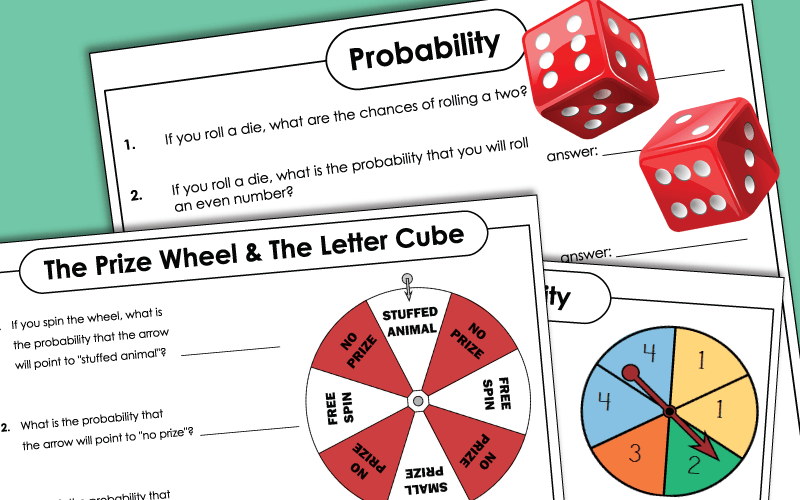
Probability Worksheets
- Kindergarten


Child Login
- Kindergarten
- Number charts
- Skip Counting
- Place Value
- Number Lines
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Word Problems
- Comparing Numbers
- Ordering Numbers
- Odd and Even
- Prime and Composite
- Roman Numerals
- Ordinal Numbers
- In and Out Boxes
- Number System Conversions
- More Number Sense Worksheets
- Size Comparison
- Measuring Length
- Metric Unit Conversion
- Customary Unit Conversion
- Temperature
- More Measurement Worksheets
- Writing Checks
- Profit and Loss
- Simple Interest
- Compound Interest
- Tally Marks
- Mean, Median, Mode, Range
- Mean Absolute Deviation
- Stem-and-leaf Plot
- Box-and-whisker Plot
- Permutation and Combination
- Probability
- Venn Diagram
- More Statistics Worksheets
- Shapes - 2D
- Shapes - 3D
- Lines, Rays and Line Segments
- Points, Lines and Planes
- Transformation
- Quadrilateral
- Ordered Pairs
- Midpoint Formula
- Distance Formula
- Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines
- Scale Factor
- Surface Area
- Pythagorean Theorem
- More Geometry Worksheets
- Converting between Fractions and Decimals
- Significant Figures
- Convert between Fractions, Decimals, and Percents
- Proportions
- Direct and Inverse Variation
- Order of Operations
- Squaring Numbers
- Square Roots
- Scientific Notations
- Speed, Distance, and Time
- Absolute Value
- More Pre-Algebra Worksheets
- Translating Algebraic Phrases
- Evaluating Algebraic Expressions
- Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
- Algebraic Identities
- Quadratic Equations
- Systems of Equations
- Polynomials
- Inequalities
- Sequence and Series
- Complex Numbers
- More Algebra Worksheets
- Trigonometry
- Math Workbooks
- English Language Arts
- Summer Review Packets
- Social Studies
- Holidays and Events
- Worksheets >
- Statistics >

Probability Worksheets
Navigate through this assortment of printable probability worksheets that includes exercises on basic probability based on more likely, less likely, equally likely, certain and impossible events, pdf worksheets based on identifying suitable events, simple spinner problems, for students in grade 4, grade 5, and grade 6. With the required introduction, the beginners get to further their knowledge with skills like probability on single coin, two coins, days in a week, months in a year, fair die, pair of dice, deck of cards, numbers and more. Mutually exclusive and inclusive events, probability on odds and other challenging probability worksheets are useful for grade 7, grade 8, and high school. Grab some of these probability worksheets for free!
Probability on Coins
Simple probability worksheets based on tossing single coin or two coins. Identify the proper sample space before finding probability.
Probability in a single coin toss
Probability in pair of coin - 1
Probability in pair of coin - 2
Probability on Days and Months
Fun filled worksheet pdfs based on days in a week and months in a year. Sample space is easy to find but care is required in identifying like events.
Days of a week
Months of a year - 1
Months of a year - 2
Probability on Fair Die
Fair die is numbered from 1 to 6. Understand the multiples, divisors and factors and apply it on these probability worksheets.
Simple numbers
Multiples and divisors
Mutually exclusive and inclusive
Probability on Pair of Dice
Sample space is little large which contains 36 elements. Write all of them in papers before start answering on probability questions for grade 7 and grade 8.
Based on numbers
Based on sum and difference
Based on multiples and divisors
Based on factors
Probability on Numbers
Students should learn the concepts of multiples, divisors and factors before start practicing these printable worksheets.
Probability on numbers - 1
Probability on numbers - 2
Probability on numbers - 3
Probability on numbers - 4
Probability on numbers - 5
Probability on Deck of Cards
Deck of cards contain 52 cards, 26 are black, 26 are red, four different flowers, each flower contain 13 cards such as A, 1, 2, ..., 10, J, Q, K.
Deck of cards worksheet - 1
Deck of cards worksheet - 2
Deck of cards worksheet - 3
Probability on Spinners
Interactive worksheets for 4th grade and 5th grade kids to understand the probability using spinners. Colorful spinners are included for more fun.
Spinner worksheets on numbers
Spinner worksheets on colors
Probability on Odds
Probability on odds worksheets can be broadly classifieds as favorable to the events or against the events.
Odds worksheet - 1
Odds worksheet - 2
Odds worksheet - 3
Probability on Independent and Dependent
Here comes our challenging probability worksheets set for 8th grade and high school students based on dependent and independent events with various real-life applications.
Based on deck of cards
Based on marbles
Based on cards
Probability on Different Events
Basic probability worksheets for beginners in 6th grade and 7th grade to understand the different type of events such as more likely, less likely, equally likely and so on.
Balls in container
Identify suitable events
Mutually inclusive and exclusive events
Related Worksheets
» Permutation
» Combination
» Permutation and Combination
» Venn Diagram
Become a Member
Membership Information
Privacy Policy
What's New?
Printing Help
Testimonial
Copyright © 2024 - Math Worksheets 4 Kids
This is a members-only feature!


Addition (Basic)
Addition (Multi-Digit)
Algebra & Pre-Algebra
Comparing Numbers
Daily Math Review
Division (Basic)
Division (Long Division)
Hundreds Charts
Measurement
Multiplication (Basic)
Multiplication (Multi-Digit)
Order of Operations
Place Value
Probability
Skip Counting
Subtraction
Telling Time
Word Problems (Daily)
More Math Worksheets
Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension Gr. 1
Reading Comprehension Gr. 2
Reading Comprehension Gr. 3
Reading Comprehension Gr. 4
Reading Comprehension Gr. 5
Reading Comprehension Gr. 6
Reading & Writing
Reading Worksheets
Cause & Effect
Fact & Opinion
Fix the Sentences
Graphic Organizers
Synonyms & Antonyms
Writing Prompts
Writing Story Pictures
Writing Worksheets
More ELA Worksheets
Consonant Sounds
Vowel Sounds
Consonant Blends
Consonant Digraphs
Word Families
More Phonics Worksheets
Early Literacy
Build Sentences
Sight Word Units
Sight Words (Individual)
More Early Literacy
Punctuation
Subjects and Predicates
More Grammar Worksheets
Spelling Lists
Spelling Grade 1
Spelling Grade 2
Spelling Grade 3
Spelling Grade 4
Spelling Grade 5
Spelling Grade 6
More Spelling Worksheets
Chapter Books
Charlotte's Web
Magic Tree House #1
Boxcar Children
More Literacy Units
Animal (Vertebrate) Groups
Butterfly Life Cycle
Electricity
Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas)
Simple Machines
Space - Solar System
More Science Worksheets
Social Studies
Maps (Geography)
Maps (Map Skills)
More Social Studies
Mother's Day
Father's Day
More Holiday Worksheets
Puzzles & Brain Teasers
Brain Teasers
Logic: Addition Squares
Mystery Graph Pictures
Number Detective
Lost in the USA
More Thinking Puzzles
Teacher Helpers
Teaching Tools
Award Certificates
More Teacher Helpers
Pre-K and Kindergarten
Alphabet (ABCs)
Numbers and Counting
Shapes (Basic)
More Kindergarten
Worksheet Generator
Word Search Generator
Multiple Choice Generator
Fill-in-the-Blanks Generator
More Generator Tools
Full Website Index
Probability Worksheets
These printable math worksheets will help students learn about probability of random events.
Logged in members can use the Super Teacher Worksheets filing cabinet to save their favorite worksheets.
Quickly access your most used files AND your custom generated worksheets!
Please login to your account or become a member and join our community today to utilize this helpful feature.

Also on Super Teacher Worksheets...
Learn basic fraction skills with these printables
Sample Worksheet Images

PDF with answer key:
PDF no answer key:
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Statistics and probability
Course: statistics and probability > unit 7.
- Intro to theoretical probability
Probability: the basics
- Simple probability: yellow marble
- Simple probability: non-blue marble
- Simple probability
- Intuitive sense of probabilities
- Comparing probabilities
- The Monty Hall problem
- The probability of an event can only be between 0 and 1 and can also be written as a percentage.
- The probability of event A is often written as P ( A ) .
- If P ( A ) > P ( B ) , then event A has a higher chance of occurring than event B .
- If P ( A ) = P ( B ) , then events A and B are equally likely to occur.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Statistics and Probability Worksheets
Welcome to the statistics and probability page at Math-Drills.com where there is a 100% chance of learning something! This page includes Statistics worksheets including collecting and organizing data, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode and range) and probability.
Students spend their lives collecting, organizing, and analyzing data, so why not teach them a few skills to help them on their way. Data management is probably best done on authentic tasks that will engage students in their own learning. They can collect their own data on topics that interest them. For example, have you ever wondered if everyone shares the same taste in music as you? Perhaps a survey, a couple of graphs and a few analysis sentences will give you an idea.
Statistics has applications in many different fields of study. Budding scientists, stock market brokers, marketing geniuses, and many other pursuits will involve managing data on a daily basis. Teaching students critical thinking skills related to analyzing data they are presented will enable them to make crucial and informed decisions throughout their lives.
Probability is a topic in math that crosses over to several other skills such as decimals, percents, multiplication, division, fractions, etc. Probability worksheets will help students to practice all of these skills with a chance of success!
Most Popular Statistics and Probability Worksheets this Week

Mean, Median, Mode and Range Worksheets

Calculating the mean, median, mode and range are staples of the upper elementary math curriculum. Here you will find worksheets for practicing the calculation of mean, median, mode and range. In case you're not familiar with these concepts, here is how to calculate each one. To calculate the mean, add all of the numbers in the set together and divide that sum by the number of numbers in the set. To calculate the median, first arrange the numbers in order, then locate the middle number. In sets where there are an even number of numbers, calculate the mean of the two middle numbers. To calculate the mode, look for numbers that repeat. If there is only one of each number, the set has no mode. If there are doubles of two different numbers and there are more numbers in the set, the set has two modes. If there are triples of three different numbers and there are more numbers in the set, the set has three modes, and so on. The range is calculated by subtracting the least number from the greatest number.
Note that all of the measures of central tendency are included on each page, but you don't need to assign them all if you aren't working on them all. If you're only working on mean, only assign students to calculate the mean.
In order to determine the median, it is necessary to have your numbers sorted. It is also helpful in determining the mode and range. To expedite the process, these first worksheets include the lists of numbers already sorted.
- Calculating Mean, Median, Mode and Range from Sorted Lists Sets of 5 Numbers from 1 to 10 Sets of 5 Numbers from 10 to 99 Sets of 5 Numbers from 100 to 999 Sets of 10 Numbers from 1 to 10 Sets of 10 Numbers from 10 to 99 Sets of 10 Numbers from 100 to 999 Sets of 20 Numbers from 10 to 99 Sets of 15 Numbers from 100 to 999
Normally, data does not come in a sorted list, so these worksheets are a little more realistic. To find some of the statistics, it will be easier for students to put the numbers in order first.
- Calculating Mean, Median, Mode and Range from Unsorted Lists Sets of 5 Numbers from 1 to 10 Sets of 5 Numbers from 10 to 99 Sets of 5 Numbers from 100 to 999 Sets of 10 Numbers from 1 to 10 Sets of 10 Numbers from 10 to 99 Sets of 10 Numbers from 100 to 999 Sets of 20 Numbers from 10 to 99 Sets of 15 Numbers from 100 to 999
Collecting and Organizing Data
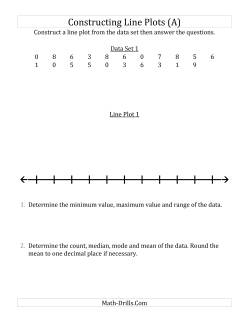
Teaching students how to collect and organize data enables them to develop skills that will enable them to study topics in statistics with more confidence and deeper understanding.
- Constructing Line Plots from Small Data Sets Construct Line Plots with Smaller Numbers and Lines with Ticks Provided (Small Data Set) Construct Line Plots with Smaller Numbers and Lines Only Provided (Small Data Set) Construct Line Plots with Smaller Numbers (Small Data Set) Construct Line Plots with Larger Numbers and Lines with Ticks Provided (Small Data Set) Construct Line Plots with Larger Numbers and Lines Only Provided (Small Data Set) Construct Line Plots with Larger Numbers (Small Data Set)
- Constructing Line Plots from Larger Data Sets Construct Line Plots with Smaller Numbers and Lines with Ticks Provided Construct Line Plots with Smaller Numbers and Lines Only Provided Construct Line Plots with Smaller Numbers Construct Line Plots with Larger Numbers and Lines with Ticks Provided Construct Line Plots with Larger Numbers and Lines Only Provided Construct Line Plots with Larger Numbers
Interpreting and Analyzing Data

Answering questions about graphs and other data helps students build critical thinking skills. Standard questions include determining the minimum, maximum, range, count, median, mode, and mean.
- Answering Questions About Stem-and-Leaf Plots Stem-and-Leaf Plots with about 25 data points Stem-and-Leaf Plots with about 50 data points Stem-and-Leaf Plots with about 100 data points
- Answering Questions About Line Plots Line Plots with Smaller Data Sets and Smaller Numbers Line Plots with Smaller Data Sets and Larger Numbers Line Plots with Larger Data Sets and Smaller Numbers Line Plots with Larger Data Sets and Larger Numbers
- Answering Questions About Broken-Line Graphs Answer Questions About Broken-Line Graphs
- Answering Questions About Circle Graphs Circle Graph Questions (Color Version) Circle Graph Questions (Black and White Version) Circle Graphs No Questions (Color Version) Circle Graphs No Questions (Black and White Version)
- Answering Questions About Pictographs Answer Questions About Pictographs
Probability Worksheets

- Calculating Probabilities with Dice Sum of Two Dice Probabilities Sum of Two Dice Probabilities (with table)
Spinners can be used for probability experiments or for theoretical probability. Students should intuitively know that a number that is more common on a spinner will come up more often. Spinning 100 or more times and tallying the results should get them close to the theoretical probability. The more sections there are, the more spins will be needed.
- Calculating Probabilities with Number Spinners Number Spinner Probability (4 Sections) Number Spinner Probability (5 Sections) Number Spinner Probability (6 Sections) Number Spinner Probability (7 Sections) Number Spinner Probability (8 Sections) Number Spinner Probability (9 Sections) Number Spinner Probability (10 Sections) Number Spinner Probability (11 Sections) Number Spinner Probability (12 Sections)
Non-numerical spinners can be used for experimental or theoretical probability. There are basic questions on every version with a couple extra questions on the A and B versions. Teachers and students can make up other questions to ask and conduct experiments or calculate the theoretical probability. Print copies for everyone or display on an interactive white board.
- Probability with Single-Event Spinners Animal Spinner Probability ( 4 Sections) Animal Spinner Probability ( 5 Sections) Animal Spinner Probability ( 10 Sections) Letter Spinner Probability ( 4 Sections) Letter Spinner Probability ( 5 Sections) Letter Spinner Probability ( 10 Sections) Color Spinner Probability ( 4 Sections) Color Spinner Probability ( 5 Sections) Color Spinner Probability ( 10 Sections)
- Probability with Multi-Event Spinners Animal/Letter Combined Spinner Probability ( 4 Sections) Animal/Letter Combined Spinner Probability ( 5 Sections) Animal/Letter Combined Spinner Probability ( 10 Sections) Animal/Letter/Color Combined Spinner Probability ( 4 Sections) Animal/Letter/Color Combined Spinner Probability ( 5 Sections) Animal/Letter/Color Combined Spinner Probability ( 10 Sections)
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.
Probability
How likely something is to happen.
Many events can't be predicted with total certainty. The best we can say is how likely they are to happen, using the idea of probability.
Tossing a Coin
When a coin is tossed, there are two possible outcomes:
Heads (H) or Tails (T)
- the probability of the coin landing H is ½
- the probability of the coin landing T is ½
Throwing Dice
When a single die is thrown, there are six possible outcomes: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 .
The probability of any one of them is 1 6
In general:
Probability of an event happening = Number of ways it can happen Total number of outcomes
Example: the chances of rolling a "4" with a die
Number of ways it can happen: 1 (there is only 1 face with a "4" on it)
Total number of outcomes: 6 (there are 6 faces altogether)
So the probability = 1 6
Example: there are 5 marbles in a bag: 4 are blue, and 1 is red. What is the probability that a blue marble gets picked?
Number of ways it can happen: 4 (there are 4 blues)
Total number of outcomes: 5 (there are 5 marbles in total)
So the probability = 4 5 = 0.8
Probability Line
We can show probability on a Probability Line :
Probability is always between 0 and 1
Probability is Just a Guide
Probability does not tell us exactly what will happen, it is just a guide
Example: toss a coin 100 times, how many Heads will come up?
Probability says that heads have a ½ chance, so we can expect 50 Heads .
But when we actually try it we might get 48 heads, or 55 heads ... or anything really, but in most cases it will be a number near 50.
Learn more at Probability Index .
Some words have special meaning in Probability:
Experiment : a repeatable procedure with a set of possible results.
Example: Throwing dice
We can throw the dice again and again, so it is repeatable.
The set of possible results from any single throw is {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Outcome: A possible result.
Example: "6" is one of the outcomes of a throw of a die.
Trial: A single performance of an experiment.
Example: I conducted a coin toss experiment. After 4 trials I got these results:
Three trials had the outcome "Head", and one trial had the outcome "Tail"
Sample Space: all the possible outcomes of an experiment.

Example: choosing a card from a deck
There are 52 cards in a deck (not including Jokers)
So the Sample Space is all 52 possible cards : {Ace of Hearts, 2 of Hearts, etc... }
The Sample Space is made up of Sample Points:
Sample Point: just one of the possible outcomes
Example: Deck of Cards
- the 5 of Clubs is a sample point
- the King of Hearts is a sample point
"King" is not a sample point. There are 4 Kings, so that is 4 different sample points.
There are 6 different sample points in that sample space.
Event: one or more outcomes of an experiment
Example Events:
An event can be just one outcome:
- Getting a Tail when tossing a coin
- Rolling a "5"
An event can include more than one outcome:
- Choosing a "King" from a deck of cards (any of the 4 Kings)
- Rolling an "even number" (2, 4 or 6)
Hey, let's use those words, so you get used to them:
Example: Alex wants to see how many times a "double" comes up when throwing 2 dice.
The Sample Space is all possible Outcomes (36 Sample Points):
{1,1} {1,2} {1,3} {1,4} ... ... ... {6,3} {6,4} {6,5} {6,6}
The Event Alex is looking for is a "double", where both dice have the same number. It is made up of these 6 Sample Points :
{1,1} {2,2} {3,3} {4,4} {5,5} and {6,6}
These are Alex's Results:
After 100 Trials , Alex has 19 "double" Events ... is that close to what you would expect?

Probability Practice Questions
Click here for questions, click here for answers, gcse revision cards.

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024

Conditional Probability

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.

Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs
- Data & Graphing
Probability

Download & Print Only $4.70
Basic probabilities expressed as fractions
In math, probability measures the likelihood of an event occurring . In these basic probability worksheets, students determine the probability of certain events and express then as a fraction.

Spinning wheel:

These worksheets are available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.
Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
- Forgot Password?
One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
This topic is relevant for:

Probability Scale
Here we will learn about the probability scale, including placing the chance of events happening on a probability scale, calculating the chance of events happening and calculating the chance of events not happening.
There are also probability scale worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is the probability scale?
The probability scale is a number line from 0 to 1 where we can place the probability of events occurring. Events can range from impossible to certain.
To do this we need to be able to identify decimals and fractions on the number line from 0 to 1 and calculate the probability of events happening or not happening.
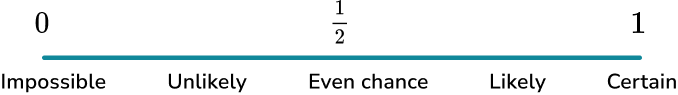
For example, let’s look at the probabilities of a few possible outcomes when a fair 6 sided dice is rolled.
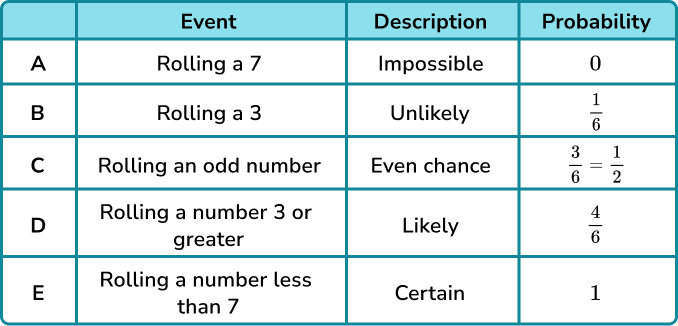
These events are placed on the probability scale below.
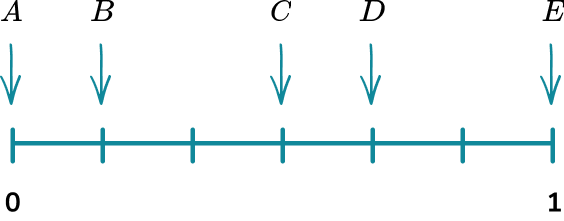
Understanding the probability scale
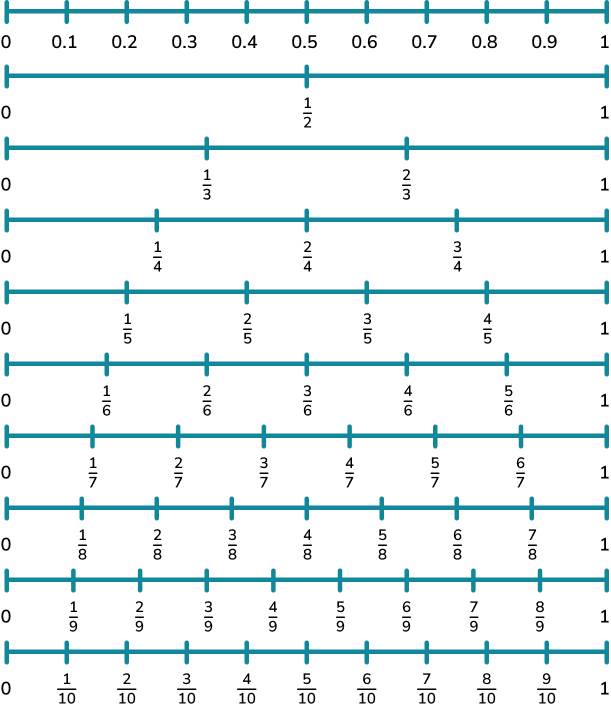
To understand the probability scale, you must be familiar with the positions of fractions and decimals on a number line between 0 and 1.
Here is the 0 to 1 number line split into decimals and fractions.
An event which is impossible would be positioned at 0.
An event which is certain would be positioned at 1.
An event with an even chance of occurring or not occurring would be positioned at \frac{1}{2} .
Events where different fractions, decimals or percentages can be used to describe the probability can be positioned onto the probability scale.
How to use a probability scale
In order to place events on a probability scale:
- Calculate the probability of the event.
Identify the probabilities on the scale.
- Indicate the probability of the event on the probability scale.
Explain how to use a probability scale
Probability scale worksheet
Get your free probability scale worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
Related lessons on describing probability
Probability scale is part of our series of lessons to support revision on describing probability . You may find it helpful to start with the main describing probability lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
- Describing probability
- Probability symbol
- Probability notation
Probability scale examples
Example 1: probability scale.
A spinner is shown below. Place the events on the probability scale below.
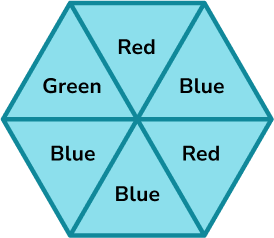
Calculate the probabilities of the events.
In this example, the probabilities have already been calculated for you.
2 Identify the probabilities on the scale.
The scale has six divisions so each line represents \frac{1}{6} .
3 Indicate the probability of the events on the scale.
Example 2: probability scale
A bag has 10 counters in it. 3 of the counters are red, 4 of the counters are blue, 1 of the counters is green and 2 of the counters are yellow. Place the events on the probability scale below.
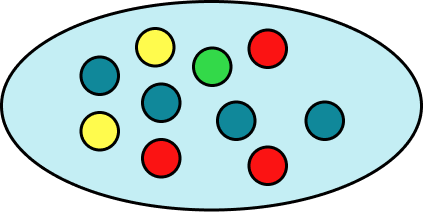
The scale has 10 divisions so each line represents 0.1 .
Indicate the probability of the events on the scale.
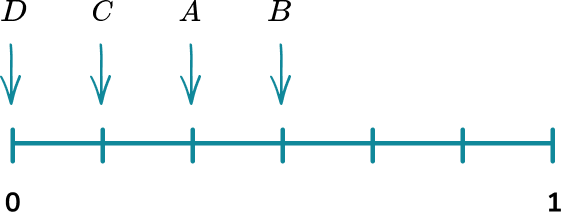
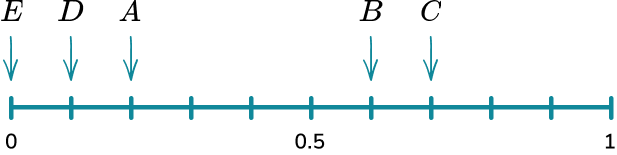
Example 3: calculating probability
A bag has 10 counters in it. 2 of the counters are red, 6 of the counters are blue, 1 of the counters is green and 1 of the counters is yellow. Place the events on the probability scale below.
The scale has 10 divisions so each line represents 0.1.
How to calculate the probability of an event happening
We could be asked to calculate probabilities before placing them onto a probability scale. In order to calculate the probability of events happening we need to know the number of ways the event can occur and the total number of possible outcomes.
We can represent the calculated probability as a fraction or a decimal.
Identify the total number of possible outcomes.
Identify the number of ways the specific event can occur.
Substitute into the formula for the probability of an event.
Indicate the calculated probability on the probability scale.
Explain how to calculate the probability of an event happening
Calculating probability examples
Example 4: calculating probability.
A bag contains six blue counters, two red counters, a green counter and a yellow counter.
Represent the probability of picking a blue counter on a probability scale.
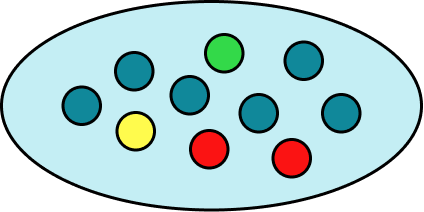
There are 10 counters in total.
There are 6 blue counters.
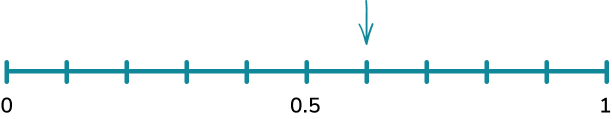
Example 5: calculating probability
A spinner is shown below. Calculate the probability of the spinner landing on green.
Represent this on a probability scale.
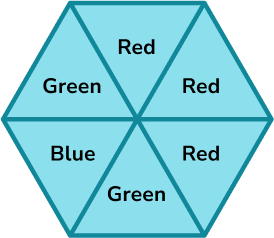
There are six equally likely outcomes on the spinner.
Two of the sections are green.

Example 6: probability of an event not happening
A bag contains six blue counters, two red counters, a green counter and a yellow counter.
Represent the probability of not picking a blue counter on a probability scale.
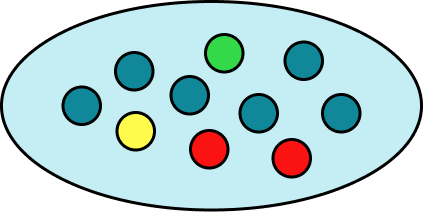
Altogether there are 10 counters which could be picked.
If you do not pick a blue counter, you could pick a yellow counter, a green counter and there are two red counters. There are 4 counters that are not blue.

Example 7: probability of an event not happening
A spinner is shown below. Calculate the probability of the spinner not landing on green.
Represent this on a probability scale.
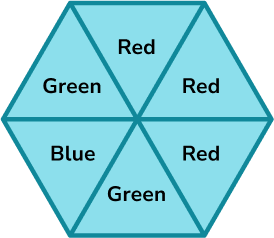
There are six equal sections on the spinner.
Four sections are not green.

Common misconceptions
- Writing probabilities as a ratio or in words
Probabilities must be written as a fraction, decimal or percentage. The chance of rolling a 1 on a fair six-sided dice is \frac{1}{6}. This cannot be written as a ratio, for example 1:6, or in words, for example ‘1 in 6’ or ‘1 out of 6’.
- Probabilities greater than \bf{1}
The chance of all outcomes of an event will always add up to one. Therefore a probability as a decimal cannot be greater than 1 or a fraction cannot be improper. For example 1.4 or \frac{6}{5} cannot be probabilities.
Practice probability scale questions
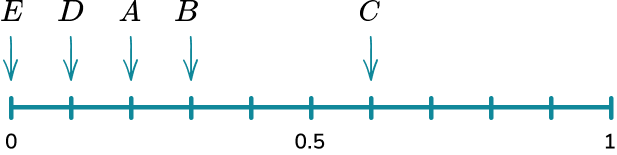
1. A spinner is shown below. Place the events on the probability scale below.
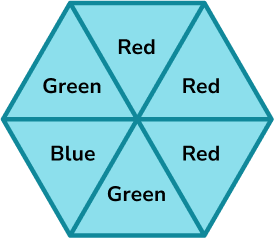
The probability scale has six equally likely outcomes so each line represents one sixth. These are then indicated with arrows and labelled with the correct letter.
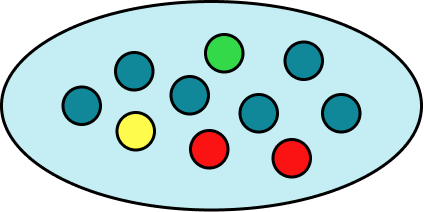
2. A bag has 10 counters in it. 4 of the counters are red, 3 of the counters are blue, 2 of the counters are green and 1 of the counters is yellow. Place the events on the probability scale below.
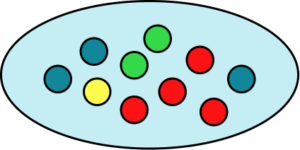
The probability scale has ten equally likely outcomes so each line represents 0.1. These are then indicated with arrows and labelled with the correct letter.
3. A bag has 10 counters in it. 1 of the counters are red, 7 of the counters are blue, 1 of the counters is green and 1 of the counters is yellow. Complete the table of probabilities below and represent the probabilities on a probability scale.
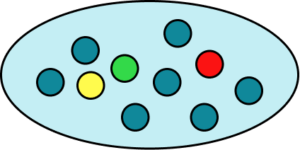
There are ten counters so you can either represent each counter as 0.1 or \frac{1}{10}.
4. A bag contains three blue counters, four red counters, two green counters and a yellow counter. Calculate the probability of picking a red counter. Represent this on a probability scale.
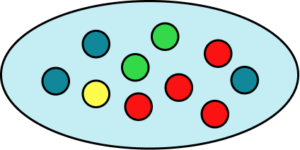
There are ten counters and four of them are red.
5. A bag contains three blue counters, four red counters, two green counters and a yellow counter. Calculate the probability of picking a green or a yellow counter. Represent this on a probability scale.
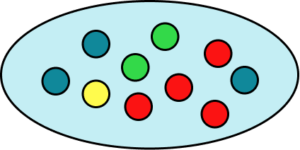
There are ten counters in total. Two of them are green and one of them is yellow, so there are three that could be picked,
6. A spinner is shown below.
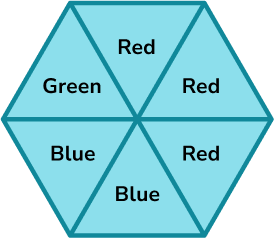
Calculate the probability of the spinner landing on green as a fraction. Represent this on a probability scale.

There are six equal sections and one of them is green,
7. A bag contains three blue counters, four red counters, two green counters and a yellow counter. Calculate the probability of not picking a green counter. Represent your answer on a probability scale.
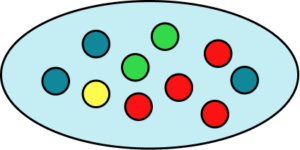
There are ten counters and two of them are green, so eight of them are not green,
8. A bag contains three blue counters, four red counters, two green counters and a yellow counter. Calculate the probability of not picking a red or a blue counter. Represent this on a probability scale.
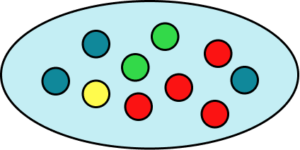
There are ten counters in total. Four of them are red and three of them are blue. This means there are 3 counters that are not red or blue,
Probability scale GCSE questions
1. An ordinary fair dice is thrown once. On the probability scale mark with a cross ( X ) the probability that the dice lands on an even number.

2. (a) A fair spinner has 6 sections. They are labelled 1, \ 2, \ 3 and 5.
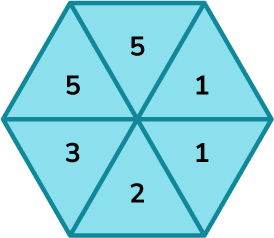
Which arrow shows the probability of the spinner landing on a 5?
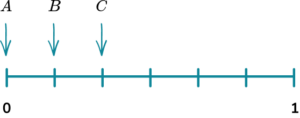
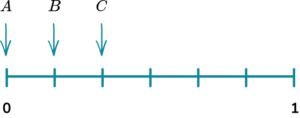
(b) Which arrow shows the probability of the spinner landing on an even number?
3. Stevie spins a fair 4 -sided spinner.
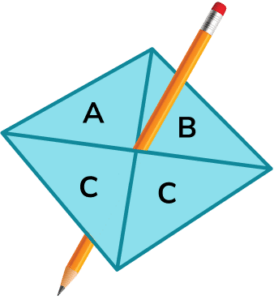
(a) On the probability scale mark with a cross ( X ) the probability that the spinner lands on A.
(b) Write down the probability that the spinner lands on C.
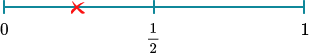
(b) 0.5 or equivalent
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- List possible outcomes for an event
- Place the probability of events on a probability scale
- Calculate the chance of an event happening
- Calculate the chance of an event not happening
The next lessons are
- Probability distribution
- How to calculate probability
- Combined events probability
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
× Description: "This worksheet is designed to introduce children to the concept of basic probability through practical examples leveraging dice and spinners. It comprises 12 engaging and thought-provoking math problems, teaching them about odds, event likelihood, and random selection. The worksheet is versatile in its application, allowing for customization, conversion into flashcards, and ...
Basic probability worksheets for beginners in 6th grade and 7th grade to understand the different type of events such as more likely, less likely, equally likely and so on. Balls in container. Identify suitable events. Mutually inclusive and exclusive events. Free probability worksheets for kids include odds, spinner problems, coins, deck of ...
Learn About Probability Theory With The Following Examples And Interactive Exercises. Choose a worksheet or answer key below. Be sure to try the interactive probability activities, too! Worksheets to Supplement our Lessons. Worksheet 1: Worksheet 1 Key:
These dynamically created Probability Worksheets are great for learning and practicing the concept of probability. These Probability Worksheets are ideal for 4th Grade, 5th Grade, 6th Grade, and 7th Grade students. Click here for a Detailed Description of all the Probability Worksheets.
Probability tells us how often some event will happen after many repeated trials. You've experienced probability when you've flipped a coin, rolled some dice, or looked at a weather forecast. Go deeper with your understanding of probability as you learn about theoretical, experimental, and compound probability, and investigate permutations, combinations, and more!
These printable math worksheets will help students learn about probability of random events. Use the pictures of the spinners to determine the probability of outcomes for events. Determine the probability of drawing certain marbles at random from a bag. Color the marble pictures. Then, write the probability of drawing certain colored marbles ...
Probability is the study of chance. It is the possibility or indications of an incident happening. The formula for calculating it translates to the number of steps of gaining victory (NSGV) / the entire amount of feasible results (EAFR). Example: Find the probability of flipping a coin in which:=> Heads = 1/2 => Possible result = 2 (head or ...
Our probability worksheets offer targeted extra practice for kids learning about concepts such as coin probability, probability graphs, and mean, median, mode. These skills are crucial to master in fifth grade before kids move on to higher level math skills in middle school. ... For example, when flipping a coin, it will land on either heads or ...
In these exercises, students determine the probability of events by counting the number of ways an event can happen (the numerator) divided by the total number of possible outcomes. Note that this method only works if each different outcome is equally likely to happen at any time. Worksheet #1 Worksheet #2 Worksheet #3. Worksheet #4 Worksheet #5.
11) P(A) =. . 6) You roll a fair six-sided die twice. The first roll shows a five and the second roll shows a six. 8) A basket contains five apples and seven peaches. You randomly select one piece of fruit and eat it. Then you randomly select another piece of fruit. The first piece of fruit is an apple and the second piece is a peach.
1. \bf {1} 1. The probabilities of all outcomes of an event will always add up to one. Therefore a probability as a decimal cannot be greater than 1 1 or a fraction cannot be improper. For example, 1.4 1.4 or \frac {6} {5} 56 cannot be probabilities. Adding probabilities instead of multiplying them.
More Lessons On Probability More Lessons for Grade 6 Math Math Worksheets. How to determine the probability of simple events, flipping a coin, rolling a 6-sided die, or drawing a card? The following diagram shows the formula and an example of simple probability. Scroll down the page for more examples and solutions for simple probability.
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC Kuta Software - Infinite Algebra 2 Probability with Combinatorics Name_____ Date_____ Period____-1-Find the probability of each event. 1) Beth and Shayna each purchase one raffle ticket. If a total of eleven raffle tickets are sold and two winners will be selected, what is the probability that both Beth and Shayna ...
3 months ago. Classical Probability (Equally Likely Outcomes): To find the probability of an event happening, you divide the number of ways the event can happen by the total number of possible outcomes. Probability of an Event Not Occurring: If you want to find the probability of an event not happening, you subtract the probability of the event ...
Welcome to the statistics and probability page at Math-Drills.com where there is a 100% chance of learning something! This page includes Statistics worksheets including collecting and organizing data, measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode and range) and probability.. Students spend their lives collecting, organizing, and analyzing data, so why not teach them a few skills to help ...
Example: there are 5 marbles in a bag: 4 are blue, and 1 is red. What is the probability that a blue marble gets picked? Number of ways it can happen: 4 (there are 4 blues). Total number of outcomes: 5 (there are 5 marbles in total). So the probability = 4 5 = 0.8
Practice Questions. Previous: Direct and Inverse Proportion Practice Questions. Next: Reverse Percentages Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Probability.
1. rolling a number less than 6 on a number cube labeled 1 through 6. 2. flipping a coin and getting heads. 3. spinning a number less than 3 on a spinner with 8 equal sections marked 1 through 8. 4. drawing a red or blue marble from a bag of red marbles and blue marbles. 5. rolling a number greater than 6 on a number. _________________ A.
Examples, videos, worksheets, solutions, and activities to help students learn about conditional probability. How to determine conditional probability using a tree diagram or a table? ... Conditional Probability Tree Diagram Example: Assume that 75% of the AP Stats students studied for the test. If 40% of those who studied got an A, but only 10 ...
Example 3: two independent events. Mary has to catch 2 2 buses to work. The probability the first bus will be late is 0.1 0.1 and the probability the second bus will be late is 0.3. 0.3. Complete the tree diagram. Work out the probability that at least one bus will be late. Fill in the probabilities on the branches.
Basic probabilities expressed as fractions. In math, probability measures the likelihood of an event occurring. In these basic probability worksheets, students determine the probability of certain events and express then as a fraction. Dice: Worksheet #1. Raffle: Worksheet #2. Cards: Worksheet #3.
A spinner is shown below. Place the events on the probability scale below. 2. A bag has 10 10 counters in it. 4 4 of the counters are red, 3 3 of the counters are blue, 2 2 of the counters are green and 1 1 of the counters is yellow. Place the events on the probability scale below. 3.