- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In

Definition of coursework
Examples of coursework in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'coursework.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1890, in the meaning defined above
Dictionary Entries Near coursework
Cite this entry.
“Coursework.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/coursework. Accessed 20 May. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 17, birds say the darndest things, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), games & quizzes.

What Is a Coursework and How to Write a Paper: A Simple Guide
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 2715 words
- Icon Clock 13 min read
Academic writing is an essential activity in higher education and comes in various forms. Basically, one of these forms is coursework writing, where instructors assess students’ level of understanding of a course during a semester. In this case, unlike other papers, coursework assignments evaluate students’ understanding of the course and not just a topic in the class. Moreover, various forms of coursework writing include essays, term papers, theses, dissertations, and report projects. Hence, students need to learn what is a coursework assignment and how to write such a paper.
What Is a Coursework Paper
College and university students undertake different kinds of academic exercises, with writing projects taking a significant portion. Basically, one of these exercises is the writing of coursework, an assignment that they submit at the end of the semester. Ideally, this kind of work assesses students’ understanding of a particular field of study within a single semester. In turn, instructors rarely require students to write a coursework assignment for things they learned during the previous semester.
Definition of a Coursework
By definition, a coursework assignment is an academic project that students undertake in the course of study and which they must submit before the closure of the semester. For example, such types of papers aim to evaluate students’ level of knowledge and skills acquisition, meaning the work contributes to students’ final grades. Ideally, coursework is what students learn during a semester, and such an assignment is meant to measure how well they have understood the subject matter. Moreover, students use reliable and relevant sources to study, examine and evaluate the chosen coursework topic. Therefore, a coursework assignment is very similar to other writing assignments, such as essays, reports, thesis writing, and dissertations.

Differences With Other Papers
In the course of their classes, students write different types of papers, including essays and reports. Basically, the major difference between coursework writing and these papers is that it assesses students’ understanding of what they have discovered throughout the semester. In contrast, essays and other papers assess students’ understanding of a specific topic, concept, result, or theory. Moreover, students may need to address an issue in their coursework that they might have addressed in an essay assignment sometime during the semester. As such, a coursework assignment is broader in scope than other papers.
Expectations
Like essays and other papers, a coursework assignment varies from one area of study to another. For example, there is a coursework for the English subject and another for the sciences. Therefore, students are expected to complete their coursework assignments according to their instructor’s or department’s instructions. In most cases, this expectation includes presenting the assignment in an essay format, where they select a title of their choice. Depending on the subject, some coursework assignments expect students to collect, examine, infer, and report data when answering a specific question.
When it comes to the grading of academic assignments, instructors look at how well a student has attended to all the requirements and expectations. For instance, these requirements include writing about a choice of themes or text excerpts in a given format. In this case, students must use an approach that they believe is likely to give them a higher grade, meaning an approach that helps them to answer the question methodically, logically, and critically by using relevant information. In essence, these are three dimensions for grading a coursework assignment.
Constructing a Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide on How to Write a Coursework Assignment
Like an essay, a coursework assignment takes a particular structure. Basically, students should understand the core components and make sure that they address them in their academic writing. In this case, the most significant issue for students is to ensure a logical flow of ideas. Moreover, developing a thesis statement is essential to provide high-quality essays with a guideline on focal issues. Primarily, these issues are the concepts and theories that the student has learned in a specific course during the semester.
Step 1: Preparation
Planning or preparation is the first step in writing a coursework paper. For instance, the essence of any form of academic writing is to measure a student’s level of understanding about a particular area of study. Since the coursework measures what a student has learned in a given course, it is paramount for each person to prepare well when executing the assignment. Here, learners have to choose a topic that they are comfortable with, one that they are passionate about. Additionally, they should generate ideas about their coursework by deciding what is relevant and what is not. In this case, the reasoning that guides this decision is the expectation outlined in assignment instructions. Lastly, students should understand their audience – consumers of their work or readers. Like any other assignment, the audience is course instructors. Hence, writers should ensure coursework satisfies a curiosity of readers.
Step 2: Setting Up
After preparation, students should set up the stage for coursework writing. Basically, the first preoccupation is to find sources relevant to the assignment prompt – those that are more likely to provide enough evidence and support needed claims. As students review credible sources, they should take notes to provide a strong argumentation in their coursework. Then, another activity involves deciding on the coursework outline, which should help answer the assignment prompt logically and critically. Lastly, learners should create an annotated bibliography, a summary of each source they intend to use as the basis of their arguments in the coursework.
Step 3: Writing the Coursework
After preparing and setting up the stage, students should start writing the coursework assignment. In this case, armed with notes taken during the review of reliable sources and the outline they have created, students should start with the first draft, where they develop a thesis statement. Basing all opinions and arguments on the thesis, writers should answer the assignment prompt methodically, logically, and critically. Moreover, the thesis statement should ‘hook’ the audience and make them interested in reading the substantial part of the paper – the body. In essence, the body is where students use all the evidence they have gathered about the topic, while the thesis informs the audience of what individuals have focused on in the paper.
Step 4: Wrapping It Up
It is normal for a writer to make mistakes when writing an academic document. For example, these mistakes include inconsistent arguments, irrelevant content, punctuation errors, and countless grammatical mistakes. Therefore, after completing the draft, students should read it through, at least twice, to identify these mistakes and correct them. Basically, the processes of correction include revising and editing the paper. Regarding revisions, students should give their work to a friend or mentor to read it through. In their feedback, these individuals are likely to point out areas where authors should make corrections for the paper to be logical and interesting to read. Concerning editing the paper, students should proofread their work to ensure it is free of spelling mistakes, punctuation errors, and other grammatical mishaps.
Step 5: Developing Body Paragraphs
The body paragraph of any academic text, including a coursework assignment, utilizes several features to make the paper logical. Basically, the first feature is the topic sentence that opens up each paragraph. Also, the purpose of this feature is to strengthen the central idea captured in the thesis statement. Then, the rest of the paragraph structure backs up this claim using evidence gathered from different sources. In turn, another feature is a concluding sentence, which closes each paragraph. For instance, the goal of this aspect is to connect the topic sentence with the thesis statement. Finally, another feature is transition words and phrases that help readers sense a logical flow of ideas throughout the paper. In short, writers use transitions within and between paragraphs to create a logical flow of information and ideas.
Step 6: Referencing Format and Peer Reviewing
Besides ensuring the paper is written methodically and logically, students should see that it meets the highest academic writing standards. In this regard, they should ensure it follows after a particular format – APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian. In most cases, the assignment prompt dictates the format that learners should use. Moreover, the referencing format informs about the structure of the paper and the format of citations. In turn, another essential activity that students should perform is to commit the paper to peer review. Here, authors give coursework papers to distinguished scholars, such as a professor or classmate, to assess the validity and quality of information used, including sources.
Step 7: Writing the Final Draft of a Coursework Paper
After subjecting the first draft to vigorous scrutiny through revisions, editions, and peer review, students should start writing the final draft of a coursework paper. Basically, this draft should be thoroughly polished, meaning it should be free of spelling, punctuation, and grammatical mistakes, as well as inconsistent arguments and irrelevant sentences. Moreover, it should indicate an effective use of transitions in the body paragraphs. In short, the final draft is an improved version of the first draft because writers have revised and edited it and incorporated feedback from a friend, mentor, or professor. However, they still need to read through the final draft, at least once, to ensure it is perfect before submission to the department. In turn, if students note several mistakes, it means another revision is necessary. Hence, the student’s focus should be the content, organization of ideas, style of writing, and format.
Types of Coursework
Given that coursework assignments test students’ level of understanding about a course’s content in a given semester, it means that it takes several forms. For example, these include a term paper, a Master’s thesis, a dissertation, or a report project. Ideally, the coursework is an essential requirement for a student to complete the course successfully. It also means the coursework is essential to be awarded a degree. In turn, the only difference between these types of coursework assignments is that they take a different approach to examining and analyzing course content, with each subject taking a unique approach.
Coursework Writing Techniques
The dream of every student is to pass any assessment and attain a higher grade. In a coursework assignment, students can utilize different techniques to ensure they attain higher grades after assessments. As indicated earlier about the grading of coursework, learners should use an approach that they believe answers the assignment prompt methodically, logically, and critically. As a result, every technique they use must allow them to answer the question in a way that satisfies these three grading dimensions.
1. Compare and Contrast Technique
A compare and contrast essay technique is about analyzing two subjects, ideas, concepts, or theories by comparing them, contrasting them, or doing both. Basically, the purpose of answering a coursework assignment through this approach is that students must not state obvious things. Instead, they need to shed light on the subtle differences or unexpected similarities between subjects, ideas, concepts, or theories.
2. Cause and Effect Technique
A cause and effect essay technique allows writers to develop their paper’s body by analyzing the reasons for and the consequences of a decision, action, or event. When organizing a paragraph, students adopt a structure that allows them to arrange the causes and effects in a chronological or reverse chronological order. Alternatively, authors can present their arguments through emphasis, starting from least important to most important aspects, or vice versa.
3. Investigation Technique
An investigation technique involves undertaking an in-depth examination of a topic, idea, concept, or theory. Basically, this technique’s primary goal is to demonstrate that students have gained a thorough knowledge of the subject, which is indicated in their methodical, logical, and critical analysis and presentation of information. In this case, ensuring that research findings are interpreted and presented in an organized manner throughout the essay is critical. Ultimately, the technique enables writers to demonstrate their articulate understanding of the various viewpoints about the issue under investigation.
How to Present Strong Arguments
For an academic paper to capture the audience’s attention and interest, students must not only develop a thesis statement but also ensure they use strong arguments to back up the central idea in the statement. Basically, the “they say, I say” technique is the simplest method to present arguments properly. In this regard, the information that the student uses in answering the coursework assignment prompt should be free of plagiarism. For instance, they need to cite sources properly. Then, another way to ensure that the writing is persuasive is to confirm that they have attained the required word count without counting footnotes, endnotes, references, and appendices. Ideally, selecting a topic that one is comfortable with and passionate about enables the writing to be high-quality in terms of argumentation. Also, students should discuss alternatives with their mentor or instructor. Finally, the thesis statement should not be complicated.
Major Mistakes in Courseworks
Students make different kinds of mistakes when writing academic texts. For example, a common mistake in coursework writing involves a scope, where students fail to focus on one area of the topic and instead try to be broad in their argumentation. In this case, the problem with this approach is that they waste space talking about irrelevant material, leaving them with little space to write about the core idea. Also, the solution to this problem is to develop a thesis statement that sets out the paper’s specific agenda. In doing so, students can realize every time they go off-topic.
Another common mistake involves colloquialism, where students use a language that is not standard for academic writing. Basically, this problem is particularly common with students who become excited about the topic and try to express their ideas creatively. Moreover, the problem is that the coursework shifts from being evidence-based to a document about the student’s opinion. In turn, the solution to this problem is to pick a topic that is exciting and critically discussed in the literature. As a result, they can identify several sources that discuss the topic to use as bases for evidence of their claims and arguments about the topic.
Sample of a General Coursework Outline
The coursework paper adopts a typical outline, as indicated below:
- Table of Contents
- Abstract or Executive Summary
- Introduction
- Body Paragraph(s)
- Reference list
Reason for Similarity of a Coursework Assignment With a Research Paper
Ideally, the outline of a coursework assignment is similar to that of a research paper. In this case, an abstract serves as a brief overview of a research paper and informs readers of the writer’s focal points. More importantly, the coursework outline has a body, where writers use different paragraphs to make an argument about the topic. Also, each of the paragraphs begins with a topic sentence and ends with a concluding sentence. Like research papers, body paragraphs of a coursework assignment serve to cement the writer’s claims and arguments, which are linked to the thesis statement.
Summing Up on What Is a Coursework Assignment and How to Write a Paper
A coursework assignment is among the writing assignments that students in colleges and universities undertake in preparation for their degree. Unlike other papers, this assignment assesses students’ understanding of what they have learned in a course in a given semester. As such, students must complete and submit it before the semester closes. Moreover, the different types of coursework include essays, term papers, theses, dissertations, and report projects.
Students should master the following tips when it comes to writing a coursework assignment:
- Choose an exciting topic and stick to it. Basically, students come across tons of exciting information about their topic. However, to avoid going off-script, they should focus on their core subject and avoid the temptation of using data that may prove irrelevant.
- Use evidence (quotes and statistics) selectively. In this case, relevancy is a significant indicator of a high-grade paper. As such, where students are not going to refer to some data directly because it adds no value to their argument, they should avoid dwelling on it in their paper.
- Cite sources correctly. When citing sources, students should note the standards of the format in use – APA, MLA, Harvard, or Chicago/Turabian – as each has a unique approach.
- Revise, edit, and proofread the paper. In turn, high-quality coursework writing should be free of inconsistent arguments, irrelevant sentences, and spelling, punctuation, and grammatical mistakes.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Cite a Court Case in MLA 9: A Simple Guide With Examples
- 7 August 2020

How to Cite a Dissertation or Thesis in Chicago/Turabian With Examples
- 5 August 2020
How to Write a Coursework

Coursework projects do not resemble essays, research papers, or dissertations. They are the combination of all three. Students spend less time writing coursework than on making a term paper, but this type of work requires more time and efforts than an ordinary essay - it is made of several essays. Thanks to our guide, each student can discover how to write coursework. If you are running out of time or lack experience to complete the specific coursework, we recommend using our coursework writing services to hire professional academic writers.
What is Coursework and Why Does It Matter?
Coursework definition: General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) coursework is a typical academic assignment, given in the course of study to evaluate the student’s knowledge, skills, and identify the final grade. Many students face this type of writing in the US colleges. One of the examples is a coursework UTD (The University of Texas at Dallas) - the requirements of this institution are strict, and many students fail to submit their papers and pass the corresponding courses.
Such type of assignment helps to have the ‘detective’ hat on: a student observes, examines, and evaluates the chosen topic using credible, up-to-date, and relevant sources. Working under controlled conditions is important. Participating in every school class will help to prepare good coursework by the end of the term. Take a look at the examples of what students of various profiles may face:
- English Composition - English coursework is an extended essay in most cases. A student has a right to pick the topic. The tutors provide their students with the list of recommended titles to choose from, sources to observe & analyze, and a format (e.g., a comparison between different relevant articles)
- Sciences - coursework for science is a complicated assignment. Such type of work appears in the form of a scientific paper to test what a writer investigates and reports independently.
- Geography - geography coursework is about collecting, reporting, and explaining information to reply to a certain geographical question or offer solutions to the problem. One idea is to explore the usage of a shopping mall or analyze the recent tornado. No matter whether you have to prepare a coursework Columbia or such paper for other educational institutions, keep in mind these differences!
Types of Coursework Explained
English Language coursework is the most common type of this assignment. At advanced GCE level, the student will be expected to write a couple of essays, totaling 3,000 words. Every assignment is 20 marks maximum.

An analytical essay : Evaluate, compare, & contrast 3 different sources of data interconnected by a common theme; written /spoken / multimedia content. Discuss different uses for targeting various audiences. Learn more on our blog.
Original essay with a supportive commentary : A student will have to come up with a single piece of media writing in the observed modes (written, spoken, or multimodal). Add a supporting piece with details about the aspects of English language. English Language & Literature coursework is a bit different. The basic requirements are the same, and the parts are:
An analytical study : Sharing an analysis of the chosen piece and its relation to the related content. It will show how well the writer understands the original piece. Tutors grade such works based on the:
- Use of the proper terminology and the coherence of the written words;
- Understanding & evaluation of the way a structure, form, and language create the written & spoken word;
- Opportunity to observe relationships between various pieces of writing.
Creative writing & commentary : Produce a creative piece that imitates the style of the assessed text. Share comments to backup your understanding. The goal is to show the knowledge, prove the competence, and use appropriate language skills in communicating with the target audience. You will also need a relevant coursework resume (review) in both cases. Keep on reading to learn how to write coursework of A level.
How to Write a Coursework: Guide for Students
Several factors may lead to the coursework being disqualified. It is a serious matter! The risk factors include:
- Plagiarism - it is the worst thing that could happen to any type of academic assignment. Lots of relevant information is available on the world wide web today, and the tutors are strict about the issue of plagiarism. Write everything in your own words! If you decide to insert the quotes from the sources, apply the suggested citation format and develop a list of references. Sign the declaration claiming it is your original project. If you're unsure about how to approach this, seeking professional help by choosing to write my coursework can be a wise decision.
- Word count - do not ignore the specific requirements concerning the length of the coursework. Specify if the footnotes, appendices, & references are included in the word count.
- Topics - go through the list of available themes. If there is an examination planned on the specific topic, try to pick another idea for the coursework.
- Tutor’s assistance - do not ignore the help of your instructor, ask them to provide guidance on what to write. Ask the questions to learn more details, but keep in mind they can go through the 1st draft once and just offer some general recommendations.
Choosing a Topic for Your Project
Dedicate enough time to this extra important question. Select the field of your interest if it is possible to relate it to the course. That is the golden rule of choosing a coursework topic - keep in mind the rest of the hints:
- Analyze the offered list of topics or develop yours
- Pick a topic from the area of your expertise related to the studied subject
- Select the topic you are interested in
- Choose the topic you’ve started to observe in the past
- Check how much relevant, up-to-date information is available on the Internet about each of the topics
- Pick what you can measure, change, & control (they call it a ‘fair test’)
- Use the ideas of previous researchers and students
- Do not choose a topic with a vast scope - you risk struggling to research it correctly
10 Good Coursework Topics
- Non-traditional Forms of Poetry with TC Tolbert
- Documentary Foundations: Usage of Oral Histories with Beth Alvarado
- Traditional Forms of Poetry
- Hermit Crabs: Type of Fiction
- Writing the Autobiographical Poem
- Creative Non-Fiction on the Examples of New Journalists
- Authors without Borders
- Writing the Sticky Stuff
- Socially Engaged Literary Arts
- Common Vocabulary
Research & Data Collection
Research is an integral part of coursework. Have you written research papers before? If yes, you will find it easier to select proper primary & secondary sources and gather the necessary information (evidence to support the main point - thesis). Depending on the required paper format, cite & reference the following sources:
- Books & e-Books
Base the project on a specific hypothesis. The research must start with minimum one hypothesis. The research stage for some topics may consist of visiting websites to collect information. Leave another time for collecting the data as it is the heart of the research. Three methods of data collection are known:
- Direct personal investigation : The one an author does individually (using literature and findings from previous studies);
- Interview/Questionnaire : The researcher should gather the data from the respondents asking questions regarding required data;
- Discussion with community leaders : Community leaders are approached to fetch information for the necessary data.
In case a student works on a scientific experiment, they should pay attention to planning the analysis with the help of rigorous scientific methods (keeping in mind the Health & Safety precautions you take). Review background information and theories. Take notes to express what you expect to occur to compare & contrast it to what happened in real life. In the write-up stage, one has to evaluate and present the findings.

Writing a Coursework Outline
The writing process follows the research. Do not start it without preparing an action plan and scheduling the work - a paper pin for English coursework is based on an extended essay . An outline will look different for the science coursework projects. The goal of creating a plan is to prevent a writer from being disorganized and waffling.

Let us explain coursework outline on the specific example - a project on the global pursuit of lower costs and the role of human rights.
Start with the brief introduction explaining why it might be a topic of interest for many people. Mention those vast corporations like Wal-Mart abuse human rights by choosing and using child labor in the factories.
Provide an overview of the problem . Define human rights and costs. Pick the definitions from the official dictionaries and cite them properly when inserting in the text. Try to explain the terms in your own words.
Develop a body of the coursework , start with the case for & against ethical business practices. Using evidence and examples, list the arguments supporting ethical business practices and another side of the coin. Include a business case for ethical practices after the opening body paragraph.
Move to discussing ethical responsibilities ; explain why business organizations should care about the ethical aspects of their activities. After three sections of the body, one can conclude the paper. It can be a good idea to share a fact or statistics stressing the importance of research problem in the essay conclusion. End up with the reference list that may look this way:
- Klein N (2000) No Logo (Flamingo, London)
- Marcousé I, Gillespie A, Martin B, Surridge M and Wall N (2003) Business Studies 2e (Hodder Arnold, Oxon)
- Royal Dutch Shell (2006) 4th Quarter Financial Report at (site example)

Additional Elements
Supporting materials and pictures are a must! The sciences & geography projects require tables, charts, graphs, and other types of images to illustrate the complicated topic. Not only should you add the pictures - it is essential to interpret and reference each of them. A separate part of the coursework where the student list and explains every visual element is Appendix , and it is an optional part. The presence of appendix increases the chances to earn an A+.
How to Write an Introduction for Coursework?
Most of the students underestimate the role of introduction & conclusion when it comes to writing an essay. An eye-catchy introduction is a key to success. The primary purposes of a coursework introduction are:
- To grab the reader’s attention
- To introduce the topic
- To explain the research importance
- To come up with a compelling thesis statement
The opening paragraph shows the depth of the writer’s acquaintance with the topic. Look at the expert tips below. They will help to learn how to write a coursework introduction to make the tutor want to read your entire paper.
What Is an Introduction?
The introduction of GCSE coursework is the opening paragraph that aims to interpret the central questions and purposes of the entire paper. It should have several elements to be effective. Those are:
- A hook sentence
- Background information
- Problem significance
- Solid thesis statement
Advice from our Experienced Writer
How to write an introduction to coursework? The quality of this part predetermines paper’s success. Look at some common mistakes writers do while working on the coursework introduction - try to prevent them!
Ignoring the prompt. Many students tend to neglect the tutor’s instructions. It is critical to read the prompt several times, highlight the main points, research question, rules, and grading rubric details.
Missing a plan. The prompt does not always say to develop a coursework outline. Without a plan for every separate section, it is impossible to write a flawless piece step-by-step. No matter whether you have to write a term paper, research paper, dissertation, or C3 coursework, get ready with the detailed plan. Once you understand how to write an introduction, it will be easier to develop the rest of the paper.
For those who need a helping hand in ensuring their work meets all the standards and deadlines, don't hesitate to buy coursework from trusted professionals.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
[ kawrs -wurk , kohrs - ]
- the work required of a student in a particular course of study; classroom work .
- curricular studies or academic work .
/ ˈkɔːsˌwɜːk /
- written or oral work completed by a student within a given period, which is assessed as an integral part of an educational course
Discover More
Word history and origins.
Origin of coursework 1
Most Popular
10 days ago
How to Write a Hook
How to do footnotes, how to write a 5 paragraph essay, how to write an opinion essay, how to write a synthesis essay, coursework writing tips.

There are elements of coursework that resemble or are constructed to run along the lines of laboratory work, other kinds of experimental work such as polls, surveys, and other observational studies, or can include scientific research in subjects such as the sciences, where it is difficult to prove the coverage of material through exams.
Steps to Carry out Successful Coursework
- Carefully select a topic and decide on the goal of your coursework. Make sure you understand all the requirements of your coursework, as well as the topic itself. When choosing your topic, try adhering to the rule of the golden middle: choose a topic that is not too hackneyed (because writing coursework on the same topic everyone does is pointless), but which is also not too specialized and under-researched (because you will need sources, and it is better that you are able to find them easily). Narrow the topic down, if it is possible—make sure there is only one way to understand it, and that it articulates your subject in a clear way.
- Consult with your teachers, especially with the teacher who is supervising your coursework. Ask his or her opinion on the topic you have chosen and for some possible advice on how to narrow or improve it. Teachers may give you a hint on whether your topic is promising and perspective, where to start your research from, what difficulties you may encounter, and so on.
- After you have decided on the topic and your goal, create an approximate plan of your coursework’s structure. Different colleges and universities may have different requirements for coursework structure and contents, so you should figure it out before you begin the process of planning. It is not final yet, and later you will correct it, but at this point you need this plan to have a point to start from.
- Decide on research methods. Depending on your topic, methods may include experiments, observations, polls, comparisons, analysis, and so on, along with standard methods such as studying resources on the subject. Check these methods with your supervising teacher.
- Figure out where you can find all the needed information, gather the equipment necessary for your research methods, and do the research. While researching, make sure to take notes. Also, check your coursework structure plan and make corrections, if needed. Your notes should be easy to read and navigate.
- Based on your structure plan and your research materials, create an outline of your coursework. Basically, an outline is a more detailed version of a structure plan. After you create it, craft the first draft of your coursework.
- Keep working on your draft unless you make it look like a final copy. Consult with your supervising teacher as often as possible.
- Before submitting your coursework, make sure to proofread and edit it. Also, you should check all the data in it for accuracy, consistency, and credibility.
Topic Selection
Proper topic selection accounts for a large portion of your academic coursework—therefore it is important to make a reasonable and balanced choice. There are several ways to pick a suitable topic. Sometimes a consultation with a tutor may help you narrow down your subject to a certain topic. However, it might happen that you will need to decide on your own. To do so, move from universals to particulars. Brainstorming and mind-mapping techniques will help you.
Define the field for your future research; say it is American literature—then decide on a school: romanticism, realism, decadency, Beat, and so on. For example, you can choose Beat literature, and one of its brightest representatives, Jack Kerouac. Keep on narrowing the subject down: choose one of his novels—let it be “On the Road.” Now, think over problems, characters, events, and relationships described in the novel. After you have finished with all the procedures as previously stated, your topic for the coursework on American literature might sound like, “The Personality of Dean Moriarty as Freedom Personified by Jack Kerouac.”
And finally, remember, that successful academic coursework can be written only successfully if the topic is of interest to you.
Key Points to Consider
- The research phase is crucial for any coursework. Anytime you feel like making a shortcut or try to skip this phase and get down to writing, do not do this. On the contrary, you should aim to gather as much data from different resources as you can; this includes books, journals, websites, results of experiments, and so on. Therefore, you should dedicate about 60% of your time to researching.
- The content of your coursework should be based on accurate, relevant, and credible information. All the data you use in your coursework should be aimed at proving your research hypothesis, or thesis statement, and the paper itself should be a deep analysis of the topic.
- Usually, students procrastinate as long as possible, and rush into writing coursework in the last week or two before the due date. Perhaps, this is one of the reasons why there are usually so many mistakes and typos in coursework. Sometimes, typos and inattentiveness can become reasons for you completely negating the whole argument of your paper. So, to be on the safe side, make sure to reread your paper before you submit it; also, use MS Word, Google Docs, or other similar text-processing software to be able to notice mistakes easier.
- Make sure your coursework is easy to read and to comprehend. Use subheadings: they are a good way to mark semantic transitions within the text. They also break the text into smaller chunks, making it more reader-friendly. Use transition words to clearly show how the ideas, arguments, and evidence in your work are connected. Mind the length and structure of your sentences; long, complicated sentences are harder to understand, but short sentences do not let you fully convey your thought. Also, you should make sure the words you are using are precise and accurate, and that you fully understand their meaning.
Dos and Don’ts
Common mistakes.
- Not allocating enough time for research. Although this is the most crucial step of writing coursework, many students tend to try to shortcut it and get down directly to writing.
- Not proofreading or editing enough. This is important, because sometimes the cost for making a mistake is too high. Overlook a simple “not” in the concluding and summarizing part of your coursework, and your entire argumentation may be denied or ruined.
- Submitting your coursework exactly on the due date. This way, students often deprive themselves of time they could use to double-check the paper and correct the mistakes.
- Missed citations, improper formatting, gullible statements, excessive simplification (or, on the contrary, complication) of the text.
- Not making the text reader-friendly.
Now that you have acquainted yourself with the basic academic coursework writing tips and rules, you can check out our academic coursework samples to link theory with practice.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from How to Write an Academic Assignment

Samples for Coursework Writing Tips
Embedded marketing as a powerful commercial tool essay sample, example, xenophobia and islamophobia among european right-wing populist parties essay sample, example, aggression in the classroom essay sample, example.
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Academic Coursework Writing Guide
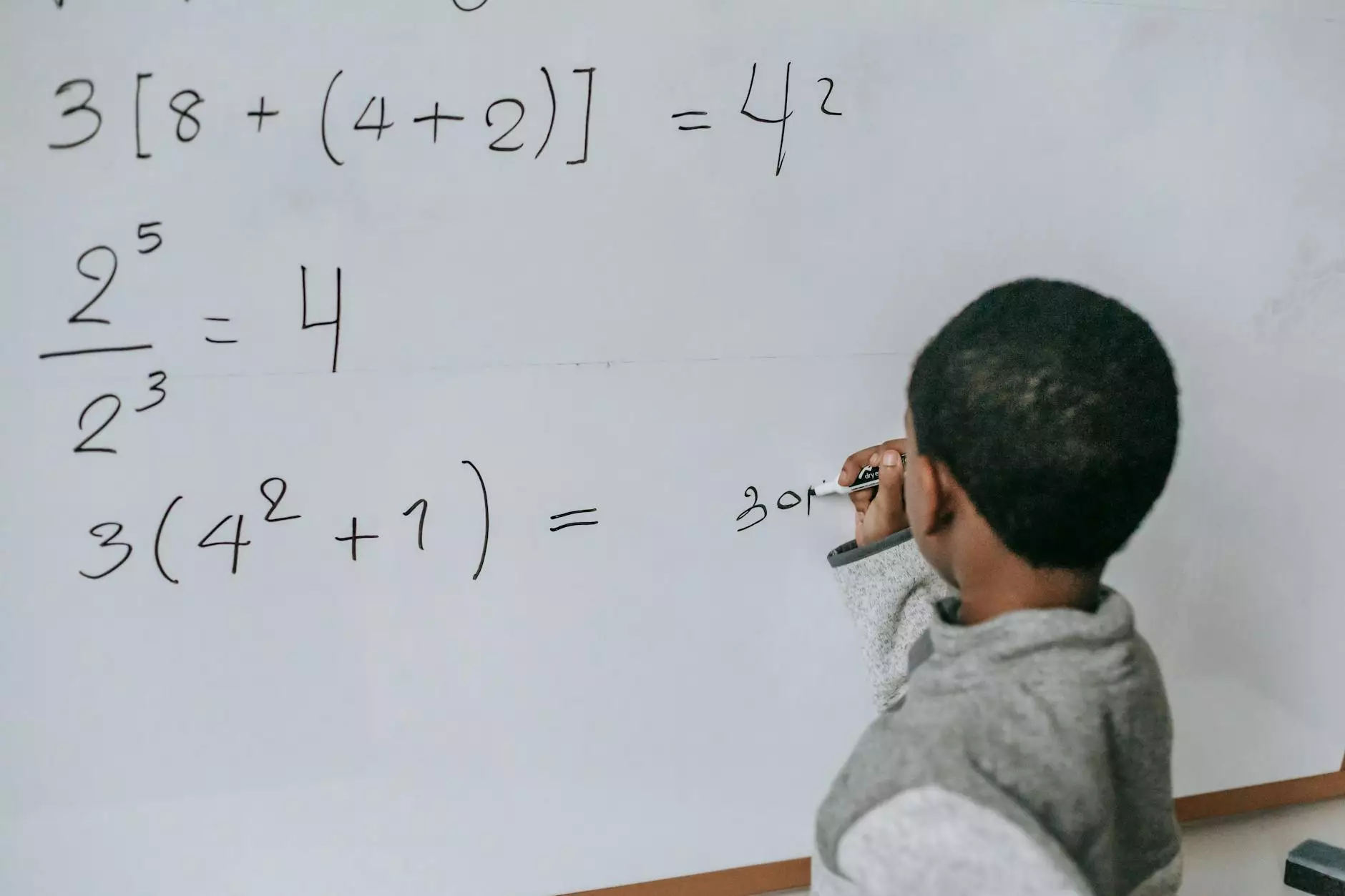
Introduction
Welcome to The Knowledge Nest's Academic Coursework Writing Guide! In this comprehensive guide, we will provide you with invaluable insights, expert tips, and effective strategies to help you excel in your academic coursework. Whether you are a high school student, college student, or pursuing advanced studies, mastering the art of coursework writing is essential for your success.
Understanding Academic Coursework
Academic coursework refers to the assignments and projects assigned to students as part of their educational curriculum. It presents an opportunity for students to demonstrate their understanding of the subject matter, apply critical thinking skills, and showcase their research capabilities. Coursework typically includes essays, research papers, laboratory reports, case studies, and more.
Importance of Well-Written Coursework
Well-written coursework plays a crucial role in achieving academic excellence. It not only contributes to your overall grades but also helps you develop essential skills such as research, analysis, and writing. Additionally, it serves as a reflection of your knowledge and commitment to your academic pursuits.
Effective Coursework Writing Strategies
1. analyze the assignment.
Before you begin writing your coursework, carefully read and analyze the assignment guidelines. Understand the requirements, topic, and any specific instructions given by your instructor. This will ensure that you stay focused and tailor your work accordingly.
2. Plan and Organize
Effective planning and organization are essential for successful coursework completion. Create a timeline for each task, allocate sufficient time for research, writing, and revision. Divide your coursework into manageable sections, allowing yourself ample time to delve into the subject matter and produce high-quality work.
3. Conduct Thorough Research
Research is a fundamental aspect of coursework writing. Gather relevant and reliable sources such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites. Take comprehensive notes, ensuring you properly attribute all sources used. This will strengthen the credibility of your coursework and showcase your ability to engage with scholarly material.
4. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement forms the foundation of your coursework. It encapsulates the main argument or perspective you will present in your work. Your thesis statement should be clear, concise, and relevant to the topic at hand. It will guide your research and help you maintain a coherent flow throughout your coursework.
5. Structure Your Coursework
Organize your coursework in a logical manner. Divide it into sections such as introduction, main body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each section should have a clear purpose and flow seamlessly into the next. Use appropriate headings and subheadings to enhance readability and highlight key arguments or concepts.
6. Write Clearly and Concisely
Effective communication is essential in coursework writing. Use clear and concise language to express your ideas. Avoid excessive use of complex vocabulary or jargon that may confuse readers. Support your arguments with evidence and examples, ensuring your reasoning is logical and well-articulated.
7. Edit and Proofread
Never underestimate the importance of editing and proofreading your coursework. Review your work for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inconsistencies. Ensure your referencing and citations adhere to the required formatting style (e.g., APA, MLA). Take the time to polish your work and make necessary revisions before submission.
Mastering the art of academic coursework writing is a valuable skill that will benefit you throughout your educational journey. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can enhance your coursework writing abilities, ultimately leading to improved academic performance. Remember, coursework is not just an assignment, but an opportunity to showcase your intellectual prowess and passion for learning.
Unlock Your Potential with The Knowledge Nest
The Knowledge Nest is your trusted partner in educational success. We strive to provide students with the tools, resources, and guidance they need to excel in their coursework. Explore our website to discover a wealth of information on various subjects, study tips, and expert advice to enhance your academic journey. Empower yourself with knowledge and unlock your full potential with The Knowledge Nest.

Chinese Homework Help - Complex Tasks Made Easy

Maths Coursework Help: the Road to Understanding - Studybay

Term Paper Writing Service - Studybay

Getting Philosophy Homework Help With Experts - Studybay

Perfecting a Health and Social Care Personal Statement

10 Tips For Balancing Work and School - Studybay

How to Answer Essay Questions on an Exam
Fast Food Cause And Effect Essay: How To Approach Writing

How to Find Someone for Coding Help Online

What Is Lidl's Organisational Structure
We have to use cookies to be sure that our website functions properly. Click here for more information about our Cookie Policy and then tap Allow to continue your work
Top Special Offer! Check discount here
Get 13% off your first order - use TopStart13 discount code now!
- Admission Essay Writing
- Essay Writers for Hire
- Essays for Sale
- Pay for Research Paper
- Research Paper Writing
- Write My Dissertation
- Write Papers for Money
- Essay Editing
- Research Paper Editing
- Buy Assignments
- How it works
- Conclusion Generator
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Testimonials
- Tips and Hacks
How to Write a Coursework ✔ Tips by Academic Experts
Writing coursework is a unique task, but it’s also extremely common. Students must work on this assignment every year, but they inevitably face problems because coursework simultaneously functions as an essay, dissertation, and research paper. It borrows elements from different academic tasks and helps determine your final grade, so it’s important to do everything correctly. Because of academic pressure, it might take months to get everything together, and you’ll have to apply much effort to succeed. But don’t worry; our thoughtful guide will show you how to deal with it. You can buy coursework online if your time is already short, but if you’re ready for intense work, study the tips we developed!

Coursework Definition and Its Types
What is a coursework? It’s an academic task involving written and practical elements that seek to demonstrate a student’s knowledge of the subject. In every case, it comprises extensive research, and the coursework grade will play a decisive role in your final performance assessment. The point of this assignment lies in encouraging students’ critical thinking and boosting their research skills.
After fulfilling every part of the task, students gain invaluable experience that is bound to facilitate their future studies. Depending on their subject, they might face coursework of different types. Writing, practical study, and experiment are the three most common options. We’ll discuss them in more depth below so that you know what you should expect.
Explaining Three Main Types of Coursework
Writing a coursework means creating something between an essay and a dissertation. It’s the simplest and the most common coursework type that can take a variety of shapes across different disciplines. For instance, if someone is studying Literature, their professor might give them a list of questions that they’ll need to answer in a written format, explaining what made them think this way and justifying their position with arguments. They might also give you a specific topic that you’ll need to explore. Learning how to write an introduction and performing a literature review would be essential here: you’ll rely on other sources and your personal interpretations to create a complete picture of your subject. Your faculty will expect to see logical links between ideas, a documented research base consisting of credible sources, as well as your thoughtful observations.
What is academic coursework practical study? This is a more complex type of work. Imagine that we study History. Our topic entails establishing how the portrayal of women evolved in China. We’ll have to do theoretical research consulting other relevant sources, but the focus will be on practical elements. Choosing forms of art depicting women through the ages and finding and selecting excerpts from ancient literature about them would form the basis of our knowledge and insights.
So, when working on your coursework, do practical research that comes from you and your unique effort. This is similar to the experiment type: the only difference is that with the latter, you’ll have to focus on a practical part in particular. Choosing your area of research is vital: you need a hypothesis, a focus group you could use as a sample, and a special research design. You could interview people, send questionnaires to them, observe them, etc. In both tasks, your professor will value your original insights and the thoroughness of your research.
Facts that Might Earn You an Automatic Falling Grade
Another crucial element students must know is the examples of coursework violations. Everyone wants to avoid it for obvious reasons, but not everyone succeeds. Plagiarism is the first and worst issue. It may ruin everything you’ve worked for. Some faculties use softer approaches: they have a threshold of about 10% plagiarism. Their coursework will be deemed original if their students don’t deviate from this norm. But other professors might fail you even for one uncited claim. That is why you must use plagiarism detectors before submitting your work anywhere. Also, pay attention to claims people don’t know about and which you use in your coursework. For example, if you claim that women wore only dresses in China in 1200, you’ll need to point out a source from which you got this info. Ask your parents or friends if they know this information: if the answer is no, make a citation.
Word count within your coursework essay is also important. If your professor told everyone to write 2000 words, yet you wrote 1500, they might fail you either entirely or partly. Take your time. Writing more isn’t a good idea as well. Sure, it might win you more points for effort, but some professors won’t be happy with having extra work, and your grade will suffer. Select a good topic that corresponds to your subject and academic level. To be safe, get approval from your supervisor in advance because there is nothing worse than wasting months on work that will bring you nothing but failure. If you worry too much or the assignment is too important, and you think you lack time or knowledge, know that TopEssayWriting is aware of all these nuances and is willing to take care of it. Get the best essay writers for hire , and they’ll craft and perfect your coursework by the day you need it. Unlike students, they have extensive experience, and they’ll guarantee solid original research, appropriate word count and topic, as well as perfect formatting.
A Plan of Writing Coursework for Students
You know coursework definition already; you have heard about its types and nuances they entail. But how to write this kind of project? We’re going to list all relevant steps and describe them. First of all, take a look at the image below. It features a summary of each step. You can save and use it whenever you need it; share it with friends who might struggle with their coursework, too.

- Choosing a topic: look for inspiring ideas online, consider your sphere of interest, or consult your professor to pick the best topic.
- Research and collecting data: use Google Scholar or any other academic database to locate relevant academic articles, books, or websites. They must be credible.
- Organization: Analyze and categorize your findings.
- Developing outline: create an outline listing the major topics you plan on working within each of your paragraphs.
- Making the first draft: write an initial version of your paper by relying on your draft and briefly explore all ideas from it.
- Editing coursework: edit your coursework and flesh out your points until everything looks perfect.
But now, let’s review each stage of writing coursework thoroughly.
Step 1: Knowing What Topic to Choose
Selecting a strong topic is one of the guarantees of success. If you like it, if it’s relevant and has a lot of materials dedicated to it, you’ll enjoy doing research, and your professor will likely enjoy reading it. Some tips for making a good final choice: consult your supervisor if you have a trust-based relationship and know they’ll welcome it. If not, try online lists. There are plenty of them — in fact, we’ll offer you three potential topics right here! Just ensure your topic is broad enough to warrant lengthy research and avoid trite ideas. No one wants to hear about capital punishment, abortions, or marijuana because these topics are incredibly overused. Check these examples out.
1) Effect of Crowd Behavior on Victim Blaming
This example of coursework topic is interesting because most people can relate to it, plus it offers a wide territory for research. Everyone was a victim once in some minor or major way. Did you feel like you were blamed for something that happened to you? Or perhaps you felt inclined to blame someone when learning about what they experienced? The area of crowd behavior is also fascinating. Twenty people can be decent and law-abiding, but they can do horrifying things when put together. Why is that? Explore both topics, combine them using logical links, and enjoy many articles that could guide you.
2) Should There Be Any Regulations Concerning Fictional Content?
This coursework example is intriguing because it concerns a relevant topic. There is an increasing number of people who think that watching TV shows about murders or unequal relationships might automatically make viewers murderers and abusers. Take one or both sides of the issue; research them, their history, and examples of bans on fiction in the past; you could also choose any perspective from which to view it, be it legal, ethical, philosophical, or even religious.
3) What Strategies Can Help a Small Country Win a War against a Large Country
The value of this topic is its relevance. The war in Ukraine demonstrates how a large empire cannot defeat a small country. Ukraine is far from winning, so explore the current situation and past examples involving similar circumstances. It could be interesting and educational both.
Step 2: Starting Your Research
Doing research is a crucial step in coursework writing. Once students pick a topic, they must find sources that will help them explore their subject and make strong points. We suggest using both primary and secondary sources. The former include raw materials like interviews, memos, or reports; the latter are typical research articles with second-hand information. You can easily find a big collection of diverse sources on Google Scholar or in your college library. Just ensure that your chosen source is credible. If it’s a blog by an enthusiast, stay away from it. Wiki is a big no since any person can edit it. Check if the article has DOI, use websites with .edu or .gov, and rely on books published by academic houses. Remember that the fresher a source is, the more its relevance increases. Some professors insist students shouldn’t use articles older than 3 or 5 years.
Step 3: Organization
Take notes as you research or make a table with sources you’ll use, might use, or won’t use. It’ll help keep your research process organized. This organization is crucial as it allows you to categorize your findings, making it easier to reference them later. By sorting the information into different themes or arguments, you can identify areas where you have enough data and areas where further research might be needed. This step also helps in avoiding redundancy and ensuring that all your sources are relevant and contribute meaningfully to your argument. An organized approach to your research not only streamlines the writing process but also ensures a well-rounded and thorough exploration of your topic.
Step 4: Working on an Outline
What is coursework outline? It’s a short summary of key points that will be present in your essay. First, deal with technical elements: make a timeline of when you’ll be doing what. If you have four months to complete your coursework, dedicate month 1 to research, month 2 to outlines and drafts, month 3 to writing, and month 4 to final polishing. Having a schedule always helps stay on track. You’ll also need to structure your outline properly. Here is a potential overview of its structure:
- Introduction: include your thesis and sketch your topic’s background here.
- Literature Review: Summarize the current state of research on your topic.
- Methodology: describe how you collected data and what samples you used.
- Main Body: List the main ideas or arguments—present data, quotes, or examples to support your points.
- Analysis & Discussion: Interpret and analyze the results of your research.
- Conclusion: make recommendations for future research
- References: List all sources cited in your coursework in the appropriate format.
- Appendices: Include any additional material like charts, graphs, or raw data.

Adding just a few lines would be sufficient here. This outline will come in handy more often than you think: it will remind you whenever you forget what you want to do.
Take nuances of your formatting style into consideration, too. APA, for example, requires a title page and an abstract. This is how to reference a claim: “King Valluar died in 1444, leaving a record number of 214 children behind (Foster, 2022).” Add a page number when using a direct quote like this: (Foster, 2022, p. 13).
Our suggestion: stay strictly on topic. Understand its final point, break it into major points, and make every section in an outline concise and clear.
Don’t forget about additional elements — preparing them at this stage could boost your productivity later. Some topics require visual illustrations or the presence of tables. Include them. Cite them, make sure they are readable and have good quality; if you’re making them yourself, double-check them repeatedly.
Step 5: Creating the Draft
Start your academic coursework by consulting your outline. Introduction is particularly important as it’s the first section your readers see. Make it engaging by starting with a hook, an intriguing claim guaranteed to secure people’s interest. It could be a controversial claim, a powerful statement, statistics, etc.
Introduce the topic background and explain what you’re trying to achieve by writing this coursework. After this, it’ll be simpler to move toward the next sections. Don’t feel compelled to develop every point to perfection: brushing against the most important aspects would be enough for now. Keep your structure clean; don’t make paragraphs longer than 200 words. Cite sources in each paragraph at least once, preferably more often.
Step 6: Starting Editing Rounds
Read your draft. Identify its weak spots and correct them. It is time to do it if you didn’t develop your points properly. Keep expanding paragraphs until you reach the required word count, and everything feels complete. Cut the pieces you consider less relevant if the word count is too long.
With this done, check your coursework again for grammar, formatting, and style. Eliminate typos, catch instances of informal language usage (contractions, phrasal verbs, slang, etc.), and compare your formatting to a template. Remember that you could edit paper online with professionals. Our editing service is affordable and accurate, and our experts could give you content and/or proofreading assistance, combing through your text and removing every problem in it.
Exclusive Tips Based on Our Writers’ Personal Experience
As you probably figured out by now, our writers have seen numerous coursework examples in their work. Their years-long experience speaks for itself. We surveyed them, and they identified the three most widespread mistakes students made in their coursework and gave three pieces of advice.
- Failure to follow instructions. It seems like such an obvious thing, but no, multiple students keep treating their instructions inattentively. If professors asked them to explore 5 points, many explored 3 or 4; if they asked to write 3000 words, some wrote much less or much more than that. Finally, some students don’t understand their prompt, research the wrong topic, or not performing the kind of study they were asked to do.
- Lack of coherence. Only some people are good writers. Students often need to be more balanced between ideas erratically, skipping over connections or not elaborating on their point.
- Technical issues. Grammar or formatting mistakes, typos, or informal words are parasites that often slip into students’ texts without them noticing it.
- Re-read your prompt several times. Even if you’re confident you understood everything correctly, better be safe than sorry. Re-read instructions slowly, lingering on each element.
- Ask for help if needed. It doesn’t matter what’s wrong: if you cannot finish your coursework but you want plagiarism free papers of the highest quality, consult experts. They’ll help you.
- Don’t worry about seemingly losing time. Some students think that writing outlines or drafts is redundant. Yes, they might take time, but you’ll save it because you’ll spend far less time on actual writing. Create a solid preparatory base for yourself.
Create Well-Crafted Coursework and Secure Your Success
You know how to define coursework, what types exist, how to protect yourself from a bad grade, and which steps to follow to write a great project. Apply this knowledge in your studies! Start working on your coursework step by step, creating section after section and polishing each until even the strictest professor feels impressed. If something is amiss, contact TopEssayWriting ASAP and formulate your request. We are here every day and each night, serving students and connecting them with the best writers. Order personalized coursework examples, ask us to write a chapter or the entire work, demand editing or grading. Our services are always open to you. Get even more knowledge and succeed in your writing!
Related Blog Posts
Coursework writing poses an endless number of problems to students. It's time-consuming and exhausting. Rely on this guide and gain a deep understanding of this task!
There are many inspiring persuasive essay topics out there, and we tried to gather many of them in one place. Choose the best one for your paper.
- Terms and Conditions
- Money Back Guarantee
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
Customer support
- Buy Argumentative Essay
- Buy Coursework
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Reaction Paper
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy College Essays
- Buy Narrative Essay
- Buy Thesis Paper
- Expository Essay Writing
- Law Essay Writing
- Dissertation Writing
- APA Paper Writing
- MBA Essay Writing
- Nursing Paper Writing
- Graduate Essay
- Plagiarism Free Essays
- Research Paper for Sale
- Write My Assignment
- Write My Research Paper
- Write My Thesis
- Write My College Essay
- Coursework Writing Service
- History Essay Writing Service
- Business Essay Writing Service
- Psychology Essay Writing Service
- Book Review Writing Service
- Literature Review Writing Service
- Finance Essay Writing Service
- Persuasive Essay Writing Service
- Economics Essay Writing Service
- Descriptive Essay Writing Service
- Analytical Essay Writing Service


What is Coursework?
Table of Contents

Definition and Meaning
So what is coursework? Coursework is an integral part of the educational process, which refers to written or practical tasks that students perform during educational courses. These assignments are typically evaluated and contribute to the final grade or mark. The coursework definition, especially the term “curriculum-mandated” signifies that instructors are required to assign coursework within certain guidelines. This aspect of academic work is crucial as it extends learning beyond the traditional classroom setting.

While some coursework may involve practical tasks conducted within the classroom, a significant portion is often completed independently by students, such as in their homes or dormitories. Notably, certain colleges in Texas are adopting policies that mandate a minimum of 20% of writing coursework to be completed in class, under the supervision of educators. This approach ensures the authenticity of students’ work and provides an opportunity for direct observation of their writing skills.
Additionally, it’s common for students to access previously submitted coursework online, serving as a resource for their own assignments. However, when utilizing such materials, it is imperative to thoroughly rewrite and adapt the content to maintain originality and avoid plagiarism.
Types and Examples of Coursework
The many faces of coursework.
So, what is coursework? Coursework isn’t a one-size-fits-all kind of deal. It morphs to fit the subject, the course, and the learning objectives. Here’s a snapshot:
- Essays and Written Assignments. From reflective pieces to extensive research papers, these are staples in humanities and social sciences.
- Lab Reports and Scientific Research. Science and engineering students often get hands-on with experiments, followed by detailed reporting.
- Art and Design Portfolios. For the creatives, it’s about showcasing their artistic journey through portfolios.
- Group Projects and Presentations. These emphasize collaboration and communication skills, common in business and management courses.
- Fieldwork and Case Studies. Especially in disciplines like anthropology or marketing, where real-world application is key.
Examples in Different Fields
- Biology Coursework. Might involve a lab-based investigation into a specific biological phenomenon.
- Literature Coursework. Could be an analysis of a particular literary work or a comparative study of multiple pieces.
- Computer Science Coursework. Often involves coding projects or developing software solutions.
Importance and Objectives
More than just grades.
What is coursework? Coursework is about more than chasing an ‘A’. It’s an integral part of the learning process. Through coursework, you:
- Develop Critical Skills. Like research, analysis, and problem-solving.
- Apply Theoretical Knowledge. It’s your chance to use what you’ve learned in a practical context.
- Prepare for the Future. Whether it’s further academic pursuits or the professional world, coursework lays the groundwork.
Educational Objectives
Graduate coursework, in particular, is designed to deepen expertise in a field. It’s less about memorizing facts and more about developing a sophisticated understanding of complex concepts.
Challenges and Strategies
Common roadblocks.
- Time Management: Juggling multiple assignments can be overwhelming.
- Understanding Requirements: Sometimes, assignment briefs are as clear as mud.
- Maintaining Academic Integrity: The line between inspiration and plagiarism can get blurry.
Navigating the Coursework Maze
- Start Early: Procrastination is your enemy. Begin as soon as you get the assignment.
- Seek Clarification: If you’re not sure, ask. Better safe than sorry.
- Use Resources Wisely: Libraries, online databases, and even study groups can be goldmines.
Helpful Sources
- Cambridge Dictionary
- Merriam-Webster
- Can you attend two colleges at once ?
Final Thoughts
In a nutshell, what is coursework? Coursework is an indispensable part of the academic journey. It’s where theory meets practice, where skills are honed, and knowledge is deepened. As education continues to evolve with technology and changing societal needs, so does coursework. It adapts, transforms, and continues to play a crucial role in shaping competent, well-rounded individuals ready to take on the world. So, embrace your coursework – it’s not just a stepping stone to a grade, but a pathway to learning, growth, and success.
How to Write a Coursework: Complete Guide

In all academic writing assignments, coursework is the most important. It reveals students` writing skills. This type of academic writing is used to assess a student’s understanding of a subject. Coursework combines all the requirements needed in all types of academic writing. This means that a perfect coursework paper requires more than just decent and basic writing skills. However, this has been made easier by our team of experts who have combined their experience and expertise to create a guide on how to write an excellent coursework paper and ultimately improve our writing.
Coursework is a type of academic writing that can show the full capabilities of a student. It offers a different environment from an exam room while giving a student a chance to excel. The coursework assignment is an opportunity if you look at it in a literal way. If you cannot perform well in your exams, it can be a lifesaver, but it can be as challenging as an exam.
If that is not enough, our experts can also craft the best coursework paper for you to reinvent your writing ultimately. They have passed through special vetting and training to allow them to provide the highest quality of work for customers. Our company’s primary goal is not to make money but to give the top quality services to students all across the world at affordable prices.
Table of Contents
Coursework Simplified – What is Coursework?
Coursework papers can be described as an extension of a school project or essay. The role of coursework varies from different disciplines that a student is majoring in. When writing your coursework paper, conducting relevant research plays a very vital role. The emphasis required is independent for various topics. Doing the research is like an investigation, and every bit of detail matters largely. Act like a detective when searching, analyzing, and investigating sources of information for your topic.
How to Write a Good Coursework
We strongly recommend you to begin your coursework as soon as you are given such a task. Brilliant coursework needs a lot of time, so you have to start as early as possible. Always stay calm so that you cannot mess up your performance due to pressure. Do not rush to complete your assignment on one sitting. Divide your workload precisely and work slowly from day to day. This way, you can have manageable work to do every day, enabling you to pay great attention to your assignment.
Brilliant Writing Tips – How to Start a Coursework
The most important and vital part of coursework writing is research. Always make sure all the sources of information you use are credible. Various sources like material written by authentic writers, visiting the libraries, surfing the internet, or written class notes can be used as great sources.
Try to be organized and make an efficient timetable before you start working on your assignments. Follow your set timetable and avoid rushing your work. Never work on your coursework when your deadline is approaching. In case of emergencies, preset a completion date before you are required to submit your work.
The Perfect Way on How to Structure a Coursework
If you want to excel in coursework writing, you need to have a good structure. This means:
- Structuring your coursework is essential for all academic writing for a reason. A structure allows a writer to thoroughly layout your assignments and plans on how your final paper will look.
- A coursework structure is created after finishing the studying of your research sources. When doing this, you can loom at good coursework written by other students.
- Be careful not to have plagiarism because it is a huge mistake that can cause you to ultimately fail your coursework paper.
- Create a structure that can provide you with reliable follow up when writing your assignment.
A Proven and Brilliant Coursework Introduction
The introduction is what draws in a reader. It should be enticing but short. Your beginning statement should always draw in your reader. This will make the argument or information interesting, leaving your reader asking for more. Once you have a great beginning and all the context needed, countercheck your paper to make sure it is consistent and coherent. Don’t be discouraged if you write your introduction many times, it means you have a grasp of the right thing to do.
A Great Coursework Body
The body is where a writer states the main argument and fully develops it. Each paragraph should contain a key point clearly supporting an argument. The follow up should support all key points and be backed up with substantial evidence. The body of the essay is the building block for the coursework assignment. The body paragraph will be quite readable if it doesn’t contain large chunks of text. Simple paragraphs of 4-5 lines are quite enough.
A Moving Coursework Conclusion
A conclusion plays an important role in paper writing. It helps to reinforce your argument or main idea of your paper. Our experts insist that you have to restate the thesis statement and main idea of the coursework. Without a good conclusion, your essay will look blunt. This will make your assignment seem incomplete.
https://www.dictionary.com/browse/coursework
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coursework
All this said, not everyone can put together with outstanding coursework. That’s why our experts have dedicated their valuable time and effort to writing brilliant coursework.
Our ‘ write my coursework for me ‘ service guarantee high-quality coursework papers that no writing service can top. Why hustle any longer with endless coursework assignments. Use our cheap coursework writing service to get outstanding academic papers. Use your time for other things while our writers toil. Order a paper now!

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Guidelines and steps for writing a coursework | Tips for good writing
What is a coursework and why to write a coursework.
A coursework is a written or practical work done by student in form of thesis, dissertation, project or paper as a part of course. This is often an essential requirement for being awarded a degree and counts towards successful completion of the course. A coursework is assessed by class instructors or by other teachers in the school. Many students cannot clearly define what is a coursework. In a nutshell, at the “A” and GSCE level , a coursework is written in the form of projects or essays. There are few guidelines and good practices which should be followed while writing a coursework. Perfect examples of a coursework include extended essay, field studies, practical activities, design studies and internal assessment test set. Conversely, each coursework have differing objectives from one course unit to another. In addition, a coursework may incorporate work for which the experiments, topics, themes or parameters of a project or essay have been designed by the teacher, or specified in the syllabus, or selected by the students themselves. Therefore, a coursework is presented in a form of a research assignment meant to reflect the understanding of topics and concepts by the student. Students can handle their coursework either at school under the controlled conditions in class sessions, and/or as homework.

Coursework writing varies from one subject to another as the need differs for each subject. For example, an English coursework differs from a geography coursework. Whereas the former requires the student to present coursework in an essay format where a student has to select a title of their choice. Whereas the latter highly focuses on collecting, and examining, inferring and reporting data, answering a certain geographical question. For example, in English coursework, a student is often assigned to choice of themes or text excerpt to write on a format of their choice. One can either employ a comparison approach or the cause-effect method. Conversely, coursework in subjects, such as geography coursework, requires scholars to conduct investigations. For example, students can explore on the desert features, river formation or usage of social facilities such as halls, schools and hospital and report the findings.
Some rules & guidelines for writing a coursework
So how to start a coursework? Just like any other academic piece, there are some rules and guidelines that determine what makes a coursework good and exceptional. It is significant for scholars to consider all the following points for writing a coursework to score good grade and avoid having their paper disqualified:
- Students are not allowed to seek help from the instructors or from fellow students unless it is a group coursework or instructed. Though, an instructor is only permitted to deliver directions on how to handle a coursework paper as well as pointing out specific areas that are critically checked by examiners.
- Students should avoid plagiarism. It is a rule that is considered as a serious academic offense if committed. Under this rule, a student is expected to submit an original work written and not copied from other source. This is checked by using various softwares that checks for plagiarism. Therefore, students should make sure there work is their own words by signing a declaration asserting that it is your own piece of work. Buying coursework is also an offense if it is discovered.
- Also, a student has to confirm the word count on their paper to ensure it has the instructed word limits without the consideration of the appendices, references and footnotes.
- Students have to be keen and careful when they are selecting the topics to avoid writing on a wrong topic that is not covered in the coursework. A topic already covered should also be checked or discussed with concerned faculty before writing.
All these rules are constantly restated in coursework prompts and rubrics to ensure one does not derail and violate them when they are figuring out on how to start a coursework.

Deciding good topic for a coursework
The capability to choose a good topic to write on is a vital skill in coursework writing. All the work and efforts will revolve around the chosen topic. If given the liberty to choose, then the topic should be something you would love to write about.
- Sometimes instructors can assign you to handle a specific topic, but often, as a writer, you are required to develop or select a topic that interests you is the one you may enjoy writing about. For example, you may decide to settle on a topic from either an area you understood well in the syllabus or from an area in the course that you enjoyed.
- However, before deciding on your topic, you need to examine whether you can control, measure and change the topic by conducting a fair taste. It is advisable not to select topics that appear ambiguous or which have a wider scope as it might affect the developing of a precise thesis statement, as they make it difficult to reach the word limit as well as failing to satisfy the topic. Also, students are allowed to seek guidance and assistance on choosing suitable topic to write in a situation where you are not sure on what to write about. For example, you can check previous assignments done by other students to get idea about their approaches on particular topics.
Steps for writing a coursework
- Before writing a coursework, a student has to plan based on duration and the materials needed and as instructed in coursework tips. Concerning the deadline, a student must not wait until the last-minute for the paper to start writing. Last minute rush in completing a paper can cause students to make common grammar mistakes that will affect their final grade.
- Deadlines are normally indicated in all the coursework assignments and a student has to understand when the deadlines are due for the final assignments as well as time for submitting a first draft for comments from your teacher.
- Proper time planning will spare you plenty of time to make corrections based on teacher’s remarks, as well as creating time for final editing and proofreading.
- To achieve this, you have to set up your own deadlines that are far or within the actual deadline to ensure you complete your coursework writing in time.
- Research is about collecting significant and supporting literature from both primary and secondary sources. You will be required to collect data and know methods of data collection as a part of this step. Conducting surveys and preparing good questionnaires will be a much needed skill in many cases.

- The actual writing of your paper commences after gathering sufficient data that will do justice to the topic.
- Student has to write down the paper structure before writing. Though, the outline provided in the essay instructions where students are expected to follow.
- A standard essay format comprises of an introduction, body and conclusion. In particular, structure planning in important for big projects, because there is a likelihood of having disorganized and waffling writing since it entails a lot of information to convey that needs to be arranged. This has a significant impact on your data analysis and presentation.
- Consequently, one has to perfect their writing abilities to produce a high quality paper that bases around the standard essay format. For complex projects in science, you need to be more analytical and interpretive to get the accurate inferences of the data collected in your writing.
- In addition, you look for a quiet and conducive environment that is free from unnecessary distractions to earn the greatest concentration required for thinking and writing. Switching off TV and logging out from all social media accounts help in reducing external distractions.
Supporting Materials – deal breaker for writing a coursework
Supporting materials are defined as the evidencing materials that are included in the writing to reinforce the theories explained. For example table, graphs, charts, and images are mostly applicable and relevant in subjects such as geography and sciences. Supporting materials are written in the appendix part of a paper to avoid cluttering of information in the main part of the paper. For instance, the coursework focus is survey oriented, you could put the raw survey responses, survey templates, questionnaires, in an appendix and present the analysis and discussions in the main body of the coursework.
Finalizing Your Coursework
The steps on how to finish a coursework is easy as it necessitates one to edit their papers prior to the submission. Prior to the submission, students would have time to proffered and confirm features such as word count, word choice, grammar errors, spellings as well as the punctuation mistakes. It is advisable to carry out a manual proofreading as the modern spell checking and grammar checking software can overlook some common mistakes. Importantly, a student is required to include in-text citation according to the writing style used. A well-written coursework is thought-provoking, enjoyable for the reader and enhances the reader’s knowledge.
About The Author
Full Guide on How to Write a Coursework with Tips and Topics

Defining What is Coursework
Coursework writing guide, additional tips for coursework writing, useful coursework topics, final advice.
Picture this: it's a sunny day, and you're walking across your university campus, feeling energized and motivated. But as you look at your schedule, you notice the looming deadlines for your coursework assignments. Suddenly, your excitement turns into anxiety as you realize you're not quite sure what coursework even entails. Fear not, as we're here to help! In this paragraph, we'll define what is coursework and explore its various forms, so you can approach your assignments with confidence and clarity.
Coursework definition goes as a set of academic assignments, exercises, or projects that students are required to complete as part of their course requirements. It can take different forms, including essays, reports, presentations, research papers, lab reports, and other assignments.
Coursework aims to assess students' knowledge, understanding, and skills in a particular subject or field of study. Coursework assignments are usually completed outside of class time and are often graded by instructors to determine the student's level of achievement in the course.
Are you feeling overwhelmed by the prospect of writing coursework? You're not alone. Coursework assignments can be challenging, especially if you're unsure of what's expected of you. But we've got you. We've prepared a comprehensive guide to fulfill your concern for 'how to write my coursework' that provides tips, strategies, and step-by-step instructions to help you produce high-quality assignments.
Our guide covers everything from choosing a topic to conducting research, developing a thesis, and structuring your coursework effectively. Whether you're a seasoned writer or new to coursework assignments, our guide is designed to help you succeed. So, let's dive in and get started.
To further ease your academic journey, you can also explore the option to buy coursework , which offers a tailored solution to meet your specific needs and ensure you achieve the best possible results.
Structure and Outline of a Coursework
The structure and outline of a coursework can vary depending on the specific type of assignment and subject matter. However, there are some commonalities between different types of coursework writing.
For instance, good coursework assignments follow a typical academic format that includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Many coursework assignments require a reference list or bibliography to cite sources used in the research process.
Thesis and dissertation projects may have slightly different structures, often requiring additional sections such as a literature review, methodology, and discussion section. Research papers may also have another format, depending on the assignment's requirements and the subject matter.

Despite these variations, coursework assignments generally adopt a typical outline format that includes the following:
- The title page - includes the assignment title, the student's name, the course title, and the date.
- Table of contents - provides a list of the major sections and subsections of the assignment.
- Abstract - a summary of the assignment that highlights the key points.
- Introduction - provides an overview of the topic and the purpose of the assignment.
- Body paragraph(s) - presents the main argument or analysis of the assignment, supported by evidence and research.
- Conclusion - summarizes the main points of the assignment and provides a final analysis or evaluation.
- Reference list - lists all sources used in the research process.
By following this coursework outline format and adapting it to the assignment's specific requirements, students can create clear, well-structured coursework papers. But if you need a professional writer's help, you can just ask us: 'Can you write my paper ?' and that's all the effort you need to make for a perfect paper.
How to Write a Coursework Introduction
The introduction is a crucial part of any coursework writing process, as it sets the tone for the rest of the paper and helps to engage the reader. Here are some points to help you master how to write a coursework introduction:
- Explain the significance of your coursework topic - Start briefly explaining why your issue is essential, and highlight its relevance and potential impact.
- Identify the main problem/question - By providing readers with a brief insight into the issue you'll be exploring, you can give them a sense of the scope and focus of your study.
- Establish clear goals - This will help you stay focused and ensure your research aligns with your objectives.
- Craft a thesis statement - By clearly stating what you hope to achieve and the results you plan to obtain, you can establish a roadmap for your research.
- End your introduction with a thought-provoking statement - This can help to capture their attention and motivate them to continue reading your work.
Following these pointers, you can create a solid and engaging introduction that sets the stage for a well-structured and impressive coursework assignment.
Not Ready to Complete Your Upcoming Coursework?
Our writers have extensive experience creating a wide range of essays and research papers

How to Write a Summary of Coursework in Resume
If you're a student, your resume may lack work experience, but that doesn't mean you have nothing to offer to potential employers. Including a summary of your relevant coursework writing can showcase the skills you're developing and help employers understand why you're a good fit for the job or internship.
To help you learn how to write a summary of coursework in resume, we gathered some tips:
- Use single-column format - list the relevant courses under a section titled 'Relevant Coursework.' This format resembles the education section on your resume and presents the coursework in a simple list form.
- Multi-column format - If you're applying for a job that requires expertise in multiple fields, you can group the columns into sections using a multi-column layout. For example:
- Academic Writing
- Internship involving Research
- Oral Communication Skills
- Detailed Format - The detailed format offers a more comprehensive view of the coursework you choose to include on your resume. This format resembles the professional experience section, where you provide details about the course and two to four bullet points highlighting the study's relevant learnings or achievements.
How to Write a Coursework Report
How to write a coursework report can be a common question among students. A coursework report allows students to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of a particular topic, concept, or issue by conducting research, analyzing data, and presenting their findings in a written report. If you find it challenging to write this report before your deadline, you can say the magic words 'write my coursework report,' and an online paper writing service will provide it to you quickly.
The structure of a coursework report typically consists of several key components, including:
1.0 The Introduction
2.0 Key Issues (provides an overview of the main topics covered in this report, leading into sections 2.1 and 2.2)
2.1 Sub-topic 1
2.2 Sub-topic 2
3.0 Key Issues (outlines the main topics covered in this section, leading into sections 3.1, 3.2, and 3.3)
3.1 Sub-topic 1
3.2 Sub-topic 2
3.3 Sub-topic 3
4.0 Conclusions (summarizes the essential findings and insights, representing 5-10% of the word count)
5.0 Recommendations (provides actionable suggestions based on the conclusions and analysis presented in the report)
In this paragraph, we provided seven coursework writing tips that will help you to write your academic paper, definition essay examples , or any coursework perfectly:

- Start Early : Begin working on your coursework as soon as possible to avoid last-minute stress and ensure you have enough time for proper planning, research, writing, and editing.
- Choose a Clear and Interesting Topic : Choose a topic that you are eager to write coursework about and is clear and specific. A precise topic will help you focus your research and writing, while an interesting topic will keep you engaged and motivated.
- Use Evidence Effectively: Use evidence such as quotes and statistics to support your arguments, but use them selectively. Ensure your evidence is relevant and supports your main points, and always cite your sources correctly.
- Follow the Instructions: Pay close attention to the instructions given by your professor, and ensure you understand the coursework requirements.
- Structure Your Paper : Organize your paper into clear sections with headings and subheadings. This will make it easier for your readers to follow your arguments and understand your ideas.
- Revise and Edit: Once you have completed your coursework, revise and edit it carefully. Check for spelling and grammar errors, and make sure your ideas are presented clearly and coherently.
- Use Feedback: If you receive feedback from your professor or peers, use it to improve your coursework. Consider the feedback carefully and make revisions where necessary.
To help you create your coursework examples effectively, we gathered some topics for you to write about:
Psychology Coursework:
- Investigating the impact of stress on memory
- Examining the effectiveness of different types of therapy for treating depression
- Analyzing the effects of social media use on mental health
History Coursework:
- Examining the causes and consequences of a particular historical event
- Analyzing the impact of a particular historical figure on their time period
- Investigating the role of propaganda in a particular historical context
Computer Science Coursework:
- Developing a computer program to solve a particular problem
- Analyzing the performance of different algorithms for a particular task
- Examining the security risks associated with a particular technology or system.
If you read the article till this paragraph, you now know what is a coursework and even how to write a resume for coursework that is effective. But if you still need further guidance, you can leave a request " write my coursework " to our coursework writing service and be sure that it will be perfectly done. You can also use our platform to write an extended essay or a research paper with any level of complexity!
How to Write an Essay: Advice From Professionals

Good Persuasive Speech Topics That Spark Intrigue

Business Essay Topics to Help Students Stay Ahead

How to Write a Synthesis Essay with Strong Arguments

How to Write a Critical Analysis Step-by-Step Guide

How to Write a Movie Review: Definition, Tips, and Best Practices

How to Write a Narrative Essay: Definition, Outline, and Writing Hints

How to Write an Argumentative Essay?

Creative Book Report Ideas to Make Reading Fun!
.png)

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Undergraduate Writing: Understanding the Assignment
Introduction, common writing terms.
Analyze = explain a multifaceted text or idea by breaking it into its parts.
Example: Analyze the relationship between hand sanitizer and disease transmission in hospitals.
Tips: Remember to state what the relationship is, but also why . The why involves critical thinking to determine all the factors in the scenario.
Assess or evaluate = determine the significance or value of something by examining it closely.
Example: Evaluate whether hand sanitizer decreases disease transmission.
Tips: Come to an overall, educated opinion on the issue based on course readings, other research, and reasoning. Write a thesis statement at the beginning of your paper to tell the reader what that opinion is.
Compare and contrast = to examine two items to discover similarities and differences.
Example : Compare and contrast three brands of hand sanitizer for effectiveness and cost.
Tips : To provide a well-rounded comparison, give equal attention to the similarities and the differences. Follow our compare/contrast guidelines before submission.
Paraphrase = restate a passage in your own words.
Example : Paraphrase the CDC's recent announcement on the use of hand sanitizer.
Tips : It can be tempting to directly quote the statement, but paraphrasing builds your academic skills. Read the announcement carefully and then open a new document on your computer. Without looking back, reword the announcement using your own vocabulary. Finally, compare yours to the original.
Reflect = think about an idea deeply and consider its impact.
Example : Reflect on your own use of hand sanitizer in the medical profession.
Tips : You might find that sitting in a quiet place, away from the computer, allows you to think easier. Even if you are reflecting on a bad situation in your workplace, remain neutral and objective when writing about the incident.
Summarize = express the main points of a reading in a shorter form.
Example : Summarize Chapter 3 of your course text on disease transmission.
Tips : While reading, pay attention to the who, what, why, where, and how in the text. It could be helpful to take notes or highlight the important information that jumps out at you.
Support your work/ideas = justify your point of view by providing evidence.
Tips : Evidence can come in the form of statistics, examples, or other research. Such evidence is usually accompanied by a citation crediting the original source.
Once you understand the assignment instructions, jot down each component or outline the paper. Keep these tools handy as you write.
Still unsure what a word or concept means? Look it up in Merriam-Webster's Online Dictionary .
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Assignment Resources
- Next Page: Discussion Posts
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Course Assessment
Course-level assessment is a process of systematically examining and refining the fit between the course activities and what students should know at the end of the course.
Conducting a course-level assessment involves considering whether all aspects of the course align with each other and whether they guide students to achieve the desired learning outcomes.
“Assessment” refers to a variety of processes for gathering, analyzing, and using information about student learning to support instructional decision-making, with the goal of improving student learning. Most instructors already engage in assessment processes all the time, ranging from informal (“hmm, there are many confused faces right now- I should stop for questions”) to formal (“nearly half the class got this quiz question wrong- I should revisit this concept”).
When approached in a formalized way, course-level assessment is a process of systematically examining and refining the fit between the course activities and what students should know at the end of the course. Conducting a course-level assessment involves considering whether all aspects of the course align with each other and whether they guide students to achieve the desired learning outcomes . Course-level assessment can be a practical process embedded within course design and teaching, that provides substantial benefits to instructors and students.
Over time, as the process is followed iteratively over several semesters, it can help instructors find a variety of pathways to designing more equitable courses in which more learners develop greater expertise in the skills and knowledge of greatest importance to the discipline or topic of the course.
Differentiating Grading from Assessment
“Assessment” is sometimes used colloquially to mean “grading,” but there are distinctions between the two. Grading is a process of evaluating individual student learning for the purposes of characterizing that student’s level of success at a particular task (or the entire course). The grade of an assignment may provide feedback to students on which concepts or skills they have mastered, which can guide them to revise their study approach, but may not be used by the instructor to decide how subsequent class sessions will be spent. Similarly, a student’s grade in a course might convey to other instructors in the curriculum or prospective employers the level of mastery that the student has demonstrated during that semester, but need not suggest changes to the design of the course as a whole for future iterations.
In contrast to grading, assessment practices focus on determining how many students achieved which learning course outcomes, and to what level of mastery, for the purpose of helping the instructor revise subsequent lessons or the course as a whole for subsequent terms. Since final course grades may include participation points, and aggregate student mastery of all course learning objectives into a single measure, they rarely give clarity on what elements of the course have been most or least successful in achieving the instructor’s goals. Differentiating assessment from grading allows instructors to plot a clear course forward toward making the changes that will have the greatest impact in the areas they define as being most important, based on the results of the assessment.
Course learning outcomes are measurable statements that describe what students should be able to do by the end of a course . Let’s parse this statement into its three component parts: student-centered, measurable, and course-level.
Student-Centered
First, learning outcomes should focus on what students will be able to do, not what the course will do. For example:
- “Introduces the fundamental ideas of computing and the principles of programming” says what a course is intended to accomplish. This is perfectly appropriate for a course description but is not a learning outcome.
- A related student learning outcome might read, “ Explain the fundamental ideas of computing and identify the principles of programming.”
Second, learning outcomes are measurable , which means that you can observe the student performing the skill or task and determine the degree to which they have done so. This does not need to be measured in quantitative terms—student learning can be observed in the characteristics of presentations, essays, projects, and many other student products created in a course (discussed more in the section on rubrics below).
To be measurable, learning outcomes should not include words like understand , learn , and appreciate , because these qualities occur within the student’s mind and are not observable. Rather, ask yourself, “What would a student be doing if they understand, have learned, or appreciate?” For example:
- “Learners should understand US political ideologies regarding social and environmental issues,” is not observable.
- “Learners should be able to compare and contrast U.S. political ideologies regarding social and environmental issues,” is observable.
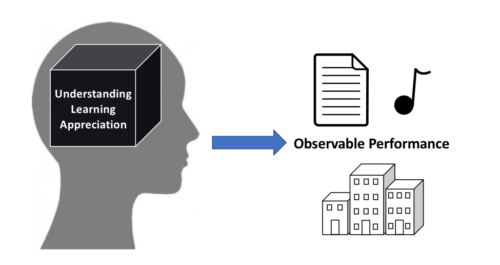
Course-Level
Finally, learning outcomes for course-level assessment focus on the knowledge and skills that learners will take away from a course as a whole. Though the final project, essay, or other assessment that will be used to measure student learning may match the outcome well, the learning outcome should articulate the overarching takeaway from the course, rather than describing the assignment. For example:
- “Identify learning principles and theories in real-world situations” is a learning outcome that describes skills learners will use beyond the course.
- “Develop a case study in which you document a learner in a real-world setting” describes a course assignment aligned with that outcome but is not a learning outcome itself.
Identify and Prioritize Your Higher-Order End Goals
Course-level learning outcomes articulate the big-picture takeaways of the course, providing context and purpose for day-to-day learning. To keep the workload of course assessment manageable, focus on no more than 5-10 learning outcomes per course (McCourt, 2007). This limit is helpful because each of these course-level learning objectives will be carefully assessed at the end of the term and used to guide iterative revision of the course in future semesters.
This is not meant to suggest that students will only learn 5-10 skills or concepts during the term. Multiple shorter-term and lower-level learning objectives are very helpful to guide student learning at the unit, week, or even class session scale (Felder & Brent, 2016). These shorter-term objectives build toward or serve as components of the course-level objectives.
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (Anderson & Krathwohl, 2001) is a helpful tool for deciding which of your objectives are course-level, which may be unit-to class-level objectives, and how they fit together. This taxonomy organizes action verbs by complexity of thinking, resulting in the following categories:
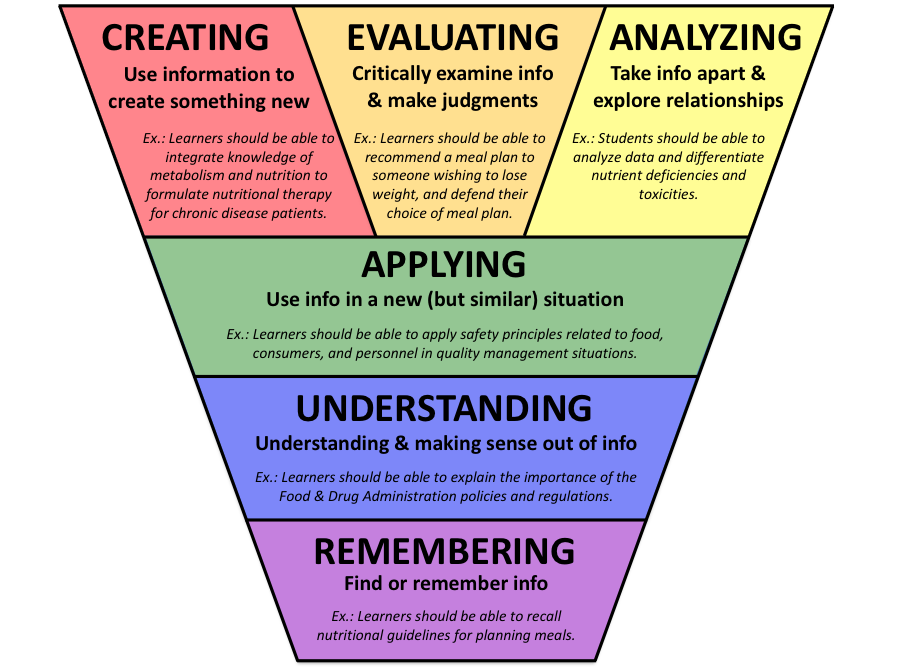
Download a list of sample learning outcomes from a variety of disciplines .
Typically, objectives at the higher end of the spectrum (“analyzing,” “evaluating,” or “creating”) are ideal course-level learning outcomes, while those at the lower end of the spectrum (“remembering,” “understanding,” or “applying”) are component parts and day, week, or unit-level outcomes. Lower-level outcomes that do not contribute substantially to students’ ability to achieve the higher-level objectives may fit better in a different course in the curriculum.
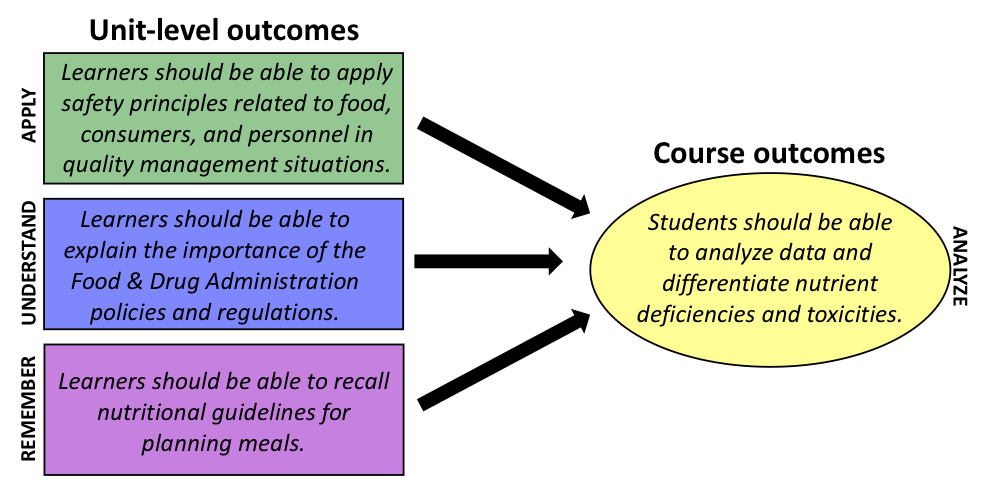
Consider Involving Your Learners
Depending on the course and the flexibility of the course structure and/or progression, some educators spend the first day of the course working with learners to craft or edit learning outcomes together. This practice of giving learners an informed voice may lead to increased motivation and ownership of learning.
Alignment, where all components work together to bolster specific student learning outcomes, occurs at multiple levels. At the course level, assignments or activities within the course are aligned with the daily or unit-level learning outcomes, which in turn are aligned with the course-level objectives. At the next level, the learning outcomes of each course in a curriculum contribute directly and strategically to programmatic learning outcomes.
Alignment Within the Course
Since learning outcomes are statements about key learning takeaways, they can be used to focus the assignments, activities, and content of the course (Wiggins & McTighe, 2005). Biggs & Tang (2011) note that, “In a constructively aligned system, all components… support each other, so the learner is enveloped within a supportive learning system.”
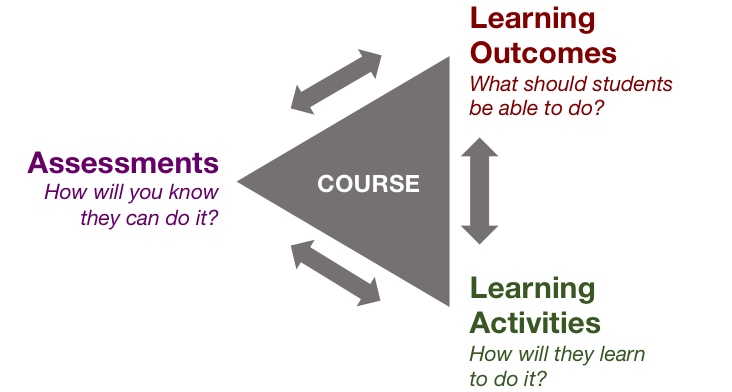
For example, for the learning outcome, “learners should be able to collaborate effectively on a team to create a marketing campaign for a product,” the course should: (1) intentionally teach learners effective ways to collaborate on a team and how to create a marketing campaign; (2) include activities that allow learners to practice and progress in their skillsets for collaboration and creation of marketing campaigns; and (3) have assessments that provide feedback to the learners on the extent that they are meeting these learning outcomes.
Alignment With Program
When developing your course learning outcomes, consider how the course contributes to your program’s mission/goals (especially if such decisions have not already been made at the programmatic level). If course learning outcomes are set at the programmatic level, familiarize yourself with possible program sequences to understand the knowledge and skills learners are bringing into your course and the level and type of mastery they may need for future courses and experiences. Explicitly sharing your understanding of this alignment with learners may help motivate them and provide more context, significance, and/or impact for their learning (Cuevas, Matveevm, & Miller, 2010).
If relevant, you will also want to ensure that a course with NUpath attributes addresses the associated outcomes . Similarly, for undergraduate or graduate courses that meet requirements set by external evaluators specific to the discipline or field, reviewing and assessing these outcomes is often a requirement for continuing accreditation.
See our program-level assessment guide for more information.
Transparency
Sharing course learning outcomes with learners makes the benchmarks for learning explicit and helps learners make connections across different elements within the course (Cuevas & Mativeev, 2010). Consider including course learning outcomes in your syllabus , so learners know what is expected of them by the end of a course and can refer to the outcomes as the term progresses. When educators refer to learning outcomes during the course before introducing new concepts or assignments, learners receive the message that the outcomes are important and are more likely to see the connections between the outcomes and course activities.
Formative Assessment
Formative assessment practices are brief, often low-stakes (minimal grade value) assignments administered during the semester to give the instructor insight into student progress toward one or more course-level learning objectives (or the day-to unit-level objectives that stair-step toward the course objectives). Common formative assessment techniques include classroom discussions , just-in-time quizzes or polls , concept maps , and informal writing techniques like minute papers or “muddiest points,” among many others (Angelo & Cross, 1993).
Refining Alignment During the Semester
While it requires a bit of flexibility built into the syllabus, student-centered courses often use the results of formative assessments in real time to revise upcoming learning activities. If students are struggling with a particular outcome, extra time might be devoted to related practice. Alternatively, if students demonstrate accomplishment of a particular outcome early in the related unit, the instructor might choose to skip activities planned to teach that outcome and jump ahead to activities related to an outcome that builds upon the first one.
Supporting Student Motivation and Engagement
Formative assessment and subsequent refinements to alignment that support student learning can be transformative for student motivation and engagement in the course, with the greatest benefits likely for novices and students worried about their ability to successfully accomplish the course outcomes, such as those impacted by stereotype threat (Steele, 2010). Take the example below, in which an instructor who sees that students are struggling decides to dedicate more time and learning activities to that outcome. If that instructor were to instead move on to instruction and activities that built upon the prior learning objective, students who did not reach the prior objective would become increasingly lost, likely recognize that their efforts at learning the new content or skill were not helping them succeed, and potentially disengage from the course as a whole.
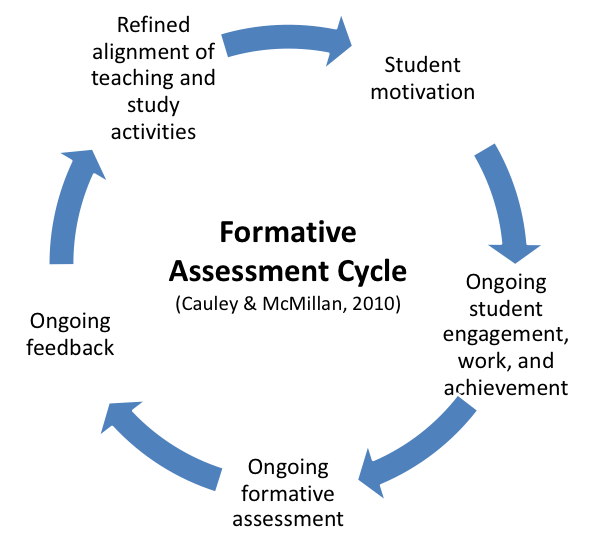
Artifacts for Summative Assessment
To determine the degree to which students have accomplished the course learning outcomes, instructors often assign some form of project , essay, presentation, portfolio, renewable assignment , or other cumulative final. The final product of these activities could serve as the “artifact” that is assessed. In this context, alignment is particularly critical—if this assignment does not adequately guide students to demonstrate their achievement of the learning outcomes, the instructor will not have concrete information to guide course design for future semesters. To keep assessment manageable, aim to design a single final assignment that create the space for students to demonstrate their performance on multiple (if not all) course learning outcomes.
Since not all courses are designed with a final assignment that allows students to demonstrate their highest level of achievement of all course learning outcomes, the assessment processes could use the course assignment that represents the highest level of achievement that students had an opportunity to demonstrate during the term. However, some learning objectives that do not come into play during the final may be better categorized as unit-level, rather than course-level, objectives.
Direct vs. Indirect Measures of Student Learning
Some instructors also use surveys, interviews, or other methods that ask learners whether and how they believe they have achieved the learning outcomes. This type of “indirect evidence” can provide valuable information about how learners understand their progress but does not directly measure students’ learning. In fact, novices commonly have difficulty accurately evaluating their own learning (Ambrose et al., 2010). For this reason, indirect evidence of student learning (on its own) is not considered sufficient for summative assessment.
Together, direct and indirect evidence of student learning can help an instructor determine whether to bolster student practice in certain areas or whether to simply focus on increasing transparency about when students are working toward which learning outcome.
Creating and Assessing Student Work with Analytic Rubrics
One tool for assessing student work is analytic rubrics (shown below) which are matrices of characteristics and descriptions of what it might look like for student products to demonstrate these characteristics at different levels of mastery. Analytic rubrics are commonly recommended for assessment purposes, since they provide more detailed feedback to guide course design in more meaningful ways than holistic rubrics. Pre-existing analytic rubrics such as the AAC&U VALUE Rubrics can be tailored to fit your course or program, or you can develop an outcome-specific rubric yourself (Moskal, 2000 is a useful reference, or contact CATLR for a one-on-one consultation). The process of refining a rubric often involves multiple iterations of applying the rubric to student work and identifying the ways in which it captures or does not capture the characteristics representing the outcome.
Summative assessment results can inform changes to any of the course components for subsequent terms. If students have underperformed on a particular course learning objective, the instructor might choose to revise the related assignments or provide additional practice opportunities related to that objective, and formative assessments might be revised or implemented to test whether those new learning activities are producing better results. If the final assessment does not provide sufficient information about student performance on a certain outcome, the instructor might revise the assessment guidelines or even implement a different assessment that is more aligned to the outcome. Finally, if an instructor notices during the assessment process that an important outcome has not been articulated, or would be more clearly stated a different way, that instructor might revise the objectives themselves.
For assistance at any stage of the course assessment cycle, contact CATLR for a one-on-one or group consultation.
Ambrose, S. A., Bridges, M. W., DiPietro, M., Lovett, M. C., & Norman, M. K. (2010). How learning works: Seven research-based principles for smart teaching . San Francisco, CA: John Wiley & Sons.
Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives . New York, NY: Longman.
Bembenutty, H. (2011). Self-regulation of learning in postsecondary education. New Directions for Teaching and Learning , 126 , 3-8. doi: 10.1002/tl.439
Biggs, J., & Tang, C. (2011). Teaching for Quality Learning at University . Maidenhead, England: Society for Research into Higher Education & Open University Press.
Cauley, K. M., & McMillan, J. H. (2010). Formative assessment techniques to support student motivation and achievement. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas , 83 (1), 1-6. doi: 10.1080/00098650903267784
Cuevas, N. M., Matveev, A. G., & Miller, K. O. (2010). Mapping general education outcomes in the major: Intentionality and transparency. Peer Review , 12 (1), 10-15.
Felder, R. M., & Brent, R. (2016). Teaching and learning STEM: A practical guide . San Francisco, CA: John Wiley & Sons.
Krathwohl, D. R. (2002). A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy: An overview. Theory into practice , 41 (4), 212-218. doi: 10.1207/s15430421tip4104_2
McCourt, Millis, B. J., (2007). Writing and Assessing Course-Level Student Learning Outcomes . Office of Planning and Assessment at the Texas Tech University.
Moskal, B. M. (2000). Scoring rubrics: What, when and how? Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation , 7 (3).
Setting Learning Outcomes . (2012). Center for Teaching Excellence at Cornell University. Retrieved from https://teaching.cornell.edu/teaching-resources/designing-your-course/setting-learning-outcomes .
Steele, C. M. (2010). Whistling Vivaldi: How Stereotypes Affect Us and What We Can Do . New York, NY: WW Norton & Company, Inc.
Wiggins, G., & McTighe, J. (2005). Understanding by Design (Expanded) . Alexandria, US: Association for Supervision & Curriculum Development (ASCD).
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of assignment in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- It was a jammy assignment - more of a holiday really.
- He took this award-winning photograph while on assignment in the Middle East .
- His two-year assignment to the Mexico office starts in September .
- She first visited Norway on assignment for the winter Olympics ten years ago.
- He fell in love with the area after being there on assignment for National Geographic in the 1950s.
- act as something
- all work and no play (makes Jack a dull boy) idiom
- be at work idiom
- be in work idiom
- housekeeping
- in the line of duty idiom
- undertaking
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
assignment | American Dictionary
Assignment | business english, examples of assignment, collocations with assignment.
These are words often used in combination with assignment .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of assignment
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
hit the road
to leave a place or begin a journey

Searching out and tracking down: talking about finding or discovering things

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- on assignment
- American Noun
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
To add assignment to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add assignment to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The meaning of COURSEWORK is work that is assigned or performed as part of a course of study. How to use coursework in a sentence.
Coursework refers to a series of assignments, projects, and other tasks that are completed by a student over the course of a semester or academic year. It is a more comprehensive form of assessment than individual assignments, as it covers a broader range of topics and requires the student to demonstrate a deeper understanding of the subject ...
By definition, a coursework assignment is an academic project that students undertake in the course of study and which they must submit before the closure of the semester. For example, such types of papers aim to evaluate students' level of knowledge and skills acquisition, meaning the work contributes to students' final grades. Ideally ...
Coursework (also course work, especially British English) is work performed by students or trainees for the purpose of learning. Coursework may be specified and assigned by teachers, or by learning guides in self-taught courses. Coursework can encompass a wide range of activities, including practice, experimentation, research, and writing (e.g ...
Coursework definition: General Certificate of Secondary Education (GCSE) coursework is a typical academic assignment, given in the course of study to evaluate the student's knowledge, skills, and identify the final grade. Many students face this type of writing in the US colleges. One of the examples is a coursework UTD (The University of ...
Define Coursework. Coursework refers to the assignments, projects, and assessments that students are required to complete as part of a course. It is the practical application of the knowledge and skills learned in the classroom and is designed to assess a student's understanding of the subject matter.
Coursework definition: the work required of a student in a particular course of study; classroom work. . See examples of COURSEWORK used in a sentence.
Steps to Carry out Successful Coursework. Carefully select a topic and decide on the goal of your coursework. Make sure you understand all the requirements of your coursework, as well as the topic itself. When choosing your topic, try adhering to the rule of the golden middle: choose a topic that is not too hackneyed (because writing coursework ...
COURSEWORK meaning: 1. work set at regular periods as part of an educational course 2. work set at regular periods as…. Learn more.
Effective Coursework Writing Strategies. 1. Analyze the Assignment. Before you begin writing your coursework, carefully read and analyze the assignment guidelines. Understand the requirements, topic, and any specific instructions given by your instructor. This will ensure that you stay focused and tailor your work accordingly.
Introduction: include your thesis and sketch your topic's background here. Literature Review: Summarize the current state of research on your topic. Methodology: describe how you collected data and what samples you used. Main Body: List the main ideas or arguments—present data, quotes, or examples to support your points.
Coursework is an integral part of the educational process, which refers to written or practical tasks that students perform during educational courses. These assignments are typically evaluated and contribute to the final grade or mark. The coursework definition, especially the term "curriculum-mandated" signifies that instructors are ...
Brilliant coursework needs a lot of time, so you have to start as early as possible. Always stay calm so that you cannot mess up your performance due to pressure. Do not rush to complete your assignment on one sitting. Divide your workload precisely and work slowly from day to day.
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
Approach coursework meaning as a good alternative to achieving academic success without risking failing an exam. It is also a great way to learn how to process information as you write and see where your learning strengths lie. Since the majority of students would like to avoid examinations, it is much better when you can take a different route ...
It is largely a part of learning exercise and a step to prepare you to handle the required work/ task effectively and efficiently. folios of essays. art and craft items. speaking tests. practical work. assignments and experiments undertaken and assessed during the course. As per Oxford dictionary "Coursework" is defined as.
Coursework definition: The various assignments, exercises, examinations, etc. completed by a student to fulfill the requirements for passing a particular class or course of study.
Many students cannot clearly define what is a coursework. In a nutshell, at the "A" and GSCE level, a coursework is written in the form of projects or essays. There are few guidelines and good practices which should be followed while writing a coursework. ... Therefore, a coursework is presented in a form of a research assignment meant to ...
Despite these variations, coursework assignments generally adopt a typical outline format that includes the following: The title page - includes the assignment title, the student's name, the course title, and the date.; Table of contents - provides a list of the major sections and subsections of the assignment.; Abstract - a summary of the assignment that highlights the key points.
Coursework is practical work or studies completed by a student in partial fulfilment of training or degree. Coursework includes projects, fieldwork, design studies, extensive college essays, and other activities. The type of work required varies on the course. It is mostly a part of the learning process and a step towards preparing students to ...
Introduction. The first step in completing an assignment is ensuring that you understand what is expected. Assignment instructions can sometimes contain language that is unfamiliar, especially if you have been out of school for a while. For help navigating this language, consult our guide to writing terms below.
Course-Level. Finally, learning outcomes for course-level assessment focus on the knowledge and skills that learners will take away from a course as a whole. Though the final project, essay, or other assessment that will be used to measure student learning may match the outcome well, the learning outcome should articulate the overarching ...
ASSIGNMENT definition: 1. a piece of work given to someone, typically as part of their studies or job: 2. a job that…. Learn more.