Our website uses cookies, which helps us to deliver the best customer experience. Cookie policy. Got It

- Yelo Hyperlocal Ordering
- Tookan Delivery Management
- Hippo Customer Engagement
- Panther Consultation Marketplace
- On-Demand Delivery Service End-to-end software to launch your hyperlocal delivery service
- Home Services Fully customizable software for home services business
- Delivery Orchestration Manage deliveries efficiently through third-party and in-house fleets
- Telemedicine Create an online medical consultation platform
- Direct-to-consumer Eliminate aggregators and deliver direct-to-consumer
- Headless Commerce Endless customization for a unique front-end experience
- Fleet management Minimize costs through efficient monitoring of your delivery fleet
- Last-mile delivery Automate your last-mile dispatches & deliver without hassle
- Customer Engagement Automation Automate your engagements and marketing activities through an omnichannel approach
- Mapping Infrastructure Optimize your delivery route efficiently
- Partner Network Home
- Partnership FAQs
- Our Integration Partners
- Try Now Request a Demo
- Whitepapers
- Infographics

FedEx Business model – Operational Insights and Revenue Streams
“Happiness is getting a package from FedEx.”
A brilliant idea owes its existence to a college assignment. The revolutionary concept that is responsible for first centralizing the courier delivery . The idea that promises you to deliver your package safely in one piece, the idea that also incited the delivery tracking system’s patent, the concept that connects people with possibilities. That idea that has so much of glory, magic, and marvel associated with it, is none other than FedEx.

The genesis of FedEx
In 1965, a Yale University graduate, in his term paper, outlined the logistic problems faced by firms and proposed a system to accommodate time-sensitive deliveries. Consequently, the foundation-stone of Federal Express was laid in Little Rock, Arkansas, in 1961. In 1994 Federal Express was officially rebranded as FedEx.
FedEx Business Model
FedEx uses wholly-owned subsidiaries to provide a portfolio of transportation, e-commerce , and business services . FedEx generates value by offering ‘high value-added’ package delivery services to 220+ countries. The inceptive bedrock of FedEx, i.e., “When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight,” encapsulates its business model. FedEx stays ahead of the curve by delivering the promise of speedy delivery with over 99% reliability. For this purpose, FedEx banks upon its ultra-efficient operating systems that are pivoted on aircraft. Fed uses a hub-spoke model where-in instead of flying directly, FedEx aircraft pass through one of the strategically placed FedEx hubs. Consequently, packages are immediately placed on outbound aircraft, and thus this operational model reduces the delivery time .

FedEx Business Model: Operating Segments
FedEx has the following key operating segments:
- FedEx Express: The global network responsible for providing time-sensitive and air-ground express service.
- FedEx Ground: Renders reliable B2B delivery or convenient residential services. Although FedEx serves customers & businesses across the globe transcending geographical barriers but FedEx Ground is exclusively for North America.
- FedEx Freight: Provides an array of LTL (less-than-truckload) choices to address customer needs.
- FedEx Services: It uses technology to address customer needs, be it global supply chain issues or e-commerce problems.
FedEx Business Model: Revenue Insights
In 1973, FedEx witnessed the growth, and since then, there’s no turning back. Apart from the four main vital segments, FedEx Logistics & FedEx Office, also contributes to the total revenue. In FY20, FedEx managed to earn $69.2B, out of which 51% was donated by FedEx Express, 33% FedEx Ground, 10% by FedEx Freight, and the rest by others and eliminations. From FT16 to FY19, FedEx witnessed an annual growth rate of 11.6%. During this period, i.e., FY16-FY19, revenue for FedEx Express & FedEx Ground grew due to higher packages being shipped. In the future, volume growth could touch high single digits owing to an increase in e-commerce . Freight shipments also grew, leading to FedEx Freight revenue growth.
Factors affecting business & revenue
- Overall customer demand for a mix of services in the FedEx portfolio of services
- Macroeconomic factors & global factors affecting the market of FedEx customers
- The volume of transportation services, gauged using shipment weight & average daily volume
- The cost controlling ability of FedEx to match with the changing volume levels
- The yield earned by FedEx measured in terms of revenue per package or revenue per hundredweight etc
What the future holds for FedEx
Market analysts forecast that a 15.5% raise will be witnessed in the EPS of FedEx shares for FY21. Its forward price ratio of 13.8 highlights that the stock provides the stock’s safety as a growth strategy is implemented. FedEx has undertaken some remarkable digital transformations. For instance, FedEx delivery managers aimed at increasing visibility and control for customers, autonomous vehicles like Roxo, the FedEx SameDay Bot inciting cutting-edge innovation, and their newest solutions FedEx Surround and SenseAware ID to advance their industry-leading tracking technology. FedEx’s realigned strategy is helping FedEx deliver its purple promise in more meaningful ways, and clearly, the best years of FedEx and its customers are ahead.
If you’re also looking for creating excellent delivery management services with real-time tracking , Tookan is the ultimate cure-all for you. Route optimization , end to end planning, automated dispatch , and geofencing are some of the many excellent features that Tookan has got in store to help you streamline your business.
If you enjoyed reading this, we’re sure you will also love checking out what we have in store on our Youtube channel . You can also head to our home page for more information!
Subscribe to stay ahead with the latest updates and entrepreneurial insights!
Share this article:

Subscribe to our newsletter
Get access to the latest industry & product insights.
Quickstart Guides

You may be interested in these articles

Yelo 14th September 2021
Tookan 21st May 2021
Tookan 20th May 2021
Yelo 20th January 2021
Find out how Jungleworks' products can help you set up & manage your online business
Have our business experts on the phone to understand your company's operations and guide you through a demo customized to your business industry.

Request a Free Demo
Our experts will contact you shortly
Step 1 of 3.
Explore our platform and launch your business with Yelo
Take a comprehensive walkthrough of the features and functionalities that Yelo provides, and learn how you can launch and grow your hyperlocal business.

Launch your Hyperlocal Business
Get started with Yelo Today
Already have an account, Sign In .
Your Theme has been Selected If you wish to proceed with this, the selected theme will be applied to your live account.
If that's okay, kindly proceed ahead ., sign up for 14 days free trial..
Learn more about Yelo and its features during Yelo's 14 days free trial. You can set up your online hyperlocal store without coding and explore the platform on your own. Upgrade your plan only when you're ready.
Start your 14 days free trial.
Make the best of this opportunity, explore the platform before you pay.
Find out how Panther can help you expand your consultation business.
Build a community of doctors, lawyers, astrologers, fitness experts and many more with Panther. Connect with our business experts & get a demo customized to your business requirements.

Launch Your Consultation Business
Sign up for 14 days free trial.
Learn more about Panther and its features during Panther's 14 days free trial. You can set up your online consultation platform without coding and explore it on your own. Upgrade your plan only when you're ready.
Find out how Yelo can help you expand your business.
Have our business experts on the phone to understand your brand's operations and guide you through a demo customized to your business industry.

Find out how Tookan can help you set up and grow your online delivery & logistics business
Connect with our product specialists to understand how the world's fastest-growing companies use Tookan to optimize deliveries.

Get in Touch
Our business experts will contact you shortly
Explore the Tookan platform for your business and get started today
Take a comprehensive walkthrough of the features and functionalities that Tookan provides, and learn how you can start managing your dispatch and delivery operations in a smoother manner.

Get Started for Free
Your online delivery platform is just one step away
Learn more about Tookan and its features during the 14 days free trial. You can start managing your operations with Tookan without coding. White-label your platform or upgrade your plan only when you're ready.
Our team will get in touch with you for the next steps, For questions or rush request please email [email protected]
Our Product Specialist will get in touch with you for the next steps. Click on the button below to see how your website will look like.
Get your Tech, sorted!

Join us for a live demo!
We'll walk you through the product suite and answer all your questions about Jungleworks.

FedEx Corporation (FDX): Business Model Canvas
- Marketing Mix
Introduction
With the global economy experiencing a rapid shift towards e-commerce and online shopping, the transportation and logistics industry has seen an exponential growth in recent years. According to a report by Statista, the global logistics market was valued at $11.5 trillion in 2020 and is expected to reach $17.9 trillion by 2026, with a CAGR of 7.5%. This significant growth can be attributed to the rise in globalization and international trade, as well as the increasing demand for faster and efficient delivery services.
One of the key players in the logistics industry is FedEx Corporation (FDX), which operates in various segments, including FedEx Express, FedEx Ground, FedEx Freight, and FedEx Trade Networks. The company's primary revenue comes from shipping services, followed by e-commerce and retail services.
In this blog post, we will delve deeper into FedEx's business model canvas, exploring key partners, activities, cost structures, customer segments, and value propositions. The post aims to provide insights into what makes FedEx a successful player in the logistics industry and how it continues to expand its business by targeting new customer segments and revenue streams.
Key Partnerships
FedEx Corporation relies on several key partnerships to ensure that its operations run smoothly and efficiently. These partnerships include:
- Suppliers: FedEx partners with suppliers to source essential materials and equipment needed for its operations. This includes partnerships with suppliers who provide technology, vehicles, fuel, and other operational resources.
- Third-party logistics providers: FedEx engages third-party logistics providers to complement its distribution network and expand its reach. These partners allow FedEx to easily reach customers in remote areas and reduce the transportation costs of certain shipments.
- Government agencies: FedEx works closely with government agencies to ensure that it complies with relevant laws and regulations regarding transportation, security, and trade. These agencies include the Federal Aviation Administration, the Department of Homeland Security, and the Department of Transportation.
- Airport operators: FedEx partners with airport operators to gain access to infrastructure, facilities, and resources needed for its air transportation operations. These partnerships also include access to customs and border control facilities.
- Retail partners: FedEx has agreements in place with several retailers, including Walmart, Walgreens, and Kroger, which allow customers to drop off and pick up packages at designated locations. This increases convenience for customers and expands FedEx's distribution network.
These partnerships are crucial to FedEx's success and allow the company to maximize efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the overall customer experience.
Key Activities
FedEx Corporation (FDX) provides courier delivery services, and its key activities are:
- Transportation Services: FedEx provides transportation services to deliver packages, documents, and freight domestically and internationally. It operates a fleet of airplanes and trucks to offer timely delivery to its customers.
- Logistics Support: FedEx offers logistics support to its customers, including supply chain management, warehousing, and distribution. The company's logistic services help its customers to optimize their businesses by reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Customs Clearance: FedEx provides customs clearance services for international packages and freight. Its experts ensure that packages comply with regulations and have the necessary documentation to cross borders.
- Tech Support: FedEx leverages technology to provide its customers with an efficient and transparent experience. Its technological support includes mobile applications, shipment tracking, and online platforms that allow customers to print labels and schedule pick-ups.
- Customer Service: FedEx values its customers, and it offers exceptional customer service. It has a team of experts who provide help to its customers through various channels, such as phone, email, and chat. FedEx also offers customer training programs to ensure that its customers use its services optimally.
These key activities allow FedEx to be the industry leader and continue its success as one of the most recognized and respected courier delivery companies worldwide.
Key Resources
Transportation Fleet: One of the most important resources for FedEx is its transportation fleet. The company has a vast fleet of aircraft, trucks and vans that are used to transport packages across the globe. The transportation fleet is critical for the timely delivery of the packages and the success of the business. The company invests heavily in expanding and maintaining its fleet to meet growing customer demands.
Technology: FedEx has a very advanced and sophisticated technological infrastructure, which includes sorting equipment, tracking systems, and computer programs. This technology helps in the efficient processing of a huge volume of deliveries and provides real-time tracking information to the customers. The technology also helps the company to optimize delivery routes and reduce costs.
Human Resources: Another key resource for FedEx is its workforce. The company has a vast team of employees consisting of pilots, drivers, maintenance staff and customer service representatives who ensure that the shipments are delivered on-time and with high-quality. The company invests heavily in employee training and development to ensure that they maintain the highest level of service quality.
Brand Reputation: FedEx has a strong brand reputation that has been built over decades. The company has always focused on providing high-quality services and building long-term relationships with its customers. This has helped it in building trust and earning customer loyalty. The brand reputation makes it easier for the company to attract new customers and expand its business.
Infrastructure: The company has a vast network of facilities including airports, distribution centers, and retail locations. These infrastructures help in the efficient transportation, sorting, and delivery of the packages. The company invests heavily in expanding and maintaining its infrastructure to meet growing customer demands.
- Relationships with Suppliers:
FedEx has relationships with numerous suppliers to ensure that it has access to the necessary supplies required for its business operations. This includes relationships with aircraft and vehicle manufacturers, fuel suppliers, and technology providers. These relationships are critical for the efficient and effective operation of FedEx.
Value Propositions
FedEx Corporation (FDX) offers a comprehensive range of shipping, logistics, and e-commerce solutions to customers across the world. Our value propositions include:
- Fast and reliable delivery: We understand the importance of timely delivery, and our extensive network ensures that your packages reach their destination as quickly as possible. We also offer a money-back guarantee for late deliveries.
- Flexibility: Whether you need to ship overnight, on the same day, or schedule a delivery in advance, we offer a variety of options to suit your needs. We also provide the option to reroute packages in transit and pick up shipments from alternative locations.
- Global reach: With a presence in over 220 countries and territories, we provide reliable and consistent service across the world. Our international solutions include customs clearance, cross-border e-commerce, and specialized delivery options for different regions.
- Innovative technology: We use cutting-edge technology to streamline the shipping process, from online booking to package tracking. Our digital solutions include a user-friendly website and mobile app, electronic signature capture, and real-time delivery updates.
- End-to-end supply chain solutions: We offer a range of logistics services, including inventory management, warehousing, transportation, and fulfillment. Our integrated solutions help businesses optimize their supply chain processes, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Dedicated customer support: Our team of customer service representatives is available 24/7 to assist with any queries or concerns. We also provide a range of resources, such as online tracking, FAQs, and shipping guides, to help customers navigate the shipping process.
By leveraging our extensive experience and expertise, we help businesses of all sizes to simplify and optimize their shipping and logistics processes. With a focus on speed, reliability, and flexibility, we empower our customers to deliver on their promises and exceed customer expectations.
Customer Relationships
FedEx Corporation (FDX) uses a multi-channel approach to reach its customers.
- Online Platform: FedEx offers an online platform for customers to book shipments, track shipments, and manage their accounts. Customers can access the platform through the company's website, mobile app, or email.
- Retail Locations: FedEx has retail locations all over the world where customers can drop off their shipments or pick up their packages. These locations also offer printing and shipping supplies.
- Customer Service: FedEx offers customer service through various channels, including phone, email, and social media. Customers can contact the company's customer service department to get help with their shipments or to ask any questions they have.
- Partnerships: FedEx has partnerships with other companies that offer complementary services. For example, the company partners with Walgreens to provide FedEx pick-up and drop-off locations at Walgreens stores across the United States.
FedEx's multi-channel approach allows customers to choose the most convenient way to interact with the company. The online platform is ideal for customers who prefer to handle everything digitally, while retail locations are ideal for customers who prefer face-to-face interaction with a FedEx representative. The company's customer service channels ensure that customers can get help whenever they need it. Finally, partnerships allow FedEx to expand its reach and provide more services to customers.
Customer Segments
Cost structure.
FedEx Corporation (FDX) operates on a cost structure that is centered on its global logistics network, transportation infrastructure, and advanced technology systems. The company's primary costs are categorized into three, namely:
- Operational Costs: This includes the expenses associated with sorting, handling, and delivering packages, fuel and energy costs, employee salaries and benefits, and legal and regulatory costs. The company invests heavily in technology to optimize its operations and reduce these costs.
- Infrastructure Costs: FedEx operates various infrastructures that are critical to its operations, including aircraft, vehicles, warehousing and distribution centers, IT systems, and communication networks. The company spends a significant amount of its revenue on maintaining and upgrading these infrastructures to meet customer demands and comply with regulations.
- Marketing and Sales Costs: FedEx invests in marketing and advertising programs to promote its services and expand its customer base. These costs include advertising, market research, promotional activities, and customer service operations.
FedEx faces various economic and market-related factors that impact its cost structure, including fluctuations in fuel prices, global trade policies, and competition from other logistics providers.
The company focuses on maintaining a balanced cost structure while ensuring that it delivers high-quality services to its customers. Through its strategic investments in technology, infrastructure, and marketing, FedEx aims to enhance efficiencies and remain competitive in the market.
Revenue Streams
- Shipping Services: FedEx generates revenue from shipping services it provides to various individuals, small and medium-sized businesses, corporate clients through air, ground, and sea transportation. The price for these services depends on the size, weight, and destination of the package.
- Print and Document Services: FedEx offers printing, copying, and document services to its customers. This includes printing presentations, flyers, business cards, etc. The revenue stream from this service is based on a per-page pricing model.
- E-commerce and Fulfillment Services: FedEx provides e-commerce and fulfillment services for businesses that sell products online. They offer various services such as warehousing, pick and pack, and shipping of products directly to the customer. The revenue stream for this service is based on a monthly fee and a per-item fee.
- Customs and Trade Services: FedEx offers customs and trade services to businesses that are involved in international trade. This includes customs clearance, documentation, and international trade advisory services. The revenue stream for this service is based on a fee for the services provided.
- Cross-border E-commerce Solutions: FedEx offers cross-border e-commerce solutions to help small and medium-sized businesses sell their products to international customers. The revenue stream for this service is based on a fee for the services provided.
- Other Services: FedEx also generates revenue from other services such as transportation consulting, insurance, and packaging services.
FedEx's revenue streams are diversified and well spread across various business segments. This diversity helps the company to better manage risks associated with any one particular revenue stream. It also allows the company to leverage its brand name and infrastructure to offer a wide range of value-added services to its customers.
After analyzing the Business Model Canvas of FedEx Corporation (FDX), we can conclude that the company has a strong and diversified presence in the logistics industry. The company's value proposition is its ability to provide fast and reliable delivery services to its customers.
It has a broad customer segment that includes individuals, small businesses, and large corporations. The company operates a well-established transportation network that provides courier, express, and package delivery services. FedEx's key resources include its fleet of aircraft, trucks, and technological infrastructure, including automation and tracking systems.
FedEx's revenue streams come from various services, including FedEx Express, FedEx Ground, FedEx Freight, FedEx Office, and other services. The company maintains a global presence in approximately 220 countries and territories, making it a formidable player in the logistics market.
Overall, FedEx Corporation (FDX) has a strong business model that has proven to be successful over time. The company's ability to adapt to changes in the market and adopt new technologies has ensured its continued growth and profitability.
- FedEx Corporation (FDX) has a strong and diversified presence in the logistics industry.
- The company's value proposition is its ability to provide fast and reliable delivery services to its customers.
- FedEx's key resources include its fleet of aircraft, trucks, and technological infrastructure, including automation and tracking systems.
- FedEx's revenue streams come from various services, including FedEx Express, FedEx Ground, FedEx Freight, FedEx Office, and other services.
- The company maintains a global presence in approximately 220 countries and territories, making it a formidable player in the logistics market.

5-Year Financial Model
40+ Charts & Metrics
DCF & Multiple Valuation
Free Email Support
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models
FedEx Business Model
The FedEx Business Model revolves around providing fast and reliable shipping services with a global network and advanced tracking. They generate revenue through shipping fees and value -added services. Their key activities include package handling, transportation, and technology innovation . FedEx serves e-commerce businesses, SMEs, and global corporations. They leverage key resources such as a global transportation network , advanced technology systems, and a skilled workforce. Strategic partnerships and cost management contribute to their success in the logistics industry.
Table of Contents
1. Revenue Streams:
- Shipping Fees: FedEx generates a significant portion of its revenue from shipping fees charged to customers for the delivery of packages and parcels.
- Value-Added Services: FedEx offers various value -added services such as customs clearance, insurance, packaging services, and freight forwarding, which contribute to additional revenue .
2. Key Activities:
- Package Handling: FedEx specializes in the efficient handling and transportation of packages, ensuring they reach their destinations intact and on time.
- Transportation: FedEx operates an extensive fleet of aircraft, vehicles, and distribution centers to facilitate the movement of packages and goods.
- Technology Innovation: Continuous technological innovation is crucial for FedEx to optimize its operations, enhance tracking capabilities, and improve customer experience.
3. Customer Segments:
- E-commerce Businesses: FedEx serves a broad range of e-commerce businesses, including online retailers and marketplaces that require reliable shipping solutions for their customers.
- Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): FedEx offers shipping and logistics services tailored to the needs of SMEs, helping them manage their supply chains effectively.
- Global Corporations: Large multinational corporations rely on FedEx for efficient international shipping, supply chain management , and logistics solutions.
4. Key Resources:
- Global Transportation Network: FedEx’s extensive network of aircraft, trucks, distribution centers, and international hubs is a critical resource that enables them to reach customers worldwide.
- Advanced Technology Systems: Cutting-edge technology systems power FedEx’s operations, including package tracking, route optimization, and customer communication.
- Skilled Workforce: A highly trained and skilled workforce is essential for ensuring the timely and secure delivery of packages.
5. Distribution Channels:
- Global Network: FedEx operates a global network of sorting facilities, distribution centers, and transportation hubs to facilitate the movement of packages across international borders.
- Online Platforms: Customers can access FedEx’s services and track their shipments through the company’s online platforms and mobile apps.
6. Cost Structure:
- Transportation Costs: These include expenses related to fuel, maintenance, and operations of FedEx’s extensive transportation fleet.
- Labor Costs: Labor costs encompass wages and benefits for the workforce involved in package handling, transportation, and customer service.
- Technology Investments: Continuous investments in technology and infrastructure are necessary to maintain a competitive edge.
- Marketing and Sales: Expenses related to marketing , advertising, and sales efforts to attract and retain customers.
- Maintenance and Facilities: Costs associated with maintaining distribution centers, sorting facilities, and other infrastructure.
7. Partnerships:
- Retail Partnerships: FedEx has partnerships with retail locations and drop-off points, allowing customers to conveniently access FedEx services.
- Customs and Trade Organizations: Collaborations with customs and trade organizations streamline the customs clearance process for international shipments.
- Supplier Partnerships: Partnerships with suppliers ensure a steady supply of resources such as fuel and vehicle components.
Key Highlights
- Reliable Shipping Services: FedEx is known for providing fast and dependable shipping services worldwide, catering to a diverse range of customers.
- Diverse Revenue Streams: The company generates revenue primarily through shipping fees, but it also offers various value -added services to increase its income .
- Efficient Package Handling: FedEx excels in efficient package handling and transportation, ensuring packages arrive at their destinations intact and on time.
- Global Transportation Network: The company boasts an extensive global network of aircraft, vehicles, distribution centers, and international hubs to facilitate global shipping.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Continuous technological innovation is a key aspect of FedEx’s operations, enabling advanced package tracking, route optimization, and enhanced customer communication.
- Customer-Centric Approach: FedEx serves a wide range of customer segments, including e-commerce businesses, SMEs, and global corporations, tailoring its services to meet their specific needs.
- Online Platforms: Customers can access FedEx’s services and track their shipments conveniently through the company’s online platforms and mobile apps.
- Skilled Workforce: A highly trained and skilled workforce is crucial for ensuring the secure and timely delivery of packages.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with retail partners, customs and trade organizations, and suppliers enhance FedEx’s operations and customer service.
- Cost Management: Effective cost management strategies help FedEx maintain its competitiveness in the logistics industry.
Related Visual Stories
FedEx Revenue

FedEx Net Income

FedEx Employees

FedEx Revenue Per Package

UPS Revenue

UPS Profits

UPS Cost Structure

UPS Average Revenue Per Piece

More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
What Is FedEx’s Business Model?
FedEx provides a portfolio of transportation, e-commerce, and business services through wholly owned subsidiaries.
Apr. 2 2016, Updated 1:06 a.m. ET
In the previous article, we saw how FedEx (FDX) grew through multiple acquisitions. Here, we will look at an overview of FDX’s business model. FedEx provides a portfolio of transportation, e-commerce, and business services through wholly owned subsidiaries. Headquartered in Memphis, the company employed 325,000 people as of May 31, 2015. In the same year, Fortune ranked the company 12th for the “world’s most admired companies” for the 14th consecutive year.
Key operating segments
FDX’s business is divided into four segments in the form of primary operating companies:
- FedEx Express: one of the world’s largest express transportation companies
- FedEx Ground Package System (or FedEx Ground): a provider of small-package ground delivery services in North America
- FedEx Freight: a provider of less-than-truckload (or LTL) services in the US
- FedEx Corporate Services (or FedEx Services): a provider of sales, marketing, administrative, and information technology support, communications, and certain back-office support to FDX’s other segments.
In addition, the FedEx Services segment provides customers with retail access to FedEx Express and FedEx Ground shipping services through FedEx Office and Print Services (or FedEx Office). The FedEx Services segment also offers customer service, technical support and billing, and collection services through FedEx TechConnect (or FedEx TechConnect).
Now let’s understand the key factors that impact FDX’s business:
- overall customer demand for FDX’s multiple services based on macroeconomic factors and the global economy.
- volume of transportation services, which is measured by FDX’s average daily volume and shipment weight
- the mix of services purchased by its customers
- the prices derived by FDX for its services measured in yield (revenue per package or pound and revenue per hundredweight and shipment for less-than-truckload freight shipments)
- FedEx’s ability to control costs to match its shifting volume levels
Investing in ETFs
The transportation sector performance is a prime indicator of economic activity for any nation. Investors who want to invest in US transportation stocks that include airlines (DAL) , railroads (CSX) , trucking (JBHT) , and other logistics companies (UPS) can opt for the First Trust Industrials/Producer Durables AlphaDEX Fund (FXR) . Major US airlines and prominent railroads make up 9.8% and 5.2% of FXR.
In the coming part, we’ll discuss FDX’s biggest segment by revenue, which is FedEx Express.
Latest Delta Air Lines Inc News and Updates
- ABOUT Market Realist
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Use
- CONNECT with Market Realist
- Link to Facebook
- Link to Instagram
- Contact us by Email

Opt-out of personalized ads
© Copyright 2024 Market Realist. Market Realist is a registered trademark. All Rights Reserved. People may receive compensation for some links to products and services on this website. Offers may be subject to change without notice.

Technology and Operations Management
Mba student perspectives.
- Assignments
- Assignment: The TOM Challenge: TOM…
FedEx: The world’s largest continuous flow process

From package pickup to final delivery, FedEx's air freight network is the world's largest continuous flow process, allowing it to deliver on its customer promise of fast, overnight, and reliable delivery.
FedEx Express is the world’s leading express delivery company. Founded in 1971 as Federal Express, the company has experienced outsized returns and growth since its inception, with a quarterly dividend and a 63% increase in share price in the last five years alone.(1) This success is directly attributable to the highly effective alignment between FedEx’s strategy and customer promise of rapid delivery and its highly automated and synchronized operating model, specifically within its major subsidiary, FedEx Express. FedEx serves as an excellent example of how executing a successful operating model is crucial to creating and capturing value.
Business Model
FedEx creates value by offering “high-value added” package delivery to over 220 countries. (2) The business model can best be summed-up in the company’s early slogan: When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight. (3) With 652 aircraft (the world’s largest freight airline) moving over 4 million packages per day, FedEx guarantees speed with a reliability of greater than 99% (4). Very few companies can make such a claim, and FedEx is able to capture value by consistently delivering on this promise to its customers.
Operating Model
Pathways to just digital future.

Any company could transport one package via aircraft from point A to point B quickly, but this is prohibitively costly without economies of scale. To deliver on its customer promise of rapid and reliable delivery while offering competitive pricing, FedEx Express relies on an extremely efficient operating model that is centered on its aircraft (Figure 1) (5). FedEx is colloquially known as an airline that owns trucks, unlike its nearest competitor UPS, a trucking company that owns airplanes.
While FedEx Express has the largest freight airline in the world, these aircraft do not fly direct. Instead, all aircraft pass through one of FedEx’s 14 major hubs placed strategically around the globe (Figure 2, illustrated in purple). (6)

Instead of aircraft taking off periodically during the day, all aircraft take off and land in waves (4 per day) within the same time windows (Figure 3). (7) This operational model reduces WIP time of delivery – packages are immediately placed on outbound aircraft instead of waiting around, yet this requires tremendous capacity to land, service, and launch aircraft as well as to sort, since all packages must be unloaded, sorted, and reloaded within tight time constraints. Therefore, hubs are located at passenger-light airports with large infrastructure to accommodate many aircraft.
Nowhere is this better exemplified than at FedEx’s “world superhub” in Memphis, Tennessee. Each night, 8,000 employees sort over 1.5 million packages. With a total of 3.3 million packages sorted per day, the Memphis hub is the largest mail and package sorting facility in the world. (8) Its efficiency relies on a continuous flow process (Figure 4 shows the superhub in action) (9). The Memphis airport is the world’s busiest airport after dark, with 140 aircraft arriving within a two and a half hour window between 10:30 pm and 1:00 am, a cycle time of one aircraft per 77 seconds.10 Aircraft take between 35 – 70 minutes to unload, equaling one container of ~245 packages entering the hub every 11 seconds. To assist in sorting, packages are placed onto one of three conveyor lines based on size and weight, then sent to the Matrix – where employees place packages face up for barcode scanning and an automated system of 42 miles of conveyor belts send the packages to the correct aircraft for outbound loading. The outbound launch of aircraft starts at 2:30 am; by 4:30 am the last of the 140 aircraft has departed. (10) This highly automated and efficient sorting and airline system is the critical competitive advantage of the company’s operating model. It’s also capital intensive, thus creating high barriers to entry and limiting competition. This unique operating capability allows FedEx to successfully deliver on its customer promise and business model of overnight delivery, thus creating and capturing value that is hard to reproduce.
Performance
In a fairly low margin industry, FedEx’s alignment of business and operating model has resulted in a healthy operating margin of between 5%-8% while generating revenues of $27.2 billion in fiscal year 2015 alone. (11) The company has also changed its pricing model recently – space is more valuable than weight and the new pricing model reflect this, resulting in increased yields (Figure 5). (5) As e-commerce increases worldwide, FedEx is well placed to leverage its highly efficient operating model to deliver on its business model in the years to come.

Sources: [1] https://www.google.com/finance?q=fedex&ei=6MZgVpC2CI-oeb-BsSg [2] http://investors.fedex.com/investor-home/default.aspx [3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/FedEx#Advertising [4] http://about.van.fedex.com/our-story/company-structure/express-fact-sheet
[5] http://marketrealist.com/analysis/stock-analysis/industrials/courier-services/charts/ featured_post=492808&featured_chart=493056 [6] https://people.hofstra.edu/GEOTRANS/eng/gallery/Map_Air_Freight_Integrators.pdf [7] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0xEczrGIy08 [8] http://www.ehow.com/info_8036798_fedex-hubs.html [9] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SNFE_1Rnsu8 [10] http://www.cnet.com/news/at-fedex-sorting-packages-1-5-million-at-a-time/ [11] http://s1.q4cdn.com/714383399/files/doc_news/earnings/2015/FedEx-Q1-FY16-Earnings-Release.pdf
Student comments on FedEx: The world’s largest continuous flow process
Excellent post – I particularly enjoyed the video depicting daily flights for FedEx. Quite impressive! I was struck by the fact that “FedEx is colloquially known as an airline that owns trucks, unlike its nearest competitor UPS, a trucking company that owns airplanes.” Does FedEx generate most of its revenue from overnight and second day delivery rather than from FedEx ground? How much of FedEx’s business is based on documents versus packages, and is this business at risk as legal documents can be more easily executed electronically?
Great question – Yes, over 60% of FedEx’s revenue comes from its Air segment (FedEx Express). See Figure 1 for the full breakdown. I agree with you that document delivery has the chance to be disrupted, however the company is well-placed to ride the rising wave of e-commerce. Even if a company like Amazon wanted to enter this space directly, it would be very capital intensive to do so.
Great post JP. As someone who grew up in a FedEx Family (Dad, Mom, and brother all worked for FedEx at one point) and grew up in Memphis, the scale is impressive. Watching the aircraft arrive at night is truly a sight to see. One point you alluded to WRT FedEx vs UPS owning trucks is actually quite interesting. FedEx is primarily an airline, meaning its employees are covered by the Railway Labor Act, and have little to no capability to unionize, whereas UPS is a trucking company whose employees are covered by the National Labor Relations Act, allowing them to unionize. This was because national coverage meant that union problems in one area could rob work from a different state. This has played out significantly in favor of FedEx, and is a huge reason they enjoy some advantages over competitors. UPS actually lobbied to change this and force FedEx to operate under the NLRA so that they become burdened with the same regulations. Obviously, this would have a HUGE impact on operations. Food for thought!
This is really impressive operating model for FedEx. Sorting packages from all 140 aircrafts and passing right packages to right destination aircraft needs highly efficient and more importantly effective operations setup. Thanks for sharing the video for US operations. On that, it raises two questions: 1) Does FedEx have same efficient operating model at international hubs? 2) Is FedEx planning to expand its network through more international hubs or the company does not feel the need for it at this stage?
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Business Model Canvas: Explained with Examples
Got a new business idea, but don’t know how to put it to work? Want to improve your existing business model? Overwhelmed by writing your business plan? There is a one-page technique that can provide you the solution you are looking for, and that’s the business model canvas.
In this guide, you’ll have the Business Model Canvas explained, along with steps on how to create one. All business model canvas examples in the post can be edited online.
What is a Business Model Canvas
A business model is simply a plan describing how a business intends to make money. It explains who your customer base is and how you deliver value to them and the related details of financing. And the business model canvas lets you define these different components on a single page.
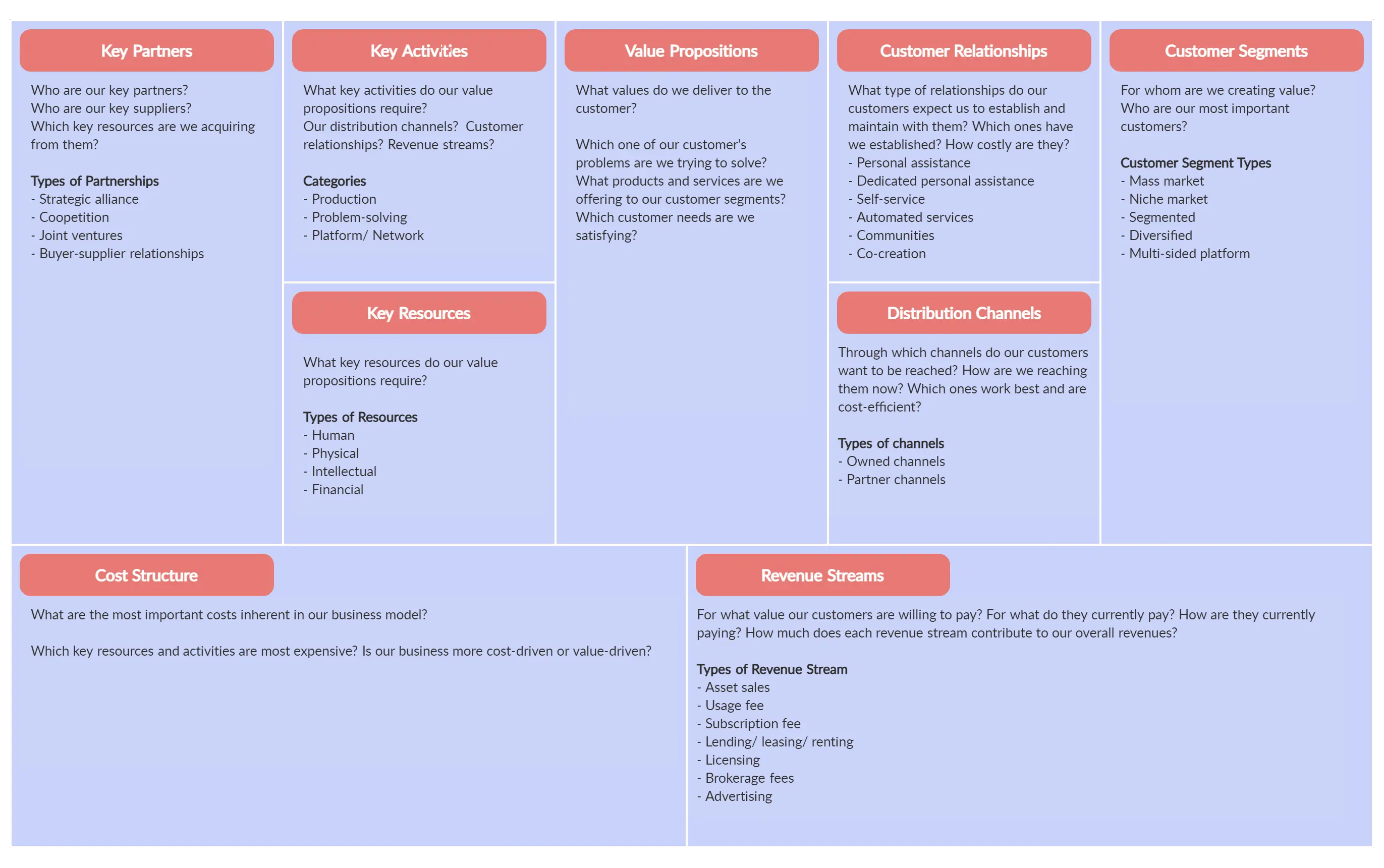
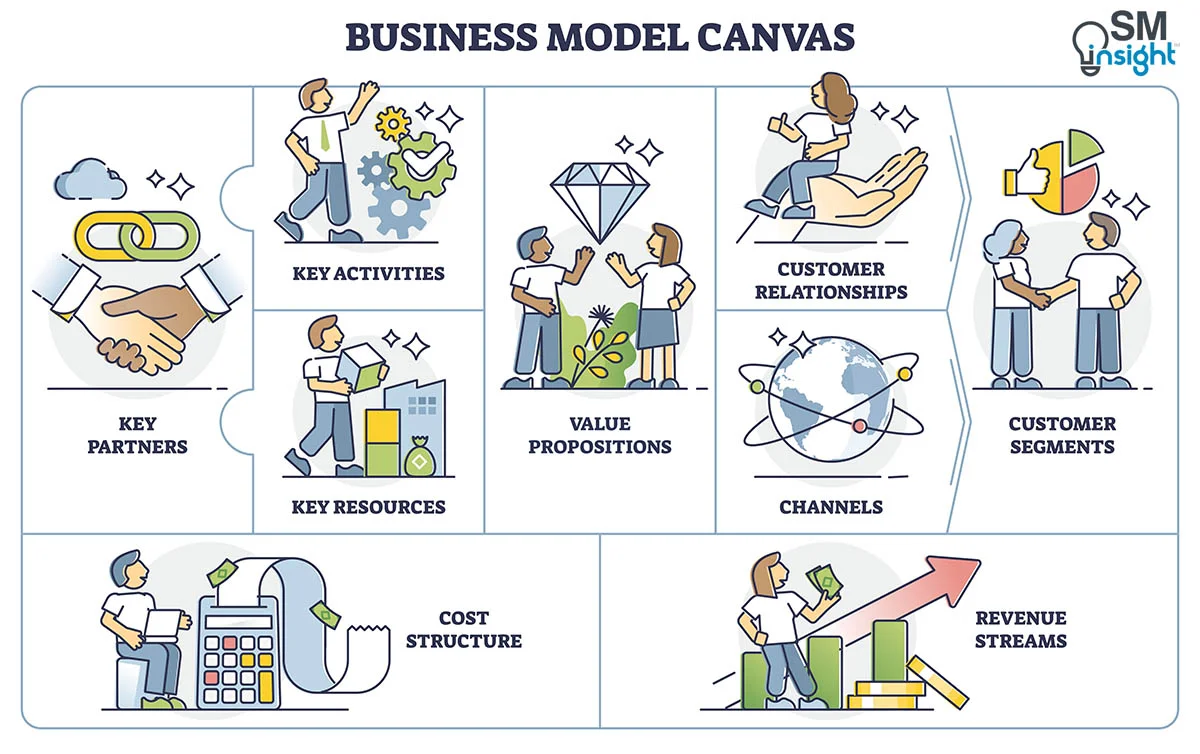
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that lets you visualize and assess your business idea or concept. It’s a one-page document containing nine boxes that represent different fundamental elements of a business.
The business model canvas beats the traditional business plan that spans across several pages, by offering a much easier way to understand the different core elements of a business.
The right side of the canvas focuses on the customer or the market (external factors that are not under your control) while the left side of the canvas focuses on the business (internal factors that are mostly under your control). In the middle, you get the value propositions that represent the exchange of value between your business and your customers.
The business model canvas was originally developed by Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur and introduced in their book ‘ Business Model Generation ’ as a visual framework for planning, developing and testing the business model(s) of an organization.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Business Model Canvas
Why do you need a business model canvas? The answer is simple. The business model canvas offers several benefits for businesses and entrepreneurs. It is a valuable tool and provides a visual and structured approach to designing, analyzing, optimizing, and communicating your business model.
- The business model canvas provides a comprehensive overview of a business model’s essential aspects. The BMC provides a quick outline of the business model and is devoid of unnecessary details compared to the traditional business plan.
- The comprehensive overview also ensures that the team considers all required components of their business model and can identify gaps or areas for improvement.
- The BMC allows the team to have a holistic and shared understanding of the business model while enabling them to align and collaborate effectively.
- The visual nature of the business model canvas makes it easier to refer to and understand by anyone. The business model canvas combines all vital business model elements in a single, easy-to-understand canvas.
- The BMC can be considered a strategic analysis tool as it enables you to examine a business model’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges.
- It’s easier to edit and can be easily shared with employees and stakeholders.
- The BMC is a flexible and adaptable tool that can be updated and revised as the business evolves. Keep your business agile and responsive to market changes and customer needs.
- The business model canvas can be used by large corporations and startups with just a few employees.
- The business model canvas effectively facilitates discussions among team members, investors, partners, customers, and other stakeholders. It clarifies how different aspects of the business are related and ensures a shared understanding of the business model.
- You can use a BMC template to facilitate discussions and guide brainstorming brainstorming sessions to generate insights and ideas to refine the business model and make strategic decisions.
- The BMC is action-oriented, encouraging businesses to identify activities and initiatives to improve their business model to drive business growth.
- A business model canvas provides a structured approach for businesses to explore possibilities and experiment with new ideas. This encourages creativity and innovation, which in turn encourages team members to think outside the box.
How to Make a Business Model Canvas
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model.
Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
While you can create a business model canvas with whiteboards, sticky notes, and markers, using an online platform like Creately will ensure that your work can be accessed from anywhere, anytime. Create a workspace in Creately and provide editing/reviewing permission to start.
Step 2: Set the context Clearly define the purpose and the scope of what you want to map out and visualize in the business model canvas. Narrow down the business or idea you want to analyze with the team and its context.
Step 3: Draw the canvas Divide the workspace into nine equal sections to represent the nine building blocks of the business model canvas.
Step 4: Identify the key building blocks Label each section as customer segment, value proposition, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, and cost structure.
Step 5: Fill in the canvas Work with your team to fill in each section of the canvas with relevant information. You can use data, keywords, diagrams, and more to represent ideas and concepts.
Step 6: Analyze and iterate Once your team has filled in the business model canvas, analyze the relationships to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and challenges. Discuss improvements and make adjustments as necessary.
Step 7: Finalize Finalize and use the model as a visual reference to communicate and align your business model with stakeholders. You can also use the model to make informed and strategic decisions and guide your business.
What are the Key Building Blocks of the Business Model Canvas?
There are nine building blocks in the business model canvas and they are:
Customer Segments
Customer relationships, revenue streams, key activities, key resources, key partners, cost structure.
- Value Proposition
When filling out a Business Model Canvas, you will brainstorm and conduct research on each of these elements. The data you collect can be placed in each relevant section of the canvas. So have a business model canvas ready when you start the exercise.
Let’s look into what the 9 components of the BMC are in more detail.
These are the groups of people or companies that you are trying to target and sell your product or service to.
Segmenting your customers based on similarities such as geographical area, gender, age, behaviors, interests, etc. gives you the opportunity to better serve their needs, specifically by customizing the solution you are providing them.
After a thorough analysis of your customer segments, you can determine who you should serve and ignore. Then create customer personas for each of the selected customer segments.
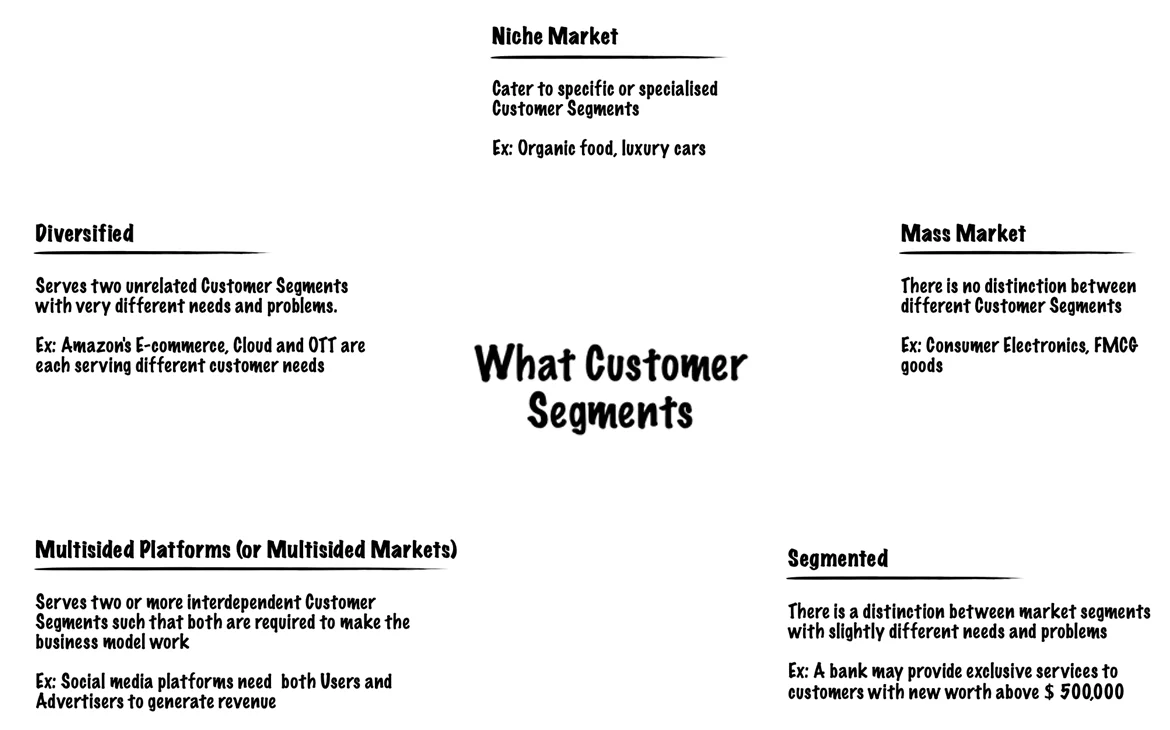
There are different customer segments a business model can target and they are;
- Mass market: A business model that focuses on mass markets doesn’t group its customers into segments. Instead, it focuses on the general population or a large group of people with similar needs. For example, a product like a phone.
- Niche market: Here the focus is centered on a specific group of people with unique needs and traits. Here the value propositions, distribution channels, and customer relationships should be customized to meet their specific requirements. An example would be buyers of sports shoes.
- Segmented: Based on slightly different needs, there could be different groups within the main customer segment. Accordingly, you can create different value propositions, distribution channels, etc. to meet the different needs of these segments.
- Diversified: A diversified market segment includes customers with very different needs.
- Multi-sided markets: this includes interdependent customer segments. For example, a credit card company caters to both their credit card holders as well as merchants who accept those cards.
Use STP Model templates for segmenting your market and developing ideal marketing campaigns
Visualize, assess, and update your business model. Collaborate on brainstorming with your team on your next business model innovation.
In this section, you need to establish the type of relationship you will have with each of your customer segments or how you will interact with them throughout their journey with your company.
There are several types of customer relationships
- Personal assistance: you interact with the customer in person or by email, through phone call or other means.
- Dedicated personal assistance: you assign a dedicated customer representative to an individual customer.
- Self-service: here you maintain no relationship with the customer, but provides what the customer needs to help themselves.
- Automated services: this includes automated processes or machinery that helps customers perform services themselves.
- Communities: these include online communities where customers can help each other solve their own problems with regard to the product or service.
- Co-creation: here the company allows the customer to get involved in the designing or development of the product. For example, YouTube has given its users the opportunity to create content for its audience.
You can understand the kind of relationship your customer has with your company through a customer journey map . It will help you identify the different stages your customers go through when interacting with your company. And it will help you make sense of how to acquire, retain and grow your customers.
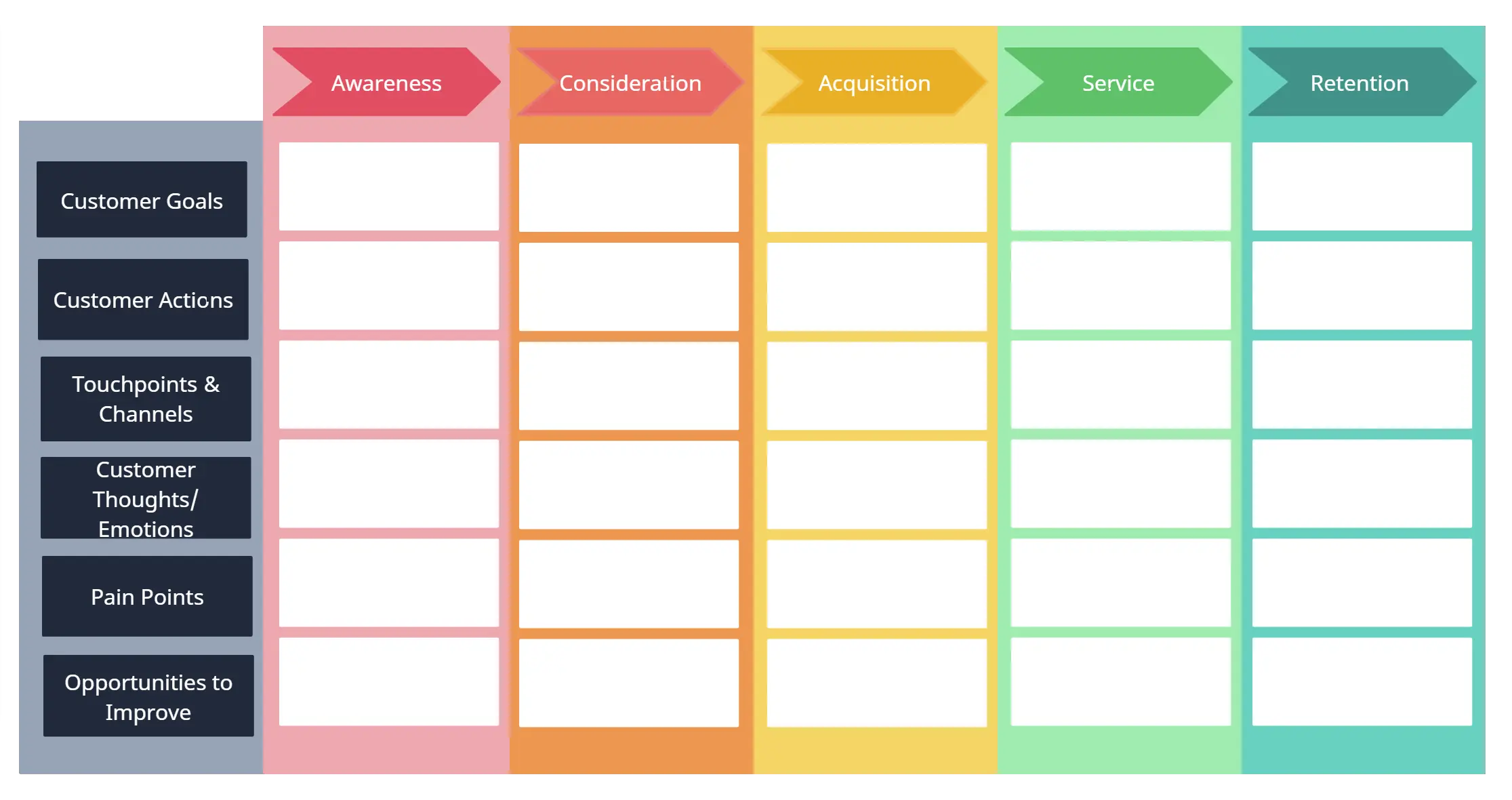
This block is to describe how your company will communicate with and reach out to your customers. Channels are the touchpoints that let your customers connect with your company.
Channels play a role in raising awareness of your product or service among customers and delivering your value propositions to them. Channels can also be used to allow customers the avenue to buy products or services and offer post-purchase support.
There are two types of channels
- Owned channels: company website, social media sites, in-house sales, etc.
- Partner channels: partner-owned websites, wholesale distribution, retail, etc.
Revenues streams are the sources from which a company generates money by selling their product or service to the customers. And in this block, you should describe how you will earn revenue from your value propositions.
A revenue stream can belong to one of the following revenue models,
- Transaction-based revenue: made from customers who make a one-time payment
- Recurring revenue: made from ongoing payments for continuing services or post-sale services
There are several ways you can generate revenue from
- Asset sales: by selling the rights of ownership for a product to a buyer
- Usage fee: by charging the customer for the use of its product or service
- Subscription fee: by charging the customer for using its product regularly and consistently
- Lending/ leasing/ renting: the customer pays to get exclusive rights to use an asset for a fixed period of time
- Licensing: customer pays to get permission to use the company’s intellectual property
- Brokerage fees: revenue generated by acting as an intermediary between two or more parties
- Advertising: by charging the customer to advertise a product, service or brand using company platforms
What are the activities/ tasks that need to be completed to fulfill your business purpose? In this section, you should list down all the key activities you need to do to make your business model work.
These key activities should focus on fulfilling its value proposition, reaching customer segments and maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue.
There are 3 categories of key activities;
- Production: designing, manufacturing and delivering a product in significant quantities and/ or of superior quality.
- Problem-solving: finding new solutions to individual problems faced by customers.
- Platform/ network: Creating and maintaining platforms. For example, Microsoft provides a reliable operating system to support third-party software products.
This is where you list down which key resources or the main inputs you need to carry out your key activities in order to create your value proposition.
There are several types of key resources and they are
- Human (employees)
- Financial (cash, lines of credit, etc.)
- Intellectual (brand, patents, IP, copyright)
- Physical (equipment, inventory, buildings)
Key partners are the external companies or suppliers that will help you carry out your key activities. These partnerships are forged in oder to reduce risks and acquire resources.
Types of partnerships are
- Strategic alliance: partnership between non-competitors
- Coopetition: strategic partnership between partners
- Joint ventures: partners developing a new business
- Buyer-supplier relationships: ensure reliable supplies
In this block, you identify all the costs associated with operating your business model.
You’ll need to focus on evaluating the cost of creating and delivering your value propositions, creating revenue streams, and maintaining customer relationships. And this will be easier to do so once you have defined your key resources, activities, and partners.
Businesses can either be cost-driven (focuses on minimizing costs whenever possible) and value-driven (focuses on providing maximum value to the customer).
Value Propositions
This is the building block that is at the heart of the business model canvas. And it represents your unique solution (product or service) for a problem faced by a customer segment, or that creates value for the customer segment.
A value proposition should be unique or should be different from that of your competitors. If you are offering a new product, it should be innovative and disruptive. And if you are offering a product that already exists in the market, it should stand out with new features and attributes.
Value propositions can be either quantitative (price and speed of service) or qualitative (customer experience or design).
What to Avoid When Creating a Business Model Canvas
One thing to remember when creating a business model canvas is that it is a concise and focused document. It is designed to capture key elements of a business model and, as such, should not include detailed information. Some of the items to avoid include,
- Detailed financial projections such as revenue forecasts, cost breakdowns, and financial ratios. Revenue streams and cost structure should be represented at a high level, providing an overview rather than detailed projections.
- Detailed operational processes such as standard operating procedures of a business. The BMC focuses on the strategic and conceptual aspects.
- Comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. The business model canvas does not provide space for comprehensive marketing or sales strategies. These should be included in marketing or sales plans, which allow you to expand into more details.
- Legal or regulatory details such as intellectual property, licensing agreements, or compliance requirements. As these require more detailed and specialized attention, they are better suited to be addressed in separate legal or regulatory documents.
- Long-term strategic goals or vision statements. While the canvas helps to align the business model with the overall strategy, it should focus on the immediate and tangible aspects.
- Irrelevant or unnecessary information that does not directly relate to the business model. Including extra or unnecessary information can clutter the BMC and make it less effective in communicating the core elements.
What Are Your Thoughts on the Business Model Canvas?
Once you have completed your business model canvas, you can share it with your organization and stakeholders and get their feedback as well. The business model canvas is a living document, therefore after completing it you need to revisit and ensure that it is relevant, updated and accurate.
What best practices do you follow when creating a business model canvas? Do share your tips with us in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.

FAQs About the Business Model Canvas
- Use clear and concise language
- Use visual-aids
- Customize for your audience
- Highlight key insights
- Be open to feedback and discussion
More Related Articles

Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.

Business Model Canvas (BMC)

What is the Business Model Canvas
Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a framework that helps determine how a business creates, delivers, and captures values. It is a visual representation of the important aspects or parts to consider when designing a Business Model.
BMC aids in constructing a shared understanding of a business by condensing it into a simple, relevant, and intuitively understandable one-page visual while not oversimplifying the complexities of how enterprises function.
This concept has been applied and tested around the world and is used in organizations such as GE, P&G, Nestlé, IBM, Ericsson, and Deloitte, including Government Services of Canada and many more [1],[2] .
The Nine Building Blocks
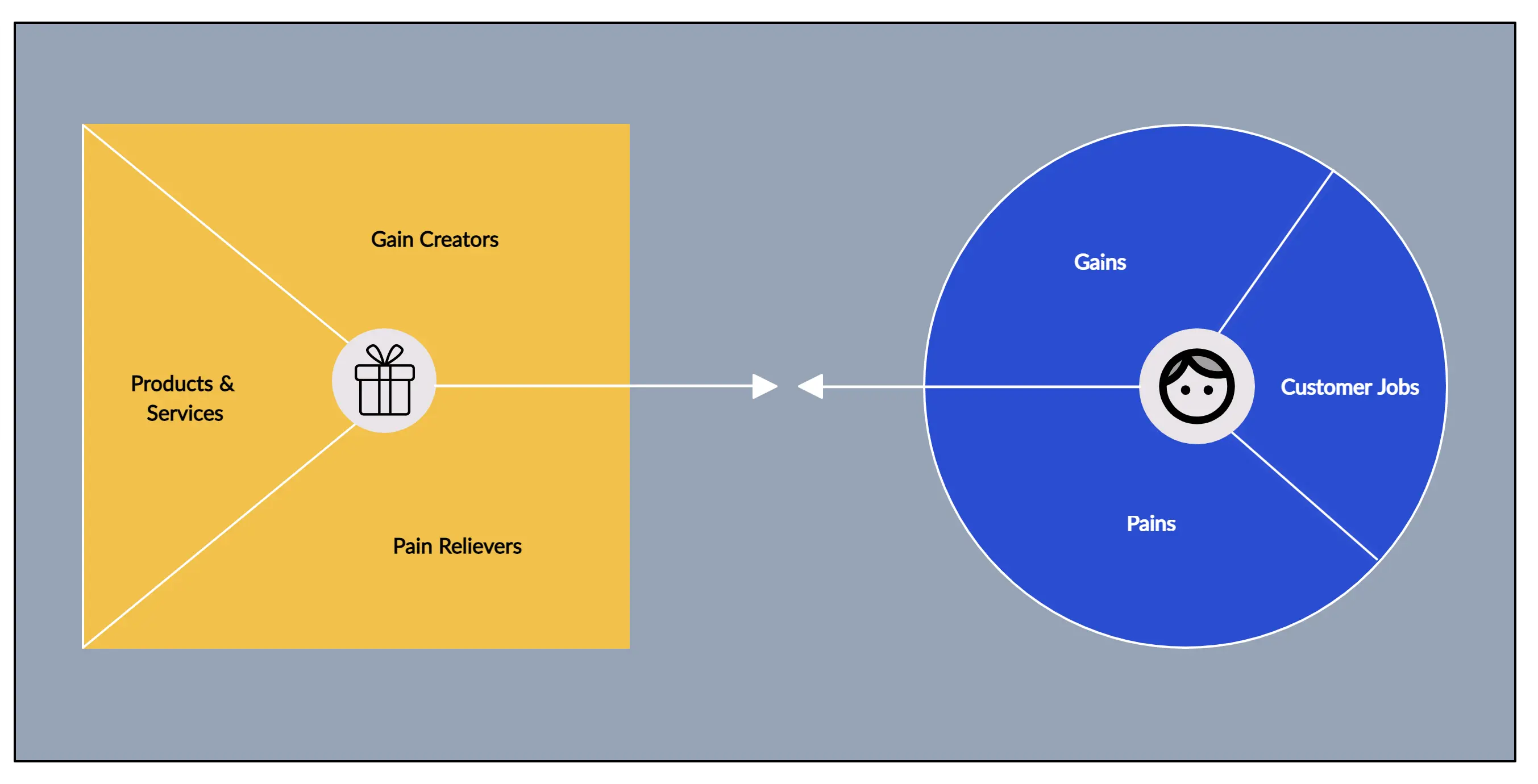
BMC describes a business through nine basic building blocks that show the logic of how a business intends to make money. These nine blocks cover the four main areas of a business: Customers, Offer, Infrastructure, and Financial Viability.
BMC acts as a shared language for describing, visualizing, assessing, and changing business models. It is like a blueprint for a strategy to be implemented through organizational structures, processes, and systems.
Each of these blocks is explained in more detail as follows:
1. Customer Segments (CS)
These are the groups of people or organizations that a business aims to reach and serve. Customers are the heart of a business model, and without (profitable) customers, a business cannot survive.
Customers are grouped into distinct segments with common needs, common behaviors, or other attributes. Customer groups represent separate segments if:
- Their needs require and justify a distinct offer.
- They are reached through different Distribution Channels.
- They require different types of relationships.
- They have substantially different profitability.
- They are willing to pay for different aspects of the offer.
An organization must make a conscious decision about which segment(s) to serve and which segments to ignore. Once this decision is made, a business model can be carefully designed around a strong understanding of specific customer needs.
The following two questions, if answered with clarity, help a business identify its CS.
- For whom are we creating value?
- Who are our most important customers?
- What are the customer archetypes?
Examples of some of the Customer Segments are shown in the figure:
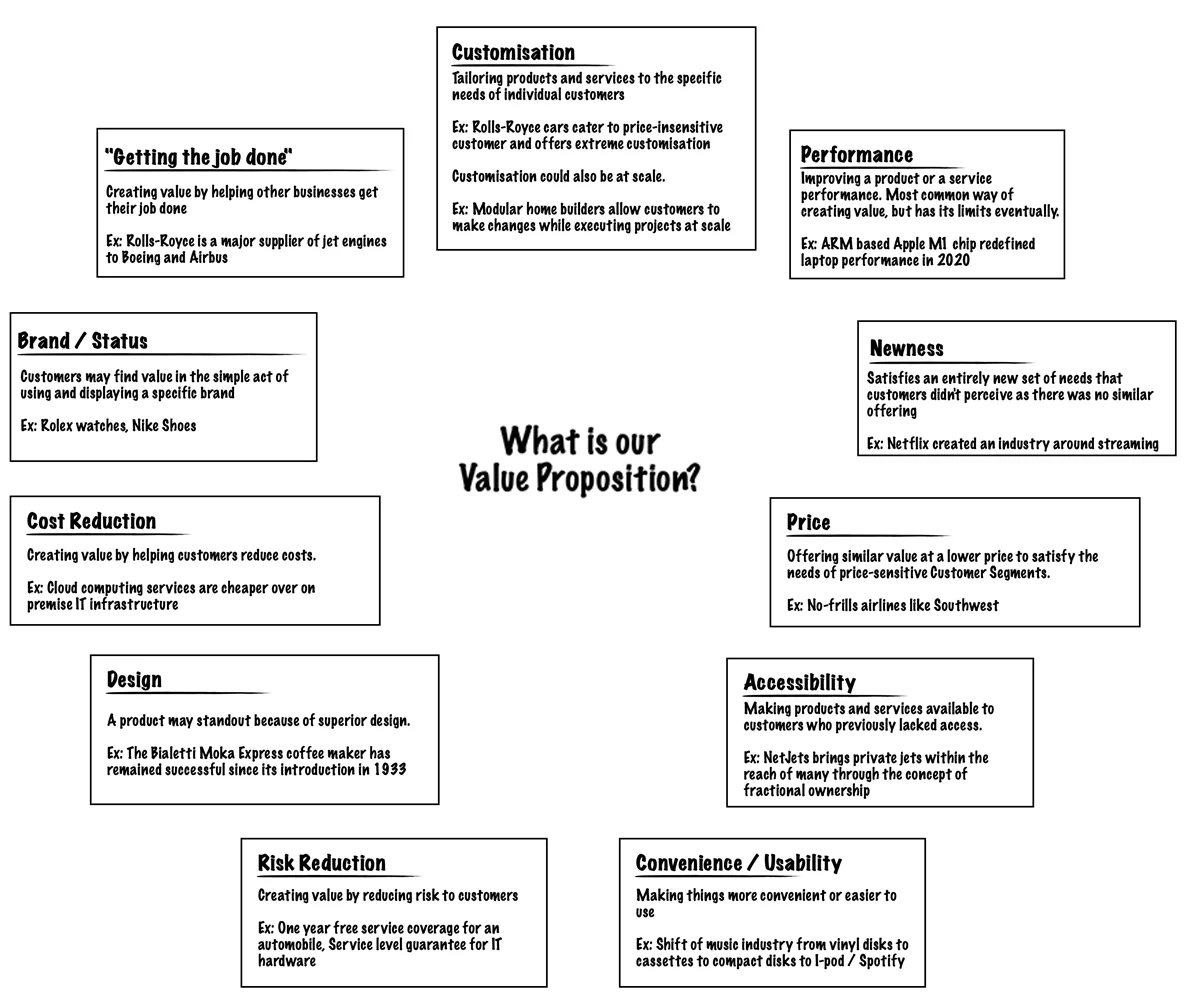
2. Value proposition (VP)
Value Proposition describes the bundle of products and services that create value for a specific Customer Segment chosen by a business.
A VP is the reason why customers turn to one company over another. VP must solve a customer’s problem or satisfy a need. A business can have more than one VP, but each must consist of a selected bundle of products and/or services that caters to the requirements of a specific Customer Segment.
While some VPs may be innovative and represent a new or disruptive offer, others may be similar to existing market offers but with added features and attributes.
An organization’s VP must answer the following questions with clarity:
- What value do we deliver to the customer?
- Which one of our customer’s problems are we helping to solve?
- Which customer needs are we satisfying?
- What bundles of products and services are we offering to each CS?
Elements from some of the following can contribute to customer value creation:
3. Channels (CH)
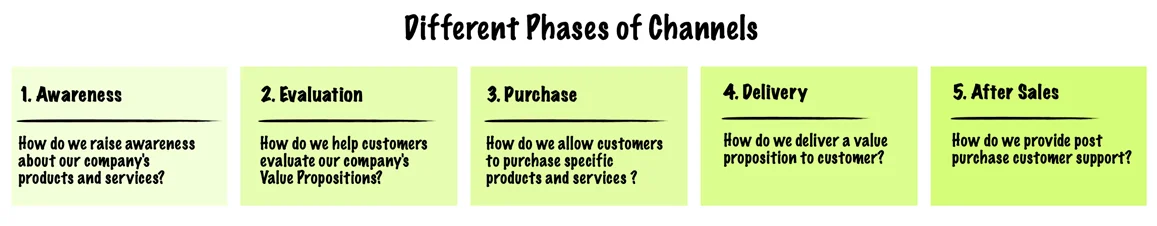
Channels describe how a company communicates with and reaches its Customer Segments to deliver a Value Proposition.
Channels are customer touch points that play an important role in the customer experience and serve several functions, including:
- Raising awareness about a company’s products and services
- Helping customers evaluate a company’s Value Proposition
- Allowing customers to purchase specific products and services
- Delivering a Value Proposition to customers
- Providing post-purchase customer support
To establish an effective channel, a company must first answer the following:
- Through which Channels do our Customer Segments want to be reached?
- How are we reaching them now?
- How are our Channels integrated?
- Which ones work best?
- Which ones are most cost-efficient?
- How are we integrating them with customer routines?
There are five distinct phases (figure below) through which a channel passes, and it could cover more than one of these phases at a time.
Channels can be either direct, indirect or hybrid, as shown:
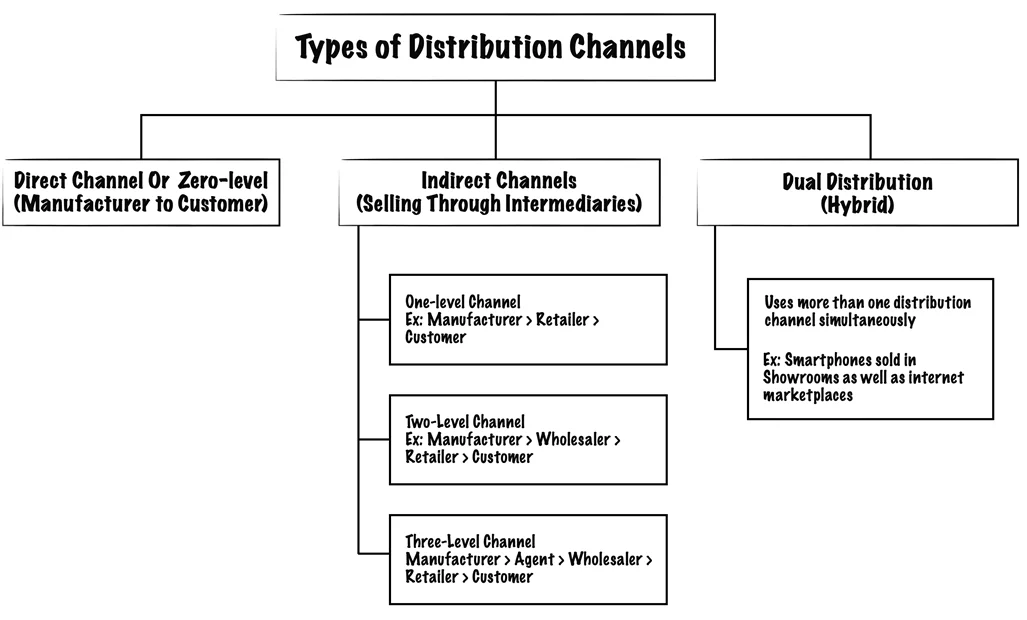
Finding the right mix of Channels to satisfy how customers want to be reached is crucial in bringing a Value Proposition to market and can create a great customer experience.
4. Customer Relationships (CR)
Customer Relationships describe the types of relationships a company establishes with specific Customer Segments. Relationships can range from personal to automated. An organization’s CR strategy may be driven by one of the following motivators:
- Customer acquisition
- Customer retention
- Boosting sales (upselling)
A business can arrive at the optimum CR by asking the following questions:
- What type of relationship does each of our Customer Segments expect us to establish and maintain with them?
- Which ones have we established?
- How costly are they?
- How are they integrated with the rest of our business model?
Several categories of Customer Relationships may co-exist in a company’s relationship with a particular Customer Segment. Some of which are:
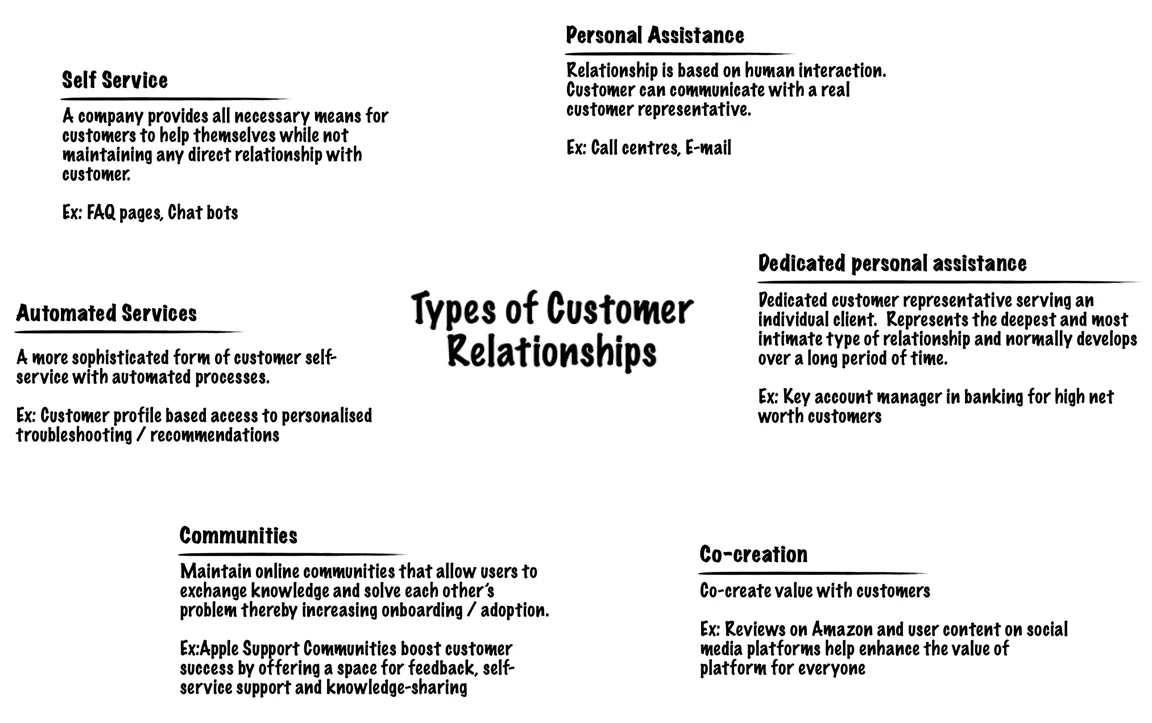
5. Revenue Streams (RS)
Revenue Streams represent the company’s cash (earnings) from each Customer Segment and are like the arteries of any business.
There are two distinct categories of Revenue Streams:
- Transaction Revenues which are one-time customer payments
- Recurring Revenues that are ongoing payments to either deliver a Value Proposition to customers or provide post-purchase customer support
A business can arrive at its ideal revenue stream by asking the following questions:
- For what value are our customers willing to pay?
- For what do they currently pay?
- How are they currently paying?
- How would they prefer to pay?
- How much does each Revenue Stream contribute to overall revenues?
There are several ways a business can generate revenue, such as:
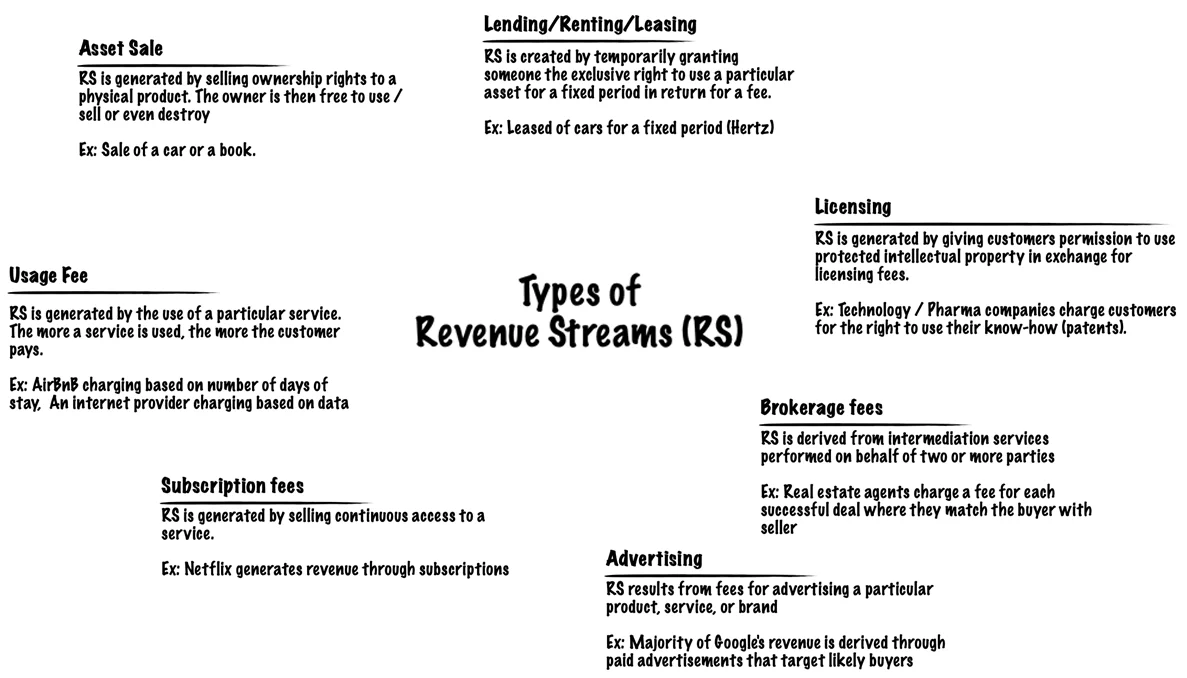
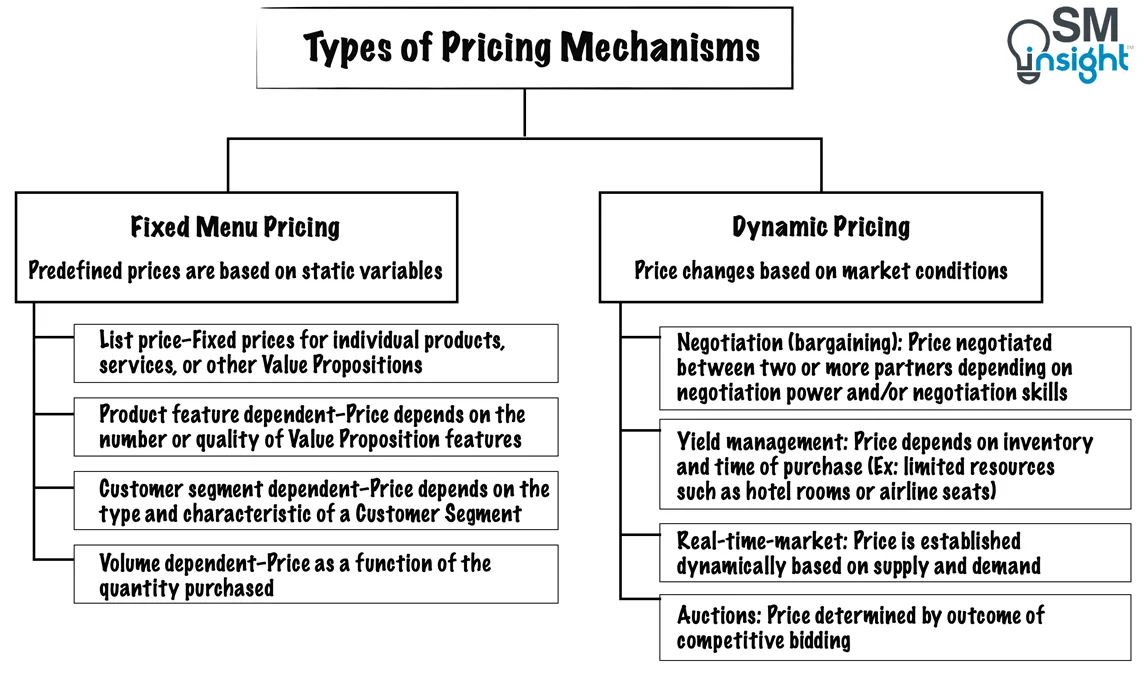
A business may have one or more Revenue Streams, each with different pricing mechanisms. The choice of pricing mechanism greatly influences the revenues generated.
There are two main types of pricing mechanisms, Fixed and Dynamic, as follows:
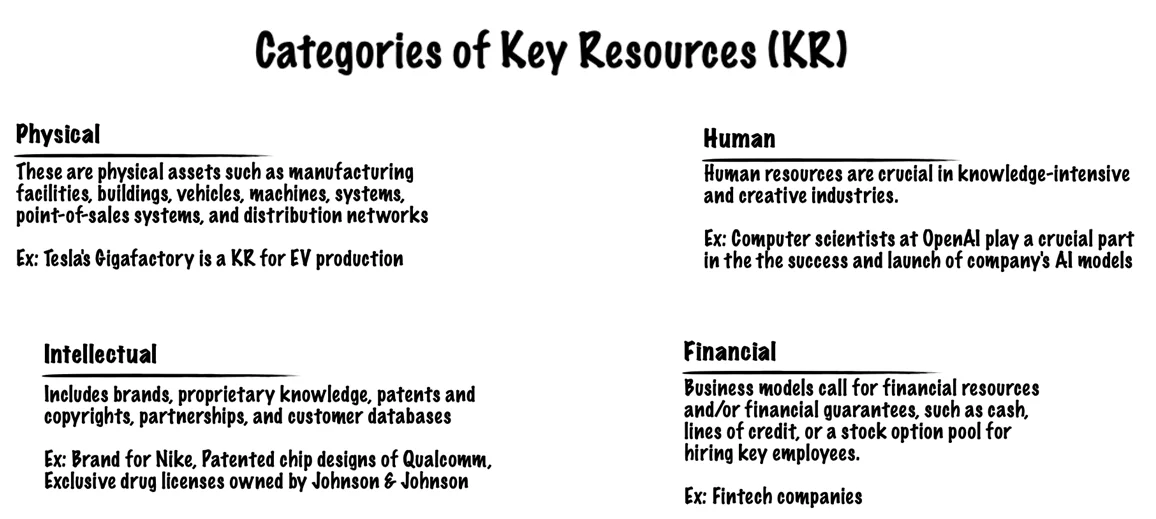
6. Key Resources (KR)
The Key Resources describe the most important assets required to make a business model work.
These resources allow an enterprise to create and offer a Value Proposition, reach markets, maintain relationships with Customer Segments, and earn revenues. Different Key Resources are needed depending on the type of business model.
For example, a chip fabrication business like TSMC [9] requires capital-intensive facilities worth billions of dollars, while a chip designer like NVIDIA [10] would need skilled manpower as its Key Resource.
Key Resources can be owned or leased by a business or acquired from its key partners. They can be identified by answering the following questions:
- What Key Resources do our Value Propositions require?
- What resources are required to sustain our Distribution Channels, Customer Relationships and Revenue Streams?
Key Resources can be categorized as follows:
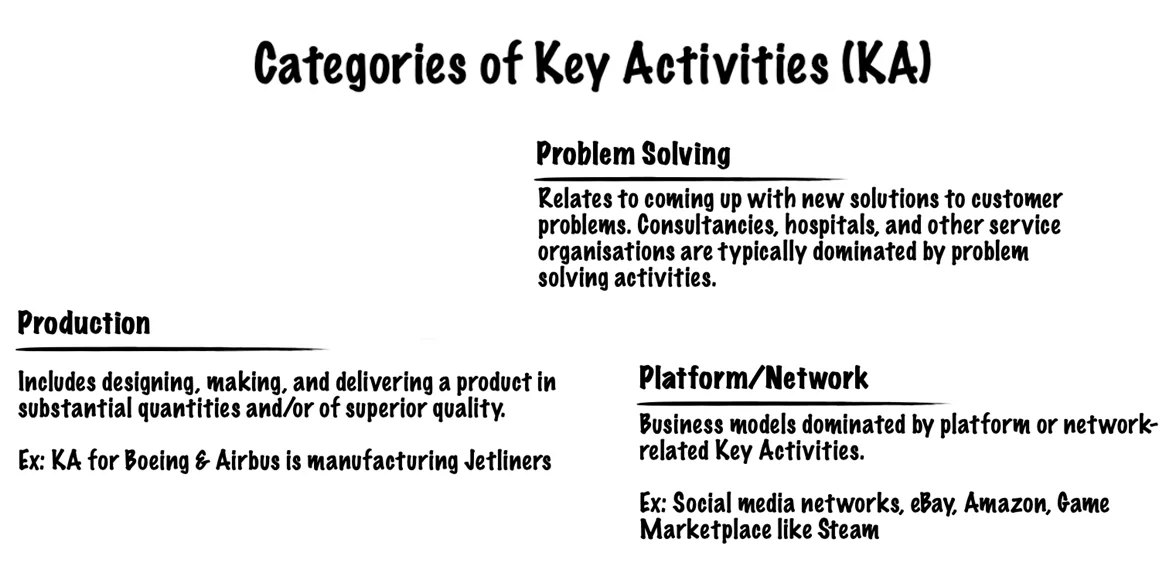
7. Key Activities (KA)
Key Activities describe the most important things a company must do to make its business model work. They are required to create and offer a Value Proposition, reach markets, maintain Customer Relationships, and earn revenues.
Key Activities differ depending on the business model type. For example, Microsoft’s Key Activity is software development, while for Dell, it is Supply Chain Management. For a consultancy firm like McKinsey, Key Activity is problem-solving.
A business can identify its Key Activities by answering the following questions:
- What Key Activities do our Value Propositions require?
- What activities directly contribute to maintaining our Distribution Channels, Customer Relationships and Revenue Streams?
Key Activities can be categorized as follows:
8. Key Partnerships (KP)
The Key Partnerships describe the network of suppliers and partners that make the business model. There are four types of partnerships:
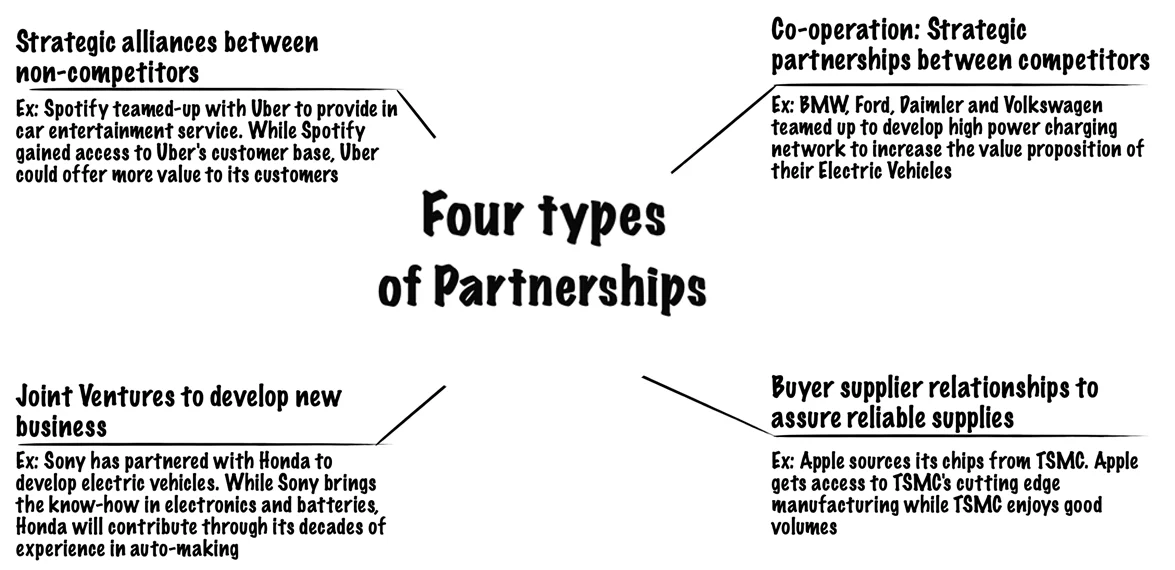
A business must ask the following questions before forming partnerships:
- Who are our key partners?
- Who are our key suppliers?
- Which Key Resources are we acquiring from partners?
- Which Key Activities do partners perform?
Primarily, there are three motivations for a business when creating partnerships, as shown:
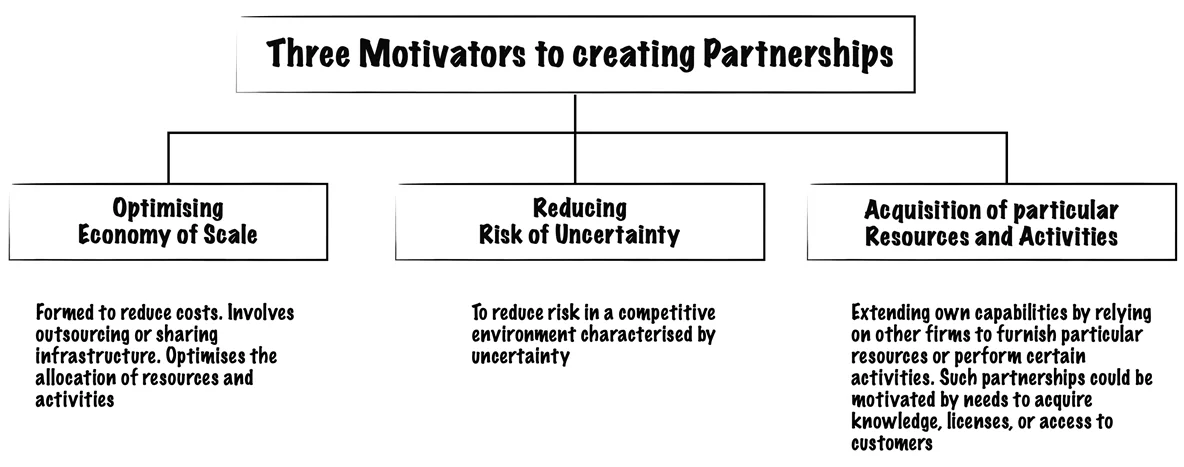
9. Cost Structure (CS)
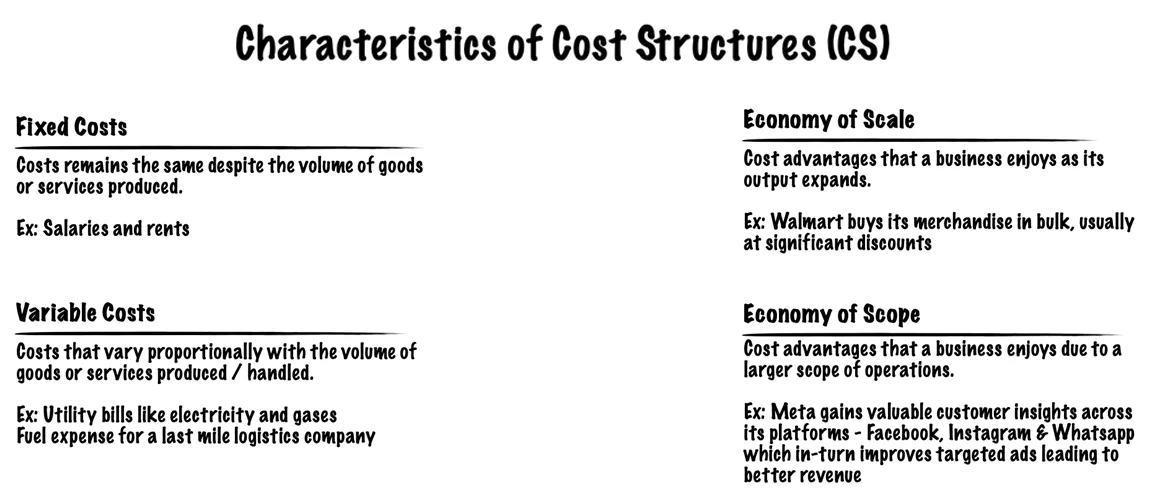
Cost Structure describes all costs incurred to operate a business model. A business incurs costs in creating and delivering value, maintaining customer relationships, and generating revenue. Costs are business-specific, where some are more cost-driven than others.
A business must answer the following questions to arrive at an optimum cost structure:
- What are the most important costs inherent in our business model?
- Which Key Resources are most expensive?
- Which Key Activities are most expensive?
While costs should be minimized in every business model, it is useful to distinguish between two broad classes of business model Cost Structures:
- Cost Driven : This model focuses on minimizing costs wherever possible. This approach aims at creating and maintaining the leanest possible Cost Structure, using low-price Value Propositions, maximum automation, and extensive outsourcing. Examples: No frills airlines like Southwest & easyJet, Fast food joints such as McDonald’s & KFC.
- Value Driven: Premium Value Propositions and a high degree of personalized service usually characterize value-driven business models. Examples: Luxury hotels, Expensive Cars like Rolls-Royce
Cost Structures can have the following characteristics:
Putting-it-all together
The nine business model Building Blocks form the basis for a handy tool, which is called the Business Model Canvas (figure below). This tool resembles a painter’s canvas preformatted with nine blocks that allow painting pictures of new or existing business models. It is a hands-on tool that fosters understanding, discussion, creativity, and analysis.
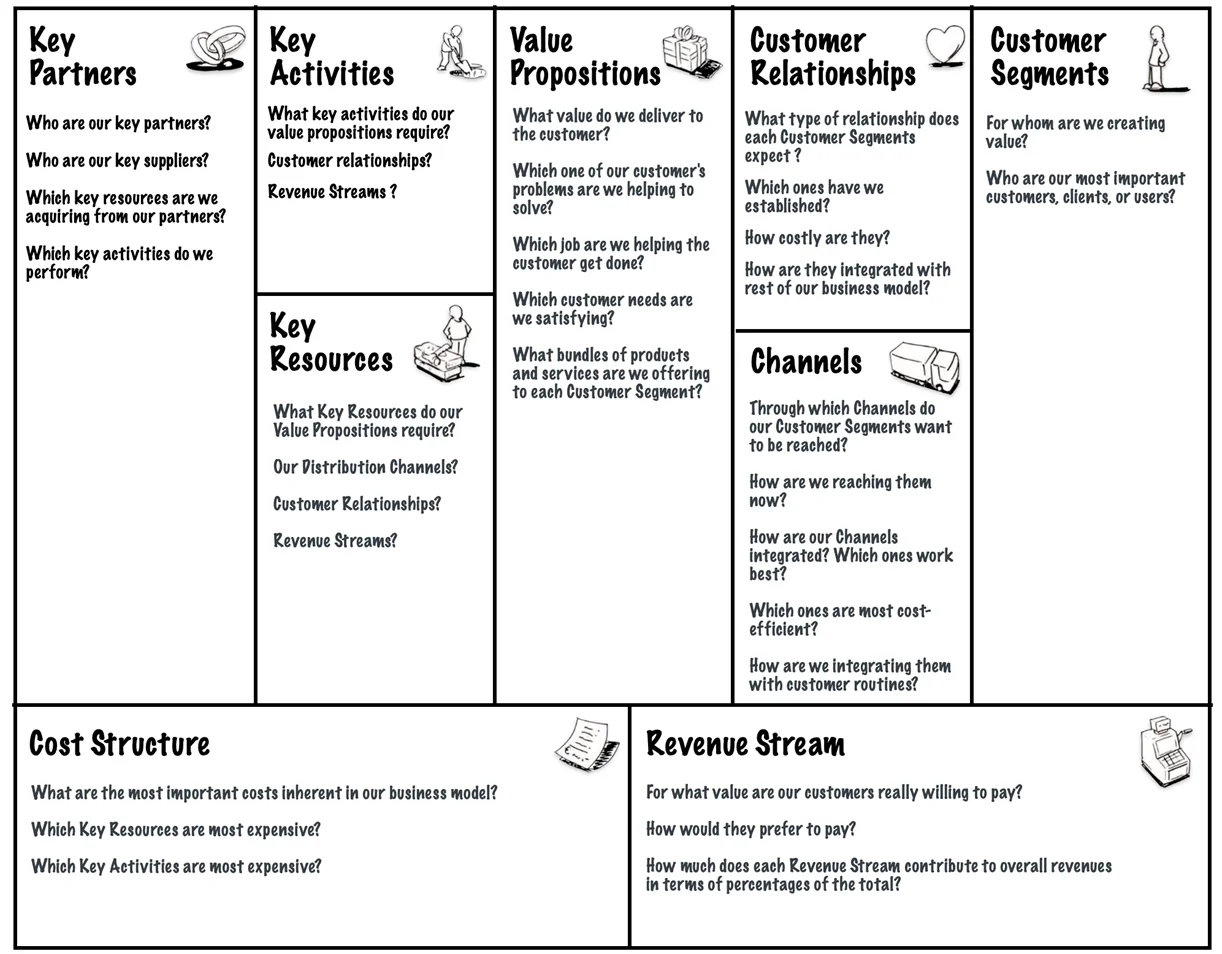
BMC works best when printed out on a large surface such that groups of people can jointly note, sketch, and discuss business model elements.
Example of Business Model Canvas
Nespresso [17] , a fully owned daughter company of Nestlé, changed the dynamics of the coffee industry by turning a transactional business (selling coffee through retail) into one with recurring revenues (selling proprietary pods through direct channels).
The two-part strategy involved selling their patented coffee machine to retail customers first to lock them into the brand. This generated a recurring demand for coffee refills (pods) that led to constant revenues. These pods were sold directly through mail/website/own stores, thereby eliminating middlemen/dealers, which further increased profits [1] .
Nespresso’s strategy plotted on a Business Model Canvas looks as follows:
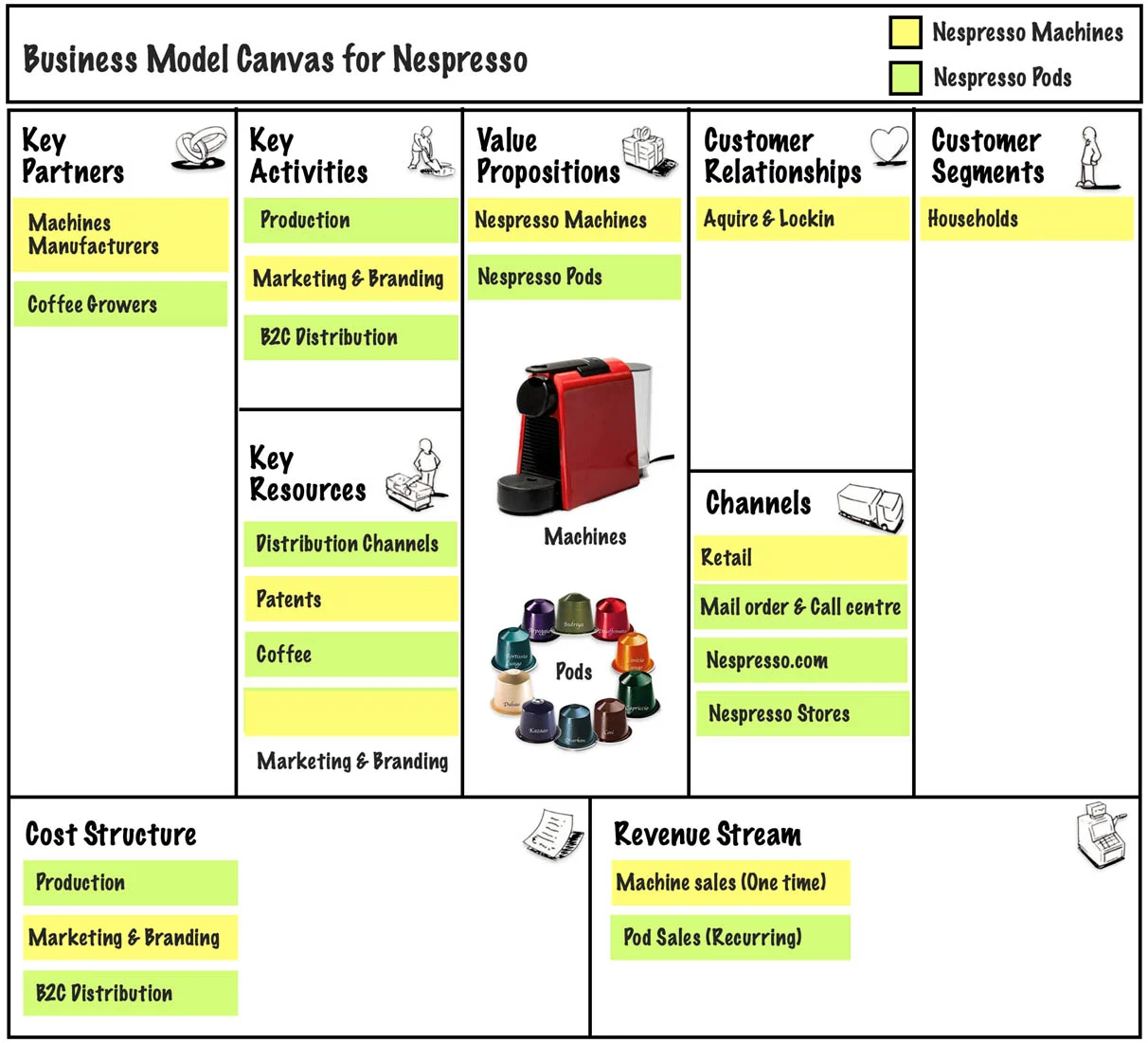
Business Model Canvas helped Nespresso establish a solid and enduring foundation by engaging consumers directly and bringing a barista-like experience within the reach of a home or an office.
Advantages & Limitations
- Encourages Collaboration – collaborative framework, which helps put different business stakeholders in sync. This improves the likelihood of generating new ideas and their quality.
- Facilitates testing of ideas before launch – allows business owners, strategists, and managers to think through business ideas as well as test concepts that would otherwise get tested with potential customers where the stakes are higher.
- Customer-centered approach – Key customer segments, relationships, activities, and value propositions are all elements that focus on creating, delivering, and capturing value for customers.
- Clarity – Analyzing the business through the lens of nine blocks brings better clarity and structure to the business model.
Limitations
- Lacks a section for defining the start-up’s mission statement, which is crucial to understanding the goals and objectives of any business.
- Overlooks the importance of a profit mechanism beyond costs and revenues, including decisions on how to use potential profits.
- The order of the canvas is not intuitive, making it difficult to read and understand the strategic decisions in a logical sequence.
- Does not depict interconnections between different elements, which can have a significant impact on the overall business model.
- Fails to acknowledge the company’s role within its ecosystem, including its impact on the environment and local communities.
- External factors such as competition, history, and other industry-specific factors are absent from the canvas, which can greatly influence the success of a business model.
1. “A Better Way to Think About Your Business Model”. Harvard Business Review, https://hbr.org/2013/05/a-better-way-to-think-about-yo . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
2. “Business Model Generation”. Alexander Osterwalder, https://www.strategyzer.com/books/business-model-generation . Accessed 28 Jul 2023
3. “The Apple M1 is a revolution that is changing the computing world”. Citymagazine, https://citymagazine.si/en/apple-m1-is-a-revolution-that-changes-the-computer-world/ . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
4. “Mass Customization”. Corporate Finance Institute, https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/management/mass-customization/ . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
5. “Moka Pot”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moka_pot . Accessed 29 Jul 2023
6. “NetJets Homepage”. NetJets, https://www.netjets.com/en-us/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
7. “Distribution Channels – Definition, Types, & Functions”. Feedough, https://www.feedough.com/distribution-channels-definition-types-functions/ . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
8. “Lease from Hertz”. Hertz, https://www.hertz.com/rentacar/rental-car/car-lease . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
9. “TSMC”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TSMC . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
10. “NVIDIA”. Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nvidia . Accessed 30 Jul 2023
11. “BMW, Daimler, Ford and Volkswagen team up on high-power charging network”. Techcrunch, https://techcrunch.com/2017/11/03/bmw-daimler-ford-and-volkswagen-team-up-on-high-power-charging-network/ . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
12. “Honda And Sony Combine Talents To Build Electric Vehicles”. Forbes, https://www.forbes.com/sites/peterlyon/2022/06/26/honda-and-sony-announce-joint-venture-to-build-electric-vehicles/ . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
13. “Uber and Spotify launch car music playlist partnership”. BBC, https://www.bbc.com/news/technology-30080974 . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
14. “Walmart Has the Scale and Infrastructure to Generate Positive Gains”. Yahoo Finance, https://finance.yahoo.com/news/walmart-scale-infrastructure-generate-positive-201822628.html . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
15. “Demand-Side Economies of Scope in Big Tech Business Modelling and Strategy”. MDPI, https://www.mdpi.com/2079-8954/10/6/246 . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
16. “The Business Model Canvas”. Strategyzer, https://www.strategyzer.com/canvas/business-model-canvas . Accessed 31 Jul 2023
17. “HomePage”. Nespresso, https://www.nespresso.com/us/en/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
18. “Business Model Canvas of Nespresso”. Alex Osterwalder, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dhQh-tryXOg . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
19. “Nespresso Capsule”. Electromall, https://electromall.net/product/nespresso-capsule/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
20. “The Best Nespresso Machine (But It’s Not for Everyone)”. Newyork Times, https://www.nytimes.com/wirecutter/reviews/best-nespresso-machine/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
21. “Business Model Canvas”. Think Design, https://think.design/user-design-research/business-model-canvas/ . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
22. “6 Problems with the Business Model Canvas”. The Pourquoi Pas, https://www.thepourquoipas.com/post/problems-with-the-business-model-canvas . Accessed 01 Aug 2023
- McKinsey 7S Model
- Elaboration Likelihood Model of Persuasion
- The Johari Window Model
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Data & Visuals

Partner Center
- Integrations
- Learning Center
How to Build a Product Roadmap Based on a Business Model Canvas
Could you list all of the key building blocks you need to develop, manage, maintain, market, and sell a product on a single sheet of paper? With the business model canvas, you can! Using the business model canvas approach is a great way to force yourself to focus on the most strategically important elements of your product. As the name suggests, the typical use case for this tool is to outline the fundamental building blocks of a business, but it also can work really well for a product.
Today we’ll show you how the business model canvas works and how you can use it to come up with a high-level product strategy.
What is a Business Model Canvas?
As you can see from the sample example below (thanks, Strategyzer.com), a business model canvas is a one-page summary describing the high-level strategic details needed to get a business (or product) successfully to market.
The categories or buckets contained in a canvas can be customized. But most will look similar to the one here—covering such key areas as:
- The product’s value propositions (what it does and promises)
- Customer segments (who it’s for)
- Key activities (the steps the team must complete to make it successful)
- Key resources (what personnel, tools, and budget the team will have access to)
- Channels (how the organization will market and sell it)
- Customer relationships (how the team will support and work with its customer base)
- Key partners (how third parties will fit into the plan)
- Cost structure (what it costs to build the product as well as how to sell and support it)
- Revenue streams (how the product will make money)
If you think about it, that’s a fairly comprehensive set of building blocks you’ll need to think through for your product before you begin developing it. There will certainly be additional factors that’ll affect your strategy, but if you can fill in these high-level details—which, as you can see, should fit comfortably on a single page—you’ll have a useful strategic guide for developing your product roadmap.
Why Should I Use a Business Model Canvas to Develop a Product Roadmap?
Okay, but why? What’s the benefit of building a business model canvas (or the, even more, stripped-down variation, the lean canvas) to guide my product roadmap ?
There are plenty of reasons. But simply put, you can think of a business model canvas as a mission statement for your product roadmap. It’s a handy reference you can refer to, to make sure your roadmap always reflects all the strategic elements needed for your product’s success.
Tweet This: “Think of a business model canvas as a mission statement for your product roadmap.”
Our co-founder Jim Semick has a couple of great short videos explaining the business model canvas concept, which you can check out in the player below.
As Jim explains, here are a few of the benefits of using a business model canvas to think through product strategies:
1. You can use a business model canvas to roadmap quickly.
You can use this canvas approach in just a few hours (and as Jim says, you can even do it with sticky-notes).
This way, rather than trying to write out every detail about your product plan beforehand, you can just document the highlights—and then you can get rolling translating the canvas into your product roadmap.

2. A business model canvas will be more agile.
One problem with the old structure of documenting a business model—the traditional business plan—was that it was almost always inaccurate as soon as the author finished drafting it.
These meaty plans included detailed cost estimates, revenue projections going years into the future, and long-term plans for growing the staff. How could any of that remain accurate for long?
In product terms, you can think of the business plan as resembling an MRD (Market Requirements Document). It’s long, detailed, and probably mostly untrue by the time it’s done.
But because you can put a canvas together so quickly, it will much more accurately reflect your strategic thinking and your company’s current reality. And if things change, it’ll be easier than a long and detailed plan to adjust. This brings us to Jim’s third benefit…
3. Business model canvas roadmaps allow you to pivot as needed.
If you build a business model canvas to guide your business roadmap , and something happens that forces you to re-prioritize or pivot your product , it will be a lot easier to update this short, high-level document than it would be if you had some monster MRD or business plan to tear apart and edit.
With a one-page business model canvas acting as the strategic undergirding for your roadmap, you’ll always be able to quickly spot any items or plans that need updating whenever priorities change or new realities demand that you adjust your approach.
How Can I Use A Business Model Canvas to Guide My Product Roadmap?
The alexa example.
Let’s talk through a hypothetical example, using Amazon’s Echo device (“Alexa”) as our guide.
Imagine that as they were talking through what belonged in the “Revenue Streams” bucket of the business model canvas, Amazon’s Echo team came up with three sources of revenue to start with:
1) Selling Echo devices.
2) Using the device to sell other stuff as customers ask it to connect to the Amazon marketplace. (“Alexa, please add laundry detergent pods to my shopping cart.”)
3) Licensing Echo’s proprietary speech-recognition technology to other businesses.
Now, if the Echo product team put these on their business model canvas, they’d know that they need to make room for budget, time, and resources on their product roadmap for all of these revenue streams.
Another Hypothetical Example of the Business Model Canvas: Channels
Or think about the Channels bucket in the business model canvas. If your team was building out a canvas, maybe you’d have several ideas for reaching customers:
1) The in-house sales team. 2) Affiliate partners. 3) Word-of-mouth advertising from users.
It’s easy to write. But how are you going to translate that “word-of-mouth” strategy into an actual plan?
Maybe you’ll need to budget time and resources for developing things right into your product that make it easier for users to share their experiences with friends, such as a handy tool to help them tweet about it. Maybe you’ll even want to include an “Invite a friend” feature that lets users easier send a trial license to friends, or a couponing feature that offers some reward to a user who brings in two more users.
The point is, your business model canvas can serve as a great strategic reminder of the things you’ve determined are important enough to make it onto your product roadmap .
So you can always look back and see immediately—it’s just one page, after all—if you’re still working on all of the essential elements of your product, or if you’ve inadvertently strayed from them and gotten lost in the wrong details.
That’s why we’re big proponents of the business model canvas approach to guiding your product roadmap .
Do you have an opinion about using the business model canvas approach for developing and documenting your product’s strategy? Feel free to share them in the comments section.

Product Management Training: 5 Excellent Resources
If you want to become a software developer, one option is to major in computer science or software engineering in...
A Product Manager’s Role in SAFe®
Agile started with software development. Although many organizations have found the principles beneficial. The ability to quickly assess, adjust, and...
5 Roadmap Templates for Product Executives
Product roadmaps shouldn’t be a one-size-fits-all proposition, as different stakeholders care about various elements and require different levels of detail....
Continue exploring
You can search or explore specific categories.
Product Updates
Company news and updates, templates and workbooks, remote product management, product metrics and analytics, product strategy example, product managers, prioritization and backlog, tools and resources, customer-centricity, product leadership, product management, roadmap and roadmap management, product strategy, agile & product development, career and interviews, try productplan free for 14 days, share on mastodon.
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
The Business Model Canvas
What is the business model canvas.
The business model canvas is a tool designers use to map out a business or product’s key actors, activities and resources, the value proposition for target customers, customer relationships, channels involved and financial matters. It gives an overview to help identify requirements to deliver the service and more.
“A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value.” — Alexander Osterwalder, Co-creator of the Business Model Canvas
Learn about the business model canvas and how it helps in design.
- Transcript loading…
The Business Model Canvas – Flexible Chart, Early-Warning System and More
In service design , two tools are essential to use early in your design process: the business model canvas and the value proposition canvas . You can use the business model canvas to build an overview of changes to be made to an existing business (e.g., a merger) or of a totally new business opportunity or market gap . At the start of your design process, it’s vital to map out the business model of your service to see how it will fit into the marketplace. You’ll also need to ensure what you propose can bring maximum value to both your customers and business, and keep doing so in terms of customer retention, profitability and more.
To gain the most accurate vision of a proposed product or service, it’s essential to understand all the components and dynamics of not only the customer experience but also the service as a whole ecosystem . This ecosystem contains all the channels and touchpoints that must work together to deliver and sustain maximum value to the customer.
This canvas gives you several important advantages, namely these:
It’s collaborative – so you can bring the various partners together on the same page to generate and analyze ideas, and have an early testing ground for concepts before you advance to service staging a prototype.
It’s human-centered – so you can keep close track on how to create and maximize value for customers as well as stakeholders and other partners.
It makes it easier to collect rich data – if you have a clear purpose and strategy in mind.
A business model canvas typically contains 10 boxes:
Key Partners – The people who will help you fulfill the key activities, using the key resources.
Key Activities – Those vital actions that go into the everyday business to get things done; these are all the activities needed to realize and maintain the value proposition, and to power everything else involved.
Key Resources – The tools needed to get those things done, stretching across all areas the canvas covers to include, for example, customer retention.
Value Proposition – The item you think will create value for your customer: e.g., a new idea, a price drop. This is a summary of what your business will deliver to customers, and feeds into the value proposition canvas, the tool you’ll use to expand this.
Customer Relationships – Where you envision the relationship each customer segment expects: e.g., customer acquisition, retention and upselling (i.e., How do you get customers? How do you keep customers? How do you continue to create value for them?).
(Note: boxes 5 and 4 are closely linked as everything you do revolves around retaining the customer and considering the customer lifecycle.)
Customer Segments – Your most important customers (e.g., seniors); consider the value of personas here.
Channels – How you deliver the value proposition. Will it be online, through physical means or a combination? Here, you identify which channels are the best (both desirable for customers as well as cost-efficient and cost-effective for the brand).
Cost Structure – Here you find the most essential cost drivers. This allows you to consider the return on investment (ROI).
Revenue Streams – Where you find potential revenue sources (e.g., advertising).
Sustainability – How sustainable your offering is overall, to the environment, to the social good, etc.
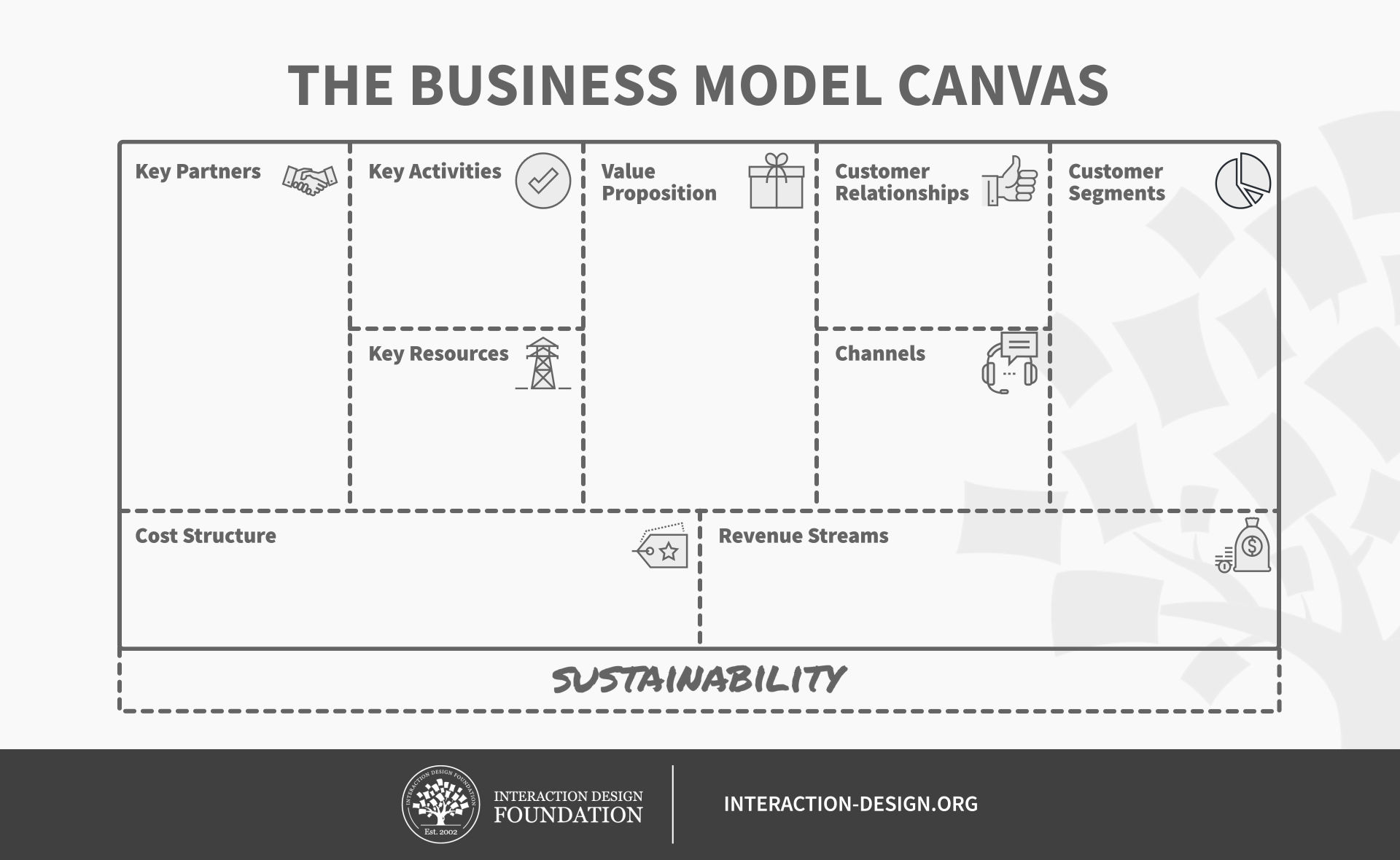
© Strategyzer AG, modified, CC-BY-SA-3.0
How to Build a Business Model Canvas
For the best results, follow these guidelines and aim to fill in all the gaps, looking out for cause-and-effect relationships that run between boxes/throughout:
Complete the top seven boxes (Key Partners to Customer Segments) – using all the information you can gather from your research.
Complete the next boxes:
Cost Structure – Determine the cost drivers from the Key Partners, Activities and Resources boxes; and
Revenue Streams – Determine these from the Customer Relationships, Customer Segments and Channels boxes.
Once you have established these, you can work to estimate them in monetary terms.
Complete the Sustainability box – according to the insights you’ve found.
Here’s an example of a business model canvas as a work in progress:
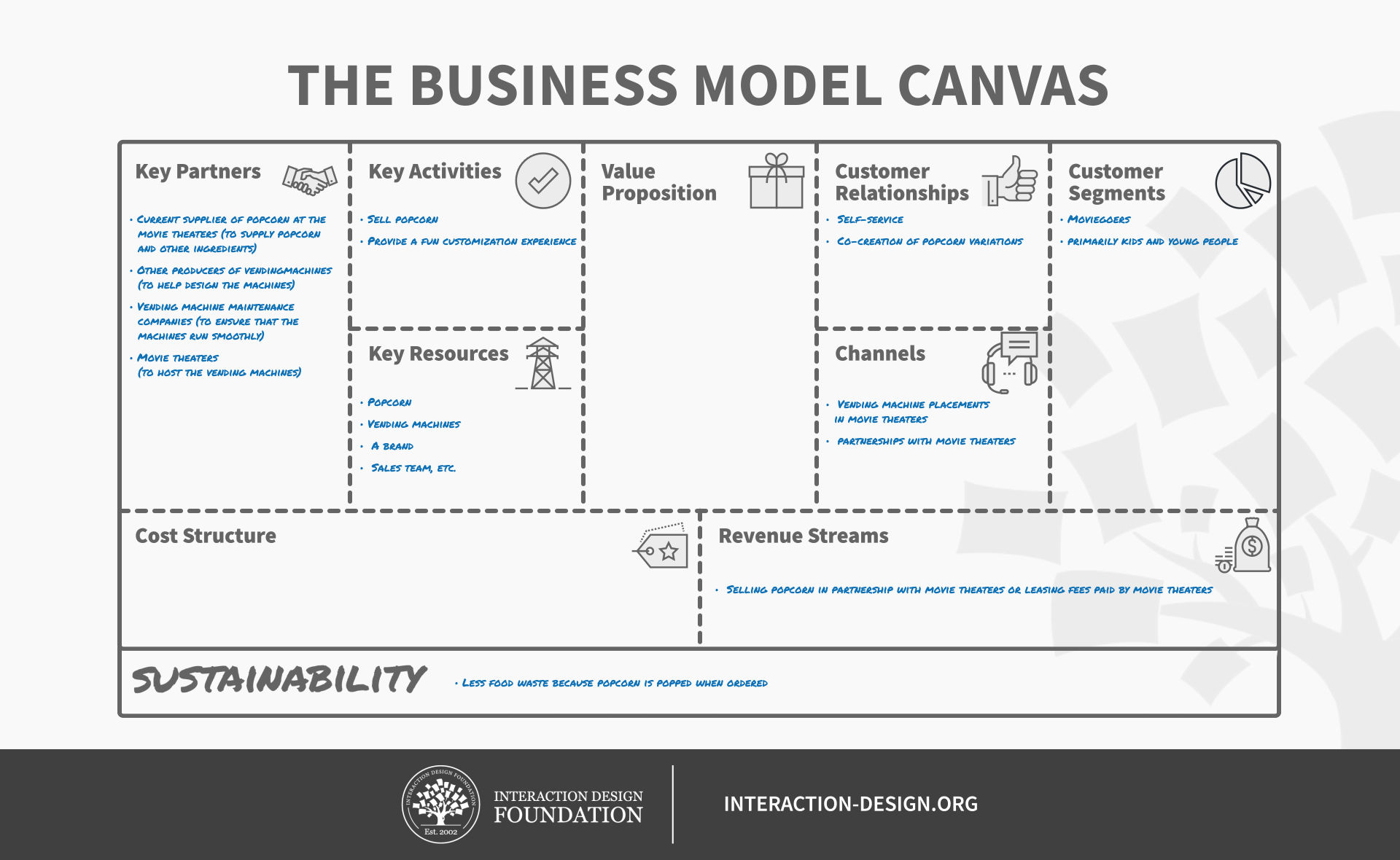
© Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0
Overall, remember your canvas is a flexible tool. It’s also a living document that you can revisit and use to find the most effective alternatives. With a clear sense of goals, a keen eye for detail and ear for input, and a readiness to refine this canvas, you can use it to fine-tune the best service prototype every time.
Learn More about The Business Model Canvas
Take our Service Design course , featuring a template for service blueprints.
Read this example-rich piece by experienced strategy designer Justin Lokitz for tips on using the business model canvas .
Find some additional tips on how to make the most of your business model canvas here .
Literature on the Business Model Canvas
Here’s the entire UX literature on the Business Model Canvas by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about the Business Model Canvas
Take a deep dive into Business Model Canvas with our course Service Design: How to Design Integrated Service Experiences .
Services are everywhere! When you get a new passport, order a pizza or make a reservation on AirBnB, you're engaging with services. How those services are designed is crucial to whether they provide a pleasant experience or an exasperating one. The experience of a service is essential to its success or failure no matter if your goal is to gain and retain customers for your app or to design an efficient waiting system for a doctor’s office.
In a service design process, you use an in-depth understanding of the business and its customers to ensure that all the touchpoints of your service are perfect and, just as importantly, that your organization can deliver a great service experience every time . It’s not just about designing the customer interactions; you also need to design the entire ecosystem surrounding those interactions.
In this course, you’ll learn how to go through a robust service design process and which methods to use at each step along the way. You’ll also learn how to create a service design culture in your organization and set up a service design team . We’ll provide you with lots of case studies to learn from as well as interviews with top designers in the field. For each practical method, you’ll get downloadable templates that guide you on how to use the methods in your own work.
This course contains a series of practical exercises that build on one another to create a complete service design project . The exercises are optional, but you’ll get invaluable hands-on experience with the methods you encounter in this course if you complete them, because they will teach you to take your first steps as a service designer. What’s equally important is that you can use your work as a case study for your portfolio to showcase your abilities to future employers! A portfolio is essential if you want to step into or move ahead in a career in service design.
Your primary instructor in the course is Frank Spillers . Frank is CXO of award-winning design agency Experience Dynamics and a service design expert who has consulted with companies all over the world. Much of the written learning material also comes from John Zimmerman and Jodi Forlizzi , both Professors in Human-Computer Interaction at Carnegie Mellon University and highly influential in establishing design research as we know it today.
You’ll earn a verifiable and industry-trusted Course Certificate once you complete the course. You can highlight it on your resume, CV, LinkedIn profile or on your website.
All open-source articles on the Business Model Canvas
Service design - design is not just for products.

The Relationship Between Visual Design and User Experience Design
- 2 years ago
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
This web app uses cookies to compile statistic information of our users visits. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies. If you wish you may change your preference or read about cookies
Or explore sectors:
6 matching canvas
Poste Italiane Business Model
Deutsche post ag business model, ups business model, bm express business model, fedex business model, japan post holdings business model.
Vizologi is a platform powered by artificial intelligence that searches, analyzes and visualizes the world’s collective business model intelligence to help answer strategic questions, it combines the simplicity of business model canvas with the innovation power of mash-up method .
See how Vizologi works View all features
Supercharge Your Business Strategy!
Before you download our exclusive content Subscribe to Vizologi’s FREE newsletter. Join 50k+ innovators shaping success with curated content. No spam, just pure value! @vizologi

Thanks for joining us!
Your exclusive content is on the way to your inbox. Ready to elevate your business with Vizologi?

The Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management and entrepreneurial tool. It allows you to describe, design, challenge, invent, and pivot your business model. This method from the bestselling management book Business Model Generation is applied in leading organizations and start-ups worldwide.

The Business Model Canvas enables you to:
- Visualize and communicate a simple story of your existing business model.
- Use the canvas to design new business models, whether you are a start-up or an existing businessManage a portfolio of business models
- You can use the canvas to easily juggle between "Explore" and "Exploit" business models.

About the speakers
Download your free copy of this whitepaper now, explore other examples.

Get Strategyzer updates straight in your inbox

Mastering business models
A self-paced online course with Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur.
Are you trying to improve your existing business model? Or trying to create a new one that can compete in today’s market?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
FedEx Business Model: Revenue Insights. In 1973, FedEx witnessed the growth, and since then, there's no turning back. Apart from the four main vital segments, FedEx Logistics & FedEx Office, also contributes to the total revenue. In FY20, FedEx managed to earn $69.2B, out of which 51% was donated by FedEx Express, 33% FedEx Ground, 10% by ...
post courier mail logistics transport commerce shipping freight packaging. Vizologi is a platform powered by artificial intelligence that searches, analyzes and visualizes the world's collective business model intelligence to help answer strategic questions, it combines the simplicity of business model canvas with the innovation power of mash ...
BUSINESS MODEL OF FedEx. FedEx provides transportation, e-commerce, and business services through wholly-owned subsidiaries. FedEx creates value by providing 220+ nations with "high value-added" package delivery services. FedEx's business philosophy is encapsulated by its founding core, "When it absolutely, positively has to get there ...
In this blog post, we will delve deeper into FedEx's business model canvas, exploring key partners, activities, cost structures, customer segments, and value propositions. The post aims to provide insights into what makes FedEx a successful player in the logistics industry and how it continues to expand its business by targeting new customer ...
The FedEx Business Model revolves around providing fast and reliable shipping services with a global network and advanced tracking. They generate revenue through shipping fees and value-added services. Their key activities include package handling, transportation, and technology innovation. FedEx serves e-commerce businesses, SMEs, and global corporations. They leverage key resources such as a ...
FedEx Express - This business is the first service that was provided by the company. It includes time-sensitive, air-ground express services. This business group was formed in 1971. Today, it ...
Here, we will look at an overview of FDX's business model. FedEx provides a portfolio of transportation, e-commerce, and business services through wholly owned subsidiaries. Headquartered in ...
Business Model. FedEx creates value by offering "high-value added" package delivery to over 220 countries. (2) The business model can best be summed-up in the company's early slogan: When it absolutely, positively has to be there overnight. (3) With 652 aircraft (the world's largest freight airline) moving over 4 million packages per ...
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a business canvas model. Step 1: Gather your team and the required material Bring a team or a group of people from your company together to collaborate. It is better to bring in a diverse group to cover all aspects.
Business model of FedEx Customer Segments. FedEx provides a range of delivery, distribution, and supply chain services to customers worldwide. The Company's customers can be categorised as follows: Residential Customers, comprising general consumers to which the Company provides consumer-to-consumer package delivery services;
Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a framework that helps determine how a business creates, delivers, and captures values. It is a visual representation of the important aspects or parts to consider when designing a Business Model. BMC aids in constructing a shared understanding of a business by condensing it into a simple, relevant, and ...
From How to Map Out Your Digital Transformation , Apr 27, 2022. Find new ideas and classic advice on strategy, innovation and leadership, for global leaders from the world's best business and ...
FedEx Express invented express distribution and is the industry's global leader, providing rapid, reliable, time-definite delivery to more than 220 countries and territories, connecting markets that comprise more than 90 percent of the world's gross domestic product within one to three business days. Unmatched air route authorities and ...
Before 2004, entrepreneurs suffered from prolonged and cumbersome business plans. Alexander Osterwalder facilitated the creation of a business model by introducing the Business Model Canvas (BMC).. By definition, it's a visual template that illustrates various objects of a business model.Osterwalder's original canvas includes nine elements, which we will have explained below in the article.
As Jim explains, here are a few of the benefits of using a business model canvas to think through product strategies: 1. You can use a business model canvas to roadmap quickly. You can use this canvas approach in just a few hours (and as Jim says, you can even do it with sticky-notes). This way, rather than trying to write out every detail ...
This post covers the next building block of the Business Model Canvas, which is Key Resources. In this post, we will look at 1) key resources, 2) types of key resources, 3) key resources and value propositions (section added), 4) key resources according to types of businesses, and 5) two case studies. KEY RESOURCES Key resources are the main inputs that your company uses to create its value ...
The Business Model Canvas - Flexible Chart, Early-Warning System and More In service design, two tools are essential to use early in your design process: the business model canvas and the value proposition canvas.You can use the business model canvas to build an overview of changes to be made to an existing business (e.g., a merger) or of a totally new business opportunity or market gap.
View all canvas. Vizologi is a platform powered by artificial intelligence that searches, analyzes and visualizes the world's collective business model intelligence to help answer strategic questions, it combines the simplicity of business model canvas with the innovation power of mash-up method. See how Vizologi works View all features.
A business model canvas is a strategic management tool that helps companies visualize new and existing business models they develop. This one-page template allows you to examine the external and internal factors that could make or break your business, such as the infrastructure running your business, what value you're offering, the customers you serve, and the finances that keep your business ...
Business Models. The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management and entrepreneurial tool. It allows you to describe, design, challenge, invent, and pivot your business model. This method from the bestselling management book Business Model Generation is applied in leading organizations and start-ups worldwide.
Build a business model canvas. Fill out each component of the business model canvas template with information on your customers, partners, key activities, value propositions, costs, and revenue streams. Easily add new text boxes or sticky notes to construct and align your business concept with your team. Personalize your business model canvas.
FedEx Business Model Canvas.FedEx Corporation (FedEx), incorporated on October 2, 1997, provides a portfolio of transportation, e-commerce and business services through companies competing collectively, operating independently and managed collaboratively, under the FedEx brand. The company's Segments include FedEx Express, TNT Express, FedEx ...
Next image. Herbag Zip retourne cabine tilt bag 50. $4,150. Customization and add to cart. Color. alezan / fauve. Product description. Travel bag in Officier canvas and Hunter cowhide with shoulder strap, collapsible handle, exterior pocket and palladium-plated Clou de Selle closure Made in France. Measures 19.7" long, 13.4" high and 8.9" deep.