demonstrate that you can stand in the shoes of your customers and see the problem as they do.
Ideally, you should be able to summarise all of this into a problem statement. This is a simple one or two-sentence explanation that describes the problem, identifies the pain points, and explains why it needs solving.
Providing data to back up your problem statement is also important, but it doesn’t have to be complicated. You’re not trying to show the size of the market, just the severity of the problem.
Having built up an understanding of the problem, you now need to explain how you plan on solving it. What is your solution? How will your startup solve this problem? What makes your product or service different?
Your solution slide should be clear, concise, and easy to understand. You should have a brief paragraph explaining what your startup does, followed by supporting information in the form of screenshots, images, or diagrams.
Remember, during live pitching or conversations, you may be able to talk about your solution in more detail – maybe even showcase a live demo – but in your pitch deck, you need to keep it simple.
If you’re having trouble boiling down your complex solution then consider how you would sell it to a potential customer. If you can pitch it to them in a way that they understand and see the value, then your pitch deck will be able to do the same.
With the problem and solution explained, it’s time to move on to your business model. This is a critical slide for any pitch deck as it demonstrates how you plan to make money from your startup idea. It’s showing your investors that you understand the business side of things and that you have a plan for growth.
This slide can be a little tricky to get right, as you don’t want to overload your audience with too much information (especially at idea stage, when you don’t have a fully formed business model). However, you need to convey that the unit economics make sense and that there is a path to profitability.
There are lots of different ways to structure this slide, but the most common model breaks it down into a one-paragraph pitch of your business model, followed by one or two diagrams showing the relationships between your costs and revenue. By using simple visuals, you can convey complex ideas far more effectively than words alone.
Unfortunately, pitch decks don’t have the space to explore every aspect of your business model. It’s a good idea to create a separate document for this, which you can then share with interested investors or partners.
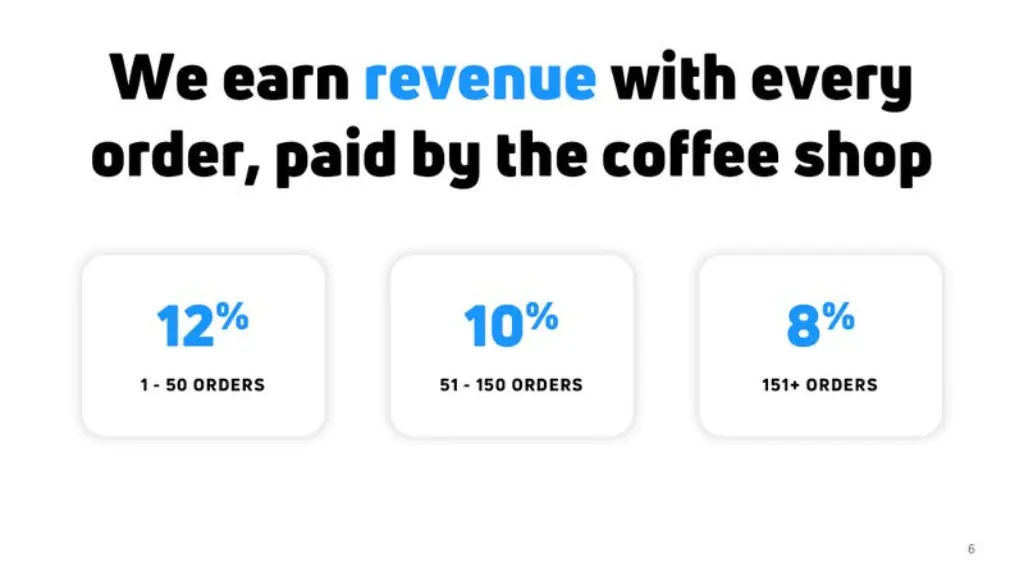
Now it’s time to move on to the all-important question of market size. Market sizing for early-stage startups can be a contentious issue.
Many entrepreneurs think that they need to show huge total addressable markets (TAM), and pitch themselves as the next billion-dollar startup. However, most sophisticated investors how that for most early-stage startups this is not appropriate.
Pitching a large TAM isn’t going to impress investors, they’ve seen it all before, but pitching yourself as the best company in your segment will demonstrate that you have a great understanding of your industry and the opportunity at hand.
It’s most important to be able to show that there is a market for your product or service, that it’s growing, and that there is room for you to compete. You don’t need to pitch yourself as a billion-dollar company, just pitch that you have a good understanding of the market segment, that people are spending money solving this type of problem, and that you’re going to be one of the best companies in your space.
For example, if your idea is to launch the next big analytics platform, don’t pitch a market size that includes every business in the world. Instead, focus on a specific industry or sector and show how behaviours in that industry are changing, paving the way for your product or service.
Again, you don’t need to go into too much detail in your pitch deck. A one-paragraph pitch of your market size is usually enough, followed by a simple diagram showing the trends that are opening up opportunities for your startup.
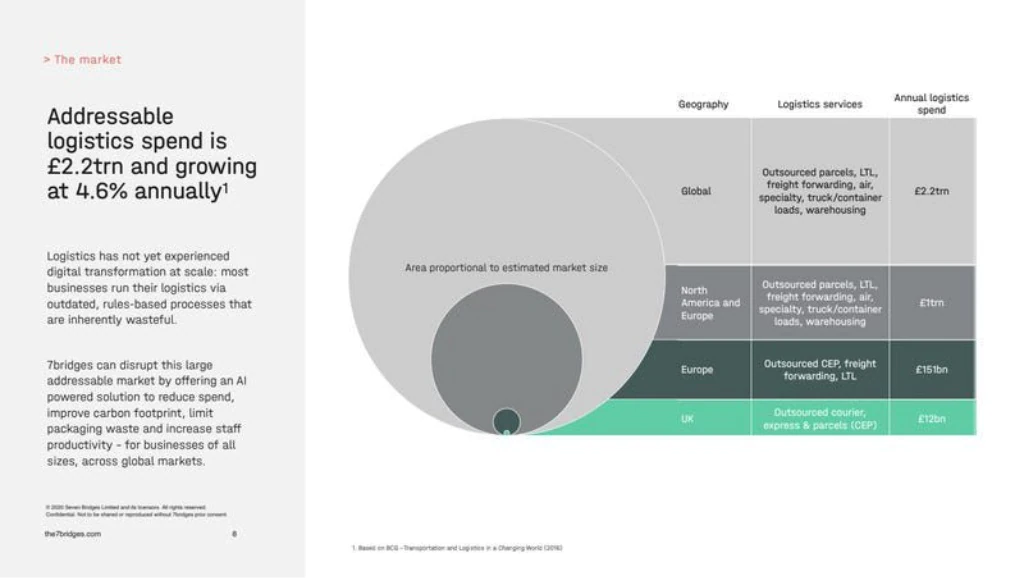
This is another key slide for any pitch deck, as it demonstrates that you have done your research and that you understand the competitive landscape.
Start by defining the market segment you are targeting, and then show the key points of differentiation when compared to your primary competitors.
Describe how they fit into the customer’s perspective of the market, show where their strengths and weaknesses lie, and how you plan to compete with them.
This isn’t the place for a full analysis of your competitors, but you should be able to pitch yourself as the best company in your space, with a clear understanding of how you’re going to win.
There are two common ways to visualise your competitor analysis, the magic quadrant (or 2×2 matrix) and a comparison table.
The magic quadrant is a way of plotting your competitors on two axes, based on two factors that you’ll pluck from thin air. These visualisations are rarely credible unless you have a lot of experience in the market you are analysing, or they’ve been produced by large consultancies like Deloitte or Gartner.
On the other hand, comparison tables can be very effective as they’re easy to digest, position you alongside recognisable brands, and allow you to highlight the key differences between your company and your competitors. By comparing factors that are demonstrably important to customers, you’ll come across as more credible and able to back up your pitch with cold, hard facts.
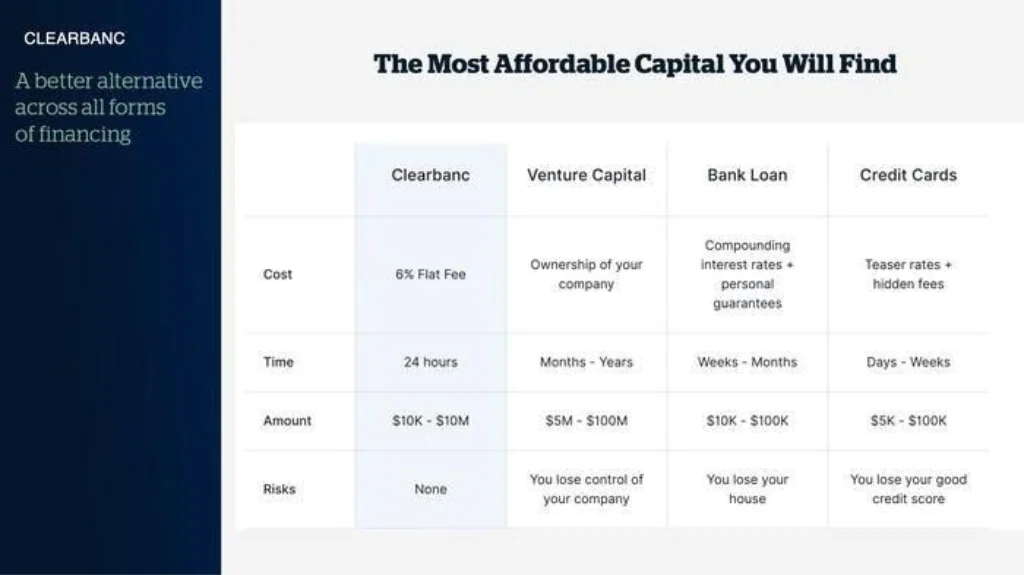
Now it’s time to talk about marketing and sales strategy, or how you’re going to get your product or service in front of customers. This is where you’ll pitch your go-to-market strategy. Your go-to-market slide should include the following elements:
- The channels you will use to reach your target audience
- The actions you will take to put your product in front of potential customers
- The milestones you will hit as you progress through your go-to-market plan
- The resources you will require to reach your target successfully
Start by describing your target market and how you plan to reach them. This might include explaining your distribution channels, sales strategy, or marketing approach. You can also use this slide to talk about any partnerships you have in place, or how you plan to leverage them.
Next, explain the actions you will take to reach your target audience, and how you plan to measure success. These actions should fit within each of the channels that you’ve already identified. For example, if you’re using digital marketing, your actions might be things like website development, SEO, or social media campaigns.
Lastly, list the key milestones you will hit as you progress through your go-to-market plan, and identify the resources you will require to achieve them. You can include your team, budget for marketing activities, or specific assets like signage.

As a startup, traction is key. Investors want to see that you’re making progress and that your product is resonating with customers. This slide is often one of the trickiest for startups at idea-stage, as it can be difficult to show commercial progress and it will be too early for product-market fit.
There are a few different ways to pitch traction, and you need to choose the one that works best with your company and the stage you’re at. Some options include user base, revenue growth, or market validation.
If you’re focusing on your user base, you’ll want to pitch a clear and compelling story about your customer base. If you have a small data set, it’s worth showcasing your first 100 customers as this makes the numbers seem more real.
If you have a large customer base, pitch your exponential growth in terms of percentage or absolute figures. For example, pitch how many customers you signed in the past quarter or year.
Revenue Growth
If you’re focusing on revenue growth, pitch your current (or projected) sales figures. You can also pitch the average ticket size or value of your deals. Alternatively, pitch your revenue growth (in terms of percentage or absolute figures) over the past year.
Market Validation
If your product is still at idea-stage and still has a long way to go before it’s ready for market, pitch your progress in terms of real-world validation. For example, pitch the number of people who have registered to use your product or service, or pitch the number of companies that have expressed interest during interviews.
Most importantly, be honest about your progress. If they are interested, investors will dig into your traction claims and you’ll need to back them up with data – if it turns out that you’ve lied or embellished the facts, you’ll not only lose trust and credibility, you’ll probably lose the investment too.

Having set the scene in which your startup operates, it’s time to introduce the management team behind your startup. Investors will be keen to learn about who is leading your company and how they will transform your idea into a profitable business.
The focus here must be you and your co-founders. People invest in people, so you’ll need to show how you have the vision, experience, and motivation required to deliver on your pitch.
Keep your team slide short and sweet. You’ll want to include the founding team, highlighting their relevant experience in the industry or field that you’re operating within.
Pictures help to make your presentation more personal, so make sure you have a good quality headshot of each team member, consistently formatted so that everyone appears the same size and in focus.
The team slide should only include the founding team, though it is acceptable to include key team members, as well as notable advisors or investors if beneficial. If you do this, ensure that there is a clear visual separation between the two groups.

This is the big one. The pitch deck wouldn’t be complete without a clear proposal of what you’re asking for from your investors. This slide should clearly state the amount of money you’re seeking, as well as what you plan to do with it.
It’s important to remember that investors are looking for a return on their investment (ROI), so your proposal must be realistic and demonstrate how you will use the funds raised to reach key growth milestones.
To convince investors, your “Ask slide” will need to answer these three questions:
- How much are you seeking to raise?
- What will you do with the money?
- What do you intend to accomplish with the funds?
Always remember to pitch the ask in terms of how it benefits the investor – not just you. For example, if you’re seeking a £100,000 investment, explain how that money will help you reach a specific milestone that will create value for your investors.
Be specific about how much you need to raise, and where you plan to deploy the money. This will show that you’ve done your homework and understand how you will grow your business.
A simple pie chart with the breakdown of how you plan to use funds can go a long way towards demonstrating to investors that you’re serious about using their money wisely. For example, if 25 percent goes towards marketing spend, 30 percent for technology development, and 45 percent for new hires, that’s a good indication you have your priorities straight.
It’s unlikely that you will be profitable before the next round of funding, but it is usually worth highlighting the key numbers from your financial projections to give investors an idea of the scale and trajectory of your business.
Perhaps the most important factor in your investment ask is demonstrating that you understand how much capital you require to hit key growth milestones without requiring further funding rounds for at least 12-18 months. This is something that almost every investor will expect you to have a solid plan for.

Pitch Deck Design
Whether you’re sharing your deck by email or presenting on stage, the design of your pitch deck matters. However, you can’t afford to hire a professional pitch deck designer to help. So, what do you do?
KEEP. IT. SIMPLE.
Your pitch deck is not the place to show off your design skills – or highlight any lack of expertise in this department! The only goal of your pitch deck is to communicate information clearly and concisely so that investors understand what you’re pitching and can get excited about it.
Keep your presentation simple, use bold typography, highlight key information, and stick to a maximum of two or three colors. Resist the urge to use lots of graphics and animations, as these can be distracting and take up valuable space on your slides.
How to design a better pitch deck
There are a lot of things to consider when designing your pitch deck presentation. Below are some tips on how to make your pitch more effective:
The average investor has a short attention span, so keep your deck concise and easy to follow. Use clear language, avoid complex graphs and charts, and stick to a maximum of 15 slides.
Use the same fonts, colors, and layouts throughout your pitch deck to create a cohesive look.
Slides that are crowded with text and images will be difficult for your audience to read and comprehend.
A pitch deck template is a great way to ensure that your pitch deck looks professional and follows the proper design guidelines.
Pitch deck design tools
Today, there is a huge selection of online design tools and no-code builders to help you build your perfect deck. Below are just a few of the design platforms that can help you craft your pitch.
An easy-to-use platform that allows startups to build a beautiful slide deck without any special design skills. Start from scratch or create your slides using predefined pitch deck templates.
https://slidebean.com/
Offers a wide range of design tools and templates for creating professional pitch decks. The free version includes limited features, while the paid plans start at $12/month.
This pitch deck design app is great for startups and entrepreneurs who need to create a pitch deck quickly. The basic plan starts at $12/month (billed annually) but there is a 14-day free trial.
https://www.beautiful.ai/
The tools provided by Pitch allow you to quickly produce a high-quality pitch. Even if you’re not a designer, you can create a strong pitch deck that looks great. The basic plan is free, but you’ll need to upgrade to the paid plans for more features.
https://pitch.com/
While these design tools can be extremely powerful, it still pays to follow the same basic guidelines to ensure that your pitch deck is easy for investors to understand; Keep it simple, avoid animation, stick to a consistent layout, and make sure your text and images are easy to read.
When you’re trying to capture investors’ attention and raise equity funding, you need to show them that you have a good plan. But startups aren’t traditional businesses and they don’t use traditional business plans.
like the Holy Grail, the business plan remains largely unattainable and mythological. Most experts wouldn’t agree, but a business plan is of limited usefulness for a startup because entrepreneurs base so much of their plans on assumptions, “visions,” and unknowns. Guy Kawasaki
This is why pitch decks are the perfect approach to sharing a startup business plan.
Fundamentally, your pitch deck is used to share your vision, attract investors, and start conversations. As a founder, you should be prepared for investors who may not “get” your pitch deck right away — this doesn’t mean that they aren’t interested in what you’re doing.
Be prepared to answer questions and have an engaging conversation about your startup. Investors want to see that you have a clear understanding of your business, the problem you’re solving, and how you plan on making money. They also want to know that you’re capable of executing your vision.
Remember, pitch decks are just one part of the overall investment process. If you’re able to create a pitch deck that effectively communicates your idea and leaves investors wanting more, then you’re on the right track!
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

- Try Tactyqal

Pitch deck vs business plan – Which do you need for your business?
What is a pitch deck.
A pitch deck is a presentation that entrepreneurs use to sell their business idea to potential investors. The purpose of a pitch deck is to give an overview of the business, its products or services, its market opportunity, and its team in order to persuade the audience to invest in the company.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that outlines the goals, strategies, and financial projections of a business. It is used to persuade potential investors to invest in the company.
Pitch deck vs Business plan
Pitch decks and business plans are different in their purpose, content, and format.
Pitch decks are typically shorter and more visual than business plans. They are used to give an overview of the business and its opportunity, and to persuade the audience to invest in the company. Business plans are longer and more detailed. They are used to outline the goals, strategies, and financial projections of the business.
Whether you need a pitch deck vs a business plan will depend a lot on the type of business you are running or planning to set up.
Both these documents help entrepreneurs navigate their businesses over the next few years. And both these documents help investors in deciding whether to fund the business or not. However, where business plans are essential for traditional businesses that have a more concrete pathway to success, startups don’t require business plans. A pitch deck is more appropriate for a startup as a lot will change in the course of business.
In this post, we will discuss the differences between pitch deck and business plan and help you determine which one is necessary for your business.
The purpose of a pitch deck is to raise money from venture capitalists and angel investors. The purpose of a business plan is for traditional businesses or late-stage companies to raise money from investors and banks and also to forge partnerships with other organizations.
A pitch deck is a summary to help investors get a decent understanding of the business and helps create opportunities for entrepreneurs to get meetings with venture capital firms and angel investors. Business plans on the other hand serve as full-proof research to help investors understand whether they should invest.
As mentioned previously, pitch decks are more apt for tech startup companies whereas business plans are prominently used by established businesses, small or big.
If I am an angel investor or a venture capitalist investing at a seed stage (up to $1 million), I am more interested in the team and the idea and how the business could disrupt a whole industry or create a new one. When the company has grown from an idea to a company with employees and millions of dollars in revenue, I am more interested in seeing how they will reach stability and become the number 1 or 2 player in the market, and I am interested in detailed strategies. That is when I want to look at the business plan and understand how they will execute their plans.
Pitch decks can range between 10-50 pages and depend on the stage of the startup. For example, investors who invest in very early-stage startups require not more than a 10-page pitch deck. However, as the startup grows and raises more money, investors who come in at a later stage would want more information and might require a detailed pitch deck that can range up to 70 pages.
Business plans on the other hand are very detailed as cover every aspect of the business and can easily be 100 pages long. A business plan can even contain forecasts for the next 5 years.
A typical investor will spend 2-3 minutes going through a pitch deck but needs to spend more time going through a business plan as there are more details.
Audience Focus
A pitch deck focuses on the team, product, market, and traction metrics. These are 4 primary features investors look at to decide whether to invest or not. And these features can easily fit into a 10-page deck.
When the relevant audience looks at a business plan, they want to know if the business they are getting into is/can be profitable and also runs stable operations. In other words, since business plans look at a much longer-term, it includes a lot of details.
Presentation
Pitch decks are more visual compared to business plans and are presented vocally to an audience or a set of investors. Business plans are presented verbally as they are read by the relevant audience. Since business plans are longer, they are not presented to an audience.
Pitch decks are usually created with software like Microsoft PowerPoint or Google slides. There is also other software like Prezi and Slidebean which specifically help in preparing pitch decks.
Business plans are usually prepared in Word format as they are heavily text-based.
These are the key differences between startup pitch decks vs business plans.
Pitch deck vs business plan, w hat comes first?
The pitch deck is a teaser and comes first. If you are running a business and have decided to raise funds from investors, it’s obvious that you probably don’t know most of them. So, a pitch deck is a great way to get your foot on the door and make a good first impression.
With many new entrepreneurs starting up, you can imagine that every investor gets plenty of pitch decks and business proposals to invest in. Probably hundreds, every month. So, if they have to read lengthy business plans, they won’t have time to actually make investments. That’s why it’s essential to capture their attention with a crisp 10-15 page pitch deck that introduces them to the team, the idea, and how the business can make investors rich.
Do you have all the elements of a good pitch deck?
A good pitch deck gives you the opportunity to grab the attention of investors. A good pitch deck contains most of the necessary information required for investors to make a decision on whether they should talk to you. Take the free assessment to find out if you have all the elements that should be included in your pitch deck .
Also, check out our post on how to create a good elevator pitch to get investors interested in what you’re building.
Tips for creating a good pitch deck
Here are a few tips for creating a successful pitch deck:
– Keep it short and sweet: Remember that you only have a few minutes to make your case, so make sure your deck is concise and to the point.
– Focus on the key points: Investors will want to know about your team, your business model, your traction, and your financial projections. Make sure you hit on all of these points in your deck.
– Use visuals: A pitch deck is a great opportunity to show off your company with some visuals. Include slides with graphs and charts to illustrate your key points.
– Practice, practice, practice: Before you ever step in front of investors, make sure you’ve practiced your pitch a few times. This will help you deliver it confidently and ensure that you don’t leave anything out.

Do you need a pitch deck and a business plan?
This is a common question for entrepreneurs. The simple answer is that it depends on your stage of business and what you’re using the documents for.
A pitch deck is a shorter, more visual version of a business plan that you use to introduce your company to potential investors, customers, or partners. A business plan, on the other hand, is a more formal document that you use to map out the details of your business, including your business model, marketing plan, financial projections, and other operational details.
So which one do you need? If you’re just starting out, you’ll probably want to focus on creating a solid business plan. Once you’ve got that in place, you can use it as the foundation for your pitch deck. If you’re further along in your business and are looking to raise money or secure partnerships, then you’ll need to create a pitch deck.
Creating a pitch deck is a good way to concisely communicate your business plan and get feedback from potential investors, customers, or partners. If you’re raising money, your pitch deck will be one of the first things investors look at, so it’s important to make a good impression.
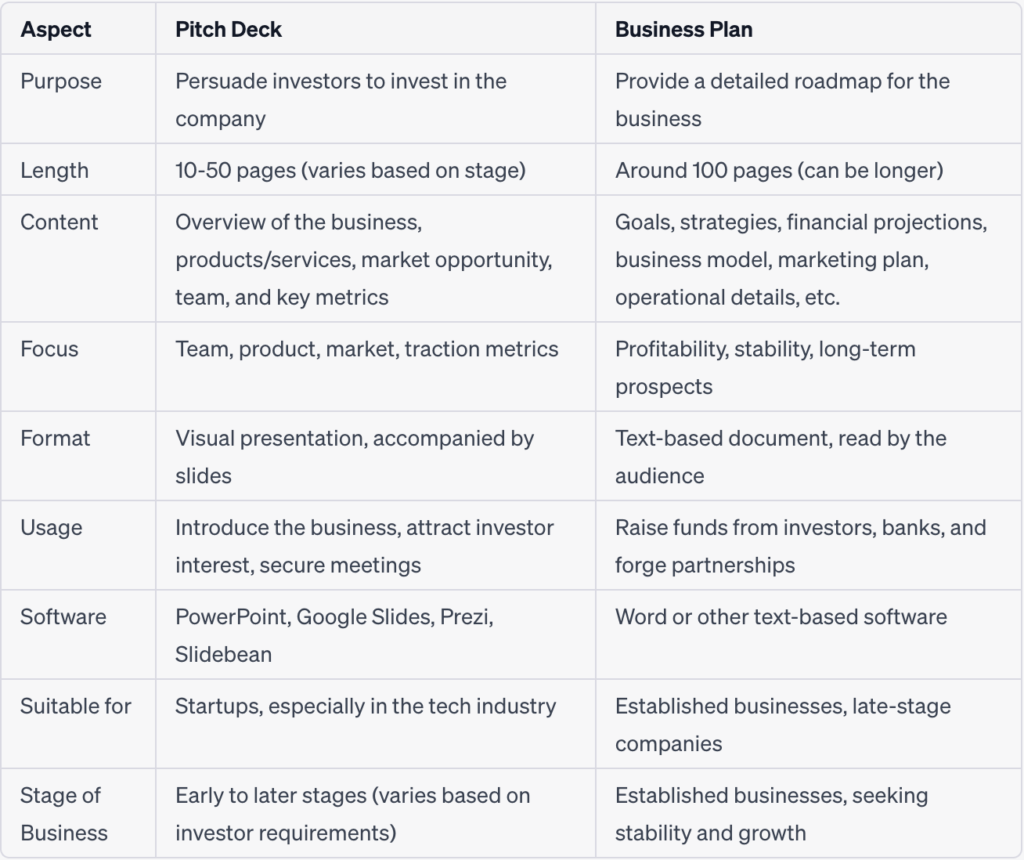
Partha Chakraborty
Partha Chakraborty is a venture capitalist turned entrepreneur with 17 years of experience. He has worked across India, China & Singapore. He is the founder of Tactyqal.com, a startup that guides other startup founders to find success. He loves to brainstorm new business ideas, and talk about growth hacking, and venture capital. In his spare time, he mentors young entrepreneurs to build successful startups.
You may also like

The Role of the Chief Growth Officer
- Uncategorized

The Inspiring Journey of Whitney Wolfe Herd- Cofounder of Tinder and Founder of Bumble
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Business Plans vs. Pitch Decks
As readers of either my Mentor’s Perspective or Mentor’s Journal series will know, one of the most common themes that I come across is that of fundraising in all its guises.
Maybe that is because it is a topic that most businesses will consider at some point in their growth, or maybe it is because it is often the area of running a business that many founders feel most uncomfortable with, or know the least about. I will discuss the art of fundraising in a future article but here I wanted to focus on two of the most important steps that must be taken before setting out to raise any funds – that is writing a business plan and producing a pitch deck.
Indeed, in my opinion, the business plan is such an important document that it is a crucial exercise that should be undertaken for any business, irrespective of whether it wishes to raise funds or not.
For any new business it is an extremely valuable exercise to write a business plan, as this will force you to analyse all of the areas that need to be taken into consideration when deciding upon the focus of your business and your product or service. The process should start with the simplified Business Model Canvas (many examples and templates are available online) as this is a bit more of a brainstorming exercise to try and make sure that you have pulled together all of the areas that need to go into the business plan and then grouped them together sensibly. Once you have spent some time on that exercise you can then start to write the business plan. This does not need to be excessively large or detailed but should go into sufficient detail to cover all aspects of the business.
Business Model Basics
- Your product / service and what differentiates it and you as a company – what are you doing differently and what factors will ensure that your company succeeds?
- Your potential market place and how much of the market you realistically hope to reach – is this just the UK or do you plan to export? How will you develop this and over what time period?
- Your competition and barriers to entry – will you compete with large players and how easy will it be for you to break into the market or indeed for others to break into your market?
- Your management team and what previous experience they have – a previous track record always adds comfort so if you do not have all the experience necessary how will you cover the gaps?
- Your financials – both actuals to date and future forecast (with detailed assumptions based on research). These must be realistic and demonstrably achievable. If they are too optimistic then they will undermine the whole business plan in the eyes of others and also set you wrong targets
- Your manufacturing / distributing / supply chain / route to market – set this out in order to show the complete process and to help the reader put the financials and everything else into perspective
- Your marketing and sales strategy – explain how you will market and sell your product or service and how you plan to grow sales over time. Again, this will help add credibility to the assumptions used in your financial projections
Do not worry if your plan brings out some areas of difficulty as this is to be expected. What is important is that it demonstrates that you know these areas exist and that you have thought about them and found solutions.
There should be a one or two page executive summary at the front that pulls out all of the really important points from the main business plan. Be warned, this summary is extremely important as many readers, especially potential investors, will only read the full plan if you have grabbed their attention sufficiently in the executive summary.
Once the initial plan is written it can be extremely beneficial to discuss it with your Mentor or other trusted advisors as it is likely that they will point out areas that they feel should be included and they should also challenge some of the assumptions made, especially in the financial forecasts. This process ensures that after any revisions that you may decide to make, either to your plan, or indeed your actual business, you have a robust plan and you are able to defend all of the assumptions made.
Once the business plan has been produced it is a very useful document to revise periodically and to update as your business grows and your needs and aspirations change over time. As I mentioned at the beginning of this article, I feel that preparing a business plan should be done simply as a good exercise to clarify your thoughts, but certainly if you are looking to raise funding by way of debt or equity then it becomes a necessity. As such, updating and refining an existing plan is a much easier task then writing one from the start, and because it is not the first attempt it should also be a better document.
If you are looking to raise equity funding then clearly the company needs to have a valuation and the only real way that this can be obtained is by producing a full business plan with financial projections and clear assumptions, together with the future plans of the company. If indeed the company is considering raising equity it is crucial that the management team provides a broad range of experience and any gaps in experience should ideally be filled with non-executive directors and a good advisory board.
Pitch Deck vs. Business plan
The pitch deck complements the business plan and stands alongside it. Just as it is important that the full business plan has a one or two page executive summary which must catch the readers’ imagination and encourage them to read the whole business plan, then the pitch deck can be seen as an alternative form of executive summary but used in a different way.
The business plan is a long, detailed document typically produced in Word, whilst the pitch deck is normally between 10 to 20 pages in length and often produced in PowerPoint, but it is a much more visual document designed entirely to sell the business to potential investors or lenders, or anyone else that reads it. It must grab the reader’s attention immediately and encourage them to want to know more.
It is important to use pictures, graphs, tables and the like, to get as much of the important information over as succinctly as possible and to reduce the number of words required. It needs to tell a story and there is of course a real art to this. Think of it as a trailer to a forthcoming blockbuster film and you start to get the right picture.
The information contained should enable the reader to understand the company’s product or service, the advantages it has over rivals, the size of the market, how much it is raising for what amount of equity and how the money will be spent. It must therefore include projected financials and a pre-money valuation of the company (that is the value of the company before any additional funds are raised). It is also best to include a timeline of significant events in the company’s history.
Producing the bones of a pitch deck is relatively easy once the business plan has been done but given that it effectively acts as the elevator pitch of the company, and first impressions are crucial, I would suggest that it is one thing that is worth spending good money on to ensure that it looks the part and includes all the required information.
Both the business plan and the pitch deck can of course be produced fully in house but I also know of some very good companies out there that can produce extremely professional documents for a modest fee. Like everything, that decision will be dependent upon the in house ability and time available, but do not underestimate the time needed to do either of these properly. Both of these documents could be crucial to securing external investment so they are well worth doing well.
To summarise, all businesses should do a business plan and keep them regularly updated whether they want to raise finance or not. Any company that wishes to raise finance must also produce a first class pitch deck.
Share This Article

- DEALMAKERS PODCAST
- BUSINESS TEMPLATES
- M&A ADVISOR
- BOOK A CALL
I hope you enjoy reading this blog post.
If you want help with your fundraising or acquisition, just book a call click here .
Business Plan vs. Pitch Deck
by Alejandro Cremades
Business plan vs. pitch deck? Which should you be focusing on first as a startup founder?
For decades entrepreneurs and business owners believed they needed to focus on building a comprehensive business plan. All before taking real action. There were good reasons for that. More recently, many entrepreneurs have gone almost exclusively with pitch decks in place of a traditional business plan.
Which of these two approaches is best? Does it depend on the type of business you are starting or if you plan any fundraising efforts? Is a hybrid approach the wisest move? Or should you stay intensely focused on one before the other?
*FREE DOWNLOAD*
The ultimate guide to pitch decks.
Here is the content that we will cover in this post. Let’s get started.
- 1. Definitions: Business Plans Vs. Pitch Decks
- 2. Uses For A Business Plan Today
- 3. The Pros & Cons Of Business Plans Today
- 4. Uses For A Pitch Deck Today
- 5. The Pros & Cons Of Pitch Decks Today
- 7. FULL TRANSCRIPTION OF THE VIDEO:
Definitions: Business Plans Vs. Pitch Decks
A traditional business plan is a fairly lengthy text-based document. It lays out all of the parts of the business.
From the corporate structure to marketing plans to startup needs and growth plans and financial forecasts for the next five years. Plus the much longer-term game plan. This is typically in a Microsoft Word style format, and can easily run 25 pages. It begins with a brief executive summary . Which can be 1-3 pages long on its own.
A pitch deck is a slide-based presentation. Think PowerPoint or Google Slides formatting. Ideally, your pitch deck will run between 5 to 20 slides. It is a very short, simple and compact version of a traditional business plan. Pitch decks emerged specifically for pitching startups to potential investors for fundraising. However, they are increasingly replacing business plans.
Uses For A Business Plan Today
Are business plans still relevant today?
Yes and no. Every business and entrepreneur should have a plan. We all know what failing to plan means. Yet, what is effective and valuable in terms of business plans may be changing and evolving.
A business plan really helps you get depth and length in your plans. It gives more clarity than you could ever fit into a pitch deck. This process helps entrepreneurs really think through the details and big vision and long term game plan. It helps you get granular with marketing plans, startup costs, cash flow needs, and financial projections.
It also helps to give you a framework to start building on. As well as really thinking through a functional business model .
Investors, advisors and other key players may be completely satisfied with seeing a one-page business plan, executive summary, and bullet-pointed action plan. Providing that accompanies a great pitch deck.
However, there may still be some scenarios in which you will be asked for your business plan. This includes applying for some types of loans, leasing space and joining certain groups or applying for licenses.
The Pros & Cons Of Business Plans Today
The advantages of business plans:.
- Being forced to think through the details
- Having an in-depth plan and awareness of your real needs
- Being able to back up the hype with something tangible
- Credibility with potential partners and early investors
- Being prepared if you are asked for it
- Having a comprehensive guide and roadmap to follow
The cons of business plans:
- Chances are no one else will ever read it
- Things move so fast, most may be irrelevant in a couple of months
- It’s a black hole for your time, energy and momentum
- Many entrepreneurs get bogged down here and miss their best opportunities
- Additional expenses with negligible returns
- Appearing like a novice to experienced investors
Uses For A Pitch Deck Today
A pitch deck is for more than just fundraising. Below is a video where I cover how to create a pitch deck.
See How I Can Help You With Your Fundraising Or Acquisition Efforts
- Fundraising or Acquisition Process: get guidance from A to Z.
- Materials: our team creates epic pitch decks and financial models.
- Investor and Buyer Access: connect with the right investors or buyers for your business and close them.
Book a Call
In fact, you’ll find pitch decks useful from before day one through your exit.
These scenarios include:
- Honing your initial concept and model, like with a business plan
- Gaining initial feedback
- Recruiting cofounders
- Enrolling advisors
- Hiring early and key team members
- Pitching investors on and offline
- Securing early customers and strategic partnerships
- Through multiple fundraising rounds
- Getting to an exit
The Pros & Cons Of Pitch Decks Today
The advantages of pitch decks:.
- Expected when raising capital
- A streamlined framework for creating a mini business plan
- Easily and efficiently updated for multiple purposes and overtime
- Much faster to create
- More likely that you will use and refer to it often
- Easier to share
- Enables you to get down to business faster
If you want to go more in detail you can view the video below where I cover this.
The cons of pitch decks:
- Can be an excuse not to have a real plan of model
- Dangerous gaps from not thinking through the details
- Not prepared when a business plan is requested
- Emphasis on fluff and hype versus substance
- Very short term outlook
Summary
There are many advantages and disadvantages of solely running on a traditional business plan or new modern pitch deck. Trying to juggle both simultaneously can further compound the cons, distraction, and length of time before you really get into the game.
Today, it seems the best-prepared entrepreneurs, especially when it comes to getting funded are those with a strong pitch deck, and at least a one-page business plan, and strong executive summary.
Do not dismiss the importance and value of having a real plan. You could be sabotaging your own mission and future. If you plan to stay small local business or solopreneur forever a real business plan is smart. Though as the founder of a fast-moving startup that needs funding, a pitch deck can be even more important. You’ll probably be moving so fast your business plan will never keep up.
If you have to choose one, it should be focusing on knocking out a winning pitch deck. This process will also give you many of the answers and framework for fleshing out your real business plan. At least this way you’ll be poised to raise money, and build out your team and gain early clients in the meantime.
Remember that storytelling plays a key role in fundraising and you will need capital to scale things up. This is being able to capture the essence of the business in 15 to 20 slides. For a winning deck, take a look at the template created by Silicon Valley legend, Peter Thiel ( see it here ) that I recently covered. Thiel was the first angel investor in Facebook with a $500K check that turned into more than $1 billion in cash.
Remember to unlock the pitch deck template that is being used by founders around the world to raise millions below.
Unlock the pitch deck template used by founders to raise millions. Just enter your email below.
FULL TRANSCRIPTION OF THE VIDEO:
Hello, everyone. This is Alejandro Cremades, and today we’re going to be talking about the main difference between a pitch deck and a business plan. Essentially, a pitch deck is a 15 to 20 slide presentation, while a business plan is a 10 page to a 100-page document. Both have been sent in the past or have been used to be sent to investors when you’re raising capital. So with that being said, let’s go into it and really understand the difference between one and the other.
In terms of the actual use: the actual use of the business fund, I think it’s a great way to give a complete inside to the business to the investor. Remember: it’s a 10 page to 100-page document. The thing about a business plan is that it tends to be lengthy. Data shows that typically investors, right off the bat, especially doing the first discussions, they’re going to be only allocating to reviewing your opportunity about 2:41. That’s it.
With that being said, the main difference here is that, for example, on the pitch deck, you’re really giving that possibility to the investor of reviewing everything in those 15 to 20 slide of the business, understanding the 30,000-foot view, and really knowing if that’s an opportunity that they want to pursue further, or perhaps that it makes no sense because maybe it’s not a fit with their investment thesis.
In terms of the actual disadvantages of maybe pitch decks or business plans, the main disadvantage of a business plan is the fact that your business is going to be constantly changing. No single business plan is completely bulletproof to the market. So you may be investing a ton of time in putting those 100 pages. Then you go to the market, and you realize that you need to either optimize or iterate on the business model in order to get it right. So that’s basically going back to the drawing board.
What I like about the pitch deck is that it’s just a 15 to 20 slide presentation where you can continue to iterate and optimize the presentation as you go based on the feedback that you’re getting from investors, from customers, from employees, whoever that is that is helping you to understand how you’re positioning this better towards the investors that are going to be reviewing the document.
In terms of the business plan today, certainly, it has taken a backstep towards the fundraising process when it comes to pitch decks. Pitch decks today are used more than business plans, and they’ve been taking the lead over the course of time.
Now, the beauty here of business plans, though, is that they’ve taken a backstep, but they’re a great document that you could use with your team and then also to showcase to investors if there’s further interest as an 18 to 24-month roadmap as to how you’re planning to execute the business.
For the pitch deck, again, it’s a great way to showcase the 30,000-foot view of your business in a way in which you can continue to change depending on the concerns and those questions that you’re receiving while you’re out there raising the capital.
Lastly, as part of the difference between the business plan, and then also the pitch deck, remember timing. Timing is the reason why you’re going to be sending a business plan is because the investor is about to make the investment. It’s one of the last things that they need in order to push forward and give you the money.
Then while you’re sending the pitch deck is because you want a secure meeting because you want to maybe convince the investor further. But, really, the difference is that one is going to be lengthy, while the other one is going to provide a 30,000-foot view of the business.
So with that being said, if you like the video, make sure that you Like this video and then also hit the Subscribe so that you don’t miss any other videos, and then leave a comment. And don’t forget to check out the fundraising training where you’re going to be able to see how we help founders from A all the way to Z with everything related to fundraising, live Q&A, templates, agreements, you name it. Thank you so much for watching.
Facebook Comments
Do You Want More Funding Or Get Acquired?
Get a custom action plan and all the help you need to start raising more capital or to get your company acquired.
About the Author
Alejandro Cremades leads the vision and execution for Panthera Advisors as its Co-Founder and…
Recent Posts
- This Entrepreneur Raised $36.5 Million To Secure Cloud-Stored Data From Hackers
- Ameesh Divatia On Raising $36.5 Million To Secure Cloud-Stored Data From Hackers
- This Serial Entrepreneur Built A P2P Finance Marketplace And Has Now Patented A New Way to Tip For Service Providers
- Oli Cavanagh On Building A P2P Finance Marketplace And Now Patenting A New Way to Tip For Service Providers
- Roberto Cipriani On Raising Over $380 Million To Bring Personalized Learning Support To Students
If you want help with your fundraising or acquisition, just book a call
Swipe Up To Get More Funding!
See How I Can Help You With Your Fundraising Or Acquisition Effort
Book a call
Want To Raise Millions?
Get the FREE bundle used by over 160,000 entrepreneurs showing you exactly what you need to do to get more funding.

Health and Wellness Startups to Watch
- Tips & Strategies

5 Ways to Boost Employee Productivity

Product Led Growth vs Sales Led Growth: Business Models

Difference between Entrepreneur and Entrepreneurship

Pitch Deck vs Business Plan: Understanding the Differences for Startup Success
The Battle of the Startup Strategies: Pitch Deck vs Business Plan
Starting a new business venture can be an exciting but daunting endeavor. As an aspiring entrepreneur, it’s crucial to have a comprehensive roadmap to guide you through the journey to success. Two common tools used in the startup world are pitch decks and business plans. Both serve as fundamental documents that outline your business concept and strategy, but they differ in format, purpose, and target audience. Understanding the differences between a pitch deck and a business plan is essential for startup success. Let’s delve into the unique aspects of each and determine which one is the right fit for your entrepreneurial aspirations.
Pitch Deck: Captivating Investors with a Compelling Story
Imagine you’re on an elevator, and you spot your dream investor stepping in. You have just a few minutes to convey your startup’s value proposition and convince them to invest their hard-earned money in your vision. This scenario perfectly encapsulates the purpose of a pitch deck – a concise, visually compelling presentation that captures the essence of your business idea and entices potential investors.
A pitch deck focuses on storytelling and aims to elicit an emotional response from the audience. It typically consists of 10-20 slides that cover essential aspects of your startup, including the problem you’re solving, your unique solution, target market, competition, business model, and financial projections. The goal is to present a captivating narrative that showcases your team’s expertise, the market potential, and the scalability of the business.
Unlike a traditional business plan, a pitch deck is designed to be concise, engaging, and visually appealing. It should provide just enough information to generate interest and leave the investors hungry for more. Think of it as a movie trailer – a teaser that leaves the audience excited and wanting to watch the full feature.
The Power of Visual Storytelling in Pitch Decks
Visual elements play a crucial role in pitch decks. Utilizing eye-catching graphics, charts, and images can effectively communicate complex ideas and data in a simplified manner. Humans are visual creatures, and a well-designed pitch deck can evoke emotions and make a lasting impression on potential investors.
Here are some key tips to create a powerful pitch deck:
- Keep the slides clutter-free and visually appealing
- Use compelling images to support your narrative
- Highlight key data and metrics through charts and graphs
- Use concise and impactful language
Remember, your pitch deck is your chance to shine and stand out among the competition. Make it a visual feast for the investors’ eyes while delivering a compelling story they won’t forget.
Business Plan: The Comprehensive Blueprint for Success
While a pitch deck captures the attention and imagination of potential investors, a business plan is a more in-depth document that serves as the foundation for your startup’s success. A business plan encompasses all aspects of your business strategy, operations, financials, and market analysis.
Unlike a pitch deck, a business plan isn’t intended to be presented in a few minutes. It’s a comprehensive written document that provides a detailed roadmap for your startup’s journey. A well-crafted business plan demonstrates your understanding of the market, competitors, target audience, and financial projections.
Typically, a business plan consists of several sections, including an executive summary, company overview, market analysis, product or service description, marketing and sales strategy, organizational structure, and financial projections. Each section delves into specific aspects of your startup, allowing you to present a comprehensive picture to potential stakeholders, including investors, partners, and lenders.
The Detail-Oriented Nature of Business Plans
Creating a business plan is a meticulous process that requires thorough research, analysis, and strategic thinking. It requires you to dive deep into your market, identify your target audience, understand your competition, and devise a winning marketing and sales strategy.
Here are some key elements to include in a business plan:
- Market analysis and competitive landscape
- Clear value proposition and unique selling points
- Comprehensive marketing and sales strategy
- Organizational structure and team composition
- Detailed financial projections and funding requirements
A well-crafted business plan demonstrates your expertise, market knowledge, and strategic thinking. It provides a solid foundation for decision-making, ensuring that your startup is on the right path to success.
Selecting the Right Tool for your Startup Journey
Now that we’ve explored the unique aspects of both pitch decks and business plans, it’s essential to understand when to use each tool. While both documents play a crucial role in the startup ecosystem, their purposes and target audiences differ.
If you’re in the early stages of your startup and seeking funding or investment, a compelling pitch deck is vital to capture the attention of potential investors. With a well-crafted pitch deck, you can pique their interest, generate curiosity, and secure a meeting to present your idea in more detail.
However, as your startup progresses and you require a more comprehensive document to present to potential stakeholders, partners, or lenders, a business plan becomes essential. A business plan allows you to showcase your strategic thinking, market knowledge, financial projections, and long-term vision in a detailed manner.
Remember, a pitch deck and a business plan aren’t mutually exclusive – they can complement each other. A compelling pitch deck can serve as a visual aid during your business plan presentations, capturing the attention of your audience and enhancing their understanding of your startup’s value proposition.
The Winning Combination: Harnessing the Power of Pitch Decks and Business Plans
As an entrepreneur, your success lies in your ability to effectively communicate your startup’s vision, strategy, and potential. By harnessing the power of both pitch decks and business plans, you can increase your chances of startup success.
Use the captivating storytelling techniques of a pitch deck to create an emotional connection with potential investors. Engage their senses with visually appealing graphics and charts, leaving a lasting impression in their minds.
Simultaneously, utilize a well-crafted business plan to showcase your strategic thinking, market knowledge, and financial projections. This comprehensive document will solidify your startup’s foundation and instill confidence in potential stakeholders.
Remember, the battle between a pitch deck and a business plan isn’t about choosing one over the other but rather understanding how to leverage each for maximum impact. Embrace the power of both tools and set your startup on the path to success.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts
- Pitch Decks & Investor Materials
- B2B Graphic Design
- Startup Consulting
- Trainings & Workshops
- Case studies
- Downloadable resources
The differences between a business plan, pitch deck and an elevator pitch
- Pitch deck design /
- Presentation design

Over the years we encountered confusions between our startup clients regarding whether they should have a business plan before making a pitch deck or if they need one in the first place. So let’s put it like this, the business plan is your house, the pitch deck is your window that shows the indoor beauty and the elevator pitch is your alley to the house.
First things first, you need all three of these materials prepared when you want to start a business. Before we start to talk about the differences between them, let’s go through some basic information.
What is a business plan?

A business plan is a document that contains a detailed description of your business. You will use it as a roadmap for how to structure, run and grow your new business. It is built to store and transmit your plans for the next 1, 3 or 5 years, including the research of the industry, the competitors. It covers the sales predictions, the marketing strategy and the operational plans.
The document is based on charts, representations of growth and financial strategy, but mainly the information is transmitted through plain text. A common business plan has a length of 10 to 100 pages. As nobody has the patience to go through a 100 pages document you should keep it simple, but well structured.
In the end you are making the business plan for you, to reflect the vision and the direction you are going. After that, the goal of a business plan is to give investors information about your company, to show them how do you plan to use their investment.
Tip: You should be honest with yourself in your business plan, which is why it’s important to consider challenges and opportunities. If you’ve got a strong idea, let it stand on its merit.
What is a pitch deck?

A pitch deck is a presentation that summarises the business plan and it gives an overview of your company. It is usually made using PowerPoint, Keynote or Prezi as a visual support and used in face-to-face/ online meetings with potential investors, customers, partners or presented in pitch competitions.
The pitch deck contains 10 – 20 slides and should include all the information required, as you may be asked to send it after the presentation. The structure can vary from business to business, but it must include company details, who it serves and why, the size of the market, you added value.
The goal of the pitch deck is to show investors where you are, where you are going and most important to get a meeting or start a conversation with one about funding you.

If you want to know more about what to put in a pitch deck read
How to create a great pitch deck .
What is an elevator pitch?

As its name says an elevator pitch is a brief description of your business, like a movie trailer, that can be presented during an average elevator ride 10 – 30 seconds. An elevator pitch should be pre – prepared so when the occasion arises you will know exactly what to say.
You can also look at it as a positioning statement. Start with Who do you help , this is also important to set for yourself. Now they are listening to you so you continue with what you help them with .
The elevator pitch can be used in other situations, such as job fairs, networking events, your LinkedIn bio. It is a great way to introduce you to people that you meet as a conversion starter.
The goal of this speech is to be short and spark interest to your elevator ride so they want to know more about your business.
Focus your elevator pitch around “ We are X and we help Y to do Z “
What are the differences?
Basically all three of them have the same content, but it’s a matter of details. You start with the business plan that has everything about the business, then make a more compact version for the pitch deck and finally you create an elevator pitch that has the essence of your business.

The link between the business plan, the pitch deck and the elevator pitch
We talked about the differences, but now let’s see what is the connection between these three.
As we know the pitch deck and the business plan include mostly the same section and while the business plan is more detailed, the pitch deck offers high level information on some sections ( problem, solution, product, market, team). We can consider the pitch deck a visual summary of the business plan.
The elevator pitch is used without an additional support, but when presenting a pitch deck the first information has the role of an elevator pitch, to catch the attention of the investors for the rest of the presentation. You open the pitch deck presentation with the elevator pitch.
Looking at the big picture we can see that the elevator pitch is included in the pitch deck, which in his turn is included in the business plan.

Download a Free Guide to design your pitch deck
We recommend having all of them prepared. For the business plan you can use all kinds of templates and platforms to build one or having a consultant working with you. The pitch deck should be made with a pitch deck designer as it needs to be compelling, but there are also a lot of tips for how to create one. And for the elevator pitch follow a structure that puts your advantages in the spotlight.
Hope this helped you to have a clear perspective about what is a business plan, a pitch deck, an elevator pitch, when to use them and what are the differences between them.
If you already decided that you need to have an stunning design for your pitch deck we are here to make that for you.
Need help designing or structuring your next presentation?
Our team can help with everything from research, to creating your presentation flow, writing the content, designing and building your slides.
Get in touch
Top articles
- Infographics
- Personal branding
- Pitch deck design
- PowerPoint tutorial
- Public speaking
- Visual communication
Sign up for our monthly newsletter
This is very helpful information
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Recently Active
- Top Discussions
- Best Content
By Industry
- Investment Banking
- Private Equity
- Hedge Funds
- Real Estate
- Venture Capital
- Asset Management
- Equity Research
- Investing, Markets Forum
- Business School
- Fashion Advice
- Technical Skills
- Deals and Transactions
Business Plan vs Pitch Deck vs Elevator Plan
These will be for those looking to secure investor financing; knowing the differences will help smooth the process of moving their business forward.

Matthew started his finance career working as an investment banking analyst for Falcon Capital Partners, a healthcare IT boutique, before moving on to work for Raymond James Financial, Inc in their specialty finance coverage group in Atlanta. Matthew then started in a role in corporate development at Babcock & Wilcox before moving to a corporate development associate role with Caesars Entertainment Corporation where he currently is. Matthew provides support to Caesars' M&A processes including evaluating inbound teasers/ CIMs to identify possible acquisition targets, due diligence, constructing financial models , corporate valuation, and interacting with potential acquisition targets.
Matthew has a Bachelor of Science in Accounting and Business Administration and a Bachelor of Arts in German from University of North Carolina.
- What Is Business Plan Vs Pitch Deck Vs Elevator Plan?
- What Is Business Plan?
- What Is Pitch Deck?
- What Is Elevator Pitch?
- Business Plan Vs Pitch Deck Vs Elevator Plan
What Is Business Plan vs Pitch Deck vs Elevator Plan?
Although they are similar, a company executive’s business plan, pitch deck , and elevator pitch are distinct. For those looking to secure investor financing, knowing the differences will help smooth the process of moving their business forward.
At a high level, the three schemes all describe a company and its plan, albeit in varying detail. Several key differences lead to different formats that serve specific objectives.
Investors review the business plan to make a final funding decision. For this reason, it is lengthy and text-heavy.
The pitch deck is the preliminary investor presentation. At this stage, we seek to gain investor attention and interest that could lead to funding down the line. Because it is not the final step, this presentation is shorter but still detailed. Lots of imagery is used to convey ideas visually.
The elevator pitch is the first step; it is meant to spark an initial interest in the company. Because it is the shortest of the three, it hits only on the absolute core ideas. This pitch is completely verbal.
An overall summary of the differences between the business plan, pitch deck, and elevator pitch, respectively:
- Tens of pages vs. a ballpark of 10–20 slides vs. a quick verbal explanation
- Text focus vs. visual focus vs. verbal focus
- Funding-oriented vs. attention-oriented vs. interest-sparking
Now let us look at each of the three in more detail to truly understand their differences.
Key Takeaways
- The business plan, pitch deck, and elevator pitch differ in length, focus, and goals.
- Business plans are comprehensive (long, text-heavy), pitch decks are concise with visuals, and elevator pitches are ultra-short verbal summaries. Business plan contents cover all aspects of the business in detailed sections.
- The pitch deck uses little text to emphasize important points visually and keeps it succinct.
- Elevator Pitch pitch should be presented in a short time frame, ideally within the length of time it takes for a lift on the elevator.The final few seconds of an elevator pitch should focus on key concepts in order to grab listeners' attention.
What is Business Plan?
A business plan is the most detailed of the three documents and explains everything there is to know about a business. However, the document is commonly lengthy because it is much more comprehensive than both the pitch deck and the elevator pitch.
Even though the business plan can be anywhere from 10 to 100 pages, it is important to write it with concision in mind. This should not necessarily be at the expense of detail, though.
What exactly is included in terms of content? The business plan is how you plan for your business to both grow and operate in the intermediate future (this can be anywhere from 1 to 5 years). Business plans should ensure that they include the following:
- The Executive Summary: It is an overview of the entire document. It hits on the key points in each section. An indication of a solid executive summary is whether or not it could stand alone as a separate document. If it could, then it is likely a sufficient summary.
- Business Overview : The business overview should describe some basics about the business. These would include how the business was formed, its legal structure, where it is located, what type of business it is, and the means of conducting business.
- Operational Plan : The operational plan should explain how the business will operate and function. Different teams and their responsibilities should be included.
- Market Analysis : The market analysis details and explains your plans to fulfill customers' needs.
- Products and Services : The section on products and services explains all the products and services being sold, how each product is categorized within the business and its model for generating revenue, and a concise description of each product.
- Sales and Marketing : The overview of sales and marketing will outline pricing and other sales information. This includes why these price points were chosen and why customers will be willing to purchase at that price point. In addition, strategies for reaching customers and driving sales will be described here.
- Competitive Analysis : In the area dedicated to competitive analysis, competitors in the market are examined. In addition, comparisons of the strengths and weaknesses of the company should be mentioned, as well as a plan to rise above the competition.
- Management Team : The management team section exists primarily to drive trust. It provides reasons why the team is uniquely qualified to tackle the challenge the market presents.
- Financial Plan : The financial plan should be very detailed and leave nothing to surprise. The cost of starting the business and expected costs for the next few years should be included. In addition, it should also cover how these costs are spread and if more funding will be needed down the road.
- Projections : Finally, projections of financial statements should be presented, including how net income will grow and what the balance sheet will look like in a few years.
Final tips: When writing, it would be helpful to be realistic with challenges and expectations. Creating a plan that overstates what can be expected will only lead to unforeseen problems. Investors will also likely be able to tell whether or not your expectations are excessive.
What is Pitch Deck?
A pitch deck is typically created for potential investors’ review. Then, it is put together to begin conversations about financing the company.
To best convey the main points of an otherwise lengthy presentation, the pitch deck summarizes a company’s information rather than going into complete detail.
As denoted in its name, a pitch deck is normally presented in the form of a deck of slides. However, instead of being text-focused, these slides tend to be image-heavy, providing visual support to investors.
While images should make up the bulk of the content, it could still be worthwhile to include some text with key business information for potential investors’ further review after the presentation.
We have already established that the full business plan ranges from 10 to 100 pages. In comparison, the pitch deck is much shorter—it is usually between 10 and 20 slides.
What should be included?
Though the content is up to the presenter’s discretion and depends on what best highlights each company, certain topics should be touched upon.
Value proposition and brand positioning
Revenue model, roadmap, sales, and marketing strategies, the team and competition, financials as well as plans for funding.
As discussed in greater detail in the elevator pitch section, the value proposition and brand positioning statement answer many simple questions about what the business offers.
In addition to answering these basic questions, the value proposition and brand positioning section should also discuss the ideal customer and the market as a whole, specifically market sizing.
The revenue model, roadmap, sales, and marketing strategies section should include figures detailing your pricing strategy and how that compares to your costs. What does the rollout of your product or service look like, or has it already begun?
Other questions investors may have that are answered in this section include growth projections and justification for those forecasts. Are prototypes generating lots of interest?
Are there existing products released, and if so, how much traction do they have? Is growth expected to come from new releases or existing products?
Then, the marketing strategy is discussed to address how and why it will expand the business's existing traction and profit expectations.
Moving forward, in the team and competition section, the reason why the business team is best prepared to deal with any challenges the market presents is listed.
Moreover, the following questions are also considered in this section:
- How does the executive team stack up against competitors?
- What is the team’s competitive advantage?
- Do comparisons present a challenge, or is the team looking to emulate other similar companies?
Finally, when investors have a more complete understanding of the company, the section about financials is presented.
The following questions are typically considered in this section:
- What is the current financial situation of the company?
- What valuation does this lead to?
- Why is the funding needed?
- How will it be used moving forward?
- Is more funding likely to be needed?
Once again, when discussing funding and valuation, it is best to be realistic. Investors will form a valuation opinion themselves anyway.
If the valuations provided by the business match the investors' expectations, it will give the investors the impression that the executive team has a solid understanding of the market. Overreaching estimates will only generate more issues for the company in the future.
What is Elevator Pitch?
Finally, we have the elevator pitch. The elevator pitch is the most summarized version of the three.
Given its name, the pitch should be presented in a short time frame, ideally within the length of time it takes for a lift on the elevator. It should not take more than 30 seconds.
Because an elevator pitch is so short, it is important to be once again concise in conveying ideas. It is, in fact, quite logical to even have a rehearsed pitch in advance to make sure all the main points are touched upon efficiently.
The key is to think of the pitch as a hook, touching on the absolute fundamentals of why the company is an innovative and profitable idea.
What might this include? We can approach it in a few ways; two examples below are through value proposition and brand positioning.
Value proposition
The value proposition asks the key questions:
- Who are we?
- What do we do?
- Why does it matter?
A well-conveyed value proposition should explain why the company exists and demonstrate that your team is internally aligned (meaning that there is motivation towards a clear purpose).
Beyond just creating interest, the value proposition helps establish a purpose for the business that is more profound than a mere market opportunity.
Communicating this concept will implicitly improve how your audiences perceive the business idea and help drive trust if they want to invest.
Brand positioning
We can also consider the fundamentals of the brand positioning statement:
- Discussing the target market shows to whom your company is relevant and frames your business in a value-focused way.
- The frame of reference further expands upon why your business idea could profit by analyzing how the competitors in the market are meeting market demands. Examining their shortcomings leads nicely to explaining why your brand would stand out.
- The critical benefit further discusses this idea with an emphasis on the customer. This section should address the following questions: What exactly is offered to customers? Is it something completely new? Or is it a modification of something already offered?
- The final section should include the reasons why your product or service is better than others from a customer's perspective. Does it check all the boxes of customer requirements? Does the company also differentiate itself from competitors in a way that makes it more appealing? Again, these concepts are the backbone of creating trust in both consumers and investors.
Other aspects that can be worth including in the elevator pitch are a brief introduction about yourself (optional) and a conclusion inviting interested investors to contact you (recommended).
Including a little about yourself at the beginning of the pitch may help build credibility with the person listening. Most of the pitch, however, should be about the business idea itself.
Closing the pitch with a call to action helps move the process forward. The goal of the pitch is not to fully sell your idea but to peak interest and lock in a second, in-depth conversation.
Business Plan Vs Pitch Deck Vs Elevator Pitch
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing.
The pitch decks are a visual aid to help businesses attract investors and clients. Understanding the elements of a pitch deck can help you reach your business goals.
The goal of the elevator plan is to capture the audience’s interest so that they want to know more about the idea presented. It assists in expanding one’s professional network and saves time and energy spent conveying ideas. Pitches attract attention and help retain or gain more money in the venture.
Everything You Need To Break into Private Equity
Sign Up to The Insider's Guide on How to Land the Most Prestigious Buyside Roles on Wall Street.
Researched and authored by Jacob Rounds | LinkedIn
Reviewed and edited by Hongmo Liu | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:
- Bailout Takeover
- Highly Leveraged Transaction (HLT)
- Hostile Bid

Get instant access to lessons taught by experienced private equity pros and bulge bracket investment bankers including financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel Modeling.
or Want to Sign up with your social account?
7 Great Pitch Deck Examples From Real Businesses
11 min. read
Updated April 9, 2024
A solid pitch deck can mean the difference between landing funding and going home empty-handed.
Your deck has to convince investors that you and your business are a good bet. Otherwise, they’ll take their money elsewhere.
But what does a good pitch deck look like? Yes, there are specific slides that you should include , but including them won’t guarantee that you get funding.
Luckily, there are hundreds of pitch decks from highly successful companies that you can look at for inspiration.
For this article, I grabbed a few favorite pitch decks and dug into why they’re so good.
- Why these pitch decks?
These pitch decks made the list because they come from highly successful startups that successfully landed one or multiple rounds of investor funding.
They’re unique with specific strengths and formatting that go beyond your typical presentation templates.
Some are more like a business plan presentation —incredibly long, use a lot of text, and focus more on data and financials. Others are short, highly visual, and meant to invoke specific emotions.
No matter your business stage or industry—these are all useful to explore and reference when crafting your pitch.
Get started with a free startup pitch deck template
Don’t get held up creating your pitch deck presentation.
Download a free investor pitch deck template with pre-built slides and instructions from experienced entrepreneurs.
This template is yours to customize and adjust as you see fit. And remember, the 11 slides in the deck are just the standard to start with.
1. Airbnb — Turning a pitch into a story
Airbnb’s pitch deck has become the go-to example for startups. Sure, the design is outdated, but the results speak for themselves. It is one of the most recognizable funding success stories of the 2000s, and many would say that’s because of their pitch deck.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Company info
- Founded: 2008
- Industry: Travel and hospitality
- Business Model: Digital marketplace
- Funding: $600,000 seed funding round in 2009
- Source: Sequoia Capital and Y Combinator
What’s great about this pitch deck?
Airbnb’s deck is simple and punchy. It gets right to the point, doesn’t overload the slides with too much information, and serves as a useful backdrop to the founder’s elevator pitch .
The deck is also fairly brief.
It doesn’t include every slide that we recommend. Instead, they prioritize crafting a story and leaning into their strengths.
In just a few slides Airbnb:
- Demonstrates a real-world problem and viable solution.
- Breaks down a clear path to enter the market.
- Details how they will make money and even show initial traction.
Key Takeaway: Tell a story and play to your strengths. You don’t need to get into every detail about your business during the initial pitch. The goal is to spark interest and start a conversation. Just be ready to answer any lingering questions after the fact.
2. Copper Cow Coffee — Showcasing expertise
Copper Cow Coffee, known for its Vietnamese coffee and portable pour-over technology, has been part of multiple funding rounds (including a stint on Shark Tank). Founder Debbie Wei’s pitch deck is less concerned about proving a business concept than showing the competitive advantages of her business.
It is a well-designed pitch deck to review if you are looking to scale and bring in additional capital.
- Founded: 2016
- Industry: Food and beverage
- Business Model: D2C, Subscription, and Wholesale
- Funding: $2 million seed round
- Source(s): Techstars, CRCM Ventures, among others
This deck does a lot with visuals. It conveys the history, innovation, and premium nature of Vietnamese-sourced coffee with virtually no text. Rather than being a distraction that investors get hung up reading, the deck is far more additive and helps punctuate specific points during the pitch.
Since this is an established business, once the unique value proposition is set, the remainder of the deck is dedicated to operational efficiency, partnerships, and revenue—areas of the business that prove Copper Cow Coffee is sustainable, has a strong competitive advantage, and has opportunities to grow.
Key Takeaway: There’s no need to dig deep into hypotheticals when your business has enough traction to prove you’re worth investing in. If you have enticing data points, use them to sell your value to investors.
3. LinkedIn — A pitch meant for knowledgeable investors
LinkedIn often gets lumped in with other social media platforms, but its purpose and user base are unique.
From the beginning, it was pitched as a network for professionals—where you could easily find and contact the right people in your industry.
So, the concept and unique value were easy to understand. But how that would work and generate consistent revenue were the bigger questions.
- Founded: 2003
- Industry: Social Media and Professional Networking
- Business Model: Freemium model with revenue from advertising, premium subscriptions, and talent solutions.
- Funding: Approximately $103 million (before going public in 2011)
- Funding Source(s): Sequoia Capital, Greylock Partners, etc.
While I praised the Airbnb deck for being lean, I’m giving LinkedIn a thumbs up for the opposite. Their deck is incredibly thorough and heavy on information and data to establish the company’s position, monetization strategies, and growth details.
That doesn’t mean that they skip establishing a narrative. They just did it in only a few slides, choosing to focus on the traction and experience of their founding team.
This makes sense when your audience of investors may actually be potential users as well. So, establishing credibility, digging into the details, and clearly defining a sustainable path for growth were necessary.
Key Takeaway: Tailor your pitch and pitch deck to your audience. This may require you to add more details, prioritize different business areas, or pull back on specific information to let the story shine.
4. Uber — Proving there’s a pain point
Uber is an interesting case of a business poking holes in a problem that most people just accepted. At the time, there were no real alternatives to paying for a taxi. And owners of these cab companies held a bit of a monopoly over the industry.
For Uber to succeed, it had to prove that innovation and harnessing new technologies were key.
This makes this deck a must-review if your business has the hurdle of pushing an established industry system to evolve.
- Founded: 2009
- Industry: Transportation and Technology
- Funding: Approximately $24.5 billion (before going public in 2019)
- Funding Source(s): SoftBank, Benchmark, GV, etc.
Uber’s pitch deck painted a visceral picture of how the taxi industry was ripe for disruption in just two slides. For anyone who has had to hail a taxi, this immediately resonates.
The rest of the deck is dedicated to how they would do it. They needed to apply reality to this futuristic vision with facts, ambitious but believable financial projections, and evidence that they had traction.
Key Takeaway: If your business is built around disruption and new technology, you must prove that people will care. Clearly and quickly outline an actual problem , present a bold vision for the future, and then back that up with tangible steps to get there.
5. DoorDash — Proving there’s a better way
Now synonymous with food delivery, DoorDash wasn’t actually the first to market with the mobile ordering concept. That honor goes to GrubHub.
In this case, arriving later was a benefit. There were still obvious gaps in mobile ordering that made the technology less impactful for consumers. No dedicated delivery drivers, a lack of up-to-date restaurant information, and extensive wait times were just the minimum.
DoorDash didn’t reinvent the wheel but honed in on the new pain points that business owners and consumers complained about. And that is the crux of their pitch.

- Founded: 2013
- Industry: Food Delivery and Technology
- Business Model: Logistics platform connecting customers, restaurants, and delivery drivers, earning fees from each order.
- Funding: Approximately $2.5 billion (before going public in 2020)
- Funding Source(s): Y Combinator, Charles River Ventures, SoftBank, etc.
DoorDash’s pitch deck for Y Combinator’s demo day clearly defines a significant problem in the food delivery industry and presents its platform as a solution that benefits consumers, restaurants, and drivers alike.
Combined with their elevator pitch, the deck effectively showcased DoorDash’s technological edge and operational efficiency. They demonstrated proven traction in an area that didn’t rely on a dense population center, further illustrating a clear vision to scale the business.
Lastly, they left a clear opening to draw in interested investors . By proving they know the industry and have a foothold that will lead to sustained growth, they didn’t need to fully explain the opportunity. Instead, they used their demonstrated success to land direct conversations after the larger pitch.
Key Takeaway: Your deck can be a backdrop to your elevator pitch. It doesn’t have to do all the talking but should elevate your point through well-timed visuals.
6. Peloton — Connecting with customers
It’s interesting to compare Peloton’s original Kickstarter campaign to their future pitch deck.
The consumer-facing Kickstarter spent little time establishing a narrative. Instead, it prioritized product features, visualized how it could fit in someone’s home, and showcased behind-the-scenes development.
Their 2018 pitch deck emphasizes how Peloton makes people feel. It informs the emotional connection with a detailed audience breakdown, brand values, and multiple customer quotes.
They wanted to prove that they had a deep understanding of their customers and had evolved as a brand. No longer just being seen as innovative exercise equipment but a recognizable brand movement.
Disclaimer: Peloton has struggled to maintain consistent growth after growing wildly successful amidst the COVID-19 pandemic. Hardware recalls, issues with user retention, high-profile executive exits, and a struggle to adapt to changing demands are all contributing factors.
However, Peloton’s deck still led to funding before their initial success and is still a strong example of how to showcase an in-depth understanding of your customers when pitching.
- Founded: 2012
- Industry: Fitness and Technology
- Business Model: D2C hardware and subscription services
- Funding: Approximately $994 million (before going public in 2019)
- Funding Source(s): Tiger Global Management, True Ventures, L Catterton, etc.
Peloton strays away from the typical business overview of most pitch decks. Investors knew the product already and needed to be sold moreso on the potential long-term retention of customers.
Peloton expertly defines its customer base beyond typical demographic and psychographic information. They string the community narrative throughout the deck, reinforcing the customer identity with every visual. You not only walk away knowing their customer base but get a sense of how they view themselves.
Key Takeaway: Don’t be afraid to diverge from the standard pitch deck structure. If you have to prove a specific point or show off a deep understanding of 1-2 business areas, craft your pitch around that instead.
7. Facebook — Let data do the talking
Facebook’s deck represents a business very different from what it is today. While social platforms like MySpace and LinkedIn were around, the scale and connectivity proposed with the platform had never been seen before.
So, the majority of the deck is dedicated to demonstrating that there is customer interest and a viable path to scaling to new customers. The business model takes a bit of a backseat, likely with the intent to flaunt how many potential people companies could engage with.
- Founded: 2004
- Industry: Social Media and Technology
- Business Model: Advertising, with ventures into hardware sales.
- Funding: Approximately $2.3 billion (before going public in 2012)
- Funding Source(s): Accel, Greylock, Peter Thiel, and others.
Facebook’s pitch deck is a masterclass in breaking down market opportunity. They demonstrate a clear product-market fit that feeds into an ambitious but achievable path to growth.
At any point, real data can be inserted, they do it. There are no questions about the business’s growth potential because it is laid out so well.
Key Takeaway: Use in-depth data to make your point. Any time you can punctuate your narrative with research or your own internal metrics, you will be far more convincing to potential investors.
Additional pitch deck resources
Hopefully, this curated guide of successful pitch decks will help you determine what to focus on in your deck.
For more guidance, check out these resources:
- Y-Combinator Startup Directory : Explore a list of 5,000+ companies funded by Y-Combinator to learn what type of businesses get early seed funding.
- PitchDeckHunt : Check out this library of over 1,000 real-world pitch deck examples for more inspiration.
- Investor Pitch Deck Template : A great starting point to develop your deck and ensure you cover all necessary information.
- Elevator Pitch Guide : A selection of resources that will help you refine your verbal pitch, impress investors, and know how to adapt it for different scenarios.
- Our Favorite Pitch Deck Tools : If you need more than a template to create your presentation, check out this round-up of pitch creation tools.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Kody Wirth is a content writer and SEO specialist for Palo Alto Software—the creator's of Bplans and LivePlan. He has 3+ years experience covering small business topics and runs a part-time content writing service in his spare time.

Table of Contents
- Free pitch deck template
- Copper Cow Coffee
- Additional resources
Related Articles

15 Min. Read
The 11 Slides You Need to Have in Your Pitch Deck for 2024

9 Min. Read
Our 5 Favorite Tools to Create Your Pitch Deck

8 Min. Read
How to Create a Business Plan Presentation
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Check out the pitch deck that helped adtech identity company ID5 raise $20 million from investors including TransUnion and Martin Sorrell's S4S
- Identifier-focused adtech company ID5 raised a $20 million Series B round.
- New investors included Martin Sorrell's S4S Ventures and TransUnion.
- ID5 plans to use the funds to expand its popular identifier to channels like CTV and mobile apps.
Adtech company ID5 said Tuesday it had raised $20 million in Series B investment. It plans to use the funds to help it expand its identifier technology from the web to more channels like mobile apps and connected TV.
Appetite in the digital ad community for alternative identifier solutions has been on the rise in recent years, thanks to the rollout of global privacy regulations and the impending death of third-party cookies . This signal loss, together with growing concerns about data privacy, have made it more challenging for advertisers to precision-target ads and measure whether their campaigns were effective.
Founded in the UK in 2017, just before Europe's General Data Protection Regulation came into effect, ID5 offers a solution that's similar to the marketing functions of a cookie. Its identifier attaches to a user's device when they visit a website or app. Publishers can enhance that with their own first-party data like hashed email addresses or phone numbers. The user is asked whether they would like to opt out, and the identifier carries strict permissions, so it can only be used by certain parties. ID5 allows a retailer, for example, to serve an ad to someone who had previously browsed its website and consented to their data being used for this purpose.
ID5 generates revenue by licensing its identifier to companies that use it to activate data or set up private marketplaces. The ID5 identifier has been deployed by more than 66,000 publishers, per the metadata company Sincera. ID5 lets publishers make their audiences addressable to buyers for free, which has helped it become the most widely adopted identifier by publishers globally, according to Sincera. In that space, it competes with the likes of Lotame's Panorama ID and The Trade Desk's Unified ID 2.0 , though many of these identifiers are also interoperable with one another.
Mathieu Roche, cofounder and CEO of ID5, said the company's revenue had grown by about 100% year-over-year, and that the company expects to be profitable by the end of this year or early next.
ID5 has now raised just over $27 million in funding to date, though the company declined to disclose its post-money valuation. New investors in this round included the credit reporting and data agency TransUnion and advertising veteran Martin Sorrell's venture capital firm S4S Ventures. Existing investors Progress Ventures, Seventure Partners, 360 Capital Partners, Axio, and Aperiam Ventures also participated in the round.
With Google's Chrome expected to cut support for third-party cookies at the end of this year , the digital ad industry on the open web is heading for a "real y2k" moment, said Sorrell, who is also executive chairman of the marketing services group S4 Capital.
"It's a real issue and very few clients are well prepared with integrated data sources," Sorrell said. "One of the biggest growth areas for us has been helping clients find their way through this, and what we're doing with ID5 supports that.'"
Matt Spiegel, executive vice president of TransUnion's TruAudience growth strategy, said ID5's and TransUnion's identity and data signals will be complimentary to each other.
"Our worldview is that the solutions for identity and the next wave isn't a single thing," Spiegel said. "It's a complex ecosystem that companies like us need to make simple, and Matt and the team are helping us do that in some key ways."
ID5 now hopes to expand its identifier into new areas like CTV, mobile apps, and audio. They all come with different sets of challenges, Roche said. The app ecosystem is more focused on measurement, for example, while the TV space is motivated by data protection because broadcasters "don't want to replicate the mistake of web publishers who have been robbed at gunpoint of their data," Roche added.
ID5 intends to grow its team from around 50 people currently to around 70 by the end of next year, hiring across the business in areas including sales, marketing, and engineering.
Check out key slides from the pitch deck that helped ID5 raise $20 million in Series B funding.
ID5 was founded in 2017 with the motivation of building a better, more privacy-conscious infrastructure for digital advertising than cookies.
While the company began in Europe, with its strict data protection regulations, it makes around 65% of its revenue in the US, the world's largest ad market.
"We've built a foundation that can make addressability and measurability possible across all digital channels so brands can actually know what happened to their ad investments and what results they generated without revealing the individual's" personal data, ID5's Roche said.
The global digital advertising market is set to reach $1 trillion by 2028, much of it fuelled by the transition of ad budgets out of linear TV into more data-driven environments.
ID5 is already the most popular identifier among global publishers, according to Sincera data.
ID5 says its identifier can maximize an ad campaign's reach while ensuring the same users aren't bombarded over and over again by the same ads.
ID5 now has a team of 50 people and it plans to grow that to about 70 by the end of 2025.
Sanja Partalo, managing partner of S4S Ventures, said the firm carried out due diligence on the identifier space for a year and found ID5 had become "the globally scaled solution that everybody talks about."
- Main content

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Captivates investors: Concisely delivers the problem, solution, market, and team. Business Plan: 1. Dominates later stages: Series B and beyond. 2. Secures substantial funding: Demonstrates viability and potential return on investment (ROI). Frequency of use. Pitch Deck: 1.
Differences Pitch Deck Business Plan; Purpose: Tell a compelling visual story about the business's potential. Provide a comprehensive roadmap of the business's strategy, operations, and financial projections. Goal: Capture investor interest and secure the subsequent meetings.
The business plan becomes your guiding star when seeking substantial investments, forging partnerships, or outlining your startup's long-term trajectory. The document demonstrates your commitment, knowledge, and foresight to potential investors and stakeholders. Main Differences Between Business Plan and Pitch Deck
Key Components of a Business Plan and a Pitch Deck. A business plan and pitch deck have different components that are essential to the success of your company. Here are the key components of each: Business Plan. Executive Summary: This section provides an overview of your entire business plan. It should be concise and highlight key points about ...
Both business plans and pitch decks contain financial information but the quantity and type usually differ. Pitch decks usually have no more than one slide dedicated to financials and prefer to zoom in on key figures. Business plans, however, include a detailed balance sheet, a profit and loss account, and a cash flow forecast.
Ongoing refinement is key. Key Differences Summarized. In summary, while a pitch deck and business plan are complementary, their key differences include: Purpose: Pitch deck - Generate interest. Business plan - In-depth evaluation. Length: Pitch deck - 10-15 slides. Business plan - 20-50 pages.
A pitch deck is a brief presentation that gives potential investors or clients an overview of your business plan, products, services and growth traction. As an entrepreneur, you probably know this: your company or idea needs financing. Oftentimes, this financing will come from external sources—i.e. people who aren't friends or family.
For the purposes of this contract, a pitch deck refers to a brief presentation that provides an overview of a business, while a business plan refers to a detailed document outlining the goals, objectives, and strategies of a business. 3. Ownership. Party A acknowledges that the pitch deck and business plan are the intellectual property of Party ...
Here are additional differences between pitch decks and business plans, expanding on the previous points with more numerical details: 6. Visual Elements. Pitch Deck: - Typically includes 10-20 slides. - Relies heavily on visuals, images, and charts to convey information. - Each slide should be concise and focused, with minimal text ...
Pitch decks and business plans are two commonly used tools in the startup world, each serving a unique purpose. In this article, we will dive deep into the world of pitch decks and business plans, understanding their differences and exploring how they can lead to startup success.
Pitch Deck and Business Plan: The Power of Both. While a pitch deck and a business plan have different formats and serve distinct purposes, they are both critical for startup success. A pitch deck helps you engage and excite potential investors by delivering a concise, visually appealing overview of your business.
Pitch deck: As descried, a pitch deck can be sent early in the process. This can be done through cold 'acquisition', but preferably from an introduction via a mutual connection. business plan: As described, a business plan doesn't get sent too often.
Well, guess what, a pitch deck touches on every single one of those topics; the difference between a pitch deck and a business plan is that a pitch deck can take a few hours to write (less than an hour if you use that a really awesome tool we've mentioned before). In contrast, a business plan will take you days and days of writing, proofreading ...
The Differences: Pitch Deck vs Business Plan. Now that we have a basic understanding of what pitch decks and business plans entail, let's explore the key differences between the two: 1. Purpose. The primary purpose of a pitch deck is to deliver a captivating and concise pitch to potential investors or stakeholders. It aims to generate ...
A pitch deck is a presentation that summarises a company's business plan. Often prepared using PowerPoint or Keynote, a pitch deck usually has 15 to 20 slides. It can either be used as a visual support for in-person meetings or sent as a standalone document to potential investors. A pitch deck is not only short, it also follows a clear ...
This is the most important slide in the whole deck, you need to grab the attention of the investor with a title slide that convinces them to keep reading. Your title slide must: Showcase your logo and brand name. In one phrase, state your value proposition. Engage the reader by promising them an interesting pitch.
Pitch decks and business plans are different in their purpose, content, and format. Pitch decks are typically shorter and more visual than business plans. They are used to give an overview of the business and its opportunity, and to persuade the audience to invest in the company. Business plans are longer and more detailed.
Pitch Deck vs. Business plan. The pitch deck complements the business plan and stands alongside it. Just as it is important that the full business plan has a one or two page executive summary which must catch the readers' imagination and encourage them to read the whole business plan, then the pitch deck can be seen as an alternative form of ...
This is Alejandro Cremades, and today we're going to be talking about the main difference between a pitch deck and a business plan. Essentially, a pitch deck is a 15 to 20 slide presentation, while a business plan is a 10 page to a 100-page document. Both have been sent in the past or have been used to be sent to investors when you're ...
The Battle of the Startup Strategies: Pitch Deck vs Business Plan. Starting a new business venture can be an exciting but daunting endeavor. As an aspiring entrepreneur, it's crucial to have a comprehensive roadmap to guide you through the journey to success. Two common tools used in the startup world are pitch decks and business plans.
As we know the pitch deck and the business plan include mostly the same section and while the business plan is more detailed, the pitch deck offers high level information on some sections ( problem, solution, product, market, team). We can consider the pitch deck a visual summary of the business plan. The elevator pitch is used without an ...
Conclusion. Both the tried-and-true business plan and the brand-new pitch deck come with their share of benefits and drawbacks. When you multitask, you increase the number of distractions you face and the amount of time it takes to get into the game. In the very competitive atmosphere of modern fundraising, the most successful entrepreneurs are ...
The business plan, pitch deck, and elevator pitch differ in length, focus, and goals. Business plans are comprehensive (long, text-heavy), pitch decks are concise with visuals, and elevator pitches are ultra-short verbal summaries. Business plan contents cover all aspects of the business in detailed sections. The pitch deck uses little text to ...
And remember, the 11 slides in the deck are just the standard to start with. 1. Airbnb — Turning a pitch into a story. Airbnb's pitch deck has become the go-to example for startups. Sure, the design is outdated, but the results speak for themselves. It is one of the most recognizable funding success stories of the 2000s, and many would say ...
Allstar, a startup that helps gamers become creators: $12 million Series A. Almost Friday Media, formerly Friday Beers, a digital media company: $6 million seed. Amagi, a media tech firm for ...
Check out key slides from the pitch deck that helped ID5 raise $20 million in Series B funding. ID5 was founded in 2017 with the motivation of building a better, more privacy-conscious ...